Neutron background in underground particle astrophysics experiments
|
|
|
- Letitia Norah Bradley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neutron background in underground particle astrophysics experiments V. A. Kudryavtsev Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Sheffield for ILIAS and the UK Dark Matter Collaboration LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 1
2 Outline Introduction. Neutrons from radioactivity and their suppression by passive shielding. Neutrons from cosmic-ray muons. Summary. See also presentations and other documentation related to ILIAS activities on background studies: links available from ilias.in2p3.fr LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 2
3 Background studies in ILIAS ILIAS - FP6 European Programme: Integrated Large Infrastructures for Astroparticle Science. A working group on background studies within N3 (Direct Dark Matter Detection - DMD) and JRA1 (Low Background Techniques for Deep Underground Science - LBT-DUSL) activities. Active participants from: France - Saclay, LSM, Lyon, Grenoble; Germany - Tuebingen, Munich-Garching, Karlsruhe, Heidelberg; Spain - Zaragoza, Canfranc; Italy -Milan, LNGS; UK - Imperial College, RAL, Sheffield. One of the objectives of ILIAS: to disseminate a new knowledge as widely as possible through the participation in international workshops and conferences, publication of scientific papers. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 3
4 Aims of the working group Simulations of various types of background in underground laboratories (in particular, for dark matter detectors), comparing the results from different MC codes with each other and with available experimental data (testing MC codes) - N3, JRA1. Investigation of methods of background suppression and rejection (passive shielding, active vetoes etc.); formulation of requirements for shieldings and veto systems - mainly N3. Calculation of background rates in dark matter detectors - N3. Another working group in JRA1: measurements of neutron and gamma fluxes (and spectra) in underground laboratories (Gran Sasso, Modane, Canfranc, Boulby) - can be used to check Monte Carlo codes. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 4
5 Backgrounds for dark matter experiments Several large-scale (~ 1 tonne) experiments are discussed for WIMP dark matter searches down pb: SuperCDMS (Ge), EURECA (EDELWEISS + CRESST), XMASS (Xe), XENON (Xe), ZEPLIN IV/MAX (Xe), CLEAN (Ne), DRIFT, WARP(Ar), ArDM (Ar), DEAP (Ar) etc. Tolerated (non-discriminated) background - no more than a few events per tonne of target per year (< 5 ev/tonne/year in Xe at kev recoil energies to reach pb); Neutrons and gammas from rock - suppression of >10 6 should be achieved for neutrons - passive shielding; Neutrons, gammas, alphas and betas from detector components - ultra-pure materials, veto, discrimination; Neutrons from cosmic-ray muons - large depth, veto; Radon - gammas, neutrons and alphas (?) - radon removal, gas-tight sealing and ventilation with radon-free air, careful treatment at the surface; Cosmogenically produced isotopes - underground storage, large depth. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 5
6 Neutron production in U/Th decay chains SOURCES-4A (Wilson et al. SOURCES4A, Technical Report LA MS, Los Alamos, 1999) - code to calculate neutron flux and energy spectrum arising from U/Th contamination in various materials. Modifications to SOURCES (Carson et al. Astropart. Phys. 21 (2004) 667; Lemrani et al., NIMA 560 (2006) 454; hep-ex/ ): Alpha energy range extended beyond 6.5 MeV upper limit; Cross-sections already present in the code library extended to higher energies using available experimental data; Some cross-sections updated according to recent experimental results; A code EMPIRE-2.19 ( is used to calculate the cross-sections to different excited states (excitation functions can be extracted) if there are no measurements; New cross-sections added ( 35 Cl, Fe, Cu, Ca, Ti etc.). Main feature in SOURCES, absent (probably) in most other calculations: Accounting for transitions of the final nucleus to the excited states (GNASH calculations of transition probabilities - excitation functions, or EMPIRE) - reduces neutron energies. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 6
7 Neutron spectra and yields Neutron production rate in NaCl cm -3 s -1 agrees with other calculations. The peak in the spectrum is usually at ~1-1.5 MeV which is lower than obtained in other calculations due to transitions to the excited states in SOURCES - less energy transferred to neutrons. Coulomb barrier suppresses the crosssections for high-z elements even if the energy threshold (calculated from the Q- value of the reaction) is small; for Fe-Cu the Coulomb barrier is about MeV for higher-z targets spontaneous fission of U-238 dominates. Similar approach when calculating neutron production rate in detector components (including shielding). Similar spectrum for Modane rock (Lemrani et al., NIMA (2006); hep-ex/ ). Neutron production spectrum in NaCl -60/300 ppb U/Th (SOURCES-4A): mainly (α,n) - Carson et al. Astropart. Phys. 21 (2004) 667. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 7
8 Neutron propagation through the shielding Neutron spectra after various shielding thicknesses (CH 2 ) - Lemrani et al, NIMA, 560 (2006) 454; simulations by Lemrani, Robinson, De Jesus (see also Carson et al. Astropart. Phys. 21 (2004) 667). Neutron spectra after various shielding thicknesses (lead + CH 2 ) - Lemrani et al, NIMA, 560 (2006) 454; simulations by Lemrani, Robinson, De Jesus (also Carson et al. Astropart. Phys. 21 (2004) 667). LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 8
9 Comparing different rocks Boulby - NaCl; Modane - O - 50%, Ca - 31%, C - 6%, Si - 7%, Mg - 1%, Al - 2%, H - 1%, Fe - 2% (Chazal et al. Astroparticle Physics (1998)). Higher U/Th concentrations in the Modane rock. Similar neutron yields due to lower thresholds of (alpha,n) reactions in Na and Cl - in Modane rock (alpha,n) reactions give 77% of neutron yield, in NaCl - 98%. Smaller neutron flux in the Modane lab - due to the presence of H: suppression by a factor of 1.8 above 1 MeV compared to the case without H. Details in Lemrani et al. NIMA 560 (2006) 454. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 9
10 Checking MC Measurements of neutron flux in underground labs. Boulby: Gd-loaded liquid scintillator; signature: two pulses (proton recoils and gammas from neutron capture) in delayed coincidences. Neutron flux at Boulby (>0.5 MeV): (2.05 ± 0.72) 10-6 n/cm 2 s (preliminary) - in agreement with MC assuming measured concentrations of U/Th. τ = 84 ± 5 μs LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 10
11 Muon-induced neutrons Inputs: Muon rate - measurements at a particular underground site. Muon spectrum and angular distribution (normalised to the total rate) - simulations or measurements (if available) - not a problem (for example, MUSIC code for muon propagation - Antonioli et al., Astrop. Phys. 7 (1997) 357, Kudryavtsev et al. Phys. Lett. B 471 (1999) 251 or MUSUN code for muon simulations underground - Kudryavtsev et al. NIMA, 505 (2003) 688). Neutrons from muons - production, propagation, detection together with all other particles (muon-induced cascades): GEANT4 (GEANT4 Coll. NIMA, 506 (2003) 250) or FLUKA (Fasso et al. Proc. MC2000 Conf., Lisbon, 2000, p. 159; ibid. p. 995). Important: all particles should be produced, propagated and detected with one code to look for simultaneous detection of neutrons and other particles, such as photons, electrons, muons, hadrons. FLUKA calculates kerma factors as average energy depositions from nuclear recoils - not very accurate treatement on event-by-event basis. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 11
