4. AC Circuit Analysis
|
|
|
- Lora Dorsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4. A icui Analysis J B A Signals sofquncy Quaniis Sinusoidal quaniy A " # a() A cos (# + " ) ampliud : maximal valu of a() and is a al posiiv numb; adian [/s]: al posiiv numb; phas []: fquncy al numb; a() A cos (" + ) A A cos (" + ) $ T # # f T $ piod [s]; naual fquncy [Hz]; -θ/ω Tπ/ω/f A T + T A cos (# + " ) d A 0,707 A Effciv valu - ms valu (oo-man-squa valu)
2 A Signals sofquncy Quaniis a() A cos (ω + θ a ) b() B cos (ω + θ b ) ϕ θ a - θ b phas shif angl (a and b a ϕ ou of phas) 0 a() and b() a in phas; > 0 a() lads b() by (advancd); < 0 a() lags b() by (dlayd). a() A cos ω b() B cos (ω ϕ) b() a() ϕ θ b 0 /ω (" a # " b ) /ω a() lads b() by b() a() 0 a() and b() in phas a() b() ±π a() and b() in opposiion of phas b() a() ±π / a() and b() 90 ou of phas A Signals: Sinusoids and Phasos Eul dniy : j cos + jsin A j(ω+θ ) A cos (ω + θ) + j A sin (ω + θ) a() A cos (ω + θ) A j(ω+θ ) A jω wh : A A jθ A jθ A cos θ + j sin θ ( ) A M A a() ( ω + θ ) m
3 A Signals: Sinusoids and Phasos j( " + ) j j" j" [ A ] [ A ] [ A ] a() A cos (" + ) wh h phaso is a cun o a volag givn by h complx A : j A A A ( cos + jsin ) A Th is a biuniqu cospondnc bwn sinusoids a h sam fquncy and phasos. $ a() (" + ) #m A Sinusoid (im domain) A cos( + ") ( A cos" ) cos + (- A sin " ) sin Phaso (fquncy domain) cangula fom Exponnial fom Pola fom A A cos + j A sin A j A A A A Signals: Sinusoids and Phasos omplx plan psnaion A A wh a b A j' A cos A sin ' ' a A a + + b ( cos' + jsin ' ) j b -& b # ' an $, wh % a " a > 0 m b A a j A A 3
4 A Signals: Sinusoids and Phasos a() A cos ( + " ) b() B cos ( + " ) a b j [ A ] [ B ] j Uniqunss: Two sinusoids a h sam fquncy a qual if and only if hy a psnd by h sam phaso a() b() A B As jω is a complx numb which oas on h complx plan whn incass, a() is qual o b() a any, if boh h al and h immaginay pas of A and B A a + jb a qual : ja ja - b a() b() A jω B jω ( cosω + j sinω) A ( cosω + j sinω) B ja m A cosω A + j sinω A cosω B + j sinω B cosω A -sinω m A cosω B -sinω m B a() b() A B and m A m B. A Signals: Sinusoids and Phasos a() A cos ( + " ) b() B cos ( + " ) a b j [ A ] [ B ] j inaiy: Th lina combinaion (wih consan and al cofficins) of phasos psns h sam lina combinaion of sinusoids a h sam fquncy c a() + c b() ca + cb suls c fom h following laion : j j [ A ] c [ B ] [( c A c B) ] j + + 4
5 A Signals: Sinusoids and Phasos a() A cos ( + " ) Divaiv: f A is h phaso of a() Acos( + (ω), ") h faso of h im divaiv of a(), da() d (ω) d d [Acos(+")], is givn by jωa suls d d fom h da() d a jω A; [ ] j A d a() jω ( jωa ) - ω A d following laion : ja j d j( ) d { [ A + " ]} { [ A ]} [ A cos( + " )] d d - A sin( ) [ j A ] [ ] j( + " ) j A j + " m A A icui Analysis n h cicui of h figu fom h lmn quaion i suls : v() i() v() di d + n a lina cicui a sinusoidal cun i() i(')d' + i() cosponds o a sinusoidal volag v() a h sam fquncy and diffn phas. dv d i d d + d i + d i v() V cos(ω +θ v ) V jω i() cos(ω +θ i ) jω jωv jω (jω ) jω + + jω jω + jω wh : jθ V V V ; jθ. jωv jω -ω jω + jω jω + jω jωv jω -ω + jω + jω jωv jω -ω + jω + jω jωv -ω + jω + 5
6 A icui Analysis i() V + j ω ω v() V Z o V Z - Elmn quaion in h fqncy domain Fom h dfiniion of h ffciv phasos i is V V and Th impdnc (complx numb) is h aio of h paso volag V and h phaso cun. wh Z + j ω ω o Z + j X sisanc X aanc, acanc, X X + X ; X ω, X - ω Th impdnc is masud in ohm [Ω]. Th cipocal of impdnc is h admianc: Y Z ( S uni : simns [S]) v() V cos(ω +θ V ) V jω i() cos(ω +θ ) jω wh V V jθ V ; jθ V Z A icui Analysis wh Z +jx o Z Z jθ Z ; Z X + X, θ Z an - V Z V Z j(θ V - θ Z ) jθ m V V Z V V + X + ω- ω X ω- θ θ V - θ Z θ V - an - θ - ω V an- 6
7 A icui Analysis Phas shif v() V cos(ω +θ V ) V jω i() cos(ω +θ ) jω wh V jθ V V ; jθ v() i() V V j(θ V -θ ) V jϕ Z Z jθ + jx Z Z V jϕ m X Z ϕ Thfo h phas shif angl ϕ θ V -θ bwn cun and volag phasos is also h angl of h load impdnc. A icui Analysis Whn assuming as h fnc : θ v 0 (his wihou any loss of gnaliy, sinc all phas angls will b fncd o h souc volag's angl) ϕ θ v - θ i - θ i v() V cos ω V jω, V V i() cos(ω ϕ) jω, -jϕ V Z wh Z + j ω ω + jx is also : Z Z jθ Z ; Z X + X ; θ Z ϕ an - V Z V Z j(θ V - θ Z ) jθ -jϕ V Z V V + X + ω- ω X ω- ϕ θ Z an - ω an- m ϕ V 7
8 A icui Analysis icui Analysis v n m i 0 v 0 (i ) ngo-diffnial Equaions f Tansfomaion fom h im domain o h fquncy domain (Sinmz ansfom) n m V 0 V 0 f ( ) Algbaic quaions Soluion and nvs Tansfomaion fom h fquncy domain o h im domain A icui Analysis Th siso: Z V v() Vcos ω V jω, V V i() cos(ω ϕ) jω, -jϕ V Z wh Z V Z V -jϕ wh V X ϕ an - 0 m v() V i() i() cos(ω ϕ) V cos ω v() i() V v() and i() in phas 8
9 A icui Analysis Th nduco: Z j ω V v() Vcos ω V jω, V V i() cos(ω ϕ) jω, -jϕ v() V Z wh Z jω i() V Z V ω -jπ V -jϕ wh ω ϕ an - i() cos(ω ϕ) v() " # ω 0 π V ω cos ω - π V ȷ ) m V i() and v() a π/ ou of phas i() lags v() by π/ (dlayd) A icui Analysis Th apacio: Z - j ω V v() Vcos ω V jω, V V i() cos(ω ϕ) jω, -jϕ v() V Z wh Z -j ω V Z V ω j π V ω -jϕ wh ϕ an - ω 0 - π i() cos(ω ϕ) V ω cos ω + π v() " & i( )d V - $% ȷ /0 m i() V i() and v() a π/ ou of phas i() lads v() by π/ (advancd) 9
10 A icui Analysis Sis sonanc v() V cos ω V jω, V V i() cos(ω ϕ) jω, -jϕ V Z -jϕ con ϕ ω ( ω ) V + ω- ω ω ω- ( ) an - A h sonanc fquncy ω 0, fo which h induciv and h capaciiv acanc in si a qual in magniud, h oal acanc is zo. Thfo i follows ha: - h impdnc is only sisiv, - h cun ampliud/ffciv valu (ω 0 ), (ω 0 ) a maximual (his is h moivaion of h m "sonanc"). - h volag and h cun a in phas. ω 0 - ω 0 0 ω 0 ϕ i() v() (ω) ω 0 ω 0 ω ω A icui Analysis Sis sonanc Z & # + j$ ' - + j( X + X ) % ' " A ' ' 0 i is X - X. V Z + j X + j X : i() v() Fo a givn " h volag phaso # is givn by h vco sum "+jx "+jx " V j X j X j X V j X j X V ω < ω 0 ω ω 0 ω > ω 0 j X 0
11 A icui Analysis Paalll sonanc: Z Z Z Z + Z, dov Z j ω, Z -j ω Z -j ω - ω ( ω ) V ω - ω A h sonanc fquncy ω 0, as h induciv and h capaciiv acanc a qual in magniud, h paalll of a capacio wih an induco has a oal acanc qual o infini. Thfo i follows ha: - h oal impdnc is infini; - h oal cun flowing hough h cicui is zo. - h cuns in h induco and h capacio a: - X V ω 0 ω ω 0 - ω 0 0 ω 0 and a ω ω j V A icui Analysis mpdanc onncions Sis of impdancs Z k q Z k Z Z Z Z n Paalll of impdancs Z q k Z k Z Z n Z Δ Z Y Wy Dla onncion Z Y Z Δ ZΔ Z Δ + Z Δ + Z Δ3 Z Δ Z Y3 ZY ZΔ3 Z Δ Z Y ZY + Z Y ZY3 + Z Y3 ZY Z Y3 3
