SECTION 6-3 Systems Involving Second-Degree Equations
|
|
|
- Sherman McBride
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 446 6 Systems of Equations and Inequalities SECTION 6-3 Systems Involving Second-Degree Equations Solution by Substitution Other Solution Methods If a system of equations contains any equations that are not linear, then the system is called a nonlinear system. In this section we investigate nonlinear systems involving second-degree terms such as y 3 y 1 y y 3y y 0 y y 0 It can be shown that such systems have at most four solutions, some of which may be imaginary. Since we are interested in finding both real and imaginary solutions to the systems we consider, we now assume that the replacement set for each variable is the set of comple numbers, rather than the set of real numbers. Solution by Substitution The substitution method used to solve linear systems of two equations in two variables is also an effective method for solving nonlinear systems. This process is best illustrated by eamples. EXAMPLE 1 Solving a Nonlinear System by Substitution Solve the system: y 3 y 1 Solution Solve the second equation for y in terms of ; then substitute for y in the first equation to obtain an equation that involves alone. 3 y 1 y 1 3 aeebeec y (1 3) ( 1)( ) 0 Substitute this epression for y in the first equation. Simplify and write in standard quadratic form. Divide through by to simplify further. 1, If we substitute these values back into the equation y 1 3, we obtain two solutions to the system:
2 6-3 Systems Involving Second-Degree Equations 447 y 1 3 y 1 y 1 3(1) y 1 3( 11 ) y A check, which you should provide, verifies that (1, ) and (, ) are both solutions to the system. These solutions are illustrated in Figure 1. However, if we substitute the values of back into the equation y, we obtain 11 FIGURE y y 4 y ( ) y y 11 y 11 It appears that we have found two additional solutions, (1, ) and (, ). But neither of these solutions satisfies the equation 3 y 1, which you should verify. So, neither is a solution of the original system. We have produced two etraneous roots, apparent solutions that do not actually satisfy both equations in the system. This is a common occurrence when solving nonlinear systems. It is always very important to check the solutions of any nonlinear system to ensure that etraneous roots have not been introduced. 11 Matched Problem 1 Solve the system: y 10 y 1 EXPLORE-DISCUSS 1 In Eample 1, we saw that the line 3 y 1 intersected the circle y in two points. (A) Consider the system y 3 y 10 Graph both equations in the same coordinate system. Are there any real solutions to this system? Are there any comple solutions? Find any real or comple solutions. (B) Consider the family of lines given by 3 y b b any real number What do all these lines have in common? Illustrate graphically the lines in this family that intersect the circle y in eactly one point. How many such lines are there? What are the corresponding value(s) of b? What are the intersection points? How are these lines related to the circle?
3 448 6 Systems of Equations and Inequalities EXAMPLE Solving a Nonlinear System by Substitution Solve: y y Solution Solve the second equation for y, substitute in the first equation, and proceed as before. y y u u 8 0 (u 4)(u ) 0 u 4, Multiply both sides by and simplify. Substitute u to transform to quadratic form and solve. FIGURE y y y Thus, For, y 1. For 4 or or, y 1. i For i, y i. i For i, y i. i Thus, the four solutions to this system are (, 1), (, 1), (i, i ), and ( i, i ). Notice that two of the solutions involve imaginary numbers. These imaginary solutions cannot be illustrated graphically (see Fig. ); however, they do satisfy both equations in the system (verify this). Matched Problem Solve: 3 y 6 y 3 EXPLORE-DISCUSS (A) Refer to the system in Eample. Could a graphing utility be used to find the real solutions of this system? The imaginary solutions?
4 6-3 Systems Involving Second-Degree Equations 449 (B) In general, eplain why graphic approimation techniques can be used to approimate the real solutions of a system, but not the comple solutions. EXAMPLE 3 Design 19 inches FIGURE 3 y Solution An engineer is to design a rectangular computer screen with a 19-inch diagonal and a 17-square-inch area. Find the dimensions of the screen to the nearest tenth of an inch. Sketch a rectangle letting be the width and y the height (Fig. 3). We obtain the following system using the Pythagorean theorem and the formula for the area of a rectangle: This system is solved using the procedures outlined in Eample. However, in this case, we are only interested in real solutions. We start by solving the second equation for y in terms of and substituting the result into the first equation. y 17 y 19 y , ,6 0 Multiply both sides by and simplify Quadratic in Solve the last equation for using the quadratic formula, then solve for : (1)(30,6) 1.0 inches or 11.7 inches Substitute each choice of into y 17/ to find the corresponding y values: For 1.0 inches, 17 y 11.7 inches 1 For 11.7 inches, y inches 11.7 Assuming the screen is wider than it is high, the dimensions are 1.0 by 11.7 inches.
5 40 6 Systems of Equations and Inequalities Matched Problem 3 An engineer is to design a rectangular television screen with a 1-inch diagonal and a 09-square-inch area. Find the dimensions of the screen to the nearest tenth of an inch. Since Eample 3 is only concerned with real solutions, graphic techniques can also be used to approimate the solutions (see Fig. 4). As we saw in Section 3-1, graphing a circle on a graphing utility requires two functions, one for the upper half of the circle and another for the lower half. [Note: since and y must be nonnegative real numbers, we ignore the intersection points in the third quadrant see Fig 4(a).] FIGURE 4 Graphic solution of y 19, y (a) y (b) Intersection point: (c) Intersection point: y 361 (11.7, 1.0) (1.0, 11.7) y 3 17 Other Solution Methods We now look at some other techniques for solving nonlinear systems of equations. EXAMPLE 4 Solving a Nonlinear System by Elimination Solve: y y 17 Solution This type of system can be solved using elimination by addition. Multiply the second equation by 1 and add: y y 17 3y 1 y 4 y Now substitute y and y back into either original equation to find. For y, For y, () 3 ( ) 3
6 6-3 Systems Involving Second-Degree Equations 41 Thus, (3, ), (3, ), ( 3, ), and ( 3, ), are the four solutions to the system. The check of the solutions is left to you. Matched Problem 4 Solve: 3y 3 4y 16 EXAMPLE Solving a Nonlinear System Using Factoring and Substitution Solve: 3y y 0 y y 0 Solution Factor the left side of the equation that has a 0 constant term: y y 0 y( y) 0 y 0 or y Thus, the original system is equivalent to the two systems: y 0 3y y 0 or or y 3y y 0 These systems are solved by substitution. First System y 0 3y y 0 Substitute y 0 in the second equation, and solve for. 3(0) (0) Second System y 3y y 0 Substitute y in the second equation and solve for Substitute these values back into y to find y.