12 Total neutron yield Total neutron yield is used to check Monte Carlo codes which can then be used to simulate fast neutrons. Usually expressed as the average number of neutrons produced by a muon crossing 1 g/cm 2 of target material. It is measured or simulated by counting neutrons produced by many muons along long tracks. Dark matter experiments should worry about fast neutrons ( > MeV) but it is difficult to measure the yield of fast neutrons because their energy degrades during transport in matter. The flux of fast neutrons can be measured by scintillators or dark matter detectors but it is possible to do so only at certain (quite big) distances from the muon track. At small distances neutron signal may coincide with the muon signal if they are detected by the same detector. Delayed signal from neutron capture is usually used to detect neutrons. It provides information about neutrons with all energies which were thermalised and captured. (Also DM and DBD detectors but small signal). LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 12
13 Dependence on muon energy Neutron production rate in (CH 2 ) n (liquid scintillator): Araujo et al., NIMA 545 (2005), 398; hep-ex/ ; FLUKA (Paper 1) - Kudryavtsev et al. NIMA, 505 (2003) 688; FLUKA (Paper 2) - Wang et al. Phys. Rev. D, 64 (2001) ; Experimental data - see Papers 1 and 2 for the full list of references for experimental data. No accurate simulations of the detector geometry and response for any of the experiments at large depths. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 13
14 Muon-induced neutrons: processes GEANT4: Araujo et al. NIMA 545 (2005), 398 FLUKA: Wang et al. PRD, 64 (2001) Contribution of different processes: real photonuclear disintegration dominates in GEANT4 at all energies and for (almost) all materials. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 14
15 Muon-induced neutrons: A-dependence GEANT4 Coll. NIMA, 506 (2003) 250. Fasso et al. Proc. MC2000 Conf., p. 159; p Contribution of different processes in various materials - GEANT4: Araujo et al. NIMA 545 (2005), 398. A-dependence of neutron production rate - GEANT4: Araujo et al., FLUKA: Kudryavtsev et al. FLUKA gives twice as many neutrons compared to GEANT4 in most materials tested. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 15
16 Energy spectrum and lateral distribution Neutron production spectrum - GEANT4: Araujo et al., FLUKA: Wang et al. ; data - LVD: LVD Collab., Proc. 26 ICRC (1999), vol. 2, p. 44; hepex/ LVD and FLUKA spectra are in arbitrary units and are normalised to the GEANT4 simulations. Neutron lateral distribution (from muon track) - GEANT4, FLUKA and LVD data. Simulations did not include detector specific features. LVD data are in arbitrary units normalised to the simulations. See also Menghetti et al. Proc. IDM2004, for more LVD data and another analysis technique. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 16
17 Neutron energy spectra are different in different materials. Typically higher neutron yield result in softer spectrum (less high energy neutrons). Should be checked for all our labs and other materials. Neutron energy spectra CH 2 NaCl From V. A. Kudryavtsev et al., NIMA, 505 (2003) 688. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 17
18 Neutron energy spectra: GEANT4 CH 2 Pb Neutron production spectra from 270 GeV muons in CH 2 (left) and lead (right) - GEANT4: Araujo and Kudryavtsev (talk at IDM2004). Energy spectra are different for different materials but the main difference is at low energies: fast neutron yield (> 20 MeV) is not much different for CH 2 and lead. Neutron yield (per muon) at >1 MeV in NaCl is 50% lower than in Gran Sasso rock (FLUKA: Carson et al., Wulandari et al., hep-ex/ ). LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 18
19 Fast neutron fluxes Neutron fluxes coming from rock at different energies in units of 10-9 cm -2 s -1. All results are from simulations with FLUKA: Carson et al. Astropart. Phys. 21 (2004) 667; Wulandari et al., hep-ex/ ; D.-M. Mei and A. Hime, Phys. Rev. D 73 (2006) Site Total > 1 kev > 1 MeV > 10 MeV > 100 MeV Boulby Mei&Hime Boulby Carson et al Gran Sasso Mei&Hime Gran Sasso Wulandari et al LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 19
20 Muon-induced neutrons: problems Differential cross-section of neutron production in thin targets for 190 GeV muons (E n >10 MeV). Upper (thick) histograms - GEANT4; dashed line - FLUKA (Araujo et al.); data - NA55 (Chazal et al. NIMA, 490 (2002) 334). Other data for lead (Bergamasco et al. Nuovo Cim. A, 13 (1973) 403; Gorshkov et al. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys., 18 (1974) 57) are old and controversial but also show significantly higher neutron production compared with simulations. Lead is important since it is used as a shield in DM experiments. Measurements using dark matter detectors or active veto systems. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 20
21 Site specific simulations Site specific (detector specific) simulation. Sampling muons according to angular distribution and energy spectrum at specific site, propagating muons, generating secondaries, propagating secondaries, everything is detected. Sampling neutrons: where? Around the detector? Or on sides only? It is not known where the tracks of muons and secondaries are and whether they will be detected by the target or veto? air μ C 10 H 20 xenon lead n salt LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 21
22 Angular distribution and multiplicity From Wang et al. (2001) Distributions peaked at 0 o relative to the muon track. To sample correctly the direction of a neutron, the muon track should be known. Total neutron yield includes different neutron multiplicities. This should be simulated correctly for each muon interaction. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 22
23 Spectra in the laboratory Neutron spectra in the lab before and after shielding - GEANT4: Araujo et al.; also Araujo&Kudryavtsev, talk at IDM2004; FLUKA: Kudryavtsev et al. - good agreement for all energies of interest (within 50%). LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 23
24 Events in xenon detector Nuclear recoil event rate as a function of measured energy (quenching = 0.2 for xenon) - GEANT4 and FLUKA: Araujo et al. - good agreement (within 30%). Energy spectrum of all events - GEANT4 and FLUKA: Araujo et al. Only <10% of nuclear recoil events contain nuclear recoils only; others have larger energy deposition from other particles. To estimate the background from nuclear recoils only, all particles should be produced, propagated and detected. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 24
25 Events in xenon detector From Araujo et al. NIMA 545 (2005), 398; hep-ex/ Neutron signal will be in time coincidence with electromagnetic signal (fast neutrons) - no big delays. If there is an active veto (100 kev threshold, 4π geometry) - no signal in anticoincidence with veto - a limit of <0.5 ev/year. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 25
