PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #9-- SOLUTIONS
|
|
|
- Marsha Ford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHYS 0 HOMEWORK #9-- SOLUTIONS. We are asked to use Dirichlet' s theorem to determine the value of f (x) as defined below at x = 0, ± /, ± f(x) = 0, - < x <, < x < Dirichlet's theorem tells us that the Fourier series will converge to the value of f(x) for those values of x where f is continuous, and will converge to the midoint of f(x) at discontinuities. The Fourier series for this function is: f x = Å 4 -Å Å cos x - cos x + cos 5 x sin x sin x - + sin x + sin 5 x - sin 6 x Let' s lot a few cycles of this grah to show it is eriodic and to see where the discontinuities lie. I will lot this using the analytical exression for the Fourier coefficients a 0, a n, and b n which you can find easily from integrating the simle ste function.
2 hys0-009hw9s.nb Plot 4 Sum Sin n Cos n x n, n,, 5 Sum ^ n Cos n Sin n x n, n,, 5, x,, The function is continuous at x = 0, so the Fourier series converges to the value of function. We know from the definition of the function above that f (0) = 0. Recalling that cos 0 = and sin 0 = 0, this imlies : f 0 = 0 = Å 4 -Å -Å +Å 5 -Å Which imlies that : Å 4 = -Å +Å 5 -Å A result that we obtained in class and is shown on. 58 of Boas. The function is discontinuous at x = /; the midoint of the jum is /, so the value of f (/) = /. All of the cos terms in this Fourier series will be zero since cos (n /) = 0 for odd values of n, and sin (n /) is zero for even values of n, and is either + or - deending on whether n=,5,9,... or n=,7,... These results imly:
3 hys0-009hw9s.nb f Å = Å = Å 4 +Å -Å +Å 5 -Å A result we already know. We can see that the function is discontinuous at x = ± by lotting several cycles of this function: The value of x at x= ± is just the midoint of the jum, so that the value of the function at ± is simly /. You should do the exercise of substituting + and - into the Fourier series exression to show that your resulting value is in fact /. Similarly, the function is continuous at x=-/, so f(-/)=0.. We need only to do the function defined in a).we will first calculate the sine/cos series, then the comlex series, then lot the function defined below. Our function is: f x = x, - < x < To find the Fourier coefficients : a 0 = Å x dx = Å - x = Å - = Å a n = Å x cos nx dx = Å - x n sin nx -Å n x sin nx dx - - = Å x n sin nx -Å n -x n cos nx - - n Å cos nx - - = Å 0 +Å n Å cos n - - cos -n + 0 = n 4 cos n n = 4 - n n To calculate b n, we could either exlicitly integrate the aroriate Fourier integral, or we can aeal to the symmetry of the functions involved. We know that x is an even function, and sin (n x) is an odd function. The roduct of an even and odd function is itself an odd function, and
4 4 hys0-009hw9s.nb the value of the integral of an odd function between limits symmetric across the origin is zero. In other words: -L Lf odd function dx = 0 Thus, by using the symmetry of these functions, we know that b n is 0. Therefore, we can write the sin/cos Fourier series for this function as: f x = + 4 S - n cos nx n= n To find the comlex series, find the comlex coefficients, c n : c n = f x e -inx dx = - x e -inx dx - In the case that n = 0, we obtain simly for c 0 : c 0 = x dx = - We solve this integral by arts; for ease of tying I will omit limits and aly those at the end. c n = x e -inx = -x in e-inx + in xe -inx dx = -x in + in -x in e-inx + in e -inx dx = e -inx in x + nx - i n - = - n 4 n In making the final evaluation, we make use of the fact that : e -in = cos (n ) - i sin(n ) = cos(n ) = - n.
5 hys0-009hw9s.nb 5 Finally, we lot three cycles of the Fourier Series using the Fourier coefficients defined above : Plot 4 Sum n Cos n x n^, n,, 7, x,, We are asked to find the Fourier series for the function : f x = e x, - < x < Finding the Fourier coefficients : a 0 = Å e x dx = - Å e - e - To find the Fourier coefficients a n and b n, lease refer to roblem 7 of HW 7 in which we solved an integral very similar to what you will need here. Quoting only the results: e x cos nx dx = - n sinh a n = Å - n + where sinh is the hyerbolic sine function defined as : sinh x = ex - e -x.
6 6 hys0-009hw9s.nb The cosh function is similarly : cosh x = ex + e -x e x sin nx dx = - - n n sinh b n = Å - n + So that our Fourier series is : f x = sinh sinh + sinh S + -cos x + cos x 5 - n S - n n sin nx cos nx - = n + n + - cos x sin x - sin x 5 + sin x () () Plotting this Fourier series over cycles : Plot Sinh Sum n Sinh Cos n x n^, n,, 9 Sum n n Sinh Sin n x n^, n,, 9, x,, And now lotting the Fourier Series from - to and overlaying two oints which we know to be on the curve; this Fourier series aears to be a very good fit to the function e x.
7 hys0-009hw9s.nb 7 g Plot Sinh Sum n Sinh Cos n x n^, n,, 9 Sum n n Sinh Sin n x n^, n,, 9, x,,, Eilog Red, PointSize Large, Point, Ex,, Ex Comlex Fourier Series : We now solve the coefficients for the comlex Fourier series. We need to comute : c 0 = e x dx and c n = - e x e -inx dx - These are both very easy integrals to evaluate : c 0 = e x dx = - e - e - = sinh c n = e x e -inx dx = - e x -in dx = - - in e e -in - e - e in = cos n + in e - e - + n = - n sinh n + + in - n sinh + n = - n sinh -Å n n + i In reducing this exression, we recognize that e in = cos n ±i sin n = cos(n ) since sin n is always zero for integer values of n. Additionally, we
8 8 hys0-009hw9s.nb multily numerator and denominator by the comlex conjugate of the term (-i n). In the last ste, we make use of the relationshi i = -, so that i = -/i. The comlex Fourier series is written as: f x = S cn e inx n=- where the index n now runs from minus infinity to lus infinity. If we grou terms as : f x = c 0 + c e ix + c - e - ix + c e ix + c e -ix +... we can write this comlex Fourier series as : f x = sinh + -e ix + eix i - e -ix - e-ix i + e ix 5 - eix 5 i + e-ix 5 - e-ix 5 i... = sinh + - cos x + sin x + cos x - sin x We roduce the final equation in () by recalling the definitions of cos nx and sin nx : cos nx = einx + e -inx and sin n x = einx - e -inx i And we find, as we exect, that the exression in () matches the exression in (). () 4. We wish to roduce the Fourier Series for the function : f x = - x on - < x < This is our first encounter with eriodic Fourier series on an interval other than. In this case, we use the following versions of Fourier equations : f x = a 0 + S an cos n x n= L + b n sin n x L
9 hys0-009hw9s.nb 9 where the coefficients are : a n = Lf L x cos n x -L L dx and b n = Lf L x sin n x -L L dx In our current case, L =, and so we roceed : a 0 = Å - x dx = 4 - a n = Å - x cos n x - dx = Integrate x Cos n x, x,,, Assumtions Element n, Integers 0 To find the b n coefficients: b n = Å - x sin n x - dx = Integrate x Sin n x, x,,, Assumtions Element n, Integers 4 n n We then write the Fourier series on this interval as : f x = +Å 4 S - n sin n x n= n = (4) +Å 4 sin x -sin x + - sin x +... (5) Plotting this series over three cycles :
