Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics
|
|
|
- Irene Owens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA35) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University
2 Chapter 7 Water Waves
3 For Airy wave, we need to determine three parameters, (A, k, ω). In fact, only two of them, (A, k), need to be determined, since a dispersion relation exists, that will be introduced soon later in this section. Acoskx t 1. Airy wave is a -dimensional cosine function, known as cosine wave, sine wave or linear sinusoidal wave. A -- wave amplitude; H = A -- wave height. λ -- wave length, the distance between two adjacent crests or troughs.
4 . k : the wave number Let t = 0, Airy wave becomes simply a cosine function of x. Acos kx kx n (n is an integer) For n = 1, it corresponds one wave form, that is, x =λ, therefore k K k = wavenumber = π/ [L -1 ]
5 3. ω : circular frequency Let x = 0, Airy wave becomes a cosine function of t. Acost t n (n is an integer) For n = 1, it corresponds one period, t = T = 1/f, therefore f T where T 1 f T = frequency = π/t [T -1 ], e.g. rad/sec
6 4. Phase velocity / Celerity ( c or V p ): wave form moving velocity Let s look at a fixed position in space where at an instant a crest located at. Then the crest moves forward. The duration until another crest arrives at that point is just one wave period. During this period, we can see the wave form moves forward just one wave length. So, velocity the wave form advances is cv p y T MWL A Vp (x,t) = y x h
7 Airy wave is also known as sinusoidal wave. It is expressed as Acoskx t Acos k x t Acos k x ct k where k T T c Phase velocity, wave length, wave period, wave frequency, circular frequency and wave number related with each other as follows: c T k
8 5. Dispersion relation: relation between circular frequency and wave number. Velocity potential ga sin Now, substituting the velocity potential in the linearized free surface condition, it yields kx t cosh k y h cosh Free surface condition g 0 (on y = 0) y t That is the dispersion relation. cosh kh gk sinh kh 0 sinh kh gk gk tanh kh cosh kh kh
9 If we want to calculate the wave number from a given water depth and a given circular frequency, it is difficult to derive an explicit expression. Instead, we can write the dispersion relation in a form below and try to find the intersection of two functions (curves), the left hand side function and the right side function of the equation. h C kh kh g C kh tanh tanh kh C kh 1 tanh kh 1/5 1 kh =f(c) 3 kh
10 Some characteristics of the related hyperbolic functions f deep water shallow water kh 3 kh 1 f kh 0 tanh 1 kh f f f 1 3 y y y cosh cosh sinh k y h cosh kh k y h sinh kh k y h sinh kh e e ky ky ky e kh y h
11 Equating function f 1 (kh) and function f (kh), we can get solution, kh, of the dispersion relation. Geometrically, the solution corresponds the intersection of the two curves of f 1 (kh) and f (kh). C f1 kh kh f kh tanh kh where C g h kh if kh 1, or, h (shallow water) kh sinh kh 1 e tanh kh 1 if kh 3, or, h kh cosh kh 1 e (deep water) (tanh )
12 For a given water depth h, wave dispersion relation gives a correspondence between the wave circular frequency ω and the wave number k. circular frequency (ω) Since c be written as k wave number (k) and k, the dispersion relation can c g h tanh k Therefore, the dispersion relation also give the correspondence between phase velocity (c) and wave length (λ), provided water depth h is given. phase velocity (c) wave length (λ)
13 tanh kh 1 Deep water waves: If kh 3, or, h 3, approximately h, then it results the deep water dispersion relation gk T g c d g k g Therefore, Since h 1 k; T; c, deep water waves are also called short waves..
14 Shallow water waves: If kh 1, or, h 1, that is, h, generally, if h 5, water depth can be considered small enough. Since ghk tanh kh T kh it results shallow water dispersion relation. gh cs gh Therefore, length any more. For h 1 5 k, T, and c does not relate to wave, shallow water waves are also known as long waves.
15 1 h 1 5 h Generally for water depth in between ( or ): 0.08 c h c tanhkh h tanh kh tanh, tanh c c kh h d s h
16 For a fixed water depth, since cs gh is a constant, phase velocity c will decrease with wave lengthλ. That is, longer waves travel faster, and shorter waves travel slower. For waves with fixed wave length, since cd is a constant, phase velocity c will increase with the water depth h. That is, deep water waves travel faster, and shallow water waves travel slower. g h
17 6. Velocity field From velocity potential of the wave flows and dispersion relation, velocity field of the wave flows can be readily derived. ga cosh k y h sin kx t, cosh kh Agk cosh k y h u coskx t x cosh kh cosh ky h A coskx t sinh kh Agk sinh k y h v sin kx t y cosh kh sinh k y h A sin kx t sinh kh gk tanh kh
18 On y = 0 : 1 U 0 A tanh kh kx t cos, V A kx t 0 sin then, velocity can be written relative to that on y = 0, it gives t u U 0 cosh k y h cosh kh, v V 0 sinh k y h sinh kh v V 0 u U 0
19 Shanghai Jiao Tong University For deep water waves, kh 3, we have u U 0 cosh k y h cosh kh e ky, v V 0 sinh k y h sinh kh e ky g k g k
20 u U Shanghai Jiao Tong University For shallow water waves, 0 cosh k y h cosh kh kh 1 1, 0, we have v sinh k y h y 1 V sinh kh h A u kx t kh g h cos, v A 1 sinkx t y h
21 Characteristics of Airy waves deep water shallow water kh 3 kh 1 dispersion relation velocity c d gk g g k u ky e U v V 0 0 e ky cs u U v V 0 ghk 0 gh 1 1 y h
22 7. Particle orbit At time t, fluid particle P takes the position (x P (t), y P (t)), and if we denote its mean position is xp, yp and P(x p,y p ) x P() t xp x P() t y () t y y () t P P P Since velocity is a time derivative of position, that is, x, y,,,, (x,y ) dx u x y t u x y t P up ux, y, t x y dt x y remaining the main first term and integrating the equation, it gives cosh k y h x P x ux, y, tdt x A coskx tdt sinh kh cosh ky h x A sin kx t sinh kh
23 7. Particle orbit At time t, fluid particle P takes the position (x P (t), y P (t)), and if we denote its mean position xp, yp and P(x p,y p ) x P() t xp x P() t y () t y y () t P P P Since velocity is a time derivative of position, that is, x, y,,,, (x,y ) dx u x y t u x y t P up ux, y, t x y dt x y remaining the main first term and integrating the equation, it gives cosh k y h x P x ux, y, tdt x A coskx tdt sinh kh cosh ky h x A sin kx t sinh kh
24 Similarly,,, v x, y, t dy v x y t P vp vx, y, t x y dt x y keeping the first term only and integrating the equation, it results sinh k y h yp y vx, y, tdt y A sinkx tdt sinh kh sinh ky h y A coskx t sinh kh Specifically, on the mean free surface,, the unknown wave elevation is obtained. y 0 y Acoskx t P
25 Then, the particle orbit of particle P is obtained. where a A P 1 x x y y P cosh a k y h sinh kh b, b A sinh k y h sinh kh Particle orbits are ellipses. Both major axis and minor axis decrease with the increase of the depth below the free surface.
