Sh. Zeynalov, O. Zeynalova, V. Smirnov
|
|
|
- Derick Gordon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 E Sh. Zeynalov, O. Zeynalova, V. Smirnov APPLICATION OF DIGITAL SIGNAL-PROCESSING TECHNIQUE TO DELAYED-NEUTRON YIELD MEASUREMENTS ON THERMAL-NEUTRON INDUCED FISSION OF 237 Np Submitted to Éμ³ Ö Ô Ö
2 ²μ., ²μ., ³ μ. E ²μ ³ Éμ μ Í Ë μ μ μ μé± ²μ ± ³ Õ ÒÌμ Ò ÕÐ Ì É μ μ ² 237 Np É ²μ Ò³ É μ ³ ³ Éμ ± ³ Ö ÒÌμ Ò ÕÐ Ì É μ μ ² Ö, μ μ Ö μ ²ÊÎ ² Ê ³ÒÌ Ö 237 Np ³μ ʲ μ Ò³ μ³μðóõ ³ Ì Î ±μ μ - Ò É ²Ö μéμ±μ³ É ²μ ÒÌ É μ μ. ˆ Ö ³ Éμ ³ É μ μ ³ μ É μ Ö, ²μ Î Ö μí Ê μ²ó Ê É Ö ²Ö μé Ð Ö Éμ μ μ μ μ ÉÊ ± Ëμ ³ Í μ Ò³ μéμ± ³. ²Ö ÔÉμ μ μéμ± ÒÌ, Î ÒÌ ²Ö - Î Î ± ²Ò Ö Ê ² Î μ μ μ ÉÊ, Î ² ³μ ʲ Ê É Ö μ³μðóõ μ - μ²ó μ ±μ μ μ μ ² μ É ²Ó μ É É ± ³ μ μ³, ÎÉμ Éμ²Ó±μ μ²êî É ²Ó, μ ² ÕРʱ μ ±μ μ μ μ ² μ É ²Ó μ ÉÓÕ, ³μ É μ É μ ÉÓ μ ²Ó ÊÕ Ëμ ³ - Í Õ. ² μ ±Í, Ò ÒÌ É ²μ Ò³ É μ ³, ±μ, μ²ó μ - Ò ²Ö ³μ ʲÖÍ É μ μ μ μéμ±, ³ Ö² Ö ²Ö ³μ ʲÖÍ ²μ É ±- Éμ Ò ÕÐ Ì É μ μ. ³ ³Ò³ É μ ² Ö Ê² μ ʲÓÉ É Éμ²Ó±μ ²Ö ²μ É ±Éμ, ±μ ² μ ÒÌ ³μ ʲÖÍ μéμ± É ²μ ÒÌ É μ μ. μé μ μ μé μ μ ³ Éμ ³ Ö ³Ò³ μ ÒÎ μ ³ Éμ ³ ²Ö μ μ ÒÌ ³ μ± Ò μ μ μ É μé μ μ ³ Éμ, ÕÐ ³Ê μ μ ÊÕ ÔËË ±É μ ÉÓ Ê ²μ ÖÌ ³ É Ê μ ±μ É μ² Ê ³Ò³ Ëμ μ Ò³ Ê ²μ Ö³. ˆ μ²ó μ ³ ÖÌ ²ÊÎ ÒÌ ±μ μ ÒÌ μ ² μ É ²Ó μ É - É Ê É ± Î É μ μé ² ÔËË ±Éμ, Ö ÒÌ ² Ê ³Ò³ Ö ² ³, μé Ëμ μ, Ò ÒÌ Ê ³ μí ³. μé Ò μ² μ Éμ É μ μ Ë ± ³. ˆ. Œ. ± ˆŸˆ. É Ñ μ μ É ÉÊÉ Ö ÒÌ ² μ. Ê, 2008 Zeynalov Sh., Zeynalova O., Smirnov V. E Application of Digital Signal-Processing Technique to Delayed-Neutron Yield Measurements on Thermal-Neutron Induced Fission of 237 Np The measurement procedure based on the continuous thermal-neutron beam modulation with a mechanical chopper was developed for delayed-neutron yield measurement of the thermal-neutron induced ˇssion of 237 Np. The idea of the procedure is similar to that which is widely used in modern communications for the nonauthorized data access prevention. The data is modulated with predeˇned pattern before transmission to the public network and only the recipient that has the modulation pattern is able to demodulate it upon reception. For the thermal-neutron induced reaction applications, the thermal-neutron beam modulation pattern was used to demodulate the measured delayed-neutron intensity signals on the detector output resulting in nonzero output only for the detector signals correlated with the beam modulation pattern. A comparison of the method with the conventional measurement procedure was provided, and it was demonstrated that the cross-correlation procedure has special features making it superior over the conventional one when the measured value difference from the background is extremely small. Due to strong sensitivity of measurement procedure on the modulation pattern of the neutron beam, one can implement the modulation pattern of speciˇc shape to separate the effect of the thermal part of the beam from the higher energy one in the most conˇdent way in a particular experiment. The investigation has been performed at the Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics, JINR. Preprint of the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research. Dubna, 2008
3 INTRODUCTION The conventional measurement procedure of the delayed-neutron yield of the thermal-neutron induced reaction product can usually be considered as a three-phase procedure in which at the ˇrst phase the sample is irradiated by thermal neutrons to produce delayed-neutron emitting nuclei. At the second phase following immediately after the ˇrst one, the thermal-neutron irradiation stopped and the delayed-neutron yield measurement started. Usually both the irradiation and measurement time intervals are equal to each other and their duration should be chosen long enough for full saturation (or decay) of the investigated nuclei. The third phase, following the second phase, is used for the background measurement and it also should be not shorter than the ˇrst two phases for statistical consistency of the result. Multiple repetition of the three phase's procedure with summing of the acquired data improves the statistical accuracy of the measurement to the acceptable level. For the investigated activity to be stabilized at both the saturated and background levels one needs time usually measured in the half-life units (T 1/2 ) of the investigated isotope. The activity measurement should be done at the stable levels preventing the transition phase to be involved in the measurement causing additional time delays, usually (6-10) T 1/2.The cross-correlation procedure contrary to conventional one utilizes the transition phases for measurement excluding hence such time delays providing more efˇcient use of the neutron beam. As is well known [1, 2], the thermal-neutron induced ˇssion cross section for 237 Np is very small ( 20 mb) in comparison with a total one (170 b). This fact causes the signiˇcant technical difˇculties because of need of a huge amount of the sample material with high intrinsic neutron radioactivity (due to (α,n) and (n th γ) reactions in sample material) for the acceptable accuracy of the measurements. The insensitivity of the method to neutron signals, that are noncorrelated with modulation pattern of the beam, was its main advantage, that additionally provided automatic subtraction of the background from any intrinsic neutron radioactivity, for example, spontaneous ˇssion or (α, n) reaction. 1
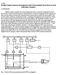
4 1. THE EXPERIMENTAL SET-UP We present the slightly modiˇed experimental set-up described already in [3Ä 6]. A simpliˇed block diagram of the set-up consisting of neutron detector, the beam chopper, and the thermal-neutron ux modulator is shown in Fig. 1. A neutron detector was made of mm polyethylene block with cylindrical channel passing through centers of both the quadrant sides of the block. The axis of the hole with the diameter of 150 mm was oriented in parallel to the neutron beam axis. The sample during the measurement was located at the center of the hole and was irradiated homogeneously by the neutron beam of approximately rectangular mm shape. The distance between sample location and the neutron source center (ight path) was about 30 m and the inner side of the hole was covered by the metallic cadmium (Cd) sheet to protect the detector from the thermal neutrons scattered on the sample. Twelve cylindrical 3 He-proportional counters with dimensions of mm were placed at equal distances from each other on the cylinder surface with diameter of 225 mm which was coaxial with the central cylindrical hole. Fig. 1. Experimental set-up IBR-2 pulsed reactor was used as a neutron source with a pulsing cycle and the mean power of the reactor about 5 per second and 1.5 MW, respectively. There were two kinds of the source neutron pulses inside single reactor burst cycle with the time structure schematically shown in Fig. 2. The neutron source pulse was created by the reactor ˇssile core and had the width of 320μs [7]. That pulse registered by the neutron detector due to part of prompt ˇssion neutrons born inside the core was able to pass through the moderator and surrounding materials almost without collisions. The thermal-neutron pulse of the source was created by neutrons thermalized inside the reactor core and could not be seen directly by the neutron detector, but they caused prompt ˇssion neutrons on the target. These prompt neutrons reproduced the TOF structure of the thermal-neutron pulse at the detector location. The reactor intensity between succeeding bursts was considered as consisting of three main parts: sharp fast neutron pulse, followed by wider 2
5 Fig. 2. TOF spectrum obtained for 237 Np(n th, f). The allocation of the sampling intervals is schematically shown in the ˇgure thermal-neutron pulse and the steady state ux of the source which was generated by the reactor core continuously with the same energy spectrum as burst neutrons but with intensity of about 7% of the total neutron ux of the IBR-2. A bent mirror neutron guide (not shown in Fig. 1) was used to reduce (by a factor of 30) the fast neutron ux at the sample position declining the thermal neutrons from the beam axis to about 15 mm. Rotating mechanical chopper consisting of metallic cadmium sheet (1 mm thick) with narrow slit transparent for thermal neutrons, served to shape thermal-neutron pulses and tailor the steady state share of the thermal-neutron ux between reactor pulses. Additional thermal-neutron beam shutter (modulator) controlled by the data acquisition system was used to create the thermal-neutron beam modulation pattern as shown in Fig. 3. When the Fig. 3. Time dependence of the PN counting rate when beam modulation was applied (full line). The CCF between PN and beam modulation pattern (dashed line) is normalized to total number of PN detected per modulation cycle 3