10 0 hys0-009hw9s.nb Plot 4 Sum ^n Sin n x n, n,, 5, x, 6, We can also check Dirichlet' s theorem by using our series in eq. (4) by solving for the value of the function at the jum at x =. We have from equation (4) : f x = +Å 4 S - n sin n x n= n f = +Å 4 S - n sin n n = fl since all sin (n ) terms are zero for integer values of n. This result equals the midoint of the jum at x =, and is consistent with Dirichlet' s theorem. Comlex Fourier Series The comlex Fourier series is given by (Boas,. 6) : f x = inx L S cn e n=- where the comlex coefficients are determined from : c 0 = Lf L x dx c n = L -L L f x e -inx L dx -L for this function, L =, f (x) = - x, and our integrals become : c 0 = Å 4 - x dx = -
11 hys0-009hw9s.nb c n = Å 4 - x e -inx dx = - Integrate x Ex n x, x,,, Assumtions Element n, Integers 4 Abs n n n n i where use the relationshi i = -/i in the last ste. We can then write the comlex Fourier series as : f x = + i - n S n=- n Look at the inut statement above. In articular, notice how we write the imaginary number in Mathematica code. If you use a simle "i" keystroke, Mathematica will assume "i" reresents a new variable name; in order to indicate the imaginary number, you enter the  iiâ; in other words, hit the escae key, the "i" key twice, followed by the escae key, with no intervening saces. We can use our comuted coefficients to write the first several terms of the comlex Fourier series : f x = c 0 + c e i x + c e -i x + c e ix + c e -ix + c e ix + c - e -ix +... = + i -ei x + e -i x + ei x - ei x + -ei x + e-i x +... = + Å sin x - sin x + sin x (6) which matches the Fourier exansion in eqs. (4) and (5) 5. Find the Fourier series for : f x = sin x on the interval -Å < x < Å Here, L = /, so we have :
12 hys0-009hw9s.nb a 0 = sin xdx = - cos - cos - = 0 - a n = sin x cos n x dx = 0 - b n = sin x sin nx dx = - Integrate Sin x Sin n x, x,,, Assumtions Element n, Integers 8 n n 4n and to be sure that we cover all ossible cases, we exlicitly evaluate the case for n = : Integrate Sin x Sin x, x,, 8 The Fourier series for this function is then : f x = Å 8 S - n n sin nx = Å 8 n= - 4 n sin x - sin 4 x 5 + sin 6 x Plotting cycles of this function gives us : Plot 8 Sum ^n n Sin n x 4 n, n,, 5, x,, How well does this Fourier series aroximate sin ( x) on the interval (-/./)? Let' s lot the Fourier exansion and the curve for sin( x) on the same set of axes (with the sin ( x) grah lotted as a thick urle line and the Fourier series lotted with a blue, thick, dashed line) :
13 hys0-009hw9s.nb Plot Sin x, 8 Sum ^n n Sin n x 4 n, n,, 5, x,,, PlotStyle Thick, Purle, Blue, Thick, Dashed And the first 5 terms of the Fourier series converge very closely to the curve of sin ( x). The Comlex Fourier series We find the coefficients : c 0 = sin x dx = - cos - cos - = 0 - c n = sin x e - inx dx = - Integrate Sin x Ex n x, x,,, Assumtions Element n, Integers 4 n n 4n We can write the result in outut line [8] as : -4i - n n - 4 n = 4 - n n i - 4 n so that our comlex Fourier series is : f x = Å 4 S - n n - i - 4 n ein x
PHYSICS 301/MATH 355 HOMEWORK #8
 PHYSICS 3/MATH 355 HOMEWORK #8 Solutions Question # We consider the integral : where m and n are both integers. We can evaluate this integral : Integrate@Cos@m xd Cos@n xd, 8x, π, π
PHYSICS 3/MATH 355 HOMEWORK #8 Solutions Question # We consider the integral : where m and n are both integers. We can evaluate this integral : Integrate@Cos@m xd Cos@n xd, 8x, π, π
2.9 Dirac Notation Vectors ji that are orthonormal hk ji = k,j span a vector space and express the identity operator I of the space as (1.
 14 Fourier Series 2.9 Dirac Notation Vectors ji that are orthonormal hk ji k,j san a vector sace and exress the identity oerator I of the sace as (1.132) I NX jihj. (2.99) Multilying from the right by
14 Fourier Series 2.9 Dirac Notation Vectors ji that are orthonormal hk ji k,j san a vector sace and exress the identity oerator I of the sace as (1.132) I NX jihj. (2.99) Multilying from the right by
Towards understanding the Lorenz curve using the Uniform distribution. Chris J. Stephens. Newcastle City Council, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK
 Towards understanding the Lorenz curve using the Uniform distribution Chris J. Stehens Newcastle City Council, Newcastle uon Tyne, UK (For the Gini-Lorenz Conference, University of Siena, Italy, May 2005)
Towards understanding the Lorenz curve using the Uniform distribution Chris J. Stehens Newcastle City Council, Newcastle uon Tyne, UK (For the Gini-Lorenz Conference, University of Siena, Italy, May 2005)
MATH 2710: NOTES FOR ANALYSIS
 MATH 270: NOTES FOR ANALYSIS The main ideas we will learn from analysis center around the idea of a limit. Limits occurs in several settings. We will start with finite limits of sequences, then cover infinite
MATH 270: NOTES FOR ANALYSIS The main ideas we will learn from analysis center around the idea of a limit. Limits occurs in several settings. We will start with finite limits of sequences, then cover infinite
Chapter 10. Classical Fourier Series
 Math 344, Male ab Manual Chater : Classical Fourier Series Real and Comle Chater. Classical Fourier Series Fourier Series in PS K, Classical Fourier Series in PS K, are aroimations obtained using orthogonal
Math 344, Male ab Manual Chater : Classical Fourier Series Real and Comle Chater. Classical Fourier Series Fourier Series in PS K, Classical Fourier Series in PS K, are aroimations obtained using orthogonal
Elementary Analysis in Q p
 Elementary Analysis in Q Hannah Hutter, May Szedlák, Phili Wirth November 17, 2011 This reort follows very closely the book of Svetlana Katok 1. 1 Sequences and Series In this section we will see some
Elementary Analysis in Q Hannah Hutter, May Szedlák, Phili Wirth November 17, 2011 This reort follows very closely the book of Svetlana Katok 1. 1 Sequences and Series In this section we will see some
FOURIER SERIES PART III: APPLICATIONS
 FOURIER SERIES PART III: APPLICATIONS We extend the construction of Fourier series to functions with arbitrary eriods, then we associate to functions defined on an interval [, L] Fourier sine and Fourier
FOURIER SERIES PART III: APPLICATIONS We extend the construction of Fourier series to functions with arbitrary eriods, then we associate to functions defined on an interval [, L] Fourier sine and Fourier
Solutions to Problem Set 5
 Solutions to Problem Set Problem 4.6. f () ( )( 4) For this simle rational function, we see immediately that the function has simle oles at the two indicated oints, and so we use equation (6.) to nd the
Solutions to Problem Set Problem 4.6. f () ( )( 4) For this simle rational function, we see immediately that the function has simle oles at the two indicated oints, and so we use equation (6.) to nd the
