Cosmology & CMB. Set6: Polarisation & Secondary Anisotropies. Davide Maino
|
|
|
- Ruth McDaniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cosmology & CMB Set6: Polarisation & Secondary Anisotropies Davide Maino
2 Polarisation How? Polarisation is generated via Compton/Thomson scattering (angular dependence of the scattering term M) Who? Only quadrupole anisotropy is able to produce linear polarisation When? Near recombination Θ 2 is at 5-10% level of Θ 0
3 Polarisation Linear polarisation is described by Stokes Q and U parameters Q measures differences of intensities along the x and y axes, while U measures same differences but in a 45 rotated frame Stokes are not in general rotationally invariant Q = Qcos(2ψ) Usin(2ψ) U = Ucos(2ψ) + Qsin(2ψ) Q ± iu = e ±2iψ (Q ± iu) (Q ± iu) transform like a spin-2 tensor
4 Polarisation: Spin weighted spherical harmonics A general spin-2 tensor on a sphere is properly represented by spin-s spherical harmonics s Y lm Under rotation: s Y lm e ±isψ sy lm Normality and completeness dˆn s Ylm (ˆn) sy l m (ˆn) = δ ll δ mm sylm (ˆn) sy lm (ˆn ) = δ(φ φ )δ(cosθ cos(θ ) lm
5 Polarisation: All-sky decomposition [Q ± iu](n) = l,m a ±2 lm ±2Y lm (n) = l,m (a E,lm ± ia B,lm ) ±2 Y lm (n) E (gradient) and B (curl) modes are a E,lm = 1 2 (a+2 lm + a 2 lm ) a B,lm = i 2 (a+2 lm a 2 lm )
6 Polarisation: Power Spectra Four parity-independent power spectra C TT = 1 2l + 1 C EE = 1 2l + 1 a T,lm a T,lm C TE = 1 a T,lm 2l + 1 a E,lm m m a E,lm a E,lm C BB = 1 a B,lm 2l + 1 a B,lm m E-modes are generated by both scalar (density) and tensor (gw) perturbation B-modes are generated only by tensor perturbation: direct probe of inflation m
7 Polarisation: Power Spectra
8 Current Status of measurements Planck-2015 provides the best current measurements of E and TE power spectra
9 Secondary Anisotropies CMB photons traverse the large-scale structure of the Universe from z 1000 to the present Having nearly scale-invariant adiabatic fluctuations (from CMB observations), structures form bottom-up i.e. small scales first. Hierarchical structure formation. First objects (starts) re-ionize the Universe between z 7 30 Gravitational: Integrated Sach-Wolfe effect (ISW), gravitational lensing Scattering: peak suppression, large-angle polarisation (Compton scattering)
10 Gravitational Secondaries
11 Transfer Function We observe the distribution of matter predominantly at late epochs (now) It is possible to relate potential at these times to the primordial one Φ(k, a) = Φ p (k) {Transfer Function(k)} {Growth Factor(a)} where Φ p is the primordial value of the potential (i.e. end of inflation). The transfer function describes the evolution of perturbation from horizon crossings to radiation/matter transition The growth factor describes wavelength-independent growth at late times
12 Transfer Function The transfer function is usually defined as T(k) Φ(k, a late ) Φ Large Scale (k, a late ) where a late is an epoch after transfer function regime (i.e. when T(k) is constant) Φ Large Scale = 9/10Φ p The growth factor is instead Φ(a) Φ(a late ) D 1(a) a a > a late Looking at matter-dominated case where Φ is constant we have D 1 (a) = a and overdensities grows with the scale factor δ a
13 Growth Factor Sensible to the actual content of the Universe (dark matter, dark energy and their relative amount)
14 Integrated Sachs-Wolfe (ISW) effect Sensible to potential decay leading to gravitational red-shift Intrinsically a large effect on the anisotropies of the CMB Net change is integrated along a given line-of-sight Θ l (k, η 0 ) 2l + 1 = η0 0 = 2Φ(k, η MD ) [ dηe τ 2 Φ(k, ] η) j l (k(η 0 η)) η0 0 dηe τ ġ(η η 0 )j l (k(η η 0 )) On small scales where k ġ/g the integral becomes η0 dη ġ(d) j l (kd) ġ(d = l/k) 1 π k 2l 0 where we used dx j l (x) = π/2l
15 Integrated Sachs-Wolfe (ISW) effect On the power spectrum C l = 2 dk k 3 Θ l (k, η 0)Θ l (k, η 0 ) π k (2l + 1) 2 = 2π2 l 3 dη Dġ 2 (η) 2 Φ(l/D, η MD ) For scale-invariant potential we have l 2 C l 1/l. Of course depends on the details of ġ: particular important for dark energy models Net effect (enhancement) on CMB is much more evident at low (l < 10) multipoles Difficult to measure due to cosmic variance and local contaminations: cross-correlate CMB results with other tracers of structure formation to get hints on D 1
16 Integrated Sachs-Wolfe (ISW) effect
17 Integrated Sachs-Wolfe (ISW) effect Power spectrum sampling errors = [(l + 1/2)f sky ] 1/2 Low multipole effects severely cosmic variance limited
18 Gravitational Lensing Lensing is a remapping conserving surface brightness of source image reprojected via the gradient of a projected potential φ(ˆn) = 2 η0 such that fields are re-mapped as η dη (D D) DD Φ(Dˆn, η) x(ˆn) x(ˆn + φ) where x {Θ, Q, U} temperature and polarization Taylor expansion leads to product of fields and Fourier mode-coupling
19 Flat-sky Treatment Taylor expand Θ(ˆn) = Θ(ˆn + φ) = Θ(ˆn) + i φ(ˆn) i Θ(ˆn) iφ(ˆn) j φ(ˆn) i j Θ(ˆn) +... Fourier decomposition φ(ˆn) = Θ(ˆn) = d 2 l (2π) 2 φ(l)eil ˆn d 2 l il ˆn Θ(l)e (2π) 2
20 Flat-sky Treatment Mode coupling harmonics Θ(l) = dˆnθ(ˆn)e il ˆn = Θ(l) d 2 l 1 (2π) Θ(l 2 1 )L(l, l 1 ) where L(l, l 1 ) = φ(l l 1 )(l l 1 ) l d 2 l 2 2 (2π) 2 φ(l 2)φ (l 2 + l 1 l)(l 2 l 1 )(l 2 + l 1 l) l 1 Represent a coupling between harmonics mess up the original CMB angular power spectrum
21 Power Spectrum Power spectra becomes C ΘΘ l Θ (l)θ(l ) = (2π) 2 δ(l l )Cl ΘΘ φ (l)φ(l ) = (2π) 2 δ(l l )C φφ l d = (1 l 2 ) C l ΘΘ 2 l 1 ΘΘ + C (2π) 2 l l 1 Cφφ l 1 [(l l 1 ) l 1 ] 2 where R = 1 dl 4π l l4 C φφ l
22 Smoothing of Power Spectra If C ΘΘ l const we can move it out from the integral d C l ΘΘ 2 l 1 (2π) 2 Cφφ l (l l 1 ) 2 l 2 R C ΘΘ Lensing acts to smooth features in the power spectrum Lensing generates power below the damping (last-scattering) scale l
23 Lensing in the Power Spectrum Lensing width l ΘΘ l(l+1)c l /2π lensed unlensed all flat error ΘΕ l(l+1)c l /2π l
24 Lensing Potential Power Spectrum Planck-2015 produces best measurement of C φφ l
