Drag Computation (1)
|
|
|
- Philomena Hensley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Drag Computation (1)
2 Why drag so concerned Its effects on aircraft performances On the Concorde, one count drag increase ( C D =.0001) requires two passengers, out of the 90 ~ 100 passenger capacity, be taken off the North Atlantic run. A drag decrease is equated to the decrease in aircraft weight required to carry a specified payload for the required distance. One advanced fighter study found the drag sensitivity in supersonic cruise was 90 lb/ct and 48 lb/ct for subsonic and transonic cruise.
3 Why drag so concerned For one executive business jet the range sensitivity is 17 miles/drag count. Advanced supersonic transports now being studied have range sensitivities of about 100 miles/drag count. Conclusion A minor changes in drag can be critical!
4 Why drag so concerned Its effects on the company The economic viability and future survival of an aircraft manufacturer depends on minimizing aerodynamic drag while maintaining good handling qualities to ensure flight safety and ride comfort. A company was willing to invest $750,000 for each count of drag reduction. Examples: Boeing 767, 777 Airbus A340
5 Why drag so concerned The designing for low drag and the ability to estimate drag is at the heart of aerodynamic design Initial drag estimates can dictate the selection of a specific configuration concept in comparison with other concepts early in the design phase. The drag projections have a huge effect on the projected configuration size and cost, and thus on the decision to proceed with the design.
6 Issues on Drag Drag cannot yet be predicted accurately with high confidence levels (especially for unusual configuration concepts) without extensive testing. No one is exactly sure what the ultimate possible drag level really is that can be achieved for a practical configuration. To this extent, aerodynamic designers are the dreamers of the engineering profession.
7 The efforts on drag estimation and reduction Conferences Aerodynamic Drag, AGARD CP-14, Aircraft Drag Prediction, AGARD-R-73, Drag Reduction Techniques, AGARD-R-787 AIAA CFD Drag Prediction workshop, 001 AIAA progress series book Thrust and Drag: Its Prediction and Verification, AIAA, New York, 1985.
8 Objective of this chapter To introduce the key concepts required to use computational aerodynamics to evaluate drag.
9 Outline Nomenclature and Concepts Farfield Drag Analysis Induced Drag Zero Lift Drag Friction and Form Drag Estimation Supersonic Wave Drag Trim Drag Current Issues for Drag Calculation Using CA
10 Some Different Ways to View Drag - Nomenclature and Concepts Simple Integration Approach Consider the distribution of forces over the surface. pressure force shear stress force due to the presence of viscosity An integration over the surface results in an estimate of the drag. This approach is known as a nearfield drag calculation.
11 Simple Integration Disadvantages This integration requires extreme precision remember that program PANEL did not predict exactly zero drag The results are difficult to interpret for aerodynamic analysis Exactly where is the drag coming from? Why does it exist, and how do you reduce it?
12 Fluid Mechanics: This viewpoint emphasizes the drag resulting from various fluid mechanics phenomena. This approach is important in conceiving a means to reduce drag. Providing a means of computing drag contributions in a systematic manner. friction drag form drag induced drag wave drag The term can be confusing!
13 The Terms on Drag Friction Drag Skin friction drag which depends mostly upon the wetted area. Form Drag ( Pressure Drag) Viscous separation drag which depends upon the location of the separation point on the body. Profile Drag ( Parasite Drag) Skin friction drag + Form drag Induced Drag Drag forces that are a strong function of lift Wave Drag The drag caused by the information of shocks at supersonic and high subsonic speeds.
14 Aerodynamics: This approach combines the fluid mechanics viewpoint with more practical considerations. Thinking in terms of contributions from a variety of aircraft features. The basic contributions from each component must be included. individual component contributions to drag base drag inlet drag with spillage boattail drag camber drag trim drag thrust-drag bookkeeping aeroelastic effects on drag
15 Performance: To calculate the performance of an airplane it is natural to define drag as the sum of the drag at zero lift and the drag due to lift. C D = C D 0 + C L πare Each term is a function of Mach number, Reynolds number (or altitude), and the particular geometric configuration (flap deflection, wing sweep, etc.). The value of the Oswald efficiency factor, E, is defined as a function of the lift coefficient and Mach number
16 Performance: To take into account the effect of wing camber and twist, drag polar become asymmetrical about the C L = 0 axis. C D = C D + C D + K( C 0 m m L C L )
17 A categorization of drag
18 Drag Term Again Pressure drag / Form drag Skin friction drag Wave drag Parasite drag Profile drag Independent of lift Additional profile drag due to lift ( should be small) Drag due to lift Due to lift generated vorticity shed into wake Additional profile drag due to lift Wave drag due to lift Zero lift drag Profile drag independent of lift Wave drag due to volume
19 A fluid mechanics refinement: transonic wave drag Transonic flow The wave drag arises at subsonic speeds when the flow accelerates locally to supersonic speeds, and then returns to subsonic speed through a shock wave. Drag divergence Mach number, M DD The Mach number at which the rapid drag increase occurs At drag divergence the additional transonic drag is divided between the explicit shock drag and the shock induced additional profile drag.
20 A fluid mechanics refinement: transonic wave drag Definitions of the drag rise Mach number dc D dm C L = conts. = 0.1 or C D = Details of wave drag increases at transonic speeds
21 An aerodynamics/flight mechanics refinement: trim drag The requirement of steady flight can lead to control surface deflections that increase the drag. The cases of significant drag: The shift in the aerodynamic center location with Mach number for supersonic aircraft The use of airfoils with large values of the zero lift pitching moment about their aerodynamic center The configurations with variable wing sweep
22 A practical aspect of aero-propulsion integration: thrust-drag bookkeeping The drag of the airframe is affected by the operation of the propulsion system a spillage drag the boattail drag over the external portion of the nozzle Approach thrust-drag bookkeeping.
23 Aerodynamic-structural interaction: aeroelastic effects on drag aerodynamic loads aerodynamic loads structure change of drag change of drag deformation
24 Farfield Drag Analysis Approach Estimate the drag on a body by considering the overall momentum balance on a control volume surface well away from the body. Advantage Less sensitive to the detailed calculations of surface pressure and integration of the pressures over the surface to obtain the drag.
25 Derivation (1) where q is the disturbance velocity vector Control volume for farfield drag evaluation.
26 Derivation () Using linearized flow relations and the small disturbance relations:
27 Derivation (3) The equation became: Where v r is the radial component
28 Derivation (4) The integral over I is zero as x -. The integral over II as x, corresponds to the so-called Trefftz Plane. The integral over III is the wave drag integral, which is zero for subsonic flow, and when any embedded shock waves do not reach III.
