Application of Hankel Transform for Solving a Fracture Problem of a Cracked Piezoelectric Strip Under Thermal Loading
|
|
|
- Dennis Edwards
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Applcaton of Hankel Tranform for Solvng a Fracture Problem of a Cracked Pezoelectrc Strp Under Thermal Loadng Se Ueda Oaka Inttute of Technology Japan. Introducton In th chapter, an example of the applcaton of Hankel tranform for olvng a fracture problem wll be explaned. In dcung axymmetrc problem, t advantageou to ue polar coordnate, and the Hankel tranform method powerful to olve the general equaton n polar coordnate. A bref account of the Hankel tranform wll be gven. Here f a functon of r, t tranform ndcated by a captal F, J ν the ν th order Beel functon of the frt knd, and the nature of the tranformaton ether by a uffx or by a charactertc new varable. It wll be aumed wthout comment that the ntegral n queton ext, and that, f neceary, the functon and ther dervatve tend to zero a the varable tend to nfnty. The Hankel tranform of order ν > /, Hν [ f( r)] or Fν (), of a functon f () r defned a and t nveron formula ν ν = ν H [ f ( r)] F ( ) rj ( r) f ( rdr ) Alo, ntegratng by part twce gve f () r = Jν( r) Fν() d d f df ν Hν + f F () = ν dr rdr r provded that rf ( r ) and rdf ( r)/ dr tend to zero a r and a r. The pezoelectrc materal have attracted conderable attenton recently. Owng to the couplng effect between the thermo-elatc and electrc feld n pezoelectrc materal, thermo-mechancal dturbance can be determned form meaurement of the nduced electrc potental, and the enung repone can be controlled through applcaton of an approprate electrc feld (Rao & Sunar, 994). For ucceful and effcent utlzaton of
2 8 Fourer Tranform Materal Analy pezoelectrc a enor and actuator n ntellgent ytem, everal reearche on pezothermo-elatc behavor have been reported (Tauchert, 99). Moreover a better undertandng of the mechanc of fracture n pezoelectrc materal under thermal load condton needed for the requrement of relablty and lfetme of thee ytem. Ung the Fourer tranform, the preent author tuded the thermally nduced fracture of a pezoelectrc trp wth a two-dmenonal crack (Ueda, 6a, 6b). Here the mxed-mode thermo-electro-mechancal fracture problem for a pezoelectrc materal trp wth a penny-haped crack condered. It aumed that the trp under the thermal loadng. The crack face are uppoed to be nulated thermally and electrcally. By ung the Hankel tranform (Sneddon & Lowengrub, 969), the thermal and electromechancal problem are reduced to a ngular ntegral equaton and a ytem of ngular ntegral equaton (Erdogan & Wu, 996), repectvely, whch are olved numercally (Sh, 97). Numercal calculaton are carred out, and detaled reult are preented to llutrate the nfluence of the crack ze and the crack locaton on the tre and electrc dplacement ntenty factor. The temperature, tre and electrc dplacement dtrbuton are alo preented.. Formulaton of the problem Fg.. Penny-haped crack n a pezoelectrc trp A penny-haped crack of radu c embedded n an nfnte long pezoelectrc trp of thckne h = h + h a hown n Fgure. The crack located parallel to the boundare and at an arbtrary poton n the trp, and the crack face are uppoed to be nulated thermally and electrcally. The cylndrcal coordnate ytem denoted by ( r, θ, z) wth t orgn at the center of the crack face and the plane r θ along the crack plane, where z the polng ax. It aumed that unform temperature T and T are mantaned over the tre-free boundare. In the followng, the ubcrpt r, θ, z wll be ued to refer to the drecton of coordnate. The materal properte, uch a the elatc tffne contant, the pezoelectrc contant, the delectrc contant, the tre-temperature coeffcent, the coeffcent of heat conducton, and the pyroelectrc contant, are denoted by c kl, e kl, ε kk, λ kk ( kl, =,, 3), κ r, κ z, and p z, repectvely. The conttutve equaton for the elatc feld are
3 Applcaton of Hankel Tranform for Solvng a Fracture Problem of a Cracked Pezoelectrc Strp Under Thermal Loadng 9 σ σ σ rr θθ zz ur ur uz φ = c + c + c3 + e3 λt, r r z z ur ur uz φ = c + c + c3 + e3 λt, r r z z ur ur uz φ = c3 + c3 + c33 + e33 λ33t, r r z z uz ur φ σ zr = c e5 r z r ( =, ) () where T ( r, z) the temperature, φ ( rz, ) the electrc potental, ur( r, z), uz( r, z) are the dplacement component, σ rr( rz, ), σ θθ( rz, ), σ zz( rz, ), σ zr( rz, )( =, ) are the tre component. The ubcrpt =, denote the thermo-electro-elatc feld n z h and h z, repectvely. For the electrc feld, the conttutve relaton are uz ur φ Dr = e5 + ε, r z r ur ur uz φ Dz = e3 + e3 + e33 ε33 + pzt r r z z ( =, ) () where D ( r, z), D ( r, z)( =, ) are the electrc dplacement component. r z The governng equaton for the thermo-electro-elatc feld of the medum may be expreed a follow: κ T T T + ( ) + = =, r r r z (3) ur ur u r ur uz φ T c + c44 ( c3 c44 ) ( e3 e5 ), r r r r = λ z rz rz r uz u z u z ur u r φ φ φ T c44 + c ( c3 + c44 ) + + e5 + + e 33 r r r z r z r z r r r = λ 33, (4) z z ( = ), uz u z u z ur u r φ φ φ T e5 e 33 ( e5 e3 ) ε ε 33 p z + r r r z + + = r z r z r r r z z where κ = κ / κ. r z The boundary condton can be wrtten a T ( r, ) = ( r < c) z (5) (, ) = (, ) ( <) T r T r c r
4 Fourer Tranform Materal Analy T( r, h) = T, T( r, ) = T( r, ), ( r <) z z T( r, h) = T (6) for thermal loadng condton and σ zz( r, ) = ( r < c) (7) u ( r, ) = u ( r, ) ( c r <) z z σ zr( r, ) = ( r < c) (8) u ( r, ) = u ( r, ) ( c r <) r r Dz( r, ) = ( r < c) (9) φ ( r, ) = φ ( r, ) ( c r <) σzz( r, ) = σzz( r, ), σzz( r, h) =, σzz( r, h) =, σzr( r, ) = σzr ( r, ), σzr( r, h) =, σzr ( r, h) =, ( r <) () D ( r, ) = D ( r, ), D ( r, h ) =, D ( r, h ) = z z z z for the electromechancal condton. 3. Temperature feld For the problem condered here, t convenent to repreent the temperature a the um of two functon. where () () T( r, z) = T ( z) + T ( r, z) ( =, ) () T () ( z ) atfe the followng equaton and boundary condton: dt dz () = () and () () = T ( h ) T, T ( h ) = T T () ( r, z)( =, ) ubjected to the relaton: κ () () () T T T + + = ( =, ) r r r z (3) (4) () d () T ( r, ) = T () ( r < c) z dz (5) T ( r, ) = T ( r, ) ( c r <) () ()
5 Applcaton of Hankel Tranform for Solvng a Fracture Problem of a Cracked Pezoelectrc Strp Under Thermal Loadng () T ( r, h) =, () () T ( r, ) = T ( r, ), ( r <) z z T ( r h ) (), = (6) It eay to fnd from Eq.() and (3) that () T ( z) = T T z+ T h + T h h + h {( ) } (7) By applyng the Hankel tranform to Eq.(4) (Sneddon & Lowengrub, 969), we have () τ (8) T ( r, z ) = D ( ) J ( r )exp( z ) d ( =, ) where D ()(, j = ), are unknown functon to be olved and τ (, =, ) are gven by τ = τ = κ, τ = τ = κ (9) Takng the econd boundary condton (5) nto conderaton, the problem may be reduced to a ngular ntegral equaton by defnng the followng new unknown functon G ( r ) (Erdogan & Wu, 996): G() r = r () () { } T ( r, ) T ( r, ) ( r < c) ( c r <) () Makng ue of the frt boundary condton (5) wth Eq.(6), we have the followng ngular ntegral equaton for the determnaton of the unknown functon () G t : { } c T T t M ( t, r) + M ( t, r) G ( t) dt = ( r < c) () () () κ h + h () In Eq.(), the kernel functon M ( tr, ) and M () ( tr, ) are gven by M () r E ( ), r < t π t t r ( t, r) = r t t E + K ( r > t) π tt ( r ) r rt r () M tr ρ ( ) ρ ( ) J rj td () (, ) = + ( ) ( ) κρ() (3) where K and E are complete ellptc ntegral of the frt and econd knd, and ρ ()( k = ),, are gven by k
6 Fourer Tranform Materal Analy { } { } ρ() = ρ() exp( κh) ρ() exp( κh), ρ() = τ τexp( κh) ( = ), (4) Once G () t obtaned from Eq.(), the temperature feld can be ealy calculated a follow: where wth () () () T ( r, z) = T ( r, z) ( =, ) (5) τ (6) T ( r, z) = R ( ) R ( ) J ( r)exp( z) d (, j =, ) c R() = tg () t J( t) dt, ρ() ρ() R() =, R() = exp( κ h), ρ() ρ() ρ() ρ() R() =, R() = exp( κ h ) ρ() ρ() (7) On the plane z =, the temperature T () ( r, )( =, ) are reduced to T () ( ) c ( ) ( r ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) G t dt R, = + r j R J r d =, = (8) 4. Thermally nduced elatc and electrc feld The non-dturbed temperature fled T () ( z ) gven by Eq.(7) doe not nduce the tre and electrc dplacement component, whch affect the ngular feld. Thu, we conder the elatc and electrc feld due to the dturbed temperature dtrbuton T () ( r, z)( =, ) only. It convenent to repreent the oluton uz( r, z), ur( r, z) and φ ( rz, )( =, ) a the um of two functon, repectvely. () () uz( r, z) = uz ( r, z) + uz ( r, z), () () ur( r, z) = ur ( r, z) + ur ( r, z), ( =, ) (9) () () φ( rz, ) = φ ( rz, ) + φ ( rz, ) where u () z ( r, z), u () r ( r, z), φ () ( rz, )( =, ) are the partcular oluton of Eq.(4) replaced T by T (), and u () ( r, z), u () r ( r, z), φ () ( rz, ) ( =, ) are the general oluton of z
