Math 121, Chapter 1 and Complex Numbers Practice Questions Hints and Answers. 2. Multiply numerator and denominator by complex conjugate and simplify:
|
|
|
- Cody Patrick Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 121, Chapter 1 and Complex Numbers Practice Questions Hints and Answers 1. (a) (3 2i)( + 1i) = i 8i 2i 2 = 12 5i 2( 1) = 1 5i. (b) i 223 = (i ) 55 (i 3 ) = i. 2. Multiply numerator and denominator by complex conjugate and simplify: (3 2i)( 5i) ( + 5i)( 5i) = 12 23i + 10i2 1 = 2 23i 1 = i. 3. (a) 2x + 5 3x 1 = 1 implies 2x + 5 = 3x 1 implies 6 = x. Thus, the solution is x = 6. (b) 3 x d = c where c > 0 implies x d = c/3 and so x d = c/3 or x d = c/3. Therefore, x = d + c/3 or x = d c/3. (c) Multiply both sides by 15 to obtain 5(21 2x) = 3(x + 6) and so x = 12x + 18 or 22x = 87 and so x = 87/22. (You should plug this back in to check your answer). (d) Distributing we have 10s 22 8s 36 = 0 and so 2s 58 = 0 or 2s = 58 and so s = 29. (As usual, you should plug this back in original equation to check.) (e) We will isolate the expression x + 7 first. Thus 3 x + 7 = 33 and so x + 7 = 11. Then x + 7 = 11 or x + 7 = 11 Thus x = or x = 18. The solutions are 18,. (f) Solve t = 70. This implies t = 70 or t = 70. Then 60 = 30t or 200 = 30t. Thus t = 2 or t = 20/ Thus Rueben will be exactly 70 miles from Barstow in 2 hours and in 6.7 hours.. (a) Let A be the amount of time in hours that it would take the assistant to build the fence alone. Because the two workers can finish the fence in 5 hours time, we get that Therefore, 5 A = 3 8 and so A = 0 3 hours A = 1. (b) The rate for the painter is 1/1 and the rate for the assistant is 1/35. Use the formula that rate times time is the portion of the job completed. Let t be the time needed for the two working together to paint the kitchen. Then t t 1 35 = 1 or 5t + 2t = 70 and so t = 10. It would take 10 hours for the two working together to paint the kitchen. 1
2 5. Let x = the amount of antifreeze solution that should be drained and replaced with pure antifreeze. Then there are 6 x liters of 20% solution, and x liters of 100% solution to produce 6 liters of 50% solution. The equation for the amount of antifreeze in the radiator is thus: (6 x)(.2) + x(1.0) = (.5)(6). Therefore, 1.2.2x + x = 3 and so x = 3 and so.8x = 1.8 and so x = 9 liters. 6. (a) A = 1h(b b 2 ) implies b 1 + b 2 = 2A implies b h 2 = 2A b h 1 implies b 2 = 2A b 1h. h (b) Multiplying both sides of 1 R = 1 R R 2 by R R 1 R 2 implies R 1 R 2 = RR 2 +RR 1. Therefore, R 1 R 2 RR 2 = RR 1 and so R 2 (R 1 R) = RR 1, and finally, R 2 = RR 1 R 1 R. (c) Solve similarly to (b), or 1 R = 1 R R 2 implies R = multiplying numerator and denominator by R 1 R 2 to obtain R = R 1R 2 R 2 + R R Simply this fraction by R 2 7. (a) Let x be the amount invested at 8%. Then interest earned = interest rate times amount invested yields the equation (2500)(.055) +.08x =.07( x) which has solution x = Thus $3750 is invested at 8%. (b) Let x be the amount invested at 11%. Then x is the amount invested at 8%. Therefore, the interest earned equation is 0.08(11000 x) x = 108 This simplifies to.03x = (11000) = 168, and so x = 168/.03 = 5600, which means x = 500. Thus $500 was invested at 8% and $5600 was invested at 11%. 8. (a) Let x be the number of grams of pure gold added. Then computing the amount of gold in the allow yields ( ) x = 18 (x + 15) 2 2 which has solution x = 10 grams. (b) Let x be the number of $6.50 per ounce silver needed in the mixture. Then 0 x is the number of $9.00 per ounce silver that is needed. This leads to the equation 6.5x + 9(0 x) = 0(8). Then, 2.5x = 320, or 5x/2 = 0, and so x = 16. Therefore, 16 ounces of $6.50 per ounce silver should be mixed with 2 ounces of $9.00 per ounce silver. 2
3 9.(a) Let d be the distance each direction, and let t be the amount of time it took the messenger to run to the palace. Using d = rt we obtain the equation 10t = (8.75 t). Therefore, 1t = 35 and so t = 2.5 hours. Therefore, the distance from the messenger s residence to the palace is d = 10 miles 2.5hours = 25 miles. hours (b) Let t be the time in seconds it took the sprinter to run to the end of the track. Then the return trip took 126 t seconds. Then t = length of track = 2(126 t). Therefore, t = 2(126 t) or 6t = 2(126) or t = 2 seconds. Then the track is (2) = 168 meters long x 2 + 3x = implies 2x 2 + 3x = 0. Now the quadratic equation implies x = 3 ± 3 2 (2)( ), thus the solutions are x = 3 ± 1. 2(2) 11. Using the difference of two squares pattern, we factor (x 5) 2 9 = ((x 5) + 3)((x 5) 3) Therefore, (x 2)(x 8) = 0 and so x = 2 or x = First, 1 2 x2 + 3 x + 1 = 0 implies that (multiply both sides of the equation by ) 2x 2 + 3x + = 0. Now, for the purposes of the quadratic equation, a = 2, b = 3 and c =, and so x = 3 ± 3 2 (2)() 2(2) = 3 ± 23. Therefore, the answer is x = 3 ± i 23 = 3 ± i (a) Let w be the width, and l be the length. The amount of fence used will be 2l + 3w (the 3w is because of the extra fence in the middle to create the two smaller rectangles). Now 2l + 3w = 600 and so l = (600 3w)/2. Also, A = lw and so we get that w(300 3 w) = 15, Thus, 3 2 w2 300w + 15, 000 = 0. Multiplying both sides by 2 to get rid of the faction, we have 3w 2 600w + 30, 000 = 0. This factors as 3(w 2 200w + 10, 000) = 3(w 100) 2. Therefore, 3(w 100) 2 = 0 and so w = 100. Hence l = (600 3(100))/2 = 150. So the enclosure s dimensions are 100 feet by 150 feet. 3
4 (b) The ball will have a height of 130 feet when 16t t + 7 = 130, or 16t 2 88t = 0. There are no real solutions to this quadratic equation (check with the quadratic formula), so the ball never reaches a height of 130 feet. The ball will land when h(t) = 0. Thus one should solve 16t t + 7 = 0. This has solutions t = 88 ± 88 2 ( 16)(7) 2( 16) = 88 ± so t is approximately 5.58 seconds or.078 seconds. But the equation is only for t 0, (time after it was thrown), so the ball hits the ground after approximately 5.58 seconds. (c) The volume is 3(x 6) 2 and so we solve 3(x 6) 2 = Then (x 6) 2 = and so x 6 = and thus x 6 = 8.5, or x = 1.5. Thus a sheet of cardboard that measures 1.5 inches by 1.5 inches is needed. (d) Let the screen have dimensions x by y. Then y = and so y = x. By the Pythagorean x 3 3 theorem ( ) = x 2 + y 2 = x x = x x2 (9)(5) and so (9)(5) 2 = 9x x 2 2 and then x = The screen measures 32. inches by 3.2 inches. = (3)(5) 5 = 32. and y = 3 (32.) = 1. (a) Rewrite as 2x = x + 1 and then square both sides to obtain (2x 5) + 2 2x = x + 1 and simplify to x 5 = 2 2x 5 and square both sides again to obtain x 2 10x + 25 = (2x 5). Therefore, x 2 18x + 5 = 0, and so (x 3)(x 15) = 0. Consequently, the proposed solutions are x = 3 or x = 15. However, x = 15 doesn t work, therefore x = 3 is the only solution. (b) Rewrite the equation as 3x + 7 = x + 1 and then square both sides to obtain 3x + 7 = x 2 + 2x + 1, or x 2 x 6 = 0. Therefore, (x 3)(x + 2) = 0, and so x = 3 and x = 2 are proposed solutions. Plugging these back into the original equation, we find that x = 3 works, while x = 2 does not. Therefore, the solution is x = Raise both sides of the equation to the th power to get that 256x 3 = x 2 Therefore, x 2 (256x 1) = 0. Thus the proposed solutions to the equation are x = 0 and x = Plugging them back into the equation, we can see that they both are solutions.