29 Drag Categorization & Farfield Drag Analysis Drag = friction drag + induced drag + wave drag + form drag 1 D = ρ [( M 1) u + v + w ] dydz ρ uvrrdθdx II III Farfield Drag Analysis
30 Consider the integral over II The induced drag integral 1 ρ [( M 1) u + v + D i = w ] dydz 1 ρ [ v + D i = w ] dydz Far downstream, u 0 Using Green s theorem II ( v + w ) ds φ = φ dc n c D i 1 = ρ φ φ dc n c
31 In this Trefftz plane, the integral vanishes around the outside contour as R and the integrals along AB and CD cancel. The only contribution comes from the slit containing the trace of vorticity shed from the wing. The value of φ is equal and opposite above and below the vortex sheet,and φ = w n
32 D i = b / 1 ρ ( φ) x= b / w dy Relation between φ and circulation φ x= = Γ(y) Using lifting line theory w x= ( y) = 1 π b / b / γ ( η) dη y η γ ( η) = d Γ / dy Relation between the trailing vorticity strength and the change in circulation D i ρ 4π b/ b/ = b/ b/ dγ( y dy 1 ) dγ( y dy ) ln y 1 y dy dy 1
33 D i ρ 4π b/ b/ = b/ b/ dγ( y dy 1 ) dγ( y dy ) ln y 1 y dy dy 1 Comments on this equation This result shows that the induced drag is a function of the Γ distribution (spanload) alone. The spanload distribution is responsible for the induced drag. Because of the double integral we can get the total drag, but we have lost the ability to get detailed distributions of the induced drag on the body. This is the price we pay to use the farfield analysis.
34 Summary The importance of drag in aircraft design Nomenclature and Concepts Don t be confused by the all those terms! Far-field Drag Analysis Formulation The Integral over Surface II: Induced Drag
The Importance of drag
 Drag Computation The Importance of drag Its effects on aircraft performances On the Concorde, one count drag increase (ΔC D =.0001) requires two passengers, out of the 90 ~ 100 passenger capacity, be taken
Drag Computation The Importance of drag Its effects on aircraft performances On the Concorde, one count drag increase (ΔC D =.0001) requires two passengers, out of the 90 ~ 100 passenger capacity, be taken
Drag (2) Induced Drag Friction Drag Form Drag Wave Drag
 Drag () Induced Drag Friction Drag Form Drag Wave Drag Outline Nomenclature and Concepts Farfield Drag Analysis Induced Drag Multiple Lifting Surfaces Zero Lift Drag :Friction and Form Drag Supersonic
Drag () Induced Drag Friction Drag Form Drag Wave Drag Outline Nomenclature and Concepts Farfield Drag Analysis Induced Drag Multiple Lifting Surfaces Zero Lift Drag :Friction and Form Drag Supersonic
Definitions. Temperature: Property of the atmosphere (τ). Function of altitude. Pressure: Property of the atmosphere (p). Function of altitude.
 Definitions Chapter 3 Standard atmosphere: A model of the atmosphere based on the aerostatic equation, the perfect gas law, an assumed temperature distribution, and standard sea level conditions. Temperature:
Definitions Chapter 3 Standard atmosphere: A model of the atmosphere based on the aerostatic equation, the perfect gas law, an assumed temperature distribution, and standard sea level conditions. Temperature:
Compressible Potential Flow: The Full Potential Equation. Copyright 2009 Narayanan Komerath
 Compressible Potential Flow: The Full Potential Equation 1 Introduction Recall that for incompressible flow conditions, velocity is not large enough to cause density changes, so density is known. Thus
Compressible Potential Flow: The Full Potential Equation 1 Introduction Recall that for incompressible flow conditions, velocity is not large enough to cause density changes, so density is known. Thus
Airfoils and Wings. Eugene M. Cliff
 Airfoils and Wings Eugene M. Cliff 1 Introduction The primary purpose of these notes is to supplement the text material related to aerodynamic forces. We are mainly interested in the forces on wings and
Airfoils and Wings Eugene M. Cliff 1 Introduction The primary purpose of these notes is to supplement the text material related to aerodynamic forces. We are mainly interested in the forces on wings and
MDTS 5705 : Aerodynamics & Propulsion Lecture 2 : Missile lift and drag. G. Leng, MDTS, NUS
 MDTS 5705 : Aerodynamics & Propulsion Lecture 2 : Missile lift and drag 2.1. The design of supersonic airfoils For efficient lift generation at subsonic speeds, airfoils look like : So why can t a similar
MDTS 5705 : Aerodynamics & Propulsion Lecture 2 : Missile lift and drag 2.1. The design of supersonic airfoils For efficient lift generation at subsonic speeds, airfoils look like : So why can t a similar
Flight Vehicle Terminology
 Flight Vehicle Terminology 1.0 Axes Systems There are 3 axes systems which can be used in Aeronautics, Aerodynamics & Flight Mechanics: Ground Axes G(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) Body Axes G(x, y, z) Aerodynamic Axes
Flight Vehicle Terminology 1.0 Axes Systems There are 3 axes systems which can be used in Aeronautics, Aerodynamics & Flight Mechanics: Ground Axes G(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) Body Axes G(x, y, z) Aerodynamic Axes
Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters 2 Lecture 20 Topics
 Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters Lecture 0 Topics 5..4 Effects of geometric parameters, Reynolds number and roughness on aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils 5..5 Choice of airfoil
Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters Lecture 0 Topics 5..4 Effects of geometric parameters, Reynolds number and roughness on aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils 5..5 Choice of airfoil
Given the water behaves as shown above, which direction will the cylinder rotate?
 water stream fixed but free to rotate Given the water behaves as shown above, which direction will the cylinder rotate? ) Clockwise 2) Counter-clockwise 3) Not enough information F y U 0 U F x V=0 V=0
water stream fixed but free to rotate Given the water behaves as shown above, which direction will the cylinder rotate? ) Clockwise 2) Counter-clockwise 3) Not enough information F y U 0 U F x V=0 V=0
Configuration Aerodynamics
 Configuration Aerodynamics William H. Mason Virginia Tech Blacksburg, VA The front cover of the brochure describing the French Exhibit at the Montreal Expo, 1967. January 2018 W.H. Mason CONTENTS i CONTENTS
Configuration Aerodynamics William H. Mason Virginia Tech Blacksburg, VA The front cover of the brochure describing the French Exhibit at the Montreal Expo, 1967. January 2018 W.H. Mason CONTENTS i CONTENTS
High Speed Aerodynamics. Copyright 2009 Narayanan Komerath
 Welcome to High Speed Aerodynamics 1 Lift, drag and pitching moment? Linearized Potential Flow Transformations Compressible Boundary Layer WHAT IS HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS? Airfoil section? Thin airfoil
Welcome to High Speed Aerodynamics 1 Lift, drag and pitching moment? Linearized Potential Flow Transformations Compressible Boundary Layer WHAT IS HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS? Airfoil section? Thin airfoil
A Novel Airfoil Circulation Augment Flow Control Method Using Co-Flow Jet
 AIAA Paper 2004-2208, 2004 A Novel Airfoil Circulation Augment Flow Control Method Using Co-Flow Jet Ge-Cheng Zha and Craig D. Paxton Dept. of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering University of Miami Coral
AIAA Paper 2004-2208, 2004 A Novel Airfoil Circulation Augment Flow Control Method Using Co-Flow Jet Ge-Cheng Zha and Craig D. Paxton Dept. of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering University of Miami Coral
Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics
 David G. Hull Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics With 125 Figures and 25 Tables y Springer Introduction to Airplane Flight Mechanics 1 1.1 Airframe Anatomy 2 1.2 Engine Anatomy 5 1.3 Equations of