7 4 6 Systems of Equations and Inequalities For, y. For, y. The solutions for the original system are (, 0), (, 0), (, ), and (, ). The check of the solutions is left to you. Matched Problem Solve: y y 9 y 0 Eample is somewhat specialized. However, it suggests a procedure that is effective for some problems. EXAMPLE 6 Graphic Approimations of Real Solutions Use a graphing utility to approimate real solutions to two decimal places: 4y y 1 y y 6 Solution Before we can enter these equations in our graphing utility, we must solve for y: 4y y 1 y 4y ( 1) 0 y y 6 y y ( 6) 0 Applying the quadratic formula to each equation, we have y ( 1) y 4 4( 6) Since each equation has two solutions, we must enter four functions in the graphing utility, as shown in Figure (a). Eamining the graph in Figure (b), we see that there are four intersection points. Using the built-in intersection routine repeatedly (details omitted), we find that the solutions to two decimal places are (.10, 0.83), ( 0.37,.79), (0.37,.79), and (.10, 0.83). FIGURE (a) (b)
8 6-3 Systems Involving Second-Degree Equations 43 Matched Problem 6 Use a graphing utility to approimate real solutions to two decimal places: 8y y 70 y y 0 Answers to Matched Problems 9 1. ( 1, 3), (, 13 ). ( 3, 3), ( 3, 3), (i, 3i), ( i, 3i) by 1. in 4. (, 1), (, 1), (, 1), (, 1). (0, 3), (0, 3), ( 3, 3), ( 3, 3) 6. ( 3.89, 1.68), ( 0.96,.3), (0.96,.3), (3.89, 1.68) EXERCISE 6-3 A Solve each system in Problems y 169. y 1 y y y. 3 y 6. y 0 7. y 8. y y 3 y 9. y y 3 y 1 y 11. y y 1 16 y 4y B Solve each system in Problems y y 6 0 y y 4 1. y y y y 1 4y 3 y 0 y 18 y y y 10 4 y 8 4y y 0. y 0 y y y 1. y 9. y 16 y 9 y y 4 3. y 3 4. y 1 y y An important type of calculus problem is to find the area between the graphs of two functions. To solve some of these problems it is necessary to find the coordinates of the points of intersections of the two graphs. In Problems 3, find the coordinates of the points of intersections of the two given equations.. y, y 6. y, y 3 7. y, y 8. y, y 3 9. y 6 9, y 30. y 3, y y 8 4, y 3. y 4 10, y Consider the circle with equation y and the family of lines given by y b, where b is any real number. (A) Illustrate graphically the lines in this family that intersect the circle in eactly one point, and describe the relationship between the circle and these lines. (B) Find the values of b corresponding to the lines in part A, and find the intersection points of the lines and the circle. (C) How is the line with equation y 0 related to this family of lines? How could this line be used to find the intersection points in part B? 34. Consider the circle with equation y and the family of lines given by 3 4y b, where b is any real number. (A) Illustrate graphically the lines in this family that intersect the circle in eactly one point, and describe the relationship between the circle and these lines. (B) Find the values of b corresponding to the lines in part A, and find the intersection points of the lines and the circle.
9 44 6 Systems of Equations and Inequalities (C) How is the line with equation 4 3y 0 related to this family of lines? How could this line be used to find the intersection points and the values of b in part B? of the circle is 6. inches, and the area of the rectangle is 1 square inches. Find the dimensions of the rectangle. C Solve each system in Problems y 7y y y 16 y 3 0 y y y y 39. y y y 0 y y y 3 y y 36 y y 3y 3 4. y y 16 4y 3y 0 y y 0 In Problems 43 48, use a graphing utility to approimate the real solutions of each system to two decimal places. 43. y y y y 3 4y y 8 y y y y 46. 4y y 4 y y 9 4 y y y y 9 4 4y y y y 1 4 4y y y 9. Construction. A rectangular swimming pool with a deck feet wide is enclosed by a fence as shown in the figure. The surface area of the pool is 7 square feet, and the total area enclosed by the fence (including the pool and the deck) is 1,1 square feet. Find the dimensions of the pool. ft Pool ft 6. inches Fence APPLICATIONS ft ft 49. Numbers. Find two numbers such that their sum is 3 and their product is Numbers. Find two numbers such that their difference is 1 and their product is 1. (Let be the larger number and y the smaller number.) 1. Geometry. Find the lengths of the legs of a right triangle with an area of 30 square inches if its hypotenuse is 13 inches long.. Geometry. Find the dimensions of a rectangle with an area of 3 square meters if its perimeter is 36 meters long. 3. Design. An engineer is designing a small portable television set. According to the design specifications, the set must have a rectangular screen with a 7.-inch diagonal and an area of 7 square inches. Find the dimensions of the screen. 4. Design. An artist is designing a logo for a business in the shape of a circle with an inscribed rectangle. The diameter 6. Construction. An open-topped rectangular bo is formed by cutting a 6-inch square from each corner of a rectangular piece of cardboard and bending up the ends and sides. The area of the cardboard before the corners are removed is 768 square inches, and the volume of the bo is 1,440 cubic inches. Find the dimensions of the original piece of cardboard. 6 in. 6 in. 6 in. 6 in. 6 in. 6 in. 6 in. 6 in. 7. Transportation. Two boats leave Bournemouth, England,
10 6-4 Systems of Linear Inequalities in Two Variables 4 at the same time and follow the same route on the 7-mile trip across the English Channel to Cherbourg, France. The average speed of boat A is miles per hour greater than the average speed of boat B. Consequently, boat A arrives at Cherbourg 30 minutes before boat B. Find the average speed of each boat. 8. Transportation. Bus A leaves Milwaukee at noon and travels west on Interstate 94. Bus B leaves Milwaukee 30 minutes later, travels the same route, and overtakes bus A at a point 10 miles west of Milwaukee. If the average speed of bus B is 10 miles per hour greater than the average speed of bus A, at what time did bus B overtake bus A? SECTION 6-4 Systems of Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Graphically Application Many applications of mathematics involve systems of inequalities rather than systems of equations. A graph is often the most convenient way to represent the solutions of a system of inequalities in two variables. In this section, we discuss techniques for graphing both a single linear inequality in two variables and a system of linear inequalities in two variables. Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables We know how to graph first-degree equations such as y 3 and 3y but how do we graph first-degree inequalities such as y 3 and 3y Actually, graphing these inequalities is almost as easy as graphing the equations. But before we begin, we must discuss some important subsets of a plane in a rectangular coordinate system. A line divides a plane into two halves called half-planes. A vertical line divides a plane into left and right half-planes [Fig. 1(a)]; a nonvertical line divides a plane into upper and lower half-planes [Fig. 1(b)]. FIGURE 1 Half-planes. y y Left half-plane Right half-plane Upper half-plane Lower half-plane (a) (b)
Remember, you may not use a calculator when you take the assessment test.
 Elementary Algebra problems you can use for practice. Remember, you may not use a calculator when you take the assessment test. Use these problems to help you get up to speed. Perform the indicated operation.
Elementary Algebra problems you can use for practice. Remember, you may not use a calculator when you take the assessment test. Use these problems to help you get up to speed. Perform the indicated operation.
