A Demand Response Calculus with Perfect Batteries
|
|
|
- Elfrieda Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Demand Response Calculus with Perfect Batteries Dan-Cristian Tomozei Joint work with Jean-Yves Le Boudec CCW, Sedona AZ, 07/11/2012
2 Demand Response by Quantity = distribution network operator may interrupt / modulate power elastic loads support graceful degradation Thermal load (Voltalis), water heaters (Romande Energie «commande centralisée»), e-cars Voltalis Bluepod switches off thermal load for 60 mn #2
3 Network Calculus? Service curve? Voltalis: At most 30 mn of interruption total per day Service curve contract Guaranteed energy delivered in (s, t) β t s, β t = superadditive function. 0 s t #3
4 #4 Real Situation: Unexpected Consumption Peaks
5 Is Demand Response a good solution? Today Aggregate demand is predictable Operators foresee reserve (primary, secondary, tertiary) E.g., gas turbines Reserve is expensive (capacity) / rare event demand response Delay ( buffer ) demand until the peak has passed ~ virtual energy storage Tomorrow? High penetration of renewables Large (unaffordable) reserve requirements E.g., fleet of e-cars DR exploits load flexibility #5
6 Demand Response by Quantity Formally: Consumption: energy (Watt-hours) U t = u s ds Allowed consumption (control): 0 G t = g s ds Demand Response imposes: 0 t t power (Watts) 0 U t U s G t G s, 0 s t [Le Boudec, Tomozei ISGT-EU 11] #6
7 Inelastic load = lights out? Inelastic (non-dispatchable) loads Lamps, TVs, Microwaves, Elastic (dispatchable) loads Heating, A/C (TCLs) Make it dispatchable! t Inelastic load L t = l s ds 0 Use a large enough battery! #7 Load sees no constraints Energy buffer Actual consumption (constrained!) Grid
8 The Perfect Battery Battery may be charged (u t > l(t)) or discharged (u t < l(t)) Load l t is given Problem is to determine a power schedule u(t), subject to 0 u t g(t) and within battery constraints #8
9 System Equations for the Perfect Battery 1. L t B 0 + U(t) no underflow 2. U t L t + B 0 B no overflow 3. U t U s G t G s, s t power constraint where U t, L t, G t are cumulative functions such as U t = t 0 u s ds #9
10 #10 Omniscient Problem Given (known) signals: The load L t = l s ds Allowed consumption 0 G t = g s ds 0 t t To be determined: Battery initial charge B 0 Max battery capacity B Schedule (consumption from grid) U t = u s ds 0 t Constraints: Demand Response: 0 U t U s G t G s, s t Perfect battery constraints: L t B 0 + U t U t L t + B 0 B
11 Main Result Theorem There exists a feasible schedule if and only if B 0 sup t L t G t B sup (L t L s G t + G(s)) 0 s t Moreover, if this is the case, then there exist a minimal and a maximal schedule: U t = 0 sup G t G τ + L τ B 0 τ t U t = G t inf s t G t G s + L s + B B 0 U t U t U t, t 0 The maximal schedule is causal & corresponds to the greedy policy (maximizes battery charge) #11
12 Service Curve Approach to Demand Response Assume we do not know the control signal G t Instead: service curve contract [Le Boudec, Tomozei, ISGT-EU 11] G t G s β t s, 0 s t β t = superadditive function. Example: At most 30 mn of interruption total per day Or reduction to z max 2 for 60mn total per day Similar theorem closed form condition on B, B 0 + min/max schedule #12
13 Service Curve + Arrival Curve Assume we don t know the load L(t) either! Instead, L(t) is constrained by a subadditive arrival curve: L t L s α t s, 0 s t Smallest arrival curve obtained via min-plus deconvolution: α t sup s 0 L s + t L s G(t) is well behaved (according to superadditive service curve): G t G s β t s, 0 s t Theorem For all (B )B 0 B sup{α s β s }, there exists a feasible s online (causal) schedule, valid for all loads and control signal compatible with α and β respectively. #13
14 Application: Transparent DR for data centers Akamai data set [Qureshi et al, SIGCOMM 2009] - Traffic at Akamai (millions of hits over 24 days) - Measured power consumption of a desktop (SPEC) - Uniform repartition of tasks => consumption of one server #14
15 Empirical arrival curve α m t sup 0 s T max t L s + t L s Intuitively = worst observed day #15
16 Choosing a SC contract and a battery Interruption time = t 0 Maximum power = z max Required battery charge = B 1h/24h Service interruption #16
17 #17 A run of the system using the greedy policy
18 Conclusion Another application of Network Calculus: Smart Grids Theoretical results for perfect battery Practical battery sizing problem Easy to compute Ongoing work Realistic battery model (losses, aging, ) #18
Worst-Case Optimal Battery Filling Policies with Constrained Adjustable Service
 Worst-Case Optimal Battery Filling Policies with Constrained Adjustable Service Jean-Yves Le Boudec, Fellow, IEEE, Dan-Cristian Tomozei, Member, IEEE Abstract We study battery filling policies with hard
Worst-Case Optimal Battery Filling Policies with Constrained Adjustable Service Jean-Yves Le Boudec, Fellow, IEEE, Dan-Cristian Tomozei, Member, IEEE Abstract We study battery filling policies with hard
Coordinated Aggregation of Distributed Resources
 Coordinated Aggregation of Distributed Resources UC Berkeley October 13, 2011 Coordinated Aggregation 1 of 39 Co-conspirators Anand Subramanian, Manuel Garcia, Josh Taylor [Berkeley Students] Duncan Callaway,
Coordinated Aggregation of Distributed Resources UC Berkeley October 13, 2011 Coordinated Aggregation 1 of 39 Co-conspirators Anand Subramanian, Manuel Garcia, Josh Taylor [Berkeley Students] Duncan Callaway,
Real-Time Calculus. LS 12, TU Dortmund
 Real-Time Calculus Prof. Dr. Jian-Jia Chen LS 12, TU Dortmund 09, Dec., 2014 Prof. Dr. Jian-Jia Chen (LS 12, TU Dortmund) 1 / 35 Arbitrary Deadlines The worst-case response time of τ i by only considering
