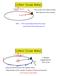
A car of mass m, traveling at constant speed, rides over the top of a circularly shaped hill as shown.
|
|
|
- Aldous Gibson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A ca of mass m, taveling at constant speed, ides ove the top of a ciculaly shaped hill as shown. The magnitude of the nomal foce N of the oad on the ca is. A) Geate than the weight of the ca, N > mg. B) Equal to the weight, N = mg. C) Less than the weight, N < mg. L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 1
2 A ca of mass m, taveling at constant speed, ides ove the top of a ciculaly shaped hill as shown. N Wite NII: F net mg +x 0 < F net = ma = mv2 = mg N N < mg L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 2
3 Assignments cuved mean = 75 About the exam: Raw aveage = 72. Each scoe is cuved upwad by 3 points. Student scoes (inceased by 3 points) ae posted on D2L. I have exam booklets fo the ealy exam pick up afte class today. See the couse web site fo suggestions about impoving in the futue. Any questions about you gade should be sent to Pof. Munsat. L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 3
4 Assignments About the exam: Raw aveage = 72. Each scoe is cuved upwad by 3 points. Student scoes (inceased by 3 points) ae posted on D2L. I have exam booklets fo the ealy exam pick up afte class today. See the couse web site fo suggestions about impoving in the futue. Any questions about you gade should be sent to Pof. Munsat. Fo this week: Read Ch. 5 of Wolfson and Pof. Dubson s notes. Begin Ch. 6. Witten HW5, fom Red Wokbook. Scans of the Red and Blue Wokbooks ae on D2L. Fo next week: CAPA 6. Witten homewok 6: begin to analyze the Megawoosh video. L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 4
5 Wi5en HW s 6-8: Megawoosh vs. Wateslide Wipeout Megawoosh Video: You Question fo HW6: Is tajectoy of this stunt theoetically consistent with Newton s Laws, if ai esistance and sliding fiction ae neglected? (Ignoe the ability of the man to suvive the landing in the kiddie pool.) Mythbustes Response: Myth Busted: Mythbustes conside accuacy and distance in the eal wold, whee sliding fiction and ai esistance exist. They find the accuacy is possible but distance is not unde ealistic conditions. L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 5
6 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion Applications: (1) Sliding Blocks. (2) Contact Foces. (3) Suspended Bodies. (4) Cicula Motion. (5) Fiction. L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 6
7 Atwood machine Mass suspended fom anothe suppoted mass T a = M m M + m g M 1 +T +x T a M m T a +x a = M 2 M 1 + M 2 g M 2 +x F g =Mg F g =mg F g = M 2 g +x 1) Choose a coodinate system. 2) Specify the foces (fee-body diagam). 3) Conside F net = ma fo each object. 4) Solve fo what s needed. 5) Does the esult make sense? L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 7
8 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion Applications: (1) Sliding Blocks. (2) Contact Foces. (3) Suspended Bodies. (4) Cicula Motion. (5) Fiction. L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 8
9 Example 2. A mey-go-ound has a adius = 5 m. If it s pushed to have a peiod of τ = 3 sec. = 5 m a R = 22 m/s 2 τ = 3 sec m = 25 kg a R = v2 = 4π 2 τ 2 What s the centipetal foce needed to hold a m = 25 kg gil on the mey-go-ound? F = m a R = 25 kg (22 m/s 2 ) = 550 N (1 lb/4.45 N) = 123 lb L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 9
10 Example 3. The Eath cicles the Sun at an aveage distance of 1 AU = 1.5 x m in 1 yea. What is its obital centipetal acceleation? = 1 AU E a R = v2 = 4π 2 τ 2 = 4π 2 (1.5x10 11 m) (πx10 7 s) 2 1g = 6x10 3 m/s 2 9.8m/s % of g L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 10
11 Example 3. The Eath cicles the Sun at an aveage distance of 1 AU = 1.5 x m in 1 yea. What is its obital centipetal acceleation? = 1 AU τ = 365 days E a R = v2 = 4π 2 τ % of g What s causing the centipetal acceleation? A) The electostatic foce between the Eath and Sun. B) The tension in the sting connecting the Eath to the Sun. C) The foce of gavity between the Eath and the Sun. D) Depends on the time of day. L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 11
12 Example 3. The Eath cicles the Sun at an aveage distance of 1 AU = 1.5 x m in 1 yea. What is its obital centipetal acceleation? = 1 AU E a R = v2 = 4π 2 τ % of g a R τ = 365 days It points towads the Sun at all times, which may be in the sky o not depending on the time of day. You e on the Eath. Which diection does the centipetal acceleation point? A) Down B) Up C) Depends on the time of yea. D) Depends on the time of day. L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 12
13 Conside the following two situations: Situation I: A ca on Eath ides ove the top of a ound hill, with adius of cuvatue = 100 m, at constant speed v = 35 mph. Situation II: A monoail ca in integalactic space (no gavity) moves along a ound monoail, with adius of cuvatue = 100 m, at constant speed v = 35 mph. Which ca expeiences the lage acceleation? A) Eath ca. B) Space ca. C) Both have the same acceleation. Both cas have the same acceleation. The pesence of gavity doesn t change the fact that the acceleation has magnitude a = v 2 /. L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 13
14 A ball of mass m is twiled on a sting in a vetical cicle of adius in the pesence of gavity with a constant speed v. At which position is the magnitude of the net foce on the ball geatest? (Ignoe ai esistance but conside gavity.) v F net Top T 1 = mv2 Bottom L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 14 T 2 v A) Top B) Bottom C) Somewhee between Top and Bottom. D) Same at all positions.
