Public Sector Employment in an Equilibrium Search and Matching Model (Work in Progress)
|
|
|
- Joseph Watkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Public Sector Employment in an Equilibrium Search and Matching Model (Work in Progress) Jim Albrecht, 1 Lucas Navarro, 2 and Susan Vroman 3 November Georgetown University and IZA 2 ILADES, Universidad Alberto Hurtado, Santiago, Chile 3 Georgetown University and IZA
2 Introduction The public sector accounts for a substantial fraction of employment in both developed and developing countries. There is a public-sector wage premium in many countries both in the raw data and after controlling for observables and endogenous sector choice. Wages in the public sector tend to be more compressed than in the private sector. The public-sector premium is higher at lower quantiles, and there is a negative public-sector premium at higher quantiles in some countries.
3 Questions How do the private- and public-sector labor markets interact? What types of workers tend to work in the public sector and in the private sector? How do the size of the public sector and the way that wages are set in that sector affect the overall unemployment rate and the distributions of productivity and wages?
4 Related Literature A natural approach to these questions is to incorporate public-sector employment into an equilibrium search and matching model. Surprisingly, there are few papers that do this. Burdett (2010) - Adds a public sector to the Burdett- Mortensen (IER 1998) model of on-the-job search. Quadrini and Trigari (ScanJE 2007) Pissarides (2000) model in which private-sector productivity varies stochastically over time. Neither paper (nor any others that we know about) allows for worker heterogeneity.
5 Model - Basic Ingredients Worker heterogeneity Y F (y) interpreted as human capital from ANV (EJ 2009) Match-specific productivity X G s (x y), s = {p, g} with a first-order stochastic dominance assumption, i.e., y > y => G s (x y ) < G s (x y). A similar idea (with a 2-point distribution for Y ) can be found in Dolado, Jansen and Jimeno (BEJournal Macro 2007) The public sector posts v g vacancies (exogenous). We formulate the hiring decision as a threshold rule, x ξ g (y), and assume that wages are set according to an exogenous rule, w g (x, y).
6 Model - Assumptions Random search only by the unemployed, no on-the-job search The rate at which unemployed workers meet prospective employers is given by an exogenous contact function, m(θ), where θ = (v p + v g )/u. The fraction of those contacts that are with private-sector vacancies is φ = v p /(v p + v g ). The rate at which prospective employers meet job seekers is m(θ)/θ Labor market tightness is endogenous there is a free-entry condition for private-sector vacancy creation
7 Model - Assumptions Not every contact leads to a match. We derive a reservation acceptance threshold for private-sector jobs for type-y workers. Public sector matches form only if x ξ g (y) Private-sector wages are determined by Nash bargaining; public-sector wages are given by w g (x, y) Steady-state analysis
8 Value Functions - Workers U(y), N p (x, y), and N g (x, y) are the values for a worker of type y associated with unemployment and with private-sector and public-sector jobs with match-specific productivity x. ru(y) = z + φm(θ)e max[n p (x, y) U(y), 0] +(1 φ)m(θ)e max[n g (x, y) U(y), 0] rn p (x, y) = w p (x, y) + δ p (U(y) N p (x, y)) rn g (x, y) = w g (x, y) + δ g (U(y) N g (x, y))
9 Value Functions - Firms J(x, y) is the value associated with a private-sector job filled by a worker of type y with match-specific productivity x. V is the value of posting a private-sector vacancy rj(x, y) = x w p (x, y) + δ p (V J(x, y)) rv = c + m(θ) E max[j(x, y) V, 0] θ The expectation is taken with respect to the joint distribution of (X, Y ) across the unemployed
10 Wages Free entry => V = 0 in steady state. With V = 0, the Nash bargaining solution with exogenous worker share β gives w p (x, y) = βx + (1 β)ru(y) Again, w g (x, y) is exogenous
11 Reservation Thresholds R p (y) is the value of x such that N p (x, y) = U(y). Using N p (R p (y), y) = U(y), the Nash bargaining solution implies R p (y) = ru(y) The reservation threshold for a public-sector job is R g (y) = ξ g (y). This is equivalent to assuming that N g (ξ g (y), y) U(y)
12 More on Reservation Thresholds To derive a recursion for R p (y), we rewrite our expression for ru(y). This gives β R p (y) = z + φm(θ) r + δ p x R p (y ) 1 +(1 φ)m(θ) r + δ g (1 G p (x y))dx x ξ g (y ) (w g (x, y) R p (y))dg g (x y) Given θ and φ, the reservation thresholds are uniquely determined
13 Free Entry The free-entry condition for private-sector vacancy creation is c = m(θ) E max[j(x, y), 0] θ Let f u (y) be the density of y across the unemployed. Substituting for J(x, y) gives c = m(θ) ( 1 β y ) θ r + δ p y x R p (y ) (1 G p (x y))dxf u (y)dy
14 Steady-State Conditions By Bayes Law f u (y) = u(y)f (y) u where u(y) is the type-y unemployment rate and u = u(y)f (y)dy is the overall unemployment rate. The type-specific unemployment rates are derived from steady-state conditions the flow of type-y workers from unemployment to private-sector employment must equal the flow in the reverse direction and similarly for transitions between unemployment and public-sector employment. u(y) = δ g δ p δ g δ p + δ g φm(θ)(1 G p (R p (y) y)) +δ p (1 φ)m(θ)(1 G g (R g (y) y))
15 A Final Unknown The final unknown is φ, the fraction of vacancies that are posted by private-sector firms. Since v p + v g = θu, φ = v p v p + v g => φ = θu v g θu
16 Equilibrium An equilibrium is a function, R p (y), and a pair of scalars, θ and φ, that satisfy the relevant equations (private-sector matches are formed iff there is positive surplus, free-entry, steady-state Equilibrium always exists. This can be seen from the free-entry condition: c = m(θ) ( 1 β y ) θ r + δ p y x R p (y ) (1 G p (x y))dxf u (y)dy The RHS of this equation can be written as a function of θ alone. It is continuous in θ, converges to as θ 0, and converges to zero as θ. Once we solve for θ, we can recover the other equilibrium objects. Note that we do not claim uniqueness
17 Wage Distributions Let H s (w) denote the distribution function of wages paid in sector s. We can develop expressions for H p (w) and H g (w) as follows. Consider first the distribution of private-sector wages across workers of type y, say H p (w y). For w < w p (R p (y), y), we have H p (w y) = 0 for w < w p (R p (y), y). H p (w y) = P[w p (R p (y), y) w p (X, y) w y] = P[R p (y) βx + (1 β)r p (y) w y] = P[R p (y) X w (1 β)r p(y) y] β ( = G p ( w (1 β)r ) p(y) ) y G p (R p (y) y) β
18 Wage Distributions The unconditional distribution of private-sector wages is where H p (w) = y y H p (w y)f p (y)dy, f p (y) = n p(y)f (y) n p is the density of Y across workers employed in the private sector. The private-sector employment rate for type-y workers, n p (y), is derived from steady-state conditions. The same approach can be used to find the distribution of public-sector wages.