5 16. (a) Make the substitution u = (3x 5) 1 3 to convert this into the quadratic equation u 2 + 6u + 8 = 0. Therefore, (u + )(u + 2) = 0 and so u = 2 or u =. Now u 3 = 3x 5 and so x = u Consequently, the solutions to the equation are x = = 1 and x = = (b) x 5x 2 + = 0 implies (x 2 )(x 2 1) = 0 and so x = 2, 2, 1, 1. (c) x 6 5x = 0 implies (x 3 1)(x 3 + 6) = 0 and so x = 1 and x = 3 6 are the real solutions. 17. Pump 1 can drain t 10 of the pool in t hours and pump 2 can drain t of the pool in t hours. 8 So, let x be the number of hours it takes the pumps to drain the pool together. Then x 10 + x 8 = 1. Multiplying both sides of the equation by 80, we get 8x + 10x = 80. Therefore, 18x = 80 and so x = 80/18 = 0/9. Thus, together the pumps can drain the pool in 9 hours. 18.(a) First, x 3 6x 2 + 8x = x(x 2)(x ). Therefore, x(x 2)(x ) = 0. Thus, the solutions are x = 0, x = 2 and x =. (b) Factor by grouping: x 2 (5x + 6) 16(5x + 6) = 0, or (x 2 16)(5x + 6) = 0. Therefore, x =, x = or x = 6/5 19. Write the equation as x 1 = 2x 8 so that the radical is alone on one side of the equation. Squaring both sides of this equation, we get x 1 = x 2 32x + 6, bringing everything to one side yields x 2 36x + 65 = 0. Factoring this quadratic, one obtains (2x 5)(2x 13) = 0. Thus the proposed solutions are x = 5 13 and x = 2 2. Plugging x = 5 back into the original 2 equation leads to 3 = 3, hence 5 13 is not a solution. Plunging x = into the original equation 2 2 leads to 5 = 5, and so it is a solution. Therefore, the original equation has solution x =
6 20. (a) 1 5x 6 < 9 is equivalent to 5 5x < 15 (by adding 6 to all sides of the inequality), which in turn is equivalent to 1 x > 3 (dividing by 3 on all sides). Therefore, the solution, in interval notation, is ( 3, 1]. (b) Let x represent the percentage on the final test. Then 75 (.7)(92) + (.3)x 85, i.e., x 85. Subtracting 6. from each side yields x Dividing each side by.3 leads to x Thus the student needs between 35.33% and 68.67% on the final exam. 21. x 2 10 is equivalent to x 2 10 or x Solving these individually leads to x 2 or x 3. In interval notation, the answer is: (, 2] [3, ). 22. (, ) because an absolute value is always larger than a negative number. 23., the emptyset, because an absolute value is never negative. 2. 6x + 3 < 15 is equivalent to 15 < 6x + 3 < 15 which leads to 3 < x < 2, or in interval notation: ( 3, 2). 25. x 2 < x + 30 is equivalent to x 2 + x 30 < 0, or (x + 6)(x 5) < 0. The critical values are 5 and 6. Next use a sign chart: x < 6 x = 6 6 < x < 5 x = 5 5 < x x + 6 neg 0 pos pos pos x 5 neg neg neg 0 pos (x + 6)(x 5) pos 0 neg 0 pos The inequality is true when the product is negative, thus the solution in interval notation is found to be ( 6, 5). 26. The inequality x + 1 x 2 yields x + 5 x 2 using this information. x is equivalent to 2 0. Simplifying the left hand side, x 2 0. Thus the critical values are x = 2 and x = 5. Next create a sign chart x < 2 x = 2 2 < x < 5 x = 5 5 < x x 2 neg 0 pos pos pos x + 5 pos pos pos 0 neg x + 5 x 2 neg und pos 0 neg In interval notation the solution is (2, 5]. 6
7 27. The problem suggest v 0 = 80 and s 0 = 33. Thus s = 16t t We then solve the inequality 16t t + 33 > 97. Thus 16t t 6 > 0 and multiplying both sides by 1 we have 16t 2 80t + 6 < 0 and dividing by 16 yields t 2 5t + < 0 and factoring gives us (t )(t 1) < 0. The critical values are 1 and. t < 1 t = 1 1 < t < t = < t t 1 neg 0 pos pos pos t neg neg neg 0 pos (t 1)(t ) pos 0 neg 0 pos Thus the inequality is true when 1 < t <. That is the ball is more than 97 feet above the ground between 1 second and seconds after it was thrown. 28. We look for when the expression is positive or 0 (note it is undefined at x = and it is 0 when x = 2 or x = 1), so we use the sign chart: x < 1 x = 1 1 < x < 2 x = 2 2 < x < x = < x x + 1 neg 0 pos pos pos pos pos x 2 neg neg neg 0 pos pos pos x neg neg neg neg neg 0 pos (x 2)(x + 1) x neg 0 pos 0 neg und pos Thus the inequality is true when 1 x 2 or when x >. In interval notation, the answer is [ 1, 2] (, ) 29. The combined variation equation is L = kd. To find k we plug in the given values: h2 6 = k2. Therefore, k = 600/16 = Now, if a column has a diameter of 3 feet and a 102 height of 1 feet, it can support up to L = (37.5)(3 ) tons. 30. Increases by a factor of 2, i.e., can support a weight 16 times greater. 7
8 31. Under these parameters, the modified column could support (.5) th of the weight of the 32 original column, that is, it can support only 1 of the amount of weight (a) Use the relation I = k where I is the sound intensity,and d is the distance from d2 the engine to the ramp meter. For the given data, k = (0.5)(25) = Thus the intensity when d = 11 is I = Thus to three decimal places, the sound intensity is W/m 2. (b) (i) If the distance doubles, the sound intenisty is one-quarter of the original intensity. (ii) If the distance triples, the sound intensity will be one-ninth of the original intensity. We obtain this from I = k, and so replacing the distance with 3d we obtain d2 I = which is 1/9 of the original intensity. k (3d) 2 = k 9d = k d The relation is L = kwd2 l new beam can support. We use 600 = k(6)(82 ) 1 L = 700(5.5)(62 ) 32(16) to find k = (1)(600) (6)(6) Thus the new beam can support approximately 271 pounds. = 700. Thus the 32 8
Math 121, Chapter 1 and Complex Numbers Practice Questions Hints and Answers. 2. Multiply numerator and denominator by complex conjugate and simplify:
 Math 2, Chapter and Complex Numbers Practice Questions Hints and Answers (a) (3 2i)( + i) = 2 + 3i 8i 2i 2 = 2 5i 2( ) = 5i (b) i 223 = (i ) 55 (i 3 ) = i 2 Multiply numerator and denominator by complex
Math 2, Chapter and Complex Numbers Practice Questions Hints and Answers (a) (3 2i)( + i) = 2 + 3i 8i 2i 2 = 2 5i 2( ) = 5i (b) i 223 = (i ) 55 (i 3 ) = i 2 Multiply numerator and denominator by complex
1 Linear and Absolute Value Equations
 1 Linear and Absolute Value Equations 1. Solve the equation 11x + 6 = 7x + 15. Solution: Use properties of equality to bring the x s to one side and the numbers to the other: 11x (7x) + 6 = 7x (7x) + 15
1 Linear and Absolute Value Equations 1. Solve the equation 11x + 6 = 7x + 15. Solution: Use properties of equality to bring the x s to one side and the numbers to the other: 11x (7x) + 6 = 7x (7x) + 15
Answers to Sample Exam Problems
 Math Answers to Sample Exam Problems () Find the absolute value, reciprocal, opposite of a if a = 9; a = ; Absolute value: 9 = 9; = ; Reciprocal: 9 ; ; Opposite: 9; () Commutative law; Associative law;
Math Answers to Sample Exam Problems () Find the absolute value, reciprocal, opposite of a if a = 9; a = ; Absolute value: 9 = 9; = ; Reciprocal: 9 ; ; Opposite: 9; () Commutative law; Associative law;
Final Exam Review for DMAT 0310
 Final Exam Review for DMAT 010 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Factor the polynomial completely. What is one of the factors? 1) x
Final Exam Review for DMAT 010 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Factor the polynomial completely. What is one of the factors? 1) x
Chapter 1 Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter Equations and Inequalities Section.. +. (r ) + (r ) r + r r r r. +. + + +. ( ) ( ) +. +.. +........ +.().( + ) +. +...... ( + )( ) (+ )( ) ( ) + + + +. [ ( )] ( + ) ( + ) + +. + ( ) + Conditional
Chapter Equations and Inequalities Section.. +. (r ) + (r ) r + r r r r. +. + + +. ( ) ( ) +. +.. +........ +.().( + ) +. +...... ( + )( ) (+ )( ) ( ) + + + +. [ ( )] ( + ) ( + ) + +. + ( ) + Conditional
Math 110 Final Exam Review Revised December 2015
 Math 110 Final Exam Review Revised December 2015 Factor out the GCF from each polynomial. 1) 60x - 15 2) 7x 8 y + 42x 6 3) x 9 y 5 - x 9 y 4 + x 7 y 2 - x 6 y 2 Factor each four-term polynomial by grouping.