Real-Time Calculus Prof. Dr. Jian-Jia Chen LS 12, TU Dortmund 09, Dec., 2014 Prof. Dr. Jian-Jia Chen (LS 12, TU Dortmund) 1 / 35 Arbitrary Deadlines The worst-case response time of τ i by only considering
Background Concrete Greedy Shapers Min-Plus Algebra Abstract Greedy Shapers Acknowledgment. Greedy Shaper
 Greedy Shaper Modular Performance Analysis and Interface-Based Design for Embedded Real-Time Systems: Section 3.1 od Reading Group on Real-Time Calculus Outline 1 Background The Curves Drawback 2 Concrete
Greedy Shaper Modular Performance Analysis and Interface-Based Design for Embedded Real-Time Systems: Section 3.1 od Reading Group on Real-Time Calculus Outline 1 Background The Curves Drawback 2 Concrete
On the Resource/Performance Tradeoff in Large Scale Queueing Systems
 On the Resource/Performance Tradeoff in Large Scale Queueing Systems David Gamarnik MIT Joint work with Patrick Eschenfeldt, John Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia (MIT) High level comments High level comments
On the Resource/Performance Tradeoff in Large Scale Queueing Systems David Gamarnik MIT Joint work with Patrick Eschenfeldt, John Tsitsiklis and Martin Zubeldia (MIT) High level comments High level comments
Different Scenarios of Concatenation at Aggregate Scheduling of Multiple Nodes
 ICNS 03 : The Ninth International Conference on Networking and Services Different Scenarios of Concatenation at Aggregate Scheduling of Multiple Nodes Ulrich Klehmet Kai-Steffen Hielscher Computer Networks
ICNS 03 : The Ninth International Conference on Networking and Services Different Scenarios of Concatenation at Aggregate Scheduling of Multiple Nodes Ulrich Klehmet Kai-Steffen Hielscher Computer Networks
Real Time Control of Electrical Distribution Grids
 ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE DE LAUSANNE Real Time Control of Electrical Distribution Grids Jean Yves Le Boudec 1,2 EPFL Simons Institute / Societal Networks Mar. 26 Mar. 29, 2018 1 https://people.epfl.ch/105633/research
ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE DE LAUSANNE Real Time Control of Electrical Distribution Grids Jean Yves Le Boudec 1,2 EPFL Simons Institute / Societal Networks Mar. 26 Mar. 29, 2018 1 https://people.epfl.ch/105633/research
An Application to Growth Theory
 An Application to Growth Theory First let s review the concepts of solution function and value function for a maximization problem. Suppose we have the problem max F (x, α) subject to G(x, β) 0, (P) x
An Application to Growth Theory First let s review the concepts of solution function and value function for a maximization problem. Suppose we have the problem max F (x, α) subject to G(x, β) 0, (P) x
Real-Time Operation of Microgrids
 ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE DE LAUSANNE Real-Time Operation of Microgrids Jean Yves Le Boudec, 1 EPFL Flexible Operation and Advanced Control for Energy Systems Isaac Newton Institute Mathematics of Energy
ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE DE LAUSANNE Real-Time Operation of Microgrids Jean Yves Le Boudec, 1 EPFL Flexible Operation and Advanced Control for Energy Systems Isaac Newton Institute Mathematics of Energy
Network Calculus Analysis of Feedback Systems with Random Service. Alireza Shekaramiz
 Network Calculus Analysis of Feedback Systems with Random Service by Alireza Shekaramiz A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Applied Science Graduate Department
Network Calculus Analysis of Feedback Systems with Random Service by Alireza Shekaramiz A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Applied Science Graduate Department
Net Export Rule 1 : Deriving the generation value of storage device G(t)
 Net Export Rule 1 : Deriving the generation value of storage device G(t) G(t) nx = n i=1 G(i, t) min{0, N(i, t)} Where, i = 1,2, n location G(i, t) storage device generation metered output at location
Net Export Rule 1 : Deriving the generation value of storage device G(t) G(t) nx = n i=1 G(i, t) min{0, N(i, t)} Where, i = 1,2, n location G(i, t) storage device generation metered output at location
A Virtual Queue Approach to Loss Estimation
 A Virtual Queue Approach to Loss Estimation Guoqiang Hu, Yuming Jiang, Anne Nevin Centre for Quantifiable Quality of Service in Communication Systems Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Norway
A Virtual Queue Approach to Loss Estimation Guoqiang Hu, Yuming Jiang, Anne Nevin Centre for Quantifiable Quality of Service in Communication Systems Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Norway
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing
 Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Effective Bandwidth for Traffic Engineering
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2-5- Effective Bandwidth for Traffic Engineering Mark J. Clement clement@cs.byu.edu Rob Kunz See next page for additional authors Follow
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2-5- Effective Bandwidth for Traffic Engineering Mark J. Clement clement@cs.byu.edu Rob Kunz See next page for additional authors Follow
CECOER. Renewable Energy Control Center. How technologies have boosted remote operations. Agder Energi-konferansen
 CECOER Renewable Energy Control Center How technologies have boosted remote operations Agder Energi-konferansen 2018 30.-31. mai, Kristiansand GLOBAL LEADER IN INFRASTRUCTURE, WATER, SERVICES AND RENEWABLE
CECOER Renewable Energy Control Center How technologies have boosted remote operations Agder Energi-konferansen 2018 30.-31. mai, Kristiansand GLOBAL LEADER IN INFRASTRUCTURE, WATER, SERVICES AND RENEWABLE
Cyclic Dependencies in Modular Performance Analysis
 Cyclic Dependencies in Modular Performance Analysis ABSTRACT Bengt Jonsson Dept. Information Technology Uppsala University Sweden bengt@it.uu.se Lothar Thiele Computer Engineering and Networks Lab. ETH