26 a b Ae Accordingly particle orbits become circles. The radius is getting smaller with the increase of depth from the free surface. On the free surface, the radius is just equal to the wave amplitude. kh 1 For deep water wave,, major and minor axes become equal ky
27
28 For shallow water waves,, the major and minor axes are a A kh const, kh 1 The particle orbits are ellipses. Major axis is horizontal and keeps constant, while the minor axis is vertical and decreases linearly with the depth from the free surface: on free surface, y = 0, it equals the wave amplitude, and on sea bottom, y = -h, it reduces to zero. b A1 y h
29
30 8. Pressure field According to the linearized dynamic condition (Bernoulli s equation), the pressure is evaluated as follows p pa gy t cosh k y h ga coskx t gy cosh kh cosh k y h g gy cosh kh
31 kh 1 cosh k y h cosh kh For deep water wave,, since we have approximation pressure is approximately written as ky p pa g e y V p gh that is, the dynamic pressure, the exponential part, decays with the increase of depth from free surface. Below half wave length, it could be reasonably neglected, where static pressure dominates. e ky V p (kh >> 1) p (kh << 1) p p d p s p d
32 For shallow water wave,, since we have approximation on the left, pressure distribution is approximated as p p g y a kh 1 cosh k y cosh kh h 1 that is, the pressure is very similar to static pressure distribution. The only difference is that the depth is measured from the instantaneous wave surface. V p gh V p (kh >> 1) p (kh << 1) p p d p s p d
33 Eg. 1 For an Airy wave, it is given that amplitude A = 0.3 m, wave period T = s, calculate its circular frequency, wave number, phase velocity, wave length and the maximum wave slope. Solution: Circular frequency: 3.14 s T 1 Wave number: gk 3.14 k g m 1 Phase velocity: c 3.14 k m/s
34 Wave length: m k Wave elevation: Acoskx t x 0.3 cos t x cos 1.01x 3.14t Wave slope: tg Ak sin kx t The maximum wave slope angle: tg max max o
35 Eg. A boat on a water wave is rolling at a rate of 30 cycles per minute. The sea is assumed deep enough. Calculate the wave length L, circular frequency ω, wave number k and the phase velocity c. Solution: Since the boat is not traveling, its rolling is assumed to be caused by an incident water waves. Then, wave period: T circular frequency: wave number: k 1 min ( s ) 30 T g 3.14(1/ s) wave length: L 6.6( m) k phase velocity: L C 3.13( m / s) T
36 Eg. 3 Consider two fluid layers, the upper fluid with densityρ 1, depth h 1, the lower fluid with densityρ, depth h. Two fluids are bounded by uppermost and lowest horizontal rigid walls. Determine phase velocity for the wave at the separating surface of the two layers with wave number k. Solution: Take origin at the mean separating surface, x- axis horizontal and y-axis vertical, upward positive.then velocity potentials of the wave in each layers are respectively as follows, in the upper layer ga cosh k yh sin cosh sin cosh kh in the lower layer kx t C k y h kx t ga cosh k y h sin cosh sin cosh kh kx t D k y h kx t y x
37 On the interface of the upper and lower fluid layers, pressure and velocity should coincide with each other. According to Bernoulli s equation, we have p p gy 0, gy 0 t t y p p On the interface,, pressure coincidence requires,, i.e. g g ( y 0) t t 1 g t t y 0
38 Next, velocity coincidence. On the interface, y-components of the upper and lower velocities should be equal, that is y y ( y 0) kc sinh k h sin kx t kd sinh kh sin kx t Thus, Csinh kh Dsinh kh From the linear kinematic condition of Airy wave, we have ( y 0) y y t
39 Therefore, 1 ( y 0) y g t t kdsinh khsin kx t Ccosh k h Dcosh kh g kdg sinh kh D cosh kh C cosh kh sin kx t
40 From above expression, finally we can get phase velocity formula. c k k Dg sinh kh k Dcosh kh C cosh kh g cosh kh C cosh kh k sinh kh D sinh kh g k tanh kh tanh kh End of Eg. 3.
Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19. Exact (nonlinear) governing equations for surface gravity waves assuming potential theory
 13.021 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 2004 Lecture 19 Copyright c 2004 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserved. Water Waves 13.021 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19 Exact (nonlinear) governing
13.021 Marine Hydrodynamics, Fall 2004 Lecture 19 Copyright c 2004 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserved. Water Waves 13.021 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19 Exact (nonlinear) governing
Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19. Exact (nonlinear) governing equations for surface gravity waves assuming potential theory
 13.021 Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19 Copyright c 2001 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserved. 13.021 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19 Water Waves Exact (nonlinear) governing equations
13.021 Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19 Copyright c 2001 MIT - Department of Ocean Engineering, All rights reserved. 13.021 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19 Water Waves Exact (nonlinear) governing equations
Chapter 4 Water Waves
 2.20 Marine Hdrodnamics, Fall 2018 Lecture 15 Copright c 2018 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserved. Chapter 4 Water Waves 2.20 - Marine Hdrodnamics Lecture 15 4.1 Exact (Nonlinear)
2.20 Marine Hdrodnamics, Fall 2018 Lecture 15 Copright c 2018 MIT - Department of Mechanical Engineering, All rights reserved. Chapter 4 Water Waves 2.20 - Marine Hdrodnamics Lecture 15 4.1 Exact (Nonlinear)
v t + fu = 1 p y w t = 1 p z g u x + v y + w
 1 For each of the waves that we will be talking about we need to know the governing equators for the waves. The linear equations of motion are used for many types of waves, ignoring the advective terms,
1 For each of the waves that we will be talking about we need to know the governing equators for the waves. The linear equations of motion are used for many types of waves, ignoring the advective terms,
13.42 LECTURE 2: REVIEW OF LINEAR WAVES
 13.42 LECTURE 2: REVIEW OF LINEAR WAVES SPRING 2003 c A.H. TECHET & M.S. TRIANTAFYLLOU 1. Basic Water Waves Laplace Equation 2 φ = 0 Free surface elevation: z = η(x, t) No vertical velocity at the bottom
13.42 LECTURE 2: REVIEW OF LINEAR WAVES SPRING 2003 c A.H. TECHET & M.S. TRIANTAFYLLOU 1. Basic Water Waves Laplace Equation 2 φ = 0 Free surface elevation: z = η(x, t) No vertical velocity at the bottom
2. Theory of Small Amplitude Waves
 . Theory of Small Amplitude Waves.1 General Discussion on Waves et us consider a one-dimensional (on -ais) propagating wave that retains its original shape. Assume that the wave can be epressed as a function
. Theory of Small Amplitude Waves.1 General Discussion on Waves et us consider a one-dimensional (on -ais) propagating wave that retains its original shape. Assume that the wave can be epressed as a function
Concepts from linear theory Extra Lecture
 Concepts from linear theory Extra Lecture Ship waves from WW II battleships and a toy boat. Kelvin s (1887) method of stationary phase predicts both. Concepts from linear theory A. Linearize the nonlinear
Concepts from linear theory Extra Lecture Ship waves from WW II battleships and a toy boat. Kelvin s (1887) method of stationary phase predicts both. Concepts from linear theory A. Linearize the nonlinear
Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University
1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs)
 c01.tex 8/10/2010 22: 55 Page 1 PART A Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) Chap. 1 First-Order ODEs Sec. 1.1 Basic Concepts. Modeling To get a good start into this chapter and this section, quickly
c01.tex 8/10/2010 22: 55 Page 1 PART A Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) Chap. 1 First-Order ODEs Sec. 1.1 Basic Concepts. Modeling To get a good start into this chapter and this section, quickly
Figure 1: Surface waves
 4 Surface Waves on Liquids 1 4 Surface Waves on Liquids 4.1 Introduction We consider waves on the surface of liquids, e.g. waves on the sea or a lake or a river. These can be generated by the wind, by
4 Surface Waves on Liquids 1 4 Surface Waves on Liquids 4.1 Introduction We consider waves on the surface of liquids, e.g. waves on the sea or a lake or a river. These can be generated by the wind, by
DRAFT - Math 101 Lecture Note - Dr. Said Algarni
 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 The Derivative of Polynomial and Exponential Functions In this section we learn how to differentiate constant functions, power functions, polynomials, and exponential functions.
