Introduction to Aerospace Engineering
|
|
|
- Curtis Green
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Aerosace Engineering Lecture slides hallenge the future
2 Introduction to Aerosace Engineering Aerodynamics & Prof. H. Bijl ir. N. Timmer
3 &. Airfoils and finite wings Anderson 5.9 end of chater 5 excl. 5.9
4 Toics lecture & Pressure distributions and lift Finite wings Swet wings 3
5 Pressure coefficient Tyical examle Definition of ressure coefficient : - uer side q lower side -.0 Stagnation oint: t t - q > 4
6 Examle 5.6 The ressure on a oint on the wing of an airlane is 7.58x0 4 N/m. The airlane is flying with a velocity of 70 m/s at conditions associated with standard altitude of 000m. alculate the ressure coefficient at this oint on the wing 000 m: N/m ρ.0066 kg/m 3.50 q 5
7 Obtaining lift from ressure distribution θ leading edge V s trailing edge ds dy θ dx ds cos θ 6
8 Obtaining lift from ressure distribution Normal force er meter san: with ds cos θ dx N N TE LE c Write dimensionless force coefficient : dx 0 l l TE cosθds cosθds n c 0 u LE dx N ρv c u N q c n l x u d q 0 c q 0 c x d n ( ) x d l u c 0 7
9 TLsinα- Dcosα NLcosα + Dsinα L R N α T D V α angle of attack 8
10 Obtaining lift from normal force coefficient L N cos α T sinα c c cosα c l n t sinα L N T cosα q c q c q c sinα For small angle of attack α 5 o : cosα, sinα 0 d x ( ) ( ) l l c 0 u 9
11 Examle 5. onsider an airfoil with chord length c and the running distance x measured along the chord. The leading edge is located at x/c0 and the trailing edge at x/c. The ressure coefficient variations over the uer and lower surfaces are given as, u, u, l x x 300 for 0 0. c c x x for 0..0 c c x x 0.95 for 0.0 c c alculate the normal force coefficient. 0
12 omressibility correction of the ressure coefficient at a certain oint omressibility correction Aroximate theoretical correction (valid for 0 < M < 0.7) :,0 M M.0 Prandtl-Glauert Rule
13 omressibility correction for lift coefficient ( ) d ( x) c c l u o l l c 0 M M c 0 ( ) ( ) d x u o c d x ( ) ( ) l,0 l c 0 l l,0 M u o l M> α
14 Examle 5. onsider an NAA 44 airfoil at an angle of attack of 4 o. If the free-stream Mach number is 0.7, what is the lift coefficient? -From A. D for angle of attack of 4 o, c l 0.83.However, these data were obtained at low seeds. 3
15 ritical Mach number and critical ressure coefficient M0.3 M eak 0.44 M0.5 M eak 0.7 M0.6 M eak.00 ritical Mach number for the airfoil 4
16 ritical ressure coefficient,min thick -.5 thick medium -.0 medium thin -0.5 thin, cr f (M ) M.0 Thicker airfoil reaches critical ressure coefficient at a lower value of M 5
17 6 ritical ressure coefficient Definition of ressure coefficient : q q Dynamic ressure : ρ ρ ρ / V V V q We have found before : ρ a thus : M a V q For isentroic flow we found : 0 M + Dividing these equations we find :... 0 M + and also :
18 7 ritical ressure coefficient )M ( )M ( + + Substitution in -equation gives : + + )M ( )M ( M q + + )M ( )M ( M or :
19 8 ritical ressure coefficient The critical ressure coefficient is found when M is reached : + + )M ( M,cr c cr ( ) M M
20 The intersection of this curve with the airfoil P,min will give the value of the M cr secific for the airfoil under consideration. +, cr M cr Airfoil indeendent curve cr [( ) / ] M + [( ) / ] M cr min,0min M Airfoil deendent curve 9
21 Drag divergence 0
22 Drag divergence M< M <M cr M> M< M cr <M <M drag divergence M< shock wave M> M< M >M drag divergence Searated flow
23 Drag divergence Develoment of suercritical airfoils -,cr x/c
24 3
25 Finite Wings 4
26 haracteristics of finite wings ti vortex Flow around the wing ti generates ti vortices low ressure high ressure 5
27 6
28 Ti vortices ross section of ti vortex R V θ Induced velocity V V local flow vector w The trailing ti vortex causes downwash, w 7
29 Induced drag α i L L geometric angle of attack α V α i α 8
30 Induced drag α i D i Lsin α i L geometric angle of attack α induced drag, D i V α i α α eff 9
31 Induced drag α i D i Lsin α i L geometric angle of attack α induced drag, D i V α i α Since α small : sinα i α i D i L α i α eff 30
32 Induced drag FRONT VIEW Examle : ellitical lift distribution ellitical lift distribution downwash, w Ellitical lift distribution results in constant downwash and therefore constant induced angle of attack From incomressible flow theory : where : A α i L πa b (Asect ratio) Thus : S D i L πa 3
33 3
34 33
35 Effect of asect ratio on induced drag High asect ratio : Low Induced Drag DG 00 DG 500 Low asect ratio : High Induced Drag Mirage
36 San efficiency factor D i L π A e san efficiency factor (Oswald factor) Ellitical loading Non-ellitical loading : e ; minimum induced drag : e < ; higher induced drag The total drag of the wing can now be written as : + D D π A Profile drag Induced drag L e 35
37 Examle 5.9 onsider a flying wing with wing area of 06 m, an asect ratio of 0, a san effectiveness factor of 0.95, and an NAA 44 airfoil. The weight of the airlane is 7.5x0 5 N. If the density altitude is 3 km and the flight velocity is 00 m/s, calculate the total drag on the aircraft. 36
38 Lift curve sloe geometric angle of attack α α eff α i V The effect of a finite wing is to reduce the wing lift curve sloe 37
39 Lift curve sloe The induced angle of attack reduces The local effective angle of attack : α eff α α i For a wing of a general lan form we may write : α α i i L π A e 57.3 L π Ae Angle is in radians! e is san effectiveness factor (theoretically different from e but in ractice more or less the same) For angle in degrees 38
40 Lift curve sloe L infinite wing (effective angle of attack) a 0 d l d α a a 0 finite wing (geometric angle of attack) d a dα L α From thin airfoil theory we find : a 0 π 39
41 Lift curve sloe Effective local angle of attack α eff α α i For an arbitrary loading distribution wing we find : d L L α i a0 πae d( α αi ) ( α α ) const, L a0 i + L a0α a + 0 πae const + a + 0 πae Integrate : a L L 0 α + Ae π const 40
