Section 2.1 Limits: Approached Numerically and Graphically
|
|
|
- Gwen Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section 2.1 Limits: Approached Numerically and Graphically Foundation Concepts: Limit Left-hand limit Right-hand limit 1 = 1 = tiny big Practice: 1. What can we say about lim,. f(x)? a) If lim, 3 4 f(x)=7 and lim f(x)=7, what can we say about lim f(x)?, 35, 3 b) If lim, 6 4 f(x)=7 and lim f(x)=9, what can we say about lim f(x)?, 65, 6 c) If lim f(x) =, what can we say about lim f(x)?, 78, 78
2 2. Use the graph on the right to find the following limits: a. lim f(x) =, 7; 5 b. lim f(x) =, 7; 4 c. lim, = f(x) = 3. Use the graph below to find lim, >/6 f(x) 4. Find the limit, if it exists: lim, 6 (x 6 + 8x 2) Problems Example 1 Use the following graph of G to find each limit. If the limit does not exist, state that fact. a) lim, 78 5 G(x) b) lim, 78 4 G(x) c) lim, 78 G(x) d) lim, = 5 G(x) e) lim, = 4 G(x) f) lim, = G(x) g) lim, 8 5 G(x) h) lim, 8 4 G(x) i) lim, 8 G(x) j) lim, ; G(x)
3 Example 2 Given Find a) lim, 8 5 F(x) b) lim, 8 4 F(x) c) lim, 8 F(x) Example 3 Given Find a) lim, 6 5 F(x) b) lim, 6 4 F(x) c) lim, 6 F(x)
4 Section 2.2 Limits and Continuity Foundation Concepts: Properties of Limits L1 lim,. c = L2 lim,. x = L3 lim,. cf(x) = L4 lim,. [f(x)] I = K L5 lim Jf(x) =,. If lim,. f(x) = L and lim,. g(x) = M, then we have the following. L6 lim,. [f(x) ± g(x)] = L7 lim,. [f(x) g(x)] = Q(,) L8 lim =,. R(R) Continuous
5 Practice: 1. Find lim, 6 (x 6 2x + 5). 2. Find lim, 6 x + 1. Use the graph below to answer questions f( 1) = ; lim f(x) = ; f is/is not (circle one) continuous at x = 1, 78 because. 4. f(1) = ; lim, 8 f(x) = ; f is/is not (circle one) continuous at x = 1 because. 5. f(3) = ; lim, ; f(x) = ; f is/is not (circle one) continuous at x = 3 because. Note: In the last space, cite the reason why the function is or is not continuous using the aspects of the definition of continuous.
6 6. Find the limit, if it exists: lim,w 7X, ;,7;. (Hint: the initiation substitution of x = 3 yields the form 0/0. Look for a way to simplify the function algebraically or use a table and/or graph to determine the limit.) 7. Find the limit, if it exists: lim, 8Y x 6 9. Problems Example 1 Use the graph below to answer the following questions. a) Find g( 1). b) Find lim g(x), lim g(x), and lim g(x)., 785 4, 78, 78 c) Is g continuous at x = 1? Why or why not? d) Find g(3).
7 e) Find lim, ; 5 g(x), lim g(x), and lim g(x)., ; 4, ; f) Is g continuous at x = 3? Why or why not? Example 2 Find lim, 8.,78, W 78. Example 3 Find lim. (8]\)^78 \ = \. Example 4 Find lim \ =. _ `4a 7_` \.
8 Section 2.3 Average Rates of Change Foundation Concepts: Average rate of change Difference quotient Practice: 1. The average price of a ticket to a minor league baseball game can be approximated by p(x) = 0.02x x , where x is the number of years after 1990 and p(x) is in dollars. (i) Find p(6). (ii) Find p(13). (iii) Find p(13) p(6). (iv) Find g(8;)7g(h), and interpret this result. 8;7h 2. Find the simplified form of the difference quotient for f(x) = 3x 2x 6. Show your work.
9 Problems Example 1 For f(x) = 2 2x 6, a) Find a simplified form of the difference quotient Q(,]\)7Q(,) \ b) Use the simplified form to compute the difference quotient for x = 1 and i. h = 0.5 ii. h = 0.1 iii. h = 0.01 iv. h = Example 2 If a rock is thrown from the ground with an initial velocity of 80 feet per second, then the height of the rock, in feet, at t seconds can be modeled by s(t) = 16t t, 0 t 5. a) Find s(2) s(0). b) Find m(6)7m(=). What does this quantity represent? 67=
10 Example 3 The number of unbreakable sunglasses sold at a specialty store during a sales promotion can be modeled by g(x) = 2x x, 0 x 10, where x represents the number of weeks since the promotion began and g(x) represents the number of sunglasses sold. a) Find g(2) g(0). What does this quantity represent? b) Find R(6)7R(=). What does this quantity represent? 67= c) Find g(10) g(8). What does this quantity represent? d) Find R(8=)7R(n). What does this quantity represent? 8=7n e) Compare the answers obtained in parts (b) and (d). Which is greater? Why?
11 Section 2.4 Differentiation Using Limits of Difference Quotients Foundation Conceptual: A. Give the definition of the derivative of f(x) using a limit of the difference quotient B. What is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of f(x) at x = a? Differentiable vs Nondifferentiable
12 Practice: 1. For f(x) = x 6 + 2x 5, find f p (x) using the difference quotient. 2. Given that f(x) = 6 and, fp (x) = 6 W, find the equation of the tangent line at x = 2., 3. If a rock is dropped from the top of a 196 ft tall building, the height of the rock, in feet, at t seconds can be modeled by s(t) = t 6, 0 t 3.5. Find v(t). Problems Example 1 For f(x) = x 6 x, a) Find a simplified form of the difference quotient Q(,]\)7Q(,). \ b) Find f p frx+hs f(x) (x) by lim using the simplified form in (a). \ = h
13 c) Compute f p (a) for the given values of a: i. a = 2 ii. a = 0 iii. a = 0.5 iv. a = 1 Example 2 For f(x) = x 6 2x + 3, a) Find f p frx+hs f(x) (x) by lim. \ = h b) Compute f p (a) for the given values of a: i. a = 2 ii. a = 0 iii. a = 1 c) Find the equation of the tangent line at point ra, f(a)s for the given values of a in part (b). i. a = 2 ii. a = 0 iii. a = 1
14 d) Graph the function and draw tangent lines at these points to confirm that the slopes match the derivatives obtained in part (b). Tip: If you have a graphing calculator, now would be a great time to use it!