12 Pow in A icuis p() v() i() Wih h assumpion : θ v 0 v() Vcosω; i() cos(ω ϕ) ( ) cos ϕ cos ω + sin ϕ sin ω i a () + i () i() cos ω cos ϕ + sin ω sin ϕ i a () cos ϕ cos ω; in phas cun, i () sin ϕ sin ω; aciv cun (π / ou of phas). Th isananous pow is h sum of h in phas isananous pow p a () and h isananous aciv pow p (). p() v() i() v() i a () + v() i () p a () + p () v() i() v() VMcos# i() cos( # " ) v() i() M Pow in A icuis nsananous in Phas and aciv Pow p a () v() i a ( ) Vcosω cos ϕ cos ω V cosϕ cos ω p a () is h in phas isananous pow. is always posiiv. Thby i is a pow flowing ino h cicui lmn and is dissipad by h sisanc of h lmn. This pow is consumd and hfo i is uilizd by h cicui lmn ha is h cicui load. p () v() i () Vcosω sn ϕ sn ω V sin ϕ sin ω V sin ϕ sin ω p () is h isananous aciv pow. s avag valu is qual o zo. cosponds o an ngy flowing ino h cicui lmn fo half piod [h piod of p is T/ π /(ω )] and ousid of i fo h nx half piod and hnc in and ou of h mmay lmns (inducanc and capacios). sananous in phas pow : p a () V cos cos " i () p a() v() i a() sananous aciv pow: p () V sin sin " v() p ()
13 Avag Pow Pow in A icuis Th avag pow P (said also al pow) is h avag of h isananosus pow ov on piod T π /ω. P T 0 +T p(') d' 0 T 0 +T as p a () V cos ϕ cos ω, i is : P V cos ϕ V cos ϕ p a (') + p (') d' 0 T 0 +T p a (') d' 0 wh V and a h ffciv valus of h nsion and h cun spcivly [hy a h ms valus of v() and i(). "cosϕ " is said o b h pow faco]. Th avag pow is h pow uilizd by h cicui loads, i is consumd by h cicui. n h S Sysm of Unis h avag pow is masud in wa [W]. aciv Pow Pow in A icuis Th aciv pow Q is h maximal valu of h isananous aciv pow p (): Q p () Max sign ϕ ( ) V sin ϕ V sin ϕ wh p () V sinϕ sinω V sinϕ sinω Q is h maximal valu of h pow xchangd by a cicui lmn, o gnally by a load, wih h cicui ino which h cicui lmn is insd (o wih h nwok o which h load is conncd). Q can b posiiv o ngaiv dpnding on h sign of ϕ. Fo an induciv load Q is posiiv, fo a capaciiv load Q is ngaiv. n h S Sism of Unis Q is masud in vol - amp aciv [VA]. 3
14 Pow in A icuis omplx Pow V * N * V ( ) $ N V j& V -j& j & V -& * V V N P + jq # " V j% P + jq V cos% + jv sin % Sinc i is N V * Z N P + jq V Z * % Z ( + j X ) + j X $ # P " Q X ( h avag pow dpnds on h sisanc) ( h aciv pow dpnds on h acanc ) Pow in A icuis A Pow onsvaion Whn wo loads Z and Z a in si wih a volag souc (op figu), KT ylds V V, + V, N V * * V, ( + V, ) V *, + V,, * N + N Whn h loads a in paalll wih h souc (midl figu), K ylds, +, N V * V *, + *, ( ) V *, + V *, N + N Fo a cicui of l lmns, whh h loads a conncd in si o in paalll o boh conncions a psn (boom figu), h oal pow supplid by h souc quals h amoun of pow dlivd o h cicui lmns. N V * N P + jq l V,k *,k Nk k l k l k ( P k + j Q k ) P Q l V + " k X k k k (P is du o h sisancs) k l X k k (Q is du o h acancs) k Z Z V + " V + " Z Z 4
15 Appan Pow Pow in A icuis Th appan pow is h poduc of h ffciv volag (ms valu) and h ffciv cun (ms valu). N V V n h S sism of unis N is masud in vol-amp [VA]. Fom h dfiniion of h avag pow P i is: P N cosϕ o N P cosϕ Ths laions indica h lvanc of h pow faco cosϕ. Whn h load angl ncass abov zo cosϕ dcass blow and h avag pow P, which is h pow uilizd by h load, dcass blow h appan pow N, which is h pow capaciy ndd by h soucs (fo xampl h lcical pow capaciy of h gnaos of h lcical pow saions). Pow in A icuis Pow Faco Th pow faco is h cosin of h phas diffnc bwn volag and cun. Hnc i is h cosin of h angl of h load impdnc: cosϕ cos(θ V θ ). P V cos N cos P cos V Th valu of h pow faco cosϕ angs bwn 0 and uniy. Fo a pu sisiv load h volag and cun a in phas, so ha θ V θ ϕ 0 and h pow faco cosϕ. Thfo h appan pow is qual o h avag pow. Fo a puly aciv load θ V θ ϕ ±π/ and h cosϕ 0. n his cas h avag pow is zo. n bwn hs wo xm cass h pow faco is said o b lading o lagging. ading pow faco mans ha h cun lads h volag (capaciiv load). agging pow faco mans ha h cun lags h volag (induciv load). P N 5
16 Pow in A icuis Pow Faco P V cos N cos Q V P V sn an cos P P cos V N & cos' cos $ an % - Q # P " P a fixd P and V cos$ # ", N V cos$ n h lcical sysms h pow faco has o b as big as possibl o uiliz h maximal pa of h appan pow gnad (P N) and o duc h cun a a givn pow uilizd (P) and a a givn volag. Many uiliis qus o pay h pow faco uilizd whn is valu is blow 0.9. Pow in A icuis G V ' V U ln Moivaions fo h ducion of h phas shif angl f h cun is ducd, h pow los along h lin dcass (P ln ). As consan volag V ' V is quid by h n and as V ' V + ln, in od o duc h volag losss along h lin h cun has o b as low as possibl. Th appan pow, ha has o b gnad by h lcical pow saion, dcass wih h dcas of h cun. 6
17 Shif Angl ocion P V cos ϕ Q P an ϕ Q V sin ϕ Mos loads a induciv and opa a a low lagging pow faco. n od o duc ϕ o a dmind ϕ' (usually cosϕ' 0,9 ) a capacio is s in paalll wih h load. Th capaciy is givn by h h capaciiv aciv pow which compnsas h induciv pow : Q P an ϕ Q + Q P an ϕ ' Q P an ϕ' - an ϕ ( ) wh Q is h aciv pow o b cocd and Q -ω V ( ωv) is h aciv pow of h capacio uilizd fo h load faco cocion. Hnc i is P - " # & an ϕ - an ϕ ' ( ) $% ' an + an + & # ω V$% # Pow in A icuis V V ϕ ϕ U Tminology admianc ampliud divaiv fquncydomain olag olad impdnc linaiy invsansfom naualfquncy opposiionofphas paalllsonanc phas phasshifangl phaso ouofphas ammnza ampizza divazion,divaa dominiodllfqunz ssiniadodifas ssinanicipodifas impdnza linaià asfomaa invsa fqunzaciclica, fqunza opposiziondifas aniisonanza fas angolodisfasamno faso sfasaodi 90 ouofphas sfasaodi90,in quadauadifas piod adianfquncy acanc sonancfquncy oo mansqua valu,ms valu sissonanc sinusoid sinusoidalquaniy Sinmzansfom imdomain uniqunss piodo pulsazion,fqunza angola aanza fqunzadiisonanza valofficac isonanza sinusoid gandzzasinusoidal asfomaadi Sinmz dominiodlmpo unicià Dpamn*of*Elcical,*Elconic,*and*nfomaion*Engining*(DE)*7 Univsiy*of*Bologna 34 7
4. AC Circuit Analysis
 4. A icui Analysis J B Dpamn of Elcical, Elconic, and nfomaion Engining (DE) - Univsiy of Bologna A Signals sofquncy Quaniis Sinusoidal quaniy A q w a() A cos ( w + q ) ampliud : maximal valu of a() and
4. A icui Analysis J B Dpamn of Elcical, Elconic, and nfomaion Engining (DE) - Univsiy of Bologna A Signals sofquncy Quaniis Sinusoidal quaniy A q w a() A cos ( w + q ) ampliud : maximal valu of a() and
1 Lecture: pp
 EE334 - Wavs and Phasos Lcu: pp -35 - -6 This cous aks vyhing ha you hav bn augh in physics, mah and cicuis and uss i. Easy, only nd o know 4 quaions: 4 wks on fou quaions D ρ Gauss's Law B No Monopols
EE334 - Wavs and Phasos Lcu: pp -35 - -6 This cous aks vyhing ha you hav bn augh in physics, mah and cicuis and uss i. Easy, only nd o know 4 quaions: 4 wks on fou quaions D ρ Gauss's Law B No Monopols
Physics 160 Lecture 3. R. Johnson April 6, 2015
 Physics 6 Lcur 3 R. Johnson April 6, 5 RC Circui (Low-Pass Filr This is h sam RC circui w lookd a arlir h im doma, bu hr w ar rsd h frquncy rspons. So w pu a s wav sad of a sp funcion. whr R C RC Complx
Physics 6 Lcur 3 R. Johnson April 6, 5 RC Circui (Low-Pass Filr This is h sam RC circui w lookd a arlir h im doma, bu hr w ar rsd h frquncy rspons. So w pu a s wav sad of a sp funcion. whr R C RC Complx
Partial Fraction Expansion
 Paial Facion Expanion Whn ying o find h inv Laplac anfom o inv z anfom i i hlpfl o b abl o bak a complicad aio of wo polynomial ino fom ha a on h Laplac Tanfom o z anfom abl. W will illa h ing Laplac anfom.