3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 The Derivative of Polynomial and Exponential Functions In this section we learn how to differentiate constant functions, power functions, polynomials, and exponential functions.
Shallow Water Gravity Waves: A Note on the Particle Orbits
 Journal of Oceanography Vol. 5, pp. 353 to 357. 1996 Shallow Water Gravity Waves: A Note on the Particle Orbits KERN E. KENYON 463 North Lane, Del Mar, CA 9014-4134, U.S.A. (Received 4 July 1995; in revised
Journal of Oceanography Vol. 5, pp. 353 to 357. 1996 Shallow Water Gravity Waves: A Note on the Particle Orbits KERN E. KENYON 463 North Lane, Del Mar, CA 9014-4134, U.S.A. (Received 4 July 1995; in revised
Chapter 15. Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
Nonlinear Wave Theory
 Nonlinear Wave Theory Weakly Nonlinear Wave Theory (WNWT): Stokes Expansion, aka Mode Coupling Method (MCM) 1) Only applied in deep or intermediate depth water ) When truncated at a relatively high order,
Nonlinear Wave Theory Weakly Nonlinear Wave Theory (WNWT): Stokes Expansion, aka Mode Coupling Method (MCM) 1) Only applied in deep or intermediate depth water ) When truncated at a relatively high order,
On Vertical Variations of Wave-Induced Radiation Stress Tensor
 Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics Vol. 55 (2008), No. 3 4, pp. 83 93 IBW PAN, ISSN 1231 3726 On Vertical Variations of Wave-Induced Radiation Stress Tensor Włodzimierz Chybicki
Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics Vol. 55 (2008), No. 3 4, pp. 83 93 IBW PAN, ISSN 1231 3726 On Vertical Variations of Wave-Induced Radiation Stress Tensor Włodzimierz Chybicki
Salmon: Introduction to ocean waves
 3 Many waves In the previous lecture, we considered the case of two basic waves propagating in one horizontal dimension. However, Proposition #2 lets us have as many basic waves as we want. Suppose we
3 Many waves In the previous lecture, we considered the case of two basic waves propagating in one horizontal dimension. However, Proposition #2 lets us have as many basic waves as we want. Suppose we
Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section 1.2 and 1.3
 Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section. and.3 Introduction of the velocity potential: irrotational motion: ω = u = identity in the vector analysis: ϕ u = ϕ Basic conservation principles:
Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section. and.3 Introduction of the velocity potential: irrotational motion: ω = u = identity in the vector analysis: ϕ u = ϕ Basic conservation principles:
Math 132 Information for Test 2
 Math 13 Information for Test Test will cover material from Sections 5.6, 5.7, 5.8, 6.1, 6., 6.3, 7.1, 7., and 7.3. The use of graphing calculators will not be allowed on the test. Some practice questions
Math 13 Information for Test Test will cover material from Sections 5.6, 5.7, 5.8, 6.1, 6., 6.3, 7.1, 7., and 7.3. The use of graphing calculators will not be allowed on the test. Some practice questions
SAMPLE CHAPTERS UNESCO EOLSS WAVES IN THE OCEANS. Wolfgang Fennel Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde (IOW) an der Universität Rostock,Germany
 WAVES IN THE OCEANS Wolfgang Fennel Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde (IOW) an der Universität Rostock,Germany Keywords: Wind waves, dispersion, internal waves, inertial oscillations, inertial waves,
WAVES IN THE OCEANS Wolfgang Fennel Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde (IOW) an der Universität Rostock,Germany Keywords: Wind waves, dispersion, internal waves, inertial oscillations, inertial waves,
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Waves in Fluids
 Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Waves in Fluids Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI (after: D.J. ACHESON s Elementary Fluid Dynamics ) bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Waves in Fluids Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI (after: D.J. ACHESON s Elementary Fluid Dynamics ) bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute
a Write down the coordinates of the point on the curve where t = 2. b Find the value of t at the point on the curve with coordinates ( 5 4, 8).
