Cosmology with CMB anisotropy
|
|
|
- Albert Cannon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cosmology with CMB anisotropy Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune WHEPP-9 (Jan 10, 2005)
2 The Isotropic Universe Serendipitous discovery of the dominant Radiation content of the universe as an extremely isotropic, Black-body bath at temperature T 0 =2.725 ±0.002 K. Clinching support for Hot Big Bang model
3 The dominant radiation component in the universe ~ 400 CMB photons per cubic cm. (D. Scott 99)
4 The most perfect Black-Body spectrum in nature COBE FIRAS The CMB temperature A single number characterizes the radiation content of the universe!! COBE website
5 COBE-FIRAS results strongly constrain any Energy input into the CMB in the not-so-early universe 60 Ghz 600 Ghz δe E ( λ = µ m) 4, ARCADE Ghz 30Ghz (figs: Bond, 1996)
6 The Perturbed Isotropic Universe Predicted as precursors to the observed large scale structure After 25 years of intense search, tiny variations (~10 p.p.m.) of CMB temperature sky map finally discovered. Holy grail of structure formation
7 Cosmic Microwave Background a probe beyond the cosmic horizon Pristine relic of a hot, dense & smooth early universe - Hot Big Bang model Pre-recombination : Tightly coupled to, and in thermal equilibrium with, ionized matter. Post-recombination :Freely propagating through (weakly perturbed) homogeneous & isotropic cosmos. CMB anisotropy is related to the tiny primordial fluctuations which formed the Large scale Structure through gravitational instability Simple linear physics allows for accurate predictions Consequently a powerful cosmological probe
8 Gravitational Instability Mildly Perturbed universe at z=1100 Present universe at z=0 Cosmic matter content Ω Ω Ω tot b DM Ω Λ H 0
9 Cosmological Parameters Multi-parameter (7-11) joint estimation (complex covariance, degeneracies, priors, marginal distributions) Strategies to search & Locate best parameters: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Dark energy Cosmic age Dark matter Baryonic matter Expansion rate Optical depth Fig.:R.Sinha, TS
10 Statistics of CMB CMB Anisotropy Sky map => Spherical Harmonic decomposition T ( θ, φ ) = l a lm Y lm ( θ, φ ) l= 2 m= l Gaussian CMB anisotropy completely specified by the angular power spectrum IF Statistical isotropy * lm l ' m' l ll ' mm' a a = C δ δ (=> Correlation function C(n,n )=h T Ti is rotationally invariant)
11 Fig. M. White 1997 The Angular power spectrum of the CMB anisotropy depends sensitively on the present matter current of the universe and the spectrum of primordial perturbations C l The Angular power spectrum of CMB anisotropy is considered a powerful tool for constraining cosmological parameters.
12 Low multipole : Sachs-Wolfe plateau Moderate multipole : Acoustic Doppler peaks High multipole : Damping tail CMB physics is very well understood!!!
13 Sensitive to curvature 1 Ω K l = 220 Fig:Hu & Dodelson 2002 l
14 Fig:Hu & Dodelson 2002 Sensitive to Baryon density T = 74µK
15 Post-COBE Ground & Balloon Experiments Python-V 1999, 2003 Boomerang 1998 DASI 2002 (Degree Angular scale Interferometer) Archeops 2002
16 Highlights of CMB Anisotropy Measurements ( )
17 NASA Launched July 2001 Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe First year data results announced on Feb. 11, 2003!
18 30% sky daily, Whole sky every 6 months
19 10 independent Difference assemblies over 5 frequencies K band 23 GHz (1 DA) Ka band 33 GHz (1 DA) CMB anisotropy signal W band 94 GHz (4 DA) Q band 41 GHz (2 DA) NASA/WMAP science team V band 61 GHz (2 DA)
20 dus saal baad.
21 NASA/WMAP science team Signal / Noise > 1for 650 Cosmic variance limited errors for 350
22 Independent, self contained analysis of WMAP multi-frequency maps Only input : CMB anisotropy is achromatic (frequency independent) No extraneous foreground info.! I.e., free of uncertainty of foreground modeling IIT Kanpur + IUCAA Black: IITK+IUCAA Red : WMAP team Saha, Jain,Souradeep 2005 (astro-ph/ )
23 Controlling other Systematics Eg.,Non-circular beam effect in CMB measurements WMAP Q beam Eccentricity =0.7 (S. Mitra, A. Sengupta, Souradeep, PRD 2004) Close to the corrections expected in the WMAP 2 nd data release
24 (74.4±0.3, 220.8±0.8) (74.7 ±0.5, ±0.8) Saha, Jain,Souradeep 2005 (astro-ph/ ) (49.6 ±1.2, 545 ±17) (48.8 ±0.9, 546 ±10) (42.2 ±0.9, ±5.5) (41.0 ± 0.5, ±3.5)
25 Power spectrum of mass distribution ( Tegmark et al. 2004)
26 CMB + (Fig: Tegmark) LSS (WMAP+SDSS analysis: Tegmark et al. 2004)
27 Near future : High resolution C l (SPT) CMB Task force report 2005
28 Gravitational Instability Mildly Perturbed universe at z=1100 Present universe at z=0 Cosmic matter content Ω Ω Ω tot b DM Ω Λ H 0
29 Present distribution of matter Few Gpc. SLOAN DIGITAL SKY SURVEY (SDSS)
30 One little telltale bump!! ξ() r = δρ( r) δρ( r ) 1 2 A small excess in correlation at 150 Mpc.! SDSS survey (astro-ph/ ) (Einsentein et al. 2005) 150 Mpc.
31 Acoustic Baryon oscillations!! 150 Mpc. (Einsentein et al. 2005)
32 Acoustic Baryon oscillations in the matter correlation function!! 2-point correlation of density contrast 105 h Strong evidence of Gravitational instability mechanism for structure formation (from adiabatic initial perturbations)!!! 150 Mpc. The same CMB oscillations at low redshifts!!! SDSS survey (astro-ph/ ) (Einsentein et al. 2005)
33 Quantum fluctuations PARAMETERS OF THE INITIAL super adiabatic CONDITIONS amplified by FROM inflation EARLY (rapid expansion) UNIVERSE Galaxy COSMOLOGICAL & Large scale Structure PARAMETERS formation Via gravitational instability Early Universe The Cosmic screen Present Universe
34 The nature of initial/primordial perturbations Power spectrum Nearly Scale invariant /scale free form ( for the Geometry & Topology of the universe) Spin characteristics Scalar --- Density perturbations Tensor --- Gravity waves Vector --- rotational modes Type of scalar perturbations Adiabatic --- no entropy fluctuations Underlying statistics Isocurvature -- no curvature fluctuations Gaussian Non-Gaussian
35 Thompson scattering of the CMB anisotropy quadrupole at the surface of last scattering generates a linear polarization pattern in the CMB. Three additional Power spectra (C l TT +.. ): two polarization modes (C l EE, C l BB ) cross correlation with temperature anisotropy C l TE. (Fig:Hu & White, 97) Initial metric perturbation mix correspondence : Scalar perturbations predominantly generate the Electric (E) polarization mode. Vector perturbations predominantly generate the magnetic (B) polarization mode. Tensor perturbations generate the both modes in comparable amounts. Temperature anisotropy Cross-correlation only with the E-mode.
36 C l TT First detection by DASI (2002) l = C l EE C l TE Regularly updated Sept 2004: CBI, DASI,CAPMAP July 2005: Boomerang
37 Proof of inflation? Anti-correlation peak = 137 ± 9, T = 35µK z reion 10 = Adiabatic IC TE peak out of phase = 300 NASA/WMAP science team Consistent with T for 20
38 (MacTavish et al. astro-ph/ ) Out of phase location of peaks Null in BB: EE, Awaiting TE relative direct to TT signature impliesof tensor perturbations, adiabatic initial a.k.a. perturbations!!! gravity waves!!!