42 Lift curve sloe Differentiating this equation results in : d dα Examle : d Infinite wing : A then L π dα L + a0 a0 πae Finite wings : A (Fokker 50) then A5 then d L dα d L dα π π π π 4
43 a d L a0 dα a0 + π Ae a 0 d l dα d L a0 dα 57.3a + π Ae 0 a 0 er degree 4
44 Examle 5. onsider a wing with an asect ratio of 0 and NAA 30 airfoil section. Assume Re 5 x 0 6. the san efficiency factor is ee If the wing is at 4 o angle of attack, calculate L and D. 43
45 Swet wings M V M cr 0.7 Λ40 44
46 Swet wings M V M cr 0.7 Λ40 V cos Λ V M cr for swet wing 0.7 cos Λ 0.9 By sweeing the wings of subsonic aircraft, the drag divergence is delayed to higher Mach numbers 45
47 Swet wings Effect of wing thickness and sweeback angle on minimum wing drag coefficient A B D,min t/c9% t/c6% t/c4% A B.0 M.0 M 46
48 Total drag D + D rofile L π Ae + + D D D D rofile f ressure w 47
49 Flas δ W L L ρv S Thus : V W ρs L and : V stall ρ W S L max The landing seed is decreased when the maximum lift coefficient is increased 48
50 Flas δ f 60 L flas extended δ δ f 5 flas retracted δ f 0 α 49
51 Flas Tyical examle 50
52 Flas and slats flas slats 5
53 Flas 5
54 Flas 53
55 Flas 54
a) Derive general expressions for the stream function Ψ and the velocity potential function φ for the combined flow. [12 Marks]
![a) Derive general expressions for the stream function Ψ and the velocity potential function φ for the combined flow. [12 Marks] a) Derive general expressions for the stream function Ψ and the velocity potential function φ for the combined flow. [12 Marks]](/thumbs/87/95430472.jpg) Question 1 A horizontal irrotational flow system results from the combination of a free vortex, rotating anticlockwise, of strength K=πv θ r, located with its centre at the origin, with a uniform flow
Question 1 A horizontal irrotational flow system results from the combination of a free vortex, rotating anticlockwise, of strength K=πv θ r, located with its centre at the origin, with a uniform flow
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT A: Fundamental Concepts
 AE3 Aerodynamics I UNIT A: Fundamental Concets ROAD MAP... A-: Engineering Fundamentals Review A-: Standard Atmoshere A-3: Governing Equations of Aerodynamics A-4: Airseed Measurements A-5: Aerodynamic
AE3 Aerodynamics I UNIT A: Fundamental Concets ROAD MAP... A-: Engineering Fundamentals Review A-: Standard Atmoshere A-3: Governing Equations of Aerodynamics A-4: Airseed Measurements A-5: Aerodynamic
Chapter 4 Estimation of wing loading and thrust loading - 8 Lecture 16 Topics
 hater 4 Estimation of wing loading and thrust loading - 8 Lecture 16 Toics 4.14.9 Selection of roeller diameter for a chosen alication Examle 4.19 4.14.1 Procedure for obtaining THP for given h, V, BHP
hater 4 Estimation of wing loading and thrust loading - 8 Lecture 16 Toics 4.14.9 Selection of roeller diameter for a chosen alication Examle 4.19 4.14.1 Procedure for obtaining THP for given h, V, BHP
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering
 4. Basic Fluid (Aero) Dynamics Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Here, we will try and look at a few basic ideas from the complicated field of fluid dynamics. The general area includes studies of incompressible,
4. Basic Fluid (Aero) Dynamics Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Here, we will try and look at a few basic ideas from the complicated field of fluid dynamics. The general area includes studies of incompressible,
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT A: Fundamental Concepts
 AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT A: Fundamental Concets ROAD MAP... A-1: Engineering Fundamentals Reiew A-: Standard Atmoshere A-3: Goerning Equations of Aerodynamics A-4: Airseed Measurements A-5: Aerodynamic
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT A: Fundamental Concets ROAD MAP... A-1: Engineering Fundamentals Reiew A-: Standard Atmoshere A-3: Goerning Equations of Aerodynamics A-4: Airseed Measurements A-5: Aerodynamic
Airfoils and Wings. Eugene M. Cliff
 Airfoils and Wings Eugene M. Cliff 1 Introduction The primary purpose of these notes is to supplement the text material related to aerodynamic forces. We are mainly interested in the forces on wings and
Airfoils and Wings Eugene M. Cliff 1 Introduction The primary purpose of these notes is to supplement the text material related to aerodynamic forces. We are mainly interested in the forces on wings and
Chapter 3 Weight estimation - 2 Lecture 7 Topics
 Chater-3 Chater 3 eight estimation - 2 ecture 7 Toics 3.5 Estimation o uel raction ( / 0 ) 3.5.1 Mission roile 3.5.2 eight ractions or various segments o mission 3.5.3 Fuel raction or warm u, taxing and
Chater-3 Chater 3 eight estimation - 2 ecture 7 Toics 3.5 Estimation o uel raction ( / 0 ) 3.5.1 Mission roile 3.5.2 eight ractions or various segments o mission 3.5.3 Fuel raction or warm u, taxing and
Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters 2 Lecture 20 Topics
 Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters Lecture 0 Topics 5..4 Effects of geometric parameters, Reynolds number and roughness on aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils 5..5 Choice of airfoil
Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters Lecture 0 Topics 5..4 Effects of geometric parameters, Reynolds number and roughness on aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils 5..5 Choice of airfoil
MAE SUMMER 2015 HOMEWORK 1 SOLUTION
 MAE 04 - SUMMER 205 HOMEWORK SOLUTION Problem :. Plot the drag coefficient, c D, the aerodynamic efficiency, AE, and the center of pressure, x cp, of the airplane as a function of the angle of attack.
MAE 04 - SUMMER 205 HOMEWORK SOLUTION Problem :. Plot the drag coefficient, c D, the aerodynamic efficiency, AE, and the center of pressure, x cp, of the airplane as a function of the angle of attack.
Definitions. Temperature: Property of the atmosphere (τ). Function of altitude. Pressure: Property of the atmosphere (p). Function of altitude.