19 What s Next? Specify functional forms for F (y) and G s (x y) Y unif [0, 1] X unif [y, y + 1] ln X N(y, σ 2 ) Specify functional forms for ξ g (y) and w g (x, y) ξ g (y) = α + R p (y) w g (x, y) = γx + (1 γ)ru(y) = γx + (1 γ)r p (y) Calibrate Run numerical policy experiments change v g, ξ g (y) and w g (x, y)
20 Assume Y unif [0, 1] and X unif [y, y + 1]. Assumed parameter values: r z 0.3 c 0.3 β 0.75 m (θ) 3θ 0.25 δ p 0.1 δ g 0.05 v g α 0 γ 0.5 Results: θ = 0.95, u = 0.094, φ = 0.86
Master 2 Macro I. Lecture notes #9 : the Mortensen-Pissarides matching model
 2012-2013 Master 2 Macro I Lecture notes #9 : the Mortensen-Pissarides matching model Franck Portier (based on Gilles Saint-Paul lecture notes) franck.portier@tse-fr.eu Toulouse School of Economics Version
2012-2013 Master 2 Macro I Lecture notes #9 : the Mortensen-Pissarides matching model Franck Portier (based on Gilles Saint-Paul lecture notes) franck.portier@tse-fr.eu Toulouse School of Economics Version
Effi ciency in Search and Matching Models: A Generalized Hosios Condition
 Effi ciency in Search and Matching Models: A Generalized Hosios Condition Sephorah Mangin and Benoît Julien 22 September 2017 Abstract When is the level of entry of buyers or sellers effi cient in markets
Effi ciency in Search and Matching Models: A Generalized Hosios Condition Sephorah Mangin and Benoît Julien 22 September 2017 Abstract When is the level of entry of buyers or sellers effi cient in markets
Diamond-Mortensen-Pissarides Model
 Diamond-Mortensen-Pissarides Model Dongpeng Liu Nanjing University March 2016 D. Liu (NJU) DMP 03/16 1 / 35 Introduction Motivation In the previous lecture, McCall s model was introduced McCall s model
Diamond-Mortensen-Pissarides Model Dongpeng Liu Nanjing University March 2016 D. Liu (NJU) DMP 03/16 1 / 35 Introduction Motivation In the previous lecture, McCall s model was introduced McCall s model
The Harris-Todaro model
 Yves Zenou Research Institute of Industrial Economics July 3, 2006 The Harris-Todaro model In two seminal papers, Todaro (1969) and Harris and Todaro (1970) have developed a canonical model of rural-urban
Yves Zenou Research Institute of Industrial Economics July 3, 2006 The Harris-Todaro model In two seminal papers, Todaro (1969) and Harris and Todaro (1970) have developed a canonical model of rural-urban
Macroeconomics 2. Lecture 9 - Labor markets: The search and matching model with endogenous job destruction March.
 Macroeconomics 2 Lecture 9 - Labor markets: The search and matching model with endogenous job destruction Zsófia L. Bárány Sciences Po 2014 March Empirical relevance of a variable job destruction rate
Macroeconomics 2 Lecture 9 - Labor markets: The search and matching model with endogenous job destruction Zsófia L. Bárány Sciences Po 2014 March Empirical relevance of a variable job destruction rate
Optimal Insurance of Search Risk
 Optimal Insurance of Search Risk Mikhail Golosov Yale University and NBER Pricila Maziero University of Pennsylvania Guido Menzio University of Pennsylvania and NBER November 2011 Introduction Search and
Optimal Insurance of Search Risk Mikhail Golosov Yale University and NBER Pricila Maziero University of Pennsylvania Guido Menzio University of Pennsylvania and NBER November 2011 Introduction Search and
1. Unemployment. March 20, Nr. 1
 1. Unemployment March 20, 2007 Nr. 1 Job destruction, and employment protection. I So far, only creation decision. Clearly both creation and destruction margins. So endogenize job destruction. Can then
1. Unemployment March 20, 2007 Nr. 1 Job destruction, and employment protection. I So far, only creation decision. Clearly both creation and destruction margins. So endogenize job destruction. Can then
Job Search Models. Jesús Fernández-Villaverde. University of Pennsylvania. February 12, 2016
 Job Search Models Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania February 12, 2016 Jesús Fernández-Villaverde (PENN) Job Search February 12, 2016 1 / 57 Motivation Introduction Trade in the labor
Job Search Models Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania February 12, 2016 Jesús Fernández-Villaverde (PENN) Job Search February 12, 2016 1 / 57 Motivation Introduction Trade in the labor
Working Time Reduction, Unpaid Overtime Work and Unemployment
 Working Time Reduction Unpaid Overtime Work and Unemployment Makoto Masui Department of Economics Soka University 1-236 Tangi-cho Hachiouji-city Tokyo 192-8577 Japan First Version: April 2007 Second Version:
Working Time Reduction Unpaid Overtime Work and Unemployment Makoto Masui Department of Economics Soka University 1-236 Tangi-cho Hachiouji-city Tokyo 192-8577 Japan First Version: April 2007 Second Version:
The Dark Corners of the Labor Market
 The Dark Corners of the Labor Market Vincent Sterk Conference on Persistent Output Gaps: Causes and Policy Remedies EABCN / University of Cambridge / INET University College London September 2015 Sterk
The Dark Corners of the Labor Market Vincent Sterk Conference on Persistent Output Gaps: Causes and Policy Remedies EABCN / University of Cambridge / INET University College London September 2015 Sterk
The Labor Market in the New Keynesian Model: Incorporating a Simple DMP Version of the Labor Market and Rediscovering the Shimer Puzzle
 The Labor Market in the New Keynesian Model: Incorporating a Simple DMP Version of the Labor Market and Rediscovering the Shimer Puzzle Lawrence J. Christiano April 1, 2013 Outline We present baseline
The Labor Market in the New Keynesian Model: Incorporating a Simple DMP Version of the Labor Market and Rediscovering the Shimer Puzzle Lawrence J. Christiano April 1, 2013 Outline We present baseline
Directed Search with Phantom Vacancies
 Directed Search with Phantom Vacancies Jim Albrecht (Georgetown University) Bruno Decreuse (Aix-Marseille U, AMSE) Susan Vroman (Georgetown University) April 2016 I am currently on the job hunt and I had
Directed Search with Phantom Vacancies Jim Albrecht (Georgetown University) Bruno Decreuse (Aix-Marseille U, AMSE) Susan Vroman (Georgetown University) April 2016 I am currently on the job hunt and I had
Efficiency in a Search and Matching Model with Endogenous Participation
