Kernels. Machine Learning CSE446 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington. October 28, Carlos Guestrin
|
|
|
- Cecil Francis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kernels Machine Learning CSE446 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 28, 2013 Carlos Guestrin Linear Separability: More formally, Using Margin Data linearly separable, if there exists a vector a margin Such that Carlos Guestrin
2 Perceptron Analysis: Linearly Separable Case Theorem [Block, Novikoff]: Given a sequence of labeled examples: Each feature vector has bounded norm: If dataset is linearly separable: Then the number of mistakes made by the online perceptron on any such sequence is bounded by Carlos Guestrin Beyond Linearly Separable Case Perceptron algorithm is super cool! No assumption about data distribution! Could be generated by an oblivious adversary, no need to be iid Makes a fixed number of mistakes, and it s done for ever! Even if you see infinite data However, real world not linearly separable Can t expect never to make mistakes again Analysis extends to non-linearly separable case Very similar bound, see Freund & Schapire Converges, but ultimately may not give good accuracy (make many many many mistakes) Carlos Guestrin
3 What if the data is not linearly separable? Use features of features of features of features. Feature space can get really large really quickly! Carlos Guestrin Higher order polynomials number of monomial terms number of input dimensions d=4 d=3 d=2 m input features d degree of polynomial grows fast! d = 6, m = 100 about 1.6 billion terms Carlos Guestrin
4 Perceptron Revisited Given weight vector w (t), predict point x by: Mistake at time t: w (t+1) ç w (t) + y (t) x (t) Thus, write weight vector in terms of mistaken data points only: Let M (t) be time steps up to t when mistakes were made: Prediction rule now: When using high dimensional features: Carlos Guestrin Dot-product of polynomials exactly d Carlos Guestrin
5 Finally the Kernel Trick!!! (Kernelized Perceptron Every time you make a mistake, remember (x (t),y (t) ) Kernelized Perceptron prediction for x: y (j) j2m (t) sign(w (t) (x)) = X (x (j) ) (x) = X y (j) k(x (j), x) j2m (t) Carlos Guestrin Polynomial kernels All monomials of degree d in O(d) operations: How about all monomials of degree up to d? Solution 0: exactly d Better solution: Carlos Guestrin
6 Common kernels Polynomials of degree exactly d Polynomials of degree up to d Gaussian (squared exponential) kernel 2 Sigmoid Carlos Guestrin What you need to know Notion of online learning Perceptron algorithm Mistake bounds and proofs The kernel trick Kernelized Perceptron Derive polynomial kernel Common kernels In online learning, report averaged weights at the end Carlos Guestrin
7 Your Midterm Content: Everything up to last Wednesday (Perceptron) Only 80mins, so arrive early and settle down quickly, we ll start and end on time Open book Textbook, Books, Course notes, Personal notes Bring a calculator that can do log J No: Computers, tablets, phones, other materials, internet devices, wireless telepathy or wandering eyes The exam: Covers key concepts and ideas, work on understanding the big picture, and differences between methods Carlos Guestrin Support Vector Machines Machine Learning CSE446 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 28, 2013 Carlos Guestrin
8 Linear classifiers Which line is better? Carlos Guestrin 15 Pick the one with the largest margin! w.x + w 0 = 0 confidence = y j (w x j + w 0 ) Carlos Guestrin 16 8
9 Maximize the margin w.x + w 0 = 0 max,w,w 0 y j (w x j + w 0 ), 8j 2 {1,...,N} Carlos Guestrin 17 But there are many planes w.x + w 0 = Carlos Guestrin 18 9
10 Review: Normal to a plane x j = x j + w w w.x + w 0 = Carlos Guestrin 19 A Convention: Normalized margin Canonical hyperplanes x j = x j + w w w.x + w 0 = +1 w.x + w 0 = 0 w.x + w 0 = -1 x + x - margin 2γ Carlos Guestrin 20 10
11 Margin maximization using canonical hyperplanes w.x + w 0 = +1 w.x + w 0 = 0 w.x + w 0 = -1 Unnormalized problem: max,w,w 0 Normalized Problem: y j (w x j + w 0 ), 8j 2 {1,...,N} margin 2γ min w,w 0 w 2 2 y j (w x j + w 0 ) 1, 8j 2 {1,...,N} Carlos Guestrin 21 Support vector machines (SVMs) w.x + w 0 = +1 w.x + w 0 = 0 w.x + w 0 = -1 min w,w 0 w 2 2 y j (w x j + w 0 ) 1, 8j 2 {1,...,N} Solve efficiently by many methods, e.g., quadratic programming (QP) Well-studied solution algorithms Stochastic gradient descent Hyperplane defined by support vectors margin 2γ Carlos Guestrin 22 11
12 What if the data is not linearly separable? Use features of features of features of features Carlos Guestrin 23 What if the data is still not linearly separable? min w,w 0 w 2 2 y j (w x j + w 0 ) 1, 8j If data is not linearly separable, some points don t satisfy margin constraint: How bad is the violation? Tradeoff margin violation with w : Carlos Guestrin 24 12