Complex Analysis Homework 1
 Comlex Analysis Homework 1 Steve Clanton Sarah Crimi January 27, 2009 Problem Claim. If two integers can be exressed as the sum of two squares, then so can their roduct. Proof. Call the two squares that
Comlex Analysis Homework 1 Steve Clanton Sarah Crimi January 27, 2009 Problem Claim. If two integers can be exressed as the sum of two squares, then so can their roduct. Proof. Call the two squares that
2 Fourier Series. 2.1 Complex Fourier Series The phases exp(inx)/ p 2, one for each integer n, are orthonormal on an interval of length 2 Z 2
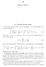 2 Fourier Series 2. Comlex Fourier Series The hases ex(inx)/, one for each integer n, are orthonormal on an interval of length e imx e inx e i(n m)x dx = dx = m,n (2.) where n,m =ifn = m, and n,m =ifn6=
2 Fourier Series 2. Comlex Fourier Series The hases ex(inx)/, one for each integer n, are orthonormal on an interval of length e imx e inx e i(n m)x dx = dx = m,n (2.) where n,m =ifn = m, and n,m =ifn6=
MATH 361: NUMBER THEORY EIGHTH LECTURE
 MATH 361: NUMBER THEORY EIGHTH LECTURE 1. Quadratic Recirocity: Introduction Quadratic recirocity is the first result of modern number theory. Lagrange conjectured it in the late 1700 s, but it was first
MATH 361: NUMBER THEORY EIGHTH LECTURE 1. Quadratic Recirocity: Introduction Quadratic recirocity is the first result of modern number theory. Lagrange conjectured it in the late 1700 s, but it was first
Advanced Calculus I. Part A, for both Section 200 and Section 501
 Sring 2 Instructions Please write your solutions on your own aer. These roblems should be treated as essay questions. A roblem that says give an examle requires a suorting exlanation. In all roblems, you
Sring 2 Instructions Please write your solutions on your own aer. These roblems should be treated as essay questions. A roblem that says give an examle requires a suorting exlanation. In all roblems, you
Computer arithmetic. Intensive Computation. Annalisa Massini 2017/2018
 Comuter arithmetic Intensive Comutation Annalisa Massini 7/8 Intensive Comutation - 7/8 References Comuter Architecture - A Quantitative Aroach Hennessy Patterson Aendix J Intensive Comutation - 7/8 3
Comuter arithmetic Intensive Comutation Annalisa Massini 7/8 Intensive Comutation - 7/8 References Comuter Architecture - A Quantitative Aroach Hennessy Patterson Aendix J Intensive Comutation - 7/8 3
Solved Problems. (a) (b) (c) Figure P4.1 Simple Classification Problems First we draw a line between each set of dark and light data points.
 Solved Problems Solved Problems P Solve the three simle classification roblems shown in Figure P by drawing a decision boundary Find weight and bias values that result in single-neuron ercetrons with the
Solved Problems Solved Problems P Solve the three simle classification roblems shown in Figure P by drawing a decision boundary Find weight and bias values that result in single-neuron ercetrons with the
Series Handout A. 1. Determine which of the following sums are geometric. If the sum is geometric, express the sum in closed form.
 Series Handout A. Determine which of the following sums are geometric. If the sum is geometric, exress the sum in closed form. 70 a) k= ( k ) b) 50 k= ( k )2 c) 60 k= ( k )k d) 60 k= (.0)k/3 2. Find the
Series Handout A. Determine which of the following sums are geometric. If the sum is geometric, exress the sum in closed form. 70 a) k= ( k ) b) 50 k= ( k )2 c) 60 k= ( k )k d) 60 k= (.0)k/3 2. Find the
Real Analysis 1 Fall Homework 3. a n.
 eal Analysis Fall 06 Homework 3. Let and consider the measure sace N, P, µ, where µ is counting measure. That is, if N, then µ equals the number of elements in if is finite; µ = otherwise. One usually
eal Analysis Fall 06 Homework 3. Let and consider the measure sace N, P, µ, where µ is counting measure. That is, if N, then µ equals the number of elements in if is finite; µ = otherwise. One usually
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 Geometry and Geometric Programming
 CMSC 425: Lecture 4 Geometry and Geometric Programming Geometry for Game Programming and Grahics: For the next few lectures, we will discuss some of the basic elements of geometry. There are many areas
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 Geometry and Geometric Programming Geometry for Game Programming and Grahics: For the next few lectures, we will discuss some of the basic elements of geometry. There are many areas
The Euler Phi Function
 The Euler Phi Function 7-3-2006 An arithmetic function takes ositive integers as inuts and roduces real or comlex numbers as oututs. If f is an arithmetic function, the divisor sum Dfn) is the sum of the
The Euler Phi Function 7-3-2006 An arithmetic function takes ositive integers as inuts and roduces real or comlex numbers as oututs. If f is an arithmetic function, the divisor sum Dfn) is the sum of the
Chapter 7 Rational and Irrational Numbers
 Chater 7 Rational and Irrational Numbers In this chater we first review the real line model for numbers, as discussed in Chater 2 of seventh grade, by recalling how the integers and then the rational numbers
Chater 7 Rational and Irrational Numbers In this chater we first review the real line model for numbers, as discussed in Chater 2 of seventh grade, by recalling how the integers and then the rational numbers
PROFIT MAXIMIZATION. π = p y Σ n i=1 w i x i (2)
 PROFIT MAXIMIZATION DEFINITION OF A NEOCLASSICAL FIRM A neoclassical firm is an organization that controls the transformation of inuts (resources it owns or urchases into oututs or roducts (valued roducts
PROFIT MAXIMIZATION DEFINITION OF A NEOCLASSICAL FIRM A neoclassical firm is an organization that controls the transformation of inuts (resources it owns or urchases into oututs or roducts (valued roducts
Introduction to Group Theory Note 1
 Introduction to Grou Theory Note July 7, 009 Contents INTRODUCTION. Examles OF Symmetry Grous in Physics................................. ELEMENT OF GROUP THEORY. De nition of Grou................................................
Introduction to Grou Theory Note July 7, 009 Contents INTRODUCTION. Examles OF Symmetry Grous in Physics................................. ELEMENT OF GROUP THEORY. De nition of Grou................................................
Economics 101. Lecture 7 - Monopoly and Oligopoly
 Economics 0 Lecture 7 - Monooly and Oligooly Production Equilibrium After having exlored Walrasian equilibria with roduction in the Robinson Crusoe economy, we will now ste in to a more general setting.
Economics 0 Lecture 7 - Monooly and Oligooly Production Equilibrium After having exlored Walrasian equilibria with roduction in the Robinson Crusoe economy, we will now ste in to a more general setting.
F(p) y + 3y + 2y = δ(t a) y(0) = 0 and y (0) = 0.