Math 110 Final Exam Review Revised December 2015 Factor out the GCF from each polynomial. 1) 60x - 15 2) 7x 8 y + 42x 6 3) x 9 y 5 - x 9 y 4 + x 7 y 2 - x 6 y 2 Factor each four-term polynomial by grouping.
INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3
 INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3 Evaluate the epression. ) a) 73 (-4)2-44 d) 4-3 e) (-)0 f) -90 g) 23 2-4 h) (-2)4 80 i) (-2)5 (-2)-7 j) 5-6 k) 3-2 l) 5-2 Simplify the epression. Write your answer
INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3 Evaluate the epression. ) a) 73 (-4)2-44 d) 4-3 e) (-)0 f) -90 g) 23 2-4 h) (-2)4 80 i) (-2)5 (-2)-7 j) 5-6 k) 3-2 l) 5-2 Simplify the epression. Write your answer
Chapter 1 Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter Equations and Inequalities Section.. +. +. ( ) ( ) +. (r ) + (r ) r + r r r r. + + +. +.. +........ +.().( + ) +. +...... ( + )( ) (+ )( ) + ( ) + + +. [ ( )] ( + ) ( + ) + +. + ( ) + Conditional
Chapter Equations and Inequalities Section.. +. +. ( ) ( ) +. (r ) + (r ) r + r r r r. + + +. +.. +........ +.().( + ) +. +...... ( + )( ) (+ )( ) + ( ) + + +. [ ( )] ( + ) ( + ) + +. + ( ) + Conditional
Math 110 Final Exam Review Revised October 2018
 Math 110 Final Exam Review Revised October 2018 Factor out the GCF from each polynomial. 1) 60x - 15 2) 7x 8 y + 42x 6 3) x 9 y 5 - x 9 y 4 + x 7 y 2 - x 6 y 2 Factor each four-term polynomial by grouping.
Math 110 Final Exam Review Revised October 2018 Factor out the GCF from each polynomial. 1) 60x - 15 2) 7x 8 y + 42x 6 3) x 9 y 5 - x 9 y 4 + x 7 y 2 - x 6 y 2 Factor each four-term polynomial by grouping.
My Math Plan Assessment #1 Study Guide
 My Math Plan Assessment #1 Study Guide 1. Find the x-intercept and the y-intercept of the linear equation. 8x y = 4. Use factoring to solve the quadratic equation. x + 9x + 1 = 17. Find the difference.
My Math Plan Assessment #1 Study Guide 1. Find the x-intercept and the y-intercept of the linear equation. 8x y = 4. Use factoring to solve the quadratic equation. x + 9x + 1 = 17. Find the difference.
Final Exam Review: Study Guide Math 3
 Final Exam Review: Study Guide Math 3 Name: Day 1 Functions, Graphing, Regression Relation: Function: Domain: Range: Asymptote: Hole: Graphs of Functions f(x) = x f(x) = f(x) = x f(x) = x 3 Key Ideas Key
Final Exam Review: Study Guide Math 3 Name: Day 1 Functions, Graphing, Regression Relation: Function: Domain: Range: Asymptote: Hole: Graphs of Functions f(x) = x f(x) = f(x) = x f(x) = x 3 Key Ideas Key
For problems 1 4, evaluate each expression, if possible. Write answers as integers or simplified fractions
 / MATH 05 TEST REVIEW SHEET TO THE STUDENT: This Review Sheet gives you an outline of the topics covered on Test as well as practice problems. Answers are at the end of the Review Sheet. I. EXPRESSIONS
/ MATH 05 TEST REVIEW SHEET TO THE STUDENT: This Review Sheet gives you an outline of the topics covered on Test as well as practice problems. Answers are at the end of the Review Sheet. I. EXPRESSIONS
3 Inequalities Absolute Values Inequalities and Intervals... 18
 Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 1. Factoring Polynomials........................................ 1. Algebraic and Fractional
Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 1. Factoring Polynomials........................................ 1. Algebraic and Fractional
Math Departmental Exit Assessment Review (Student Version)
 Math 03 - Departmental Eit Assessment Review (Student Version) Factor completel. (Factoring Review) ) 6-6 - 0 ) 3-343 3) 3 - + 8-40 4) - 36 ) + - 6 + 9 + 8 - + + Add or subtract as indicated. Simplif completel.
Math 03 - Departmental Eit Assessment Review (Student Version) Factor completel. (Factoring Review) ) 6-6 - 0 ) 3-343 3) 3 - + 8-40 4) - 36 ) + - 6 + 9 + 8 - + + Add or subtract as indicated. Simplif completel.