6 modulator was at the Beam-On state, the thermal neutron ux at the sample location was estimated from measurement of ˇssion rate of the 235 U sample ( 12.5 mg of enrichment) found to be n/(s sm 2 ) with the stability value no worse than 1%. Neutron signals detected inside each reactor burst cycle were assigned to the fast, prompt, and delayed neutrons in respect of the beam neutron TOF values as shown in Fig. 2. These signals were normalized to the 5 neutron source burst cycles creating fast, prompt, and delayed neutron counting rate samples per source cycle. The sequence of the samples versus the source cycle number was treated as discrete analog of the corresponding continuous neutron counting rate function sampled with the neutron source cycle. During the open state of the modulator, the delayed neutron counting rate was continuously increasing until reaching the saturation level as schematically shown in Fig. 4. Then the modulator phase was Fig. 4. The simulated time dependence of DN counting rate (full line) along with CCF (dashed line) between DN counting rate and the beam modulation pattern turned to the Beam-Off phase terminating the thermal neutron ux for the same time interval as at the Beam-On phase. At the Beam-Off phase of the modulator the fast neutron intensity was not terminated, but weakened by the scattering on the modulator to the 0.98 of the value at the Beam-On phase as it was evaluated from the attenuation of the fast neutron pulse. The delayedneutron counting rate at the saturation level in respect to the background level for the given target depended on the ˇssion rate of the target nuclei. The ˇssion rate of the target can be evaluated from simultaneously measured total number of prompt and delayed neutrons using the ν p value available from the literature and using 235 U(n th,f) reaction for the calibration as explained in the next chapter. 4
7 2. DATA ACQUISITION AND DATA ANALYSIS SYSTEM The specialized data acquisition system based on IBM-PC plug-in card associated with the data acquisition and data analysis software was developed for measurement and evaluation of the prompt and the delayed neutron counting rate functions. In the present report only a brief review of the electronics was provided, the detailed description is available in [3]. The data acquisition electronics was triggered by the reactor T-Zero signal for the thermal neutron TOF measurement. The data acquisition card had 4096 channels of 48 μs each, and it sampled neutron intensity function during 197 ms out of the 200 ms time interval between successive bursts of the reactor. After collecting 5 successive bursts of the reactor, the acquired TOF spectrum was recorded to the PC hard disk along with the information on the beam modulation phase. The beam modulation phase was controlled by the part of the data acquisition software for the synchronization of the beam modulation with the data acquisition. The duration of the beam modulation phase was chosen to be 200 seconds, so for both the phases 1000 TOF distributions were recorded. As was described in the previous chapter, the TOF distributions were used to produce fast (FN), prompt (PN), and delayed neutron (DN) counting rates. All signals making up the TOF distribution were divided into three groups related to the fast (0 < TOF < 1.5 ms), prompt (1.5 < TOF < 24 ms), and delayed (24 < TOF < 180 ms) neutrons according to the TOF values. The numbers of counts in the individual groups were considered as discrete samples of the corresponding counting rates. The prompt neutron counting rate measured for 237 Np(n th, f) reaction is shown in Fig. 3 (solid line) along with the cross-correlation function (CCF) between the beam modulation and the PN rate (dashed line) calculated using the formula: PN CCF (t) = 1 T PN(τ)M(t τ)dτ, where M N = 1 T M(t)dt. (1) M N T 0 0 The CCF was normalized to the total number of PN detected per period of modulation function. Because the DN counting rate measured in the same experiment had signiˇcant constant background and noise basement, the simulated DN counting rate is presented in Fig. 4 along with the CCF for reference. The time dependence of the measured DN counting rate is shown in Fig. 5, and the corresponding CCF presented in Fig. 6 was calculated using the following formula: DN CCF (t) = 1 N T 0 DN N (τ) M(t τ)dτ, where the N = 1 T T 0 M(τ)dτ. (2) 5
8 Fig. 5. The time dependence of DN counting rate measured in 237 Np(n th, f) reaction with 20 g neptunium sample when beam modulation was applied Fig. 6. The time dependence of the CCF between DN counting rate and beam modulation pattern measured in 237 Np(n th, f) reaction with 20 g neptunium sample when beam modulation was applied It is clear from the comparison of the CCF with the original counting rate functions that the CCF had better signal-to-noise ratio due to that CCF is suppressing the frequency components in the original signal which are not present in the modulation function. For further improvement of the signal-to-noise ratio, the CCF and ACF functions were reduced to the single period of the modulation function by summing. We used the ACF for the DN because it produced better signal-to-noise ratio than the CCF. Analyzing the correlation of the FN counting rate with the neutron beam modulation we found the modulation pattern similar to that presented in Fig, 3 for PN. That fact we explained by loss of the fast neutrons after scattering on the cadmium sheet of the beam modulator. The 6
9 value of the modulation was found to be compatible with the delayed-neutron counting rate and it was taken into account in data analysis for correct evaluation of the delayed-neutron yield as follows. As was mentioned earlier the constant background in the TOF spectrum was created by the steady state ux of the IBR-2 core and it had the same spectrum as the pulsed ux. That is why the same ux reduction due to scattering at the modulator can be expected for the steady state background as for the FN pulse. When the correlation functions are properly normalized, then their average values for the period of modulation function are equal to the number of FN, PN, or DN detected per period plus the average constant background counting rate. Denoting the integral values of PN and DN counts per period as N PN and N DN, respectively, one can write the following equation: N PN ν p ε p = N DN ν d ε d. (3) Right and left sides of the equation represent the thermal neutron induced ˇssion rates calculated using PN and DN counts for the same measurement time interval. The values ν p, ε p are the average number of prompt neutrons per ˇssion event and neutron detector efˇciency for PN, and ν d, ε d are corresponding values for DN. Rewriting formula (3) to the following form: ν d = N PN N DN ε p ε d ν p, (4) one can ˇnd ν d using measured values N PN, N DN and available from the literature the ν p value. The remaining parameter ε p can be obtained from calibration ε d measurement with 235 U sample considering formula (5) as the equation in respect Fig. 7. The time dependence of the CCF between PN counting rate and beam modulation pattern measured in 237 Np(n th, f) reaction with 20 g neptunium sample reduced to the one cycle of the beam modulation pattern 7
10 Fig. 8. The time dependence of the CCF between FN counting rate and beam modulation pattern measured in 237 Np(n th, f) reaction with 20 g neptunium sample reduced to the one cycle of the beam modulation pattern Fig. 9. The time dependence of the CCF between DN counting rate and beam modulation pattern measured in 237 Np(n th, f) reaction with 20 g neptunium sample reduced to the one cycle of the beam modulation pattern to ε p ε d using value of ν d for the 235 U from the literature. Finally the measurement of delayed neutron yield reduces to the measurement of values N PN, N DN,which evaluated using functions measured for 237 Np(n th, f) reaction and presented in Figs. 7Ä9. 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The method discussed above was applied to delayed-neutron yield measurement of thermal-neutron induced ˇssion of 237 Np and the following result was 8
11 found for 90 hours measurement: ν d = ± Comparing the value ν d for the 237 Np(n th, f) reaction with the previous result reported in [6], one can found difference of about 3% which we explain by the neglecting in [6] of the background modulation by the beam shutter described above. To demonstrate the power and the sensitivity of the developed method, a series of special measurements was carried out with very small 1 mg sample of the 235 U with background conditions as for 237 Np target. Under this condition measured in the different series, the delayed-neutron yield for thermal-neutron induced ˇssion of 235 U was in good agreement with the results obtained with a 235 U sample of 12.5 mg measured in normal background conditions. Finally, the presented method provides at least twice higher value of the thermal-neutron beam utilization efˇciency in comparison with the traditional procedure as was implemented in [6]. REFERENCES 1. Thierens H. et al. // Nucl. Phys. A V P Mughabghab S. F. et al. Neutron Cross Sections. New York: Academic, V. 1 Part B. 3. Zeinalov Sh. S., Zeinalova O. V., Smirnov V. I. Measurements of Delayed Neutron Yield on Thermal Neutron Induced Fission of 237 Np Using Cross-Correlation Technique. JINR, P Dubna, 1998 (in Russian). 4. Borzakov S. B. et al. Measurements of Delayed Neutron Yields from Thermal Neutron Induced Fission of 235 U, 233 U, 239 Pu, and 237 Np. JINR, E Dubna, Zeinalov Sh. S., Zeinalova O. V., Smirnov V. I. Measurements of Delayed Neutron Yield on Thermal Neutron Induced Fission of 237 Np Using Cross-Correlation Technique. JINR, E Dubna, Borzakov S. B. // Physics of Atomic Nuclei V. 63. P Shabalin E. P. Fast Pulsed and Burst Reactors. Oxford: Pergamon Press, Received on February 19, 2008.