 Page 5- Chater 5: Lalace Transforms The Lalace Transform is a useful tool that is used to solve many mathematical and alied roblems. In articular, the Lalace transform is a technique that can be used to
Page 5- Chater 5: Lalace Transforms The Lalace Transform is a useful tool that is used to solve many mathematical and alied roblems. In articular, the Lalace transform is a technique that can be used to
Homework 2 - Solutions
 Homework 2 - Solutions Carbon Nanotubes Part 4) We can write the wavefunction of the grahene sheet within the tight-binding model in the usual way ( ~ R)= e i~ k ~R Then, to imose eriodic boundary condition
Homework 2 - Solutions Carbon Nanotubes Part 4) We can write the wavefunction of the grahene sheet within the tight-binding model in the usual way ( ~ R)= e i~ k ~R Then, to imose eriodic boundary condition
PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #13-- SOLUTIONS
 PHYS 31 HOMEWORK #13-- SOLUTIONS 1. The wave equation is : 2 u x = 1 2 u 2 v 2 t 2 Since we have that u = f (x - vt) and u = f (x + vt), we substitute these expressions into the wave equation.starting
PHYS 31 HOMEWORK #13-- SOLUTIONS 1. The wave equation is : 2 u x = 1 2 u 2 v 2 t 2 Since we have that u = f (x - vt) and u = f (x + vt), we substitute these expressions into the wave equation.starting
4. Score normalization technical details We now discuss the technical details of the score normalization method.
 SMT SCORING SYSTEM This document describes the scoring system for the Stanford Math Tournament We begin by giving an overview of the changes to scoring and a non-technical descrition of the scoring rules
SMT SCORING SYSTEM This document describes the scoring system for the Stanford Math Tournament We begin by giving an overview of the changes to scoring and a non-technical descrition of the scoring rules
Math 104B: Number Theory II (Winter 2012)
 Math 104B: Number Theory II (Winter 01) Alina Bucur Contents 1 Review 11 Prime numbers 1 Euclidean algorithm 13 Multilicative functions 14 Linear diohantine equations 3 15 Congruences 3 Primes as sums
Math 104B: Number Theory II (Winter 01) Alina Bucur Contents 1 Review 11 Prime numbers 1 Euclidean algorithm 13 Multilicative functions 14 Linear diohantine equations 3 15 Congruences 3 Primes as sums
I Poles & zeros. I First-order systems. I Second-order systems. I E ect of additional poles. I E ect of zeros. I E ect of nonlinearities
 EE C28 / ME C34 Lecture Chater 4 Time Resonse Alexandre Bayen Deartment of Electrical Engineering & Comuter Science University of California Berkeley Lecture abstract Toics covered in this resentation
EE C28 / ME C34 Lecture Chater 4 Time Resonse Alexandre Bayen Deartment of Electrical Engineering & Comuter Science University of California Berkeley Lecture abstract Toics covered in this resentation
ute measures of uncertainty called standard errors for these b j estimates and the resulting forecasts if certain conditions are satis- ed. Note the e
 Regression with Time Series Errors David A. Dickey, North Carolina State University Abstract: The basic assumtions of regression are reviewed. Grahical and statistical methods for checking the assumtions
Regression with Time Series Errors David A. Dickey, North Carolina State University Abstract: The basic assumtions of regression are reviewed. Grahical and statistical methods for checking the assumtions
MATH 361: NUMBER THEORY ELEVENTH LECTURE
 MATH 361: NUMBER THEORY ELEVENTH LECTURE The subjects of this lecture are characters, Gauss sums, Jacobi sums, and counting formulas for olynomial equations over finite fields. 1. Definitions, Basic Proerties
MATH 361: NUMBER THEORY ELEVENTH LECTURE The subjects of this lecture are characters, Gauss sums, Jacobi sums, and counting formulas for olynomial equations over finite fields. 1. Definitions, Basic Proerties
Periodic functions: simple harmonic oscillator
 Periodic functions: simple harmonic oscillator Recall the simple harmonic oscillator (e.g. mass-spring system) d 2 y dt 2 + ω2 0y = 0 Solution can be written in various ways: y(t) = Ae iω 0t y(t) = A cos
Periodic functions: simple harmonic oscillator Recall the simple harmonic oscillator (e.g. mass-spring system) d 2 y dt 2 + ω2 0y = 0 Solution can be written in various ways: y(t) = Ae iω 0t y(t) = A cos
HENSEL S LEMMA KEITH CONRAD
 HENSEL S LEMMA KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction In the -adic integers, congruences are aroximations: for a and b in Z, a b mod n is the same as a b 1/ n. Turning information modulo one ower of into similar
HENSEL S LEMMA KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction In the -adic integers, congruences are aroximations: for a and b in Z, a b mod n is the same as a b 1/ n. Turning information modulo one ower of into similar
1. Solve the boundary-value problems or else show that no solutions exist. y (x) = c 1 e 2x + c 2 e 3x. (3)
 Diff. Eqns. Problem Set 6 Solutions. Solve the boundary-value problems or else show that no solutions exist. a y + y 6y, y, y 4 b y + 9y x + e x, y, yπ a Assuming y e rx is a solution, we get the characteristic
Diff. Eqns. Problem Set 6 Solutions. Solve the boundary-value problems or else show that no solutions exist. a y + y 6y, y, y 4 b y + 9y x + e x, y, yπ a Assuming y e rx is a solution, we get the characteristic
Pretest (Optional) Use as an additional pacing tool to guide instruction. August 21
 Trimester 1 Pretest (Otional) Use as an additional acing tool to guide instruction. August 21 Beyond the Basic Facts In Trimester 1, Grade 8 focus on multilication. Daily Unit 1: Rational vs. Irrational
Trimester 1 Pretest (Otional) Use as an additional acing tool to guide instruction. August 21 Beyond the Basic Facts In Trimester 1, Grade 8 focus on multilication. Daily Unit 1: Rational vs. Irrational
ECE 534 Information Theory - Midterm 2
 ECE 534 Information Theory - Midterm Nov.4, 009. 3:30-4:45 in LH03. You will be given the full class time: 75 minutes. Use it wisely! Many of the roblems have short answers; try to find shortcuts. You
ECE 534 Information Theory - Midterm Nov.4, 009. 3:30-4:45 in LH03. You will be given the full class time: 75 minutes. Use it wisely! Many of the roblems have short answers; try to find shortcuts. You
Fourier Series Tutorial
 Fourier Series Tutorial INTRODUCTION This document is designed to overview the theory behind the Fourier series and its alications. It introduces the Fourier series and then demonstrates its use with a
Fourier Series Tutorial INTRODUCTION This document is designed to overview the theory behind the Fourier series and its alications. It introduces the Fourier series and then demonstrates its use with a
Supplementary Materials for Robust Estimation of the False Discovery Rate
 Sulementary Materials for Robust Estimation of the False Discovery Rate Stan Pounds and Cheng Cheng This sulemental contains roofs regarding theoretical roerties of the roosed method (Section S1), rovides
Sulementary Materials for Robust Estimation of the False Discovery Rate Stan Pounds and Cheng Cheng This sulemental contains roofs regarding theoretical roerties of the roosed method (Section S1), rovides
Session 5: Review of Classical Astrodynamics
 Session 5: Review of Classical Astrodynamics In revious lectures we described in detail the rocess to find the otimal secific imulse for a articular situation. Among the mission requirements that serve
Session 5: Review of Classical Astrodynamics In revious lectures we described in detail the rocess to find the otimal secific imulse for a articular situation. Among the mission requirements that serve
Elliptic Curves Spring 2015 Problem Set #1 Due: 02/13/2015
 18.783 Ellitic Curves Sring 2015 Problem Set #1 Due: 02/13/2015 Descrition These roblems are related to the material covered in Lectures 1-2. Some of them require the use of Sage, and you will need to
18.783 Ellitic Curves Sring 2015 Problem Set #1 Due: 02/13/2015 Descrition These roblems are related to the material covered in Lectures 1-2. Some of them require the use of Sage, and you will need to
COMPUTING FOURIER SERIES
 COMPUTING FOURIER SERIES Overview We have see i revious otes how we ca use the fact that si ad cos rereset comlete orthogoal fuctios over the iterval [-,] to allow us to determie the coefficiets of a Fourier
COMPUTING FOURIER SERIES Overview We have see i revious otes how we ca use the fact that si ad cos rereset comlete orthogoal fuctios over the iterval [-,] to allow us to determie the coefficiets of a Fourier
Approximating min-max k-clustering
 Aroximating min-max k-clustering Asaf Levin July 24, 2007 Abstract We consider the roblems of set artitioning into k clusters with minimum total cost and minimum of the maximum cost of a cluster. The cost
Aroximating min-max k-clustering Asaf Levin July 24, 2007 Abstract We consider the roblems of set artitioning into k clusters with minimum total cost and minimum of the maximum cost of a cluster. The cost
ANALYTIC NUMBER THEORY AND DIRICHLET S THEOREM
 ANALYTIC NUMBER THEORY AND DIRICHLET S THEOREM JOHN BINDER Abstract. In this aer, we rove Dirichlet s theorem that, given any air h, k with h, k) =, there are infinitely many rime numbers congruent to
ANALYTIC NUMBER THEORY AND DIRICHLET S THEOREM JOHN BINDER Abstract. In this aer, we rove Dirichlet s theorem that, given any air h, k with h, k) =, there are infinitely many rime numbers congruent to
f(r) = a d n) d + + a0 = 0
 Math 400-00/Foundations of Algebra/Fall 07 Polynomials at the Foundations: Roots Next, we turn to the notion of a root of a olynomial in Q[x]. Definition 8.. r Q is a rational root of fx) Q[x] if fr) 0.
