Chapter 03: Bayesian Networks
|
|
|
- Clifford Webster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LEARNING AND INFERENCE IN GRAPHICAL MODELS Chapter 03: Bayesian Networks Dr. Martin Lauer University of Freiburg Machine Learning Lab Karlsruhe Institute of Technology Institute of Measurement and Control Systems Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 1/15
2 References for this chapter Christopher M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, ch. 8, Springer, 2006 Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig, Artificial Intelligenece: A Modern Approach, ch. 14, Prentice Hall, 2003 Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 2/15
3 Motivation Bayesian inference very useful for non-trivial problems: modeling with several random variables which depend in a complex way on each other understanding the inference process becomes hard graphical representation of dependencies in a graph structure Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 3/15
4 Bayesian networks a Bayesian network is a directed, weakly connected, acyclic graph each node represents a random variable open circles indicate non-observed random variables filled circles indicate observed random variables dots indicate given constants A B C links (arrows) indicate an explicitly modeled stochastic dependence in the form of a conditional density D Bayesian networks are also called belief networks. Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 4/15
5 Bayesian networks Joint probability in a Bayesian network over all nodes Definition: the joint probability of a Bayesian network with nodesa 1,...,A ν is given by A p(a 1,...,A ν ) = ν p(a j Pred(A j )) B C j=1 wherepred(a) denotes the set of all nodesb for which a connectionb A exists in the network. D Example: p(a,b,c,d) = p(a) p(b A) p(c) p(d B,C) Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 5/15
6 Bayesian networks Examples: tossing a coin 5 times (α 1,α 2 ) (q 1,q 2 ) X 1 X 2 X 3 X 4 X 5 p(q 1,q 2,X 1,...,X 5 ) = p(q 1,q 2 α 1,α 2 ) p(x 1 q 1,q 2 ) p(x 2 q 1,q 2 ) p(x 3 q 1,q 2 ) p(x 4 q 1,q 2 ) p(x 5 q 1,q 2 ) Remark: constants do not contribute to the left side of conditionals Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 6/15
7 Bayesian networks Copying nodes for independently identically distributed random variables is annoying plates (α 1,α 2 ) (q 1,q 2 ) X i 5 Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 7/15
8 Independence in Bayesian networks Example: consider the network on the right how can we simplify p(e A,B,C,D,F,G,H)? node E is independent on which of the other nodes? blackboard A B C D p(e A,B,C,D,F,G,H) = p(e B,C,F,G) E F E is stochastically independent of A, D, and H if we know B,C,F, and G G H Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 8/15
9 Independence in Bayesian networks More general: p(x rest) = p(x Pred(X) Succ(X) Cop(X)) with Cop(X) = ( Y Succ(X) Pred(Y)) \{X} the coparents of X Proof: let s definen = Succ(X) Pred(X) Cop(X) andr = {all nodes}\(n {X}) then, by definition of a Bayesian network, the joint probability can be split as p(x,n,r)=p(x Pred(X)) Y Succ(X) p(y X,Pred(Y)\{X}) } {{ } =:V(X,N) =V(X,N) C(N,R)... }{{} =:C(N,R) Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 9/15
10 Independence in Bayesian networks Then, p(x =x N = n,r = r) = = p(x = x,n = n,r = r) p(n = n,r = r) p(x = x,n = n,r = r) p(x = x,n = n,r = r)dx = V(x,n) C(n,r) V(x,n) C(n,r)dx = V(x,n) C(n,r) V(x,n)dx C(n,r) = V(x,n) V(x,n)dx V(x,n) C(n,r )dr = = V(x,n)dx C(n,r )dr V(x,n) C(n,r )dr V(x,n) C(n,r )dx dr = p(x = x,n = n,r = r )dr p(x = x,n = n,r = r )dx dr = p(x = x,n = n) p(n = n) = p(x = x N = n) Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 10/15
11 Independence in Bayesian networks The set Pred(X) Succ(X) Cop(X) is called the Markov blanket ofx Why do the coparents belong to the Markov blanket? X Example: the exam problem the lecturer cannot access the mental mood. Hence, he will consider p(comprehension exam) the student knows his mental state. He want s the lecturer to consider p(comprehension exam, mood) level of comprehension mental mood result of exam Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 11/15
12 Examples Develop Bayesian networks for the following tasks on the blackboard. Discuss the structure of the network, the type of network nodes, and conditional distribution that can be assigned to each node. level of maturity fruit type classification of euro coins depending on diameter, thickness, and weight color size shape extend the exam problem making multiple measurements with a biased measurement tool/calibrating a biased measurement tool contour linear regression reconsider the fruit type problem from chapter 1 image Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 12/15
13 Gibbs distribution A Gibbs distribution is often useful for things that can be described hardly with standard distributions for which a function E can be determined which models whether an outcome is likely (E(x) small) or unlikely (E(x) large) IfE(x) is a real-valued function andβ > 0 and e βe(x) dx <, then p(x) = 1 Z(β) e βe(x) is a Gibbs distribution (or Boltzmann distribution). The normalization constant Z(β) = e βe(x) dx is called the partition function. Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 13/15
14 Gibbs distribution Examples: modeling the distribution of images of apples function E measures the similarity of template and image pixelwise, e.g. E(image) = u v g(u,v) t(u,v) β can be used to model how much deviation from the template is tolerated β large: only images contribute to the distribution which are very similar to the template β close to0: images which are dissimilar also have a probability significantly larger than0 template of an applet(u,v) image of an appleg(u,v) Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 14/15
15 Summary structure of Bayesian networks joint probability independence in Bayesian networks examples Gibbs distribution follows in subsequent chapters: various methods for stochastic inference in Bayesian networks hidden Markov models as special form of Bayesian networks Learning and Inference in Graphical Models. Chapter 03 p. 15/15
Chapter 04: Exact Inference in Bayesian Networks
 LEARNING AND INFERENCE IN GRAPHICAL MODELS Chapter 04: Exact Inference in Bayesian Networks Dr. Martin Lauer University of Freiburg Machine Learning Lab Karlsruhe Institute of Technology Institute of Measurement
