11. Collision in Two Dimensions*
|
|
|
- Lionel Morris Garrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 11. Collision in Two Dimensions* The objective in this unit is to learn about collisions in two dimensions. Learning Objectives: 1. Solve a two dimensional momentum problem illustrating momentum conservation that especially emphasizing the vector nature of momentum. 2. Taking full advantage of separation of vector components, use free fall along z direction to time motion in the x-y plane. 3. Recognize proportionality between time of fall and distance traveled when velocities are constant. Your group is part of a team investigating an air crash in which a small aircraft collided with a helicopter carrying a news crew. The plan is to set up model mid-air collisions in the laboratory. In the actual air crash, the collision is not inelastic, although the laboratory simulation will study first the case of a nearly elastic collision. (Later the inelastic case will be taken up, perhaps by a different group.) In the case under study, the plane and the helicopter were about the same mass. They collided at exactly the same altitude, so the collision was two dimensional. Reading: Before coming to lab, read the section on collisions in your textbook. In particular, read material on collisions in two and three dimensions, both elastic and inelastic collisions. Knight, Jones & Field (161): 3.3 Coordinate Systems and vector Components, 9.6 Momentum and Collision in Two Dimensions Serway and Vuille (211): 6.3 Collisions s, 6.4 Glancing Collisions Serway and Jewett (251): 9.5 Collisions in Two Dimensions PRE-LAB EXERCISES Complete the following exercises before you come to lab. As usual, your TA will check to be sure you have done them when you enter the lab. You will turn them in with your report. 1. Answer the following from your reading. a. Write a formula defining the total momentum p of a system consisting of three particles, with masses m 1, m 2 and m 3. Use proper vector notation. b. Under what conditions will the total momentum be the same before and after a certain process? (In other words, when is momentum conserved?) c. If a collision is elastic, what other quantity besides total momentum is the same before and after the collision? d. What two conditions must be met in order that when two spheres collide, one of them being at rest initially, that the angle between the velocity vectors after the collision will be 90 o? * William A Schwalm
2 2. (Phys 211 and 251, not Phys 161) In an air hockey game with two pucks of unequal mass, one puck has mass m and the other has mass 2m. The heavier puck is initially at rest and the lighter one is moving along some direction with speed v o, and hits the other one at a glancing angle. After the collision, the lighter puck moves away from the point of impact at an angle of 90 o with respect to its initial direction. If the collision is elastic, find out how fast the lighter puck is moving and also the two components of the velocity of the heavier puck after the collision. 3. Now consider the air crash. Suppose that at the instant of the crash, neither aircraft is given an initial vertical velocity. The motion of each just after the crash is in the horizontal plane. If the collision takes place at an altitude h, at what time t (how long after the crash) will the two objects both strike the ground? Show your work and explain, as always. 4. If the horizontal velocity vectors on the aircraft and the helicopter, just milliseconds after the crash, are va and vh respectively, explain how you could calculate exactly where each one should strike the ground, measured from the point on the ground directly under the crash. Be specific. 11-2
3 5. On the other hand, suppose you did not know the initial horizontal velocities. Explain how you could find the velocity vectors, knowing where the collision took place, including the altitude, and knowing where each aircraft crashed. Explain in sufficient detail. 6. Suppose the plane crashed at 470 meters west and 150 meters north of the collision, and the helicopter crashed at 220 meters south and 70 meters west of the collision. Figure out the x and y components of the two initial horizontal velocities after the crash, if the collision was at an altitude of 650 meters. Show your work and explain your reasoning in complete sentences. 7. Suppose for simplicity that the helicopter and the airplane have the same mass m. Can you figure out what the initial velocity vector of the plane was before the collision, assuming that the helicopter was stopped? Include in your explanation a statement of what physical quantity would necessarily be conserved, and why. 11-3
4 Equipment: You will be using two steel balls to model the crash. One is given an initial velocity by having it roll down an incline (on a plastic ruler) while the other ball is initially at rest, sitting on top of a leveling screw. You have the plastic ruler ramp, which cab be fixed to the table, a leveling screw for positioning the target ball, a string and plumb bob for finding the point on the floor under where the collision takes place, and some butcher s paper and carbon copy paper for recording data (crash sites). Meter sticks will also be available. Problem 1 First we need to get a handle on controlling initial speed in the modeling process. So the first thing to do is to have a way of measuring the initial speed of the moving ball before collision. One way to do it using the equipment at hand is to launch a steel ball horizontally of the edge of the table, without any collision, and to see where it falls. Doing this a few times will give some idea of how to control the initial speed before impact. 1. Prediction question: What do you know, in general, about the horizontal motion of a projectile? Explain why. 2. Prediction question: If you know the initial height above the floor, how can this be used to figure the time of flight? We need a formula here. 3. Method question: Using materials provided in the list above, how can you find a point on the floor directly under the point where the ball starts to drop? 4. Method question: By making several shots and recording where the ball hits each time, how can you estimate the precision of the measurement? Plan: After a discussion with your group members, write out an outline of how you plan to determine the initial speed of the ball before impact in the modeling experiments. You also need to know about measurement precision, so figure out how to determine that too. Implementation: Carry out your plan. Collect the data you need in order to determine the initial velocity under controlled conditions. See whether you can even vary the initial velocity in a controlled way. 11-4