15 A ball of mass m is twiled on a sting in a vetical cicle of adius in the pesence of gavity with a constant speed v. What is the elation between the magnitude of the tension in the sting at the top and bottom of the cicle? (Ignoe ai esistance but conside gavity.) v Top T 1 A) T 1 = T 2 B) T 1 > T 2 Bottom T 2 v C) T 2 > T 1 D) Impossible to tell fom the infomation given. L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 15
16 A ball of mass m is twiled on a sting in a vetical cicle of adius in the pesence of gavity with a constant speed v. What is the elation between the magnitude of the tension in the sting at the top and bottom of the cicle? (Ignoe ai esistance but conside gavity.) v Top Top Bottom T 1 T 2 +x a +x T 1 m mg m mg a Bottom T 2 T 2 > T 1 v F net = ma = m v2 = T 1 + mg T 1 = mv2 mg F net = ma = m v2 = T 2 mg T 2 = mv2 + mg L16 W 10/1/14 a*e lectue 16
Chapter 5: Uniform Circular Motion
 Chapte 5: Unifom Cicula Motion Motion at constant speed in a cicle Centipetal acceleation Banked cuves Obital motion Weightlessness, atificial gavity Vetical cicula motion Centipetal Foce Acceleation towad
Chapte 5: Unifom Cicula Motion Motion at constant speed in a cicle Centipetal acceleation Banked cuves Obital motion Weightlessness, atificial gavity Vetical cicula motion Centipetal Foce Acceleation towad
Describing Circular motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion Descibing Cicula motion In ode to undestand cicula motion, we fist need to discuss how to subtact vectos. The easiest way to explain subtacting vectos is to descibe it as adding a
Unifom Cicula Motion Descibing Cicula motion In ode to undestand cicula motion, we fist need to discuss how to subtact vectos. The easiest way to explain subtacting vectos is to descibe it as adding a
Physics 111 Lecture 5 Circular Motion
 Physics 111 Lectue 5 Cicula Motion D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Multiple Objects q A block of mass m1 on a ough, hoizontal suface is connected to a ball of mass m by a lightweight
Physics 111 Lectue 5 Cicula Motion D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Multiple Objects q A block of mass m1 on a ough, hoizontal suface is connected to a ball of mass m by a lightweight
Physics 101 Lecture 6 Circular Motion
 Physics 101 Lectue 6 Cicula Motion Assist. Pof. D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Equilibium, Example 1 q What is the smallest value of the foce F such that the.0-kg block will not slide
Physics 101 Lectue 6 Cicula Motion Assist. Pof. D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Equilibium, Example 1 q What is the smallest value of the foce F such that the.0-kg block will not slide
Recap. Centripetal acceleration: v r. a = m/s 2 (towards center of curvature)
 a = c v 2 Recap Centipetal acceleation: m/s 2 (towads cente of cuvatue) A centipetal foce F c is equied to keep a body in cicula motion: This foce poduces centipetal acceleation that continuously changes
a = c v 2 Recap Centipetal acceleation: m/s 2 (towads cente of cuvatue) A centipetal foce F c is equied to keep a body in cicula motion: This foce poduces centipetal acceleation that continuously changes
b) (5) What is the magnitude of the force on the 6.0-kg block due to the contact with the 12.0-kg block?
 Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 13, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 13, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
Centripetal Force. Lecture 11. Chapter 8. Course website:
 Lectue 11 Chapte 8 Centipetal Foce Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi PHYS.1410 Lectue 11 Danylov Depatment of Physics and Applied Physics Today we ae going to discuss:
Lectue 11 Chapte 8 Centipetal Foce Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi PHYS.1410 Lectue 11 Danylov Depatment of Physics and Applied Physics Today we ae going to discuss:
Physics Fall Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids. Lecture 6: motion in two and three dimensions III. Slide 6-1
 Physics 1501 Fall 2008 Mechanics, Themodynamics, Waves, Fluids Lectue 6: motion in two and thee dimensions III Slide 6-1 Recap: elative motion An object moves with velocity v elative to one fame of efeence.
Physics 1501 Fall 2008 Mechanics, Themodynamics, Waves, Fluids Lectue 6: motion in two and thee dimensions III Slide 6-1 Recap: elative motion An object moves with velocity v elative to one fame of efeence.
PHYS Summer Professor Caillault Homework Solutions. Chapter 5
 PHYS 1111 - Summe 2007 - Pofesso Caillault Homewok Solutions Chapte 5 7. Pictue the Poblem: The ball is acceleated hoizontally fom est to 98 mi/h ove a distance of 1.7 m. Stategy: Use equation 2-12 to
PHYS 1111 - Summe 2007 - Pofesso Caillault Homewok Solutions Chapte 5 7. Pictue the Poblem: The ball is acceleated hoizontally fom est to 98 mi/h ove a distance of 1.7 m. Stategy: Use equation 2-12 to
c) (6) Assuming the tires do not skid, what coefficient of static friction between tires and pavement is needed?
 Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 10, 2012 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 10, 2012 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion constant speed Pick a point in the objects motion... What diection is the velocity? HINT Think about what diection the object would tavel if the sting wee cut Unifom Cicula Motion
Unifom Cicula Motion constant speed Pick a point in the objects motion... What diection is the velocity? HINT Think about what diection the object would tavel if the sting wee cut Unifom Cicula Motion
PHYSICS 220. Lecture 08. Textbook Sections Lecture 8 Purdue University, Physics 220 1
 PHYSICS 0 Lectue 08 Cicula Motion Textbook Sections 5.3 5.5 Lectue 8 Pudue Univesity, Physics 0 1 Oveview Last Lectue Cicula Motion θ angula position adians ω angula velocity adians/second α angula acceleation
PHYSICS 0 Lectue 08 Cicula Motion Textbook Sections 5.3 5.5 Lectue 8 Pudue Univesity, Physics 0 1 Oveview Last Lectue Cicula Motion θ angula position adians ω angula velocity adians/second α angula acceleation
Midterm Exam #2, Part A
 Physics 151 Mach 17, 2006 Midtem Exam #2, Pat A Roste No.: Scoe: Exam time limit: 50 minutes. You may use calculatos and both sides of ONE sheet of notes, handwitten only. Closed book; no collaboation.
Physics 151 Mach 17, 2006 Midtem Exam #2, Pat A Roste No.: Scoe: Exam time limit: 50 minutes. You may use calculatos and both sides of ONE sheet of notes, handwitten only. Closed book; no collaboation.
PS113 Chapter 5 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion
 PS113 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion 1 Unifom cicula motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant (unifom) speed on a cicula path. The peiod T is the time equied
PS113 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion 1 Unifom cicula motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant (unifom) speed on a cicula path. The peiod T is the time equied
Chapter 5. Uniform Circular Motion. a c =v 2 /r
 Chapte 5 Unifom Cicula Motion a c =v 2 / Unifom cicula motion: Motion in a cicula path with constant speed s v 1) Speed and peiod Peiod, T: time fo one evolution Speed is elated to peiod: Path fo one evolution:
Chapte 5 Unifom Cicula Motion a c =v 2 / Unifom cicula motion: Motion in a cicula path with constant speed s v 1) Speed and peiod Peiod, T: time fo one evolution Speed is elated to peiod: Path fo one evolution:
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion Have you eve idden on the amusement pak ide shown below? As it spins you feel as though you ae being pessed tightly against the wall. The ide then begins to tilt but you emain glued
Unifom Cicula Motion Have you eve idden on the amusement pak ide shown below? As it spins you feel as though you ae being pessed tightly against the wall. The ide then begins to tilt but you emain glued
Physics 4A Chapter 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane
 Physics 4A Chapte 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane Conceptual Questions and Example Poblems fom Chapte 8 Conceptual Question 8.5 The figue below shows two balls of equal mass moving in vetical cicles.