 Efficienc in a Search an Matching Moel with Enogenous Participation James Albrecht a Department of Economics, Georgetown Universit an IZA Lucas Navarro Department of Economics, ILADES-Universia Alberto
Efficienc in a Search an Matching Moel with Enogenous Participation James Albrecht a Department of Economics, Georgetown Universit an IZA Lucas Navarro Department of Economics, ILADES-Universia Alberto
Equilibrium Directed Search with Multiple Applications
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 719 Equilibrium Directed Search with Multiple Applications James Albrecht Pieter Gautier Susan Vroman February 003 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 719 Equilibrium Directed Search with Multiple Applications James Albrecht Pieter Gautier Susan Vroman February 003 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute
Mortenson Pissarides Model
 Mortenson Pissarides Model Prof. Lutz Hendricks Econ720 November 22, 2017 1 / 47 Mortenson / Pissarides Model Search models are popular in many contexts: labor markets, monetary theory, etc. They are distinguished
Mortenson Pissarides Model Prof. Lutz Hendricks Econ720 November 22, 2017 1 / 47 Mortenson / Pissarides Model Search models are popular in many contexts: labor markets, monetary theory, etc. They are distinguished
Online Appendix to Asymmetric Information and Search Frictions: A Neutrality Result
 Online Appendix to Asymmetric Information and Search Frictions: A Neutrality Result Neel Rao University at Buffalo, SUNY August 26, 2016 Abstract The online appendix extends the analysis to the case where
Online Appendix to Asymmetric Information and Search Frictions: A Neutrality Result Neel Rao University at Buffalo, SUNY August 26, 2016 Abstract The online appendix extends the analysis to the case where
On-the-Job Search with Match-Specific Amenities
 On-the-Job Search with Match-Specific Amenities James Albrecht Georgetown University, CESifo, and IZA Carlos Carrillo-Tudela University of Essex, CEPR, CESifo, and IZA Susan Vroman Georgetown University,
On-the-Job Search with Match-Specific Amenities James Albrecht Georgetown University, CESifo, and IZA Carlos Carrillo-Tudela University of Essex, CEPR, CESifo, and IZA Susan Vroman Georgetown University,
Efficiency in Search and Matching Models: A Generalized Hosios Condition *
 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS ISSN 1441-5429 DISCUSSION PAPER 28/16 Efficiency in Search and Matching Models: A Generalized Hosios Condition * Benoît Julien and Sephorah Mangin Abstract: This paper generalizes
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS ISSN 1441-5429 DISCUSSION PAPER 28/16 Efficiency in Search and Matching Models: A Generalized Hosios Condition * Benoît Julien and Sephorah Mangin Abstract: This paper generalizes
Labor-market Volatility in Matching Models with Endogenous Separations
 Scand. J. of Economics 109(4), 645 665, 2007 DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-9442.2007.00515.x Labor-market Volatility in Matching Models with Endogenous Separations Dale Mortensen Northwestern University, Evanston,
Scand. J. of Economics 109(4), 645 665, 2007 DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-9442.2007.00515.x Labor-market Volatility in Matching Models with Endogenous Separations Dale Mortensen Northwestern University, Evanston,
The Joint Effect of Firing Costs on Employment and Productivity in Search and Matching Models
 The Joint Effect of Firing Costs on Employment and Productivity in Search and Matching Models Björn Brügemann October 2006 Abstract In the textbook search and matching model the effect of firing costs
The Joint Effect of Firing Costs on Employment and Productivity in Search and Matching Models Björn Brügemann October 2006 Abstract In the textbook search and matching model the effect of firing costs
NASH BARGAINING, ON-THE-JOB SEARCH AND LABOR MARKET EQUILIBRIUM
 NASH BARGAINING, ON-THE-JOB SEARCH AND LABOR MARKET EQUILIBRIUM Roberto Bonilla Department of Economics University of Newcastle Business School University of Newcastle upon Tyne Newcastle upon Tyne U.K.
NASH BARGAINING, ON-THE-JOB SEARCH AND LABOR MARKET EQUILIBRIUM Roberto Bonilla Department of Economics University of Newcastle Business School University of Newcastle upon Tyne Newcastle upon Tyne U.K.
Directed Search on the Job, Heterogeneity, and Aggregate Fluctuations
 Directed Search on the Job, Heterogeneity, and Aggregate Fluctuations By GUIDO MENZIO AND SHOUYONG SHI In models of search on the job (e.g. Kenneth Burdett and Dale Mortensen 1998, Burdett and Melvyn Coles
Directed Search on the Job, Heterogeneity, and Aggregate Fluctuations By GUIDO MENZIO AND SHOUYONG SHI In models of search on the job (e.g. Kenneth Burdett and Dale Mortensen 1998, Burdett and Melvyn Coles
(a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
Labor Economics, Lecture 11: Partial Equilibrium Sequential Search
 Labor Economics, 14.661. Lecture 11: Partial Equilibrium Sequential Search Daron Acemoglu MIT December 6, 2011. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Sequential Search December 6, 2011. 1 / 43 Introduction Introduction
Labor Economics, 14.661. Lecture 11: Partial Equilibrium Sequential Search Daron Acemoglu MIT December 6, 2011. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Sequential Search December 6, 2011. 1 / 43 Introduction Introduction
Directed Search with Multiple Vacancies
 Directed Search with Multiple Vacancies Benjamin Lester University of Western Ontario July 9, 2008 Abstract Preliminary and incomplete: please do not circulate. Contact: blester@uwo.ca. I would like to
Directed Search with Multiple Vacancies Benjamin Lester University of Western Ontario July 9, 2008 Abstract Preliminary and incomplete: please do not circulate. Contact: blester@uwo.ca. I would like to
Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions
 Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions Daniel Němec Faculty of Economics and Administrations Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic nemecd@econ.muni.cz ESF MU (Brno)
Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions Daniel Němec Faculty of Economics and Administrations Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic nemecd@econ.muni.cz ESF MU (Brno)
A Centralized or a Decentralized Labor Market?