25 Polarisation Lensing Since E and B are relationships between polarisation amplitude and direction we expect lensing to create B modes Original Lensed E Lensed B
26 Polarisation Lensing Polarisation field harmonics lensed similarly [Q ± iu](ˆn) = Again with Taylor expansion [Q ± iu](ˆn) = [ Q ± iũ](ˆn + φ) d 2 l (2π) 2 [E ± ib] (l)e±2iφ l e l ˆn [ Q ± iũ](ˆn) + i φ(ˆn) i [ Q ± iũ](ˆn) iφ(ˆn) j φ(ˆn) i j [ Q ± iũ](ˆn)
27 Polarisation Lensing: power spectra In terms of power spectra (Zaldarriaga & Seljak 98) C TT = C TT + W l C EE = C EE + 1 [ 2 1l C TT W l 1l + Wl 2l [ W l 1l Wl 2l C BB = C BB C TE = C TE + W3l l TE ] C EE ] C EE 1 2 [ W1l 2l] l C Wl BB [ W1l 2l] l + C Wl EE Lensing mixes E and B modes: even with no primordial GW, B-modes are generated at small scales
28 Polarisation Lensing: power spectra
29 Scattering Secondaries
30 Scattering Secondaries Optical depth during reionization ( Ωb h 2 ) ( Ωm h 2 ) 1/2 ( ) 1 + z 3/2 τ Anisotropies suppressed as e τ Θ l (k, η 0 ) η0 2l + 1 = dηe τ [2 Φ(k, η)] j l (k(η 0 η)) Large scale fluctuations not suppressed since scattering acts on smaller scales Quadrupole from Sachs-Wolfe effect scatters into a large scale polarization bump
31 Thermal SZ effect Thermal velocities lead to Doppler effect but cancels out at first order due to random directions Residual effect of the order v 2 τ T e /m e τ and could be important for T e 10keV (gas within cluster of galaxies) RJ decrement and Wien enhancement described by second order collision term in Boltzmann equation: Kompaneets equation Clusters are rare objects so contribution to power spectrum suppressed but has been detected already by Planck: sensitive to (matter) power spectrum normalization σ 8
32 Thermal SZ effect
33 Thermal SZ effect
34 tsz & ksz effects - Unresolved sources Un-resolved sources contributes as a background noise on very small angular scales Both radio and ir-sources contributes and multi-frequency experiments can distinguish contributions
35 Where to go?
36 Where to go?
Ast 448 Set 2: Polarization and Secondaries. Wayne Hu
 Ast 448 Set 2: Polarization and Secondaries Wayne Hu Stokes Parameters Specific intensity is related to quadratic combinations of the electric field. Define the intensity matrix (time averaged over oscillations)
Ast 448 Set 2: Polarization and Secondaries Wayne Hu Stokes Parameters Specific intensity is related to quadratic combinations of the electric field. Define the intensity matrix (time averaged over oscillations)
Observational Cosmology
 The Cosmic Microwave Background Part I: CMB Theory Kaustuv Basu Course website: http://www.astro.uni-bonn.de/~kbasu/obscosmo CMB parameter cheat sheet 2 Make your own CMB experiment! Design experiment
The Cosmic Microwave Background Part I: CMB Theory Kaustuv Basu Course website: http://www.astro.uni-bonn.de/~kbasu/obscosmo CMB parameter cheat sheet 2 Make your own CMB experiment! Design experiment
Gravitational Lensing of the CMB
 Gravitational Lensing of the CMB SNAP Planck 1 Ω DE 1 w a.5-2 -1.5 w -1 -.5 Wayne Hu Leiden, August 26-1 Outline Gravitational Lensing of Temperature and Polarization Fields Cosmological Observables from
Gravitational Lensing of the CMB SNAP Planck 1 Ω DE 1 w a.5-2 -1.5 w -1 -.5 Wayne Hu Leiden, August 26-1 Outline Gravitational Lensing of Temperature and Polarization Fields Cosmological Observables from
KIPMU Set 4: Power Spectra. Wayne Hu
 KIPMU Set 4: Power Spectra Wayne Hu Planck Power Spectrum B-modes: Auto & Cross Scalar Primary Power Spectrum 10 3 10 2 temperature Power (µk 2 ) 10 1 10 0 reion. τ=0.1 cross 10-1 E-pol. 10-2 10 1 10 2
KIPMU Set 4: Power Spectra Wayne Hu Planck Power Spectrum B-modes: Auto & Cross Scalar Primary Power Spectrum 10 3 10 2 temperature Power (µk 2 ) 10 1 10 0 reion. τ=0.1 cross 10-1 E-pol. 10-2 10 1 10 2
Secondary Polarization
 Secondary Polarization z i =25 0.4 Transfer function 0.2 0 z=1 z i =8 10 100 l Reionization and Gravitational Lensing Wayne Hu Minnesota, March 2003 Outline Reionization Bump Model independent treatment
Secondary Polarization z i =25 0.4 Transfer function 0.2 0 z=1 z i =8 10 100 l Reionization and Gravitational Lensing Wayne Hu Minnesota, March 2003 Outline Reionization Bump Model independent treatment
Lecture 4. - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum (continued) - Polarisation
 Lecture 4 - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum (continued) - Polarisation Planck Collaboration (2016) Let s understand the peak heights Silk+Landau Damping Sachs-Wolfe
Lecture 4 - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum (continued) - Polarisation Planck Collaboration (2016) Let s understand the peak heights Silk+Landau Damping Sachs-Wolfe
CMB Polarization and Cosmology
 CMB Polarization and Cosmology Wayne Hu KIPAC, May 2004 Outline Reionization and its Applications Dark Energy The Quadrupole Gravitational Waves Acoustic Polarization and Initial Power Gravitational Lensing
CMB Polarization and Cosmology Wayne Hu KIPAC, May 2004 Outline Reionization and its Applications Dark Energy The Quadrupole Gravitational Waves Acoustic Polarization and Initial Power Gravitational Lensing
The Silk Damping Tail of the CMB l. Wayne Hu Oxford, December 2002
 The Silk Damping Tail of the CMB 100 T (µk) 10 10 100 1000 l Wayne Hu Oxford, December 2002 Outline Damping tail of temperature power spectrum and its use as a standard ruler Generation of polarization
The Silk Damping Tail of the CMB 100 T (µk) 10 10 100 1000 l Wayne Hu Oxford, December 2002 Outline Damping tail of temperature power spectrum and its use as a standard ruler Generation of polarization
The Once and Future CMB
 The Once and Future CMB DOE, Jan. 2002 Wayne Hu The On(c)e Ring Original Power Spectra of Maps 64º Band Filtered Ringing in the New Cosmology Gravitational Ringing Potential wells = inflationary seeds
The Once and Future CMB DOE, Jan. 2002 Wayne Hu The On(c)e Ring Original Power Spectra of Maps 64º Band Filtered Ringing in the New Cosmology Gravitational Ringing Potential wells = inflationary seeds
Really, really, what universe do we live in?
 Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
Really, really, what universe do we live in? Fluctuations in cosmic microwave background Origin Amplitude Spectrum Cosmic variance CMB observations and cosmological parameters COBE, balloons WMAP Parameters
Second Order CMB Perturbations
 Second Order CMB Perturbations Looking At Times Before Recombination September 2012 Evolution of the Universe Second Order CMB Perturbations 1/ 23 Observations before recombination Use weakly coupled particles
Second Order CMB Perturbations Looking At Times Before Recombination September 2012 Evolution of the Universe Second Order CMB Perturbations 1/ 23 Observations before recombination Use weakly coupled particles
Priming the BICEP. Wayne Hu Chicago, March BB
 Priming the BICEP 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01 0 0.01 BB 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 Wayne Hu Chicago, March 2014 A BICEP Primer How do gravitational waves affect the CMB temperature and polarization spectrum?
Priming the BICEP 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01 0 0.01 BB 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 Wayne Hu Chicago, March 2014 A BICEP Primer How do gravitational waves affect the CMB temperature and polarization spectrum?
Polarization of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Polarization of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Yasin Memari, March 2007 The CMB radiation is completely characterized by its temperature anisotropy and polarization in each direction in the
Polarization of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Yasin Memari, March 2007 The CMB radiation is completely characterized by its temperature anisotropy and polarization in each direction in the
Lecture 3. - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum. - Polarisation of the CMB
 Lecture 3 - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum - Polarisation of the CMB Planck Collaboration (2016) Let s understand the peak heights Silk+Landau Damping Sachs-Wolfe Sound
Lecture 3 - Cosmological parameter dependence of the temperature power spectrum - Polarisation of the CMB Planck Collaboration (2016) Let s understand the peak heights Silk+Landau Damping Sachs-Wolfe Sound
The cosmic microwave background radiation
 The cosmic microwave background radiation László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 May 18, 2018. Origin of the cosmic microwave radiation Photons in the plasma are
The cosmic microwave background radiation László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 May 18, 2018. Origin of the cosmic microwave radiation Photons in the plasma are
The AfterMap Wayne Hu EFI, February 2003
 The AfterMap Wayne Hu EFI, February 2003 Connections to the Past Outline What does MAP alone add to the cosmology? What role do other anisotropy experiments still have to play? How do you use the MAP analysis
The AfterMap Wayne Hu EFI, February 2003 Connections to the Past Outline What does MAP alone add to the cosmology? What role do other anisotropy experiments still have to play? How do you use the MAP analysis
Power spectrum exercise
 Power spectrum exercise In this exercise, we will consider different power spectra and how they relate to observations. The intention is to give you some intuition so that when you look at a microwave
Power spectrum exercise In this exercise, we will consider different power spectra and how they relate to observations. The intention is to give you some intuition so that when you look at a microwave
Primordial Gravitational waves and the polarization of the CMB. José Alberto Rubiño Martín (IAC, Tenerife)
 Primordial Gravitational waves and the polarization of the CMB José Alberto Rubiño Martín (IAC, Tenerife) Outline Lecture 1. Theory of CMB polarization. E and B modes. Primordial Gravitational waves. Observational
Primordial Gravitational waves and the polarization of the CMB José Alberto Rubiño Martín (IAC, Tenerife) Outline Lecture 1. Theory of CMB polarization. E and B modes. Primordial Gravitational waves. Observational
COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND ANISOTROPIES
 COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND ANISOTROPIES Anthony Challinor Institute of Astronomy & Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge, U.K. a.d.challinor@ast.cam.ac.uk 26
COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND ANISOTROPIES Anthony Challinor Institute of Astronomy & Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge, U.K. a.d.challinor@ast.cam.ac.uk 26
Modern Cosmology / Scott Dodelson Contents
 Modern Cosmology / Scott Dodelson Contents The Standard Model and Beyond p. 1 The Expanding Universe p. 1 The Hubble Diagram p. 7 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis p. 9 The Cosmic Microwave Background p. 13 Beyond
Modern Cosmology / Scott Dodelson Contents The Standard Model and Beyond p. 1 The Expanding Universe p. 1 The Hubble Diagram p. 7 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis p. 9 The Cosmic Microwave Background p. 13 Beyond
Rayleigh scattering:
 Rayleigh scattering: blue sky thinking for future CMB observations arxiv:1307.8148; previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Rayleigh scattering: blue sky thinking for future CMB observations arxiv:1307.8148; previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
CMB studies with Planck
 CMB studies with Planck Antony Lewis Institute of Astronomy & Kavli Institute for Cosmology, Cambridge http://cosmologist.info/ Thanks to Anthony Challinor & Anthony Lasenby for a few slides (almost) uniform
CMB studies with Planck Antony Lewis Institute of Astronomy & Kavli Institute for Cosmology, Cambridge http://cosmologist.info/ Thanks to Anthony Challinor & Anthony Lasenby for a few slides (almost) uniform
A5682: Introduction to Cosmology Course Notes. 11. CMB Anisotropy
 Reading: Chapter 9, sections 9.4 and 9.5 11. CMB Anisotropy Gravitational instability and structure formation Today s universe shows structure on scales from individual galaxies to galaxy groups and clusters
Reading: Chapter 9, sections 9.4 and 9.5 11. CMB Anisotropy Gravitational instability and structure formation Today s universe shows structure on scales from individual galaxies to galaxy groups and clusters
Microwave Background Polarization: Theoretical Perspectives
 Microwave Background Polarization: Theoretical Perspectives Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Pittsburgh CMBpol Technology Workshop Outline Tensor Perturbations and Microwave Polarization
Microwave Background Polarization: Theoretical Perspectives Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Pittsburgh CMBpol Technology Workshop Outline Tensor Perturbations and Microwave Polarization
The causal structure of the CMB or: how to fit the CMB into a box
 The causal structure of the CMB or: how to fit the CMB into a box L. Raul Abramo University of São Paulo, Physics Dept. & Princeton University, Dept. of Astrophysical Sciences & University of Pennsylvannia,