David G. Hull Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics With 125 Figures and 25 Tables y Springer Introduction to Airplane Flight Mechanics 1 1.1 Airframe Anatomy 2 1.2 Engine Anatomy 5 1.3 Equations of
LONGITUDINAL STABILITY AND TRIM OF AN ARIANE 5 FLY-BACK BOOSTER
 12th AIAA International Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies 1-19 December 23, Norfolk, Virginia AIAA 23-7 LONGITUDINAL STABILITY AND TRIM OF AN ARIANE FLY-BACK BOOSTER Th. Eggers DLR,
12th AIAA International Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies 1-19 December 23, Norfolk, Virginia AIAA 23-7 LONGITUDINAL STABILITY AND TRIM OF AN ARIANE FLY-BACK BOOSTER Th. Eggers DLR,
Applied Aerodynamics - I
 Applied Aerodynamics - I o Course Contents (Tentative) Introductory Thoughts Historical Perspective Flow Similarity Aerodynamic Coefficients Sources of Aerodynamic Forces Fundamental Equations & Principles
Applied Aerodynamics - I o Course Contents (Tentative) Introductory Thoughts Historical Perspective Flow Similarity Aerodynamic Coefficients Sources of Aerodynamic Forces Fundamental Equations & Principles
FLIGHT DYNAMICS. Robert F. Stengel. Princeton University Press Princeton and Oxford
 FLIGHT DYNAMICS Robert F. Stengel Princeton University Press Princeton and Oxford Preface XV Chapter One Introduction 1 1.1 ELEMENTS OF THE AIRPLANE 1 Airframe Components 1 Propulsion Systems 4 1.2 REPRESENTATIVE
FLIGHT DYNAMICS Robert F. Stengel Princeton University Press Princeton and Oxford Preface XV Chapter One Introduction 1 1.1 ELEMENTS OF THE AIRPLANE 1 Airframe Components 1 Propulsion Systems 4 1.2 REPRESENTATIVE
Evaluation of nacelle drag using Computational Fluid Dynamics
 doi: 10.5028/jatm.2010.02026410 Luis Gustavo Trapp* Empresa Brasileira de Aeronáutica S.A. São José dos Campos Brazil gustavo.trapp@embraer.com.br Henrique Gustavo Argentieri Empresa Brasileira de Aeronáutica
doi: 10.5028/jatm.2010.02026410 Luis Gustavo Trapp* Empresa Brasileira de Aeronáutica S.A. São José dos Campos Brazil gustavo.trapp@embraer.com.br Henrique Gustavo Argentieri Empresa Brasileira de Aeronáutica
An Investigation of the Attainable Efficiency of Flight at Mach One or Just Beyond
 An Investigation of the Attainable Efficiency of Flight at Mach One or Just Beyond Antony Jameson Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, NV AIAA Paper 2007-0037
An Investigation of the Attainable Efficiency of Flight at Mach One or Just Beyond Antony Jameson Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, NV AIAA Paper 2007-0037
AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics. Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2017
 AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2017 Lift curve 2 Lift curve slope 3 Subsonic lift curve slope C Lα = 2 + 4 + AR2 β 2 η
AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2017 Lift curve 2 Lift curve slope 3 Subsonic lift curve slope C Lα = 2 + 4 + AR2 β 2 η
MODIFICATION OF AERODYNAMIC WING LOADS BY FLUIDIC DEVICES
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 21, No. 2 2014 MODIFICATION OF AERODYNAMIC WING LOADS BY FLUIDIC DEVICES Institute of Aviation Department of Aerodynamics and Flight Mechanics Krakowska
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 21, No. 2 2014 MODIFICATION OF AERODYNAMIC WING LOADS BY FLUIDIC DEVICES Institute of Aviation Department of Aerodynamics and Flight Mechanics Krakowska
Supersonic Aerodynamics. Methods and Applications
 Supersonic Aerodynamics Methods and Applications Outline Introduction to Supersonic Flow Governing Equations Numerical Methods Aerodynamic Design Applications Introduction to Supersonic Flow What does
Supersonic Aerodynamics Methods and Applications Outline Introduction to Supersonic Flow Governing Equations Numerical Methods Aerodynamic Design Applications Introduction to Supersonic Flow What does
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : LOW SPEED AERODYNAMICS Course Code : AAE004 Regulation : IARE
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : LOW SPEED AERODYNAMICS Course Code : AAE004 Regulation : IARE
To highlight the change in drag with lift: Drag = Zero-Lift Drag + Lift-Dependent Drag + Compressibility Drag
 Drag Drag Bookkeeping Drag may be divided into components in several ways: To highlight the change in drag with lift: Drag = Zero-Lift Drag + Lift-Dependent Drag + Compressibility Drag To emphasize the
Drag Drag Bookkeeping Drag may be divided into components in several ways: To highlight the change in drag with lift: Drag = Zero-Lift Drag + Lift-Dependent Drag + Compressibility Drag To emphasize the
AEROSPACE ENGINEERING
 AEROSPACE ENGINEERING Subject Code: AE Course Structure Sections/Units Topics Section A Engineering Mathematics Topics (Core) 1 Linear Algebra 2 Calculus 3 Differential Equations 1 Fourier Series Topics
AEROSPACE ENGINEERING Subject Code: AE Course Structure Sections/Units Topics Section A Engineering Mathematics Topics (Core) 1 Linear Algebra 2 Calculus 3 Differential Equations 1 Fourier Series Topics
Masters in Mechanical Engineering Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 2015/16
 Masters in Mechanical Engineering Aerodynamics st Semester 05/6 Exam st season, 8 January 06 Name : Time : 8:30 Number: Duration : 3 hours st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed nd Part : Textbooks allowed
Masters in Mechanical Engineering Aerodynamics st Semester 05/6 Exam st season, 8 January 06 Name : Time : 8:30 Number: Duration : 3 hours st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed nd Part : Textbooks allowed
SPC Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30
 SPC 307 - Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30 1. The maximum velocity at which an aircraft can cruise occurs when the thrust available with the engines operating with the
SPC 307 - Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30 1. The maximum velocity at which an aircraft can cruise occurs when the thrust available with the engines operating with the
and K becoming functions of Mach number i.e.: (3.49)
 Chapter 3 Lecture 11 Drag polar 6 Topics 3.3.4 Parabolic drag polar at high speeds 3.3.5 Guidelines for variations of C Do and K for subsonic jet transport airplanes 3.3.6 Variations of C Do and K for
Chapter 3 Lecture 11 Drag polar 6 Topics 3.3.4 Parabolic drag polar at high speeds 3.3.5 Guidelines for variations of C Do and K for subsonic jet transport airplanes 3.3.6 Variations of C Do and K for
A COUPLED-ADJOINT METHOD FOR HIGH-FIDELITY AERO-STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION
 A COUPLED-ADJOINT METHOD FOR HIGH-FIDELITY AERO-STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION Joaquim Rafael Rost Ávila Martins Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Stanford University Ph.D. Oral Examination, Stanford
A COUPLED-ADJOINT METHOD FOR HIGH-FIDELITY AERO-STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION Joaquim Rafael Rost Ávila Martins Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Stanford University Ph.D. Oral Examination, Stanford
Introduction to Atmospheric Flight. Dr. Guven Aerospace Engineer (P.hD)
 Introduction to Atmospheric Flight Dr. Guven Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) What is Atmospheric Flight? There are many different ways in which Aerospace engineering is associated with atmospheric flight concepts.
Introduction to Atmospheric Flight Dr. Guven Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) What is Atmospheric Flight? There are many different ways in which Aerospace engineering is associated with atmospheric flight concepts.
Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Mecânica Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 2012/13
 Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Mecânica Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 212/13 Exam 2ª época, 2 February 213 Name : Time : 8: Number: Duration : 3 hours 1 st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed 2 nd Part :
Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Mecânica Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 212/13 Exam 2ª época, 2 February 213 Name : Time : 8: Number: Duration : 3 hours 1 st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed 2 nd Part :
1. Fluid Dynamics Around Airfoils
 1. Fluid Dynamics Around Airfoils Two-dimensional flow around a streamlined shape Foces on an airfoil Distribution of pressue coefficient over an airfoil The variation of the lift coefficient with the
1. Fluid Dynamics Around Airfoils Two-dimensional flow around a streamlined shape Foces on an airfoil Distribution of pressue coefficient over an airfoil The variation of the lift coefficient with the
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering
 4. Basic Fluid (Aero) Dynamics Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Here, we will try and look at a few basic ideas from the complicated field of fluid dynamics. The general area includes studies of incompressible,
4. Basic Fluid (Aero) Dynamics Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Here, we will try and look at a few basic ideas from the complicated field of fluid dynamics. The general area includes studies of incompressible,
AERODYNAMICS STUDY NOTES UNIT I REVIEW OF BASIC FLUID MECHANICS. Continuity, Momentum and Energy Equations. Applications of Bernouli s theorem
 AERODYNAMICS STUDY NOTES UNIT I REVIEW OF BASIC FLUID MECHANICS. Continuity, Momentum and Energy Equations. Applications of Bernouli s theorem UNIT II TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS Complex Potential, Point Source
AERODYNAMICS STUDY NOTES UNIT I REVIEW OF BASIC FLUID MECHANICS. Continuity, Momentum and Energy Equations. Applications of Bernouli s theorem UNIT II TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS Complex Potential, Point Source
Aerodynamics. High-Lift Devices
 High-Lift Devices Devices to increase the lift coefficient by geometry changes (camber and/or chord) and/or boundary-layer control (avoid flow separation - Flaps, trailing edge devices - Slats, leading
High-Lift Devices Devices to increase the lift coefficient by geometry changes (camber and/or chord) and/or boundary-layer control (avoid flow separation - Flaps, trailing edge devices - Slats, leading
Aeroelastic Gust Response
 Aeroelastic Gust Response Civil Transport Aircraft - xxx Presented By: Fausto Gill Di Vincenzo 04-06-2012 What is Aeroelasticity? Aeroelasticity studies the effect of aerodynamic loads on flexible structures,
Aeroelastic Gust Response Civil Transport Aircraft - xxx Presented By: Fausto Gill Di Vincenzo 04-06-2012 What is Aeroelasticity? Aeroelasticity studies the effect of aerodynamic loads on flexible structures,
Mechanics of Flight. Warren F. Phillips. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Professor Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Utah State University WILEY
 Mechanics of Flight Warren F. Phillips Professor Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Utah State University WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Inc. CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgments xi xiii 1. Overview of Aerodynamics
Mechanics of Flight Warren F. Phillips Professor Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Utah State University WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Inc. CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgments xi xiii 1. Overview of Aerodynamics
AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics. Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2015
 AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2015 Lift curve 2 Lift curve slope 3 Subsonic lift curve slope C Lα = 2 + 4 + AR2 β 2 η
AE 451 Aeronautical Engineering Design I Aerodynamics Prof. Dr. Serkan Özgen Dept. Aerospace Engineering December 2015 Lift curve 2 Lift curve slope 3 Subsonic lift curve slope C Lα = 2 + 4 + AR2 β 2 η
COMPLETE CONFIGURATION AERO-STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION USING A COUPLED SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS METHOD
 COMPLETE CONFIGURATION AERO-STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION USING A COUPLED SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS METHOD Joaquim R. R. A. Martins Juan J. Alonso James J. Reuther Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Stanford
COMPLETE CONFIGURATION AERO-STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION USING A COUPLED SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS METHOD Joaquim R. R. A. Martins Juan J. Alonso James J. Reuther Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Stanford
Investigation potential flow about swept back wing using panel method
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENERGY AND ENVIRONMENT Volume 7, Issue 4, 2016 pp.317-326 Journal homepage: www.ijee.ieefoundation.org Investigation potential flow about swept back wing using panel method Wakkas
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENERGY AND ENVIRONMENT Volume 7, Issue 4, 2016 pp.317-326 Journal homepage: www.ijee.ieefoundation.org Investigation potential flow about swept back wing using panel method Wakkas
PEMP ACD2501. M.S. Ramaiah School of Advanced Studies, Bengaluru
 Aircraft Aerodynamics Session delivered by: Mr. Ramjan Pathan 1 Session Objectives At the end of this session students would have understood Basics of Fluid Mechanics Definition of fluid, Fluid flow applications
Aircraft Aerodynamics Session delivered by: Mr. Ramjan Pathan 1 Session Objectives At the end of this session students would have understood Basics of Fluid Mechanics Definition of fluid, Fluid flow applications
DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING, IIT MADRAS M.Tech. Curriculum
 DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING, IIT MADRAS M.Tech. Curriculum SEMESTER I AS5010 Engg. Aerodyn. & Flt. Mech. 3 0 0 3 AS5020 Elements of Gas Dyn. & Propln. 3 0 0 3 AS5030 Aircraft and Aerospace Structures
DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING, IIT MADRAS M.Tech. Curriculum SEMESTER I AS5010 Engg. Aerodyn. & Flt. Mech. 3 0 0 3 AS5020 Elements of Gas Dyn. & Propln. 3 0 0 3 AS5030 Aircraft and Aerospace Structures
The polar for uncambered and cambered airfoils. The angel of attack α
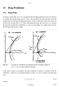 13-1 13 Drag Prediction 13.1 Drag Polar In Section under Step 14 it was a requirement that the flight performance has to be checked to complete the aircraft design process. This is only possible if the
13-1 13 Drag Prediction 13.1 Drag Polar In Section under Step 14 it was a requirement that the flight performance has to be checked to complete the aircraft design process. This is only possible if the
Air Loads. Airfoil Geometry. Upper surface. Lower surface
 AE1 Jha Loads-1 Air Loads Airfoil Geometry z LE circle (radius) Chord line Upper surface thickness Zt camber Zc Zl Zu Lower surface TE thickness Camber line line joining the midpoints between upper and
AE1 Jha Loads-1 Air Loads Airfoil Geometry z LE circle (radius) Chord line Upper surface thickness Zt camber Zc Zl Zu Lower surface TE thickness Camber line line joining the midpoints between upper and
Aerodynamic force analysis in high Reynolds number flows by Lamb vector integration
 Aerodynamic force analysis in high Reynolds number flows by Lamb vector integration Claudio Marongiu, Renato Tognaccini 2 CIRA, Italian Center for Aerospace Research, Capua (CE), Italy E-mail: c.marongiu@cira.it
Aerodynamic force analysis in high Reynolds number flows by Lamb vector integration Claudio Marongiu, Renato Tognaccini 2 CIRA, Italian Center for Aerospace Research, Capua (CE), Italy E-mail: c.marongiu@cira.it