13 SVMs for Non-Linearly Separable meet my friend the Perceptron Perceptron was minimizing the hinge loss: NX j=1 y j (w x j + w 0 ) + SVMs minimizes the regularized hinge loss!! w C NX j=1 1 y j (w x j + w 0 ) + Carlos Guestrin Stochastic Gradient Descent for SVMs NX j=1 Perceptron minimization: y j (w x j + w 0 ) + SGD for Perceptron: SVMs minimization: NX w C 1 y j (w x j + w 0 ) + j=1 SGD for SVMs: w (t+1) w (t) + h i y (t) (w (t) x (t) ) apple 0 y (t) x (t) Carlos Guestrin
14 What you need to know Maximizing margin Derivation of SVM formulation Non-linearly separable case Hinge loss A.K.A. adding slack variables SVMs = Perceptron + L2 regularization Can also use kernels with SVMs Can optimize SVMs with SGD Many other approaches possible Carlos Guestrin 27 14
Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines
 Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines Emily Fox University of Washington February 13, 2017 What is the perceptron optimizing? 1 The perceptron algorithm [Rosenblatt 58, 62] Classification setting:
Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines Emily Fox University of Washington February 13, 2017 What is the perceptron optimizing? 1 The perceptron algorithm [Rosenblatt 58, 62] Classification setting:
Logistic Regression Logistic
 Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities L2 Regularization for Logistic Regression Machine Learning/Statistics for Big Data CSE599C1/STAT592, University of Washington Carlos Guestrin January 10 th,
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities L2 Regularization for Logistic Regression Machine Learning/Statistics for Big Data CSE599C1/STAT592, University of Washington Carlos Guestrin January 10 th,
Support Vector Machines
 Two SVM tutorials linked in class website (please, read both): High-level presentation with applications (Hearst 1998) Detailed tutorial (Burges 1998) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning 10701/15781
Two SVM tutorials linked in class website (please, read both): High-level presentation with applications (Hearst 1998) Detailed tutorial (Burges 1998) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning 10701/15781
Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression
 Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression Boss gives you a bunch of data on loans defaulting or not: {(x i,y i )} n i= x i 2 R d, y i 2 {, } You model the data as: P (Y = y x, w) = + exp( yw T
Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression Boss gives you a bunch of data on loans defaulting or not: {(x i,y i )} n i= x i 2 R d, y i 2 {, } You model the data as: P (Y = y x, w) = + exp( yw T
SVMs, Duality and the Kernel Trick
 SVMs, Duality and the Kernel Trick Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University February 26 th, 2007 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 1 SVMs reminder 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 2 Today
SVMs, Duality and the Kernel Trick Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University February 26 th, 2007 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 1 SVMs reminder 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 2 Today
Support vector machines Lecture 4
 Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
CSE546: SVMs, Dual Formula5on, and Kernels Winter 2012
 CSE546: SVMs, Dual Formula5on, and Kernels Winter 2012 Luke ZeClemoyer Slides adapted from Carlos Guestrin Linear classifiers Which line is becer? w. = j w (j) x (j) Data Example i Pick the one with the
CSE546: SVMs, Dual Formula5on, and Kernels Winter 2012 Luke ZeClemoyer Slides adapted from Carlos Guestrin Linear classifiers Which line is becer? w. = j w (j) x (j) Data Example i Pick the one with the
PAC-learning, VC Dimension and Margin-based Bounds
 More details: General: http://www.learning-with-kernels.org/ Example of more complex bounds: http://www.research.ibm.com/people/t/tzhang/papers/jmlr02_cover.ps.gz PAC-learning, VC Dimension and Margin-based
More details: General: http://www.learning-with-kernels.org/ Example of more complex bounds: http://www.research.ibm.com/people/t/tzhang/papers/jmlr02_cover.ps.gz PAC-learning, VC Dimension and Margin-based
PAC-learning, VC Dimension and Margin-based Bounds
 More details: General: http://www.learning-with-kernels.org/ Example of more complex bounds: http://www.research.ibm.com/people/t/tzhang/papers/jmlr02_cover.ps.gz PAC-learning, VC Dimension and Margin-based
More details: General: http://www.learning-with-kernels.org/ Example of more complex bounds: http://www.research.ibm.com/people/t/tzhang/papers/jmlr02_cover.ps.gz PAC-learning, VC Dimension and Margin-based
Warm up. Regrade requests submitted directly in Gradescope, do not instructors.