Math 060/Final Exam Review Guide/ / College of the Canyons
 Math 060/Final Exam Review Guide/ 010-011/ College of the Canyons General Information: The final exam is a -hour timed exam. There will be approximately 40 questions. There will be no calculators or notes
Math 060/Final Exam Review Guide/ 010-011/ College of the Canyons General Information: The final exam is a -hour timed exam. There will be approximately 40 questions. There will be no calculators or notes
Math Exam Jam Solutions. Contents. 1 Linear Inequalities and Absolute Value Equations 2
 Math 11100 Exam Jam Solutions Contents 1 Linear Inequalities and Absolute Value Equations 2 2 Linear Equations, Graphing and Solving Systems of Equations 4 3 Polynomials and Rational Expressions 13 4 Radical
Math 11100 Exam Jam Solutions Contents 1 Linear Inequalities and Absolute Value Equations 2 2 Linear Equations, Graphing and Solving Systems of Equations 4 3 Polynomials and Rational Expressions 13 4 Radical
MAT 1033 Final Review for Intermediate Algebra (Revised April 2013)
 1 This review corresponds to the Charles McKeague textbook. Answers will be posted separately. Section 2.1: Solve a Linear Equation in One Variable 1. Solve: " = " 2. Solve: "# = " 3. Solve: " " = " Section
1 This review corresponds to the Charles McKeague textbook. Answers will be posted separately. Section 2.1: Solve a Linear Equation in One Variable 1. Solve: " = " 2. Solve: "# = " 3. Solve: " " = " Section
Lesson
 Lesson 28 Zeros of a function: - the inputs that make the function equal to zero (same values as the x- coordinates of the x-intercepts) o if ( ), ( ) when o zeros are 2 and - when a function is graphed,
Lesson 28 Zeros of a function: - the inputs that make the function equal to zero (same values as the x- coordinates of the x-intercepts) o if ( ), ( ) when o zeros are 2 and - when a function is graphed,
My Math Plan Assessment #2 Study Guide
 My Math Plan Assessment #2 Study Guide 1. Find the x-intercept and the y-intercept of the linear equation. 8x y = 4 2. Use factoring to solve the quadratic equation. x 2 + 9x + 1 = 17. Multiply and simplify
My Math Plan Assessment #2 Study Guide 1. Find the x-intercept and the y-intercept of the linear equation. 8x y = 4 2. Use factoring to solve the quadratic equation. x 2 + 9x + 1 = 17. Multiply and simplify
= = =
 . D - To evaluate the expression, we can regroup the numbers and the powers of ten, multiply, and adjust the decimal and exponent to put the answer in correct scientific notation format: 5 0 0 7 = 5 0
. D - To evaluate the expression, we can regroup the numbers and the powers of ten, multiply, and adjust the decimal and exponent to put the answer in correct scientific notation format: 5 0 0 7 = 5 0
MAT Intermediate Algebra - Final Exam Review Textbook: Beginning & Intermediate Algebra, 5th Ed., by Martin-Gay
 MAT0 - Intermediate Algebra - Final Eam Review Tetbook: Beginning & Intermediate Algebra, 5th Ed., by Martin-Gay Section 2. Solve the equation. ) 9 - ( - ) = 2 Section 2.8 Solve the inequality. Graph the
MAT0 - Intermediate Algebra - Final Eam Review Tetbook: Beginning & Intermediate Algebra, 5th Ed., by Martin-Gay Section 2. Solve the equation. ) 9 - ( - ) = 2 Section 2.8 Solve the inequality. Graph the
Algebra 1. Math Review Packet. Equations, Inequalities, Linear Functions, Linear Systems, Exponents, Polynomials, Factoring, Quadratics, Radicals
 Algebra 1 Math Review Packet Equations, Inequalities, Linear Functions, Linear Systems, Exponents, Polynomials, Factoring, Quadratics, Radicals 2017 Math in the Middle 1. Clear parentheses using the distributive
Algebra 1 Math Review Packet Equations, Inequalities, Linear Functions, Linear Systems, Exponents, Polynomials, Factoring, Quadratics, Radicals 2017 Math in the Middle 1. Clear parentheses using the distributive
Skill: determine an approximate value of a radical expression using a variety of methods.
 Skill: determine an approximate value of a radical expression using a variety of methods. N.RN.A. Extend the properties of exponents to rational exponents. Rewrite expressions involving radicals and rational
Skill: determine an approximate value of a radical expression using a variety of methods. N.RN.A. Extend the properties of exponents to rational exponents. Rewrite expressions involving radicals and rational
CCR Math - Grade 7 Practice Test
 R Math - Grade 7 Practice Test You may use a calculator for questions -7.. Use the picture below to answer the question. A B What is the probability of spinning a? A. B.. D. 5 3 5 3 5 A 3 Go on to the
R Math - Grade 7 Practice Test You may use a calculator for questions -7.. Use the picture below to answer the question. A B What is the probability of spinning a? A. B.. D. 5 3 5 3 5 A 3 Go on to the
Solving Problems with Labeled Numbers
 Solving Problems with Labeled Numbers When solving problems with labeled numbers (those with units such as grams or liters), the labels are treated in the same way as P or y in algebra. The problem is
Solving Problems with Labeled Numbers When solving problems with labeled numbers (those with units such as grams or liters), the labels are treated in the same way as P or y in algebra. The problem is
MATH 125 ELAC SPRING 2018 TEST 3 TAKE HOME NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 125 ELAC SPRING 2018 TEST 3 TAKE HOME NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Write an equation of the circle with the given center
MATH 125 ELAC SPRING 2018 TEST 3 TAKE HOME NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Write an equation of the circle with the given center
Chapter 1 Notes: Quadratic Functions
 19 Chapter 1 Notes: Quadratic Functions (Textbook Lessons 1.1 1.2) Graphing Quadratic Function A function defined by an equation of the form, The graph is a U-shape called a. Standard Form Vertex Form
19 Chapter 1 Notes: Quadratic Functions (Textbook Lessons 1.1 1.2) Graphing Quadratic Function A function defined by an equation of the form, The graph is a U-shape called a. Standard Form Vertex Form
Big Ideas: determine an approximate value of a radical expression using a variety of methods. REVIEW Radicals
 Big Ideas: determine an approximate value of a radical expression using a variety of methods. REVIEW N.RN. Rewrite expressions involving radicals and rational exponents using the properties of exponents.
Big Ideas: determine an approximate value of a radical expression using a variety of methods. REVIEW N.RN. Rewrite expressions involving radicals and rational exponents using the properties of exponents.
2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
 .1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions A term is a number or the product of a number and variables raised to powers. The numerical coefficient of a term is the numerical factor. The numerical coefficient
.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions A term is a number or the product of a number and variables raised to powers. The numerical coefficient of a term is the numerical factor. The numerical coefficient
6 th Grade Math. Full Curriculum Book. Sample file. A+ Interactive Math (by A+ TutorSoft, Inc.)
 6 th Grade Math Full Curriculum Book Release 7 A+ Interactive Math (by A+ TutorSoft, Inc.) Email: info@aplustutorsoft.com www.aplustutorsoft.com Page 3 of 518 Copyright 2014 A+ TutorSoft Inc., All Rights
6 th Grade Math Full Curriculum Book Release 7 A+ Interactive Math (by A+ TutorSoft, Inc.) Email: info@aplustutorsoft.com www.aplustutorsoft.com Page 3 of 518 Copyright 2014 A+ TutorSoft Inc., All Rights
Solving Multi-Step Equations
 1. Clear parentheses using the distributive property. 2. Combine like terms within each side of the equal sign. Solving Multi-Step Equations 3. Add/subtract terms to both sides of the equation to get the
1. Clear parentheses using the distributive property. 2. Combine like terms within each side of the equal sign. Solving Multi-Step Equations 3. Add/subtract terms to both sides of the equation to get the
lsolve. 25(x + 3)2-2 = 0
 II nrm!: lsolve. 25(x + 3)2-2 = 0 ISolve. 4(x - 7) 2-5 = 0 Isolate the squared term. Move everything but the term being squared to the opposite side of the equal sign. Use opposite operations. Isolate
II nrm!: lsolve. 25(x + 3)2-2 = 0 ISolve. 4(x - 7) 2-5 = 0 Isolate the squared term. Move everything but the term being squared to the opposite side of the equal sign. Use opposite operations. Isolate
DIRECT, JOINT, AND INVERSE VARIATION
 DIRECT, JOINT, AND INVERSE VARIATION DIRECT VARIATION A linear equation of the form y = kx with k! 0 is called direct variation. The variable y varies directly with the variable x. In other words, the
DIRECT, JOINT, AND INVERSE VARIATION DIRECT VARIATION A linear equation of the form y = kx with k! 0 is called direct variation. The variable y varies directly with the variable x. In other words, the
Mt. Douglas Secondary
 Foundations of Math 11 Section 7.3 Quadratic Equations 31 7.3 Quadratic Equations Quadratic Equation Definition of a Quadratic Equation An equation that can be written in the form ax + bx + c = 0 where
Foundations of Math 11 Section 7.3 Quadratic Equations 31 7.3 Quadratic Equations Quadratic Equation Definition of a Quadratic Equation An equation that can be written in the form ax + bx + c = 0 where
Solve. Label any contradictions or identities. 1) -4x + 2(3x - 3) = 5-9x. 2) 7x - (3x - 1) = 2. 3) 2x 5 - x 3 = 2 4) 15. 5) -4.2q =
 Spring 2011 Name Math 115 Elementary Algebra Review Wednesday, June 1, 2011 All problems must me done on 8.5" x 11" lined paper. Solve. Label any contradictions or identities. 1) -4x + 2(3x - 3) = 5-9x
Spring 2011 Name Math 115 Elementary Algebra Review Wednesday, June 1, 2011 All problems must me done on 8.5" x 11" lined paper. Solve. Label any contradictions or identities. 1) -4x + 2(3x - 3) = 5-9x
North Seattle Community College Math 084 Chapter 1 Review. Perform the operation. Write the product using exponents.
