PHYS 172: Modern Mechanics. Summer r p. Lecture 9 Motion Along a Curve Read Ch 5
|
|
|
- Christal Cannon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHYS 172: Moden Mechanics Summe 2010 Δ sys = F net Δt ΔE = W + Q sys su su ΔL sys = τ net Δt Lectue 9 Motion Along a Cuve Read Ch 5
2
3 Statics Static means that something doesn t change in time. What do we exect fo ou measues of inteactions in a statics oblem?
4 Clicke Question Which of the following statements is tue? A) If = 0 d then = 0 dt = 0 d 0 d dt = 0 dt = 0 d 0 0 dt d = 0 dt B) If then C) If then D) If then E) If then may o may not be zeo
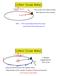
5 Motion Along a Cuve An object is following the cuved tajectoy shown below. The object is at constant t seed. Let s look at what kind of foce is necessay to get the Let s look at what kind of foce is necessay to get the object to move like this!
6 Motion Along a Cuve An object is following the cuved tajectoy shown below. The object is at constant t seed. Let s look at what kind of foce is necessay to get the Let s look at what kind of foce is necessay to get the object to move like this!
7 Peendicula and Paallel Comonents seed = constant Δ Δ Peendicula foces change the diection of momentum, but not magnitude.
8 Motion Along a Cuve An object is following the cuved tajectoy shown below. The object is seeding u. Let s look at what kind of foce is necessay to get the Let s look at what kind of foce is necessay to get the object to move like this!
9 Paallel and Peendicula Comonents Δ i Δ Δ Δ sys = Fnet Δt F aticle must be aallel with the F F g net f The net foce on the change in momentum.
10 Motion Along a Cuve Δ Δ Δ Δ Δ In comaison with the motion at a constant seed, hee we have a aallel comonent of the change in momentum and thus a aallel comonent to the net foce. Since the only thing that has changed fom the evious examle is that the object is seeding u, we conclude that the aallel comonent of the net foce is esonsible fo the change in magnitude of the momentum.
11 Detailed Fomulae = ˆ d d = ˆ + dt dt dˆ d t change in diection of momentum change in magnitude of momentum dˆ dt = v R nˆ R = adius of kissing cicle
12 Paallel and Peendicula Comonents dˆ v = nˆ = F dt R d ˆ dt = F fo magnitudes only: v R = F Often called the centietal foce
13 Centietal Foce The centietal foce is simly a new name fo foces aleady esent. It is not an additional (new) foce! Rathe it is the label given to the foce o Rathe it is the label given to the foce o the sum of foces that cause the cicula motion
14 Unifom Cicula Motion v v R = F
15 CLICKER QUESTION In Lab #5 you ll ty to secify an initial seed v such that the caft will move in a cicula obit about the Eath. R = 6.4e7 m M E = 6e24 kg M C = 15e3 kg G = 6.67x10-11 Nm 2 /kg 2 g=9.8 m/s 2 Fist, what is the magnitude of the gavitational ti foce on the caft? v= v =? Caft A N F = F ˆ B N C. 147,000 N D e10 N E. Need moe infomation. ( ) CE CE CE R Eath MEMC F CE = G = N 2 CE
16 CLICKER QUESTION In Lab #5 you ll ty to secify an initial seed v such that the caft will move in a cicula obit about the Eath. You just calculated that the Eath exets a foce of magnitude N on the caft. What seed does the caft need to go in a cicula obit? R = 6.4e7 m m E = 6e24 kg E m C = 15e3 kg v = v =? Eath G = -6.67x10-11 Nm 2 /kg 2 Caft R A. 17, ms B m/s v C m/s Fgav, CE = F = R D m/s E. Need moe infomation. v RF gav, CE m = = m s
17 Clicke Question: Tazan Tazan swings on a vine to coss a ive. At the bottom of his swing what is the diection? a) d) b) e) has no magnitude c)
18 Clicke Question: Tazan Assume Tazan has some momentum to the ight. What is the net foce on Tazan? = 0 2 F net F net =< 0, mg, 0 > ml F net =< 0, mg, 0 > 2 mv F net = mg 2 L F net =< 0,, 0 ml A) = 0 D) B) E) C) >
19 Clicke Question: Tazan What is the foce that Tazan exets on the vine? 2 F Tazan F Tazan =< 0, mg, 0 2mL A) =< 0, mg, 0 > D)F > 2 ml B) =< 0, mg, 0 > E) F Tazan 2 ml C) F Tazan =< 0, mg, 0 > F Tazan =< 0,0, 0 >
20 Clicke Question The vine snas and sends Tazan in to the ive, what should Tazan do if he wants to make it acoss the ive? A) Ty a longe vine B) Ty a shote vine C) This was clealy a fluke ty again with the same length
21 Clicke Question Tazan successfully swings acoss the ive. As he aoaches the othe side what should haen to the magnitude of his momentum? A) Inceases B) Deceases C) Stays the same
PHYS 172: Modern Mechanics. Summer Lecture 4 The Momentum Principle & Predicting Motion Read
 PHYS 172: Moden Mechanics Summe 2010 Δp sys = F net Δt ΔE = W + Q sys su su ΔL sys = τ net Δt Lectue 4 The Momentum Pinciple & Pedicting Motion Read 2.6-2.9 READING QUESTION #1 Reading Question Which of
PHYS 172: Moden Mechanics Summe 2010 Δp sys = F net Δt ΔE = W + Q sys su su ΔL sys = τ net Δt Lectue 4 The Momentum Pinciple & Pedicting Motion Read 2.6-2.9 READING QUESTION #1 Reading Question Which of
Fri Angular Momentum Quiz 10 RE 11.a; HW10: 13*, 21, 30, 39 Mon , (.12) Rotational + Translational RE 11.b Tues.