12 ±Éμ.. ˆ ϱ Î μ μ Î ÉÓ μ ³ É 60 90/16. ʳ μë É Ö. Î ÉÓ μë É Ö. ². Î. ². 0,75. Î.-. ². 1, Ô±. ± º ˆ É ²Ó ± μé ² Ñ μ μ É ÉÊÉ Ö ÒÌ ² μ ,. Ê, Œμ ±μ ± Ö μ ²., ʲ. μ² μ-šõ,
E NUCLEAR PROCESSES INDUCED BY MUON DECAY AT THE K-ORBIT OF MUONIC ATOM. 1 Nuclear Physics Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia
 E15-2012-61 B. Sabirov, V. Abazov, A. Demyanov, I. Falomkin, V. Gordeev 1, K. Grama 2, S. Kutuzov, Do Khoang Kyong, M. Lewandowski 3, I. Mitropolsky 1, G. Solyakin 1 NUCLEAR PROCESSES INDUCED BY MUON DECAY
E15-2012-61 B. Sabirov, V. Abazov, A. Demyanov, I. Falomkin, V. Gordeev 1, K. Grama 2, S. Kutuzov, Do Khoang Kyong, M. Lewandowski 3, I. Mitropolsky 1, G. Solyakin 1 NUCLEAR PROCESSES INDUCED BY MUON DECAY
USE OF ORTHONORMAL POLYNOMIAL EXPANSION METHOD TO THE DESCRIPTION OF THE ENERGY SPECTRA OF BIOLOGICAL LIQUIDS
 E10-2015-67 N. B. Bogdanova 1,2,, S. T. Todorov 1,, G.A.Ososkov 2, USE OF ORTHONORMAL POLYNOMIAL EXPANSION METHOD TO THE DESCRIPTION OF THE ENERGY SPECTRA OF BIOLOGICAL LIQUIDS 1 Institute for Nuclear
E10-2015-67 N. B. Bogdanova 1,2,, S. T. Todorov 1,, G.A.Ososkov 2, USE OF ORTHONORMAL POLYNOMIAL EXPANSION METHOD TO THE DESCRIPTION OF THE ENERGY SPECTRA OF BIOLOGICAL LIQUIDS 1 Institute for Nuclear
NEW METHOD FOR DETERMINING AVALANCHE BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE OF SILICON PHOTOMULTIPLIERS
 D13-2017-28 I. Chirikov-Zorin NEW METHOD FOR DETERMINING AVALANCHE BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE OF SILICON PHOTOMULTIPLIERS Presented at the International Conference Instrumentation for Colliding Beam Physicsª (INSTR17),
D13-2017-28 I. Chirikov-Zorin NEW METHOD FOR DETERMINING AVALANCHE BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE OF SILICON PHOTOMULTIPLIERS Presented at the International Conference Instrumentation for Colliding Beam Physicsª (INSTR17),
E. V. Samsonov, B. N. Gikal, O. N. Borisov, I. A. Ivanenko NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF ION ACCELERATION AND EXTRACTION IN CYCLOTRON DC-110
 E9-2013-121 E. V. Samsonov, B. N. Gikal, O. N. Borisov, I. A. Ivanenko NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF ION ACCELERATION AND EXTRACTION IN CYCLOTRON DC-110 Submitted to Ó³ Ÿ ³ μ μ... E9-2013-121 ² μ ³μ ² μ Ê ±μ
E9-2013-121 E. V. Samsonov, B. N. Gikal, O. N. Borisov, I. A. Ivanenko NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF ION ACCELERATION AND EXTRACTION IN CYCLOTRON DC-110 Submitted to Ó³ Ÿ ³ μ μ... E9-2013-121 ² μ ³μ ² μ Ê ±μ
THE FORWARD DETECTOR OF THE ANKE SPECTROMETER. SCINTILLATION AND CHERENKOV HODOSCOPES
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2002. º 4[113] Particles and Nuclei, Letters. 2002. No. 4[113] Š 539.1.07 THE FORWARD DETECTOR OF THE ANKE SPECTROMETER. SCINTILLATION AND CHERENKOV HODOSCOPES B. Chiladze a,s.dymov b, R. Esser c,
Ó³ Ÿ. 2002. º 4[113] Particles and Nuclei, Letters. 2002. No. 4[113] Š 539.1.07 THE FORWARD DETECTOR OF THE ANKE SPECTROMETER. SCINTILLATION AND CHERENKOV HODOSCOPES B. Chiladze a,s.dymov b, R. Esser c,
A STUDY OF AN AIR MEDIUM INFLUENCE ON THE RECTILINEARITY OF LASER RAY PROLIFERATION TOWARDS THE USING FOR LARGE DISTANCES AND HIGH-PRECISION METROLOGY
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2007.. 4, º 1(137).. 150Ä156 Œ ˆŠ ˆ ˆ Š ƒ Š ˆŒ A STUDY OF AN AIR MEDIUM INFLUENCE ON THE RECTILINEARITY OF LASER RAY PROLIFERATION TOWARDS THE USING FOR LARGE DISTANCES AND HIGH-PRECISION METROLOGY
Ó³ Ÿ. 2007.. 4, º 1(137).. 150Ä156 Œ ˆŠ ˆ ˆ Š ƒ Š ˆŒ A STUDY OF AN AIR MEDIUM INFLUENCE ON THE RECTILINEARITY OF LASER RAY PROLIFERATION TOWARDS THE USING FOR LARGE DISTANCES AND HIGH-PRECISION METROLOGY
SPIN ASSIGNMENT OF NEUTRON RESONANCES VIA (n, γ) AND(n, α) REACTIONS F. Corvi
 ˆ ˆŠ Œ ˆ ˆ Œ ƒ Ÿ 2004.. 35.. 6 Š 539.125.5 SPIN ASSIGNMENT OF NEUTRON RESONANCES VIA (n, γ) AND(n, α) REACTIONS F. Corvi EC-JRC, Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements, Geel, Belgium M. Przytula
ˆ ˆŠ Œ ˆ ˆ Œ ƒ Ÿ 2004.. 35.. 6 Š 539.125.5 SPIN ASSIGNMENT OF NEUTRON RESONANCES VIA (n, γ) AND(n, α) REACTIONS F. Corvi EC-JRC, Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements, Geel, Belgium M. Przytula
E Submitted to Physical Review C
 E7-2004-160 MEASUREMENTS OF CROSS SECTIONS AND DECAY PROPERTIES OF THE ISOTOPES OF ELEMENTS 112, 114 AND 116 PRODUCED IN THE FUSION REACTIONS 233,238 U, 242 Pu, AND 248 Cm + 48 Ca Submitted to Physical
E7-2004-160 MEASUREMENTS OF CROSS SECTIONS AND DECAY PROPERTIES OF THE ISOTOPES OF ELEMENTS 112, 114 AND 116 PRODUCED IN THE FUSION REACTIONS 233,238 U, 242 Pu, AND 248 Cm + 48 Ca Submitted to Physical
POSITRON EMISSION ISOTOPE PRODUCTION CYCLOTRON AT DLNP JINR (STATUS REPORT)
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2008.. 5, º 7(149).. 74Ä79 ˆ ˆŠ ˆ ˆŠ Š ˆ POSITRON EMISSION ISOTOPE PRODUCTION CYCLOTRON AT DLNP JINR (STATUS REPORT) Yu. G. Alenitsky 1, Yu. N. Denisov, A. F. Chesnov, A. A. Glazov, S. V. Gurskiy,
Ó³ Ÿ. 2008.. 5, º 7(149).. 74Ä79 ˆ ˆŠ ˆ ˆŠ Š ˆ POSITRON EMISSION ISOTOPE PRODUCTION CYCLOTRON AT DLNP JINR (STATUS REPORT) Yu. G. Alenitsky 1, Yu. N. Denisov, A. F. Chesnov, A. A. Glazov, S. V. Gurskiy,
MEASUREMENT OF TUBE TENSION IN STRAW DETECTORS
 E13-2014-68 A. D. Volkov MEASUREMENT OF TUBE TENSION IN STRAW DETECTORS Submitted to Uspekhi Prikladnoi Fiziki μ²±μ.. E13-2014-68 ˆ ³ ÉÖ Ö É Ê ± É μê- É ±Éμ Ì ³μÉ μ Ê É μ É μ ²Ö ±μ É μ²ö ÉÖ Ö É Ê μ± É
E13-2014-68 A. D. Volkov MEASUREMENT OF TUBE TENSION IN STRAW DETECTORS Submitted to Uspekhi Prikladnoi Fiziki μ²±μ.. E13-2014-68 ˆ ³ ÉÖ Ö É Ê ± É μê- É ±Éμ Ì ³μÉ μ Ê É μ É μ ²Ö ±μ É μ²ö ÉÖ Ö É Ê μ± É
Fig. 1 Sketch of the experimental setup for PFN investigation.
 1) Title Prompt Fission Neutron Investigation with Frisch-gridded Twin Back-to-back Ionization Chamber. 2) Introduction Modern models consider the nuclear fission process as a result of competition between
1) Title Prompt Fission Neutron Investigation with Frisch-gridded Twin Back-to-back Ionization Chamber. 2) Introduction Modern models consider the nuclear fission process as a result of competition between
E MEASUREMENT OF THE TOP QUARK MASS USING NEUTRINO WEIGHTING METHOD IN DILEPTON EVENTS AT CDF ОБЪЕДИНЕННЫЙ ИНСТИТУТ ЯДЕРНЫХ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЙ
 ОБЪЕДИНЕННЫЙ ИНСТИТУТ ЯДЕРНЫХ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЙ Дубна E1-2005-129 1 2 2 3, G. Bellettini, J. Budagov, G. Chlachidze, N. Giokaris V. Glagolev 2, F. Prakoshyn 2, A. Sissakian 2, I. Suslov 2, G. Velev4 (On behalf
ОБЪЕДИНЕННЫЙ ИНСТИТУТ ЯДЕРНЫХ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЙ Дубна E1-2005-129 1 2 2 3, G. Bellettini, J. Budagov, G. Chlachidze, N. Giokaris V. Glagolev 2, F. Prakoshyn 2, A. Sissakian 2, I. Suslov 2, G. Velev4 (On behalf
Measurements of Neutron Total and Capture Cross Sections at the TOF spectrometers of the Moscow Meson Factory
 Measurements of Neutron Total and Capture Cross Sections at the TOF spectrometers of the Moscow Meson Factory Yu.V. Grigoriev 1,2, D.V. Khlustin 1, Zh.V. Mezentseva 2, Yu.V. Ryabov 1 1 Institute for Nuclear
Measurements of Neutron Total and Capture Cross Sections at the TOF spectrometers of the Moscow Meson Factory Yu.V. Grigoriev 1,2, D.V. Khlustin 1, Zh.V. Mezentseva 2, Yu.V. Ryabov 1 1 Institute for Nuclear
Method of active correlations in the experiment 249 Cf+ 48 Ca n
 Method of active correlations in the experiment 249 Cf+ 48 Ca 297 118 +3n Yu.S.Tsyganov, A.M.Sukhov, A.N.Polyakov Abstract Two decay chains originated from the even-even isotope 294 118 produced in the
Method of active correlations in the experiment 249 Cf+ 48 Ca 297 118 +3n Yu.S.Tsyganov, A.M.Sukhov, A.N.Polyakov Abstract Two decay chains originated from the even-even isotope 294 118 produced in the
THE CALIBRATION OF THE PRECISION LASER INCLINOMETER
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2015.. 12, º 7(198).. 1272Ä1278 Œ ˆŠ ˆ ˆ Š ƒ Š ˆŒ THE CALIBRATION OF THE PRECISION LASER INCLINOMETER V. Batusov a, J. Budagov a, M. Lyablin a, 1, G. Shirkov a, J.-Ch. Gayde b, D. Mergelkuhl b a
Ó³ Ÿ. 2015.. 12, º 7(198).. 1272Ä1278 Œ ˆŠ ˆ ˆ Š ƒ Š ˆŒ THE CALIBRATION OF THE PRECISION LASER INCLINOMETER V. Batusov a, J. Budagov a, M. Lyablin a, 1, G. Shirkov a, J.-Ch. Gayde b, D. Mergelkuhl b a
PRODUCTION OF PHOTOFISSION FRAGMENTS AND STUDY OF THEIR NUCLEAR STRUCTURE BY LASER SPECTROSCOPY
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2005.. 2, º 2(125).. 50Ä59 Š 539.183+539.143 PRODUCTION OF PHOTOFISSION FRAGMENTS AND STUDY OF THEIR NUCLEAR STRUCTURE BY LASER SPECTROSCOPY Yu. P. Gangrsky, S. G. Zemlyanoi, D. V. Karaivanov, K.