 Warm up Regrade requests submitted directly in Gradescope, do not email instructors. 1 float in NumPy = 8 bytes 10 6 2 20 bytes = 1 MB 10 9 2 30 bytes = 1 GB For each block compute the memory required
Warm up Regrade requests submitted directly in Gradescope, do not email instructors. 1 float in NumPy = 8 bytes 10 6 2 20 bytes = 1 MB 10 9 2 30 bytes = 1 GB For each block compute the memory required
Linear classifiers Lecture 3
 Linear classifiers Lecture 3 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin ML Methodology Data: labeled instances, e.g. emails marked spam/ham
Linear classifiers Lecture 3 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin ML Methodology Data: labeled instances, e.g. emails marked spam/ham
Stochastic Gradient Descent
 Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 9, 2013 1 Logistic Regression Logistic function (or Sigmoid): Learn P(Y X) directly Assume a particular
Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 9, 2013 1 Logistic Regression Logistic function (or Sigmoid): Learn P(Y X) directly Assume a particular
Learning Theory. Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington. November 25, Carlos Guestrin
 Learning Theory Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington November 25, 2013 Carlos Guestrin 2005-2013 1 What now n We have explored many ways of learning from data n But How good
Learning Theory Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington November 25, 2013 Carlos Guestrin 2005-2013 1 What now n We have explored many ways of learning from data n But How good
Announcements - Homework
 Announcements - Homework Homework 1 is graded, please collect at end of lecture Homework 2 due today Homework 3 out soon (watch email) Ques 1 midterm review HW1 score distribution 40 HW1 total score 35
Announcements - Homework Homework 1 is graded, please collect at end of lecture Homework 2 due today Homework 3 out soon (watch email) Ques 1 midterm review HW1 score distribution 40 HW1 total score 35
Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Kernel CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2012
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Kernel CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Linear classifier Which classifier? x 2 x 1 2 Linear classifier Margin concept x 2
Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Kernel CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Linear classifier Which classifier? x 2 x 1 2 Linear classifier Margin concept x 2
Topics we covered. Machine Learning. Statistics. Optimization. Systems! Basics of probability Tail bounds Density Estimation Exponential Families
 Midterm Review Topics we covered Machine Learning Optimization Basics of optimization Convexity Unconstrained: GD, SGD Constrained: Lagrange, KKT Duality Linear Methods Perceptrons Support Vector Machines
Midterm Review Topics we covered Machine Learning Optimization Basics of optimization Convexity Unconstrained: GD, SGD Constrained: Lagrange, KKT Duality Linear Methods Perceptrons Support Vector Machines
Kernel Machines. Pradeep Ravikumar Co-instructor: Manuela Veloso. Machine Learning
 Kernel Machines Pradeep Ravikumar Co-instructor: Manuela Veloso Machine Learning 10-701 SVM linearly separable case n training points (x 1,, x n ) d features x j is a d-dimensional vector Primal problem:
Kernel Machines Pradeep Ravikumar Co-instructor: Manuela Veloso Machine Learning 10-701 SVM linearly separable case n training points (x 1,, x n ) d features x j is a d-dimensional vector Primal problem:
Support Vector Machines: Training with Stochastic Gradient Descent. Machine Learning Fall 2017
 Support Vector Machines: Training with Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Support vector machines Training by maximizing margin The SVM objective Solving the SVM optimization problem
Support Vector Machines: Training with Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Support vector machines Training by maximizing margin The SVM objective Solving the SVM optimization problem
Support Vector Machines. Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar
 Data Mining Support Vector Machines Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 02/03/2018 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Support Vector Machines Find a linear hyperplane
Data Mining Support Vector Machines Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 02/03/2018 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Support Vector Machines Find a linear hyperplane
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2014 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2014 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Machine Learning and Data Mining. Support Vector Machines. Kalev Kask
 Machine Learning and Data Mining Support Vector Machines Kalev Kask Linear classifiers Which decision boundary is better? Both have zero training error (perfect training accuracy) But, one of them seems
Machine Learning and Data Mining Support Vector Machines Kalev Kask Linear classifiers Which decision boundary is better? Both have zero training error (perfect training accuracy) But, one of them seems
Introduction to Support Vector Machines
 Introduction to Support Vector Machines Shivani Agarwal Support Vector Machines (SVMs) Algorithm for learning linear classifiers Motivated by idea of maximizing margin Efficient extension to non-linear
Introduction to Support Vector Machines Shivani Agarwal Support Vector Machines (SVMs) Algorithm for learning linear classifiers Motivated by idea of maximizing margin Efficient extension to non-linear
Learning Theory Continued
 Learning Theory Continued Machine Learning CSE446 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington May 13, 2013 1 A simple setting n Classification N data points Finite number of possible hypothesis (e.g., dec.
Learning Theory Continued Machine Learning CSE446 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington May 13, 2013 1 A simple setting n Classification N data points Finite number of possible hypothesis (e.g., dec.