26 Low-energy neutron production: Summary - I Modified code SOURCES is probably OK for this job - tested. Softer spectrum compared to earlier calculations. Missing cross-sections and excitation functions can be calculated with EMPIRE: the accuracy is about 20% if you choose right model. Low-energy neutron propagation and detection: Accurate measurements underground (and simulations of the whole experiment) are needed to test neutron yields and spectra - not easy. MCNP vs GEANT4 - good agreement: 50% difference after 6 orders of magnitude suppression by shielding. Designing dark matter detector: 55 g/cm 2 of CH 2 (or 20 cm of lead + 45 g/cm 2 of CH 2 ) should suppress the neutron flux below 1 event/ton/year at kev nuclear recoil energies; the required thickness of CH 2 depends on the fraction of H, density, use of lead (10 cm of Pb is equivalent to 5 g/cm 2 of CH 2 ), holes, neutron spectrum; detector components (+ shielding) will become the dominant background. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 26
27 Summary - II Muon-induced neutrons: FLUKA and GEANT4 (also modified GEANT3) agree within a factor of 2 (even better for some materials and energies). Most experimental data (although with large uncertainties) are also in agreement with simulations within a factor of 2; some data show significantly higher neutron yield in heavy materials; Designing dark matter detector: 40 g/cm 2 of CH 2 (after lead) suppress the muon-induced neutron flux down to a few events/year/tonne at a depth of about 3 km.w.e.; self-vetoing is important: most neutron events have accompanying particles - gammas, electrons, muons; (3 5) ((1 2) ) pb is reachable at ~2.5 (~3.0) km w. e. even without active veto (tested for a large xenon detector and NaCl as a rock). However, active veto is good for diagnostic and against neutrons (gammas) from the detector components. LRT /10/ Modane Vitaly Kudryavtsev 27
Neutron- and muoninduced. underground physics experiments. L. Pandola, V. Tomasello and V. Kudryavtsev. for the JRA1 and N3 simulation groups
 Neutron- and muoninduced background in underground physics experiments L. Pandola, V. Tomasello and V. Kudryavtsev for the JRA1 and N3 simulation groups ILIAS 4 th Annual Meeting, Chambery, 2007 ILIAS
Neutron- and muoninduced background in underground physics experiments L. Pandola, V. Tomasello and V. Kudryavtsev for the JRA1 and N3 simulation groups ILIAS 4 th Annual Meeting, Chambery, 2007 ILIAS
Background simulations and shielding calculations
 Background simulations and shielding calculations Vitaly A. Kudryavtsev University of Sheffield Contributions from many others Outline Note 1: results are relevant to many experiments and techniques (mainly
Background simulations and shielding calculations Vitaly A. Kudryavtsev University of Sheffield Contributions from many others Outline Note 1: results are relevant to many experiments and techniques (mainly
Low energy neutron propagation in MCNPX and GEANT4
 Low energy neutron propagation in and R. Lemrani a M. Robinson b V. A. Kudryavtsev b M. De Jesus c G. Gerbier a N. J. C. Spooner b arxiv:hep-ex/06030 v1 17 Jan 2006 a DAPNIA-SPP, CEA-Saclay, Gif-Sur-Yvette,
Low energy neutron propagation in and R. Lemrani a M. Robinson b V. A. Kudryavtsev b M. De Jesus c G. Gerbier a N. J. C. Spooner b arxiv:hep-ex/06030 v1 17 Jan 2006 a DAPNIA-SPP, CEA-Saclay, Gif-Sur-Yvette,
Simulations and other stuff
 Simulations and other stuff Vitaly A. Kudryavtsev University of Sheffield Contributions from many others Outline Muon generators: MUSIC, MUSUN. Neutrons from muons. Neutrons from radioactivity. Some notes
Simulations and other stuff Vitaly A. Kudryavtsev University of Sheffield Contributions from many others Outline Muon generators: MUSIC, MUSUN. Neutrons from muons. Neutrons from radioactivity. Some notes
Neutron background in large-scale xenon detectors for dark matter searches
 Astroparticle Physics xxx (2004) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/astropart Neutron background in large-scale xenon detectors for dark matter searches M.J. Carson, J.C. Davies, E. Daw, R.J. Hollingworth,
Astroparticle Physics xxx (2004) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/astropart Neutron background in large-scale xenon detectors for dark matter searches M.J. Carson, J.C. Davies, E. Daw, R.J. Hollingworth,
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches
 Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
NEUTRON BACKGROUND STUDIES FOR THE EDELWEISS WIMP SEARCH
 NEUTRON BACKGROUND STUDIES FOR THE EDELWEISS WIMP SEARCH G. CHARDIN AND G. GERBIER FOR THE EDELWEISS COLLABORATION DSM/DAPNIA/SPP, CEA/Saclay. F-91191 Gif-sur-Yvette Cedex, France E-mail: gabriel.chardin@cea.fr
NEUTRON BACKGROUND STUDIES FOR THE EDELWEISS WIMP SEARCH G. CHARDIN AND G. GERBIER FOR THE EDELWEISS COLLABORATION DSM/DAPNIA/SPP, CEA/Saclay. F-91191 Gif-sur-Yvette Cedex, France E-mail: gabriel.chardin@cea.fr
Neutron background studies for
 Neutron background studies for Edelweiss programs Introducing ETNomSiQ working group - Past measurements - Monte Carlo studies - Program of measurements and protections for EDELW II G. Gerbier CEA/Saclay,
Neutron background studies for Edelweiss programs Introducing ETNomSiQ working group - Past measurements - Monte Carlo studies - Program of measurements and protections for EDELW II G. Gerbier CEA/Saclay,
arxiv:hep-ex/ v4 4 Feb 2005
 Muon-induced neutron production and detection with GEANT4 and FLUKA H. M. Araújo a,, V. A. Kudryavtsev b, N. J. C. Spooner b, T. J. Sumner a arxiv:hep-ex/0411026v4 4 Feb 2005 Abstract a Blackett Laboratory,
Muon-induced neutron production and detection with GEANT4 and FLUKA H. M. Araújo a,, V. A. Kudryavtsev b, N. J. C. Spooner b, T. J. Sumner a arxiv:hep-ex/0411026v4 4 Feb 2005 Abstract a Blackett Laboratory,
Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment. Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH
 Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH The XENON dark matter search program Target Volume 62 kg Total
Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH The XENON dark matter search program Target Volume 62 kg Total
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment
 The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
The XENON100 Dark Matter Experiment
 The XENON0 Dark Matter Experiment Marc Schumann 1, Eirini Tziaferi 2 for the XENON0 collaboration 1 Rice University, 60 Main St., Houston TX, USA 2 University of Zürich, Winterthurerstr. 190, Zürich, Switzerland
The XENON0 Dark Matter Experiment Marc Schumann 1, Eirini Tziaferi 2 for the XENON0 collaboration 1 Rice University, 60 Main St., Houston TX, USA 2 University of Zürich, Winterthurerstr. 190, Zürich, Switzerland
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter
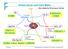 Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Studies of the XENON100 Electromagnetic Background
 Studies of the XENON100 Electromagnetic Background Daniel Mayani Physik-Institut University of Zurich PhD Seminar PSI, August 26-27, 2015 Searching for elusive particles The main challenge for experiments
Studies of the XENON100 Electromagnetic Background Daniel Mayani Physik-Institut University of Zurich PhD Seminar PSI, August 26-27, 2015 Searching for elusive particles The main challenge for experiments
Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search
 Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search Federica Petricca on behalf of the CRESST collaboration: Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München TU München University of Oxford Universität
Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search Federica Petricca on behalf of the CRESST collaboration: Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München TU München University of Oxford Universität
Recent results from the UK Dark Matter Search at Boulby Mine.