39 (MacTavish et al. astro-ph/ ) BUT, please read the fine print! Data combos, priors, parameterization BUT, please read the fine print! Data combos, priors, parameterization,
40 (MacTavish et al. astro-ph/ )
41 The curvature (density) of the Universe (MacTavish et al. astro-ph/ ) Ω K =-0.037±0.04 Ω K =-0.027±0.016 Ω K =-0.022±0.017
42 Cosmological constraints on ν mass (MacTavish et al. astro-ph/ ) 3-ν degenerate mass Ω ν = 3 m ν /(94.0 ev) f ν = Ω ν /Ω DM m ν m ν m ν (95% CL) < 1.0 ev < 0.4 ev < 0.16 ev
43 The nature of dark energy (MacTavish et al. astro-ph/ ) Constant equation of state, w w=-0.86±0.4 w=-0.94±0.1
44 (MacTavish et al. astro-ph/ ) Tensor to scalar ratio is a crucial discriminant of EU scenarios Tensor to scalar ratio A T /A S < 0.71 A T /A S < 0.36
45 CMB Task force report 2005
46 CMB Task force report 2005
47 Courtesy: A. Coorey (EPIC) 10-3 : reasonable low end of inflationary possibilities
48 PARAMETERS OF THE INITIAL CONDITIONS FROM EARLY UNIVERSE COSMOLOGICAL PARAMETERS Early Universe The Cosmic screen Present Universe
49 CMB anisotropy has two independent aspects: C l dk = Pk ( ) G ( k) k P( k) Primordial power spectrum from Early universe G( k) Post recombination Radiation transport in a given cosmology (Tegmark & Zaldariagga 97, Gawaiser & Silk 00, Matsumiya et al. 02..) l
50 Suppression of power on low multipoles (l=2,3) NASA/WMAP science team Low Quadrupole T 2 = 8 ± 2 µ K (COBE T = + 4 µ K ) = 2
51 Recovering the primordial power spectrum (Shafieloo & Souradeep, 2004 PRD ) Primordial power spectrum from Early universe can deconvolved from CMB anisotropyspectrum Horizon scale C l = dk k P( k) G ( k) l Improved Error sensitive iterative Richardson-Lucy deconvolution method Recovered spectrum shows an infra-red cut-off on Horizon scale!!! Is it cosmic topology? Signature of pre-inflationary phase? New physics?.
52
53
54
55 Wavelet Decomposition of features (TS+ Rangarajan, Panigrahi, Manimaran: in progress) Infrared cutoff Superimposed Oscillations
56 Recovery of the primordial power spectrum A reconfirmation of our results using different deconvolution method! (Tocchini-Vaentini, Hoffman, Silk astro-ph/ )
57 Two independent aspects of CMB anisotropy : C C C C PS( k), PT( k), Piso( k) TT EE BB TE Primordial power spectra from Early universe = = = = dk k dk k dk k dk k Pk ( ) Pk ( ) P( k) G G G TT EE BB ( k) ( k) ( k) TE Pk ( ) G ( k) TT EE BB TE G ( k), G ( k), G ( k), G ( k) Post recombination Radiative transport kernels in a given cosmology
58 Absence of large scale power Intriguing lack of correlations at large angular scales (θ 60 ) Can imply more than just the suppression of power in the low multipoles! NASA/WMAP science team
59 Asymmetries in the CMB anisotropy N-S asymmetry Eriksen, et al. 2004, Hansen et al (in local power) Larson & Wandelt 2004, Park 2004 (genus stat.) Special directions Axis of Evil Tegmark et al (l=2,3 aligned) Copi et al (multipole vectors) Land & Magueijo 2004 (cubic anomalies) Prunet et al., 2004 (mode coupling) Underlying `template pattern Jaffe et al (Bianchi VIIh:mild cosmic rotation?).. WMAP first year data Bianchi template Difference map Broadly, statistical properties are not invariant under rotations I.e., Breakdown of Statistical Isotropy? Low N-S asymmetry High N-S asymmetry Fig: H. K. Eriksen, et al. 2003
60 Statistics of CMB Possibilities: Cn ( ˆ, nˆ ) Cn ( ˆ nˆ ) Statistically Isotropic, Gaussian models Statistically Isotropic, non-gaussian models Statistically An-isotropic, Gaussian models Statistically An-isotropic, non-gaussian models * lm l ' m' l ll ' mm' a a C δ δ
61 Sources of Statistical Anisotropy Ultra large scale structure and cosmic topology. Anisotropic cosmology Primordial magnetic fields (based on Durrer et al. 98, Chen et al. 04) Observational artifacts: Anisotropic noise Non-circular beam Incomplete/unequal sky coverage Residuals from foreground removal
62 Figs. J. Levin Cn ( ˆ, nˆ ) Cn ( ˆ nˆ ) Beautiful Correlation patterns could underlie the CMB tapestry Can we measure correlation patterns? the COSMIC CATCH is
63 Bipolar Power spectrum (BiPS( BiPS) ) : A Generic Measure of Statistical Anisotropy 1 Recall: C( nˆ ˆ ) ( ˆ, ˆ 1 n2 = dr C Rn1 Rn2) 2 8π Bipolar multipole index κ 1 = 8π dω dω ( ) ( 2 1, dr χ n n R C Rn Rn ˆ ˆ ) 2 A weighted average of the correlation function over all rotations Hajian & Souradeep ApJ. Lett 2003 Hajian, Souradeep & Cornish ApJ. Lett χ ( R ) = ( R ) m = D mm Characteristic Wigner function rotation matrix
64 Statistical Isotropy κ = κ 0 δ 0 Correlation is invariant under rotations C ( Rnˆ, ˆ ) ( ˆ, ˆ 1 Rn2 = C n1 n2) κ 2 1 = ( 2 + 1) dω 2 8π 2 ( ˆ ˆ n dω C n1, n2)[ drχ ( R 1 n 2 )] 2 dr ( ) δ 0 χ R =
65 BiPS: : In Harmonic Space Correlation is a two point function on a sphere C LM ( n1, n2) Al l { Yl ( n ) Yl ( n l l LM Inverse-transform A LM l l 1 2 = = 1 2 dω n 1 dω n 2 C( n { Y = l 1 ( n1 ) Y LM C m m 1 2 l l 1 2 )} m m 1 l LM 2 2 ( n Y 1 2 l m 1 )} ( n LM 1 ) Y n Yl n Yl n * 1, 2){ ( 1) ( 2)} LM 1 Clebsch-Gordan 2 BiPoSH Bipolar spherical harmonics. l 2 m 2 ( n 2 ) = m m 1 2 a l m 1 1 a l 2 m 2 CLM l 1m12 l m2 Linear combination of off-diagonal elements
66 Recall: Coupling of angular momentum states l m l m M l l l + m + m + M , 1 2 = 0 BiPoSH coefficients : A M l l 1 2 = a a * l1m 1 l2 M + m m 1 1 M C l 1m1 l2 M + m1 Complete,Independent linear combinations of off-diagonal correlations. Encompasses other specific measures of off-diagonal terms, such as D a - Durrer et al. l 98 : lm a l + 2 m = - Prunet et al. 04 : ( i) M M D a a + + = A C + + l lm M M A C ll ' l + 2 M l 1 m i M m ll' l m l 1 m i l m BiPS: rotationally invariant κ M, l 1, l 2 A M l l
67 SI violation : a lm a * l ' m ' C l δ ll' δ mm' Radical breakdown a l ' m ' a a lm a * l ' m ' * l ' m ' a lm a * lm (Bond, Pogosyan & Souradeep 1998, 2002)
68 SI violation: a a C δ δ * lm l ' m' l ll ' mm' Understanding BiPoSH coefficients A 4 M ll ' LM A ll ' = almalm' C mm' LM lml ' m ' Measure cross correlation in a lm A 2 M ll '
69 Spherical harmonics alm Spherical Harmonic coefficents C l Angular power spectrum Bipolar spherical harmonics M A ll' BiPoSH coefficents κ BiPS Bipolar Power spectrum (BiPS( BiPS) ) : A Generic Measure of Statistical Anisotropy
70 Spherical harmonics Spherical Harmonic Transforms C l alm Angular power spectrum Bipolar spherical harmonics M A ll' BipoSH Transforms κ BiPS (Bipolar Power Spectrum) Bipolar Power spectrum (BiPS( BiPS) ) : A Generic Measure of Statistical Anisotropy
71 Orientation independent. Measure of Statistical Isotropy A κ M ll' = = ll' M Stat.isotropy mm' A a M ll' lm κ 2 a l' m' = B κ 0 C δ M lml ' m' 0 SH transform of the map bias Averaging over l,l & M beats down Cosmic variance. Fast: Advantage of fast SH transform. (1 min. /alpha 1.25 GHz proc.: Healpix 512, BiPS upto 20 )
72 Statistical Isotropy of CMB Anisotropy WMAP CMB anisotropy map Fig: NASA/WMAP science team Hajian & Souradeep ApJ. Lett 2003 Hajian, Souradeep & Cornish ApJ. Lett WMAP Angular power spectrum Fig: NASA/WMAP science team W(l) WMAP Bipolar power spectrum BiPS imply (BiPS) WMAP is Statistically Isotropic!!
