Introduction to Macroeconomics
|
|
|
- Justin Edgar Merritt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Macroeconomics Martin Ellison Nuffi eld College Michaelmas Term 2018 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
2 Macroeconomics is Dynamic Decisions are taken over time t 1 t t+1 Expectations Expectations make economics special Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
3 Macroeconomics is Stochastic The economy is hit by shocks - Frisch-Slutsky paradigm Impulses Propagation Fluctuations Shocks to: technology monetary policy consumer confidence oil prices exchange rate Microfounded (Lucas) from deep parameters: i) tastes and preferences ii) production technology iii) market structure Decisions have to account for uncertainty Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
4 Macroeconomics is General Equilibrium Markets are interconnected Income ( ) Labour maximise utility Households Goods Firms maximise profit Expenditure ( ) Need to analyse all markets together Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
5 Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (DSGE) Work with Frisch-Slutsky paradigm backwards Impulses Propagation Fluctuations What do fluctuations look like? underlying trend business cycle seasonality random fluctuations measurement error Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
6 Macroeconomic data 10 9 LGNPC LPCECC Log GNP and non-durable consumption in the US Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
7 Filtering Hodrick-Prescott filter decomposes data y t into trend τ t and cycle c t y t = τ t + c t Trend should be smooth but follow data closely min {τ t } T t=1 ( T t=1 λ is weighting parameter (y t τ t ) 2 T 1 + λ t=2 λ = 0 means τ t = y t and trend is data λ means 2 τ t = 0 and trend is linear [(τ t+1 τ t ) (τ t τ t 1 )] 2 ) Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
8 Hodrick-Prescott filter LGNPC96 LGNPC96( =400) LGNPC96( =800) LGNPC96( =1600) US GNP and Hodrick-Prescott trends Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
9 Hodrick-Prescott as a band-pass filter λ = 6400 dots; λ = 1600 solid; λ = 400 dashes λ = 1600 defines business cycle as fluctuations less than about 40 quarters Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
10 Comments on filtering HP is a 2-sided filter that brings future information into the present and so violates informational assumptions of rational expectations Identification of cycles not invariant to filter others may be better Filtering may induce spurious cycles, e.g. linear detrending of a random walk Can remove propagation from a model entirely and still get cycles Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
11 Long run properties of macroeconomic data 10 9 LGNPC96 LGNPC96( =1600) DLGNPC96( =1600) Trend growth in US GNP per capita is approximately constant Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
12 Long run properties of macroeconomic data labour share C/Y I/Y Labour share and the Great Ratios in the US are approximately constant Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
13 Kaldor (1957) facts 1 Output per worker grows at a roughly constant rate 2 Capital per worker grows over time 3 Capital/output ratio is roughly constant 4 Rate of return to capital is constant 5 Shares of capital and labour in net income are nearly constant 6 Real wage grows over time 7 Ratios of consumption and investment to GDP are constant Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
14 Short run properties of macroeconomic data Detrended GNP and non-durable consumption LGNPC96(hp) LPCECC96(hp) σ Y > σ C ; strong correlation; C leads Y by a quarter or two? Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
15 Short run properties of macroeconomic data Variable Sd% Cross-correlation of output with: t-3 t-2 t-1 t t+1 t+2 t+3 GNP CND CD I H Ave H L GNP/H Ave W Cyclical behaviour of the US economy Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
16 Stylised facts Non-durable consumption less volatile than output Volatility of output and hours similar Employment more volatile than average hours Wages less volatile than productivity Productivity slightly procyclical Wage acyclical Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
17 Vector autoregressions (VARs) Flexible form that describes wide range of real data sets R t = R 0 + a 11 R t a p1 R t p + b 11 π t b p1 π t p + e 1t π t = π 0 + a 12 R t a p2 R t p + b 12 π t b p2 π t p + e 2t p-th order vector autoregression in interest rate R t and inflation π t Can be estimated by Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
18 The identification problem VAR residuals and fundamental shocks ( ) ( ) ( ) e1t θ1 θ = 2 u1t ; e 2t θ 3 θ 4 u 2t ( u1t u 2t ) N [ ( 1 0 0; 0 1 )] Problem is that both u 1t and u 2t may affect both e 1t and e 2t Not identified Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
19 Causal ordering Assume R t reacts to π t with a lag VAR residuals and fundamental shocks ( ) ( ) ( e1t θ1 0 u1t = e 2t θ 3 θ 4 u 2t ) N [ ( σ1 σ 0; 12 σ 12 σ 2 )] Unique identification σ 1 = θ 2 1, σ 12 = θ 1 θ 3, σ 2 = θ θ 2 4 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
20 Notes on causal ordering Identified VAR is a structural vector autoregression (SVAR) Ordering could be so π t reacts to R t with a lag not unique Known as Wold decomposition or Choleski ordering Generalisable to more than two variables Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
21 Impulse response functions Shock to u 2t t R t π t θ 4 1 b 11 θ 4 b 12 θ 4 2 a 11 b 11 θ 4 + b 11 b 12 θ 4 + b 21 θ 4 a 12 b 11 θ 4 + b 12 b 12 θ 4 + b 22 θ 4... Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
22 Sims (1992) Six variable VAR for UK 1965q4 to 1990:12 Causal ordering 1 Short interest rate R 2 Index of foreign exchange value of domestic currency XR 3 Commodity price index PC 4 Monetary aggregate M 5 Consumer price index P 6 Industrial production index Y Innovations only affect variables lower in causal ordering Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
23 Sims (1992) Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
24 Christiano, Eichenbaum and Evans (2005) Nine variable VAR for US 1965:3 to 1995:3 Causal ordering 1 Real GDP, real consumption, GDP deflator, real investment, real wage, labour productivity 2 Interest rate 3 Real profit and growth rate of M2 R shocks only affect real profit and M2 R affected by all shocks except real profit and M2 shocks Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
25 Christiano, Eichenbaum and Evans (2005) Solid lines with plus signs are VAR-based estimates Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
26 Christiano, Eichenbaum and Evans (2005) Results suggest that after an expansionary monetary policy shock: 1 output, consumption, and investment respond in a hump-shape, peaking after about one and a half years and returning to pre-shock levels after about three years 2 inflation responds in a hump-shape, peaking after about two years 3 interest rate falls for roughly one year 4 real profits, real wages, and labor productivity rise 5 growth rate of money rises immediately Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
