Entropy Gradient Maximization for Systems with Discoupled Time
|
|
|
- Sophia Pierce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Entropy Gradient Maximization for Systems with Discoupled Time I. V. Drozdov Abstract The conventional definition of time based on the period of oscillations or fluctuations around equilibrium states is considered in the framework of the local formalism of entropy gradient maximization. This definition is shown to be an arbitrary chioce of the time scale in a special case of systems with discoupled clock -degree of freedom. The relation between the conventional definition of time and the timereference degree of freedom in the local formalism of entropy gradient maximization is established. In this framework it is entirely a restriction on the special case of the entropy function with the separated time-reference degree of freedom. A transformation to this special form is discussed and illustrated with a standard example. 1 Introduction 1.1 Motivation In the entropy gradient maximization (EGM) formalism recently developed [1], the subject of time was sufficiently revised, so that it does not exist anymore in an usual sense. In terms of this formalism the concept of time (especially, since the time is arbitrary eligible), appears to be physically not well-defined and meaningless. Since the only measurable quantities can be viewed as physically relevant, but a measurement of time in EGM is entirely a comparison of substates of two subsystems, then instead of a question for a time interval between Corresponding author, drosdow@uni-koblenz.de 1
2 two states {A 1, B 1 } and {A 2, B 2 } of subsystems A, B, the formalism allows for, to compare A, B with each other immediately, avoiding the usage of the third subsystem C (clock) of the same closed system. In other words, the only physically meaningful question is, instead of asking for a time interval between states A 1 and A 2 in order to compare this interval with the one between states B 1 and B 2, we ask, which substate B 2 corresponds to the total state including the substate A 2, provided the A 1 and B 1 are substates of the same total state. It has been shown in the present remark that this concept is quite compliant with the usual definition of time and the latter is a particular case of EGM with discoupled time reference, in which the conventional view is implemented. In turn, this case includes a particular formulation of true hamiltonian ergodicity condition, which establishes the agreeabilty with a conventional definition of time units based on closed loop-processes like oscillations and fluctuations. 1.2 Formulation of the entropy-gradient-maximization The local formalism of entropy gradient maximization (EGM), recently proposed in[1] produces the dynamical equations. for a closed system with n + 1 degrees of freedom (DoF s). q i = {q 1, q 2,..., q n+1 = τ} where the states {q i } are ordered with respect to increasing values of scalar function S(q i ) -entropy - a scalar field on the space {q i } the degree of freedom τ is any of the dofs {q 1,..., q n+1 } which is timeeligible so that τ S := S τ 0 for a continuum (1) The EGM formalism maximizes the entropy variation δs around the given state {q = (q 1, q 2,..., q n+1 = τ)} δs(q i ) = n S qi dq i + S τ dτ + (higher orders) (2) i=1 2
3 The maximization of the entropy variation (2 ) with the additional condition - ergodicity h(q i, τ; dq i, dτ) = ε 0 (3) provides i) the first order equation (system of equations) for dq i dτ, δs τ = 0 (4) δs qi = 0, (5) which defines the trajectory in the state space {q i, τ} and ii) the set of second order differential inequalities [ ] δsττ δs τ qi { 0} matrix [n + 1 n + 1] is non-positive (6) δs qk τ δs qi q k - causality condition for S and/or h 2 Discoupled time 2.1 EGM compared with the canonical formalism In the canonical (hamiltonian) formalism the state space is determined by the double set of DoF s q i, p i by means of local scalar function H = H(q i, p i ), Hamilton function - the key object generating the evolution in the state space, the time dependence - dynamics- is introduced externally by imposing the dynamical equations dq dt = H p; dp dt = H q - the Hamiltonian equations. Disadvantages of this approach which should be mentioned are ˆ redundant degrees of freedom (2n instead of n), although p i are generically connected with time derivatives of q i ; ˆ time is an external parameter - the time scale of the dynamics is not an intrinsic feature of the system and can be chosen arbitrary. 3
4 2.2 Definition of a conventinal time as a discoupled degree of freedom The EGM formalism outlined above claims in paricular, a closed system in an equilibrium cannot posess any eigentime, since the local maximum of entropy as equilibrium condition q i S(q i ) = 0, for all q i excludes an existence of a degree of freedom τ := q t satisfying the time eligibility S(q i ) > 0 q t For oscillations, which are closed paths in the state space around the stable equilibrium states (attractors), only partial intervals of values q t can be chosen, where this condition is satisfied. Thus the internal eigentime of the closed system can be defined for example piecewiese like τ := { qt q t q t S > 0 q t S < 0 The following helpful definition is in order: degree of freedom τ is called discoupled (from other degrees of freedom q i ) in the total entropy S(τ, q i ), if S(τ, q i ) = σ(τ) + s(q i ) (7) This condition is equivalent to the requirement for all second derivatives mixed with τ to disappear: S qi τ = 0, i = 1,..., n If additionally, the ergodicity does not depend on τ, dτ (in extended global and local sense): h dτ = h τ = 0 then the system can be called true hamiltonian by comparison with the canonical form. 4
5 The definition of unbounded time scale in a conventional sense in units of fluctuation periods around some equilibrium state, mentioned above, is explained for this case as follows: Suppose, the external degree of freedom τ of the clock-subsystem is discoupled in the total entropy S(τ, x, y) of e.g. three degrees of freedom, S(τ, x, y) = σ(τ) + s(x, y) (8) while the degree of freedom τ is also not contained in the ergodicity condition h = h(x, y) (9) (the ergodicity for x(τ), y(τ) is true hamiltonian. Then the differentiation according to the entropy gradient maximization formalism [1] provides: (the dot denotes d, the prime τ dτ t : = σ (τ) = s x (x, y)ẋ + s y (x, y)ẏ (10) dx = ẋ dy ẏ = h y(x, y) (11) h x (x, y) respectively) The latter itself provides the path P(x, y) = 0 - a trajectory in the state subspace {x, y} uniquely (together with an initial condition P(x 0, y 0 ) = 0). and the former is only the parametrization of the latter, thus its solutions are parametrizations of P(x, y) = 0. The existence of closed paths is therefore only a property of ergodicity function h(x, y), like a Hamilton function for harmonic oscillator H(p, q) = p 2 + q 2 = ε 0 A time period is assigned only by the parametrization τ, which is not unique. Thus the definition of time σ(τ) in terms of oscillation or fluctuation periods taken for time units, by means of (8) is a pure clock choice, which does not depend on the geometry of state space or entropy structure, unless the clock degree of freedom is not discoupled (in that general case S(τ, q i ) τ = S(τ, q i) q i q i ) 5