 Recent results from the UK Dark Matter Search at Boulby Mine. Nigel Smith Rutherford Appleton Laboratory on behalf of the UK Dark Matter Collaboration (Imperial College, Sheffield, RAL) NaI scintillation
Recent results from the UK Dark Matter Search at Boulby Mine. Nigel Smith Rutherford Appleton Laboratory on behalf of the UK Dark Matter Collaboration (Imperial College, Sheffield, RAL) NaI scintillation
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
Background Characterization and Rejection in the LZ Detector. David Malling Brown University IDM 2012 July 25, 2012
 Background Characterization and Rejection in the LZ Detector David Malling Brown University IDM 2012 July 25, 2012 LZ Construction 2 Background Sources Ti cryostats 1500 kg
Background Characterization and Rejection in the LZ Detector David Malling Brown University IDM 2012 July 25, 2012 LZ Construction 2 Background Sources Ti cryostats 1500 kg
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector. WIMP Search. Mani Tripathi, INPAC Meeting. Berkeley, May 5, 2007
 LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors. David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011
 Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011 1 Summary LUX screening program limits background contributions
Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011 1 Summary LUX screening program limits background contributions
School of Mathematics and Physics, Fujian University of Technology, Fuzhou , China
 Evaluation of the neutron background in cryogenic Germanium target for WIMP direct detection when using a reactor neutrino detector as a neutron veto system arxiv:1205.0428v4 [astro-ph.im] 3 Dec 2015 Ye
Evaluation of the neutron background in cryogenic Germanium target for WIMP direct detection when using a reactor neutrino detector as a neutron veto system arxiv:1205.0428v4 [astro-ph.im] 3 Dec 2015 Ye
Muon-induced background study for underground laboratories
 PHYSICAL REVIEW D 73, 053004 (006 Muon-induced background study for underground laboratories D.-M. Mei and A. Hime Physics Division, MS H803, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico 87545,
PHYSICAL REVIEW D 73, 053004 (006 Muon-induced background study for underground laboratories D.-M. Mei and A. Hime Physics Division, MS H803, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico 87545,
DARK MATTER SEARCH AT BOULBY MINE
 DARK MATTER SEARCH AT BOULBY MINE R. LUSCHER on behalf of the Boulby Dark Matter Collaboration (RAL, Imperial College, Sheffield, UCLA, Texas A&M, Pisa, ITEP, Coimbra, Temple and Occidental) Rutherford
DARK MATTER SEARCH AT BOULBY MINE R. LUSCHER on behalf of the Boulby Dark Matter Collaboration (RAL, Imperial College, Sheffield, UCLA, Texas A&M, Pisa, ITEP, Coimbra, Temple and Occidental) Rutherford
Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments
 Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments Jingke Xu Princeton University June 7 th, 2013 1 Evidences for Dark Matter Rotation Curve Gravitational Lensing CMB Power Spectrum
Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments Jingke Xu Princeton University June 7 th, 2013 1 Evidences for Dark Matter Rotation Curve Gravitational Lensing CMB Power Spectrum
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search
 Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Universität Zürich E-mail: marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Liquid noble gases have proven a great potential as detector medium for dark matter searches. Particles interacting in these media produce ionized and
Universität Zürich E-mail: marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Liquid noble gases have proven a great potential as detector medium for dark matter searches. Particles interacting in these media produce ionized and
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Dark Matter Search. Dark Matter
 Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
Network on Direct Dark Matter Search ILIAS N3
 Network on Direct Dark Matter Search ILIAS N3 N3 Dark Matter 2/25/2008 ILIAS 1 ILIAS-N3 Dark Matter Network Participating Institutions France: CNRS/CEA CNRS/SPM/CRTBT Grenoble CNRS/IN2P3/IPN Lyon CNRS/IN2P3/CSNSM
Network on Direct Dark Matter Search ILIAS N3 N3 Dark Matter 2/25/2008 ILIAS 1 ILIAS-N3 Dark Matter Network Participating Institutions France: CNRS/CEA CNRS/SPM/CRTBT Grenoble CNRS/IN2P3/IPN Lyon CNRS/IN2P3/CSNSM
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 24 Jun 2004
 LATEST RESULTS OF THE EDELWEISS EXPERIMENT arxiv:astro-ph/46537v 24 Jun 24 V. SANGLARD for the Edelweiss collaboration Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, 4 rue Enrico Fermi, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
LATEST RESULTS OF THE EDELWEISS EXPERIMENT arxiv:astro-ph/46537v 24 Jun 24 V. SANGLARD for the Edelweiss collaboration Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, 4 rue Enrico Fermi, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
Results on geoneutrinos at Borexino experiment. Heavy Quarks and Leptons Yamagata Davide Basilico
 Results on geoneutrinos at Borexino experiment Heavy Quarks and Leptons 2018 - Yamagata Davide Basilico Outline 1. Geoneutrinos 2. Borexino 3. Analysis and results 2 What are geoneutrinos? Distribution
Results on geoneutrinos at Borexino experiment Heavy Quarks and Leptons 2018 - Yamagata Davide Basilico Outline 1. Geoneutrinos 2. Borexino 3. Analysis and results 2 What are geoneutrinos? Distribution
arxiv:hep-ex/ v2 7 Apr 2004
 Neutron background at the Canfranc Underground Laboratory and its contribution to the IGEX-DM dark matter experiment arxiv:hep-ex/0403009 v2 7 Apr 2004 J.M. Carmona, S. Cebrián, E. García, I.G. Irastorza,
Neutron background at the Canfranc Underground Laboratory and its contribution to the IGEX-DM dark matter experiment arxiv:hep-ex/0403009 v2 7 Apr 2004 J.M. Carmona, S. Cebrián, E. García, I.G. Irastorza,
DARK MATTER SEARCHES
 DARK MATTER SEARCHES N.J.C. SPOONER Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Sheffield, Hicks Building, Hounsfield Road, Sheffield S3 7RH E-mail: n.spooner@sheffield.ac.uk A brief review is presented
DARK MATTER SEARCHES N.J.C. SPOONER Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Sheffield, Hicks Building, Hounsfield Road, Sheffield S3 7RH E-mail: n.spooner@sheffield.ac.uk A brief review is presented
The GERmanium Detector Array
 The GERmanium Detector Array n n ν=v p e - e - p Outline: Exp. issues of 0νββ-decay of 76 Ge Concept of GERDA Status of the experiment Summary and conclusions Kevin Kröninger (Max-Planck-Institut für Physik,
The GERmanium Detector Array n n ν=v p e - e - p Outline: Exp. issues of 0νββ-decay of 76 Ge Concept of GERDA Status of the experiment Summary and conclusions Kevin Kröninger (Max-Planck-Institut für Physik,
Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments
 Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments Debasish Majumdar Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata WIMP Hunting Going beyond gravity, three ways to detect
Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments Debasish Majumdar Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata WIMP Hunting Going beyond gravity, three ways to detect