27 Problems with causal orderings Sims (1992) and Christiano, Eichenbaum and Evans (2005) find prices for a while after an unexpected in R t Could be a cost channel effect (firm borrowing costs rise so they increase prices) but more likely faulty identification Sign restriction VARs designed to rule out such anomalies Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
28 Mapping all identifications Relationship between residuals and fundamental shocks e 1t = (θ 1 cos λ) u 1t + (θ 1 sin λ) u 2t e 2t = (θ 3 cos λ θ 4 sin λ) u 1t + (θ 3 sin λ + θ 4 cos λ) u 2t λ = 0 recover standard causal ordering ( ) λ = tan 1 θ3 θ4 recovers alternative causal ordering By looking at λ [ π, π] can map all possible identifications Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
29 Mapping all identifications Matrix form ( e1t e 2t ) ( θ1 0 = θ 3 θ 4 ) ( cos λ sin λ sin λ cos λ ) ( u1t u 2t ) Distribution of residuals ( ) e1t N for all λ [ π, π] e 2t [ ( θ 2 0; 1 θ 1 θ 3 θ 1 θ 3 θ θ 2 4 In linear algebra we are rotating matrices )] Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
30 Sign restrictions First variable is R t and second variable is inflation π t Standard VAR with causal ordering identifies θ 1, θ 3, θ 4 All possible rotations e 1t = (θ 1 cos λ) u 1t + (θ 1 sin λ) u 2t e 2t = (θ 3 cos λ θ 4 sin λ) u 1t + (θ 3 sin λ + θ 4 cos λ) u 2t Monetary policy shock raises R t and lowers π t Search for rotations that satisfy θ 1 cos λ > 0 θ 3 cos λ θ 4 sin λ < 0 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
31 Illustrative example Suppose standard VAR identifies θ 1 = θ 3 = θ 4 = 1 Permissible rotations θ 1 cos λ > 0 θ 3 cos λ θ 4 sin λ < 0 λ is in region [ π 4, π ] 2 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
32 Canova (2007) Responses to a US policy shock, 1964:1-2001:10 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
33 Canova and Paustian (2010) Sign restrictions Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
34 Canova and Paustian (2010) Response intervals to monetary shocks Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
35 Identification using high frequency information ECB monthly press conference January 15, 2009 Traders expect interest rate cut on February 5, 2009 Trichet announces no policy change expected next meeting Traders revise up expectations Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
36 Rosa (2008) Link Time zero when Trichet starts answering a journalist s question Mid-quote on 3-month Euribor future expiring in March 2009 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
37 Kuttner (2001) Spot-month futures rate on day t of month s interpreted as conditional expectation of the average funds rate in month s plus term premium fs,t 0 1 = E t m r i + µ 0 s,t i s Policy surprise measure computed from the 1-day change in the spot-month future rate r t u = m ( f 0 m t s,t fs,t 1 0 ) Policy surprise is proxied by change in futures rate proxy VAR Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
38 Proxy Correlated with u 1t so E (u 1t z t ) = φ Uncorrelated with u 2t so E (u 2t z t ) = 0 Correlated with both residuals [( ) ] [( ) ( e1t θ1 θ E z e t = E 2 u1t 2t θ 3 θ 4 u 2t ) ] ( θ1 φ (φu 1t + ν t ) = θ 3 φ ) Proxy VAR identified by restriction for known E (e 1t z t ) and E (e 2t z t ) θ 1 = E (e 1tz t ) θ 3 E (e 2t z t ) Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
39 Kuttner (2001) 1-month response of interest rates to Fed funds surprises Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term / 39
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999)
 Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium and Growth
 Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium and Growth Martin Ellison Nuffi eld College Michaelmas Term 2018 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) D(S)GE and Growth Michaelmas Term 2018 1 / 43 Macroeconomics is Dynamic
Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium and Growth Martin Ellison Nuffi eld College Michaelmas Term 2018 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) D(S)GE and Growth Michaelmas Term 2018 1 / 43 Macroeconomics is Dynamic
Assessing Structural VAR s
 ... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Zurich, September 2005 1 Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Address the Following Type of Question:
... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Zurich, September 2005 1 Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Address the Following Type of Question:
LECTURE 3 The Effects of Monetary Changes: Statistical Identification. September 5, 2018
 Economics 210c/236a Fall 2018 Christina Romer David Romer LECTURE 3 The Effects of Monetary Changes: Statistical Identification September 5, 2018 I. SOME BACKGROUND ON VARS A Two-Variable VAR Suppose the
Economics 210c/236a Fall 2018 Christina Romer David Romer LECTURE 3 The Effects of Monetary Changes: Statistical Identification September 5, 2018 I. SOME BACKGROUND ON VARS A Two-Variable VAR Suppose the
Toulouse School of Economics, Macroeconomics II Franck Portier. Homework 1. Problem I An AD-AS Model
 Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Real Business Cycle Model (RBC)
 Real Business Cycle Model (RBC) Seyed Ali Madanizadeh November 2013 RBC Model Lucas 1980: One of the functions of theoretical economics is to provide fully articulated, artificial economic systems that
Real Business Cycle Model (RBC) Seyed Ali Madanizadeh November 2013 RBC Model Lucas 1980: One of the functions of theoretical economics is to provide fully articulated, artificial economic systems that
Assessing Structural VAR s
 ... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Columbia, October 2005 1 Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Can be Used to Address the Following
... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Columbia, October 2005 1 Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Can be Used to Address the Following
Lecture 2. Business Cycle Measurement. Randall Romero Aguilar, PhD II Semestre 2017 Last updated: August 18, 2017
 Lecture 2 Business Cycle Measurement Randall Romero Aguilar, PhD II Semestre 2017 Last updated: August 18, 2017 Universidad de Costa Rica EC3201 - Teoría Macroeconómica 2 Table of contents 1. Introduction
Lecture 2 Business Cycle Measurement Randall Romero Aguilar, PhD II Semestre 2017 Last updated: August 18, 2017 Universidad de Costa Rica EC3201 - Teoría Macroeconómica 2 Table of contents 1. Introduction
Assessing Structural VAR s
 ... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Yale, October 2005 1 Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Can be Used to Address the Following Type
... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Yale, October 2005 1 Background Structural Vector Autoregressions Can be Used to Address the Following Type
Can News be a Major Source of Aggregate Fluctuations?