5 Record here with appropriate units and notes. Remember you need to be able to define the initial conditions so that another student from a different physics course could reproduce the results, given the same equipment. Analysis: From your data, see if you can find the way the initial speed is related to the conditions you tried. Show enough of your work and explain what you re doing. Give a quantitative estimate of the error involved, and state whether or not you can actually control the initial speed effectively and repeatably. Conclusions: What did you learn? 1. Describe what you have learned about controlling the speed of the moving ball before impact. 2. Explain how you expect to make use of this in the next phase of the research. 11-5
6 Problem 2 Now you need to set up a collision to simulate the air crash. 1. Prediction question: Write down a conservation law that should always hold for collisions. What quantity should be the same before and after any collision? Express this in proper mathematical notation. 2. Prediction question: (Phys 251 only) Recall two things about vector dot products: (a) dotting a vector into itself gives the square of its magnitude, and (b) when you dot two vectors together you get zero if and only if they are perpendicular. Two identical balls have the same mass. Initially, one ball is moving with initial velocity v and the other is at rest. After the collision, the two are moving with o velocity vectors v 1 and v 2 respectively. Take the total momentum vector before the collision and dot it into itself. Then take the total momentum vector after the collision and dot it into itself. Write these expressions down. These quantities should be equal. (Why?) 3. Prediction question: (251 only) Suppose the collision is elastic. Then what quantity should also be the same before and after the collision? Assuming that this additional quantity is indeed conserved, and using the formula from the previous question, what does this tell you about the dot product v1 v2? Thus, what can you conclude about the relative directions of motion of the two balls after the collision? 4. Method question: In the previous questions you showed that if the masses are equal and also the collision is elastic, then the angle between the final velocity vectors is 90 o. How will you be able to tell from measurements whether or not the laboratory collisions are elastic, or nearly elastic? 11-6
7 Plan: Devise amongst yourselves a plan for making measurements to tell (a) whether or not momentum is actually conserved in laboratory conditions, and (b) whether the collisions you observe are actually elastic or not. What data do you need? What role will each group member play in taking the data? How will the data be analyzed? Record your group plan here. Implementation: Implement your plan and record the necessary data here, including correct units and comments as needed. Analysis: Now carry out the analysis needed to solve the measurement problems (a) and (b). Show example calculations and explain your analysis. 11-7
8 Conclusions: What have you learned? 1. To what extent (quantitatively) do the data support your predictions? Is either or both of the two quantities we have been discussing conserved during the model collisions in the laboratory? 2. If your predictions were more or less correct, how can the model be used to study the air crash? If not, what do you thing the difficulty is in the method? 11-8
10. Ballistic Pendulum*
 10. Ballistic Pendulum* Use is made of a ballistic pendulum to determine projectile velocity. Learning Objectives: 1. Explore the ideas of energy and momentum conservation, particularly the conditions
10. Ballistic Pendulum* Use is made of a ballistic pendulum to determine projectile velocity. Learning Objectives: 1. Explore the ideas of energy and momentum conservation, particularly the conditions
Conservation of Momentum: Marble Collisions Student Version
 Conservation of Momentum: Marble Collisions Student Version In this lab you will roll a marble down a ramp, and at the bottom of the ramp the marble will collide with another marble. You will measure the
Conservation of Momentum: Marble Collisions Student Version In this lab you will roll a marble down a ramp, and at the bottom of the ramp the marble will collide with another marble. You will measure the
Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions
 Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions Consider the two-dimensional (glancing) collision shown below. Here, mass m 1 travels to the right along the x-axis with velocity v 1o and strikes mass m 2 initially
Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions Consider the two-dimensional (glancing) collision shown below. Here, mass m 1 travels to the right along the x-axis with velocity v 1o and strikes mass m 2 initially
CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM. Object: To study the law of conservation of momentum by analyzing collisions in two dimensions.
 CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM Object: To study the law of conservation of momentum by analyzing collisions in two dimensions. Apparatus: Digital scale, Ramp, two steel balls, one hollow or plastic ball, C-clamp,
CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM Object: To study the law of conservation of momentum by analyzing collisions in two dimensions. Apparatus: Digital scale, Ramp, two steel balls, one hollow or plastic ball, C-clamp,
Projectile Motion. x = v ox t (1)
 Projectile Motion Theory Projectile motion is the combination of different motions in the x and y directions. In the x direction, which is taken as parallel to the surface of the earth, the projectile
Projectile Motion Theory Projectile motion is the combination of different motions in the x and y directions. In the x direction, which is taken as parallel to the surface of the earth, the projectile
Physics 11 Honours. x-dir px : m1 v1 = (m1 + m2 ) V cos y-dir py : m2 v2 = (m1 + m2 ) V sin A Collision at an Intersection Example 1:
 Name: Physics 11 Honours Date: Unit 7 Momentum and Its Conservation 7.4 A perfectly inelastic collision in 2-D Consider a collision in 2-D (cars crashing at a slippery intersection...no friction). Because
Name: Physics 11 Honours Date: Unit 7 Momentum and Its Conservation 7.4 A perfectly inelastic collision in 2-D Consider a collision in 2-D (cars crashing at a slippery intersection...no friction). Because
Notes Momentum. Momentum and Impulse. - The product (multiplication) of an objects mass and velocity is called momentum.
 Notes Momentum Momentum and Impulse - The product (multiplication) of an objects mass and velocity is called momentum. Momentum is the energy of motion of an object. Momentum is represented by the letter.
Notes Momentum Momentum and Impulse - The product (multiplication) of an objects mass and velocity is called momentum. Momentum is the energy of motion of an object. Momentum is represented by the letter.
General Physics I Lab. M7 Conservation of Angular Momentum
 Purpose In this experiment, you will investigate the conservation law of angular momentum in a collision between a ball falling along an inclined ramp and a ball catcher fixed on a freely rotating disk.
Purpose In this experiment, you will investigate the conservation law of angular momentum in a collision between a ball falling along an inclined ramp and a ball catcher fixed on a freely rotating disk.