7 Applcaton of Hankel Tranform for Solvng a Fracture Problem of a Cracked Pezoelectrc Strp Under Thermal Loadng 3 homogeneou equaton obtaned by ettng T = ( = ), n Eq.(4). In the followng, the upercrpt () and () ndcate the partcular and general oluton of Eq.(4). Subttutng Eq.(9) nto Eq.() and (), one obtan tre σ rr( rz, ), σ θθ( rz, ), σ zz( rz, ), σ zr( rz, ) and electrc dplacement D ( r, z), D ( r, z)( =, ) expreon. r Ung the dplacement potental functon method (Ueda, 6a), the partcular oluton can be obtaned a follow: z () () σzz ( rz, ) = p R( R ) ( J ) ( r)exp( τ zd ), () () σzr ( rz, ) = p R( R ) ( J ) ( r)exp( τ zd ), () () Dz ( r, z) = p 3 R( ) R( ) J( r)exp( τ z) d, ( =, ) u r z p R () R () J ( r)exp( τ z) d, () ( ) z (, ) = 4 u r z p R R J r z d () () r (, ) = 5 ( ) ( ) ( )exp( τ ), () (), = 6 φ ( rz) p R() R() J( r)exp( τ zd ) (3) where the contant p () k (, j =,, k =,,..., 6) are gven n Appendx A. The general oluton are obtaned by ung the Hankel tranform technque (Sneddon & Lowengrub, 969): 6 () () σzz ( rz, ) = p A ( J ) ( r)exp( γzd ), 6 () () σzr ( rz, ) = p A ( J ) ( r)exp( γzd ), 6 () () Dz ( r, z) = p 3 A( ) J( r)exp( γ z) d, ( =, ) u ( r z) p A ( ) J ( r) exp( γ z) d, 6 () () z, = 4 6 () () r (, ) = 5 ( ) ( )exp( γ ), u r z p A J r z d 6 () (), = 6 φ ( rz) p A ( J ) ( r)exp( γzd ) (3) where A( ) ( =,, j =,,..., 6) are the unknown functon to be olved, and the contant γ and p () ( =,, j, k =,,..., 6) are gven n Appendx B. k
8 4 Fourer Tranform Materal Analy Smlar to the temperature analy, the problem may be reduced to a ytem of ngular ntegral equaton by takng the econd boundary condton (7)-(9) nto conderaton and by defnng the followng new unknown functon Gl( r)( l =,, 3) : G() r = r () () { z z } u ( r, ) u ( r, ) ( r < c) ( c r <) () () { r r } r u ( r, ) u ( r, ) ( r < c) G() r = r r ( c r <) () () { φ φ } ( r, ) ( r, ) ( r < c) G3() r = r ( c r <) Makng ue of the frt boundary condton (7)-(9) wth Eq.(), we have the followng ytem of ngular ntegral equaton for the determnaton of the unknown functon G ()( t l = 3),, : l () { } () { } (3) (33) (34) c t[ Z M ( t, r) + M( t, r) G( t) + M( t, r) G( t) + (35) + Z M ( t, r) + M ( t, r) G ( t)] dt = σ ( r) ( r < c) zz () { } c tm [ ( trg, ) ( t) + ZM ( tr, ) + M( tr, ) G( t) + (36) + M ( t, r) G ( t)] dt = σ ( r) ( r < c) 3 3 zr () { } () { } c t[ Z 3M ( t, r) + M3( t, r) G( t) + M3( t, r) G( t) + (37) + Z M ( t, r) + M ( t, r) G ( t)] dt = D ( r) ( r < c) z () where the kernel functon M ( tr, ), Mkl ( tr, ) and the contant Zkl ( k, l=,, 3) are gven by M () 4 r r t r r K E + E K ( r t), < πrt t t πrt t r t t ( t, r) = 4 t t t K E E ( r t) + > πt r r π t r r { kl kl } { kl kl } { kl kl } { kl kl } Z () Z J ( rj ) ( td ) ( k= 3,, l= 3),, Z () Z J ( rj ) ( td ) ( k= 3,, l= ), Mkl( t, r) = Z () Z J ( rj ) ( td ) ( k=, l= 3),, Z () Z J ( rj ) ( td ) ( k=, l= ) (38) (39)
9 Applcaton of Hankel Tranform for Solvng a Fracture Problem of a Cracked Pezoelectrc Strp Under Thermal Loadng 5 6 () kl k j jl kl kl Z () = p d (), Z = lm Z () ( k, l= 3),, (4) In Eq.(4), the functon d jl()( j =,,..., 6, l= 3),, are gven n Appendx C. The functon σ zz ( r ), σ zr ( r ) and Dz ( r ), whch correpond to the tre and electrc dplacement component nduced by the dturbed temperature feld T () ( r, z)( =, ) on the r -ax n the plate wthout crack, are obtaned a follow: 6 () T () σ zz() r = R () p jdj() + p jrj() J( r) d, 6 () T () σ zr() r = R () p jdj() + p jrj() J( r) d, 6 () T () Dz() r = R () p3 jdj() p3 jrj() J ( r ) d (4) T where the functon d j() ( j =,,..., 6) are alo gven n Appendx C. Thee component are uperfcal quantte and have no phycal meanng n th analy. However, they are equvalent to the crack face tracton n olvng the crack problem by a proper uperpoton. To olve the ngular ntegral equaton () and (35)- (37) by ung the Gau-Jacob ntegraton formula (Sh, 97), we ntroduce the followng functon Φ ()( l= 3),,, : l t / c+ t Gl() t = Φl() t ( l= 3),,, c t (4) Then the tre ntenty factor K I, may be defned and evaluated a: K II and the electrc dplacement ntenty factor K D { } / / KI = lm{ π( c r)} σzz( r, ) = ( πc) ZΦ() c + Z3Φ3(), c + r c / / KII = lm { π( c r)} σzr( r, ) = ( πc) ZΦ ( c), + r c / / KD = lm{ π( c r)} Dz( r, ) = ( πc) { Z3Φ() c + Z33Φ3() c } + r c (43) 5. Numercal reult and dcuon For the numercal calculaton, the thermo-electro-elatc properte of the plate are aumed to be one of cadmum elende wth the followng properte (Ahda & Tauchert, 998). The value of the coeffcent of heat conducton for cadmum elende could not be found n the lterature. Snce the value of them for orthotropc Alumna (Al O 3 ) are κ r =.5[W/mK] and κ z = 9.8[W/mK] (Dag, 6), the value κ = κr / κz = / 5. aumed. To examne the effect of the normalzed crack ze c/ h and the normalzed crack
10 6 Fourer Tranform Materal Analy locaton h / h on the tre and electrc dplacement ntenty factor, the oluton of the ytem of the ngular ntegral equaton have been computed numercally. 9 9 c = 74. [ N/ m ], c = 45. [ N/ m ], 9 9 c3 = [ N/ m ], c33 = [ N/ m ], 9 c44 = 3. [ N/ m ], e3 =. 6[ C/ m ], e33 =. 347[ C/ m ], e5 =. 38[ C/ m ], ε =. / ε33 =. / 6 6 λ =. 6 [ N/ Km λ33 =. N/ Km 6 p z 94 [ CK m ] 8 6 [C Vm], 9 3 [C Vm], ], 55 [ ], =.. (44) In the frt et of calculaton, we conder the temperature feld and the electro-elatc feld wthout crack. Fgure how the normalzed temperature ( T ( x) T )/ T ( =, ) on the ± crack face ( r < c, z ) and the crack extended lne ( c r c, z= ) for h / h = 5. and c/ h =. 5, where T = T T. The maxmum local temperature dfference acro the crack occur at the center of the crack. Fgure 3 exhbt the normalzed tre component ( σzz( r), σzr( r)) / λ33t and the electrc dplacement component Dz( r) / pzt on the r -ax n the trp wthout crack due to the temperature hown n Fgure. The maxmum abolute value of σ zz ( r ) and Dz ( r ) occur at the center of the crack ( r / c =. ), wherea the maxmum value of σ zr ( r ) occur at the crack tp ( r/ c = )...8 (T -T )/T.6.4 h /h=.5 c/h=.5 : = (z + ) : = (z - ). r/c Fg.. The temperature on the crack face and the crack extended lne for c/ h =. 5 and h / h = 5. In the econd et of calculaton, we tudy the nfluence of the crack ze on the tre and electrc dplacement ntenty factor. Fgure 4(a)-(c) how the plot of the normalzed / tre and electrc dplacement ntenty factor ( KI, KII) / λ33t( πc), KD pzt ( πc ) / / veru c / h for h / h = 5.,.5 and.75. Becaue of ymmetry, the value of K I and K D
11 Applcaton of Hankel Tranform for Solvng a Fracture Problem of a Cracked Pezoelectrc Strp Under Thermal Loadng 7. (σ zz, σ zr )/λ 33 T.6.4. h /h=.5 c/h=.5 D z σ zr D z /p z T σ zz -.4 r/c Fg. 3. The tre component σ zz, σ zr and the electrc dplacement component Dz r -ax wthout crack due to the temperature hown n Fg. on the / K I/λ 33T (πc).. -. (a) h /h=.5 h /h=.5 h /h=.75 / K II/λ 33T (πc) (b) h /h=.5 h /h=.5, c/h c/h.. (c) h /h=.75 K D /p T (πc) Z / -. h /h=.5 h /h=.5 -. c/h Fg. 4. (a) The effect of the crack ze on the tre ntenty factor K I. (b) The effect of the crack ze on the tre ntenty factor K II. (c) The effect of the crack ze on the electrc dplacement ntenty factor K D
12 8 Fourer Tranform Materal Analy / =. are zero, and [ K ] h for h h 5 [ K ] h D / h.5 = [ ] D h / h=.75 I / h.5 = K. The abolute value of = = [ KI ], [ K ] h / h=.75 h.75 monotoncally ncreae wth ncreang c/ h, but the value of / II / h.5 = K = [ ] h II / h=.75 K I λ 33 T ( π c) / / for h / h = 5. and K II λ 33 T ( π c) / / and the abolute value of KD / pzt ( πc ) ncreae at frt, reach maxmum value and then decreae wth ncreang c / h. The value of K I for h / h = 75. become negatve o that the contact of the crack face would occur. The reult preented here wthout conderng th effect may not be exact but would be more conervatve. Snce the contact of the crack face wll ncreae the frcton between the face and make thermo-electrcal tranfer acro the crack face eaer, the tre and electrc dplacement ntenty factor would be lowered by thee two factor. In the fnal et of calculaton, we nvetgate the nfluence of the crack locaton on the ntenty factor. Fgure 5 ndcate the effect of the crack locaton on K I, K II and K D for c/ h = 5.. A h / h ncreae, the value of K I and K D tend to decreae or ncreae monotoncally. The value of K II λ 33 T ( π c) / / decreae f the crack approache the free boundare ( h / h.or.), and the peak value of K II λ 33 T ( π c) / / =.77 occur at h / h = K II (K I, K II )/λ 33 T (πc) /.. K D K I. -. K D /p z T (πc) / -. c/h= h /h Fg. 5 The effect of the crack locaton on the tre ntenty factor dplacement ntenty factor K 6. Concluon D K I, K II and the electrc An example of the applcaton of Hankel tranform for olvng a mxed-mode thermoelectro-elatc fracture problem of a pezoelectrc materal trp wth a parallel penny-haped crack explaned. The effect of the crack ze ( c / h) and the crack locaton ( h / h) on the fracture behavor are analyzed. The followng fact can be found from the numercal reult.. The large hear tre occur n the trp wthout crack due to the dturbed temperature feld.. The normalzed ntenty factor are under the great nfluence of the geometrc parameter h / h and c / h.