 ömmföäflsäafaäsflassflassflas ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Discussion Papers A Centralized or a Decentralized Labor Market? Juha Virrankoski Aalto University and HECER Discussion Paper No. 42 November
ömmföäflsäafaäsflassflassflas ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Discussion Papers A Centralized or a Decentralized Labor Market? Juha Virrankoski Aalto University and HECER Discussion Paper No. 42 November
Frictional Wage Dispersion in Search Models: A Quantitative Assessment
 Frictional Wage Dispersion in Search Models: A Quantitative Assessment Andreas Hornstein Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Per Krusell Princeton University, IIES-Stockholm and CEPR Gianluca Violante New
Frictional Wage Dispersion in Search Models: A Quantitative Assessment Andreas Hornstein Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Per Krusell Princeton University, IIES-Stockholm and CEPR Gianluca Violante New
McCall Model. Prof. Lutz Hendricks. November 22, Econ720
 McCall Model Prof. Lutz Hendricks Econ720 November 22, 2017 1 / 30 Motivation We would like to study basic labor market data: unemployment and its duration wage heterogeneity among seemingly identical
McCall Model Prof. Lutz Hendricks Econ720 November 22, 2017 1 / 30 Motivation We would like to study basic labor market data: unemployment and its duration wage heterogeneity among seemingly identical
Important job creation - job destruction rate Account for labor supply and labor demand behavior to explain unemployment
 Labor Economics and Employment Policies Pierre Cahuc and Sébastien Roux, 2007-2008 Lecture 5: Job creations, job destructions and unemployment: the matching model Important job creation - job destruction
Labor Economics and Employment Policies Pierre Cahuc and Sébastien Roux, 2007-2008 Lecture 5: Job creations, job destructions and unemployment: the matching model Important job creation - job destruction
Labor Economics, Lectures 11-13: Search, Matching and Unemployment
 Labor Economics, 14.661. Lectures 11-13: Search, Matching and Unemployment Daron Acemoglu MIT December 4, 6 and 11, 2018 Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Search, Matching, Unemployment December 4, 6 and 11, 2018 1
Labor Economics, 14.661. Lectures 11-13: Search, Matching and Unemployment Daron Acemoglu MIT December 4, 6 and 11, 2018 Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Search, Matching, Unemployment December 4, 6 and 11, 2018 1
Asymmetric Information and Search Frictions: A Neutrality Result
 Asymmetric Information and Search Frictions: A Neutrality Result Neel Rao University at Buffalo, SUNY August 26, 2016 Abstract This paper integrates asymmetric information between firms into a canonical
Asymmetric Information and Search Frictions: A Neutrality Result Neel Rao University at Buffalo, SUNY August 26, 2016 Abstract This paper integrates asymmetric information between firms into a canonical
MONOPOLISTICALLY COMPETITIVE SEARCH EQUILIBRIUM JANUARY 26, 2018
 MONOPOLISTICALLY COMPETITIVE SEARCH EQUILIBRIUM JANUARY 26, 2018 Introduction LABOR MARKET INTERMEDIATION Recruiting Sector aka Labor Market Intermediaries aka Headhunters aka Middlemen January 26, 2018
MONOPOLISTICALLY COMPETITIVE SEARCH EQUILIBRIUM JANUARY 26, 2018 Introduction LABOR MARKET INTERMEDIATION Recruiting Sector aka Labor Market Intermediaries aka Headhunters aka Middlemen January 26, 2018
Toulouse School of Economics, M2 Macroeconomics 1 Professor Franck Portier. Exam Solution
 Toulouse School of Economics, 2013-2014 M2 Macroeconomics 1 Professor Franck Portier Exam Solution This is a 3 hours exam. Class slides and any handwritten material are allowed. You must write legibly.
Toulouse School of Economics, 2013-2014 M2 Macroeconomics 1 Professor Franck Portier Exam Solution This is a 3 hours exam. Class slides and any handwritten material are allowed. You must write legibly.
On-the-job search and sorting
 On-the-job search and sorting Pieter A. Gautier Coen N. Teulings Aico van Vuuren July, 27 Abstract We characterize the equilibrium for a general class of search models with two sided heterogeneity and
On-the-job search and sorting Pieter A. Gautier Coen N. Teulings Aico van Vuuren July, 27 Abstract We characterize the equilibrium for a general class of search models with two sided heterogeneity and
Revisiting Nash Wages Negotiations in Matching Models
 Introduction Revisiting Nash Wages Negotiations in Matching Models S. Amine 1 S. Baumann 2 P. Lages Dos Santos 2 F. Valognes 3 1 CIRANO University of Quebec en Outaouais 2 CERENE University of Le Havre
Introduction Revisiting Nash Wages Negotiations in Matching Models S. Amine 1 S. Baumann 2 P. Lages Dos Santos 2 F. Valognes 3 1 CIRANO University of Quebec en Outaouais 2 CERENE University of Le Havre
Residual Wage Disparity and Coordination Unemployment
 Residual Wage Disparity and Coordination Unemployment Benoit Julien, John Kennes, and Ian King First Draft: June 2001 This Draft: April 2005 Abstract How much of residual wage dispersion can be explained
Residual Wage Disparity and Coordination Unemployment Benoit Julien, John Kennes, and Ian King First Draft: June 2001 This Draft: April 2005 Abstract How much of residual wage dispersion can be explained
Wages, Unemployment and Inequality with Heterogeneous Firms and Workers
 Wages, Unemployment and Inequality with Heterogeneous Firms and Workers Elhanan Helpman Oleg Itskhoki Stephen Redding Harvard and CIFAR Harvard LSE and CEP Penn State June 12, 2008 1 / 28 Introduction
Wages, Unemployment and Inequality with Heterogeneous Firms and Workers Elhanan Helpman Oleg Itskhoki Stephen Redding Harvard and CIFAR Harvard LSE and CEP Penn State June 12, 2008 1 / 28 Introduction
Do employment contract reforms affect welfare?
 Do employment contract reforms affect welfare? Cristina Tealdi IMT Lucca Institute for Advanced Studies April 26, 2013 Cristina Tealdi (NU / IMT Lucca) Employment contract reforms April 26, 2013 1 Motivation:
Do employment contract reforms affect welfare? Cristina Tealdi IMT Lucca Institute for Advanced Studies April 26, 2013 Cristina Tealdi (NU / IMT Lucca) Employment contract reforms April 26, 2013 1 Motivation:
Social Networks in a Frictional Labour Market
 Social Networks in a Frictional Labour Market Dissertation zur Erlangung des Grades eines Doktors der Wirtschaftswissentschaften (Dr. rer. pol.) der Fakultät für Wirtschaftswissentschaften der Universität
Social Networks in a Frictional Labour Market Dissertation zur Erlangung des Grades eines Doktors der Wirtschaftswissentschaften (Dr. rer. pol.) der Fakultät für Wirtschaftswissentschaften der Universität
An adaptation of Pissarides (1990) by using random job destruction rate
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive An adaptation of Pissarides (990) by using random job destruction rate Huiming Wang December 2009 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/203/ MPRA Paper No. 203, posted
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive An adaptation of Pissarides (990) by using random job destruction rate Huiming Wang December 2009 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/203/ MPRA Paper No. 203, posted