Physics 30 - Ballistic Pendulum Lab 2010, Science Kit All Rights Reserved
 BACKGROUND Energy The maximum height achieved by the pendulum on the Ballistic Pendulum apparatus can be determined by using the angle it achieved. Figure S1 shows the pendulum in two different positions,
BACKGROUND Energy The maximum height achieved by the pendulum on the Ballistic Pendulum apparatus can be determined by using the angle it achieved. Figure S1 shows the pendulum in two different positions,
IMPACT (Section 15.4)
 IMPACT (Section 15.4) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Understand and analyze the mechanics of impact. b) Analyze the motion of bodies undergoing a collision, in both central and oblique
IMPACT (Section 15.4) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Understand and analyze the mechanics of impact. b) Analyze the motion of bodies undergoing a collision, in both central and oblique
Student Exploration: 2D Collisions
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: 2D Collisions Vocabulary: center of mass, conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, elasticity, kinetic energy, momentum, speed, vector, velocity Prior Knowledge
Name: Date: Student Exploration: 2D Collisions Vocabulary: center of mass, conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, elasticity, kinetic energy, momentum, speed, vector, velocity Prior Knowledge
Exercise 6: The conservation of energy and momentum
 Physics 221 Name: Exercise 6: The conservation of energy and momentum Part 1: The projectile launcher s spring constant Objective: Through the use of the principle of conservation of energy (first law
Physics 221 Name: Exercise 6: The conservation of energy and momentum Part 1: The projectile launcher s spring constant Objective: Through the use of the principle of conservation of energy (first law
12-Nov-17 PHYS Inelastic Collision. To study the laws of conservation of linear momentum and energy in a completely inelastic collision.
 Objectives Inelastic Collision To study the laws of conservation of linear momentum and energy in a completely inelastic collision. Introduction If no net external force acts on a system of particles,
Objectives Inelastic Collision To study the laws of conservation of linear momentum and energy in a completely inelastic collision. Introduction If no net external force acts on a system of particles,
Conservation of Momentum: Marble Collisions Advanced Version
 Conservation of Momentum: Marble Collisions Advanced Version In this lab you will roll a marble down a ramp, and at the bottom of the ramp the marble will collide with another marble. You will measure
Conservation of Momentum: Marble Collisions Advanced Version In this lab you will roll a marble down a ramp, and at the bottom of the ramp the marble will collide with another marble. You will measure
(D) Based on Ft = m v, doubling the mass would require twice the time for same momentum change
 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass, what time would be required to stop a car of mass m traveling
1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass, what time would be required to stop a car of mass m traveling
Energy in Collisions Problems AP Physics C
 1. A bullet of mass m and velocity v 0 is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity
1. A bullet of mass m and velocity v 0 is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity
Gravity Pre-Lab 1. Why do you need an inclined plane to measure the effects due to gravity?
 Lab Exercise: Gravity (Report) Your Name & Your Lab Partner s Name Due Date Gravity Pre-Lab 1. Why do you need an inclined plane to measure the effects due to gravity? 2. What are several advantage of
Lab Exercise: Gravity (Report) Your Name & Your Lab Partner s Name Due Date Gravity Pre-Lab 1. Why do you need an inclined plane to measure the effects due to gravity? 2. What are several advantage of
Chapter Assessment Use with Chapter 9.
 Date Period 9 Use with Chapter 9. Momentum and Its Conservation Understanding Concepts Part A Write the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The linear momentum
Date Period 9 Use with Chapter 9. Momentum and Its Conservation Understanding Concepts Part A Write the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The linear momentum
PHYS 154 Practice Test 3 Spring 2018
 The actual test contains 1 multiple choice questions and 2 problems. However, for extra exercise, this practice test includes 4 problems. Questions: N.B. Make sure that you justify your answers explicitly
The actual test contains 1 multiple choice questions and 2 problems. However, for extra exercise, this practice test includes 4 problems. Questions: N.B. Make sure that you justify your answers explicitly
Lab 10: Ballistic Pendulum
 Lab Section (circle): Day: Monday Tuesday Time: 8:00 9:30 1:10 2:40 Lab 10: Ballistic Pendulum Name: Partners: Pre-Lab You are required to finish this section before coming to the lab it will be checked
Lab Section (circle): Day: Monday Tuesday Time: 8:00 9:30 1:10 2:40 Lab 10: Ballistic Pendulum Name: Partners: Pre-Lab You are required to finish this section before coming to the lab it will be checked
11 M36 M36.1 ANALYSIS OF A COMPLETELY INELASTIC COLLISION OBJECT The object of this experiment is to examine a completely inelastic collision between
 11 M36 M36.1 ANALYSIS OF A COMPLETELY INELASTIC COLLISION OBJECT The object of this experiment is to examine a completely inelastic collision between a steel ball and a ballistic pendulum. NOTE: Before
11 M36 M36.1 ANALYSIS OF A COMPLETELY INELASTIC COLLISION OBJECT The object of this experiment is to examine a completely inelastic collision between a steel ball and a ballistic pendulum. NOTE: Before
(A) 0 (B) mv (C) 2mv (D) 2mv sin θ (E) 2mv cos θ
 Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
Experiment 4: Projectile Motion
 Experiment 4: Projectile Motion EQUIPMENT Figure 4.1: Ballistic Pendulum (Spring Gun) Pasco Ballistic Pendulum (Spring Gun) 2-Meter Stick Meter Stick Ruler Plumb Bob Carbon Paper Target Paper Launch Platform
Experiment 4: Projectile Motion EQUIPMENT Figure 4.1: Ballistic Pendulum (Spring Gun) Pasco Ballistic Pendulum (Spring Gun) 2-Meter Stick Meter Stick Ruler Plumb Bob Carbon Paper Target Paper Launch Platform
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum)
 AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum) 1980M2. A block of mass m slides at velocity v o across a horizontal frictionless surface toward a large curved movable ramp
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum) 1980M2. A block of mass m slides at velocity v o across a horizontal frictionless surface toward a large curved movable ramp
11 M36 M36.1 ANALYSIS OF A PERFECTLY INELASTIC COLLISION The object of this experiment is to examine a perfectly inelastic collision between a steel
 11 M36 M36.1 OBJECT THEORY ANALYSIS OF A PERFECTLY INELASTIC COLLISION The object of this experiment is to examine a perfectly inelastic collision between a steel ball and a ballistic pendulum. NOTE: Before
11 M36 M36.1 OBJECT THEORY ANALYSIS OF A PERFECTLY INELASTIC COLLISION The object of this experiment is to examine a perfectly inelastic collision between a steel ball and a ballistic pendulum. NOTE: Before
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions
 Physics Topics Elastic and Inelastic Collisions If necessary, review the following topics and relevant textbook sections from Serway / Jewett Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 9th Ed. Kinetic Energy