 Fi. 11.1 Angula Momentum Quiz 10 R 11.a; HW10: 13*, 1, 30, 39 Mon. 11.-.3, (.1) Rotational + Tanslational R 11.b Tues. P10 Mon. 11.4-.6, (.13) Angula Momentum & Toque Tues. Wed. 11.7 -.9, (.11) Toque R
Fi. 11.1 Angula Momentum Quiz 10 R 11.a; HW10: 13*, 1, 30, 39 Mon. 11.-.3, (.1) Rotational + Tanslational R 11.b Tues. P10 Mon. 11.4-.6, (.13) Angula Momentum & Toque Tues. Wed. 11.7 -.9, (.11) Toque R
Physics 111 Lecture 5 Circular Motion
 Physics 111 Lectue 5 Cicula Motion D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Multiple Objects q A block of mass m1 on a ough, hoizontal suface is connected to a ball of mass m by a lightweight
Physics 111 Lectue 5 Cicula Motion D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Multiple Objects q A block of mass m1 on a ough, hoizontal suface is connected to a ball of mass m by a lightweight
Physics C Rotational Motion Name: ANSWER KEY_ AP Review Packet
 Linea and angula analogs Linea Rotation x position x displacement v velocity a T tangential acceleation Vectos in otational motion Use the ight hand ule to detemine diection of the vecto! Don t foget centipetal
Linea and angula analogs Linea Rotation x position x displacement v velocity a T tangential acceleation Vectos in otational motion Use the ight hand ule to detemine diection of the vecto! Don t foget centipetal
Chapter 5: Uniform Circular Motion
 Chapte 5: Unifom Cicula Motion Motion at constant speed in a cicle Centipetal acceleation Banked cuves Obital motion Weightlessness, atificial gavity Vetical cicula motion Centipetal Foce Acceleation towad
Chapte 5: Unifom Cicula Motion Motion at constant speed in a cicle Centipetal acceleation Banked cuves Obital motion Weightlessness, atificial gavity Vetical cicula motion Centipetal Foce Acceleation towad
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion constant speed Pick a point in the objects motion... What diection is the velocity? HINT Think about what diection the object would tavel if the sting wee cut Unifom Cicula Motion
Unifom Cicula Motion constant speed Pick a point in the objects motion... What diection is the velocity? HINT Think about what diection the object would tavel if the sting wee cut Unifom Cicula Motion
c) (6) Assuming the tires do not skid, what coefficient of static friction between tires and pavement is needed?
 Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 10, 2012 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 10, 2012 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
constant t [rad.s -1 ] v / r r [m.s -2 ] (direction: towards centre of circle / perpendicular to circle)
![constant t [rad.s -1 ] v / r r [m.s -2 ] (direction: towards centre of circle / perpendicular to circle) constant t [rad.s -1 ] v / r r [m.s -2 ] (direction: towards centre of circle / perpendicular to circle)](/thumbs/87/96959272.jpg) VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 5 ADVANCED MECHANICS NON-UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION Equation of a cicle x y Angula displacement [ad] Angula speed d constant t [ad.s -1 ] dt Tangential velocity v v [m.s -1 ]
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 5 ADVANCED MECHANICS NON-UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION Equation of a cicle x y Angula displacement [ad] Angula speed d constant t [ad.s -1 ] dt Tangential velocity v v [m.s -1 ]
Physics 231 Lecture 17
 Physics 31 Lectue 17 Main points of today s lectue: Centipetal acceleation: a c = a c t Rotational motion definitions: Δω Δω α =, α = limδ t 0 Δt Δt Δ s= Δ θ;t = ω;at = α Rotational kinematics equations:
Physics 31 Lectue 17 Main points of today s lectue: Centipetal acceleation: a c = a c t Rotational motion definitions: Δω Δω α =, α = limδ t 0 Δt Δt Δ s= Δ θ;t = ω;at = α Rotational kinematics equations:
Lecture 19 Angular momentum. Chapter
 PHYS 172H: Moden Mechanics Fall 2010 Lectue 19 ngula momentum Chapte 11.4 11.7 The angula momentum pinciple dp = F dl =? net d ( p ) d dp = p+ = v γ mv = = 0 The angula momentum pinciple fo a point paticle
PHYS 172H: Moden Mechanics Fall 2010 Lectue 19 ngula momentum Chapte 11.4 11.7 The angula momentum pinciple dp = F dl =? net d ( p ) d dp = p+ = v γ mv = = 0 The angula momentum pinciple fo a point paticle
Chapter 5. Uniform Circular Motion. a c =v 2 /r
 Chapte 5 Unifom Cicula Motion a c =v 2 / Unifom cicula motion: Motion in a cicula path with constant speed s v 1) Speed and peiod Peiod, T: time fo one evolution Speed is elated to peiod: Path fo one evolution:
Chapte 5 Unifom Cicula Motion a c =v 2 / Unifom cicula motion: Motion in a cicula path with constant speed s v 1) Speed and peiod Peiod, T: time fo one evolution Speed is elated to peiod: Path fo one evolution:
Quiz 6--Work, Gravitation, Circular Motion, Torque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible)
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
KEPLER S LAWS AND PLANETARY ORBITS
 KEPE S AWS AND PANETAY OBITS 1. Selected popeties of pola coodinates and ellipses Pola coodinates: I take a some what extended view of pola coodinates in that I allow fo a z diection (cylindical coodinates
KEPE S AWS AND PANETAY OBITS 1. Selected popeties of pola coodinates and ellipses Pola coodinates: I take a some what extended view of pola coodinates in that I allow fo a z diection (cylindical coodinates
Extra notes for circular motion: Circular motion : v keeps changing, maybe both speed and
 Exta notes fo cicula motion: Cicula motion : v keeps changing, maybe both speed and diection ae changing. At least v diection is changing. Hence a 0. Acceleation NEEDED to stay on cicula obit: a cp v /,
Exta notes fo cicula motion: Cicula motion : v keeps changing, maybe both speed and diection ae changing. At least v diection is changing. Hence a 0. Acceleation NEEDED to stay on cicula obit: a cp v /,
Physics 101 Lecture 6 Circular Motion
 Physics 101 Lectue 6 Cicula Motion Assist. Pof. D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Equilibium, Example 1 q What is the smallest value of the foce F such that the.0-kg block will not slide
Physics 101 Lectue 6 Cicula Motion Assist. Pof. D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Equilibium, Example 1 q What is the smallest value of the foce F such that the.0-kg block will not slide
13.10 Worked Examples
 13.10 Woked Examples Example 13.11 Wok Done in a Constant Gavitation Field The wok done in a unifom gavitation field is a faily staightfowad calculation when the body moves in the diection of the field.
13.10 Woked Examples Example 13.11 Wok Done in a Constant Gavitation Field The wok done in a unifom gavitation field is a faily staightfowad calculation when the body moves in the diection of the field.