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
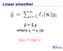 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines. Prof. Matteo Matteucci
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Prof. Matteo Matteucci Discriminative vs. Generative Approaches 2 o Generative approach: we derived the classifier from some generative hypothesis about the way
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Prof. Matteo Matteucci Discriminative vs. Generative Approaches 2 o Generative approach: we derived the classifier from some generative hypothesis about the way
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2015 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2015 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
About this class. Maximizing the Margin. Maximum margin classifiers. Picture of large and small margin hyperplanes
 About this class Maximum margin classifiers SVMs: geometric derivation of the primal problem Statement of the dual problem The kernel trick SVMs as the solution to a regularization problem Maximizing the
About this class Maximum margin classifiers SVMs: geometric derivation of the primal problem Statement of the dual problem The kernel trick SVMs as the solution to a regularization problem Maximizing the
Machine Learning Practice Page 2 of 2 10/28/13
 Machine Learning 10-701 Practice Page 2 of 2 10/28/13 1. True or False Please give an explanation for your answer, this is worth 1 pt/question. (a) (2 points) No classifier can do better than a naive Bayes
Machine Learning 10-701 Practice Page 2 of 2 10/28/13 1. True or False Please give an explanation for your answer, this is worth 1 pt/question. (a) (2 points) No classifier can do better than a naive Bayes
Machine Learning. Support Vector Machines. Fabio Vandin November 20, 2017
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Fabio Vandin November 20, 2017 1 Classification and Margin Consider a classification problem with two classes: instance set X = R d label set Y = { 1, 1}. Training
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Fabio Vandin November 20, 2017 1 Classification and Margin Consider a classification problem with two classes: instance set X = R d label set Y = { 1, 1}. Training
10/05/2016. Computational Methods for Data Analysis. Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES. Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers
 Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers 1 Linear Classifiers denotes +1 denotes -1 w x + b>0 f(x,w,b) = sign(w x + b) How
Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers 1 Linear Classifiers denotes +1 denotes -1 w x + b>0 f(x,w,b) = sign(w x + b) How
Support Vector Machines. Machine Learning Fall 2017
 Support Vector Machines Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Where are we? Learning algorithms Decision Trees Perceptron AdaBoost 2 Where are we? Learning algorithms Decision Trees Perceptron AdaBoost Produce
Support Vector Machines Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Where are we? Learning algorithms Decision Trees Perceptron AdaBoost 2 Where are we? Learning algorithms Decision Trees Perceptron AdaBoost Produce
Nearest Neighbor. Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington. October 26, Kevin Jamieson 2
 Nearest Neighbor Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington October 26, 2017 2017 Kevin Jamieson 2 Some data, Bayes Classifier Training data: True label: +1 True label: -1 Optimal
Nearest Neighbor Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington October 26, 2017 2017 Kevin Jamieson 2 Some data, Bayes Classifier Training data: True label: +1 True label: -1 Optimal
Machine Learning Basics Lecture 4: SVM I. Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang
 Machine Learning Basics Lecture 4: SVM I Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Review: machine learning basics Math formulation Given training data x i, y i : 1 i n i.i.d. from distribution
Machine Learning Basics Lecture 4: SVM I Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Review: machine learning basics Math formulation Given training data x i, y i : 1 i n i.i.d. from distribution
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities. Kakade Announcements: Project Proposals: due this Friday!
 Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Intro Logistic Regression Gradient Descent + SGD Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade April 4, 017 1 Announcements:
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Intro Logistic Regression Gradient Descent + SGD Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade April 4, 017 1 Announcements:
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 28, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Today Two important concepts: Margins Kernels Large Margin Classification
Support Vector Machines INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 28, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Today Two important concepts: Margins Kernels Large Margin Classification
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
 What s learning, revisited Overfitting Generative versus Discriminative Logistic Regression Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University September 19 th, 2007 Bias-Variance Tradeoff
What s learning, revisited Overfitting Generative versus Discriminative Logistic Regression Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University September 19 th, 2007 Bias-Variance Tradeoff
SVMs: nonlinearity through kernels
 Non-separable data e-8. Support Vector Machines 8.. The Optimal Hyperplane Consider the following two datasets: SVMs: nonlinearity through kernels ER Chapter 3.4, e-8 (a) Few noisy data. (b) Nonlinearly
Non-separable data e-8. Support Vector Machines 8.. The Optimal Hyperplane Consider the following two datasets: SVMs: nonlinearity through kernels ER Chapter 3.4, e-8 (a) Few noisy data. (b) Nonlinearly
A short introduction to supervised learning, with applications to cancer pathway analysis Dr. Christina Leslie
 A short introduction to supervised learning, with applications to cancer pathway analysis Dr. Christina Leslie Computational Biology Program Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center http://cbio.mskcc.org/leslielab
A short introduction to supervised learning, with applications to cancer pathway analysis Dr. Christina Leslie Computational Biology Program Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center http://cbio.mskcc.org/leslielab
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter
 Classification / Regression Support Vector Machines Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter 2012 1 Topics SVM classifiers for linearly separable classes SVM classifiers for non-linearly separable