For problems 1 4, evaluate each expression, if possible. Write answers as integers or simplified fractions
 / MATH 05 TEST REVIEW SHEET TO THE STUDENT: This Review Sheet gives you an outline of the topics covered on Test as well as practice problems. Answers are at the end of the Review Sheet. I. EXPRESSIONS
/ MATH 05 TEST REVIEW SHEET TO THE STUDENT: This Review Sheet gives you an outline of the topics covered on Test as well as practice problems. Answers are at the end of the Review Sheet. I. EXPRESSIONS
Module 2, Section 2 Solving Equations
 Principles of Mathematics Section, Introduction 03 Introduction Module, Section Solving Equations In this section, you will learn to solve quadratic equations graphically, by factoring, and by applying
Principles of Mathematics Section, Introduction 03 Introduction Module, Section Solving Equations In this section, you will learn to solve quadratic equations graphically, by factoring, and by applying
MATH 110: FINAL EXAM REVIEW
 MATH 0: FINAL EXAM REVIEW Can you solve linear equations algebraically and check your answer on a graphing calculator? (.) () y y= y + = 7 + 8 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) y+ 7 7 y = 9 (d) ( ) ( ) 6 = + + Can you set
MATH 0: FINAL EXAM REVIEW Can you solve linear equations algebraically and check your answer on a graphing calculator? (.) () y y= y + = 7 + 8 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) y+ 7 7 y = 9 (d) ( ) ( ) 6 = + + Can you set
SECTION 4-3 Approximating Real Zeros of Polynomials Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Polynomial and Rational Functions 79. P() 9 9 8. P() 6 6 8 7 8 8. The solutions to the equation are all the cube roots of. (A) How many cube roots of are there? (B) is obviously a cube root of ; find all
Polynomial and Rational Functions 79. P() 9 9 8. P() 6 6 8 7 8 8. The solutions to the equation are all the cube roots of. (A) How many cube roots of are there? (B) is obviously a cube root of ; find all
13.1 NONLINEAR SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS
 690 (3 ) Chapter 3 Nonlinear Systems and the Conic Sections 3. NONLINEAR SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS In this section Solving by Elimination Applications E X A M P L E y 5 4 (, 3) 3 y = x (, 0) 4 3 3 4 3 4 y =
690 (3 ) Chapter 3 Nonlinear Systems and the Conic Sections 3. NONLINEAR SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS In this section Solving by Elimination Applications E X A M P L E y 5 4 (, 3) 3 y = x (, 0) 4 3 3 4 3 4 y =
Chapter 5: Systems of Equations and Inequalities. Section 5.4. Check Point Exercises
 Chapter : Systems of Equations and Inequalities Section. Check Point Eercises. = y y = Solve the first equation for y. y = + Substitute the epression + for y in the second equation and solve for. ( + )
Chapter : Systems of Equations and Inequalities Section. Check Point Eercises. = y y = Solve the first equation for y. y = + Substitute the epression + for y in the second equation and solve for. ( + )
7.6 Radical Equations and Problem Solving
 Section 7.6 Radical Equations and Problem Solving 447 Use rational eponents to write each as a single radical epression. 9. 2 4 # 2 20. 25 # 2 3 2 Simplify. 2. 240 22. 2 4 6 7 y 0 23. 2 3 54 4 24. 2 5-64b
Section 7.6 Radical Equations and Problem Solving 447 Use rational eponents to write each as a single radical epression. 9. 2 4 # 2 20. 25 # 2 3 2 Simplify. 2. 240 22. 2 4 6 7 y 0 23. 2 3 54 4 24. 2 5-64b
MATH 111 Departmental Midterm Exam Review Exam date: Tuesday, March 1 st. Exam will cover sections and will be NON-CALCULATOR EXAM.
 MATH Departmental Midterm Eam Review Eam date: Tuesday, March st Eam will cover sections -9 + - and will be NON-CALCULATOR EXAM Terms to know: quadratic function, ais of symmetry, verte, minimum/maimum
MATH Departmental Midterm Eam Review Eam date: Tuesday, March st Eam will cover sections -9 + - and will be NON-CALCULATOR EXAM Terms to know: quadratic function, ais of symmetry, verte, minimum/maimum
How can you find decimal approximations of square roots that are not rational? ACTIVITY: Approximating Square Roots
 . Approximating Square Roots How can you find decimal approximations of square roots that are not rational? ACTIVITY: Approximating Square Roots Work with a partner. Archimedes was a Greek mathematician,
. Approximating Square Roots How can you find decimal approximations of square roots that are not rational? ACTIVITY: Approximating Square Roots Work with a partner. Archimedes was a Greek mathematician,
1 Linear and Absolute Value Equations
 1 Linear and Absolute Value Equations 1. Solve the equation 11x + 6 = 7x + 15. Solution: Use properties of equality to bring the x s to one side and the numbers to the other: 11x (7x) + 6 = 7x (7x) + 15
1 Linear and Absolute Value Equations 1. Solve the equation 11x + 6 = 7x + 15. Solution: Use properties of equality to bring the x s to one side and the numbers to the other: 11x (7x) + 6 = 7x (7x) + 15
Chapter 7: Practice/review problems The collection of problems listed below contains questions taken from previous MA123 exams.
 Word problems Chapter 7: Practice/review problems The collection of problems listed below contains questions taken from previous MA3 exams. Max-min problems []. A field has the shape of a rectangle with
Word problems Chapter 7: Practice/review problems The collection of problems listed below contains questions taken from previous MA3 exams. Max-min problems []. A field has the shape of a rectangle with
CHAPTER 2 Solving Equations and Inequalities
 CHAPTER Solving Equations and Inequalities Section. Linear Equations and Problem Solving........... 8 Section. Solving Equations Graphically............... 89 Section. Comple Numbers......................
CHAPTER Solving Equations and Inequalities Section. Linear Equations and Problem Solving........... 8 Section. Solving Equations Graphically............... 89 Section. Comple Numbers......................
Equations and Inequalities
 Equations and Inequalities Figure 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE.1 The Rectangular Coordinate Systems and Graphs. Linear Equations in One Variable.3 Models and Applications. Comple Numbers.5 Quadratic Equations.6 Other
Equations and Inequalities Figure 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE.1 The Rectangular Coordinate Systems and Graphs. Linear Equations in One Variable.3 Models and Applications. Comple Numbers.5 Quadratic Equations.6 Other
Solving and Graphing Polynomials
 UNIT 9 Solving and Graphing Polynomials You can see laminar and turbulent fl ow in a fountain. Copyright 009, K1 Inc. All rights reserved. This material may not be reproduced in whole or in part, including
UNIT 9 Solving and Graphing Polynomials You can see laminar and turbulent fl ow in a fountain. Copyright 009, K1 Inc. All rights reserved. This material may not be reproduced in whole or in part, including
(b) Find the difference quotient. Interpret your result. 3. Find the average rate of change of ƒ(x) = x 2-3x from
 6360_ch0pp00-075.qd 0/6/08 4:8 PM Page 67 CHAPTER Summar 67 69. ƒ() = 3 70. ƒ() = -5 (b) Find the difference quotient. Interpret our result. 7. ƒ() = - 7. ƒ() = 0 73. ƒ() = + 74. ƒ() = -3 + 4 75. ƒ() =
6360_ch0pp00-075.qd 0/6/08 4:8 PM Page 67 CHAPTER Summar 67 69. ƒ() = 3 70. ƒ() = -5 (b) Find the difference quotient. Interpret our result. 7. ƒ() = - 7. ƒ() = 0 73. ƒ() = + 74. ƒ() = -3 + 4 75. ƒ() =
CHAPTER 8 Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities
 CHAPTER Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities Section. Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring and Special Forms..................... 7 Section. Completing the Square................... 9 Section.
CHAPTER Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities Section. Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring and Special Forms..................... 7 Section. Completing the Square................... 9 Section.
Algebra I Semester 2 Practice Exam DRAFT
 Algebra I Semester Practice Eam 1. What is the -coordinate of the point of intersection for the two lines below? 6 7 y y 640 8 13 4 13. What is the y-coordinate of the point of intersection for the two
Algebra I Semester Practice Eam 1. What is the -coordinate of the point of intersection for the two lines below? 6 7 y y 640 8 13 4 13. What is the y-coordinate of the point of intersection for the two
Particle Motion Problems
 Particle Motion Problems Particle motion problems deal with particles that are moving along the x or y axis. Thus, we are speaking of horizontal or vertical movement. The position, velocity, or acceleration
Particle Motion Problems Particle motion problems deal with particles that are moving along the x or y axis. Thus, we are speaking of horizontal or vertical movement. The position, velocity, or acceleration
Practice Test - Chapter 4
 Find the value of x. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 1. An acute angle measure and the length of the hypotenuse are given, so the sine function can be used to find the length of the side opposite.
Find the value of x. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 1. An acute angle measure and the length of the hypotenuse are given, so the sine function can be used to find the length of the side opposite.