15 Section 2.5 Basic Derivative Formulas and Properties Foundation Conceptual: A. Write two different notations to express the derivative of function f(x). B. If y = f(x) = C, then y p = f p (x) = (Derivative of a Constant Function) C. If y = f(x) = x v, then y p = f p (x) = (Power Rule) D. If y = f(x) = e,, then y p = f p (x) = (Natural Exponential Function Rule) E. If F(x) = k f(x), then y F(x) = (Constant Multiple Property) y, F. If F(x) = g(x) ± h(x), then y F(x) = (Sum and Difference Properties) y, G. Higher Order Derivatives Practice: 1. Find the derivative of y = 5x 6 2.1x. 2. Given that f(x) = 5x 6 7x + 9, find f p (x).
16 3. Differentiate y = 6 x. 4. Given y = ;, dy, compute., 6 dx 5. Given s(t) = t 6, find s p (t) and s pp (t). Problems Example 1 For each of the following functions, find f p (x). 5 a) f(x) = 3 Jx 3 b) f(x) = 6, W c) f(x) = 6,
17 Example 2 For each of the following functions, find y. a) y = 3, } +3 x 3 ^, W b) y =,W ; + ;, W c) y = 5e, x ~ Example 3 a) y W Differentiate. y, W (8x6 6x + 4) b) y y, x} c) y y, (3e, ) Example 4 Find the points on the curve where the tangent line is horizontal. If such a point does not exist, state that fact. a) f(x) = 8 6 x6 1 b) f(x) = 2x ; + 3x 6 12x + 1 c) f(x) = 3x 1
18 Example 5 If a rock is thrown from the ground with an initial velocity of 80 feet per second, then the height of the rock, in feet, at t seconds can be modeled by s(t) = 16t t, 0 t 5. a) Find v(t) and a(t). b) Find v(3). What does this quantity represent? c) At t = 3 seconds, is the rock rising up or falling down? How do you know? d) At what time does the rock reach the highest height, and what is that height? e) What is the acceleration of the rock when it reaches the highest height?
19 Section 2.6 Differentiation Techniques: Product & Quotient Rules Foundation Conceptual: A. If F(x) = f(x) g(x), then F (x) = (Product Rule) B. If F(x) = Q(,), then y F(x) = (Quotient Rule) R(,) y, Practice: 1. Differentiate g(x) = (x )(x 7; + 5). 2. For the function f(x) = (3x 6 + 2)e,, a. Find f p (x). b. Find f p (0). c. Find an equation of the tangent line to the graph of the function at (0,2).
20 ,^ 3. Differentiate (x) =,78. Problems Example 1 For each of the following functions, find f p (x). a) f(x) = 3 x + n, (e, + x 6 + 4) b) f(x) = 6, ~` Example 2 For y = 3 xe, + 6 yƒ, find., y,
21 Example 3 Differentiate: yw y, W (x6 e, ) Example 4 A men s suit manufacturer finds that the cost, in dollars, of producing x suits is given by C(x) = x. Find the derivative of the average cost per item. Example 5 Find an equation of the tangent line to the graph of the function f(x) = a) x = 0 Y, W ]6 at b) x = 1
22 Section 2.7 Extended Power and Natural Exponential Rules Foundation Conceptual: A. If F(x) = [g(x)] v, then F (x) = (Extended Power Rule) B. If F(x) = e R(,), then F (x) = (Extended Natural Exponential Rule) Practice: Differentiate the following functions. 1. f(x) = (3 3x) 6;= 2. f(x) = 2 4x 3 + 3x 6 3. f(x) = 2e ;,W ]6,
23 4. f(x) = 8 (3, W 7},7;) Problems Example 1 For each of the following functions, indicate which rule(s) (Power Rule, Natural Exponential Rule, Sum and Difference, Product Rule, Quotient Rule, Extended Power Rule, Extended Natural Exponential Rule, etc.) should be used to find f p (x). (You do not need to compute f p (x).) a) f(x) = (2x ; + 5x 6 3) } b) f(x) = 5e =.=h c) f(x) = 3e Y,^73, d) f(x) = (x + 1) } (3x 2) 6 e) f(x) = 4x 3 e ;,W f) f(x) = x x f) f(x) = 3,]; },76 ; h) f(x) = } (6,]8)^ Example 2 For each of the following functions, find f p (x). (Tip: See above!) a) f(x) = x x 6 + 1
24 b) f(x) = 3,]; },76 ; c) f(x) = } (6,]8)^ Example 3 Differentiate: yw y, W re,w s
25 Section 2.8 Chain Rule and Derivatives of Log Functions Foundation Conceptual: A. If y = F(x) = frg(x)s, call y = f(u) with u = g(x), then y p = F p (x) = or yƒ = (Chain Rule) y, B. D. y ln x = C. y ln g(x) = y, y, y y, log. x = E. y y, a, = Practice: 1. For f(x) = 5x ; + 8 and g(x) = 2x, a. Find (f g)(x). b. Find (g f)(x). 2. Differentiate: a. y = ln(9x ; x 6 ) b. f(t) = ln(t ; + t) 3
26 3. Differentiate: a. y = 3 7, b. y = log 3 7x Problems Example 1 For each of the following, find yƒ, yœ yƒ and. yœ y, y, a) y = u ; and u = 3e, + 2 b) y = e Œ and u = 3x c) y = ln u and u = x Y + 1 Example 2 Find y p for y = 3 x ln(6x).
27 Example 3 Differentiate: yw y, W (x6 ln x) Example 4 at (1,0). Find an equation of the tangent line to the graph of the function f(x) = (3x + 2) ln x Example 5 In one city, 35% of all aluminum cans distributed will be recycled each year. A juice company distributes 110,000 cans. The number still in use after time t, in years, is given by N(t) = 110,000(0.35) Ž. Find N (t).
OBJECTIVE Find limits of functions, if they exist, using numerical or graphical methods.
 1.1 Limits: A Numerical and Graphical Approach OBJECTIVE Find limits of functions, if they exist, using numerical or graphical methods. 1.1 Limits: A Numerical and Graphical Approach DEFINITION: As x approaches
1.1 Limits: A Numerical and Graphical Approach OBJECTIVE Find limits of functions, if they exist, using numerical or graphical methods. 1.1 Limits: A Numerical and Graphical Approach DEFINITION: As x approaches
Chapter 4. Section Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 4 Section 4.2 - Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Objectives: The student will be able to calculate the derivative of e x and of lnx. The student will be able to compute the
Chapter 4 Section 4.2 - Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Objectives: The student will be able to calculate the derivative of e x and of lnx. The student will be able to compute the
MAC 2233 Chapter 3 Practice for the Test
 Class: Date: MAC 33 Chapter 3 Practice for the Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. At which labeled point is the slope of the tangent
Class: Date: MAC 33 Chapter 3 Practice for the Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. At which labeled point is the slope of the tangent
Final Exam Review. MATH Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri. Name:. Show all your work.
 MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri Dr. Kracht Name:. 1. Consider the function f depicted below. Final Exam Review Show all your work. y 1 1 x (a) Find each of the following
MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri Dr. Kracht Name:. 1. Consider the function f depicted below. Final Exam Review Show all your work. y 1 1 x (a) Find each of the following
MATH 236 ELAC FALL 2017 CA 9 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 236 ELAC FALL 207 CA 9 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. ) 27 p 3 27 p 3 ) 2) If 9 t 3 4t 9-2t = 3, find t. 2) Solve the equation.
MATH 236 ELAC FALL 207 CA 9 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. ) 27 p 3 27 p 3 ) 2) If 9 t 3 4t 9-2t = 3, find t. 2) Solve the equation.
e) Find the average revenue when 100 units are made and sold.
 Math 142 Week in Review Set of Problems Week 7 1) Find the derivative, y ', if a) y=x 5 x 3/2 e 4 b) y= 1 5 x 4 c) y=7x 2 0.5 5 x 2 d) y=x 2 1.5 x 10 x e) y= x7 5x 5 2 x 4 2) The price-demand function
Math 142 Week in Review Set of Problems Week 7 1) Find the derivative, y ', if a) y=x 5 x 3/2 e 4 b) y= 1 5 x 4 c) y=7x 2 0.5 5 x 2 d) y=x 2 1.5 x 10 x e) y= x7 5x 5 2 x 4 2) The price-demand function
3. Find the slope of the tangent line to the curve given by 3x y e x+y = 1 + ln x at (1, 1).
 1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
Math 1120 Calculus Final Exam
 May 4, 2001 Name The first five problems count 7 points each (total 35 points) and rest count as marked. There are 195 points available. Good luck. 1. Consider the function f defined by: { 2x 2 3 if x
May 4, 2001 Name The first five problems count 7 points each (total 35 points) and rest count as marked. There are 195 points available. Good luck. 1. Consider the function f defined by: { 2x 2 3 if x
Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems
 Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems Coverage of the midterm: Sections 10.1-10.7, 11.2-11.6 Sections or topics NOT on the midterm: Section 11.1 (The constant e and continuous compound interest, Section
Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems Coverage of the midterm: Sections 10.1-10.7, 11.2-11.6 Sections or topics NOT on the midterm: Section 11.1 (The constant e and continuous compound interest, Section
Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review
 Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review Note to students: The final exam for MAT10, MAT 11 and MAT1 will consist of 30 multiple-choice questions and a few open-ended questions. The exam itself will cover
Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review Note to students: The final exam for MAT10, MAT 11 and MAT1 will consist of 30 multiple-choice questions and a few open-ended questions. The exam itself will cover
3.4 The Chain Rule. F (x) = f (g(x))g (x) Alternate way of thinking about it: If y = f(u) and u = g(x) where both are differentiable functions, then
 3.4 The Chain Rule To find the derivative of a function that is the composition of two functions for which we already know the derivatives, we can use the Chain Rule. The Chain Rule: Suppose F (x) = f(g(x)).
3.4 The Chain Rule To find the derivative of a function that is the composition of two functions for which we already know the derivatives, we can use the Chain Rule. The Chain Rule: Suppose F (x) = f(g(x)).
x C) y = - A) $20000; 14 years B) $28,000; 14 years C) $28,000; 28 years D) $30,000; 15 years
 Dr. Lee - Math 35 - Calculus for Business - Review of 3 - Show Complete Work for Each Problem MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find
Dr. Lee - Math 35 - Calculus for Business - Review of 3 - Show Complete Work for Each Problem MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find
Section 2.1, Section 3.1 Rate of change, Tangents and Derivatives at a point
 Section 2.1, Section 3.1 Rate of change, Tangents and Derivatives at a point Line through P and Q approaches to the tangent line at P as Q approaches P. That is as a + h a = h gets smaller. Slope of the
Section 2.1, Section 3.1 Rate of change, Tangents and Derivatives at a point Line through P and Q approaches to the tangent line at P as Q approaches P. That is as a + h a = h gets smaller. Slope of the
Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A
 Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A Name: While every attempt was made to be complete in the types of problems given below, we make no guarantees about the completeness of the problems. Specifically,
Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A Name: While every attempt was made to be complete in the types of problems given below, we make no guarantees about the completeness of the problems. Specifically,
Study Guide - Part 2
 Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 2 1. Which of the following describes the derivative function f (x) of a quadratic function f(x)? (A) Cubic (B) Quadratic (C) Linear (D) Constant 2. Find the derivative
Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 2 1. Which of the following describes the derivative function f (x) of a quadratic function f(x)? (A) Cubic (B) Quadratic (C) Linear (D) Constant 2. Find the derivative
INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems. (1) Let us consider the circle with equation. (b) Find the center and the radius of the circle given above.
 INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (b) Find the center and
INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (b) Find the center and
UNIT 2 DERIVATIVES 2.1 EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION APPLICATIONS. Pre-Class:
 1830 UNIT 2 DERIVATIVES 2.1 EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION APPLICATIONS Pre-Class: Take notes on the videos and readings (use the space below). Work and check problem #1 in the 2.1 NOTES section.
1830 UNIT 2 DERIVATIVES 2.1 EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION APPLICATIONS Pre-Class: Take notes on the videos and readings (use the space below). Work and check problem #1 in the 2.1 NOTES section.
UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE
 Calculus I UNIT 3: Derivatives REVIEW Name: Date: UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE Section 1: Section 2: Limit Definition (Derivative as the Slope of the Tangent Line) Calculating Rates of Change (Average
Calculus I UNIT 3: Derivatives REVIEW Name: Date: UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE Section 1: Section 2: Limit Definition (Derivative as the Slope of the Tangent Line) Calculating Rates of Change (Average
Homework 1. 3x 12, 61.P (x) = 3t 21 Section 1.2
 Section 1.1 Homework 1 (34, 36) Determine whether the equation defines y as a function of x. 34. x + h 2 = 1, 36. y = 3x 1 x + 2. (40, 44) Find the following for each function: (a) f(0) (b) f(1) (c) f(
Section 1.1 Homework 1 (34, 36) Determine whether the equation defines y as a function of x. 34. x + h 2 = 1, 36. y = 3x 1 x + 2. (40, 44) Find the following for each function: (a) f(0) (b) f(1) (c) f(
Calculus I Sample Exam #01
 Calculus I Sample Exam #01 1. Sketch the graph of the function and define the domain and range. 1 a) f( x) 3 b) g( x) x 1 x c) hx ( ) x x 1 5x6 d) jx ( ) x x x 3 6 . Evaluate the following. a) 5 sin 6
Calculus I Sample Exam #01 1. Sketch the graph of the function and define the domain and range. 1 a) f( x) 3 b) g( x) x 1 x c) hx ( ) x x 1 5x6 d) jx ( ) x x x 3 6 . Evaluate the following. a) 5 sin 6
Calculus with Applications Good Problems. Justin M. Ryan. Mathematics Department Butler Community College Andover, Kansas USA
 DGS GPBC Calculus with Applications Good Problems Justin M. Ryan Mathematics Department Butler Community College Andover, Kansas USA jryan10@butlercc.edu DRAFT 13 March 2017 These notes consist of a collection
DGS GPBC Calculus with Applications Good Problems Justin M. Ryan Mathematics Department Butler Community College Andover, Kansas USA jryan10@butlercc.edu DRAFT 13 March 2017 These notes consist of a collection
Math Practice Final - solutions
 Math 151 - Practice Final - solutions 2 1-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Problem 1 Indicate the following from looking at the graph of f(x) above. All answers are small integers, ±, or DNE for does not exist. a) lim x 1
Math 151 - Practice Final - solutions 2 1-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Problem 1 Indicate the following from looking at the graph of f(x) above. All answers are small integers, ±, or DNE for does not exist. a) lim x 1
Math 110 Final Exam General Review. Edward Yu
 Math 110 Final Exam General Review Edward Yu Da Game Plan Solving Limits Regular limits Indeterminate Form Approach Infinities One sided limits/discontinuity Derivatives Power Rule Product/Quotient Rule
Math 110 Final Exam General Review Edward Yu Da Game Plan Solving Limits Regular limits Indeterminate Form Approach Infinities One sided limits/discontinuity Derivatives Power Rule Product/Quotient Rule
1 + x 2 d dx (sec 1 x) =
 Page This exam has: 8 multiple choice questions worth 4 points each. hand graded questions worth 4 points each. Important: No graphing calculators! Any non-graphing, non-differentiating, non-integrating
Page This exam has: 8 multiple choice questions worth 4 points each. hand graded questions worth 4 points each. Important: No graphing calculators! Any non-graphing, non-differentiating, non-integrating
Chapter 4 Notes, Calculus I with Precalculus 3e Larson/Edwards
 4.1 The Derivative Recall: For the slope of a line we need two points (x 1,y 1 ) and (x 2,y 2 ). Then the slope is given by the formula: m = y x = y 2 y 1 x 2 x 1 On a curve we can find the slope of a
4.1 The Derivative Recall: For the slope of a line we need two points (x 1,y 1 ) and (x 2,y 2 ). Then the slope is given by the formula: m = y x = y 2 y 1 x 2 x 1 On a curve we can find the slope of a
MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29,
 MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29, This review includes typical exam problems. It is not designed to be comprehensive, but to be representative of topics covered
MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29, This review includes typical exam problems. It is not designed to be comprehensive, but to be representative of topics covered
CALCULUS. Berkant Ustaoğlu CRYPTOLOUNGE.NET
 CALCULUS Berkant Ustaoğlu CRYPTOLOUNGE.NET Secant 1 Definition Let f be defined over an interval I containing u. If x u and x I then f (x) f (u) Q = x u is the difference quotient. Also if h 0, such that
CALCULUS Berkant Ustaoğlu CRYPTOLOUNGE.NET Secant 1 Definition Let f be defined over an interval I containing u. If x u and x I then f (x) f (u) Q = x u is the difference quotient. Also if h 0, such that
Find all points where the function is discontinuous. 1) Find all vertical asymptotes of the given function. x(x - 1) 2) f(x) =
 Math 90 Final Review Find all points where the function is discontinuous. ) Find all vertical asymptotes of the given function. x(x - ) 2) f(x) = x3 + 4x Provide an appropriate response. 3) If x 3 f(x)
Math 90 Final Review Find all points where the function is discontinuous. ) Find all vertical asymptotes of the given function. x(x - ) 2) f(x) = x3 + 4x Provide an appropriate response. 3) If x 3 f(x)
Week 1: need to know. November 14, / 20
 Week 1: need to know How to find domains and ranges, operations on functions (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, composition), behaviors of functions (even/odd/ increasing/decreasing), library
Week 1: need to know How to find domains and ranges, operations on functions (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, composition), behaviors of functions (even/odd/ increasing/decreasing), library
Purdue University Study Guide for MA Credit Exam
 Purdue University Study Guide for MA 16010 Credit Exam Students who pass the credit exam will gain credit in MA16010. The credit exam is a two-hour long exam with multiple choice questions. No books or
Purdue University Study Guide for MA 16010 Credit Exam Students who pass the credit exam will gain credit in MA16010. The credit exam is a two-hour long exam with multiple choice questions. No books or
Limits, Continuity, and the Derivative
 Unit #2 : Limits, Continuity, and the Derivative Goals: Study and define continuity Review limits Introduce the derivative as the limit of a difference quotient Discuss the derivative as a rate of change
Unit #2 : Limits, Continuity, and the Derivative Goals: Study and define continuity Review limits Introduce the derivative as the limit of a difference quotient Discuss the derivative as a rate of change
Midterm 1 Review Problems Business Calculus
 Midterm 1 Review Problems Business Calculus 1. (a) Show that the functions f and g are inverses of each other by showing that f g(x) = g f(x) given that (b) Sketch the functions and the line y = x f(x)
Midterm 1 Review Problems Business Calculus 1. (a) Show that the functions f and g are inverses of each other by showing that f g(x) = g f(x) given that (b) Sketch the functions and the line y = x f(x)
Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20. ), and f(a + 1).
 Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20 # 18, page 18: If f(x) = x2 x 2 1, find f( 1 2 ), f( 1 2 ), and f(a + 1). # 22, page 18: When a solution of acetylcholine
Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20 # 18, page 18: If f(x) = x2 x 2 1, find f( 1 2 ), f( 1 2 ), and f(a + 1). # 22, page 18: When a solution of acetylcholine
Formulas that must be memorized:
 Formulas that must be memorized: Position, Velocity, Acceleration Speed is increasing when v(t) and a(t) have the same signs. Speed is decreasing when v(t) and a(t) have different signs. Section I: Limits
Formulas that must be memorized: Position, Velocity, Acceleration Speed is increasing when v(t) and a(t) have the same signs. Speed is decreasing when v(t) and a(t) have different signs. Section I: Limits
Math 142 (Summer 2018) Business Calculus 5.8 Notes
 Math 142 (Summer 2018) Business Calculus 5.8 Notes Implicit Differentiation and Related Rates Why? We have learned how to take derivatives of functions, and we have seen many applications of this. However
Math 142 (Summer 2018) Business Calculus 5.8 Notes Implicit Differentiation and Related Rates Why? We have learned how to take derivatives of functions, and we have seen many applications of this. However
Section 11.3 Rates of Change:
 Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 f(t) Distance
Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 f(t) Distance
Final Exam Study Guide
 Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam Coverage: Sections 10.1-10.2, 10.4-10.5, 10.7, 11.2-11.4, 12.1-12.6, 13.1-13.2, 13.4-13.5, and 14.1 Sections/topics NOT on the exam: Sections 10.3 (Continuity, it definition
Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam Coverage: Sections 10.1-10.2, 10.4-10.5, 10.7, 11.2-11.4, 12.1-12.6, 13.1-13.2, 13.4-13.5, and 14.1 Sections/topics NOT on the exam: Sections 10.3 (Continuity, it definition
2.1 The Tangent and Velocity Problems
 2.1 The Tangent and Velocity Problems Tangents What is a tangent? Tangent lines and Secant lines Estimating slopes from discrete data: Example: 1. A tank holds 1000 gallons of water, which drains from
2.1 The Tangent and Velocity Problems Tangents What is a tangent? Tangent lines and Secant lines Estimating slopes from discrete data: Example: 1. A tank holds 1000 gallons of water, which drains from
Sample Math 115 Midterm Exam Spring, 2014
 Sample Math 5 Midterm Exam Spring, 04 The midterm examination is on Wednesday, March at 5:45PM 7:45PM The midterm examination will be in Budig 0 Look for your instructor who will direct you where to sit
Sample Math 5 Midterm Exam Spring, 04 The midterm examination is on Wednesday, March at 5:45PM 7:45PM The midterm examination will be in Budig 0 Look for your instructor who will direct you where to sit
Applied Calculus I Practice Final Exam Solution Notes
 AMS 5 (Fall, 2009). Solve for x: 0 3 2x = 3 (.2) x Taking the natural log of both sides, we get Applied Calculus I Practice Final Exam Solution Notes Joe Mitchell ln 0 + 2xln 3 = ln 3 + xln.2 x(2ln 3 ln.2)
AMS 5 (Fall, 2009). Solve for x: 0 3 2x = 3 (.2) x Taking the natural log of both sides, we get Applied Calculus I Practice Final Exam Solution Notes Joe Mitchell ln 0 + 2xln 3 = ln 3 + xln.2 x(2ln 3 ln.2)
MATH 2554 (Calculus I)
 MATH 2554 (Calculus I) Dr. Ashley K. University of Arkansas February 21, 2015 Table of Contents Week 6 1 Week 6: 16-20 February 3.5 Derivatives as Rates of Change 3.6 The Chain Rule 3.7 Implicit Differentiation
MATH 2554 (Calculus I) Dr. Ashley K. University of Arkansas February 21, 2015 Table of Contents Week 6 1 Week 6: 16-20 February 3.5 Derivatives as Rates of Change 3.6 The Chain Rule 3.7 Implicit Differentiation
Math 131 Exam 2 Spring 2016
 Math 3 Exam Spring 06 Name: ID: 7 multiple choice questions worth 4.7 points each. hand graded questions worth 0 points each. 0. free points (so the total will be 00). Exam covers sections.7 through 3.0
Math 3 Exam Spring 06 Name: ID: 7 multiple choice questions worth 4.7 points each. hand graded questions worth 0 points each. 0. free points (so the total will be 00). Exam covers sections.7 through 3.0
University of Connecticut Department of Mathematics
 University of Connecticut Department of Mathematics Math 1131 Sample Exam 1 Fall 2013 Name: This sample exam is just a guide to prepare for the actual exam. Questions on the actual exam may or may not
University of Connecticut Department of Mathematics Math 1131 Sample Exam 1 Fall 2013 Name: This sample exam is just a guide to prepare for the actual exam. Questions on the actual exam may or may not
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7)
 Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 2) h(x) = x2-5x + 5
 Assignment 7 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Using the derivative of f(x) given below, determine the critical points of f(x).
Assignment 7 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Using the derivative of f(x) given below, determine the critical points of f(x).
Marginal Propensity to Consume/Save
 Marginal Propensity to Consume/Save The marginal propensity to consume is the increase (or decrease) in consumption that an economy experiences when income increases (or decreases). The marginal propensity
Marginal Propensity to Consume/Save The marginal propensity to consume is the increase (or decrease) in consumption that an economy experiences when income increases (or decreases). The marginal propensity
INTERNET MAT 117. Solution for the Review Problems. (1) Let us consider the circle with equation. x 2 + 2x + y 2 + 3y = 3 4. (x + 1) 2 + (y + 3 2
 INTERNET MAT 117 Solution for the Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (i) Group
INTERNET MAT 117 Solution for the Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (i) Group
Doug Clark The Learning Center 100 Student Success Center learningcenter.missouri.edu Overview
 Math 1400 Final Exam Review Saturday, December 9 in Ellis Auditorium 1:00 PM 3:00 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part 1: Derivatives and Applications of Derivatives 3:30 PM 5:30 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part
Math 1400 Final Exam Review Saturday, December 9 in Ellis Auditorium 1:00 PM 3:00 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part 1: Derivatives and Applications of Derivatives 3:30 PM 5:30 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part
AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER PREVIEW
 AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER PREVIEW Name: Your summer homework assignment is to write complete solutions for all of the problems listed in this packet. It is important that you have mastered the concepts covered
AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER PREVIEW Name: Your summer homework assignment is to write complete solutions for all of the problems listed in this packet. It is important that you have mastered the concepts covered
Name Date Period. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 AB Fall Final Exam Review 200-20 Name Date Period MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. ) The position of a particle
AB Fall Final Exam Review 200-20 Name Date Period MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. ) The position of a particle
a b c d e GOOD LUCK! 3. a b c d e 12. a b c d e 4. a b c d e 13. a b c d e 5. a b c d e 14. a b c d e 6. a b c d e 15. a b c d e
 MA Elem. Calculus Fall 07 Exam 07-09- Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. No books or notes may be used. You may use an ACT-approved calculator during the exam,
MA Elem. Calculus Fall 07 Exam 07-09- Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. No books or notes may be used. You may use an ACT-approved calculator during the exam,
Sec 4.1 Limits, Informally. When we calculated f (x), we first started with the difference quotient. f(x + h) f(x) h
 1 Sec 4.1 Limits, Informally When we calculated f (x), we first started with the difference quotient f(x + h) f(x) h and made h small. In other words, f (x) is the number f(x+h) f(x) approaches as h gets
1 Sec 4.1 Limits, Informally When we calculated f (x), we first started with the difference quotient f(x + h) f(x) h and made h small. In other words, f (x) is the number f(x+h) f(x) approaches as h gets
What will you learn?