Physics Topics Elastic and Inelastic Collisions If necessary, review the following topics and relevant textbook sections from Serway / Jewett Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 9th Ed. Kinetic Energy
AAPT UNITED STATES PHYSICS TEAM AIP 2017
 2017 F = ma Exam 1 AAPT UNITED STATES PHYSICS TEAM AIP 2017 2017 F = ma Contest 25 QUESTIONS - 75 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO BEGIN Use g = 10 N/kg throughout this
2017 F = ma Exam 1 AAPT UNITED STATES PHYSICS TEAM AIP 2017 2017 F = ma Contest 25 QUESTIONS - 75 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO BEGIN Use g = 10 N/kg throughout this
Chapter 3 Kinematics
 Chapter 3 Kinematics GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Use the following terms to describe the physical state of a system:
Chapter 3 Kinematics GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Use the following terms to describe the physical state of a system:
Glancing Collisions and Conservation of Momentum
 Bob Somers 12/16/04 Per. 4 Daniel Lau, Patrick Noland Glancing Collisions and Conservation of Momentum Purpose In this lab we set out to prove that momentum is conserved in the real world, even in glancing,
Bob Somers 12/16/04 Per. 4 Daniel Lau, Patrick Noland Glancing Collisions and Conservation of Momentum Purpose In this lab we set out to prove that momentum is conserved in the real world, even in glancing,
Changes in Energy and Momentum
 Changes in Energy and Momentum Name: Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Learning Objectives: 1. Understanding the relationship between force, distance and changes in kinetic energy. 2. Understanding the relationship
Changes in Energy and Momentum Name: Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Learning Objectives: 1. Understanding the relationship between force, distance and changes in kinetic energy. 2. Understanding the relationship
Review Session 1. Page 1
 Review Session 1 1. Which combination of fundamental units can be used to express the amount of work done on an object? 2. The height of a typical kitchen table is approximately A) 10-2 m B) 10 0 m C)
Review Session 1 1. Which combination of fundamental units can be used to express the amount of work done on an object? 2. The height of a typical kitchen table is approximately A) 10-2 m B) 10 0 m C)
IMPACT Today s Objectives: In-Class Activities:
 Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Understand and analyze the mechanics of impact. 2. Analyze the motion of bodies undergoing a collision, in both central and oblique cases of impact. IMPACT
Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Understand and analyze the mechanics of impact. 2. Analyze the motion of bodies undergoing a collision, in both central and oblique cases of impact. IMPACT
Ballistic Pendulum and Projectile Motion
 Ballistic Pendulum and Projectile Motion The initial velocity of a ball shot from a spring gun is determined by the equations for projectile motion and by the equations for a ballistic pendulum. Projectile
Ballistic Pendulum and Projectile Motion The initial velocity of a ball shot from a spring gun is determined by the equations for projectile motion and by the equations for a ballistic pendulum. Projectile
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions
 Elastic and Inelastic Collisions - TA Version Physics Topics If necessary, review the following topics and relevant textbook sections from Serway / Jewett Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 9th Ed.
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions - TA Version Physics Topics If necessary, review the following topics and relevant textbook sections from Serway / Jewett Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 9th Ed.
A) 4.0 m/s B) 5.0 m/s C) 0 m/s D) 3.0 m/s E) 2.0 m/s. Ans: Q2.
 Coordinator: Dr. W. Al-Basheer Thursday, July 30, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. A constant force F ( 7.0ˆ i 2.0 ˆj ) N acts on a 2.0 kg block, initially at rest, on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the force causes
Coordinator: Dr. W. Al-Basheer Thursday, July 30, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. A constant force F ( 7.0ˆ i 2.0 ˆj ) N acts on a 2.0 kg block, initially at rest, on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the force causes
Academic Physics! Work and Momentum Summary! Name
 Academic Physics! Work and Summary! Name 1. A child with a mass of 23kg rides a bike with a mass of 5.5 kg at a velocity of 4.5 m/s to the south. Compare the momentum of the child and the momentum of the
Academic Physics! Work and Summary! Name 1. A child with a mass of 23kg rides a bike with a mass of 5.5 kg at a velocity of 4.5 m/s to the south. Compare the momentum of the child and the momentum of the
The Role of the Lab Practicum in Modeling
 The Role of the Lab Practicum in Modeling The lab practicum, as advocated by Jon Barber and Henry Ryan, serves as an excellent deployment activity for the application and reinforcement of the models and
The Role of the Lab Practicum in Modeling The lab practicum, as advocated by Jon Barber and Henry Ryan, serves as an excellent deployment activity for the application and reinforcement of the models and
Final EXAM. Physics 203. Prof. Daniel A. Martens Yaverbaum. John Jay College of Criminal Justice, the CUNY. Sections 1, 2. Wednesday, 5/21/14
 Final EXAM Physics 203 Prof. Daniel A. Martens Yaverbaum John Jay College of Criminal Justice, the CUNY Sections 1, 2 Wednesday, 5/21/14 (Revised, Clarified, 5/28/14) Name: Section # : SCORE: DIRECTIONS
Final EXAM Physics 203 Prof. Daniel A. Martens Yaverbaum John Jay College of Criminal Justice, the CUNY Sections 1, 2 Wednesday, 5/21/14 (Revised, Clarified, 5/28/14) Name: Section # : SCORE: DIRECTIONS
Two Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems
 Two Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems Problem 1: Suppose a MIT student wants to row across the Charles River. Suppose the water is moving downstream at a constant rate of 1.0 m/s. A second boat
Two Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems Problem 1: Suppose a MIT student wants to row across the Charles River. Suppose the water is moving downstream at a constant rate of 1.0 m/s. A second boat
11 M36 M36.1 ANALYSIS OF A PERFECTLY INELASTIC COLLISION OBJECT The object of this experiment is to examine a perfectly inelastic collision between a
 11 M36 M36.1 ANALYSIS OF A PERFECTLY INELASTIC COLLISION OBJECT The object of this experiment is to examine a perfectly inelastic collision between a steel ball and a ballistic pendulum. THEORY Reference:
11 M36 M36.1 ANALYSIS OF A PERFECTLY INELASTIC COLLISION OBJECT The object of this experiment is to examine a perfectly inelastic collision between a steel ball and a ballistic pendulum. THEORY Reference:
4.) A baseball that weighs 1.6 N leaves a bat with a speed of 40.0 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the ball. 130 J
 AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
Cart A Cart B Cart C Cart D Mass (kg) 4.0kg 1.0kg 3.5kg 12kg Velocity (m/s)
 Position (m) -40-20 20 40 Physics 03_14 Momentum Remediation 1. A 65 kg person runs to catch the bus at 1.31 m/s. What is their momentum? Name 4. A 10.2 kg ball has a momentum of 4340 kg m/s. What is the
Position (m) -40-20 20 40 Physics 03_14 Momentum Remediation 1. A 65 kg person runs to catch the bus at 1.31 m/s. What is their momentum? Name 4. A 10.2 kg ball has a momentum of 4340 kg m/s. What is the
Projectile Motion. Figure 1. The system of coordinates for the projectile motion.