Paial Facion Expanion Whn ying o find h inv Laplac anfom o inv z anfom i i hlpfl o b abl o bak a complicad aio of wo polynomial ino fom ha a on h Laplac Tanfom o z anfom abl. W will illa h ing Laplac anfom.
DSP-First, 2/e. This Lecture: LECTURE #3 Complex Exponentials & Complex Numbers. Introduce more tools for manipulating complex numbers
 DSP-Fis, / LECTURE #3 Compl Eponnials & Compl umbs READIG ASSIGMETS This Lcu: Chap, Scs. -3 o -5 Appndi A: Compl umbs Appndi B: MATLAB Lcu: Compl Eponnials Aug 016 003-016, JH McClllan & RW Schaf 3 LECTURE
DSP-Fis, / LECTURE #3 Compl Eponnials & Compl umbs READIG ASSIGMETS This Lcu: Chap, Scs. -3 o -5 Appndi A: Compl umbs Appndi B: MATLAB Lcu: Compl Eponnials Aug 016 003-016, JH McClllan & RW Schaf 3 LECTURE
Chapter 2 : Fundamental parameters of antennas
 Chap : Fundamnal paams of annnas Fom adiaion an adiaion innsiy Bamwidh Diciviy nnna fficincy Gain olaizaion Fom Cicui viwpoin Inpu Impdanc 1 Chap : opics nnna ffciv lngh and ffciv aa Fiis ansmission quaion
Chap : Fundamnal paams of annnas Fom adiaion an adiaion innsiy Bamwidh Diciviy nnna fficincy Gain olaizaion Fom Cicui viwpoin Inpu Impdanc 1 Chap : opics nnna ffciv lngh and ffciv aa Fiis ansmission quaion
4. Fundamental of A.C. Circuit
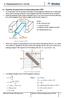 4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
Review Lecture 5. The source-free R-C/R-L circuit Step response of an RC/RL circuit. The time constant = RC The final capacitor voltage v( )
 Rviw Lcur 5 Firs-ordr circui Th sourc-fr R-C/R-L circui Sp rspons of an RC/RL circui v( ) v( ) [ v( 0) v( )] 0 Th i consan = RC Th final capacior volag v() Th iniial capacior volag v( 0 ) Volag/currn-division
Rviw Lcur 5 Firs-ordr circui Th sourc-fr R-C/R-L circui Sp rspons of an RC/RL circui v( ) v( ) [ v( 0) v( )] 0 Th i consan = RC Th final capacior volag v() Th iniial capacior volag v( 0 ) Volag/currn-division
What is an Antenna? Not an antenna + - Now this is an antenna. Time varying charges cause radiation but NOT everything that radiates is an antenna!
 Wha is an Annna? Tim vaying chags caus adiaion bu NOT vyhing ha adias is an annna! No an annna + - Now his is an annna Wha is an Annna? An annna is a dvic ha fficinly ansiions bwn ansmission lin o guidd
Wha is an Annna? Tim vaying chags caus adiaion bu NOT vyhing ha adias is an annna! No an annna + - Now his is an annna Wha is an Annna? An annna is a dvic ha fficinly ansiions bwn ansmission lin o guidd
Lecture 1: Growth and decay of current in RL circuit. Growth of current in LR Circuit. D.K.Pandey
 cur : Growh and dcay of currn in circui Growh of currn in Circui us considr an inducor of slf inducanc is conncd o a DC sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc and a ky K in sris. Whn h ky K is swichd
cur : Growh and dcay of currn in circui Growh of currn in Circui us considr an inducor of slf inducanc is conncd o a DC sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc and a ky K in sris. Whn h ky K is swichd
Charging of capacitor through inductor and resistor
 cur 4&: R circui harging of capacior hrough inducor and rsisor us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R, an inducor of inducanc and a y K in sris.
cur 4&: R circui harging of capacior hrough inducor and rsisor us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R, an inducor of inducanc and a y K in sris.
Voltage v(z) ~ E(z)D. We can actually get to this wave behavior by using circuit theory, w/o going into details of the EM fields!
 Considr a pair of wirs idal wirs ngh >, say, infinily long olag along a cabl can vary! D olag v( E(D W can acually g o his wav bhavior by using circui hory, w/o going ino dails of h EM filds! Thr
Considr a pair of wirs idal wirs ngh >, say, infinily long olag along a cabl can vary! D olag v( E(D W can acually g o his wav bhavior by using circui hory, w/o going ino dails of h EM filds! Thr
Chapter 4 The Fourier Series and Fourier Transform
 Represenaion of Signals in Terms of Frequency Componens Chaper 4 The Fourier Series and Fourier Transform Consider he CT signal defined by x () = Acos( ω + θ ), = The frequencies `presen in he signal are
Represenaion of Signals in Terms of Frequency Componens Chaper 4 The Fourier Series and Fourier Transform Consider he CT signal defined by x () = Acos( ω + θ ), = The frequencies `presen in he signal are
k of the incident wave) will be greater t is too small to satisfy the required kinematics boundary condition, (19)
 TOTAL INTRNAL RFLTION Kmacs pops Sc h vcos a coplaa, l s cosd h cd pla cocds wh h X pla; hc 0. y y y osd h cas whch h lgh s cd fom h mdum of hgh dx of faco >. Fo cd agls ga ha h ccal agl s 1 ( /, h hooal
TOTAL INTRNAL RFLTION Kmacs pops Sc h vcos a coplaa, l s cosd h cd pla cocds wh h X pla; hc 0. y y y osd h cas whch h lgh s cd fom h mdum of hgh dx of faco >. Fo cd agls ga ha h ccal agl s 1 ( /, h hooal
Lecture 20. Transmission Lines: The Basics
 Lcu 0 Tansmissin Lins: Th Basics n his lcu u will lan: Tansmissin lins Diffn ps f ansmissin lin sucus Tansmissin lin quains Pw flw in ansmissin lins Appndi C 303 Fall 006 Fahan Rana Cnll Univsi Guidd Wavs
Lcu 0 Tansmissin Lins: Th Basics n his lcu u will lan: Tansmissin lins Diffn ps f ansmissin lin sucus Tansmissin lin quains Pw flw in ansmissin lins Appndi C 303 Fall 006 Fahan Rana Cnll Univsi Guidd Wavs
AC Circuits AC Circuit with only R AC circuit with only L AC circuit with only C AC circuit with LRC phasors Resonance Transformers
 A ircuis A ircui wih only A circui wih only A circui wih only A circui wih phasors esonance Transformers Phys 435: hap 31, Pg 1 A ircuis New Topic Phys : hap. 6, Pg Physics Moivaion as ime we discovered
A ircuis A ircui wih only A circui wih only A circui wih only A circui wih phasors esonance Transformers Phys 435: hap 31, Pg 1 A ircuis New Topic Phys : hap. 6, Pg Physics Moivaion as ime we discovered
AC STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS
 AC STEADY-STATE ANAYSS SNUSODA AND COPEX FOCNG FUNCTONS Bhavior of circuis wih sinusoidal indpndn sourcs and modling of sinusoids in rms of complx xponnials PHASOS prsnaion of complx xponnials as vcors.
AC STEADY-STATE ANAYSS SNUSODA AND COPEX FOCNG FUNCTONS Bhavior of circuis wih sinusoidal indpndn sourcs and modling of sinusoids in rms of complx xponnials PHASOS prsnaion of complx xponnials as vcors.