Cyclic Dependencies in Modular Performance Analysis ABSTRACT Bengt Jonsson Dept. Information Technology Uppsala University Sweden bengt@it.uu.se Lothar Thiele Computer Engineering and Networks Lab. ETH
Stochastic Unit Commitment with Topology Control Recourse for Renewables Integration
 1 Stochastic Unit Commitment with Topology Control Recourse for Renewables Integration Jiaying Shi and Shmuel Oren University of California, Berkeley IPAM, January 2016 33% RPS - Cumulative expected VERs
1 Stochastic Unit Commitment with Topology Control Recourse for Renewables Integration Jiaying Shi and Shmuel Oren University of California, Berkeley IPAM, January 2016 33% RPS - Cumulative expected VERs
Impact of Demand-Response on the Efficiency and Prices in Real-Time Electricity Markets
 Impact of Demand-Response on the Efficiency and Prices in Real-Time Electricity Markets Nicolas Gast, Jean-Yves Le Boudec, Dan-Cristian Tomozei To cite this version: Nicolas Gast, Jean-Yves Le Boudec,
Impact of Demand-Response on the Efficiency and Prices in Real-Time Electricity Markets Nicolas Gast, Jean-Yves Le Boudec, Dan-Cristian Tomozei To cite this version: Nicolas Gast, Jean-Yves Le Boudec,
Some properties of variable length packet shapers
 Some properties of variable length packet shapers Jean-Yves Le Boudec EPFL-DSC CH-1015 Lausanne, Switzerland EPFL-DSC esearch eport DSC/2000/037 20 Decembre 2000 Abstract The
Some properties of variable length packet shapers Jean-Yves Le Boudec EPFL-DSC CH-1015 Lausanne, Switzerland EPFL-DSC esearch eport DSC/2000/037 20 Decembre 2000 Abstract The
Timing Analysis of AVB Traffic in TSN Networks using Network Calculus
 Timing Analysis of AVB Traffic in TSN Networks using Network Calculus Luxi Zao, Paul Pop Tecnical University of Denmark Zong Zeng, Qiao Li Beiang University Outline Introduction System Model Arcitecture
Timing Analysis of AVB Traffic in TSN Networks using Network Calculus Luxi Zao, Paul Pop Tecnical University of Denmark Zong Zeng, Qiao Li Beiang University Outline Introduction System Model Arcitecture
Scheduling I. Today. Next Time. ! Introduction to scheduling! Classical algorithms. ! Advanced topics on scheduling
 Scheduling I Today! Introduction to scheduling! Classical algorithms Next Time! Advanced topics on scheduling Scheduling out there! You are the manager of a supermarket (ok, things don t always turn out
Scheduling I Today! Introduction to scheduling! Classical algorithms Next Time! Advanced topics on scheduling Scheduling out there! You are the manager of a supermarket (ok, things don t always turn out
Technion - Computer Science Department - Technical Report CS On Centralized Smooth Scheduling
 On Centralized Smooth Scheduling Ami Litman January 25, 2005 Abstract Shiri Moran-Schein This paper studies evenly distributed sets of natural numbers and their applications to scheduling in a centralized
On Centralized Smooth Scheduling Ami Litman January 25, 2005 Abstract Shiri Moran-Schein This paper studies evenly distributed sets of natural numbers and their applications to scheduling in a centralized
Stochastic-Process Limits
 Ward Whitt Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues With 68 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface vii 1 Experiencing Statistical Regularity
Ward Whitt Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues With 68 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface vii 1 Experiencing Statistical Regularity
On the Impact of Link Scheduling on End-to-End Delays in Large Networks
 1 On the Impact of Link Scheduling on End-to-End Delays in Large Networks Jörg Liebeherr, Yashar Ghiassi-Farrokhfal, Almut Burchard Abstract We seek to provide an analytical answer whether the impact of
1 On the Impact of Link Scheduling on End-to-End Delays in Large Networks Jörg Liebeherr, Yashar Ghiassi-Farrokhfal, Almut Burchard Abstract We seek to provide an analytical answer whether the impact of
Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks
 Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks X 14 (t) X 12 (t) 1 3 4 k a P ak () t P a tot X 21 (t) 2 N X 2N (t) X N4 (t) µ ab () rate µ ab µ ab (p, S 3 ) µ ab µ ac () µ ab (p,
Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks X 14 (t) X 12 (t) 1 3 4 k a P ak () t P a tot X 21 (t) 2 N X 2N (t) X N4 (t) µ ab () rate µ ab µ ab (p, S 3 ) µ ab µ ac () µ ab (p,
Cyclic Dependencies in Modular Performance Analysis
 Cyclic Dependencies in Modular Performance Analysis ABSTRACT Bengt Jonsson Dept. Information Technology Uppsala University Box 337, 751 05 Uppsala bengt@it.uu.se Lothar Thiele Computer Engineering and
Cyclic Dependencies in Modular Performance Analysis ABSTRACT Bengt Jonsson Dept. Information Technology Uppsala University Box 337, 751 05 Uppsala bengt@it.uu.se Lothar Thiele Computer Engineering and
Duration and deadline differentiated demand: a model of flexible demand
 Duration and deadline differentiated demand: a model of flexible demand A. Nayyar, M. Negrete-Pincetić, K. Poolla, W. Chen, Y.Mo, L. Qiu, P. Varaiya May, 2016 1 / 21 Outline Duration-differentiated (DD)
Duration and deadline differentiated demand: a model of flexible demand A. Nayyar, M. Negrete-Pincetić, K. Poolla, W. Chen, Y.Mo, L. Qiu, P. Varaiya May, 2016 1 / 21 Outline Duration-differentiated (DD)
Optimal Media Streaming in a Rate-Distortion Sense For Guaranteed Service Networks
 Optimal Media Streaming in a Rate-Distortion Sense For Guaranteed Service Networks Olivier Verscheure and Pascal Frossard Jean-Yves Le Boudec IBM Watson Research Center Swiss Federal Institute of Tech.
Optimal Media Streaming in a Rate-Distortion Sense For Guaranteed Service Networks Olivier Verscheure and Pascal Frossard Jean-Yves Le Boudec IBM Watson Research Center Swiss Federal Institute of Tech.
