An Elastic Contact Problem with Normal Compliance and Memory Term
|
|
|
- Doreen Casey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Machine Dynamics Research 2012, Vol. 36, No 1, Abstract An Elastic Contact Problem with Normal Compliance and Memory Term Mikäel Barboteu, Ahmad Ramadan, Mircea Sofonea Uniersité de Perpignan, France 1 barboteu@uni-perp.fr, ahmad.ramadan@uni-perp.fr, sofonea@uni-perp.fr Flaius Patrulescu Tiberiu Popoiciu Institute of Numerical Analysis, Cluj-Napoca, Romania flaius.patrulescu@ictp.acad.ro. We consider a history-dependent problem which describes the contact between an elastic body and an obstacle, the so-called foundation. The contact is frictionless and is modeled with a ersion of the normal compliance condition in which the memory effects are taken into account. The mathematical analysis of the problem, including existence, uniqueness and conergence results, was proided in (Barboteu et al., in preparation). Here we present the analytic expression of the solution and numerical simulations, in the study of one and two-dimensional examples, respectiely. 1. Introduction Phenomena of contact between deformable bodies abound in industry and eeryday life. Owing to their inherent complexity, they lead to nonlinear and nonsmooth mathematical models. To construct a mathematical model which describes a specific contact process we need to precise the material s behaior and the contact conditions, among others. In this paper we model the behaior of the material with an elastic constitutie law of the form σ Fε(u) (1) where u denotes the displacement field, σ represents the stress, ε(u) is the linearized strain tensor and F is a nonlinear constitutie function. Also, we use the contact condition 1 Laboratoire de Mathématiques et Physique
2 16 M. Barboteu, A. Ramadan, M. Sofonea, F. Patrulescu t ( p( u ( ) b( t s) u ( s)ds (2) in which σ ν and u ν are the normal stress and the normal displacement, respectiely, p and b are gien functions, and r + denotes the positie part of r, i.e. r + = max {0, r}. The contact condition (2) was first introduced by Petrulescu (2011). It shows that at each time moment t R + the normal stress has an additie decomposition of the form in which the functions D ( ( ( D M and are gien by D M ( p( u ( ), ( b( t s) u ( s) ds. 0 M D It follows from aboe that satisfies a normal compliance contact condition and, M therefore, it describes the deformability of the foundation. Also, satisfies a history dependent condition and, therefore, it describes the memory properties of the foundation. Moreoer, we conclude from (2) that at each moment t, the reaction of the foundation depends both on the current alue of the penetration (represented by the term p(u ν ()) as well as on the history of the penetration (represented by the integral term). The analysis of arious frictional and frictionless contact problems with elastic materials was proided in many papers, see for instance (Han and Sofonea, 2002; Shillor et al., 2004; Sofonea and Matei, 2012) and the references therein. In particular, results on the unique weak solability can be found in (Shillor et al., 2004; Sofonea and Matei, 2012); fully discrete schemes for the numerical approximation of the models, including error estimates and numerical simulations can be found in (Han and Sofonea, 2002). In all these papers the mechanical process was studied in a finite interal of time and the contact was modeled either with the normal compliance condition or the Signorini condition, or was assumed to be bilateral. A mathematical model constructed by using the constitutie law (1) and the contact condition (2) has been considered by Barboteu et al., (in preparation). There, the unique weak solability of the model was proed by using arguments on historydependent ariational inequalities obtained by Sofonea and Matei (2011). Various conergence results were proed and their numerical alidation was also proided. The current paper represents a continuation of (Barboteu et al., in preparation). Its aim is to present additional results in the study of the mathematical model considered
3 An Elastic Contact Problem with Normal Compliance and Memory Term 17 there, which highlight the behaior of the solution of the corresponding historydependent contact problem. The manuscript is structured as follows. In section 2 we describe the physical setting and present the classical formulation of the problem. Then, in section 3 we present the analytic expression of the solution in the one-dimensional case and, in section 4, we present numerical simulations in the study of an academic twodimensional example. Finally, we end this paper with section 5, in which we present some conclusions, comments and problems for further research. 2. The model The physical setting is as follows. An elastic body occupies a bounded domain Ω R d (d = 1, 2, 3) with a Lipschitz continuous boundary Γ, diided into three measurable parts Γ 1, Γ 2 and Γ 3, such that meas (Γ 1 ) > 0. The body is subject to the action of body forces of density f 0. We also assume that it is fixed on Γ 1 and surface tractions of density f 2 act on Γ 2. On Γ 3, the body is in frictionless contact with a deformable obstacle, the so-called foundation. We assume that the contact process is history-dependent, and we study it in the interal of time R +. We denote by S d the space of second order symmetric tensors on R d or, equialently, the space of symmetric matrices of order d. We use the notation x = (x i ) for a typical point in Ω Γ and we denote by ν = (ν i ) the outward unit normal at Γ. Here and below the indices i, j, k, l run between 1 and d and, unless stated otherwise, the summation conention oer repeated indices is used. An index that follows a comma represents the partial deriatie with respect to the corresponding component of the spatial ariable x, e.g. u i,j = u i / x j. Also, ε and Di will represent the deformation and the diergence operators, respectiely, i.e. ε(υ) = (ε ij (υ)), ε ij (υ) = 0.5(υ i,j + υ j,i ), Di σ = (σ ij,j ). We denote by υ ν and υ τ the normal and tangential components of υ on Γ gien by υ ν = υ ν, υ τ = υ υ ν ν. Also, for a regular stress function σ we use the notation σ ν and σ τ for the normal and the tangential traces on the boundary, i.e. σ ν = (σν) ν and σ τ = σν σ ν ν. With these preliminaries, the classical formulation of the contact problem is as follows. Problem P Find a displacement field u : Ω R + R d and a stress field σ : Ω R + S d such that, for each t R +, σ( = Fε(u() in Ω R + (3) Di σ( + f 0 ( = 0 in Ω R + (4)
4 18 M. Barboteu, A. Ramadan, M. Sofonea, F. Patrulescu u( = 0 on Γ 1 R + (5) σ(ν = f 2 ( on Γ 2 R + (6) t σ ν ( + p(u () b ( t s) u ( s)ds 0 on Γ 3 R + (7) 0 σ τ ( = 0 on Γ 3 R + (8) Here and below, in order to simplify the notation, we do not indicate explicitly the dependence of arious functions on the spatial ariable x. Equation (3) represents the elastic constitutie law of the material, see (1). Equation (4) is the equation of equilibrium, conditions (5), (6) represent the displacement and traction boundary conditions, respectiely, and condition (7) is the contact condition with normal compliance and memory term, see (2). Finally, (8) represents the frictionless condition. The well-posedness of Problem P was obtained by Barboteu et al. (in preparation), see also (Petrulescu, 2012) for details and complements. In the next two sections we turn to the study of one and two-dimensional examples which underline the influence of the memory term on the solution. 3. One dimensional example We consider a cantileer elastic rod which is fixed at its left end x = 0, is in contact at its right end x = 1, and is subjected to the action of a body force of density f 0 in the x-direction, as shown in Fig. 1. This problem corresponds to problem (3) (8) with Ω = (0,1), Γ 1 = {0}, Γ 2 =, Γ 3 = {1}. We use the linearly elastic constitutie law σ = Eε(u) where E > 0 represents the Young modulus of the material and ε(u) = u/ x. Moreoer, we assume that f 0 and b are constant functions, i.e. f 0 (x, = f and b( = b for all x (0,1) and t R + where f, b > 0. Finally, we suppose that the compliance function has the form p(r) = cr +, where c > 0. With these assumptions, the one-dimensional problem we consider is as follows. Problem P 1 Find a displacement field u : (0,1) R + R and a stress field σ : (0,1) R + R such that, for each t R +, u σ(x, = E ( x, in (0,1) R + (9) x ( x, f 0 in (0,1) R + (10) x σ(1, + p(u(1,) + b u u(0, = 0 for all t R + (11) t 0 ( 1, s)ds 0 for all t R + (12)