6 2.3 Separable time-refernce degree of freedom The special case considered above gives rise to the following reverse question: For a dynamical system S = S(p, q) Does a transformation exists, such that ε 0 = h(p, q) {p, q} {x, τ} S(p, q) = S(x, τ) = Σ(x) + σ(τ) h(p, q) = h(x, τ) i.e. in terms of transformed degrees of freedom it becomes a system with the separated time τ. In such a case the system can be called a system with the separable time Example of a time separation For a system with 2 degrees of freedom {q, p} with global ergodicity h(q, p) = q 2 p 2 it is natural if the entropy is a linear function of the volume of state space: S(q, p) = L(qp), L some linear function. The transformation brings the system to the form n = q p 2, τ = p + q 2 and q = τ + n; p = τ n S(n, τ) = L(τ 2 ) L(n 2 ) h(n, τ) = 4nτ with the separated time τ, e.g. a quantum system with the occupation number n, where the ergodicity function transporms to the action, and the entropy corresponds the quantum system with the external clock of the macroscopic labor-system. 6
7 3 Conclusions As it has been shown in the note, the formalism proposed in [1] includes also the definition of external time as a special case of discoupled clock (8). By the way, this case is physically non-realisable, on the basis of the fact alone, that both subsystems - an observable system {q i } and the external clock {τ} - should be compared with each other in a total frame of reference; therefore, the information exchange means an interaction between them. For instance, it can be never neglected in a quantum case, since getting any information of a system changes the quantum state. References [1] I.V. Drozdov On a local formalism for time evolution of dynamical systems arxiv: physics.class-ph
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. Canonical Transformations-1
 1 Introduction Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics Canonical Transformations The choice of generalized coordinates used to describe a physical system is completely arbitrary, but the Lagrangian is invariant
1 Introduction Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics Canonical Transformations The choice of generalized coordinates used to describe a physical system is completely arbitrary, but the Lagrangian is invariant
The Principle of Least Action
 The Principle of Least Action Anders Svensson Abstract In this paper, the principle of least action in classical mechanics is studied. The term is used in several different contexts, mainly for Hamilton
The Principle of Least Action Anders Svensson Abstract In this paper, the principle of least action in classical mechanics is studied. The term is used in several different contexts, mainly for Hamilton
Under evolution for a small time δt the area A(t) = q p evolves into an area
 Physics 106a, Caltech 6 November, 2018 Lecture 11: Hamiltonian Mechanics II Towards statistical mechanics Phase space volumes are conserved by Hamiltonian dynamics We can use many nearby initial conditions
Physics 106a, Caltech 6 November, 2018 Lecture 11: Hamiltonian Mechanics II Towards statistical mechanics Phase space volumes are conserved by Hamiltonian dynamics We can use many nearby initial conditions
Classical Statistical Mechanics: Part 1
 Classical Statistical Mechanics: Part 1 January 16, 2013 Classical Mechanics 1-Dimensional system with 1 particle of mass m Newton s equations of motion for position x(t) and momentum p(t): ẋ(t) dx p =
Classical Statistical Mechanics: Part 1 January 16, 2013 Classical Mechanics 1-Dimensional system with 1 particle of mass m Newton s equations of motion for position x(t) and momentum p(t): ẋ(t) dx p =
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Statistical Physics I Spring Term 2013 Notes on the Microcanonical Ensemble
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department 8.044 Statistical Physics I Spring Term 2013 Notes on the Microcanonical Ensemble The object of this endeavor is to impose a simple probability
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department 8.044 Statistical Physics I Spring Term 2013 Notes on the Microcanonical Ensemble The object of this endeavor is to impose a simple probability
for changing independent variables. Most simply for a function f(x) the Legendre transformation f(x) B(s) takes the form B(s) = xs f(x) with s = df
 Physics 106a, Caltech 1 November, 2018 Lecture 10: Hamiltonian Mechanics I The Hamiltonian In the Hamiltonian formulation of dynamics each second order ODE given by the Euler- Lagrange equation in terms
Physics 106a, Caltech 1 November, 2018 Lecture 10: Hamiltonian Mechanics I The Hamiltonian In the Hamiltonian formulation of dynamics each second order ODE given by the Euler- Lagrange equation in terms
LANGEVIN EQUATION AND THERMODYNAMICS
 LANGEVIN EQUATION AND THERMODYNAMICS RELATING STOCHASTIC DYNAMICS WITH THERMODYNAMIC LAWS November 10, 2017 1 / 20 MOTIVATION There are at least three levels of description of classical dynamics: thermodynamic,
LANGEVIN EQUATION AND THERMODYNAMICS RELATING STOCHASTIC DYNAMICS WITH THERMODYNAMIC LAWS November 10, 2017 1 / 20 MOTIVATION There are at least three levels of description of classical dynamics: thermodynamic,
HAMILTON S PRINCIPLE
 HAMILTON S PRINCIPLE In our previous derivation of Lagrange s equations we started from the Newtonian vector equations of motion and via D Alembert s Principle changed coordinates to generalised coordinates
HAMILTON S PRINCIPLE In our previous derivation of Lagrange s equations we started from the Newtonian vector equations of motion and via D Alembert s Principle changed coordinates to generalised coordinates
Nonlinear Single-Particle Dynamics in High Energy Accelerators
 Nonlinear Single-Particle Dynamics in High Energy Accelerators Part 2: Basic tools and concepts Nonlinear Single-Particle Dynamics in High Energy Accelerators This course consists of eight lectures: 1.
Nonlinear Single-Particle Dynamics in High Energy Accelerators Part 2: Basic tools and concepts Nonlinear Single-Particle Dynamics in High Energy Accelerators This course consists of eight lectures: 1.