The causal structure of the CMB or: how to fit the CMB into a box L. Raul Abramo University of São Paulo, Physics Dept. & Princeton University, Dept. of Astrophysical Sciences & University of Pennsylvannia,
The Outtakes. Back to Talk. Foregrounds Doppler Peaks? SNIa Complementarity Polarization Primer Gamma Approximation ISW Effect
 The Outtakes CMB Transfer Function Testing Inflation Weighing Neutrinos Decaying Neutrinos Testing Λ Testing Quintessence Polarization Sensitivity SDSS Complementarity Secondary Anisotropies Doppler Effect
The Outtakes CMB Transfer Function Testing Inflation Weighing Neutrinos Decaying Neutrinos Testing Λ Testing Quintessence Polarization Sensitivity SDSS Complementarity Secondary Anisotropies Doppler Effect
A5682: Introduction to Cosmology Course Notes. 11. CMB Anisotropy
 Reading: Chapter 8, sections 8.4 and 8.5 11. CMB Anisotropy Gravitational instability and structure formation Today s universe shows structure on scales from individual galaxies to galaxy groups and clusters
Reading: Chapter 8, sections 8.4 and 8.5 11. CMB Anisotropy Gravitational instability and structure formation Today s universe shows structure on scales from individual galaxies to galaxy groups and clusters
Investigation of CMB Power Spectra Phase Shifts
 Investigation of CMB Power Spectra Phase Shifts Brigid Mulroe Fordham University, Bronx, NY, 1458 Lloyd Knox, Zhen Pan University of California, Davis, CA, 95616 ABSTRACT Analytical descriptions of anisotropies
Investigation of CMB Power Spectra Phase Shifts Brigid Mulroe Fordham University, Bronx, NY, 1458 Lloyd Knox, Zhen Pan University of California, Davis, CA, 95616 ABSTRACT Analytical descriptions of anisotropies
Polarization from Rayleigh scattering
 Polarization from Rayleigh scattering Blue sky thinking for future CMB observations Previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
Polarization from Rayleigh scattering Blue sky thinking for future CMB observations Previous work: Takahara et al. 91, Yu, et al. astro-ph/0103149 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/rayleigh_scattering Antony
We finally come to the determination of the CMB anisotropy power spectrum. This set of lectures will be divided into five parts:
 Primary CMB anisotropies We finally come to the determination of the CMB anisotropy power spectrum. This set of lectures will be divided into five parts: CMB power spectrum formalism. Radiative transfer:
Primary CMB anisotropies We finally come to the determination of the CMB anisotropy power spectrum. This set of lectures will be divided into five parts: CMB power spectrum formalism. Radiative transfer:
Testing parity violation with the CMB
 Testing parity violation with the CMB Paolo Natoli Università di Ferrara (thanks to Alessandro Gruppuso)! ISSS L Aquila 24 April 2014 Introduction The aim is to use observed properties of CMB pattern to
Testing parity violation with the CMB Paolo Natoli Università di Ferrara (thanks to Alessandro Gruppuso)! ISSS L Aquila 24 April 2014 Introduction The aim is to use observed properties of CMB pattern to
CMB beyond a single power spectrum: Non-Gaussianity and frequency dependence. Antony Lewis
 CMB beyond a single power spectrum: Non-Gaussianity and frequency dependence Antony Lewis http://cosmologist.info/ Evolution of the universe Opaque Transparent Hu & White, Sci. Am., 290 44 (2004) CMB temperature
CMB beyond a single power spectrum: Non-Gaussianity and frequency dependence Antony Lewis http://cosmologist.info/ Evolution of the universe Opaque Transparent Hu & White, Sci. Am., 290 44 (2004) CMB temperature
Week 10: Theoretical predictions for the CMB temperature power spectrum
 Week 10: Theoretical predictions for the CMB temperature power spectrum April 5, 2012 1 Introduction Last week we defined various observable quantities to describe the statistics of CMB temperature fluctuations,
Week 10: Theoretical predictions for the CMB temperature power spectrum April 5, 2012 1 Introduction Last week we defined various observable quantities to describe the statistics of CMB temperature fluctuations,
Planck was conceived to confirm the robustness of the ΛCDM concordance model when the relevant quantities are measured with much higher accuracy
 12-14 April 2006, Rome, Italy Francesco Melchiorri Memorial Conference Planck was conceived to confirm the robustness of the ΛCDM concordance model when the relevant quantities are measured with much higher
12-14 April 2006, Rome, Italy Francesco Melchiorri Memorial Conference Planck was conceived to confirm the robustness of the ΛCDM concordance model when the relevant quantities are measured with much higher
Ringing in the New Cosmology
 Ringing in the New Cosmology 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI 500 1000 1500 l (multipole) Acoustic Peaks in the CMB Wayne Hu Temperature Maps CMB Isotropy Actual Temperature Data COBE 1992 Dipole
Ringing in the New Cosmology 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI 500 1000 1500 l (multipole) Acoustic Peaks in the CMB Wayne Hu Temperature Maps CMB Isotropy Actual Temperature Data COBE 1992 Dipole
CMB Anisotropies Episode II :
 CMB Anisotropies Episode II : Attack of the C l ones Approximation Methods & Cosmological Parameter Dependencies By Andy Friedman Astronomy 200, Harvard University, Spring 2003 Outline Elucidating the
CMB Anisotropies Episode II : Attack of the C l ones Approximation Methods & Cosmological Parameter Dependencies By Andy Friedman Astronomy 200, Harvard University, Spring 2003 Outline Elucidating the
Physical Cosmology 6/6/2016
 Physical Cosmology 6/6/2016 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2016 CMB anisotropies The temperature fluctuation in
Physical Cosmology 6/6/2016 Alessandro Melchiorri alessandro.melchiorri@roma1.infn.it slides can be found here: oberon.roma1.infn.it/alessandro/cosmo2016 CMB anisotropies The temperature fluctuation in
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results. Alexander Schmah
 The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
The cosmic background radiation II: The WMAP results Alexander Schmah 27.01.05 General Aspects - WMAP measures temperatue fluctuations of the CMB around 2.726 K - Reason for the temperature fluctuations
Cosmic Microwave Background Introduction
 Cosmic Microwave Background Introduction Matt Chasse chasse@hawaii.edu Department of Physics University of Hawaii at Manoa Honolulu, HI 96816 Matt Chasse, CMB Intro, May 3, 2005 p. 1/2 Outline CMB, what
Cosmic Microwave Background Introduction Matt Chasse chasse@hawaii.edu Department of Physics University of Hawaii at Manoa Honolulu, HI 96816 Matt Chasse, CMB Intro, May 3, 2005 p. 1/2 Outline CMB, what
Tomography with CMB polarization A line-of-sight approach in real space
 Tomography with CMB polarization A line-of-sight approach in real space University of Pennsylvania - feb/2009 L. Raul Abramo Instituto de Física University of Sao Paulo L. Raul Abramo & H. Xavier, Phys.