 Section 2.2 Basic Differentiation Rules & Rates of Change Calc What will you learn? Find the derivative using the Constant Rule Find the derivative using the Power Rule Find the derivative using the Constant
Section 2.2 Basic Differentiation Rules & Rates of Change Calc What will you learn? Find the derivative using the Constant Rule Find the derivative using the Power Rule Find the derivative using the Constant
Math 142 Week-in-Review #4 (Sections , 4.1, and 4.2)
 Math 142 WIR, copyright Angie Allen, Fall 2018 1 Math 142 Week-in-Review #4 (Sections 3.1-3.3, 4.1, and 4.2) Note: This collection of questions is intended to be a brief overview of the exam material (with
Math 142 WIR, copyright Angie Allen, Fall 2018 1 Math 142 Week-in-Review #4 (Sections 3.1-3.3, 4.1, and 4.2) Note: This collection of questions is intended to be a brief overview of the exam material (with
Section 11.7 The Chain Rule
 Section.7 The Chain Rule Composition of Functions There is another way of combining two functions to obtain a new function. For example, suppose that y = fu) = u and u = gx) = x 2 +. Since y is a function
Section.7 The Chain Rule Composition of Functions There is another way of combining two functions to obtain a new function. For example, suppose that y = fu) = u and u = gx) = x 2 +. Since y is a function
Math 131. Rolle s and Mean Value Theorems Larson Section 3.2
 Math 3. Rolle s and Mean Value Theorems Larson Section 3. Many mathematicians refer to the Mean Value theorem as one of the if not the most important theorems in mathematics. Rolle s Theorem. Suppose f
Math 3. Rolle s and Mean Value Theorems Larson Section 3. Many mathematicians refer to the Mean Value theorem as one of the if not the most important theorems in mathematics. Rolle s Theorem. Suppose f
Math 1314 Test 2 Review Lessons 2 8
 Math 1314 Test Review Lessons 8 CASA reservation required. GGB will be provided on the CASA computers. 50 minute exam. 15 multiple choice questions. Do Practice Test for extra practice and extra credit.
Math 1314 Test Review Lessons 8 CASA reservation required. GGB will be provided on the CASA computers. 50 minute exam. 15 multiple choice questions. Do Practice Test for extra practice and extra credit.
Math 611b Assignment #6 Name. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 611b Assignment #6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a formula for the function graphed. 1) 1) A) f(x) = 5 + x, x < -
Math 611b Assignment #6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a formula for the function graphed. 1) 1) A) f(x) = 5 + x, x < -
A) (-1, -1, -2) B) No solution C) Infinite solutions D) (1, 1, 2) A) (6, 5, -3) B) No solution C) Infinite solutions D) (1, -3, -7)
 Algebra st Semester Final Exam Review Multiple Choice. Write an equation that models the data displayed in the Interest-Free Loan graph that is provided. y = x + 80 y = -0x + 800 C) y = 0x 00 y = 0x +
Algebra st Semester Final Exam Review Multiple Choice. Write an equation that models the data displayed in the Interest-Free Loan graph that is provided. y = x + 80 y = -0x + 800 C) y = 0x 00 y = 0x +
Mth Review Problems for Test 2 Stewart 8e Chapter 3. For Test #2 study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework.
 For Test # study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework. Derivative Rules D [u n ] = nu n 1 du D [ln u] = du u D [log b u] = du u ln b D [e u ] = e u du D [a u ] = a u ln a du D [sin
For Test # study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework. Derivative Rules D [u n ] = nu n 1 du D [ln u] = du u D [log b u] = du u ln b D [e u ] = e u du D [a u ] = a u ln a du D [sin
MATH150-E01 Test #2 Summer 2016 Show all work. Name 1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3).
 1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3). 2. Let the supply and demand functions for sugar be given by p = S(q) = 1.4q 0.6 and p = D(q) = 2q + 3.2 where p is the
1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3). 2. Let the supply and demand functions for sugar be given by p = S(q) = 1.4q 0.6 and p = D(q) = 2q + 3.2 where p is the
This Week. Basic Problem. Instantaneous Rate of Change. Compute the tangent line to the curve y = f (x) at x = a.
 This Week Basic Problem Compute the tangent line to the curve y = f (x) at x = a. Read Sections 2.7,2.8 and 3.1 in Stewart Homework #2 due 11:30 Thursday evening worksheet #3 in section on Tuesday slope
This Week Basic Problem Compute the tangent line to the curve y = f (x) at x = a. Read Sections 2.7,2.8 and 3.1 in Stewart Homework #2 due 11:30 Thursday evening worksheet #3 in section on Tuesday slope
Chapter 2 Differentiation. 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes. Calculus: A Complete Course, 8e Chapter 2: Differentiation
 Chapter 2 Differentiation 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes 1) Find the slope of the tangent line to the curve y = 4x x 2 at the point (-1, 0). A) -1 2 C) 6 D) 2 1 E) -2 2) Find the equation of the tangent
Chapter 2 Differentiation 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes 1) Find the slope of the tangent line to the curve y = 4x x 2 at the point (-1, 0). A) -1 2 C) 6 D) 2 1 E) -2 2) Find the equation of the tangent
Free Response Questions Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom
 Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Exam 1 KEY MATH 142 Summer 18 Version A. Name (printed):
 Exam 1 KEY MATH 1 Summer 18 Version A Name (printed): On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work. Name (signature): Section: Instructions: You must
Exam 1 KEY MATH 1 Summer 18 Version A Name (printed): On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work. Name (signature): Section: Instructions: You must
Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation
 2301107 Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation Chapter 5:Applications of differentiation C05-2 Outline 5.1. Extreme values 5.2. Curvature and Inflection point 5.3. Curve sketching 5.4. Related rate
2301107 Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation Chapter 5:Applications of differentiation C05-2 Outline 5.1. Extreme values 5.2. Curvature and Inflection point 5.3. Curve sketching 5.4. Related rate
Lecture 26: Section 5.3 Higher Derivatives and Concavity
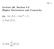 L26-1 Lecture 26: Section 5.3 Higher Derivatives and Concavity ex. Let f(x) = ln(e 2x + 1) 1) Find f (x). 2) Find d dx [f (x)]. L26-2 We define f (x) = Higher Order Derivatives For y = f(x), we can write
L26-1 Lecture 26: Section 5.3 Higher Derivatives and Concavity ex. Let f(x) = ln(e 2x + 1) 1) Find f (x). 2) Find d dx [f (x)]. L26-2 We define f (x) = Higher Order Derivatives For y = f(x), we can write
Name. 3) f(x) = -x2-2. Sketch the graph of the function and find the domain and range. 1) f(x) = x2-4. 4) f(x) = x ) f(x) = -3(x + 3)2-2
 Exam 3 Final Preparation Ch 7, 9, etal v0 There will be 5 questions on Exam 3 (Final). Twenty questions from chapters 7 & 9. Five questions from chapter 5. No Book/No Notes/No Ipod/ No Phone/Yes Calculator/55
Exam 3 Final Preparation Ch 7, 9, etal v0 There will be 5 questions on Exam 3 (Final). Twenty questions from chapters 7 & 9. Five questions from chapter 5. No Book/No Notes/No Ipod/ No Phone/Yes Calculator/55
AP Calculus Chapter 3 Testbank (Mr. Surowski)
 AP Calculus Chapter 3 Testbank (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.). If f(x) = 0x 4 3 + x, then f (8) = (A) (B) 4 3 (C) 83 3 (D) 2 3 (E) 2
AP Calculus Chapter 3 Testbank (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.). If f(x) = 0x 4 3 + x, then f (8) = (A) (B) 4 3 (C) 83 3 (D) 2 3 (E) 2
Chapter. Integration. 1. Antidifferentiation: The Indefinite Integral. 2. Integration by Substitution. 3. Introduction to Differential Equations
 Integration Chapter. Antidifferentiation: The Indefinite Integral 2. Integration by Substitution 3. Introduction to Differential Equations 4. Integration by Parts Chapter Summary and Review Problems Antidifferentiation:
Integration Chapter. Antidifferentiation: The Indefinite Integral 2. Integration by Substitution 3. Introduction to Differential Equations 4. Integration by Parts Chapter Summary and Review Problems Antidifferentiation:
Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules
 Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules Derivative constant function if c is any real number, then Example: The Power Rule: If n is a positive integer, then Example: Extended Power Rule: If r is any real number,
Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules Derivative constant function if c is any real number, then Example: The Power Rule: If n is a positive integer, then Example: Extended Power Rule: If r is any real number,
THE USE OF A CALCULATOR, CELL PHONE, OR ANY OTHER ELECTRONIC DEVICE IS NOT PERMITTED IN THIS EXAMINATION.