Canonical transformations (Lecture 4)
 Canonical transformations (Lecture 4) January 26, 2016 61/441 Lecture outline We will introduce and discuss canonical transformations that conserve the Hamiltonian structure of equations of motion. Poisson
Canonical transformations (Lecture 4) January 26, 2016 61/441 Lecture outline We will introduce and discuss canonical transformations that conserve the Hamiltonian structure of equations of motion. Poisson
Typicality paradigm in Quantum Statistical Thermodynamics Barbara Fresch, Giorgio Moro Dipartimento Scienze Chimiche Università di Padova
 Typicality paradigm in Quantum Statistical Thermodynamics Barbara Fresch, Giorgio Moro Dipartimento Scienze Chimiche Università di Padova Outline 1) The framework: microcanonical statistics versus the
Typicality paradigm in Quantum Statistical Thermodynamics Barbara Fresch, Giorgio Moro Dipartimento Scienze Chimiche Università di Padova Outline 1) The framework: microcanonical statistics versus the
Deriving quantum mechanics from statistical assumptions
 from statistical assumptions U. Klein University of Linz, Institute for Theoretical Physics, A-4040 Linz, Austria Joint Annual Meeting of ÖPG/SPS/ÖGAA - Innsbruck 2009 The interpretation of quantum mechanics
from statistical assumptions U. Klein University of Linz, Institute for Theoretical Physics, A-4040 Linz, Austria Joint Annual Meeting of ÖPG/SPS/ÖGAA - Innsbruck 2009 The interpretation of quantum mechanics
An Outline of (Classical) Statistical Mechanics and Related Concepts in Machine Learning
 An Outline of (Classical) Statistical Mechanics and Related Concepts in Machine Learning Chang Liu Tsinghua University June 1, 2016 1 / 22 What is covered What is Statistical mechanics developed for? What
An Outline of (Classical) Statistical Mechanics and Related Concepts in Machine Learning Chang Liu Tsinghua University June 1, 2016 1 / 22 What is covered What is Statistical mechanics developed for? What
Chapter 2 Thermodynamics 2.1 Thermodynamic Description
 Chapter 2 Thermodynamics 2.1 Thermodynamic Description In some cases, mechanical systems with many degrees of freedom admit a simpler description using a small number of parameters. Consider, for example,
Chapter 2 Thermodynamics 2.1 Thermodynamic Description In some cases, mechanical systems with many degrees of freedom admit a simpler description using a small number of parameters. Consider, for example,
Euclidean path integral formalism: from quantum mechanics to quantum field theory
 : from quantum mechanics to quantum field theory Dr. Philippe de Forcrand Tutor: Dr. Marco Panero ETH Zürich 30th March, 2009 Introduction Real time Euclidean time Vacuum s expectation values Euclidean
: from quantum mechanics to quantum field theory Dr. Philippe de Forcrand Tutor: Dr. Marco Panero ETH Zürich 30th March, 2009 Introduction Real time Euclidean time Vacuum s expectation values Euclidean
Electric and Magnetic Forces in Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Formalism
 Electric and Magnetic Forces in Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Formalism Benjamin Hornberger 1/26/1 Phy 55, Classical Electrodynamics, Prof. Goldhaber Lecture notes from Oct. 26, 21 Lecture held by Prof. Weisberger
Electric and Magnetic Forces in Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Formalism Benjamin Hornberger 1/26/1 Phy 55, Classical Electrodynamics, Prof. Goldhaber Lecture notes from Oct. 26, 21 Lecture held by Prof. Weisberger
Two recent works on molecular systems out of equilibrium
 Two recent works on molecular systems out of equilibrium Frédéric Legoll ENPC and INRIA joint work with M. Dobson, T. Lelièvre, G. Stoltz (ENPC and INRIA), A. Iacobucci and S. Olla (Dauphine). CECAM workshop:
Two recent works on molecular systems out of equilibrium Frédéric Legoll ENPC and INRIA joint work with M. Dobson, T. Lelièvre, G. Stoltz (ENPC and INRIA), A. Iacobucci and S. Olla (Dauphine). CECAM workshop:
15. Hamiltonian Mechanics
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Classical Dynamics Physics Course Materials 2015 15. Hamiltonian Mechanics Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu Creative Commons License
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Classical Dynamics Physics Course Materials 2015 15. Hamiltonian Mechanics Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu Creative Commons License
Quantum field theory and the Ricci flow
 Quantum field theory and the Ricci flow Daniel Friedan Department of Physics & Astronomy Rutgers the State University of New Jersey, USA Natural Science Institute, University of Iceland Mathematics Colloquium
Quantum field theory and the Ricci flow Daniel Friedan Department of Physics & Astronomy Rutgers the State University of New Jersey, USA Natural Science Institute, University of Iceland Mathematics Colloquium
Gauge Fixing and Constrained Dynamics in Numerical Relativity
 Gauge Fixing and Constrained Dynamics in Numerical Relativity Jon Allen The Dirac formalism for dealing with constraints in a canonical Hamiltonian formulation is reviewed. Gauge freedom is discussed and
Gauge Fixing and Constrained Dynamics in Numerical Relativity Jon Allen The Dirac formalism for dealing with constraints in a canonical Hamiltonian formulation is reviewed. Gauge freedom is discussed and
Part II. Classical Dynamics. Year
 Part II Year 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 28 Paper 1, Section I 8B Derive Hamilton s equations from an action principle. 22 Consider a two-dimensional phase space with the Hamiltonian
Part II Year 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 28 Paper 1, Section I 8B Derive Hamilton s equations from an action principle. 22 Consider a two-dimensional phase space with the Hamiltonian
Homework 4. Goldstein 9.7. Part (a) Theoretical Dynamics October 01, 2010 (1) P i = F 1. Q i. p i = F 1 (3) q i (5) P i (6)
 Theoretical Dynamics October 01, 2010 Instructor: Dr. Thomas Cohen Homework 4 Submitted by: Vivek Saxena Goldstein 9.7 Part (a) F 1 (q, Q, t) F 2 (q, P, t) P i F 1 Q i (1) F 2 (q, P, t) F 1 (q, Q, t) +
Theoretical Dynamics October 01, 2010 Instructor: Dr. Thomas Cohen Homework 4 Submitted by: Vivek Saxena Goldstein 9.7 Part (a) F 1 (q, Q, t) F 2 (q, P, t) P i F 1 Q i (1) F 2 (q, P, t) F 1 (q, Q, t) +
Derivation of the GENERIC form of nonequilibrium thermodynamics from a statistical optimization principle
 Derivation of the GENERIC form of nonequilibrium thermodynamics from a statistical optimization principle Bruce Turkington Univ. of Massachusetts Amherst An optimization principle for deriving nonequilibrium
Derivation of the GENERIC form of nonequilibrium thermodynamics from a statistical optimization principle Bruce Turkington Univ. of Massachusetts Amherst An optimization principle for deriving nonequilibrium