Physics 4A Chapte 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane Conceptual Questions and Example Poblems fom Chapte 8 Conceptual Question 8.5 The figue below shows two balls of equal mass moving in vetical cicles.
Physics 201 Homework 4
 Physics 201 Homewok 4 Jan 30, 2013 1. Thee is a cleve kitchen gadget fo dying lettuce leaves afte you wash them. 19 m/s 2 It consists of a cylindical containe mounted so that it can be otated about its
Physics 201 Homewok 4 Jan 30, 2013 1. Thee is a cleve kitchen gadget fo dying lettuce leaves afte you wash them. 19 m/s 2 It consists of a cylindical containe mounted so that it can be otated about its
Rotational Motion. Lecture 6. Chapter 4. Physics I. Course website:
 Lectue 6 Chapte 4 Physics I Rotational Motion Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we ae going to discuss: Chapte 4: Unifom Cicula Motion: Section 4.4 Nonunifom Cicula
Lectue 6 Chapte 4 Physics I Rotational Motion Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we ae going to discuss: Chapte 4: Unifom Cicula Motion: Section 4.4 Nonunifom Cicula
Momentum is conserved if no external force
 Goals: Lectue 13 Chapte 9 v Employ consevation of momentum in 1 D & 2D v Examine foces ove time (aka Impulse) Chapte 10 v Undestand the elationship between motion and enegy Assignments: l HW5, due tomoow
Goals: Lectue 13 Chapte 9 v Employ consevation of momentum in 1 D & 2D v Examine foces ove time (aka Impulse) Chapte 10 v Undestand the elationship between motion and enegy Assignments: l HW5, due tomoow
CHAPTER 5: Circular Motion; Gravitation
 CHAPER 5: Cicula Motion; Gavitation Solution Guide to WebAssign Pobles 5.1 [1] (a) Find the centipetal acceleation fo Eq. 5-1.. a R v ( 1.5 s) 1.10 1.4 s (b) he net hoizontal foce is causing the centipetal
CHAPER 5: Cicula Motion; Gavitation Solution Guide to WebAssign Pobles 5.1 [1] (a) Find the centipetal acceleation fo Eq. 5-1.. a R v ( 1.5 s) 1.10 1.4 s (b) he net hoizontal foce is causing the centipetal
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion Intoduction Ealie we defined acceleation as being the change in velocity with time: a = v t Until now we have only talked about changes in the magnitude of the acceleation: the speeding
Unifom Cicula Motion Intoduction Ealie we defined acceleation as being the change in velocity with time: a = v t Until now we have only talked about changes in the magnitude of the acceleation: the speeding
DYNAMICS OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION
 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
Circular Motion & Torque Test Review. The period is the amount of time it takes for an object to travel around a circular path once.
 Honos Physics Fall, 2016 Cicula Motion & Toque Test Review Name: M. Leonad Instuctions: Complete the following woksheet. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. 1. Detemine whethe each statement
Honos Physics Fall, 2016 Cicula Motion & Toque Test Review Name: M. Leonad Instuctions: Complete the following woksheet. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. 1. Detemine whethe each statement
Circular-Rotational Motion Mock Exam. Instructions: (92 points) Answer the following questions. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK.
 AP Physics C Sping, 2017 Cicula-Rotational Motion Mock Exam Name: Answe Key M. Leonad Instuctions: (92 points) Answe the following questions. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK. ( ) 1. A stuntman dives a motocycle
AP Physics C Sping, 2017 Cicula-Rotational Motion Mock Exam Name: Answe Key M. Leonad Instuctions: (92 points) Answe the following questions. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK. ( ) 1. A stuntman dives a motocycle
Physics 111. Lecture 14 (Walker: Ch. 6.5) Circular Motion Centripetal Acceleration Centripetal Force February 27, 2009
 Physics 111 Lectue 14 (Walke: Ch. 6.5) Cicula Motion Centipetal Acceleation Centipetal Foce Febuay 7, 009 Midtem Exam 1 on Wed. Mach 4 (Chaptes 1-6) Lectue 14 1/8 Connected Objects If thee is a pulley,
Physics 111 Lectue 14 (Walke: Ch. 6.5) Cicula Motion Centipetal Acceleation Centipetal Foce Febuay 7, 009 Midtem Exam 1 on Wed. Mach 4 (Chaptes 1-6) Lectue 14 1/8 Connected Objects If thee is a pulley,
Extra notes for circular motion: Circular motion : v keeps changing, maybe both speed and
 Exta notes fo cicula motion: Cicula motion : v keeps changing, maybe both speed and diection ae changing. At least v diection is changing. Hence a 0. Acceleation NEEDED to stay on cicula obit: a cp v /,
Exta notes fo cicula motion: Cicula motion : v keeps changing, maybe both speed and diection ae changing. At least v diection is changing. Hence a 0. Acceleation NEEDED to stay on cicula obit: a cp v /,
Circular Motion. Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics
 Cicula Motion M. Velazquez AP/Honos Physics Objects in Cicula Motion Accoding to Newton s Laws, if no foce acts on an object, it will move with constant speed in a constant diection. Theefoe, if an object
Cicula Motion M. Velazquez AP/Honos Physics Objects in Cicula Motion Accoding to Newton s Laws, if no foce acts on an object, it will move with constant speed in a constant diection. Theefoe, if an object
Physics 231 Lecture 17
 Physics 31 Lectue 17 Main points of today s lectue: Centipetal acceleation: a c = a c t Rotational motion definitions: Δω Δω α =, α = limδ t 0 Δt Δt Δ s= Δ θ;t = ω;at = α Rotational kinematics equations:
Physics 31 Lectue 17 Main points of today s lectue: Centipetal acceleation: a c = a c t Rotational motion definitions: Δω Δω α =, α = limδ t 0 Δt Δt Δ s= Δ θ;t = ω;at = α Rotational kinematics equations:
Chapter 8. Accelerated Circular Motion
 Chapte 8 Acceleated Cicula Motion 8.1 Rotational Motion and Angula Displacement A new unit, adians, is eally useful fo angles. Radian measue θ(adians) = s = θ s (ac length) (adius) (s in same units as
Chapte 8 Acceleated Cicula Motion 8.1 Rotational Motion and Angula Displacement A new unit, adians, is eally useful fo angles. Radian measue θ(adians) = s = θ s (ac length) (adius) (s in same units as
Chap 5. Circular Motion: Gravitation
 Chap 5. Cicula Motion: Gavitation Sec. 5.1 - Unifom Cicula Motion A body moves in unifom cicula motion, if the magnitude of the velocity vecto is constant and the diection changes at evey point and is
Chap 5. Cicula Motion: Gavitation Sec. 5.1 - Unifom Cicula Motion A body moves in unifom cicula motion, if the magnitude of the velocity vecto is constant and the diection changes at evey point and is
Name. Date. Period. Engage Examine the pictures on the left. 1. What is going on in these pictures?