Quadratic Graphs and Their Properties
 - Think About a Plan Quadratic Graphs and Their Properties Physics In a physics class demonstration, a ball is dropped from the roof of a building, feet above the ground. The height h (in feet) of the
- Think About a Plan Quadratic Graphs and Their Properties Physics In a physics class demonstration, a ball is dropped from the roof of a building, feet above the ground. The height h (in feet) of the
Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 SECTION.1 Linear and Quadratic Functions Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions Section.1: Linear and Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Definition of a Linear
SECTION.1 Linear and Quadratic Functions Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions Section.1: Linear and Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Definition of a Linear
Math 111, Spring 2009 Final Exam
 Math 111, Spring 009 Final Exam Name (print) Instructor s name Directions 1. Time limit: 1 hour 50 minutes. Each test should have 8 pages. Points for each problem are to the right of the blank.. To receive
Math 111, Spring 009 Final Exam Name (print) Instructor s name Directions 1. Time limit: 1 hour 50 minutes. Each test should have 8 pages. Points for each problem are to the right of the blank.. To receive
Modeling and Optimization (Word Problems ALL DAY) Let the first number and = the second number. The boundaries of this problem are [0, 30].
![Modeling and Optimization (Word Problems ALL DAY) Let the first number and = the second number. The boundaries of this problem are [0, 30]. Modeling and Optimization (Word Problems ALL DAY) Let the first number and = the second number. The boundaries of this problem are [0, 30].](/thumbs/76/73837032.jpg) New Calculus 5.4 Modeling and Optimization (Word Problems ALL DAY) The sum of two non-negative numbers is 30. a) Find the numbers if the sum of their squares is as large as possible. b) Find the numbers
New Calculus 5.4 Modeling and Optimization (Word Problems ALL DAY) The sum of two non-negative numbers is 30. a) Find the numbers if the sum of their squares is as large as possible. b) Find the numbers
Fixed Perimeter Rectangles
 Rectangles You have a flexible fence of length L = 13 meters. You want to use all of this fence to enclose a rectangular plot of land of at least 8 square meters in area. 1. Determine a function for the
Rectangles You have a flexible fence of length L = 13 meters. You want to use all of this fence to enclose a rectangular plot of land of at least 8 square meters in area. 1. Determine a function for the
Math 108 Skills Assessment
 Math 08 Assessment Test Page Math 08 Skills Assessment The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses). All of the
Math 08 Assessment Test Page Math 08 Skills Assessment The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses). All of the
150. a. Clear fractions in the following equation and write in. b. For the equation you wrote in part (a), compute. The Quadratic Formula
 75 CHAPTER Quadratic Equations and Functions Preview Eercises Eercises 8 50 will help you prepare for the material covered in the net section. 8. a. Solve by factoring: 8 + - 0. b. The quadratic equation
75 CHAPTER Quadratic Equations and Functions Preview Eercises Eercises 8 50 will help you prepare for the material covered in the net section. 8. a. Solve by factoring: 8 + - 0. b. The quadratic equation
Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
 Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square Learning Objectives: 1. Use the square root propert to solve quadratic equations.. Solve quadratic equations b completing the square.
Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square Learning Objectives: 1. Use the square root propert to solve quadratic equations.. Solve quadratic equations b completing the square.
MA Review Worksheet for Exam 1, Summer 2016
 MA 15800 Review Worksheet for Eam 1, Summer 016 1) Choose which of the following relations represent functions and give the domain and/or range. a) {(,5), (,5), ( 1,5)} b) equation: y 4 1 y 4 (5, ) 1 (
MA 15800 Review Worksheet for Eam 1, Summer 016 1) Choose which of the following relations represent functions and give the domain and/or range. a) {(,5), (,5), ( 1,5)} b) equation: y 4 1 y 4 (5, ) 1 (
Functions and Their Graphs
 Functions and Their Graphs 015 College Board. All rights reserved. Unit Overview In this unit you will study polynomial and rational functions, their graphs, and their zeros. You will also learn several
Functions and Their Graphs 015 College Board. All rights reserved. Unit Overview In this unit you will study polynomial and rational functions, their graphs, and their zeros. You will also learn several
Name Date. Analyzing Graphs of Polynomial Functions For use with Exploration 2.7
 Name Date.7 Analyzing Graphs of Polynomial Functions For use with Eploration.7 Essential Question How many turning points can the graph of a polynomial function have? 1 EXPLORATION: Approimating Turning
Name Date.7 Analyzing Graphs of Polynomial Functions For use with Eploration.7 Essential Question How many turning points can the graph of a polynomial function have? 1 EXPLORATION: Approimating Turning
1. sin 2. csc 2 3. tan 1 2. Cos 8) Sin 10. sec. Honors Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review 2 nd semester. TRIGONOMETRY Solve for 0 2
 Honors Pre-Calculus Final Eam Review nd semester Name: TRIGONOMETRY Solve for 0 without using a calculator: 1 1. sin. csc 3. tan 1 4. cos 1) ) 3) 4) Solve for in degrees giving all solutions. 5. sin 1
Honors Pre-Calculus Final Eam Review nd semester Name: TRIGONOMETRY Solve for 0 without using a calculator: 1 1. sin. csc 3. tan 1 4. cos 1) ) 3) 4) Solve for in degrees giving all solutions. 5. sin 1
SYSTEMS OF THREE EQUATIONS
 SYSTEMS OF THREE EQUATIONS 11.2.1 11.2.4 This section begins with students using technology to eplore graphing in three dimensions. By using strategies that they used for graphing in two dimensions, students
SYSTEMS OF THREE EQUATIONS 11.2.1 11.2.4 This section begins with students using technology to eplore graphing in three dimensions. By using strategies that they used for graphing in two dimensions, students
1. sin 2. Honors Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review 2 nd semester June TRIGONOMETRY Solve for 0 2. without using a calculator: 2. csc 2 3.
 Honors Pre-Calculus Name: Final Eam Review nd semester June 05 TRIGONOMETRY Solve for 0 without using a calculator:. sin. csc. tan. cos ) ) ) ) Solve for in degrees giving all solutions. 5. sin 6. cos
Honors Pre-Calculus Name: Final Eam Review nd semester June 05 TRIGONOMETRY Solve for 0 without using a calculator:. sin. csc. tan. cos ) ) ) ) Solve for in degrees giving all solutions. 5. sin 6. cos
[1] [2.3 b,c] [2] [2.3b] 3. Solve for x: 3x 4 2x. [3] [2.7 c] [4] [2.7 d] 5. Solve for h : [5] [2.4 b] 6. Solve for k: 3 x = 4k
![[1] [2.3 b,c] [2] [2.3b] 3. Solve for x: 3x 4 2x. [3] [2.7 c] [4] [2.7 d] 5. Solve for h : [5] [2.4 b] 6. Solve for k: 3 x = 4k [1] [2.3 b,c] [2] [2.3b] 3. Solve for x: 3x 4 2x. [3] [2.7 c] [4] [2.7 d] 5. Solve for h : [5] [2.4 b] 6. Solve for k: 3 x = 4k](/thumbs/78/77023587.jpg) 1. Solve for x: 4( x 5) = (4 x) [1] [. b,c]. Solve for x: x 1.6 =.4 +. 8x [] [.b]. Solve for x: x 4 x 14 [] [.7 c] 4. Solve for x:.x. 4 [4] [.7 d] 5. Solve for h : 1 V = Ah [5] [.4 b] 6. Solve for k: x
1. Solve for x: 4( x 5) = (4 x) [1] [. b,c]. Solve for x: x 1.6 =.4 +. 8x [] [.b]. Solve for x: x 4 x 14 [] [.7 c] 4. Solve for x:.x. 4 [4] [.7 d] 5. Solve for h : 1 V = Ah [5] [.4 b] 6. Solve for k: x
Quadratic Applications Name: Block: 3. The product of two consecutive odd integers is equal to 30 more than the first. Find the integers.