G : Statistical Mechanics Notes for Lecture 3 I. MICROCANONICAL ENSEMBLE: CONDITIONS FOR THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM Consider bringing two systems into
 G25.2651: Statistical Mechanics Notes for Lecture 3 I. MICROCANONICAL ENSEMBLE: CONDITIONS FOR THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM Consider bringing two systems into thermal contact. By thermal contact, we mean that the
G25.2651: Statistical Mechanics Notes for Lecture 3 I. MICROCANONICAL ENSEMBLE: CONDITIONS FOR THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM Consider bringing two systems into thermal contact. By thermal contact, we mean that the
ChE 503 A. Z. Panagiotopoulos 1
 ChE 503 A. Z. Panagiotopoulos 1 STATISTICAL MECHANICAL ENSEMLES 1 MICROSCOPIC AND MACROSCOPIC ARIALES The central question in Statistical Mechanics can be phrased as follows: If particles (atoms, molecules,
ChE 503 A. Z. Panagiotopoulos 1 STATISTICAL MECHANICAL ENSEMLES 1 MICROSCOPIC AND MACROSCOPIC ARIALES The central question in Statistical Mechanics can be phrased as follows: If particles (atoms, molecules,
Averaging II: Adiabatic Invariance for Integrable Systems (argued via the Averaging Principle)
 Averaging II: Adiabatic Invariance for Integrable Systems (argued via the Averaging Principle In classical mechanics an adiabatic invariant is defined as follows[1]. Consider the Hamiltonian system with
Averaging II: Adiabatic Invariance for Integrable Systems (argued via the Averaging Principle In classical mechanics an adiabatic invariant is defined as follows[1]. Consider the Hamiltonian system with
First Problem Set for Physics 847 (Statistical Physics II)
 First Problem Set for Physics 847 (Statistical Physics II) Important dates: Feb 0 0:30am-:8pm midterm exam, Mar 6 9:30am-:8am final exam Due date: Tuesday, Jan 3. Review 0 points Let us start by reviewing
First Problem Set for Physics 847 (Statistical Physics II) Important dates: Feb 0 0:30am-:8pm midterm exam, Mar 6 9:30am-:8am final exam Due date: Tuesday, Jan 3. Review 0 points Let us start by reviewing
9.1 System in contact with a heat reservoir
 Chapter 9 Canonical ensemble 9. System in contact with a heat reservoir We consider a small system A characterized by E, V and N in thermal interaction with a heat reservoir A 2 characterized by E 2, V
Chapter 9 Canonical ensemble 9. System in contact with a heat reservoir We consider a small system A characterized by E, V and N in thermal interaction with a heat reservoir A 2 characterized by E 2, V
Elements of Statistical Mechanics
 Elements of Statistical Mechanics Thermodynamics describes the properties of macroscopic bodies. Statistical mechanics allows us to obtain the laws of thermodynamics from the laws of mechanics, classical
Elements of Statistical Mechanics Thermodynamics describes the properties of macroscopic bodies. Statistical mechanics allows us to obtain the laws of thermodynamics from the laws of mechanics, classical
Curves in the configuration space Q or in the velocity phase space Ω satisfying the Euler-Lagrange (EL) equations,
 Physics 6010, Fall 2010 Hamiltonian Formalism: Hamilton s equations. Conservation laws. Reduction. Poisson Brackets. Relevant Sections in Text: 8.1 8.3, 9.5 The Hamiltonian Formalism We now return to formal
Physics 6010, Fall 2010 Hamiltonian Formalism: Hamilton s equations. Conservation laws. Reduction. Poisson Brackets. Relevant Sections in Text: 8.1 8.3, 9.5 The Hamiltonian Formalism We now return to formal
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701
 Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/24//2017 Physics 5701 Lecture Commutation of Observables and First Consequences of the Postulates Outline 1 Commutation Relations 2 Uncertainty Relations
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/24//2017 Physics 5701 Lecture Commutation of Observables and First Consequences of the Postulates Outline 1 Commutation Relations 2 Uncertainty Relations
1. Diagonalize the matrix A if possible, that is, find an invertible matrix P and a diagonal
 . Diagonalize the matrix A if possible, that is, find an invertible matrix P and a diagonal 3 9 matrix D such that A = P DP, for A =. 3 4 3 (a) P = 4, D =. 3 (b) P = 4, D =. (c) P = 4 8 4, D =. 3 (d) P
. Diagonalize the matrix A if possible, that is, find an invertible matrix P and a diagonal 3 9 matrix D such that A = P DP, for A =. 3 4 3 (a) P = 4, D =. 3 (b) P = 4, D =. (c) P = 4 8 4, D =. 3 (d) P
Modelling and Mathematical Methods in Process and Chemical Engineering
 Modelling and Mathematical Methods in Process and Chemical Engineering Solution Series 3 1. Population dynamics: Gendercide The system admits two steady states The Jacobi matrix is ẋ = (1 p)xy k 1 x ẏ
Modelling and Mathematical Methods in Process and Chemical Engineering Solution Series 3 1. Population dynamics: Gendercide The system admits two steady states The Jacobi matrix is ẋ = (1 p)xy k 1 x ẏ
Mesoscale Simulation Methods. Ronojoy Adhikari The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai
 Mesoscale Simulation Methods Ronojoy Adhikari The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai Outline What is mesoscale? Mesoscale statics and dynamics through coarse-graining. Coarse-grained equations
Mesoscale Simulation Methods Ronojoy Adhikari The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai Outline What is mesoscale? Mesoscale statics and dynamics through coarse-graining. Coarse-grained equations
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7)
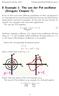 8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
Kinematics. Chapter Multi-Body Systems
 Chapter 2 Kinematics This chapter first introduces multi-body systems in conceptual terms. It then describes the concept of a Euclidean frame in the material world, following the concept of a Euclidean
Chapter 2 Kinematics This chapter first introduces multi-body systems in conceptual terms. It then describes the concept of a Euclidean frame in the material world, following the concept of a Euclidean
Quantum Field Theory Notes. Ryan D. Reece
 Quantum Field Theory Notes Ryan D. Reece November 27, 2007 Chapter 1 Preliminaries 1.1 Overview of Special Relativity 1.1.1 Lorentz Boosts Searches in the later part 19th century for the coordinate transformation
Quantum Field Theory Notes Ryan D. Reece November 27, 2007 Chapter 1 Preliminaries 1.1 Overview of Special Relativity 1.1.1 Lorentz Boosts Searches in the later part 19th century for the coordinate transformation
Limiting shapes of Ising droplets, fingers, and corners
 Limiting shapes of Ising droplets, fingers, and corners Pavel Krapivsky Boston University Plan and Motivation Evolving limiting shapes in the context of Ising model endowed with T=0 spin-flip dynamics.