13 Applcaton of Hankel Tranform for Solvng a Fracture Problem of a Cracked Pezoelectrc Strp Under Thermal Loadng 9 3. For the cae of h / h >.5, mode I tre ntenty factor become negatve o that the contact of the crack face would occur. 4. The ntenty factor of crack near the free urface due to the thermal load are not o large. Appendx A The contant where p () (, j =,, k =,,..., 6) are k ( ) () ( ) ( τ ) () p = c3 c33kτ C e33τ N λ33, p = c44 + k τ C + e5n, () p3 = e3 e33k C + ε33τ N + pz, () () () p4 = kτ C, p5 = C, p6 = N (, =, ) (A.) wth b b τ C =, () () m + km () () n + kn N =, ( ) () (), j =, m + km () () τ n + n k = () () τ n + n (A.) () m = a 4 a 4τ, () m = ( a 44τ a 43) τ, () () n = {( Hr + H3r) ( b b τ) + H4rm } τ, () () n = {( Hz + H3z) ( b b τ) + H4zm } τ, () () n = {( Hr Hrτ )( b b τ ) + H4rm } τ, () () n = {( Hz Hzτ ) ( b ) } b τ + H 4 zm τ (, j =,) (A.3) c44ε33 + e5e33 c44ε + e5 c33ε33 + e33 c33ε + e5e 33 Hr =, Hz =, Hr =, Hz =, e33ε e5ε33 e5ε33 e33ε e33ε e5ε33 e5ε33 e33ε c3ε33 + e3e33 c3ε + e5e3 pe z 33 λ33ε33 pe z 5 λ33ε H3r =, H3z =, H4r =, H4z = e33ε e5ε33 e5ε33 e33ε e33ε e5ε33 e5ε33 e33ε (A.4)
14 Fourer Tranform Materal Analy a = c, a = c + ( e + e )( H + H ), r 3r 43 = c3 + c44 + ( e5 + e3) Hr, a 44 = ( e5 + e3) Hr, = λ, b = ( e5 + e3) H 4r a b (A.5) Appendx B The contant γ ( =,, j =,,..., 6) are the root of the followng charactertc equaton: 6 4 ( f4g g4f ) γ ( f4g fg g4f gf ) γ ( fg fg gf gf ) γ ( fg gf ) = j ( =,, j =,,..., 6) (B.) where R [ γ j] <R [ γ j + ], R [ γ j] >R [ γ j+ ]( j =,,..., 5) and f4 = c44e33, f = ( c3 + c44)( e5 + e3) ce33 c44e5, f = ce5, f = c33( e5 + e3) e33( c3 + c44), f = c44( e5 + e3) + e5( c3 + c44) g4 = c44ε 33, g = ( e5 + e3) cε33 c44ε, g = cε, g = e33( e5 + e3) + ε 33( c3 + c44), g = e5( e5 + e3) ε( c3 + c44) (B.) (B.3) The functon p () ()( =,, j, k =,,..., 6) are k () () 3 () γ ( ), ( γ ), γ ( ε ) p = c a + c e b p = c a + e b 44 5 p e a e b = p p () 4 () 5 p () 6 =, = a = b where a and b ( =,, j =,,..., 6) are gven by b,, g γ + g a =, 4 g4γ + gγ + g ( c44γ c) a c3 c44 = e5 + e3 ( =,, j =,,..., 6) ( =,, j =,,..., 6) (B.4) (B.5)
15 Applcaton of Hankel Tranform for Solvng a Fracture Problem of a Cracked Pezoelectrc Strp Under Thermal Loadng Appendx C The functon d ( ) ( =,, j =,,..., 6, k =,, 3) are gven by k djk() = qj, k+ 9(), ( j =,,..., 6, k =,, 3) djk() = qj+ 6, k+ 9() (C.) where the functon qjk, ()( j, k =,,..., ) are the element of a quare matrx Q = Δ of order. The element δ, ( ) ( j, k =,,..., ) of the quare matrx Δ are gven by jk () δjk, ( ) = pjkexp( γkh) ( j =,, 3), () δj+ 3, k+ 6() = pjkexp( γkh) ( j = 3),,, ( 6) () k =,,..., δ j+ 6, k() = pjk ( j =,,..., 6), () δ j+ 6, k+ 6() = pjk ( j =,,..., 6) (C.) T The functon d ( ) ( =,, j =,,..., 6) are T d j() = qj, k() uk(), k= ( 6) j =,,..., T dj() = qj+ 6, k() uk() k= (C.3) where u () = p R ()exp( h ) ( k = 3),,, R() () k k j j τ j R() () k+ 3 k j j τ j u () = p R ()exp( h ) ( k = 3),,, R() () () uk+ 6() = { pkjrj() pkjrj() } ( k 6) =,,..., (C.4) 7. Reference Ahda, F. & Tauchert, T.R. (998). Tranent Repone of a Pezothermoelatc Crcular Dk under Axymmetrc Heatng. Acta Mechanca, Vol. 8, pp. -4, -597 Dag, S., Ilhan, K.A. & Erdogan, F. (6), Mxed-Mode Stre Intenty Factor for an Embedded Crack n an Orthotropc FGM Coatng, Proceedng of the Internatonal Conference FGM IX, , Oahu Iland, Hawa, October 6 Erdogan, F. & Wu, B.H. (996). Crack Problem n FGM Layer under Thermal Stree. Journal of Thermal Stree, Vol. 9, pp ,
16 Fourer Tranform Materal Analy Rao, S.S. & Sunar, M. (994). Pezoelectrcty and It Ue n Dturbance Senng and Control of Flexble Structure: a Survey. Appled Mechanc Revew, Vol. 47, pp. 3-3, 3-69 Sh, G.C. (Ed.). (97). Method of Analy and Soluton of Crack Problem, Noordhoff, Internatonal Publhng, , Leyden Sneddon, I.N. & Lowengrub, M. (969). Crack Problem n the Clacal Theory of Elatcty, John Wley & Son, Inc., , New York Tauchert, T.R. (99). Pezothermoelatc Behavor of a Lamnated Plate. Journal of Thermal Stree, Vol. 5, pp. 5-37, Ueda, S. (6a). The Crack Problem n Pezoelectrc Strp under Thermoelectrc Loadng. Journal of Thermal Stree, Vol. 9, pp , Ueda, S. (6b). Thermal Stre Intenty Factor for a Normal Crack n a Pezoelectrc Strp. Journal of Thermal Stree, Vol. 9, pp. 7-6,
17 Fourer Tranform - Materal Analy Edted by Dr Salh Salh ISBN Hard cover, 6 page Publher InTech Publhed onlne 3, May, Publhed n prnt edton May, The feld of materal analy ha een explove growth durng the pat decade. Almot all the textbook on materal analy have a ecton devoted to the Fourer tranform theory. For th reaon, the book focue on the materal analy baed on Fourer tranform theory. The book chapter are related to FTIR and the other method ued for analyzng dfferent type of materal. It hoped that th book wll provde the background, reference and ncentve to encourage further reearch and reult n th area a well a provde tool for practcal applcaton. It provde an applcaton-orented approach to materal analy wrtten prmarly for phyct, Chemt, Agrculturalt, Electrcal Engneer, Mechancal Engneer, Sgnal Proceng Engneer, and the Academc Reearcher and for the Graduate Student who wll alo fnd t ueful a a reference for ther reearch actvte. How to reference In order to correctly reference th cholarly work, feel free to copy and pate the followng: Se Ueda (). Applcaton of Hankel Tranform for Solvng a Fracture Problem of a Cracked Pezoelectrc Strp Under Thermal Loadng, Fourer Tranform - Materal Analy, Dr Salh Salh (Ed.), ISBN: , InTech, Avalable from: InTech Europe Unverty Campu STeP R Slavka Krautzeka 83/A 5 Reka, Croata Phone: +385 (5) Fax: +385 (5) InTech Chna Unt 45, Offce Block, Hotel Equatoral Shangha No.65, Yan An Road (Wet), Shangha, 4, Chna Phone: Fax:
Method Of Fundamental Solutions For Modeling Electromagnetic Wave Scattering Problems
 Internatonal Workhop on MehFree Method 003 1 Method Of Fundamental Soluton For Modelng lectromagnetc Wave Scatterng Problem Der-Lang Young (1) and Jhh-We Ruan (1) Abtract: In th paper we attempt to contruct
Internatonal Workhop on MehFree Method 003 1 Method Of Fundamental Soluton For Modelng lectromagnetc Wave Scatterng Problem Der-Lang Young (1) and Jhh-We Ruan (1) Abtract: In th paper we attempt to contruct
Harmonic oscillator approximation
 armonc ocllator approxmaton armonc ocllator approxmaton Euaton to be olved We are fndng a mnmum of the functon under the retrcton where W P, P,..., P, Q, Q,..., Q P, P,..., P, Q, Q,..., Q lnwgner functon
armonc ocllator approxmaton armonc ocllator approxmaton Euaton to be olved We are fndng a mnmum of the functon under the retrcton where W P, P,..., P, Q, Q,..., Q P, P,..., P, Q, Q,..., Q lnwgner functon
Two-Layered Model of Blood Flow through Composite Stenosed Artery
 Avalable at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 93-9466 Vol. 4, Iue (December 9), pp. 343 354 (Prevouly, Vol. 4, No.) Applcaton Appled Mathematc: An Internatonal Journal (AAM) Two-ayered Model
Avalable at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 93-9466 Vol. 4, Iue (December 9), pp. 343 354 (Prevouly, Vol. 4, No.) Applcaton Appled Mathematc: An Internatonal Journal (AAM) Two-ayered Model
Chapter 11. Supplemental Text Material. The method of steepest ascent can be derived as follows. Suppose that we have fit a firstorder
 S-. The Method of Steepet cent Chapter. Supplemental Text Materal The method of teepet acent can be derved a follow. Suppoe that we have ft a frtorder model y = β + β x and we wh to ue th model to determne