 Worksheet A 1 A curve is given by the parametric equations x = t + 1, y = 4 t. a Write down the coordinates of the point on the curve where t =. b Find the value of t at the point on the curve with coordinates
Worksheet A 1 A curve is given by the parametric equations x = t + 1, y = 4 t. a Write down the coordinates of the point on the curve where t =. b Find the value of t at the point on the curve with coordinates
1 The Derivative and Differrentiability
 1 The Derivative and Differrentiability 1.1 Derivatives and rate of change Exercise 1 Find the equation of the tangent line to f (x) = x 2 at the point (1, 1). Exercise 2 Suppose that a ball is dropped
1 The Derivative and Differrentiability 1.1 Derivatives and rate of change Exercise 1 Find the equation of the tangent line to f (x) = x 2 at the point (1, 1). Exercise 2 Suppose that a ball is dropped
Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 3 (9/13/06) Bound States in One Dimensional Systems Particle in a Square Well
 22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 3 (9/13/06) Bound States in One Dimensional Systems Particle in a Square Well References - R. L. Liboff, Introductory Quantum Mechanics (Holden Day, New
22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 3 (9/13/06) Bound States in One Dimensional Systems Particle in a Square Well References - R. L. Liboff, Introductory Quantum Mechanics (Holden Day, New
Lecture 10. (2) Functions of two variables. Partial derivatives. Dan Nichols February 27, 2018
 Lecture 10 Partial derivatives Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts February 27, 2018 Last time: functions of two variables f(x, y) x and y are the independent
Lecture 10 Partial derivatives Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts February 27, 2018 Last time: functions of two variables f(x, y) x and y are the independent
7.1. Calculus of inverse functions. Text Section 7.1 Exercise:
 Contents 7. Inverse functions 1 7.1. Calculus of inverse functions 2 7.2. Derivatives of exponential function 4 7.3. Logarithmic function 6 7.4. Derivatives of logarithmic functions 7 7.5. Exponential
Contents 7. Inverse functions 1 7.1. Calculus of inverse functions 2 7.2. Derivatives of exponential function 4 7.3. Logarithmic function 6 7.4. Derivatives of logarithmic functions 7 7.5. Exponential
Chapter 2. The continuous equations
 Chapter. The continuous equations Fig. 1.: Schematic of a forecast with slowly varying weather-related variations and superimposed high frequency Lamb waves. Note that even though the forecast of the slow
Chapter. The continuous equations Fig. 1.: Schematic of a forecast with slowly varying weather-related variations and superimposed high frequency Lamb waves. Note that even though the forecast of the slow
Water is sloshing back and forth between two infinite vertical walls separated by a distance L: h(x,t) Water L
 ME9a. SOLUTIONS. Nov., 29. Due Nov. 7 PROBLEM 2 Water is sloshing back and forth between two infinite vertical walls separated by a distance L: y Surface Water L h(x,t x Tank The flow is assumed to be
ME9a. SOLUTIONS. Nov., 29. Due Nov. 7 PROBLEM 2 Water is sloshing back and forth between two infinite vertical walls separated by a distance L: y Surface Water L h(x,t x Tank The flow is assumed to be
ENGI 9420 Lecture Notes 1 - ODEs Page 1.01
 ENGI 940 Lecture Notes - ODEs Page.0. Ordinary Differential Equations An equation involving a function of one independent variable and the derivative(s) of that function is an ordinary differential equation
ENGI 940 Lecture Notes - ODEs Page.0. Ordinary Differential Equations An equation involving a function of one independent variable and the derivative(s) of that function is an ordinary differential equation
CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation
 CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University September 26, 2005 1 Sinusoids Sinusoids
CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University September 26, 2005 1 Sinusoids Sinusoids
OPAC102. The Acoustic Wave Equation
 OPAC102 The Acoustic Wave Equation Acoustic waves in fluid Acoustic waves constitute one kind of pressure fluctuation that can exist in a compressible fluid. The restoring forces responsible for propagating
OPAC102 The Acoustic Wave Equation Acoustic waves in fluid Acoustic waves constitute one kind of pressure fluctuation that can exist in a compressible fluid. The restoring forces responsible for propagating
) 2 ψ +β ψ. x = 0. (71) ν = uk βk/k 2, (74) c x u = β/k 2. (75)
 3 Rossby Waves 3.1 Free Barotropic Rossby Waves The dispersion relation for free barotropic Rossby waves can be derived by linearizing the barotropic vortiticy equation in the form (21). This equation
3 Rossby Waves 3.1 Free Barotropic Rossby Waves The dispersion relation for free barotropic Rossby waves can be derived by linearizing the barotropic vortiticy equation in the form (21). This equation
Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules (continued)
 Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules (continued) Sec 3.5: Implicit Differentiation (continued) Implicit Differentiation What if you want to find the slope of the tangent line to a curve that is not the graph
Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules (continued) Sec 3.5: Implicit Differentiation (continued) Implicit Differentiation What if you want to find the slope of the tangent line to a curve that is not the graph
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB
 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
II TheLaplace equacon and potencal fluid flow
 THE WAVE EQUATION (3) I Main Topics A The aplace equacon and fluid potencal B AssumpCons and boundary condicons of D small wave theory C SoluCon of the wave equacon D Energy in a wave E Shoaling of waves
THE WAVE EQUATION (3) I Main Topics A The aplace equacon and fluid potencal B AssumpCons and boundary condicons of D small wave theory C SoluCon of the wave equacon D Energy in a wave E Shoaling of waves
THE PHYSICS OF WAVES CHAPTER 1. Problem 1.1 Show that Ψ(x, t) = (x vt) 2. is a traveling wave.
 CHAPTER 1 THE PHYSICS OF WAVES Problem 1.1 Show that Ψ(x, t) = (x vt) is a traveling wave. Show thatψ(x, t) is a wave by substitutioninto Equation 1.1. Proceed as in Example 1.1. On line version uses Ψ(x,
CHAPTER 1 THE PHYSICS OF WAVES Problem 1.1 Show that Ψ(x, t) = (x vt) is a traveling wave. Show thatψ(x, t) is a wave by substitutioninto Equation 1.1. Proceed as in Example 1.1. On line version uses Ψ(x,
Traveling Harmonic Waves
 Traveling Harmonic Waves 6 January 2016 PHYC 1290 Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Functional Form for Traveling Waves We can show that traveling waves whose shape does not change with time
Traveling Harmonic Waves 6 January 2016 PHYC 1290 Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Functional Form for Traveling Waves We can show that traveling waves whose shape does not change with time
m(x) = f(x) + g(x) m (x) = f (x) + g (x) (The Sum Rule) n(x) = f(x) g(x) n (x) = f (x) g (x) (The Difference Rule)
 Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Aka The Short Cuts! Yay! f(x) = c f (x) = 0 g(x) = x g (x) = 1 h(x) = x n h (x) = n x n-1 (The Power Rule) k(x)
Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Aka The Short Cuts! Yay! f(x) = c f (x) = 0 g(x) = x g (x) = 1 h(x) = x n h (x) = n x n-1 (The Power Rule) k(x)
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 559
 Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Possible C4 questions from past papers P1 P3
 Possible C4 questions from past papers P1 P3 Source of the original question is given in brackets, e.g. [P January 001 Question 1]; a question which has been edited is indicated with an asterisk, e.g.
Possible C4 questions from past papers P1 P3 Source of the original question is given in brackets, e.g. [P January 001 Question 1]; a question which has been edited is indicated with an asterisk, e.g.
Sinusoids. Amplitude and Magnitude. Phase and Period. CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation
 Sinusoids CMPT 889: Lecture Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University September 6, 005 Sinusoids are
Sinusoids CMPT 889: Lecture Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University September 6, 005 Sinusoids are
THE NCUK INTERNATIONAL FOUNDATION YEAR (IFY) Further Mathematics
 IFYFM00 Further Maths THE NCUK INTERNATIONAL FOUNDATION YEAR (IFY) Further Mathematics Examination Session Summer 009 Time Allowed hours 0 minutes (Including 0 minutes reading time) INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS
IFYFM00 Further Maths THE NCUK INTERNATIONAL FOUNDATION YEAR (IFY) Further Mathematics Examination Session Summer 009 Time Allowed hours 0 minutes (Including 0 minutes reading time) INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS
SECOND-ORDER PARTIAL STANDING WAVE SOLUTION FOR A SLOPING BOTTOM
 SECOND-ORDER PARTIAL STANDING WAVE SOLUTION FOR A SLOPING BOTTOM Meng-Syue Li Qingping Zou Yang-Yih Chen 3 and Hung-Chu Hsu This paper presents a second-order asymptotic solution in Lagrangian description
SECOND-ORDER PARTIAL STANDING WAVE SOLUTION FOR A SLOPING BOTTOM Meng-Syue Li Qingping Zou Yang-Yih Chen 3 and Hung-Chu Hsu This paper presents a second-order asymptotic solution in Lagrangian description
MATH 2250 Final Exam Solutions
 MATH 225 Final Exam Solutions Tuesday, April 29, 28, 6: 8:PM Write your name and ID number at the top of this page. Show all your work. You may refer to one double-sided sheet of notes during the exam
MATH 225 Final Exam Solutions Tuesday, April 29, 28, 6: 8:PM Write your name and ID number at the top of this page. Show all your work. You may refer to one double-sided sheet of notes during the exam
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension
 Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Reading Quiz 16.05 f = c Slide 16-2 Reading Quiz 16.06 Slide 16-3 Reading Quiz 16.07 Heavier portion looks like a fixed end, pulse is inverted on reflection.