 Definitions Chapter 3 Standard atmosphere: A model of the atmosphere based on the aerostatic equation, the perfect gas law, an assumed temperature distribution, and standard sea level conditions. Temperature:
Definitions Chapter 3 Standard atmosphere: A model of the atmosphere based on the aerostatic equation, the perfect gas law, an assumed temperature distribution, and standard sea level conditions. Temperature:
Hypersonic flow: introduction
 Hyersonic flow: introduction Van Dyke: Hyersonic flow is flow ast a body at high ach number, where nonlinearity is an essential feature of the flow. Also understood, for thin bodies, that if is the thickness-to-chord
Hyersonic flow: introduction Van Dyke: Hyersonic flow is flow ast a body at high ach number, where nonlinearity is an essential feature of the flow. Also understood, for thin bodies, that if is the thickness-to-chord
Thin airfoil theory. Chapter Compressible potential flow The full potential equation
 hapter 4 Thin airfoil theory 4. ompressible potential flow 4.. The full potential equation In compressible flow, both the lift and drag of a thin airfoil can be determined to a reasonable level of accuracy
hapter 4 Thin airfoil theory 4. ompressible potential flow 4.. The full potential equation In compressible flow, both the lift and drag of a thin airfoil can be determined to a reasonable level of accuracy
AIRFRAME NOISE MODELING APPROPRIATE FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION
 AIRFRAME NOISE MODELING APPROPRIATE FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION AIAA-2004-0689 Serhat Hosder, Joseph A. Schetz, Bernard Grossman and William H. Mason Virginia Tech Work sponsored by NASA
AIRFRAME NOISE MODELING APPROPRIATE FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION AIAA-2004-0689 Serhat Hosder, Joseph A. Schetz, Bernard Grossman and William H. Mason Virginia Tech Work sponsored by NASA
High Speed Aerodynamics. Copyright 2009 Narayanan Komerath
 Welcome to High Speed Aerodynamics 1 Lift, drag and pitching moment? Linearized Potential Flow Transformations Compressible Boundary Layer WHAT IS HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS? Airfoil section? Thin airfoil
Welcome to High Speed Aerodynamics 1 Lift, drag and pitching moment? Linearized Potential Flow Transformations Compressible Boundary Layer WHAT IS HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS? Airfoil section? Thin airfoil
Continuity Equation for Compressible Flow
 Continuity Equation for Compressible Flow Velocity potential irrotational steady compressible Momentum (Euler) Equation for Compressible Flow Euler's equation isentropic velocity potential equation for
Continuity Equation for Compressible Flow Velocity potential irrotational steady compressible Momentum (Euler) Equation for Compressible Flow Euler's equation isentropic velocity potential equation for
Flight Vehicle Terminology
 Flight Vehicle Terminology 1.0 Axes Systems There are 3 axes systems which can be used in Aeronautics, Aerodynamics & Flight Mechanics: Ground Axes G(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) Body Axes G(x, y, z) Aerodynamic Axes
Flight Vehicle Terminology 1.0 Axes Systems There are 3 axes systems which can be used in Aeronautics, Aerodynamics & Flight Mechanics: Ground Axes G(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) Body Axes G(x, y, z) Aerodynamic Axes
Given a stream function for a cylinder in a uniform flow with circulation: a) Sketch the flow pattern in terms of streamlines.
 Question Given a stream function for a cylinder in a uniform flow with circulation: R Γ r ψ = U r sinθ + ln r π R a) Sketch the flow pattern in terms of streamlines. b) Derive an expression for the angular
Question Given a stream function for a cylinder in a uniform flow with circulation: R Γ r ψ = U r sinθ + ln r π R a) Sketch the flow pattern in terms of streamlines. b) Derive an expression for the angular
Air Loads. Airfoil Geometry. Upper surface. Lower surface
 AE1 Jha Loads-1 Air Loads Airfoil Geometry z LE circle (radius) Chord line Upper surface thickness Zt camber Zc Zl Zu Lower surface TE thickness Camber line line joining the midpoints between upper and
AE1 Jha Loads-1 Air Loads Airfoil Geometry z LE circle (radius) Chord line Upper surface thickness Zt camber Zc Zl Zu Lower surface TE thickness Camber line line joining the midpoints between upper and
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : LOW SPEED AERODYNAMICS Course Code : AAE004 Regulation : IARE
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : LOW SPEED AERODYNAMICS Course Code : AAE004 Regulation : IARE
Consider a wing of finite span with an elliptic circulation distribution:
 Question 1 (a) onsider a wing of finite span with an elliptic circulation distribution: Γ( y) Γo y + b = 1, - s y s where s=b/ denotes the wing semi-span. Use this equation, in conjunction with the Kutta-Joukowsky
Question 1 (a) onsider a wing of finite span with an elliptic circulation distribution: Γ( y) Γo y + b = 1, - s y s where s=b/ denotes the wing semi-span. Use this equation, in conjunction with the Kutta-Joukowsky
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering
 Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Lecture slides Challenge the future 3-0-0 Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Aerodynamics 5 & 6 Prof. H. Bijl ir. N. Timmer Delft University of Technology 5. Compressibility
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Lecture slides Challenge the future 3-0-0 Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Aerodynamics 5 & 6 Prof. H. Bijl ir. N. Timmer Delft University of Technology 5. Compressibility
SPC Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30
 SPC 307 - Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30 1. The maximum velocity at which an aircraft can cruise occurs when the thrust available with the engines operating with the
SPC 307 - Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30 1. The maximum velocity at which an aircraft can cruise occurs when the thrust available with the engines operating with the
Given the water behaves as shown above, which direction will the cylinder rotate?
 water stream fixed but free to rotate Given the water behaves as shown above, which direction will the cylinder rotate? ) Clockwise 2) Counter-clockwise 3) Not enough information F y U 0 U F x V=0 V=0
water stream fixed but free to rotate Given the water behaves as shown above, which direction will the cylinder rotate? ) Clockwise 2) Counter-clockwise 3) Not enough information F y U 0 U F x V=0 V=0
Incompressible Flow Over Airfoils
 Chapter 7 Incompressible Flow Over Airfoils Aerodynamics of wings: -D sectional characteristics of the airfoil; Finite wing characteristics (How to relate -D characteristics to 3-D characteristics) How
Chapter 7 Incompressible Flow Over Airfoils Aerodynamics of wings: -D sectional characteristics of the airfoil; Finite wing characteristics (How to relate -D characteristics to 3-D characteristics) How
The polar for uncambered and cambered airfoils. The angel of attack α
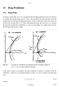 13-1 13 Drag Prediction 13.1 Drag Polar In Section under Step 14 it was a requirement that the flight performance has to be checked to complete the aircraft design process. This is only possible if the
13-1 13 Drag Prediction 13.1 Drag Polar In Section under Step 14 it was a requirement that the flight performance has to be checked to complete the aircraft design process. This is only possible if the
for what specific application did Henri Pitot develop the Pitot tube? what was the name of NACA s (now NASA) first research laboratory?
 1. 5% short answers for what specific application did Henri Pitot develop the Pitot tube? what was the name of NACA s (now NASA) first research laboratory? in what country (per Anderson) was the first
1. 5% short answers for what specific application did Henri Pitot develop the Pitot tube? what was the name of NACA s (now NASA) first research laboratory? in what country (per Anderson) was the first
Random Problems. Problem 1 (30 pts)
 Random Problems Problem (3 pts) An untwisted wing with an elliptical planform has an aspect ratio of 6 and a span of m. The wing loading (defined as the lift per unit area of the wing) is 9N/m when flying
Random Problems Problem (3 pts) An untwisted wing with an elliptical planform has an aspect ratio of 6 and a span of m. The wing loading (defined as the lift per unit area of the wing) is 9N/m when flying
Simplifications to Conservation Equations
 Chater 5 Simlifications to Conservation Equations 5.1 Steady Flow If fluid roerties at a oint in a field do not change with time, then they are a function of sace only. They are reresented by: ϕ = ϕq 1,
Chater 5 Simlifications to Conservation Equations 5.1 Steady Flow If fluid roerties at a oint in a field do not change with time, then they are a function of sace only. They are reresented by: ϕ = ϕq 1,
MODELING OF UNSTEADY AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTCS OF DELTA WINGS.