Optimal Demand Response
 Optimal Demand Response Libin Jiang Steven Low Computing + Math Sciences Electrical Engineering Caltech Oct 2011 Outline Caltech smart grid research Optimal demand response Global trends 1 Exploding renewables
Optimal Demand Response Libin Jiang Steven Low Computing + Math Sciences Electrical Engineering Caltech Oct 2011 Outline Caltech smart grid research Optimal demand response Global trends 1 Exploding renewables
A Generalized Processor Sharing Approach to Flow Control in Integrated Services Networks: The Single Node Case. 1
 A Generalized Processor Sharing Approach to Flow Control in Integrated Services Networks: The Single Node Case 1 Abhay K Parekh 2 3 and Robert G Gallager 4 Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems
A Generalized Processor Sharing Approach to Flow Control in Integrated Services Networks: The Single Node Case 1 Abhay K Parekh 2 3 and Robert G Gallager 4 Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems
MODELING AND CONTROL OF THERMOSTATICALLY CONTROLLED LOADS
 MODELING AND CONTROL OF THERMOSTATICALLY CONTROLLED LOADS Soumya Kundu Nikolai Sinitsyn Scott Backhaus University of Michigan Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos National Laboratory Ann Arbor USA
MODELING AND CONTROL OF THERMOSTATICALLY CONTROLLED LOADS Soumya Kundu Nikolai Sinitsyn Scott Backhaus University of Michigan Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos National Laboratory Ann Arbor USA
Power Engineering II. Fundamental terms and definitions
 Fundamental terms and definitions Power engineering A scientific discipline that focuses on: Generation of electrical energy (EE) Transmission and distribution of EE Consumption of EE Power grid operation
Fundamental terms and definitions Power engineering A scientific discipline that focuses on: Generation of electrical energy (EE) Transmission and distribution of EE Consumption of EE Power grid operation
Optimal Demand Response
 Optimal Demand Response Libin Jiang Steven Low Computing + Math Sciences Electrical Engineering Caltech June 2011 Outline o Motivation o Demand response model o Some results Wind power over land (outside
Optimal Demand Response Libin Jiang Steven Low Computing + Math Sciences Electrical Engineering Caltech June 2011 Outline o Motivation o Demand response model o Some results Wind power over land (outside
Fair Scheduling in Input-Queued Switches under Inadmissible Traffic
 Fair Scheduling in Input-Queued Switches under Inadmissible Traffic Neha Kumar, Rong Pan, Devavrat Shah Departments of EE & CS Stanford University {nehak, rong, devavrat@stanford.edu Abstract In recent
Fair Scheduling in Input-Queued Switches under Inadmissible Traffic Neha Kumar, Rong Pan, Devavrat Shah Departments of EE & CS Stanford University {nehak, rong, devavrat@stanford.edu Abstract In recent
Window Flow Control Systems with Random Service
 Window Flow Control Systems with Random Service Alireza Shekaramiz Joint work with Prof. Jörg Liebeherr and Prof. Almut Burchard April 6, 2016 1 / 20 Content 1 Introduction 2 Related work 3 State-of-the-art
Window Flow Control Systems with Random Service Alireza Shekaramiz Joint work with Prof. Jörg Liebeherr and Prof. Almut Burchard April 6, 2016 1 / 20 Content 1 Introduction 2 Related work 3 State-of-the-art
1 Introduction Future high speed digital networks aim to provide integrated services, including voice, video, fax, and data. To control interaction am
 A Min-Plus System Theory for Constrained Trac Regulation and Dynamic Service Guarantees Cheng-Shang Chang, Rene L. Cruz y, Jean-Yves Le Boudec z, and Patrick Thiran x May 6, 1999 Abstract: By extending
A Min-Plus System Theory for Constrained Trac Regulation and Dynamic Service Guarantees Cheng-Shang Chang, Rene L. Cruz y, Jean-Yves Le Boudec z, and Patrick Thiran x May 6, 1999 Abstract: By extending
Queueing Theory I Summary! Little s Law! Queueing System Notation! Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K "
 Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Resource Provisioning in the Electrical Grid
 Resource Provisioning in the Electrical Grid by Omid Ardakanian A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree of Master of Mathematics in Computer
Resource Provisioning in the Electrical Grid by Omid Ardakanian A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree of Master of Mathematics in Computer
ECG 740 GENERATION SCHEDULING (UNIT COMMITMENT)
 1 ECG 740 GENERATION SCHEDULING (UNIT COMMITMENT) 2 Unit Commitment Given a load profile, e.g., values of the load for each hour of a day. Given set of units available, When should each unit be started,
1 ECG 740 GENERATION SCHEDULING (UNIT COMMITMENT) 2 Unit Commitment Given a load profile, e.g., values of the load for each hour of a day. Given set of units available, When should each unit be started,
Multi-Area Stochastic Unit Commitment for High Wind Penetration
 Multi-Area Stochastic Unit Commitment for High Wind Penetration Workshop on Optimization in an Uncertain Environment Anthony Papavasiliou, UC Berkeley Shmuel S. Oren, UC Berkeley March 25th, 2011 Outline
Multi-Area Stochastic Unit Commitment for High Wind Penetration Workshop on Optimization in an Uncertain Environment Anthony Papavasiliou, UC Berkeley Shmuel S. Oren, UC Berkeley March 25th, 2011 Outline
A Mechanism for Pricing Service Guarantees
 A Mechanism for Pricing Service Guarantees Bruce Hajek Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and the Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Sichao Yang Qualcomm
A Mechanism for Pricing Service Guarantees Bruce Hajek Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and the Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Sichao Yang Qualcomm
Stochastic Optimization for Undergraduate Computer Science Students
 Stochastic Optimization for Undergraduate Computer Science Students Professor Joongheon Kim School of Computer Science and Engineering, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Republic of Korea 1 Reference 2 Outline
Stochastic Optimization for Undergraduate Computer Science Students Professor Joongheon Kim School of Computer Science and Engineering, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Republic of Korea 1 Reference 2 Outline
Recent Progress on a Statistical Network Calculus
 Recent Progress on a Statistical Network Calculus Jorg Liebeherr Deartment of Comuter Science University of Virginia Collaborators Almut Burchard Robert Boorstyn Chaiwat Oottamakorn Stehen Patek Chengzhi
Recent Progress on a Statistical Network Calculus Jorg Liebeherr Deartment of Comuter Science University of Virginia Collaborators Almut Burchard Robert Boorstyn Chaiwat Oottamakorn Stehen Patek Chengzhi
Energy-Efficient Real-Time Task Scheduling in Multiprocessor DVS Systems
 Energy-Efficient Real-Time Task Scheduling in Multiprocessor DVS Systems Jian-Jia Chen *, Chuan Yue Yang, Tei-Wei Kuo, and Chi-Sheng Shih Embedded Systems and Wireless Networking Lab. Department of Computer
Energy-Efficient Real-Time Task Scheduling in Multiprocessor DVS Systems Jian-Jia Chen *, Chuan Yue Yang, Tei-Wei Kuo, and Chi-Sheng Shih Embedded Systems and Wireless Networking Lab. Department of Computer
Latency and Backlog Bounds in Time- Sensitive Networking with Credit Based Shapers and Asynchronous Traffic Shaping
 Latency and Backlog Bounds in Time- Sensitive Networking with Credit Based Shapers and Asynchronous Traffic Shaping Ehsan Mohammadpour, Eleni Stai, Maaz Mohuiddin, Jean-Yves Le Boudec September 7 th 2018,
Latency and Backlog Bounds in Time- Sensitive Networking with Credit Based Shapers and Asynchronous Traffic Shaping Ehsan Mohammadpour, Eleni Stai, Maaz Mohuiddin, Jean-Yves Le Boudec September 7 th 2018,
Scheduling Coflows in Datacenter Networks: Improved Bound for Total Weighted Completion Time
 1 1 2 Scheduling Coflows in Datacenter Networs: Improved Bound for Total Weighted Completion Time Mehrnoosh Shafiee and Javad Ghaderi Abstract Coflow is a recently proposed networing abstraction to capture
1 1 2 Scheduling Coflows in Datacenter Networs: Improved Bound for Total Weighted Completion Time Mehrnoosh Shafiee and Javad Ghaderi Abstract Coflow is a recently proposed networing abstraction to capture
1 Introduction Future high speed digital networks aim to serve integrated trac, such as voice, video, fax, and so forth. To control interaction among
 On Deterministic Trac Regulation and Service Guarantees: A Systematic Approach by Filtering Cheng-Shang Chang Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Tsing Hua University Hsinchu 30043 Taiwan, R.O.C.