73 Cosmology with CMB anisotropy Precise values of the parameters of the working model of cosmology. Direct evidence of gravitational instability being responsible for structure formation. Initial/primordial perturbations from (simple) inflation adiabatic density perturbations Gaussian random fields A non-zero tensor component? (cosmic gravity wave background ) Observable signatures of Ultra-large structure of the cosmos, or, new physics in early universe infra-red cutoff & feature in the primordial power spectrum Violation of statistical isotropy : Are C l adequate descriptor of CMB? (Detection of cosmic topology? Is the universe observably finite?)
74 Thank you!!! CMB Task force report 2005
Cosmology with CMB: the perturbed universe
 Cosmology with CMB: the perturbed universe Utkal Univ. (Jan 11-12, 2008) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India How do we know so much now about this model Universe? Cosmic Microwave Background Pristine
Cosmology with CMB: the perturbed universe Utkal Univ. (Jan 11-12, 2008) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India How do we know so much now about this model Universe? Cosmic Microwave Background Pristine
CMB anisotropy. Tarun Souradeep. ICSW-07 IPM, Tehran (Jun 2-9, 2007) I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India
 CMB anisotropy ICSW-07 IPM, Tehran (Jun 2-9, 2007) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India Cosmic Microwave Background X R H /33 Cosmic Super IMAX theater 0.5 Myr Here & Now (14 Gyr) 14 GPc Transparent
CMB anisotropy ICSW-07 IPM, Tehran (Jun 2-9, 2007) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India Cosmic Microwave Background X R H /33 Cosmic Super IMAX theater 0.5 Myr Here & Now (14 Gyr) 14 GPc Transparent
Cosmology with CMB & LSS:
 Cosmology with CMB & LSS: the Early universe VSP08 lecture 4 (May 12-16, 2008) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India Ω +Ω +Ω +Ω + Ω +... = 1 0 0 0 0... 1 m DE K r r The Cosmic Triangle (Ostriker & Steinhardt)
Cosmology with CMB & LSS: the Early universe VSP08 lecture 4 (May 12-16, 2008) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India Ω +Ω +Ω +Ω + Ω +... = 1 0 0 0 0... 1 m DE K r r The Cosmic Triangle (Ostriker & Steinhardt)
Observational evidence for Dark energy
 Observational evidence for Dark energy ICSW-07 (Jun 2-9, 2007) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India Email: tarun@iucaa.ernet.in Observational evidence for DE poses a major challenge for theoretical cosmology.
Observational evidence for Dark energy ICSW-07 (Jun 2-9, 2007) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India Email: tarun@iucaa.ernet.in Observational evidence for DE poses a major challenge for theoretical cosmology.
CMB anisotropy & Large Scale Structure : Dark energy perspective
 CMB anisotropy & Large Scale Structure : Dark energy perspective ICSW-07 IPM, Tehran (Jun 2-9, 2007) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India India I.U.C.A.A., Pune, India The Realm of Cosmology Basic unit:
CMB anisotropy & Large Scale Structure : Dark energy perspective ICSW-07 IPM, Tehran (Jun 2-9, 2007) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India India I.U.C.A.A., Pune, India The Realm of Cosmology Basic unit:
Cosmic Microwave Background Introduction
 Cosmic Microwave Background Introduction Matt Chasse chasse@hawaii.edu Department of Physics University of Hawaii at Manoa Honolulu, HI 96816 Matt Chasse, CMB Intro, May 3, 2005 p. 1/2 Outline CMB, what
Cosmic Microwave Background Introduction Matt Chasse chasse@hawaii.edu Department of Physics University of Hawaii at Manoa Honolulu, HI 96816 Matt Chasse, CMB Intro, May 3, 2005 p. 1/2 Outline CMB, what
A5682: Introduction to Cosmology Course Notes. 11. CMB Anisotropy
 Reading: Chapter 9, sections 9.4 and 9.5 11. CMB Anisotropy Gravitational instability and structure formation Today s universe shows structure on scales from individual galaxies to galaxy groups and clusters
Reading: Chapter 9, sections 9.4 and 9.5 11. CMB Anisotropy Gravitational instability and structure formation Today s universe shows structure on scales from individual galaxies to galaxy groups and clusters
A5682: Introduction to Cosmology Course Notes. 11. CMB Anisotropy
 Reading: Chapter 8, sections 8.4 and 8.5 11. CMB Anisotropy Gravitational instability and structure formation Today s universe shows structure on scales from individual galaxies to galaxy groups and clusters
Reading: Chapter 8, sections 8.4 and 8.5 11. CMB Anisotropy Gravitational instability and structure formation Today s universe shows structure on scales from individual galaxies to galaxy groups and clusters
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results. Alexander Schmah
 The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
Anisotropy in the CMB
 Anisotropy in the CMB Antony Lewis Institute of Astronomy & Kavli Institute for Cosmology, Cambridge http://cosmologist.info/ Hanson & Lewis: 0908.0963 Evolution of the universe Opaque Transparent Hu &
Anisotropy in the CMB Antony Lewis Institute of Astronomy & Kavli Institute for Cosmology, Cambridge http://cosmologist.info/ Hanson & Lewis: 0908.0963 Evolution of the universe Opaque Transparent Hu &
Really, really, what universe do we live in?
 Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
Power spectrum exercise
 Power spectrum exercise In this exercise, we will consider different power spectra and how they relate to observations. The intention is to give you some intuition so that when you look at a microwave
Power spectrum exercise In this exercise, we will consider different power spectra and how they relate to observations. The intention is to give you some intuition so that when you look at a microwave
Modern Cosmology / Scott Dodelson Contents
 Modern Cosmology / Scott Dodelson Contents The Standard Model and Beyond p. 1 The Expanding Universe p. 1 The Hubble Diagram p. 7 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis p. 9 The Cosmic Microwave Background p. 13 Beyond
Modern Cosmology / Scott Dodelson Contents The Standard Model and Beyond p. 1 The Expanding Universe p. 1 The Hubble Diagram p. 7 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis p. 9 The Cosmic Microwave Background p. 13 Beyond
Galaxies 626. Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
CMB studies with Planck
 CMB studies with Planck Antony Lewis Institute of Astronomy & Kavli Institute for Cosmology, Cambridge http://cosmologist.info/ Thanks to Anthony Challinor & Anthony Lasenby for a few slides (almost) uniform
CMB studies with Planck Antony Lewis Institute of Astronomy & Kavli Institute for Cosmology, Cambridge http://cosmologist.info/ Thanks to Anthony Challinor & Anthony Lasenby for a few slides (almost) uniform
The cosmic microwave background radiation
 The cosmic microwave background radiation László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 May 18, 2018. Origin of the cosmic microwave radiation Photons in the plasma are
The cosmic microwave background radiation László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 May 18, 2018. Origin of the cosmic microwave radiation Photons in the plasma are
Ringing in the New Cosmology
 Ringing in the New Cosmology 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI 500 1000 1500 l (multipole) Acoustic Peaks in the CMB Wayne Hu Temperature Maps CMB Isotropy Actual Temperature Data COBE 1992 Dipole
Ringing in the New Cosmology 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI 500 1000 1500 l (multipole) Acoustic Peaks in the CMB Wayne Hu Temperature Maps CMB Isotropy Actual Temperature Data COBE 1992 Dipole
CMB Polarization and Cosmology
 CMB Polarization and Cosmology Wayne Hu KIPAC, May 2004 Outline Reionization and its Applications Dark Energy The Quadrupole Gravitational Waves Acoustic Polarization and Initial Power Gravitational Lensing
CMB Polarization and Cosmology Wayne Hu KIPAC, May 2004 Outline Reionization and its Applications Dark Energy The Quadrupole Gravitational Waves Acoustic Polarization and Initial Power Gravitational Lensing
The AfterMap Wayne Hu EFI, February 2003
 The AfterMap Wayne Hu EFI, February 2003 Connections to the Past Outline What does MAP alone add to the cosmology? What role do other anisotropy experiments still have to play? How do you use the MAP analysis
The AfterMap Wayne Hu EFI, February 2003 Connections to the Past Outline What does MAP alone add to the cosmology? What role do other anisotropy experiments still have to play? How do you use the MAP analysis
CMB Anisotropies: The Acoustic Peaks. Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI. l (multipole) Astro 280, Spring 2002 Wayne Hu
 CMB Anisotropies: The Acoustic Peaks 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI 500 1000 1500 l (multipole) Astro 280, Spring 2002 Wayne Hu Physical Landscape 100 IAB Sask 80 Viper BAM TOCO Sound Waves
CMB Anisotropies: The Acoustic Peaks 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI 500 1000 1500 l (multipole) Astro 280, Spring 2002 Wayne Hu Physical Landscape 100 IAB Sask 80 Viper BAM TOCO Sound Waves
n=0 l (cos θ) (3) C l a lm 2 (4)
 Cosmic Concordance What does the power spectrum of the CMB tell us about the universe? For that matter, what is a power spectrum? In this lecture we will examine the current data and show that we now have
Cosmic Concordance What does the power spectrum of the CMB tell us about the universe? For that matter, what is a power spectrum? In this lecture we will examine the current data and show that we now have
An Estimator for statistical anisotropy from the CMB. CMB bispectrum
 An Estimator for statistical anisotropy from the CMB bispectrum 09/29/2012 1 2 3 4 5 6 ...based on: N. Bartolo, E. D., M. Liguori, S. Matarrese, A. Riotto JCAP 1201:029 N. Bartolo, E. D., S. Matarrese,
An Estimator for statistical anisotropy from the CMB bispectrum 09/29/2012 1 2 3 4 5 6 ...based on: N. Bartolo, E. D., M. Liguori, S. Matarrese, A. Riotto JCAP 1201:029 N. Bartolo, E. D., S. Matarrese,
Observational Cosmology
 The Cosmic Microwave Background Part I: CMB Theory Kaustuv Basu Course website: http://www.astro.uni-bonn.de/~kbasu/obscosmo CMB parameter cheat sheet 2 Make your own CMB experiment! Design experiment
The Cosmic Microwave Background Part I: CMB Theory Kaustuv Basu Course website: http://www.astro.uni-bonn.de/~kbasu/obscosmo CMB parameter cheat sheet 2 Make your own CMB experiment! Design experiment
Cosmology with cosmic microwave background anisotropy
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 4 journal of October 2006 physics pp. 699 710 Cosmology with cosmic microwave background anisotropy TARUN SOURADEEP Inter-University Centre for Astronomy
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 4 journal of October 2006 physics pp. 699 710 Cosmology with cosmic microwave background anisotropy TARUN SOURADEEP Inter-University Centre for Astronomy
CMB Anisotropies Episode II :
 CMB Anisotropies Episode II : Attack of the C l ones Approximation Methods & Cosmological Parameter Dependencies By Andy Friedman Astronomy 200, Harvard University, Spring 2003 Outline Elucidating the
CMB Anisotropies Episode II : Attack of the C l ones Approximation Methods & Cosmological Parameter Dependencies By Andy Friedman Astronomy 200, Harvard University, Spring 2003 Outline Elucidating the
The Once and Future CMB
 The Once and Future CMB DOE, Jan. 2002 Wayne Hu The On(c)e Ring Original Power Spectra of Maps 64º Band Filtered Ringing in the New Cosmology Gravitational Ringing Potential wells = inflationary seeds
The Once and Future CMB DOE, Jan. 2002 Wayne Hu The On(c)e Ring Original Power Spectra of Maps 64º Band Filtered Ringing in the New Cosmology Gravitational Ringing Potential wells = inflationary seeds
What can we Learn from the Cosmic Microwave Background
 What can we Learn from the Cosmic Microwave Background Problem Set #3 will be due in part on April 8 and in full on April 11 Solutions to Problem Set #2 are online... graded versions soon Again I m asking
What can we Learn from the Cosmic Microwave Background Problem Set #3 will be due in part on April 8 and in full on April 11 Solutions to Problem Set #2 are online... graded versions soon Again I m asking
CMB Theory, Observations and Interpretation
 CMB Theory, Observations and Interpretation Danielle Wills Seminar on Astroparticle Physics 14 May 2010 Physikalisches Institut Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn Outline of what will follow
CMB Theory, Observations and Interpretation Danielle Wills Seminar on Astroparticle Physics 14 May 2010 Physikalisches Institut Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn Outline of what will follow
COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND ANISOTROPIES
 COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND ANISOTROPIES Anthony Challinor Institute of Astronomy & Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge, U.K. a.d.challinor@ast.cam.ac.uk 26
COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND ANISOTROPIES Anthony Challinor Institute of Astronomy & Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge, U.K. a.d.challinor@ast.cam.ac.uk 26
Priming the BICEP. Wayne Hu Chicago, March BB
 Priming the BICEP 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01 0 0.01 BB 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 Wayne Hu Chicago, March 2014 A BICEP Primer How do gravitational waves affect the CMB temperature and polarization spectrum?
Priming the BICEP 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01 0 0.01 BB 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 Wayne Hu Chicago, March 2014 A BICEP Primer How do gravitational waves affect the CMB temperature and polarization spectrum?
Microwave Background Polarization: Theoretical Perspectives
 Microwave Background Polarization: Theoretical Perspectives Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Pittsburgh CMBpol Technology Workshop Outline Tensor Perturbations and Microwave Polarization
Microwave Background Polarization: Theoretical Perspectives Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Pittsburgh CMBpol Technology Workshop Outline Tensor Perturbations and Microwave Polarization
Deconvoluting CMB (and other data sets)
 University of Warsaw 4th February 29 Introduction The WMAP results show that the primordial density perturbations are coherent, predominantly adiabatic and generated on superhorizon scales. Why is the
University of Warsaw 4th February 29 Introduction The WMAP results show that the primordial density perturbations are coherent, predominantly adiabatic and generated on superhorizon scales. Why is the
The ultimate measurement of the CMB temperature anisotropy field UNVEILING THE CMB SKY
 The ultimate measurement of the CMB temperature anisotropy field UNVEILING THE CMB SKY PARAMETRIC MODEL 16 spectra in total C(θ) = CMB theoretical spectra plus physically motivated templates for the
The ultimate measurement of the CMB temperature anisotropy field UNVEILING THE CMB SKY PARAMETRIC MODEL 16 spectra in total C(θ) = CMB theoretical spectra plus physically motivated templates for the
Wavelets Applied to CMB Analysis
 Wavelets Applied to CMB Analysis CMB non-gaussianity Constraining the Primordial Power Spectrum IPAM, Nov 2004 Pia Mukherjee, Astronomy Centre, University of Sussex The Universe.. is a perturbed Robertson
Wavelets Applied to CMB Analysis CMB non-gaussianity Constraining the Primordial Power Spectrum IPAM, Nov 2004 Pia Mukherjee, Astronomy Centre, University of Sussex The Universe.. is a perturbed Robertson
Introduction. How did the universe evolve to what it is today?