 Can News be a Major Source of Aggregate Fluctuations? A Bayesian DSGE Approach Ippei Fujiwara 1 Yasuo Hirose 1 Mototsugu 2 1 Bank of Japan 2 Vanderbilt University August 4, 2009 Contributions of this paper
Can News be a Major Source of Aggregate Fluctuations? A Bayesian DSGE Approach Ippei Fujiwara 1 Yasuo Hirose 1 Mototsugu 2 1 Bank of Japan 2 Vanderbilt University August 4, 2009 Contributions of this paper
Financial Factors in Economic Fluctuations. Lawrence Christiano Roberto Motto Massimo Rostagno
 Financial Factors in Economic Fluctuations Lawrence Christiano Roberto Motto Massimo Rostagno Background Much progress made on constructing and estimating models that fit quarterly data well (Smets-Wouters,
Financial Factors in Economic Fluctuations Lawrence Christiano Roberto Motto Massimo Rostagno Background Much progress made on constructing and estimating models that fit quarterly data well (Smets-Wouters,
Macroeconomics Field Exam. August 2007
 Macroeconomics Field Exam August 2007 Answer all questions in the exam. Suggested times correspond to the questions weights in the exam grade. Make your answers as precise as possible, using graphs, equations,
Macroeconomics Field Exam August 2007 Answer all questions in the exam. Suggested times correspond to the questions weights in the exam grade. Make your answers as precise as possible, using graphs, equations,
Lecture 4 The Centralized Economy: Extensions
 Lecture 4 The Centralized Economy: Extensions Leopold von Thadden University of Mainz and ECB (on leave) Advanced Macroeconomics, Winter Term 2013 1 / 36 I Motivation This Lecture considers some applications
Lecture 4 The Centralized Economy: Extensions Leopold von Thadden University of Mainz and ECB (on leave) Advanced Macroeconomics, Winter Term 2013 1 / 36 I Motivation This Lecture considers some applications
Assessing Structural VAR s
 ... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Minneapolis, August 2005 1 Background In Principle, Impulse Response Functions from SVARs are useful as
... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson Minneapolis, August 2005 1 Background In Principle, Impulse Response Functions from SVARs are useful as
1.2. Structural VARs
 1. Shocks Nr. 1 1.2. Structural VARs How to identify A 0? A review: Choleski (Cholesky?) decompositions. Short-run restrictions. Inequality restrictions. Long-run restrictions. Then, examples, applications,
1. Shocks Nr. 1 1.2. Structural VARs How to identify A 0? A review: Choleski (Cholesky?) decompositions. Short-run restrictions. Inequality restrictions. Long-run restrictions. Then, examples, applications,
A. Recursively orthogonalized. VARs
 Orthogonalized VARs A. Recursively orthogonalized VAR B. Variance decomposition C. Historical decomposition D. Structural interpretation E. Generalized IRFs 1 A. Recursively orthogonalized Nonorthogonal
Orthogonalized VARs A. Recursively orthogonalized VAR B. Variance decomposition C. Historical decomposition D. Structural interpretation E. Generalized IRFs 1 A. Recursively orthogonalized Nonorthogonal
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models. Basic Economic Models
 4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
Vector Autoregressions as a Guide to Constructing Dynamic General Equilibrium Models
 Vector Autoregressions as a Guide to Constructing Dynamic General Equilibrium Models by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson 1 Background We Use VAR Impulse Response Functions
Vector Autoregressions as a Guide to Constructing Dynamic General Equilibrium Models by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson 1 Background We Use VAR Impulse Response Functions
PANEL DISCUSSION: THE ROLE OF POTENTIAL OUTPUT IN POLICYMAKING
 PANEL DISCUSSION: THE ROLE OF POTENTIAL OUTPUT IN POLICYMAKING James Bullard* Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis 33rd Annual Economic Policy Conference St. Louis, MO October 17, 2008 Views expressed are
PANEL DISCUSSION: THE ROLE OF POTENTIAL OUTPUT IN POLICYMAKING James Bullard* Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis 33rd Annual Economic Policy Conference St. Louis, MO October 17, 2008 Views expressed are
Lecture 1: Information and Structural VARs
 Lecture 1: Information and Structural VARs Luca Gambetti 1 1 Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona LBS, May 6-8 2013 Introduction The study of the dynamic effects of economic shocks is one of the key applications
Lecture 1: Information and Structural VARs Luca Gambetti 1 1 Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona LBS, May 6-8 2013 Introduction The study of the dynamic effects of economic shocks is one of the key applications
Solving a Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium Model under the Discrete Time Framework
 Solving a Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium Model under the Discrete Time Framework Dongpeng Liu Nanjing University Sept 2016 D. Liu (NJU) Solving D(S)GE 09/16 1 / 63 Introduction Targets of the
Solving a Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium Model under the Discrete Time Framework Dongpeng Liu Nanjing University Sept 2016 D. Liu (NJU) Solving D(S)GE 09/16 1 / 63 Introduction Targets of the
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco Nova SBE February 2012 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/31 Housekeeping Website TA: none No "Mas-Collel" in macro One midterm, one final, problem sets
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco Nova SBE February 2012 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/31 Housekeeping Website TA: none No "Mas-Collel" in macro One midterm, one final, problem sets
RBC Model with Indivisible Labor. Advanced Macroeconomic Theory
 RBC Model with Indivisible Labor Advanced Macroeconomic Theory 1 Last Class What are business cycles? Using HP- lter to decompose data into trend and cyclical components Business cycle facts Standard RBC
RBC Model with Indivisible Labor Advanced Macroeconomic Theory 1 Last Class What are business cycles? Using HP- lter to decompose data into trend and cyclical components Business cycle facts Standard RBC
S TICKY I NFORMATION Fabio Verona Bank of Finland, Monetary Policy and Research Department, Research Unit
 B USINESS C YCLE DYNAMICS UNDER S TICKY I NFORMATION Fabio Verona Bank of Finland, Monetary Policy and Research Department, Research Unit fabio.verona@bof.fi O BJECTIVE : analyze how and to what extent
B USINESS C YCLE DYNAMICS UNDER S TICKY I NFORMATION Fabio Verona Bank of Finland, Monetary Policy and Research Department, Research Unit fabio.verona@bof.fi O BJECTIVE : analyze how and to what extent
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2016 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/23 Housekeeping. Class organization. Website with notes and papers as no "Mas-Collel" in macro
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2016 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/23 Housekeeping. Class organization. Website with notes and papers as no "Mas-Collel" in macro
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle
 Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
Assessing Structural VAR s
 ... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson University of Maryland, September 2005 1 Background In Principle, Impulse Response Functions from SVARs
... Assessing Structural VAR s by Lawrence J. Christiano, Martin Eichenbaum and Robert Vigfusson University of Maryland, September 2005 1 Background In Principle, Impulse Response Functions from SVARs
Chapter 11 The Stochastic Growth Model and Aggregate Fluctuations
 George Alogoskoufis, Dynamic Macroeconomics, 2016 Chapter 11 The Stochastic Growth Model and Aggregate Fluctuations In previous chapters we studied the long run evolution of output and consumption, real
George Alogoskoufis, Dynamic Macroeconomics, 2016 Chapter 11 The Stochastic Growth Model and Aggregate Fluctuations In previous chapters we studied the long run evolution of output and consumption, real
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2011 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/34 The log-linear plain vanilla RBC and ν(σ n )= ĉ t = Y C ẑt +(1 α) Y C ˆn t + K βc ˆk t 1 + K
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2011 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/34 The log-linear plain vanilla RBC and ν(σ n )= ĉ t = Y C ẑt +(1 α) Y C ˆn t + K βc ˆk t 1 + K
Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions
 Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions Daniel Němec Faculty of Economics and Administrations Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic nemecd@econ.muni.cz ESF MU (Brno)
Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions Daniel Němec Faculty of Economics and Administrations Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic nemecd@econ.muni.cz ESF MU (Brno)
Oil price and macroeconomy in Russia. Abstract
 Oil price and macroeconomy in Russia Katsuya Ito Fukuoka University Abstract In this note, using the VEC model we attempt to empirically investigate the effects of oil price and monetary shocks on the
Oil price and macroeconomy in Russia Katsuya Ito Fukuoka University Abstract In this note, using the VEC model we attempt to empirically investigate the effects of oil price and monetary shocks on the
Public Economics The Macroeconomic Perspective Chapter 2: The Ramsey Model. Burkhard Heer University of Augsburg, Germany
 Public Economics The Macroeconomic Perspective Chapter 2: The Ramsey Model Burkhard Heer University of Augsburg, Germany October 3, 2018 Contents I 1 Central Planner 2 3 B. Heer c Public Economics: Chapter
Public Economics The Macroeconomic Perspective Chapter 2: The Ramsey Model Burkhard Heer University of Augsburg, Germany October 3, 2018 Contents I 1 Central Planner 2 3 B. Heer c Public Economics: Chapter
ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I
 Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Lars Svensson 2/16/06. Y t = Y. (1) Assume exogenous constant government consumption (determined by government), G t = G<Y. (2)
 Eco 504, part 1, Spring 2006 504_L3_S06.tex Lars Svensson 2/16/06 Specify equilibrium under perfect foresight in model in L2 Assume M 0 and B 0 given. Determine {C t,g t,y t,m t,b t,t t,r t,i t,p t } that
Eco 504, part 1, Spring 2006 504_L3_S06.tex Lars Svensson 2/16/06 Specify equilibrium under perfect foresight in model in L2 Assume M 0 and B 0 given. Determine {C t,g t,y t,m t,b t,t t,r t,i t,p t } that
Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models
 Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 2011 This note describes very briefly how to conduct quantitative analysis on a linearized
Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 2011 This note describes very briefly how to conduct quantitative analysis on a linearized
Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3.
 Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Inference when identifying assumptions are doubted. A. Theory B. Applications
 Inference when identifying assumptions are doubted A. Theory B. Applications 1 A. Theory Structural model of interest: A y t B 1 y t1 B m y tm u t nn n1 u t i.i.d. N0, D D diagonal 2 Bayesian approach:
Inference when identifying assumptions are doubted A. Theory B. Applications 1 A. Theory Structural model of interest: A y t B 1 y t1 B m y tm u t nn n1 u t i.i.d. N0, D D diagonal 2 Bayesian approach:
Inference when identifying assumptions are doubted. A. Theory. Structural model of interest: B 1 y t1. u t. B m y tm. u t i.i.d.
 Inference when identifying assumptions are doubted A. Theory B. Applications Structural model of interest: A y t B y t B m y tm nn n i.i.d. N, D D diagonal A. Theory Bayesian approach: Summarize whatever
Inference when identifying assumptions are doubted A. Theory B. Applications Structural model of interest: A y t B y t B m y tm nn n i.i.d. N, D D diagonal A. Theory Bayesian approach: Summarize whatever
Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded areas indicate US recessions research.stlouisfed.org
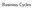 Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Computational Macroeconomics. Prof. Dr. Maik Wolters Friedrich Schiller University Jena
 Computational Macroeconomics Prof. Dr. Maik Wolters Friedrich Schiller University Jena Overview Objective: Learn doing empirical and applied theoretical work in monetary macroeconomics Implementing macroeconomic
Computational Macroeconomics Prof. Dr. Maik Wolters Friedrich Schiller University Jena Overview Objective: Learn doing empirical and applied theoretical work in monetary macroeconomics Implementing macroeconomic
Macroeconomics II. Dynamic AD-AS model
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Dynamic AD-AS model vs. AD-AS model Notes. Dynamic AD-AS model in a few words Notes. Notation to incorporate time-dimension Notes
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model
 Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam?
 The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
The Price Puzzle: Mixing the Temporary and Permanent Monetary Policy Shocks.
 The Price Puzzle: Mixing the Temporary and Permanent Monetary Policy Shocks. Ida Wolden Bache Norges Bank Kai Leitemo Norwegian School of Management BI September 2, 2008 Abstract We argue that the correct
The Price Puzzle: Mixing the Temporary and Permanent Monetary Policy Shocks. Ida Wolden Bache Norges Bank Kai Leitemo Norwegian School of Management BI September 2, 2008 Abstract We argue that the correct
The Neo Fisher Effect and Exiting a Liquidity Trap
 The Neo Fisher Effect and Exiting a Liquidity Trap Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé and Martín Uribe Columbia University European Central Bank Conference on Monetary Policy Frankfurt am Main, October 29-3, 218
The Neo Fisher Effect and Exiting a Liquidity Trap Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé and Martín Uribe Columbia University European Central Bank Conference on Monetary Policy Frankfurt am Main, October 29-3, 218
The Ramsey Model. (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 2013)
 The Ramsey Model (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 213) 1 Introduction The Ramsey model (or neoclassical growth model) is one of the prototype models in dynamic macroeconomics.