 Quadratic Applications Name: Block: This problem packet is due before 4pm on Friday, October 26. It is a formative assessment and worth 20 points. Complete the following problems. Circle or box your answer.
Quadratic Applications Name: Block: This problem packet is due before 4pm on Friday, October 26. It is a formative assessment and worth 20 points. Complete the following problems. Circle or box your answer.
x and y, called the coordinates of the point.
 P.1 The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane (also called the rectangular coordinate system) is the plane that allows you to represent ordered pairs of real numbers by points. It is
P.1 The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane (also called the rectangular coordinate system) is the plane that allows you to represent ordered pairs of real numbers by points. It is
Equations and Inequalities
 Equations and Inequalities Figure 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE 1 The Rectangular Coordinate Systems and Graphs Linear Equations in One Variable Models and Applications Comple Numbers Quadratic Equations 6 Other Types
Equations and Inequalities Figure 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE 1 The Rectangular Coordinate Systems and Graphs Linear Equations in One Variable Models and Applications Comple Numbers Quadratic Equations 6 Other Types
Part II) Practice Problems
 Part II) Practice Problems 1. Calculate the value of to the nearest tenth: sin 38 80 2. Calculate the value of y to the nearest tenth: y cos 52 80 3. Calculate the value of to the nearest hundredth: tan
Part II) Practice Problems 1. Calculate the value of to the nearest tenth: sin 38 80 2. Calculate the value of y to the nearest tenth: y cos 52 80 3. Calculate the value of to the nearest hundredth: tan
Using the distance formula Using formulas to solve unknowns. Pythagorean Theorem. Finding Legs of Right Triangles
 Math 154 Chapter 9.6: Applications of Radical Equations Objectives: Finding legs of right triangles Finding hypotenuse of right triangles Solve application problems involving right triangles Pythagorean
Math 154 Chapter 9.6: Applications of Radical Equations Objectives: Finding legs of right triangles Finding hypotenuse of right triangles Solve application problems involving right triangles Pythagorean
Quadratic Inequalities in One Variable
 Quadratic Inequalities in One Variable Quadratic inequalities in one variable can be written in one of the following forms: a b c + + 0 a b c + + 0 a b c + + 0 a b c + + 0 Where a, b, and c are real and
Quadratic Inequalities in One Variable Quadratic inequalities in one variable can be written in one of the following forms: a b c + + 0 a b c + + 0 a b c + + 0 a b c + + 0 Where a, b, and c are real and
Lesson 4.1 (Part 1): Roots & Pythagorean Theorem
 Lesson 4.1 (Part 1): Roots & Pythagorean Theorem Objectives Students will understand how roots are used to undo powers. how the Pythagorean theorem is used in applications. Students will be able to use
Lesson 4.1 (Part 1): Roots & Pythagorean Theorem Objectives Students will understand how roots are used to undo powers. how the Pythagorean theorem is used in applications. Students will be able to use
= = =
 . D - To evaluate the expression, we can regroup the numbers and the powers of ten, multiply, and adjust the decimal and exponent to put the answer in correct scientific notation format: 5 0 0 7 = 5 0
. D - To evaluate the expression, we can regroup the numbers and the powers of ten, multiply, and adjust the decimal and exponent to put the answer in correct scientific notation format: 5 0 0 7 = 5 0
Math 1050 REVIEW for Exam 1. Use synthetic division to find the quotient and the remainder. 1) x3 - x2 + 6 is divided by x + 2
 Math 0 REVIEW for Eam 1 Use snthetic division to find the quotient and the remainder. 1) 3-2 + 6 is divided b + 2 Use snthetic division to determine whether - c is a factor of the given polnomial. 2) 3-32
Math 0 REVIEW for Eam 1 Use snthetic division to find the quotient and the remainder. 1) 3-2 + 6 is divided b + 2 Use snthetic division to determine whether - c is a factor of the given polnomial. 2) 3-32
Section 3.4. from Verbal Descriptions and from Data. Quick Review. Quick Review Solutions. Functions. Solve the equation or inequality. x. 1.
 .4: Quadratic Models Starter.4 Section.4 Building Quadratic at Models from Verbal Descriptions and from Data DO:,, p. 60 Solve the given formula for the required variable. ) Area of a Triangle Solve for
.4: Quadratic Models Starter.4 Section.4 Building Quadratic at Models from Verbal Descriptions and from Data DO:,, p. 60 Solve the given formula for the required variable. ) Area of a Triangle Solve for
PreCalculus. American Heritage Upper School Summer Math Packet
 ! PreCalculus American Heritage Upper School Summer Math Packet All Upper School American Heritage math students are required to complete a summer math packet. This packet is intended for all students
! PreCalculus American Heritage Upper School Summer Math Packet All Upper School American Heritage math students are required to complete a summer math packet. This packet is intended for all students
One of the most common applications of Calculus involves determining maximum or minimum values.
 8 LESSON 5- MAX/MIN APPLICATIONS (OPTIMIZATION) One of the most common applications of Calculus involves determining maimum or minimum values. Procedure:. Choose variables and/or draw a labeled figure..
8 LESSON 5- MAX/MIN APPLICATIONS (OPTIMIZATION) One of the most common applications of Calculus involves determining maimum or minimum values. Procedure:. Choose variables and/or draw a labeled figure..
Review Algebra and Functions & Equations (10 questions)
 Paper 1 Review No calculator allowed [ worked solutions included ] 1. Find the set of values of for which e e 3 e.. Given that 3 k 1 is positive for all values of, find the range of possible values for
Paper 1 Review No calculator allowed [ worked solutions included ] 1. Find the set of values of for which e e 3 e.. Given that 3 k 1 is positive for all values of, find the range of possible values for
Park Forest Math Team. Meet #5. Algebra. Self-study Packet
 Park Forest Math Team Meet #5 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet: 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. Geometry: Angle measures in plane figures including supplements and complements 3. Number
Park Forest Math Team Meet #5 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet: 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. Geometry: Angle measures in plane figures including supplements and complements 3. Number
More Differentiation Page 1
 More Differentiation Page 1 Directions: Solve the following problems using the available space for scratchwork. Indicate your answers on the front page. Do not spend too much time on any one problem. Note:
More Differentiation Page 1 Directions: Solve the following problems using the available space for scratchwork. Indicate your answers on the front page. Do not spend too much time on any one problem. Note:
18.01 Exercises. December 23, Unit 2. Applications of Differentiation. 2A. Approximation
 8.0 Eercises December 23, 200 Unit 2. Applications of Differentiation 2A. Approimation 2A- Find the linearization of a + b at 0, by using (2), and also by using the basic approimation formulas. (Here a
8.0 Eercises December 23, 200 Unit 2. Applications of Differentiation 2A. Approimation 2A- Find the linearization of a + b at 0, by using (2), and also by using the basic approimation formulas. (Here a
June Dear Future Functions/Analytic Geometry Students,
 June 016 Dear Future Functions/Analytic Geometry Students, Welcome to pre-calculus! Since we have so very many topics to cover during our 016-17 school year, it is important that each one of you is able
June 016 Dear Future Functions/Analytic Geometry Students, Welcome to pre-calculus! Since we have so very many topics to cover during our 016-17 school year, it is important that each one of you is able
Math Review for Incoming Geometry Honors Students
 Solve each equation. 1. 5x + 8 = 3 + 2(3x 4) 2. 5(2n 3) = 7(3 n) Math Review for Incoming Geometry Honors Students 3. Victoria goes to the mall with $60. She purchases a skirt for $12 and perfume for $35.99.
Solve each equation. 1. 5x + 8 = 3 + 2(3x 4) 2. 5(2n 3) = 7(3 n) Math Review for Incoming Geometry Honors Students 3. Victoria goes to the mall with $60. She purchases a skirt for $12 and perfume for $35.99.