 Cosmology 8 1 Introduction 8 2 Cosmology: science of the universe as a whole How did the universe evolve to what it is today? Based on four basic facts: The universe expands, is isotropic, and is homogeneous.
Cosmology 8 1 Introduction 8 2 Cosmology: science of the universe as a whole How did the universe evolve to what it is today? Based on four basic facts: The universe expands, is isotropic, and is homogeneous.
Rayleigh scattering:
 Rayleigh scattering: blue sky thinking for future CMB observations arxiv:1307.8148; previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Rayleigh scattering: blue sky thinking for future CMB observations arxiv:1307.8148; previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Polarization from Rayleigh scattering
 Polarization from Rayleigh scattering Blue sky thinking for future CMB observations Previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Polarization from Rayleigh scattering Blue sky thinking for future CMB observations Previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
BipoSH Representation: Modulation & Systematics
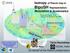 Isotropy of Planck map in C l L=0 BipoSH Representation: Modulation & Systematics Planck 2013 results. XXIII. Isotropy and statistics of the CMB L=10 Spherical harmonic l Planck unveils the Cosmic Microwave
Isotropy of Planck map in C l L=0 BipoSH Representation: Modulation & Systematics Planck 2013 results. XXIII. Isotropy and statistics of the CMB L=10 Spherical harmonic l Planck unveils the Cosmic Microwave
The oldest science? One of the most rapidly evolving fields of modern research. Driven by observations and instruments
 The oldest science? One of the most rapidly evolving fields of modern research. Driven by observations and instruments Intersection of physics (fundamental laws) and astronomy (contents of the universe)
The oldest science? One of the most rapidly evolving fields of modern research. Driven by observations and instruments Intersection of physics (fundamental laws) and astronomy (contents of the universe)
The first light in the universe
 The first light in the universe Aniello Mennella Università degli Studi di Milano Dipartimento di Fisica Photons in the early universe Early universe is a hot and dense expanding plasma 14 May 1964, 11:15
The first light in the universe Aniello Mennella Università degli Studi di Milano Dipartimento di Fisica Photons in the early universe Early universe is a hot and dense expanding plasma 14 May 1964, 11:15
Physics 661. Particle Physics Phenomenology. October 2, Physics 661, lecture 2
 Physics 661 Particle Physics Phenomenology October 2, 2003 Evidence for theory: Hot Big Bang Model Present expansion of the Universe Existence of cosmic microwave background radiation Relative abundance
Physics 661 Particle Physics Phenomenology October 2, 2003 Evidence for theory: Hot Big Bang Model Present expansion of the Universe Existence of cosmic microwave background radiation Relative abundance
Lecture 03. The Cosmic Microwave Background
 The Cosmic Microwave Background 1 Photons and Charge Remember the lectures on particle physics Photons are the bosons that transmit EM force Charged particles interact by exchanging photons But since they
The Cosmic Microwave Background 1 Photons and Charge Remember the lectures on particle physics Photons are the bosons that transmit EM force Charged particles interact by exchanging photons But since they
The Silk Damping Tail of the CMB l. Wayne Hu Oxford, December 2002
 The Silk Damping Tail of the CMB 100 T (µk) 10 10 100 1000 l Wayne Hu Oxford, December 2002 Outline Damping tail of temperature power spectrum and its use as a standard ruler Generation of polarization
The Silk Damping Tail of the CMB 100 T (µk) 10 10 100 1000 l Wayne Hu Oxford, December 2002 Outline Damping tail of temperature power spectrum and its use as a standard ruler Generation of polarization
An Acoustic Primer. Wayne Hu Astro 448. l (multipole) BOOMERanG MAXIMA Previous COBE. W. Hu Dec. 2000
 An Acoustic Primer 100 BOOMERanG MAXIMA Previous 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 COBE W. Hu Dec. 2000 10 100 l (multipole) Wayne Hu Astro 448 CMB Anisotropies COBE Maxima Hanany, et al. (2000) BOOMERanG de Bernardis,
An Acoustic Primer 100 BOOMERanG MAXIMA Previous 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 COBE W. Hu Dec. 2000 10 100 l (multipole) Wayne Hu Astro 448 CMB Anisotropies COBE Maxima Hanany, et al. (2000) BOOMERanG de Bernardis,
 COSMOLOGY PHYS 30392 COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND RADIATION Giampaolo Pisano - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics The University of Manchester - April 2013 http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~gp/ giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk
COSMOLOGY PHYS 30392 COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND RADIATION Giampaolo Pisano - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics The University of Manchester - April 2013 http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~gp/ giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk
Cosmology & CMB. Set6: Polarisation & Secondary Anisotropies. Davide Maino
 Cosmology & CMB Set6: Polarisation & Secondary Anisotropies Davide Maino Polarisation How? Polarisation is generated via Compton/Thomson scattering (angular dependence of the scattering term M) Who? Only
Cosmology & CMB Set6: Polarisation & Secondary Anisotropies Davide Maino Polarisation How? Polarisation is generated via Compton/Thomson scattering (angular dependence of the scattering term M) Who? Only
CMB beyond a single power spectrum: Non-Gaussianity and frequency dependence. Antony Lewis
 CMB beyond a single power spectrum: Non-Gaussianity and frequency dependence Antony Lewis http://cosmologist.info/ Evolution of the universe Opaque Transparent Hu & White, Sci. Am., 290 44 (2004) CMB temperature
CMB beyond a single power spectrum: Non-Gaussianity and frequency dependence Antony Lewis http://cosmologist.info/ Evolution of the universe Opaque Transparent Hu & White, Sci. Am., 290 44 (2004) CMB temperature
Cosmic Variance of the Three-Point Correlation Function of the Cosmic Microwave Background
 CfPA 93 th 18 astro-ph/9306012 June 1993 REVISED arxiv:astro-ph/9306012v2 14 Jul 1993 Cosmic Variance of the Three-Point Correlation Function of the Cosmic Microwave Background Mark Srednicki* Center for
CfPA 93 th 18 astro-ph/9306012 June 1993 REVISED arxiv:astro-ph/9306012v2 14 Jul 1993 Cosmic Variance of the Three-Point Correlation Function of the Cosmic Microwave Background Mark Srednicki* Center for
Correlations between the Cosmic Microwave Background and Infrared Galaxies
 Correlations between the Cosmic Microwave Background and Infrared Galaxies Brett Scheiner & Jake McCoy Based on work by Goto, Szapudi and Granett (2012) http://cdsads.u-strasbg.fr/abs/2012mnras.422l..77g
Correlations between the Cosmic Microwave Background and Infrared Galaxies Brett Scheiner & Jake McCoy Based on work by Goto, Szapudi and Granett (2012) http://cdsads.u-strasbg.fr/abs/2012mnras.422l..77g
Cosmology. Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick.