 Projectile Motion (1) Introduction and Theory: Consider a projectile motion of a ball as shown in Fig. 1. At t = 0 the ball is released at the position (0, y0) with horizontal velocity vx. Figure 1. The
Projectile Motion (1) Introduction and Theory: Consider a projectile motion of a ball as shown in Fig. 1. At t = 0 the ball is released at the position (0, y0) with horizontal velocity vx. Figure 1. The
Chapter 9. 9 Momentum. Momentum. PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Momentum PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition 9 Momentum Slide 9-2 Slide 9-3 1 Slide 9-4 Reading Quiz 1. Impulse is A. a force that is applied at a random
Chapter 9 Momentum PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition 9 Momentum Slide 9-2 Slide 9-3 1 Slide 9-4 Reading Quiz 1. Impulse is A. a force that is applied at a random
Unit 7, 8, 9 Physics Review
 Unit 7, 8, 9 Physics Review 1. A 2 kg mass is held 4 m above the ground. What is the approximate potential energy due to gravity of the mass with respect to the ground? a. 20 J. b. 40 J. c. 60 J. d. 80
Unit 7, 8, 9 Physics Review 1. A 2 kg mass is held 4 m above the ground. What is the approximate potential energy due to gravity of the mass with respect to the ground? a. 20 J. b. 40 J. c. 60 J. d. 80
PSI AP Physics I Momentum
 PSI AP Physics I Momentum Multiple-Choice questions 1. A truck moves along a frictionless level road at a constant speed. The truck is open on top. A large load of gravel is suddenly dumped into the truck.
PSI AP Physics I Momentum Multiple-Choice questions 1. A truck moves along a frictionless level road at a constant speed. The truck is open on top. A large load of gravel is suddenly dumped into the truck.
Dynamics-Newton's 2nd Law
 1. A constant unbalanced force is applied to an object for a period of time. Which graph best represents the acceleration of the object as a function of elapsed time? 2. The diagram below shows a horizontal
1. A constant unbalanced force is applied to an object for a period of time. Which graph best represents the acceleration of the object as a function of elapsed time? 2. The diagram below shows a horizontal
Comprehensive Exam Session III Classical Mechanics Physics Department- Proctor: Dr. Jack Straton (Sun. Jan 11 th, 2015) (3 hours long 1:00 to 4:00 PM)
 Letter Comprehensive Exam Session III Classical Mechanics Physics Department- Proctor: Dr. Jack Straton (Sun. Jan 11 th, 2015) (3 hours long 1:00 to 4:00 PM) If you cannot solve the whole problem, write
Letter Comprehensive Exam Session III Classical Mechanics Physics Department- Proctor: Dr. Jack Straton (Sun. Jan 11 th, 2015) (3 hours long 1:00 to 4:00 PM) If you cannot solve the whole problem, write
Linear Acceleration and Projectile Path
 Linear Acceleration and Projectile Path Objective To study the motion of a body when projected at an angle above the horizontal on an inclined plane. Introduction In this experiment we ll use an air table
Linear Acceleration and Projectile Path Objective To study the motion of a body when projected at an angle above the horizontal on an inclined plane. Introduction In this experiment we ll use an air table
Experiment 7: Conservation of Energy and Momentum in a Collision
 Experiment 7: Conservation of Energy and Momentum in a Collision You will check for conservation of kinetic energy and for conservation of momentum in a collision between two ball bearings. One ball bearing
Experiment 7: Conservation of Energy and Momentum in a Collision You will check for conservation of kinetic energy and for conservation of momentum in a collision between two ball bearings. One ball bearing
Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 BROCK UNIVERSITY
 Tutorial #: Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 Name: Student #: BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 7: November 2015 Number of pages: 5 Course: PHYS 1P21/1P91 Number of students: 218 Examination date: 17
Tutorial #: Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 Name: Student #: BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 7: November 2015 Number of pages: 5 Course: PHYS 1P21/1P91 Number of students: 218 Examination date: 17
THE BALLISTIC PENDULUM AND THE LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY
 THE BALLISTIC PENDULUM AND THE LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Objectives 1) To study the laws of conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, and the elements of projectile motion using the ballistic
THE BALLISTIC PENDULUM AND THE LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Objectives 1) To study the laws of conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, and the elements of projectile motion using the ballistic
Prelab: Complete the prelab section BEFORE class Purpose:
 Lab: Projectile Motion Prelab: Complete the prelab section BEFORE class Purpose: What is the Relationship between and for the situation of a cannon ball shot off a with an angle of from the horizontal.
Lab: Projectile Motion Prelab: Complete the prelab section BEFORE class Purpose: What is the Relationship between and for the situation of a cannon ball shot off a with an angle of from the horizontal.