 MATH 110 FINAL EXAM SPRING 2008 FORM A NAME STUDENT NUMBER INSTRUCTOR SECTION NUMBER This examination will be machine processed by the University Testing Service. Use only a number 2 pencil on your scantron.
MATH 110 FINAL EXAM SPRING 2008 FORM A NAME STUDENT NUMBER INSTRUCTOR SECTION NUMBER This examination will be machine processed by the University Testing Service. Use only a number 2 pencil on your scantron.
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. x )
 Midterm Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the arrow diagram defines a function. 1) Domain Range 1) Determine
Midterm Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the arrow diagram defines a function. 1) Domain Range 1) Determine
2.2 THE DERIVATIVE 2.3 COMPUTATION OF DERIVATIVES: THE POWER RULE 2.4 THE PRODUCT AND QUOTIENT RULES 2.6 DERIVATIVES OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 Differentiation CHAPTER 2 2.1 TANGENT LINES AND VELOCITY 2.2 THE DERIVATIVE 2.3 COMPUTATION OF DERIVATIVES: THE POWER RULE 2.4 THE PRODUCT AND QUOTIENT RULES 25 2.5 THE CHAIN RULE 2.6 DERIVATIVES OF TRIGONOMETRIC
Differentiation CHAPTER 2 2.1 TANGENT LINES AND VELOCITY 2.2 THE DERIVATIVE 2.3 COMPUTATION OF DERIVATIVES: THE POWER RULE 2.4 THE PRODUCT AND QUOTIENT RULES 25 2.5 THE CHAIN RULE 2.6 DERIVATIVES OF TRIGONOMETRIC
Section Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions
 Section 3.1 - Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Constant Function Rule: If f(x)=c where c is a constant then Power Rule: If f(x)=x n, where n is a real number, then Constant Multiple
Section 3.1 - Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Constant Function Rule: If f(x)=c where c is a constant then Power Rule: If f(x)=x n, where n is a real number, then Constant Multiple
NO CALCULATOR 1. Find the interval or intervals on which the function whose graph is shown is increasing:
 AP Calculus AB PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM Read each choice carefully and find the best answer. Your midterm exam will be made up of 8 of these questions. I reserve the right to change numbers and answers on
AP Calculus AB PRACTICE MIDTERM EXAM Read each choice carefully and find the best answer. Your midterm exam will be made up of 8 of these questions. I reserve the right to change numbers and answers on
m(x) = f(x) + g(x) m (x) = f (x) + g (x) (The Sum Rule) n(x) = f(x) g(x) n (x) = f (x) g (x) (The Difference Rule)
 Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Aka The Short Cuts! Yay! f(x) = c f (x) = 0 g(x) = x g (x) = 1 h(x) = x n h (x) = n x n-1 (The Power Rule) k(x)
Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Aka The Short Cuts! Yay! f(x) = c f (x) = 0 g(x) = x g (x) = 1 h(x) = x n h (x) = n x n-1 (The Power Rule) k(x)
3. Go over old quizzes (there are blank copies on my website try timing yourself!)
 final exam review General Information The time and location of the final exam are as follows: Date: Tuesday, June 12th Time: 10:15am-12:15pm Location: Straub 254 The exam will be cumulative; that is, it
final exam review General Information The time and location of the final exam are as follows: Date: Tuesday, June 12th Time: 10:15am-12:15pm Location: Straub 254 The exam will be cumulative; that is, it
MATH 115 SECOND MIDTERM EXAM
 MATH 115 SECOND MIDTERM EXAM November 22, 2005 NAME: SOLUTION KEY INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NO: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has 10 pages including this cover. There are
MATH 115 SECOND MIDTERM EXAM November 22, 2005 NAME: SOLUTION KEY INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NO: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has 10 pages including this cover. There are
The Quadratic Formula. ax 2 bx c 0 where a 0. Deriving the Quadratic Formula. Isolate the constant on the right side of the equation.
 SECTION 11.2 11.2 The Quadratic Formula 11.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve quadratic equations by using the quadratic formula 2. Determine the nature of the solutions of a quadratic equation by using the discriminant
SECTION 11.2 11.2 The Quadratic Formula 11.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve quadratic equations by using the quadratic formula 2. Determine the nature of the solutions of a quadratic equation by using the discriminant
Average rates of change May be used to estimate the derivative at a point
 Derivatives Big Ideas Rule of Four: Numerically, Graphically, Analytically, and Verbally Average rate of Change: Difference Quotient: y x f( a+ h) f( a) f( a) f( a h) f( a+ h) f( a h) h h h Average rates
Derivatives Big Ideas Rule of Four: Numerically, Graphically, Analytically, and Verbally Average rate of Change: Difference Quotient: y x f( a+ h) f( a) f( a) f( a h) f( a+ h) f( a h) h h h Average rates
Sample Mathematics 106 Questions
 Sample Mathematics 106 Questions x 2 + 8x 65 (1) Calculate lim x 5. x 5 (2) Consider an object moving in a straight line for which the distance s (measured in feet) it s travelled from its starting point
Sample Mathematics 106 Questions x 2 + 8x 65 (1) Calculate lim x 5. x 5 (2) Consider an object moving in a straight line for which the distance s (measured in feet) it s travelled from its starting point
Math 1101 Test 2 Practice Problems
 Math 1101 Test 2 Practice Problems These problems are not intended to cover all possible test topics. These problems should serve as on activity in preparing for your test, but other study is required
Math 1101 Test 2 Practice Problems These problems are not intended to cover all possible test topics. These problems should serve as on activity in preparing for your test, but other study is required
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB
 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
Final Exam Review Packet
 1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
Final Exam Review Packet
 1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
Announcements. Topics: Homework: - sections 4.5 and * Read these sections and study solved examples in your textbook!