The Ramsey Model (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 213) 1 Introduction The Ramsey model (or neoclassical growth model) is one of the prototype models in dynamic macroeconomics.
Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment
 Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment Pascal Michaillat (LSE) & Emmanuel Saez (Berkeley) September 2014 1 / 44 Motivation 11% Unemployment rate 9% 7% 5% 3% 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 2 / 44 Motivation
Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment Pascal Michaillat (LSE) & Emmanuel Saez (Berkeley) September 2014 1 / 44 Motivation 11% Unemployment rate 9% 7% 5% 3% 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 2 / 44 Motivation
Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment
 Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment Pascal Michaillat (LSE) & Emmanuel Saez (Berkeley) July 2014 1 / 46 Motivation 11% Unemployment rate 9% 7% 5% 3% 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 2 / 46 Motivation
Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment Pascal Michaillat (LSE) & Emmanuel Saez (Berkeley) July 2014 1 / 46 Motivation 11% Unemployment rate 9% 7% 5% 3% 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 2 / 46 Motivation
Asymmetry of the exchange rate pass-through: An exercise on the Polish data
 National Bank of Poland Asymmetry of the exchange rate pass-through: An exercise on the Polish data Jan Przystupa Ewa Wróbel 0th Annual NBP - SNB Seminar June 4, 03 Zurich PLN/USD fluctuations Band +/-5%
National Bank of Poland Asymmetry of the exchange rate pass-through: An exercise on the Polish data Jan Przystupa Ewa Wróbel 0th Annual NBP - SNB Seminar June 4, 03 Zurich PLN/USD fluctuations Band +/-5%
Warwick Business School Forecasting System. Summary. Ana Galvao, Anthony Garratt and James Mitchell November, 2014
 Warwick Business School Forecasting System Summary Ana Galvao, Anthony Garratt and James Mitchell November, 21 The main objective of the Warwick Business School Forecasting System is to provide competitive
Warwick Business School Forecasting System Summary Ana Galvao, Anthony Garratt and James Mitchell November, 21 The main objective of the Warwick Business School Forecasting System is to provide competitive
Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4
 Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4 1 Basic Model 1.1 Uzawa Utility E 0 t=0 θ t U (c t, h t ) θ 0 = 1 θ t+1 = β (c t, h t ) θ t ; β c < 0; β h > 0. Time-varying discount factor With a constant
Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4 1 Basic Model 1.1 Uzawa Utility E 0 t=0 θ t U (c t, h t ) θ 0 = 1 θ t+1 = β (c t, h t ) θ t ; β c < 0; β h > 0. Time-varying discount factor With a constant
1 The Basic RBC Model
 IHS 2016, Macroeconomics III Michael Reiter Ch. 1: Notes on RBC Model 1 1 The Basic RBC Model 1.1 Description of Model Variables y z k L c I w r output level of technology (exogenous) capital at end of
IHS 2016, Macroeconomics III Michael Reiter Ch. 1: Notes on RBC Model 1 1 The Basic RBC Model 1.1 Description of Model Variables y z k L c I w r output level of technology (exogenous) capital at end of
A primer on Structural VARs
 A primer on Structural VARs Claudia Foroni Norges Bank 10 November 2014 Structural VARs 1/ 26 Refresh: what is a VAR? VAR (p) : where y t K 1 y t = ν + B 1 y t 1 +... + B p y t p + u t, (1) = ( y 1t...
A primer on Structural VARs Claudia Foroni Norges Bank 10 November 2014 Structural VARs 1/ 26 Refresh: what is a VAR? VAR (p) : where y t K 1 y t = ν + B 1 y t 1 +... + B p y t p + u t, (1) = ( y 1t...
Foundation of (virtually) all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model) is Solow growth model
 THE BASELINE RBC MODEL: THEORY AND COMPUTATION FEBRUARY, 202 STYLIZED MACRO FACTS Foundation of (virtually all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model is Solow growth model So want/need/desire business-cycle models
THE BASELINE RBC MODEL: THEORY AND COMPUTATION FEBRUARY, 202 STYLIZED MACRO FACTS Foundation of (virtually all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model is Solow growth model So want/need/desire business-cycle models
Estimating and Accounting for the Output Gap with Large Bayesian Vector Autoregressions
 Estimating and Accounting for the Output Gap with Large Bayesian Vector Autoregressions James Morley 1 Benjamin Wong 2 1 University of Sydney 2 Reserve Bank of New Zealand The view do not necessarily represent
Estimating and Accounting for the Output Gap with Large Bayesian Vector Autoregressions James Morley 1 Benjamin Wong 2 1 University of Sydney 2 Reserve Bank of New Zealand The view do not necessarily represent
Precautionary Demand for Money in a Monetary Business Cycle Model
 Discussion of Precautionary Demand for Money in a Monetary Business Cycle Model by I. Telyukova and L. Visschers Makoto Nakajima FRB Philadelphia March 27, 2009 Makoto Nakajima (FRB Philadelphia) Discussion
Discussion of Precautionary Demand for Money in a Monetary Business Cycle Model by I. Telyukova and L. Visschers Makoto Nakajima FRB Philadelphia March 27, 2009 Makoto Nakajima (FRB Philadelphia) Discussion
MFx Macroeconomic Forecasting
 MFx Macroeconomic Forecasting Structural Vector Autoregressive Models Part II IMFx This training material is the property of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and is intended for use in IMF Institute
MFx Macroeconomic Forecasting Structural Vector Autoregressive Models Part II IMFx This training material is the property of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and is intended for use in IMF Institute
Online Appendix (Not intended for Publication): Decomposing the Effects of Monetary Policy Using an External Instruments SVAR
 Online Appendix (Not intended for Publication): Decomposing the Effects of Monetary Policy Using an External Instruments SVAR Aeimit Lakdawala Michigan State University December 7 This appendix contains
Online Appendix (Not intended for Publication): Decomposing the Effects of Monetary Policy Using an External Instruments SVAR Aeimit Lakdawala Michigan State University December 7 This appendix contains
Gaussian Mixture Approximations of Impulse Responses and the Non-Linear Effects of Monetary Shocks
 Gaussian Mixture Approximations of Impulse Responses and the Non-Linear Effects of Monetary Shocks Regis Barnichon (CREI, Universitat Pompeu Fabra) Christian Matthes (Richmond Fed) Effects of monetary