Limiting shapes of Ising droplets, fingers, and corners Pavel Krapivsky Boston University Plan and Motivation Evolving limiting shapes in the context of Ising model endowed with T=0 spin-flip dynamics.
Estimating Lyapunov Exponents from Time Series. Gerrit Ansmann
 Estimating Lyapunov Exponents from Time Series Gerrit Ansmann Example: Lorenz system. Two identical Lorenz systems with initial conditions; one is slightly perturbed (10 14 ) at t = 30: 20 x 2 1 0 20 20
Estimating Lyapunov Exponents from Time Series Gerrit Ansmann Example: Lorenz system. Two identical Lorenz systems with initial conditions; one is slightly perturbed (10 14 ) at t = 30: 20 x 2 1 0 20 20
Physics 6010, Fall 2016 Constraints and Lagrange Multipliers. Relevant Sections in Text:
 Physics 6010, Fall 2016 Constraints and Lagrange Multipliers. Relevant Sections in Text: 1.3 1.6 Constraints Often times we consider dynamical systems which are defined using some kind of restrictions
Physics 6010, Fall 2016 Constraints and Lagrange Multipliers. Relevant Sections in Text: 1.3 1.6 Constraints Often times we consider dynamical systems which are defined using some kind of restrictions
IV. Classical Statistical Mechanics
 IV. Classical Statistical Mechanics IV.A General Definitions Statistical Mechanics is a probabilistic approach to equilibrium macroscopic properties of large numbers of degrees of freedom. As discussed
IV. Classical Statistical Mechanics IV.A General Definitions Statistical Mechanics is a probabilistic approach to equilibrium macroscopic properties of large numbers of degrees of freedom. As discussed
Lecture 5. Alexey Boyarsky. October 21, Legendre transformation and the Hamilton equations of motion
 Lecture 5 Alexey Boyarsky October 1, 015 1 The Hamilton equations of motion 1.1 Legendre transformation and the Hamilton equations of motion First-order equations of motion. In the Lagrangian formulation,
Lecture 5 Alexey Boyarsky October 1, 015 1 The Hamilton equations of motion 1.1 Legendre transformation and the Hamilton equations of motion First-order equations of motion. In the Lagrangian formulation,
5. Systems in contact with a thermal bath
 5. Systems in contact with a thermal bath So far, isolated systems (micro-canonical methods) 5.1 Constant number of particles:kittel&kroemer Chap. 3 Boltzmann factor Partition function (canonical methods)
5. Systems in contact with a thermal bath So far, isolated systems (micro-canonical methods) 5.1 Constant number of particles:kittel&kroemer Chap. 3 Boltzmann factor Partition function (canonical methods)
A Brief Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
 A Brief Introduction to Statistical Mechanics E. J. Maginn, J. K. Shah Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556 USA Monte Carlo Workshop Universidade
A Brief Introduction to Statistical Mechanics E. J. Maginn, J. K. Shah Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556 USA Monte Carlo Workshop Universidade
The Quantum Theory of Finite-Temperature Fields: An Introduction. Florian Divotgey. Johann Wolfgang Goethe Universität Frankfurt am Main
 he Quantum heory of Finite-emperature Fields: An Introduction Florian Divotgey Johann Wolfgang Goethe Universität Franfurt am Main Fachbereich Physi Institut für heoretische Physi 1..16 Outline 1 he Free
he Quantum heory of Finite-emperature Fields: An Introduction Florian Divotgey Johann Wolfgang Goethe Universität Franfurt am Main Fachbereich Physi Institut für heoretische Physi 1..16 Outline 1 he Free
Local time path integrals and their application to Lévy random walks
 Local time path integrals and their application to Lévy random walks Václav Zatloukal (www.zatlovac.eu) Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague talk given
Local time path integrals and their application to Lévy random walks Václav Zatloukal (www.zatlovac.eu) Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague talk given
Thermodynamics of phase transitions
 Thermodynamics of phase transitions Katarzyna Sznajd-Weron Department of Theoretical of Physics Wroc law University of Science and Technology, Poland March 12, 2017 Katarzyna Sznajd-Weron (WUST) Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics of phase transitions Katarzyna Sznajd-Weron Department of Theoretical of Physics Wroc law University of Science and Technology, Poland March 12, 2017 Katarzyna Sznajd-Weron (WUST) Thermodynamics
Collective Effects. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics
 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 5, April 14, 2006 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 5, April 14, 2006 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Hamiltonian flow in phase space and Liouville s theorem (Lecture 5)
 Hamiltonian flow in phase space and Liouville s theorem (Lecture 5) January 26, 2016 90/441 Lecture outline We will discuss the Hamiltonian flow in the phase space. This flow represents a time dependent
Hamiltonian flow in phase space and Liouville s theorem (Lecture 5) January 26, 2016 90/441 Lecture outline We will discuss the Hamiltonian flow in the phase space. This flow represents a time dependent
Quantum Mechanical Foundations of Causal Entropic Forces
 Quantum Mechanical Foundations of Causal Entropic Forces Swapnil Shah North Carolina State University, USA snshah4@ncsu.edu Abstract. The theory of Causal Entropic Forces was introduced to explain the
Quantum Mechanical Foundations of Causal Entropic Forces Swapnil Shah North Carolina State University, USA snshah4@ncsu.edu Abstract. The theory of Causal Entropic Forces was introduced to explain the
The Hamiltonian formulation of gauge theories
 The Hamiltonian formulation of gauge theories I [p, q] = dt p i q i H(p, q) " # q i = @H @p i =[q i, H] ṗ i = @H =[p @q i i, H] 1. Symplectic geometry, Hamilton-Jacobi theory,... 2. The first (general)
The Hamiltonian formulation of gauge theories I [p, q] = dt p i q i H(p, q) " # q i = @H @p i =[q i, H] ṗ i = @H =[p @q i i, H] 1. Symplectic geometry, Hamilton-Jacobi theory,... 2. The first (general)
Physics 106a, Caltech 13 November, Lecture 13: Action, Hamilton-Jacobi Theory. Action-Angle Variables
 Physics 06a, Caltech 3 November, 08 Lecture 3: Action, Hamilton-Jacobi Theory Starred sections are advanced topics for interest and future reference. The unstarred material will not be tested on the final
Physics 06a, Caltech 3 November, 08 Lecture 3: Action, Hamilton-Jacobi Theory Starred sections are advanced topics for interest and future reference. The unstarred material will not be tested on the final
Legendre Transforms, Calculus of Varations, and Mechanics Principles