 North Seattle Community College Math 084 Chapter 1 Review For the test, be sure to show all work! Turn off cell phones. Perform the operation. Perform the operation. Write the product using exponents.
North Seattle Community College Math 084 Chapter 1 Review For the test, be sure to show all work! Turn off cell phones. Perform the operation. Perform the operation. Write the product using exponents.
CHAPTER 1 Equations, Inequalities, and Mathematical Modeling
 CHAPTER Equations, Inequalities, and Mathematical Modeling Section. Graphs of Equations.................... 9 Section. Linear Equations in One Variable............. Section. Modeling with Linear Equations..............
CHAPTER Equations, Inequalities, and Mathematical Modeling Section. Graphs of Equations.................... 9 Section. Linear Equations in One Variable............. Section. Modeling with Linear Equations..............
Important: You must show your work on a separate sheet of paper. 1. There are 2 red balls and 5 green balls. Write the ratio of red to green balls.
 Math Department Math Summer Packet: Incoming 8 th -Graders, 2018-2019 Student Name: Period: Math Teacher: Important: You must show your work on a separate sheet of paper. Remember: It is important to arrive
Math Department Math Summer Packet: Incoming 8 th -Graders, 2018-2019 Student Name: Period: Math Teacher: Important: You must show your work on a separate sheet of paper. Remember: It is important to arrive
Math 120 online. Practice Midterm Exam #2 Prof. Kinoshita. Fall (Actual midterm will have 100 pts)
 Note: The format of this practice midterm will be similar to the real midterm. However, the actual midterm will have less questions and be worth 100 points. There will also be more room to work on the
Note: The format of this practice midterm will be similar to the real midterm. However, the actual midterm will have less questions and be worth 100 points. There will also be more room to work on the
( 3x 2 y) 6 (6x 3 y 2 ) x 4 y 4 b.
 1. Simplify 3 x 5 4 64x Algebra Practice Problems for MDPT Pre Calculus a. 1 18x 10 b. 7 18x 7 c. x 6 3x d. 8x 1 x 4. Solve 1 (x 3) + x 3 = 3 4 (x 1) + 1 9 a. 77 51 b. 3 17 c. 3 17 d. 3 51 3. Simplify
1. Simplify 3 x 5 4 64x Algebra Practice Problems for MDPT Pre Calculus a. 1 18x 10 b. 7 18x 7 c. x 6 3x d. 8x 1 x 4. Solve 1 (x 3) + x 3 = 3 4 (x 1) + 1 9 a. 77 51 b. 3 17 c. 3 17 d. 3 51 3. Simplify
1) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-1) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-1)(2) =
 Extra Practice for Lesson Add or subtract. ) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = Multiply. 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-)(2) = Division is
Extra Practice for Lesson Add or subtract. ) (-3) + (-6) = 2) (2) + (-5) = 3) (-7) + (-) = 4) (-3) - (-6) = 5) (+2) - (+5) = 6) (-7) - (-4) = Multiply. 7) (5)(-4) = 8) (-3)(-6) = 9) (-)(2) = Division is
degree -6x 3 + 5x 3 Coefficients:
 Date P3 Polynomials and Factoring leading coefficient degree -6 3 + 5 3 constant term coefficients Degree: the largest sum of eponents in a term Polynomial: a n n + a n-1 n-1 + + a 1 + a 0 where a n 0
Date P3 Polynomials and Factoring leading coefficient degree -6 3 + 5 3 constant term coefficients Degree: the largest sum of eponents in a term Polynomial: a n n + a n-1 n-1 + + a 1 + a 0 where a n 0
CURRICULUM CATALOG MATHEMATICS 1 (21032X0) NC
 2018-19 CURRICULUM CATALOG MATHEMATICS 1 (21032X0) NC Table of Contents MATHEMATICS 1 (21032X0) NC COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: FOUNDATIONS OF ALGEBRA... 1 UNIT 2: EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES... 1 UNIT
2018-19 CURRICULUM CATALOG MATHEMATICS 1 (21032X0) NC Table of Contents MATHEMATICS 1 (21032X0) NC COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: FOUNDATIONS OF ALGEBRA... 1 UNIT 2: EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES... 1 UNIT
Study Guide For use with pages 63 68
 2.1 For use with pages 63 68 GOAL Use properties of addition and multiplication. VOCABULARY Lesson 2.1 Commutative Property of Addition: In a sum, you can add the numbers in any order. Associative Property
2.1 For use with pages 63 68 GOAL Use properties of addition and multiplication. VOCABULARY Lesson 2.1 Commutative Property of Addition: In a sum, you can add the numbers in any order. Associative Property
Math 096--Quadratic Formula page 1
 Math 096--Quadratic Formula page 1 A Quadratic Formula. Use the quadratic formula to solve quadratic equations ax + bx + c = 0 when the equations can t be factored. To use the quadratic formula, the equation
Math 096--Quadratic Formula page 1 A Quadratic Formula. Use the quadratic formula to solve quadratic equations ax + bx + c = 0 when the equations can t be factored. To use the quadratic formula, the equation
South Brunswick Schools
 South Brunswick Schools Summer Packet For Rising Honors Algebra students Directions: All students entering Honors Algebra are expected to be proficient in all their previously-learned algebra and geometry
South Brunswick Schools Summer Packet For Rising Honors Algebra students Directions: All students entering Honors Algebra are expected to be proficient in all their previously-learned algebra and geometry
Algebra I. Course Requirements
 Algebra I Algebra I is a full year, high school credit course that is intended for the student who has successfully mastered the core algebraic concepts covered in the prerequisite course, Pre- Algebra.
Algebra I Algebra I is a full year, high school credit course that is intended for the student who has successfully mastered the core algebraic concepts covered in the prerequisite course, Pre- Algebra.
Curriculum Catalog
 2016-2017 Curriculum Catalog 2016 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents ALGEBRA I FUNDAMENTALS COURSE OVERVIEW... ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED. UNIT 1: FOUNDATIONS OF ALGEBRA... ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
2016-2017 Curriculum Catalog 2016 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents ALGEBRA I FUNDAMENTALS COURSE OVERVIEW... ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED. UNIT 1: FOUNDATIONS OF ALGEBRA... ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
1.2 Constructing Models to Solve Problems
 1.2 Constructing Models to Solve Problems In the previous section, we learned how to solve linear equations. In this section, we will put those skills to use in order to solve a variety of application
1.2 Constructing Models to Solve Problems In the previous section, we learned how to solve linear equations. In this section, we will put those skills to use in order to solve a variety of application
PAP Geometry Summer Assignment 2017
 PAP Geometry Summer Assignment 2017 Name This assignment should be completed without the use of a calculator or an EOC chart. Show all work on separate paper for credit. A. Solve. Leave answers as improper
PAP Geometry Summer Assignment 2017 Name This assignment should be completed without the use of a calculator or an EOC chart. Show all work on separate paper for credit. A. Solve. Leave answers as improper
Review for Mastery. Integer Exponents. Zero Exponents Negative Exponents Negative Exponents in the Denominator. Definition.