Gaussian Mixture Approximations of Impulse Responses and the Non-Linear Effects of Monetary Shocks Regis Barnichon (CREI, Universitat Pompeu Fabra) Christian Matthes (Richmond Fed) Effects of monetary
A Primer on Vector Autoregressions
 A Primer on Vector Autoregressions Ambrogio Cesa-Bianchi VAR models 1 [DISCLAIMER] These notes are meant to provide intuition on the basic mechanisms of VARs As such, most of the material covered here
A Primer on Vector Autoregressions Ambrogio Cesa-Bianchi VAR models 1 [DISCLAIMER] These notes are meant to provide intuition on the basic mechanisms of VARs As such, most of the material covered here
Study of Causal Relationships in Macroeconomics
 Study of Causal Relationships in Macroeconomics Contributions of Thomas Sargent and Christopher Sims, Nobel Laureates in Economics 2011. 1 1. Personal Background Thomas J. Sargent: PhD Harvard University
Study of Causal Relationships in Macroeconomics Contributions of Thomas Sargent and Christopher Sims, Nobel Laureates in Economics 2011. 1 1. Personal Background Thomas J. Sargent: PhD Harvard University
Identifying SVARs with Sign Restrictions and Heteroskedasticity
 Identifying SVARs with Sign Restrictions and Heteroskedasticity Srečko Zimic VERY PRELIMINARY AND INCOMPLETE NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION February 13, 217 Abstract This paper introduces a new method to identify
Identifying SVARs with Sign Restrictions and Heteroskedasticity Srečko Zimic VERY PRELIMINARY AND INCOMPLETE NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION February 13, 217 Abstract This paper introduces a new method to identify
The 2001 recession displayed unique characteristics in comparison to other
 Smoothing the Shocks of a Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Model ANDREW BAUER NICHOLAS HALTOM AND JUAN F RUBIO-RAMÍREZ Bauer and Haltom are senior economic analysts and Rubio-Ramírez is an economist
Smoothing the Shocks of a Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Model ANDREW BAUER NICHOLAS HALTOM AND JUAN F RUBIO-RAMÍREZ Bauer and Haltom are senior economic analysts and Rubio-Ramírez is an economist
Gold Rush Fever in Business Cycles
 Gold Rush Fever in Business Cycles Paul Beaudry, Fabrice Collard & Franck Portier University of British Columbia & Université de Toulouse UAB Seminar Barcelona November, 29, 26 The Klondike Gold Rush of
Gold Rush Fever in Business Cycles Paul Beaudry, Fabrice Collard & Franck Portier University of British Columbia & Université de Toulouse UAB Seminar Barcelona November, 29, 26 The Klondike Gold Rush of
Quarterly Journal of Economics and Modelling Shahid Beheshti University SVAR * SVAR * **
 1392 Quarterly Journal of Economics and Modelling Shahid Beheshti University : SVAR * ** 93/9/2 93/2/15 SVAR h-dargahi@sbuacir esedaghatparast@ibiacir ( 1 * ** 1392 13 2 SVAR H30, C32, E62, E52, E32 JEL
1392 Quarterly Journal of Economics and Modelling Shahid Beheshti University : SVAR * ** 93/9/2 93/2/15 SVAR h-dargahi@sbuacir esedaghatparast@ibiacir ( 1 * ** 1392 13 2 SVAR H30, C32, E62, E52, E32 JEL
Animal Spirits, Fundamental Factors and Business Cycle Fluctuations
 Animal Spirits, Fundamental Factors and Business Cycle Fluctuations Stephane Dées Srečko Zimic Banque de France European Central Bank January 6, 218 Disclaimer Any views expressed represent those of the
Animal Spirits, Fundamental Factors and Business Cycle Fluctuations Stephane Dées Srečko Zimic Banque de France European Central Bank January 6, 218 Disclaimer Any views expressed represent those of the
Signaling Effects of Monetary Policy
 Signaling Effects of Monetary Policy Leonardo Melosi London Business School 24 May 2012 Motivation Disperse information about aggregate fundamentals Morris and Shin (2003), Sims (2003), and Woodford (2002)
Signaling Effects of Monetary Policy Leonardo Melosi London Business School 24 May 2012 Motivation Disperse information about aggregate fundamentals Morris and Shin (2003), Sims (2003), and Woodford (2002)
Endogenous Information Choice
 Endogenous Information Choice Lecture 7 February 11, 2015 An optimizing trader will process those prices of most importance to his decision problem most frequently and carefully, those of less importance
Endogenous Information Choice Lecture 7 February 11, 2015 An optimizing trader will process those prices of most importance to his decision problem most frequently and carefully, those of less importance
Identifying Aggregate Liquidity Shocks with Monetary Policy Shocks: An Application using UK Data
 Identifying Aggregate Liquidity Shocks with Monetary Policy Shocks: An Application using UK Data Michael Ellington and Costas Milas Financial Services, Liquidity and Economic Activity Bank of England May
Identifying Aggregate Liquidity Shocks with Monetary Policy Shocks: An Application using UK Data Michael Ellington and Costas Milas Financial Services, Liquidity and Economic Activity Bank of England May
Modern Macroeconomics and Regional Economic Modeling
 Modern Macroeconomics and Regional Economic Modeling by Dan S. Rickman Oklahoma State University prepared for presentation in the JRS 50 th Anniversary Symposium at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York
Modern Macroeconomics and Regional Economic Modeling by Dan S. Rickman Oklahoma State University prepared for presentation in the JRS 50 th Anniversary Symposium at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York
Estimating and Identifying Vector Autoregressions Under Diagonality and Block Exogeneity Restrictions
 Estimating and Identifying Vector Autoregressions Under Diagonality and Block Exogeneity Restrictions William D. Lastrapes Department of Economics Terry College of Business University of Georgia Athens,
Estimating and Identifying Vector Autoregressions Under Diagonality and Block Exogeneity Restrictions William D. Lastrapes Department of Economics Terry College of Business University of Georgia Athens,
Problem Set 4. Graduate Macro II, Spring 2011 The University of Notre Dame Professor Sims
 Problem Set 4 Graduate Macro II, Spring 2011 The University of Notre Dame Professor Sims Instructions: You may consult with other members of the class, but please make sure to turn in your own work. Where
Problem Set 4 Graduate Macro II, Spring 2011 The University of Notre Dame Professor Sims Instructions: You may consult with other members of the class, but please make sure to turn in your own work. Where
The Real Business Cycle Model
 The Real Business Cycle Model Macroeconomics II 2 The real business cycle model. Introduction This model explains the comovements in the fluctuations of aggregate economic variables around their trend.