5 An Elastic Contact Problem with Normal Compliance and Memory Term 19 The exact solution of Problem P 1 can be obtained through an elementary calculus which we present in what follows. Let t R +. First, we integrate (10) with respect to x and obtain σ(x, = fx + α( x (0,1) (13) where α( is a constant of integration. Then we combine (9) and (13) to deduce that u f ( t ( x, x ) x (0,1) (14) x E E And, finally, we integrate (14) with respect to x and use condition (11) to see that f 2 ( u( x, ( x, x x x (0,1) (15) 2E E Fig. 1. Contact rod with a foundation We turn now to determinate α( and, to this end, we use the contact condition (12). It follows from (12), (13) and (15) that t c f b f ( f ( ( ds 0 t R (16) E 2 E 2 0 The existence of a unique solution to the nonlinear integral equation (16) follows from a general abstract result, as shown in (Petrulescu, 2012). Moreoer, an elementary calculus shows that the function b t Ec R fe ( e 2( E c) f 2 satisfies (16). Therefore, using (13) and (15) we obtain and E ( x, fx e E c 1 f 2 t (17) b t Ec (, (0,1) R x (18)
6 20 M. Barboteu, A. Ramadan, M. Sofonea, F. Patrulescu u( x, f 2E x 2 E e E c b t Ec 1 f 2E x ( x, (0,1) R (19) Assume now that E = 1, f = 2, b = c = 1. Then, the stress σ(1, and the displacement u(1, are plotted in Fig. 2. Moreoer, the stress function (18) and the displacement function (19) are plotted in Figs. 3 and 4, respectiely. Finally, we note that lim u(1, 0, lim f (1, (20) t t 2 We deduce that in x = 1 the displacement anishes and the stress reach the residual alue f /2, as t tends to infinity. This behaior of the solution represents one of the effects of the memory term in the contact condition. Fig. 2. The stress σ(1, and the displacement u(1, for t [0,10] Fig. 3. The stress σ(x, for (x, (0,1) [0,10]
7 An Elastic Contact Problem with Normal Compliance and Memory Term 21 Fig. 4. The displacement u(x, for (x, (0,1) [0,10] Fig. 5. Initial configuration of the two-dimensional example 4. Two dimensional example The numerical solution of the contact problem P is based on a classical Newton method combined with a penalized method for the compliance contact and a trapezoidale rule for the time integration of the memory term. More details on this discretization step and the corresponding numerical method can be found in (Alart and Curnier, 1991; Laursen, 2002; Wriggers, 2002). In order to keep this paper in a reasonable length, we skip the presentation of the numerical algorithm and we describe in what follows a two-dimensional numerical example. We consider the physical setting depicted in Fig. 5. There, Ω = (0,2) (0,1) R 2 with Γ 1 = ({0} [0.5,1]) ({2} [0.5,1]), Γ 2 = ([0,2] {1}) ({0} [0,0.5]) ({2} [0,0.5]), Γ 3 = [0,2] {0}. The domain Ω represents the cross section of a three-dimensional deformable body subjected to the action of tractions in such a way that a plane stress hypothesis is assumed. On the part Γ 1 the body is clamped and, therefore, the displacement field anishes there. Vertical tractions act on the part
8 22 M. Barboteu, A. Ramadan, M. Sofonea, F. Patrulescu [0,2] {1} of the boundary Γ 2 and the part ({0} [0,0.5]) ({2} [0,0.5]) is traction and displacement free. No body forces are assumed to act on the body during the process. The body is in frictionless contact with an obstacle on the part Γ3 = [0,2] {0} of the boundary. For the discretization we use 7935 elastic finite elements and 129 contact elements. The total number of degrees of freedom is equal to 8326 and we take a time step equal to 0.1 s. We model the material s behaior with a constitutie law of the form (1) in which the elasticity tensor F satisfies E E F 1, 2 (21) 1 1 ( ε) ( ), Here E is the Young modulus, κ the Poisson ratio of the material and δ αβ denotes the Kronecker symbol. For the computation below we used the following data: t [0,T], T = 3.6 s, E = N/m 2, κ = 0.3, f 0 = (0,0) N/m 2, (0,0) N/m on ({0} [0,0.5]) ({2} [0,0.5] f 2, (-2000,0) N/m on [0,2] {1} p(r) = c ν r +, c ν = 200 N/m 2. Our results are presented in Figs. 6 9 and are described in what follows. Fig. 6. Deformed mesh and contact interface forces for b = c ν Fig. 7. Deformed mesh and contact interface forces for b = 0
9 An Elastic Contact Problem with Normal Compliance and Memory Term 23 Fig. 8. Deformed mesh and contact interface forces for b = c ν Fig. 9. Deformed meshes and contact interface forces for t = 0.8, 1.6, 2.4 and 3.6 s First, in Figs. 6, 7 and 8 the deformed mesh and the contact interface forces are presented in the case b = c ν > 0, b = c ν = 0 and b = c ν < 0, respectiely. We note that when b = c ν > 0 the penetration is less important than in the case when the memory term anishes (i.e. b = 0). Also, when b = c ν < 0 the penetration is more important than in the case when b = 0. We conclude from here that in function of the sign of b, the memory term describes either the hardness or the softness of the foundation. In Fig. 9 we present the eolution of the contact in time, for b = c ν. There we present the deformed meshes as well as the associated contact forces for t = 0.8, 1.6, 2.4 and 3.2 s, respectiely. We note that the penetration is smaller at t = 3.2 s than at t = 0.8 s and it decreases in time. These results suggest that for a large time interal the penetration conerges to zero, which represents a similar behaior to that obsered in the one-dimensional case, see the first equality in (20).
10 24 M. Barboteu, A. Ramadan, M. Sofonea, F. Patrulescu 5. Conclusions In this paper we presented a model for the history-dependent process of frictionless contact of an elastic body. The contact was goerned by a normal compliance condition with memory. Our aim was to study the behaiour of the solution and to underline the effects of the memory terms in the process of contact. To this end we considered a one-dimensional example and we proided an analytic expression of the solution. Then, we proided numerical simulations in the study of a two-dimensional model. We used an algorithm based on a Newton method combined with a penalized method for the compliance contact and a trapezoidal rule for the time integration of the contact memory term. Based on the simulations, we found that the algorithm worked well and the conergence was rapid. Subsequent stages of the research presented in this paper will consist to add friction in the model and to extend these results to dynamic frictional or frictionless contact processes. Acknowledgement The work of the fourth author was supported within the Sectorial Operational Programme for Human Resources Deelopment , co-financed by the European Social Fund, under the project number POSDRU/88/1.5/S/60185 entitled Modern Doctoral Studies: Innoatie Doctoral Studies in a Knowledge Based Society, at Uniersity Babeş-Bolyai, Cluj-Napoca, Romania. References Alart, P., Curnier, A., 1991, A mixed formulation for frictional contact problems prone to Newton like solution methods, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 92, Barboteu, M., Patrulescu, F., Sofonea, M., Analysis of a contact problem with normal compliance and memory term, in preparation. Han, W., Sofonea M., 2002, Quasistatic Contact Problems in Viscoelasticity and Viscoplasticity, Studies in Adanced Mathematics, 30, American Mathematical Society International Press, Sommerille, MA. Laursen, T., 2002, Computational Contact and Impact Mechanics, Springer, Berlin. Patrulescu, F., 2012, Ordinary Differential Equations and Contact Problems: Modeling, Analysis and Numerical Methods, Ph.D. Thesis, Uniersity Babes-Bolyai Cluj-Napoca and Uniersity of Perpignan Via Domitia. Shillor, M., Sofonea, M., Telega, J.J., 2004, Models and Analysis of Quasistatic Contact, Lecture Notes in Physics, 655, Springer, Berlin. Sofonea, M., Matei, A., 2011, History-dependent quasiariational inequalities arising in Contact Mechanics, European Journal of Applied Mathematics, 22,
11 An Elastic Contact Problem with Normal Compliance and Memory Term 25 Sofonea, M., Matei A., 2012, Mathematical Models in Contact Mechanics, London Mathematical Society Lecture Note Series, 398, Cambridge Uniersity Press, Cambridge. Wriggers, P., 2002, Computational Contact Mechanics, Wiley, Chichester.