Analyses of Diamond - Shaped and Circular Arc Airfoils in Supersonic Wind Tunnel Airflows
 Analyses of Diamond - Shaped and Circular Arc Airfoils in Supersonic Wind Tunnel Airflows Modo U. P, Chukwuneke J. L, Omenyi Sam 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka,
Analyses of Diamond - Shaped and Circular Arc Airfoils in Supersonic Wind Tunnel Airflows Modo U. P, Chukwuneke J. L, Omenyi Sam 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka,
AIRFRAME NOISE MODELING APPROPRIATE FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION
 AIRFRAME NOISE MODELING APPROPRIATE FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION AIAA-2004-0689 Serhat Hosder, Joseph A. Schetz, Bernard Grossman and William H. Mason Virginia Tech Work sponsored by NASA
AIRFRAME NOISE MODELING APPROPRIATE FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION AIAA-2004-0689 Serhat Hosder, Joseph A. Schetz, Bernard Grossman and William H. Mason Virginia Tech Work sponsored by NASA
F-35: A case study. Eugene Heim Leifur Thor Leifsson Evan Neblett. AOE 4124 Configuration Aerodynamics Virginia Tech April 2003
 F-35: A case study Eugene Heim Leifur Thor Leifsson Evan Neblett AOE 4124 Configuration Aerodynamics Virginia Tech April 2003 Course: AOE 4124 Configuration Aerodynamics Project: A case study of the F-35
F-35: A case study Eugene Heim Leifur Thor Leifsson Evan Neblett AOE 4124 Configuration Aerodynamics Virginia Tech April 2003 Course: AOE 4124 Configuration Aerodynamics Project: A case study of the F-35
Computational Fluid Dynamics Study Of Fluid Flow And Aerodynamic Forces On An Airfoil S.Kandwal 1, Dr. S. Singh 2
 Computational Fluid Dynamics Study Of Fluid Flow And Aerodynamic Forces On An Airfoil S.Kandwal 1, Dr. S. Singh 2 1 M. Tech Scholar, 2 Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bipin Tripathi
Computational Fluid Dynamics Study Of Fluid Flow And Aerodynamic Forces On An Airfoil S.Kandwal 1, Dr. S. Singh 2 1 M. Tech Scholar, 2 Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bipin Tripathi
The E80 Wind Tunnel Experiment the experience will blow you away. by Professor Duron Spring 2012
 The E80 Wind Tunnel Experiment the experience will blow you away by Professor Duron Spring 2012 Objectives To familiarize the student with the basic operation and instrumentation of the HMC wind tunnel
The E80 Wind Tunnel Experiment the experience will blow you away by Professor Duron Spring 2012 Objectives To familiarize the student with the basic operation and instrumentation of the HMC wind tunnel
Based on the Aircraft Design Lecture Notes and Master Thesis of Roberto Segovia García. Hamburg University of Applied Sciences.
 Dieter Scholz Drag Estimation Based on the Aircraft Design Lecture Notes and Master Thesis of Roberto Segovia García. Hamburg University of Applied Sciences. 2017 In cruise we calculate the drag coefficient
Dieter Scholz Drag Estimation Based on the Aircraft Design Lecture Notes and Master Thesis of Roberto Segovia García. Hamburg University of Applied Sciences. 2017 In cruise we calculate the drag coefficient
Study of Preliminary Configuration Design of F-35 using simple CFD
 Study of Preliminary Configuration Design of F-35 using simple CFD http://www.aerospaceweb.org/aircraft/research/x35/pics.shtml David Hall Sangeon Chun David Andrews Center of Gravity Estimation.5873 Conventional
Study of Preliminary Configuration Design of F-35 using simple CFD http://www.aerospaceweb.org/aircraft/research/x35/pics.shtml David Hall Sangeon Chun David Andrews Center of Gravity Estimation.5873 Conventional
Investigation on Boundary Layer Ingestion Propulsion for UAVs
 International Micro Air Vehicle Conference and Flight Competition (IMAV) 2017 293 Investigation on Boundary Layer Ingestion Propulsion for UAVs L. Teperin, M. El-Salamony, A. Moharam, and M. Shehata, Central
International Micro Air Vehicle Conference and Flight Competition (IMAV) 2017 293 Investigation on Boundary Layer Ingestion Propulsion for UAVs L. Teperin, M. El-Salamony, A. Moharam, and M. Shehata, Central
Performance. 5. More Aerodynamic Considerations
 Performance 5. More Aerodynamic Considerations There is an alternative way of looking at aerodynamic flow problems that is useful for understanding certain phenomena. Rather than tracking a particle of
Performance 5. More Aerodynamic Considerations There is an alternative way of looking at aerodynamic flow problems that is useful for understanding certain phenomena. Rather than tracking a particle of
Design of a Droopnose Configuration for a Coanda Active Flap Application. Marco Burnazzi and Rolf Radespiel
 Design of a Droopnose Configuration for a Coanda Active Flap Application Marco Burnazzi and Rolf Radespiel Institute of Fluid Mechanics, Technische Universität Braunschweig, 38108 Braunschweig, Germany
Design of a Droopnose Configuration for a Coanda Active Flap Application Marco Burnazzi and Rolf Radespiel Institute of Fluid Mechanics, Technische Universität Braunschweig, 38108 Braunschweig, Germany
AE 2020: Low Speed Aerodynamics. I. Introductory Remarks Read chapter 1 of Fundamentals of Aerodynamics by John D. Anderson
 AE 2020: Low Speed Aerodynamics I. Introductory Remarks Read chapter 1 of Fundamentals of Aerodynamics by John D. Anderson Text Book Anderson, Fundamentals of Aerodynamics, 4th Edition, McGraw-Hill, Inc.
AE 2020: Low Speed Aerodynamics I. Introductory Remarks Read chapter 1 of Fundamentals of Aerodynamics by John D. Anderson Text Book Anderson, Fundamentals of Aerodynamics, 4th Edition, McGraw-Hill, Inc.
Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig L. Hilmes Boeing Commercial Airplane Group, Seattle, Washington, 98124
 AIAA--2007-0684 Pressures and Drag Characteristics of Bodies of Revolution at Near Sonic Speeds Including the Effects of Viscosity and Wind Tunnel Walls Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig
AIAA--2007-0684 Pressures and Drag Characteristics of Bodies of Revolution at Near Sonic Speeds Including the Effects of Viscosity and Wind Tunnel Walls Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig
Transonic Aerodynamics Wind Tunnel Testing Considerations. W.H. Mason Configuration Aerodynamics Class
 Transonic Aerodynamics Wind Tunnel Testing Considerations W.H. Mason Configuration Aerodynamics Class Transonic Aerodynamics History Pre WWII propeller tip speeds limited airplane speed Props did encounter
Transonic Aerodynamics Wind Tunnel Testing Considerations W.H. Mason Configuration Aerodynamics Class Transonic Aerodynamics History Pre WWII propeller tip speeds limited airplane speed Props did encounter
Aeroelasticity. Lecture 9: Supersonic Aeroelasticity. G. Dimitriadis. AERO0032-1, Aeroelasticity and Experimental Aerodynamics, Lecture 9
 Aeroelasticity Lecture 9: Supersonic Aeroelasticity G. Dimitriadis AERO0032-1, Aeroelasticity and Experimental Aerodynamics, Lecture 9 1 Introduction All the material presented up to now concerned incompressible
Aeroelasticity Lecture 9: Supersonic Aeroelasticity G. Dimitriadis AERO0032-1, Aeroelasticity and Experimental Aerodynamics, Lecture 9 1 Introduction All the material presented up to now concerned incompressible
ν δ - 1 -
 ν δ - 1 - δ ν ν δ ν ν - 2 - ρ δ ρ θ θ θ δ τ ρ θ δ δ θ δ δ δ δ τ μ δ μ δ ν δ δ δ - 3 - τ ρ δ ρ δ ρ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ - 4 - ρ μ ρ μ ρ ρ μ μ ρ - 5 - ρ τ μ τ μ ρ δ δ δ - 6 - τ ρ μ τ ρ μ ρ δ θ θ δ θ - 7
ν δ - 1 - δ ν ν δ ν ν - 2 - ρ δ ρ θ θ θ δ τ ρ θ δ δ θ δ δ δ δ τ μ δ μ δ ν δ δ δ - 3 - τ ρ δ ρ δ ρ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ - 4 - ρ μ ρ μ ρ ρ μ μ ρ - 5 - ρ τ μ τ μ ρ δ δ δ - 6 - τ ρ μ τ ρ μ ρ δ θ θ δ θ - 7
Contents. I Introduction 1. Preface. xiii
 Contents Preface xiii I Introduction 1 1 Continuous matter 3 1.1 Molecules................................ 4 1.2 The continuum approximation.................... 6 1.3 Newtonian mechanics.........................