 IAS00 ONGRESS MODEING OF UNSTEADY AERODYNAMI HARATERISTS OF DETA WINGS. Jouannet hristoher, rus Petter inköings Uniersity eywords: Delta wings, Unsteady, Modeling, Preliminary design, Aerodynamic coefficient.
IAS00 ONGRESS MODEING OF UNSTEADY AERODYNAMI HARATERISTS OF DETA WINGS. Jouannet hristoher, rus Petter inköings Uniersity eywords: Delta wings, Unsteady, Modeling, Preliminary design, Aerodynamic coefficient.
On Optimization of Power Coefficient of HAWT
 Journal of Power and Energy Engineering, 14,, 198- Published Online Aril 14 in Scies htt://wwwscirorg/journal/jee htt://dxdoiorg/1436/jee1448 On Otimization of Power Coefficient of HAWT Marat Z Dosaev
Journal of Power and Energy Engineering, 14,, 198- Published Online Aril 14 in Scies htt://wwwscirorg/journal/jee htt://dxdoiorg/1436/jee1448 On Otimization of Power Coefficient of HAWT Marat Z Dosaev
df da df = force on one side of da due to pressure
 I. Review of Fundamental Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 1. 1 Some fundamental aerodynamic variables htt://en.wikiedia.org/wiki/hurricane_ivan_(2004) 1) Pressure: the normal force er unit area exerted
I. Review of Fundamental Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 1. 1 Some fundamental aerodynamic variables htt://en.wikiedia.org/wiki/hurricane_ivan_(2004) 1) Pressure: the normal force er unit area exerted
Lifting Airfoils in Incompressible Irrotational Flow. AA210b Lecture 3 January 13, AA210b - Fundamentals of Compressible Flow II 1
 Lifting Airfoils in Incompressible Irrotational Flow AA21b Lecture 3 January 13, 28 AA21b - Fundamentals of Compressible Flow II 1 Governing Equations For an incompressible fluid, the continuity equation
Lifting Airfoils in Incompressible Irrotational Flow AA21b Lecture 3 January 13, 28 AA21b - Fundamentals of Compressible Flow II 1 Governing Equations For an incompressible fluid, the continuity equation
AE 2020: Low Speed Aerodynamics. I. Introductory Remarks Read chapter 1 of Fundamentals of Aerodynamics by John D. Anderson
 AE 2020: Low Speed Aerodynamics I. Introductory Remarks Read chapter 1 of Fundamentals of Aerodynamics by John D. Anderson Text Book Anderson, Fundamentals of Aerodynamics, 4th Edition, McGraw-Hill, Inc.
AE 2020: Low Speed Aerodynamics I. Introductory Remarks Read chapter 1 of Fundamentals of Aerodynamics by John D. Anderson Text Book Anderson, Fundamentals of Aerodynamics, 4th Edition, McGraw-Hill, Inc.
Aerodynamics. High-Lift Devices
 High-Lift Devices Devices to increase the lift coefficient by geometry changes (camber and/or chord) and/or boundary-layer control (avoid flow separation - Flaps, trailing edge devices - Slats, leading
High-Lift Devices Devices to increase the lift coefficient by geometry changes (camber and/or chord) and/or boundary-layer control (avoid flow separation - Flaps, trailing edge devices - Slats, leading
The E80 Wind Tunnel Experiment the experience will blow you away. by Professor Duron Spring 2012
 The E80 Wind Tunnel Experiment the experience will blow you away by Professor Duron Spring 2012 Objectives To familiarize the student with the basic operation and instrumentation of the HMC wind tunnel
The E80 Wind Tunnel Experiment the experience will blow you away by Professor Duron Spring 2012 Objectives To familiarize the student with the basic operation and instrumentation of the HMC wind tunnel
Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Mecânica Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 2012/13
 Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Mecânica Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 212/13 Exam 2ª época, 2 February 213 Name : Time : 8: Number: Duration : 3 hours 1 st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed 2 nd Part :
Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Mecânica Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 212/13 Exam 2ª época, 2 February 213 Name : Time : 8: Number: Duration : 3 hours 1 st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed 2 nd Part :
University of California at Berkeley Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 163 ENGINEERING AERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM, 13TH DECEMBER 2005
 University of California at Berkeley Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 163 ENGINEERING AERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM, 13TH DECEMBER 2005 Answer both questions. Question 1 is worth 30 marks and question
University of California at Berkeley Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 163 ENGINEERING AERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM, 13TH DECEMBER 2005 Answer both questions. Question 1 is worth 30 marks and question
FUNDAMENTALS OF AERODYNAMICS
 *A \ FUNDAMENTALS OF AERODYNAMICS Second Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Professor of Aerospace Engineering University of Maryland H ' McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas
*A \ FUNDAMENTALS OF AERODYNAMICS Second Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Professor of Aerospace Engineering University of Maryland H ' McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas
Blade Element Momentum Theory
 Blade Element Theory has a number of assumptions. The biggest (and worst) assumption is that the inflow is uniform. In reality, the inflow is non-uniform. It may be shown that uniform inflow yields the
Blade Element Theory has a number of assumptions. The biggest (and worst) assumption is that the inflow is uniform. In reality, the inflow is non-uniform. It may be shown that uniform inflow yields the
Fluid Mechanics Prof. T. I. Eldho Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Fluid Mechanics Prof. T. I. Eldho Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 35 Boundary Layer Theory and Applications Welcome back to the video course on fluid
Fluid Mechanics Prof. T. I. Eldho Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 35 Boundary Layer Theory and Applications Welcome back to the video course on fluid
1. Fluid Dynamics Around Airfoils
 1. Fluid Dynamics Around Airfoils Two-dimensional flow around a streamlined shape Foces on an airfoil Distribution of pressue coefficient over an airfoil The variation of the lift coefficient with the
1. Fluid Dynamics Around Airfoils Two-dimensional flow around a streamlined shape Foces on an airfoil Distribution of pressue coefficient over an airfoil The variation of the lift coefficient with the
AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics. Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2017
 AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2017 Lift curve 2 Lift curve slope 3 Subsonic lift curve slope C Lα = 2 + 4 + AR2 β 2 η
AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2017 Lift curve 2 Lift curve slope 3 Subsonic lift curve slope C Lα = 2 + 4 + AR2 β 2 η
High speed wind tunnels 2.0 Definition of high speed. 2.1 Types of high speed wind tunnels
 Module Lectures 6 to 1 High Seed Wind Tunnels Keywords: Blow down wind tunnels, Indraft wind tunnels, suersonic wind tunnels, c-d nozzles, second throat diffuser, shocks, condensation in wind tunnels,
Module Lectures 6 to 1 High Seed Wind Tunnels Keywords: Blow down wind tunnels, Indraft wind tunnels, suersonic wind tunnels, c-d nozzles, second throat diffuser, shocks, condensation in wind tunnels,
Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics
 David G. Hull Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics With 125 Figures and 25 Tables y Springer Introduction to Airplane Flight Mechanics 1 1.1 Airframe Anatomy 2 1.2 Engine Anatomy 5 1.3 Equations of
David G. Hull Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics With 125 Figures and 25 Tables y Springer Introduction to Airplane Flight Mechanics 1 1.1 Airframe Anatomy 2 1.2 Engine Anatomy 5 1.3 Equations of
Notes on pressure coordinates Robert Lindsay Korty October 1, 2002
 Notes on ressure coordinates Robert Lindsay Korty October 1, 2002 Obviously, it makes no difference whether the quasi-geostrohic equations are hrased in height coordinates (where x, y,, t are the indeendent
Notes on ressure coordinates Robert Lindsay Korty October 1, 2002 Obviously, it makes no difference whether the quasi-geostrohic equations are hrased in height coordinates (where x, y,, t are the indeendent
AAE 251 Formulas. Standard Atmosphere. Compiled Fall 2016 by Nicholas D. Turo-Shields, student at Purdue University. Gradient Layer.