Tomography with CMB polarization A line-of-sight approach in real space University of Pennsylvania - feb/2009 L. Raul Abramo Instituto de Física University of Sao Paulo L. Raul Abramo & H. Xavier, Phys.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 2 Sep 2004
 Sunyaev-Zel dovich polarization simulation Alexandre Amblard a,1, Martin White a,b,2 a Department of Astronomy, University of California, Berkeley, CA, 94720 b Department of Physics, University of California,
Sunyaev-Zel dovich polarization simulation Alexandre Amblard a,1, Martin White a,b,2 a Department of Astronomy, University of California, Berkeley, CA, 94720 b Department of Physics, University of California,
20 Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation continued
 PHYS 652: Astrophysics 103 20 Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation continued Innocent light-minded men, who think that astronomy can be learnt by looking at the stars without knowledge of
PHYS 652: Astrophysics 103 20 Lecture 20: Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation continued Innocent light-minded men, who think that astronomy can be learnt by looking at the stars without knowledge of
The ultimate measurement of the CMB temperature anisotropy field UNVEILING THE CMB SKY
 The ultimate measurement of the CMB temperature anisotropy field UNVEILING THE CMB SKY PARAMETRIC MODEL 16 spectra in total C(θ) = CMB theoretical spectra plus physically motivated templates for the
The ultimate measurement of the CMB temperature anisotropy field UNVEILING THE CMB SKY PARAMETRIC MODEL 16 spectra in total C(θ) = CMB theoretical spectra plus physically motivated templates for the
An Acoustic Primer. Wayne Hu Astro 448. l (multipole) BOOMERanG MAXIMA Previous COBE. W. Hu Dec. 2000
 An Acoustic Primer 100 BOOMERanG MAXIMA Previous 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 COBE W. Hu Dec. 2000 10 100 l (multipole) Wayne Hu Astro 448 CMB Anisotropies COBE Maxima Hanany, et al. (2000) BOOMERanG de Bernardis,
An Acoustic Primer 100 BOOMERanG MAXIMA Previous 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 COBE W. Hu Dec. 2000 10 100 l (multipole) Wayne Hu Astro 448 CMB Anisotropies COBE Maxima Hanany, et al. (2000) BOOMERanG de Bernardis,
Cosmic Microwave Background Polarization. Gil Holder
 Cosmic Microwave Background Polarization Gil Holder Outline 1: Overview of Primary CMB Anisotropies and Polarization 2: Primary, Secondary Anisotropies and Foregrounds 3: CMB Polarization Measurements
Cosmic Microwave Background Polarization Gil Holder Outline 1: Overview of Primary CMB Anisotropies and Polarization 2: Primary, Secondary Anisotropies and Foregrounds 3: CMB Polarization Measurements
NeoClassical Probes. of the Dark Energy. Wayne Hu COSMO04 Toronto, September 2004
 NeoClassical Probes in of the Dark Energy Wayne Hu COSMO04 Toronto, September 2004 Structural Fidelity Dark matter simulations approaching the accuracy of CMB calculations WMAP Kravtsov et al (2003) Equation
NeoClassical Probes in of the Dark Energy Wayne Hu COSMO04 Toronto, September 2004 Structural Fidelity Dark matter simulations approaching the accuracy of CMB calculations WMAP Kravtsov et al (2003) Equation
n=0 l (cos θ) (3) C l a lm 2 (4)
 Cosmic Concordance What does the power spectrum of the CMB tell us about the universe? For that matter, what is a power spectrum? In this lecture we will examine the current data and show that we now have
Cosmic Concordance What does the power spectrum of the CMB tell us about the universe? For that matter, what is a power spectrum? In this lecture we will examine the current data and show that we now have
Variation in the cosmic baryon fraction and the CMB
 Variation in the cosmic baryon fraction and the CMB with D. Hanson, G. Holder, O. Doré, and M. Kamionkowski Daniel Grin (KICP/Chicago) Presentation for CAP workshop 09/24/2013 arxiv: 1107.1716 (DG, OD,
Variation in the cosmic baryon fraction and the CMB with D. Hanson, G. Holder, O. Doré, and M. Kamionkowski Daniel Grin (KICP/Chicago) Presentation for CAP workshop 09/24/2013 arxiv: 1107.1716 (DG, OD,
KIPMU Set 1: CMB Statistics. Wayne Hu
 KIPMU Set 1: CMB Statistics Wayne Hu CMB Blackbody COBE FIRAS spectral measurement. yellblackbody spectrum. T = 2.725K giving Ω γ h 2 = 2.471 10 5 12 GHz 200 400 600 10 B ν ( 10 5 ) 8 6 4 error 50 2 0
KIPMU Set 1: CMB Statistics Wayne Hu CMB Blackbody COBE FIRAS spectral measurement. yellblackbody spectrum. T = 2.725K giving Ω γ h 2 = 2.471 10 5 12 GHz 200 400 600 10 B ν ( 10 5 ) 8 6 4 error 50 2 0
Galaxies 626. Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Secondary CMB Anisotropy
 Secondary CMB Anisotropy III: Dark Energy Wayne Hu Cabo, January 2009 Integrated Sachs-Wolfe Effect Smooth Energy Density & Potential Decay Regardless of the equation of state an energy component that
Secondary CMB Anisotropy III: Dark Energy Wayne Hu Cabo, January 2009 Integrated Sachs-Wolfe Effect Smooth Energy Density & Potential Decay Regardless of the equation of state an energy component that
Probing the Dark Ages with 21 cm Absorption
 May 13, 2008 Probing the Dark Ages with 21 cm Absorption Emil Polisensky (UMD/NRL) ABSTRACT A brief overview of detecting neutral hydrogen gas during the cosmic Dark Ages in absorption against the background
May 13, 2008 Probing the Dark Ages with 21 cm Absorption Emil Polisensky (UMD/NRL) ABSTRACT A brief overview of detecting neutral hydrogen gas during the cosmic Dark Ages in absorption against the background
Weak gravitational lensing of CMB
 Weak gravitational lensing of CMB (Recent progress and future prospects) Toshiya Namikawa (YITP) Lunch meeting @YITP, May 08, 2013 Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) Precise measurements of CMB fluctuations
Weak gravitational lensing of CMB (Recent progress and future prospects) Toshiya Namikawa (YITP) Lunch meeting @YITP, May 08, 2013 Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) Precise measurements of CMB fluctuations
Weak Lensing of CMB by Cosmic Strings and its Detectability
 Weak Lensing of CMB by Cosmic Strings and its Detectability YAMAUCHI, Daisuke Research Center for the Early Universe (RESCEU), U. Tokyo Based on the collaboration with T. Namikawa (Kyoto), A. Taruya (Kyoto),
Weak Lensing of CMB by Cosmic Strings and its Detectability YAMAUCHI, Daisuke Research Center for the Early Universe (RESCEU), U. Tokyo Based on the collaboration with T. Namikawa (Kyoto), A. Taruya (Kyoto),
B-mode Polarization of The Cosmic Microwave Background
 B-mode Polarization of The Cosmic Microwave Background Yuri Hayashida May 27, 2015 1 / 19 Index Reference Introduction Polarization Observation Summary 2 / 19 Reference [1] Baumann,D. (2012). TASI Lectures
B-mode Polarization of The Cosmic Microwave Background Yuri Hayashida May 27, 2015 1 / 19 Index Reference Introduction Polarization Observation Summary 2 / 19 Reference [1] Baumann,D. (2012). TASI Lectures
Imprint of Scalar Dark Energy on CMB polarization
 Imprint of Scalar Dark Energy on CMB polarization Kin-Wang Ng ( 吳建宏 ) Institute of Physics & Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, Taiwan Cosmology and Gravity Pre-workshop NTHU, Apr
Imprint of Scalar Dark Energy on CMB polarization Kin-Wang Ng ( 吳建宏 ) Institute of Physics & Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, Taiwan Cosmology and Gravity Pre-workshop NTHU, Apr
The Cosmic Background Radiation
 The Cosmic Background Radiation 1. Expansion history of the universe At time of inflation, we have three fundamental scalar fields: Higgs, inflaton, dark energy. We still don t know what dark energy is,
The Cosmic Background Radiation 1. Expansion history of the universe At time of inflation, we have three fundamental scalar fields: Higgs, inflaton, dark energy. We still don t know what dark energy is,