Gravitation. AP/Honors Physics 1 Mr. Velazquez
 Gavitation AP/Honos Physics 1 M. Velazquez Newton s Law of Gavitation Newton was the fist to make the connection between objects falling on Eath and the motion of the planets To illustate this connection
Gavitation AP/Honos Physics 1 M. Velazquez Newton s Law of Gavitation Newton was the fist to make the connection between objects falling on Eath and the motion of the planets To illustate this connection
Physics 2001 Problem Set 5 Solutions
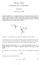 Physics 2001 Poblem Set 5 Solutions Jeff Kissel Octobe 16, 2006 1. A puck attached to a sting undegoes cicula motion on an ai table. If the sting beaks at the point indicated in the figue, which path (A,
Physics 2001 Poblem Set 5 Solutions Jeff Kissel Octobe 16, 2006 1. A puck attached to a sting undegoes cicula motion on an ai table. If the sting beaks at the point indicated in the figue, which path (A,
Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
 Potential Enegy and Consevation of Enegy Consevative Foces Definition: Consevative Foce If the wok done by a foce in moving an object fom an initial point to a final point is independent of the path (A
Potential Enegy and Consevation of Enegy Consevative Foces Definition: Consevative Foce If the wok done by a foce in moving an object fom an initial point to a final point is independent of the path (A
Physics 4A Chapter 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane
 Physics 4A Chapte 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane Conceptual Questions and Example Poblems fom Chapte 8 Conceptual Question 8.5 The figue below shows two balls of equal mass moving in vetical cicles.
Physics 4A Chapte 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane Conceptual Questions and Example Poblems fom Chapte 8 Conceptual Question 8.5 The figue below shows two balls of equal mass moving in vetical cicles.
PS113 Chapter 5 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion
 PS113 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion 1 Unifom cicula motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant (unifom) speed on a cicula path. The peiod T is the time equied
PS113 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion 1 Unifom cicula motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant (unifom) speed on a cicula path. The peiod T is the time equied
Mon , (.12) Rotational + Translational RE 11.b Tues.
 Mon..-.3, (.) Rotational + Tanlational RE.b Tue. EP0 Mon..4-.6, (.3) Angula Momentum & Toque RE.c Tue. Wed..7 -.9, (.) Toque EP RE.d ab Fi. Rotation Coue Eval.0 Quantization, Quiz RE.e Mon. Review fo Final
Mon..-.3, (.) Rotational + Tanlational RE.b Tue. EP0 Mon..4-.6, (.3) Angula Momentum & Toque RE.c Tue. Wed..7 -.9, (.) Toque EP RE.d ab Fi. Rotation Coue Eval.0 Quantization, Quiz RE.e Mon. Review fo Final
Chap 5. Circular Motion: Gravitation
 Chap 5. Cicula Motion: Gavitation Sec. 5.1 - Unifom Cicula Motion A body moves in unifom cicula motion, if the magnitude of the velocity vecto is constant and the diection changes at evey point and is
Chap 5. Cicula Motion: Gavitation Sec. 5.1 - Unifom Cicula Motion A body moves in unifom cicula motion, if the magnitude of the velocity vecto is constant and the diection changes at evey point and is
6.4 Period and Frequency for Uniform Circular Motion
 6.4 Peiod and Fequency fo Unifom Cicula Motion If the object is constained to move in a cicle and the total tangential foce acting on the total object is zeo, F θ = 0, then (Newton s Second Law), the tangential
6.4 Peiod and Fequency fo Unifom Cicula Motion If the object is constained to move in a cicle and the total tangential foce acting on the total object is zeo, F θ = 0, then (Newton s Second Law), the tangential
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion Intoduction Ealie we defined acceleation as being the change in velocity with time: a = v t Until now we have only talked about changes in the magnitude of the acceleation: the speeding
Unifom Cicula Motion Intoduction Ealie we defined acceleation as being the change in velocity with time: a = v t Until now we have only talked about changes in the magnitude of the acceleation: the speeding
Physics NYB problem set 5 solution
 Physics NY poblem set 5 solutions 1 Physics NY poblem set 5 solution Hello eveybody, this is ED. Hi ED! ED is useful fo dawing the ight hand ule when you don t know how to daw. When you have a coss poduct
Physics NY poblem set 5 solutions 1 Physics NY poblem set 5 solution Hello eveybody, this is ED. Hi ED! ED is useful fo dawing the ight hand ule when you don t know how to daw. When you have a coss poduct
Circular Motion. x-y coordinate systems. Other coordinates... PHY circular-motion - J. Hedberg
 Cicula Motion PHY 207 - cicula-motion - J. Hedbeg - 2017 x-y coodinate systems Fo many situations, an x-y coodinate system is a geat idea. Hee is a map on Manhattan. The steets ae laid out in a ectangula
Cicula Motion PHY 207 - cicula-motion - J. Hedbeg - 2017 x-y coodinate systems Fo many situations, an x-y coodinate system is a geat idea. Hee is a map on Manhattan. The steets ae laid out in a ectangula
Spring 2001 Physics 2048 Test 3 solutions
 Sping 001 Physics 048 Test 3 solutions Poblem 1. (Shot Answe: 15 points) a. 1 b. 3 c. 4* d. 9 e. 8 f. 9 *emembe that since KE = ½ mv, KE must be positive Poblem (Estimation Poblem: 15 points) Use momentum-impulse
Sping 001 Physics 048 Test 3 solutions Poblem 1. (Shot Answe: 15 points) a. 1 b. 3 c. 4* d. 9 e. 8 f. 9 *emembe that since KE = ½ mv, KE must be positive Poblem (Estimation Poblem: 15 points) Use momentum-impulse
Physics 107 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8
 Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
Describing Circular motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion Descibing Cicula motion In ode to undestand cicula motion, we fist need to discuss how to subtact vectos. The easiest way to explain subtacting vectos is to descibe it as adding a
Unifom Cicula Motion Descibing Cicula motion In ode to undestand cicula motion, we fist need to discuss how to subtact vectos. The easiest way to explain subtacting vectos is to descibe it as adding a
Math Notes on Kepler s first law 1. r(t) kp(t)
 Math 7 - Notes on Keple s fist law Planetay motion and Keple s Laws We conside the motion of a single planet about the sun; fo simplicity, we assign coodinates in R 3 so that the position of the sun is
Math 7 - Notes on Keple s fist law Planetay motion and Keple s Laws We conside the motion of a single planet about the sun; fo simplicity, we assign coodinates in R 3 so that the position of the sun is
OSCILLATIONS AND GRAVITATION
 1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
Phys 201A. Homework 6 Solutions. F A and F r. B. According to Newton s second law, ( ) ( )2. j = ( 6.0 m / s 2 )ˆ i ( 10.4m / s 2 )ˆ j.