 AAE 51 Formulas Compiled Fall 016 by Nicholas D. Turo-Shields, student at Purdue University Standard Atmosphere p 0 = 1.0135 10 5 Pascals ρ 0 = 1.5 kg m 3 R = 87 J kg K γ = 1.4 for air p = ρrt ; Equation
AAE 51 Formulas Compiled Fall 016 by Nicholas D. Turo-Shields, student at Purdue University Standard Atmosphere p 0 = 1.0135 10 5 Pascals ρ 0 = 1.5 kg m 3 R = 87 J kg K γ = 1.4 for air p = ρrt ; Equation
Flight and Orbital Mechanics
 Flight and Orbital Mechanics Lecture slides Challenge the future 1 Flight and orbital mechanics Flight Mechanics practice questions Dr. ir. Mark Voskuijl 20-11-2013 Delft University of Technology Challenge
Flight and Orbital Mechanics Lecture slides Challenge the future 1 Flight and orbital mechanics Flight Mechanics practice questions Dr. ir. Mark Voskuijl 20-11-2013 Delft University of Technology Challenge
Chapter 5 Lecture 19. Performance analysis I Steady level flight 3. Topics. Chapter-5
 Chapter 5 Lecture 19 Performance analysis I Steady level flight 3 Topics 5.8 Influence of level flight analysis on airplane design 5.9 Steady level flight performance with a given engine 5.10 Steady level
Chapter 5 Lecture 19 Performance analysis I Steady level flight 3 Topics 5.8 Influence of level flight analysis on airplane design 5.9 Steady level flight performance with a given engine 5.10 Steady level
Drag Computation (1)
 Drag Computation (1) Why drag so concerned Its effects on aircraft performances On the Concorde, one count drag increase ( C D =.0001) requires two passengers, out of the 90 ~ 100 passenger capacity, be
Drag Computation (1) Why drag so concerned Its effects on aircraft performances On the Concorde, one count drag increase ( C D =.0001) requires two passengers, out of the 90 ~ 100 passenger capacity, be
A Study of Transonic Flow and Airfoils. Presented by: Huiliang Lui 30 th April 2007
 A Study of Transonic Flow and Airfoils Presented by: Huiliang Lui 3 th April 7 Contents Background Aims Theory Conservation Laws Irrotational Flow Self-Similarity Characteristics Numerical Modeling Conclusion
A Study of Transonic Flow and Airfoils Presented by: Huiliang Lui 3 th April 7 Contents Background Aims Theory Conservation Laws Irrotational Flow Self-Similarity Characteristics Numerical Modeling Conclusion
Analyses of Diamond - Shaped and Circular Arc Airfoils in Supersonic Wind Tunnel Airflows
 Analyses of Diamond - Shaped and Circular Arc Airfoils in Supersonic Wind Tunnel Airflows Modo U. P, Chukwuneke J. L, Omenyi Sam 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka,
Analyses of Diamond - Shaped and Circular Arc Airfoils in Supersonic Wind Tunnel Airflows Modo U. P, Chukwuneke J. L, Omenyi Sam 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka,
Stability and Control Some Characteristics of Lifting Surfaces, and Pitch-Moments
 Stability and Control Some Characteristics of Lifting Surfaces, and Pitch-Moments The lifting surfaces of a vehicle generally include the wings, the horizontal and vertical tail, and other surfaces such
Stability and Control Some Characteristics of Lifting Surfaces, and Pitch-Moments The lifting surfaces of a vehicle generally include the wings, the horizontal and vertical tail, and other surfaces such
Steady, 1-d, constant area, adiabatic flow with no external work but with friction Conserved quantities
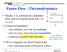 School of Aerosace Engineering Stead, -d, constant area, adiabatic flow with no external work but with friction Conserved quantities since adiabatic, no work: h o constant since Aconst: mass fluxρvconstant
School of Aerosace Engineering Stead, -d, constant area, adiabatic flow with no external work but with friction Conserved quantities since adiabatic, no work: h o constant since Aconst: mass fluxρvconstant
Lab Reports Due on Monday, 11/24/2014
 AE 3610 Aerodynamics I Wind Tunnel Laboratory: Lab 4 - Pressure distribution on the surface of a rotating circular cylinder Lab Reports Due on Monday, 11/24/2014 Objective In this lab, students will be
AE 3610 Aerodynamics I Wind Tunnel Laboratory: Lab 4 - Pressure distribution on the surface of a rotating circular cylinder Lab Reports Due on Monday, 11/24/2014 Objective In this lab, students will be
Introduction to Atmospheric Flight. Dr. Guven Aerospace Engineer (P.hD)
 Introduction to Atmospheric Flight Dr. Guven Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) What is Atmospheric Flight? There are many different ways in which Aerospace engineering is associated with atmospheric flight concepts.
Introduction to Atmospheric Flight Dr. Guven Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) What is Atmospheric Flight? There are many different ways in which Aerospace engineering is associated with atmospheric flight concepts.