LEARNING AND INFERENCE IN GRAPHICAL MODELS Chapter 04: Exact Inference in Bayesian Networks Dr. Martin Lauer University of Freiburg Machine Learning Lab Karlsruhe Institute of Technology Institute of Measurement
Chapter 05: Hidden Markov Models
 LEARNING AND INFERENCE IN GRAPHICAL MODELS Chapter 05: Hidden Markov Models Dr. Martin Lauer University of Freiburg Machine Learning Lab Karlsruhe Institute of Technology Institute of Measurement and Control
LEARNING AND INFERENCE IN GRAPHICAL MODELS Chapter 05: Hidden Markov Models Dr. Martin Lauer University of Freiburg Machine Learning Lab Karlsruhe Institute of Technology Institute of Measurement and Control
Bayesian Machine Learning
 Bayesian Machine Learning Andrew Gordon Wilson ORIE 6741 Lecture 4 Occam s Razor, Model Construction, and Directed Graphical Models https://people.orie.cornell.edu/andrew/orie6741 Cornell University September
Bayesian Machine Learning Andrew Gordon Wilson ORIE 6741 Lecture 4 Occam s Razor, Model Construction, and Directed Graphical Models https://people.orie.cornell.edu/andrew/orie6741 Cornell University September
Chris Bishop s PRML Ch. 8: Graphical Models
 Chris Bishop s PRML Ch. 8: Graphical Models January 24, 2008 Introduction Visualize the structure of a probabilistic model Design and motivate new models Insights into the model s properties, in particular
Chris Bishop s PRML Ch. 8: Graphical Models January 24, 2008 Introduction Visualize the structure of a probabilistic model Design and motivate new models Insights into the model s properties, in particular
Part I. C. M. Bishop PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 8: GRAPHICAL MODELS
 Part I C. M. Bishop PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 8: GRAPHICAL MODELS Probabilistic Graphical Models Graphical representation of a probabilistic model Each variable corresponds to a
Part I C. M. Bishop PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 8: GRAPHICAL MODELS Probabilistic Graphical Models Graphical representation of a probabilistic model Each variable corresponds to a
Bayesian Networks BY: MOHAMAD ALSABBAGH
 Bayesian Networks BY: MOHAMAD ALSABBAGH Outlines Introduction Bayes Rule Bayesian Networks (BN) Representation Size of a Bayesian Network Inference via BN BN Learning Dynamic BN Introduction Conditional
Bayesian Networks BY: MOHAMAD ALSABBAGH Outlines Introduction Bayes Rule Bayesian Networks (BN) Representation Size of a Bayesian Network Inference via BN BN Learning Dynamic BN Introduction Conditional
Machine Learning Lecture 14
 Many slides adapted from B. Schiele, S. Roth, Z. Gharahmani Machine Learning Lecture 14 Undirected Graphical Models & Inference 23.06.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de
Many slides adapted from B. Schiele, S. Roth, Z. Gharahmani Machine Learning Lecture 14 Undirected Graphical Models & Inference 23.06.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de
Probabilistic Graphical Models (I)
 Probabilistic Graphical Models (I) Hongxin Zhang zhx@cad.zju.edu.cn State Key Lab of CAD&CG, ZJU 2015-03-31 Probabilistic Graphical Models Modeling many real-world problems => a large number of random
Probabilistic Graphical Models (I) Hongxin Zhang zhx@cad.zju.edu.cn State Key Lab of CAD&CG, ZJU 2015-03-31 Probabilistic Graphical Models Modeling many real-world problems => a large number of random
Undirected Graphical Models
 Outline Hong Chang Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Machine Learning Methods (Fall 2012) Outline Outline I 1 Introduction 2 Properties Properties 3 Generative vs. Conditional
Outline Hong Chang Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Machine Learning Methods (Fall 2012) Outline Outline I 1 Introduction 2 Properties Properties 3 Generative vs. Conditional
Probabilistic Machine Learning
 Probabilistic Machine Learning Bayesian Nets, MCMC, and more Marek Petrik 4/18/2017 Based on: P. Murphy, K. (2012). Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective. Chapter 10. Conditional Independence Independent
Probabilistic Machine Learning Bayesian Nets, MCMC, and more Marek Petrik 4/18/2017 Based on: P. Murphy, K. (2012). Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective. Chapter 10. Conditional Independence Independent
Probabilistic Graphical Networks: Definitions and Basic Results
 This document gives a cursory overview of Probabilistic Graphical Networks. The material has been gleaned from different sources. I make no claim to original authorship of this material. Bayesian Graphical
This document gives a cursory overview of Probabilistic Graphical Networks. The material has been gleaned from different sources. I make no claim to original authorship of this material. Bayesian Graphical
Lecture 6: Graphical Models
 Lecture 6: Graphical Models Kai-Wei Chang CS @ Uniersity of Virginia kw@kwchang.net Some slides are adapted from Viek Skirmar s course on Structured Prediction 1 So far We discussed sequence labeling tasks:
Lecture 6: Graphical Models Kai-Wei Chang CS @ Uniersity of Virginia kw@kwchang.net Some slides are adapted from Viek Skirmar s course on Structured Prediction 1 So far We discussed sequence labeling tasks:
Rapid Introduction to Machine Learning/ Deep Learning
 Rapid Introduction to Machine Learning/ Deep Learning Hyeong In Choi Seoul National University 1/32 Lecture 5a Bayesian network April 14, 2016 2/32 Table of contents 1 1. Objectives of Lecture 5a 2 2.Bayesian
Rapid Introduction to Machine Learning/ Deep Learning Hyeong In Choi Seoul National University 1/32 Lecture 5a Bayesian network April 14, 2016 2/32 Table of contents 1 1. Objectives of Lecture 5a 2 2.Bayesian
Sampling Methods (11/30/04)
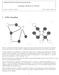 CS281A/Stat241A: Statistical Learning Theory Sampling Methods (11/30/04) Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Jaspal S. Sandhu 1 Gibbs Sampling Figure 1: Undirected and directed graphs, respectively, with
CS281A/Stat241A: Statistical Learning Theory Sampling Methods (11/30/04) Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Jaspal S. Sandhu 1 Gibbs Sampling Figure 1: Undirected and directed graphs, respectively, with
Introduction to Graphical Models. Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah
 Introduction to Graphical Models Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah Reference Christopher M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, Jonathan S. Yedidia, William T. Freeman,
Introduction to Graphical Models Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah Reference Christopher M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, Jonathan S. Yedidia, William T. Freeman,