 Cosmology Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick http://astro.uni-tuebingen.de/~wilms/teach/cosmo Contents 2 Old Cosmology Space and Time Friedmann Equations World Models Modern Cosmology
Cosmology Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick http://astro.uni-tuebingen.de/~wilms/teach/cosmo Contents 2 Old Cosmology Space and Time Friedmann Equations World Models Modern Cosmology
Structures in the early Universe. Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4
 Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview Part 1: problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Part : Need for
Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview Part 1: problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Part : Need for
Thermal History of the Universe and the Cosmic Microwave Background. II. Structures in the Microwave Background
 Thermal History of the Universe and the Cosmic Microwave Background. II. Structures in the Microwave Background Matthias Bartelmann Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik IMPRS Lecture, March 2003 Part 2:
Thermal History of the Universe and the Cosmic Microwave Background. II. Structures in the Microwave Background Matthias Bartelmann Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik IMPRS Lecture, March 2003 Part 2:
Structure in the CMB
 Cosmic Microwave Background Anisotropies = structure in the CMB Structure in the CMB Boomerang balloon flight. Mapped Cosmic Background Radiation with far higher angular resolution than previously available.
Cosmic Microwave Background Anisotropies = structure in the CMB Structure in the CMB Boomerang balloon flight. Mapped Cosmic Background Radiation with far higher angular resolution than previously available.
Variation in the cosmic baryon fraction and the CMB
 Variation in the cosmic baryon fraction and the CMB with D. Hanson, G. Holder, O. Doré, and M. Kamionkowski Daniel Grin (KICP/Chicago) Presentation for CAP workshop 09/24/2013 arxiv: 1107.1716 (DG, OD,
Variation in the cosmic baryon fraction and the CMB with D. Hanson, G. Holder, O. Doré, and M. Kamionkowski Daniel Grin (KICP/Chicago) Presentation for CAP workshop 09/24/2013 arxiv: 1107.1716 (DG, OD,
WMAP 9-Year Results and Cosmological Implications: The Final Results
 WMAP 9-Year Results and Cosmological Implications: The Final Results Eiichiro Komatsu (Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik) 17th Paris Cosmology Colloquium 2013 Observatoire de Paris, July 24, 2013 1 used
WMAP 9-Year Results and Cosmological Implications: The Final Results Eiichiro Komatsu (Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik) 17th Paris Cosmology Colloquium 2013 Observatoire de Paris, July 24, 2013 1 used
Astronomy 422. Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background
 Astronomy 422 Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background Key concepts: The CMB Recombination Radiation and matter eras Next time: Astro 422 Peer Review - Make sure to read all 6 proposals and send in rankings
Astronomy 422 Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background Key concepts: The CMB Recombination Radiation and matter eras Next time: Astro 422 Peer Review - Make sure to read all 6 proposals and send in rankings
Testing parity violation with the CMB
 Testing parity violation with the CMB Paolo Natoli Università di Ferrara (thanks to Alessandro Gruppuso)! ISSS L Aquila 24 April 2014 Introduction The aim is to use observed properties of CMB pattern to
Testing parity violation with the CMB Paolo Natoli Università di Ferrara (thanks to Alessandro Gruppuso)! ISSS L Aquila 24 April 2014 Introduction The aim is to use observed properties of CMB pattern to
The Cosmic Background Radiation
 The Cosmic Background Radiation 1. Expansion history of the universe At time of inflation, we have three fundamental scalar fields: Higgs, inflaton, dark energy. We still don t know what dark energy is,
The Cosmic Background Radiation 1. Expansion history of the universe At time of inflation, we have three fundamental scalar fields: Higgs, inflaton, dark energy. We still don t know what dark energy is,
Lecture 3+1: Cosmic Microwave Background
 Lecture 3+1: Cosmic Microwave Background Structure Formation and the Dark Sector Wayne Hu Trieste, June 2002 Large Angle Anisotropies Actual Temperature Data Really Isotropic! Large Angle Anisotropies
Lecture 3+1: Cosmic Microwave Background Structure Formation and the Dark Sector Wayne Hu Trieste, June 2002 Large Angle Anisotropies Actual Temperature Data Really Isotropic! Large Angle Anisotropies
20 Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation continued
 PHYS 652: Astrophysics 103 20 Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation continued Innocent light-minded men, who think that astronomy can be learnt by looking at the stars without knowledge of
PHYS 652: Astrophysics 103 20 Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation continued Innocent light-minded men, who think that astronomy can be learnt by looking at the stars without knowledge of
The Theory of Inflationary Perturbations
 The Theory of Inflationary Perturbations Jérôme Martin Institut d Astrophysique de Paris (IAP) Indian Institute of Technology, Chennai 03/02/2012 1 Introduction Outline A brief description of inflation
The Theory of Inflationary Perturbations Jérôme Martin Institut d Astrophysique de Paris (IAP) Indian Institute of Technology, Chennai 03/02/2012 1 Introduction Outline A brief description of inflation
Connecting Quarks to the Cosmos
 Connecting Quarks to the Cosmos Institute for Nuclear Theory 29 June to 10 July 2009 Inflationary Cosmology II Michael S. Turner Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Michael
Connecting Quarks to the Cosmos Institute for Nuclear Theory 29 June to 10 July 2009 Inflationary Cosmology II Michael S. Turner Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Michael
Primordial gravitational waves detected? Atsushi Taruya
 21 May 2014 Lunch seminar @YITP Primordial gravitational waves detected? Atsushi Taruya Contents Searching for primordial gravitational waves from cosmic microwave background polarizations Gravitational-wave
21 May 2014 Lunch seminar @YITP Primordial gravitational waves detected? Atsushi Taruya Contents Searching for primordial gravitational waves from cosmic microwave background polarizations Gravitational-wave
El Universo en Expansion. Juan García-Bellido Inst. Física Teórica UAM Benasque, 12 Julio 2004
 El Universo en Expansion Juan García-Bellido Inst. Física Teórica UAM Benasque, 12 Julio 2004 5 billion years (you are here) Space is Homogeneous and Isotropic General Relativity An Expanding Universe
El Universo en Expansion Juan García-Bellido Inst. Física Teórica UAM Benasque, 12 Julio 2004 5 billion years (you are here) Space is Homogeneous and Isotropic General Relativity An Expanding Universe
The Outtakes. Back to Talk. Foregrounds Doppler Peaks? SNIa Complementarity Polarization Primer Gamma Approximation ISW Effect
 The Outtakes CMB Transfer Function Testing Inflation Weighing Neutrinos Decaying Neutrinos Testing Λ Testing Quintessence Polarization Sensitivity SDSS Complementarity Secondary Anisotropies Doppler Effect
The Outtakes CMB Transfer Function Testing Inflation Weighing Neutrinos Decaying Neutrinos Testing Λ Testing Quintessence Polarization Sensitivity SDSS Complementarity Secondary Anisotropies Doppler Effect
Cosmology after Planck
 Cosmology after Planck Raphael Flauger Rencontres de Moriond, March 23, 2014 Looking back Until ca. 1997 data was consistent with defects (such as strings) generating the primordial perturbations. (Pen,
Cosmology after Planck Raphael Flauger Rencontres de Moriond, March 23, 2014 Looking back Until ca. 1997 data was consistent with defects (such as strings) generating the primordial perturbations. (Pen,
Cosmology II: The thermal history of the Universe