Classification / Regression Support Vector Machines Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter 2012 1 Topics SVM classifiers for linearly separable classes SVM classifiers for non-linearly separable
Support Vector Machines: Maximum Margin Classifiers
 Support Vector Machines: Maximum Margin Classifiers Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition: September 16, 2008 Piotr Mirowski Based on slides by Sumit Chopra and Fu-Jie Huang 1 Outline What is behind
Support Vector Machines: Maximum Margin Classifiers Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition: September 16, 2008 Piotr Mirowski Based on slides by Sumit Chopra and Fu-Jie Huang 1 Outline What is behind
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines
 Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 6 Support Vector Machines Defining Characteristics Like logistic regression, good for continuous input features, discrete
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 6 Support Vector Machines Defining Characteristics Like logistic regression, good for continuous input features, discrete
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines
 Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Lecture 11: Review. Henry Chai 10/02/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
Perceptron Revisited: Linear Separators. Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Perceptron Revisited: Linear Separators Binary classification can be viewed as the task of separating classes in feature space: w T x + b > 0 w T x + b = 0 w T x + b < 0 Department
Support Vector Machines Perceptron Revisited: Linear Separators Binary classification can be viewed as the task of separating classes in feature space: w T x + b > 0 w T x + b = 0 w T x + b < 0 Department
COMP 875 Announcements
 Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Remember: Monday before the week of the presentation you must send me the final paper list (for posting
Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Remember: Monday before the week of the presentation you must send me the final paper list (for posting
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine
 CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
Deep Learning for Computer Vision
 Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 4: Curse of Dimensionality, High Dimensional Feature Spaces, Linear Classifiers, Linear Regression, Python, and Jupyter Notebooks Peter Belhumeur Computer Science
Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 4: Curse of Dimensionality, High Dimensional Feature Spaces, Linear Classifiers, Linear Regression, Python, and Jupyter Notebooks Peter Belhumeur Computer Science
Classification Logistic Regression
 Announcements: Classification Logistic Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Sham Kakade University of Washington HW due on Friday. Today: Review: sub-gradients,lasso Logistic Regression October 3, 26 Sham
Announcements: Classification Logistic Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Sham Kakade University of Washington HW due on Friday. Today: Review: sub-gradients,lasso Logistic Regression October 3, 26 Sham
Kernels and the Kernel Trick. Machine Learning Fall 2017
 Kernels and the Kernel Trick Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Support vector machines Training by maximizing margin The SVM objective Solving the SVM optimization problem Support vectors, duals and kernels
Kernels and the Kernel Trick Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Support vector machines Training by maximizing margin The SVM objective Solving the SVM optimization problem Support vectors, duals and kernels
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear Classifiers: predictions Original version of these slides by Mark Schmidt, with modifications by Mike Gelbart. 1 Admin Assignment 4: Due Friday of next
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear Classifiers: predictions Original version of these slides by Mark Schmidt, with modifications by Mike Gelbart. 1 Admin Assignment 4: Due Friday of next
Dan Roth 461C, 3401 Walnut
 CIS 519/419 Applied Machine Learning www.seas.upenn.edu/~cis519 Dan Roth danroth@seas.upenn.edu http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~danroth/ 461C, 3401 Walnut Slides were created by Dan Roth (for CIS519/419 at Penn
CIS 519/419 Applied Machine Learning www.seas.upenn.edu/~cis519 Dan Roth danroth@seas.upenn.edu http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~danroth/ 461C, 3401 Walnut Slides were created by Dan Roth (for CIS519/419 at Penn
Logistic Regression. Machine Learning Fall 2018
 Logistic Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are e? We have seen the folloing ideas Linear models Learning as loss minimization Bayesian learning criteria (MAP and MLE estimation) The Naïve Bayes
Logistic Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are e? We have seen the folloing ideas Linear models Learning as loss minimization Bayesian learning criteria (MAP and MLE estimation) The Naïve Bayes
Linear Classifiers and the Perceptron
 Linear Classifiers and the Perceptron William Cohen February 4, 2008 1 Linear classifiers Let s assume that every instance is an n-dimensional vector of real numbers x R n, and there are only two possible
Linear Classifiers and the Perceptron William Cohen February 4, 2008 1 Linear classifiers Let s assume that every instance is an n-dimensional vector of real numbers x R n, and there are only two possible
Machine Learning : Support Vector Machines
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines 05/01/2014 Machine Learning : Support Vector Machines Linear Classifiers (recap) A building block for almost all a mapping, a partitioning of the input space into
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines 05/01/2014 Machine Learning : Support Vector Machines Linear Classifiers (recap) A building block for almost all a mapping, a partitioning of the input space into
Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron
 CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
Multiclass Classification-1
 CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 27, 2016 Multiclass Classification Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng Overview Binary to multiclass Multiclass SVM Constraint classification 1 Introduction Multiclass
CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 27, 2016 Multiclass Classification Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng Overview Binary to multiclass Multiclass SVM Constraint classification 1 Introduction Multiclass
SVMs: Non-Separable Data, Convex Surrogate Loss, Multi-Class Classification, Kernels
 SVMs: Non-Separable Data, Convex Surrogate Loss, Multi-Class Classification, Kernels Karl Stratos June 21, 2018 1 / 33 Tangent: Some Loose Ends in Logistic Regression Polynomial feature expansion in logistic