Introduction to Graphical Models. Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah
 Introduction to Graphical Models Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah Reference Christopher M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, Jonathan S. Yedidia, William T. Freeman,
Introduction to Graphical Models Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah Reference Christopher M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, Jonathan S. Yedidia, William T. Freeman,
Deep Learning Srihari. Deep Belief Nets. Sargur N. Srihari
 Deep Belief Nets Sargur N. Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu Topics 1. Boltzmann machines 2. Restricted Boltzmann machines 3. Deep Belief Networks 4. Deep Boltzmann machines 5. Boltzmann machines for continuous
Deep Belief Nets Sargur N. Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu Topics 1. Boltzmann machines 2. Restricted Boltzmann machines 3. Deep Belief Networks 4. Deep Boltzmann machines 5. Boltzmann machines for continuous
A graph contains a set of nodes (vertices) connected by links (edges or arcs)
 BOLTZMANN MACHINES Generative Models Graphical Models A graph contains a set of nodes (vertices) connected by links (edges or arcs) In a probabilistic graphical model, each node represents a random variable,
BOLTZMANN MACHINES Generative Models Graphical Models A graph contains a set of nodes (vertices) connected by links (edges or arcs) In a probabilistic graphical model, each node represents a random variable,
Using Graphs to Describe Model Structure. Sargur N. Srihari
 Using Graphs to Describe Model Structure Sargur N. srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics in Structured PGMs for Deep Learning 0. Overview 1. Challenge of Unstructured Modeling 2. Using graphs to describe
Using Graphs to Describe Model Structure Sargur N. srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics in Structured PGMs for Deep Learning 0. Overview 1. Challenge of Unstructured Modeling 2. Using graphs to describe
Chapter 10: Random Fields
 LEARNING AND INFERENCE IN GRAPHICAL MODELS Chapter 10: Random Fields Dr. Martin Lauer University of Freiburg Machine Learning Lab Karlsruhe Institute of Technology Institute of Measurement and Control
LEARNING AND INFERENCE IN GRAPHICAL MODELS Chapter 10: Random Fields Dr. Martin Lauer University of Freiburg Machine Learning Lab Karlsruhe Institute of Technology Institute of Measurement and Control
Recall from last time. Lecture 3: Conditional independence and graph structure. Example: A Bayesian (belief) network.
 ecall from last time Lecture 3: onditional independence and graph structure onditional independencies implied by a belief network Independence maps (I-maps) Factorization theorem The Bayes ball algorithm
ecall from last time Lecture 3: onditional independence and graph structure onditional independencies implied by a belief network Independence maps (I-maps) Factorization theorem The Bayes ball algorithm
CS Lecture 3. More Bayesian Networks
 CS 6347 Lecture 3 More Bayesian Networks Recap Last time: Complexity challenges Representing distributions Computing probabilities/doing inference Introduction to Bayesian networks Today: D-separation,
CS 6347 Lecture 3 More Bayesian Networks Recap Last time: Complexity challenges Representing distributions Computing probabilities/doing inference Introduction to Bayesian networks Today: D-separation,
CS 2750: Machine Learning. Bayesian Networks. Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh March 14, 2016
 CS 2750: Machine Learning Bayesian Networks Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh March 14, 2016 Plan for today and next week Today and next time: Bayesian networks (Bishop Sec. 8.1) Conditional
CS 2750: Machine Learning Bayesian Networks Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh March 14, 2016 Plan for today and next week Today and next time: Bayesian networks (Bishop Sec. 8.1) Conditional
Intelligent Systems I
 Intelligent Systems I 00 INTRODUCTION Stefan Harmeling & Philipp Hennig 24. October 2013 Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems Dptmt. of Empirical Inference Which Card? Opening Experiment Which
Intelligent Systems I 00 INTRODUCTION Stefan Harmeling & Philipp Hennig 24. October 2013 Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems Dptmt. of Empirical Inference Which Card? Opening Experiment Which
Intelligent Systems (AI-2)
 Intelligent Systems (AI-2) Computer Science cpsc422, Lecture 11 Oct, 3, 2016 CPSC 422, Lecture 11 Slide 1 422 big picture: Where are we? Query Planning Deterministic Logics First Order Logics Ontologies
Intelligent Systems (AI-2) Computer Science cpsc422, Lecture 11 Oct, 3, 2016 CPSC 422, Lecture 11 Slide 1 422 big picture: Where are we? Query Planning Deterministic Logics First Order Logics Ontologies
Probabilistic Representation and Reasoning
 Probabilistic Representation and Reasoning Alessandro Panella Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Chicago May 4, 2010 Alessandro Panella (CS Dept. - UIC) Probabilistic Representation
Probabilistic Representation and Reasoning Alessandro Panella Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Chicago May 4, 2010 Alessandro Panella (CS Dept. - UIC) Probabilistic Representation
CS Lecture 4. Markov Random Fields
 CS 6347 Lecture 4 Markov Random Fields Recap Announcements First homework is available on elearning Reminder: Office hours Tuesday from 10am-11am Last Time Bayesian networks Today Markov random fields
CS 6347 Lecture 4 Markov Random Fields Recap Announcements First homework is available on elearning Reminder: Office hours Tuesday from 10am-11am Last Time Bayesian networks Today Markov random fields
Final Examination CS540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Final Examination CS540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence May 9, 2018 LAST NAME: SOLUTIONS FIRST NAME: Directions 1. This exam contains 33 questions worth a total of 100 points 2. Fill in your
Final Examination CS540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence May 9, 2018 LAST NAME: SOLUTIONS FIRST NAME: Directions 1. This exam contains 33 questions worth a total of 100 points 2. Fill in your
Chapter 16. Structured Probabilistic Models for Deep Learning
 Peng et al.: Deep Learning and Practice 1 Chapter 16 Structured Probabilistic Models for Deep Learning Peng et al.: Deep Learning and Practice 2 Structured Probabilistic Models way of using graphs to describe