Aerodynamics SYST 460/560. George Mason University Fall 2008 CENTER FOR AIR TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS RESEARCH. Copyright Lance Sherry (2008)
 Aerodynamics SYST 460/560 George Mason University Fall 2008 1 CENTER FOR AIR TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS RESEARCH Copyright Lance Sherry (2008) Ambient & Static Pressure Ambient Pressure Static Pressure 2 Ambient
Aerodynamics SYST 460/560 George Mason University Fall 2008 1 CENTER FOR AIR TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS RESEARCH Copyright Lance Sherry (2008) Ambient & Static Pressure Ambient Pressure Static Pressure 2 Ambient
Masters in Mechanical Engineering Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 2015/16
 Masters in Mechanical Engineering Aerodynamics st Semester 05/6 Exam st season, 8 January 06 Name : Time : 8:30 Number: Duration : 3 hours st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed nd Part : Textbooks allowed
Masters in Mechanical Engineering Aerodynamics st Semester 05/6 Exam st season, 8 January 06 Name : Time : 8:30 Number: Duration : 3 hours st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed nd Part : Textbooks allowed
Lifting-Line Predictions for Induced Drag and Lift in Ground Effect
 Utah State University gitalommons@usu Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Faculty Publications Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering 8-1-013 ifting-ine Predictions for Induced Drag and ift in Ground Effect
Utah State University gitalommons@usu Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Faculty Publications Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering 8-1-013 ifting-ine Predictions for Induced Drag and ift in Ground Effect
Aeroelasticity. Lecture 9: Supersonic Aeroelasticity. G. Dimitriadis. AERO0032-1, Aeroelasticity and Experimental Aerodynamics, Lecture 9
 Aeroelasticity Lecture 9: Supersonic Aeroelasticity G. Dimitriadis AERO0032-1, Aeroelasticity and Experimental Aerodynamics, Lecture 9 1 Introduction All the material presented up to now concerned incompressible
Aeroelasticity Lecture 9: Supersonic Aeroelasticity G. Dimitriadis AERO0032-1, Aeroelasticity and Experimental Aerodynamics, Lecture 9 1 Introduction All the material presented up to now concerned incompressible
AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics. Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2015
 AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2015 Lift curve 2 Lift curve slope 3 Subsonic lift curve slope C Lα = 2 + 4 + AR2 β 2 η
AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2015 Lift curve 2 Lift curve slope 3 Subsonic lift curve slope C Lα = 2 + 4 + AR2 β 2 η
Syllabus for AE3610, Aerodynamics I
 Syllabus for AE3610, Aerodynamics I Current Catalog Data: AE 3610 Aerodynamics I Credit: 4 hours A study of incompressible aerodynamics of flight vehicles with emphasis on combined application of theory
Syllabus for AE3610, Aerodynamics I Current Catalog Data: AE 3610 Aerodynamics I Credit: 4 hours A study of incompressible aerodynamics of flight vehicles with emphasis on combined application of theory
Theory of turbomachinery. Chapter 1
 Theory of turbomachinery Chater Introduction: Basic Princiles Take your choice of those that can best aid your action. (Shakeseare, Coriolanus) Introduction Definition Turbomachinery describes machines
Theory of turbomachinery Chater Introduction: Basic Princiles Take your choice of those that can best aid your action. (Shakeseare, Coriolanus) Introduction Definition Turbomachinery describes machines
Compressible Flow Introduction. Afshin J. Ghajar
 36 Comressible Flow Afshin J. Ghajar Oklahoma State University 36. Introduction...36-36. he Mach Number and Flow Regimes...36-36.3 Ideal Gas Relations...36-36.4 Isentroic Flow Relations...36-4 36.5 Stagnation
36 Comressible Flow Afshin J. Ghajar Oklahoma State University 36. Introduction...36-36. he Mach Number and Flow Regimes...36-36.3 Ideal Gas Relations...36-36.4 Isentroic Flow Relations...36-4 36.5 Stagnation
Study of Preliminary Configuration Design of F-35 using simple CFD
 Study of Preliminary Configuration Design of F-35 using simple CFD http://www.aerospaceweb.org/aircraft/research/x35/pics.shtml David Hall Sangeon Chun David Andrews Center of Gravity Estimation.5873 Conventional
Study of Preliminary Configuration Design of F-35 using simple CFD http://www.aerospaceweb.org/aircraft/research/x35/pics.shtml David Hall Sangeon Chun David Andrews Center of Gravity Estimation.5873 Conventional
Introduction to Flight Dynamics
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Flight Dynamics Flight dynamics deals principally with the response of aerospace vehicles to perturbations in their flight environments and to control inputs. In order to understand
Chapter 1 Introduction to Flight Dynamics Flight dynamics deals principally with the response of aerospace vehicles to perturbations in their flight environments and to control inputs. In order to understand
Module3: Waves in Supersonic Flow Lecture14: Waves in Supersonic Flow (Contd.)
 1 Module3: Waves in Supersonic Flow Lecture14: Waves in Supersonic Flow (Contd.) Mach Reflection: The appearance of subsonic regions in the flow complicates the problem. The complications are also encountered
1 Module3: Waves in Supersonic Flow Lecture14: Waves in Supersonic Flow (Contd.) Mach Reflection: The appearance of subsonic regions in the flow complicates the problem. The complications are also encountered
Flight Dynamics and Control. Lecture 3: Longitudinal stability Derivatives G. Dimitriadis University of Liege
 Flight Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Longitudinal stability Derivatives G. Dimitriadis University of Liege Previously on AERO0003-1 We developed linearized equations of motion Longitudinal direction
Flight Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Longitudinal stability Derivatives G. Dimitriadis University of Liege Previously on AERO0003-1 We developed linearized equations of motion Longitudinal direction
Introduction to Aeronautics
 Introduction to Aeronautics ARO 101 Sections 03 & 04 Sep 30, 2015 thru Dec 9, 2015 Instructor: Raymond A. Hudson Week #8 Lecture Material 1 Topics For Week #8 Airfoil Geometry & Nomenclature Identify the
Introduction to Aeronautics ARO 101 Sections 03 & 04 Sep 30, 2015 thru Dec 9, 2015 Instructor: Raymond A. Hudson Week #8 Lecture Material 1 Topics For Week #8 Airfoil Geometry & Nomenclature Identify the
Chapter 5 Performance analysis I Steady level flight (Lectures 17 to 20) Keywords: Steady level flight equations of motion, minimum power required,
 Chapter 5 Performance analysis I Steady level flight (Lectures 17 to 20) Keywords: Steady level flight equations of motion, minimum power required, minimum thrust required, minimum speed, maximum speed;
Chapter 5 Performance analysis I Steady level flight (Lectures 17 to 20) Keywords: Steady level flight equations of motion, minimum power required, minimum thrust required, minimum speed, maximum speed;
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering
 Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Lecture slides Challenge the future 1 Introduction Aerospace Engineering Flight Mechanics Dr. ir. Mark Voskuijl 15-12-2012 Delft University of Technology Challenge
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Lecture slides Challenge the future 1 Introduction Aerospace Engineering Flight Mechanics Dr. ir. Mark Voskuijl 15-12-2012 Delft University of Technology Challenge
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering
 Introduction to Aerospace Engineering 5. Aircraft Performance 5.1 Equilibrium Flight In order to discuss performance, stability, and control, we must first establish the concept of equilibrium flight.
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering 5. Aircraft Performance 5.1 Equilibrium Flight In order to discuss performance, stability, and control, we must first establish the concept of equilibrium flight.