 .. Cosmology II: The thermal history of the Universe Ruth Durrer Département de Physique Théorique et CAP Université de Genève Suisse August 6, 2014 Ruth Durrer (Université de Genève) Cosmology II August
.. Cosmology II: The thermal history of the Universe Ruth Durrer Département de Physique Théorique et CAP Université de Genève Suisse August 6, 2014 Ruth Durrer (Université de Genève) Cosmology II August
Concordance Cosmology and Particle Physics. Richard Easther (Yale University)
 Concordance Cosmology and Particle Physics Richard Easther (Yale University) Concordance Cosmology The standard model for cosmology Simplest model that fits the data Smallest number of free parameters
Concordance Cosmology and Particle Physics Richard Easther (Yale University) Concordance Cosmology The standard model for cosmology Simplest model that fits the data Smallest number of free parameters
V. The Thermal Beginning of the Universe
 V. The Thermal Beginning of the Universe I. Aretxaga Jan 2014 CMB discovery time-line -1947-1948 Gamow, Alpher and Hermans model of nucleosynthesis predicts relic millimeter radiation, but the models have
V. The Thermal Beginning of the Universe I. Aretxaga Jan 2014 CMB discovery time-line -1947-1948 Gamow, Alpher and Hermans model of nucleosynthesis predicts relic millimeter radiation, but the models have
Brief Introduction to Cosmology
 Brief Introduction to Cosmology Matias Zaldarriaga Harvard University August 2006 Basic Questions in Cosmology: How does the Universe evolve? What is the universe made off? How is matter distributed? How
Brief Introduction to Cosmology Matias Zaldarriaga Harvard University August 2006 Basic Questions in Cosmology: How does the Universe evolve? What is the universe made off? How is matter distributed? How
Imprint of Scalar Dark Energy on CMB polarization
 Imprint of Scalar Dark Energy on CMB polarization Kin-Wang Ng ( 吳建宏 ) Institute of Physics & Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, Taiwan Cosmology and Gravity Pre-workshop NTHU, Apr
Imprint of Scalar Dark Energy on CMB polarization Kin-Wang Ng ( 吳建宏 ) Institute of Physics & Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, Taiwan Cosmology and Gravity Pre-workshop NTHU, Apr
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 9 Aug 2006
 Angular power spectrum of CMB anisotropy from WMAP Tarun Souradeep 1, Rajib Saha 1,2 and Pankaj Jain 2 arxiv:astro-ph/0608199v1 9 Aug 2006 1 Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA),
Angular power spectrum of CMB anisotropy from WMAP Tarun Souradeep 1, Rajib Saha 1,2 and Pankaj Jain 2 arxiv:astro-ph/0608199v1 9 Aug 2006 1 Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA),
Cosmic Microwave Background
 Cosmic Microwave Background Following recombination, photons that were coupled to the matter have had very little subsequent interaction with matter. Now observed as the cosmic microwave background. Arguably
Cosmic Microwave Background Following recombination, photons that were coupled to the matter have had very little subsequent interaction with matter. Now observed as the cosmic microwave background. Arguably
STUDY OF THE LARGE-SCALE STRUCTURE OF THE UNIVERSE USING GALAXY CLUSTERS
 STUDY OF THE LARGE-SCALE STRUCTURE OF THE UNIVERSE USING GALAXY CLUSTERS BÙI VĂN TUẤN Advisors: Cyrille Rosset, Michel Crézé, James G. Bartlett ASTROPARTICLE AND COSMOLOGY LABORATORY PARIS DIDEROT UNIVERSITY
STUDY OF THE LARGE-SCALE STRUCTURE OF THE UNIVERSE USING GALAXY CLUSTERS BÙI VĂN TUẤN Advisors: Cyrille Rosset, Michel Crézé, James G. Bartlett ASTROPARTICLE AND COSMOLOGY LABORATORY PARIS DIDEROT UNIVERSITY
Tomography with CMB polarization A line-of-sight approach in real space
 Tomography with CMB polarization A line-of-sight approach in real space University of Pennsylvania - feb/2009 L. Raul Abramo Instituto de Física University of Sao Paulo L. Raul Abramo & H. Xavier, Phys.
Tomography with CMB polarization A line-of-sight approach in real space University of Pennsylvania - feb/2009 L. Raul Abramo Instituto de Física University of Sao Paulo L. Raul Abramo & H. Xavier, Phys.
Simulating Cosmic Microwave Background Fluctuations
 Simulating Cosmic Microwave Background Fluctuations Mario Bisi Emma Kerswill Picture taken from: http://astro.uchicago.edu/~tyler/omegab.html Introduction What is the CMB and how was it formed? Why is
Simulating Cosmic Microwave Background Fluctuations Mario Bisi Emma Kerswill Picture taken from: http://astro.uchicago.edu/~tyler/omegab.html Introduction What is the CMB and how was it formed? Why is
Archaeology of Our Universe YIFU CAI ( 蔡一夫 )
 Archaeology of Our Universe YIFU CAI ( 蔡一夫 ) 2013-11-05 Thermal History Primordial era 13.8 billion years by WMAP/NASA Large Scale Structure (LSS) by 2MASS Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) by ESA/Planck
Archaeology of Our Universe YIFU CAI ( 蔡一夫 ) 2013-11-05 Thermal History Primordial era 13.8 billion years by WMAP/NASA Large Scale Structure (LSS) by 2MASS Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) by ESA/Planck
Physics Nobel Prize 2006
 Physics Nobel Prize 2006 Ghanashyam Date The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai http://www.imsc.res.in shyam@imsc.res.in Nov 4, 2006. Organization of the Talk Organization of the Talk Nobel Laureates
Physics Nobel Prize 2006 Ghanashyam Date The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai http://www.imsc.res.in shyam@imsc.res.in Nov 4, 2006. Organization of the Talk Organization of the Talk Nobel Laureates
Physics of CMB Polarization and Its Measurement
 Physics of CMB Polarization and Its Measurement HEP seminar at Kyoto University April 13 th, 2007 Akito KUSAKA University of Tokyo Outline Physics of CMB and its Polarization What does WMAP shed light
Physics of CMB Polarization and Its Measurement HEP seminar at Kyoto University April 13 th, 2007 Akito KUSAKA University of Tokyo Outline Physics of CMB and its Polarization What does WMAP shed light
MASAHIDE YAMAGUCHI. Quantum generation of density perturbations in the early Universe. (Tokyo Institute of Technology)
 Quantum generation of density perturbations in the early Universe MASAHIDE YAMAGUCHI (Tokyo Institute of Technology) 03/07/16@Symposium: New Generation Quantum Theory -Particle Physics, Cosmology, and
Quantum generation of density perturbations in the early Universe MASAHIDE YAMAGUCHI (Tokyo Institute of Technology) 03/07/16@Symposium: New Generation Quantum Theory -Particle Physics, Cosmology, and
MODERN COSMOLOGY LECTURE FYTN08
 1/43 MODERN COSMOLOGY LECTURE Lund University bijnens@thep.lu.se http://www.thep.lu.se/ bijnens Lecture Updated 2015 2/43 3/43 1 2 Some problems with a simple expanding universe 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Credit many
1/43 MODERN COSMOLOGY LECTURE Lund University bijnens@thep.lu.se http://www.thep.lu.se/ bijnens Lecture Updated 2015 2/43 3/43 1 2 Some problems with a simple expanding universe 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Credit many
Physics 463, Spring 07. Formation and Evolution of Structure: Growth of Inhomogenieties & the Linear Power Spectrum
 Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 3 Formation and Evolution of Structure: Growth of Inhomogenieties & the Linear Power Spectrum last time: how fluctuations are generated and how the smooth Universe grows
Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 3 Formation and Evolution of Structure: Growth of Inhomogenieties & the Linear Power Spectrum last time: how fluctuations are generated and how the smooth Universe grows
AST5220 lecture 2 An introduction to the CMB power spectrum. Hans Kristian Eriksen
 AST5220 lecture 2 An introduction to the CMB power spectrum Hans Kristian Eriksen Cosmology in ~five slides The basic ideas of Big Bang: 1) The Big Bang model The universe expands today Therefore it must
AST5220 lecture 2 An introduction to the CMB power spectrum Hans Kristian Eriksen Cosmology in ~five slides The basic ideas of Big Bang: 1) The Big Bang model The universe expands today Therefore it must