Math 400-00/Foundations of Algebra/Fall 07 Polynomials at the Foundations: Roots Next, we turn to the notion of a root of a olynomial in Q[x]. Definition 8.. r Q is a rational root of fx) Q[x] if fr) 0.
Section 0.10: Complex Numbers from Precalculus Prerequisites a.k.a. Chapter 0 by Carl Stitz, PhD, and Jeff Zeager, PhD, is available under a Creative
 Section 0.0: Comlex Numbers from Precalculus Prerequisites a.k.a. Chater 0 by Carl Stitz, PhD, and Jeff Zeager, PhD, is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike.0 license.
Section 0.0: Comlex Numbers from Precalculus Prerequisites a.k.a. Chater 0 by Carl Stitz, PhD, and Jeff Zeager, PhD, is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike.0 license.
Almost 4000 years ago, Babylonians had discovered the following approximation to. x 2 dy 2 =1, (5.0.2)
 Chater 5 Pell s Equation One of the earliest issues graled with in number theory is the fact that geometric quantities are often not rational. For instance, if we take a right triangle with two side lengths
Chater 5 Pell s Equation One of the earliest issues graled with in number theory is the fact that geometric quantities are often not rational. For instance, if we take a right triangle with two side lengths
3. Show that if there are 23 people in a room, the probability is less than one half that no two of them share the same birthday.
 N12c Natural Sciences Part IA Dr M. G. Worster Mathematics course B Examles Sheet 1 Lent erm 2005 Please communicate any errors in this sheet to Dr Worster at M.G.Worster@damt.cam.ac.uk. Note that there
N12c Natural Sciences Part IA Dr M. G. Worster Mathematics course B Examles Sheet 1 Lent erm 2005 Please communicate any errors in this sheet to Dr Worster at M.G.Worster@damt.cam.ac.uk. Note that there
Convex Analysis and Economic Theory Winter 2018
 Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences Ec 181 KC Border Conve Analysis and Economic Theory Winter 2018 Toic 16: Fenchel conjugates 16.1 Conjugate functions Recall from Proosition 14.1.1 that is
Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences Ec 181 KC Border Conve Analysis and Economic Theory Winter 2018 Toic 16: Fenchel conjugates 16.1 Conjugate functions Recall from Proosition 14.1.1 that is
Participation Factors. However, it does not give the influence of each state on the mode.
 Particiation Factors he mode shae, as indicated by the right eigenvector, gives the relative hase of each state in a articular mode. However, it does not give the influence of each state on the mode. We
Particiation Factors he mode shae, as indicated by the right eigenvector, gives the relative hase of each state in a articular mode. However, it does not give the influence of each state on the mode. We
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 2012/2013 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math : Calculus - Fall 0/0 Review of Precalculus Concets Welcome to Math - Calculus, Fall 0/0! This roblems in this acket are designed to hel you review the toics from Algebra and Precalculus
Introduction Math : Calculus - Fall 0/0 Review of Precalculus Concets Welcome to Math - Calculus, Fall 0/0! This roblems in this acket are designed to hel you review the toics from Algebra and Precalculus
Lecture 6. 2 Recurrence/transience, harmonic functions and martingales
 Lecture 6 Classification of states We have shown that all states of an irreducible countable state Markov chain must of the same tye. This gives rise to the following classification. Definition. [Classification
Lecture 6 Classification of states We have shown that all states of an irreducible countable state Markov chain must of the same tye. This gives rise to the following classification. Definition. [Classification
Use of Transformations and the Repeated Statement in PROC GLM in SAS Ed Stanek
 Use of Transformations and the Reeated Statement in PROC GLM in SAS Ed Stanek Introduction We describe how the Reeated Statement in PROC GLM in SAS transforms the data to rovide tests of hyotheses of interest.
Use of Transformations and the Reeated Statement in PROC GLM in SAS Ed Stanek Introduction We describe how the Reeated Statement in PROC GLM in SAS transforms the data to rovide tests of hyotheses of interest.
PRIME NUMBERS YANKI LEKILI
 PRIME NUMBERS YANKI LEKILI We denote by N the set of natural numbers:,2,..., These are constructed using Peano axioms. We will not get into the hilosohical questions related to this and simly assume the
PRIME NUMBERS YANKI LEKILI We denote by N the set of natural numbers:,2,..., These are constructed using Peano axioms. We will not get into the hilosohical questions related to this and simly assume the
PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #4
 PHYS HOMEWORK #4 Due : February 7 Do all integrals by hand; you may check your answers via Mathematica but must show all work.. Show for m, n integers :, m n sin (m x) sin (n x) dx = -, m = n - sin (n
PHYS HOMEWORK #4 Due : February 7 Do all integrals by hand; you may check your answers via Mathematica but must show all work.. Show for m, n integers :, m n sin (m x) sin (n x) dx = -, m = n - sin (n
Pell's Equation and Fundamental Units Pell's equation was first introduced to me in the number theory class at Caltech that I never comleted. It was r
 Pell's Equation and Fundamental Units Kaisa Taiale University of Minnesota Summer 000 1 Pell's Equation and Fundamental Units Pell's equation was first introduced to me in the number theory class at Caltech
Pell's Equation and Fundamental Units Kaisa Taiale University of Minnesota Summer 000 1 Pell's Equation and Fundamental Units Pell's equation was first introduced to me in the number theory class at Caltech
Problem set 6 for Quantum Field Theory course
 Problem set 6 or Quantum Field Theory course 2018.03.13. Toics covered Scattering cross-section and decay rate Yukawa theory and Yukawa otential Scattering in external electromagnetic ield, Rutherord ormula
Problem set 6 or Quantum Field Theory course 2018.03.13. Toics covered Scattering cross-section and decay rate Yukawa theory and Yukawa otential Scattering in external electromagnetic ield, Rutherord ormula
8.7 Associated and Non-associated Flow Rules
 8.7 Associated and Non-associated Flow Rules Recall the Levy-Mises flow rule, Eqn. 8.4., d ds (8.7.) The lastic multilier can be determined from the hardening rule. Given the hardening rule one can more