S-. The Method of Steepet cent Chapter. Supplemental Text Materal The method of teepet acent can be derved a follow. Suppoe that we have ft a frtorder model y = β + β x and we wh to ue th model to determne
FEEDDBACK CONTROL OF PIEZO-LAMINATE COMPOSITE PLATE. Hafez Ave, Tehran 15914, Iran
 ICSV14 Carn Autrala 9-12 July, 2007 FEEDDBACK CONTROL OF PIEZO-LAMINATE COMPOSITE PLATE A. Yelagh Tamjan 1, M. Abouhamze 1, R. Mrzaefar 1, A.R. Ohad 1, M.R. Elam 1 1 Department of Mechancal Engneerng,
ICSV14 Carn Autrala 9-12 July, 2007 FEEDDBACK CONTROL OF PIEZO-LAMINATE COMPOSITE PLATE A. Yelagh Tamjan 1, M. Abouhamze 1, R. Mrzaefar 1, A.R. Ohad 1, M.R. Elam 1 1 Department of Mechancal Engneerng,
Chapter 6 The Effect of the GPS Systematic Errors on Deformation Parameters
 Chapter 6 The Effect of the GPS Sytematc Error on Deformaton Parameter 6.. General Beutler et al., (988) dd the frt comprehenve tudy on the GPS ytematc error. Baed on a geometrc approach and aumng a unform
Chapter 6 The Effect of the GPS Sytematc Error on Deformaton Parameter 6.. General Beutler et al., (988) dd the frt comprehenve tudy on the GPS ytematc error. Baed on a geometrc approach and aumng a unform
Module 5. Cables and Arches. Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpur
 odule 5 Cable and Arche Veron CE IIT, Kharagpur Leon 33 Two-nged Arch Veron CE IIT, Kharagpur Intructonal Objectve: After readng th chapter the tudent wll be able to 1. Compute horzontal reacton n two-hnged
odule 5 Cable and Arche Veron CE IIT, Kharagpur Leon 33 Two-nged Arch Veron CE IIT, Kharagpur Intructonal Objectve: After readng th chapter the tudent wll be able to 1. Compute horzontal reacton n two-hnged
Improvements on Waring s Problem
 Improvement on Warng Problem L An-Png Bejng, PR Chna apl@nacom Abtract By a new recurve algorthm for the auxlary equaton, n th paper, we wll gve ome mprovement for Warng problem Keyword: Warng Problem,
Improvement on Warng Problem L An-Png Bejng, PR Chna apl@nacom Abtract By a new recurve algorthm for the auxlary equaton, n th paper, we wll gve ome mprovement for Warng problem Keyword: Warng Problem,
Specification -- Assumptions of the Simple Classical Linear Regression Model (CLRM) 1. Introduction
 ECONOMICS 35* -- NOTE ECON 35* -- NOTE Specfcaton -- Aumpton of the Smple Clacal Lnear Regreon Model (CLRM). Introducton CLRM tand for the Clacal Lnear Regreon Model. The CLRM alo known a the tandard lnear
ECONOMICS 35* -- NOTE ECON 35* -- NOTE Specfcaton -- Aumpton of the Smple Clacal Lnear Regreon Model (CLRM). Introducton CLRM tand for the Clacal Lnear Regreon Model. The CLRM alo known a the tandard lnear
Small signal analysis
 Small gnal analy. ntroducton Let u conder the crcut hown n Fg., where the nonlnear retor decrbed by the equaton g v havng graphcal repreentaton hown n Fg.. ( G (t G v(t v Fg. Fg. a D current ource wherea
Small gnal analy. ntroducton Let u conder the crcut hown n Fg., where the nonlnear retor decrbed by the equaton g v havng graphcal repreentaton hown n Fg.. ( G (t G v(t v Fg. Fg. a D current ource wherea
FREE VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF CLAMPED-FREE COMPOSITE CYLINDRICAL SHELLS WITH AN INTERIOR RECTANGULAR PLATE
 FREE VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF CLAPED-FREE COPOSITE CYLINDRICAL SHELLS WITH AN INTERIOR RECTANGULAR PLATE Young-Shn Lee and young-hwan Cho Department of echancal Degn Engneerng, Chungnam Natonal Unverty, 0
FREE VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF CLAPED-FREE COPOSITE CYLINDRICAL SHELLS WITH AN INTERIOR RECTANGULAR PLATE Young-Shn Lee and young-hwan Cho Department of echancal Degn Engneerng, Chungnam Natonal Unverty, 0
Electrical Circuits II (ECE233b)
 Electrcal Crcut II (ECE33b) Applcaton of Laplace Tranform to Crcut Analy Anet Dounav The Unverty of Wetern Ontaro Faculty of Engneerng Scence Crcut Element Retance Tme Doman (t) v(t) R v(t) = R(t) Frequency
Electrcal Crcut II (ECE33b) Applcaton of Laplace Tranform to Crcut Analy Anet Dounav The Unverty of Wetern Ontaro Faculty of Engneerng Scence Crcut Element Retance Tme Doman (t) v(t) R v(t) = R(t) Frequency
Improvements on Waring s Problem
 Imrovement on Warng Problem L An-Png Bejng 85, PR Chna al@nacom Abtract By a new recurve algorthm for the auxlary equaton, n th aer, we wll gve ome mrovement for Warng roblem Keyword: Warng Problem, Hardy-Lttlewood
Imrovement on Warng Problem L An-Png Bejng 85, PR Chna al@nacom Abtract By a new recurve algorthm for the auxlary equaton, n th aer, we wll gve ome mrovement for Warng roblem Keyword: Warng Problem, Hardy-Lttlewood
On the SO 2 Problem in Thermal Power Plants. 2.Two-steps chemical absorption modeling
 Internatonal Journal of Engneerng Reearch ISSN:39-689)(onlne),347-53(prnt) Volume No4, Iue No, pp : 557-56 Oct 5 On the SO Problem n Thermal Power Plant Two-tep chemcal aborpton modelng hr Boyadjev, P
Internatonal Journal of Engneerng Reearch ISSN:39-689)(onlne),347-53(prnt) Volume No4, Iue No, pp : 557-56 Oct 5 On the SO Problem n Thermal Power Plant Two-tep chemcal aborpton modelng hr Boyadjev, P
728. Mechanical and electrical elements in reduction of vibrations
 78. Mechancal and electrcal element n reducton of vbraton Katarzyna BIAŁAS The Slean Unverty of Technology, Faculty of Mechancal Engneerng Inttute of Engneerng Procee Automaton and Integrated Manufacturng
78. Mechancal and electrcal element n reducton of vbraton Katarzyna BIAŁAS The Slean Unverty of Technology, Faculty of Mechancal Engneerng Inttute of Engneerng Procee Automaton and Integrated Manufacturng
CHAPTER X PHASE-CHANGE PROBLEMS
 Chapter X Phae-Change Problem December 3, 18 917 CHAPER X PHASE-CHANGE PROBLEMS X.1 Introducton Clacal Stefan Problem Geometry of Phae Change Problem Interface Condton X. Analytcal Soluton for Soldfcaton
Chapter X Phae-Change Problem December 3, 18 917 CHAPER X PHASE-CHANGE PROBLEMS X.1 Introducton Clacal Stefan Problem Geometry of Phae Change Problem Interface Condton X. Analytcal Soluton for Soldfcaton
Scattering of two identical particles in the center-of. of-mass frame. (b)
 Lecture # November 5 Scatterng of two dentcal partcle Relatvtc Quantum Mechanc: The Klen-Gordon equaton Interpretaton of the Klen-Gordon equaton The Drac equaton Drac repreentaton for the matrce α and
Lecture # November 5 Scatterng of two dentcal partcle Relatvtc Quantum Mechanc: The Klen-Gordon equaton Interpretaton of the Klen-Gordon equaton The Drac equaton Drac repreentaton for the matrce α and
Electric and magnetic field sensor and integrator equations
 Techncal Note - TN12 Electrc and magnetc feld enor and ntegrator uaton Bertrand Da, montena technology, 1728 oen, Swtzerland Table of content 1. Equaton of the derate electrc feld enor... 1 2. Integraton
Techncal Note - TN12 Electrc and magnetc feld enor and ntegrator uaton Bertrand Da, montena technology, 1728 oen, Swtzerland Table of content 1. Equaton of the derate electrc feld enor... 1 2. Integraton
Lateral stresses caused by uniform rectangular area loads on a cross-anisotropic backfill
 Wang, C. D. (). Géotechnque 5, No. 9, 5 [do:./geot..5.9.5] TECHNICAL NOTE Lateral tree caued by unform rectangular area load on a cro-anotropc backfll C. D. WANG* KEYWORDS: anotropy; degn; earth preure;
Wang, C. D. (). Géotechnque 5, No. 9, 5 [do:./geot..5.9.5] TECHNICAL NOTE Lateral tree caued by unform rectangular area load on a cro-anotropc backfll C. D. WANG* KEYWORDS: anotropy; degn; earth preure;
Pythagorean triples. Leen Noordzij.