 LESSON 6- Review for Mastery Integer Exponents Remember that means 8. The base is, the exponent is positive. Exponents can also be 0 or negative. Zero Exponents Negative Exponents Negative Exponents in
LESSON 6- Review for Mastery Integer Exponents Remember that means 8. The base is, the exponent is positive. Exponents can also be 0 or negative. Zero Exponents Negative Exponents Negative Exponents in
MATH 121: EXTRA PRACTICE FOR TEST 2. Disclaimer: Any material covered in class and/or assigned for homework is a fair game for the exam.
 MATH 121: EXTRA PRACTICE FOR TEST 2 Disclaimer: Any material covered in class and/or assigned for homework is a fair game for the exam. 1 Linear Functions 1. Consider the functions f(x) = 3x + 5 and g(x)
MATH 121: EXTRA PRACTICE FOR TEST 2 Disclaimer: Any material covered in class and/or assigned for homework is a fair game for the exam. 1 Linear Functions 1. Consider the functions f(x) = 3x + 5 and g(x)
a 17 9 d rt 700 (72)t P 2L 2W 19 2L 2(3) L 13 A LW 50 12W W 50 9a a a a 17 9a / 9 17 / 9 9a
 Free Pre-Algebra Lesson 0 page Lesson 0 Equations with Fractions Here we practice solving equations that involve fractions. The Solution is A Fraction Even equations with all whole numbers can have a fraction
Free Pre-Algebra Lesson 0 page Lesson 0 Equations with Fractions Here we practice solving equations that involve fractions. The Solution is A Fraction Even equations with all whole numbers can have a fraction
Polynomials 370 UNIT 10 WORKING WITH POLYNOMIALS. The railcars are linked together.
 UNIT 10 Working with Polynomials The railcars are linked together. 370 UNIT 10 WORKING WITH POLYNOMIALS Just as a train is built from linking railcars together, a polynomial is built by bringing terms
UNIT 10 Working with Polynomials The railcars are linked together. 370 UNIT 10 WORKING WITH POLYNOMIALS Just as a train is built from linking railcars together, a polynomial is built by bringing terms
QUEEN ELIZABETH REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS 2201 MIDTERM EXAM
 QUEEN ELIZABETH REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS 0 MIDTERM EXAM JANUARY 0 NAME: TIME: HOURS 0 MINUTES ( INCLUDES EXTRA TIME ) PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE ( Value: 0 % ) Shade the letter of the correct response
QUEEN ELIZABETH REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS 0 MIDTERM EXAM JANUARY 0 NAME: TIME: HOURS 0 MINUTES ( INCLUDES EXTRA TIME ) PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE ( Value: 0 % ) Shade the letter of the correct response
Algebra I Unit Report Summary
 Algebra I Unit Report Summary No. Objective Code NCTM Standards Objective Title Real Numbers and Variables Unit - ( Ascend Default unit) 1. A01_01_01 H-A-B.1 Word Phrases As Algebraic Expressions 2. A01_01_02
Algebra I Unit Report Summary No. Objective Code NCTM Standards Objective Title Real Numbers and Variables Unit - ( Ascend Default unit) 1. A01_01_01 H-A-B.1 Word Phrases As Algebraic Expressions 2. A01_01_02
STUDY GUIDE FOR TEST 2. Project 3: Fill in the blanks and do the assigned questions. 11/6/07
 STUDY GUIDE FOR TEST 2 Name: Project 3: Fill in the blanks and do the assigned questions. 11/6/07 Quadrant II Quadrant I ORDERED PAIR: The first number in the ordered pair is the -coordinate and the second
STUDY GUIDE FOR TEST 2 Name: Project 3: Fill in the blanks and do the assigned questions. 11/6/07 Quadrant II Quadrant I ORDERED PAIR: The first number in the ordered pair is the -coordinate and the second
Curriculum Catalog
 2017-2018 Curriculum Catalog 2017 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents ALGEBRA I COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: FOUNDATIONS OF ALGEBRA... 1 UNIT 2: LINEAR EQUATIONS... 2 UNIT 3: FUNCTIONS... 2 UNIT 4: INEQUALITIES...
2017-2018 Curriculum Catalog 2017 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents ALGEBRA I COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: FOUNDATIONS OF ALGEBRA... 1 UNIT 2: LINEAR EQUATIONS... 2 UNIT 3: FUNCTIONS... 2 UNIT 4: INEQUALITIES...
The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide
 The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide Copyright 007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Ch. Numerical Operations - Integers... - Fractions... - Proportion and Percent...
The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide Copyright 007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Ch. Numerical Operations - Integers... - Fractions... - Proportion and Percent...
CAHSEE on Target UC Davis, School and University Partnerships
 UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 2006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
UC Davis, School and University Partnerships CAHSEE on Target Mathematics Curriculum Published by The University of California, Davis, School/University Partnerships Program 2006 Director Sarah R. Martinez,
= 9 = x + 8 = = -5x 19. For today: 2.5 (Review) and. 4.4a (also review) Objectives:
 Math 65 / Notes & Practice #1 / 20 points / Due. / Name: Home Work Practice: Simplify the following expressions by reducing the fractions: 16 = 4 = 8xy =? = 9 40 32 38x 64 16 Solve the following equations
Math 65 / Notes & Practice #1 / 20 points / Due. / Name: Home Work Practice: Simplify the following expressions by reducing the fractions: 16 = 4 = 8xy =? = 9 40 32 38x 64 16 Solve the following equations
All work must be shown or no credit will be awarded. Box all answers!! Order of Operations
 Steps: All work must be shown or no credit will be awarded. Box all answers!! Order of Operations 1. Do operations that occur within grouping symbols. If there is more than one set of symbols, work from
Steps: All work must be shown or no credit will be awarded. Box all answers!! Order of Operations 1. Do operations that occur within grouping symbols. If there is more than one set of symbols, work from
, passing through the point 4, 2
 MATD 090 INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA Review for Test Test covers all cumulative material, including new sections.-.8,.-.,.6-.7, and 6.-6.. Bring a non-graphing calculator and something to write with and erase
MATD 090 INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA Review for Test Test covers all cumulative material, including new sections.-.8,.-.,.6-.7, and 6.-6.. Bring a non-graphing calculator and something to write with and erase
Intermediate Algebra Semester Summary Exercises. 1 Ah C. b = h
 . Solve: 3x + 8 = 3 + 8x + 3x A. x = B. x = 4 C. x = 8 8 D. x =. Solve: w 3 w 5 6 8 A. w = 4 B. w = C. w = 4 D. w = 60 3. Solve: 3(x ) + 4 = 4(x + ) A. x = 7 B. x = 5 C. x = D. x = 4. The perimeter of
. Solve: 3x + 8 = 3 + 8x + 3x A. x = B. x = 4 C. x = 8 8 D. x =. Solve: w 3 w 5 6 8 A. w = 4 B. w = C. w = 4 D. w = 60 3. Solve: 3(x ) + 4 = 4(x + ) A. x = 7 B. x = 5 C. x = D. x = 4. The perimeter of
Unit 1 - INTRODUCTION MEDICAL MATH Listening guide
 Unit 1 - INTRODUCTION MEDICAL MATH Listening guide Name Period 1. List one important reason that healthcare workers must be proficient in math. 2. Number forms: 3. Basic math: Counting numbers and zero
Unit 1 - INTRODUCTION MEDICAL MATH Listening guide Name Period 1. List one important reason that healthcare workers must be proficient in math. 2. Number forms: 3. Basic math: Counting numbers and zero
5. 2. The solution set is 7 6 i, 7 x. Since b = 20, add
 Chapter : Quadratic Equations and Functions Chapter Review Eercises... 5 8 6 8 The solution set is 8, 8. 5 5 5 5 5 5 The solution set is 5,5. Rationalize the denominator. 6 The solution set is. 8 8 9 6
Chapter : Quadratic Equations and Functions Chapter Review Eercises... 5 8 6 8 The solution set is 8, 8. 5 5 5 5 5 5 The solution set is 5,5. Rationalize the denominator. 6 The solution set is. 8 8 9 6
MTH 111 Fall 2017 Mathematics Department Missouri State University-West Plains
 MTH 111 Fall 2017 Mathematics Department Missouri State University-West Plains 2 MTH 111 Unit Objectives Unit 1: 1. Simplify numeric expressions using the Order of Operations. 2. Simplify variable expressions
MTH 111 Fall 2017 Mathematics Department Missouri State University-West Plains 2 MTH 111 Unit Objectives Unit 1: 1. Simplify numeric expressions using the Order of Operations. 2. Simplify variable expressions
Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 3.1 Power and Polynomial Functions 155 Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions Section 3.1 Power Functions & Polynomial Functions... 155 Section 3. Quadratic Functions... 163 Section 3.3 Graphs of
3.1 Power and Polynomial Functions 155 Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions Section 3.1 Power Functions & Polynomial Functions... 155 Section 3. Quadratic Functions... 163 Section 3.3 Graphs of
CHAPTER 8 Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities
 CHAPTER Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities Section. Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring and Special Forms..................... 7 Section. Completing the Square................... 9 Section.