 page 437 Appendix C Legendre Transforms, Calculus of Varations, and Mechanics Principles C.1 Legendre Transforms Legendre transforms map functions in a vector space to functions in the dual space. From
page 437 Appendix C Legendre Transforms, Calculus of Varations, and Mechanics Principles C.1 Legendre Transforms Legendre transforms map functions in a vector space to functions in the dual space. From
22.2. Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 22.2 Introduction Many applications of matrices in both engineering and science utilize eigenvalues and, sometimes, eigenvectors. Control theory, vibration
Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors 22.2 Introduction Many applications of matrices in both engineering and science utilize eigenvalues and, sometimes, eigenvectors. Control theory, vibration
Physics 562: Statistical Mechanics Spring 2003, James P. Sethna Homework 5, due Wednesday, April 2 Latest revision: April 4, 2003, 8:53 am
 Physics 562: Statistical Mechanics Spring 2003, James P. Sethna Homework 5, due Wednesday, April 2 Latest revision: April 4, 2003, 8:53 am Reading David Chandler, Introduction to Modern Statistical Mechanics,
Physics 562: Statistical Mechanics Spring 2003, James P. Sethna Homework 5, due Wednesday, April 2 Latest revision: April 4, 2003, 8:53 am Reading David Chandler, Introduction to Modern Statistical Mechanics,
Motivation: Can the equations of physics be derived from information-theoretic principles?
 10. Physics from Fisher Information. Motivation: Can the equations of physics e derived from information-theoretic principles? I. Fisher Information. Task: To otain a measure of the accuracy of estimated
10. Physics from Fisher Information. Motivation: Can the equations of physics e derived from information-theoretic principles? I. Fisher Information. Task: To otain a measure of the accuracy of estimated
Lecture 5. Hartree-Fock Theory. WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics
 Lecture 5 Hartree-Fock Theory WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics Particle-number representation: General formalism The simplest starting point for a many-body state is a system of
Lecture 5 Hartree-Fock Theory WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics Particle-number representation: General formalism The simplest starting point for a many-body state is a system of
Statistical thermodynamics for MD and MC simulations
 Statistical thermodynamics for MD and MC simulations knowing 2 atoms and wishing to know 10 23 of them Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař 22 June 2016 Introduction Thermodynamic properties of molecular systems
Statistical thermodynamics for MD and MC simulations knowing 2 atoms and wishing to know 10 23 of them Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař 22 June 2016 Introduction Thermodynamic properties of molecular systems
Relativistic Mechanics
 Physics 411 Lecture 9 Relativistic Mechanics Lecture 9 Physics 411 Classical Mechanics II September 17th, 2007 We have developed some tensor language to describe familiar physics we reviewed orbital motion
Physics 411 Lecture 9 Relativistic Mechanics Lecture 9 Physics 411 Classical Mechanics II September 17th, 2007 We have developed some tensor language to describe familiar physics we reviewed orbital motion
Chapter 2 Ensemble Theory in Statistical Physics: Free Energy Potential
 Chapter Ensemble Theory in Statistical Physics: Free Energy Potential Abstract In this chapter, we discuss the basic formalism of statistical physics Also, we consider in detail the concept of the free
Chapter Ensemble Theory in Statistical Physics: Free Energy Potential Abstract In this chapter, we discuss the basic formalism of statistical physics Also, we consider in detail the concept of the free
Collective Effects. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics
 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 5, April 14, 2006 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/
1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 5, April 14, 2006 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/
then the substitution z = ax + by + c reduces this equation to the separable one.
 7 Substitutions II Some of the topics in this lecture are optional and will not be tested at the exams. However, for a curious student it should be useful to learn a few extra things about ordinary differential
7 Substitutions II Some of the topics in this lecture are optional and will not be tested at the exams. However, for a curious student it should be useful to learn a few extra things about ordinary differential
The Microcanonical Approach. (a) The volume of accessible phase space for a given total energy is proportional to. dq 1 dq 2 dq N dp 1 dp 2 dp N,
 8333: Statistical Mechanics I Problem Set # 6 Solutions Fall 003 Classical Harmonic Oscillators: The Microcanonical Approach a The volume of accessible phase space for a given total energy is proportional
8333: Statistical Mechanics I Problem Set # 6 Solutions Fall 003 Classical Harmonic Oscillators: The Microcanonical Approach a The volume of accessible phase space for a given total energy is proportional
Feynman s path integral approach to quantum physics and its relativistic generalization
 Feynman s path integral approach to quantum physics and its relativistic generalization Jürgen Struckmeier j.struckmeier@gsi.de, www.gsi.de/ struck Vortrag im Rahmen des Winterseminars Aktuelle Probleme
Feynman s path integral approach to quantum physics and its relativistic generalization Jürgen Struckmeier j.struckmeier@gsi.de, www.gsi.de/ struck Vortrag im Rahmen des Winterseminars Aktuelle Probleme
4 Insect outbreak model
 4 Insect outbreak model In this lecture I will put to a good use all the mathematical machinery we discussed so far. Consider an insect population, which is subject to predation by birds. It is a very
4 Insect outbreak model In this lecture I will put to a good use all the mathematical machinery we discussed so far. Consider an insect population, which is subject to predation by birds. It is a very
Lecture 4: Entropy. Chapter I. Basic Principles of Stat Mechanics. A.G. Petukhov, PHYS 743. September 7, 2017
 Lecture 4: Entropy Chapter I. Basic Principles of Stat Mechanics A.G. Petukhov, PHYS 743 September 7, 2017 Chapter I. Basic Principles of Stat Mechanics A.G. Petukhov, Lecture PHYS4: 743 Entropy September
Lecture 4: Entropy Chapter I. Basic Principles of Stat Mechanics A.G. Petukhov, PHYS 743 September 7, 2017 Chapter I. Basic Principles of Stat Mechanics A.G. Petukhov, Lecture PHYS4: 743 Entropy September
From quantum to classical statistical mechanics. Polyatomic ideal gas.