Set 9: CMB and Large Scale Structure
 Set 9: CMB and Large Scale Structure CMB Temperature Anisotropy Planck 2015 map of the temperature anisotropy (first discovered by COBE) from recombination: 300 200 100 0 µkcmb 100 200 300 CMB Temperature
Set 9: CMB and Large Scale Structure CMB Temperature Anisotropy Planck 2015 map of the temperature anisotropy (first discovered by COBE) from recombination: 300 200 100 0 µkcmb 100 200 300 CMB Temperature
OVERVIEW OF NEW CMB RESULTS
 OVERVIEW OF NEW CMB RESULTS C. R. Lawrence, JPL for the Planck Collaboration UCLA Dark Matter 2016 2016 February 17 Overview of new CMB results Lawrence 1 UCLA, 2016 February 17 Introduction Planck First
OVERVIEW OF NEW CMB RESULTS C. R. Lawrence, JPL for the Planck Collaboration UCLA Dark Matter 2016 2016 February 17 Overview of new CMB results Lawrence 1 UCLA, 2016 February 17 Introduction Planck First
A theorist s take-home message from CMB Supratik Pal
 A theorist s take-home message from CMB Supratik Pal Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata Outline CMB à la WMAP and Planck Inflation Dark energy New horizons 1 A cosmologist s wishlist To explain... 2
A theorist s take-home message from CMB Supratik Pal Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata Outline CMB à la WMAP and Planck Inflation Dark energy New horizons 1 A cosmologist s wishlist To explain... 2
Constraining the topology of the Universe using CMB maps
 Constraining the topology of the Universe using CMB maps P. Bielewicz, A.J. Banday K.M. Górski, JPL Outline topology of the Universe signatures of topology in the CMB maps search for signatures of topology
Constraining the topology of the Universe using CMB maps P. Bielewicz, A.J. Banday K.M. Górski, JPL Outline topology of the Universe signatures of topology in the CMB maps search for signatures of topology
Cosmology with CMB & LSS:
 Cosmology with CMB & LSS: the Early universe VSP08 lecture 4 (May 12-16, 2008) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India Ω +Ω +Ω +Ω + Ω +... = 1 0 0 0 0... 1 m DE K r r The Cosmic Triangle (Ostriker & Steinhardt)
Cosmology with CMB & LSS: the Early universe VSP08 lecture 4 (May 12-16, 2008) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India Ω +Ω +Ω +Ω + Ω +... = 1 0 0 0 0... 1 m DE K r r The Cosmic Triangle (Ostriker & Steinhardt)
Concordance Cosmology and Particle Physics. Richard Easther (Yale University)
 Concordance Cosmology and Particle Physics Richard Easther (Yale University) Concordance Cosmology The standard model for cosmology Simplest model that fits the data Smallest number of free parameters
Concordance Cosmology and Particle Physics Richard Easther (Yale University) Concordance Cosmology The standard model for cosmology Simplest model that fits the data Smallest number of free parameters
Instrumental Systematics on Lensing Reconstruction and primordial CMB B-mode Diagnostics. Speaker: Meng Su. Harvard University
 Instrumental Systematics on Lensing Reconstruction and primordial CMB B-mode Diagnostics Speaker: Meng Su Harvard University Collaborators: Amit P.S. Yadav, Matias Zaldarriaga Berkeley CMB Lensing workshop
Instrumental Systematics on Lensing Reconstruction and primordial CMB B-mode Diagnostics Speaker: Meng Su Harvard University Collaborators: Amit P.S. Yadav, Matias Zaldarriaga Berkeley CMB Lensing workshop
Observational Cosmology
 (C. Porciani / K. Basu) Lecture 7 Cosmology with galaxy clusters (Mass function, clusters surveys) Course website: http://www.astro.uni-bonn.de/~kbasu/astro845.html Outline of the two lecture Galaxy clusters
(C. Porciani / K. Basu) Lecture 7 Cosmology with galaxy clusters (Mass function, clusters surveys) Course website: http://www.astro.uni-bonn.de/~kbasu/astro845.html Outline of the two lecture Galaxy clusters
Physics of CMB Polarization and Its Measurement
 Physics of CMB Polarization and Its Measurement HEP seminar at Kyoto University April 13 th, 2007 Akito KUSAKA University of Tokyo Outline Physics of CMB and its Polarization What does WMAP shed light
Physics of CMB Polarization and Its Measurement HEP seminar at Kyoto University April 13 th, 2007 Akito KUSAKA University of Tokyo Outline Physics of CMB and its Polarization What does WMAP shed light
Cosmic Microwave Background
 Cosmic Microwave Background Following recombination, photons that were coupled to the matter have had very little subsequent interaction with matter. Now observed as the cosmic microwave background. Arguably
Cosmic Microwave Background Following recombination, photons that were coupled to the matter have had very little subsequent interaction with matter. Now observed as the cosmic microwave background. Arguably
Astro 448 Lecture Notes Set 1 Wayne Hu
 Astro 448 Lecture Notes Set 1 Wayne Hu Recombination Equilibrium number density distribution of a non-relativistic species n i = g i ( mi T 2π ) 3/2 e m i/t Apply to the e + p H system: Saha Equation n
Astro 448 Lecture Notes Set 1 Wayne Hu Recombination Equilibrium number density distribution of a non-relativistic species n i = g i ( mi T 2π ) 3/2 e m i/t Apply to the e + p H system: Saha Equation n
Modern Cosmology Final Examination Solutions 60 Pts
 Modern Cosmology Final Examination Solutions 6 Pts Name:... Matr. Nr.:... February,. Observable Universe [4 Pts] 6 Pt: Complete the plot of Redshift vs Luminosity distance in the range < z < and plot (i)
Modern Cosmology Final Examination Solutions 6 Pts Name:... Matr. Nr.:... February,. Observable Universe [4 Pts] 6 Pt: Complete the plot of Redshift vs Luminosity distance in the range < z < and plot (i)
Useful Quantities and Relations
 189 APPENDIX B. USEFUL QUANTITIES AND RELATIONS 190 Appendix B Useful Quantities and Relations B.1 FRW Parameters The expansion rate is given by the Hubble parameter ( ) 1 H 2 da 2 (ȧ ) a 2 0 = a dt a
189 APPENDIX B. USEFUL QUANTITIES AND RELATIONS 190 Appendix B Useful Quantities and Relations B.1 FRW Parameters The expansion rate is given by the Hubble parameter ( ) 1 H 2 da 2 (ȧ ) a 2 0 = a dt a
The physics of the cosmic microwave background
 The physics of the cosmic microwave background V(φ) φ Hiranya Peiris STFC Advanced Fellow University of Cambridge Before we start... Acknowledgment: Anthony Challinor (University of Cambridge) for invaluable
The physics of the cosmic microwave background V(φ) φ Hiranya Peiris STFC Advanced Fellow University of Cambridge Before we start... Acknowledgment: Anthony Challinor (University of Cambridge) for invaluable
Details create the big picture the physics behind the famous image of the cosmic microwave background. Marieke Postma
 Details create the big picture the physics behind the famous image of the cosmic microwave background Marieke Postma last week Inflation period of accelerated expansion a(t) eht - creates homogeneous and
Details create the big picture the physics behind the famous image of the cosmic microwave background Marieke Postma last week Inflation period of accelerated expansion a(t) eht - creates homogeneous and
Dark Energy in Light of the CMB. (or why H 0 is the Dark Energy) Wayne Hu. February 2006, NRAO, VA
 Dark Energy in Light of the CMB (or why H 0 is the Dark Energy) Wayne Hu February 2006, NRAO, VA If its not dark, it doesn't matter! Cosmic matter-energy budget: Dark Energy Dark Matter Dark Baryons Visible
Dark Energy in Light of the CMB (or why H 0 is the Dark Energy) Wayne Hu February 2006, NRAO, VA If its not dark, it doesn't matter! Cosmic matter-energy budget: Dark Energy Dark Matter Dark Baryons Visible
Observational evidence for Dark energy
 Observational evidence for Dark energy ICSW-07 (Jun 2-9, 2007) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India Email: tarun@iucaa.ernet.in Observational evidence for DE poses a major challenge for theoretical cosmology.