SVMs: Non-Separable Data, Convex Surrogate Loss, Multi-Class Classification, Kernels Karl Stratos June 21, 2018 1 / 33 Tangent: Some Loose Ends in Logistic Regression Polynomial feature expansion in logistic
Multi-class SVMs. Lecture 17: Aykut Erdem April 2016 Hacettepe University
 Multi-class SVMs Lecture 17: Aykut Erdem April 2016 Hacettepe University Administrative We will have a make-up lecture on Saturday April 23, 2016. Project progress reports are due April 21, 2016 2 days
Multi-class SVMs Lecture 17: Aykut Erdem April 2016 Hacettepe University Administrative We will have a make-up lecture on Saturday April 23, 2016. Project progress reports are due April 21, 2016 2 days
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Hypothesis Space variable size deterministic continuous parameters Learning Algorithm linear and quadratic programming eager batch SVMs combine three important ideas Apply optimization
Support Vector Machines Hypothesis Space variable size deterministic continuous parameters Learning Algorithm linear and quadratic programming eager batch SVMs combine three important ideas Apply optimization
COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning. Nakul Verma
 COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning Nakul Verma Announcements HW1 due next lecture Project details are available decide on the group and topic by Thursday Last time Generative vs. Discriminative
COMS 4771 Introduction to Machine Learning Nakul Verma Announcements HW1 due next lecture Project details are available decide on the group and topic by Thursday Last time Generative vs. Discriminative
Announcements. Proposals graded
 Announcements Proposals graded Kevin Jamieson 2018 1 Bayesian Methods Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington November 1, 2018 2018 Kevin Jamieson 2 MLE Recap - coin flips Data:
Announcements Proposals graded Kevin Jamieson 2018 1 Bayesian Methods Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington November 1, 2018 2018 Kevin Jamieson 2 MLE Recap - coin flips Data:
(Kernels +) Support Vector Machines
 (Kernels +) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning Torsten Möller Reading Chapter 5 of Machine Learning An Algorithmic Perspective by Marsland Chapter 6+7 of Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning
(Kernels +) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning Torsten Möller Reading Chapter 5 of Machine Learning An Algorithmic Perspective by Marsland Chapter 6+7 of Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning
Support Vector Machines. CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington
 Support Vector Machines CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 A Linearly Separable Problem Consider the binary classification
Support Vector Machines CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 A Linearly Separable Problem Consider the binary classification
Review: Support vector machines. Machine learning techniques and image analysis
 Review: Support vector machines Review: Support vector machines Margin optimization min (w,w 0 ) 1 2 w 2 subject to y i (w 0 + w T x i ) 1 0, i = 1,..., n. Review: Support vector machines Margin optimization
Review: Support vector machines Review: Support vector machines Margin optimization min (w,w 0 ) 1 2 w 2 subject to y i (w 0 + w T x i ) 1 0, i = 1,..., n. Review: Support vector machines Margin optimization
Lecture 10: A brief introduction to Support Vector Machine
 Lecture 10: A brief introduction to Support Vector Machine Advanced Applied Multivariate Analysis STAT 2221, Fall 2013 Sungkyu Jung Department of Statistics, University of Pittsburgh Xingye Qiao Department
Lecture 10: A brief introduction to Support Vector Machine Advanced Applied Multivariate Analysis STAT 2221, Fall 2013 Sungkyu Jung Department of Statistics, University of Pittsburgh Xingye Qiao Department
Neural networks and support vector machines
 Neural netorks and support vector machines Perceptron Input x 1 Weights 1 x 2 x 3... x D 2 3 D Output: sgn( x + b) Can incorporate bias as component of the eight vector by alays including a feature ith
Neural netorks and support vector machines Perceptron Input x 1 Weights 1 x 2 x 3... x D 2 3 D Output: sgn( x + b) Can incorporate bias as component of the eight vector by alays including a feature ith
Support Vector Machine (continued)
 Support Vector Machine continued) Overlapping class distribution: In practice the class-conditional distributions may overlap, so that the training data points are no longer linearly separable. We need
Support Vector Machine continued) Overlapping class distribution: In practice the class-conditional distributions may overlap, so that the training data points are no longer linearly separable. We need
Linear classifiers: Overfitting and regularization
 Linear classifiers: Overfitting and regularization Emily Fox University of Washington January 25, 2017 Logistic regression recap 1 . Thus far, we focused on decision boundaries Score(x i ) = w 0 h 0 (x
Linear classifiers: Overfitting and regularization Emily Fox University of Washington January 25, 2017 Logistic regression recap 1 . Thus far, we focused on decision boundaries Score(x i ) = w 0 h 0 (x
Midterm. Introduction to Machine Learning. CS 189 Spring You have 1 hour 20 minutes for the exam.
 CS 189 Spring 2013 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 1 hour 20 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. Please use non-programmable calculators
CS 189 Spring 2013 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 1 hour 20 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. Please use non-programmable calculators
Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers)
 Support vector machines In a nutshell Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers) Solution only depends on a small subset of training
Support vector machines In a nutshell Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers) Solution only depends on a small subset of training
Statistical Machine Learning from Data
 Samy Bengio Statistical Machine Learning from Data 1 Statistical Machine Learning from Data Support Vector Machines Samy Bengio IDIAP Research Institute, Martigny, Switzerland, and Ecole Polytechnique
Samy Bengio Statistical Machine Learning from Data 1 Statistical Machine Learning from Data Support Vector Machines Samy Bengio IDIAP Research Institute, Martigny, Switzerland, and Ecole Polytechnique
Support Vector Machines, Kernel SVM
 Support Vector Machines, Kernel SVM Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 27, 2017 1 / 40 Outline 1 Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 SVM
Support Vector Machines, Kernel SVM Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 27, 2017 1 / 40 Outline 1 Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 SVM
Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington. September 30, What about continuous variables?