CSE 245: Computer Aided Circuit Simulation and Verification
 CSE 45: Compur Aidd Circui Simulaion and Vrificaion Fall 4, Sp 8 Lcur : Dynamic Linar Sysm Oulin Tim Domain Analysis Sa Equaions RLC Nwork Analysis by Taylor Expansion Impuls Rspons in im domain Frquncy
CSE 45: Compur Aidd Circui Simulaion and Vrificaion Fall 4, Sp 8 Lcur : Dynamic Linar Sysm Oulin Tim Domain Analysis Sa Equaions RLC Nwork Analysis by Taylor Expansion Impuls Rspons in im domain Frquncy
H is equal to the surface current J S
 Chapr 6 Rflcion and Transmission of Wavs 6.1 Boundary Condiions A h boundary of wo diffrn mdium, lcromagnic fild hav o saisfy physical condiion, which is drmind by Maxwll s quaion. This is h boundary condiion
Chapr 6 Rflcion and Transmission of Wavs 6.1 Boundary Condiions A h boundary of wo diffrn mdium, lcromagnic fild hav o saisfy physical condiion, which is drmind by Maxwll s quaion. This is h boundary condiion
GUIDE FOR SUPERVISORS 1. This event runs most efficiently with two to four extra volunteers to help proctor students and grade the student
 GUIDE FOR SUPERVISORS 1. This vn uns mos fficinly wih wo o fou xa voluns o hlp poco sudns and gad h sudn scoshs. 2. EVENT PARAMETERS: Th vn supviso will povid scoshs. You will nd o bing a im, pns and pncils
GUIDE FOR SUPERVISORS 1. This vn uns mos fficinly wih wo o fou xa voluns o hlp poco sudns and gad h sudn scoshs. 2. EVENT PARAMETERS: Th vn supviso will povid scoshs. You will nd o bing a im, pns and pncils
Boyce/DiPrima 9 th ed, Ch 2.1: Linear Equations; Method of Integrating Factors
 Boc/DiPrima 9 h d, Ch.: Linar Equaions; Mhod of Ingraing Facors Elmnar Diffrnial Equaions and Boundar Valu Problms, 9 h diion, b William E. Boc and Richard C. DiPrima, 009 b John Wil & Sons, Inc. A linar
Boc/DiPrima 9 h d, Ch.: Linar Equaions; Mhod of Ingraing Facors Elmnar Diffrnial Equaions and Boundar Valu Problms, 9 h diion, b William E. Boc and Richard C. DiPrima, 009 b John Wil & Sons, Inc. A linar
Basic Circuit Elements Professor J R Lucas November 2001
 Basic Circui Elemens - J ucas An elecrical circui is an inerconnecion of circui elemens. These circui elemens can be caegorised ino wo ypes, namely acive and passive elemens. Some Definiions/explanaions
Basic Circui Elemens - J ucas An elecrical circui is an inerconnecion of circui elemens. These circui elemens can be caegorised ino wo ypes, namely acive and passive elemens. Some Definiions/explanaions
MEMS 0031 Electric Circuits
 MEMS 0031 Elecric Circuis Chaper 1 Circui variables Chaper/Lecure Learning Objecives A he end of his lecure and chaper, you should able o: Represen he curren and volage of an elecric circui elemen, paying
MEMS 0031 Elecric Circuis Chaper 1 Circui variables Chaper/Lecure Learning Objecives A he end of his lecure and chaper, you should able o: Represen he curren and volage of an elecric circui elemen, paying
EE 224 Signals and Systems I Complex numbers sinusodal signals Complex exponentials e jωt phasor addition
 EE 224 Signals and Sysems I Complex numbers sinusodal signals Complex exponenials e jω phasor addiion 1/28 Complex Numbers Recangular Polar y z r z θ x Good for addiion/subracion Good for muliplicaion/division
EE 224 Signals and Sysems I Complex numbers sinusodal signals Complex exponenials e jω phasor addiion 1/28 Complex Numbers Recangular Polar y z r z θ x Good for addiion/subracion Good for muliplicaion/division
Phys Nov. 3, 2017 Today s Topics. Continue Chapter 2: Electromagnetic Theory, Photons, and Light Reading for Next Time
 Phys 31. No. 3, 17 Today s Topcs Cou Chap : lcomagc Thoy, Phoos, ad Lgh Radg fo Nx Tm 1 By Wdsday: Radg hs Wk Fsh Fowls Ch. (.3.11 Polazao Thoy, Jos Macs, Fsl uaos ad Bws s Agl Homwok hs Wk Chap Homwok
Phys 31. No. 3, 17 Today s Topcs Cou Chap : lcomagc Thoy, Phoos, ad Lgh Radg fo Nx Tm 1 By Wdsday: Radg hs Wk Fsh Fowls Ch. (.3.11 Polazao Thoy, Jos Macs, Fsl uaos ad Bws s Agl Homwok hs Wk Chap Homwok
University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics. Appendix. DC Circuits Capacitors and Inductors AC Circuits Operational Amplifiers
 Universiy of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Opics Appendix DC Circuis Capaciors and Inducors AC Circuis Operaional Amplifiers Circui Elemens An elecrical circui consiss of circui elemens such as
Universiy of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Opics Appendix DC Circuis Capaciors and Inducors AC Circuis Operaional Amplifiers Circui Elemens An elecrical circui consiss of circui elemens such as
Lecture 2: Current in RC circuit D.K.Pandey
 Lcur 2: urrn in circui harging of apacior hrough Rsisr L us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R and a ky K in sris. Whn h ky K is swichd on, h charging
Lcur 2: urrn in circui harging of apacior hrough Rsisr L us considr a capacior of capacianc is conncd o a D sourc of.m.f. E hrough a rsisr of rsisanc R and a ky K in sris. Whn h ky K is swichd on, h charging
Dynamics of Bloch Electrons 1
 Dynamics of Bloch Elcons 7h Spmb 003 c 003, Michal Mad Dfiniions Dud modl Smiclassical dynamics Bloch oscillaions K P mhod Effciv mass Houson sas Zn unnling Wav pacs Anomalous vlociy Wanni Sa ladds d Haas
Dynamics of Bloch Elcons 7h Spmb 003 c 003, Michal Mad Dfiniions Dud modl Smiclassical dynamics Bloch oscillaions K P mhod Effciv mass Houson sas Zn unnling Wav pacs Anomalous vlociy Wanni Sa ladds d Haas
EXERCISE - 01 CHECK YOUR GRASP
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION EXERCISE - CHECK YOUR GRASP 7. m hn D() m m, D () m m. hn givn D () m m D D D + m m m m m m + m m m m + ( m ) (m ) (m ) (m + ) m,, Hnc numbr of valus of mn will b. n ( ) + c sinc
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION EXERCISE - CHECK YOUR GRASP 7. m hn D() m m, D () m m. hn givn D () m m D D D + m m m m m m + m m m m + ( m ) (m ) (m ) (m + ) m,, Hnc numbr of valus of mn will b. n ( ) + c sinc
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits
 Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Module 4 Single-phase AC Circuits Lesson 14 Solution of Current in R-L-C Series Circuits In the last lesson, two points were described: 1. How to represent a sinusoidal (ac) quantity, i.e. voltage/current
Lecture 2: Bayesian inference - Discrete probability models
 cu : Baysian infnc - Disc obabiliy modls Many hings abou Baysian infnc fo disc obabiliy modls a simila o fqunis infnc Disc obabiliy modls: Binomial samling Samling a fix numb of ials fom a Bnoulli ocss
cu : Baysian infnc - Disc obabiliy modls Many hings abou Baysian infnc fo disc obabiliy modls a simila o fqunis infnc Disc obabiliy modls: Binomial samling Samling a fix numb of ials fom a Bnoulli ocss
Study of Tyre Damping Ratio and In-Plane Time Domain Simulation with Modal Parameter Tyre Model (MPTM)
 Sudy o Ty Damping aio and In-Plan Tim Domain Simulaion wih Modal Paam Ty Modl (MPTM D. Jin Shang, D. Baojang Li, and Po. Dihua Guan Sa Ky Laboaoy o Auomoiv Say and Engy, Tsinghua Univsiy, Bijing, China
Sudy o Ty Damping aio and In-Plan Tim Domain Simulaion wih Modal Paam Ty Modl (MPTM D. Jin Shang, D. Baojang Li, and Po. Dihua Guan Sa Ky Laboaoy o Auomoiv Say and Engy, Tsinghua Univsiy, Bijing, China
E F. and H v. or A r and F r are dual of each other.