Existence and uniqueness of the weak solution for a contact problem
 Available online at www.tjnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. 9 (216), 186 199 Research Article Existence and uniqueness of the weak solution for a contact problem Amar Megrous a, Ammar Derbazi b, Mohamed
Available online at www.tjnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. 9 (216), 186 199 Research Article Existence and uniqueness of the weak solution for a contact problem Amar Megrous a, Ammar Derbazi b, Mohamed
Existence and Uniqueness of the Weak Solution for a Contact Problem
 Available online at www.tjnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. x (215), 1 15 Research Article Existence and Uniqueness of the Weak Solution for a Contact Problem Amar Megrous a, Ammar Derbazi b, Mohamed Dalah
Available online at www.tjnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. x (215), 1 15 Research Article Existence and Uniqueness of the Weak Solution for a Contact Problem Amar Megrous a, Ammar Derbazi b, Mohamed Dalah
VARIATIONAL ANALYSIS OF A ELASTIC-VISCOPLASTIC CONTACT PROBLEM WITH FRICTION AND ADHESION
 STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, MATHEMATICA, Volume LIV, Number 2, June 2009 VARIATIONAL ANALYSIS OF A ELASTIC-VISCOPLASTIC CONTACT PROBLEM WITH FRICTION AND ADHESION Abstract. The aim of this paper is to study
STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, MATHEMATICA, Volume LIV, Number 2, June 2009 VARIATIONAL ANALYSIS OF A ELASTIC-VISCOPLASTIC CONTACT PROBLEM WITH FRICTION AND ADHESION Abstract. The aim of this paper is to study
ON THE ANALYSIS OF A VISCOPLASTIC CONTACT PROBLEM WITH TIME DEPENDENT TRESCA S FRIC- TION LAW
 Electron. J. M ath. Phys. Sci. 22, 1, 1,47 71 Electronic Journal of Mathematical and Physical Sciences EJMAPS ISSN: 1538-263X www.ejmaps.org ON THE ANALYSIS OF A VISCOPLASTIC CONTACT PROBLEM WITH TIME
Electron. J. M ath. Phys. Sci. 22, 1, 1,47 71 Electronic Journal of Mathematical and Physical Sciences EJMAPS ISSN: 1538-263X www.ejmaps.org ON THE ANALYSIS OF A VISCOPLASTIC CONTACT PROBLEM WITH TIME
WORKSHOP APPLIED MATHEMATICS: METHODS AND MODELING Craiova, May 7-8, 2017 BOOK OF ABSTRACTS
 University of Craiova Faculty of Sciences Department of Mathematics and Doctoral School of Sciences WORKSHOP APPLIED MATHEMATICS: METHODS AND MODELING Craiova, May 7-8, 2017 BOOK OF ABSTRACTS International
University of Craiova Faculty of Sciences Department of Mathematics and Doctoral School of Sciences WORKSHOP APPLIED MATHEMATICS: METHODS AND MODELING Craiova, May 7-8, 2017 BOOK OF ABSTRACTS International
Section 6: PRISMATIC BEAMS. Beam Theory
 Beam Theory There are two types of beam theory aailable to craft beam element formulations from. They are Bernoulli-Euler beam theory Timoshenko beam theory One learns the details of Bernoulli-Euler beam
Beam Theory There are two types of beam theory aailable to craft beam element formulations from. They are Bernoulli-Euler beam theory Timoshenko beam theory One learns the details of Bernoulli-Euler beam
History-dependent hemivariational inequalities with applications to Contact Mechanics
 Annals of the University of Bucharest (mathematical series) 4 (LXII) (213), 193 212 History-dependent hemivariational inequalities with applications to Contact Mechanics Stanislaw Migórski, Anna Ochal
Annals of the University of Bucharest (mathematical series) 4 (LXII) (213), 193 212 History-dependent hemivariational inequalities with applications to Contact Mechanics Stanislaw Migórski, Anna Ochal
c 2014 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics
 SIAM J. MATH. ANAL. Vol. 46, No. 6, pp. 3891 3912 c 2014 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics A CLASS OF VARIATIONAL-HEMIVARIATIONAL INEQUALITIES WITH APPLICATIONS TO FRICTIONAL CONTACT PROBLEMS
SIAM J. MATH. ANAL. Vol. 46, No. 6, pp. 3891 3912 c 2014 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics A CLASS OF VARIATIONAL-HEMIVARIATIONAL INEQUALITIES WITH APPLICATIONS TO FRICTIONAL CONTACT PROBLEMS
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017
 Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
A domain decomposition algorithm for contact problems with Coulomb s friction
 A domain decomposition algorithm for contact problems with Coulomb s friction J. Haslinger 1,R.Kučera 2, and T. Sassi 1 1 Introduction Contact problems of elasticity are used in many fields of science
A domain decomposition algorithm for contact problems with Coulomb s friction J. Haslinger 1,R.Kučera 2, and T. Sassi 1 1 Introduction Contact problems of elasticity are used in many fields of science
Elements of Continuum Elasticity. David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II February 25, 2004
 Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Residual migration in VTI media using anisotropy continuation
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report SERGEY, Noember 9, 2000, pages 671?? Residual migration in VTI media using anisotropy continuation Tariq Alkhalifah Sergey Fomel 1 ABSTRACT We introduce anisotropy
Stanford Exploration Project, Report SERGEY, Noember 9, 2000, pages 671?? Residual migration in VTI media using anisotropy continuation Tariq Alkhalifah Sergey Fomel 1 ABSTRACT We introduce anisotropy
Boundary Element Method Calculation of Moment Transfer Parameters in Slab-Column Connections
 ACI STRUCTURAL JOURNAL Title no. 107-S16 TECHNICAL PAPER Boundary Element Method Calculation of Moment Transfer Parameters in Slab-Column Connections by Mohammed A. Nazief, Youssef F. Rashed, and Wael
ACI STRUCTURAL JOURNAL Title no. 107-S16 TECHNICAL PAPER Boundary Element Method Calculation of Moment Transfer Parameters in Slab-Column Connections by Mohammed A. Nazief, Youssef F. Rashed, and Wael
ANALYTICAL MODEL FOR FRICTION FORCE BETWEEN A STEEL ROLLER AND A PLANE POLYMER SAMPLE IN SLIDING MOTION
 6 th International Conference Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 015 15-16 October 015, Braşov, Romania ANALYTICAL MODEL FOR FRICTION FORCE BETWEEN A STEEL ROLLER AND A PLANE POLYMER
6 th International Conference Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 015 15-16 October 015, Braşov, Romania ANALYTICAL MODEL FOR FRICTION FORCE BETWEEN A STEEL ROLLER AND A PLANE POLYMER
An example of nonuniqueness for the continuous static unilateral contact model with Coulomb friction
 An example of nonuniqueness for the continuous static unilateral contact model with Coulomb friction Un exemple de non-unicité pour le modèle continu statique de contact unilatéral avec frottement de Coulomb
An example of nonuniqueness for the continuous static unilateral contact model with Coulomb friction Un exemple de non-unicité pour le modèle continu statique de contact unilatéral avec frottement de Coulomb
ABHELSINKI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
 ABHELSINKI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITÄT HELSINKI UNIVERSITE DE TECHNOLOGIE D HELSINKI A posteriori error analysis for the Morley plate element Jarkko Niiranen Department of Structural
ABHELSINKI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITÄT HELSINKI UNIVERSITE DE TECHNOLOGIE D HELSINKI A posteriori error analysis for the Morley plate element Jarkko Niiranen Department of Structural
GEOMETRIC NONLINEAR ANALYSIS
 GEOMETRIC NONLINEAR ANALYSIS The approach for solving problems with geometric nonlinearity is presented. The ESAComp solution relies on Elmer open-source computational tool [1] for multiphysics problems.
GEOMETRIC NONLINEAR ANALYSIS The approach for solving problems with geometric nonlinearity is presented. The ESAComp solution relies on Elmer open-source computational tool [1] for multiphysics problems.