Ó³ Ÿ. 2005.. 2, º 2(125).. 50Ä59 Š 539.183+539.143 PRODUCTION OF PHOTOFISSION FRAGMENTS AND STUDY OF THEIR NUCLEAR STRUCTURE BY LASER SPECTROSCOPY Yu. P. Gangrsky, S. G. Zemlyanoi, D. V. Karaivanov, K.
Nuclear Reactions A Z. Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q > 0. Exothermic Endothermic
 Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reactions A Z 4 P D+ He + Q A 4 Z 2 Q > 0 Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q = ( m + m m m ) c 2 x X Y y Q > 0 Q < 0 Exothermic Endothermic 2
Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reactions A Z 4 P D+ He + Q A 4 Z 2 Q > 0 Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q = ( m + m m m ) c 2 x X Y y Q > 0 Q < 0 Exothermic Endothermic 2
A New MCNPX PTRAC Coincidence Capture File Capability: A Tool for Neutron Detector Design
 Abstract A New MCNPX PTRAC Coincidence Capture File Capability: A Tool for Neutron Detector Design L. G. Evans, M.A. Schear, J. S. Hendricks, M.T. Swinhoe, S.J. Tobin and S. Croft Los Alamos National Laboratory
Abstract A New MCNPX PTRAC Coincidence Capture File Capability: A Tool for Neutron Detector Design L. G. Evans, M.A. Schear, J. S. Hendricks, M.T. Swinhoe, S.J. Tobin and S. Croft Los Alamos National Laboratory
This paper should be understood as an extended version of a talk given at the
 This paper should be understood as an extended version of a talk given at the Abstract: 1 st JINA workshop at Gull Lake, 2002. Recent experimental developments at LANL (Los Alamos, NM, USA) and CERN (Geneva,
This paper should be understood as an extended version of a talk given at the Abstract: 1 st JINA workshop at Gull Lake, 2002. Recent experimental developments at LANL (Los Alamos, NM, USA) and CERN (Geneva,
VERDI a double (v, E) fission-fragment fragment spectrometer
 EFNUDAT Slow and Resonance Neutrons, Budapest (HU), Sep. 23-25, 2009 1 VERDI a double (v, E) fission-fragment fragment spectrometer S. Oberstedt, R. Borcea,, Th. Gamboni,, W. Geerts, F.-J. Hambsch, A.
EFNUDAT Slow and Resonance Neutrons, Budapest (HU), Sep. 23-25, 2009 1 VERDI a double (v, E) fission-fragment fragment spectrometer S. Oberstedt, R. Borcea,, Th. Gamboni,, W. Geerts, F.-J. Hambsch, A.
SILVER NEUTRON ACTIVATION DETECTOR FOR MEASURING BURSTS OF 14 MEV NEUTRONS
 SILVER NEUTRON ACTIVATION DETECTOR FOR MEASURING BURSTS OF 14 MEV NEUTRONS Song Zhaohui, Guan Xinyin, Zhang Zichuan Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology, Xi an, 71004, China In order to measure bursts
SILVER NEUTRON ACTIVATION DETECTOR FOR MEASURING BURSTS OF 14 MEV NEUTRONS Song Zhaohui, Guan Xinyin, Zhang Zichuan Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology, Xi an, 71004, China In order to measure bursts
A POSITION SENSITIVE ALPHA PARTICLE DETECTOR BASED ON A LYSO CRYSTAL AND A MICRO-PIXEL AVALANCHE PHOTODIODE
 A POSITION SENSITIVE ALPHA PARTICLE DETECTOR BASED ON A LYSO CRYSTAL AND A MICRO-PIXEL AVALANCHE PHOTODIODE Ahmadov G.S. a,b,c, Ahmadov F.I. b,c, Kopatch Yu.N. a, Telezhnikov S.A. a, Nuriyev S.M. a,b,
A POSITION SENSITIVE ALPHA PARTICLE DETECTOR BASED ON A LYSO CRYSTAL AND A MICRO-PIXEL AVALANCHE PHOTODIODE Ahmadov G.S. a,b,c, Ahmadov F.I. b,c, Kopatch Yu.N. a, Telezhnikov S.A. a, Nuriyev S.M. a,b,
The neutron multiplicity study at spontaneous fission of short-lived isotopes (z > 100) using VASSILISSA recoil separator
 The neutron multiplicity study at spontaneous fission of short-lived isotopes (z > 100) using VASSILISSA recoil separator Svirikhin A.I. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia Manipal University,
The neutron multiplicity study at spontaneous fission of short-lived isotopes (z > 100) using VASSILISSA recoil separator Svirikhin A.I. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia Manipal University,
Photoneutron Interrogation of Uranium Samples by a 4 MeV LINAC. A Feasibility Study
 Photoneutron Interrogation of Uranium Samples by a 4 MeV LINAC. A Feasibility Study L. Lakosi, C. T. Nguyen, J. Bagi Institute of Isotopes, Hungarian Academy of Sciences P. O. Box 77, H-1525 Budapest,
Photoneutron Interrogation of Uranium Samples by a 4 MeV LINAC. A Feasibility Study L. Lakosi, C. T. Nguyen, J. Bagi Institute of Isotopes, Hungarian Academy of Sciences P. O. Box 77, H-1525 Budapest,
Pulsed Neutron Interrogation Test Assembly - PUNITA
 Pulsed Neutron Interrogation Test Assembly - PUNITA Bent Pedersen Nuclear Security Unit Institute for Transuranium Elements - ITU Joint Research Centre presented at IPNDV WG3 meeting, 12-13 May 2016 JRC,
Pulsed Neutron Interrogation Test Assembly - PUNITA Bent Pedersen Nuclear Security Unit Institute for Transuranium Elements - ITU Joint Research Centre presented at IPNDV WG3 meeting, 12-13 May 2016 JRC,
J. Ritman*, O. I. Yuldashev, M. B. Yuldasheva
 E11-2005-49 J. Ritman*, O. I. Yuldashev, M. B. Yuldasheva AN ALGORITHM FOR CONSTRUCTION OF DIPOLE MAGNETS COMPUTER MODELS WITH QUALITY CONTROL AND ITS APPLICATION FOR THE PANDA FORWARD SPECTROMETER Institute
E11-2005-49 J. Ritman*, O. I. Yuldashev, M. B. Yuldasheva AN ALGORITHM FOR CONSTRUCTION OF DIPOLE MAGNETS COMPUTER MODELS WITH QUALITY CONTROL AND ITS APPLICATION FOR THE PANDA FORWARD SPECTROMETER Institute
PROBING NEW PHYSICS SCALE WITH HIGH-ENERGY NEUTRINOS
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2013.. 10, º 3(180).. 326Ä331 ˆ ˆŠ Œ ˆ ˆ Œ ƒ Ÿ. ˆŸ PROBING NEW PHYSICS SCALE WITH HIGH-ENERGY NEUTRINOS Salah Eddine Ennadiˇ 1 Laboratory of High Energy Physics, Modeling and Simulation, Faculty
Ó³ Ÿ. 2013.. 10, º 3(180).. 326Ä331 ˆ ˆŠ Œ ˆ ˆ Œ ƒ Ÿ. ˆŸ PROBING NEW PHYSICS SCALE WITH HIGH-ENERGY NEUTRINOS Salah Eddine Ennadiˇ 1 Laboratory of High Energy Physics, Modeling and Simulation, Faculty
FISSILE MATERIALS DETECTION VIA NEUTRON DIFFERENTIAL DIE-AWAY TECHNIQUE
 Applications of Nuclear Techniques (CRETE13) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 27 (2014) 1460130 (8 pages) The Authors DOI: 10.1142/S2010194514601306 FISSILE MATERIALS DETECTION
Applications of Nuclear Techniques (CRETE13) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 27 (2014) 1460130 (8 pages) The Authors DOI: 10.1142/S2010194514601306 FISSILE MATERIALS DETECTION
Radioactivity III: Measurement of Half Life.