 A Duality Thom: Consid th following quations as an xampl = A = F μ ε H A E A = jωa j ωμε A + β A = μ J μ A x y, z = J, y, z 4π E F ( A = jω F j ( F j β H F ωμε F + β F = ε M jβ ε F x, y, z = M, y, z 4π
A Duality Thom: Consid th following quations as an xampl = A = F μ ε H A E A = jωa j ωμε A + β A = μ J μ A x y, z = J, y, z 4π E F ( A = jω F j ( F j β H F ωμε F + β F = ε M jβ ε F x, y, z = M, y, z 4π
CHAPTER 2 Signals And Spectra
 CHAPER Signals And Specra Properies of Signals and Noise In communicaion sysems he received waveform is usually caegorized ino he desired par conaining he informaion, and he undesired par. he desired par
CHAPER Signals And Specra Properies of Signals and Noise In communicaion sysems he received waveform is usually caegorized ino he desired par conaining he informaion, and he undesired par. he desired par
8.022 (E&M) Lecture 16
 8. (E&M) ecure 16 Topics: Inducors in circuis circuis circuis circuis as ime Our second lecure on elecromagneic inducance 3 ways of creaing emf using Faraday s law: hange area of circui S() hange angle
8. (E&M) ecure 16 Topics: Inducors in circuis circuis circuis circuis as ime Our second lecure on elecromagneic inducance 3 ways of creaing emf using Faraday s law: hange area of circui S() hange angle
Wave Equation (2 Week)
 Rfrnc Wav quaion ( Wk 6.5 Tim-armonic filds 7. Ovrviw 7. Plan Wavs in Losslss Mdia 7.3 Plan Wavs in Loss Mdia 7.5 Flow of lcromagnic Powr and h Poning Vcor 7.6 Normal Incidnc of Plan Wavs a Plan Boundaris
Rfrnc Wav quaion ( Wk 6.5 Tim-armonic filds 7. Ovrviw 7. Plan Wavs in Losslss Mdia 7.3 Plan Wavs in Loss Mdia 7.5 Flow of lcromagnic Powr and h Poning Vcor 7.6 Normal Incidnc of Plan Wavs a Plan Boundaris
Active Harmonic Filtering and Reactive Power Control
 Session 3, Page /34 Acive Harmonic Filering and Reacive Power Conrol Imiaion Measured Currens: Define array of ime and define angular frequency: Δ Δ.3 4 s 86Hz 6 secδ ω 6Hz π6hz ω() ω Load curren as a
Session 3, Page /34 Acive Harmonic Filering and Reacive Power Conrol Imiaion Measured Currens: Define array of ime and define angular frequency: Δ Δ.3 4 s 86Hz 6 secδ ω 6Hz π6hz ω() ω Load curren as a
ACCUMULATION. Section 7.5 Calculus AP/Dual, Revised /26/2018 7:27 PM 7.5A: Accumulation 1
 ACCUMULATION Secion 7.5 Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 2019 vie.dang@humbleisd.ne 12/26/2018 7:27 PM 7.5A: Accumulaion 1 APPLICATION PROBLEMS A. Undersand he quesion. I is ofen no necessary o as much compuaion
ACCUMULATION Secion 7.5 Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 2019 vie.dang@humbleisd.ne 12/26/2018 7:27 PM 7.5A: Accumulaion 1 APPLICATION PROBLEMS A. Undersand he quesion. I is ofen no necessary o as much compuaion
Module 4. Single-phase AC Circuits. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 4 Single-phase A ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur esson 4 Solution of urrent in -- Series ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur In the last lesson, two points were described:. How to represent a sinusoidal
Module 4 Single-phase A ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur esson 4 Solution of urrent in -- Series ircuits ersion EE IIT, Kharagpur In the last lesson, two points were described:. How to represent a sinusoidal
Fourier transforms (Chapter 15) Fourier integrals are generalizations of Fourier series. The series representation
 Pof. D. I. Nass Phys57 (T-3) Sptmb 8, 03 Foui_Tansf_phys57_T3 Foui tansfoms (Chapt 5) Foui intgals a gnalizations of Foui sis. Th sis psntation a0 nπx nπx f ( x) = + [ an cos + bn sin ] n = of a function
Pof. D. I. Nass Phys57 (T-3) Sptmb 8, 03 Foui_Tansf_phys57_T3 Foui tansfoms (Chapt 5) Foui intgals a gnalizations of Foui sis. Th sis psntation a0 nπx nπx f ( x) = + [ an cos + bn sin ] n = of a function
Estimation of a Random Variable
 Estimation of a andom Vaiabl Obsv and stimat. ˆ is an stimat of. ζ : outcom Estimation ul ˆ Sampl Spac Eampl: : Pson s Hight, : Wight. : Ailin Company s Stock Pic, : Cud Oil Pic. Cost of Estimation Eo
Estimation of a andom Vaiabl Obsv and stimat. ˆ is an stimat of. ζ : outcom Estimation ul ˆ Sampl Spac Eampl: : Pson s Hight, : Wight. : Ailin Company s Stock Pic, : Cud Oil Pic. Cost of Estimation Eo
Derivation of the differential equation of motion
 Divion of h iffnil quion of oion Fis h noions fin h will us fo h ivion of h iffnil quion of oion. Rollo is hough o -insionl isk. xnl ius of h ll isnc cn of ll (O) - IDU s cn of gviy (M) θ ngl of inclinion
Divion of h iffnil quion of oion Fis h noions fin h will us fo h ivion of h iffnil quion of oion. Rollo is hough o -insionl isk. xnl ius of h ll isnc cn of ll (O) - IDU s cn of gviy (M) θ ngl of inclinion
Wave Motion Sections 1,2,4,5, I. Outlook II. What is wave? III.Kinematics & Examples IV. Equation of motion Wave equations V.
 Secions 1,,4,5, I. Oulook II. Wha is wave? III.Kinemaics & Eamples IV. Equaion of moion Wave equaions V. Eamples Oulook Translaional and Roaional Moions wih Several phsics quaniies Energ (E) Momenum (p)
Secions 1,,4,5, I. Oulook II. Wha is wave? III.Kinemaics & Eamples IV. Equaion of moion Wave equaions V. Eamples Oulook Translaional and Roaional Moions wih Several phsics quaniies Energ (E) Momenum (p)
8 - GRAVITATION Page 1
 8 GAVITATION Pag 1 Intoduction Ptolmy, in scond cntuy, gav gocntic thoy of plantay motion in which th Eath is considd stationay at th cnt of th univs and all th stas and th plants including th Sun volving
8 GAVITATION Pag 1 Intoduction Ptolmy, in scond cntuy, gav gocntic thoy of plantay motion in which th Eath is considd stationay at th cnt of th univs and all th stas and th plants including th Sun volving
Lecture 9: Space-Vector Models
 1 / 30 Lecture 9: Space-Vector Models ELEC-E8405 Electric Drives (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Autumn 2017 2 / 30 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises you will be able to: Include the number of
1 / 30 Lecture 9: Space-Vector Models ELEC-E8405 Electric Drives (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Autumn 2017 2 / 30 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises you will be able to: Include the number of
Chapter 5 The Laplace Transform. x(t) input y(t) output Dynamic System
 EE 422G No: Chapr 5 Inrucor: Chung Chapr 5 Th Laplac Tranform 5- Inroducion () Sym analyi inpu oupu Dynamic Sym Linar Dynamic ym: A procor which proc h inpu ignal o produc h oupu dy ( n) ( n dy ( n) +
EE 422G No: Chapr 5 Inrucor: Chung Chapr 5 Th Laplac Tranform 5- Inroducion () Sym analyi inpu oupu Dynamic Sym Linar Dynamic ym: A procor which proc h inpu ignal o produc h oupu dy ( n) ( n dy ( n) +
Voltage/current relationship Stored Energy. RL / RC circuits Steady State / Transient response Natural / Step response
 Review Capaciors/Inducors Volage/curren relaionship Sored Energy s Order Circuis RL / RC circuis Seady Sae / Transien response Naural / Sep response EE4 Summer 5: Lecure 5 Insrucor: Ocavian Florescu Lecure
Review Capaciors/Inducors Volage/curren relaionship Sored Energy s Order Circuis RL / RC circuis Seady Sae / Transien response Naural / Sep response EE4 Summer 5: Lecure 5 Insrucor: Ocavian Florescu Lecure
European and American options with a single payment of dividends. (About formula Roll, Geske & Whaley) Mark Ioffe. Abstract
 866 Uni Naions Plaza i 566 Nw Yo NY 7 Phon: + 3 355 Fa: + 4 668 info@gach.com www.gach.com Eoan an Amican oions wih a singl amn of ivins Abo fomla Roll Gs & Whal Ma Ioff Absac Th aicl ovis a ivaion of
866 Uni Naions Plaza i 566 Nw Yo NY 7 Phon: + 3 355 Fa: + 4 668 info@gach.com www.gach.com Eoan an Amican oions wih a singl amn of ivins Abo fomla Roll Gs & Whal Ma Ioff Absac Th aicl ovis a ivaion of
Part I- Wave Reflection and Transmission at Normal Incident. Part II- Wave Reflection and Transmission at Oblique Incident