Ballistic Pendulum. Caution
 Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the ball,
Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the ball,
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum
 Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the
General Physics I Momentum
 General Physics I Momentum Linear Momentum: Definition: For a single particle, the momentum p is defined as: p = mv (p is a vector since v is a vector). So p x = mv x etc. Units of linear momentum are
General Physics I Momentum Linear Momentum: Definition: For a single particle, the momentum p is defined as: p = mv (p is a vector since v is a vector). So p x = mv x etc. Units of linear momentum are
9 Momentum and Its Conservation 2 Conservation of Momentum MAINIDEA
 9 Momentum and Its Conservation 2 Conservation of Momentum MAINIDEA Write the Main Idea for this section. REVIEW VOCABULARY Recall and write the definition of the Review Vocabulary term. NEW VOCABULARY
9 Momentum and Its Conservation 2 Conservation of Momentum MAINIDEA Write the Main Idea for this section. REVIEW VOCABULARY Recall and write the definition of the Review Vocabulary term. NEW VOCABULARY
Ballistic Pendulum. Equipment- ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale PRECAUTION
 Ballistic Pendulum Equipment- ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale PRECAUTION In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally
Ballistic Pendulum Equipment- ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale PRECAUTION In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally
Chapter 9. Momentum. PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Momentum PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition 9 Momentum Slide 9-2 Slide 9-3 Slide 9-4 Reading Quiz 1. Impulse is A. a force that is applied at a random
Chapter 9 Momentum PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition 9 Momentum Slide 9-2 Slide 9-3 Slide 9-4 Reading Quiz 1. Impulse is A. a force that is applied at a random
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7
 Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7 1. Kinetic energy is defined to be one-half the a. mass times the speed. b. mass times the speed squared. c. mass times the acceleration. d.
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7 1. Kinetic energy is defined to be one-half the a. mass times the speed. b. mass times the speed squared. c. mass times the acceleration. d.
Practice Test for Midterm Exam
 A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity of o
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Momentum and Impulse 1976B2. A bullet of mass m and velocity v o is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface.
AP Physics Free Response Practice Momentum and Impulse 1976B2. A bullet of mass m and velocity v o is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface.
Conservation Laws (Collisions)
 PHYS-101 LAB-04 Conservation Laws (Collisions) 1. Objective The objectives of this experiment are: Measurement of momentum and kinetic energy in collisions. Experimentally test the validity of the principles
PHYS-101 LAB-04 Conservation Laws (Collisions) 1. Objective The objectives of this experiment are: Measurement of momentum and kinetic energy in collisions. Experimentally test the validity of the principles
Multiple Choice Review for Final Exam ~ Physics 1020
 Multiple Choice Review for Final Exam ~ Physics 1020 1. You are throwing a ball straight up in the air. At the highest point, the ball s a) velocity and acceleration are zero b) velocity is nonzero, but
Multiple Choice Review for Final Exam ~ Physics 1020 1. You are throwing a ball straight up in the air. At the highest point, the ball s a) velocity and acceleration are zero b) velocity is nonzero, but
Vector and Relative motion discussion/ in class notes. Projectile Motion discussion and launch angle problem. Finish 2 d motion and review for test
 AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
It would be appropriate to pull out your phone or planner and write these dates down.
 Upcoming dates 11/11 (A) + 11/12 (B): Virtual Collision Lab 11/13 (A) + 11/14 (B): Momentum and Impulse Quiz and Collision Lab 11/17 (A) + 11/18 (B): Momentum and Impulse Vocabulary Quiz and Test Review
Upcoming dates 11/11 (A) + 11/12 (B): Virtual Collision Lab 11/13 (A) + 11/14 (B): Momentum and Impulse Quiz and Collision Lab 11/17 (A) + 11/18 (B): Momentum and Impulse Vocabulary Quiz and Test Review
Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions
 Conseration of Momentum in Two Dimensions Name Section Linear momentum p is defined as the product of the mass of an object and its elocity. If there is no (or negligible) external force in a collision,
Conseration of Momentum in Two Dimensions Name Section Linear momentum p is defined as the product of the mass of an object and its elocity. If there is no (or negligible) external force in a collision,
Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3
 Name: Date: _ Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3 Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above Please write and bubble your Name and Student
Name: Date: _ Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3 Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above Please write and bubble your Name and Student
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE. This file can only be used to produce a handout master:
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE This file can only be used to produce a handout master: Use print from the File menu to make a printout of the test. You may not modify the contents of this file. IMPORTANT NOTICE:
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE This file can only be used to produce a handout master: Use print from the File menu to make a printout of the test. You may not modify the contents of this file. IMPORTANT NOTICE:
Conservation of Momentum
 Conservation of Momentum 1 Introduction In this lab you will investigate conservation of momentum and the concepts of elastic and inelastic collisions. You will use similar techniques that you developed
Conservation of Momentum 1 Introduction In this lab you will investigate conservation of momentum and the concepts of elastic and inelastic collisions. You will use similar techniques that you developed
General Physics I Lab (PHYS-2011) Experiment MECH-1: Projectile Motion
 MECH-1: Projectile Motion Page 1 of 7 1 EQUIPMENT General Physics I Lab (PHYS-2011) Experiment MECH-1: Projectile Motion 1 Mini Launcher ME-6825 1 Time of Flight Accessory ME-6810 1 Phone Jack Extender
MECH-1: Projectile Motion Page 1 of 7 1 EQUIPMENT General Physics I Lab (PHYS-2011) Experiment MECH-1: Projectile Motion 1 Mini Launcher ME-6825 1 Time of Flight Accessory ME-6810 1 Phone Jack Extender
Conservation of Momentum
 Conservation of Momentum Law of Conservation of Momentum The sum of the momenta before a collision equal the sum of the momenta after the collision in an isolated system (=no external forces acting).
Conservation of Momentum Law of Conservation of Momentum The sum of the momenta before a collision equal the sum of the momenta after the collision in an isolated system (=no external forces acting).