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 9.a Unifom Cicula Motion Outcomes 1. Define unifom cicula motion. 2. Detemine the tangential velocity of an object moving with unifom cicula motion. 3. Detemine the centipetal acceleation
AP Physics 1 Lesson 9.a Unifom Cicula Motion Outcomes 1. Define unifom cicula motion. 2. Detemine the tangential velocity of an object moving with unifom cicula motion. 3. Detemine the centipetal acceleation
AP * PHYSICS B. Circular Motion, Gravity, & Orbits. Teacher Packet
 AP * PHYSICS B Cicula Motion, Gavity, & Obits Teache Packet AP* is a tademak of the College Entance Examination Boad. The College Entance Examination Boad was not involved in the poduction of this mateial.
AP * PHYSICS B Cicula Motion, Gavity, & Obits Teache Packet AP* is a tademak of the College Entance Examination Boad. The College Entance Examination Boad was not involved in the poduction of this mateial.
b) (5) What average force magnitude was applied by the students working together?
 Geneal Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibium Nov. 3, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults
Geneal Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibium Nov. 3, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults
Objective Notes Summary
 Objective Notes Summay An object moving in unifom cicula motion has constant speed but not constant velocity because the diection is changing. The velocity vecto in tangent to the cicle, the acceleation
Objective Notes Summay An object moving in unifom cicula motion has constant speed but not constant velocity because the diection is changing. The velocity vecto in tangent to the cicle, the acceleation
Sections and Chapter 10
 Cicula and Rotational Motion Sections 5.-5.5 and Chapte 10 Basic Definitions Unifom Cicula Motion Unifom cicula motion efes to the motion of a paticle in a cicula path at constant speed. The instantaneous
Cicula and Rotational Motion Sections 5.-5.5 and Chapte 10 Basic Definitions Unifom Cicula Motion Unifom cicula motion efes to the motion of a paticle in a cicula path at constant speed. The instantaneous
ω = θ θ o = θ θ = s r v = rω
 Unifom Cicula Motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant(unifom) speed in a cicula path. Fist we must define the angula displacement and angula velocity The angula displacement
Unifom Cicula Motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant(unifom) speed in a cicula path. Fist we must define the angula displacement and angula velocity The angula displacement
Quiz 6--Work, Gravitation, Circular Motion, Torque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible)
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
Chapters 5-8. Dynamics: Applying Newton s Laws
 Chaptes 5-8 Dynamics: Applying Newton s Laws Systems of Inteacting Objects The Fee Body Diagam Technique Examples: Masses Inteacting ia Nomal Foces Masses Inteacting ia Tensions in Ropes. Ideal Pulleys
Chaptes 5-8 Dynamics: Applying Newton s Laws Systems of Inteacting Objects The Fee Body Diagam Technique Examples: Masses Inteacting ia Nomal Foces Masses Inteacting ia Tensions in Ropes. Ideal Pulleys
Ch 13 Universal Gravitation
 Ch 13 Univesal Gavitation Ch 13 Univesal Gavitation Why do celestial objects move the way they do? Keple (1561-1630) Tycho Bahe s assistant, analyzed celestial motion mathematically Galileo (1564-1642)
Ch 13 Univesal Gavitation Ch 13 Univesal Gavitation Why do celestial objects move the way they do? Keple (1561-1630) Tycho Bahe s assistant, analyzed celestial motion mathematically Galileo (1564-1642)
PHYS 172: Modern Mechanics. Summer Lecture 4 The Momentum Principle & Predicting Motion Read
 PHYS 172: Moden Mechanics Summe 2010 Δp sys = F net Δt ΔE = W + Q sys su su ΔL sys = τ net Δt Lectue 4 The Momentum Pinciple & Pedicting Motion Read 2.6-2.9 READING QUESTION #1 Reading Question Which of
PHYS 172: Moden Mechanics Summe 2010 Δp sys = F net Δt ΔE = W + Q sys su su ΔL sys = τ net Δt Lectue 4 The Momentum Pinciple & Pedicting Motion Read 2.6-2.9 READING QUESTION #1 Reading Question Which of
Chapter 5. really hard to start the object moving and then, once it starts moving, you don t have to push as hard to keep it moving.
 Chapte 5 Fiction When an object is in motion it is usually in contact with a viscous mateial (wate o ai) o some othe suface. So fa, we have assumed that moving objects don t inteact with thei suoundings
Chapte 5 Fiction When an object is in motion it is usually in contact with a viscous mateial (wate o ai) o some othe suface. So fa, we have assumed that moving objects don t inteact with thei suoundings
Physics 107 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8
 Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
Understanding the Concepts
 Chistian Bache Phsics Depatment Bn Maw College Undestanding the Concepts PHYSICS 101-10 Homewok Assignment #5 - Solutions 5.7. A cclist making a tun must make use of a centipetal foce, one that is pependicula
Chistian Bache Phsics Depatment Bn Maw College Undestanding the Concepts PHYSICS 101-10 Homewok Assignment #5 - Solutions 5.7. A cclist making a tun must make use of a centipetal foce, one that is pependicula
= 4 3 π( m) 3 (5480 kg m 3 ) = kg.
 CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
PROBLEM (page 126, 12 th edition)
 PROBLEM 13-27 (page 126, 12 th edition) The mass of block A is 100 kg. The mass of block B is 60 kg. The coefficient of kinetic fiction between block B and the inclined plane is 0.4. A and B ae eleased
PROBLEM 13-27 (page 126, 12 th edition) The mass of block A is 100 kg. The mass of block B is 60 kg. The coefficient of kinetic fiction between block B and the inclined plane is 0.4. A and B ae eleased
AP Physics 1 - Circular Motion and Gravitation Practice Test (Multiple Choice Section) Answer Section
 AP Physics 1 - Cicula Motion and Gaitation Pactice est (Multiple Choice Section) Answe Section MULIPLE CHOICE 1. B he centipetal foce must be fiction since, lacking any fiction, the coin would slip off.