APPENDIX C DRAG POLAR, STABILITY DERIVATIVES AND CHARACTERISTIC ROOTS OF A JET AIRPLANE (Lectures 37 to 40)
 APPENDIX C DRAG POLAR, STABILITY DERIVATIVES AND CHARACTERISTIC ROOTS OF A JET AIRPLANE (Lectures 37 to 40 E.G. TULAPURKARA YASHKUMAR A. VENKATTRAMAN REPORT NO: AE TR 2007-3 APRIL 2007 (REVISED NOVEMBER
APPENDIX C DRAG POLAR, STABILITY DERIVATIVES AND CHARACTERISTIC ROOTS OF A JET AIRPLANE (Lectures 37 to 40 E.G. TULAPURKARA YASHKUMAR A. VENKATTRAMAN REPORT NO: AE TR 2007-3 APRIL 2007 (REVISED NOVEMBER
Continuum Mechanics Lecture 7 Theory of 2D potential flows
 Continuum Mechanics ecture 7 Theory of 2D potential flows Prof. http://www.itp.uzh.ch/~teyssier Outline - velocity potential and stream function - complex potential - elementary solutions - flow past a
Continuum Mechanics ecture 7 Theory of 2D potential flows Prof. http://www.itp.uzh.ch/~teyssier Outline - velocity potential and stream function - complex potential - elementary solutions - flow past a
Aircraft Design I Tail loads
 Horizontal tail loads Aircraft Design I Tail loads What is the source of loads? How to compute it? What cases should be taken under consideration? Tail small wing but strongly deflected Linearized pressure
Horizontal tail loads Aircraft Design I Tail loads What is the source of loads? How to compute it? What cases should be taken under consideration? Tail small wing but strongly deflected Linearized pressure
An-Najah National University Civil Engineering Departemnt. Fluid Mechanics. Chapter [2] Fluid Statics
![An-Najah National University Civil Engineering Departemnt. Fluid Mechanics. Chapter [2] Fluid Statics An-Najah National University Civil Engineering Departemnt. Fluid Mechanics. Chapter [2] Fluid Statics](/thumbs/89/101171273.jpg) An-Najah National University Civil Engineering Deartemnt Fluid Mechanics Chater [2] Fluid Statics 1 Fluid Statics Problems Fluid statics refers to the study of fluids at rest or moving in such a manner
An-Najah National University Civil Engineering Deartemnt Fluid Mechanics Chater [2] Fluid Statics 1 Fluid Statics Problems Fluid statics refers to the study of fluids at rest or moving in such a manner
Supersonic Aerodynamics. Methods and Applications
 Supersonic Aerodynamics Methods and Applications Outline Introduction to Supersonic Flow Governing Equations Numerical Methods Aerodynamic Design Applications Introduction to Supersonic Flow What does
Supersonic Aerodynamics Methods and Applications Outline Introduction to Supersonic Flow Governing Equations Numerical Methods Aerodynamic Design Applications Introduction to Supersonic Flow What does
Fluids Applications of Fluid Dynamics
 Fluids Applications of Fluid Dynamics Lana Sheridan De Anza College April 16, 2018 Last time fluid dynamics the continuity equation Bernoulli s equation Overview Torricelli s law applications of Bernoulli
Fluids Applications of Fluid Dynamics Lana Sheridan De Anza College April 16, 2018 Last time fluid dynamics the continuity equation Bernoulli s equation Overview Torricelli s law applications of Bernoulli
AE Stability and Control of Aerospace Vehicles
 AE 430 - Stability and ontrol of Aerospace Vehicles Static/Dynamic Stability Longitudinal Static Stability Static Stability We begin ith the concept of Equilibrium (Trim). Equilibrium is a state of an
AE 430 - Stability and ontrol of Aerospace Vehicles Static/Dynamic Stability Longitudinal Static Stability Static Stability We begin ith the concept of Equilibrium (Trim). Equilibrium is a state of an
Flight and Orbital Mechanics
 Flight and Orbital Mechanics Lecture slides Challenge the future 1 Flight and Orbital Mechanics Lecture hours 3, 4 Minimum time to climb Mark Voskuijl Semester 1-2012 Delft University of Technology Challenge
Flight and Orbital Mechanics Lecture slides Challenge the future 1 Flight and Orbital Mechanics Lecture hours 3, 4 Minimum time to climb Mark Voskuijl Semester 1-2012 Delft University of Technology Challenge
Module 4 : Lecture 1 COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS (Fundamental Aspects: Part - I)
 Module 4 : Lecture COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS (Fundamental Asects: Part - I) Overview In general, the liquids and gases are the states of a matter that comes under the same category as fluids. The incomressible
Module 4 : Lecture COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS (Fundamental Asects: Part - I) Overview In general, the liquids and gases are the states of a matter that comes under the same category as fluids. The incomressible
Induced Drag and High-Speed Aerodynamics Robert Stengel, Aircraft Flight Dynamics, MAE 331, 2018
 Induced Drag and High-Speed Aerodynamics Robert Stengel, Aircraft Flight Dynamics, MAE 331, 2018 Drag-due-to-lift and effects of wing planform Effect of angle of attack on lift and drag coefficients Mach
Induced Drag and High-Speed Aerodynamics Robert Stengel, Aircraft Flight Dynamics, MAE 331, 2018 Drag-due-to-lift and effects of wing planform Effect of angle of attack on lift and drag coefficients Mach
Week 8 lectures. ρ t +u ρ+ρ u = 0. where µ and λ are viscosity and second viscosity coefficients, respectively and S is the strain tensor:
 Week 8 lectures. Equations for motion of fluid without incomressible assumtions Recall from week notes, the equations for conservation of mass and momentum, derived generally without any incomressibility
Week 8 lectures. Equations for motion of fluid without incomressible assumtions Recall from week notes, the equations for conservation of mass and momentum, derived generally without any incomressibility
Lecture 7 Boundary Layer
 SPC 307 Introduction to Aerodynamics Lecture 7 Boundary Layer April 9, 2017 Sep. 18, 2016 1 Character of the steady, viscous flow past a flat plate parallel to the upstream velocity Inertia force = ma
SPC 307 Introduction to Aerodynamics Lecture 7 Boundary Layer April 9, 2017 Sep. 18, 2016 1 Character of the steady, viscous flow past a flat plate parallel to the upstream velocity Inertia force = ma
PEMP ACD2505. Finite Wing Theory. M.S. Ramaiah School of Advanced Studies, Bengaluru
 Finite Wing Theory Session delivered by: Prof. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives -- At the end of this session the delegate would have understood The finite wing theory Lifting line theory Elliptic
Finite Wing Theory Session delivered by: Prof. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives -- At the end of this session the delegate would have understood The finite wing theory Lifting line theory Elliptic
except assume the parachute has diameter of 3.5 meters and calculate how long it takes to stop. (Must solve differential equation)
 Homework 5 Due date: Thursday, Mar. 3 hapter 7 Problems 1. 7.88. 7.9 except assume the parachute has diameter of 3.5 meters and calculate how long it takes to stop. (Must solve differential equation) 3.
Homework 5 Due date: Thursday, Mar. 3 hapter 7 Problems 1. 7.88. 7.9 except assume the parachute has diameter of 3.5 meters and calculate how long it takes to stop. (Must solve differential equation) 3.