Observational evidence for Dark energy ICSW-07 (Jun 2-9, 2007) Tarun Souradeep I.U.C.A.A, Pune, India Email: tarun@iucaa.ernet.in Observational evidence for DE poses a major challenge for theoretical cosmology.
Anisotropy in the CMB
 Anisotropy in the CMB Antony Lewis Institute of Astronomy & Kavli Institute for Cosmology, Cambridge http://cosmologist.info/ Hanson & Lewis: 0908.0963 Evolution of the universe Opaque Transparent Hu &
Anisotropy in the CMB Antony Lewis Institute of Astronomy & Kavli Institute for Cosmology, Cambridge http://cosmologist.info/ Hanson & Lewis: 0908.0963 Evolution of the universe Opaque Transparent Hu &
Cross-correlation studies with CMB polarization maps
 PHYSICAL REVIEW D 70, 023508 2004 Cross-correlation studies with CMB polarization maps Asantha Cooray* California Institute of Technology, Mail Code 130-33, Pasadena, California 91125, USA Received 21
PHYSICAL REVIEW D 70, 023508 2004 Cross-correlation studies with CMB polarization maps Asantha Cooray* California Institute of Technology, Mail Code 130-33, Pasadena, California 91125, USA Received 21
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam for AST5220 Cosmology II Date: Tuesday, June 4th, 2013 Time: 09.00 13.00 The exam set consists of 13 pages. Appendix: Equation summary
UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Exam for AST5220 Cosmology II Date: Tuesday, June 4th, 2013 Time: 09.00 13.00 The exam set consists of 13 pages. Appendix: Equation summary
Thermal History of the Universe and the Cosmic Microwave Background. II. Structures in the Microwave Background
 Thermal History of the Universe and the Cosmic Microwave Background. II. Structures in the Microwave Background Matthias Bartelmann Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik IMPRS Lecture, March 2003 Part 2:
Thermal History of the Universe and the Cosmic Microwave Background. II. Structures in the Microwave Background Matthias Bartelmann Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik IMPRS Lecture, March 2003 Part 2:
Primordial nongaussianities I: cosmic microwave background. Uros Seljak, UC Berkeley Rio de Janeiro, August 2014
 Primordial nongaussianities I: cosmic microwave bacground Uros Selja, UC Bereley Rio de Janeiro, August 2014 Outline Primordial nongaussianity Introduction and basic physics CMB temperature power spectrum
Primordial nongaussianities I: cosmic microwave bacground Uros Selja, UC Bereley Rio de Janeiro, August 2014 Outline Primordial nongaussianity Introduction and basic physics CMB temperature power spectrum
Connecting Quarks to the Cosmos
 Connecting Quarks to the Cosmos Institute for Nuclear Theory 29 June to 10 July 2009 Inflationary Cosmology II Michael S. Turner Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Michael
Connecting Quarks to the Cosmos Institute for Nuclear Theory 29 June to 10 July 2009 Inflationary Cosmology II Michael S. Turner Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Michael
Probing Primordial Magnetic Fields with Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Probing Primordial Magnetic Fields with Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi IIT Madras, May 17, 2012 Collaborators: K. Subramanian, Pranjal
Probing Primordial Magnetic Fields with Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi IIT Madras, May 17, 2012 Collaborators: K. Subramanian, Pranjal
The Physics of CMB Polarization
 The Physics of CMB Polarization Wayne Hu Chicago, March 2004 Chicago s Polarization Orientation Thomson Radiative Transfer (Chandrashekhar 1960 ;-) Reionization (WMAP 2003; Planck?) Gravitational Waves
The Physics of CMB Polarization Wayne Hu Chicago, March 2004 Chicago s Polarization Orientation Thomson Radiative Transfer (Chandrashekhar 1960 ;-) Reionization (WMAP 2003; Planck?) Gravitational Waves
Astro 448 Lecture Notes Set 1 Wayne Hu
 Astro 448 Lecture Notes Set 1 Wayne Hu Recombination Equilibrium number density distribution of a non-relativistic species n i = g i ( mi T 2π ) 3/2 e m i/t Apply to the e + p H system: Saha Equation n
Astro 448 Lecture Notes Set 1 Wayne Hu Recombination Equilibrium number density distribution of a non-relativistic species n i = g i ( mi T 2π ) 3/2 e m i/t Apply to the e + p H system: Saha Equation n
Analyzing the CMB Brightness Fluctuations. Position of first peak measures curvature universe is flat
 Analyzing the CMB Brightness Fluctuations (predicted) 1 st rarefaction Power = Average ( / ) 2 of clouds of given size scale 1 st compression 2 nd compression (deg) Fourier analyze WMAP image: Measures
Analyzing the CMB Brightness Fluctuations (predicted) 1 st rarefaction Power = Average ( / ) 2 of clouds of given size scale 1 st compression 2 nd compression (deg) Fourier analyze WMAP image: Measures
Lecture 3+1: Cosmic Microwave Background
 Lecture 3+1: Cosmic Microwave Background Structure Formation and the Dark Sector Wayne Hu Trieste, June 2002 Large Angle Anisotropies Actual Temperature Data Really Isotropic! Large Angle Anisotropies
Lecture 3+1: Cosmic Microwave Background Structure Formation and the Dark Sector Wayne Hu Trieste, June 2002 Large Angle Anisotropies Actual Temperature Data Really Isotropic! Large Angle Anisotropies
CMB Anisotropies: The Acoustic Peaks. Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI. l (multipole) Astro 280, Spring 2002 Wayne Hu
 CMB Anisotropies: The Acoustic Peaks 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI 500 1000 1500 l (multipole) Astro 280, Spring 2002 Wayne Hu Physical Landscape 100 IAB Sask 80 Viper BAM TOCO Sound Waves
CMB Anisotropies: The Acoustic Peaks 80 T (µk) 60 40 20 Boom98 CBI Maxima-1 DASI 500 1000 1500 l (multipole) Astro 280, Spring 2002 Wayne Hu Physical Landscape 100 IAB Sask 80 Viper BAM TOCO Sound Waves
CMB Polarization in Einstein-Aether Theory
 CMB Polarization in Einstein-Aether Theory Masahiro Nakashima (The Univ. of Tokyo, RESCEU) With Tsutomu Kobayashi (RESCEU) COSMO/CosPa 2010 Introduction Two Big Mysteries of Cosmology Dark Energy & Dark
CMB Polarization in Einstein-Aether Theory Masahiro Nakashima (The Univ. of Tokyo, RESCEU) With Tsutomu Kobayashi (RESCEU) COSMO/CosPa 2010 Introduction Two Big Mysteries of Cosmology Dark Energy & Dark
Theory of Cosmological Perturbations
 Theory of Cosmological Perturbations Part III CMB anisotropy 1. Photon propagation equation Definitions Lorentz-invariant distribution function: fp µ, x µ ) Lorentz-invariant volume element on momentum
Theory of Cosmological Perturbations Part III CMB anisotropy 1. Photon propagation equation Definitions Lorentz-invariant distribution function: fp µ, x µ ) Lorentz-invariant volume element on momentum
extra dimensions? Are they necessary? Andrew Beckwith, AIBEP.org
 extra dimensions? Are they necessary? Andrew Beckwith, AIBEP.org beckwith@aibep.org,abeckwith@uh.edu Plan of the talk What is known about string theory, LQG, and also other models Deceleration parameter,
extra dimensions? Are they necessary? Andrew Beckwith, AIBEP.org beckwith@aibep.org,abeckwith@uh.edu Plan of the talk What is known about string theory, LQG, and also other models Deceleration parameter,
Delensing CMB B-modes: results from SPT.