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Reading Quiz 16.05 f = c Slide 16-2 Reading Quiz 16.06 Slide 16-3 Reading Quiz 16.07 Heavier portion looks like a fixed end, pulse is inverted on reflection.
Wave-Body Interaction Theory (Theory of Ship Waves) Lecture Notes for Graduate Course
 Wave-Body Interaction Theory (Theory of Ship Waves) Lecture Notes for Graduate Course ( April 018 ) Lab of Seakeeping & Floating-Body Dynamics in Waves Dept of Naval Architecture & Ocean Engineering Osaka
Wave-Body Interaction Theory (Theory of Ship Waves) Lecture Notes for Graduate Course ( April 018 ) Lab of Seakeeping & Floating-Body Dynamics in Waves Dept of Naval Architecture & Ocean Engineering Osaka
Solutions to Section 1.1
 Solutions to Section True-False Review: FALSE A derivative must involve some derivative of the function y f(x), not necessarily the first derivative TRUE The initial conditions accompanying a differential
Solutions to Section True-False Review: FALSE A derivative must involve some derivative of the function y f(x), not necessarily the first derivative TRUE The initial conditions accompanying a differential
SHIP WAVE CRESTS IN INTERMEDIATE-DEPTH WATER
 Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts (APAC 011) December 14 16, 011, Hong Kong, China SHIP WAVE CRESTS IN INTERMEDIATE-DEPTH WATER C. LEE, B.W. LEE Department of
Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts (APAC 011) December 14 16, 011, Hong Kong, China SHIP WAVE CRESTS IN INTERMEDIATE-DEPTH WATER C. LEE, B.W. LEE Department of
Waves Primer II Basic wave form. Waves are: 1. Important 2. Easy 3. Neat
 Waves Primer II Waves are: 1. Important 2. Easy 3. Neat 23.1 Basic wave form The wave form that you will almost always use is a = Re[A c e i(kx+ly ωt) ] (23.1) Where a variable A c waveamplitude(complexinthiscase)
Waves Primer II Waves are: 1. Important 2. Easy 3. Neat 23.1 Basic wave form The wave form that you will almost always use is a = Re[A c e i(kx+ly ωt) ] (23.1) Where a variable A c waveamplitude(complexinthiscase)
Chapter 10: Conic Sections; Polar Coordinates; Parametric Equations
 Chapter 10: Conic Sections; Polar Coordinates; Parametric Equations Section 10.1 Geometry of Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola a. Geometric Definition b. Parabola c. Ellipse d. Hyperbola e. Translations f.
Chapter 10: Conic Sections; Polar Coordinates; Parametric Equations Section 10.1 Geometry of Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola a. Geometric Definition b. Parabola c. Ellipse d. Hyperbola e. Translations f.
Foundations of quantum mechanics
 CHAPTER 4 Foundations of quantum mechanics de Broglie s Ansatz, the basis of Schrödinger s equation, operators, complex numbers and functions, momentum, free particle wavefunctions, expectation values
CHAPTER 4 Foundations of quantum mechanics de Broglie s Ansatz, the basis of Schrödinger s equation, operators, complex numbers and functions, momentum, free particle wavefunctions, expectation values
Fluid Dynamics for Ocean and Environmental Engineering Homework #2 Viscous Flow
 OCEN 678-600 Fluid Dynamics for Ocean and Environmental Engineering Homework #2 Viscous Flow Date distributed : 9.18.2005 Date due : 9.29.2005 at 5:00 pm Return your solution either in class or in my mail
OCEN 678-600 Fluid Dynamics for Ocean and Environmental Engineering Homework #2 Viscous Flow Date distributed : 9.18.2005 Date due : 9.29.2005 at 5:00 pm Return your solution either in class or in my mail
Free Response Questions Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom
 Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
MATHEMATICS LEARNING AREA. Methods Units 1 and 2 Course Outline. Week Content Sadler Reference Trigonometry
 MATHEMATICS LEARNING AREA Methods Units 1 and 2 Course Outline Text: Sadler Methods and 2 Week Content Sadler Reference Trigonometry Cosine and Sine rules Week 1 Trigonometry Week 2 Radian Measure Radian
MATHEMATICS LEARNING AREA Methods Units 1 and 2 Course Outline Text: Sadler Methods and 2 Week Content Sadler Reference Trigonometry Cosine and Sine rules Week 1 Trigonometry Week 2 Radian Measure Radian
Math 122 Test 3. April 17, 2018
 SI: Math Test 3 April 7, 08 EF: 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Total Name Directions:. No books, notes or April showers. You may use a calculator to do routine arithmetic computations. You may not use your calculator
SI: Math Test 3 April 7, 08 EF: 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Total Name Directions:. No books, notes or April showers. You may use a calculator to do routine arithmetic computations. You may not use your calculator
Do not turn over until you are told to do so by the Invigilator.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2014 15 FLUID DYNAMICS - THEORY AND COMPUTATION MTHA5002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt QUESTIONS 1 and 2, and THREE other questions.
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2014 15 FLUID DYNAMICS - THEORY AND COMPUTATION MTHA5002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt QUESTIONS 1 and 2, and THREE other questions.
Practice Problems For Test 3
 Practice Problems For Test 3 Power Series Preliminary Material. Find the interval of convergence of the following. Be sure to determine the convergence at the endpoints. (a) ( ) k (x ) k (x 3) k= k (b)
Practice Problems For Test 3 Power Series Preliminary Material. Find the interval of convergence of the following. Be sure to determine the convergence at the endpoints. (a) ( ) k (x ) k (x 3) k= k (b)
Strauss PDEs 2e: Section Exercise 4 Page 1 of 6
 Strauss PDEs 2e: Section 5.3 - Exercise 4 Page of 6 Exercise 4 Consider the problem u t = ku xx for < x < l, with the boundary conditions u(, t) = U, u x (l, t) =, and the initial condition u(x, ) =, where
Strauss PDEs 2e: Section 5.3 - Exercise 4 Page of 6 Exercise 4 Consider the problem u t = ku xx for < x < l, with the boundary conditions u(, t) = U, u x (l, t) =, and the initial condition u(x, ) =, where
m(x) = f(x) + g(x) m (x) = f (x) + g (x) (The Sum Rule) n(x) = f(x) g(x) n (x) = f (x) g (x) (The Difference Rule) thing CFAIHIHD fkthf.
 . Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Aka The Short Cuts! Yay! f(x) c f (x) 0 g(x) x g (x) 1 h(x) x n h (x) n x n-1 (The Power Rule) k(x) c f(x) k (x)
. Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Aka The Short Cuts! Yay! f(x) c f (x) 0 g(x) x g (x) 1 h(x) x n h (x) n x n-1 (The Power Rule) k(x) c f(x) k (x)
Practice Problems For Test 3
 Practice Problems For Test 3 Power Series Preliminary Material. Find the interval of convergence of the following. Be sure to determine the convergence at the endpoints. (a) ( ) k (x ) k (x 3) k= k (b)
Practice Problems For Test 3 Power Series Preliminary Material. Find the interval of convergence of the following. Be sure to determine the convergence at the endpoints. (a) ( ) k (x ) k (x 3) k= k (b)
MA 242 Review Exponential and Log Functions Notes for today s class can be found at
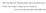 MA 242 Review Exponential and Log Functions Notes for today s class can be found at www.xecu.net/jacobs/index242.htm Example: If y = x n If y = x 2 then then dy dx = nxn 1 dy dx = 2x1 = 2x Power Function
MA 242 Review Exponential and Log Functions Notes for today s class can be found at www.xecu.net/jacobs/index242.htm Example: If y = x n If y = x 2 then then dy dx = nxn 1 dy dx = 2x1 = 2x Power Function
Lecture 18: Wave-Mean Flow Interaction, Part I
 Lecture 18: Wave-Mean Flow Interaction, Part I Lecturer: Roger Grimshaw. Write-up: Hiroki Yamamoto June 5, 009 1 Introduction Nonlinearity in water waves can lead to wave breaking. We can observe easily
Lecture 18: Wave-Mean Flow Interaction, Part I Lecturer: Roger Grimshaw. Write-up: Hiroki Yamamoto June 5, 009 1 Introduction Nonlinearity in water waves can lead to wave breaking. We can observe easily
SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION PRACTICAL (Keith Priestley)
 SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION PRACTICAL (Keith Priestley) This practical deals with surface waves, which are usually the largest amplitude arrivals on the seismogram. The velocity at which surface waves propagate
SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION PRACTICAL (Keith Priestley) This practical deals with surface waves, which are usually the largest amplitude arrivals on the seismogram. The velocity at which surface waves propagate
4. Factor the expression completely. Begin by factoring out the lowest power of each common factor: 20x 1/2 + 9x 1/2 + x 3/2
 M180 Final Exam practice 1.Simplify each expression, and eliminate any negative exponents. st 7 4 1 s t. Simplify the expression. Assume that x, y, and z denote any positive real numbers. 3. Rationalize
M180 Final Exam practice 1.Simplify each expression, and eliminate any negative exponents. st 7 4 1 s t. Simplify the expression. Assume that x, y, and z denote any positive real numbers. 3. Rationalize
Magnets and Lattices. - Accelerator building blocks - Transverse beam dynamics - coordinate system
 Magnets and Lattices - Accelerator building blocks - Transverse beam dynamics - coordinate system Both electric field and magnetic field can be used to guide the particles path. r F = q( r E + r V r B
Magnets and Lattices - Accelerator building blocks - Transverse beam dynamics - coordinate system Both electric field and magnetic field can be used to guide the particles path. r F = q( r E + r V r B
1D Wave PDE. Introduction to Partial Differential Equations part of EM, Scalar and Vector Fields module (PHY2064) Richard Sear.
 Introduction to Partial Differential Equations part of EM, Scalar and Vector Fields module (PHY2064) November 12, 2018 Wave equation in one dimension This lecture Wave PDE in 1D Method of Separation of
Introduction to Partial Differential Equations part of EM, Scalar and Vector Fields module (PHY2064) November 12, 2018 Wave equation in one dimension This lecture Wave PDE in 1D Method of Separation of
Fourier transforms. c n e inπx. f (x) = Write same thing in an equivalent form, using n = 1, f (x) = l π
 Fourier transforms We can imagine our periodic function having periodicity taken to the limits ± In this case, the function f (x) is not necessarily periodic, but we can still use Fourier transforms (related
Fourier transforms We can imagine our periodic function having periodicity taken to the limits ± In this case, the function f (x) is not necessarily periodic, but we can still use Fourier transforms (related
4.1 Analysis of functions I: Increase, decrease and concavity
 4.1 Analysis of functions I: Increase, decrease and concavity Definition Let f be defined on an interval and let x 1 and x 2 denote points in that interval. a) f is said to be increasing on the interval
4.1 Analysis of functions I: Increase, decrease and concavity Definition Let f be defined on an interval and let x 1 and x 2 denote points in that interval. a) f is said to be increasing on the interval
Indefinite Integration
 Indefinite Integration 1 An antiderivative of a function y = f(x) defined on some interval (a, b) is called any function F(x) whose derivative at any point of this interval is equal to f(x): F'(x) = f(x)
Indefinite Integration 1 An antiderivative of a function y = f(x) defined on some interval (a, b) is called any function F(x) whose derivative at any point of this interval is equal to f(x): F'(x) = f(x)
On the Deformed Theory of Special Relativity
 Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics Vol. 11, 2017, no. 6, 275-282 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/astp.2017.61140 On the Deformed Theory of Special Relativity Won Sang Chung 1
Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics Vol. 11, 2017, no. 6, 275-282 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/astp.2017.61140 On the Deformed Theory of Special Relativity Won Sang Chung 1
2. (i) Find the equation of the circle which passes through ( 7, 1) and has centre ( 4, 3).
 Circle 1. (i) Find the equation of the circle with centre ( 7, 3) and of radius 10. (ii) Find the centre of the circle 2x 2 + 2y 2 + 6x + 8y 1 = 0 (iii) What is the radius of the circle 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 5x
Circle 1. (i) Find the equation of the circle with centre ( 7, 3) and of radius 10. (ii) Find the centre of the circle 2x 2 + 2y 2 + 6x + 8y 1 = 0 (iii) What is the radius of the circle 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 5x
Math 2413 t2rsu14. Name: 06/06/ Find the derivative of the following function using the limiting process.