Under-Employment and the Trickle-Down of Unemployment - Online Appendix Not for Publication
 Under-Employment and the Trickle-Down of Unemployment - Online Appendix Not for Publication Regis Barnichon Yanos Zylberberg July 21, 2016 This online Appendix contains a more comprehensive description
Under-Employment and the Trickle-Down of Unemployment - Online Appendix Not for Publication Regis Barnichon Yanos Zylberberg July 21, 2016 This online Appendix contains a more comprehensive description
Lecture 5 Search and matching theory
 Lecture 5 Search and matching theory Leszek Wincenciak, Ph.D. Warsaw University December 16th, 2009 2/48 Lecture outline: Introduction Search and matching theory Search and matching theory The dynamics
Lecture 5 Search and matching theory Leszek Wincenciak, Ph.D. Warsaw University December 16th, 2009 2/48 Lecture outline: Introduction Search and matching theory Search and matching theory The dynamics
Under-Employment and the Trickle-Down of Unemployment Online Appendix Not for Publication
 Under-Employment and the Trickle-Down of Unemployment Online Appendix Not for Publication Regis Barnichon Yanos Zylberberg March 30, 2018 Section 1 contains the proofs of Propositions 1 to 3 pertaining
Under-Employment and the Trickle-Down of Unemployment Online Appendix Not for Publication Regis Barnichon Yanos Zylberberg March 30, 2018 Section 1 contains the proofs of Propositions 1 to 3 pertaining
Variable Search Intensity in an Economy with Coordination Unemployment
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 3697 Variable Search Intensity in an Economy with Coordination Unemployment Leo Kaas September 2008 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the Study
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 3697 Variable Search Intensity in an Economy with Coordination Unemployment Leo Kaas September 2008 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the Study
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics B. J. Heijdra & F. van der Ploeg Chapter 9: Search in the Labour Market
 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics: Chapter 9 1 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics B. J. Heijdra & F. van der Ploeg Chapter 9: Search in the Labour Market Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics: Chapter
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics: Chapter 9 1 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics B. J. Heijdra & F. van der Ploeg Chapter 9: Search in the Labour Market Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics: Chapter
Comments on News and Noise in the Post-Great Recession Recovery by Renato Faccini and Leonardo Melosi
 Comments on News and Noise in the Post-Great Recession Recovery by Renato Faccini and Leonardo Melosi Federico Ravenna Danmarks Nationalbank and University of Copenhagen Konstanz, May 2018 The views expressed
Comments on News and Noise in the Post-Great Recession Recovery by Renato Faccini and Leonardo Melosi Federico Ravenna Danmarks Nationalbank and University of Copenhagen Konstanz, May 2018 The views expressed
On-The-Job Search and Sorting
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 1687 On-The-Job Search and Sorting Pieter A. Gautier Coen N. Teulings Aico van Vuuren July 2005 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the Study of Labor
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 1687 On-The-Job Search and Sorting Pieter A. Gautier Coen N. Teulings Aico van Vuuren July 2005 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute for the Study of Labor
THE SLOW JOB RECOVERY IN A MACRO MODEL OF SEARCH AND RECRUITING INTENSITY. I. Introduction
 THE SLOW JOB RECOVERY IN A MACRO MODEL OF SEARCH AND RECRUITING INTENSITY SYLVAIN LEDUC AND ZHENG LIU Abstract. Despite steady declines in the unemployment rate and increases in the job openings rate after
THE SLOW JOB RECOVERY IN A MACRO MODEL OF SEARCH AND RECRUITING INTENSITY SYLVAIN LEDUC AND ZHENG LIU Abstract. Despite steady declines in the unemployment rate and increases in the job openings rate after
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES EQUILIBRIUM WAGE AND EMPLOYMENT DYNAMICS IN A MODEL OF WAGE POSTING WITHOUT COMMITMENT. Melvyn G. Coles Dale T.
 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES EQUILIBRIUM WAGE AND EMPLOYMENT DYNAMICS IN A MODEL OF WAGE POSTING WITHOUT COMMITMENT Melvyn G. Coles Dale T. Mortensen Working Paper 17284 http://www.nber.org/papers/w17284
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES EQUILIBRIUM WAGE AND EMPLOYMENT DYNAMICS IN A MODEL OF WAGE POSTING WITHOUT COMMITMENT Melvyn G. Coles Dale T. Mortensen Working Paper 17284 http://www.nber.org/papers/w17284
Introduction Static Dynamic Welfare Extensions The End. Recruiting Talent. Simon Board Moritz Meyer-ter-Vehn Tomasz Sadzik UCLA.
 Recruiting Talent Simon Board Moritz Meyer-ter-Vehn Tomasz Sadzik UCLA July 13, 2016 Motivation Talent is source of competitive advantage Universities: Faculty are key asset. Netflix: We endeavor to have
Recruiting Talent Simon Board Moritz Meyer-ter-Vehn Tomasz Sadzik UCLA July 13, 2016 Motivation Talent is source of competitive advantage Universities: Faculty are key asset. Netflix: We endeavor to have
On the Efficiency of Wage-Setting Mechanisms with Search Frictions and Human Capital Investment
 On the Efficiency of Wage-Setting Mechanisms with Search Frictions and Human Capital Investment Darong Dai Guoqiang Tian This version: November, 2017 Abstract A challenge facing labor economists is to
On the Efficiency of Wage-Setting Mechanisms with Search Frictions and Human Capital Investment Darong Dai Guoqiang Tian This version: November, 2017 Abstract A challenge facing labor economists is to
Housing and the Labor Market: Time to Move and Aggregate Unemployment
 Housing and the Labor Market: Time to Move and Aggregate Unemployment Peter Rupert 1 Etienne Wasmer 2 1 University of California, Santa Barbara 2 Sciences-Po. Paris and OFCE search class April 1, 2011
Housing and the Labor Market: Time to Move and Aggregate Unemployment Peter Rupert 1 Etienne Wasmer 2 1 University of California, Santa Barbara 2 Sciences-Po. Paris and OFCE search class April 1, 2011
Why Almost Similar Regions Have Di erent Unemployment Rates Preliminary version
 Why Almost Similar Regions Have Di erent Unemployment Rates Preliminary version Roger ANTOUN y Université Panthéon-Assas Paris 2 ERMES April, 2009 Abstract I present a two-region labor matching model of
Why Almost Similar Regions Have Di erent Unemployment Rates Preliminary version Roger ANTOUN y Université Panthéon-Assas Paris 2 ERMES April, 2009 Abstract I present a two-region labor matching model of
Job Contact Networks JET Antoni Calvó-Armengol
 Job Contact Networks JET 2004 Antoni Calvó-Armengol About half of jobs are filled through contacts networks of personal contacts and word-of-mouth communication play a central role in many labor markets
Job Contact Networks JET 2004 Antoni Calvó-Armengol About half of jobs are filled through contacts networks of personal contacts and word-of-mouth communication play a central role in many labor markets