 PHY 192 Half Life Spring 2010 1 Radioactivity III: Measurement of Half Life. Introduction This experiment will once again use the apparatus of the first experiment, this time to measure radiation intensity
PHY 192 Half Life Spring 2010 1 Radioactivity III: Measurement of Half Life. Introduction This experiment will once again use the apparatus of the first experiment, this time to measure radiation intensity
Research in NDA Techniques for Waste Characterization at the JRC
 1 Research in NDA Techniques for Waste Characterization at the JRC Bent Pedersen Nuclear Security Unit Institute for Transuranium Elements Joint Research Centre presented at Annual meeting of LABONET Network
1 Research in NDA Techniques for Waste Characterization at the JRC Bent Pedersen Nuclear Security Unit Institute for Transuranium Elements Joint Research Centre presented at Annual meeting of LABONET Network
Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis
 Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis 3.1. Neutron Activation Techniques 3.2. Neutron Activation of Paintings 3.3. From Qumran to Napoleon 3.4. Neutron Activation with Accelerators 3.5. Isotope
Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis 3.1. Neutron Activation Techniques 3.2. Neutron Activation of Paintings 3.3. From Qumran to Napoleon 3.4. Neutron Activation with Accelerators 3.5. Isotope
P ³ É ÕÉ Ö µí Ê Ò ± ² µ ± µ³ É Î ±µ µ Ò É Ö Î - É ²Ö² Ó µ³µðóõ ÒÌ µ ±Í Ê Ê µ µ p(d, p)d Ö Ö É ³ Í É ³, µ²êî ÒÌ µí µ Ö Ô± ³ É µ ÊÎ Õ Ê Ê- INTRODUCTION
 Ó³ Ÿ º3[100]-2000 Particles and Nuclei, Letters No.3[100]-2000 Š 539.1.08 CALIBRATION OF SPES4-π SET-UP IN EXPERIMENTS ON SATURNE-II L.V. Malinina, E.A. Strokovsky Calibration and alignment of the SPES4-π
Ó³ Ÿ º3[100]-2000 Particles and Nuclei, Letters No.3[100]-2000 Š 539.1.08 CALIBRATION OF SPES4-π SET-UP IN EXPERIMENTS ON SATURNE-II L.V. Malinina, E.A. Strokovsky Calibration and alignment of the SPES4-π
Preparatory experiments for cold-neutron induced fission studies at IKI
 Preparatory experiments for cold-neutron induced fission studies at IKI A. Oberstedt 1, S. Oberstedt 2, R. Billnert 1, J. Karlsson 1, X. Ledoux 3, J.-G. Marmouget 3 and F.-J. Hambsch 2 1 School of Science
Preparatory experiments for cold-neutron induced fission studies at IKI A. Oberstedt 1, S. Oberstedt 2, R. Billnert 1, J. Karlsson 1, X. Ledoux 3, J.-G. Marmouget 3 and F.-J. Hambsch 2 1 School of Science
INTERPRETATION OF THE MECHANISM OF SPONTANEOUS FISSION OF HEAVY NUCLEI IN THE FRAMEWORK OF DINUCLEAR SYSTEM CONCEPTION
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2016.. 13, º 6(204).. 1131Ä1142 ˆ ˆŠ Œ ˆ ˆ Œ ƒ Ÿ. ˆŸ INTERPRETATION OF THE MECHANISM OF SPONTANEOUS FISSION OF HEAVY NUCLEI IN THE FRAMEWORK OF DINUCLEAR SYSTEM CONCEPTION V. V. Volkov a, E. A. Cherepanov
Ó³ Ÿ. 2016.. 13, º 6(204).. 1131Ä1142 ˆ ˆŠ Œ ˆ ˆ Œ ƒ Ÿ. ˆŸ INTERPRETATION OF THE MECHANISM OF SPONTANEOUS FISSION OF HEAVY NUCLEI IN THE FRAMEWORK OF DINUCLEAR SYSTEM CONCEPTION V. V. Volkov a, E. A. Cherepanov
Double-neutron capture reaction and natural abundance of 183 W, 195 Pt and 199 Hg isotopes
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Double-neutron capture reaction and natural abundance of 183 W, 195 Pt and 199 Hg isotopes To cite this article: S. A. Karamian et al 2016 J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Double-neutron capture reaction and natural abundance of 183 W, 195 Pt and 199 Hg isotopes To cite this article: S. A. Karamian et al 2016 J. Phys.:
Characterization and Monte Carlo simulations for a CLYC detector
 Characterization and Monte Carlo simulations for a CLYC detector A. Borella 1, E. Boogers 1, R.Rossa 1, P. Schillebeeckx 1 aborella@sckcen.be 1 SCK CEN, Belgian Nuclear Research Centre JRC-Geel, Joint
Characterization and Monte Carlo simulations for a CLYC detector A. Borella 1, E. Boogers 1, R.Rossa 1, P. Schillebeeckx 1 aborella@sckcen.be 1 SCK CEN, Belgian Nuclear Research Centre JRC-Geel, Joint
Instrumental Neutron Activation Analysis
 Instrumental Neutron Activation Analysis The fifth Advanced Summer School, JINR, Dubna, Russia May 12 - June 2, 2013 SUPERVISOR Prof. M.V.FRONTASYEVA Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics PARTICIPANTS Fatma
Instrumental Neutron Activation Analysis The fifth Advanced Summer School, JINR, Dubna, Russia May 12 - June 2, 2013 SUPERVISOR Prof. M.V.FRONTASYEVA Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics PARTICIPANTS Fatma
Alpha-Energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer
 Physical Structure of Matter Radioactivity Alpha-Energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer What you can learn about Decay series Radioactive equilibrium Isotopic properties Decay energy
Physical Structure of Matter Radioactivity Alpha-Energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer What you can learn about Decay series Radioactive equilibrium Isotopic properties Decay energy
Activation Analysis. Characteristic decay mechanisms, α, β, γ Activity A reveals the abundance N:
 2.5. Isotope analysis and neutron activation techniques The previously discussed techniques of material analysis are mainly based on the characteristic atomic structure of the elements and the associated
2.5. Isotope analysis and neutron activation techniques The previously discussed techniques of material analysis are mainly based on the characteristic atomic structure of the elements and the associated
Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics, JINR ISINN, May 2017, Dubna A 15-year forward look at neutron facilities in JINR
 Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics, JINR ISINN, 22 26 May 2017, Dubna A 15-year forward look at neutron facilities in JINR V.L.Aksenov E.P. Shabalin 1. Aksenov V.L., Ananiev V.D., Komyshev G.G., Rogov
Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics, JINR ISINN, 22 26 May 2017, Dubna A 15-year forward look at neutron facilities in JINR V.L.Aksenov E.P. Shabalin 1. Aksenov V.L., Ananiev V.D., Komyshev G.G., Rogov
A Measurement of Monoenergetic Neutrons from 9 Be(p,n) 9 B
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, No. 4, April 1998, pp. 462 467 A Measurement of Monoenergetic Neutrons from 9 Be(p,n) 9 B J. H. Kim, H. Bhang, J. H. Ha, J. C. Kim, M. J. Kim, Y. D. Kim
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, No. 4, April 1998, pp. 462 467 A Measurement of Monoenergetic Neutrons from 9 Be(p,n) 9 B J. H. Kim, H. Bhang, J. H. Ha, J. C. Kim, M. J. Kim, Y. D. Kim
REFERENCE SOURCES FOR THE CALIBRATION OF THE AUTOCORRELATION SINGLE-CRYSTAL SCINTILLATION TIME SPECTROMETER
 REFERENCE SOURCES FOR THE CALIBRATION OF THE AUTOCORRELATION SINGLE-CRYSTAL SCINTILLATION TIME SPECTROMETER V.A. MOROZOV 1, N.V. MOROZOVA 1, T. BĂDICĂ 2, D. DELEANU 2,3, D. GHIŢĂ 2, S. PASCU 2,3 1 Joint
REFERENCE SOURCES FOR THE CALIBRATION OF THE AUTOCORRELATION SINGLE-CRYSTAL SCINTILLATION TIME SPECTROMETER V.A. MOROZOV 1, N.V. MOROZOVA 1, T. BĂDICĂ 2, D. DELEANU 2,3, D. GHIŢĂ 2, S. PASCU 2,3 1 Joint
(a) (i) State the proton number and the nucleon number of X.
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Nuclei of 218 84Po decay by the emission of an particle to form a stable isotope of an element X. You may assume that no emission accompanies the decay. (a) (i) State the
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Nuclei of 218 84Po decay by the emission of an particle to form a stable isotope of an element X. You may assume that no emission accompanies the decay. (a) (i) State the
BEAM DYNAMICS STUDY IN THE C235 CYCLOTRON FOR PROTON THERAPY
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2009.. 6, º 1(150).. 134Ä144 ˆ ˆ ƒˆÿ, Š ƒˆÿ ˆ Ÿ Ÿ Œ ˆ ˆ BEAM DYNAMICS STUDY IN THE C235 CYCLOTRON FOR PROTON THERAPY G. A. Karamysheva, S. A. Kostromin Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna
Ó³ Ÿ. 2009.. 6, º 1(150).. 134Ä144 ˆ ˆ ƒˆÿ, Š ƒˆÿ ˆ Ÿ Ÿ Œ ˆ ˆ BEAM DYNAMICS STUDY IN THE C235 CYCLOTRON FOR PROTON THERAPY G. A. Karamysheva, S. A. Kostromin Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna
Digital simulation of neutron and gamma measurement devices
 3Security of radioactive materials and transport 3 2 Digital simulation of neutron and gamma measurement devices A.-L. WEBER (IRSN) 1 - Maximum activity that a radioactive element can present without being
3Security of radioactive materials and transport 3 2 Digital simulation of neutron and gamma measurement devices A.-L. WEBER (IRSN) 1 - Maximum activity that a radioactive element can present without being
Dependence Of Gamma Ray Attenuation On Concentration Of Manganese (II) Chloride Solution
 Dependence Of Gamma Ray Attenuation On Concentration Of Manganese (II) Chloride Solution Chikkappa Udagani Abstract: This paper presents the precise method to estimate the dependence of linear and mass
Dependence Of Gamma Ray Attenuation On Concentration Of Manganese (II) Chloride Solution Chikkappa Udagani Abstract: This paper presents the precise method to estimate the dependence of linear and mass
Experiments with massive uranium targets - on the way to technologies for Relativistic Nuclear Energy
 Experiments with massive uranium targets - on the way to technologies for Relativistic Nuclear Energy A.Baldin, V.Furman, N.Gundorin, M.Kadykov, Yu. Kopatch, A.Rogov, S.Tyutyunnikov Joint Institute for
Experiments with massive uranium targets - on the way to technologies for Relativistic Nuclear Energy A.Baldin, V.Furman, N.Gundorin, M.Kadykov, Yu. Kopatch, A.Rogov, S.Tyutyunnikov Joint Institute for
A. Aleksanyan, S. Amirkhanyan, H. Gulkanyan*, T. Kotanjyan, L. Poghosyan, V. Pogosov
 Armenian Journal of Physics, 2015, vol. 8, issue 3, pp. 102-111 SEARCHING FOR LONG-LIVING RARE PRODUCTS OF THE 252 Cf SPONTANEOUS FISSION A. Aleksanyan, S. Amirkhanyan, H. Gulkanyan*, T. Kotanjyan, L.