 Pythagorean trple. Leen Noordz Dr.l.noordz@leennoordz.nl www.leennoordz.me Content A Roadmap for generatng Pythagorean Trple.... Pythagorean Trple.... 3 Dcuon Concluon.... 5 A Roadmap for generatng Pythagorean
Pythagorean trple. Leen Noordz Dr.l.noordz@leennoordz.nl www.leennoordz.me Content A Roadmap for generatng Pythagorean Trple.... Pythagorean Trple.... 3 Dcuon Concluon.... 5 A Roadmap for generatng Pythagorean
Electromagnetic scattering. Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Communications) 1 st Semester, Sharif University of Technology
 Electromagnetc catterng Graduate Coure Electrcal Engneerng (Communcaton) 1 t Semeter, 1390-1391 Sharf Unverty of Technology Content of lecture Lecture : Bac catterng parameter Formulaton of the problem
Electromagnetc catterng Graduate Coure Electrcal Engneerng (Communcaton) 1 t Semeter, 1390-1391 Sharf Unverty of Technology Content of lecture Lecture : Bac catterng parameter Formulaton of the problem
Additional File 1 - Detailed explanation of the expression level CPD
 Addtonal Fle - Detaled explanaton of the expreon level CPD A mentoned n the man text, the man CPD for the uterng model cont of two ndvdual factor: P( level gen P( level gen P ( level gen 2 (.).. CPD factor
Addtonal Fle - Detaled explanaton of the expreon level CPD A mentoned n the man text, the man CPD for the uterng model cont of two ndvdual factor: P( level gen P( level gen P ( level gen 2 (.).. CPD factor
8 Waves in Uniform Magnetized Media
 8 Wave n Unform Magnetzed Meda 81 Suceptblte The frt order current can be wrtten j = j = q d 3 p v f 1 ( r, p, t) = ɛ 0 χ E For Maxwellan dtrbuton Y n (λ) = f 0 (v, v ) = 1 πvth exp (v V ) v th 1 πv th
8 Wave n Unform Magnetzed Meda 81 Suceptblte The frt order current can be wrtten j = j = q d 3 p v f 1 ( r, p, t) = ɛ 0 χ E For Maxwellan dtrbuton Y n (λ) = f 0 (v, v ) = 1 πvth exp (v V ) v th 1 πv th
The multivariate Gaussian probability density function for random vector X (X 1,,X ) T. diagonal term of, denoted
 Appendx Proof of heorem he multvarate Gauan probablty denty functon for random vector X (X,,X ) px exp / / x x mean and varance equal to the th dagonal term of, denoted he margnal dtrbuton of X Gauan wth
Appendx Proof of heorem he multvarate Gauan probablty denty functon for random vector X (X,,X ) px exp / / x x mean and varance equal to the th dagonal term of, denoted he margnal dtrbuton of X Gauan wth
A NUMERICAL MODELING OF MAGNETIC FIELD PERTURBATED BY THE PRESENCE OF SCHIP S HULL
 A NUMERCAL MODELNG OF MAGNETC FELD PERTURBATED BY THE PRESENCE OF SCHP S HULL M. Dennah* Z. Abd** * Laboratory Electromagnetc Sytem EMP BP b Ben-Aknoun 606 Alger Algera ** Electronc nttute USTHB Alger
A NUMERCAL MODELNG OF MAGNETC FELD PERTURBATED BY THE PRESENCE OF SCHP S HULL M. Dennah* Z. Abd** * Laboratory Electromagnetc Sytem EMP BP b Ben-Aknoun 606 Alger Algera ** Electronc nttute USTHB Alger
Introduction to Interfacial Segregation. Xiaozhe Zhang 10/02/2015
 Introducton to Interfacal Segregaton Xaozhe Zhang 10/02/2015 Interfacal egregaton Segregaton n materal refer to the enrchment of a materal conttuent at a free urface or an nternal nterface of a materal.
Introducton to Interfacal Segregaton Xaozhe Zhang 10/02/2015 Interfacal egregaton Segregaton n materal refer to the enrchment of a materal conttuent at a free urface or an nternal nterface of a materal.
Modeling of Wave Behavior of Substrate Noise Coupling for Mixed-Signal IC Design
 Modelng of Wave Behavor of Subtrate Noe Couplng for Mxed-Sgnal IC Degn Georgo Veron, Y-Chang Lu, and Robert W. Dutton Center for Integrated Sytem, Stanford Unverty, Stanford, CA 9435 yorgo@gloworm.tanford.edu
Modelng of Wave Behavor of Subtrate Noe Couplng for Mxed-Sgnal IC Degn Georgo Veron, Y-Chang Lu, and Robert W. Dutton Center for Integrated Sytem, Stanford Unverty, Stanford, CA 9435 yorgo@gloworm.tanford.edu
Buckling analysis of piezoelectric composite plates using NURBSbased isogeometric finite elements and higher-order shear deformation theory
 Proceedng of the 3 rd nternatonal Conference on Fracture Fatgue and Wear, pp. 134-140, 014 Bucklng analy of pezoelectrc compote plate ung NURBSbaed ogeometrc fnte element and hgher-order hear deformaton
Proceedng of the 3 rd nternatonal Conference on Fracture Fatgue and Wear, pp. 134-140, 014 Bucklng analy of pezoelectrc compote plate ung NURBSbaed ogeometrc fnte element and hgher-order hear deformaton
MODIFIED GENERAL TRANSFER MATRIX METHOD FOR LINEAR ROTOR BEARING SYSTEMS , Dhenkanal, Orissa, India
 IV arn Autrala 9- July, 007 Abtract MODIFIED GENERAL TRANFER MATRIX METHOD FOR LINEAR ROTOR BEARING YTEM B B Maharath, R R Dah and T Rout Department of Mechancal Engneerng, IGIT, arang 769 6, Dhenkanal,
IV arn Autrala 9- July, 007 Abtract MODIFIED GENERAL TRANFER MATRIX METHOD FOR LINEAR ROTOR BEARING YTEM B B Maharath, R R Dah and T Rout Department of Mechancal Engneerng, IGIT, arang 769 6, Dhenkanal,
Statistical Properties of the OLS Coefficient Estimators. 1. Introduction
 ECOOMICS 35* -- OTE 4 ECO 35* -- OTE 4 Stattcal Properte of the OLS Coeffcent Etmator Introducton We derved n ote the OLS (Ordnary Leat Square etmator ˆβ j (j, of the regreon coeffcent βj (j, n the mple
ECOOMICS 35* -- OTE 4 ECO 35* -- OTE 4 Stattcal Properte of the OLS Coeffcent Etmator Introducton We derved n ote the OLS (Ordnary Leat Square etmator ˆβ j (j, of the regreon coeffcent βj (j, n the mple
Root Locus Techniques
 Root Locu Technque ELEC 32 Cloed-Loop Control The control nput u t ynthezed baed on the a pror knowledge of the ytem plant, the reference nput r t, and the error gnal, e t The control ytem meaure the output,
Root Locu Technque ELEC 32 Cloed-Loop Control The control nput u t ynthezed baed on the a pror knowledge of the ytem plant, the reference nput r t, and the error gnal, e t The control ytem meaure the output,
CHAPTER 14 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY
 CHAPTER 4 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY 4 Introducton A partcle n orbt around a pont mass or a sphercally symmetrc mass dstrbuton s movng n a gravtatonal potental of the form GM / r In ths potental t moves
CHAPTER 4 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY 4 Introducton A partcle n orbt around a pont mass or a sphercally symmetrc mass dstrbuton s movng n a gravtatonal potental of the form GM / r In ths potental t moves
Indeterminate pin-jointed frames (trusses)
 Indetermnate pn-jonted frames (trusses) Calculaton of member forces usng force method I. Statcal determnacy. The degree of freedom of any truss can be derved as: w= k d a =, where k s the number of all
Indetermnate pn-jonted frames (trusses) Calculaton of member forces usng force method I. Statcal determnacy. The degree of freedom of any truss can be derved as: w= k d a =, where k s the number of all
MODELLING OF TRANSIENT HEAT TRANSPORT IN TWO-LAYERED CRYSTALLINE SOLID FILMS USING THE INTERVAL LATTICE BOLTZMANN METHOD
 Journal o Appled Mathematc and Computatonal Mechanc 7, 6(4), 57-65 www.amcm.pcz.pl p-issn 99-9965 DOI:.75/jamcm.7.4.6 e-issn 353-588 MODELLING OF TRANSIENT HEAT TRANSPORT IN TWO-LAYERED CRYSTALLINE SOLID
Journal o Appled Mathematc and Computatonal Mechanc 7, 6(4), 57-65 www.amcm.pcz.pl p-issn 99-9965 DOI:.75/jamcm.7.4.6 e-issn 353-588 MODELLING OF TRANSIENT HEAT TRANSPORT IN TWO-LAYERED CRYSTALLINE SOLID
A new Approach for Solving Linear Ordinary Differential Equations
 , ISSN 974-57X (Onlne), ISSN 974-5718 (Prnt), Vol. ; Issue No. 1; Year 14, Copyrght 13-14 by CESER PUBLICATIONS A new Approach for Solvng Lnear Ordnary Dfferental Equatons Fawz Abdelwahd Department of
, ISSN 974-57X (Onlne), ISSN 974-5718 (Prnt), Vol. ; Issue No. 1; Year 14, Copyrght 13-14 by CESER PUBLICATIONS A new Approach for Solvng Lnear Ordnary Dfferental Equatons Fawz Abdelwahd Department of
Module 1 : The equation of continuity. Lecture 1: Equation of Continuity
 1 Module 1 : The equaton of contnuty Lecture 1: Equaton of Contnuty 2 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer: Modules 1. THE EQUATION OF CONTINUITY : Lectures 1-6 () () () (v) (v) Overall Mass Balance Momentum
1 Module 1 : The equaton of contnuty Lecture 1: Equaton of Contnuty 2 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer: Modules 1. THE EQUATION OF CONTINUITY : Lectures 1-6 () () () (v) (v) Overall Mass Balance Momentum
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
 COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS INTRODUCTION We know that x 0 for all x R e the square of a real number (whether postve, negatve or ero) s non-negatve Hence the equatons x, x, x + 7 0 etc are not
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS INTRODUCTION We know that x 0 for all x R e the square of a real number (whether postve, negatve or ero) s non-negatve Hence the equatons x, x, x + 7 0 etc are not
In this section is given an overview of the common elasticity models.