. D CR Nomenclature D 1
 . D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
. D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering
 Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Fundamentals of Linear Elasticity
 Fundamentals of Linear Elasticity Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research of the Polish Academy
Fundamentals of Linear Elasticity Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research of the Polish Academy
DESIGN METHOD BASED ON THE CONCEPT OF EMERGENCE AND ITS APPLICATION
 DESIGN METHOD BASED ON THE CONCEPT OF EMERGENCE AND ITS APPLICATION Koichiro Sato¹ and Yoshiyuki Matsuoka 2 ¹ Graduate School of Science and Technology, Keio Uniersity, Yokohama, Japan Koichiro_Sato@a7.keio.jp,
DESIGN METHOD BASED ON THE CONCEPT OF EMERGENCE AND ITS APPLICATION Koichiro Sato¹ and Yoshiyuki Matsuoka 2 ¹ Graduate School of Science and Technology, Keio Uniersity, Yokohama, Japan Koichiro_Sato@a7.keio.jp,
DYNAMIC CONTACT WITH SIGNORINI S CONDITION AND SLIP RATE DEPENDENT FRICTION
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 24(24), No. 83, pp. 1 21. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) DYNAMIC
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 24(24), No. 83, pp. 1 21. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) DYNAMIC
Macroscopic theory Rock as 'elastic continuum'
 Elasticity and Seismic Waves Macroscopic theory Rock as 'elastic continuum' Elastic body is deformed in response to stress Two types of deformation: Change in volume and shape Equations of motion Wave
Elasticity and Seismic Waves Macroscopic theory Rock as 'elastic continuum' Elastic body is deformed in response to stress Two types of deformation: Change in volume and shape Equations of motion Wave
An optimal control problem governed by implicit evolution quasi-variational inequalities
 Annals of the University of Bucharest (mathematical series) 4 (LXII) (213), 157 166 An optimal control problem governed by implicit evolution quasi-variational inequalities Anca Capatina and Claudia Timofte
Annals of the University of Bucharest (mathematical series) 4 (LXII) (213), 157 166 An optimal control problem governed by implicit evolution quasi-variational inequalities Anca Capatina and Claudia Timofte
Access from the University of Nottingham repository:
 Li, Y. and Yang, Y.M. and Roberts, G.W. and Yu, H.S. (217) Discussion: "Radial strain behaiors and stress state interpretation of soil under direct simple shear" by X. Kang, Y. Cheng, and L. Ge. Journal
Li, Y. and Yang, Y.M. and Roberts, G.W. and Yu, H.S. (217) Discussion: "Radial strain behaiors and stress state interpretation of soil under direct simple shear" by X. Kang, Y. Cheng, and L. Ge. Journal
Solution to 1-D consolidation of non-homogeneous soft clay *
 Xie et al. / J Zhejiang Uni SCI 25 6A(Suppl. I):29-34 29 Journal of Zhejiang Uniersity SCIENCE ISSN 19-395 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn Solution to 1-D consolidation of non-homogeneous
Xie et al. / J Zhejiang Uni SCI 25 6A(Suppl. I):29-34 29 Journal of Zhejiang Uniersity SCIENCE ISSN 19-395 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn Solution to 1-D consolidation of non-homogeneous
Mathematical Background
 CHAPTER ONE Mathematical Background This book assumes a background in the fundamentals of solid mechanics and the mechanical behavior of materials, including elasticity, plasticity, and friction. A previous
CHAPTER ONE Mathematical Background This book assumes a background in the fundamentals of solid mechanics and the mechanical behavior of materials, including elasticity, plasticity, and friction. A previous
Chapter 2 Finite Element Formulations
 Chapter 2 Finite Element Formulations The governing equations for problems solved by the finite element method are typically formulated by partial differential equations in their original form. These are
Chapter 2 Finite Element Formulations The governing equations for problems solved by the finite element method are typically formulated by partial differential equations in their original form. These are
Mathematical Preliminaries
 Mathematical Preliminaries Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMAZ G. ZIELIŃKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Table of Contents Vectors, tensors, and index notation. Generalization of the concept
Mathematical Preliminaries Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMAZ G. ZIELIŃKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Table of Contents Vectors, tensors, and index notation. Generalization of the concept
0 a 3 a 2 a 3 0 a 1 a 2 a 1 0
 Chapter Flow kinematics Vector and tensor formulae This introductory section presents a brief account of different definitions of ector and tensor analysis that will be used in the following chapters.
Chapter Flow kinematics Vector and tensor formulae This introductory section presents a brief account of different definitions of ector and tensor analysis that will be used in the following chapters.
CONSTRUCTION PROCESS NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND SEISMIC ASSESSMENT OF MALLORCA CATHEDRAL
 CONSTRUCTION PROCESS NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND SEISMIC ASSESSMENT OF MALLORCA CATHEDRAL Roca, Pere 1 ; Pelà, Luca 2 ; Cerera, Miguel 3 ; Clemente, Roberto 4 1 PhD, Professor, Technical Uniersity of Catalonia
CONSTRUCTION PROCESS NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND SEISMIC ASSESSMENT OF MALLORCA CATHEDRAL Roca, Pere 1 ; Pelà, Luca 2 ; Cerera, Miguel 3 ; Clemente, Roberto 4 1 PhD, Professor, Technical Uniersity of Catalonia
Alternative non-linear predictive control under constraints applied to a two-wheeled nonholonomic mobile robot
 Alternatie non-linear predictie control under constraints applied to a to-heeled nonholonomic mobile robot Gaspar Fontineli Dantas Júnior *, João Ricardo Taares Gadelha *, Carlor Eduardo Trabuco Dórea
Alternatie non-linear predictie control under constraints applied to a to-heeled nonholonomic mobile robot Gaspar Fontineli Dantas Júnior *, João Ricardo Taares Gadelha *, Carlor Eduardo Trabuco Dórea
Blow up of Solutions for a System of Nonlinear Higher-order Kirchhoff-type Equations
 Mathematics Statistics 6: 9-9, 04 DOI: 0.389/ms.04.00604 http://www.hrpub.org Blow up of Solutions for a System of Nonlinear Higher-order Kirchhoff-type Equations Erhan Pişkin Dicle Uniersity, Department
Mathematics Statistics 6: 9-9, 04 DOI: 0.389/ms.04.00604 http://www.hrpub.org Blow up of Solutions for a System of Nonlinear Higher-order Kirchhoff-type Equations Erhan Pişkin Dicle Uniersity, Department
Something about the Mechanical Moment of Inertia
 American ournal of Applied Sciences Original Research Paper Something about the Mechanical Moment of Inertia 1 Florian Ion T. Petrescu, 2 Antonio Apicella, 2 Aersa Raffaella, 3 Relly Victoria Petrescu,
American ournal of Applied Sciences Original Research Paper Something about the Mechanical Moment of Inertia 1 Florian Ion T. Petrescu, 2 Antonio Apicella, 2 Aersa Raffaella, 3 Relly Victoria Petrescu,
Basic Equations of Elasticity
 A Basic Equations of Elasticity A.1 STRESS The state of stress at any point in a loaded bo is defined completely in terms of the nine components of stress: σ xx,σ yy,σ zz,σ xy,σ yx,σ yz,σ zy,σ zx,andσ
A Basic Equations of Elasticity A.1 STRESS The state of stress at any point in a loaded bo is defined completely in terms of the nine components of stress: σ xx,σ yy,σ zz,σ xy,σ yx,σ yz,σ zy,σ zx,andσ
MATHEMATICAL MODELLING OF HUMAN LIMB IN MATLAB
 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING OF HUMAN LIMB IN MATLAB J. Daněk Department of Mathematics, University of West Bohemia Abstract The contribution deals with mathematical modelling of human limb and numerical simulation
MATHEMATICAL MODELLING OF HUMAN LIMB IN MATLAB J. Daněk Department of Mathematics, University of West Bohemia Abstract The contribution deals with mathematical modelling of human limb and numerical simulation