On Deterministic Trac Regulation and Service Guarantees: A Systematic Approach by Filtering Cheng-Shang Chang Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Tsing Hua University Hsinchu 30043 Taiwan, R.O.C.
Schedulability analysis of global Deadline-Monotonic scheduling
 Schedulability analysis of global Deadline-Monotonic scheduling Sanjoy Baruah Abstract The multiprocessor Deadline-Monotonic (DM) scheduling of sporadic task systems is studied. A new sufficient schedulability
Schedulability analysis of global Deadline-Monotonic scheduling Sanjoy Baruah Abstract The multiprocessor Deadline-Monotonic (DM) scheduling of sporadic task systems is studied. A new sufficient schedulability
Performance, Power & Energy. ELEC8106/ELEC6102 Spring 2010 Hayden Kwok-Hay So
 Performance, Power & Energy ELEC8106/ELEC6102 Spring 2010 Hayden Kwok-Hay So Recall: Goal of this class Performance Reconfiguration Power/ Energy H. So, Sp10 Lecture 3 - ELEC8106/6102 2 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
Performance, Power & Energy ELEC8106/ELEC6102 Spring 2010 Hayden Kwok-Hay So Recall: Goal of this class Performance Reconfiguration Power/ Energy H. So, Sp10 Lecture 3 - ELEC8106/6102 2 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
Some Fixed-Point Results for the Dynamic Assignment Problem
 Some Fixed-Point Results for the Dynamic Assignment Problem Michael Z. Spivey Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Samford University, Birmingham, AL 35229 Warren B. Powell Department of Operations
Some Fixed-Point Results for the Dynamic Assignment Problem Michael Z. Spivey Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Samford University, Birmingham, AL 35229 Warren B. Powell Department of Operations
Scheduling Policies for Two-State Smart-Home Appliances in Dynamic Electricity Pricing Environments
 Scheduling Policies for Two-State Smart-Home Appliances in Dynamic Electricity Pricing Environments John S. Vardakas a,, Nizar Zorba b, Christos V. Verikoukis c a Iquadrat, Barcelona, Spain b QMIC, Al-Doha,
Scheduling Policies for Two-State Smart-Home Appliances in Dynamic Electricity Pricing Environments John S. Vardakas a,, Nizar Zorba b, Christos V. Verikoukis c a Iquadrat, Barcelona, Spain b QMIC, Al-Doha,
Resource Allocation for Video Streaming in Wireless Environment
 Resource Allocation for Video Streaming in Wireless Environment Shahrokh Valaee and Jean-Charles Gregoire Abstract This paper focuses on the development of a new resource allocation scheme for video streaming
Resource Allocation for Video Streaming in Wireless Environment Shahrokh Valaee and Jean-Charles Gregoire Abstract This paper focuses on the development of a new resource allocation scheme for video streaming
Envelope Modeling for Renewable Energy Intermittency and Capacity
 Envelope Modeling for Renewable Energy Intermittency and Capacity Xiaoyue Jiang, Geoffrey Parker, Ekundayo Shittu Tulane Energy Institute Tulane University New Orleans, LA Efforts to integrate renewable
Envelope Modeling for Renewable Energy Intermittency and Capacity Xiaoyue Jiang, Geoffrey Parker, Ekundayo Shittu Tulane Energy Institute Tulane University New Orleans, LA Efforts to integrate renewable
M/G/FQ: STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF FAIR QUEUEING SYSTEMS
 M/G/FQ: STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF FAIR QUEUEING SYSTEMS MOHAMMED HAWA AND DAVID W. PETR Information and Telecommunications Technology Center University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas, 66045 email: {hawa, dwp}@ittc.ku.edu
M/G/FQ: STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF FAIR QUEUEING SYSTEMS MOHAMMED HAWA AND DAVID W. PETR Information and Telecommunications Technology Center University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas, 66045 email: {hawa, dwp}@ittc.ku.edu
Energy Management Systems and Demand Response
 Energy Management Systems and Demand Response W. van Ackooij, A. P. Chorobura, C. Sagastizábal, H. Zidani PGMO Days 2017 November 14, 2017 (PGMO) November 14, 2017 1 / 24 Goals For a toy power mix problem,
Energy Management Systems and Demand Response W. van Ackooij, A. P. Chorobura, C. Sagastizábal, H. Zidani PGMO Days 2017 November 14, 2017 (PGMO) November 14, 2017 1 / 24 Goals For a toy power mix problem,
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling
 NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
ENERGY STORAGE MANAGEMENT AND LOAD SCHEDULING WITH RENEWABLE INTEGRATION. Tianyi Li. Doctor of Philosophy
 ENERGY STORAGE MANAGEMENT AND LOAD SCHEDULING WITH RENEWABLE INTEGRATION by Tianyi Li A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in The Faculty
ENERGY STORAGE MANAGEMENT AND LOAD SCHEDULING WITH RENEWABLE INTEGRATION by Tianyi Li A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in The Faculty
1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours)
 1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours) Student Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This exam is open-book 2. No cooperation is permitted 3. Please write down your name
1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours) Student Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This exam is open-book 2. No cooperation is permitted 3. Please write down your name
Scheduling I. Today Introduction to scheduling Classical algorithms. Next Time Advanced topics on scheduling
 Scheduling I Today Introduction to scheduling Classical algorithms Next Time Advanced topics on scheduling Scheduling out there You are the manager of a supermarket (ok, things don t always turn out the
Scheduling I Today Introduction to scheduling Classical algorithms Next Time Advanced topics on scheduling Scheduling out there You are the manager of a supermarket (ok, things don t always turn out the
Discrete Event Simulation. Motive
 Discrete Event Simulation These slides are created by Dr. Yih Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang's courses at GMU can make a single machine-readable copy and print a single
Discrete Event Simulation These slides are created by Dr. Yih Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang's courses at GMU can make a single machine-readable copy and print a single