 Secton 4.1 4.1 Elastc Solds In ths secton s gven an overvew of the common elastcty models. 4.1.1 The Lnear Elastc Sold The classcal Lnear Elastc model, or Hooean model, has the followng lnear relatonshp
Secton 4.1 4.1 Elastc Solds In ths secton s gven an overvew of the common elastcty models. 4.1.1 The Lnear Elastc Sold The classcal Lnear Elastc model, or Hooean model, has the followng lnear relatonshp
HEAT TRANSFER THROUGH ANNULAR COMPOSITE FINS
 Journal of Mechancal Engneerng and Technology (JMET) Volume 4, Issue 1, Jan-June 2016, pp. 01-10, Artcle ID: JMET_04_01_001 Avalable onlne at http://www.aeme.com/jmet/ssues.asp?jtype=jmet&vtype=4&itype=1
Journal of Mechancal Engneerng and Technology (JMET) Volume 4, Issue 1, Jan-June 2016, pp. 01-10, Artcle ID: JMET_04_01_001 Avalable onlne at http://www.aeme.com/jmet/ssues.asp?jtype=jmet&vtype=4&itype=1
Wind - Induced Vibration Control of Long - Span Bridges by Multiple Tuned Mass Dampers
 Tamkang Journal of Scence and Engneerng, Vol. 3, o., pp. -3 (000) Wnd - Induced Vbraton Control of Long - Span Brdge by Multple Tuned Ma Damper Yuh-Y Ln, Ch-Mng Cheng and Davd Sun Department of Cvl Engneerng
Tamkang Journal of Scence and Engneerng, Vol. 3, o., pp. -3 (000) Wnd - Induced Vbraton Control of Long - Span Brdge by Multple Tuned Ma Damper Yuh-Y Ln, Ch-Mng Cheng and Davd Sun Department of Cvl Engneerng
BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHODS FOR VIBRATION PROBLEMS. Ashok D. Belegundu Professor of Mechanical Engineering Penn State University
 BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHODS FOR VIBRATION PROBLEMS by Aho D. Belegundu Profeor of Mechancal Engneerng Penn State Unverty ahobelegundu@yahoo.com ASEE Fello, Summer 3 Colleague at NASA Goddard: Danel S. Kaufman
BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHODS FOR VIBRATION PROBLEMS by Aho D. Belegundu Profeor of Mechancal Engneerng Penn State Unverty ahobelegundu@yahoo.com ASEE Fello, Summer 3 Colleague at NASA Goddard: Danel S. Kaufman
Variable Structure Control ~ Basics
 Varable Structure Control ~ Bac Harry G. Kwatny Department of Mechancal Engneerng & Mechanc Drexel Unverty Outlne A prelmnary example VS ytem, ldng mode, reachng Bac of dcontnuou ytem Example: underea
Varable Structure Control ~ Bac Harry G. Kwatny Department of Mechancal Engneerng & Mechanc Drexel Unverty Outlne A prelmnary example VS ytem, ldng mode, reachng Bac of dcontnuou ytem Example: underea
Open Systems: Chemical Potential and Partial Molar Quantities Chemical Potential
 Open Systems: Chemcal Potental and Partal Molar Quanttes Chemcal Potental For closed systems, we have derved the followng relatonshps: du = TdS pdv dh = TdS + Vdp da = SdT pdv dg = VdP SdT For open systems,
Open Systems: Chemcal Potental and Partal Molar Quanttes Chemcal Potental For closed systems, we have derved the followng relatonshps: du = TdS pdv dh = TdS + Vdp da = SdT pdv dg = VdP SdT For open systems,
AGC Introduction
 . Introducton AGC 3 The prmary controller response to a load/generaton mbalance results n generaton adjustment so as to mantan load/generaton balance. However, due to droop, t also results n a non-zero
. Introducton AGC 3 The prmary controller response to a load/generaton mbalance results n generaton adjustment so as to mantan load/generaton balance. However, due to droop, t also results n a non-zero
A Computational Method for Solving Two Point Boundary Value Problems of Order Four
 Yoge Gupta et al, Int. J. Comp. Tec. Appl., Vol (5), - ISSN:9-09 A Computatonal Metod for Solvng Two Pont Boundary Value Problem of Order Four Yoge Gupta Department of Matematc Unted College of Engg and
Yoge Gupta et al, Int. J. Comp. Tec. Appl., Vol (5), - ISSN:9-09 A Computatonal Metod for Solvng Two Pont Boundary Value Problem of Order Four Yoge Gupta Department of Matematc Unted College of Engg and
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Calculus of Variations II
 1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Calculus of Varatons II 2 Calculus of Varatons: Generalzaton (no constrant yet) Suppose now that F depends on several dependent varables : We need to fnd such that has a statonary
1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Calculus of Varatons II 2 Calculus of Varatons: Generalzaton (no constrant yet) Suppose now that F depends on several dependent varables : We need to fnd such that has a statonary
MATHEMATICAL AND COMPUTER HOMOGENIZATION MODELS FOR BULK MIXTURE COMPOSITE MATERIALS WITH IMPERFECT INTERFACES
 Materal Phyc and Mechanc 37 (218) 34-41 Receved: December 22, 217 MATHEMATICAL AND COMPUTER HOMOGENIZATION MODELS FOR BULK MIXTURE COMPOSITE MATERIALS WITH IMPERFECT INTERFACES A.A. Naedkna 1 *, A. Rajagopal
Materal Phyc and Mechanc 37 (218) 34-41 Receved: December 22, 217 MATHEMATICAL AND COMPUTER HOMOGENIZATION MODELS FOR BULK MIXTURE COMPOSITE MATERIALS WITH IMPERFECT INTERFACES A.A. Naedkna 1 *, A. Rajagopal
Problem #1. Known: All required parameters. Schematic: Find: Depth of freezing as function of time. Strategy:
 BEE 3500 013 Prelm Soluton Problem #1 Known: All requred parameter. Schematc: Fnd: Depth of freezng a functon of tme. Strategy: In thee mplfed analy for freezng tme, a wa done n cla for a lab geometry,
BEE 3500 013 Prelm Soluton Problem #1 Known: All requred parameter. Schematc: Fnd: Depth of freezng a functon of tme. Strategy: In thee mplfed analy for freezng tme, a wa done n cla for a lab geometry,
A NEW APPROACH IN THE RAYLEIGH - SCHRÖDINGER PERTURBATION THEORY FOR THE ROVIBRATIONAL PROBLEM
 Lebanee Scence Journal, Vol., No., A NEW APPROACH IN THE RAYLEIGH - SCHRÖDINGER PERTURBATION THEORY FOR THE ROVIBRATIONAL PROBLEM M. Korek Faculty of Scence, Berut Arab Unerty, P.O.Box - Rad El Solh, Berut
Lebanee Scence Journal, Vol., No., A NEW APPROACH IN THE RAYLEIGH - SCHRÖDINGER PERTURBATION THEORY FOR THE ROVIBRATIONAL PROBLEM M. Korek Faculty of Scence, Berut Arab Unerty, P.O.Box - Rad El Solh, Berut
Thermal-Fluids I. Chapter 18 Transient heat conduction. Dr. Primal Fernando Ph: (850)
 hermal-fluds I Chapter 18 ransent heat conducton Dr. Prmal Fernando prmal@eng.fsu.edu Ph: (850) 410-6323 1 ransent heat conducton In general, he temperature of a body vares wth tme as well as poston. In
hermal-fluds I Chapter 18 ransent heat conducton Dr. Prmal Fernando prmal@eng.fsu.edu Ph: (850) 410-6323 1 ransent heat conducton In general, he temperature of a body vares wth tme as well as poston. In
PROBABILITY-CONSISTENT SCENARIO EARTHQUAKE AND ITS APPLICATION IN ESTIMATION OF GROUND MOTIONS
 PROBABILITY-COSISTET SCEARIO EARTHQUAKE AD ITS APPLICATIO I ESTIATIO OF GROUD OTIOS Q-feng LUO SUARY Th paper preent a new defnton of probablty-content cenaro earthquae PCSE and an evaluaton method of
PROBABILITY-COSISTET SCEARIO EARTHQUAKE AD ITS APPLICATIO I ESTIATIO OF GROUD OTIOS Q-feng LUO SUARY Th paper preent a new defnton of probablty-content cenaro earthquae PCSE and an evaluaton method of
Scattering cross section (scattering width)
 Scatterng cro ecton (catterng wdth) We aw n the begnnng how a catterng cro ecton defned for a fnte catterer n ter of the cattered power An nfnte cylnder, however, not a fnte object The feld radated by
Scatterng cro ecton (catterng wdth) We aw n the begnnng how a catterng cro ecton defned for a fnte catterer n ter of the cattered power An nfnte cylnder, however, not a fnte object The feld radated by
COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD
 COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD Ákos Jósef Lengyel, István Ecsed Assstant Lecturer, Professor of Mechancs, Insttute of Appled Mechancs, Unversty of Mskolc, Mskolc-Egyetemváros,
COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD Ákos Jósef Lengyel, István Ecsed Assstant Lecturer, Professor of Mechancs, Insttute of Appled Mechancs, Unversty of Mskolc, Mskolc-Egyetemváros,
Transfer Functions. Convenient representation of a linear, dynamic model. A transfer function (TF) relates one input and one output: ( ) system
 Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
DUE: WEDS FEB 21ST 2018
 HOMEWORK # 1: FINITE DIFFERENCES IN ONE DIMENSION DUE: WEDS FEB 21ST 2018 1. Theory Beam bendng s a classcal engneerng analyss. The tradtonal soluton technque makes smplfyng assumptons such as a constant
HOMEWORK # 1: FINITE DIFFERENCES IN ONE DIMENSION DUE: WEDS FEB 21ST 2018 1. Theory Beam bendng s a classcal engneerng analyss. The tradtonal soluton technque makes smplfyng assumptons such as a constant
LECTURER: PM DR MAZLAN ABDUL WAHID PM Dr Mazlan Abdul Wahid
 H E A R A N S F E R HEA RANSFER SME 4463 LECURER: PM DR MAZLAN ABDUL WAHID http://www.fkm.utm.my/~mazlan C H A P E R 3 Dr Mazlan - SME 4463 H E A R A N S F E R Chapter 5 ranent Conducton PM Dr Mazlan Abdul
H E A R A N S F E R HEA RANSFER SME 4463 LECURER: PM DR MAZLAN ABDUL WAHID http://www.fkm.utm.my/~mazlan C H A P E R 3 Dr Mazlan - SME 4463 H E A R A N S F E R Chapter 5 ranent Conducton PM Dr Mazlan Abdul
M. Mechee, 1,2 N. Senu, 3 F. Ismail, 3 B. Nikouravan, 4 and Z. Siri Introduction
 Hndaw Publhng Corporaton Mathematcal Problem n Engneerng Volume 23, Artcle ID 795397, 7 page http://dx.do.org/.55/23/795397 Reearch Artcle A Three-Stage Ffth-Order Runge-Kutta Method for Drectly Solvng
Hndaw Publhng Corporaton Mathematcal Problem n Engneerng Volume 23, Artcle ID 795397, 7 page http://dx.do.org/.55/23/795397 Reearch Artcle A Three-Stage Ffth-Order Runge-Kutta Method for Drectly Solvng
Finite Element Modelling of truss/cable structures
 Pet Schreurs Endhoven Unversty of echnology Department of Mechancal Engneerng Materals echnology November 3, 214 Fnte Element Modellng of truss/cable structures 1 Fnte Element Analyss of prestressed structures
Pet Schreurs Endhoven Unversty of echnology Department of Mechancal Engneerng Materals echnology November 3, 214 Fnte Element Modellng of truss/cable structures 1 Fnte Element Analyss of prestressed structures
Quick Visit to Bernoulli Land
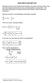 Although we have een the Bernoull equaton and een t derved before, th next note how t dervaton for an uncopreble & nvcd flow. The dervaton follow that of Kuethe &Chow ot cloely (I lke t better than Anderon).