The Real Business Cycle Model Macroeconomics II 2 The real business cycle model. Introduction This model explains the comovements in the fluctuations of aggregate economic variables around their trend.
Taylor Rules and Technology Shocks
 Taylor Rules and Technology Shocks Eric R. Sims University of Notre Dame and NBER January 17, 2012 Abstract In a standard New Keynesian model, a Taylor-type interest rate rule moves the equilibrium real
Taylor Rules and Technology Shocks Eric R. Sims University of Notre Dame and NBER January 17, 2012 Abstract In a standard New Keynesian model, a Taylor-type interest rate rule moves the equilibrium real
Perceived productivity and the natural rate of interest
 Perceived productivity and the natural rate of interest Gianni Amisano and Oreste Tristani European Central Bank IRF 28 Frankfurt, 26 June Amisano-Tristani (European Central Bank) Productivity and the
Perceived productivity and the natural rate of interest Gianni Amisano and Oreste Tristani European Central Bank IRF 28 Frankfurt, 26 June Amisano-Tristani (European Central Bank) Productivity and the
Test code: ME I/ME II, 2004 Syllabus for ME I. Matrix Algebra: Matrices and Vectors, Matrix Operations, Determinants,
 Test code: ME I/ME II, 004 Syllabus for ME I Matri Algebra: Matrices and Vectors, Matri Operations, Determinants, Nonsingularity, Inversion, Cramer s rule. Calculus: Limits, Continuity, Differentiation
Test code: ME I/ME II, 004 Syllabus for ME I Matri Algebra: Matrices and Vectors, Matri Operations, Determinants, Nonsingularity, Inversion, Cramer s rule. Calculus: Limits, Continuity, Differentiation
Are Structural VARs Useful Guides for Developing Business Cycle Theories? by Larry Christiano
 Discussion of: Chari-Kehoe-McGrattan: Are Structural VARs Useful Guides for Developing Business Cycle Theories? by Larry Christiano 1 Chari-Kehoe-McGrattan: Are Structural VARs Useful Guides for Developing
Discussion of: Chari-Kehoe-McGrattan: Are Structural VARs Useful Guides for Developing Business Cycle Theories? by Larry Christiano 1 Chari-Kehoe-McGrattan: Are Structural VARs Useful Guides for Developing
Gold Rush Fever in Business Cycles
 Gold Rush Fever in Business Cycles Paul Beaudry, Fabrice Collard & Franck Portier University of British Columbia & Université de Toulouse Banque Nationale Nationale Bank Belgischen de Belgique van Belgïe
Gold Rush Fever in Business Cycles Paul Beaudry, Fabrice Collard & Franck Portier University of British Columbia & Université de Toulouse Banque Nationale Nationale Bank Belgischen de Belgique van Belgïe
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital
 Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano January 5, 2018 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand.
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano January 5, 2018 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand.
Monetary Policy in a Macro Model
 Monetary Policy in a Macro Model ECON 40364: Monetary Theory & Policy Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 1 / 67 Readings Mishkin Ch. 20 Mishkin Ch. 21 Mishkin Ch. 22 Mishkin Ch. 23, pg. 553-569
Monetary Policy in a Macro Model ECON 40364: Monetary Theory & Policy Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 1 / 67 Readings Mishkin Ch. 20 Mishkin Ch. 21 Mishkin Ch. 22 Mishkin Ch. 23, pg. 553-569
Resolving the Missing Deflation Puzzle. June 7, 2018
 Resolving the Missing Deflation Puzzle Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin June 7, 218 Motivation Key observations during the Great Recession: Extraordinary contraction
Resolving the Missing Deflation Puzzle Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin June 7, 218 Motivation Key observations during the Great Recession: Extraordinary contraction
Fresh perspectives on unobservable variables: Data decomposition of the Kalman smoother
 Fresh perspectives on unobservable variables: Data decomposition of the Kalman smoother AN 2013/09 Nicholas Sander December 2013 Reserve Bank of New Zealand Analytical Note series ISSN 2230 5505 Reserve
Fresh perspectives on unobservable variables: Data decomposition of the Kalman smoother AN 2013/09 Nicholas Sander December 2013 Reserve Bank of New Zealand Analytical Note series ISSN 2230 5505 Reserve
Is there a flight to quality due to inflation uncertainty?
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Is there a flight to quality due to inflation uncertainty? Bulent Guler and Umit Ozlale Bilkent University, Bilkent University 18. August 2004 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/7929/
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Is there a flight to quality due to inflation uncertainty? Bulent Guler and Umit Ozlale Bilkent University, Bilkent University 18. August 2004 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/7929/
Recent Developments in Monetary Economics. Lawrence Christiano
 MACRO-LINKAGES, OIL PRICES AND DEFLATION WORKSHOP JANUARY 6 9, 2009 Recent Developments in Monetary Economics Lawrence Christiano Recent Developments in Monetary Economics Lawrence Christiano Northwestern
MACRO-LINKAGES, OIL PRICES AND DEFLATION WORKSHOP JANUARY 6 9, 2009 Recent Developments in Monetary Economics Lawrence Christiano Recent Developments in Monetary Economics Lawrence Christiano Northwestern
(a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
Discussion of Riccardo DiCecio \Comovement: It's not a Puzzle" Matteo Iacoviello Boston College
 Discussion of Riccardo DiCecio \Comovement: It's not a Puzzle" Matteo Iacoviello Boston College THE QUESTION Question: can we construct a coherent DSGE macro model that explains the comovement puzzle?