 Linear Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington September 30, 2014 1 What about continuous variables? n Billionaire says: If I am measuring a continuous variable, what
Linear Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington September 30, 2014 1 What about continuous variables? n Billionaire says: If I am measuring a continuous variable, what
Announcements Kevin Jamieson
 Announcements Project proposal due next week: Tuesday 10/24 Still looking for people to work on deep learning Phytolith project, join #phytolith slack channel 2017 Kevin Jamieson 1 Gradient Descent Machine
Announcements Project proposal due next week: Tuesday 10/24 Still looking for people to work on deep learning Phytolith project, join #phytolith slack channel 2017 Kevin Jamieson 1 Gradient Descent Machine
Mark your answers ON THE EXAM ITSELF. If you are not sure of your answer you may wish to provide a brief explanation.
 CS 189 Spring 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 80 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. No calculators or electronic items.
CS 189 Spring 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 80 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. No calculators or electronic items.
Support Vector Machines
 EE 17/7AT: Optimization Models in Engineering Section 11/1 - April 014 Support Vector Machines Lecturer: Arturo Fernandez Scribe: Arturo Fernandez 1 Support Vector Machines Revisited 1.1 Strictly) Separable
EE 17/7AT: Optimization Models in Engineering Section 11/1 - April 014 Support Vector Machines Lecturer: Arturo Fernandez Scribe: Arturo Fernandez 1 Support Vector Machines Revisited 1.1 Strictly) Separable
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1396 1 / 44 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1396 1 / 44 Table
1 Machine Learning Concepts (16 points)
 CSCI 567 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam DO NOT OPEN EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO PLEASE TURN OFF ALL CELL PHONES Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Max 16 10 16 42 24 12 120 Points Please read the following instructions
CSCI 567 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam DO NOT OPEN EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO PLEASE TURN OFF ALL CELL PHONES Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Max 16 10 16 42 24 12 120 Points Please read the following instructions
Machine Learning A Geometric Approach
 Machine Learning A Geometric Approach CIML book Chap 7.7 Linear Classification: Support Vector Machines (SVM) Professor Liang Huang some slides from Alex Smola (CMU) Linear Separator Ham Spam From Perceptron
Machine Learning A Geometric Approach CIML book Chap 7.7 Linear Classification: Support Vector Machines (SVM) Professor Liang Huang some slides from Alex Smola (CMU) Linear Separator Ham Spam From Perceptron
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning
 ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting PAC Learning Readings: Murphy 16.4;; Hastie 16 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Fighting the bias-variance tradeoff Simple
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting PAC Learning Readings: Murphy 16.4;; Hastie 16 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Fighting the bias-variance tradeoff Simple
Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington. September 30, 2013
 Bayesian Methods Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington September 30, 2013 1 What about prior n Billionaire says: Wait, I know that the thumbtack is close to 50-50. What can you
Bayesian Methods Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington September 30, 2013 1 What about prior n Billionaire says: Wait, I know that the thumbtack is close to 50-50. What can you
Name (NetID): (1 Point)
 CS446: Machine Learning (D) Spring 2017 March 16 th, 2017 This is a closed book exam. Everything you need in order to solve the problems is supplied in the body of this exam. This exam booklet contains
CS446: Machine Learning (D) Spring 2017 March 16 th, 2017 This is a closed book exam. Everything you need in order to solve the problems is supplied in the body of this exam. This exam booklet contains
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Ryan M. Rifkin Google, Inc. 2008 Plan Regularization derivation of SVMs Geometric derivation of SVMs Optimality, Duality and Large Scale SVMs The Regularization Setting (Again)
Support Vector Machines Ryan M. Rifkin Google, Inc. 2008 Plan Regularization derivation of SVMs Geometric derivation of SVMs Optimality, Duality and Large Scale SVMs The Regularization Setting (Again)
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Some material on these is slides borrowed from Andrew Moore's excellent machine learning tutorials located at: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~awm/tutorials/ Where Should We Draw the Line????
Support Vector Machines Some material on these is slides borrowed from Andrew Moore's excellent machine learning tutorials located at: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~awm/tutorials/ Where Should We Draw the Line????