Energy Optimal Control for Time Varying Wireless Networks. Michael J. Neely University of Southern California
 Energy Optimal Control for Time Varying Wireless Networks Michael J. Neely University of Southern California http://www-rcf.usc.edu/~mjneely Part 1: A single wireless downlink (L links) L 2 1 S={Totally
Energy Optimal Control for Time Varying Wireless Networks Michael J. Neely University of Southern California http://www-rcf.usc.edu/~mjneely Part 1: A single wireless downlink (L links) L 2 1 S={Totally
R O B U S T E N E R G Y M AN AG E M E N T S Y S T E M F O R I S O L AT E D M I C R O G R I D S
 ROBUST ENERGY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM FOR ISOLATED MICROGRIDS Jose Daniel La r a Claudio Cañizares Ka nka r Bhattacharya D e p a r t m e n t o f E l e c t r i c a l a n d C o m p u t e r E n g i n e e r i n
ROBUST ENERGY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM FOR ISOLATED MICROGRIDS Jose Daniel La r a Claudio Cañizares Ka nka r Bhattacharya D e p a r t m e n t o f E l e c t r i c a l a n d C o m p u t e r E n g i n e e r i n
Energy Cooperation and Traffic Management in Cellular Networks with Renewable Energy
 Energy Cooperation and Traffic Management in Cellular Networks with Renewable Energy Hyun-Suk Lee Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Eng., Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea Jang-Won Lee Dept. of Electrical
Energy Cooperation and Traffic Management in Cellular Networks with Renewable Energy Hyun-Suk Lee Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Eng., Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea Jang-Won Lee Dept. of Electrical
Congestion Control In The Internet Part 1: Theory. JY Le Boudec 2018
 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 1: Theory JY Le Boudec 2018 1 Contents 1. What is the problem; congestion collapse 2. Efficiency versus Fairness 3. Definitions of fairness 4. Additive Increase
Congestion Control In The Internet Part 1: Theory JY Le Boudec 2018 1 Contents 1. What is the problem; congestion collapse 2. Efficiency versus Fairness 3. Definitions of fairness 4. Additive Increase
A STAFFING ALGORITHM FOR CALL CENTERS WITH SKILL-BASED ROUTING: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 A STAFFING ALGORITHM FOR CALL CENTERS WITH SKILL-BASED ROUTING: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL by Rodney B. Wallace IBM and The George Washington University rodney.wallace@us.ibm.com Ward Whitt Columbia University
A STAFFING ALGORITHM FOR CALL CENTERS WITH SKILL-BASED ROUTING: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL by Rodney B. Wallace IBM and The George Washington University rodney.wallace@us.ibm.com Ward Whitt Columbia University
Embedded Systems 23 BF - ES
 Embedded Systems 23-1 - Measurement vs. Analysis REVIEW Probability Best Case Execution Time Unsafe: Execution Time Measurement Worst Case Execution Time Upper bound Execution Time typically huge variations
Embedded Systems 23-1 - Measurement vs. Analysis REVIEW Probability Best Case Execution Time Unsafe: Execution Time Measurement Worst Case Execution Time Upper bound Execution Time typically huge variations
Berge s Maximum Theorem
 Berge s Maximum Theorem References: Acemoglu, Appendix A.6 Stokey-Lucas-Prescott, Section 3.3 Ok, Sections E.1-E.3 Claude Berge, Topological Spaces (1963), Chapter 6 Berge s Maximum Theorem So far, we
Berge s Maximum Theorem References: Acemoglu, Appendix A.6 Stokey-Lucas-Prescott, Section 3.3 Ok, Sections E.1-E.3 Claude Berge, Topological Spaces (1963), Chapter 6 Berge s Maximum Theorem So far, we
Set Point Control of a Thermal Load Population
 Set Point Control of a Thermal Load Population 1/15 Set Point Control of a Thermal Load Population CE 291F Final Project Travis Walter Civil Systems Program Civil and Environmental Engineering Department
Set Point Control of a Thermal Load Population 1/15 Set Point Control of a Thermal Load Population CE 291F Final Project Travis Walter Civil Systems Program Civil and Environmental Engineering Department
Strong Performance Guarantees for Asynchronous Buffered Crossbar Schedulers
 Strong Performance Guarantees for Asynchronous Buffered Crossbar Schedulers Jonathan Turner Washington University jon.turner@wustl.edu January 30, 2008 Abstract Crossbar-based switches are commonly used
Strong Performance Guarantees for Asynchronous Buffered Crossbar Schedulers Jonathan Turner Washington University jon.turner@wustl.edu January 30, 2008 Abstract Crossbar-based switches are commonly used
POWER systems are one of the most critical infrastructures
 1 Capacity Controlled Demand Side Management: A Stochastic Pricing Analysis Kostas Margellos, Member, IEEE, and Shmuel Oren, Fellow, IEEE Abstract We consider a novel paradigm for demand side management,
1 Capacity Controlled Demand Side Management: A Stochastic Pricing Analysis Kostas Margellos, Member, IEEE, and Shmuel Oren, Fellow, IEEE Abstract We consider a novel paradigm for demand side management,
Optimal dispatch strategy for the agile virtual power plant Petersen, Mette Kirschmeyer; Bendtsen, Jan Dimon; Stoustrup, Jakob
 Aalborg Universitet Optimal dispatch strategy for the agile virtual power plant Petersen, Mette Kirschmeyer; Bendtsen, Jan Dimon; Stoustrup, Jakob Published in: 2012 American Control Conference Publication
Aalborg Universitet Optimal dispatch strategy for the agile virtual power plant Petersen, Mette Kirschmeyer; Bendtsen, Jan Dimon; Stoustrup, Jakob Published in: 2012 American Control Conference Publication
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
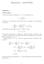 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Performance, Power & Energy
 Recall: Goal of this class Performance, Power & Energy ELE8106/ELE6102 Performance Reconfiguration Power/ Energy Spring 2010 Hayden Kwok-Hay So H. So, Sp10 Lecture 3 - ELE8106/6102 2 What is good performance?
Recall: Goal of this class Performance, Power & Energy ELE8106/ELE6102 Performance Reconfiguration Power/ Energy Spring 2010 Hayden Kwok-Hay So H. So, Sp10 Lecture 3 - ELE8106/6102 2 What is good performance?