Discussion of Riccardo DiCecio \Comovement: It's not a Puzzle" Matteo Iacoviello Boston College THE QUESTION Question: can we construct a coherent DSGE macro model that explains the comovement puzzle?
Optimal Simple And Implementable Monetary and Fiscal Rules
 Optimal Simple And Implementable Monetary and Fiscal Rules Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe Duke University September 2007 1 Welfare-Based Policy Evaluation: Related Literature (ex: Rotemberg and Woodford,
Optimal Simple And Implementable Monetary and Fiscal Rules Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe Duke University September 2007 1 Welfare-Based Policy Evaluation: Related Literature (ex: Rotemberg and Woodford,
1. Shocks. This version: February 15, Nr. 1
 1. Shocks This version: February 15, 2006 Nr. 1 1.3. Factor models What if there are more shocks than variables in the VAR? What if there are only a few underlying shocks, explaining most of fluctuations?
1. Shocks This version: February 15, 2006 Nr. 1 1.3. Factor models What if there are more shocks than variables in the VAR? What if there are only a few underlying shocks, explaining most of fluctuations?
Macroeconomics - Data & Theory
 Macroeconomics - Data & Theory Wouter J. Den Haan University of Amsterdam October 24, 2009 How to isolate the business cycle component? Easy way is to use the Hodrick-Prescott (HP) lter min fx τ,t g T
Macroeconomics - Data & Theory Wouter J. Den Haan University of Amsterdam October 24, 2009 How to isolate the business cycle component? Easy way is to use the Hodrick-Prescott (HP) lter min fx τ,t g T
Mortenson Pissarides Model
 Mortenson Pissarides Model Prof. Lutz Hendricks Econ720 November 22, 2017 1 / 47 Mortenson / Pissarides Model Search models are popular in many contexts: labor markets, monetary theory, etc. They are distinguished
Mortenson Pissarides Model Prof. Lutz Hendricks Econ720 November 22, 2017 1 / 47 Mortenson / Pissarides Model Search models are popular in many contexts: labor markets, monetary theory, etc. They are distinguished
Econometría 2: Análisis de series de Tiempo
 Econometría 2: Análisis de series de Tiempo Karoll GOMEZ kgomezp@unal.edu.co http://karollgomez.wordpress.com Segundo semestre 2016 IX. Vector Time Series Models VARMA Models A. 1. Motivation: The vector
Econometría 2: Análisis de series de Tiempo Karoll GOMEZ kgomezp@unal.edu.co http://karollgomez.wordpress.com Segundo semestre 2016 IX. Vector Time Series Models VARMA Models A. 1. Motivation: The vector
DATABASE AND METHODOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3 DATABASE AND METHODOLOGY In the present chapter, sources of database used and methodology applied for the empirical analysis has been presented The whole chapter has been divided into three sections
CHAPTER 3 DATABASE AND METHODOLOGY In the present chapter, sources of database used and methodology applied for the empirical analysis has been presented The whole chapter has been divided into three sections
Matching DSGE models,vars, and state space models. Fabio Canova EUI and CEPR September 2012
 Matching DSGE models,vars, and state space models Fabio Canova EUI and CEPR September 2012 Outline Alternative representations of the solution of a DSGE model. Fundamentalness and finite VAR representation
Matching DSGE models,vars, and state space models Fabio Canova EUI and CEPR September 2012 Outline Alternative representations of the solution of a DSGE model. Fundamentalness and finite VAR representation
General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory SPRING 2013
 HARVARD UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory SPRING 203 You have FOUR hours. Answer all questions Part A (Prof. Laibson): 48 minutes Part B (Prof. Aghion): 48
HARVARD UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory SPRING 203 You have FOUR hours. Answer all questions Part A (Prof. Laibson): 48 minutes Part B (Prof. Aghion): 48
Business Cycle Dating Committee of the Centre for Economic Policy Research. 1. The CEPR Business Cycle Dating Committee
 Business Cycle Dating Committee of the Centre for Economic Policy Research Michael Artis Fabio Canova Jordi Gali Francesco Giavazzi Richard Portes (President, CEPR) Lucrezia Reichlin (Chair) Harald Uhlig
Business Cycle Dating Committee of the Centre for Economic Policy Research Michael Artis Fabio Canova Jordi Gali Francesco Giavazzi Richard Portes (President, CEPR) Lucrezia Reichlin (Chair) Harald Uhlig
DSGE-Models. Calibration and Introduction to Dynare. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics
 DSGE-Models Calibration and Introduction to Dynare Dr. Andrea Beccarini Willi Mutschler, M.Sc. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics willi.mutschler@uni-muenster.de Summer 2012 Willi Mutschler
DSGE-Models Calibration and Introduction to Dynare Dr. Andrea Beccarini Willi Mutschler, M.Sc. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics willi.mutschler@uni-muenster.de Summer 2012 Willi Mutschler
Building and simulating DSGE models part 2
 Building and simulating DSGE models part II DSGE Models and Real Life I. Replicating business cycles A lot of papers consider a smart calibration to replicate business cycle statistics (e.g. Kydland Prescott).
Building and simulating DSGE models part II DSGE Models and Real Life I. Replicating business cycles A lot of papers consider a smart calibration to replicate business cycle statistics (e.g. Kydland Prescott).
The Dark Corners of the Labor Market
 The Dark Corners of the Labor Market Vincent Sterk Conference on Persistent Output Gaps: Causes and Policy Remedies EABCN / University of Cambridge / INET University College London September 2015 Sterk
The Dark Corners of the Labor Market Vincent Sterk Conference on Persistent Output Gaps: Causes and Policy Remedies EABCN / University of Cambridge / INET University College London September 2015 Sterk
Formulating, Estimating, and Solving Dynamic Equilibrium Models: an Introduction. Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania
 Formulating, Estimating, and Solving Dynamic Equilibrium Models: an Introduction Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Models Tradition in macroeconomics of using models: 1. Policy Analysis.
Formulating, Estimating, and Solving Dynamic Equilibrium Models: an Introduction Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Models Tradition in macroeconomics of using models: 1. Policy Analysis.