Dark matter search with the SABRE experiment
 Dark matter search with the SABRE experiment Giulia D Imperio* for the SABRE collaboration *INFN Roma 1 25-07-2017 TAUP 2017 Sudbury, Canada 1 Dark matter detection through annual modulation WIMP is one
Dark matter search with the SABRE experiment Giulia D Imperio* for the SABRE collaboration *INFN Roma 1 25-07-2017 TAUP 2017 Sudbury, Canada 1 Dark matter detection through annual modulation WIMP is one
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX
 Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
Latest results of EDELWEISS II
 Latest results of EDELWEISS II Ana Torrentó CEA/IRFU/SPP Saclay Rencontres de Moriond 2011 «EW and Unified Theories» WIMP search Motivated by the «WIMP miracle» Very small rate of WIMPnucleus scattering
Latest results of EDELWEISS II Ana Torrentó CEA/IRFU/SPP Saclay Rencontres de Moriond 2011 «EW and Unified Theories» WIMP search Motivated by the «WIMP miracle» Very small rate of WIMPnucleus scattering
Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids
 Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Recontres de Moriond 2012, Cosmology Session, La Thuile, March 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Recontres de Moriond 2012, Cosmology Session, La Thuile, March 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search. Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration
 SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background
 Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background A cryogenic detector for Dark Matter with heat (phonon) readout and light (scintillation) readout MPI, TUM, Oxford, Tübingen, LNGS What we re looking for: M W imp =
Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background A cryogenic detector for Dark Matter with heat (phonon) readout and light (scintillation) readout MPI, TUM, Oxford, Tübingen, LNGS What we re looking for: M W imp =
Neutron flux measurement using fast-neutron activation of 12 B and 12 N isotopes in hydrocarbonate scintillators
 Neutron flux measurement using fast-neutron activation of 12 B and 12 N isotopes in hydrocarbonate scintillators M. M. Boliev E-mail: kchkrv@rambler.ru Yu. F. Novoseltsev R. V. Novoseltseva V. B. Petkov
Neutron flux measurement using fast-neutron activation of 12 B and 12 N isotopes in hydrocarbonate scintillators M. M. Boliev E-mail: kchkrv@rambler.ru Yu. F. Novoseltsev R. V. Novoseltseva V. B. Petkov
Low Background Experiments and Material Assay. Tessa Johnson NSSC Summer School July 2016
 Low Background Experiments and Material Assay Tessa Johnson NSSC Summer School July 2016 Outline How do we detect particles? Some interesting questions relating to particle physics How can particle detection
Low Background Experiments and Material Assay Tessa Johnson NSSC Summer School July 2016 Outline How do we detect particles? Some interesting questions relating to particle physics How can particle detection
DARK MATTER SEARCHES AT CANFRANC: ANAIS AND ROSEBUD: an update INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL GOALS SUMMARY OF RECENT ACHIEVEMENTS AND EFFORTS
 DARK MATTER SEARCHES AT CANFRANC: ANAIS AND ROSEBUD: an update María Luisa Sarsa (Universidad de Zaragoza) On behalf of ANAIS & ROSEBUD Collaborations OUTLINE ANAIS INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL GOALS
DARK MATTER SEARCHES AT CANFRANC: ANAIS AND ROSEBUD: an update María Luisa Sarsa (Universidad de Zaragoza) On behalf of ANAIS & ROSEBUD Collaborations OUTLINE ANAIS INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL GOALS
arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 15 Dec 2009
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 15 Dec 2009 arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 15 Dec 2009](/thumbs/92/110667636.jpg) The expected background spectrum in NaI dark matter detectors and the DAMA result V. A. Kudryavtsev 1, M. Robinson, N. J. C. Spooner Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Sheffield, Sheffield,
The expected background spectrum in NaI dark matter detectors and the DAMA result V. A. Kudryavtsev 1, M. Robinson, N. J. C. Spooner Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Sheffield, Sheffield,
LOW ENERGY SOLAR NEUTRINOS WITH BOREXINO. Lea Di Noto on behalf of the Borexino collaboration
 LOW ENERGY SOLAR NEUTRINOS WITH BOREXINO Lea Di Noto on behalf of the Borexino collaboration Vulcano Workshop 20 th -26 th May 2018 [cm -2 s -1 MeV -1 ] SOLAR NEUTRINOS Electrons neutrinos are produced
LOW ENERGY SOLAR NEUTRINOS WITH BOREXINO Lea Di Noto on behalf of the Borexino collaboration Vulcano Workshop 20 th -26 th May 2018 [cm -2 s -1 MeV -1 ] SOLAR NEUTRINOS Electrons neutrinos are produced
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 25 Nov 1999
 1 Narrow muon bundles from muon pair production in rock V. A. Kudryavtsev a, E. V. Korolkova b and N. J. C. Spooner a arxiv:hep-ph/9911493v1 25 Nov 1999 a Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
1 Narrow muon bundles from muon pair production in rock V. A. Kudryavtsev a, E. V. Korolkova b and N. J. C. Spooner a arxiv:hep-ph/9911493v1 25 Nov 1999 a Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
Dark Matter Detection with XENON100 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future
 Dark Matter Detection with XENON0 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future http://xenon.astro.columbia.edu Kaixuan Ni Columbia University TeV Particle Astrophysics IHEP, Beijing, Sep.4-8, 008 The Challenges
Dark Matter Detection with XENON0 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future http://xenon.astro.columbia.edu Kaixuan Ni Columbia University TeV Particle Astrophysics IHEP, Beijing, Sep.4-8, 008 The Challenges
Looking for WIMPs with EDELWEISS. Results and status of EDW I Prospects for EDW II + DAMA /LIBRA: brief status/future
 Looking for WIMPs with EDELWEISS Results and status of EDW I Prospects for EDW II + DAMA /LIBRA: brief status/future G. Gerbier CEA/Saclay/DAPNIA G. Gerbier NESS 2002 1 The Edelweiss Collaboration CEA-
Looking for WIMPs with EDELWEISS Results and status of EDW I Prospects for EDW II + DAMA /LIBRA: brief status/future G. Gerbier CEA/Saclay/DAPNIA G. Gerbier NESS 2002 1 The Edelweiss Collaboration CEA-
The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III
 The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III Adam Cox Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT) on behalf of the EDELWEISS Collaboration CEA, Saclay (IRFU and IRAMIS) IPNL (CNRS/IN2P3 and Université de
The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III Adam Cox Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT) on behalf of the EDELWEISS Collaboration CEA, Saclay (IRFU and IRAMIS) IPNL (CNRS/IN2P3 and Université de
The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100
 The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100 Symmetries and Fundamental Interactions 01 05 September 2014 Chiemsee Fraueninsel Boris Bauermeister on behalf of the XENON collaboration Boris.Bauermeister@uni-mainz.de
The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100 Symmetries and Fundamental Interactions 01 05 September 2014 Chiemsee Fraueninsel Boris Bauermeister on behalf of the XENON collaboration Boris.Bauermeister@uni-mainz.de