Peng et al.: Deep Learning and Practice 1 Chapter 16 Structured Probabilistic Models for Deep Learning Peng et al.: Deep Learning and Practice 2 Structured Probabilistic Models way of using graphs to describe
Graphical Models - Part I
 Graphical Models - Part I Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 8, some slides from Russell and Norvig AIMA2e Outline Probabilistic Models Bayesian Networks Markov Random Fields Inference Outline Probabilistic
Graphical Models - Part I Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 8, some slides from Russell and Norvig AIMA2e Outline Probabilistic Models Bayesian Networks Markov Random Fields Inference Outline Probabilistic
9/12/17. Types of learning. Modeling data. Supervised learning: Classification. Supervised learning: Regression. Unsupervised learning: Clustering
 Types of learning Modeling data Supervised: we know input and targets Goal is to learn a model that, given input data, accurately predicts target data Unsupervised: we know the input only and want to make
Types of learning Modeling data Supervised: we know input and targets Goal is to learn a model that, given input data, accurately predicts target data Unsupervised: we know the input only and want to make
Bayesian Networks. instructor: Matteo Pozzi. x 1. x 2. x 3 x 4. x 5. x 6. x 7. x 8. x 9. Lec : Urban Systems Modeling
 12735: Urban Systems Modeling Lec. 09 Bayesian Networks instructor: Matteo Pozzi x 1 x 2 x 3 x 4 x 5 x 6 x 7 x 8 x 9 1 outline example of applications how to shape a problem as a BN complexity of the inference
12735: Urban Systems Modeling Lec. 09 Bayesian Networks instructor: Matteo Pozzi x 1 x 2 x 3 x 4 x 5 x 6 x 7 x 8 x 9 1 outline example of applications how to shape a problem as a BN complexity of the inference
Intelligent Systems (AI-2)
 Intelligent Systems (AI-2) Computer Science cpsc422, Lecture 18 Oct, 21, 2015 Slide Sources Raymond J. Mooney University of Texas at Austin D. Koller, Stanford CS - Probabilistic Graphical Models CPSC
Intelligent Systems (AI-2) Computer Science cpsc422, Lecture 18 Oct, 21, 2015 Slide Sources Raymond J. Mooney University of Texas at Austin D. Koller, Stanford CS - Probabilistic Graphical Models CPSC
Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition. Reasoning with Bayesian Networks
 Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition James L. Crowley ENSIMAG 2 / MoSIG M1 Second Semester 2016/2017 Lesson 13 24 march 2017 Reasoning with Bayesian Networks Naïve Bayesian Systems...2 Example
Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition James L. Crowley ENSIMAG 2 / MoSIG M1 Second Semester 2016/2017 Lesson 13 24 march 2017 Reasoning with Bayesian Networks Naïve Bayesian Systems...2 Example
Directed Graphical Models
 CS 2750: Machine Learning Directed Graphical Models Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh March 28, 2017 Graphical Models If no assumption of independence is made, must estimate an exponential
CS 2750: Machine Learning Directed Graphical Models Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh March 28, 2017 Graphical Models If no assumption of independence is made, must estimate an exponential
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 24
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 24 Graphical Models: Approximate Inference Course Webpage : http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs4786/2016sp/ BELIEF PROPAGATION OR MESSAGE PASSING Each
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 24 Graphical Models: Approximate Inference Course Webpage : http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs4786/2016sp/ BELIEF PROPAGATION OR MESSAGE PASSING Each
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 3 Linear
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 3 Linear
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models David Sontag New York University Lecture 4, February 16, 2012 David Sontag (NYU) Graphical Models Lecture 4, February 16, 2012 1 / 27 Undirected graphical models Reminder
Probabilistic Graphical Models David Sontag New York University Lecture 4, February 16, 2012 David Sontag (NYU) Graphical Models Lecture 4, February 16, 2012 1 / 27 Undirected graphical models Reminder
Directed and Undirected Graphical Models
 Directed and Undirected Graphical Models Adrian Weller MLSALT4 Lecture Feb 26, 2016 With thanks to David Sontag (NYU) and Tony Jebara (Columbia) for use of many slides and illustrations For more information,
Directed and Undirected Graphical Models Adrian Weller MLSALT4 Lecture Feb 26, 2016 With thanks to David Sontag (NYU) and Tony Jebara (Columbia) for use of many slides and illustrations For more information,
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 17: Representing Joint PMFs and Bayesian Networks Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: April 7, 2017 Warm Up: Joint distributions Recall
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 17: Representing Joint PMFs and Bayesian Networks Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: April 7, 2017 Warm Up: Joint distributions Recall
STATISTICAL METHODS IN AI/ML Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas. Bayesian networks: Representation
 STATISTICAL METHODS IN AI/ML Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Bayesian networks: Representation Motivation Explicit representation of the joint distribution is unmanageable Computationally:
STATISTICAL METHODS IN AI/ML Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Bayesian networks: Representation Motivation Explicit representation of the joint distribution is unmanageable Computationally:
Machine learning: lecture 20. Tommi S. Jaakkola MIT CSAIL
 Machine learning: lecture 20 ommi. Jaakkola MI CAI tommi@csail.mit.edu opics Representation and graphical models examples Bayesian networks examples, specification graphs and independence associated distribution
Machine learning: lecture 20 ommi. Jaakkola MI CAI tommi@csail.mit.edu opics Representation and graphical models examples Bayesian networks examples, specification graphs and independence associated distribution
Bayesian networks. Chapter 14, Sections 1 4
 Bayesian networks Chapter 14, Sections 1 4 Artificial Intelligence, spring 2013, Peter Ljunglöf; based on AIMA Slides c Stuart Russel and Peter Norvig, 2004 Chapter 14, Sections 1 4 1 Bayesian networks
Bayesian networks Chapter 14, Sections 1 4 Artificial Intelligence, spring 2013, Peter Ljunglöf; based on AIMA Slides c Stuart Russel and Peter Norvig, 2004 Chapter 14, Sections 1 4 1 Bayesian networks
BAYESIAN MACHINE LEARNING.