8.7 Associated and Non-associated Flow Rules Recall the Levy-Mises flow rule, Eqn. 8.4., d ds (8.7.) The lastic multilier can be determined from the hardening rule. Given the hardening rule one can more
Various Proofs for the Decrease Monotonicity of the Schatten s Power Norm, Various Families of R n Norms and Some Open Problems
 Int. J. Oen Problems Comt. Math., Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2010 ISSN 1998-6262; Coyright c ICSRS Publication, 2010 www.i-csrs.org Various Proofs for the Decrease Monotonicity of the Schatten s Power Norm, Various
Int. J. Oen Problems Comt. Math., Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2010 ISSN 1998-6262; Coyright c ICSRS Publication, 2010 www.i-csrs.org Various Proofs for the Decrease Monotonicity of the Schatten s Power Norm, Various
Statics and dynamics: some elementary concepts
 1 Statics and dynamics: some elementary concets Dynamics is the study of the movement through time of variables such as heartbeat, temerature, secies oulation, voltage, roduction, emloyment, rices and
1 Statics and dynamics: some elementary concets Dynamics is the study of the movement through time of variables such as heartbeat, temerature, secies oulation, voltage, roduction, emloyment, rices and
The Fekete Szegő theorem with splitting conditions: Part I
 ACTA ARITHMETICA XCIII.2 (2000) The Fekete Szegő theorem with slitting conditions: Part I by Robert Rumely (Athens, GA) A classical theorem of Fekete and Szegő [4] says that if E is a comact set in the
ACTA ARITHMETICA XCIII.2 (2000) The Fekete Szegő theorem with slitting conditions: Part I by Robert Rumely (Athens, GA) A classical theorem of Fekete and Szegő [4] says that if E is a comact set in the
A construction of bent functions from plateaued functions
 A construction of bent functions from lateaued functions Ayça Çeşmelioğlu, Wilfried Meidl Sabancı University, MDBF, Orhanlı, 34956 Tuzla, İstanbul, Turkey. Abstract In this resentation, a technique for
A construction of bent functions from lateaued functions Ayça Çeşmelioğlu, Wilfried Meidl Sabancı University, MDBF, Orhanlı, 34956 Tuzla, İstanbul, Turkey. Abstract In this resentation, a technique for
Math 205b Homework 2 Solutions
 Math 5b Homework Solutions January 5, 5 Problem (R-S, II.) () For the R case, we just expand the right hand side and use the symmetry of the inner product: ( x y x y ) = = ((x, x) (y, y) (x, y) (y, x)
Math 5b Homework Solutions January 5, 5 Problem (R-S, II.) () For the R case, we just expand the right hand side and use the symmetry of the inner product: ( x y x y ) = = ((x, x) (y, y) (x, y) (y, x)
{ sin(t), t [0, sketch the graph of this f(t) = L 1 {F(p)}.
 EM Solved roblems Lalace & Fourier transform c Habala 3 EM Solved roblems Lalace & Fourier transform Find the Lalace transform of the following functions: ft t sint; ft e 3t cos3t; 3 ft e 3s ds; { sint,
EM Solved roblems Lalace & Fourier transform c Habala 3 EM Solved roblems Lalace & Fourier transform Find the Lalace transform of the following functions: ft t sint; ft e 3t cos3t; 3 ft e 3s ds; { sint,
Cryptanalysis of Pseudorandom Generators
 CSE 206A: Lattice Algorithms and Alications Fall 2017 Crytanalysis of Pseudorandom Generators Instructor: Daniele Micciancio UCSD CSE As a motivating alication for the study of lattice in crytograhy we
CSE 206A: Lattice Algorithms and Alications Fall 2017 Crytanalysis of Pseudorandom Generators Instructor: Daniele Micciancio UCSD CSE As a motivating alication for the study of lattice in crytograhy we
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION COURSE III. Wednesday, August 16, :30 to 11:30 a.m.
 The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION THREE-YEAR SEQUENCE FOR HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS COURSE III Wednesday, August 6, 000 8:0 to :0 a.m., only Notice... Scientific calculators
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION THREE-YEAR SEQUENCE FOR HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS COURSE III Wednesday, August 6, 000 8:0 to :0 a.m., only Notice... Scientific calculators
CSC165H, Mathematical expression and reasoning for computer science week 12
 CSC165H, Mathematical exression and reasoning for comuter science week 1 nd December 005 Gary Baumgartner and Danny Hea hea@cs.toronto.edu SF4306A 416-978-5899 htt//www.cs.toronto.edu/~hea/165/s005/index.shtml
CSC165H, Mathematical exression and reasoning for comuter science week 1 nd December 005 Gary Baumgartner and Danny Hea hea@cs.toronto.edu SF4306A 416-978-5899 htt//www.cs.toronto.edu/~hea/165/s005/index.shtml
ON THE SET a x + b g x (mod p) 1 Introduction
 PORTUGALIAE MATHEMATICA Vol 59 Fasc 00 Nova Série ON THE SET a x + b g x (mod ) Cristian Cobeli, Marian Vâjâitu and Alexandru Zaharescu Abstract: Given nonzero integers a, b we rove an asymtotic result
PORTUGALIAE MATHEMATICA Vol 59 Fasc 00 Nova Série ON THE SET a x + b g x (mod ) Cristian Cobeli, Marian Vâjâitu and Alexandru Zaharescu Abstract: Given nonzero integers a, b we rove an asymtotic result
Round-off Errors and Computer Arithmetic - (1.2)
 Round-off Errors and Comuter Arithmetic - (.). Round-off Errors: Round-off errors is roduced when a calculator or comuter is used to erform real number calculations. That is because the arithmetic erformed
Round-off Errors and Comuter Arithmetic - (.). Round-off Errors: Round-off errors is roduced when a calculator or comuter is used to erform real number calculations. That is because the arithmetic erformed
Ordered and disordered dynamics in random networks
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 5 March 998 Eurohys. Lett., 4 (6),. 599-604 (998) Ordered and disordered dynamics in random networks L. Glass ( )andc. Hill 2,3 Deartment of Physiology, McGill University 3655 Drummond
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 5 March 998 Eurohys. Lett., 4 (6),. 599-604 (998) Ordered and disordered dynamics in random networks L. Glass ( )andc. Hill 2,3 Deartment of Physiology, McGill University 3655 Drummond
we get our formula for the saddle-point integral (5.294) h(w) e xf(w). (5.301) xf 00 (w) (w j )
 5.3 The Abel-Plana Formula and the Casimir E ect 9 and using f (w) = e i and + = to show that e i = e i i = e i = f (w) (5.3) we get our formula for the saddle-oint integral (5.94) I(x) / h(w) e xf(w).
5.3 The Abel-Plana Formula and the Casimir E ect 9 and using f (w) = e i and + = to show that e i = e i i = e i = f (w) (5.3) we get our formula for the saddle-oint integral (5.94) I(x) / h(w) e xf(w).