The Beveridge Curve, Job Creation and the Propagation of Shocks
 The Beveridge Curve, Job Creation and the Propagation of Shocks Shigeru Fujita University of California San Diego June 1, 2003 Abstract This paper proposes modifications to the popular model of equilibrium
The Beveridge Curve, Job Creation and the Propagation of Shocks Shigeru Fujita University of California San Diego June 1, 2003 Abstract This paper proposes modifications to the popular model of equilibrium
U(w) = w + βu(w) U(w) =
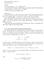 Economics 250a Lecture 11 Search Theory 2 Outline a) search intensity - a very simple model b) The Burdett-Mortensen equilibrium age-posting model (from Manning) c) Brief mention - Christensen et al (2005)
Economics 250a Lecture 11 Search Theory 2 Outline a) search intensity - a very simple model b) The Burdett-Mortensen equilibrium age-posting model (from Manning) c) Brief mention - Christensen et al (2005)
Equilibrium Unemployment in a General Equilibrium Model 1
 Equilibrium Unemployment in a General Equilibrium Model 1 Application to the UK Economy Keshab Bhattarai 2 Hull University Bus. School July 19, 2012 1 Based on the paper for the 4th World Congress of the
Equilibrium Unemployment in a General Equilibrium Model 1 Application to the UK Economy Keshab Bhattarai 2 Hull University Bus. School July 19, 2012 1 Based on the paper for the 4th World Congress of the
Choosy search and the mismatch of talents
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Choosy search and the mismatch of talents Bruno Decreuse GREQAM 2003 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/3636/ MPRA Paper No. 3636, posted 20. June 2007 Choosy search
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Choosy search and the mismatch of talents Bruno Decreuse GREQAM 2003 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/3636/ MPRA Paper No. 3636, posted 20. June 2007 Choosy search
Multidimensional Sorting Under Random Search
 Multidimensional Sorting Under Random Search Ilse Lindenlaub Fabien Postel-Vinay July 217 Abstract We analyze sorting in a standard market environment with search frictions and random search, where both
Multidimensional Sorting Under Random Search Ilse Lindenlaub Fabien Postel-Vinay July 217 Abstract We analyze sorting in a standard market environment with search frictions and random search, where both
DOCUMENTOS DE TRABAJO Serie Economía
 DOCUMENTOS DE TRABAJO Serie Economía Nº 287 MINIMUM WAGES STRIKE BACK: THE EFFECTS ON CAPITAL AND LABOR DEMANDS IN A LARGE-FIRM FRAMEWORK SOFÍA BAUDUCCO Y ALEXANDRE JANIAK s strike back: the effects on
DOCUMENTOS DE TRABAJO Serie Economía Nº 287 MINIMUM WAGES STRIKE BACK: THE EFFECTS ON CAPITAL AND LABOR DEMANDS IN A LARGE-FIRM FRAMEWORK SOFÍA BAUDUCCO Y ALEXANDRE JANIAK s strike back: the effects on
Competitive Search: A Test of Direction and Efficiency
 Bryan Engelhardt 1 Peter Rupert 2 1 College of the Holy Cross 2 University of California, Santa Barbara November 20, 2009 1 / 26 Introduction Search & Matching: Important framework for labor market analysis
Bryan Engelhardt 1 Peter Rupert 2 1 College of the Holy Cross 2 University of California, Santa Barbara November 20, 2009 1 / 26 Introduction Search & Matching: Important framework for labor market analysis
Lecture 3: Introduction to search theory. 1 Job search with an exogenous wage distribution
 BURNABY SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY BRITISH COLUMBIA Paul Klein Office: WMC 3635 Phone: TBA Email: paul klein 2@sfu.ca URL: http://paulklein.ca/newsite/teaching/89.php Economics 89 Advanced macroeconomic theory
BURNABY SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY BRITISH COLUMBIA Paul Klein Office: WMC 3635 Phone: TBA Email: paul klein 2@sfu.ca URL: http://paulklein.ca/newsite/teaching/89.php Economics 89 Advanced macroeconomic theory
Job search and earnings mobility
 Department of Economics- FEA/USP Job search and earnings mobility DAVID TURCHICK WORKING PAPER SERIES Nº 2014-16 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS, FEA-USP WORKING PAPER Nº 2014-16 Job Search and Earnings Mobility
Department of Economics- FEA/USP Job search and earnings mobility DAVID TURCHICK WORKING PAPER SERIES Nº 2014-16 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS, FEA-USP WORKING PAPER Nº 2014-16 Job Search and Earnings Mobility
Remarks on Structural Estimation The Search Framework
 Remarks on Structural Estimation The Search Framework Christopher Flinn NYU and Collegio Carlo Alberto November 2009 1 The Estimation of Search Models We develop a simple model of single agent search set
Remarks on Structural Estimation The Search Framework Christopher Flinn NYU and Collegio Carlo Alberto November 2009 1 The Estimation of Search Models We develop a simple model of single agent search set
Residual Wage Disparity in Directed Search Equilibrium
 Residual Wage Disparity in Directed Search Equilibrium John Kennes,IanKing and Benoit Julien University of Copenhagen First Version: June 2001 Revised: February 2003 Abstract We examine how much of the
Residual Wage Disparity in Directed Search Equilibrium John Kennes,IanKing and Benoit Julien University of Copenhagen First Version: June 2001 Revised: February 2003 Abstract We examine how much of the
Frictional Labor Markets, Bargaining Wedges, and Optimal Tax-Rate Volatility
 Frictional Labor Markets, Bargaining Wedges, and Optimal Tax-Rate Volatility David M. Arseneau Federal Reserve Board Sanjay K. Chugh University of Maryland First Draft: January 2008 This Draft: April 18,
Frictional Labor Markets, Bargaining Wedges, and Optimal Tax-Rate Volatility David M. Arseneau Federal Reserve Board Sanjay K. Chugh University of Maryland First Draft: January 2008 This Draft: April 18,
Introduction to Game Theory
 Introduction to Game Theory Part 3. Dynamic games of incomplete information Chapter 2. Signaling Games Ciclo Profissional 2 o Semestre / 2011 Graduação em Ciências Econômicas V. Filipe Martins-da-Rocha
Introduction to Game Theory Part 3. Dynamic games of incomplete information Chapter 2. Signaling Games Ciclo Profissional 2 o Semestre / 2011 Graduação em Ciências Econômicas V. Filipe Martins-da-Rocha
Global Dynamics in a Search and Matching Model of the Labor Market
 Global Dynamics in a Search and Matching Model of the Labor Market WP 17-12 Nika Lazaryan Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Thomas A. Lubik Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Global Dynamics in a Search and
Global Dynamics in a Search and Matching Model of the Labor Market WP 17-12 Nika Lazaryan Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Thomas A. Lubik Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Global Dynamics in a Search and
Simultaneous Search, On-the-Job Search, and the Shape of the Wage Distribution
 Simultaneous Search, On-the-Job Search, and the Shape of the Wage Distribution Ronald P. Wolthoff VU University Amsterdam, Tinbergen Institute preliminary June 16, 2008 Abstract I present an equilibrium