CHAPTER Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities Section. Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring and Special Forms..................... 7 Section. Completing the Square................... 9 Section.
EX: Simplify the expression. EX: Simplify the expression. EX: Simplify the expression
 SIMPLIFYING RADICALS EX: Simplify the expression 84x 4 y 3 1.) Start by creating a factor tree for the constant. In this case 84. Keep factoring until all of your nodes are prime. Two factor trees are
SIMPLIFYING RADICALS EX: Simplify the expression 84x 4 y 3 1.) Start by creating a factor tree for the constant. In this case 84. Keep factoring until all of your nodes are prime. Two factor trees are
Math 141. Chapter 1: Equations and Inequalities. Notes. Name...
 Math 141 Chapter 1: Equations and Inequalities Notes Name... 1 1.1 The Coordinate Plane Graphing Regions in the Coordinate Plane 1. Example: Sketch the region given by the set (a) {(x, y) x = 3} (b) {(x,
Math 141 Chapter 1: Equations and Inequalities Notes Name... 1 1.1 The Coordinate Plane Graphing Regions in the Coordinate Plane 1. Example: Sketch the region given by the set (a) {(x, y) x = 3} (b) {(x,
B) 75k k D) 75k k C) 3 5
 Fall 018 Preview Exam Math 110 This is only provided to you are a resource to help you practice and prepare for an upcoming exam. It is not a contract of inclusion and/or exclusion. You are still responsible
Fall 018 Preview Exam Math 110 This is only provided to you are a resource to help you practice and prepare for an upcoming exam. It is not a contract of inclusion and/or exclusion. You are still responsible
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 3 from the book Advanced Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0).
 This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 3 from the book Advanced Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 3 from the book Advanced Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
Part I: SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR REQUIRED. 1. [6 points] Compute each number rounded to 3 decimal places. Please double check your answer.
![Part I: SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR REQUIRED. 1. [6 points] Compute each number rounded to 3 decimal places. Please double check your answer. Part I: SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR REQUIRED. 1. [6 points] Compute each number rounded to 3 decimal places. Please double check your answer.](/thumbs/77/74747136.jpg) Chapter 1 Sample Pretest Part I: SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR REQUIRED 1. [6 points] Compute each number rounded to 3 decimal places. Please double check your answer. 3 2+3 π2 +7 (a) (b) π 1.3+ 7 Part II: NO
Chapter 1 Sample Pretest Part I: SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR REQUIRED 1. [6 points] Compute each number rounded to 3 decimal places. Please double check your answer. 3 2+3 π2 +7 (a) (b) π 1.3+ 7 Part II: NO
Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions Section 3.1 Power Functions & Polynomial Functions... 155 Section 3. Quadratic Functions... 163 Section 3.3 Graphs of Polynomial Functions... 176 Section 3.4
Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions Section 3.1 Power Functions & Polynomial Functions... 155 Section 3. Quadratic Functions... 163 Section 3.3 Graphs of Polynomial Functions... 176 Section 3.4
Algebra 1 S1 Lesson Summaries. Lesson Goal: Mastery 70% or higher
 Algebra 1 S1 Lesson Summaries For every lesson, you need to: Read through the LESSON REVIEW which is located below or on the last page of the lesson and 3-hole punch into your MATH BINDER. Read and work
Algebra 1 S1 Lesson Summaries For every lesson, you need to: Read through the LESSON REVIEW which is located below or on the last page of the lesson and 3-hole punch into your MATH BINDER. Read and work
MATH 110: FINAL EXAM REVIEW
 MATH 0: FINAL EXAM REVIEW Can you solve linear equations algebraically and check your answer on a graphing calculator? (.) () y y= y + = 7 + 8 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) y+ 7 7 y = 9 (d) ( ) ( ) 6 = + + Can you set
MATH 0: FINAL EXAM REVIEW Can you solve linear equations algebraically and check your answer on a graphing calculator? (.) () y y= y + = 7 + 8 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) y+ 7 7 y = 9 (d) ( ) ( ) 6 = + + Can you set
Strategic Math. General Review of Algebra I. With Answers. By: Shirly Boots
 Strategic Math General Review of Algebra I With Answers By: Shirly Boots 1/6 Add/Subtract/Multiply/Divide Addmoves to the right -3-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Subtract moves to the left Ex: -2 + 8 = 6 Ex: -2 8 = - 10
Strategic Math General Review of Algebra I With Answers By: Shirly Boots 1/6 Add/Subtract/Multiply/Divide Addmoves to the right -3-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Subtract moves to the left Ex: -2 + 8 = 6 Ex: -2 8 = - 10
Contents Decimals Averages Percentages Metric Units Scientific Notation Dimensional Analysis
 This year in APES you will hear the two words most dreaded by high school students NO CALCULATORS! That s right, you cannot use a calculator on the AP Environmental Science exam. Since the regular tests
This year in APES you will hear the two words most dreaded by high school students NO CALCULATORS! That s right, you cannot use a calculator on the AP Environmental Science exam. Since the regular tests
MATH 121: EXTRA PRACTICE FOR TEST 2. Disclaimer: Any material covered in class and/or assigned for homework is a fair game for the exam.
 MATH 121: EXTRA PRACTICE FOR TEST 2 Disclaimer: Any material covered in class and/or assigned for homework is a fair game for the exam. 1 Linear Functions 1. Consider the functions f(x) = 3x + 5 and g(x)
MATH 121: EXTRA PRACTICE FOR TEST 2 Disclaimer: Any material covered in class and/or assigned for homework is a fair game for the exam. 1 Linear Functions 1. Consider the functions f(x) = 3x + 5 and g(x)
June Dear Future Functions/Analytic Geometry Students,
 June 016 Dear Future Functions/Analytic Geometry Students, Welcome to pre-calculus! Since we have so very many topics to cover during our 016-17 school year, it is important that each one of you is able
June 016 Dear Future Functions/Analytic Geometry Students, Welcome to pre-calculus! Since we have so very many topics to cover during our 016-17 school year, it is important that each one of you is able
REVIEW SHEETS ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA MATH 65
 REVIEW SHEETS ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA MATH 65 A Summary of Concepts Needed to be Successful in Mathematics The following sheets list the key concepts which are taught in the specified math course. The sheets
REVIEW SHEETS ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA MATH 65 A Summary of Concepts Needed to be Successful in Mathematics The following sheets list the key concepts which are taught in the specified math course. The sheets
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 3, Lesson 3. Solving Quadratic Relations
 Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 3, Lesson 3 Solving Quadratic Relations Suggested Time: 75 minutes What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will learn how to solve a variety of quadratic relations.