NOTE: x and d are both variables for distance. Either may be used. x f = x i + v t
 Motion Equations NOTE: x and d are both variables for distance. Either may be used. Special case when a=g, up and down problems, parabolic motion Kinematics REMEMBER DISTANCE MY BE INDICATED BY EITHER
Motion Equations NOTE: x and d are both variables for distance. Either may be used. Special case when a=g, up and down problems, parabolic motion Kinematics REMEMBER DISTANCE MY BE INDICATED BY EITHER
Assignment 6 solutions
 Assignment 6 solutions 1) You are traveling on a hilly road. At a particular spot, when your car is perfectly horizontal, the road follows a circular arc of some unknown radius. Your speedometer reads
Assignment 6 solutions 1) You are traveling on a hilly road. At a particular spot, when your car is perfectly horizontal, the road follows a circular arc of some unknown radius. Your speedometer reads
Free Response- Exam Review
 Free Response- Exam Review Name Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the information and diagram below and on your knowledge of physics. A 150-newton force, applied to a wooden crate at an angle
Free Response- Exam Review Name Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the information and diagram below and on your knowledge of physics. A 150-newton force, applied to a wooden crate at an angle
FM: WARM-UP. Students gather evidence about the velocity change of objects in a collision. (10 min)
 CH.3 COLLISIONS FM: 3.3.1 WARM-UP Students gather evidence about the velocity change of objects in a collision. (10 min) Both Objects will Change Velocity Only 1 Object will Change Velocity Neither Object
CH.3 COLLISIONS FM: 3.3.1 WARM-UP Students gather evidence about the velocity change of objects in a collision. (10 min) Both Objects will Change Velocity Only 1 Object will Change Velocity Neither Object
Name Period Date. (m 1 + m 2. m 1. v 2i. v 1i
 Example Problems 8.2 Conservation of Momentum Brake Apart: p i p f ( )v 1,2i v 1f v 2 f Stick Together: p i p f v 1i v 2i ( )v 1,2 f Bouncing/Pass Through: p i p f v 1i v 2i v 1f v 2 f Example 1: - A monkey
Example Problems 8.2 Conservation of Momentum Brake Apart: p i p f ( )v 1,2i v 1f v 2 f Stick Together: p i p f v 1i v 2i ( )v 1,2 f Bouncing/Pass Through: p i p f v 1i v 2i v 1f v 2 f Example 1: - A monkey
The world is charged with the grandeur of God.
 Name: Course: HS Physics Date: Mr. Szopiak FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Final Exam Focus on Dynamic Systems Forces and their Effect on Particle Motion Conservation of Energy Transferring and Converting Energy
Name: Course: HS Physics Date: Mr. Szopiak FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Final Exam Focus on Dynamic Systems Forces and their Effect on Particle Motion Conservation of Energy Transferring and Converting Energy
Slide 1 / 40. Multiple Choice AP Physics 1 Momentum
 Slide 1 / 40 Multiple Choice AP Physics 1 Momentum Slide 2 / 40 1 A truck moves along a frictionless level road at a constant speed. The truck is open on top. A large load of gravel is suddenly dumped
Slide 1 / 40 Multiple Choice AP Physics 1 Momentum Slide 2 / 40 1 A truck moves along a frictionless level road at a constant speed. The truck is open on top. A large load of gravel is suddenly dumped
PHY 221 Lab 8. Momentum and Collisions: Conservation of momentum and kinetic energy
 Name: Partner: Partner: PHY 221 Lab 8 Momentum and Collisions: Conservation of momentum and kinetic energy Goals: To be able to explore how different collisions between carts can be studied to illustrate
Name: Partner: Partner: PHY 221 Lab 8 Momentum and Collisions: Conservation of momentum and kinetic energy Goals: To be able to explore how different collisions between carts can be studied to illustrate
4) Vector = and vector = What is vector = +? A) B) C) D) E)
 1) Suppose that an object is moving with constant nonzero acceleration. Which of the following is an accurate statement concerning its motion? A) In equal times its speed changes by equal amounts. B) In
1) Suppose that an object is moving with constant nonzero acceleration. Which of the following is an accurate statement concerning its motion? A) In equal times its speed changes by equal amounts. B) In
AP Physics C. Momentum. Free Response Problems
 AP Physics C Momentum Free Response Problems 1. A bullet of mass m moves at a velocity v 0 and collides with a stationary block of mass M and length L. The bullet emerges from the block with a velocity
AP Physics C Momentum Free Response Problems 1. A bullet of mass m moves at a velocity v 0 and collides with a stationary block of mass M and length L. The bullet emerges from the block with a velocity
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 8
 Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 8 Bin Chen NJIT Physics Department Chapter 8 Momentum, Impulse, and Collisions q q q q q q 8.1 Momentum and Impulse 8.2 Conservation of Momentum 8.3 Momentum Conservation
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 8 Bin Chen NJIT Physics Department Chapter 8 Momentum, Impulse, and Collisions q q q q q q 8.1 Momentum and Impulse 8.2 Conservation of Momentum 8.3 Momentum Conservation
PHYSICS LAB: CONSTANT MOTION
 PHYSICS LAB: CONSTANT MOTION Introduction Experimentation is fundamental to physics (and all science, for that matter) because it allows us to prove or disprove our hypotheses about how the physical world
PHYSICS LAB: CONSTANT MOTION Introduction Experimentation is fundamental to physics (and all science, for that matter) because it allows us to prove or disprove our hypotheses about how the physical world
Projectiles: Target Practice Student Advanced Version
 Projectiles: Target Practice Student Advanced Version In this lab you will shoot a chopstick across the room with a rubber band and measure how different variables affect the distance it flies. You will
Projectiles: Target Practice Student Advanced Version In this lab you will shoot a chopstick across the room with a rubber band and measure how different variables affect the distance it flies. You will
Lab 8. Ballistic Pendulum
 Lab 8. Ballistic Pendulum Goals To determine launch speed of a steel ball for short, medium, and long range settings on projectile launcher apparatus using equations for projectile motion. To use concepts
Lab 8. Ballistic Pendulum Goals To determine launch speed of a steel ball for short, medium, and long range settings on projectile launcher apparatus using equations for projectile motion. To use concepts
December 2015 Exam Review July :39 AM. Here are solutions to the December 2014 final exam.