 7. We denote the two foces F A + F B = ma,sof B = ma F A. (a) In unit vecto notation F A = ( 20.0 N)ˆ i and Theefoe, Phys 201A Homewok 6 Solutions F A and F B. Accoding to Newton s second law, a = [ (
7. We denote the two foces F A + F B = ma,sof B = ma F A. (a) In unit vecto notation F A = ( 20.0 N)ˆ i and Theefoe, Phys 201A Homewok 6 Solutions F A and F B. Accoding to Newton s second law, a = [ (
Kepler s problem gravitational attraction
 Kele s oblem gavitational attaction Summay of fomulas deived fo two-body motion Let the two masses be m and m. The total mass is M = m + m, the educed mass is µ = m m /(m + m ). The gavitational otential
Kele s oblem gavitational attaction Summay of fomulas deived fo two-body motion Let the two masses be m and m. The total mass is M = m + m, the educed mass is µ = m m /(m + m ). The gavitational otential
Objective Notes Summary
 Objective Notes Summay An object moving in unifom cicula motion has constant speed but not constant velocity because the diection is changing. The velocity vecto in tangent to the cicle, the acceleation
Objective Notes Summay An object moving in unifom cicula motion has constant speed but not constant velocity because the diection is changing. The velocity vecto in tangent to the cicle, the acceleation
PHYS 172: Modern Mechanics. Fall Lecture 6 Fundamental Forces, Reciprocity Read
 PHYS 172: Moden Mechanics Fall 2009 Lectue 6 Fundamental Foces, Recipocity Read 3.9 3.14 Exam 1 - Tuesday Septembe 15, 8:00-10:00 PM Elliott Hall of Music 1. The exam will be witten as a standad 1 hou
PHYS 172: Moden Mechanics Fall 2009 Lectue 6 Fundamental Foces, Recipocity Read 3.9 3.14 Exam 1 - Tuesday Septembe 15, 8:00-10:00 PM Elliott Hall of Music 1. The exam will be witten as a standad 1 hou
Translation and Rotation Kinematics
 Tanslation and Rotation Kinematics Oveview: Rotation and Tanslation of Rigid Body Thown Rigid Rod Tanslational Motion: the gavitational extenal foce acts on cente-of-mass F ext = dp sy s dt dv total cm
Tanslation and Rotation Kinematics Oveview: Rotation and Tanslation of Rigid Body Thown Rigid Rod Tanslational Motion: the gavitational extenal foce acts on cente-of-mass F ext = dp sy s dt dv total cm
Physics Fall Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids. Lecture 6: motion in two and three dimensions III. Slide 6-1
 Physics 1501 Fall 2008 Mechanics, Themodynamics, Waves, Fluids Lectue 6: motion in two and thee dimensions III Slide 6-1 Recap: elative motion An object moves with velocity v elative to one fame of efeence.
Physics 1501 Fall 2008 Mechanics, Themodynamics, Waves, Fluids Lectue 6: motion in two and thee dimensions III Slide 6-1 Recap: elative motion An object moves with velocity v elative to one fame of efeence.
Chapter 5. really hard to start the object moving and then, once it starts moving, you don t have to push as hard to keep it moving.
 Chapte 5 Fiction When an object is in motion it is usually in contact with a viscous mateial (wate o ai) o some othe suface. So fa, we have assumed that moving objects don t inteact with thei suoundings
Chapte 5 Fiction When an object is in motion it is usually in contact with a viscous mateial (wate o ai) o some othe suface. So fa, we have assumed that moving objects don t inteact with thei suoundings
DYNAMICS OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION
 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
Chapter 8. Accelerated Circular Motion
 Chapte 8 Acceleated Cicula Motion 8.1 Rotational Motion and Angula Displacement A new unit, adians, is eally useful fo angles. Radian measue θ(adians) = s = θ s (ac length) (adius) (s in same units as
Chapte 8 Acceleated Cicula Motion 8.1 Rotational Motion and Angula Displacement A new unit, adians, is eally useful fo angles. Radian measue θ(adians) = s = θ s (ac length) (adius) (s in same units as
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION
 MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
b) (5) What is the magnitude of the force on the 6.0-kg block due to the contact with the 12.0-kg block?
 Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 13, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 13, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
Centripetal Force. Lecture 11. Chapter 8. Course website:
 Lectue 11 Chapte 8 Centipetal Foce Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi PHYS.1410 Lectue 11 Danylov Depatment of Physics and Applied Physics Today we ae going to discuss:
Lectue 11 Chapte 8 Centipetal Foce Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi PHYS.1410 Lectue 11 Danylov Depatment of Physics and Applied Physics Today we ae going to discuss:
CHAPTER 5: Circular Motion; Gravitation
 CHAPER 5: Cicula Motion; Gavitation Solution Guide to WebAssign Pobles 5.1 [1] (a) Find the centipetal acceleation fo Eq. 5-1.. a R v ( 1.5 s) 1.10 1.4 s (b) he net hoizontal foce is causing the centipetal
CHAPER 5: Cicula Motion; Gavitation Solution Guide to WebAssign Pobles 5.1 [1] (a) Find the centipetal acceleation fo Eq. 5-1.. a R v ( 1.5 s) 1.10 1.4 s (b) he net hoizontal foce is causing the centipetal
kg 2 ) 1.9!10 27 kg = Gm 1
 Section 6.1: Newtonian Gavitation Tutoial 1 Pactice, page 93 1. Given: 1.0 10 0 kg; m 3.0 10 0 kg;. 10 9 N; G 6.67 10 11 N m /kg Requied: Analysis: G m ; G m G m Solution: G m N m 6.67!10 11 kg ) 1.0!100
Section 6.1: Newtonian Gavitation Tutoial 1 Pactice, page 93 1. Given: 1.0 10 0 kg; m 3.0 10 0 kg;. 10 9 N; G 6.67 10 11 N m /kg Requied: Analysis: G m ; G m G m Solution: G m N m 6.67!10 11 kg ) 1.0!100
Rotational Motion. Every quantity that we have studied with translational motion has a rotational counterpart
 Rotational Motion & Angula Momentum Rotational Motion Evey quantity that we have studied with tanslational motion has a otational countepat TRANSLATIONAL ROTATIONAL Displacement x Angula Position Velocity
Rotational Motion & Angula Momentum Rotational Motion Evey quantity that we have studied with tanslational motion has a otational countepat TRANSLATIONAL ROTATIONAL Displacement x Angula Position Velocity
r cos, and y r sin with the origin of coordinate system located at
 Lectue 3-3 Kinematics of Rotation Duing ou peious lectues we hae consideed diffeent examples of motion in one and seeal dimensions. But in each case the moing object was consideed as a paticle-like object,
Lectue 3-3 Kinematics of Rotation Duing ou peious lectues we hae consideed diffeent examples of motion in one and seeal dimensions. But in each case the moing object was consideed as a paticle-like object,
Understanding the Concepts
 Chistian Bache Phsics Depatment Bn Maw College Undestanding the Concepts PHYSICS 101-10 Homewok Assignment #5 - Solutions 5.7. A cclist making a tun must make use of a centipetal foce, one that is pependicula
Chistian Bache Phsics Depatment Bn Maw College Undestanding the Concepts PHYSICS 101-10 Homewok Assignment #5 - Solutions 5.7. A cclist making a tun must make use of a centipetal foce, one that is pependicula
Gaia s Place in Space
 Gaia s Place in Space The impotance of obital positions fo satellites Obits and Lagange Points Satellites can be launched into a numbe of diffeent obits depending on thei objectives and what they ae obseving.