Although we have een the Bernoull equaton and een t derved before, th next note how t dervaton for an uncopreble & nvcd flow. The dervaton follow that of Kuethe &Chow ot cloely (I lke t better than Anderon).
This appendix presents the derivations and proofs omitted from the main text.
 Onlne Appendx A Appendx: Omtted Dervaton and Proof Th appendx preent the dervaton and proof omtted from the man text A Omtted dervaton n Secton Mot of the analy provded n the man text Here, we formally
Onlne Appendx A Appendx: Omtted Dervaton and Proof Th appendx preent the dervaton and proof omtted from the man text A Omtted dervaton n Secton Mot of the analy provded n the man text Here, we formally
A P PL I CA TIONS OF FRACTIONAL EXTERIOR DI F F ER EN TIAL IN THR EE- DI M ENSIONAL S PAC E Ξ
 Appled Mathematcs and Mechancs ( Englsh Edton, Vol 24, No 3, Mar 2003) Publshed by Shangha Unversty, Shangha, Chna Artcle ID : 0253-4827 (2003) 03-0256-05 A P PL I CA TIONS OF FRACTIONAL EXTERIOR DI F
Appled Mathematcs and Mechancs ( Englsh Edton, Vol 24, No 3, Mar 2003) Publshed by Shangha Unversty, Shangha, Chna Artcle ID : 0253-4827 (2003) 03-0256-05 A P PL I CA TIONS OF FRACTIONAL EXTERIOR DI F
STATIC ANALYSIS OF TWO-LAYERED PIEZOELECTRIC BEAMS WITH IMPERFECT SHEAR CONNECTION
 STATIC ANALYSIS OF TWO-LERED PIEZOELECTRIC BEAMS WITH IMPERFECT SHEAR CONNECTION Ákos József Lengyel István Ecsed Assstant Lecturer Emertus Professor Insttute of Appled Mechancs Unversty of Mskolc Mskolc-Egyetemváros
STATIC ANALYSIS OF TWO-LERED PIEZOELECTRIC BEAMS WITH IMPERFECT SHEAR CONNECTION Ákos József Lengyel István Ecsed Assstant Lecturer Emertus Professor Insttute of Appled Mechancs Unversty of Mskolc Mskolc-Egyetemváros
Team. Outline. Statistics and Art: Sampling, Response Error, Mixed Models, Missing Data, and Inference
 Team Stattc and Art: Samplng, Repone Error, Mxed Model, Mng Data, and nference Ed Stanek Unverty of Maachuett- Amhert, USA 9/5/8 9/5/8 Outlne. Example: Doe-repone Model n Toxcology. ow to Predct Realzed
Team Stattc and Art: Samplng, Repone Error, Mxed Model, Mng Data, and nference Ed Stanek Unverty of Maachuett- Amhert, USA 9/5/8 9/5/8 Outlne. Example: Doe-repone Model n Toxcology. ow to Predct Realzed
Module 3: Element Properties Lecture 1: Natural Coordinates
 Module 3: Element Propertes Lecture : Natural Coordnates Natural coordnate system s bascally a local coordnate system whch allows the specfcaton of a pont wthn the element by a set of dmensonless numbers
Module 3: Element Propertes Lecture : Natural Coordnates Natural coordnate system s bascally a local coordnate system whch allows the specfcaton of a pont wthn the element by a set of dmensonless numbers
Electrical double layer: revisit based on boundary conditions
 Electrcal double layer: revst based on boundary condtons Jong U. Km Department of Electrcal and Computer Engneerng, Texas A&M Unversty College Staton, TX 77843-318, USA Abstract The electrcal double layer
Electrcal double layer: revst based on boundary condtons Jong U. Km Department of Electrcal and Computer Engneerng, Texas A&M Unversty College Staton, TX 77843-318, USA Abstract The electrcal double layer
Two Approaches to Proving. Goldbach s Conjecture
 Two Approache to Provng Goldbach Conecture By Bernard Farley Adved By Charle Parry May 3 rd 5 A Bref Introducton to Goldbach Conecture In 74 Goldbach made h mot famou contrbuton n mathematc wth the conecture
Two Approache to Provng Goldbach Conecture By Bernard Farley Adved By Charle Parry May 3 rd 5 A Bref Introducton to Goldbach Conecture In 74 Goldbach made h mot famou contrbuton n mathematc wth the conecture
Supplemental document
 Electronc Supplementary Materal (ESI) for Physcal Chemstry Chemcal Physcs. Ths journal s the Owner Socetes 01 Supplemental document Behnam Nkoobakht School of Chemstry, The Unversty of Sydney, Sydney,
Electronc Supplementary Materal (ESI) for Physcal Chemstry Chemcal Physcs. Ths journal s the Owner Socetes 01 Supplemental document Behnam Nkoobakht School of Chemstry, The Unversty of Sydney, Sydney,
Chapter 5. Solution of System of Linear Equations. Module No. 6. Solution of Inconsistent and Ill Conditioned Systems
 Numercal Analyss by Dr. Anta Pal Assstant Professor Department of Mathematcs Natonal Insttute of Technology Durgapur Durgapur-713209 emal: anta.bue@gmal.com 1 . Chapter 5 Soluton of System of Lnear Equatons
Numercal Analyss by Dr. Anta Pal Assstant Professor Department of Mathematcs Natonal Insttute of Technology Durgapur Durgapur-713209 emal: anta.bue@gmal.com 1 . Chapter 5 Soluton of System of Lnear Equatons
Inductance Calculation for Conductors of Arbitrary Shape
 CRYO/02/028 Aprl 5, 2002 Inductance Calculaton for Conductors of Arbtrary Shape L. Bottura Dstrbuton: Internal Summary In ths note we descrbe a method for the numercal calculaton of nductances among conductors
CRYO/02/028 Aprl 5, 2002 Inductance Calculaton for Conductors of Arbtrary Shape L. Bottura Dstrbuton: Internal Summary In ths note we descrbe a method for the numercal calculaton of nductances among conductors
I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 ME 270 Fall 2012 Fnal Exam Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem
ME 270 Fall 2012 Fnal Exam Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem
Physics 111. CQ1: springs. con t. Aristocrat at a fixed angle. Wednesday, 8-9 pm in NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm in CCLIR 468.
 c Announcement day, ober 8, 004 Ch 8: Ch 10: Work done by orce at an angle Power Rotatonal Knematc angular dplacement angular velocty angular acceleraton Wedneday, 8-9 pm n NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm
c Announcement day, ober 8, 004 Ch 8: Ch 10: Work done by orce at an angle Power Rotatonal Knematc angular dplacement angular velocty angular acceleraton Wedneday, 8-9 pm n NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm
PHY2049 Exam 2 solutions Fall 2016 Solution:
 PHY2049 Exam 2 solutons Fall 2016 General strategy: Fnd two resstors, one par at a tme, that are connected ether n SERIES or n PARALLEL; replace these two resstors wth one of an equvalent resstance. Now
PHY2049 Exam 2 solutons Fall 2016 General strategy: Fnd two resstors, one par at a tme, that are connected ether n SERIES or n PARALLEL; replace these two resstors wth one of an equvalent resstance. Now
KEY POINTS FOR NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF INCLINATION OF BUILDINGS ON LIQUEFIABLE SOIL LAYERS
 KY POINTS FOR NUMRICAL SIMULATION OF INCLINATION OF BUILDINGS ON LIQUFIABL SOIL LAYRS Jn Xu 1, Xaomng Yuan, Jany Zhang 3,Fanchao Meng 1 1 Student, Dept. of Geotechncal ngneerng, Inttute of ngneerng Mechanc,
KY POINTS FOR NUMRICAL SIMULATION OF INCLINATION OF BUILDINGS ON LIQUFIABL SOIL LAYRS Jn Xu 1, Xaomng Yuan, Jany Zhang 3,Fanchao Meng 1 1 Student, Dept. of Geotechncal ngneerng, Inttute of ngneerng Mechanc,
Circuit Theorems. Introduction
 //5 Crcut eorem ntroducton nearty Property uperpoton ource Tranformaton eenn eorem orton eorem Maxmum Power Tranfer ummary ntroducton To deelop analy technque applcable to lnear crcut. To mplfy crcut analy
//5 Crcut eorem ntroducton nearty Property uperpoton ource Tranformaton eenn eorem orton eorem Maxmum Power Tranfer ummary ntroducton To deelop analy technque applcable to lnear crcut. To mplfy crcut analy
Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer
 Master degree n Mechancal Engneerng Numercal Heat and Mass Transfer 06-Fnte-Dfference Method (One-dmensonal, steady state heat conducton) Fausto Arpno f.arpno@uncas.t Introducton Why we use models and
Master degree n Mechancal Engneerng Numercal Heat and Mass Transfer 06-Fnte-Dfference Method (One-dmensonal, steady state heat conducton) Fausto Arpno f.arpno@uncas.t Introducton Why we use models and
CuiYing Fan, MingHao Zhao, JiaPeng Wang & Ernian Pan
 Analyss of an arbtrarly orented crack n a fnte pezoelectrc plane va the hybrd extended dsplacement dscontnutyfundamental soluton method CuYng Fan, MngHao Zhao, JaPeng Wang & Ernan Pan Computatonal Mechancs
Analyss of an arbtrarly orented crack n a fnte pezoelectrc plane va the hybrd extended dsplacement dscontnutyfundamental soluton method CuYng Fan, MngHao Zhao, JaPeng Wang & Ernan Pan Computatonal Mechancs
( ) + + REFLECTION FROM A METALLIC SURFACE
 REFLECTION FROM A METALLIC SURFACE For a metallc medum the delectrc functon and the ndex of refracton are complex valued functons. Ths s also the case for semconductors and nsulators n certan frequency
REFLECTION FROM A METALLIC SURFACE For a metallc medum the delectrc functon and the ndex of refracton are complex valued functons. Ths s also the case for semconductors and nsulators n certan frequency
Lecture 10 Support Vector Machines II
 Lecture 10 Support Vector Machnes II 22 February 2016 Taylor B. Arnold Yale Statstcs STAT 365/665 1/28 Notes: Problem 3 s posted and due ths upcomng Frday There was an early bug n the fake-test data; fxed
Lecture 10 Support Vector Machnes II 22 February 2016 Taylor B. Arnold Yale Statstcs STAT 365/665 1/28 Notes: Problem 3 s posted and due ths upcomng Frday There was an early bug n the fake-test data; fxed
Joint Source Coding and Higher-Dimension Modulation
 Jont Codng and Hgher-Dmenon Modulaton Tze C. Wong and Huck M. Kwon Electrcal Engneerng and Computer Scence Wchta State Unvert, Wchta, Kana 676, USA {tcwong; huck.kwon}@wchta.edu Abtract Th paper propoe
Jont Codng and Hgher-Dmenon Modulaton Tze C. Wong and Huck M. Kwon Electrcal Engneerng and Computer Scence Wchta State Unvert, Wchta, Kana 676, USA {tcwong; huck.kwon}@wchta.edu Abtract Th paper propoe
The Tangential Force Distribution on Inner Cylinder of Power Law Fluid Flowing in Eccentric Annuli with the Inner Cylinder Reciprocating Axially
 Open Journal of Flud Dynamcs, 2015, 5, 183-187 Publshed Onlne June 2015 n ScRes. http://www.scrp.org/journal/ojfd http://dx.do.org/10.4236/ojfd.2015.52020 The Tangental Force Dstrbuton on Inner Cylnder
Open Journal of Flud Dynamcs, 2015, 5, 183-187 Publshed Onlne June 2015 n ScRes. http://www.scrp.org/journal/ojfd http://dx.do.org/10.4236/ojfd.2015.52020 The Tangental Force Dstrbuton on Inner Cylnder
Z Patch Antenna Embedded in Superstrates Anisotropic Media
 IOSR Journal of Electronc and Communcaton Engneerng (IOSR-JECE e-issn: 78-834,p- ISSN: 78-8735.Volume 11, Iue 6, Ver. III (Nov.-Dec.016, PP 35-45 www.orournal.org Adnan Affand 1, Mamdoh Gharb 1,Abdullah
IOSR Journal of Electronc and Communcaton Engneerng (IOSR-JECE e-issn: 78-834,p- ISSN: 78-8735.Volume 11, Iue 6, Ver. III (Nov.-Dec.016, PP 35-45 www.orournal.org Adnan Affand 1, Mamdoh Gharb 1,Abdullah
ENTROPY BOUNDS USING ARITHMETIC- GEOMETRIC-HARMONIC MEAN INEQUALITY. Guru Nanak Dev University Amritsar, , INDIA
 Internatonal Journal of Pure and Appled Mathematc Volume 89 No. 5 2013, 719-730 ISSN: 1311-8080 prnted veron; ISSN: 1314-3395 on-lne veron url: http://.jpam.eu do: http://dx.do.org/10.12732/jpam.v895.8
Internatonal Journal of Pure and Appled Mathematc Volume 89 No. 5 2013, 719-730 ISSN: 1311-8080 prnted veron; ISSN: 1314-3395 on-lne veron url: http://.jpam.eu do: http://dx.do.org/10.12732/jpam.v895.8
Physics 4B. A positive value is obtained, so the current is counterclockwise around the circuit.
 Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM
 ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
Integral Transforms and Dual Integral Equations to Solve Heat Equation with Mixed Conditions
 Int J Open Probles Copt Math, Vol 7, No 4, Deceber 214 ISSN 1998-6262; Copyrght ICSS Publcaton, 214 www-csrsorg Integral Transfors and Dual Integral Equatons to Solve Heat Equaton wth Mxed Condtons Naser
Int J Open Probles Copt Math, Vol 7, No 4, Deceber 214 ISSN 1998-6262; Copyrght ICSS Publcaton, 214 www-csrsorg Integral Transfors and Dual Integral Equatons to Solve Heat Equaton wth Mxed Condtons Naser
Appendix B. The Finite Difference Scheme
 140 APPENDIXES Appendx B. The Fnte Dfference Scheme In ths appendx we present numercal technques whch are used to approxmate solutons of system 3.1 3.3. A comprehensve treatment of theoretcal and mplementaton
140 APPENDIXES Appendx B. The Fnte Dfference Scheme In ths appendx we present numercal technques whch are used to approxmate solutons of system 3.1 3.3. A comprehensve treatment of theoretcal and mplementaton
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Winter 16 Final, March 16, 2016
 ME140 - Lnear rcuts - Wnter 16 Fnal, March 16, 2016 Instructons () The exam s open book. You may use your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator wth no communcaton capabltes. () You have
ME140 - Lnear rcuts - Wnter 16 Fnal, March 16, 2016 Instructons () The exam s open book. You may use your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator wth no communcaton capabltes. () You have
MULTIPLE REGRESSION ANALYSIS For the Case of Two Regressors
 MULTIPLE REGRESSION ANALYSIS For the Cae of Two Regreor In the followng note, leat-quare etmaton developed for multple regreon problem wth two eplanator varable, here called regreor (uch a n the Fat Food
MULTIPLE REGRESSION ANALYSIS For the Cae of Two Regreor In the followng note, leat-quare etmaton developed for multple regreon problem wth two eplanator varable, here called regreor (uch a n the Fat Food
Electrostatic Potential from Transmembrane Currents
 Electrostatc Potental from Transmembrane Currents Let s assume that the current densty j(r, t) s ohmc;.e., lnearly proportonal to the electrc feld E(r, t): j = σ c (r)e (1) wth conductvty σ c = σ c (r).
Electrostatc Potental from Transmembrane Currents Let s assume that the current densty j(r, t) s ohmc;.e., lnearly proportonal to the electrc feld E(r, t): j = σ c (r)e (1) wth conductvty σ c = σ c (r).
Physics 120. Exam #1. April 15, 2011
 Phyc 120 Exam #1 Aprl 15, 2011 Name Multple Choce /16 Problem #1 /28 Problem #2 /28 Problem #3 /28 Total /100 PartI:Multple Choce:Crclethebetanwertoeachqueton.Anyothermark wllnotbegvencredt.eachmultple
Phyc 120 Exam #1 Aprl 15, 2011 Name Multple Choce /16 Problem #1 /28 Problem #2 /28 Problem #3 /28 Total /100 PartI:Multple Choce:Crclethebetanwertoeachqueton.Anyothermark wllnotbegvencredt.eachmultple
MAGNUM - A Fortran Library for the Calculation of Magnetic Configurations
 CRYO/6/34 September, 3, 6 MAGNUM - A Fortran Lbrary for the Calculaton of Magnetc Confguratons L. Bottura Dstrbuton: Keywords: P. Bruzzone, M. Calv, J. Lster, C. Marnucc (EPFL/CRPP), A. Portone (EFDA-
CRYO/6/34 September, 3, 6 MAGNUM - A Fortran Lbrary for the Calculaton of Magnetc Confguratons L. Bottura Dstrbuton: Keywords: P. Bruzzone, M. Calv, J. Lster, C. Marnucc (EPFL/CRPP), A. Portone (EFDA-
MEASUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTIA
 1. measurement MESUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTI The am of ths measurement s to determne the moment of nerta of the rotor of an electrc motor. 1. General relatons Rotatng moton and moment of nerta Let us
1. measurement MESUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTI The am of ths measurement s to determne the moment of nerta of the rotor of an electrc motor. 1. General relatons Rotatng moton and moment of nerta Let us
n α j x j = 0 j=1 has a nontrivial solution. Here A is the n k matrix whose jth column is the vector for all t j=0
 MODULE 2 Topcs: Lnear ndependence, bass and dmenson We have seen that f n a set of vectors one vector s a lnear combnaton of the remanng vectors n the set then the span of the set s unchanged f that vector
MODULE 2 Topcs: Lnear ndependence, bass and dmenson We have seen that f n a set of vectors one vector s a lnear combnaton of the remanng vectors n the set then the span of the set s unchanged f that vector
Pressure Measurements Laboratory
 Lab # Pressure Measurements Laboratory Objectves:. To get hands-on experences on how to make pressure (surface pressure, statc pressure and total pressure nsde flow) measurements usng conventonal pressuremeasurng
Lab # Pressure Measurements Laboratory Objectves:. To get hands-on experences on how to make pressure (surface pressure, statc pressure and total pressure nsde flow) measurements usng conventonal pressuremeasurng
Phys 402: Raman Scattering. Spring Introduction: Brillouin and Raman spectroscopy. Raman scattering: how does it look like?
 Phy 402: Raman Scatterng Sprng 2008 1 Introducton: Brlloun and Raman pectrocopy Inelatc lght catterng medated by the electronc polarzablty of the medum a materal or a molecule catter rradant lght from
Phy 402: Raman Scatterng Sprng 2008 1 Introducton: Brlloun and Raman pectrocopy Inelatc lght catterng medated by the electronc polarzablty of the medum a materal or a molecule catter rradant lght from
AN ADVANCED 1D FINITE ELEMENT SOLUTION FOR THERMOELASTICITY PROBLEMS IN LAMINATED BEAMS
 AN ADVANCED 1D FINIE ELEMEN SOLUION FOR HERMOELASICIY PROBLEMS IN LAMINAED BEAMS E. Carrera 1, M. Flpp 2 and A. Entezar 3 1 DIMEAS, Poltecnco d orno, erao.carrera@polto.t, www.ul2.polto.t 2 DIMEAS, Poltecnco
AN ADVANCED 1D FINIE ELEMEN SOLUION FOR HERMOELASICIY PROBLEMS IN LAMINAED BEAMS E. Carrera 1, M. Flpp 2 and A. Entezar 3 1 DIMEAS, Poltecnco d orno, erao.carrera@polto.t, www.ul2.polto.t 2 DIMEAS, Poltecnco
Implicit Integration Henyey Method
 Implct Integraton Henyey Method In realstc stellar evoluton codes nstead of a drect ntegraton usng for example the Runge-Kutta method one employs an teratve mplct technque. Ths s because the structure
Implct Integraton Henyey Method In realstc stellar evoluton codes nstead of a drect ntegraton usng for example the Runge-Kutta method one employs an teratve mplct technque. Ths s because the structure
χ x B E (c) Figure 2.1.1: (a) a material particle in a body, (b) a place in space, (c) a configuration of the body
 Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
Parametric Study of Steel-Lined Pressure Shafts in Anisotropic Rock
 SEE Tunnel:Promotng Tunnelng n SEE Regon May 22-28, 2015, Lacroma Valamar Congre Center, Dubrovnk, Croata Parametrc Study of Steel-Lned Preure Shaft n Anotropc Rock Alexandre J. PACHOUD, Laboratory of
SEE Tunnel:Promotng Tunnelng n SEE Regon May 22-28, 2015, Lacroma Valamar Congre Center, Dubrovnk, Croata Parametrc Study of Steel-Lned Preure Shaft n Anotropc Rock Alexandre J. PACHOUD, Laboratory of