Simultaneous Search, On-the-Job Search, and the Shape of the Wage Distribution Ronald P. Wolthoff VU University Amsterdam, Tinbergen Institute preliminary June 16, 2008 Abstract I present an equilibrium
On-the-Job Search, Human Capital. Accumulation and Endogenous Firm. Productivity
 On-the-Job Search, Human Capital Accumulation and Endogenous Firm Productivity Emil Kostadinov University of Essex March 21, 2017 Abstract This paper studies the implications of human capital accumulation
On-the-Job Search, Human Capital Accumulation and Endogenous Firm Productivity Emil Kostadinov University of Essex March 21, 2017 Abstract This paper studies the implications of human capital accumulation
Declining Search Frictions, Unemployment and Growth
 The Ronald O. Perelman Center for Political Science and Economics (PCPSE) 133 South 36 th Street Philadelphia, PA 19104-6297 pier@econ.upenn.edu http://economics.sas.upenn.edu/pier PIER Working Paper 18-005
The Ronald O. Perelman Center for Political Science and Economics (PCPSE) 133 South 36 th Street Philadelphia, PA 19104-6297 pier@econ.upenn.edu http://economics.sas.upenn.edu/pier PIER Working Paper 18-005
Productivity and Job Flows: Heterogeneity of New Hires and Continuing Jobs in the Business Cycle
 Productivity and Job Flows: Heterogeneity of New Hires and Continuing Jobs in the Business Cycle Juha Kilponen Bank of Finland Juuso Vanhala y Bank of Finland April 3, 29 Abstract This paper focuses on
Productivity and Job Flows: Heterogeneity of New Hires and Continuing Jobs in the Business Cycle Juha Kilponen Bank of Finland Juuso Vanhala y Bank of Finland April 3, 29 Abstract This paper focuses on
evelopmnet iscussion
 2 IDEC DP D Series Vol. 3 No. 6 evelopmnet iscussion P olicy aper Work Hour Mismatch and On-the-job Search Keisuke Kawata October, 2013 Department of Development Policy Division of Development Science
2 IDEC DP D Series Vol. 3 No. 6 evelopmnet iscussion P olicy aper Work Hour Mismatch and On-the-job Search Keisuke Kawata October, 2013 Department of Development Policy Division of Development Science
Multidimensional Sorting Under Random Search
 Multidimensional Sorting Under Random Search Ilse Lindenlaub Fabien Postel-Vinay September 216 Abstract We analyze sorting in a standard market environment characterized by search frictions and random
Multidimensional Sorting Under Random Search Ilse Lindenlaub Fabien Postel-Vinay September 216 Abstract We analyze sorting in a standard market environment characterized by search frictions and random
A Pure Theory of Wage Dispersion
 A Pure Theory of Wage Dispersion Cheng Wang and Youzhi Yang February 13, 2017 Abstract We look for equilibrium wage dispersion in a labor market model with search and on-the-job search, identical firms
A Pure Theory of Wage Dispersion Cheng Wang and Youzhi Yang February 13, 2017 Abstract We look for equilibrium wage dispersion in a labor market model with search and on-the-job search, identical firms
Online Appendix H for. Discrimination and Employment Protection
 Online Appendix H for Discrimination and Employment Protection Steinar Holden 1 and Åsa Rosén 2 January 6, 2014 1 Department of Economics, University of Oslo, Steinar.Holden@econ.uio.no. 2 Stockholm University
Online Appendix H for Discrimination and Employment Protection Steinar Holden 1 and Åsa Rosén 2 January 6, 2014 1 Department of Economics, University of Oslo, Steinar.Holden@econ.uio.no. 2 Stockholm University
Subsidizing low-skilled jobs in a dual labor market
 Subsidizing low-skilled jobs in a dual labor market Pascal Belan LEMNA, Université de Nantes Martine Carré CEPII and THEMA, Université de Cergy Stéphane Gregoir EDHEC Business School February 2009 Abstract
Subsidizing low-skilled jobs in a dual labor market Pascal Belan LEMNA, Université de Nantes Martine Carré CEPII and THEMA, Université de Cergy Stéphane Gregoir EDHEC Business School February 2009 Abstract
Network Search: Climbing the Ladder Faster
 Network Search: Climbing the Ladder Faster Marcelo Arbex Dennis O Dea David Wiczer University of Windsor University of Washington Fed Reserve Bank of St. Louis. October 3, 2016 The views expressed herein
Network Search: Climbing the Ladder Faster Marcelo Arbex Dennis O Dea David Wiczer University of Windsor University of Washington Fed Reserve Bank of St. Louis. October 3, 2016 The views expressed herein
Economics 2450A: Public Economics Section 8: Optimal Minimum Wage and Introduction to Capital Taxation
 Economics 2450A: Public Economics Section 8: Optimal Minimum Wage and Introduction to Capital Taxation Matteo Paradisi November 1, 2016 In this Section we develop a theoretical analysis of optimal minimum
Economics 2450A: Public Economics Section 8: Optimal Minimum Wage and Introduction to Capital Taxation Matteo Paradisi November 1, 2016 In this Section we develop a theoretical analysis of optimal minimum
Unemployment Benefits and Matching Efficiency in an. Estimated DSGE Model with Labor Market Search. Frictions
 Unemployment Benefits and Matching Efficiency in an Estimated DSGE Model with Labor Market Search Frictions Ji Zhang PBC School of Finance, Tsinghua University Abstract To explain the high and persistent
Unemployment Benefits and Matching Efficiency in an Estimated DSGE Model with Labor Market Search Frictions Ji Zhang PBC School of Finance, Tsinghua University Abstract To explain the high and persistent
Wage Inequality, Labor Market Participation and Unemployment
 Wage Inequality, Labor Market Participation and Unemployment Testing the Implications of a Search-Theoretical Model with Regional Data Joachim Möller Alisher Aldashev Universität Regensburg www.wiwi.uni-regensburg.de/moeller/
Wage Inequality, Labor Market Participation and Unemployment Testing the Implications of a Search-Theoretical Model with Regional Data Joachim Möller Alisher Aldashev Universität Regensburg www.wiwi.uni-regensburg.de/moeller/
Lecture 5: Labour Economics and Wage-Setting Theory
 Lecture 5: Labour Economics and Wage-Setting Theory Spring 2017 Lars Calmfors Literature: Chapter 7 Cahuc-Carcillo-Zylberberg: 435-445 1 Topics Weakly efficient bargaining Strongly efficient bargaining
Lecture 5: Labour Economics and Wage-Setting Theory Spring 2017 Lars Calmfors Literature: Chapter 7 Cahuc-Carcillo-Zylberberg: 435-445 1 Topics Weakly efficient bargaining Strongly efficient bargaining
Labor-Market Matching with Precautionary Savings
 Labor-Market Matching with Precautionary Savings Bence Bardóczy * October 25, 27 Introduction In this note, I discuss how to solve Krusell, Mukoyama, and Şahin (2) (KMS) in a continuous-time setting using
Labor-Market Matching with Precautionary Savings Bence Bardóczy * October 25, 27 Introduction In this note, I discuss how to solve Krusell, Mukoyama, and Şahin (2) (KMS) in a continuous-time setting using
A Stock-Flow Theory of Unemployment with Endogenous Match Formation
 A Stock-Flow Theory of Unemployment with Endogenous Match Formation Carlos Carrillo-Tudela University of Essex, CEPR, CESifo and IZA William Hawkins Yeshiva University March 25, 206 Preliminary and Incomplete