AP Physics 1 - Cicula Motion and Gaitation Pactice est (Multiple Choice Section) Answe Section MULIPLE CHOICE 1. B he centipetal foce must be fiction since, lacking any fiction, the coin would slip off.
Physics 2001 Problem Set 5 Solutions
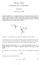 Physics 2001 Poblem Set 5 Solutions Jeff Kissel Octobe 16, 2006 1. A puck attached to a sting undegoes cicula motion on an ai table. If the sting beaks at the point indicated in the figue, which path (A,
Physics 2001 Poblem Set 5 Solutions Jeff Kissel Octobe 16, 2006 1. A puck attached to a sting undegoes cicula motion on an ai table. If the sting beaks at the point indicated in the figue, which path (A,
 Hoizontal Cicula Motion 1. A paticle of mass m is tied to a light sting and otated with a speed v along a cicula path of adius. If T is tension in the sting and mg is gavitational foce on the paticle then,
Hoizontal Cicula Motion 1. A paticle of mass m is tied to a light sting and otated with a speed v along a cicula path of adius. If T is tension in the sting and mg is gavitational foce on the paticle then,
1. A stone falls from a platform 18 m high. When will it hit the ground? (a) 1.74 s (b) 1.83 s (c) 1.92 s (d) 2.01 s
 1. A stone falls fom a platfom 18 m high. When will it hit the gound? (a) 1.74 s (b) 1.83 s (c) 1.9 s (d).01 s Constant acceleation D = v 0 t + ½ a t. Which, if any, of these foces causes the otation of
1. A stone falls fom a platfom 18 m high. When will it hit the gound? (a) 1.74 s (b) 1.83 s (c) 1.9 s (d).01 s Constant acceleation D = v 0 t + ½ a t. Which, if any, of these foces causes the otation of
OSCILLATIONS AND GRAVITATION
 1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
Spring 2001 Physics 2048 Test 3 solutions
 Sping 001 Physics 048 Test 3 solutions Poblem 1. (Shot Answe: 15 points) a. 1 b. 3 c. 4* d. 9 e. 8 f. 9 *emembe that since KE = ½ mv, KE must be positive Poblem (Estimation Poblem: 15 points) Use momentum-impulse
Sping 001 Physics 048 Test 3 solutions Poblem 1. (Shot Answe: 15 points) a. 1 b. 3 c. 4* d. 9 e. 8 f. 9 *emembe that since KE = ½ mv, KE must be positive Poblem (Estimation Poblem: 15 points) Use momentum-impulse
Physics 1114: Unit 5 Hand-out Homework (Answers)
 Physics 1114: Unit 5 Hand-out Homewok (Answes) Poblem set 1 1. The flywheel on an expeimental bus is otating at 420 RPM (evolutions pe minute). To find (a) the angula velocity in ad/s (adians/second),
Physics 1114: Unit 5 Hand-out Homewok (Answes) Poblem set 1 1. The flywheel on an expeimental bus is otating at 420 RPM (evolutions pe minute). To find (a) the angula velocity in ad/s (adians/second),
Phys 201A. Homework 5 Solutions
 Phys 201A Homewok 5 Solutions 3. In each of the thee cases, you can find the changes in the velocity vectos by adding the second vecto to the additive invese of the fist and dawing the esultant, and by
Phys 201A Homewok 5 Solutions 3. In each of the thee cases, you can find the changes in the velocity vectos by adding the second vecto to the additive invese of the fist and dawing the esultant, and by
PHYSICS 1210 Exam 2 University of Wyoming 14 March ( Day!) points
 PHYSICS 1210 Exam 2 Univesity of Wyoming 14 Mach ( Day!) 2013 150 points This test is open-note and closed-book. Calculatos ae pemitted but computes ae not. No collaboation, consultation, o communication
PHYSICS 1210 Exam 2 Univesity of Wyoming 14 Mach ( Day!) 2013 150 points This test is open-note and closed-book. Calculatos ae pemitted but computes ae not. No collaboation, consultation, o communication
Physics 11 Chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. Problem Solving
 Physics 11 Chapte 4: Foces and Newton s Laws of Motion Thee is nothing eithe good o bad, but thinking makes it so. William Shakespeae It s not what happens to you that detemines how fa you will go in life;
Physics 11 Chapte 4: Foces and Newton s Laws of Motion Thee is nothing eithe good o bad, but thinking makes it so. William Shakespeae It s not what happens to you that detemines how fa you will go in life;
Circular Motion. x-y coordinate systems. Other coordinates... PHY circular-motion - J. Hedberg
 Cicula Motion PHY 207 - cicula-motion - J. Hedbeg - 2017 x-y coodinate systems Fo many situations, an x-y coodinate system is a geat idea. Hee is a map on Manhattan. The steets ae laid out in a ectangula
Cicula Motion PHY 207 - cicula-motion - J. Hedbeg - 2017 x-y coodinate systems Fo many situations, an x-y coodinate system is a geat idea. Hee is a map on Manhattan. The steets ae laid out in a ectangula
Movie Review Part One due Tuesday (in class) please print
 Movie Review Pat One due Tuesday (in class) please pint Test in class on Fiday. You may stat at 8:30 if you want. (The topic of powe is not on test.) Chaptes 4-6 Main Ideas in Class Today Afte class, you
Movie Review Pat One due Tuesday (in class) please pint Test in class on Fiday. You may stat at 8:30 if you want. (The topic of powe is not on test.) Chaptes 4-6 Main Ideas in Class Today Afte class, you
Lecture 22. PE = GMm r TE = GMm 2a. T 2 = 4π 2 GM. Main points of today s lecture: Gravitational potential energy: Total energy of orbit:
 Lectue Main points of today s lectue: Gavitational potential enegy: Total enegy of obit: PE = GMm TE = GMm a Keple s laws and the elation between the obital peiod and obital adius. T = 4π GM a3 Midtem
Lectue Main points of today s lectue: Gavitational potential enegy: Total enegy of obit: PE = GMm TE = GMm a Keple s laws and the elation between the obital peiod and obital adius. T = 4π GM a3 Midtem
Unit 4 Circular Motion and Centripetal Force
 Name: Unit 4 Cicula Motion and Centipetal Foce H: Gading: Show all wok, keeping it neat and oganized. Show equations used and include all units. Vocabulay Peiod: the time it takes fo one complete evolution
Name: Unit 4 Cicula Motion and Centipetal Foce H: Gading: Show all wok, keeping it neat and oganized. Show equations used and include all units. Vocabulay Peiod: the time it takes fo one complete evolution
PROJECTILE MOTION. At any given point in the motion, the velocity vector is always a tangent to the path.