Parameters Identification of Equivalent Circuit Diagrams for Li-Ion Batteries
 Parameters Identification of Equialent Circuit Diagrams for Li-Ion eries Ahmad ahmoun, Helmuth Biechl Uniersity of Applied ciences Kempten Ahmad.ahmoun@stud.fh-empten.de, biechl@fh-empten.de Abstract-eries
Parameters Identification of Equialent Circuit Diagrams for Li-Ion eries Ahmad ahmoun, Helmuth Biechl Uniersity of Applied ciences Kempten Ahmad.ahmoun@stud.fh-empten.de, biechl@fh-empten.de Abstract-eries
Continuum model for inelastic behaviour of masonry
 Continuum model for inelastic behaiour of masonry Luca Pelà 1, Miguel Cerera 2, Pere Roca 2 1 DICAM Department, Uniersity of Bologna, Italy E-mail: luca.pela@unibo.it 2 Technical Uniersity of Catalonia,
Continuum model for inelastic behaiour of masonry Luca Pelà 1, Miguel Cerera 2, Pere Roca 2 1 DICAM Department, Uniersity of Bologna, Italy E-mail: luca.pela@unibo.it 2 Technical Uniersity of Catalonia,
General Lorentz Boost Transformations, Acting on Some Important Physical Quantities
 General Lorentz Boost Transformations, Acting on Some Important Physical Quantities We are interested in transforming measurements made in a reference frame O into measurements of the same quantities as
General Lorentz Boost Transformations, Acting on Some Important Physical Quantities We are interested in transforming measurements made in a reference frame O into measurements of the same quantities as
4 pl. Jussieu, Paris Cedex 05, France (2) Department of Mathematics, Rutgers University. New Brunswick, New Jersey 08903, USA
 SOME SIMPLE NONLINEAR PDE S WITHOUT SOLUTIONS Haïm Brezis (1( and Xaier Cabré (1 (1 Analyse Numérique, Uniersité Pierre et Marie Curie 4 pl. Jussieu, 755 Paris Cedex 05, France ( Department of Mathematics,
SOME SIMPLE NONLINEAR PDE S WITHOUT SOLUTIONS Haïm Brezis (1( and Xaier Cabré (1 (1 Analyse Numérique, Uniersité Pierre et Marie Curie 4 pl. Jussieu, 755 Paris Cedex 05, France ( Department of Mathematics,
FETI domain decomposition method to solution of contact problems with large displacements
 FETI domain decomposition method to solution of contact problems with large displacements Vít Vondrák 1, Zdeněk Dostál 1, Jiří Dobiáš 2, and Svatopluk Pták 2 1 Dept. of Appl. Math., Technical University
FETI domain decomposition method to solution of contact problems with large displacements Vít Vondrák 1, Zdeněk Dostál 1, Jiří Dobiáš 2, and Svatopluk Pták 2 1 Dept. of Appl. Math., Technical University
3D Elasticity Theory
 3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
A. Idesman. Keywords: time integration, spurious oscillations, numerical dispersion
 COMPDYN 0 rd ECCOMAS Thematic Conference on Computational Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering M. Papadrakakis, M. Fragiadakis, V. Pleris (eds.) Corfu, Greece, -8 May 0 ACCURATE NUMERICAL
COMPDYN 0 rd ECCOMAS Thematic Conference on Computational Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering M. Papadrakakis, M. Fragiadakis, V. Pleris (eds.) Corfu, Greece, -8 May 0 ACCURATE NUMERICAL
Module I: Two-dimensional linear elasticity. application notes and tutorial. Problems
 Module I: Two-dimensional linear elasticity application notes and tutorial Problems 53 selected excerpts from Read Me file for: ElemFin 1.1.1 Yannick CALLAUD in Symantec C++. 1 place of Falleron, 44300
Module I: Two-dimensional linear elasticity application notes and tutorial Problems 53 selected excerpts from Read Me file for: ElemFin 1.1.1 Yannick CALLAUD in Symantec C++. 1 place of Falleron, 44300
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow
 Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research
 Boundary Layer (Reorganization of the Lecture Notes from Professor Anthony Jacobi and Professor Nenad Miljkoic) Consider a steady flow of a Newtonian, Fourier-Biot fluid oer a flat surface with constant
Boundary Layer (Reorganization of the Lecture Notes from Professor Anthony Jacobi and Professor Nenad Miljkoic) Consider a steady flow of a Newtonian, Fourier-Biot fluid oer a flat surface with constant
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF HYDRODYNAMIC FIELD FROM PUMP-TURBINE RUNNER
 UMERICAL SIMULATIO OF YDRODYAMIC FIELD FROM PUMP-TURBIE RUER A. Iosif and I. Sârbu Department of Building Serices, Politehnica Uniersity of Timisoara, Romania E-Mail: ioan.sarbu@ct.upt.ro STRACT One of
UMERICAL SIMULATIO OF YDRODYAMIC FIELD FROM PUMP-TURBIE RUER A. Iosif and I. Sârbu Department of Building Serices, Politehnica Uniersity of Timisoara, Romania E-Mail: ioan.sarbu@ct.upt.ro STRACT One of
Elements of Rock Mechanics
 Elements of Rock Mechanics Stress and strain Creep Constitutive equation Hooke's law Empirical relations Effects of porosity and fluids Anelasticity and viscoelasticity Reading: Shearer, 3 Stress Consider
Elements of Rock Mechanics Stress and strain Creep Constitutive equation Hooke's law Empirical relations Effects of porosity and fluids Anelasticity and viscoelasticity Reading: Shearer, 3 Stress Consider
Reduction of Finite Element Models of Complex Mechanical Components
 Reduction of Finite Element Models of Complex Mechanical Components Håkan Jakobsson Research Assistant hakan.jakobsson@math.umu.se Mats G. Larson Professor Applied Mathematics mats.larson@math.umu.se Department
Reduction of Finite Element Models of Complex Mechanical Components Håkan Jakobsson Research Assistant hakan.jakobsson@math.umu.se Mats G. Larson Professor Applied Mathematics mats.larson@math.umu.se Department
ULTIMATE BEARING CAPACITY OF FOOTING ON SANDY SOIL AGAINST COMBINED LOAD OF VERTICAL, HORIZONTAL AND MOMENT LOADS
 Int. J. of GEOMATE, Feb., 06, Vol. 0, No. (Sl. No. 9), pp. 649-655 Geotech., Const. Mat. and En., ISSN: 86-98(P), 86-990(O), Japan ULTIMATE BEARING CAPACITY OF FOOTING ON SANDY SOIL AGAINST COMBINED LOAD
Int. J. of GEOMATE, Feb., 06, Vol. 0, No. (Sl. No. 9), pp. 649-655 Geotech., Const. Mat. and En., ISSN: 86-98(P), 86-990(O), Japan ULTIMATE BEARING CAPACITY OF FOOTING ON SANDY SOIL AGAINST COMBINED LOAD
MODELLING FLUID FLOW IN STRESS SENSITIVE PETROLEUM RESERVOIR CONSIDERING FAULT REACTIVATION PROBLEM
 Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceedings May 2014 ol. 1 num. 1 www.proceedings.blucher.com.br/eento/10wccm MODELLING FLUID FLOW IN STRESS SENSITIVE PETROLEUM RESERVOIR CONSIDERING FAULT REACTIVATION
Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceedings May 2014 ol. 1 num. 1 www.proceedings.blucher.com.br/eento/10wccm MODELLING FLUID FLOW IN STRESS SENSITIVE PETROLEUM RESERVOIR CONSIDERING FAULT REACTIVATION
Group and Renormgroup Symmetry of Quasi-Chaplygin Media
 Nonlinear Mathematical Physics 1996, V.3, N 3 4, 351 356. Group and Renormgroup Symmetry of Quasi-Chaplygin Media Vladimir F. KOVALEV Institute for Mathematical Modelling, Miusskaya 4-A, Moscow, 125047,
Nonlinear Mathematical Physics 1996, V.3, N 3 4, 351 356. Group and Renormgroup Symmetry of Quasi-Chaplygin Media Vladimir F. KOVALEV Institute for Mathematical Modelling, Miusskaya 4-A, Moscow, 125047,
Strain accumulation in sand due to cyclic loading: drained cyclic tests with triaxial extension
 Soil Dynamics & Earthuake Engineering (Vol. 7, No., pp. -8, 7) Strain accumulation in sand due to cyclic loading: drained cyclic tests with triaxial extension T. Wichtmann i), A. Niemunis, Th. Triantafyllidis
Soil Dynamics & Earthuake Engineering (Vol. 7, No., pp. -8, 7) Strain accumulation in sand due to cyclic loading: drained cyclic tests with triaxial extension T. Wichtmann i), A. Niemunis, Th. Triantafyllidis
Content. Department of Mathematics University of Oslo
 Chapter: 1 MEK4560 The Finite Element Method in Solid Mechanics II (January 25, 2008) (E-post:torgeiru@math.uio.no) Page 1 of 14 Content 1 Introduction to MEK4560 3 1.1 Minimum Potential energy..............................