Chapter 7 Quadratic Equations
 Chapter 7 Quadratic Equations We have worked with trinomials of the form ax 2 + bx + c. Now we are going to work with equations of this form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 quadratic equations. When we write a quadratic
Chapter 7 Quadratic Equations We have worked with trinomials of the form ax 2 + bx + c. Now we are going to work with equations of this form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 quadratic equations. When we write a quadratic
Exponents 4-1. Lesson Objectives. Vocabulary. Additional Examples. Evaluate expressions with exponents. exponential form (p. 162) exponent (p.
 LESSON 4-1 Exponents Lesson Objectives Evaluate expressions with exponents Vocabulary exponential form (p. 16) exponent (p. 16) base (p. 16) power (p. 16) Additional Examples Example 1 Write in exponential
LESSON 4-1 Exponents Lesson Objectives Evaluate expressions with exponents Vocabulary exponential form (p. 16) exponent (p. 16) base (p. 16) power (p. 16) Additional Examples Example 1 Write in exponential
ALGEBRA I SEMESTER EXAMS PRACTICE MATERIALS SEMESTER 2 27? 1. (7.2) What is the value of (A) 1 9 (B) 1 3 (C) 9 (D) 3
 014-015 SEMESTER EXAMS SEMESTER 1. (7.) What is the value of 1 3 7? (A) 1 9 (B) 1 3 (C) 9 (D) 3. (7.3) The graph shows an eponential function. What is the equation of the function? (A) y 3 (B) y 3 (C)
014-015 SEMESTER EXAMS SEMESTER 1. (7.) What is the value of 1 3 7? (A) 1 9 (B) 1 3 (C) 9 (D) 3. (7.3) The graph shows an eponential function. What is the equation of the function? (A) y 3 (B) y 3 (C)
C. 3 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM. 1. Simplify B. 2. D. E. None of the above. 2. Factor. completely. E. None of the above. 3.
 MA 1500 1. Simplify ; A. B. 2 C. 2. Factor 8 completely. A. x y x + y B. x 2y C. 2x y 2x + y 2x y. Simplify ( ) ; A. a b c B. C. a b c a b 6c c a b 1 MA 1500 4. Subtract and simplify. + 2 A. x: x ; x;
MA 1500 1. Simplify ; A. B. 2 C. 2. Factor 8 completely. A. x y x + y B. x 2y C. 2x y 2x + y 2x y. Simplify ( ) ; A. a b c B. C. a b c a b 6c c a b 1 MA 1500 4. Subtract and simplify. + 2 A. x: x ; x;
5. Determine the discriminant for each and describe the nature of the roots.
 4. Quadratic Equations Notes Day 1 1. Solve by factoring: a. 3 16 1 b. 3 c. 8 0 d. 9 18 0. Quadratic Formula: The roots of a quadratic equation of the form A + B + C = 0 with a 0 are given by the following
4. Quadratic Equations Notes Day 1 1. Solve by factoring: a. 3 16 1 b. 3 c. 8 0 d. 9 18 0. Quadratic Formula: The roots of a quadratic equation of the form A + B + C = 0 with a 0 are given by the following
f x and the x axis on an interval from x a and
 Unit 6: Chapter 8 Areas and Volumes & Density Functions Part 1: Areas To find the area bounded by a function bwe use the integral: f d b a b 0 f d f d. a b a f and the ais on an interval from a and. This
Unit 6: Chapter 8 Areas and Volumes & Density Functions Part 1: Areas To find the area bounded by a function bwe use the integral: f d b a b 0 f d f d. a b a f and the ais on an interval from a and. This
10.3 Solving Nonlinear Systems of Equations
 60 CHAPTER 0 Conic Sections Identif whether each equation, when graphed, will be a parabola, circle, ellipse, or hperbola. Then graph each equation.. - 7 + - =. = +. = + + 6. + 9 =. 9-9 = 6. 6 - = 7. 6
60 CHAPTER 0 Conic Sections Identif whether each equation, when graphed, will be a parabola, circle, ellipse, or hperbola. Then graph each equation.. - 7 + - =. = +. = + + 6. + 9 =. 9-9 = 6. 6 - = 7. 6
8.2 Solving Quadratic Equations by the Quadratic Formula
 Section 8. Solving Quadratic Equations by the Quadratic Formula 85 8. Solving Quadratic Equations by the Quadratic Formula S Solve Quadratic Equations by Using the Quadratic Formula. Determine the Number
Section 8. Solving Quadratic Equations by the Quadratic Formula 85 8. Solving Quadratic Equations by the Quadratic Formula S Solve Quadratic Equations by Using the Quadratic Formula. Determine the Number
Rancho Bernardo High School/Math Department Honors Pre-Calculus Exit Exam
 Rancho Bernardo High School/Math Department Honors Pre-Calculus Eit Eam You are about to take an eam that will test our knowledge of the RBHS Honors Pre-Calculus curriculum. You must demonstrate genuine
Rancho Bernardo High School/Math Department Honors Pre-Calculus Eit Eam You are about to take an eam that will test our knowledge of the RBHS Honors Pre-Calculus curriculum. You must demonstrate genuine
16x y 8x. 16x 81. U n i t 3 P t 1 H o n o r s P a g e 1. Math 3 Unit 3 Day 1 - Factoring Review. I. Greatest Common Factor GCF.
 P a g e 1 Math 3 Unit 3 Day 1 - Factoring Review I. Greatest Common Factor GCF Eamples: A. 3 6 B. 4 8 4 C. 16 y 8 II. Difference of Two Squares Draw ( - ) ( + ) Square Root 1 st and Last Term Eamples:
P a g e 1 Math 3 Unit 3 Day 1 - Factoring Review I. Greatest Common Factor GCF Eamples: A. 3 6 B. 4 8 4 C. 16 y 8 II. Difference of Two Squares Draw ( - ) ( + ) Square Root 1 st and Last Term Eamples:
Classwork 8.1. Perform the indicated operation and simplify each as much as possible. 1) 24 2) ) 54w y 11) wy 6) 5 9.
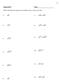 - 7 - Classwork 8.1 Name Perform the indicated operation and simplify each as much as possible. 1) 4 7) 16+ 5 49 ) 5 4 8) 11 6 81 ) 5 4x 9) 9 x + 49x 4) 75w 10) 6 5 54w y 5) 80wy 11) 15 6 6) 5 9 1) 15x
- 7 - Classwork 8.1 Name Perform the indicated operation and simplify each as much as possible. 1) 4 7) 16+ 5 49 ) 5 4 8) 11 6 81 ) 5 4x 9) 9 x + 49x 4) 75w 10) 6 5 54w y 5) 80wy 11) 15 6 6) 5 9 1) 15x
Pre-Calculus 110 Review
 Pre-Calculus 0 eview Trigonometry (eference Chapter, Sections. -., pages 74-99) Outcomes: Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, 0 60 Solve problems, using the three primary trigonometric
Pre-Calculus 0 eview Trigonometry (eference Chapter, Sections. -., pages 74-99) Outcomes: Demonstrate an understanding of angles in standard position, 0 60 Solve problems, using the three primary trigonometric
Math 2412 Activity 2(Due by EOC Feb. 27) Find the quadratic function that satisfies the given conditions. Show your work!