Contents Preface xiii I Introduction 1 1 Continuous matter 3 1.1 Molecules................................ 4 1.2 The continuum approximation.................... 6 1.3 Newtonian mechanics.........................
Nonlinear Aerodynamic Predictions Of Aircraft and Missiles Employing Trailing-Edge Flaps
 Nonlinear Aerodynamic Predictions Of Aircraft and Missiles Employing Trailing-Edge Flaps Daniel J. Lesieutre 1 Nielsen Engineering & Research, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, 95054 The nonlinear missile aerodynamic
Nonlinear Aerodynamic Predictions Of Aircraft and Missiles Employing Trailing-Edge Flaps Daniel J. Lesieutre 1 Nielsen Engineering & Research, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, 95054 The nonlinear missile aerodynamic
Consider a wing of finite span with an elliptic circulation distribution:
 Question 1 (a) onsider a wing of finite span with an elliptic circulation distribution: Γ( y) Γo y + b = 1, - s y s where s=b/ denotes the wing semi-span. Use this equation, in conjunction with the Kutta-Joukowsky
Question 1 (a) onsider a wing of finite span with an elliptic circulation distribution: Γ( y) Γo y + b = 1, - s y s where s=b/ denotes the wing semi-span. Use this equation, in conjunction with the Kutta-Joukowsky
Introduction to Aerodynamics. Dr. Guven Aerospace Engineer (P.hD)
 Introduction to Aerodynamics Dr. Guven Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) Aerodynamic Forces All aerodynamic forces are generated wither through pressure distribution or a shear stress distribution on a body. The
Introduction to Aerodynamics Dr. Guven Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) Aerodynamic Forces All aerodynamic forces are generated wither through pressure distribution or a shear stress distribution on a body. The
FREQUENCY DOMAIN FLUTTER ANALYSIS OF AIRCRAFT WING IN SUBSONIC FLOW
 FREQUENCY DOMAIN FLUTTER ANALYSIS OF AIRCRAFT WING IN SUBSONIC FLOW Ms.K.Niranjana 1, Mr.A.Daniel Antony 2 1 UG Student, Department of Aerospace Engineering, Karunya University, (India) 2 Assistant professor,
FREQUENCY DOMAIN FLUTTER ANALYSIS OF AIRCRAFT WING IN SUBSONIC FLOW Ms.K.Niranjana 1, Mr.A.Daniel Antony 2 1 UG Student, Department of Aerospace Engineering, Karunya University, (India) 2 Assistant professor,
Momentum (Newton s 2nd Law of Motion)
 Dr. Nikos J. Mourtos AE 160 / ME 111 Momentum (Newton s nd Law of Motion) Case 3 Airfoil Drag A very important application of Momentum in aerodynamics and hydrodynamics is the calculation of the drag of
Dr. Nikos J. Mourtos AE 160 / ME 111 Momentum (Newton s nd Law of Motion) Case 3 Airfoil Drag A very important application of Momentum in aerodynamics and hydrodynamics is the calculation of the drag of
Development of Two-Dimensional Convergent-Divergent Nozzle Performance Rapid Analysis Project
 International Forum on Energy, Environment Science and Materials (IFEESM 015) Development of Two-Dimensional Convergent-Divergent Nozzle Performance Rapid Analysis Project Yaxiong YANG 1,a *, Eri Qitai,b,
International Forum on Energy, Environment Science and Materials (IFEESM 015) Development of Two-Dimensional Convergent-Divergent Nozzle Performance Rapid Analysis Project Yaxiong YANG 1,a *, Eri Qitai,b,
RECENT near-sonic and low-sonic boom transport aircraft
 JOURNAL OF AIRCRAFT Vol. 44, No. 6, November December 2007 Aerodynamic Characteristics of Bodies of Revolution at Near-Sonic Speeds Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig L. Hilmes The Boeing
JOURNAL OF AIRCRAFT Vol. 44, No. 6, November December 2007 Aerodynamic Characteristics of Bodies of Revolution at Near-Sonic Speeds Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig L. Hilmes The Boeing
X-31 Vector Aircraft, Low Speed Stability & Control, Comparisons of Wind Tunnel Data & Theory (Focus on Linear & Panel Codes)
 39th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference 22-25 June 2009, San Antonio, Texas AIAA 2009-3898 27 th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, 22-25 June. 2009, San Antonio, TX, USA X-31 Vector Aircraft, Low Speed
39th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference 22-25 June 2009, San Antonio, Texas AIAA 2009-3898 27 th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, 22-25 June. 2009, San Antonio, TX, USA X-31 Vector Aircraft, Low Speed
Design and Computational Studies on Plain Flaps
 Bonfring International Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management Science, Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2013 33 Design and Computational Studies on Plain Flaps M. Senthil Kumar and K. Naveen Kumar Abstract---
Bonfring International Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management Science, Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2013 33 Design and Computational Studies on Plain Flaps M. Senthil Kumar and K. Naveen Kumar Abstract---
Lecture-4. Flow Past Immersed Bodies
 Lecture-4 Flow Past Immersed Bodies Learning objectives After completing this lecture, you should be able to: Identify and discuss the features of external flow Explain the fundamental characteristics
Lecture-4 Flow Past Immersed Bodies Learning objectives After completing this lecture, you should be able to: Identify and discuss the features of external flow Explain the fundamental characteristics
Rocket Dynamics. Forces on the Rocket
 Rocket Dynamics Forces on the Rockets - Drag Rocket Stability Rocket Equation Specific Impulse Rocket otors F Thrust Forces on the Rocket Equation of otion: Need to minimize total mass to maximize acceleration
Rocket Dynamics Forces on the Rockets - Drag Rocket Stability Rocket Equation Specific Impulse Rocket otors F Thrust Forces on the Rocket Equation of otion: Need to minimize total mass to maximize acceleration
Concept: AERODYNAMICS
 1 Concept: AERODYNAMICS 2 Narayanan Komerath 3 4 Keywords: Flow Potential Flow Lift, Drag, Dynamic Pressure, Irrotational, Mach Number, Reynolds Number, Incompressible 5 6 7 1. Definition When objects
1 Concept: AERODYNAMICS 2 Narayanan Komerath 3 4 Keywords: Flow Potential Flow Lift, Drag, Dynamic Pressure, Irrotational, Mach Number, Reynolds Number, Incompressible 5 6 7 1. Definition When objects
a) Derive general expressions for the stream function Ψ and the velocity potential function φ for the combined flow. [12 Marks]
![a) Derive general expressions for the stream function Ψ and the velocity potential function φ for the combined flow. [12 Marks] a) Derive general expressions for the stream function Ψ and the velocity potential function φ for the combined flow. [12 Marks]](/thumbs/87/95430472.jpg) Question 1 A horizontal irrotational flow system results from the combination of a free vortex, rotating anticlockwise, of strength K=πv θ r, located with its centre at the origin, with a uniform flow
Question 1 A horizontal irrotational flow system results from the combination of a free vortex, rotating anticlockwise, of strength K=πv θ r, located with its centre at the origin, with a uniform flow
Aero-Propulsive-Elastic Modeling Using OpenVSP
 Aero-Propulsive-Elastic Modeling Using OpenVSP August 8, 213 Kevin W. Reynolds Intelligent Systems Division, Code TI NASA Ames Research Center Our Introduction To OpenVSP Overview! Motivation and Background!