Armenian Journal of Physics, 2015, vol. 8, issue 3, pp. 102-111 SEARCHING FOR LONG-LIVING RARE PRODUCTS OF THE 252 Cf SPONTANEOUS FISSION A. Aleksanyan, S. Amirkhanyan, H. Gulkanyan*, T. Kotanjyan, L.
Development of an active scintillating target for fission studies. J. Aupiais, G. Bélier CEA, DAM, DIF, F Arpajon France
 Development of an active scintillating target for fission studies J. Aupiais, G. Bélier CEA, DAM, DIF, F-91297 Arpajon France 1 Motivations Fast neutron induced reactions are important for future nuclear
Development of an active scintillating target for fission studies J. Aupiais, G. Bélier CEA, DAM, DIF, F-91297 Arpajon France 1 Motivations Fast neutron induced reactions are important for future nuclear
PARAMETERISATION OF FISSION NEUTRON SPECTRA (TRIGA REACTOR) FOR NEUTRON ACTIVATION WITHOUT THE USED OF STANDARD
 Parameterisation of Fission Neutron Spectra (TRIGA Reactor) 81 7 PARAMETERISATION OF FISSION NEUTRON SPECTRA (TRIGA REACTOR) FOR NEUTRON ACTIVATION WITHOUT THE USED OF STANDARD Liew Hwi Fen Noorddin Ibrahim
Parameterisation of Fission Neutron Spectra (TRIGA Reactor) 81 7 PARAMETERISATION OF FISSION NEUTRON SPECTRA (TRIGA REACTOR) FOR NEUTRON ACTIVATION WITHOUT THE USED OF STANDARD Liew Hwi Fen Noorddin Ibrahim
Determination of the boron content in polyethylene samples using the reactor Orphée
 Determination of the boron content in polyethylene samples using the reactor Orphée F. Gunsing, A. Menelle CEA Saclay, F-91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France O. Aberle European Organization for Nuclear Research
Determination of the boron content in polyethylene samples using the reactor Orphée F. Gunsing, A. Menelle CEA Saclay, F-91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France O. Aberle European Organization for Nuclear Research
Neutron flux measurement using fast-neutron activation of 12 B and 12 N isotopes in hydrocarbonate scintillators
 Neutron flux measurement using fast-neutron activation of 12 B and 12 N isotopes in hydrocarbonate scintillators M. M. Boliev E-mail: kchkrv@rambler.ru Yu. F. Novoseltsev R. V. Novoseltseva V. B. Petkov
Neutron flux measurement using fast-neutron activation of 12 B and 12 N isotopes in hydrocarbonate scintillators M. M. Boliev E-mail: kchkrv@rambler.ru Yu. F. Novoseltsev R. V. Novoseltseva V. B. Petkov
Past searches for kev neutrinos in beta-ray spectra
 Past searches for kev neutrinos in beta-ray spectra Otokar Dragoun Nuclear Physics Institute of the ASCR Rez near Prague dragoun@ujf.cas.cz supported by GAČR, P203/12/1896 The ν-dark 2015 Workshop TUM
Past searches for kev neutrinos in beta-ray spectra Otokar Dragoun Nuclear Physics Institute of the ASCR Rez near Prague dragoun@ujf.cas.cz supported by GAČR, P203/12/1896 The ν-dark 2015 Workshop TUM
INTERACTIONS OF RELATIVISTIC HEAVY IONS IN THICK HEAVY ELEMENT TARGETS AND SOME UNRESOLVED PROBLEMS
 E1-2005-167 INTERACTIONS OF RELATIVISTIC HEAVY IONS IN THICK HEAVY ELEMENT TARGETS AND SOME UNRESOLVED PROBLEMS Submitted to the journal Particles and Nuclei É.. E1-2005-167 ³μ É ²ÖÉ É ± Ì μ μ Éμ² ÉÒ³
E1-2005-167 INTERACTIONS OF RELATIVISTIC HEAVY IONS IN THICK HEAVY ELEMENT TARGETS AND SOME UNRESOLVED PROBLEMS Submitted to the journal Particles and Nuclei É.. E1-2005-167 ³μ É ²ÖÉ É ± Ì μ μ Éμ² ÉÒ³
Troitsk ADS project S.Sidorkin, E.Koptelov, L.Kravchuk, A.Rogov
 Troitsk ADS project S.Sidorkin, E.Koptelov, L.Kravchuk, A.Rogov Institute for Nuclear Research RAS, Moscow, Russia Outline Linac and experimental complex Pulse neutron sources and its infrastructure Development
Troitsk ADS project S.Sidorkin, E.Koptelov, L.Kravchuk, A.Rogov Institute for Nuclear Research RAS, Moscow, Russia Outline Linac and experimental complex Pulse neutron sources and its infrastructure Development
Spectroscopy of fission fragments using prompt-delayed coincidence technique
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. journal of September 5 physics pp. 95 Spectroscopy of fission fragments using prompt-delayed coincidence technique RPALIT and S BISWAS Department of Nuclear
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. journal of September 5 physics pp. 95 Spectroscopy of fission fragments using prompt-delayed coincidence technique RPALIT and S BISWAS Department of Nuclear
M. S. Krick D. G. Langner J. E. Stewart.
 LA-UR-97-3427 Title: Energy-Dependent Bias in Plutonium Verification Measurements Using Thermal Neutron Multiplicity Counters Author(s): M. S. Krick D. G. Langner J. E. Stewart Submitted to: http://lib-www.lanl.gov/la-pubs/00412753.pdf
LA-UR-97-3427 Title: Energy-Dependent Bias in Plutonium Verification Measurements Using Thermal Neutron Multiplicity Counters Author(s): M. S. Krick D. G. Langner J. E. Stewart Submitted to: http://lib-www.lanl.gov/la-pubs/00412753.pdf
CDF SILICON VERTEX TRACKER: TEVATRON RUN II PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2002. º 5[114] Particles and Nuclei, Letters. 2002. No. 5[114] Š 539.1.075:621.374.3 + 539.1.05 CDF SILICON VERTEX TRACKER: TEVATRON RUN II PRELIMINARY RESULTS W. Ashmanskas a, S. Belforte b, J.
Ó³ Ÿ. 2002. º 5[114] Particles and Nuclei, Letters. 2002. No. 5[114] Š 539.1.075:621.374.3 + 539.1.05 CDF SILICON VERTEX TRACKER: TEVATRON RUN II PRELIMINARY RESULTS W. Ashmanskas a, S. Belforte b, J.
STUDY OF SLOW AND FAST EXTRACTION FOR THE ULTRALOW ENERGY STORAGE RING (USR)
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2011.. 8, º 1(164).. 85Ä99 Œ ˆŠ ˆ ˆ Š ƒ Š ˆŒ STUDY OF SLOW AND FAST EXTRACTION FOR THE ULTRALOW ENERGY STORAGE RING (USR) G. A. Karamysheva a, A. I. Papash a,b,c,c.p.welsch d,e a Joint Institute
Ó³ Ÿ. 2011.. 8, º 1(164).. 85Ä99 Œ ˆŠ ˆ ˆ Š ƒ Š ˆŒ STUDY OF SLOW AND FAST EXTRACTION FOR THE ULTRALOW ENERGY STORAGE RING (USR) G. A. Karamysheva a, A. I. Papash a,b,c,c.p.welsch d,e a Joint Institute
L 37 Modern Physics [3] The atom and the nucleus. Structure of the nucleus. Terminology of nuclear physics SYMBOL FOR A NUCLEUS FOR A CHEMICAL X
![L 37 Modern Physics [3] The atom and the nucleus. Structure of the nucleus. Terminology of nuclear physics SYMBOL FOR A NUCLEUS FOR A CHEMICAL X L 37 Modern Physics [3] The atom and the nucleus. Structure of the nucleus. Terminology of nuclear physics SYMBOL FOR A NUCLEUS FOR A CHEMICAL X](/thumbs/83/87876806.jpg) L 37 Modern Physics [3] [L37] Nuclear physics what s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity carbon dating [L38] Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear reactors
L 37 Modern Physics [3] [L37] Nuclear physics what s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity carbon dating [L38] Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear reactors
Alpha-energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer (Item No.: P )
 Alpha-energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer (Item No.: P2522015) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: ILIAS Education Level: Physik Topic: Hochschule Subtopic: Moderne Physik Experiment:
Alpha-energies of different sources with Multi Channel Analyzer (Item No.: P2522015) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: ILIAS Education Level: Physik Topic: Hochschule Subtopic: Moderne Physik Experiment:
Delayed neutrons in nuclear fission chain reaction
 Delayed neutrons in nuclear fission chain reaction 1 Critical state Temporal flow Loss by leakage Loss by Absorption If the number of neutrons (the number of fission reactions) is practically constant
Delayed neutrons in nuclear fission chain reaction 1 Critical state Temporal flow Loss by leakage Loss by Absorption If the number of neutrons (the number of fission reactions) is practically constant
3. State each of the four types of inelastic collisions, giving an example of each (zaa type example is acceptable)
 Nuclear Theory - Course 227 OBJECTIVES to: At the conclusion of this course the trainee will be able 227.00-1 Nuclear Structure 1. Explain and use the ZXA notation. 2. Explain the concept of binding energy.
Nuclear Theory - Course 227 OBJECTIVES to: At the conclusion of this course the trainee will be able 227.00-1 Nuclear Structure 1. Explain and use the ZXA notation. 2. Explain the concept of binding energy.