 Name: 06/06/014 Math 413 trsu14 1. Find the derivative of the following function using the limiting process. f( x) = 4x + 5x. Find the derivative of the following function using the limiting process. f(
Name: 06/06/014 Math 413 trsu14 1. Find the derivative of the following function using the limiting process. f( x) = 4x + 5x. Find the derivative of the following function using the limiting process. f(
Theory of Ship Waves (Wave-Body Interaction Theory) Quiz No. 2, April 25, 2018
 Quiz No. 2, April 25, 2018 (1) viscous effects (2) shear stress (3) normal pressure (4) pursue (5) bear in mind (6) be denoted by (7) variation (8) adjacent surfaces (9) be composed of (10) integrand (11)
Quiz No. 2, April 25, 2018 (1) viscous effects (2) shear stress (3) normal pressure (4) pursue (5) bear in mind (6) be denoted by (7) variation (8) adjacent surfaces (9) be composed of (10) integrand (11)
Theory of linear gravity waves April 1987
 April 1987 By Tim Palmer European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Table of contents 1. Simple properties of internal gravity waves 2. Gravity-wave drag REFERENCES 1. SIMPLE PROPERTIES OF INTERNAL
April 1987 By Tim Palmer European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Table of contents 1. Simple properties of internal gravity waves 2. Gravity-wave drag REFERENCES 1. SIMPLE PROPERTIES OF INTERNAL
MATH Non-Euclidean Geometry Exercise Set #9 Solutions
 MATH 6118-090 Non-Euclidean Geometry Exercise Set #9 Solutions 1. Consider the doubly asymptotic triangle AMN in H where What is the image of AMN under the isometry γ 1? Use this to find the hyperbolic
MATH 6118-090 Non-Euclidean Geometry Exercise Set #9 Solutions 1. Consider the doubly asymptotic triangle AMN in H where What is the image of AMN under the isometry γ 1? Use this to find the hyperbolic
Kelvin Helmholtz Instability
 Kelvin Helmholtz Instability A. Salih Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram November 00 One of the most well known instabilities in fluid
Kelvin Helmholtz Instability A. Salih Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram November 00 One of the most well known instabilities in fluid
Chapter 2 Solutions. Chapter 2 Solutions 1. 4( z t) ( z t) z t
 Chapter Solutions 1 Chapter Solutions.1. 1 z t ( z t) z z ( z t) t t It s a twice differentiable function of ( z t ), where is in the negative z direction. 1 y t ( y, t) ( y4 t) ( y 4 t) y y 8( y 4 t)
Chapter Solutions 1 Chapter Solutions.1. 1 z t ( z t) z z ( z t) t t It s a twice differentiable function of ( z t ), where is in the negative z direction. 1 y t ( y, t) ( y4 t) ( y 4 t) y y 8( y 4 t)
ENGI 2422 First Order ODEs - Separable Page 3-01
 ENGI 4 First Order ODEs - Separable Page 3-0 3. Ordinary Differential Equations Equations involving only one independent variable and one or more dependent variables, together with their derivatives with
ENGI 4 First Order ODEs - Separable Page 3-0 3. Ordinary Differential Equations Equations involving only one independent variable and one or more dependent variables, together with their derivatives with
Making Waves in Multivariable Calculus
 Making Waves in Multivariable Calculus J. B. Thoo Yuba College 2014 CMC3 Fall Conference, Monterey, Ca This presentation
Making Waves in Multivariable Calculus J. B. Thoo Yuba College 2014 CMC3 Fall Conference, Monterey, Ca This presentation
+ 1 for x > 2 (B) (E) (B) 2. (C) 1 (D) 2 (E) Nonexistent
 dx = (A) 3 sin(3x ) + C 1. cos ( 3x) 1 (B) sin(3x ) + C 3 1 (C) sin(3x ) + C 3 (D) sin( 3x ) + C (E) 3 sin(3x ) + C 6 3 2x + 6x 2. lim 5 3 x 0 4x + 3x (A) 0 1 (B) 2 (C) 1 (D) 2 (E) Nonexistent is 2 x 3x
dx = (A) 3 sin(3x ) + C 1. cos ( 3x) 1 (B) sin(3x ) + C 3 1 (C) sin(3x ) + C 3 (D) sin( 3x ) + C (E) 3 sin(3x ) + C 6 3 2x + 6x 2. lim 5 3 x 0 4x + 3x (A) 0 1 (B) 2 (C) 1 (D) 2 (E) Nonexistent is 2 x 3x
A( x) B( x) C( x) y( x) 0, A( x) 0
 3.1 Lexicon Revisited The nonhomogeneous nd Order ODE has the form: d y dy A( x) B( x) C( x) y( x) F( x), A( x) dx dx The homogeneous nd Order ODE has the form: d y dy A( x) B( x) C( x) y( x), A( x) dx
3.1 Lexicon Revisited The nonhomogeneous nd Order ODE has the form: d y dy A( x) B( x) C( x) y( x) F( x), A( x) dx dx The homogeneous nd Order ODE has the form: d y dy A( x) B( x) C( x) y( x), A( x) dx
single uniform density, but has a step change in density at x = 0, with the string essentially y(x, t) =A sin(!t k 1 x), (5.1)
 Chapter 5 Waves II 5.1 Reflection & Transmission of waves et us now consider what happens to a wave travelling along a string which no longer has a single uniform density, but has a step change in density
Chapter 5 Waves II 5.1 Reflection & Transmission of waves et us now consider what happens to a wave travelling along a string which no longer has a single uniform density, but has a step change in density
( ) b.! = 7" 3 has coordinates 1
 Chapter 4: Circular Functions Lesson 4.. 4-. a.! b.! c. i. 0!! " radians 80! = " 6 radians 4-. a. and b. ii. iii. 45!! " radians 80! = " 4 radians 60!! " radians 80! = " radians 4-. Possible patterns that
Chapter 4: Circular Functions Lesson 4.. 4-. a.! b.! c. i. 0!! " radians 80! = " 6 radians 4-. a. and b. ii. iii. 45!! " radians 80! = " 4 radians 60!! " radians 80! = " radians 4-. Possible patterns that
2 Recollection of elementary functions. II
 Recollection of elementary functions. II Last updated: October 5, 08. In this section we continue recollection of elementary functions. In particular, we consider exponential, trigonometric and hyperbolic
Recollection of elementary functions. II Last updated: October 5, 08. In this section we continue recollection of elementary functions. In particular, we consider exponential, trigonometric and hyperbolic
Solution: APPM 1350 Final Exam Spring 2014
 APPM 135 Final Exam Spring 214 1. (a) (5 pts. each) Find the following derivatives, f (x), for the f given: (a) f(x) = x 2 sin 1 (x 2 ) (b) f(x) = 1 1 + x 2 (c) f(x) = x ln x (d) f(x) = x x d (b) (15 pts)
APPM 135 Final Exam Spring 214 1. (a) (5 pts. each) Find the following derivatives, f (x), for the f given: (a) f(x) = x 2 sin 1 (x 2 ) (b) f(x) = 1 1 + x 2 (c) f(x) = x ln x (d) f(x) = x x d (b) (15 pts)
Monday, 6 th October 2008
 MA211 Lecture 9: 2nd order differential eqns Monday, 6 th October 2008 MA211 Lecture 9: 2nd order differential eqns 1/19 Class test next week... MA211 Lecture 9: 2nd order differential eqns 2/19 This morning
MA211 Lecture 9: 2nd order differential eqns Monday, 6 th October 2008 MA211 Lecture 9: 2nd order differential eqns 1/19 Class test next week... MA211 Lecture 9: 2nd order differential eqns 2/19 This morning
AN-NAJ. J. RES., JAN.1988, SEC. II, VOL. I, NO. 5,
 AN-NAJ. J. RES., JAN.1988, SEC. II, VOL. I, NO. 5, 12-27. 12 A DETAILED AND SIMPLIFIED SOLUTION TO HYDRODYNAMIC FORCES ON A SUBMERGED TANK SUBJECT TO LATERAL GROUND EXCITATION. A.H.Helou Civil Engineering