Single-part-type, multiple stage systems
 MIT 2.853/2.854 Introduction to Manufacturing Systems Single-part-type, multiple stage systems Stanley B. Gershwin Laboratory for Manufacturing and Productivity Massachusetts Institute of Technology Single-stage,
MIT 2.853/2.854 Introduction to Manufacturing Systems Single-part-type, multiple stage systems Stanley B. Gershwin Laboratory for Manufacturing and Productivity Massachusetts Institute of Technology Single-stage,
Worst Case Burstiness Increase due to FIFO Multiplexing
 Worst Case Burstiness Increase due to FIFO Multiplexing EPFL esearch eport IC/22/17 Vicent Cholvi DLSI Universitat Jaume I 1271 Castelló (Spain) vcholvi@lsi.uji.es Juan Echagüe DICC Universitat Jaume I
Worst Case Burstiness Increase due to FIFO Multiplexing EPFL esearch eport IC/22/17 Vicent Cholvi DLSI Universitat Jaume I 1271 Castelló (Spain) vcholvi@lsi.uji.es Juan Echagüe DICC Universitat Jaume I
Multi-Area Stochastic Unit Commitment for High Wind Penetration in a Transmission Constrained Network
 Multi-Area Stochastic Unit Commitment for High Wind Penetration in a Transmission Constrained Network Anthony Papavasiliou Center for Operations Research and Econometrics Université catholique de Louvain,
Multi-Area Stochastic Unit Commitment for High Wind Penetration in a Transmission Constrained Network Anthony Papavasiliou Center for Operations Research and Econometrics Université catholique de Louvain,
Deregulated Electricity Market for Smart Grid: A Network Economic Approach
 Deregulated Electricity Market for Smart Grid: A Network Economic Approach Chenye Wu Institute for Interdisciplinary Information Sciences (IIIS) Tsinghua University Chenye Wu (IIIS) Network Economic Approach
Deregulated Electricity Market for Smart Grid: A Network Economic Approach Chenye Wu Institute for Interdisciplinary Information Sciences (IIIS) Tsinghua University Chenye Wu (IIIS) Network Economic Approach
Modeling Buffers with Data Refresh Semantics in Automotive Architectures
 Modeling Buffers with Data Refresh Semantics in Automotive Architectures Linh T.X. Phan 1 Reinhard Schneider 2 Samarjit Chakraborty 2 Insup Lee 1 1 Department of Computer and Information Science, University
Modeling Buffers with Data Refresh Semantics in Automotive Architectures Linh T.X. Phan 1 Reinhard Schneider 2 Samarjit Chakraborty 2 Insup Lee 1 1 Department of Computer and Information Science, University
Component-based Analysis of Worst-case Temperatures
 Component-based Analysis of Worst-case Temperatures Lothar Thiele, Iuliana Bacivarov, Jian-Jia Chen, Devendra Rai, Hoeseok Yang 1 How can we analyze timing properties in a compositional framework? 2 Modular
Component-based Analysis of Worst-case Temperatures Lothar Thiele, Iuliana Bacivarov, Jian-Jia Chen, Devendra Rai, Hoeseok Yang 1 How can we analyze timing properties in a compositional framework? 2 Modular
Modeling Buffers With Data Refresh Semantics in Automotive Architectures
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (CIS) Department of Computer & Information Science 10-2010 Modeling Buffers With Data Refresh Semantics in Automotive Architectures Linh
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (CIS) Department of Computer & Information Science 10-2010 Modeling Buffers With Data Refresh Semantics in Automotive Architectures Linh
RUN-TIME EFFICIENT FEASIBILITY ANALYSIS OF UNI-PROCESSOR SYSTEMS WITH STATIC PRIORITIES
 RUN-TIME EFFICIENT FEASIBILITY ANALYSIS OF UNI-PROCESSOR SYSTEMS WITH STATIC PRIORITIES Department for Embedded Systems/Real-Time Systems, University of Ulm {name.surname}@informatik.uni-ulm.de Abstract:
RUN-TIME EFFICIENT FEASIBILITY ANALYSIS OF UNI-PROCESSOR SYSTEMS WITH STATIC PRIORITIES Department for Embedded Systems/Real-Time Systems, University of Ulm {name.surname}@informatik.uni-ulm.de Abstract:
Integrated Electricity Demand and Price Forecasting
 Integrated Electricity Demand and Price Forecasting Create and Evaluate Forecasting Models The many interrelated factors which influence demand for electricity cannot be directly modeled by closed-form
Integrated Electricity Demand and Price Forecasting Create and Evaluate Forecasting Models The many interrelated factors which influence demand for electricity cannot be directly modeled by closed-form
A Calculus for End-to-end Statistical Service Guarantees
 A Calculus for End-to-end Statistical Service Guarantees Almut Burchard y Jörg Liebeherr Stephen Patek y Department of Mathematics Department of Computer Science Department of Systems and Information Engineering
A Calculus for End-to-end Statistical Service Guarantees Almut Burchard y Jörg Liebeherr Stephen Patek y Department of Mathematics Department of Computer Science Department of Systems and Information Engineering
CycleTandem: Energy-Saving Scheduling for Real-Time Systems with Hardware Accelerators
 CycleTandem: Energy-Saving Scheduling for Real-Time Systems with Hardware Accelerators Sandeep D souza and Ragunathan (Raj) Rajkumar Carnegie Mellon University High (Energy) Cost of Accelerators Modern-day
CycleTandem: Energy-Saving Scheduling for Real-Time Systems with Hardware Accelerators Sandeep D souza and Ragunathan (Raj) Rajkumar Carnegie Mellon University High (Energy) Cost of Accelerators Modern-day
Temperature-Aware Analysis and Scheduling
 Temperature-Aware Analysis and Scheduling Lothar Thiele, Pratyush Kumar Overview! Introduction! Power and Temperature Models! Analysis Real-time Analysis Worst-case Temperature Analysis! Scheduling Stop-and-go
Temperature-Aware Analysis and Scheduling Lothar Thiele, Pratyush Kumar Overview! Introduction! Power and Temperature Models! Analysis Real-time Analysis Worst-case Temperature Analysis! Scheduling Stop-and-go
Modeling Fixed Priority Non-Preemptive Scheduling with Real-Time Calculus
 Modeling Fixed Priority Non-Preemptive Scheduling with Real-Time Calculus Devesh B. Chokshi and Purandar Bhaduri Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati,
Modeling Fixed Priority Non-Preemptive Scheduling with Real-Time Calculus Devesh B. Chokshi and Purandar Bhaduri Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati,
Firming Renewable Power with Demand Response: An End-to-end Aggregator Business Model
 Firming Renewable Power with Demand Response: An End-to-end Aggregator Business Model Clay Campaigne joint work with Shmuel Oren November 5, 2015 1 / 16 Motivation Problem: Expansion of renewables increases