 From quantum to classical statistical mechanics. Polyatomic ideal gas. Peter Košovan peter.kosovan@natur.cuni.cz Dept. of Physical and Macromolecular Chemistry Lecture 5, Statistical Thermodynamics, MC260P105,
From quantum to classical statistical mechanics. Polyatomic ideal gas. Peter Košovan peter.kosovan@natur.cuni.cz Dept. of Physical and Macromolecular Chemistry Lecture 5, Statistical Thermodynamics, MC260P105,
Appendix C extra - Concepts of statistical physics Cextra1-1
 Appendix C extra - Concepts of statistical physics Cextra1-1 Appendix C extra - Concepts of statistical physics A conventional introductory course in physics concentrates on one-body motion: the change
Appendix C extra - Concepts of statistical physics Cextra1-1 Appendix C extra - Concepts of statistical physics A conventional introductory course in physics concentrates on one-body motion: the change
Nosé-Hoover Thermostats
 Nosé- Nosé- Texas A & M, UT Austin, St. Olaf College October 29, 2013 Physical Model Nosé- q Figure: Simple Oscillator p Physical Model Continued Heat Bath T p Nosé- q Figure: Simple Oscillator in a heat
Nosé- Nosé- Texas A & M, UT Austin, St. Olaf College October 29, 2013 Physical Model Nosé- q Figure: Simple Oscillator p Physical Model Continued Heat Bath T p Nosé- q Figure: Simple Oscillator in a heat
763620SS STATISTICAL PHYSICS Solutions 5 Autumn 2012
 7660SS STATISTICAL PHYSICS Solutions 5 Autumn 01 1 Classical Flow in Phase Space Determine the trajectories of classical Hamiltonian flow in -dim corresponding to a particle in a constant gravitational
7660SS STATISTICAL PHYSICS Solutions 5 Autumn 01 1 Classical Flow in Phase Space Determine the trajectories of classical Hamiltonian flow in -dim corresponding to a particle in a constant gravitational
Symplectic integration. Yichao Jing
 Yichao Jing Hamiltonian & symplecticness Outline Numerical integrator and symplectic integration Application to accelerator beam dynamics Accuracy and integration order Hamiltonian dynamics In accelerator,
Yichao Jing Hamiltonian & symplecticness Outline Numerical integrator and symplectic integration Application to accelerator beam dynamics Accuracy and integration order Hamiltonian dynamics In accelerator,
Newtonian Mechanics. Chapter Classical space-time
 Chapter 1 Newtonian Mechanics In these notes classical mechanics will be viewed as a mathematical model for the description of physical systems consisting of a certain (generally finite) number of particles
Chapter 1 Newtonian Mechanics In these notes classical mechanics will be viewed as a mathematical model for the description of physical systems consisting of a certain (generally finite) number of particles
An efficient homomtopy-based Poincaré-Lindstedt method for the periodic steady-state analysis of nonlinear autonomous oscillators
 An efficient homomtopy-based Poincaré-Lindstedt method for the periodic steady-state analysis of nonlinear autonomous oscillators Zhongming Chen, Kim Batselier, Haotian Liu, Ngai Wong The University of
An efficient homomtopy-based Poincaré-Lindstedt method for the periodic steady-state analysis of nonlinear autonomous oscillators Zhongming Chen, Kim Batselier, Haotian Liu, Ngai Wong The University of
Newton s laws. Chapter 1. Not: Quantum Mechanics / Relativistic Mechanics
 PHYB54 Revision Chapter 1 Newton s laws Not: Quantum Mechanics / Relativistic Mechanics Isaac Newton 1642-1727 Classical mechanics breaks down if: 1) high speed, v ~ c 2) microscopic/elementary particles
PHYB54 Revision Chapter 1 Newton s laws Not: Quantum Mechanics / Relativistic Mechanics Isaac Newton 1642-1727 Classical mechanics breaks down if: 1) high speed, v ~ c 2) microscopic/elementary particles
Phys460.nb Back to our example. on the same quantum state. i.e., if we have initial condition (5.241) ψ(t = 0) = χ n (t = 0)
 Phys46.nb 89 on the same quantum state. i.e., if we have initial condition ψ(t ) χ n (t ) (5.41) then at later time ψ(t) e i ϕ(t) χ n (t) (5.4) This phase ϕ contains two parts ϕ(t) - E n(t) t + ϕ B (t)
Phys46.nb 89 on the same quantum state. i.e., if we have initial condition ψ(t ) χ n (t ) (5.41) then at later time ψ(t) e i ϕ(t) χ n (t) (5.4) This phase ϕ contains two parts ϕ(t) - E n(t) t + ϕ B (t)
Application of Information Theory, Lecture 7. Relative Entropy. Handout Mode. Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University.
 Application of Information Theory, Lecture 7 Relative Entropy Handout Mode Iftach Haitner Tel Aviv University. December 1, 2015 Iftach Haitner (TAU) Application of Information Theory, Lecture 7 December
Application of Information Theory, Lecture 7 Relative Entropy Handout Mode Iftach Haitner Tel Aviv University. December 1, 2015 Iftach Haitner (TAU) Application of Information Theory, Lecture 7 December
The Particle in a Box
 Page 324 Lecture 17: Relation of Particle in a Box Eigenstates to Position and Momentum Eigenstates General Considerations on Bound States and Quantization Continuity Equation for Probability Date Given:
Page 324 Lecture 17: Relation of Particle in a Box Eigenstates to Position and Momentum Eigenstates General Considerations on Bound States and Quantization Continuity Equation for Probability Date Given:
PHY411 Lecture notes Part 2
 PHY411 Lecture notes Part 2 Alice Quillen April 6, 2017 Contents 1 Canonical Transformations 2 1.1 Poisson Brackets................................. 2 1.2 Canonical transformations............................