 Apl 6, 3 Uboudd Mda Gudd Mda Chap 7 Chap 8 3 mls 3 o 3 M F bad Lgh wavs md by h su Pa I- Wav Rlo ad Tasmsso a Nomal Id Pa II- Wav Rlo ad Tasmsso a Oblqu Id Pa III- Gal Rlao Bw ad Wavguds ad Cavy Rsoao
Apl 6, 3 Uboudd Mda Gudd Mda Chap 7 Chap 8 3 mls 3 o 3 M F bad Lgh wavs md by h su Pa I- Wav Rlo ad Tasmsso a Nomal Id Pa II- Wav Rlo ad Tasmsso a Oblqu Id Pa III- Gal Rlao Bw ad Wavguds ad Cavy Rsoao
SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORMS
 SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORMS The sinusoidal waveform is he only waveform whose shape is no affeced by he response characerisics of R, L, and C elemens. Enzo Paerno CIRCUIT ELEMENTS R [ Ω ] Resisance: Ω: Ohms Georg
SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORMS The sinusoidal waveform is he only waveform whose shape is no affeced by he response characerisics of R, L, and C elemens. Enzo Paerno CIRCUIT ELEMENTS R [ Ω ] Resisance: Ω: Ohms Georg
Representing a Signal. Continuous-Time Fourier Methods. Linearity and Superposition. Real and Complex Sinusoids. Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier
 Represening a Signal Coninuous-ime ourier Mehods he convoluion mehod for finding he response of a sysem o an exciaion aes advanage of he lineariy and imeinvariance of he sysem and represens he exciaion
Represening a Signal Coninuous-ime ourier Mehods he convoluion mehod for finding he response of a sysem o an exciaion aes advanage of he lineariy and imeinvariance of he sysem and represens he exciaion
( r) E (r) Phasor. Function of space only. Fourier series Synthesis equations. Sinusoidal EM Waves. For complex periodic signals
 Inoducon Snusodal M Was.MB D Yan Pllo Snusodal M.3MB 3. Snusodal M.3MB 3. Inoducon Inoducon o o dsgn h communcaons sd of a sall? Fqunc? Oms oagaon? Oms daa a? Annnas? Dc? Gan? Wa quaons Sgnal analss Wa
Inoducon Snusodal M Was.MB D Yan Pllo Snusodal M.3MB 3. Snusodal M.3MB 3. Inoducon Inoducon o o dsgn h communcaons sd of a sall? Fqunc? Oms oagaon? Oms daa a? Annnas? Dc? Gan? Wa quaons Sgnal analss Wa
IE1206 Embedded Electronics
 E06 Embedded Elecronics Le Le3 Le4 Le Ex Ex P-block Documenaion, Seriecom Pulse sensors,, R, P, serial and parallel K LAB Pulse sensors, Menu program Sar of programing ask Kirchhoffs laws Node analysis
E06 Embedded Elecronics Le Le3 Le4 Le Ex Ex P-block Documenaion, Seriecom Pulse sensors,, R, P, serial and parallel K LAB Pulse sensors, Menu program Sar of programing ask Kirchhoffs laws Node analysis
Extinction Ratio and Power Penalty
 Application Not: HFAN-.. Rv.; 4/8 Extinction Ratio and ow nalty AVALABLE Backgound Extinction atio is an impotant paamt includd in th spcifications of most fib-optic tanscivs. h pupos of this application
Application Not: HFAN-.. Rv.; 4/8 Extinction Ratio and ow nalty AVALABLE Backgound Extinction atio is an impotant paamt includd in th spcifications of most fib-optic tanscivs. h pupos of this application
Elementary Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems
 Elmnar Diffrnial Equaions and Boundar Valu Problms Boc. & DiPrima 9 h Ediion Chapr : Firs Ordr Diffrnial Equaions 00600 คณ ตศาสตร ว ศวกรรม สาขาว ชาว ศวกรรมคอมพ วเตอร ป การศ กษา /55 ผศ.ดร.อร ญญา ผศ.ดร.สมศ
Elmnar Diffrnial Equaions and Boundar Valu Problms Boc. & DiPrima 9 h Ediion Chapr : Firs Ordr Diffrnial Equaions 00600 คณ ตศาสตร ว ศวกรรม สาขาว ชาว ศวกรรมคอมพ วเตอร ป การศ กษา /55 ผศ.ดร.อร ญญา ผศ.ดร.สมศ
Optimal design of full disks with respect to mixed creep rupture time
 Compu Aidd Opimum Dsign in Engining XII 83 Opimal dsign of full disks wih spc o mixd cp upu im K. Szuwalski & A. Uszycka Cacow Univsiy of Tchnology, Poland Absac Th mixd upu hoy o h opimizaion poblm fo
Compu Aidd Opimum Dsign in Engining XII 83 Opimal dsign of full disks wih spc o mixd cp upu im K. Szuwalski & A. Uszycka Cacow Univsiy of Tchnology, Poland Absac Th mixd upu hoy o h opimizaion poblm fo
AC STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS
 EANNG GOAS AC STEAD-STATE ANASS SNUSODS viw basic facs abou sinusoidal signals SNUSODA AND COPEX FOCNG FUNCTONS Bhavior of circuis wih sinusoidal indpndn sourcs and modling of sinusoids in rms of complx
EANNG GOAS AC STEAD-STATE ANASS SNUSODS viw basic facs abou sinusoidal signals SNUSODA AND COPEX FOCNG FUNCTONS Bhavior of circuis wih sinusoidal indpndn sourcs and modling of sinusoids in rms of complx
GRAVITATION. (d) If a spring balance having frequency f is taken on moon (having g = g / 6) it will have a frequency of (a) 6f (b) f / 6
 GVITTION 1. Two satllits and o ound a plant P in cicula obits havin adii 4 and spctivly. If th spd of th satllit is V, th spd of th satllit will b 1 V 6 V 4V V. Th scap vlocity on th sufac of th ath is
GVITTION 1. Two satllits and o ound a plant P in cicula obits havin adii 4 and spctivly. If th spd of th satllit is V, th spd of th satllit will b 1 V 6 V 4V V. Th scap vlocity on th sufac of th ath is
Introduction to AC Power, RMS RMS. ECE 2210 AC Power p1. Use RMS in power calculations. AC Power P =? DC Power P =. V I = R =. I 2 R. V p.
 ECE MS I DC Power P I = Inroducion o AC Power, MS I AC Power P =? A Solp //9, // // correced p4 '4 v( ) = p cos( ω ) v( ) p( ) Couldn' we define an "effecive" volage ha would allow us o use he same relaionships
ECE MS I DC Power P I = Inroducion o AC Power, MS I AC Power P =? A Solp //9, // // correced p4 '4 v( ) = p cos( ω ) v( ) p( ) Couldn' we define an "effecive" volage ha would allow us o use he same relaionships
EX12 EX140 EX180 EX260 EX250 EX600 EX500 EX510
 Fo Inpu/Oupu Sis Enclosu IP67 Maximum inpus/ oupus Conncion of snsos wih M8/M conncos is possibl SY//7 VQC//4/ S7 SV// u y w No) SY//7, VQC//4/, S7 a no y UL-compaibl. No. Typ Funcion 4 6 7 Oupu block
Fo Inpu/Oupu Sis Enclosu IP67 Maximum inpus/ oupus Conncion of snsos wih M8/M conncos is possibl SY//7 VQC//4/ S7 SV// u y w No) SY//7, VQC//4/, S7 a no y UL-compaibl. No. Typ Funcion 4 6 7 Oupu block
Chapter 33 Alternating Current
 hapte 33 Altenating uent icuits Most of the electical enegy is poduced by electical geneatos in the fom of sinusoidal altenating cuent. Why do we use the sinusoidal electic potential but neithe the tiangula
hapte 33 Altenating uent icuits Most of the electical enegy is poduced by electical geneatos in the fom of sinusoidal altenating cuent. Why do we use the sinusoidal electic potential but neithe the tiangula
Existence and Stability of Non-Collinear Librations Points in the Restricted Problem with Poynting Robertson Light Drag Effect
 Eisnc and Sabili of Non-Collina Libaions Poins in h sicd Poblm wih Ponin obson Lih Da Effc Mama Jain ajiv Aawal Shi Vnashwaa Univsi UP India Si Auobindo Coll Univsi of Dlhi Dlhi India ABSTACT This pap
Eisnc and Sabili of Non-Collina Libaions Poins in h sicd Poblm wih Ponin obson Lih Da Effc Mama Jain ajiv Aawal Shi Vnashwaa Univsi UP India Si Auobindo Coll Univsi of Dlhi Dlhi India ABSTACT This pap
Direct Current Circuits. February 19, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 26 1
 Direc Curren Circuis February 19, 2014 Physics for Scieniss & Engineers 2, Chaper 26 1 Ammeers and Volmeers! A device used o measure curren is called an ammeer! A device used o measure poenial difference
Direc Curren Circuis February 19, 2014 Physics for Scieniss & Engineers 2, Chaper 26 1 Ammeers and Volmeers! A device used o measure curren is called an ammeer! A device used o measure poenial difference
ME 452 Fourier Series and Fourier Transform
 ME 452 Fourier Series and Fourier ransform Fourier series From Joseph Fourier in 87 as a resul of his sudy on he flow of hea. If f() is almos any periodic funcion i can be wrien as an infinie sum of sines
ME 452 Fourier Series and Fourier ransform Fourier series From Joseph Fourier in 87 as a resul of his sudy on he flow of hea. If f() is almos any periodic funcion i can be wrien as an infinie sum of sines