Gaia s Place in Space The impotance of obital positions fo satellites Obits and Lagange Points Satellites can be launched into a numbe of diffeent obits depending on thei objectives and what they ae obseving.
Motion in Two Dimensions
 SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS Motion in Two Dimensions Section 3.1 The Position, Velocity, and Acceleation Vectos P3.1 x( m) 0!3 000!1 70!4 70 m y( m)!3 600 0 1 70! 330 m (a) Net displacement x + y 4.87 km at
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS Motion in Two Dimensions Section 3.1 The Position, Velocity, and Acceleation Vectos P3.1 x( m) 0!3 000!1 70!4 70 m y( m)!3 600 0 1 70! 330 m (a) Net displacement x + y 4.87 km at
Recap. Centripetal acceleration: v r. a = m/s 2 (towards center of curvature)
 a = c v 2 Recap Centipetal acceleation: m/s 2 (towads cente of cuvatue) A centipetal foce F c is equied to keep a body in cicula motion: This foce poduces centipetal acceleation that continuously changes
a = c v 2 Recap Centipetal acceleation: m/s 2 (towads cente of cuvatue) A centipetal foce F c is equied to keep a body in cicula motion: This foce poduces centipetal acceleation that continuously changes
Chapters 5-8. Dynamics: Applying Newton s Laws
 Chaptes 5-8 Dynamics: Applying Newton s Laws Systems of Inteacting Objects The Fee Body Diagam Technique Examples: Masses Inteacting ia Nomal Foces Masses Inteacting ia Tensions in Ropes. Ideal Pulleys
Chaptes 5-8 Dynamics: Applying Newton s Laws Systems of Inteacting Objects The Fee Body Diagam Technique Examples: Masses Inteacting ia Nomal Foces Masses Inteacting ia Tensions in Ropes. Ideal Pulleys
Physics 111. Lecture 14 (Walker: Ch. 6.5) Circular Motion Centripetal Acceleration Centripetal Force February 27, 2009
 Physics 111 Lectue 14 (Walke: Ch. 6.5) Cicula Motion Centipetal Acceleation Centipetal Foce Febuay 7, 009 Midtem Exam 1 on Wed. Mach 4 (Chaptes 1-6) Lectue 14 1/8 Connected Objects If thee is a pulley,
Physics 111 Lectue 14 (Walke: Ch. 6.5) Cicula Motion Centipetal Acceleation Centipetal Foce Febuay 7, 009 Midtem Exam 1 on Wed. Mach 4 (Chaptes 1-6) Lectue 14 1/8 Connected Objects If thee is a pulley,
Gauss Law. Physics 231 Lecture 2-1
 Gauss Law Physics 31 Lectue -1 lectic Field Lines The numbe of field lines, also known as lines of foce, ae elated to stength of the electic field Moe appopiately it is the numbe of field lines cossing
Gauss Law Physics 31 Lectue -1 lectic Field Lines The numbe of field lines, also known as lines of foce, ae elated to stength of the electic field Moe appopiately it is the numbe of field lines cossing
Chapter 4. Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapte 4 Newton s Laws of Motion 4.1 Foces and Inteactions A foce is a push o a pull. It is that which causes an object to acceleate. The unit of foce in the metic system is the Newton. Foce is a vecto
Chapte 4 Newton s Laws of Motion 4.1 Foces and Inteactions A foce is a push o a pull. It is that which causes an object to acceleate. The unit of foce in the metic system is the Newton. Foce is a vecto
 Basic oces an Keple s Laws 1. Two ientical sphees of gol ae in contact with each othe. The gavitational foce of attaction between them is Diectly popotional to the squae of thei aius ) Diectly popotional
Basic oces an Keple s Laws 1. Two ientical sphees of gol ae in contact with each othe. The gavitational foce of attaction between them is Diectly popotional to the squae of thei aius ) Diectly popotional
1 2 U CV. K dq I dt J nqv d J V IR P VI
 o 5 o T C T F 9 T K T o C 7.5 L L T V VT Q mct nct Q F V ml F V dq A H k TH TC dt L pv nt Kt nt CV ideal monatomic gas 5 CV ideal diatomic gas w/o vibation V W pdv V U Q W W Q e Q Q e Canot H C T T S C
o 5 o T C T F 9 T K T o C 7.5 L L T V VT Q mct nct Q F V ml F V dq A H k TH TC dt L pv nt Kt nt CV ideal monatomic gas 5 CV ideal diatomic gas w/o vibation V W pdv V U Q W W Q e Q Q e Canot H C T T S C
Momentum is conserved if no external force
 Goals: Lectue 13 Chapte 9 v Employ consevation of momentum in 1 D & 2D v Examine foces ove time (aka Impulse) Chapte 10 v Undestand the elationship between motion and enegy Assignments: l HW5, due tomoow
Goals: Lectue 13 Chapte 9 v Employ consevation of momentum in 1 D & 2D v Examine foces ove time (aka Impulse) Chapte 10 v Undestand the elationship between motion and enegy Assignments: l HW5, due tomoow
A car of mass m, traveling at constant speed, rides over the top of a circularly shaped hill as shown.