 Announcements Topics: - sections 4.5 and 5.1-5.5 * Read these sections and study solved examples in your textbook! Homework: - review lecture notes thoroughly - work on practice problems from the textbook
Announcements Topics: - sections 4.5 and 5.1-5.5 * Read these sections and study solved examples in your textbook! Homework: - review lecture notes thoroughly - work on practice problems from the textbook
(b) x = (d) x = (b) x = e (d) x = e4 2 ln(3) 2 x x. is. (b) 2 x, x 0. (d) x 2, x 0
 1. Solve the equation 3 4x+5 = 6 for x. ln(6)/ ln(3) 5 (a) x = 4 ln(3) ln(6)/ ln(3) 5 (c) x = 4 ln(3)/ ln(6) 5 (e) x = 4. Solve the equation e x 1 = 1 for x. (b) x = (d) x = ln(5)/ ln(3) 6 4 ln(6) 5/ ln(3)
1. Solve the equation 3 4x+5 = 6 for x. ln(6)/ ln(3) 5 (a) x = 4 ln(3) ln(6)/ ln(3) 5 (c) x = 4 ln(3)/ ln(6) 5 (e) x = 4. Solve the equation e x 1 = 1 for x. (b) x = (d) x = ln(5)/ ln(3) 6 4 ln(6) 5/ ln(3)
Exp, Log, Poly Functions Quarter 3 Review Name
 Exp, Log, Poly Functions Quarter 3 Review Name Textbook problems for practice: p. 285-293; p. 293 #9-14, p. 294-5 #1-34, 49-52, 55,56, 57; p. 297-321 logs; p. 280-1 #11-84 *Blood Alcohol, Bungee-from binder
Exp, Log, Poly Functions Quarter 3 Review Name Textbook problems for practice: p. 285-293; p. 293 #9-14, p. 294-5 #1-34, 49-52, 55,56, 57; p. 297-321 logs; p. 280-1 #11-84 *Blood Alcohol, Bungee-from binder
Math 1314 Lesson 7 Applications of the Derivative. rate of change, instantaneous rate of change, velocity, => the derivative
 Math 1314 Lesson 7 Applications of the Derivative In word problems, whenever it s anything about a: rate of change, instantaneous rate of change, velocity, => the derivative average rate of change, difference
Math 1314 Lesson 7 Applications of the Derivative In word problems, whenever it s anything about a: rate of change, instantaneous rate of change, velocity, => the derivative average rate of change, difference
Lecture 2. Derivative. 1 / 26
 Lecture 2. Derivative. 1 / 26 Basic Concepts Suppose we wish to nd the rate at which a given function f (x) is changing with respect to x when x = c. The simplest idea is to nd the average rate of change
Lecture 2. Derivative. 1 / 26 Basic Concepts Suppose we wish to nd the rate at which a given function f (x) is changing with respect to x when x = c. The simplest idea is to nd the average rate of change
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Spring 2014 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers R.6 8) 27, 30) 25
 ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Spring 2014, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Review Assignment: Precalculus Even Answers to Sections R1 R7 R.1 24) 4a 2 16ab + 16b 2 R.2 24) Prime 5x
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Spring 2014, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Review Assignment: Precalculus Even Answers to Sections R1 R7 R.1 24) 4a 2 16ab + 16b 2 R.2 24) Prime 5x
MATH 019: Final Review December 3, 2017
 Name: MATH 019: Final Review December 3, 2017 1. Given f(x) = x 5, use the first or second derivative test to complete the following (a) Calculate f (x). If using the second derivative test, calculate
Name: MATH 019: Final Review December 3, 2017 1. Given f(x) = x 5, use the first or second derivative test to complete the following (a) Calculate f (x). If using the second derivative test, calculate
MA 123 Recitation Activity Sheets
 MA 123 Recitation Activity Sheets You will need to bring this packet with you to recitation each week. Some of the exercises included in this packet closely follow the lecture material and homework problems.
MA 123 Recitation Activity Sheets You will need to bring this packet with you to recitation each week. Some of the exercises included in this packet closely follow the lecture material and homework problems.
y2 + 4y - 5 c a + b 27 i C) ) (16, ) B) (16 3 3, )
 MAT 107 Final, Version A, Spring 2008 1) If (4, 4) is the endpoint of a line segment, and (2, 1) is its midpoint, find the other endpoint. A) (0, 7) B) (-2, 0) C) (8, 10) D) (0, -2) 2) Solve for x: A)
MAT 107 Final, Version A, Spring 2008 1) If (4, 4) is the endpoint of a line segment, and (2, 1) is its midpoint, find the other endpoint. A) (0, 7) B) (-2, 0) C) (8, 10) D) (0, -2) 2) Solve for x: A)
Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not
 Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not They do The exam represent the entirety of what you could be expected to know on the exam; reflect distribution
Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not They do The exam represent the entirety of what you could be expected to know on the exam; reflect distribution
Review Assignment II
 MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus KSU Name:. Review Assignment II 1. Let C(x) be the cost, in dollars, of manufacturing x widgets. Fill in the table with a mathematical expression and appropriate units corresponding
MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus KSU Name:. Review Assignment II 1. Let C(x) be the cost, in dollars, of manufacturing x widgets. Fill in the table with a mathematical expression and appropriate units corresponding
Math 116: Business Calculus Chapter 4 - Calculating Derivatives
 Math 116: Business Calculus Chapter 4 - Calculating Derivatives Instructor: Colin Clark Spring 2017 Exam 2 - Thursday March 9. 4.1 Techniques for Finding Derivatives. 4.2 Derivatives of Products and Quotients.
Math 116: Business Calculus Chapter 4 - Calculating Derivatives Instructor: Colin Clark Spring 2017 Exam 2 - Thursday March 9. 4.1 Techniques for Finding Derivatives. 4.2 Derivatives of Products and Quotients.
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION
 4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.9 Antiderivatives In this section, we will learn about: Antiderivatives and how they are useful in solving certain scientific problems.
4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.9 Antiderivatives In this section, we will learn about: Antiderivatives and how they are useful in solving certain scientific problems.
Math 131. The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Larson Section 2.1
 Math 131. The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Larson Section.1 From precalculus, the secant line through the two points (c, f(c)) and (c +, f(c + )) is given by m sec = rise f(c + ) f(c) f(c +
Math 131. The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Larson Section.1 From precalculus, the secant line through the two points (c, f(c)) and (c +, f(c + )) is given by m sec = rise f(c + ) f(c) f(c +