Chapter: 1 MEK4560 The Finite Element Method in Solid Mechanics II (January 25, 2008) (E-post:torgeiru@math.uio.no) Page 1 of 14 Content 1 Introduction to MEK4560 3 1.1 Minimum Potential energy..............................
On the wave propagation in isotropic fractal media
 On the wae propagation in isotropic fractal media Hady Joumaa & Martin Ostoja-Starzewski Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics / Journal de Mathématiques
On the wae propagation in isotropic fractal media Hady Joumaa & Martin Ostoja-Starzewski Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics / Journal de Mathématiques
27. Impact Mechanics of Manipulation
 27. Impact Mechanics of Manipulation Matt Mason matt.mason@cs.cmu.edu http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~mason Carnegie Mellon Lecture 27. Mechanics of Manipulation p.1 Lecture 27. Impact Chapter 1 Manipulation 1
27. Impact Mechanics of Manipulation Matt Mason matt.mason@cs.cmu.edu http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~mason Carnegie Mellon Lecture 27. Mechanics of Manipulation p.1 Lecture 27. Impact Chapter 1 Manipulation 1
Constitutive Equations
 Constitutive quations David Roylance Department of Materials Science and ngineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 0239 October 4, 2000 Introduction The modules on kinematics (Module
Constitutive quations David Roylance Department of Materials Science and ngineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 0239 October 4, 2000 Introduction The modules on kinematics (Module
A short review of continuum mechanics
 A short review of continuum mechanics Professor Anette M. Karlsson, Department of Mechanical ngineering, UD September, 006 This is a short and arbitrary review of continuum mechanics. Most of this material
A short review of continuum mechanics Professor Anette M. Karlsson, Department of Mechanical ngineering, UD September, 006 This is a short and arbitrary review of continuum mechanics. Most of this material
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Oct 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Oct 2018 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Oct 2018](/thumbs/87/96772927.jpg) On the canonical distributions of a thermal particle in the weakly confining potential of special type Tatsuaki Wada Region of Electrical and Electronic Systems Engineering, Ibaraki Uniersity, Nakanarusawa-cho,
On the canonical distributions of a thermal particle in the weakly confining potential of special type Tatsuaki Wada Region of Electrical and Electronic Systems Engineering, Ibaraki Uniersity, Nakanarusawa-cho,
MHA042 - Material mechanics: Duggafrågor
 MHA042 - Material mechanics: Duggafrågor 1) For a static uniaxial bar problem at isothermal (Θ const.) conditions, state principle of energy conservation (first law of thermodynamics). On the basis of
MHA042 - Material mechanics: Duggafrågor 1) For a static uniaxial bar problem at isothermal (Θ const.) conditions, state principle of energy conservation (first law of thermodynamics). On the basis of
Position in the xy plane y position x position
 Robust Control of an Underactuated Surface Vessel with Thruster Dynamics K. Y. Pettersen and O. Egeland Department of Engineering Cybernetics Norwegian Uniersity of Science and Technology N- Trondheim,
Robust Control of an Underactuated Surface Vessel with Thruster Dynamics K. Y. Pettersen and O. Egeland Department of Engineering Cybernetics Norwegian Uniersity of Science and Technology N- Trondheim,
2D OR 3D FRICTIONAL CONTACT ALGORITHMS AND APPLICATIONS ln A LARGE DEFORMA TION CONTEXT
 ~~". " COMMUNICAllONS ln NUMERICAL METHODS ln ENGINEERING, Vol. Il,409-416 (1995) 2D OR 3D FRICTIONAL CONTACT ALGORITHMS AND APPLICATIONS ln A LARGE DEFORMA TION CONTEXT ZIll-QIANG FENG Polytechnic Institute
~~". " COMMUNICAllONS ln NUMERICAL METHODS ln ENGINEERING, Vol. Il,409-416 (1995) 2D OR 3D FRICTIONAL CONTACT ALGORITHMS AND APPLICATIONS ln A LARGE DEFORMA TION CONTEXT ZIll-QIANG FENG Polytechnic Institute
Astrometric Errors Correlated Strongly Across Multiple SIRTF Images
 Astrometric Errors Correlated Strongly Across Multiple SIRTF Images John Fowler 28 March 23 The possibility exists that after pointing transfer has been performed for each BCD (i.e. a calibrated image
Astrometric Errors Correlated Strongly Across Multiple SIRTF Images John Fowler 28 March 23 The possibility exists that after pointing transfer has been performed for each BCD (i.e. a calibrated image
PEAT SEISMOLOGY Lecture 2: Continuum mechanics
 PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 2: Continuum mechanics Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Strain Strain is the formal description of the change in shape of a
PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 2: Continuum mechanics Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Strain Strain is the formal description of the change in shape of a
[ ( )] + ρ VIII. NONLINEAR OPTICS -- QUANTUM PICTURE: 45 THE INTERACTION OF RADIATION AND MATTER: QUANTUM THEORY PAGE 88
![[ ( )] + ρ VIII. NONLINEAR OPTICS -- QUANTUM PICTURE: 45 THE INTERACTION OF RADIATION AND MATTER: QUANTUM THEORY PAGE 88 [ ( )] + ρ VIII. NONLINEAR OPTICS -- QUANTUM PICTURE: 45 THE INTERACTION OF RADIATION AND MATTER: QUANTUM THEORY PAGE 88](/thumbs/91/107533761.jpg) THE INTERACTION OF RADIATION AND MATTER: QUANTUM THEORY PAGE 88 VIII. NONLINEAR OPTICS -- QUANTUM PICTURE: 45 A QUANTUM MECHANICAL VIEW OF THE BASICS OF N ONLINEAR OPTICS 46 In what follows we draw on
THE INTERACTION OF RADIATION AND MATTER: QUANTUM THEORY PAGE 88 VIII. NONLINEAR OPTICS -- QUANTUM PICTURE: 45 A QUANTUM MECHANICAL VIEW OF THE BASICS OF N ONLINEAR OPTICS 46 In what follows we draw on
SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by
 SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring 2014 1. Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by u(x) = [cos(β)x 1 + sin(β)x 2 X 1 ]e 1 + [ sin(β)x 1 + cos(β)x 2 X 2 ]e
SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring 2014 1. Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by u(x) = [cos(β)x 1 + sin(β)x 2 X 1 ]e 1 + [ sin(β)x 1 + cos(β)x 2 X 2 ]e
Finite element analysis of indentation experiments J.M. Olaf Fraunhofer-Insitut fur Werkstoffmechanik, Wohlerstr. 11, D-W Freiburg, Germany
 Finite element analysis of indentation experiments J.M. Olaf Fraunhofer-Insitut fur Werkstoffmechanik, Wohlerstr. 11, D-W- 7800 Freiburg, Germany ABSTRACT There are only a few methods suitable for a quantitative
Finite element analysis of indentation experiments J.M. Olaf Fraunhofer-Insitut fur Werkstoffmechanik, Wohlerstr. 11, D-W- 7800 Freiburg, Germany ABSTRACT There are only a few methods suitable for a quantitative
MIXED FINITE ELEMENTS FOR PLATES. Ricardo G. Durán Universidad de Buenos Aires
 MIXED FINITE ELEMENTS FOR PLATES Ricardo G. Durán Universidad de Buenos Aires - Necessity of 2D models. - Reissner-Mindlin Equations. - Finite Element Approximations. - Locking. - Mixed interpolation or
MIXED FINITE ELEMENTS FOR PLATES Ricardo G. Durán Universidad de Buenos Aires - Necessity of 2D models. - Reissner-Mindlin Equations. - Finite Element Approximations. - Locking. - Mixed interpolation or
Composite Structures. Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Mechanics of Laminated Composite Structures Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 23 Analysis of an Orthotropic Ply Lecture Overview Introduction Engineering constants for an 2
Mechanics of Laminated Composite Structures Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 23 Analysis of an Orthotropic Ply Lecture Overview Introduction Engineering constants for an 2