 A ca of mass m, taveling at constant speed, ides ove the top of a ciculaly shaped hill as shown. The magnitude of the nomal foce N of the oad on the ca is. A) Geate than the weight of the ca, N > mg. B)
A ca of mass m, taveling at constant speed, ides ove the top of a ciculaly shaped hill as shown. The magnitude of the nomal foce N of the oad on the ca is. A) Geate than the weight of the ca, N > mg. B)
Circular Motion & Torque Test Review. The period is the amount of time it takes for an object to travel around a circular path once.
 Honos Physics Fall, 2016 Cicula Motion & Toque Test Review Name: M. Leonad Instuctions: Complete the following woksheet. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. 1. Detemine whethe each statement
Honos Physics Fall, 2016 Cicula Motion & Toque Test Review Name: M. Leonad Instuctions: Complete the following woksheet. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. 1. Detemine whethe each statement
( )( )( ) ( ) + ( ) ( ) ( )
 3.7. Moel: The magnetic fiel is that of a moving chage paticle. Please efe to Figue Ex3.7. Solve: Using the iot-savat law, 7 19 7 ( ) + ( ) qvsinθ 1 T m/a 1.6 1 C. 1 m/s sin135 1. 1 m 1. 1 m 15 = = = 1.13
3.7. Moel: The magnetic fiel is that of a moving chage paticle. Please efe to Figue Ex3.7. Solve: Using the iot-savat law, 7 19 7 ( ) + ( ) qvsinθ 1 T m/a 1.6 1 C. 1 m/s sin135 1. 1 m 1. 1 m 15 = = = 1.13
Chap13. Universal Gravitation
 Chap13. Uniesal Gaitation Leel : AP Physics Instucto : Kim 13.1 Newton s Law of Uniesal Gaitation - Fomula fo Newton s Law of Gaitation F g = G m 1m 2 2 F21 m1 F12 12 m2 - m 1, m 2 is the mass of the object,
Chap13. Uniesal Gaitation Leel : AP Physics Instucto : Kim 13.1 Newton s Law of Uniesal Gaitation - Fomula fo Newton s Law of Gaitation F g = G m 1m 2 2 F21 m1 F12 12 m2 - m 1, m 2 is the mass of the object,
Chapter 7-8 Rotational Motion
 Chapte 7-8 Rotational Motion What is a Rigid Body? Rotational Kinematics Angula Velocity ω and Acceleation α Unifom Rotational Motion: Kinematics Unifom Cicula Motion: Kinematics and Dynamics The Toque,
Chapte 7-8 Rotational Motion What is a Rigid Body? Rotational Kinematics Angula Velocity ω and Acceleation α Unifom Rotational Motion: Kinematics Unifom Cicula Motion: Kinematics and Dynamics The Toque,
PY208 Matter & Interactions Final Exam S2005
 PY Matte & Inteactions Final Exam S2005 Name (pint) Please cicle you lectue section below: 003 (Ramakishnan 11:20 AM) 004 (Clake 1:30 PM) 005 (Chabay 2:35 PM) When you tun in the test, including the fomula
PY Matte & Inteactions Final Exam S2005 Name (pint) Please cicle you lectue section below: 003 (Ramakishnan 11:20 AM) 004 (Clake 1:30 PM) 005 (Chabay 2:35 PM) When you tun in the test, including the fomula
 Hoizontal Cicula Motion 1. A paticle of mass m is tied to a light sting and otated with a speed v along a cicula path of adius. If T is tension in the sting and mg is gavitational foce on the paticle then,
Hoizontal Cicula Motion 1. A paticle of mass m is tied to a light sting and otated with a speed v along a cicula path of adius. If T is tension in the sting and mg is gavitational foce on the paticle then,
( ) ( ) Review of Force. Review of Force. r = =... Example 1. What is the dot product for F r. Solution: Example 2 ( )
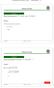 : PHYS 55 (Pat, Topic ) Eample Solutions p. Review of Foce Eample ( ) ( ) What is the dot poduct fo F =,,3 and G = 4,5,6? F G = F G + F G + F G = 4 +... = 3 z z Phs55 -: Foce Fields Review of Foce Eample
: PHYS 55 (Pat, Topic ) Eample Solutions p. Review of Foce Eample ( ) ( ) What is the dot poduct fo F =,,3 and G = 4,5,6? F G = F G + F G + F G = 4 +... = 3 z z Phs55 -: Foce Fields Review of Foce Eample
PHYSICS 1210 Exam 2 University of Wyoming 14 March ( Day!) points
 PHYSICS 1210 Exam 2 Univesity of Wyoming 14 Mach ( Day!) 2013 150 points This test is open-note and closed-book. Calculatos ae pemitted but computes ae not. No collaboation, consultation, o communication
PHYSICS 1210 Exam 2 Univesity of Wyoming 14 Mach ( Day!) 2013 150 points This test is open-note and closed-book. Calculatos ae pemitted but computes ae not. No collaboation, consultation, o communication
m1 m2 M 2 = M -1 L 3 T -2
 GAVITATION Newton s Univesal law of gavitation. Evey paticle of matte in this univese attacts evey othe paticle with a foce which vaies diectly as the poduct of thei masses and invesely as the squae of
GAVITATION Newton s Univesal law of gavitation. Evey paticle of matte in this univese attacts evey othe paticle with a foce which vaies diectly as the poduct of thei masses and invesely as the squae of
Gravitation. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman. Lectures by James Pazun
 Chapte 12 Gavitation PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 5_31_2012 Goals fo Chapte 12 To study Newton s Law
Chapte 12 Gavitation PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 5_31_2012 Goals fo Chapte 12 To study Newton s Law
Central Force Motion
 Cental Foce Motion Cental Foce Poblem Find the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): m1m F 1, ( ) =! G ˆ Linea estoing foce: F 1, ( ) =! k ˆ Two
Cental Foce Motion Cental Foce Poblem Find the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): m1m F 1, ( ) =! G ˆ Linea estoing foce: F 1, ( ) =! k ˆ Two
F g. = G mm. m 1. = 7.0 kg m 2. = 5.5 kg r = 0.60 m G = N m 2 kg 2 = = N
 Chapte answes Heinemann Physics 4e Section. Woked example: Ty youself.. GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION BETWEEN SMALL OBJECTS Two bowling balls ae sitting next to each othe on a shelf so that the centes of the
Chapte answes Heinemann Physics 4e Section. Woked example: Ty youself.. GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION BETWEEN SMALL OBJECTS Two bowling balls ae sitting next to each othe on a shelf so that the centes of the
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion Have you eve idden on the amusement pak ide shown below? As it spins you feel as though you ae being pessed tightly against the wall. The ide then begins to tilt but you emain glued
Unifom Cicula Motion Have you eve idden on the amusement pak ide shown below? As it spins you feel as though you ae being pessed tightly against the wall. The ide then begins to tilt but you emain glued
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8. Lab 5. Magnetism
 Physics 2020, Sping 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8 Lab 5. Magnetism PART I: INTRODUCTION TO MAGNETS This week we will begin wok with magnets and the foces that they poduce. By now you ae an expet on setting up
Physics 2020, Sping 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8 Lab 5. Magnetism PART I: INTRODUCTION TO MAGNETS This week we will begin wok with magnets and the foces that they poduce. By now you ae an expet on setting up
= 4 3 π( m) 3 (5480 kg m 3 ) = kg.
 CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
Chapter 13 Gravitation
 Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Chapter 4: The laws of motion. Newton s first law
 Chapte 4: The laws of motion gavitational Electic magnetic Newton s fist law If the net foce exeted on an object is zeo, the object continues in its oiginal state of motion: - an object at est, emains
Chapte 4: The laws of motion gavitational Electic magnetic Newton s fist law If the net foce exeted on an object is zeo, the object continues in its oiginal state of motion: - an object at est, emains
Physics 181. Assignment 4
 Physics 181 Assignment 4 Solutions 1. A sphee has within it a gavitational field given by g = g, whee g is constant and is the position vecto of the field point elative to the cente of the sphee. This
Physics 181 Assignment 4 Solutions 1. A sphee has within it a gavitational field given by g = g, whee g is constant and is the position vecto of the field point elative to the cente of the sphee. This
Rotational Motion: Statics and Dynamics
 Physics 07 Lectue 17 Goals: Lectue 17 Chapte 1 Define cente of mass Analyze olling motion Intoduce and analyze toque Undestand the equilibium dynamics of an extended object in esponse to foces Employ consevation
Physics 07 Lectue 17 Goals: Lectue 17 Chapte 1 Define cente of mass Analyze olling motion Intoduce and analyze toque Undestand the equilibium dynamics of an extended object in esponse to foces Employ consevation
PHYSICS 220. Lecture 08. Textbook Sections Lecture 8 Purdue University, Physics 220 1
 PHYSICS 0 Lectue 08 Cicula Motion Textbook Sections 5.3 5.5 Lectue 8 Pudue Univesity, Physics 0 1 Oveview Last Lectue Cicula Motion θ angula position adians ω angula velocity adians/second α angula acceleation
PHYSICS 0 Lectue 08 Cicula Motion Textbook Sections 5.3 5.5 Lectue 8 Pudue Univesity, Physics 0 1 Oveview Last Lectue Cicula Motion θ angula position adians ω angula velocity adians/second α angula acceleation
AMM PBL Members: Chin Guan Wei p Huang Pengfei p Lim Wilson p Yap Jun Da p Class: ME/MS803M/AM05
 AMM PBL Membes: Chin Guan Wei p3674 Huang Pengfei p36783 Lim Wilson p36808 Yap Jun Da p36697 Class: MEMS803MAM05 The common values that we use ae: G=6.674 x 0 - m 3 kg - s - Radius of Eath ()= 637km [Fom
AMM PBL Membes: Chin Guan Wei p3674 Huang Pengfei p36783 Lim Wilson p36808 Yap Jun Da p36697 Class: MEMS803MAM05 The common values that we use ae: G=6.674 x 0 - m 3 kg - s - Radius of Eath ()= 637km [Fom
Lecture 22. PE = GMm r TE = GMm 2a. T 2 = 4π 2 GM. Main points of today s lecture: Gravitational potential energy: Total energy of orbit:
 Lectue Main points of today s lectue: Gavitational potential enegy: Total enegy of obit: PE = GMm TE = GMm a Keple s laws and the elation between the obital peiod and obital adius. T = 4π GM a3 Midtem
Lectue Main points of today s lectue: Gavitational potential enegy: Total enegy of obit: PE = GMm TE = GMm a Keple s laws and the elation between the obital peiod and obital adius. T = 4π GM a3 Midtem
Module 18: Outline. Magnetic Dipoles Magnetic Torques
 Module 18: Magnetic Dipoles 1 Module 18: Outline Magnetic Dipoles Magnetic Toques 2 IA nˆ I A Magnetic Dipole Moment μ 3 Toque on a Cuent Loop in a Unifom Magnetic Field 4 Poblem: Cuent Loop Place ectangula
Module 18: Magnetic Dipoles 1 Module 18: Outline Magnetic Dipoles Magnetic Toques 2 IA nˆ I A Magnetic Dipole Moment μ 3 Toque on a Cuent Loop in a Unifom Magnetic Field 4 Poblem: Cuent Loop Place ectangula
AP Physics 1 - Circular Motion and Gravitation Practice Test (Multiple Choice Section) Answer Section
 AP Physics 1 - Cicula Motion and Gaitation Pactice est (Multiple Choice Section) Answe Section MULIPLE CHOICE 1. B he centipetal foce must be fiction since, lacking any fiction, the coin would slip off.
AP Physics 1 - Cicula Motion and Gaitation Pactice est (Multiple Choice Section) Answe Section MULIPLE CHOICE 1. B he centipetal foce must be fiction since, lacking any fiction, the coin would slip off.