Chapter 4 Circular and Curvilinear Motions
 Chp 4 Cicul n Cuilin Moions H w consi picls moing no long sigh lin h cuilin moion. W fis su h cicul moion, spcil cs of cuilin moion. Anoh mpl w h l sui li is h pojcil..1 Cicul Moion Unifom Cicul Moion
Chp 4 Cicul n Cuilin Moions H w consi picls moing no long sigh lin h cuilin moion. W fis su h cicul moion, spcil cs of cuilin moion. Anoh mpl w h l sui li is h pojcil..1 Cicul Moion Unifom Cicul Moion
Bethe-Salpeter Equation Green s Function and the Bethe-Salpeter Equation for Effective Interaction in the Ladder Approximation
 Bh-Salp Equaon n s Funcon and h Bh-Salp Equaon fo Effcv Inacon n h Ladd Appoxmaon Csa A. Z. Vasconcllos Insuo d Físca-UFRS - upo: Físca d Hadons Sngl-Pacl Popagao. Dagam xpanson of popagao. W consd as
Bh-Salp Equaon n s Funcon and h Bh-Salp Equaon fo Effcv Inacon n h Ladd Appoxmaon Csa A. Z. Vasconcllos Insuo d Físca-UFRS - upo: Físca d Hadons Sngl-Pacl Popagao. Dagam xpanson of popagao. W consd as
Physics 111. Lecture 38 (Walker: ) Phase Change Latent Heat. May 6, The Three Basic Phases of Matter. Solid Liquid Gas
 Physics 111 Lctu 38 (Walk: 17.4-5) Phas Chang May 6, 2009 Lctu 38 1/26 Th Th Basic Phass of Matt Solid Liquid Gas Squnc of incasing molcul motion (and ngy) Lctu 38 2/26 If a liquid is put into a sald contain
Physics 111 Lctu 38 (Walk: 17.4-5) Phas Chang May 6, 2009 Lctu 38 1/26 Th Th Basic Phass of Matt Solid Liquid Gas Squnc of incasing molcul motion (and ngy) Lctu 38 2/26 If a liquid is put into a sald contain
Basic Principles of Sinusoidal Oscillators
 Basic Principles of Sinusoidal Oscillaors Linear oscillaor Linear region of circui : linear oscillaion Nonlinear region of circui : ampliudes sabilizaion Barkhausen crierion X S Amplifier A X O X f Frequency-selecive
Basic Principles of Sinusoidal Oscillaors Linear oscillaor Linear region of circui : linear oscillaion Nonlinear region of circui : ampliudes sabilizaion Barkhausen crierion X S Amplifier A X O X f Frequency-selecive
Circuit Analysis-III. Circuit Analysis-II Lecture # 3 Friday 06 th April, 18
 Circuit Analysis-III Sinusoids Example #1 ü Find the amplitude, phase, period and frequency of the sinusoid: v (t ) =12cos(50t +10 ) Signal Conversion ü From sine to cosine and vice versa. ü sin (A ± B)
Circuit Analysis-III Sinusoids Example #1 ü Find the amplitude, phase, period and frequency of the sinusoid: v (t ) =12cos(50t +10 ) Signal Conversion ü From sine to cosine and vice versa. ü sin (A ± B)
Transfer function and the Laplace transformation
 Lab No PH-35 Porland Sa Univriy A. La Roa Tranfr funcion and h Laplac ranformaion. INTRODUTION. THE LAPLAE TRANSFORMATION L 3. TRANSFER FUNTIONS 4. ELETRIAL SYSTEMS Analyi of h hr baic paiv lmn R, and
Lab No PH-35 Porland Sa Univriy A. La Roa Tranfr funcion and h Laplac ranformaion. INTRODUTION. THE LAPLAE TRANSFORMATION L 3. TRANSFER FUNTIONS 4. ELETRIAL SYSTEMS Analyi of h hr baic paiv lmn R, and
( ) is the stretch factor, and x the
 (Lecures 7-8) Liddle, Chaper 5 Simple cosmological models (i) Hubble s Law revisied Self-similar srech of he universe All universe models have his characerisic v r ; v = Hr since only his conserves homogeneiy
(Lecures 7-8) Liddle, Chaper 5 Simple cosmological models (i) Hubble s Law revisied Self-similar srech of he universe All universe models have his characerisic v r ; v = Hr since only his conserves homogeneiy
I. Define the Situation
 I. efine he Siuaion This exam explores he relaionship beween he applied volage o a permanen magne C moond he linear velociy (speed) of he elecric vehicle (EV) he moor drives. The moor oupu is fed ino a
I. efine he Siuaion This exam explores he relaionship beween he applied volage o a permanen magne C moond he linear velociy (speed) of he elecric vehicle (EV) he moor drives. The moor oupu is fed ino a
ECE 145A / 218 C, notes set 1: Transmission Line Properties and Analysis
 class nos, M. Rodwll, copyrighd 9 ECE 145A 18 C, nos s 1: Transmission in Propris and Analysis Mark Rodwll Univrsiy of California, Sana Barbara rodwll@c.ucsb.du 85-893-344, 85-893-36 fax Transmission in
class nos, M. Rodwll, copyrighd 9 ECE 145A 18 C, nos s 1: Transmission in Propris and Analysis Mark Rodwll Univrsiy of California, Sana Barbara rodwll@c.ucsb.du 85-893-344, 85-893-36 fax Transmission in
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS 2008
 [E5] IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS 008 EEE/ISE PART II MEng BEng and ACGI SIGNALS AND LINEAR SYSTEMS Time allowed: :00 hours There are FOUR quesions
[E5] IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS 008 EEE/ISE PART II MEng BEng and ACGI SIGNALS AND LINEAR SYSTEMS Time allowed: :00 hours There are FOUR quesions
Hilbert Inner Product Space (2B) Young Won Lim 2/23/12
 Hilber nner Produc Space (2B) Copyrigh (c) 2009-2011 Young W. Lim. Permission is graned o copy, disribue and/or modify his documen under he erms of he GNU Free Documenaion License, Version 1.2 or any laer
Hilber nner Produc Space (2B) Copyrigh (c) 2009-2011 Young W. Lim. Permission is graned o copy, disribue and/or modify his documen under he erms of he GNU Free Documenaion License, Version 1.2 or any laer
( ) = 0.43 kj = 430 J. Solutions 9 1. Solutions to Miscellaneous Exercise 9 1. Let W = work done then 0.
 Soluions 9 Soluions o Miscellaneous Exercise 9. Le W work done hen.9 W PdV Using Simpson's rule (9.) we have. W { 96 + [ 58 + 6 + 77 + 5 ] + [ + 99 + 6 ]+ }. kj. Using Simpson's rule (9.) again: W.5.6
Soluions 9 Soluions o Miscellaneous Exercise 9. Le W work done hen.9 W PdV Using Simpson's rule (9.) we have. W { 96 + [ 58 + 6 + 77 + 5 ] + [ + 99 + 6 ]+ }. kj. Using Simpson's rule (9.) again: W.5.6
Signals and Systems Profs. Byron Yu and Pulkit Grover Fall Midterm 1 Solutions
 8-90 Signals and Sysems Profs. Byron Yu and Pulki Grover Fall 07 Miderm Soluions Name: Andrew ID: Problem Score Max 0 8 4 6 5 0 6 0 7 8 9 0 6 Toal 00 Miderm Soluions. (0 poins) Deermine wheher he following
8-90 Signals and Sysems Profs. Byron Yu and Pulki Grover Fall 07 Miderm Soluions Name: Andrew ID: Problem Score Max 0 8 4 6 5 0 6 0 7 8 9 0 6 Toal 00 Miderm Soluions. (0 poins) Deermine wheher he following
Section 3.8, Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations
 Secion 3.8, Mechanical and Elecrical Vibraions Mechanical Unis in he U.S. Cusomary and Meric Sysems Disance Mass Time Force g (Earh) Uni U.S. Cusomary MKS Sysem CGS Sysem fee f slugs seconds sec pounds
Secion 3.8, Mechanical and Elecrical Vibraions Mechanical Unis in he U.S. Cusomary and Meric Sysems Disance Mass Time Force g (Earh) Uni U.S. Cusomary MKS Sysem CGS Sysem fee f slugs seconds sec pounds
STATISTICAL MECHANICS OF DIATOMIC GASES
 Pof. D. I. ass Phys54 7 -Ma-8 Diatomic_Gas (Ashly H. Cat chapt 5) SAISICAL MECHAICS OF DIAOMIC GASES - Fo monatomic gas whos molculs hav th dgs of fdom of tanslatoy motion th intnal u 3 ngy and th spcific
Pof. D. I. ass Phys54 7 -Ma-8 Diatomic_Gas (Ashly H. Cat chapt 5) SAISICAL MECHAICS OF DIAOMIC GASES - Fo monatomic gas whos molculs hav th dgs of fdom of tanslatoy motion th intnal u 3 ngy and th spcific
5. An object moving along an x-coordinate axis with its scale measured in meters has a velocity of 6t
 AP CALCULUS FINAL UNIT WORKSHEETS ACCELERATION, VELOCTIY AND POSITION In problms -, drmin h posiion funcion, (), from h givn informaion.. v (), () = 5. v ()5, () = b g. a (), v() =, () = -. a (), v() =
AP CALCULUS FINAL UNIT WORKSHEETS ACCELERATION, VELOCTIY AND POSITION In problms -, drmin h posiion funcion, (), from h givn informaion.. v (), () = 5. v ()5, () = b g. a (), v() =, () = -. a (), v() =
C From Faraday's Law, the induced voltage is, C The effect of electromagnetic induction in the coil itself is called selfinduction.