EE 511 Online Learning Perceptron
 Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi, Mari Ostendorf, Pedro Domingos, Carlos Guestrin, and Luke Zettelmoyer, Kevin Jamison EE 511 Online Learning Perceptron Instructor: Hanna Hajishirzi hannaneh@washington.edu
Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi, Mari Ostendorf, Pedro Domingos, Carlos Guestrin, and Luke Zettelmoyer, Kevin Jamison EE 511 Online Learning Perceptron Instructor: Hanna Hajishirzi hannaneh@washington.edu
Perceptron. Subhransu Maji. CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning. 3 February February 2015
 Perceptron Subhransu Maji CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning 3 February 2015 5 February 2015 So far in the class Decision trees Inductive bias: use a combination of small number of features Nearest neighbor
Perceptron Subhransu Maji CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning 3 February 2015 5 February 2015 So far in the class Decision trees Inductive bias: use a combination of small number of features Nearest neighbor
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2016 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2016 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
6.036 midterm review. Wednesday, March 18, 15
 6.036 midterm review 1 Topics covered supervised learning labels available unsupervised learning no labels available semi-supervised learning some labels available - what algorithms have you learned that
6.036 midterm review 1 Topics covered supervised learning labels available unsupervised learning no labels available semi-supervised learning some labels available - what algorithms have you learned that
Learning Theory. Aar$ Singh and Barnabas Poczos. Machine Learning / Apr 17, Slides courtesy: Carlos Guestrin
 Learning Theory Aar$ Singh and Barnabas Poczos Machine Learning 10-701/15-781 Apr 17, 2014 Slides courtesy: Carlos Guestrin Learning Theory We have explored many ways of learning from data But How good
Learning Theory Aar$ Singh and Barnabas Poczos Machine Learning 10-701/15-781 Apr 17, 2014 Slides courtesy: Carlos Guestrin Learning Theory We have explored many ways of learning from data But How good
Support Vector Machines and Kernel Methods
 Support Vector Machines and Kernel Methods Geoff Gordon ggordon@cs.cmu.edu July 10, 2003 Overview Why do people care about SVMs? Classification problems SVMs often produce good results over a wide range
Support Vector Machines and Kernel Methods Geoff Gordon ggordon@cs.cmu.edu July 10, 2003 Overview Why do people care about SVMs? Classification problems SVMs often produce good results over a wide range
Applied Machine Learning Annalisa Marsico
 Applied Machine Learning Annalisa Marsico OWL RNA Bionformatics group Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics Free University of Berlin 29 April, SoSe 2015 Support Vector Machines (SVMs) 1. One of
Applied Machine Learning Annalisa Marsico OWL RNA Bionformatics group Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics Free University of Berlin 29 April, SoSe 2015 Support Vector Machines (SVMs) 1. One of
Online Learning With Kernel
 CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 SEP 27, 2016 Online Learning With Kernel Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: Ben Zhou, C. Cervantes Overview Stochastic Gradient Descent Algorithms Regularization Algorithm Issues
CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 SEP 27, 2016 Online Learning With Kernel Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: Ben Zhou, C. Cervantes Overview Stochastic Gradient Descent Algorithms Regularization Algorithm Issues
Discriminative Models
 No.5 Discriminative Models Hui Jiang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Lassonde School of Engineering York University, Toronto, Canada Outline Generative vs. Discriminative models
No.5 Discriminative Models Hui Jiang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Lassonde School of Engineering York University, Toronto, Canada Outline Generative vs. Discriminative models
Machine Learning Basics
 Security and Fairness of Deep Learning Machine Learning Basics Anupam Datta CMU Spring 2019 Image Classification Image Classification Image classification pipeline Input: A training set of N images, each
Security and Fairness of Deep Learning Machine Learning Basics Anupam Datta CMU Spring 2019 Image Classification Image Classification Image classification pipeline Input: A training set of N images, each
Natural Language Processing. Classification. Features. Some Definitions. Classification. Feature Vectors. Classification I. Dan Klein UC Berkeley
 Natural Language Processing Classification Classification I Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example:
Natural Language Processing Classification Classification I Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example:
18.9 SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES
 744 Chapter 8. Learning from Examples is the fact that each regression problem will be easier to solve, because it involves only the examples with nonzero weight the examples whose kernels overlap the
744 Chapter 8. Learning from Examples is the fact that each regression problem will be easier to solve, because it involves only the examples with nonzero weight the examples whose kernels overlap the
More about the Perceptron
 More about the Perceptron CMSC 422 MARINE CARPUAT marine@cs.umd.edu Credit: figures by Piyush Rai and Hal Daume III Recap: Perceptron for binary classification Classifier = hyperplane that separates positive
More about the Perceptron CMSC 422 MARINE CARPUAT marine@cs.umd.edu Credit: figures by Piyush Rai and Hal Daume III Recap: Perceptron for binary classification Classifier = hyperplane that separates positive
SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE
 SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE Mainly based on https://nlp.stanford.edu/ir-book/pdf/15svm.pdf 1 Overview SVM is a huge topic Integration of MMDS, IIR, and Andrew Moore s slides here Our foci: Geometric intuition
SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE Mainly based on https://nlp.stanford.edu/ir-book/pdf/15svm.pdf 1 Overview SVM is a huge topic Integration of MMDS, IIR, and Andrew Moore s slides here Our foci: Geometric intuition
Machine Learning. Support Vector Machines. Manfred Huber
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Manfred Huber 2015 1 Support Vector Machines Both logistic regression and linear discriminant analysis learn a linear discriminant function to separate the data
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Manfred Huber 2015 1 Support Vector Machines Both logistic regression and linear discriminant analysis learn a linear discriminant function to separate the data