Aero-Propulsive-Elastic Modeling Using OpenVSP August 8, 213 Kevin W. Reynolds Intelligent Systems Division, Code TI NASA Ames Research Center Our Introduction To OpenVSP Overview! Motivation and Background!
Chapter 5 Performance analysis I Steady level flight (Lectures 17 to 20) Keywords: Steady level flight equations of motion, minimum power required,
 Chapter 5 Performance analysis I Steady level flight (Lectures 17 to 20) Keywords: Steady level flight equations of motion, minimum power required, minimum thrust required, minimum speed, maximum speed;
Chapter 5 Performance analysis I Steady level flight (Lectures 17 to 20) Keywords: Steady level flight equations of motion, minimum power required, minimum thrust required, minimum speed, maximum speed;
Vishwakarma Institute of Technology. Honors in Aerospace Engineering
 Page 1 of 15 Bansilal Ramnath Agarwal Charitable Trust s Vishwakarma Institute of Technology (An Autonomous Institute affiliated to Savitribai Phule Pune University formerly University of Pune) Structure
Page 1 of 15 Bansilal Ramnath Agarwal Charitable Trust s Vishwakarma Institute of Technology (An Autonomous Institute affiliated to Savitribai Phule Pune University formerly University of Pune) Structure
A simplified model for a small propeller with different airfoils along the blade
 A simplified model for a small propeller with different airfoils along the blade Kamal A. R. Ismail 1) and *Célia V. A. G. Rosolen 2) 1), 2) State University of Campinas, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
A simplified model for a small propeller with different airfoils along the blade Kamal A. R. Ismail 1) and *Célia V. A. G. Rosolen 2) 1), 2) State University of Campinas, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
Math 575-Lecture Failure of ideal fluid; Vanishing viscosity. 1.1 Drawbacks of ideal fluids. 1.2 vanishing viscosity
 Math 575-Lecture 12 In this lecture, we investigate why the ideal fluid is not suitable sometimes; try to explain why the negative circulation appears in the airfoil and introduce the vortical wake to
Math 575-Lecture 12 In this lecture, we investigate why the ideal fluid is not suitable sometimes; try to explain why the negative circulation appears in the airfoil and introduce the vortical wake to
Thin airfoil theory. Chapter Compressible potential flow The full potential equation
 hapter 4 Thin airfoil theory 4. ompressible potential flow 4.. The full potential equation In compressible flow, both the lift and drag of a thin airfoil can be determined to a reasonable level of accuracy
hapter 4 Thin airfoil theory 4. ompressible potential flow 4.. The full potential equation In compressible flow, both the lift and drag of a thin airfoil can be determined to a reasonable level of accuracy
Degree Project in Aeronautics
 DEGREE PROJECT IN VEHICLE ENGINEERING, SECOND CYCLE, 30 CREDITS STOCKHOLM, SWEDEN 2017 Degree Project in Aeronautics Conceptual design, flying and handling qualities of a supersonic transport aircraft.
DEGREE PROJECT IN VEHICLE ENGINEERING, SECOND CYCLE, 30 CREDITS STOCKHOLM, SWEDEN 2017 Degree Project in Aeronautics Conceptual design, flying and handling qualities of a supersonic transport aircraft.
CFD COMPUTATION OF THE GROUND EFFECT ON AIRPLANE WITH HIGH ASPECT RATIO WING
 28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES CFD COMPUTATION OF THE GROUND EFFECT ON AIRPLANE WITH HIGH ASPECT RATIO WING Sun Tae Kim*, Youngtae Kim**, Tae Kyu Reu* *Agency for Defense Development,
28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES CFD COMPUTATION OF THE GROUND EFFECT ON AIRPLANE WITH HIGH ASPECT RATIO WING Sun Tae Kim*, Youngtae Kim**, Tae Kyu Reu* *Agency for Defense Development,
PEMP ACD2505. Finite Wing Theory. M.S. Ramaiah School of Advanced Studies, Bengaluru
 Finite Wing Theory Session delivered by: Prof. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives -- At the end of this session the delegate would have understood The finite wing theory Lifting line theory Elliptic
Finite Wing Theory Session delivered by: Prof. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives -- At the end of this session the delegate would have understood The finite wing theory Lifting line theory Elliptic
Chapter 9 Flow over Immersed Bodies
 57:00 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes Chapter 9 Professor Fred Stern Fall 009 1 Chapter 9 Flow over Immersed Bodies Fluid flows are broadly categorized: 1. Internal flows such as ducts/pipes,
57:00 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes Chapter 9 Professor Fred Stern Fall 009 1 Chapter 9 Flow over Immersed Bodies Fluid flows are broadly categorized: 1. Internal flows such as ducts/pipes,
Wings and Bodies in Compressible Flows
 Wings and Bodies in Compressible Flows Prandtl-Glauert-Goethert Transformation Potential equation: 1 If we choose and Laplace eqn. The transformation has stretched the x co-ordinate by 2 Values of at corresponding
Wings and Bodies in Compressible Flows Prandtl-Glauert-Goethert Transformation Potential equation: 1 If we choose and Laplace eqn. The transformation has stretched the x co-ordinate by 2 Values of at corresponding
PEMP ACD2505. M.S. Ramaiah School of Advanced Studies, Bengaluru
 Governing Equations of Fluid Flow Session delivered by: M. Sivapragasam 1 Session Objectives -- At the end of this session the delegate would have understood The principle of conservation laws Different
Governing Equations of Fluid Flow Session delivered by: M. Sivapragasam 1 Session Objectives -- At the end of this session the delegate would have understood The principle of conservation laws Different
Given a stream function for a cylinder in a uniform flow with circulation: a) Sketch the flow pattern in terms of streamlines.