 Inducors and Inducanc C For inducors, v() is proporional o h ra of chang of i(). Inducanc (con d) C Th proporionaliy consan is h inducanc, L, wih unis of Hnris. 1 Hnry = 1 Wb / A or 1 V sc / A. C L dpnds
Inducors and Inducanc C For inducors, v() is proporional o h ra of chang of i(). Inducanc (con d) C Th proporionaliy consan is h inducanc, L, wih unis of Hnris. 1 Hnry = 1 Wb / A or 1 V sc / A. C L dpnds
Lecture #6: Continuous-Time Signals
 EEL5: Discree-Time Signals and Sysems Lecure #6: Coninuous-Time Signals Lecure #6: Coninuous-Time Signals. Inroducion In his lecure, we discussed he ollowing opics:. Mahemaical represenaion and ransormaions
EEL5: Discree-Time Signals and Sysems Lecure #6: Coninuous-Time Signals Lecure #6: Coninuous-Time Signals. Inroducion In his lecure, we discussed he ollowing opics:. Mahemaical represenaion and ransormaions
A Simple Method for Determining the Manoeuvring Indices K and T from Zigzag Trial Data
 Rind 8-- Wbsi: wwwshimoionsnl Ro 67, Jun 97, Dlf Univsiy of chnoloy, Shi Hydomchnics Lbooy, Mklw, 68 CD Dlf, h Nhlnds A Siml Mhod fo Dminin h Mnouvin Indics K nd fom Ziz il D JMJ Jouné Dlf Univsiy of chnoloy
Rind 8-- Wbsi: wwwshimoionsnl Ro 67, Jun 97, Dlf Univsiy of chnoloy, Shi Hydomchnics Lbooy, Mklw, 68 CD Dlf, h Nhlnds A Siml Mhod fo Dminin h Mnouvin Indics K nd fom Ziz il D JMJ Jouné Dlf Univsiy of chnoloy
Q Q N, V, e, Quantum Statistics for Ideal Gas and Black Body Radiation. The Canonical Ensemble
 Quantum Statistics fo Idal Gas and Black Body Radiation Physics 436 Lctu #0 Th Canonical Ensmbl Ei Q Q N V p i 1 Q E i i Bos-Einstin Statistics Paticls with intg valu of spin... qi... q j...... q j...
Quantum Statistics fo Idal Gas and Black Body Radiation Physics 436 Lctu #0 Th Canonical Ensmbl Ei Q Q N V p i 1 Q E i i Bos-Einstin Statistics Paticls with intg valu of spin... qi... q j...... q j...
Lecture 5. Chapter 3. Electromagnetic Theory, Photons, and Light
 Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Circuits and Systems I
 Circuis and Sysms I LECTURE #3 Th Spcrum, Priodic Signals, and h Tim-Varying Spcrum lions@pfl Prof. Dr. Volan Cvhr LIONS/Laboraory for Informaion and Infrnc Sysms Licns Info for SPFirs Slids This wor rlasd
Circuis and Sysms I LECTURE #3 Th Spcrum, Priodic Signals, and h Tim-Varying Spcrum lions@pfl Prof. Dr. Volan Cvhr LIONS/Laboraory for Informaion and Infrnc Sysms Licns Info for SPFirs Slids This wor rlasd
GRAVITATION 4) R. max. 2 ..(1) ...(2)
 GAVITATION PVIOUS AMCT QUSTIONS NGINING. A body is pojctd vtically upwads fom th sufac of th ath with a vlocity qual to half th scap vlocity. If is th adius of th ath, maximum hight attaind by th body
GAVITATION PVIOUS AMCT QUSTIONS NGINING. A body is pojctd vtically upwads fom th sufac of th ath with a vlocity qual to half th scap vlocity. If is th adius of th ath, maximum hight attaind by th body
3. Alternating Current
 3. Alernaing Curren TOPCS Definiion and nroducion AC Generaor Componens of AC Circuis Series LRC Circuis Power in AC Circuis Transformers & AC Transmission nroducion o AC The elecric power ou of a home
3. Alernaing Curren TOPCS Definiion and nroducion AC Generaor Componens of AC Circuis Series LRC Circuis Power in AC Circuis Transformers & AC Transmission nroducion o AC The elecric power ou of a home
Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves
 Phsics 36: Waves Lecure 3 /9/8 Maxwell s quaions and lecromagneic Waves Four Laws of lecromagneism. Gauss Law qenc all da ρdv Inegral From From he vecor ideni da dv Therefore, we ma wrie Gauss Law as ρ
Phsics 36: Waves Lecure 3 /9/8 Maxwell s quaions and lecromagneic Waves Four Laws of lecromagneism. Gauss Law qenc all da ρdv Inegral From From he vecor ideni da dv Therefore, we ma wrie Gauss Law as ρ
Lecture 18: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System: general kinetics analysis based on the dilute-solution approximation
 Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
The Black-Scholes Formula
 lack & chols h lack-chols Fomula D. Guillmo Lópz Dumauf dumauf@fibl.com.a Copyigh 6 by D. Guillmo Lópz Dumauf. No pa of his publicaion may b poducd, sod in a ival sysm, o ansmid in any fom o by any mans
lack & chols h lack-chols Fomula D. Guillmo Lópz Dumauf dumauf@fibl.com.a Copyigh 6 by D. Guillmo Lópz Dumauf. No pa of his publicaion may b poducd, sod in a ival sysm, o ansmid in any fom o by any mans
( ) C R. υ in RC 1. cos. ,sin. ω ω υ + +
 Oscillaors. Thory of Oscillaions. Th lad circui, h lag circui and h lad-lag circui. Th Win Bridg oscillaor. Ohr usful oscillaors. Th 555 Timr. Basic Dscripion. Th S flip flop. Monosabl opraion of h 555
Oscillaors. Thory of Oscillaions. Th lad circui, h lag circui and h lad-lag circui. Th Win Bridg oscillaor. Ohr usful oscillaors. Th 555 Timr. Basic Dscripion. Th S flip flop. Monosabl opraion of h 555
ESE (Prelims) - Offline Test Series ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING SUBJECT: Electrical Machines & Systems and Signal Processing SOLUTIONS
 TEST ID: 30 ESE- 09 (Plims) - Offlin Tst Sis ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Tst-3 SUBJECT: Elctical Machins & Systms and Signal Pocssing SOLUTIONS 0. Ans: (c) Sol: With hot-olld stl laminations max [B m ] A. A
TEST ID: 30 ESE- 09 (Plims) - Offlin Tst Sis ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Tst-3 SUBJECT: Elctical Machins & Systms and Signal Pocssing SOLUTIONS 0. Ans: (c) Sol: With hot-olld stl laminations max [B m ] A. A
Chapter 1 Fundamental Concepts
 Chaper 1 Fundamenal Conceps 1 Signals A signal is a paern of variaion of a physical quaniy, ofen as a funcion of ime (bu also space, disance, posiion, ec). These quaniies are usually he independen variables
Chaper 1 Fundamenal Conceps 1 Signals A signal is a paern of variaion of a physical quaniy, ofen as a funcion of ime (bu also space, disance, posiion, ec). These quaniies are usually he independen variables
EE 101 Electrical Engineering. vrect
 EE Elecrical Engineering ac heory 3. Alernaing urren heory he advanage of he alernaing waveform for elecric power is ha i can be sepped up or sepped down in poenial easily for ransmission and uilisaion.
EE Elecrical Engineering ac heory 3. Alernaing urren heory he advanage of he alernaing waveform for elecric power is ha i can be sepped up or sepped down in poenial easily for ransmission and uilisaion.
Name: Total Points: Multiple choice questions [120 points]
![Name: Total Points: Multiple choice questions [120 points] Name: Total Points: Multiple choice questions [120 points]](/thumbs/88/115221528.jpg) Name: Toal Poins: (Las) (Firs) Muliple choice quesions [1 poins] Answer all of he following quesions. Read each quesion carefully. Fill he correc bubble on your scanron shee. Each correc answer is worh
Name: Toal Poins: (Las) (Firs) Muliple choice quesions [1 poins] Answer all of he following quesions. Read each quesion carefully. Fill he correc bubble on your scanron shee. Each correc answer is worh
( ) ( ) ( ) 0. dt dt dt ME203 PROBLEM SET #6. 1. Text Section 4.5
 ME PROBLEM SET #6 T Sion 45 d w 6 dw 4 5 w d d Solion: Fis mlil his qaion b (whih w an do sin > o ansfom i ino h Cah- El qaion givn b w ( 6w ( 4 Thn b making h sbsiion (and sing qaion (7 on ag 88 of h,
ME PROBLEM SET #6 T Sion 45 d w 6 dw 4 5 w d d Solion: Fis mlil his qaion b (whih w an do sin > o ansfom i ino h Cah- El qaion givn b w ( 6w ( 4 Thn b making h sbsiion (and sing qaion (7 on ag 88 of h,
Chapter 2 : Fourier Series. Chapter 3 : Fourier Series
 Chaper 2 : Fourier Series.0 Inroducion Fourier Series : represenaion of periodic signals as weighed sums of harmonically relaed frequencies. If a signal x() is periodic signal, hen x() can be represened
Chaper 2 : Fourier Series.0 Inroducion Fourier Series : represenaion of periodic signals as weighed sums of harmonically relaed frequencies. If a signal x() is periodic signal, hen x() can be represened
General Article Application of differential equation in L-R and C-R circuit analysis by classical method. Abstract
 Applicaion of Diffrnial... Gnral Aricl Applicaion of diffrnial uaion in - and C- circui analysis by classical mhod. ajndra Prasad gmi curr, Dparmn of Mahmaics, P.N. Campus, Pokhara Email: rajndraprasadrgmi@yahoo.com
Applicaion of Diffrnial... Gnral Aricl Applicaion of diffrnial uaion in - and C- circui analysis by classical mhod. ajndra Prasad gmi curr, Dparmn of Mahmaics, P.N. Campus, Pokhara Email: rajndraprasadrgmi@yahoo.com
PHYS PRACTICE EXAM 2
 PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