A Stock-Flow Theory of Unemployment with Endogenous Match Formation Carlos Carrillo-Tudela University of Essex, CEPR, CESifo and IZA William Hawkins Yeshiva University March 25, 206 Preliminary and Incomplete
A Distributional Framework for Matched Employer Employee Data. Nov 2017
 A Distributional Framework for Matched Employer Employee Data Nov 2017 Introduction Many important labor questions rely on rich worker and firm heterogeneity - decomposing wage inequality, understanding
A Distributional Framework for Matched Employer Employee Data Nov 2017 Introduction Many important labor questions rely on rich worker and firm heterogeneity - decomposing wage inequality, understanding
Economics Bulletin, 2012, Vol. 32 No. 1 pp Introduction
 1. Introduction The past decades have been harsh for young workers as their unemployment rate was double the rest of the populations in many developed countries. In Europe the youth unemployment rate (15
1. Introduction The past decades have been harsh for young workers as their unemployment rate was double the rest of the populations in many developed countries. In Europe the youth unemployment rate (15
Public Sector Wage Policy and Labour Market Equilibrium: a Structural Model
 Public Sector Wage Policy and Labour Maret Equilibrium: a Structural Model Jae Bradley University of Bristol Fabien Postel-Vinay University of Bristol, Paris School of Economics, CEP and IZA April 2011
Public Sector Wage Policy and Labour Maret Equilibrium: a Structural Model Jae Bradley University of Bristol Fabien Postel-Vinay University of Bristol, Paris School of Economics, CEP and IZA April 2011
The Pervasive Importance of Tightness in Labor-Market Volatility
 The Pervasive Importance of Tightness in Labor-Market Volatility Robert E. Hall Hoover Institution and Department of Economics, Stanford University National Bureau of Economic Research rehall@stanford.edu;
The Pervasive Importance of Tightness in Labor-Market Volatility Robert E. Hall Hoover Institution and Department of Economics, Stanford University National Bureau of Economic Research rehall@stanford.edu;
Optimal Insurance of Search Risk
 Optimal Insurance of Search Risk Mikhail Golosov Yale University and NBER Pricila Maziero University of Pennsylvania Guido Menzio University of Pennsylvania and NBER May 27, 2011 Introduction Search and
Optimal Insurance of Search Risk Mikhail Golosov Yale University and NBER Pricila Maziero University of Pennsylvania Guido Menzio University of Pennsylvania and NBER May 27, 2011 Introduction Search and
Structural Econometrics: Equilibrium search models. Jean-Marc Robin
 Structural Econometrics: Equilibrium search models Jean-Marc Robin Plan 1. Facts on wage distributions 2. On-the-job search and wage posting { Burdett-Mortensen 3. Sequential auctions { Postel-Vinay Robin
Structural Econometrics: Equilibrium search models Jean-Marc Robin Plan 1. Facts on wage distributions 2. On-the-job search and wage posting { Burdett-Mortensen 3. Sequential auctions { Postel-Vinay Robin
Unemployment Compensation and the Allocation of Labor in Developing Countries
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 7233 Unemployment Compensation and the Allocation of Labor in Developing Countries Olivier Charlot Franck Malherbet Mustafa Ulus February 203 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 7233 Unemployment Compensation and the Allocation of Labor in Developing Countries Olivier Charlot Franck Malherbet Mustafa Ulus February 203 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft
LABOR MATCHING MODELS: EFFICIENCY PROPERTIES FEBRUARY 1, 2019
 LABOR MATCHING MODELS: EFFICIENCY PROPERTIES FEBRUARY, 209 Eiciency Considerations LABOR-MATCHING EFFICIENCY Social Planning problem Social Planner also subject to matcing TECHNOLOGY t max ( t ct, vt,
LABOR MATCHING MODELS: EFFICIENCY PROPERTIES FEBRUARY, 209 Eiciency Considerations LABOR-MATCHING EFFICIENCY Social Planning problem Social Planner also subject to matcing TECHNOLOGY t max ( t ct, vt,
The Cyclicality of Search Intensity in a Competitive Search Model
 The Cyclicality of Search Intensity in a Competitive Search Model Paul Gomme Damba Lkhagvasuren May 28, 2013 Abstract Reasonably calibrated versions of the Diamond-Mortensen-Pissarides search and matching
The Cyclicality of Search Intensity in a Competitive Search Model Paul Gomme Damba Lkhagvasuren May 28, 2013 Abstract Reasonably calibrated versions of the Diamond-Mortensen-Pissarides search and matching
Measuring Mismatch in the U.S. Labor Market
 Measuring Mismatch in the U.S. Labor Market Ayşegül Şahin Federal Reserve Bank of New York Joseph Song Federal Reserve Bank of New York Giorgio Topa Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and IZA Gianluca Violante
Measuring Mismatch in the U.S. Labor Market Ayşegül Şahin Federal Reserve Bank of New York Joseph Song Federal Reserve Bank of New York Giorgio Topa Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and IZA Gianluca Violante
Subsidizing low-skilled jobs in a dual labor market
 Subsidizing low-skilled jobs in a dual labor market Pascal Belan LEN, Université de Nantes Martine Carré CEPII, CREST and THEMA, Université de Cergy Stéphane Gregoir CREST-INSEE May 2007 Abstract A large
Subsidizing low-skilled jobs in a dual labor market Pascal Belan LEN, Université de Nantes Martine Carré CEPII, CREST and THEMA, Université de Cergy Stéphane Gregoir CREST-INSEE May 2007 Abstract A large
Università degli studi di Torino
 Università degli studi di Torino Corso di laurea in Economics Tesi di laurea: Exploring labor market policies. Insights from a simulation model. Relatore: Pietro Terna Controrelatore: Sergio Margarita
Università degli studi di Torino Corso di laurea in Economics Tesi di laurea: Exploring labor market policies. Insights from a simulation model. Relatore: Pietro Terna Controrelatore: Sergio Margarita
HCEO WORKING PAPER SERIES
 HCEO WORKING PAPER SERIES Working Paper The University of Chicago 1126 E. 59th Street Box 107 Chicago IL 60637 www.hceconomics.org Firms Choices of Wage-Setting Protocols in the Presence of Minimum Wages
HCEO WORKING PAPER SERIES Working Paper The University of Chicago 1126 E. 59th Street Box 107 Chicago IL 60637 www.hceconomics.org Firms Choices of Wage-Setting Protocols in the Presence of Minimum Wages
Advanced Tools in Macroeconomics
 Advanced Tools in Macroeconomics Continuous time models (and methods) Pontus Rendahl August 21, 2017 Introduction In this lecture we will take a look at models in continuous, as opposed to discrete, time.
Advanced Tools in Macroeconomics Continuous time models (and methods) Pontus Rendahl August 21, 2017 Introduction In this lecture we will take a look at models in continuous, as opposed to discrete, time.
The employment effect of reforming a public employment agency
 The employment effect of reforming a public employment agency Andrey Launov and Klaus Wälde (European Economic Review, 2016) Presented by Ismael Gálvez March 15, 2017 Motivation Rich literature on the
The employment effect of reforming a public employment agency Andrey Launov and Klaus Wälde (European Economic Review, 2016) Presented by Ismael Gálvez March 15, 2017 Motivation Rich literature on the