Control of the fission chain reaction
 Control of the fission chain reaction Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 April 8, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 30) April 8, 2011 1 / 29 Outline 1 Fission chain reaction
Control of the fission chain reaction Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 April 8, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 30) April 8, 2011 1 / 29 Outline 1 Fission chain reaction
arxiv: v2 [nucl-ex] 24 Jul 2015
![arxiv: v2 [nucl-ex] 24 Jul 2015 arxiv: v2 [nucl-ex] 24 Jul 2015](/thumbs/89/98742193.jpg) The study of the thermal neutron flux in the deep underground laboratory DULB-4900 1 V.V. Alekseenko, Yu.M. Gavrilyuk, A.M. Gangapshev, A.M. Gezhaev, D.D. Dzhappuev, V.V. Kazalov, A.U. Kudzhaev, V.V. Kuzminov,
The study of the thermal neutron flux in the deep underground laboratory DULB-4900 1 V.V. Alekseenko, Yu.M. Gavrilyuk, A.M. Gangapshev, A.M. Gezhaev, D.D. Dzhappuev, V.V. Kazalov, A.U. Kudzhaev, V.V. Kuzminov,
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF NEUTRON FIELDS PRODUCED IN PROTON REACTIONS WITH HEAVY TARGETS. Nuclear Physics Institute AS CR, Rez Czech Republic
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF NEUTRON FIELDS PRODUCED IN PROTON REACTIONS WITH HEAVY TARGETS A. Kugler, V. Wagner Nuclear Physics Institute AS CR, 25068 Rez Czech Republic I. Introduction One of important aspects
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF NEUTRON FIELDS PRODUCED IN PROTON REACTIONS WITH HEAVY TARGETS A. Kugler, V. Wagner Nuclear Physics Institute AS CR, 25068 Rez Czech Republic I. Introduction One of important aspects
Measurement of the Westcott Conventionality Thermal Neutron Flux and Suchlike at Irradiation Facilities of the KUR
 Measurement of e Westcott Conventionality Thermal Neutron Flux and Suchlike at Irradiation Facilities of e KUR Hiroshi CHATANI Research Reactor Institute, Kyoto University Kumatori-cho, Sennan-gun, Osaka
Measurement of e Westcott Conventionality Thermal Neutron Flux and Suchlike at Irradiation Facilities of e KUR Hiroshi CHATANI Research Reactor Institute, Kyoto University Kumatori-cho, Sennan-gun, Osaka
Introduction to Radiological Sciences Neutron Detectors. Theory of operation. Types of detectors Source calibration Survey for Dose
 Introduction to Radiological Sciences Neutron Detectors Neutron counting Theory of operation Slow neutrons Fast neutrons Types of detectors Source calibration Survey for Dose 2 Neutrons, what are they?
Introduction to Radiological Sciences Neutron Detectors Neutron counting Theory of operation Slow neutrons Fast neutrons Types of detectors Source calibration Survey for Dose 2 Neutrons, what are they?
arxiv: v2 [physics.ins-det] 8 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v2 [physics.ins-det] 8 Feb 2013 arxiv: v2 [physics.ins-det] 8 Feb 2013](/thumbs/91/107598870.jpg) Preprint typeset in JINST style - HYPER VERSION arxiv:1302.0278v2 [physics.ins-det] 8 Feb 2013 Investigation of gamma ray detection performance of thin LFS scintillator with MAPD readout E.Guliyev a, F.Ahmadov
Preprint typeset in JINST style - HYPER VERSION arxiv:1302.0278v2 [physics.ins-det] 8 Feb 2013 Investigation of gamma ray detection performance of thin LFS scintillator with MAPD readout E.Guliyev a, F.Ahmadov
Verification measurements of alpha active waste
 Verification measurements of alpha active waste Bent Pedersen Nuclear Security Unit Directorate Nuclear Safety and Security JRC 9th Edition of the International Summer School on Nuclear Decommissioning
Verification measurements of alpha active waste Bent Pedersen Nuclear Security Unit Directorate Nuclear Safety and Security JRC 9th Edition of the International Summer School on Nuclear Decommissioning
Nuclear Fission. 1/v Fast neutrons. U thermal cross sections σ fission 584 b. σ scattering 9 b. σ radiative capture 97 b.
 Nuclear Fission 1/v Fast neutrons should be moderated. 235 U thermal cross sections σ fission 584 b. σ scattering 9 b. σ radiative capture 97 b. Fission Barriers 1 Nuclear Fission Q for 235 U + n 236 U
Nuclear Fission 1/v Fast neutrons should be moderated. 235 U thermal cross sections σ fission 584 b. σ scattering 9 b. σ radiative capture 97 b. Fission Barriers 1 Nuclear Fission Q for 235 U + n 236 U
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 29 Jun 2011
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 29 Jun 2011 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 29 Jun 2011](/thumbs/74/71147369.jpg) Investigation of Large LGB Detectors for Antineutrino Detection P. Nelson a,, N. S. Bowden b, a Department of Physics, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA 99, USA b Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory,
Investigation of Large LGB Detectors for Antineutrino Detection P. Nelson a,, N. S. Bowden b, a Department of Physics, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA 99, USA b Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory,
Verification measurements of alpha active waste
 Verification measurements of alpha active waste Bent Pedersen Nuclear Security Unit Institute for Transuranium Elements (ITU), JRC Operational Issues in Radioactive Waste Management and Nuclear Decommissioning
Verification measurements of alpha active waste Bent Pedersen Nuclear Security Unit Institute for Transuranium Elements (ITU), JRC Operational Issues in Radioactive Waste Management and Nuclear Decommissioning
DEVELOPMENT OF JINR FLNR HEAVY-ION ACCELERATOR COMPLEX IN THE NEXT 7 YEARS
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2010.. 7, º 7(163).. 827Ä834 ˆ ˆŠ ˆ ˆŠ Š ˆ DEVELOPMENT OF JINR FLNR HEAVY-ION ACCELERATOR COMPLEX IN THE NEXT 7 YEARS G. Gulbekyan, B. Gikal, I. Kalagin, N. Kazarinov Joint Institute for Nuclear
Ó³ Ÿ. 2010.. 7, º 7(163).. 827Ä834 ˆ ˆŠ ˆ ˆŠ Š ˆ DEVELOPMENT OF JINR FLNR HEAVY-ION ACCELERATOR COMPLEX IN THE NEXT 7 YEARS G. Gulbekyan, B. Gikal, I. Kalagin, N. Kazarinov Joint Institute for Nuclear
SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY
 Section 9: SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY This section briefly describes various sources of radioactive nuclei, both naturally occurring and those produced artificially (man-made) in, for example, reactors or
Section 9: SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY This section briefly describes various sources of radioactive nuclei, both naturally occurring and those produced artificially (man-made) in, for example, reactors or
1 Introduction MCNPX SIMULATIONS OF THE ENERGY PLUS TRANSMUTATION SYSTEM: NUCLEAR TRACK DETECTORS
 MCNPX SIMULATIONS OF THE ENERGY PLUS TRANSMUTATION SYSTEM: NUCLEAR TRACK DETECTORS M. Majerle 1,2, V. Wagner 1,2, A. Krása 1,2, J. Adam 1,3, S.R. Hashemi-Nezhad 4, M.I. Krivopustov 3, A. Kugler 1, V.M.
MCNPX SIMULATIONS OF THE ENERGY PLUS TRANSMUTATION SYSTEM: NUCLEAR TRACK DETECTORS M. Majerle 1,2, V. Wagner 1,2, A. Krása 1,2, J. Adam 1,3, S.R. Hashemi-Nezhad 4, M.I. Krivopustov 3, A. Kugler 1, V.M.
Application of prompt gamma activation analysis with neutron beams for the detection and analysis of nuclear materials in containers
 Application of prompt gamma activation analysis with neutron beams for the detection and analysis of nuclear materials in containers Zsolt Révay Institute of Isotopes, Budapest, Hungary Dept. of Nuclear
Application of prompt gamma activation analysis with neutron beams for the detection and analysis of nuclear materials in containers Zsolt Révay Institute of Isotopes, Budapest, Hungary Dept. of Nuclear
Alpha-particle Stopping Powers in Air and Argon
 Alpha-particle Stopping Powers in Air and Argon Mohammad QH 1* and Maghdid HA 2 1 Department of Physics, College of Science, Raparin University, Sulaimanyah, Iraqi Kurdistan, Iraq 2 Department of Physics,
Alpha-particle Stopping Powers in Air and Argon Mohammad QH 1* and Maghdid HA 2 1 Department of Physics, College of Science, Raparin University, Sulaimanyah, Iraqi Kurdistan, Iraq 2 Department of Physics,
High efficiency 3 He neutron detector TETRA for DESIR.
 DESIR workshop, May 2010 High efficiency 3 He neutron detector TETRA for DESIR. Yuri Penionzhkevich Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna Beta Decay of Exotic Nuclei: Goal to study Neutron emission
DESIR workshop, May 2010 High efficiency 3 He neutron detector TETRA for DESIR. Yuri Penionzhkevich Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna Beta Decay of Exotic Nuclei: Goal to study Neutron emission
A new method to acquire nuclear fission data using heavy ion reactions a way to understand the fission phenomenon
 press release date Friday 26 August 15:00 (material distribution) Education, Culture, Sports, Science Press conf., Nuclear Regulatory Agency Press conf., Ibaraki Pref.. Government press conf., Osaka Science
press release date Friday 26 August 15:00 (material distribution) Education, Culture, Sports, Science Press conf., Nuclear Regulatory Agency Press conf., Ibaraki Pref.. Government press conf., Osaka Science
Measurement of neutron total cross-sections of 209 Bi at the Pohang Neutron Facility* WANG Tao-Feng ( 王涛峰 ) 1,2,
 Measurement of neutron total cross-sections of 209 Bi at the Pohang Neutron Facility* WANG Tao-Feng ( 王涛峰 ) 1,2,, A.K.M.M.H.Meaze 3, Guinyun KIM 4 1 International Research Center for Nuclei and Particles
Measurement of neutron total cross-sections of 209 Bi at the Pohang Neutron Facility* WANG Tao-Feng ( 王涛峰 ) 1,2,, A.K.M.M.H.Meaze 3, Guinyun KIM 4 1 International Research Center for Nuclei and Particles
Neutron Physics. The De Broglie relation for matter is: h mv (1) λ =
 Neutron Physics Emily P. Wang MIT Department of Physics (Dated: November 11, 2004) Thermal neutrons in a beam emerging from the MIT research reactor were used to study the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution,
Neutron Physics Emily P. Wang MIT Department of Physics (Dated: November 11, 2004) Thermal neutrons in a beam emerging from the MIT research reactor were used to study the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution,
A VERY HIGH EFFICIENCY NEUTRON COUNTER FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF PLUTONIUM IN DECOMMISSIONING WASTES. J.A. Mason/A.N. Technology Ltd.