Absolute Neutrino Mass from Cosmology. Manoj Kaplinghat UC Davis
 Absolute Neutrino Mass from Cosmology Manoj Kaplinghat UC Davis Kinematic Constraints on Neutrino Mass Tritium decay (Mainz Collaboration, Bloom et al, Nucl. Phys. B91, 273, 2001) p and t decay Future
Absolute Neutrino Mass from Cosmology Manoj Kaplinghat UC Davis Kinematic Constraints on Neutrino Mass Tritium decay (Mainz Collaboration, Bloom et al, Nucl. Phys. B91, 273, 2001) p and t decay Future
Inflation. Week 9. ASTR/PHYS 4080: Introduction to Cosmology
 Inflation ASTR/PHYS 4080: Intro to Cosmology Week 9 1 Successes of the Hot Big Bang Model Consists of: General relativity Cosmological principle Known atomic/nuclear/particle physics Explains: dark night
Inflation ASTR/PHYS 4080: Intro to Cosmology Week 9 1 Successes of the Hot Big Bang Model Consists of: General relativity Cosmological principle Known atomic/nuclear/particle physics Explains: dark night
Large Scale Structure After these lectures, you should be able to: Describe the matter power spectrum Explain how and why the peak position depends on
 Observational cosmology: Large scale structure Filipe B. Abdalla Kathleen Lonsdale Building G.22 http://zuserver2.star.ucl.ac.uk/~hiranya/phas3136/phas3136 Large Scale Structure After these lectures, you
Observational cosmology: Large scale structure Filipe B. Abdalla Kathleen Lonsdale Building G.22 http://zuserver2.star.ucl.ac.uk/~hiranya/phas3136/phas3136 Large Scale Structure After these lectures, you
Physical Cosmology 6/6/2016
 Physical Cosmology 6/6/2016 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2016 CMB anisotropies The temperature fluctuation in
Physical Cosmology 6/6/2016 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2016 CMB anisotropies The temperature fluctuation in
From inflation to the CMB to today s universe. I - How it all begins
 From inflation to the CMB to today s universe I - How it all begins Raul Abramo Physics Institute - University of São Paulo abramo@fma.if.usp.br redshift Very brief cosmic history 10 9 200 s BBN 1 MeV
From inflation to the CMB to today s universe I - How it all begins Raul Abramo Physics Institute - University of São Paulo abramo@fma.if.usp.br redshift Very brief cosmic history 10 9 200 s BBN 1 MeV
Taking the Measure of the Universe. Gary Hinshaw University of British Columbia TRIUMF Saturday Series 24 November 2012
 Taking the Measure of the Universe Gary Hinshaw University of British Columbia TRIUMF Saturday Series 24 November 2012 The Big Bang Theory What is wrong with this picture? The Big Bang Theory The Big bang
Taking the Measure of the Universe Gary Hinshaw University of British Columbia TRIUMF Saturday Series 24 November 2012 The Big Bang Theory What is wrong with this picture? The Big Bang Theory The Big bang
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 7 Galaxy Sample
 Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 7 Galaxy Sample BOMEE LEE 1. Brief Introduction about BAO In our previous class we learned what is the Baryon Acoustic Oscillations(BAO).
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 7 Galaxy Sample BOMEE LEE 1. Brief Introduction about BAO In our previous class we learned what is the Baryon Acoustic Oscillations(BAO).
Gravitational Lensing of the CMB
 Gravitational Lensing of the CMB SNAP Planck 1 Ω DE 1 w a.5-2 -1.5 w -1 -.5 Wayne Hu Leiden, August 26-1 Outline Gravitational Lensing of Temperature and Polarization Fields Cosmological Observables from
Gravitational Lensing of the CMB SNAP Planck 1 Ω DE 1 w a.5-2 -1.5 w -1 -.5 Wayne Hu Leiden, August 26-1 Outline Gravitational Lensing of Temperature and Polarization Fields Cosmological Observables from
4 Evolution of density perturbations
 Spring term 2014: Dark Matter lecture 3/9 Torsten Bringmann (torsten.bringmann@fys.uio.no) reading: Weinberg, chapters 5-8 4 Evolution of density perturbations 4.1 Statistical description The cosmological
Spring term 2014: Dark Matter lecture 3/9 Torsten Bringmann (torsten.bringmann@fys.uio.no) reading: Weinberg, chapters 5-8 4 Evolution of density perturbations 4.1 Statistical description The cosmological
AST5220 lecture 2 An introduction to the CMB power spectrum. Hans Kristian Eriksen
 AST5220 lecture 2 An introduction to the CMB power spectrum Hans Kristian Eriksen Cosmology in ~five slides The basic ideas of Big Bang: 1) The Big Bang model The universe expands today Therefore it must
AST5220 lecture 2 An introduction to the CMB power spectrum Hans Kristian Eriksen Cosmology in ~five slides The basic ideas of Big Bang: 1) The Big Bang model The universe expands today Therefore it must
Primordial Gravitational waves and the polarization of the CMB. José Alberto Rubiño Martín (IAC, Tenerife)
 Primordial Gravitational waves and the polarization of the CMB José Alberto Rubiño Martín (IAC, Tenerife) Outline Lecture 1. Theory of CMB polarization. E and B modes. Primordial Gravitational waves. Observational
Primordial Gravitational waves and the polarization of the CMB José Alberto Rubiño Martín (IAC, Tenerife) Outline Lecture 1. Theory of CMB polarization. E and B modes. Primordial Gravitational waves. Observational
BARYON ACOUSTIC OSCILLATIONS. Cosmological Parameters and You
 BARYON ACOUSTIC OSCILLATIONS Cosmological Parameters and You OUTLINE OF TOPICS Definitions of Terms Big Picture (Cosmology) What is going on (History) An Acoustic Ruler(CMB) Measurements in Time and Space
BARYON ACOUSTIC OSCILLATIONS Cosmological Parameters and You OUTLINE OF TOPICS Definitions of Terms Big Picture (Cosmology) What is going on (History) An Acoustic Ruler(CMB) Measurements in Time and Space
Observing the Dimensionality of Our Parent Vacuum
 Observing the Dimensionality of Our Parent Vacuum Surjeet Rajendran, Johns Hopkins with Peter Graham and Roni Harnik arxiv:1003.0236 Inspiration Why is the universe 3 dimensional? What is the overall shape
Observing the Dimensionality of Our Parent Vacuum Surjeet Rajendran, Johns Hopkins with Peter Graham and Roni Harnik arxiv:1003.0236 Inspiration Why is the universe 3 dimensional? What is the overall shape
Structures in the early Universe. Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4
 Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Need for an exponential
Structures in the early Universe Particle Astrophysics chapter 8 Lecture 4 overview problems in Standard Model of Cosmology: horizon and flatness problems presence of structures Need for an exponential
Mysteries of the large-angle microwave sky
 Mysteries of the large-angle microwave sky Dragan Huterer Physics Department University of Michigan Collaborators: Craig Copi (CWRU), Dominik Schwarz (Bielefeld), Glenn Starkman (CWRU) Chris Gordon, Wayne
Mysteries of the large-angle microwave sky Dragan Huterer Physics Department University of Michigan Collaborators: Craig Copi (CWRU), Dominik Schwarz (Bielefeld), Glenn Starkman (CWRU) Chris Gordon, Wayne
Looking Beyond the Cosmological Horizon
 Looking Beyond the Cosmological Horizon 175 µk 175 µk Observable Universe Adrienne Erickcek in collaboration with Sean Carroll and Marc Kamionkowski A Hemispherical Power Asymmetry from Inflation Phys.
Looking Beyond the Cosmological Horizon 175 µk 175 µk Observable Universe Adrienne Erickcek in collaboration with Sean Carroll and Marc Kamionkowski A Hemispherical Power Asymmetry from Inflation Phys.
Primordial nongaussianities I: cosmic microwave background. Uros Seljak, UC Berkeley Rio de Janeiro, August 2014
 Primordial nongaussianities I: cosmic microwave bacground Uros Selja, UC Bereley Rio de Janeiro, August 2014 Outline Primordial nongaussianity Introduction and basic physics CMB temperature power spectrum
Primordial nongaussianities I: cosmic microwave bacground Uros Selja, UC Bereley Rio de Janeiro, August 2014 Outline Primordial nongaussianity Introduction and basic physics CMB temperature power spectrum