Firming Renewable Power with Demand Response: An End-to-end Aggregator Business Model Clay Campaigne joint work with Shmuel Oren November 5, 2015 1 / 16 Motivation Problem: Expansion of renewables increases
Networked Embedded Systems WS 2016/17
 Networked Embedded Systems WS 2016/17 Lecture 2: Real-time Scheduling Marco Zimmerling Goal of Today s Lecture Introduction to scheduling of compute tasks on a single processor Tasks need to finish before
Networked Embedded Systems WS 2016/17 Lecture 2: Real-time Scheduling Marco Zimmerling Goal of Today s Lecture Introduction to scheduling of compute tasks on a single processor Tasks need to finish before
A Theory of Rate-Based Execution. A Theory of Rate-Based Execution
 Kevin Jeffay Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill jeffay@cs cs.unc.edu Steve Goddard Computer Science & Engineering University of Nebraska Ð Lincoln goddard@cse cse.unl.edu
Kevin Jeffay Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill jeffay@cs cs.unc.edu Steve Goddard Computer Science & Engineering University of Nebraska Ð Lincoln goddard@cse cse.unl.edu
A Starvation-free Algorithm For Achieving 100% Throughput in an Input- Queued Switch
 A Starvation-free Algorithm For Achieving 00% Throughput in an Input- Queued Switch Abstract Adisak ekkittikul ick ckeown Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford CA 9405-400 Tel
A Starvation-free Algorithm For Achieving 00% Throughput in an Input- Queued Switch Abstract Adisak ekkittikul ick ckeown Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford CA 9405-400 Tel
Efficient Nonlinear Optimizations of Queuing Systems
 Efficient Nonlinear Optimizations of Queuing Systems Mung Chiang, Arak Sutivong, and Stephen Boyd Electrical Engineering Department, Stanford University, CA 9435 Abstract We present a systematic treatment
Efficient Nonlinear Optimizations of Queuing Systems Mung Chiang, Arak Sutivong, and Stephen Boyd Electrical Engineering Department, Stanford University, CA 9435 Abstract We present a systematic treatment
On Two Class-Constrained Versions of the Multiple Knapsack Problem
 On Two Class-Constrained Versions of the Multiple Knapsack Problem Hadas Shachnai Tami Tamir Department of Computer Science The Technion, Haifa 32000, Israel Abstract We study two variants of the classic
On Two Class-Constrained Versions of the Multiple Knapsack Problem Hadas Shachnai Tami Tamir Department of Computer Science The Technion, Haifa 32000, Israel Abstract We study two variants of the classic
A Network Calculus with Effective Bandwidth
 A Network Calculus with Effective Bandwidth Technical Report: University of Virginia, CS-2003-20, November 2003 Chengzhi Li Almut Burchard Jörg Liebeherr Department of Computer Science Department of Mathematics
A Network Calculus with Effective Bandwidth Technical Report: University of Virginia, CS-2003-20, November 2003 Chengzhi Li Almut Burchard Jörg Liebeherr Department of Computer Science Department of Mathematics
Battery Energy Storage
 Battery Energy Storage Implications for Load Shapes and Forecasting April 28, 2017 TOPICS» What is Energy Storage» Storage Market, Costs, Regulatory Background» Behind the Meter (BTM) Battery Storage Where
Battery Energy Storage Implications for Load Shapes and Forecasting April 28, 2017 TOPICS» What is Energy Storage» Storage Market, Costs, Regulatory Background» Behind the Meter (BTM) Battery Storage Where
A Hierarchy of Suboptimal Policies for the Multi-period, Multi-echelon, Robust Inventory Problem
 A Hierarchy of Suboptimal Policies for the Multi-period, Multi-echelon, Robust Inventory Problem Dimitris J. Bertsimas Dan A. Iancu Pablo A. Parrilo Sloan School of Management and Operations Research Center,
A Hierarchy of Suboptimal Policies for the Multi-period, Multi-echelon, Robust Inventory Problem Dimitris J. Bertsimas Dan A. Iancu Pablo A. Parrilo Sloan School of Management and Operations Research Center,
EE 466/586 VLSI Design. Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University
 EE 466/586 VLSI Design Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University pande@eecs.wsu.edu Lecture 9 Propagation delay Power and delay Tradeoffs Follow board notes Propagation Delay Switching Time
EE 466/586 VLSI Design Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University pande@eecs.wsu.edu Lecture 9 Propagation delay Power and delay Tradeoffs Follow board notes Propagation Delay Switching Time
Storing energy or Storing Consumption?
 Storing energy or Storing Consumption? It is not the same! Joachim Geske, Richard Green, Qixin Chen, Yi Wang 40th IAEE International Conference 18-21 June 2017, Singapore Motivation Electricity systems
Storing energy or Storing Consumption? It is not the same! Joachim Geske, Richard Green, Qixin Chen, Yi Wang 40th IAEE International Conference 18-21 June 2017, Singapore Motivation Electricity systems
Modeling Buffers with Data Refresh Semantics in Automotive Architectures
 Modeling Buffers with Data Refresh Semantics in Automotive Architectures Linh T.X. Phan Reinhard Schneider Samarjit Chakraborty Insup Lee Department of Computer and Information Science, University of Pennsylvania,
Modeling Buffers with Data Refresh Semantics in Automotive Architectures Linh T.X. Phan Reinhard Schneider Samarjit Chakraborty Insup Lee Department of Computer and Information Science, University of Pennsylvania,
Network management and QoS provisioning - Network Calculus
 Network Calculus Network calculus is a metodology to study in a deterministic approach theory of queues. First a linear modelization is needed: it means that, for example, a system like: ρ can be modelized
Network Calculus Network calculus is a metodology to study in a deterministic approach theory of queues. First a linear modelization is needed: it means that, for example, a system like: ρ can be modelized
Optimal Sensing and Transmission in Energy Harvesting Sensor Networks
 University of Arkansas, Fayetteville ScholarWorks@UARK Theses and Dissertations 2-206 Optimal Sensing and Transmission in Energy Harvesting Sensor Networks Xianwen Wu University of Arkansas, Fayetteville
University of Arkansas, Fayetteville ScholarWorks@UARK Theses and Dissertations 2-206 Optimal Sensing and Transmission in Energy Harvesting Sensor Networks Xianwen Wu University of Arkansas, Fayetteville