p-adic Measures and Bernoulli Numbers
 -Adic Measures and Bernoulli Numbers Adam Bowers Introduction The constants B k in the Taylor series exansion t e t = t k B k k! k=0 are known as the Bernoulli numbers. The first few are,, 6, 0, 30, 0,
-Adic Measures and Bernoulli Numbers Adam Bowers Introduction The constants B k in the Taylor series exansion t e t = t k B k k! k=0 are known as the Bernoulli numbers. The first few are,, 6, 0, 30, 0,
Sets of Real Numbers
 Chater 4 Sets of Real Numbers 4. The Integers Z and their Proerties In our revious discussions about sets and functions the set of integers Z served as a key examle. Its ubiquitousness comes from the fact
Chater 4 Sets of Real Numbers 4. The Integers Z and their Proerties In our revious discussions about sets and functions the set of integers Z served as a key examle. Its ubiquitousness comes from the fact
Principal Components Analysis and Unsupervised Hebbian Learning
 Princial Comonents Analysis and Unsuervised Hebbian Learning Robert Jacobs Deartment of Brain & Cognitive Sciences University of Rochester Rochester, NY 1467, USA August 8, 008 Reference: Much of the material
Princial Comonents Analysis and Unsuervised Hebbian Learning Robert Jacobs Deartment of Brain & Cognitive Sciences University of Rochester Rochester, NY 1467, USA August 8, 008 Reference: Much of the material
3.4 Design Methods for Fractional Delay Allpass Filters
 Chater 3. Fractional Delay Filters 15 3.4 Design Methods for Fractional Delay Allass Filters Above we have studied the design of FIR filters for fractional delay aroximation. ow we show how recursive or
Chater 3. Fractional Delay Filters 15 3.4 Design Methods for Fractional Delay Allass Filters Above we have studied the design of FIR filters for fractional delay aroximation. ow we show how recursive or
ECON Answers Homework #2
 ECON 33 - Answers Homework #2 Exercise : Denote by x the number of containers of tye H roduced, y the number of containers of tye T and z the number of containers of tye I. There are 3 inut equations that
ECON 33 - Answers Homework #2 Exercise : Denote by x the number of containers of tye H roduced, y the number of containers of tye T and z the number of containers of tye I. There are 3 inut equations that
John Weatherwax. Analysis of Parallel Depth First Search Algorithms
 Sulementary Discussions and Solutions to Selected Problems in: Introduction to Parallel Comuting by Viin Kumar, Ananth Grama, Anshul Guta, & George Karyis John Weatherwax Chater 8 Analysis of Parallel
Sulementary Discussions and Solutions to Selected Problems in: Introduction to Parallel Comuting by Viin Kumar, Ananth Grama, Anshul Guta, & George Karyis John Weatherwax Chater 8 Analysis of Parallel
ALGEBRAIC TOPOLOGY MASTERMATH (FALL 2014) Written exam, 21/01/2015, 3 hours Outline of solutions
 ALGERAIC TOPOLOGY MASTERMATH FALL 014) Written exam, 1/01/015, 3 hours Outline of solutions Exercise 1. i) There are various definitions in the literature. ased on the discussion on. 5 of Lecture 3, as
ALGERAIC TOPOLOGY MASTERMATH FALL 014) Written exam, 1/01/015, 3 hours Outline of solutions Exercise 1. i) There are various definitions in the literature. ased on the discussion on. 5 of Lecture 3, as
SUMS OF TWO SQUARES PAIR CORRELATION & DISTRIBUTION IN SHORT INTERVALS
 SUMS OF TWO SQUARES PAIR CORRELATION & DISTRIBUTION IN SHORT INTERVALS YOTAM SMILANSKY Abstract. In this work we show that based on a conjecture for the air correlation of integers reresentable as sums
SUMS OF TWO SQUARES PAIR CORRELATION & DISTRIBUTION IN SHORT INTERVALS YOTAM SMILANSKY Abstract. In this work we show that based on a conjecture for the air correlation of integers reresentable as sums
Elementary theory of L p spaces
 CHAPTER 3 Elementary theory of L saces 3.1 Convexity. Jensen, Hölder, Minkowski inequality. We begin with two definitions. A set A R d is said to be convex if, for any x 0, x 1 2 A x = x 0 + (x 1 x 0 )
CHAPTER 3 Elementary theory of L saces 3.1 Convexity. Jensen, Hölder, Minkowski inequality. We begin with two definitions. A set A R d is said to be convex if, for any x 0, x 1 2 A x = x 0 + (x 1 x 0 )
1 Gambler s Ruin Problem
 Coyright c 2017 by Karl Sigman 1 Gambler s Ruin Problem Let N 2 be an integer and let 1 i N 1. Consider a gambler who starts with an initial fortune of $i and then on each successive gamble either wins
Coyright c 2017 by Karl Sigman 1 Gambler s Ruin Problem Let N 2 be an integer and let 1 i N 1. Consider a gambler who starts with an initial fortune of $i and then on each successive gamble either wins
Simplifications to Conservation Equations
 Chater 5 Simlifications to Conservation Equations 5.1 Steady Flow If fluid roerties at a oint in a field do not change with time, then they are a function of sace only. They are reresented by: ϕ = ϕq 1,
Chater 5 Simlifications to Conservation Equations 5.1 Steady Flow If fluid roerties at a oint in a field do not change with time, then they are a function of sace only. They are reresented by: ϕ = ϕq 1,
DIRICHLET S THEOREM ON PRIMES IN ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS. 1. Introduction
 DIRICHLET S THEOREM ON PRIMES IN ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS INNA ZAKHAREVICH. Introduction It is a well-known fact that there are infinitely many rimes. However, it is less clear how the rimes are distributed
DIRICHLET S THEOREM ON PRIMES IN ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS INNA ZAKHAREVICH. Introduction It is a well-known fact that there are infinitely many rimes. However, it is less clear how the rimes are distributed
19th Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad. Problems and Solutions. February 28, 2017
 th Bay Area Mathematical Olymiad February, 07 Problems and Solutions BAMO- and BAMO- are each 5-question essay-roof exams, for middle- and high-school students, resectively. The roblems in each exam are
th Bay Area Mathematical Olymiad February, 07 Problems and Solutions BAMO- and BAMO- are each 5-question essay-roof exams, for middle- and high-school students, resectively. The roblems in each exam are
ON POLYNOMIAL SELECTION FOR THE GENERAL NUMBER FIELD SIEVE
 MATHEMATICS OF COMPUTATIO Volume 75, umber 256, October 26, Pages 237 247 S 25-5718(6)187-9 Article electronically ublished on June 28, 26 O POLYOMIAL SELECTIO FOR THE GEERAL UMBER FIELD SIEVE THORSTE
MATHEMATICS OF COMPUTATIO Volume 75, umber 256, October 26, Pages 237 247 S 25-5718(6)187-9 Article electronically ublished on June 28, 26 O POLYOMIAL SELECTIO FOR THE GEERAL UMBER FIELD SIEVE THORSTE
Estimation of Separable Representations in Psychophysical Experiments
 Estimation of Searable Reresentations in Psychohysical Exeriments Michele Bernasconi (mbernasconi@eco.uninsubria.it) Christine Choirat (cchoirat@eco.uninsubria.it) Raffaello Seri (rseri@eco.uninsubria.it)
Estimation of Searable Reresentations in Psychohysical Exeriments Michele Bernasconi (mbernasconi@eco.uninsubria.it) Christine Choirat (cchoirat@eco.uninsubria.it) Raffaello Seri (rseri@eco.uninsubria.it)
Pretest (Optional) Use as an additional pacing tool to guide instruction. August 21
 Trimester 1 Pretest (Otional) Use as an additional acing tool to guide instruction. August 21 Beyond the Basic Facts In Trimester 1, Grade 7 focus on multilication. Daily Unit 1: The Number System Part
Trimester 1 Pretest (Otional) Use as an additional acing tool to guide instruction. August 21 Beyond the Basic Facts In Trimester 1, Grade 7 focus on multilication. Daily Unit 1: The Number System Part
AMS10 HW1 Grading Rubric
 AMS10 HW1 Grading Rubric Problem 1 (16ts- ts/each). Left hand side is shown to equal right hand side using examles with real vectors. A vector sace is a set V on which two oerations, vector addition and
AMS10 HW1 Grading Rubric Problem 1 (16ts- ts/each). Left hand side is shown to equal right hand side using examles with real vectors. A vector sace is a set V on which two oerations, vector addition and
Brownian Motion and Random Prime Factorization
 Brownian Motion and Random Prime Factorization Kendrick Tang June 4, 202 Contents Introduction 2 2 Brownian Motion 2 2. Develoing Brownian Motion.................... 2 2.. Measure Saces and Borel Sigma-Algebras.........