 Math 4 Activity (Due by EOC Feb 7) Find the quadratic function that satisfies the given conditions Show your work! The graph has a verte at 5, and it passes through the point, 0 7 The graph passes through
Math 4 Activity (Due by EOC Feb 7) Find the quadratic function that satisfies the given conditions Show your work! The graph has a verte at 5, and it passes through the point, 0 7 The graph passes through
Math 110 Final Exam Review Revised December 2015
 Math 110 Final Exam Review Revised December 2015 Factor out the GCF from each polynomial. 1) 60x - 15 2) 7x 8 y + 42x 6 3) x 9 y 5 - x 9 y 4 + x 7 y 2 - x 6 y 2 Factor each four-term polynomial by grouping.
Math 110 Final Exam Review Revised December 2015 Factor out the GCF from each polynomial. 1) 60x - 15 2) 7x 8 y + 42x 6 3) x 9 y 5 - x 9 y 4 + x 7 y 2 - x 6 y 2 Factor each four-term polynomial by grouping.
Math 20-1 Functions and Equations Multiple Choice Questions
 Math 0- Functions and Equations Multiple Choice Questions 8 simplifies to: A. 9 B. 0 C. 90 ( )( ) simplifies to: A. B. C. 8 A. 9 B. C. simplifies to: The area of the shaded region below is: 0 0 A. B. 0
Math 0- Functions and Equations Multiple Choice Questions 8 simplifies to: A. 9 B. 0 C. 90 ( )( ) simplifies to: A. B. C. 8 A. 9 B. C. simplifies to: The area of the shaded region below is: 0 0 A. B. 0
MATH 125 ELAC SPRING 2018 TEST 3 TAKE HOME NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 125 ELAC SPRING 2018 TEST 3 TAKE HOME NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Write an equation of the circle with the given center
MATH 125 ELAC SPRING 2018 TEST 3 TAKE HOME NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Write an equation of the circle with the given center
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 3.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Get Radical or (Be)! Radicals and the Pythagorean Theorem Vocabulary Write the term that best completes each statement. 1. An expression that includes
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Get Radical or (Be)! Radicals and the Pythagorean Theorem Vocabulary Write the term that best completes each statement. 1. An expression that includes
AP Calculus AB - Mrs. Mora. Summer packet 2010
 AP Calculus AB - Mrs. Mora Summer packet 010 These eercises represent some of the more fundamental concepts needed upon entering AP Calculus AB This "packet is epected to be completed and brought to class
AP Calculus AB - Mrs. Mora Summer packet 010 These eercises represent some of the more fundamental concepts needed upon entering AP Calculus AB This "packet is epected to be completed and brought to class
3.1 Graphs of Polynomials
 3.1 Graphs of Polynomials Three of the families of functions studied thus far: constant, linear and quadratic, belong to a much larger group of functions called polynomials. We begin our formal study of
3.1 Graphs of Polynomials Three of the families of functions studied thus far: constant, linear and quadratic, belong to a much larger group of functions called polynomials. We begin our formal study of
Precalculus Notes: Unit P Prerequisite Skills
 Syllabus Objective Note: Because this unit contains all prerequisite skills that were taught in courses prior to precalculus, there will not be any syllabus objectives listed. Teaching this unit within
Syllabus Objective Note: Because this unit contains all prerequisite skills that were taught in courses prior to precalculus, there will not be any syllabus objectives listed. Teaching this unit within
Atlanta Public Schools
 Atlanta Public Schools Curriculum Supplement Student Edition Mathematics I: Unit 5 This document has been made possible by funding from the GE Foundation Developing Futures grant, in partnership with Atlanta
Atlanta Public Schools Curriculum Supplement Student Edition Mathematics I: Unit 5 This document has been made possible by funding from the GE Foundation Developing Futures grant, in partnership with Atlanta
Extra Problems: Unit 0
 Extra Problems: Unit 0 These are example problems, mostly from tests and quizzes that I have given in the past. Make sure you understand and can do all assigned textbook problems, activities, problems
Extra Problems: Unit 0 These are example problems, mostly from tests and quizzes that I have given in the past. Make sure you understand and can do all assigned textbook problems, activities, problems
Radical and Rational Functions
 Radical and Rational Functions 5 015 College Board. All rights reserved. Unit Overview In this unit, you will etend your study of functions to radical, rational, and inverse functions. You will graph radical
Radical and Rational Functions 5 015 College Board. All rights reserved. Unit Overview In this unit, you will etend your study of functions to radical, rational, and inverse functions. You will graph radical
Chapter 4 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions - Polynomial Functions Pages 09 0 Check for Understanding. A zero is the value of the variable for which a polynomial function in one variable equals zero. A root
Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions - Polynomial Functions Pages 09 0 Check for Understanding. A zero is the value of the variable for which a polynomial function in one variable equals zero. A root
P.7 Solving Inequalities Algebraically and Graphically
 54 CHAPTER P Prerequisites What you ll learn about Solving Absolute Value Inequalities Solving Quadratic Inequalities Approximating Solutions to Inequalities Projectile Motion... and why These techniques
54 CHAPTER P Prerequisites What you ll learn about Solving Absolute Value Inequalities Solving Quadratic Inequalities Approximating Solutions to Inequalities Projectile Motion... and why These techniques
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 2 Stud Guide-Chapters 8 and 9 Name Date: Time: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find all square roots of the number. ) 600 9,
Math 2 Stud Guide-Chapters 8 and 9 Name Date: Time: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find all square roots of the number. ) 600 9,
Honors Precalculus Notes Packet
 Honors Precalculus Notes Packet 03-04 Academic Magnet High School Contents Unit : Inequalities, Equations, and Graphs... Unit : Functions and Graphs... 6 Unit 3: New Functions from Old... 37 Unit 4: Polynomial
Honors Precalculus Notes Packet 03-04 Academic Magnet High School Contents Unit : Inequalities, Equations, and Graphs... Unit : Functions and Graphs... 6 Unit 3: New Functions from Old... 37 Unit 4: Polynomial
Math 110 Final Exam Review Revised October 2018
 Math 110 Final Exam Review Revised October 2018 Factor out the GCF from each polynomial. 1) 60x - 15 2) 7x 8 y + 42x 6 3) x 9 y 5 - x 9 y 4 + x 7 y 2 - x 6 y 2 Factor each four-term polynomial by grouping.
Math 110 Final Exam Review Revised October 2018 Factor out the GCF from each polynomial. 1) 60x - 15 2) 7x 8 y + 42x 6 3) x 9 y 5 - x 9 y 4 + x 7 y 2 - x 6 y 2 Factor each four-term polynomial by grouping.
Unit #7 - Optimization, Optimal Marginal Rates
 Unit #7 - Optimization, Optimal Marginal Rates Some problems and solutions selected or adapted from Hughes-Hallett Calculus. Optimization Introduction. Let f() = 0 +, and consider the interval [0, 0].
Unit #7 - Optimization, Optimal Marginal Rates Some problems and solutions selected or adapted from Hughes-Hallett Calculus. Optimization Introduction. Let f() = 0 +, and consider the interval [0, 0].
Math Analysis Chapter 2 Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Math Analysis Chapter Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions Day 13: Section -1 Comple Numbers; Sections - Quadratic Functions -1: Comple Numbers After completing section -1 you should be able to do
Math Analysis Chapter Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions Day 13: Section -1 Comple Numbers; Sections - Quadratic Functions -1: Comple Numbers After completing section -1 you should be able to do
18 19 Find the extreme values of f on the region described by the inequality. 20. Consider the problem of maximizing the function
 940 CHAPTER 14 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 14.8 EXERCISES 1. Pictured are a contour map of f and a curve with equation t, y 8. Estimate the maimum and minimum values of f subject to the constraint that t, y 8.
940 CHAPTER 14 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 14.8 EXERCISES 1. Pictured are a contour map of f and a curve with equation t, y 8. Estimate the maimum and minimum values of f subject to the constraint that t, y 8.