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 3, Lesson 3 Solving Quadratic Relations Suggested Time: 75 minutes What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will learn how to solve a variety of quadratic relations.
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt Algebra 2 2
 8-8 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 2 Warm Up Simplify each expression. Assume all variables are positive. 1. 2. 3. 4. Write each expression in radical form. 5. 6. Objective Solve radical equations
8-8 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 2 Warm Up Simplify each expression. Assume all variables are positive. 1. 2. 3. 4. Write each expression in radical form. 5. 6. Objective Solve radical equations
. Solve: x+ <7. a) x x< c) x <x. A painter can be paid in one of two ways: Plan A: $0 plus $8.00 per hour. Plan B: Straight $6.00 per hour. b) x x< x
 Intermediate Algebra Test for the Internet. Evaluate: x y when x =and y =. a) b) 6 c) 77. Add: 9:6+( :). a).9 b) -.9 c). -.. Subtract: 8 ( ). a) - b) c) -. Multiply: a) 8. Divide: a) 8 9 8 b). 6 b) 0 7
Intermediate Algebra Test for the Internet. Evaluate: x y when x =and y =. a) b) 6 c) 77. Add: 9:6+( :). a).9 b) -.9 c). -.. Subtract: 8 ( ). a) - b) c) -. Multiply: a) 8. Divide: a) 8 9 8 b). 6 b) 0 7
p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change
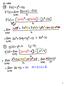 1 2 3 4 p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative
1 2 3 4 p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative
Sample Math Placement Exam Questions
 Sample Math Placement Exam Questions This review is not intended to cover all of the material on the Math Placement Exam. Material on the Math Placement Exam that is not covered in this review includes:
Sample Math Placement Exam Questions This review is not intended to cover all of the material on the Math Placement Exam. Material on the Math Placement Exam that is not covered in this review includes:
CH 56 APPLYING THE QUADRATIC FORMULA
 1 CH 56 APPLYING THE QUADRATIC FORMULA Rectangles Notice that our first example is a geometry word problem that is almost identical to a type that we had before, except that the word perimeter has been
1 CH 56 APPLYING THE QUADRATIC FORMULA Rectangles Notice that our first example is a geometry word problem that is almost identical to a type that we had before, except that the word perimeter has been
Chapter 1 Stephen Milczanowski
 Chapter 1 Stephen Milczanowski Chemistry is the study of matter and energy. Phases of matter: solid, liquid and gas. Matter is composed of atoms. An atom is one of the 100+ elements. Each element has a
Chapter 1 Stephen Milczanowski Chemistry is the study of matter and energy. Phases of matter: solid, liquid and gas. Matter is composed of atoms. An atom is one of the 100+ elements. Each element has a
MATH98 Intermediate Algebra Practice Test Form B
 MATH98 Intermediate Algebra Practice Test Form B MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the equation. 1) (y - 4) - (y + 9) = y 1) -
MATH98 Intermediate Algebra Practice Test Form B MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the equation. 1) (y - 4) - (y + 9) = y 1) -
Multiplication and Division
 UNIT 3 Multiplication and Division Skaters work as a pair to put on quite a show. Multiplication and division work as a pair to solve many types of problems. 82 UNIT 3 MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION Isaac
UNIT 3 Multiplication and Division Skaters work as a pair to put on quite a show. Multiplication and division work as a pair to solve many types of problems. 82 UNIT 3 MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION Isaac
SECTION 6-3 Systems Involving Second-Degree Equations
 446 6 Systems of Equations and Inequalities SECTION 6-3 Systems Involving Second-Degree Equations Solution by Substitution Other Solution Methods If a system of equations contains any equations that are
446 6 Systems of Equations and Inequalities SECTION 6-3 Systems Involving Second-Degree Equations Solution by Substitution Other Solution Methods If a system of equations contains any equations that are
Course Text. Course Description. Course Objectives. Course Prerequisites. Important Terms. StraighterLine Introductory Algebra
 Introductory Algebra Course Text Dugopolski, Mark. Elementary Algebra, 6th edition. McGraw-Hill, 2009. ISBN 9780077224790 [This text is available as an etextbook at purchase or students may find used,
Introductory Algebra Course Text Dugopolski, Mark. Elementary Algebra, 6th edition. McGraw-Hill, 2009. ISBN 9780077224790 [This text is available as an etextbook at purchase or students may find used,
8 th Grade Intensive Math
 8 th Grade Intensive Math Ready Florida MAFS Student Edition August-September 2014 Lesson 1 Part 1: Introduction Properties of Integer Exponents Develop Skills and Strategies MAFS 8.EE.1.1 In the past,
8 th Grade Intensive Math Ready Florida MAFS Student Edition August-September 2014 Lesson 1 Part 1: Introduction Properties of Integer Exponents Develop Skills and Strategies MAFS 8.EE.1.1 In the past,
MAT 0022C/0028C Final Exam Review. BY: West Campus Math Center
 MAT 0022C/0028C Final Exam Review BY: West Campus Math Center Factoring Topics #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 Problem Solving (Word Problems) #19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,
MAT 0022C/0028C Final Exam Review BY: West Campus Math Center Factoring Topics #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 Problem Solving (Word Problems) #19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,
Linear equations are equations involving only polynomials of degree one.
 Chapter 2A Solving Equations Solving Linear Equations Linear equations are equations involving only polynomials of degree one. Examples include 2t +1 = 7 and 25x +16 = 9x 4 A solution is a value or a set
Chapter 2A Solving Equations Solving Linear Equations Linear equations are equations involving only polynomials of degree one. Examples include 2t +1 = 7 and 25x +16 = 9x 4 A solution is a value or a set
Part I : Multiple Choice.
 Math 1010 Final Exam Intermediate Algebra Spring Semester 013 Form A Instructor Name Student ID ID Verification Section Number Time Limit: 10 minutes All problems are weighted equally. Graphing/programmable
Math 1010 Final Exam Intermediate Algebra Spring Semester 013 Form A Instructor Name Student ID ID Verification Section Number Time Limit: 10 minutes All problems are weighted equally. Graphing/programmable
Inverse Variation Read 7.1 Examples 1-4
 CC Algebra II HW #52 Name Period Row Date Inverse Variation Read 7.1 Eamples 1-4 Section 7.1 1. Vocabulary Eplain how direct variation equations and inverse variation equations are different. Tell whether
CC Algebra II HW #52 Name Period Row Date Inverse Variation Read 7.1 Eamples 1-4 Section 7.1 1. Vocabulary Eplain how direct variation equations and inverse variation equations are different. Tell whether
7.1 Solving Systems of Equations
 Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations Syllabus Objectives: 8.1 The student will solve a given system of equations or system of inequalities.
Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations Syllabus Objectives: 8.1 The student will solve a given system of equations or system of inequalities.
ALGEBRA 1 FINAL EXAM TOPICS
 ALGEBRA 1 FINAL EXAM TOPICS Chapter 2 2-1 Writing Equations 2-2 Solving One Step Equations 2-3 Solving Multi-Step Equations 2-4 Solving Equations with the Variable on Each Side 2-5 Solving Equations Involving
ALGEBRA 1 FINAL EXAM TOPICS Chapter 2 2-1 Writing Equations 2-2 Solving One Step Equations 2-3 Solving Multi-Step Equations 2-4 Solving Equations with the Variable on Each Side 2-5 Solving Equations Involving