 Question Given a stream function for a cylinder in a uniform flow with circulation: R Γ r ψ = U r sinθ + ln r π R a) Sketch the flow pattern in terms of streamlines. b) Derive an expression for the angular
Question Given a stream function for a cylinder in a uniform flow with circulation: R Γ r ψ = U r sinθ + ln r π R a) Sketch the flow pattern in terms of streamlines. b) Derive an expression for the angular
Basic Information to Help Select the Correct Propeller
 Propeller Performance Factors - Basic Information to Help Select the Correct Propeller The performance of a propeller in flight involves several complex subjects, and the high performance propellers we
Propeller Performance Factors - Basic Information to Help Select the Correct Propeller The performance of a propeller in flight involves several complex subjects, and the high performance propellers we
Part 3. Stability and Transition
 Part 3 Stability and Transition 281 Overview T. Cebeci 1 Recent interest in the reduction of drag of underwater vehicles and aircraft components has rekindled research in the area of stability and transition.
Part 3 Stability and Transition 281 Overview T. Cebeci 1 Recent interest in the reduction of drag of underwater vehicles and aircraft components has rekindled research in the area of stability and transition.
REYNOLDS NUMBER EFFECTS ON LEADING EDGE RADIUS VARIATIONS OF A SUPERSONIC TRANSPORT AT TRANSONIC CONDITIONS
 REYNOLDS NUMBER EFFECTS ON LEADING EDGE RADIUS VARIATIONS OF A SUPERSONIC TRANSPORT AT TRANSONIC CONDITIONS S. M. B. Rivers *, R. A. Wahls, and L. R. Owens Aerodynamics, Aerothermodynamics, and Acoustics
REYNOLDS NUMBER EFFECTS ON LEADING EDGE RADIUS VARIATIONS OF A SUPERSONIC TRANSPORT AT TRANSONIC CONDITIONS S. M. B. Rivers *, R. A. Wahls, and L. R. Owens Aerodynamics, Aerothermodynamics, and Acoustics
Transonic Flutter Prediction of Supersonic Jet Trainer with Various External Store Configurations
 Transonic Flutter Prediction of Supersonic Jet Trainer with Various External Store Configurations In Lee * Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, 305-701, Korea Hyuk-Jun Kwon Agency
Transonic Flutter Prediction of Supersonic Jet Trainer with Various External Store Configurations In Lee * Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, 305-701, Korea Hyuk-Jun Kwon Agency
AOE 3114 Compressible Aerodynamics
 AOE 114 Compressible Aerodynamics Primary Learning Objectives The student will be able to: 1. Identify common situations in which compressibility becomes important in internal and external aerodynamics
AOE 114 Compressible Aerodynamics Primary Learning Objectives The student will be able to: 1. Identify common situations in which compressibility becomes important in internal and external aerodynamics
Torsion of Solid Sections. Introduction
 Introduction Torque is a common load in aircraft structures In torsion of circular sections, shear strain is a linear function of radial distance Plane sections are assumed to rotate as rigid bodies These
Introduction Torque is a common load in aircraft structures In torsion of circular sections, shear strain is a linear function of radial distance Plane sections are assumed to rotate as rigid bodies These
Detailed Outline, M E 320 Fluid Flow, Spring Semester 2015
 Detailed Outline, M E 320 Fluid Flow, Spring Semester 2015 I. Introduction (Chapters 1 and 2) A. What is Fluid Mechanics? 1. What is a fluid? 2. What is mechanics? B. Classification of Fluid Flows 1. Viscous
Detailed Outline, M E 320 Fluid Flow, Spring Semester 2015 I. Introduction (Chapters 1 and 2) A. What is Fluid Mechanics? 1. What is a fluid? 2. What is mechanics? B. Classification of Fluid Flows 1. Viscous
AERO-STRUCTURAL MDO OF A SPAR-TANK-TYPE WING FOR AIRCRAFT CONCEPTUAL DESIGN
 1 26th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES AERO-STRUCTURAL MDO OF A SPAR-TANK-TYPE WING FOR AIRCRAFT CONCEPTUAL DESIGN Paulo R. Caixeta Jr., Álvaro M. Abdalla, Flávio D. Marques, Fernando
1 26th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES AERO-STRUCTURAL MDO OF A SPAR-TANK-TYPE WING FOR AIRCRAFT CONCEPTUAL DESIGN Paulo R. Caixeta Jr., Álvaro M. Abdalla, Flávio D. Marques, Fernando
The Fighter of the 21 st Century. Presented By Michael Weisman Configuration Aerodynamics 4/23/01
 The Fighter of the 21 st Century Presented By Michael Weisman Configuration Aerodynamics 4/23/01 1 Joint Strike Fighter (JSF) Program Its purpose is to develop and field an affordable and highly common
The Fighter of the 21 st Century Presented By Michael Weisman Configuration Aerodynamics 4/23/01 1 Joint Strike Fighter (JSF) Program Its purpose is to develop and field an affordable and highly common
58:160 Intermediate Fluid Mechanics Bluff Body Professor Fred Stern Fall 2014
 Professor Fred Stern Fall 04 Chapter 7 Bluff Body Fluid flows are broadly categorized:. Internal flows such as ducts/pipes, turbomachinery, open channel/river, which are bounded by walls or fluid interfaces:
Professor Fred Stern Fall 04 Chapter 7 Bluff Body Fluid flows are broadly categorized:. Internal flows such as ducts/pipes, turbomachinery, open channel/river, which are bounded by walls or fluid interfaces:
SIMULATION OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL INCOMPRESSIBLE CAVITY FLOWS
 ICAS 2000 CONGRESS SIMULATION OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL INCOMPRESSIBLE CAVITY FLOWS H Yao, R K Cooper, and S Raghunathan School of Aeronautical Engineering The Queen s University of Belfast, Belfast BT7 1NN,
ICAS 2000 CONGRESS SIMULATION OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL INCOMPRESSIBLE CAVITY FLOWS H Yao, R K Cooper, and S Raghunathan School of Aeronautical Engineering The Queen s University of Belfast, Belfast BT7 1NN,
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE DYNAMIC STABILITY DERIVATIVES FOR A FIGHTER MODEL
 24 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE DYNAMIC STABILITY DERIVATIVES FOR A FIGHTER MODEL MR Soltani*, Ali R Davari** *Associate Professor, **PhD Student
24 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE DYNAMIC STABILITY DERIVATIVES FOR A FIGHTER MODEL MR Soltani*, Ali R Davari** *Associate Professor, **PhD Student
The Truth About Elliptic Spanloads or Optimum Spanloads Incorporating Wing Structural Weight
 The Truth About Elliptic Spanloads or Optimum Spanloads Incorporating Wing Structural Weight Sergio Iglesias and William H. Mason AIAA Paper 2001-5234 as presented at the 1st AIAA Aircraft Technology,
The Truth About Elliptic Spanloads or Optimum Spanloads Incorporating Wing Structural Weight Sergio Iglesias and William H. Mason AIAA Paper 2001-5234 as presented at the 1st AIAA Aircraft Technology,
Introduction to Flight
 l_ Introduction to Flight Fifth Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Curator for Aerodynamics, National Air and Space Museum Smithsonian Institution Professor Emeritus University of Maryland Me Graw Higher Education
l_ Introduction to Flight Fifth Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Curator for Aerodynamics, National Air and Space Museum Smithsonian Institution Professor Emeritus University of Maryland Me Graw Higher Education