PHY326/426 Dark Matter and the Universe. Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev F9b, Tel.:
 PHY326/426 Dark Matter and the Universe Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev F9b, Tel.: 0114 2224531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk Indirect searches for dark matter WIMPs Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev Dark Matter and the Universe
PHY326/426 Dark Matter and the Universe Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev F9b, Tel.: 0114 2224531 v.kudryavtsev@sheffield.ac.uk Indirect searches for dark matter WIMPs Dr. Vitaly Kudryavtsev Dark Matter and the Universe
Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration. Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016
 Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016 The DarkSide program 2 Double Phase Liquid Argon TPC, a staged approach:
Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016 The DarkSide program 2 Double Phase Liquid Argon TPC, a staged approach:
Background optimization for a new spherical gas detector for very light WIMP detection
 Background optimization for a new spherical gas detector for very light WIMP detection a, I. Giomataris b, G. Gerbier b, J. Derré b, M. Gros b, P. Magnier b, D. Jourde b, E.Bougamont b, X-F. Navick b,
Background optimization for a new spherical gas detector for very light WIMP detection a, I. Giomataris b, G. Gerbier b, J. Derré b, M. Gros b, P. Magnier b, D. Jourde b, E.Bougamont b, X-F. Navick b,
Rivelazione di neutrini solari - Borexino Lino Miramonti 6 Giugno 2006 Gran Sasso
 Rivelazione di neutrini solari - Borexino Lino Miramonti 6 Giugno 2006 Gran Sasso 1 RADIOCHEMICAL Integrated in energy and time CHERENKOV Less than 0.01% of the solar neutrino flux is been measured in
Rivelazione di neutrini solari - Borexino Lino Miramonti 6 Giugno 2006 Gran Sasso 1 RADIOCHEMICAL Integrated in energy and time CHERENKOV Less than 0.01% of the solar neutrino flux is been measured in
XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector
 XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector Katsuki Hiraide, the university of Tokyo for the XMASS Collaboration October 3 rd, 2016 IPRD16@Siena, Italy 1 XMASS project XMASS: a multi purpose experiment
XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector Katsuki Hiraide, the university of Tokyo for the XMASS Collaboration October 3 rd, 2016 IPRD16@Siena, Italy 1 XMASS project XMASS: a multi purpose experiment
Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON. Kaixuan Ni (Columbia)
 Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON Kaixuan Ni (Columbia) University of Maryland, 11-25-2008 A well-known mystery for astronomers Fritz Zwicky, The Astrophysical Journal, 85
Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON Kaixuan Ni (Columbia) University of Maryland, 11-25-2008 A well-known mystery for astronomers Fritz Zwicky, The Astrophysical Journal, 85
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 26 May 2015
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 26 May 2015 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 26 May 2015](/thumbs/75/72820229.jpg) GeMSE: A new Low-Background Facility for Meteorite and Material Screening arxiv:1505.07015v1 [physics.ins-det] 26 May 2015 M. v. Sivers 1, B. A. Hofmann 2,3, A. V. Rosén 2, and M. Schumann 1 1 Albert Einstein
GeMSE: A new Low-Background Facility for Meteorite and Material Screening arxiv:1505.07015v1 [physics.ins-det] 26 May 2015 M. v. Sivers 1, B. A. Hofmann 2,3, A. V. Rosén 2, and M. Schumann 1 1 Albert Einstein
Cosmogenic background for the GERDA experiment. Luciano Pandola INFN, Laboratori del Gran Sasso, Italy
 Cosmogenic background for the GERDA experiment Luciano Pandola INFN, Laboratori del Gran Sasso, Italy Cosmogenic Activity and Background Workshop, Berkeley April 15 th, 2011 GERDA experiment at LNGS The
Cosmogenic background for the GERDA experiment Luciano Pandola INFN, Laboratori del Gran Sasso, Italy Cosmogenic Activity and Background Workshop, Berkeley April 15 th, 2011 GERDA experiment at LNGS The
ANAIS: Status and prospects
 LSC Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc ANAIS: Status and prospects Miguel Ángel Oliván on behalf of the ANAIS team Universidad de Zaragoza Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc RICAP 2014 Roma International
LSC Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc ANAIS: Status and prospects Miguel Ángel Oliván on behalf of the ANAIS team Universidad de Zaragoza Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc RICAP 2014 Roma International
The XENON Dark Matter Project: Status of the XENON100 Phase. Elena Aprile Columbia University
 The XENON Dark Matter Project: Status of the XENON100 Phase Elena Aprile Columbia University 8th UCLA Symposium Marina del Rey, Feb 22, 2008 The XENON Dark Matter Phased Program Detect WIMPS through their
The XENON Dark Matter Project: Status of the XENON100 Phase Elena Aprile Columbia University 8th UCLA Symposium Marina del Rey, Feb 22, 2008 The XENON Dark Matter Phased Program Detect WIMPS through their
China Jinping Underground Laboratory and experiments inside. Qian YUE Tsinghua University Mar. 28, 2017
 China Jinping Underground Laboratory and experiments inside Qian YUE Tsinghua University Mar. 28, 2017 Outline: Physics based on UL China Jinping Underground Laboratory (CJPL) Experiments in CJPL-I CJPL-II
China Jinping Underground Laboratory and experiments inside Qian YUE Tsinghua University Mar. 28, 2017 Outline: Physics based on UL China Jinping Underground Laboratory (CJPL) Experiments in CJPL-I CJPL-II
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 15 Feb 2005
 The XENON Dark Matter Experiment Elena Aprile (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027 age@astro.columbia.edu
The XENON Dark Matter Experiment Elena Aprile (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027 age@astro.columbia.edu
XENON100. Marc Schumann. Physik Institut, Universität Zürich. IDM 2010, Montpellier, July 26 th,
 XENON100 Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich IDM 2010, Montpellier, July 26 th, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ Why WIMP search with Xenon? efficient, fast scintillator (178nm)
XENON100 Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich IDM 2010, Montpellier, July 26 th, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ Why WIMP search with Xenon? efficient, fast scintillator (178nm)
DARWIN: dark matter WIMP search with noble liquids
 DARWIN: dark matter WIMP search with noble liquids Physik Institut, University of Zurich E-mail: laura.baudis@physik.uzh.ch DARWIN (DARk matter WImp search with Noble liquids) is an R&D and design study
DARWIN: dark matter WIMP search with noble liquids Physik Institut, University of Zurich E-mail: laura.baudis@physik.uzh.ch DARWIN (DARk matter WImp search with Noble liquids) is an R&D and design study
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions
 Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Vincenzo Caracciolo for the ADAMO collaboration National Laboratory of Gran Sasso - INFN.