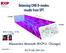 Delensing CMB B-modes: results from SPT. E mode B mode With: K.Story, K.Wu and SPT Alessandro Manzotti (KICP-U. Chicago) arxiv:1612. BCCP talk 25th Oct not in this talk: LSS and CMB ISW map reconstruction
Delensing CMB B-modes: results from SPT. E mode B mode With: K.Story, K.Wu and SPT Alessandro Manzotti (KICP-U. Chicago) arxiv:1612. BCCP talk 25th Oct not in this talk: LSS and CMB ISW map reconstruction
What can we Learn from the Cosmic Microwave Background
 What can we Learn from the Cosmic Microwave Background Problem Set #3 will be due in part on April 8 and in full on April 11 Solutions to Problem Set #2 are online... graded versions soon Again I m asking
What can we Learn from the Cosmic Microwave Background Problem Set #3 will be due in part on April 8 and in full on April 11 Solutions to Problem Set #2 are online... graded versions soon Again I m asking
CMB Anisotropies and Fundamental Physics. Lecture II. Alessandro Melchiorri University of Rome «La Sapienza»
 CMB Anisotropies and Fundamental Physics Lecture II Alessandro Melchiorri University of Rome «La Sapienza» Lecture II CMB & PARAMETERS (Mostly Dark Energy) Things we learned from lecture I Theory of CMB
CMB Anisotropies and Fundamental Physics Lecture II Alessandro Melchiorri University of Rome «La Sapienza» Lecture II CMB & PARAMETERS (Mostly Dark Energy) Things we learned from lecture I Theory of CMB
Primordial gravitational waves detected? Atsushi Taruya
 21 May 2014 Lunch seminar @YITP Primordial gravitational waves detected? Atsushi Taruya Contents Searching for primordial gravitational waves from cosmic microwave background polarizations Gravitational-wave
21 May 2014 Lunch seminar @YITP Primordial gravitational waves detected? Atsushi Taruya Contents Searching for primordial gravitational waves from cosmic microwave background polarizations Gravitational-wave
Observing the Dimensionality of Our Parent Vacuum
 Observing the Dimensionality of Our Parent Vacuum Surjeet Rajendran, Johns Hopkins with Peter Graham and Roni Harnik arxiv:1003.0236 Inspiration Why is the universe 3 dimensional? What is the overall shape
Observing the Dimensionality of Our Parent Vacuum Surjeet Rajendran, Johns Hopkins with Peter Graham and Roni Harnik arxiv:1003.0236 Inspiration Why is the universe 3 dimensional? What is the overall shape
Cosmological Structure Formation Dr. Asa Bluck
 Cosmological Structure Formation Dr. Asa Bluck Week 6 Structure Formation in the Linear Regime II CMB as Rosetta Stone for Structure Formation Week 7 Observed Scale of the Universe in Space & Time Week
Cosmological Structure Formation Dr. Asa Bluck Week 6 Structure Formation in the Linear Regime II CMB as Rosetta Stone for Structure Formation Week 7 Observed Scale of the Universe in Space & Time Week
Effects of Entanglement during Inflation on Cosmological Observables
 Effects of Entanglement during Inflation on Cosmological Observables Nadia Bolis 1 Andreas Albrecht 1 Rich Holman 2 1 University of California Davis 2 Carnegie Mellon University September 5, 2015 Inflation
Effects of Entanglement during Inflation on Cosmological Observables Nadia Bolis 1 Andreas Albrecht 1 Rich Holman 2 1 University of California Davis 2 Carnegie Mellon University September 5, 2015 Inflation
Gravitational Waves and the Microwave Background
 Gravitational Waves and the Microwave Background Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Pittsburgh KICP Inaugural Symposium, December 11, 2005 Outline Tensor Perturbations and Microwave Polarization
Gravitational Waves and the Microwave Background Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Pittsburgh KICP Inaugural Symposium, December 11, 2005 Outline Tensor Perturbations and Microwave Polarization
DES Galaxy Clusters x Planck SZ Map. ASTR 448 Kuang Wei Nov 27
 DES Galaxy Clusters x Planck SZ Map ASTR 448 Kuang Wei Nov 27 Origin of Thermal Sunyaev-Zel'dovich (tsz) Effect Inverse Compton Scattering Figure Courtesy to J. Carlstrom Observables of tsz Effect Decrease
DES Galaxy Clusters x Planck SZ Map ASTR 448 Kuang Wei Nov 27 Origin of Thermal Sunyaev-Zel'dovich (tsz) Effect Inverse Compton Scattering Figure Courtesy to J. Carlstrom Observables of tsz Effect Decrease
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 16 Jun 1997
 A CMB Polarization Primer Wayne Hu 1 Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, NJ 08540 arxiv:astro-ph/9706147v1 16 Jun 1997 Martin White Enrico Fermi Institute, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637
A CMB Polarization Primer Wayne Hu 1 Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, NJ 08540 arxiv:astro-ph/9706147v1 16 Jun 1997 Martin White Enrico Fermi Institute, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637
Hemispherical CMB power asymmetry: observation vs. models
 Helsinki May 2014 Hemispherical CMB power asymmetry: observation vs. models EnqFest May 2014 Helsinki John McDonald, Dept. of Physics, University of Lancaster Outline 1. Observed Hemispherical Asymmetry
Helsinki May 2014 Hemispherical CMB power asymmetry: observation vs. models EnqFest May 2014 Helsinki John McDonald, Dept. of Physics, University of Lancaster Outline 1. Observed Hemispherical Asymmetry