 BAYESIAN MACHINE LEARNING frederic.pennerath@centralesupelec.fr What is this Bayesian Machine Learning course about? A course emphasizing the few essential theoretical ingredients Probabilistic generative
BAYESIAN MACHINE LEARNING frederic.pennerath@centralesupelec.fr What is this Bayesian Machine Learning course about? A course emphasizing the few essential theoretical ingredients Probabilistic generative
Bayesian Networks. Machine Learning, Fall Slides based on material from the Russell and Norvig AI Book, Ch. 14
 Bayesian Networks Machine Learning, Fall 2010 Slides based on material from the Russell and Norvig AI Book, Ch. 14 1 Administrativia Bayesian networks The inference problem: given a BN, how to make predictions
Bayesian Networks Machine Learning, Fall 2010 Slides based on material from the Russell and Norvig AI Book, Ch. 14 1 Administrativia Bayesian networks The inference problem: given a BN, how to make predictions
Course Introduction. Probabilistic Modelling and Reasoning. Relationships between courses. Dealing with Uncertainty. Chris Williams.
 Course Introduction Probabilistic Modelling and Reasoning Chris Williams School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh September 2008 Welcome Administration Handout Books Assignments Tutorials Course
Course Introduction Probabilistic Modelling and Reasoning Chris Williams School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh September 2008 Welcome Administration Handout Books Assignments Tutorials Course
MODULE 10 Bayes Classifier LESSON 20
 MODULE 10 Bayes Classifier LESSON 20 Bayesian Belief Networks Keywords: Belief, Directed Acyclic Graph, Graphical Model 1 Bayesian Belief Network A Bayesian network is a graphical model of a situation
MODULE 10 Bayes Classifier LESSON 20 Bayesian Belief Networks Keywords: Belief, Directed Acyclic Graph, Graphical Model 1 Bayesian Belief Network A Bayesian network is a graphical model of a situation
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence. Unit # 11
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Unit # 11 1 Course Outline Overview of Artificial Intelligence State Space Representation Search Techniques Machine Learning Logic Probabilistic Reasoning/Bayesian
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Unit # 11 1 Course Outline Overview of Artificial Intelligence State Space Representation Search Techniques Machine Learning Logic Probabilistic Reasoning/Bayesian
Undirected Graphical Models: Markov Random Fields
 Undirected Graphical Models: Markov Random Fields 40-956 Advanced Topics in AI: Probabilistic Graphical Models Sharif University of Technology Soleymani Spring 2015 Markov Random Field Structure: undirected
Undirected Graphical Models: Markov Random Fields 40-956 Advanced Topics in AI: Probabilistic Graphical Models Sharif University of Technology Soleymani Spring 2015 Markov Random Field Structure: undirected
Conditional Independence
 Conditional Independence Sargur Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Conditional Independence Topics 1. What is Conditional Independence? Factorization of probability distribution into marginals 2. Why
Conditional Independence Sargur Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Conditional Independence Topics 1. What is Conditional Independence? Factorization of probability distribution into marginals 2. Why
Outline. CSE 573: Artificial Intelligence Autumn Agent. Partial Observability. Markov Decision Process (MDP) 10/31/2012
 CSE 573: Artificial Intelligence Autumn 2012 Reasoning about Uncertainty & Hidden Markov Models Daniel Weld Many slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer 1 Outline
CSE 573: Artificial Intelligence Autumn 2012 Reasoning about Uncertainty & Hidden Markov Models Daniel Weld Many slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer 1 Outline
Bayesian Networks. Motivation
 Bayesian Networks Computer Sciences 760 Spring 2014 http://pages.cs.wisc.edu/~dpage/cs760/ Motivation Assume we have five Boolean variables,,,, The joint probability is,,,, How many state configurations
Bayesian Networks Computer Sciences 760 Spring 2014 http://pages.cs.wisc.edu/~dpage/cs760/ Motivation Assume we have five Boolean variables,,,, The joint probability is,,,, How many state configurations
Artificial Intelligence Bayesian Networks
 Artificial Intelligence Bayesian Networks Stephan Dreiseitl FH Hagenberg Software Engineering & Interactive Media Stephan Dreiseitl (Hagenberg/SE/IM) Lecture 11: Bayesian Networks Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence Bayesian Networks Stephan Dreiseitl FH Hagenberg Software Engineering & Interactive Media Stephan Dreiseitl (Hagenberg/SE/IM) Lecture 11: Bayesian Networks Artificial Intelligence
Bayesian Networks (Part II)
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Bayesian Networks (Part II) Graphical Model Readings: Murphy 10 10.2.1 Bishop 8.1,
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Bayesian Networks (Part II) Graphical Model Readings: Murphy 10 10.2.1 Bishop 8.1,
COS402- Artificial Intelligence Fall Lecture 10: Bayesian Networks & Exact Inference
 COS402- Artificial Intelligence Fall 2015 Lecture 10: Bayesian Networks & Exact Inference Outline Logical inference and probabilistic inference Independence and conditional independence Bayes Nets Semantics
COS402- Artificial Intelligence Fall 2015 Lecture 10: Bayesian Networks & Exact Inference Outline Logical inference and probabilistic inference Independence and conditional independence Bayes Nets Semantics
Naïve Bayes classification
 Naïve Bayes classification 1 Probability theory Random variable: a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenon. Examples: A person s height, the outcome of a coin toss
Naïve Bayes classification 1 Probability theory Random variable: a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenon. Examples: A person s height, the outcome of a coin toss
Bayesian Networks Introduction to Machine Learning. Matt Gormley Lecture 24 April 9, 2018
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Bayesian Networks Matt Gormley Lecture 24 April 9, 2018 1 Homework 7: HMMs Reminders
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Bayesian Networks Matt Gormley Lecture 24 April 9, 2018 1 Homework 7: HMMs Reminders
ECE521 Tutorial 11. Topic Review. ECE521 Winter Credits to Alireza Makhzani, Alex Schwing, Rich Zemel and TAs for slides. ECE521 Tutorial 11 / 4