 Vincenzo Caracciolo for the ADAMO collaboration National Laboratory of Gran Sasso - INFN. Signatures for direct detection experiments In direct detection experiments to provide a Dark Matter signal identification
Vincenzo Caracciolo for the ADAMO collaboration National Laboratory of Gran Sasso - INFN. Signatures for direct detection experiments In direct detection experiments to provide a Dark Matter signal identification
Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE
 Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE Kyungeun E. Lim (on behalf of the CUORE collaboration) Oct. 30. 015, APS Division of Nuclear Physics meeting, Santa Fe, NM The CUORE Experiment CUORE
Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE Kyungeun E. Lim (on behalf of the CUORE collaboration) Oct. 30. 015, APS Division of Nuclear Physics meeting, Santa Fe, NM The CUORE Experiment CUORE
European Underground Laboratories and ILIAS
 LRT wokshop, Aussois, October,1-4 2006 European Underground Laboratories and ILIAS F. Piquemal (CENBG and LSM) Acknowlegement to N. Spooner (USFD and Boulby), J. Morales, (Zaragoza and Canfranc) and G.
LRT wokshop, Aussois, October,1-4 2006 European Underground Laboratories and ILIAS F. Piquemal (CENBG and LSM) Acknowlegement to N. Spooner (USFD and Boulby), J. Morales, (Zaragoza and Canfranc) and G.
Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search
 Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search KIT Institute Centre for Particle Nuclear and Physics Astroparticle Physics KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Research Center of
Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search KIT Institute Centre for Particle Nuclear and Physics Astroparticle Physics KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Research Center of
Status and Prospects of China JinPing Deep Underground Laboratory (CJPL) and China Dark Matter EXperiment (CDEX)
 Status and Prospects of China JinPing Deep Underground Laboratory (CJPL) and China Dark Matter EXperiment (CDEX) Qian Yue Department of Engineering Physics TsingHua University May 13, 2010 Outline: Survey
Status and Prospects of China JinPing Deep Underground Laboratory (CJPL) and China Dark Matter EXperiment (CDEX) Qian Yue Department of Engineering Physics TsingHua University May 13, 2010 Outline: Survey
Neutrino detectors. V. Lozza,
 Neutrino detectors, 5.10.2011 Outline - Introduction to neutrinos Sources of neutrinos Detection techniques Why we need to go underground? Background components What to do? Summary A brief of history 1914:
Neutrino detectors, 5.10.2011 Outline - Introduction to neutrinos Sources of neutrinos Detection techniques Why we need to go underground? Background components What to do? Summary A brief of history 1914:
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Backgrounds and Sensitivity Expectations for XENON100
 Backgrounds and Sensitivity Expectations for XENON100 IDM08, Stockholm, August 19, 2008 Laura Baudis University of Zurich For the XENON100 Collaboration LNGS collaboration meeting, Oct. 2007 1 ??? The
Backgrounds and Sensitivity Expectations for XENON100 IDM08, Stockholm, August 19, 2008 Laura Baudis University of Zurich For the XENON100 Collaboration LNGS collaboration meeting, Oct. 2007 1 ??? The
DarkSide new results and prospects
 DarkSide new results and prospects Stefano Davini - INFN Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration La Thuile, March 20, 2018 The DarkSide WIMP-argon program at LNGS 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
DarkSide new results and prospects Stefano Davini - INFN Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration La Thuile, March 20, 2018 The DarkSide WIMP-argon program at LNGS 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Search for low-mass WIMPs with Spherical Detectors : NEWS-LSM and NEWS-SNO
 Search for low-mass WIMPs with Spherical Detectors : NEWS-LSM and NEWS-SNO G. Gerbier 1 for the NEWS collaboration 2, 1 Queen s University, Physics Department, Kingston, Canada 2 New Experiments With Spheres
Search for low-mass WIMPs with Spherical Detectors : NEWS-LSM and NEWS-SNO G. Gerbier 1 for the NEWS collaboration 2, 1 Queen s University, Physics Department, Kingston, Canada 2 New Experiments With Spheres
- The CONUS Experiment - COherent elastic NeUtrino nucleus Scattering
 - The CONUS Experiment - COherent elastic NeUtrino nucleus Scattering C. Buck, J. Hakenmüller, G. Heusser, M. Lindner, W. Maneschg, T. Rink, H. Strecker, T. Schierhuber and V. Wagner Max-Planck-Institut
- The CONUS Experiment - COherent elastic NeUtrino nucleus Scattering C. Buck, J. Hakenmüller, G. Heusser, M. Lindner, W. Maneschg, T. Rink, H. Strecker, T. Schierhuber and V. Wagner Max-Planck-Institut
Status of KIMS-NaI experiment
 Status of KIMS-NaI experiment Hyun Su Lee Institute for Basic Science, Korea On behalf of the KIMS Collaboration XIV International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics KIMS-NaI
Status of KIMS-NaI experiment Hyun Su Lee Institute for Basic Science, Korea On behalf of the KIMS Collaboration XIV International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics KIMS-NaI
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment. 1 Abstract. 2 Introduction
 Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
Background rejection techniques in Germanium 0νββ-decay experiments. ν=v
 Background rejection techniques in Germanium 0νββ-decay experiments n p ν=v n eep II. Physikalisches Institut Universität Göttingen Institutsseminar des Inst. für Kern- und Teilchenphysik, Outline Neutrinos
Background rejection techniques in Germanium 0νββ-decay experiments n p ν=v n eep II. Physikalisches Institut Universität Göttingen Institutsseminar des Inst. für Kern- und Teilchenphysik, Outline Neutrinos
Modane underground laboratory (Fréjus)
 Modane underground laboratory (Fréjus) Present and Future IDM 2006, Rhodes F. Piquemal (CENBG, CNRS-IN2P3, U. Bordeaux I) Presented by G. Gerbier (CEA-Dapnia Saclay) Modane Underground Laboratory (Fréjus)
Modane underground laboratory (Fréjus) Present and Future IDM 2006, Rhodes F. Piquemal (CENBG, CNRS-IN2P3, U. Bordeaux I) Presented by G. Gerbier (CEA-Dapnia Saclay) Modane Underground Laboratory (Fréjus)
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter
 Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments
 Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@mpi-hd.mpg.de DM@LHC Heidelberg, April 5th, 2018 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (MPIK) Liquid noble gases Heidelberg,
Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@mpi-hd.mpg.de DM@LHC Heidelberg, April 5th, 2018 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (MPIK) Liquid noble gases Heidelberg,
Shielding Strategies. Karl Tasso Knöpfle MPI Kernphysik, Heidelberg
 Shielding Strategies Karl Tasso Knöpfle MPI Kernphysik, Heidelberg ktkno@mpi-hd.mpg.de Application of Germanium Detector in Fundamental Research Tsinghua University Bejing, March 24-26, 20011 outline Introduction
Shielding Strategies Karl Tasso Knöpfle MPI Kernphysik, Heidelberg ktkno@mpi-hd.mpg.de Application of Germanium Detector in Fundamental Research Tsinghua University Bejing, March 24-26, 20011 outline Introduction