 Proceedings of ICEM 03: The 9 th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management September 1 5, 003, Examination Schools, Oxford, England ICEM03-4659 A VERY HIGH
Proceedings of ICEM 03: The 9 th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management September 1 5, 003, Examination Schools, Oxford, England ICEM03-4659 A VERY HIGH
Introduction to Environmental Measurement Techniques Radioactivity. Dana Pittauer 1of 48
 Introduction to Environmental Measurement Techniques 2016 Radioactivity Dana Pittauer (dpittauer@marum.de) 1of 48 Introduction Radioisotopes are of interest in environmental physics for several reasons:
Introduction to Environmental Measurement Techniques 2016 Radioactivity Dana Pittauer (dpittauer@marum.de) 1of 48 Introduction Radioisotopes are of interest in environmental physics for several reasons:
A Photofission Delayed γ-ray Spectra Calculation Tool for the Conception of a Nuclear Material Characterization Facility
 A Photofission Delayed γ-ray Spectra Calculation Tool for the Conception of a Nuclear Material Characterization Facility D. BERNARD *, O. SEROT *, E. SIMON *, L. BOUCHER * and S. PLUMERI + Abstract The
A Photofission Delayed γ-ray Spectra Calculation Tool for the Conception of a Nuclear Material Characterization Facility D. BERNARD *, O. SEROT *, E. SIMON *, L. BOUCHER * and S. PLUMERI + Abstract The
Thesis and PhD themes
 Thesis and PhD themes DETERMINATION OF MASSES OF THE SUPER HEAVY ELEMENTS IN THE EXPERIMENTS ON SYNTHESIS OF 112 AND 114 ELEMENTS USING THE REACTIONS 48 CA+ 238 U AND 48 CA+ 242 PU Traditionally, in experiments
Thesis and PhD themes DETERMINATION OF MASSES OF THE SUPER HEAVY ELEMENTS IN THE EXPERIMENTS ON SYNTHESIS OF 112 AND 114 ELEMENTS USING THE REACTIONS 48 CA+ 238 U AND 48 CA+ 242 PU Traditionally, in experiments
QUANTUM DECOHERENCE IN THE THEORY OF OPEN SYSTEMS
 Ó³ Ÿ. 007.. 4, º 38.. 3Ä36 Š Œ œ ƒˆˆ ˆ ˆŠˆ QUANTUM DECOHERENCE IN THE THEORY OF OPEN SYSTEMS A. Isar Department of Theoretical Physics, Institute of Physics and Nuclear Engineering, Bucharest-Magurele,
Ó³ Ÿ. 007.. 4, º 38.. 3Ä36 Š Œ œ ƒˆˆ ˆ ˆŠˆ QUANTUM DECOHERENCE IN THE THEORY OF OPEN SYSTEMS A. Isar Department of Theoretical Physics, Institute of Physics and Nuclear Engineering, Bucharest-Magurele,
Angular and energy distributions of the prompt fission neutrons from thermal neutron-induced fission of 239 Pu
 Angular and energy distributions of the prompt fission neutrons from thermal neutron-induced fission of 239 Pu Vorobyev AS, Shcherbakov OA, Gagarski AM, Val ski GV, Petrov GA National Research Center Kurchatov
Angular and energy distributions of the prompt fission neutrons from thermal neutron-induced fission of 239 Pu Vorobyev AS, Shcherbakov OA, Gagarski AM, Val ski GV, Petrov GA National Research Center Kurchatov
I. Pre-Lab Introduction
 I. Pre-Lab Introduction Please complete the following pages before the lab by filling in the requested items. A. Atomic notation: Atoms are composed of a nucleus containing neutrons and protons surrounded
I. Pre-Lab Introduction Please complete the following pages before the lab by filling in the requested items. A. Atomic notation: Atoms are composed of a nucleus containing neutrons and protons surrounded
Precision neutron flux measurement with a neutron beam monitor
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Precision neutron flux measurement with a neutron beam monitor To cite this article: T Ino et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 528 012039 View the article
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Precision neutron flux measurement with a neutron beam monitor To cite this article: T Ino et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 528 012039 View the article
Write down the nuclear equation that represents the decay of neptunium 239 into plutonium 239.
 Q1.A rod made from uranium 238 ( U) is placed in the core of a nuclear reactor where it absorbs free neutrons. When a nucleus of uranium 238 absorbs a neutron it becomes unstable and decays to neptunium
Q1.A rod made from uranium 238 ( U) is placed in the core of a nuclear reactor where it absorbs free neutrons. When a nucleus of uranium 238 absorbs a neutron it becomes unstable and decays to neptunium
STUDY OF NEUTRON IRRADIATION-INDUCED COLOR IN TOPAZ AT THE PULSED REACTOR IBR-2. Abstract
 STUDY OF NEUTRON IRRADIATION-INDUCED COLOR IN TOPAZ AT THE PULSED REACTOR IBR-2 Yu. Khatchenko 1, T. Enik 2, M. Kovalenko 1, O. Ryabukhin 1, M. Bulavin 2, A. Verkhoglyadov 2, S. Borzakov 2, K. Khramko
STUDY OF NEUTRON IRRADIATION-INDUCED COLOR IN TOPAZ AT THE PULSED REACTOR IBR-2 Yu. Khatchenko 1, T. Enik 2, M. Kovalenko 1, O. Ryabukhin 1, M. Bulavin 2, A. Verkhoglyadov 2, S. Borzakov 2, K. Khramko
Nuclear Fission. ~200 MeV. Nuclear Reactor Theory, BAU, Second Semester, (Saed Dababneh).
 Surface effect Coulomb effect ~200 MeV 1 B.E. per nucleon for 238 U (BE U ) and 119 Pd (BE Pd )? 2x119xBE Pd 238xBE U =?? K.E. of the fragments 10 11 J/g Burning coal 10 5 J/g Why not spontaneous? Two
Surface effect Coulomb effect ~200 MeV 1 B.E. per nucleon for 238 U (BE U ) and 119 Pd (BE Pd )? 2x119xBE Pd 238xBE U =?? K.E. of the fragments 10 11 J/g Burning coal 10 5 J/g Why not spontaneous? Two
HANAA* Humans Applying Neutron Activation Analysis Hassan Amany Noura Ahmed Ali
 HANAA* Humans Applying Neutron Activation Analysis Hassan Amany Noura Ahmed Ali Neutron & Gamma ray Spectrometry Ahmed Mohamed Hassan, Assistant Lecturer, Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Mansoura
HANAA* Humans Applying Neutron Activation Analysis Hassan Amany Noura Ahmed Ali Neutron & Gamma ray Spectrometry Ahmed Mohamed Hassan, Assistant Lecturer, Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Mansoura
Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface
 Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface 2005 2006 Time: 60 minutes Total Value: 33 Marks Formulae and Constants v = f λ E = hf h f = E k + W 0 E = m c 2 p = h λ 1 A= A T 0 2 t 1 2 E k = ½ mv 2
Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface 2005 2006 Time: 60 minutes Total Value: 33 Marks Formulae and Constants v = f λ E = hf h f = E k + W 0 E = m c 2 p = h λ 1 A= A T 0 2 t 1 2 E k = ½ mv 2
PoS(ICHEP2016)474. SoLid: Search for Oscillations with a Lithium-6 Detector at the SCK CEN BR2 reactor
 SoLid: Search for Oscillations with a Lithium-6 Detector at the SCK CEN BR2 reactor University of Bristol E-mail: dan.saunders@bristol.ac.uk The disappearance of reactor antineutrinos into a new neutral
SoLid: Search for Oscillations with a Lithium-6 Detector at the SCK CEN BR2 reactor University of Bristol E-mail: dan.saunders@bristol.ac.uk The disappearance of reactor antineutrinos into a new neutral
Photofission of 238-U Nuclei
 Photofission of 238-U Nuclei International Thorium Energy Conference - ThEC18, 29-31st of October 2018, Belgium İsmail Boztosun This research has been supported by TÜBİTAK with grant number 114F220 Motivations
Photofission of 238-U Nuclei International Thorium Energy Conference - ThEC18, 29-31st of October 2018, Belgium İsmail Boztosun This research has been supported by TÜBİTAK with grant number 114F220 Motivations
STUDIES OF INTERACTION OF PARTIALLY COHERENT LASER RADIATION WITH PLASMA
 1 STUDIES OF INTERACTION OF PARTIALLY COHERENT LASER RADIATION WITH PLASMA Starodub A.N, Fedotov S.I., Fronya A.A., Kruglov B.V., Mal kova S.V., Osipov M.V., Puzyrev V.N., Sahakyan A.T., Vasin B.L., Yakushev
1 STUDIES OF INTERACTION OF PARTIALLY COHERENT LASER RADIATION WITH PLASMA Starodub A.N, Fedotov S.I., Fronya A.A., Kruglov B.V., Mal kova S.V., Osipov M.V., Puzyrev V.N., Sahakyan A.T., Vasin B.L., Yakushev
The possibility to use energy plus transmutation set-up for neutron production and transport benchmark studies
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 68, No. 2 journal of February 2007 physics pp. 297 306 The possibility to use energy plus transmutation set-up for neutron production and transport benchmark studies
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 68, No. 2 journal of February 2007 physics pp. 297 306 The possibility to use energy plus transmutation set-up for neutron production and transport benchmark studies
Correction of the electric resistivity distribution of Si wafers using selective neutron transmutation doping (SNTD) in MARIA nuclear research reactor
 NUKLEONIKA 2012;57(3):363 367 ORIGINAL PAPER Correction of the electric resistivity distribution of Si wafers using selective neutron transmutation doping (SNTD) in MARIA nuclear research reactor Mikołaj
NUKLEONIKA 2012;57(3):363 367 ORIGINAL PAPER Correction of the electric resistivity distribution of Si wafers using selective neutron transmutation doping (SNTD) in MARIA nuclear research reactor Mikołaj