 ECE52 Tutorial Topic Review ECE52 Winter 206 Credits to Alireza Makhzani, Alex Schwing, Rich Zemel and TAs for slides ECE52 Tutorial ECE52 Winter 206 Credits to Alireza / 4 Outline K-means, PCA 2 Bayesian
ECE52 Tutorial Topic Review ECE52 Winter 206 Credits to Alireza Makhzani, Alex Schwing, Rich Zemel and TAs for slides ECE52 Tutorial ECE52 Winter 206 Credits to Alireza / 4 Outline K-means, PCA 2 Bayesian
Statistical and Learning Techniques in Computer Vision Lecture 1: Random Variables Jens Rittscher and Chuck Stewart
 Statistical and Learning Techniques in Computer Vision Lecture 1: Random Variables Jens Rittscher and Chuck Stewart 1 Motivation Imaging is a stochastic process: If we take all the different sources of
Statistical and Learning Techniques in Computer Vision Lecture 1: Random Variables Jens Rittscher and Chuck Stewart 1 Motivation Imaging is a stochastic process: If we take all the different sources of
Chapter 08: Direct Maximum Likelihood/MAP Estimation and Incomplete Data Problems
 LEARNING AND INFERENCE IN GRAPHICAL MODELS Chapter 08: Direct Maximum Likelihood/MAP Estimation and Incomplete Data Problems Dr. Martin Lauer University of Freiburg Machine Learning Lab Karlsruhe Institute
LEARNING AND INFERENCE IN GRAPHICAL MODELS Chapter 08: Direct Maximum Likelihood/MAP Estimation and Incomplete Data Problems Dr. Martin Lauer University of Freiburg Machine Learning Lab Karlsruhe Institute
Conditional probabilities and graphical models
 Conditional probabilities and graphical models Thomas Mailund Bioinformatics Research Centre (BiRC), Aarhus University Probability theory allows us to describe uncertainty in the processes we model within
Conditional probabilities and graphical models Thomas Mailund Bioinformatics Research Centre (BiRC), Aarhus University Probability theory allows us to describe uncertainty in the processes we model within
Machine Learning: Probability Theory
 Machine Learning: Probability Theory Prof. Dr. Martin Riedmiller Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg AG Maschinelles Lernen Theories p.1/28 Probabilities probabilistic statements subsume different effects
Machine Learning: Probability Theory Prof. Dr. Martin Riedmiller Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg AG Maschinelles Lernen Theories p.1/28 Probabilities probabilistic statements subsume different effects
Directed Graphical Models (aka. Bayesian Networks)
 School of Computer Science 10-601B Introduction to Machine Learning Directed Graphical Models (aka. Bayesian Networks) Readings: Bishop 8.1 and 8.2.2 Mitchell 6.11 Murphy 10 Matt Gormley Lecture 21 November
School of Computer Science 10-601B Introduction to Machine Learning Directed Graphical Models (aka. Bayesian Networks) Readings: Bishop 8.1 and 8.2.2 Mitchell 6.11 Murphy 10 Matt Gormley Lecture 21 November
NPFL108 Bayesian inference. Introduction. Filip Jurčíček. Institute of Formal and Applied Linguistics Charles University in Prague Czech Republic
 NPFL108 Bayesian inference Introduction Filip Jurčíček Institute of Formal and Applied Linguistics Charles University in Prague Czech Republic Home page: http://ufal.mff.cuni.cz/~jurcicek Version: 21/02/2014
NPFL108 Bayesian inference Introduction Filip Jurčíček Institute of Formal and Applied Linguistics Charles University in Prague Czech Republic Home page: http://ufal.mff.cuni.cz/~jurcicek Version: 21/02/2014
Introduction to Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Introduction to Probabilistic Graphical Models Sargur Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics 1. What are probabilistic graphical models (PGMs) 2. Use of PGMs Engineering and AI 3. Directionality in
Introduction to Probabilistic Graphical Models Sargur Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics 1. What are probabilistic graphical models (PGMs) 2. Use of PGMs Engineering and AI 3. Directionality in
Probabilistic Classification
 Bayesian Networks Probabilistic Classification Goal: Gather Labeled Training Data Build/Learn a Probability Model Use the model to infer class labels for unlabeled data points Example: Spam Filtering...
Bayesian Networks Probabilistic Classification Goal: Gather Labeled Training Data Build/Learn a Probability Model Use the model to infer class labels for unlabeled data points Example: Spam Filtering...
Directed and Undirected Graphical Models
 Directed and Undirected Davide Bacciu Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Pisa bacciu@di.unipi.it Machine Learning: Neural Networks and Advanced Models (AA2) Last Lecture Refresher Lecture Plan Directed
Directed and Undirected Davide Bacciu Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Pisa bacciu@di.unipi.it Machine Learning: Neural Networks and Advanced Models (AA2) Last Lecture Refresher Lecture Plan Directed
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder. Canberra February June 2018
 Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression
Bayesian Networks Inference with Probabilistic Graphical Models
 4190.408 2016-Spring Bayesian Networks Inference with Probabilistic Graphical Models Byoung-Tak Zhang intelligence Lab Seoul National University 4190.408 Artificial (2016-Spring) 1 Machine Learning? Learning
4190.408 2016-Spring Bayesian Networks Inference with Probabilistic Graphical Models Byoung-Tak Zhang intelligence Lab Seoul National University 4190.408 Artificial (2016-Spring) 1 Machine Learning? Learning
Exercises, II part Exercises, II part
 Inference: 12 Jul 2012 Consider the following Joint Probability Table for the three binary random variables A, B, C. Compute the following queries: 1 P(C A=T,B=T) 2 P(C A=T) P(A, B, C) A B C 0.108 T T
Inference: 12 Jul 2012 Consider the following Joint Probability Table for the three binary random variables A, B, C. Compute the following queries: 1 P(C A=T,B=T) 2 P(C A=T) P(A, B, C) A B C 0.108 T T
An Introduction to Bayesian Machine Learning
 1 An Introduction to Bayesian Machine Learning José Miguel Hernández-Lobato Department of Engineering, Cambridge University April 8, 2013 2 What is Machine Learning? The design of computational systems
1 An Introduction to Bayesian Machine Learning José Miguel Hernández-Lobato Department of Engineering, Cambridge University April 8, 2013 2 What is Machine Learning? The design of computational systems
Learning Bayesian Networks (part 1) Goals for the lecture
 Learning Bayesian Networks (part 1) Mark Craven and David Page Computer Scices 760 Spring 2018 www.biostat.wisc.edu/~craven/cs760/ Some ohe slides in these lectures have been adapted/borrowed from materials