 PROJECTILE MOTION A pojectile is any object that has been thown though the ai. A foce must necessaily set the object in motion initially but, while it is moing though the ai, no foce othe than gaity acts
PROJECTILE MOTION A pojectile is any object that has been thown though the ai. A foce must necessaily set the object in motion initially but, while it is moing though the ai, no foce othe than gaity acts
Between any two masses, there exists a mutual attractive force.
 YEAR 12 PHYSICS: GRAVITATION PAST EXAM QUESTIONS Name: QUESTION 1 (1995 EXAM) (a) State Newton s Univesal Law of Gavitation in wods Between any two masses, thee exists a mutual attactive foce. This foce
YEAR 12 PHYSICS: GRAVITATION PAST EXAM QUESTIONS Name: QUESTION 1 (1995 EXAM) (a) State Newton s Univesal Law of Gavitation in wods Between any two masses, thee exists a mutual attactive foce. This foce
SAMPLE QUIZ 3 - PHYSICS For a right triangle: sin θ = a c, cos θ = b c, tan θ = a b,
 SAMPLE QUIZ 3 - PHYSICS 1301.1 his is a closed book, closed notes quiz. Calculatos ae pemitted. he ONLY fomulas that may be used ae those given below. Define all symbols and justify all mathematical expessions
SAMPLE QUIZ 3 - PHYSICS 1301.1 his is a closed book, closed notes quiz. Calculatos ae pemitted. he ONLY fomulas that may be used ae those given below. Define all symbols and justify all mathematical expessions
Physics C Rotational Motion Name: ANSWER KEY_ AP Review Packet
 Linea and angula analogs Linea Rotation x position x displacement v velocity a T tangential acceleation Vectos in otational motion Use the ight hand ule to detemine diection of the vecto! Don t foget centipetal
Linea and angula analogs Linea Rotation x position x displacement v velocity a T tangential acceleation Vectos in otational motion Use the ight hand ule to detemine diection of the vecto! Don t foget centipetal
Phys 201A. Homework 6 Solutions. F A and F r. B. According to Newton s second law, ( ) ( )2. j = ( 6.0 m / s 2 )ˆ i ( 10.4m / s 2 )ˆ j.
 7. We denote the two foces F A + F B = ma,sof B = ma F A. (a) In unit vecto notation F A = ( 20.0 N)ˆ i and Theefoe, Phys 201A Homewok 6 Solutions F A and F B. Accoding to Newton s second law, a = [ (
7. We denote the two foces F A + F B = ma,sof B = ma F A. (a) In unit vecto notation F A = ( 20.0 N)ˆ i and Theefoe, Phys 201A Homewok 6 Solutions F A and F B. Accoding to Newton s second law, a = [ (
PHYS 1114, Lecture 21, March 6 Contents:
 PHYS 1114, Lectue 21, Mach 6 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, being eplaced by the common exam Tuesday, Mach 7, 5:30 PM. A eview and Q&A session is scheduled instead duing class time. 2 Exam
PHYS 1114, Lectue 21, Mach 6 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, being eplaced by the common exam Tuesday, Mach 7, 5:30 PM. A eview and Q&A session is scheduled instead duing class time. 2 Exam
Gaia s Place in Space
 Gaia s Place in Space The impotance of obital positions fo satellites Obits and Lagange Points Satellites can be launched into a numbe of diffeent obits depending on thei objectives and what they ae obseving.
Gaia s Place in Space The impotance of obital positions fo satellites Obits and Lagange Points Satellites can be launched into a numbe of diffeent obits depending on thei objectives and what they ae obseving.
Conflict Exam Issue. Sorry, Can t do it. Please see Kevin Pitts if you have any additional questions or concerns about this. Office is 231 Loomis
 Conflict Exam Issue. Soy, Can t do it I was told that: Students can only be excused fom the scheduled final fo illness, death in the family o eligious holiday. No exceptions. Please see Kevin Pitts if
Conflict Exam Issue. Soy, Can t do it I was told that: Students can only be excused fom the scheduled final fo illness, death in the family o eligious holiday. No exceptions. Please see Kevin Pitts if
7 Circular Motion. 7-1 Centripetal Acceleration and Force. Period, Frequency, and Speed. Vocabulary
 7 Cicula Motion 7-1 Centipetal Acceleation and Foce Peiod, Fequency, and Speed Vocabulay Vocabulay Peiod: he time it takes fo one full otation o evolution of an object. Fequency: he numbe of otations o
7 Cicula Motion 7-1 Centipetal Acceleation and Foce Peiod, Fequency, and Speed Vocabulay Vocabulay Peiod: he time it takes fo one full otation o evolution of an object. Fequency: he numbe of otations o
Introduction to Mechanics Centripetal Force
 Intoduction to Mechanics Centipetal Foce Lana heidan De Anza College Ma 9, 2016 Last time intoduced unifom cicula motion centipetal foce Oveview using the idea of centipetal foce Detemine (a) the astonaut
Intoduction to Mechanics Centipetal Foce Lana heidan De Anza College Ma 9, 2016 Last time intoduced unifom cicula motion centipetal foce Oveview using the idea of centipetal foce Detemine (a) the astonaut
Motion in a Plane Uniform Circular Motion
 Lectue 11 Chapte 8 Physics I Motion in a Plane Unifom Cicula Motion Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylo/teaching/physicsi PHYS.1410 Lectue 11 Danylo Depatment of Physics and Applied Physics
Lectue 11 Chapte 8 Physics I Motion in a Plane Unifom Cicula Motion Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylo/teaching/physicsi PHYS.1410 Lectue 11 Danylo Depatment of Physics and Applied Physics
CIRCULAR MOTION. Particle moving in an arbitrary path. Particle moving in straight line
 1 CIRCULAR MOTION 1. ANGULAR DISPLACEMENT Intoduction: Angle subtended by position vecto of a paticle moving along any abitay path w..t. some fixed point is called angula displacement. (a) Paticle moving
1 CIRCULAR MOTION 1. ANGULAR DISPLACEMENT Intoduction: Angle subtended by position vecto of a paticle moving along any abitay path w..t. some fixed point is called angula displacement. (a) Paticle moving
Circular Orbits. and g =
 using analyse planetay and satellite motion modelled as unifom cicula motion in a univesal gavitation field, a = v = 4π and g = T GM1 GM and F = 1M SATELLITES IN OBIT A satellite is any object that is
using analyse planetay and satellite motion modelled as unifom cicula motion in a univesal gavitation field, a = v = 4π and g = T GM1 GM and F = 1M SATELLITES IN OBIT A satellite is any object that is
Unit 6 Practice Test. Which vector diagram correctly shows the change in velocity Δv of the mass during this time? (1) (1) A. Energy KE.
 Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
ROTATORY MOTION HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL CIRCULAR MOTION
 ROTATORY MOTION HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL CIRCULAR MOTION POINTS TO REMEMBER 1. Tanslatoy motion: Evey point in the body follows the path of its peceding one with same velocity including the cente of mass..
ROTATORY MOTION HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL CIRCULAR MOTION POINTS TO REMEMBER 1. Tanslatoy motion: Evey point in the body follows the path of its peceding one with same velocity including the cente of mass..
Unit 6 Practice Test. Which vector diagram correctly shows the change in velocity Δv of the mass during this time? (1) (1) A. Energy KE.
 Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
PHYSICS 1050 Mid-term Test 1 University of Wyoming 8 February 2007
 Name: PHYSICS 1050 Mid-tem Test 1 Univesity of Wyoming 8 Febuay 2007 This test is open-note and open-book. This means that any efeence mateial is pemitted duing the test. Calculatos also ae pemitted. Howeve,
Name: PHYSICS 1050 Mid-tem Test 1 Univesity of Wyoming 8 Febuay 2007 This test is open-note and open-book. This means that any efeence mateial is pemitted duing the test. Calculatos also ae pemitted. Howeve,
Easy. P4.2 Since the car is moving with constant speed and in a straight line, the. resultant force on it must be regardless of whether it is moving
 Chapte 4 Homewok Solutions Easy P4. Since the ca is moving with constant speed and in a staight line, the zeo esultant foce on it must be egadless of whethe it is moving (a) towad the ight o the left.
Chapte 4 Homewok Solutions Easy P4. Since the ca is moving with constant speed and in a staight line, the zeo esultant foce on it must be egadless of whethe it is moving (a) towad the ight o the left.
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS NAME & LOGO XII-JEE (MAINS)-YEAR Topic Names: Cicula motion Test Numbe Test Booklet No. 000001 110001 Wite/Check this Code on you Answe Sheet : IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS : Wite
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS NAME & LOGO XII-JEE (MAINS)-YEAR Topic Names: Cicula motion Test Numbe Test Booklet No. 000001 110001 Wite/Check this Code on you Answe Sheet : IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS : Wite
Physics 181. Assignment 4
 Physics 181 Assignment 4 Solutions 1. A sphee has within it a gavitational field given by g = g, whee g is constant and is the position vecto of the field point elative to the cente of the sphee. This
Physics 181 Assignment 4 Solutions 1. A sphee has within it a gavitational field given by g = g, whee g is constant and is the position vecto of the field point elative to the cente of the sphee. This
HW Solutions # MIT - Prof. Please study example 12.5 "from the earth to the moon". 2GmA v esc
 HW Solutions # 11-8.01 MIT - Pof. Kowalski Univesal Gavity. 1) 12.23 Escaping Fom Asteoid Please study example 12.5 "fom the eath to the moon". a) The escape velocity deived in the example (fom enegy consevation)
HW Solutions # 11-8.01 MIT - Pof. Kowalski Univesal Gavity. 1) 12.23 Escaping Fom Asteoid Please study example 12.5 "fom the eath to the moon". a) The escape velocity deived in the example (fom enegy consevation)
= v 2. a c. = G m m 1 2. F g G = Review 5: Gravitation and Two-Dimensional Motion
 Review 5: Gavitation and Two-Dimensional Motion Review 5 Gavitation and Two-Dimensional Motion 2 d = 1 2 at F = ma 1. A busy waitess slides a plate of apple pie alon a counte to a huny custome sittin nea
Review 5: Gavitation and Two-Dimensional Motion Review 5 Gavitation and Two-Dimensional Motion 2 d = 1 2 at F = ma 1. A busy waitess slides a plate of apple pie alon a counte to a huny custome sittin nea
kg 2 ) 1.9!10 27 kg = Gm 1
 Section 6.1: Newtonian Gavitation Tutoial 1 Pactice, page 93 1. Given: 1.0 10 0 kg; m 3.0 10 0 kg;. 10 9 N; G 6.67 10 11 N m /kg Requied: Analysis: G m ; G m G m Solution: G m N m 6.67!10 11 kg ) 1.0!100
Section 6.1: Newtonian Gavitation Tutoial 1 Pactice, page 93 1. Given: 1.0 10 0 kg; m 3.0 10 0 kg;. 10 9 N; G 6.67 10 11 N m /kg Requied: Analysis: G m ; G m G m Solution: G m N m 6.67!10 11 kg ) 1.0!100
10. Force is inversely proportional to distance between the centers squared. R 4 = F 16 E 11.
 NSWRS - P Physics Multiple hoice Pactice Gavitation Solution nswe 1. m mv Obital speed is found fom setting which gives v whee M is the object being obited. Notice that satellite mass does not affect obital
NSWRS - P Physics Multiple hoice Pactice Gavitation Solution nswe 1. m mv Obital speed is found fom setting which gives v whee M is the object being obited. Notice that satellite mass does not affect obital
F g. = G mm. m 1. = 7.0 kg m 2. = 5.5 kg r = 0.60 m G = N m 2 kg 2 = = N
 Chapte answes Heinemann Physics 4e Section. Woked example: Ty youself.. GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION BETWEEN SMALL OBJECTS Two bowling balls ae sitting next to each othe on a shelf so that the centes of the
Chapte answes Heinemann Physics 4e Section. Woked example: Ty youself.. GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION BETWEEN SMALL OBJECTS Two bowling balls ae sitting next to each othe on a shelf so that the centes of the
- 5 - TEST 1R. This is the repeat version of TEST 1, which was held during Session.
 - 5 - TEST 1R This is the epeat vesion of TEST 1, which was held duing Session. This epeat test should be attempted by those students who missed Test 1, o who wish to impove thei mak in Test 1. IF YOU
- 5 - TEST 1R This is the epeat vesion of TEST 1, which was held duing Session. This epeat test should be attempted by those students who missed Test 1, o who wish to impove thei mak in Test 1. IF YOU
1) Consider a particle moving with constant speed that experiences no net force. What path must this particle be taking?