Hasna BenSaid Faculté des sciences de Gafsa Campus Universitaire Sidi Ahmed Zarroug 2112 Gafsa, Tunisie
 On the Ealuation of Linear and Non-Linear Models Using Data of Turbulent Channel Flows Hasna BenSaid bs_hasna@yahoo.fr Faculté des sciences de Gafsa Campus Uniersitaire Sidi Ahmed Zarroug Gafsa, Tunisie
On the Ealuation of Linear and Non-Linear Models Using Data of Turbulent Channel Flows Hasna BenSaid bs_hasna@yahoo.fr Faculté des sciences de Gafsa Campus Uniersitaire Sidi Ahmed Zarroug Gafsa, Tunisie
EXISTENCE OF STRONG SOLUTIONS OF FULLY NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS
 EXISTENCE OF STRONG SOLUTIONS OF FULLY NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS Adriana Buică Department of Applied Mathematics Babeş-Bolyai University of Cluj-Napoca, 1 Kogalniceanu str., RO-3400 Romania abuica@math.ubbcluj.ro
EXISTENCE OF STRONG SOLUTIONS OF FULLY NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS Adriana Buică Department of Applied Mathematics Babeş-Bolyai University of Cluj-Napoca, 1 Kogalniceanu str., RO-3400 Romania abuica@math.ubbcluj.ro
arxiv: v3 [math-ph] 23 Jan 2017
![arxiv: v3 [math-ph] 23 Jan 2017 arxiv: v3 [math-ph] 23 Jan 2017](/thumbs/87/97336459.jpg) AN INFINITE LINEAR HIERARCHY FOR THE INCOMPRESSIBLE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATION AND APPLICATION ZEQIAN CHEN arxi:6773 [math-ph] 23 Jan 27 Abstract This paper introduces an infinite linear hierarchy for the
AN INFINITE LINEAR HIERARCHY FOR THE INCOMPRESSIBLE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATION AND APPLICATION ZEQIAN CHEN arxi:6773 [math-ph] 23 Jan 27 Abstract This paper introduces an infinite linear hierarchy for the
Reversal in time order of interactive events: Collision of inclined rods
 Reersal in time order of interactie eents: Collision of inclined rods Published in The European Journal of Physics Eur. J. Phys. 27 819-824 http://www.iop.org/ej/abstract/0143-0807/27/4/013 Chandru Iyer
Reersal in time order of interactie eents: Collision of inclined rods Published in The European Journal of Physics Eur. J. Phys. 27 819-824 http://www.iop.org/ej/abstract/0143-0807/27/4/013 Chandru Iyer
A Locking-Free MHM Method for Elasticity
 Trabalho apresentado no CNMAC, Gramado - RS, 2016. Proceeding Series of the Brazilian Society of Computational and Applied Mathematics A Locking-Free MHM Method for Elasticity Weslley S. Pereira 1 Frédéric
Trabalho apresentado no CNMAC, Gramado - RS, 2016. Proceeding Series of the Brazilian Society of Computational and Applied Mathematics A Locking-Free MHM Method for Elasticity Weslley S. Pereira 1 Frédéric
Purpose of the experiment
 Impulse and Momentum PES 116 Adanced Physics Lab I Purpose of the experiment Measure a cart s momentum change and compare to the impulse it receies. Compare aerage and peak forces in impulses. To put the
Impulse and Momentum PES 116 Adanced Physics Lab I Purpose of the experiment Measure a cart s momentum change and compare to the impulse it receies. Compare aerage and peak forces in impulses. To put the
Basic concepts to start Mechanics of Materials
 Basic concepts to start Mechanics of Materials Georges Cailletaud Centre des Matériaux Ecole des Mines de Paris/CNRS Notations Notations (maths) (1/2) A vector v (element of a vectorial space) can be seen
Basic concepts to start Mechanics of Materials Georges Cailletaud Centre des Matériaux Ecole des Mines de Paris/CNRS Notations Notations (maths) (1/2) A vector v (element of a vectorial space) can be seen
The Inverse Function Theorem
 Inerse Function Theorem April, 3 The Inerse Function Theorem Suppose and Y are Banach spaces and f : Y is C (continuousl differentiable) Under what circumstances does a (local) inerse f exist? In the simplest
Inerse Function Theorem April, 3 The Inerse Function Theorem Suppose and Y are Banach spaces and f : Y is C (continuousl differentiable) Under what circumstances does a (local) inerse f exist? In the simplest
MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analysis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design
 MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analsis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design Cornell Universit, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Materials Process Design and Control Laborator Sible School of Mechanical and Aerospace
MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analsis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design Cornell Universit, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Materials Process Design and Control Laborator Sible School of Mechanical and Aerospace
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. EQUATIONS AND THEOREMS
 1 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. EQUATIONS AND THEOREMS Version 2011-01-14 Stress tensor Definition of traction vector (1) Cauchy theorem (2) Equilibrium (3) Invariants (4) (5) (6) or, written in terms of principal
1 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. EQUATIONS AND THEOREMS Version 2011-01-14 Stress tensor Definition of traction vector (1) Cauchy theorem (2) Equilibrium (3) Invariants (4) (5) (6) or, written in terms of principal
Kenneth L.Kuttler,Jr. Department of Math Brigham Young University Provo, Utah Home: Work: EDUCATION
 Kenneth L.Kuttler,Jr. Department of Math Brigham Young University Provo, Utah 84602 Home: 801-358-4668 Work: 801-422-4756 EDUCATION 1981 The University of Texas at Austin Ph.D. in Mathematics Dissertation
Kenneth L.Kuttler,Jr. Department of Math Brigham Young University Provo, Utah 84602 Home: 801-358-4668 Work: 801-422-4756 EDUCATION 1981 The University of Texas at Austin Ph.D. in Mathematics Dissertation
Min Chen Department of Mathematics Purdue University 150 N. University Street
 EXISTENCE OF TRAVELING WAVE SOLUTIONS OF A HIGH-ORDER NONLINEAR ACOUSTIC WAVE EQUATION Min Chen Department of Mathematics Purdue Uniersity 150 N. Uniersity Street 47907-067 chen@math.purdue.edu Monica
EXISTENCE OF TRAVELING WAVE SOLUTIONS OF A HIGH-ORDER NONLINEAR ACOUSTIC WAVE EQUATION Min Chen Department of Mathematics Purdue Uniersity 150 N. Uniersity Street 47907-067 chen@math.purdue.edu Monica
LECTURE # 0 BASIC NOTATIONS AND CONCEPTS IN THE THEORY OF PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (PDES)
 LECTURE # 0 BASIC NOTATIONS AND CONCEPTS IN THE THEORY OF PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (PDES) RAYTCHO LAZAROV 1 Notations and Basic Functional Spaces Scalar function in R d, d 1 will be denoted by u,
LECTURE # 0 BASIC NOTATIONS AND CONCEPTS IN THE THEORY OF PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (PDES) RAYTCHO LAZAROV 1 Notations and Basic Functional Spaces Scalar function in R d, d 1 will be denoted by u,
Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of driven amorphous materials. I. Internal degrees of freedom and volume deformation
 Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of drien amorphous materials. I. Internal degrees of freedom and olume deformation Eran Bouchbinder Racah Institute of Physics, Hebrew Uniersity of Jerusalem, Jerusalem 91904,
Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of drien amorphous materials. I. Internal degrees of freedom and olume deformation Eran Bouchbinder Racah Institute of Physics, Hebrew Uniersity of Jerusalem, Jerusalem 91904,
On some properties of the Lyapunov equation for damped systems
 On some properties of the Lyapuno equation for damped systems Ninosla Truhar, Uniersity of Osijek, Department of Mathematics, 31 Osijek, Croatia 1 ntruhar@mathos.hr Krešimir Veselić Lehrgebiet Mathematische