6.1 According to Handbook of Chemistry and Physics the composition of air is
 6. Compressible flow 6.1 According to Handbook of Chemistry and Physics the composition of air is From this, compute the gas constant R for air. 6. The figure shows a, Pitot-static tube used for velocity
6. Compressible flow 6.1 According to Handbook of Chemistry and Physics the composition of air is From this, compute the gas constant R for air. 6. The figure shows a, Pitot-static tube used for velocity
Validation of Noise Footprint Calculation Model for a High Performance Military Aircraft
 Validation of Noise Footrint Calculation Model for a High Performance Military Aircraft Dr. Ernst Grigat, Airbus Defence and Sace GmbH 30 th May 2017 Contents The following questions (hoefully) will be
Validation of Noise Footrint Calculation Model for a High Performance Military Aircraft Dr. Ernst Grigat, Airbus Defence and Sace GmbH 30 th May 2017 Contents The following questions (hoefully) will be
Experimental Evaluation of Aerodynamics Characteristics of a Baseline Airfoil
 Research Paper American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-4, Issue-1, pp-91-96 www.ajer.org Open Access Experimental Evaluation of Aerodynamics Characteristics
Research Paper American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-4, Issue-1, pp-91-96 www.ajer.org Open Access Experimental Evaluation of Aerodynamics Characteristics
Drag (2) Induced Drag Friction Drag Form Drag Wave Drag
 Drag () Induced Drag Friction Drag Form Drag Wave Drag Outline Nomenclature and Concepts Farfield Drag Analysis Induced Drag Multiple Lifting Surfaces Zero Lift Drag :Friction and Form Drag Supersonic
Drag () Induced Drag Friction Drag Form Drag Wave Drag Outline Nomenclature and Concepts Farfield Drag Analysis Induced Drag Multiple Lifting Surfaces Zero Lift Drag :Friction and Form Drag Supersonic
Investigation potential flow about swept back wing using panel method
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENERGY AND ENVIRONMENT Volume 7, Issue 4, 2016 pp.317-326 Journal homepage: www.ijee.ieefoundation.org Investigation potential flow about swept back wing using panel method Wakkas
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENERGY AND ENVIRONMENT Volume 7, Issue 4, 2016 pp.317-326 Journal homepage: www.ijee.ieefoundation.org Investigation potential flow about swept back wing using panel method Wakkas
A SIMPLIFIED ANALYSIS OF NONLINEAR LONGITUDINAL DYNAMICS AND CONCEPTUAL CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN
 A SIMPLIFIED ANALYSIS OF NONLINEAR LONGITUDINAL DYNAMICS AND CONCEPTUAL CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN ROBBIE BUNGE 1. Introduction The longitudinal dynamics of fixed-wing aircraft are a case in which classical
A SIMPLIFIED ANALYSIS OF NONLINEAR LONGITUDINAL DYNAMICS AND CONCEPTUAL CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN ROBBIE BUNGE 1. Introduction The longitudinal dynamics of fixed-wing aircraft are a case in which classical
Fundamentals of Aerodynamics
 Fundamentals of Aerodynamics Fourth Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Curator of Aerodynamics National Air and Space Museum Smithsonian Institution and Professor Emeritus University of Maryland Me Graw Hill
Fundamentals of Aerodynamics Fourth Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Curator of Aerodynamics National Air and Space Museum Smithsonian Institution and Professor Emeritus University of Maryland Me Graw Hill
Copyright 2007 N. Komerath. Other rights may be specified with individual items. All rights reserved.
 Low Speed Aerodynamics Notes 5: Potential ti Flow Method Objective: Get a method to describe flow velocity fields and relate them to surface shapes consistently. Strategy: Describe the flow field as the
Low Speed Aerodynamics Notes 5: Potential ti Flow Method Objective: Get a method to describe flow velocity fields and relate them to surface shapes consistently. Strategy: Describe the flow field as the
Aeroelastic Wind Tunnel Testing of Very Flexible High-Aspect-Ratio Wings
 Aeroelastic Wind Tunnel Testing of Very Flexible High-Aspect-Ratio Wings Justin Jaworski Workshop on Recent Advances in Aeroelasticity, Experiment and Theory July 2, 2010 Problem and Scope High altitude
Aeroelastic Wind Tunnel Testing of Very Flexible High-Aspect-Ratio Wings Justin Jaworski Workshop on Recent Advances in Aeroelasticity, Experiment and Theory July 2, 2010 Problem and Scope High altitude
1. (20 pts total 2pts each) - Circle the most correct answer for the following questions.
 ME 50 Gas Dynamics Spring 009 Final Exam NME:. (0 pts total pts each) - Circle the most correct answer for the following questions. i. normal shock propagated into still air travels with a speed (a) equal
ME 50 Gas Dynamics Spring 009 Final Exam NME:. (0 pts total pts each) - Circle the most correct answer for the following questions. i. normal shock propagated into still air travels with a speed (a) equal
Fundamentals of Aerodynamits
 Fundamentals of Aerodynamits Fifth Edition in SI Units John D. Anderson, Jr. Curator of Aerodynamics National Air and Space Museum Smithsonian Institution and Professor Emeritus University of Maryland
Fundamentals of Aerodynamits Fifth Edition in SI Units John D. Anderson, Jr. Curator of Aerodynamics National Air and Space Museum Smithsonian Institution and Professor Emeritus University of Maryland
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale Tesi di Laurea Magistrale in Ingegneria Aerospaziale Improvement of a low-order panel method by far-field computation of induced
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale Tesi di Laurea Magistrale in Ingegneria Aerospaziale Improvement of a low-order panel method by far-field computation of induced
Numerical Simulation of Unsteady Aerodynamic Coefficients for Wing Moving Near Ground
 ISSN -6 International Journal of Advances in Computer Science and Technology (IJACST), Vol., No., Pages : -7 Special Issue of ICCEeT - Held during -5 November, Dubai Numerical Simulation of Unsteady Aerodynamic
ISSN -6 International Journal of Advances in Computer Science and Technology (IJACST), Vol., No., Pages : -7 Special Issue of ICCEeT - Held during -5 November, Dubai Numerical Simulation of Unsteady Aerodynamic
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Ideal Flow Theory & Basic Aerodynamics
 Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Ideal Flow Theory & Basic Aerodynamics Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI (after: D.J. ACHESON s Elementary Fluid Dynamics ) bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Ideal Flow Theory & Basic Aerodynamics Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI (after: D.J. ACHESON s Elementary Fluid Dynamics ) bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/
Flight and Orbital Mechanics. Exams
 1 Flight and Orbital Mechanics Exams Exam AE2104-11: Flight and Orbital Mechanics (23 January 2013, 09.00 12.00) Please put your name, student number and ALL YOUR INITIALS on your work. Answer all questions
1 Flight and Orbital Mechanics Exams Exam AE2104-11: Flight and Orbital Mechanics (23 January 2013, 09.00 12.00) Please put your name, student number and ALL YOUR INITIALS on your work. Answer all questions