Brownian Motion and Random Prime Factorization Kendrick Tang June 4, 202 Contents Introduction 2 2 Brownian Motion 2 2. Develoing Brownian Motion.................... 2 2.. Measure Saces and Borel Sigma-Algebras.........
A Special Case of the Filon Quadrature
 A Secial Case of the Filon Quadrature Formula* By Lloyd D. Fosdick Introduction. The Filon quadrature formula [1] is used for the numerical evaluation of integrals of the form (1) = J / fix) sin ikx)dx,
A Secial Case of the Filon Quadrature Formula* By Lloyd D. Fosdick Introduction. The Filon quadrature formula [1] is used for the numerical evaluation of integrals of the form (1) = J / fix) sin ikx)dx,
Number Theory Naoki Sato
 Number Theory Naoki Sato 0 Preface This set of notes on number theory was originally written in 1995 for students at the IMO level. It covers the basic background material that an IMO
Number Theory Naoki Sato 0 Preface This set of notes on number theory was originally written in 1995 for students at the IMO level. It covers the basic background material that an IMO
On the Rank of the Elliptic Curve y 2 = x(x p)(x 2)
 On the Rank of the Ellitic Curve y = x(x )(x ) Jeffrey Hatley Aril 9, 009 Abstract An ellitic curve E defined over Q is an algebraic variety which forms a finitely generated abelian grou, and the structure
On the Rank of the Ellitic Curve y = x(x )(x ) Jeffrey Hatley Aril 9, 009 Abstract An ellitic curve E defined over Q is an algebraic variety which forms a finitely generated abelian grou, and the structure
Beam-Beam Stability in Electron-Positron Storage Rings
 Beam-Beam Stability in Electron-Positron Storage Rings Bjoern S. Schmekel, Joseh T. Rogers Cornell University, Deartment of Physics, Ithaca, New York 4853, USA Abstract At the interaction oint of a storage
Beam-Beam Stability in Electron-Positron Storage Rings Bjoern S. Schmekel, Joseh T. Rogers Cornell University, Deartment of Physics, Ithaca, New York 4853, USA Abstract At the interaction oint of a storage
GENERICITY OF INFINITE-ORDER ELEMENTS IN HYPERBOLIC GROUPS
 GENERICITY OF INFINITE-ORDER ELEMENTS IN HYPERBOLIC GROUPS PALLAVI DANI 1. Introduction Let Γ be a finitely generated grou and let S be a finite set of generators for Γ. This determines a word metric on
GENERICITY OF INFINITE-ORDER ELEMENTS IN HYPERBOLIC GROUPS PALLAVI DANI 1. Introduction Let Γ be a finitely generated grou and let S be a finite set of generators for Γ. This determines a word metric on
Theoretical Statistical Physics
 Janosh Riebesell, Adrian van Kan Lecturer: Manfred Salmhofer December nd, 06 Theoretical Statistical Physics Solution to Exercise Sheet 5 Ideal gas work (3 oints Within the kinetic model of an ideal gas,
Janosh Riebesell, Adrian van Kan Lecturer: Manfred Salmhofer December nd, 06 Theoretical Statistical Physics Solution to Exercise Sheet 5 Ideal gas work (3 oints Within the kinetic model of an ideal gas,
On the stability and integration of Hamilton-Poisson systems on so(3)
 Rendiconti di Matematica, Serie VII Volume 37, Roma (016), 1 4 On the stability and integration of Hamilton-Poisson systems on so(3) R. M. ADAMS R. BIGGS W. HOLDERBAUM C. C. REMSING Abstract: We consider
Rendiconti di Matematica, Serie VII Volume 37, Roma (016), 1 4 On the stability and integration of Hamilton-Poisson systems on so(3) R. M. ADAMS R. BIGGS W. HOLDERBAUM C. C. REMSING Abstract: We consider
Solutions to Homework #05 MATH ln z 2 + x 2 1 = 2x2 z 2 + x 2 + ln z2 + x 2. = x. ln z 2 + x 2 2z z 2 + x 2 = 2xz
 Solutions to Homeork #05 MATH Kaai Section. (I) Exercise #. g x and g z : Product Rule: g x = x @ ln z + x + ln z + x @ [x] = x x z + x + ln z + x = x z + x + ln z + x x is eld constant. g z = x @ ln z
Solutions to Homeork #05 MATH Kaai Section. (I) Exercise #. g x and g z : Product Rule: g x = x @ ln z + x + ln z + x @ [x] = x x z + x + ln z + x = x z + x + ln z + x x is eld constant. g z = x @ ln z
Solution Week 75 (2/16/04) Hanging chain
 Catenary Catenary is idealized shae of chain or cable hanging under its weight with the fixed end oints. The chain (cable) curve is catenary that minimizes the otential energy PHY 322, Sring 208 Solution
Catenary Catenary is idealized shae of chain or cable hanging under its weight with the fixed end oints. The chain (cable) curve is catenary that minimizes the otential energy PHY 322, Sring 208 Solution
A glimpse of Fourier analysis
 Chapter 7 A glimpse of Fourier analysis 7.1 Fourier series In the middle of the 18th century, mathematicians and physicists started to study the motion of a vibrating string (think of the strings of a
Chapter 7 A glimpse of Fourier analysis 7.1 Fourier series In the middle of the 18th century, mathematicians and physicists started to study the motion of a vibrating string (think of the strings of a
Lecture 10: Hypercontractivity
 CS 880: Advanced Comlexity Theory /15/008 Lecture 10: Hyercontractivity Instructor: Dieter van Melkebeek Scribe: Baris Aydinlioglu This is a technical lecture throughout which we rove the hyercontractivity
CS 880: Advanced Comlexity Theory /15/008 Lecture 10: Hyercontractivity Instructor: Dieter van Melkebeek Scribe: Baris Aydinlioglu This is a technical lecture throughout which we rove the hyercontractivity
RANDOM WALKS AND PERCOLATION: AN ANALYSIS OF CURRENT RESEARCH ON MODELING NATURAL PROCESSES
 RANDOM WALKS AND PERCOLATION: AN ANALYSIS OF CURRENT RESEARCH ON MODELING NATURAL PROCESSES AARON ZWIEBACH Abstract. In this aer we will analyze research that has been recently done in the field of discrete
RANDOM WALKS AND PERCOLATION: AN ANALYSIS OF CURRENT RESEARCH ON MODELING NATURAL PROCESSES AARON ZWIEBACH Abstract. In this aer we will analyze research that has been recently done in the field of discrete
DIVISIBILITY CRITERIA FOR CLASS NUMBERS OF IMAGINARY QUADRATIC FIELDS
 IVISIBILITY CRITERIA FOR CLASS NUMBERS OF IMAGINARY QUARATIC FIELS PAUL JENKINS AN KEN ONO Abstract. In a recent aer, Guerzhoy obtained formulas for certain class numbers as -adic limits of traces of singular
IVISIBILITY CRITERIA FOR CLASS NUMBERS OF IMAGINARY QUARATIC FIELS PAUL JENKINS AN KEN ONO Abstract. In a recent aer, Guerzhoy obtained formulas for certain class numbers as -adic limits of traces of singular