Learning Bayesian Networks (part 1) Mark Craven and David Page Computer Scices 760 Spring 2018 www.biostat.wisc.edu/~craven/cs760/ Some ohe slides in these lectures have been adapted/borrowed from materials
Outline. CSE 573: Artificial Intelligence Autumn Bayes Nets: Big Picture. Bayes Net Semantics. Hidden Markov Models. Example Bayes Net: Car
 CSE 573: Artificial Intelligence Autumn 2012 Bayesian Networks Dan Weld Many slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer Outline Probabilistic models (and inference)
CSE 573: Artificial Intelligence Autumn 2012 Bayesian Networks Dan Weld Many slides adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore & Luke Zettlemoyer Outline Probabilistic models (and inference)
Naïve Bayes classification. p ij 11/15/16. Probability theory. Probability theory. Probability theory. X P (X = x i )=1 i. Marginal Probability
 Probability theory Naïve Bayes classification Random variable: a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenon. s: A person s height, the outcome of a coin toss Distinguish
Probability theory Naïve Bayes classification Random variable: a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenon. s: A person s height, the outcome of a coin toss Distinguish
Directed Graphical Models or Bayesian Networks
 Directed Graphical Models or Bayesian Networks Le Song Machine Learning II: Advanced Topics CSE 8803ML, Spring 2012 Bayesian Networks One of the most exciting recent advancements in statistical AI Compact
Directed Graphical Models or Bayesian Networks Le Song Machine Learning II: Advanced Topics CSE 8803ML, Spring 2012 Bayesian Networks One of the most exciting recent advancements in statistical AI Compact
Artificial Intelligence: Cognitive Agents
 Artificial Intelligence: Cognitive Agents AI, Uncertainty & Bayesian Networks 2015-03-10 / 03-12 Kim, Byoung-Hee Biointelligence Laboratory Seoul National University http://bi.snu.ac.kr A Bayesian network
Artificial Intelligence: Cognitive Agents AI, Uncertainty & Bayesian Networks 2015-03-10 / 03-12 Kim, Byoung-Hee Biointelligence Laboratory Seoul National University http://bi.snu.ac.kr A Bayesian network
COURSE INTRODUCTION. J. Elder CSE 6390/PSYC 6225 Computational Modeling of Visual Perception
 COURSE INTRODUCTION COMPUTATIONAL MODELING OF VISUAL PERCEPTION 2 The goal of this course is to provide a framework and computational tools for modeling visual inference, motivated by interesting examples
COURSE INTRODUCTION COMPUTATIONAL MODELING OF VISUAL PERCEPTION 2 The goal of this course is to provide a framework and computational tools for modeling visual inference, motivated by interesting examples
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning Undirected Graphical Models Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2016 Admin Assignment 3: 2 late days to hand it in today, Thursday is final day. Assignment 4:
CPSC 540: Machine Learning Undirected Graphical Models Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2016 Admin Assignment 3: 2 late days to hand it in today, Thursday is final day. Assignment 4:
Lecture 1: Bayesian Framework Basics
 Lecture 1: Bayesian Framework Basics Melih Kandemir melih.kandemir@iwr.uni-heidelberg.de April 21, 2014 What is this course about? Building Bayesian machine learning models Performing the inference of
Lecture 1: Bayesian Framework Basics Melih Kandemir melih.kandemir@iwr.uni-heidelberg.de April 21, 2014 What is this course about? Building Bayesian machine learning models Performing the inference of
Machine Learning using Bayesian Approaches
 Machine Learning using Bayesian Approaches Sargur N. Srihari University at Buffalo, State University of New York 1 Outline 1. Progress in ML and PR 2. Fully Bayesian Approach 1. Probability theory Bayes
Machine Learning using Bayesian Approaches Sargur N. Srihari University at Buffalo, State University of New York 1 Outline 1. Progress in ML and PR 2. Fully Bayesian Approach 1. Probability theory Bayes
Lecture 11: Maximum Entropy
 Lecture 11: Maximum Entropy Maximum entropy principle Maximum entropy distribution Applications Dr. Yao Xie, ECE587, Information Theory, Duke University Berger s Burger Item Price Calories Burger $1 1000
Lecture 11: Maximum Entropy Maximum entropy principle Maximum entropy distribution Applications Dr. Yao Xie, ECE587, Information Theory, Duke University Berger s Burger Item Price Calories Burger $1 1000
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Matrix Data: Classification: Part 2 Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu September 21, 2014 Methods to Learn Matrix Data Set Data Sequence Data Time Series Graph & Network
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Matrix Data: Classification: Part 2 Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu September 21, 2014 Methods to Learn Matrix Data Set Data Sequence Data Time Series Graph & Network
Introduction to Bayesian Learning
 Course Information Introduction Introduction to Bayesian Learning Davide Bacciu Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Pisa bacciu@di.unipi.it Apprendimento Automatico: Fondamenti - A.A. 2016/2017 Outline
Course Information Introduction Introduction to Bayesian Learning Davide Bacciu Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Pisa bacciu@di.unipi.it Apprendimento Automatico: Fondamenti - A.A. 2016/2017 Outline
Data Modeling & Analysis Techniques. Probability & Statistics. Manfred Huber
 Data Modeling & Analysis Techniques Probability & Statistics Manfred Huber 2017 1 Probability and Statistics Probability and statistics are often used interchangeably but are different, related fields
Data Modeling & Analysis Techniques Probability & Statistics Manfred Huber 2017 1 Probability and Statistics Probability and statistics are often used interchangeably but are different, related fields
Terminology. Experiment = Prior = Posterior =
 Review: probability RVs, events, sample space! Measures, distributions disjoint union property (law of total probability book calls this sum rule ) Sample v. population Law of large numbers Marginals,
Review: probability RVs, events, sample space! Measures, distributions disjoint union property (law of total probability book calls this sum rule ) Sample v. population Law of large numbers Marginals,
Bayesian Methods in Artificial Intelligence
 WDS'10 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part I, 25 30, 2010. ISBN 978-80-7378-139-2 MATFYZPRESS Bayesian Methods in Artificial Intelligence M. Kukačka Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics,