Status of the ANAIS experiment at Canfranc
 Status of the ANAIS experiment at Canfranc J. Amaré, B. Beltrán, J. M. Carmona, S. Cebrián, E. García, H. Gómez, G. Luzón,, J. Morales, A. Ortiz de Solórzano, C. Pobes, J. Puimedón, A. Rodriguez, J. Ruz,
Status of the ANAIS experiment at Canfranc J. Amaré, B. Beltrán, J. M. Carmona, S. Cebrián, E. García, H. Gómez, G. Luzón,, J. Morales, A. Ortiz de Solórzano, C. Pobes, J. Puimedón, A. Rodriguez, J. Ruz,
Collaborazione DAMA & INR-Kiev. XCVIII Congresso SIF Napoli, 18 Settembre F. Cappella
 Collaborazione DAMA & INR-Kiev http://people.roma2.infn.it/dama XCVIII Congresso SIF Napoli, 18 Settembre 2012 F. Cappella Based on the study of the correlation between the Earth motion in the galactic
Collaborazione DAMA & INR-Kiev http://people.roma2.infn.it/dama XCVIII Congresso SIF Napoli, 18 Settembre 2012 F. Cappella Based on the study of the correlation between the Earth motion in the galactic
Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment
 Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment by A. Lyashenko Yale University On behalf of LUX collaboration LUX Large Underground Xenon experiment LUX Collaboration: Yale, CWRU, UC Santa Barbara, Brown,
Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment by A. Lyashenko Yale University On behalf of LUX collaboration LUX Large Underground Xenon experiment LUX Collaboration: Yale, CWRU, UC Santa Barbara, Brown,
Study well-shaped germanium detectors for lowbackground
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Study well-shaped germanium detectors for lowbackground counting To cite this article: W-Z Wei et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 606 012019 View the
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Study well-shaped germanium detectors for lowbackground counting To cite this article: W-Z Wei et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 606 012019 View the
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST
 Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Simulations, backgrounds, and uncertainties in PICO-2L. Alan Robinson May 20, 2015 AARM, Rapid City South Dakota
 Simulations, backgrounds, and uncertainties in Alan Robinson May 20, 2015 AARM, Rapid City South Dakota Calibrations of Nuclear Recoils in C3F8 Calibration Slide 2/33 CAM 2013 Aug 16, 2013 Simulations
Simulations, backgrounds, and uncertainties in Alan Robinson May 20, 2015 AARM, Rapid City South Dakota Calibrations of Nuclear Recoils in C3F8 Calibration Slide 2/33 CAM 2013 Aug 16, 2013 Simulations
Detectors for astroparticle physics
 Detectors for astroparticle physics Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Universität Zürich Kern und Teilchenphysik II, Zürich 07.05.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (UZH) Detectors for astroparticle
Detectors for astroparticle physics Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Universität Zürich Kern und Teilchenphysik II, Zürich 07.05.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (UZH) Detectors for astroparticle
Light Dark Matter and XENON100. For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University
 Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
UCLA Dark Matter 2014 Symposium. Origins and Distributions of the Backgrounds. 15 min
 S. Fiorucci Brown University UCLA Dark Matter 2014 Symposium Origins and Distributions of the Backgrounds 15 min What is a signal for LUX? Nuclear recoil Single scatter Signal Low energy, typically < 25
S. Fiorucci Brown University UCLA Dark Matter 2014 Symposium Origins and Distributions of the Backgrounds 15 min What is a signal for LUX? Nuclear recoil Single scatter Signal Low energy, typically < 25
Direct and Indirect Searches for WIMP Dark Matter
 Direct and Indirect Searches for WIMP Dark Matter Neil Spooner 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Sheffield, Hounsfield Road, Sheffield, S3 7RH, UK I briefly review the present status
Direct and Indirect Searches for WIMP Dark Matter Neil Spooner 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Sheffield, Hounsfield Road, Sheffield, S3 7RH, UK I briefly review the present status
Neutron Flux Underground Revisited
 Neutron Flux Underground Revisited H. Wulandari, J. Jochum, W. Rau, F. von Feilitzsch Physikdept. E-15, Technische Universität München, James-Franckstr.- 85747 Garching, Germany Abstract The neutron flux
Neutron Flux Underground Revisited H. Wulandari, J. Jochum, W. Rau, F. von Feilitzsch Physikdept. E-15, Technische Universität München, James-Franckstr.- 85747 Garching, Germany Abstract The neutron flux
THE CRYOGENIC UNDERGROUND OBSERVATORY FOR RARE EVENTS: STATUS AND PROSPECTS
 THE CRYOGENIC UNDERGROUND OBSERVATORY FOR RARE EVENTS: STATUS AND PROSPECTS Eric B. Norman Dept. of Nuclear Engineering Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA U. S. A. Recent results in n physics Neutrinos
THE CRYOGENIC UNDERGROUND OBSERVATORY FOR RARE EVENTS: STATUS AND PROSPECTS Eric B. Norman Dept. of Nuclear Engineering Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA U. S. A. Recent results in n physics Neutrinos
Universal formula for the muon-induced neutron yield
 Universal formula for the muon-induced neutron yield N. Yu. Agafonova and A. S. Malgin Institute For Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences 60th October Anniversary Prospect 7a, 117312 Moscow,
Universal formula for the muon-induced neutron yield N. Yu. Agafonova and A. S. Malgin Institute For Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences 60th October Anniversary Prospect 7a, 117312 Moscow,
The XENON100 Dark Matter Experiment at LNGS: Status and Sensitivity
 The XENON100 Dark Matter Experiment at LNGS: Status and Sensitivity Elena Aprile (on behalf of the XENON Collaboration) Columbia University,Physics Department, New York,NY, USA E-mail: age@astro.columbia.edu
The XENON100 Dark Matter Experiment at LNGS: Status and Sensitivity Elena Aprile (on behalf of the XENON Collaboration) Columbia University,Physics Department, New York,NY, USA E-mail: age@astro.columbia.edu
Two Neutrino Double Beta (2νββ) Decays into Excited States
 Two Neutrino Double Beta (2νββ) Decays into Excited States International School of Subnuclear Physics 54 th Course: The new physics frontiers in the LHC-2 era Erice, 17/06/2016 Björn Lehnert TU-Dresden,
Two Neutrino Double Beta (2νββ) Decays into Excited States International School of Subnuclear Physics 54 th Course: The new physics frontiers in the LHC-2 era Erice, 17/06/2016 Björn Lehnert TU-Dresden,
Backgrounds in PICO. Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB. AARM Meeting Fermilab; Batavia IL, USA; March 19, 2014
 Backgrounds in PICO Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB AARM Meeting Fermilab; Batavia IL, USA; March 19, 2014 PICO at SNOLAB SNOLAB deepest and cleanest large-space international facility in the world 2 km
Backgrounds in PICO Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB AARM Meeting Fermilab; Batavia IL, USA; March 19, 2014 PICO at SNOLAB SNOLAB deepest and cleanest large-space international facility in the world 2 km