 December 2015 Exam Review July-15-14 10:39 AM Here are solutions to the December 2014 final exam. 1. [5 marks] A soccer ball is kicked from the ground so that it is projected at an initial angle of 39
December 2015 Exam Review July-15-14 10:39 AM Here are solutions to the December 2014 final exam. 1. [5 marks] A soccer ball is kicked from the ground so that it is projected at an initial angle of 39
Section 4: Newton s Laws and Momentum
 Section 4: Newton s Laws and Momentum The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Physics TAC 112.39(c). 4.01 Newton s First Law Physics (4)(D) 4.02 Newton
Section 4: Newton s Laws and Momentum The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Physics TAC 112.39(c). 4.01 Newton s First Law Physics (4)(D) 4.02 Newton
Solution Figure 2(a) shows the situation. Since there is no net force acting on the system, momentum is conserved. Thus,
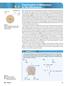 large rock Mars 5.4 small fragments to Earth Figure 1 The two-dimensional nature of the collision between a rock and the surface of Mars Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions How could a chunk of
large rock Mars 5.4 small fragments to Earth Figure 1 The two-dimensional nature of the collision between a rock and the surface of Mars Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions How could a chunk of
Force Concept Inventory
 Force Concept Inventory 1. Two metal balls are the same size but one weighs twice as much as the other. The balls are dropped from the roof of a single story building at the same instant of time. The time
Force Concept Inventory 1. Two metal balls are the same size but one weighs twice as much as the other. The balls are dropped from the roof of a single story building at the same instant of time. The time
Dynamics-Newton's 2nd Law
 1. A constant unbalanced force is applied to an object for a period of time. Which graph best represents the acceleration of the object as a function of elapsed time? 2. The diagram below shows a horizontal
1. A constant unbalanced force is applied to an object for a period of time. Which graph best represents the acceleration of the object as a function of elapsed time? 2. The diagram below shows a horizontal
What are two forms of Potential Energy that we commonly use? Explain Conservation of Energy and how we utilize it for problem-solving technics.
 Bell Ringer: Define Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy, and Work. What are two forms of Potential Energy that we commonly use? Explain Conservation of Energy and how we utilize it for problem-solving technics.
Bell Ringer: Define Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy, and Work. What are two forms of Potential Energy that we commonly use? Explain Conservation of Energy and how we utilize it for problem-solving technics.
Conservation of Momentum
 Learning Goals Conservation of Momentum After you finish this lab, you will be able to: 1. Use Logger Pro to analyze video and calculate position, velocity, and acceleration. 2. Use the equations for 2-dimensional
Learning Goals Conservation of Momentum After you finish this lab, you will be able to: 1. Use Logger Pro to analyze video and calculate position, velocity, and acceleration. 2. Use the equations for 2-dimensional
Physics Momentum. CQ8. A train and a bird are both moving with the same velocity of 50 m/s. Compare their momenta.
 Homework Procedure: Read pages specified in Honors Physics Essentials by Dan Fullerton. Questions labeled TQ will be questions about the text you read. These TQ s can be answered in one word, one phrase,
Homework Procedure: Read pages specified in Honors Physics Essentials by Dan Fullerton. Questions labeled TQ will be questions about the text you read. These TQ s can be answered in one word, one phrase,
Angular Momentum. Brown University Physics 0030 Physics Department Lab 4
 Angular Momentum Introduction In this experiment, we use a specially designed air table on which we cause the collisions of a ball and a disk, and so observe the consequence of angular momentum conservation.
Angular Momentum Introduction In this experiment, we use a specially designed air table on which we cause the collisions of a ball and a disk, and so observe the consequence of angular momentum conservation.
Momentum Practice Problems
 Momentum Practice Problems PSI AP Physics C Name Multiple Choice 1. A steel ball and a piece of clay have equal mass. They are dropped from the same height on a horizontal steel platform. The ball bounces
Momentum Practice Problems PSI AP Physics C Name Multiple Choice 1. A steel ball and a piece of clay have equal mass. They are dropped from the same height on a horizontal steel platform. The ball bounces
1. Which one of the following situations is an example of an object with a non-zero kinetic energy?
 Name: Date: 1. Which one of the following situations is an example of an object with a non-zero kinetic energy? A) a drum of diesel fuel on a parked truck B) a stationary pendulum C) a satellite in geosynchronous
Name: Date: 1. Which one of the following situations is an example of an object with a non-zero kinetic energy? A) a drum of diesel fuel on a parked truck B) a stationary pendulum C) a satellite in geosynchronous
Rolling, Torque & Angular Momentum
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 11 Rolling, Torque & Angular Momentum Rolling motion Torque Angular momentum Conservation of angular momentum 1. A uniform hoop (ring) is rolling smoothly from the
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 11 Rolling, Torque & Angular Momentum Rolling motion Torque Angular momentum Conservation of angular momentum 1. A uniform hoop (ring) is rolling smoothly from the
Outline. Collisions in 1- and 2-D. Energies from Binary Star Expt. Energy Plot. Energies with Linear Fit. Energy Plot
 Collisions in 1- and 2-D Momentum and Energy Conservation Physics 109, Class Period 9 Experiment Number 6 in the Physics 121 Lab Manual 16 October 2007 Outline Brief summary of Binary Star Experiment Description
Collisions in 1- and 2-D Momentum and Energy Conservation Physics 109, Class Period 9 Experiment Number 6 in the Physics 121 Lab Manual 16 October 2007 Outline Brief summary of Binary Star Experiment Description
Projectile Motion. v = v 2 + ( v 1 )
 What do the following situations have in common? Projectile Motion A monkey jumps from the branch of one tree to the branch of an adjacent tree. A snowboarder glides at top speed off the end of a ramp
What do the following situations have in common? Projectile Motion A monkey jumps from the branch of one tree to the branch of an adjacent tree. A snowboarder glides at top speed off the end of a ramp