WDS'10 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part I, 25 30, 2010. ISBN 978-80-7378-139-2 MATFYZPRESS Bayesian Methods in Artificial Intelligence M. Kukačka Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics,
Probabilistic Graphical Models and Bayesian Networks. Artificial Intelligence Bert Huang Virginia Tech
 Probabilistic Graphical Models and Bayesian Networks Artificial Intelligence Bert Huang Virginia Tech Concept Map for Segment Probabilistic Graphical Models Probabilistic Time Series Models Particle Filters
Probabilistic Graphical Models and Bayesian Networks Artificial Intelligence Bert Huang Virginia Tech Concept Map for Segment Probabilistic Graphical Models Probabilistic Time Series Models Particle Filters
Inference in Bayesian Networks
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Inference in graphical models Description Assume we have evidence e on the state of a subset of variables E in the model (i.e. Bayesian Network)
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Inference in graphical models Description Assume we have evidence e on the state of a subset of variables E in the model (i.e. Bayesian Network)
Based on slides by Richard Zemel
 CSC 412/2506 Winter 2018 Probabilistic Learning and Reasoning Lecture 3: Directed Graphical Models and Latent Variables Based on slides by Richard Zemel Learning outcomes What aspects of a model can we
CSC 412/2506 Winter 2018 Probabilistic Learning and Reasoning Lecture 3: Directed Graphical Models and Latent Variables Based on slides by Richard Zemel Learning outcomes What aspects of a model can we
Statistical Approaches to Learning and Discovery
 Statistical Approaches to Learning and Discovery Graphical Models Zoubin Ghahramani & Teddy Seidenfeld zoubin@cs.cmu.edu & teddy@stat.cmu.edu CALD / CS / Statistics / Philosophy Carnegie Mellon University
Statistical Approaches to Learning and Discovery Graphical Models Zoubin Ghahramani & Teddy Seidenfeld zoubin@cs.cmu.edu & teddy@stat.cmu.edu CALD / CS / Statistics / Philosophy Carnegie Mellon University
Graphical Models and Kernel Methods
 Graphical Models and Kernel Methods Jerry Zhu Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison, USA MLSS June 17, 2014 1 / 123 Outline Graphical Models Probabilistic Inference Directed vs.
Graphical Models and Kernel Methods Jerry Zhu Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison, USA MLSS June 17, 2014 1 / 123 Outline Graphical Models Probabilistic Inference Directed vs.
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Bayes Nets: Sampling Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley.
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Bayes Nets: Sampling Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley.
Objectives. Probabilistic Reasoning Systems. Outline. Independence. Conditional independence. Conditional independence II.
 Copyright Richard J. Povinelli rev 1.0, 10/1//2001 Page 1 Probabilistic Reasoning Systems Dr. Richard J. Povinelli Objectives You should be able to apply belief networks to model a problem with uncertainty.
Copyright Richard J. Povinelli rev 1.0, 10/1//2001 Page 1 Probabilistic Reasoning Systems Dr. Richard J. Povinelli Objectives You should be able to apply belief networks to model a problem with uncertainty.
Final Exam December 12, 2017
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence CSE 473, Autumn 2017 Dieter Fox Final Exam December 12, 2017 Directions This exam has 7 problems with 111 points shown in the table below, and you have 110 minutes
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence CSE 473, Autumn 2017 Dieter Fox Final Exam December 12, 2017 Directions This exam has 7 problems with 111 points shown in the table below, and you have 110 minutes
T Machine Learning: Basic Principles
 Machine Learning: Basic Principles Bayesian Networks Laboratory of Computer and Information Science (CIS) Department of Computer Science and Engineering Helsinki University of Technology (TKK) Autumn 2007
Machine Learning: Basic Principles Bayesian Networks Laboratory of Computer and Information Science (CIS) Department of Computer Science and Engineering Helsinki University of Technology (TKK) Autumn 2007
Bayesian Networks (Part I)
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Bayesian Networks (Part I) Graphical Model Readings: Murphy 10 10.2.1 Bishop 8.1,
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Bayesian Networks (Part I) Graphical Model Readings: Murphy 10 10.2.1 Bishop 8.1,
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Introduction. Basic Probability and Bayes Volkan Cevher, Matthias Seeger Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne 26/9/2011 (EPFL) Graphical Models 26/9/2011 1 / 28 Outline
Probabilistic Graphical Models Introduction. Basic Probability and Bayes Volkan Cevher, Matthias Seeger Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne 26/9/2011 (EPFL) Graphical Models 26/9/2011 1 / 28 Outline
Lecture 6: Entropy Rate
 Lecture 6: Entropy Rate Entropy rate H(X) Random walk on graph Dr. Yao Xie, ECE587, Information Theory, Duke University Coin tossing versus poker Toss a fair coin and see and sequence Head, Tail, Tail,
Lecture 6: Entropy Rate Entropy rate H(X) Random walk on graph Dr. Yao Xie, ECE587, Information Theory, Duke University Coin tossing versus poker Toss a fair coin and see and sequence Head, Tail, Tail,
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Belief networks
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Belief networks Chapter 15.1 2 Dieter Fox Based on AIMA Slides c S. Russell and P. Norvig, 1998 Chapter 15.1 2 0-0 Outline Bayesian networks: syntax and semantics
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Belief networks Chapter 15.1 2 Dieter Fox Based on AIMA Slides c S. Russell and P. Norvig, 1998 Chapter 15.1 2 0-0 Outline Bayesian networks: syntax and semantics
Introduction: MLE, MAP, Bayesian reasoning (28/8/13)
 STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Introduction: MLE, MAP, Bayesian reasoning (28/8/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: K. Ulrich, J. Subramanian, N. Raval, J. O Hollaren 1 Classifiers In this
STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Introduction: MLE, MAP, Bayesian reasoning (28/8/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: K. Ulrich, J. Subramanian, N. Raval, J. O Hollaren 1 Classifiers In this