AN-NAJ. J. RES., JAN.1988, SEC. II, VOL. I, NO. 5, 12-27. 12 A DETAILED AND SIMPLIFIED SOLUTION TO HYDRODYNAMIC FORCES ON A SUBMERGED TANK SUBJECT TO LATERAL GROUND EXCITATION. A.H.Helou Civil Engineering
Sound Waves Sound Waves:
 3//18 Sound Waves Sound Waves: 1 3//18 Sound Waves Linear Waves compression rarefaction Inference of Sound Wave equation: Sound Waves We look at small disturbances in a compressible medium (note: compressible
3//18 Sound Waves Sound Waves: 1 3//18 Sound Waves Linear Waves compression rarefaction Inference of Sound Wave equation: Sound Waves We look at small disturbances in a compressible medium (note: compressible
3.1 Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions. m(x) = f(x) + g(x) m (x) = f (x) + g (x) (The Sum Rule)
 f Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Aka The Short Cuts! Yay! f(x) c f (x) 0 g(x) x g (x) 1 h(x) x n h (x) n x n1 (The Power Rule) k(x) c f(x) k (x)
f Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Aka The Short Cuts! Yay! f(x) c f (x) 0 g(x) x g (x) 1 h(x) x n h (x) n x n1 (The Power Rule) k(x) c f(x) k (x)
ENGI 9420 Lecture Notes 8 - PDEs Page 8.01
 ENGI 940 ecture Notes 8 - PDEs Page 8.0 8. Partial Differential Equations Partial differential equations (PDEs) are equations involving functions of more than one variable and their partial derivatives
ENGI 940 ecture Notes 8 - PDEs Page 8.0 8. Partial Differential Equations Partial differential equations (PDEs) are equations involving functions of more than one variable and their partial derivatives
arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 28 Mar 2017
![arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 28 Mar 2017 arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 28 Mar 2017](/thumbs/89/99058783.jpg) J. Indones. Math. Soc. (MIHMI) Vol., No. (006), pp. 4 57. arxiv:703.09445v [physics.flu-dyn 8 Mar 07 LINEAR THEORY FOR SINGLE AND DOUBLE FLAP WAVEMAKERS W.M. Kusumawinahyu, N. Karjanto and G. Klopman Abstract.
J. Indones. Math. Soc. (MIHMI) Vol., No. (006), pp. 4 57. arxiv:703.09445v [physics.flu-dyn 8 Mar 07 LINEAR THEORY FOR SINGLE AND DOUBLE FLAP WAVEMAKERS W.M. Kusumawinahyu, N. Karjanto and G. Klopman Abstract.
Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 9, 1996 WIT Press, ISSN
 Fundamentals concerning Stokes waves M. Rahman Department of Applied Mathematics, Technical University of Nova Scotia, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B3J 2X4 Abstract In the study of water waves, it is well
Fundamentals concerning Stokes waves M. Rahman Department of Applied Mathematics, Technical University of Nova Scotia, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B3J 2X4 Abstract In the study of water waves, it is well
4. Sinusoidal solutions
 16 4. Sinusoidal solutions Many things in nature are periodic, even sinusoidal. We will begin by reviewing terms surrounding periodic functions. If an LTI system is fed a periodic input signal, we have
16 4. Sinusoidal solutions Many things in nature are periodic, even sinusoidal. We will begin by reviewing terms surrounding periodic functions. If an LTI system is fed a periodic input signal, we have
Math 113 Final Exam Practice
 Math Final Exam Practice The Final Exam is comprehensive. You should refer to prior reviews when studying material in chapters 6, 7, 8, and.-9. This review will cover.0- and chapter 0. This sheet has three
Math Final Exam Practice The Final Exam is comprehensive. You should refer to prior reviews when studying material in chapters 6, 7, 8, and.-9. This review will cover.0- and chapter 0. This sheet has three
Sample Questions Exam II, FS2009 Paulette Saab Calculators are neither needed nor allowed.
 Sample Questions Exam II, FS2009 Paulette Saab Calculators are neither needed nor allowed. Part A: (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) Do the following problems. Write the answer in the space provided. Only the answers
Sample Questions Exam II, FS2009 Paulette Saab Calculators are neither needed nor allowed. Part A: (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) Do the following problems. Write the answer in the space provided. Only the answers
Welcome to Math 104. D. DeTurck. January 16, University of Pennsylvania. D. DeTurck Math A: Welcome 1 / 44
 Welcome to Math 104 D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 16, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Welcome 1 / 44 Welcome to the course Math 104 Calculus I Topics: Quick review of Math 103 topics,
Welcome to Math 104 D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 16, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Welcome 1 / 44 Welcome to the course Math 104 Calculus I Topics: Quick review of Math 103 topics,
α(t) = ω 2 θ (t) κ I ω = g L L g T = 2π mgh rot com I rot
 α(t) = ω 2 θ (t) ω = κ I ω = g L T = 2π L g ω = mgh rot com I rot T = 2π I rot mgh rot com Chapter 16: Waves Mechanical Waves Waves and particles Vibration = waves - Sound - medium vibrates - Surface ocean
α(t) = ω 2 θ (t) ω = κ I ω = g L T = 2π L g ω = mgh rot com I rot T = 2π I rot mgh rot com Chapter 16: Waves Mechanical Waves Waves and particles Vibration = waves - Sound - medium vibrates - Surface ocean
Aalborg Universitet. Lecture Notes for the Course in Water Wave Mechanics Andersen, Thomas Lykke; Frigaard, Peter Bak. Publication date: 2007
 Aalborg Universitet Lecture Notes for the Course in Water Wave Mechanics Andersen, Thomas Lykke; Frigaard, Peter Bak Publication date: 2007 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record
Aalborg Universitet Lecture Notes for the Course in Water Wave Mechanics Andersen, Thomas Lykke; Frigaard, Peter Bak Publication date: 2007 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record
Higher Mathematics Skills Checklist
 Higher Mathematics Skills Checklist 1.1 The Straight Line (APP) I know how to find the distance between 2 points using the Distance Formula or Pythagoras I know how to find gradient from 2 points, angle
Higher Mathematics Skills Checklist 1.1 The Straight Line (APP) I know how to find the distance between 2 points using the Distance Formula or Pythagoras I know how to find gradient from 2 points, angle
5 t + t2 4. (ii) f(x) = ln(x 2 1). (iii) f(x) = e 2x 2e x + 3 4
 Study Guide for Final Exam 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its expression to be well-defined. Some examples of the conditions are: What
Study Guide for Final Exam 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its expression to be well-defined. Some examples of the conditions are: What
First Order Linear Ordinary Differential Equations
 First Order Linear Ordinary Differential Equations The most general first order linear ODE is an equation of the form p t dy dt q t y t f t. 1 Herepqarecalledcoefficients f is referred to as the forcing
First Order Linear Ordinary Differential Equations The most general first order linear ODE is an equation of the form p t dy dt q t y t f t. 1 Herepqarecalledcoefficients f is referred to as the forcing