UNIT #2 LINEAR EXPRESSIONS, EQUATIONS, AND INEQUALITIES REVIEW QUESTIONS
 Name: Date: Part I Questions UNIT # LINEAR EXPRESSIONS, EQUATIONS, AND INEQUALITIES REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. The value 4 is a solution to all of the following equations ecept which? 1. () (1) 7 15 3 1 11 (3)
Name: Date: Part I Questions UNIT # LINEAR EXPRESSIONS, EQUATIONS, AND INEQUALITIES REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. The value 4 is a solution to all of the following equations ecept which? 1. () (1) 7 15 3 1 11 (3)
ACTIVITY 14 Continued
 015 College Board. All rights reserved. Postal Service Write your answers on notebook paper. Show your work. Lesson 1-1 1. The volume of a rectangular bo is given by the epression V = (10 6w)w, where w
015 College Board. All rights reserved. Postal Service Write your answers on notebook paper. Show your work. Lesson 1-1 1. The volume of a rectangular bo is given by the epression V = (10 6w)w, where w
Expressions and the Number System
 Name: 8 th Grade Math 1 st Semester Review Pd: Expressions and the Number System 1. A square rug has an area of 225 square feet. How long is each side of the rug? A 15 feet B 22.5 feet C 23 feet D 25 feet
Name: 8 th Grade Math 1 st Semester Review Pd: Expressions and the Number System 1. A square rug has an area of 225 square feet. How long is each side of the rug? A 15 feet B 22.5 feet C 23 feet D 25 feet
Advanced Algebra 2 Final Review Packet KG Page 1 of Find the slope of the line passing through (3, -1) and (6, 4).
 Advanced Algebra Final Review Packet KG 0 Page of 8. Evaluate (7 ) 0 when and. 7 7. Solve the equation.. Solve the equation.. Solve the equation. 6. An awards dinner costs $ plus $ for each person making
Advanced Algebra Final Review Packet KG 0 Page of 8. Evaluate (7 ) 0 when and. 7 7. Solve the equation.. Solve the equation.. Solve the equation. 6. An awards dinner costs $ plus $ for each person making
2. Which of the following expressions represents the product of four less than three times x and two more than x?
 Algebra Topics COMPASS Review You will be allowed to use a calculator on the COMPASS test. Acceptable calculators are: basic calculators, scientific calculators, and graphing calculators up through the
Algebra Topics COMPASS Review You will be allowed to use a calculator on the COMPASS test. Acceptable calculators are: basic calculators, scientific calculators, and graphing calculators up through the
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of work b Horia Varlan;
Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of work b Horia Varlan;
22.1 Solving Equations by Taking Square Roots
 Name Class Date 22.1 Solving Equations by Taking Square Roots Essential Question: How can you solve quadratic equations using square roots? Resource Locker Explore Exploring Square Roots Recall that the
Name Class Date 22.1 Solving Equations by Taking Square Roots Essential Question: How can you solve quadratic equations using square roots? Resource Locker Explore Exploring Square Roots Recall that the
Pre-Algebra Semester 2 Practice Exam DRAFT
 . There are 0 yellow and purple marbles in a bag. If one marble is randomly picked from the bag, what are the odds in favor of it being yellow? A. : B. : C. :3 D. 3: 3. The data below shows the number
. There are 0 yellow and purple marbles in a bag. If one marble is randomly picked from the bag, what are the odds in favor of it being yellow? A. : B. : C. :3 D. 3: 3. The data below shows the number
Part I: SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR REQUIRED. 1. [6 points] Compute each number rounded to 3 decimal places. Please double check your answer.
![Part I: SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR REQUIRED. 1. [6 points] Compute each number rounded to 3 decimal places. Please double check your answer. Part I: SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR REQUIRED. 1. [6 points] Compute each number rounded to 3 decimal places. Please double check your answer.](/thumbs/77/74747136.jpg) Chapter 1 Sample Pretest Part I: SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR REQUIRED 1. [6 points] Compute each number rounded to 3 decimal places. Please double check your answer. 3 2+3 π2 +7 (a) (b) π 1.3+ 7 Part II: NO
Chapter 1 Sample Pretest Part I: SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR REQUIRED 1. [6 points] Compute each number rounded to 3 decimal places. Please double check your answer. 3 2+3 π2 +7 (a) (b) π 1.3+ 7 Part II: NO
Mesa Public Schools. Q3 practice test. Assessment Summary: Powered by SchoolCity Inc. Page 1 of 44
 Mesa Public Schools Assessment Summary: Q3 practice test Powered by SchoolCity Inc. www.schoolcity.com Page 1 of 44 Assessment Summary: Q3 practice test Year: 2016-2017 Subject: Math Total Items: 43 Total
Mesa Public Schools Assessment Summary: Q3 practice test Powered by SchoolCity Inc. www.schoolcity.com Page 1 of 44 Assessment Summary: Q3 practice test Year: 2016-2017 Subject: Math Total Items: 43 Total
Recall that when you multiply or divide both sides of an inequality by a negative number, you must
 Unit 3, Lesson 5.3 Creating Rational Inequalities Recall that a rational equation is an equation that includes the ratio of two rational epressions, in which a variable appears in the denominator of at
Unit 3, Lesson 5.3 Creating Rational Inequalities Recall that a rational equation is an equation that includes the ratio of two rational epressions, in which a variable appears in the denominator of at
Honors Calculus Summer Preparation 2018
 Honors Calculus Summer Preparation 08 Name: ARCHBISHOP CURLEY HIGH SCHOOL Honors Calculus Summer Preparation 08 Honors Calculus Summer Work and List of Topical Understandings In order to be a successful
Honors Calculus Summer Preparation 08 Name: ARCHBISHOP CURLEY HIGH SCHOOL Honors Calculus Summer Preparation 08 Honors Calculus Summer Work and List of Topical Understandings In order to be a successful
Study Guide and Intervention. The Quadratic Formula and the Discriminant. Quadratic Formula. Replace a with 1, b with -5, and c with -14.
 Study Guide and Intervention Quadratic Formula The Quadratic Formula can be used to solve any quadratic equation once it is written in the form a 2 + b + c = 0. Quadratic Formula The solutions of a 2 +
Study Guide and Intervention Quadratic Formula The Quadratic Formula can be used to solve any quadratic equation once it is written in the form a 2 + b + c = 0. Quadratic Formula The solutions of a 2 +
Absolute Extrema and Constrained Optimization
 Calculus 1 Lia Vas Absolute Extrema and Constrained Optimization Recall that a function f (x) is said to have a relative maximum at x = c if f (c) f (x) for all values of x in some open interval containing
Calculus 1 Lia Vas Absolute Extrema and Constrained Optimization Recall that a function f (x) is said to have a relative maximum at x = c if f (c) f (x) for all values of x in some open interval containing
Full Name. Remember, lots of space, thus lots of pages!
 Rising Pre-Calculus student Summer Packet for 016 (school year 016-17) Dear Advanced Algebra: Pre-Calculus student: To be successful in Advanced Algebra: Pre-Calculus, you must be proficient at solving
Rising Pre-Calculus student Summer Packet for 016 (school year 016-17) Dear Advanced Algebra: Pre-Calculus student: To be successful in Advanced Algebra: Pre-Calculus, you must be proficient at solving
Review Document MTH
 Review Document MTH-2101-3 Created by Martine Blais Commission scolaire des Premières-Seigneuries Mai 2010 Translated by Marie-Hélène Lebeault November 2017 Producing an algebraic model 1. How do you go
Review Document MTH-2101-3 Created by Martine Blais Commission scolaire des Premières-Seigneuries Mai 2010 Translated by Marie-Hélène Lebeault November 2017 Producing an algebraic model 1. How do you go