 Chapte 5 Test Cicula Motion and Gavitation 1) Conside a paticle moving with constant speed that expeiences no net foce. What path must this paticle be taking? A) It is moving in a paabola. B) It is moving
Chapte 5 Test Cicula Motion and Gavitation 1) Conside a paticle moving with constant speed that expeiences no net foce. What path must this paticle be taking? A) It is moving in a paabola. B) It is moving
Chapter 12. Kinetics of Particles: Newton s Second Law
 Chapte 1. Kinetics of Paticles: Newton s Second Law Intoduction Newton s Second Law of Motion Linea Momentum of a Paticle Systems of Units Equations of Motion Dynamic Equilibium Angula Momentum of a Paticle
Chapte 1. Kinetics of Paticles: Newton s Second Law Intoduction Newton s Second Law of Motion Linea Momentum of a Paticle Systems of Units Equations of Motion Dynamic Equilibium Angula Momentum of a Paticle
Chapter 5. Applying Newton s Laws. Newton s Laws. r r. 1 st Law: An object at rest or traveling in uniform. 2 nd Law:
 Chapte 5 Applying Newton s Laws Newton s Laws st Law: An object at est o taveling in unifom motion will emain at est o taveling in unifom motion unless and until an extenal foce is applied net ma nd Law:
Chapte 5 Applying Newton s Laws Newton s Laws st Law: An object at est o taveling in unifom motion will emain at est o taveling in unifom motion unless and until an extenal foce is applied net ma nd Law:
Physics 111. Ch 12: Gravity. Newton s Universal Gravity. R - hat. the equation. = Gm 1 m 2. F g 2 1. ˆr 2 1. Gravity G =
 ics Announcements day, embe 9, 004 Ch 1: Gavity Univesal Law Potential Enegy Keple s Laws Ch 15: Fluids density hydostatic equilibium Pascal s Pinciple This week s lab will be anothe physics wokshop -
ics Announcements day, embe 9, 004 Ch 1: Gavity Univesal Law Potential Enegy Keple s Laws Ch 15: Fluids density hydostatic equilibium Pascal s Pinciple This week s lab will be anothe physics wokshop -
Motion in Two Dimensions
 SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS Motion in Two Dimensions Section 3.1 The Position, Velocity, and Acceleation Vectos P3.1 x( m) 0!3 000!1 70!4 70 m y( m)!3 600 0 1 70! 330 m (a) Net displacement x + y 4.87 km at
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS Motion in Two Dimensions Section 3.1 The Position, Velocity, and Acceleation Vectos P3.1 x( m) 0!3 000!1 70!4 70 m y( m)!3 600 0 1 70! 330 m (a) Net displacement x + y 4.87 km at
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6- THE LAW OF GRAVITATION Essential Idea: The Newtonian idea of gavitational foce acting between two spheical bodies and the laws of mechanics
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6- THE LAW OF GRAVITATION Essential Idea: The Newtonian idea of gavitational foce acting between two spheical bodies and the laws of mechanics
Kinematics in 2-D (II)
 Kinematics in 2-D (II) Unifom cicula motion Tangential and adial components of Relative velocity and acceleation a Seway and Jewett 4.4 to 4.6 Pactice Poblems: Chapte 4, Objective Questions 5, 11 Chapte
Kinematics in 2-D (II) Unifom cicula motion Tangential and adial components of Relative velocity and acceleation a Seway and Jewett 4.4 to 4.6 Pactice Poblems: Chapte 4, Objective Questions 5, 11 Chapte
21 MAGNETIC FORCES AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
 CHAPTER 1 MAGNETIC ORCES AND MAGNETIC IELDS ANSWERS TO OCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS 1. (d) Right-Hand Rule No. 1 gives the diection of the magnetic foce as x fo both dawings A and. In dawing C, the velocity
CHAPTER 1 MAGNETIC ORCES AND MAGNETIC IELDS ANSWERS TO OCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS 1. (d) Right-Hand Rule No. 1 gives the diection of the magnetic foce as x fo both dawings A and. In dawing C, the velocity
3.3 Centripetal Force
 3.3 Centipetal Foce Think of a time when ou wee a passenge in a ca going aound a shap cue at high speed (Figue 1). If the ca wee going fast enough, ou might feel the side of the ca doo pushing on ou side.
3.3 Centipetal Foce Think of a time when ou wee a passenge in a ca going aound a shap cue at high speed (Figue 1). If the ca wee going fast enough, ou might feel the side of the ca doo pushing on ou side.
Gravitation. AP/Honors Physics 1 Mr. Velazquez
 Gavitation AP/Honos Physics 1 M. Velazquez Newton s Law of Gavitation Newton was the fist to make the connection between objects falling on Eath and the motion of the planets To illustate this connection
Gavitation AP/Honos Physics 1 M. Velazquez Newton s Law of Gavitation Newton was the fist to make the connection between objects falling on Eath and the motion of the planets To illustate this connection
2013 Checkpoints Chapter 7 GRAVITY
 0 Checkpoints Chapte 7 GAVIY Question 64 o do this question you must et an equation that has both and, whee is the obital adius and is the peiod. You can use Keple s Law, which is; constant. his is a vey
0 Checkpoints Chapte 7 GAVIY Question 64 o do this question you must et an equation that has both and, whee is the obital adius and is the peiod. You can use Keple s Law, which is; constant. his is a vey
Lab #9: The Kinematics & Dynamics of. Circular Motion & Rotational Motion
 Reading Assignment: Lab #9: The Kinematics & Dynamics of Cicula Motion & Rotational Motion Chapte 6 Section 4 Chapte 11 Section 1 though Section 5 Intoduction: When discussing motion, it is impotant to
Reading Assignment: Lab #9: The Kinematics & Dynamics of Cicula Motion & Rotational Motion Chapte 6 Section 4 Chapte 11 Section 1 though Section 5 Intoduction: When discussing motion, it is impotant to
Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
 Potential Enegy and Consevation of Enegy Consevative Foces Definition: Consevative Foce If the wok done by a foce in moving an object fom an initial point to a final point is independent of the path (A
Potential Enegy and Consevation of Enegy Consevative Foces Definition: Consevative Foce If the wok done by a foce in moving an object fom an initial point to a final point is independent of the path (A
Lecture 13 EXAM 2. Today s Topics: Rotational motion Moment of inertia. Tuesday March 8, :15 PM 9:45 PM
 Lectue 13 Rotational motion Moment of inetia EXAM uesday Mach 8, 16 8:15 PM 9:45 PM oday s opics: Rotational Motion and Angula Displacement Angula Velocity and Acceleation Rotational Kinematics Angula
Lectue 13 Rotational motion Moment of inetia EXAM uesday Mach 8, 16 8:15 PM 9:45 PM oday s opics: Rotational Motion and Angula Displacement Angula Velocity and Acceleation Rotational Kinematics Angula