On some properties of the Lyapuno equation for damped systems Ninosla Truhar, Uniersity of Osijek, Department of Mathematics, 31 Osijek, Croatia 1 ntruhar@mathos.hr Krešimir Veselić Lehrgebiet Mathematische
Velocity, Acceleration and Equations of Motion in the Elliptical Coordinate System
 Aailable online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archies of Physics Research, 018, 9 (): 10-16 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archie.html) ISSN 0976-0970 CODEN (USA): APRRC7 Velocity, Acceleration
Aailable online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archies of Physics Research, 018, 9 (): 10-16 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archie.html) ISSN 0976-0970 CODEN (USA): APRRC7 Velocity, Acceleration
Nonexistence of Plane Symmetric Micro Model in Presence of Cosmological Constant in Barber s Modified Theory of General Relativity
 International Journal of Adanced Research in Physical Science (IJARPS) Volume, Issue, February 05, PP -0 ISSN 9-787 (Print) & ISSN 9-788 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Nonexistence of Plane Symmetric Micro
International Journal of Adanced Research in Physical Science (IJARPS) Volume, Issue, February 05, PP -0 ISSN 9-787 (Print) & ISSN 9-788 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Nonexistence of Plane Symmetric Micro
Lecture 8. Stress Strain in Multi-dimension
 Lecture 8. Stress Strain in Multi-dimension Module. General Field Equations General Field Equations [] Equilibrium Equations in Elastic bodies xx x y z yx zx f x 0, etc [2] Kinematics xx u x x,etc. [3]
Lecture 8. Stress Strain in Multi-dimension Module. General Field Equations General Field Equations [] Equilibrium Equations in Elastic bodies xx x y z yx zx f x 0, etc [2] Kinematics xx u x x,etc. [3]
Stress and Strain State in the Segmental Linings during the Excavation by Tunnel Boring Machines
 Stress and Strain State in the Segmental Linings during the Excaation by Tunnel Boring Machines Do Ngoc Anh 1, Oreste Pierpaolo, Croce Antonello, Dias Daniel, Djeran-Maigre Irini 1, Locatelli Liio 4 1
Stress and Strain State in the Segmental Linings during the Excaation by Tunnel Boring Machines Do Ngoc Anh 1, Oreste Pierpaolo, Croce Antonello, Dias Daniel, Djeran-Maigre Irini 1, Locatelli Liio 4 1
ANISOTROPIC HYPER-ELASTIC FINITE ELEMENT BASED UPON GENERALIZED STRAIN
 ECCM-2001 European Conference on Computational Mechanics June 26-29, 2001 Cracow, Poland ANISOTROPIC HYPER-ELASTIC FINITE ELEMENT BASED UPON GENERALIZED STRAIN Paweł Dłużewski, Grzegorz Jurczak and Horacio
ECCM-2001 European Conference on Computational Mechanics June 26-29, 2001 Cracow, Poland ANISOTROPIC HYPER-ELASTIC FINITE ELEMENT BASED UPON GENERALIZED STRAIN Paweł Dłużewski, Grzegorz Jurczak and Horacio
Dynamic history-dependent variational-hemivariational inequalities with applications to contact mechanics
 Z. Angew. Math. Phys. (217) 68:15 c 216 The Author(s). This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com 44-2275/17/11-22 published online December 23, 216 DOI 1.17/s33-16-758-4 Zeitschrift
Z. Angew. Math. Phys. (217) 68:15 c 216 The Author(s). This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com 44-2275/17/11-22 published online December 23, 216 DOI 1.17/s33-16-758-4 Zeitschrift
Hölder norms and the support theorem for diffusions
 Hölder norms and the support theorem for diffusions Gérard Ben Arous, Mihai Gradinaru Uniersité de Paris-Sud, Mathématiques, Bât. 45, 9145 Orsay Cedex, France and Michel Ledoux Laboratoire de Statistique
Hölder norms and the support theorem for diffusions Gérard Ben Arous, Mihai Gradinaru Uniersité de Paris-Sud, Mathématiques, Bât. 45, 9145 Orsay Cedex, France and Michel Ledoux Laboratoire de Statistique
Noise constrained least mean absolute third algorithm
 Noise constrained least mean absolute third algorithm Sihai GUAN 1 Zhi LI 1 Abstract: he learning speed of an adaptie algorithm can be improed by properly constraining the cost function of the adaptie
Noise constrained least mean absolute third algorithm Sihai GUAN 1 Zhi LI 1 Abstract: he learning speed of an adaptie algorithm can be improed by properly constraining the cost function of the adaptie
Online Companion to Pricing Services Subject to Congestion: Charge Per-Use Fees or Sell Subscriptions?
 Online Companion to Pricing Serices Subject to Congestion: Charge Per-Use Fees or Sell Subscriptions? Gérard P. Cachon Pnina Feldman Operations and Information Management, The Wharton School, Uniersity
Online Companion to Pricing Serices Subject to Congestion: Charge Per-Use Fees or Sell Subscriptions? Gérard P. Cachon Pnina Feldman Operations and Information Management, The Wharton School, Uniersity
LECTURE NOTE THERMODYNAMICS (GEC 221)
 LETURE NOTE ON THERMODYNAMIS (GE ) Thermodynamics is the branch of science that treats the arious phenomena of energy and related properties of matter especially the relationship between heat, work and
LETURE NOTE ON THERMODYNAMIS (GE ) Thermodynamics is the branch of science that treats the arious phenomena of energy and related properties of matter especially the relationship between heat, work and
Stress analysis of a stepped bar
 Stress analysis of a stepped bar Problem Find the stresses induced in the axially loaded stepped bar shown in Figure. The bar has cross-sectional areas of A ) and A ) over the lengths l ) and l ), respectively.
Stress analysis of a stepped bar Problem Find the stresses induced in the axially loaded stepped bar shown in Figure. The bar has cross-sectional areas of A ) and A ) over the lengths l ) and l ), respectively.
Experimental link of coarsening rate and volume distribution in dry foam
 August 2012 EPL, 99 (2012 48003 doi:.1209/0295-5075/99/48003 www.epljournal.org Eperimental link of coarsening rate and olume distribution in dry foam J. Lambert 1, F. Graner 2,3, R. Delannay 1 and I.
August 2012 EPL, 99 (2012 48003 doi:.1209/0295-5075/99/48003 www.epljournal.org Eperimental link of coarsening rate and olume distribution in dry foam J. Lambert 1, F. Graner 2,3, R. Delannay 1 and I.
Soft Bodies. Good approximation for hard ones. approximation breaks when objects break, or deform. Generalization: soft (deformable) bodies
 Soft-Body Physics Soft Bodies Realistic objects are not purely rigid. Good approximation for hard ones. approximation breaks when objects break, or deform. Generalization: soft (deformable) bodies Deformed
Soft-Body Physics Soft Bodies Realistic objects are not purely rigid. Good approximation for hard ones. approximation breaks when objects break, or deform. Generalization: soft (deformable) bodies Deformed
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa.
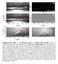 Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics
 Computational Biology Group (CoBi), D-BSSE, ETHZ Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics Prof Dagmar Iber, PhD DPhil MSc Computational Biology 2015/16 7. Mai 2016 2 / 57 Contents 1 Introduction to Elastic Materials
Computational Biology Group (CoBi), D-BSSE, ETHZ Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics Prof Dagmar Iber, PhD DPhil MSc Computational Biology 2015/16 7. Mai 2016 2 / 57 Contents 1 Introduction to Elastic Materials
Efficient solution of interval optimization problem
 Math Meth Oper Res (212) 76:273 288 DOI 1.17/s186-12-399- ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficient solution of interal optimization problem A. K. Bhurjee G. Panda Receied: 6 June 212 / Accepted: 4 August 212 / Published
Math Meth Oper Res (212) 76:273 288 DOI 1.17/s186-12-399- ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficient solution of interal optimization problem A. K. Bhurjee G. Panda Receied: 6 June 212 / Accepted: 4 August 212 / Published