Physics 312 Introduction to Astrophysics Lecture 7
 Physics 312 Intoduction to Astophysics Lectue 7 James Buckley buckley@wuphys.wustl.edu Lectue 7 Eath/Moon System Tidal Foces Tides M= mass of moon o sun F 1 = GMm 2 F 2 = GMm ( + ) 2 Diffeence in gavitational
Physics 312 Intoduction to Astophysics Lectue 7 James Buckley buckley@wuphys.wustl.edu Lectue 7 Eath/Moon System Tidal Foces Tides M= mass of moon o sun F 1 = GMm 2 F 2 = GMm ( + ) 2 Diffeence in gavitational
Flux. Area Vector. Flux of Electric Field. Gauss s Law
 Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Physics: Work & Energy Beyond Earth Guided Inquiry
 Physics: Wok & Enegy Beyond Eath Guided Inquiy Elliptical Obits Keple s Fist Law states that all planets move in an elliptical path aound the Sun. This concept can be extended to celestial bodies beyond
Physics: Wok & Enegy Beyond Eath Guided Inquiy Elliptical Obits Keple s Fist Law states that all planets move in an elliptical path aound the Sun. This concept can be extended to celestial bodies beyond
PHYS 1114, Lecture 21, March 6 Contents:
 PHYS 1114, Lectue 21, Mach 6 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, being eplaced by the common exam Tuesday, Mach 7, 5:30 PM. A eview and Q&A session is scheduled instead duing class time. 2 Exam
PHYS 1114, Lectue 21, Mach 6 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, being eplaced by the common exam Tuesday, Mach 7, 5:30 PM. A eview and Q&A session is scheduled instead duing class time. 2 Exam
Physics 1114: Unit 5 Hand-out Homework (Answers)
 Physics 1114: Unit 5 Hand-out Homewok (Answes) Poblem set 1 1. The flywheel on an expeimental bus is otating at 420 RPM (evolutions pe minute). To find (a) the angula velocity in ad/s (adians/second),
Physics 1114: Unit 5 Hand-out Homewok (Answes) Poblem set 1 1. The flywheel on an expeimental bus is otating at 420 RPM (evolutions pe minute). To find (a) the angula velocity in ad/s (adians/second),
1. A stone falls from a platform 18 m high. When will it hit the ground? (a) 1.74 s (b) 1.83 s (c) 1.92 s (d) 2.01 s
 1. A stone falls fom a platfom 18 m high. When will it hit the gound? (a) 1.74 s (b) 1.83 s (c) 1.9 s (d).01 s Constant acceleation D = v 0 t + ½ a t. Which, if any, of these foces causes the otation of
1. A stone falls fom a platfom 18 m high. When will it hit the gound? (a) 1.74 s (b) 1.83 s (c) 1.9 s (d).01 s Constant acceleation D = v 0 t + ½ a t. Which, if any, of these foces causes the otation of
Magnetic Fields Due to Currents
 PH -C Fall 1 Magnetic Fields Due to Cuents Lectue 14 Chapte 9 (Halliday/esnick/Walke, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapte 9 Magnetic Fields Due to Cuents In this chapte we will exploe the elationship
PH -C Fall 1 Magnetic Fields Due to Cuents Lectue 14 Chapte 9 (Halliday/esnick/Walke, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapte 9 Magnetic Fields Due to Cuents In this chapte we will exploe the elationship
Physics 2112 Unit 14
 Physics 2112 Unit 14 Today s Concept: What Causes Magnetic Fields d 0I ds ˆ 2 4 Unit 14, Slide 1 You Comments Can you give a summay fo eveything we use the ight hand ule fo? Wasn't too clea on this topic.
Physics 2112 Unit 14 Today s Concept: What Causes Magnetic Fields d 0I ds ˆ 2 4 Unit 14, Slide 1 You Comments Can you give a summay fo eveything we use the ight hand ule fo? Wasn't too clea on this topic.
Force between two parallel current wires and Newton s. third law
 Foce between two paallel cuent wies and Newton s thid law Yannan Yang (Shanghai Jinjuan Infomation Science and Technology Co., Ltd.) Abstact: In this pape, the essence of the inteaction between two paallel
Foce between two paallel cuent wies and Newton s thid law Yannan Yang (Shanghai Jinjuan Infomation Science and Technology Co., Ltd.) Abstact: In this pape, the essence of the inteaction between two paallel
FZX: Personal Lecture Notes from Daniel W. Koon St. Lawrence University Physics Department CHAPTER 7
 FZX: Pesonal Lectue Notes fom Daniel W. Koon St. Lawence Univesity Physics Depatment CHAPTER 7 Please epot any glitches, bugs o eos to the autho: dkoon at stlawu.edu. 7. Momentum and Impulse Impulse page
FZX: Pesonal Lectue Notes fom Daniel W. Koon St. Lawence Univesity Physics Depatment CHAPTER 7 Please epot any glitches, bugs o eos to the autho: dkoon at stlawu.edu. 7. Momentum and Impulse Impulse page
PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture #20
 PHYSICS 151 Notes fo Online Lectue #20 Toque: The whole eason that we want to woy about centes of mass is that we ae limited to looking at point masses unless we know how to deal with otations. Let s evisit
PHYSICS 151 Notes fo Online Lectue #20 Toque: The whole eason that we want to woy about centes of mass is that we ae limited to looking at point masses unless we know how to deal with otations. Let s evisit
Physics Spring 2012 Announcements: Mar 07, 2012
 Physics 00 - Sping 01 Announcements: Ma 07, 01 HW#6 due date has been extended to the moning of Wed. Ma 1. Test # (i. Ma ) will cove only chaptes 0 and 1 All of chapte will be coveed in Test #4!!! Test
Physics 00 - Sping 01 Announcements: Ma 07, 01 HW#6 due date has been extended to the moning of Wed. Ma 1. Test # (i. Ma ) will cove only chaptes 0 and 1 All of chapte will be coveed in Test #4!!! Test
Phys 201A. Homework 5 Solutions
 Phys 201A Homewok 5 Solutions 3. In each of the thee cases, you can find the changes in the velocity vectos by adding the second vecto to the additive invese of the fist and dawing the esultant, and by
Phys 201A Homewok 5 Solutions 3. In each of the thee cases, you can find the changes in the velocity vectos by adding the second vecto to the additive invese of the fist and dawing the esultant, and by
Force and Work: Reminder
 Electic Potential Foce and Wok: Reminde Displacement d a: initial point b: final point Reminde fom Mechanics: Foce F if thee is a foce acting on an object (e.g. electic foce), this foce may do some wok
Electic Potential Foce and Wok: Reminde Displacement d a: initial point b: final point Reminde fom Mechanics: Foce F if thee is a foce acting on an object (e.g. electic foce), this foce may do some wok
SAMPLE QUIZ 3 - PHYSICS For a right triangle: sin θ = a c, cos θ = b c, tan θ = a b,
 SAMPLE QUIZ 3 - PHYSICS 1301.1 his is a closed book, closed notes quiz. Calculatos ae pemitted. he ONLY fomulas that may be used ae those given below. Define all symbols and justify all mathematical expessions
SAMPLE QUIZ 3 - PHYSICS 1301.1 his is a closed book, closed notes quiz. Calculatos ae pemitted. he ONLY fomulas that may be used ae those given below. Define all symbols and justify all mathematical expessions