PHY411 Lecture notes Part 2 Alice Quillen April 6, 2017 Contents 1 Canonical Transformations 2 1.1 Poisson Brackets................................. 2 1.2 Canonical transformations............................
Stochastic Behavior of Dissipative Hamiltonian Systems with Limit Cycles
 Stochastic Behavior of Dissipative Hamiltonian Systems with Limit Cycles Wolfgang Mathis Florian Richter Richard Mathis Institut für Theoretische Elektrotechnik, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität Hannover,
Stochastic Behavior of Dissipative Hamiltonian Systems with Limit Cycles Wolfgang Mathis Florian Richter Richard Mathis Institut für Theoretische Elektrotechnik, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität Hannover,
Information Theory and Predictability Lecture 6: Maximum Entropy Techniques
 Information Theory and Predictability Lecture 6: Maximum Entropy Techniques 1 Philosophy Often with random variables of high dimensional systems it is difficult to deduce the appropriate probability distribution
Information Theory and Predictability Lecture 6: Maximum Entropy Techniques 1 Philosophy Often with random variables of high dimensional systems it is difficult to deduce the appropriate probability distribution
Basics of Statistical Mechanics
 Basics of Statistical Mechanics Review of ensembles Microcanonical, canonical, Maxwell-Boltzmann Constant pressure, temperature, volume, Thermodynamic limit Ergodicity (see online notes also) Reading assignment:
Basics of Statistical Mechanics Review of ensembles Microcanonical, canonical, Maxwell-Boltzmann Constant pressure, temperature, volume, Thermodynamic limit Ergodicity (see online notes also) Reading assignment:
We start with some important background material in classical and quantum mechanics.
 Chapter Basics We start with some important background material in classical and quantum mechanics.. Classical mechanics Lagrangian mechanics Compared to Newtonian mechanics, Lagrangian mechanics has the
Chapter Basics We start with some important background material in classical and quantum mechanics.. Classical mechanics Lagrangian mechanics Compared to Newtonian mechanics, Lagrangian mechanics has the
The Particle-Field Hamiltonian
 The Particle-Field Hamiltonian For a fundamental understanding of the interaction of a particle with the electromagnetic field we need to know the total energy of the system consisting of particle and
The Particle-Field Hamiltonian For a fundamental understanding of the interaction of a particle with the electromagnetic field we need to know the total energy of the system consisting of particle and
Liouville Equation. q s = H p s
 Liouville Equation In this section we will build a bridge from Classical Mechanics to Statistical Physics. The bridge is Liouville equation. We start with the Hamiltonian formalism of the Classical Mechanics,
Liouville Equation In this section we will build a bridge from Classical Mechanics to Statistical Physics. The bridge is Liouville equation. We start with the Hamiltonian formalism of the Classical Mechanics,
arxiv:quant-ph/ v5 10 Feb 2003
 Quantum entanglement of identical particles Yu Shi Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom and Theory of
Quantum entanglement of identical particles Yu Shi Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom and Theory of
L2 gains and system approximation quality 1
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.242, Fall 24: MODEL REDUCTION L2 gains and system approximation quality 1 This lecture discusses the utility
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.242, Fall 24: MODEL REDUCTION L2 gains and system approximation quality 1 This lecture discusses the utility
Chaos in Hamiltonian systems
 Chaos in Hamiltonian systems Teemu Laakso April 26, 2013 Course material: Chapter 7 from Ott 1993/2002, Chaos in Dynamical Systems, Cambridge http://matriisi.ee.tut.fi/courses/mat-35006 Useful reading:
Chaos in Hamiltonian systems Teemu Laakso April 26, 2013 Course material: Chapter 7 from Ott 1993/2002, Chaos in Dynamical Systems, Cambridge http://matriisi.ee.tut.fi/courses/mat-35006 Useful reading:
Energy-preserving Pseudo-spectral Methods for Klein-Gordon-Schrödinger Equations
 .. Energy-preserving Pseudo-spectral Methods for Klein-Gordon-Schrödinger Equations Jingjing Zhang Henan Polytechnic University December 9, 211 Outline.1 Background.2 Aim, Methodology And Motivation.3
.. Energy-preserving Pseudo-spectral Methods for Klein-Gordon-Schrödinger Equations Jingjing Zhang Henan Polytechnic University December 9, 211 Outline.1 Background.2 Aim, Methodology And Motivation.3
Classical Mechanics in Hamiltonian Form
 Classical Mechanics in Hamiltonian Form We consider a point particle of mass m, position x moving in a potential V (x). It moves according to Newton s law, mẍ + V (x) = 0 (1) This is the usual and simplest
Classical Mechanics in Hamiltonian Form We consider a point particle of mass m, position x moving in a potential V (x). It moves according to Newton s law, mẍ + V (x) = 0 (1) This is the usual and simplest
Canonical transformations and exact invariants for time-dependent Hamiltonian systems
 Ann. Phys. Leipzig 11 00 1, 15 38 Canonical transformations and exact invariants for time-dependent Hamiltonian systems Jürgen Struckmeier a and Claus Riedel Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung GSI,
Ann. Phys. Leipzig 11 00 1, 15 38 Canonical transformations and exact invariants for time-dependent Hamiltonian systems Jürgen Struckmeier a and Claus Riedel Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung GSI,
Concepts in Materials Science I. StatMech Basics. VBS/MRC Stat Mech Basics 0
 StatMech Basics VBS/MRC Stat Mech Basics 0 Goal of Stat Mech Concepts in Materials Science I Quantum (Classical) Mechanics gives energy as a function of configuration Macroscopic observables (state) (P,
StatMech Basics VBS/MRC Stat Mech Basics 0 Goal of Stat Mech Concepts in Materials Science I Quantum (Classical) Mechanics gives energy as a function of configuration Macroscopic observables (state) (P,
An introduction to Birkhoff normal form
 An introduction to Birkhoff normal form Dario Bambusi Dipartimento di Matematica, Universitá di Milano via Saldini 50, 0133 Milano (Italy) 19.11.14 1 Introduction The aim of this note is to present an
An introduction to Birkhoff normal form Dario Bambusi Dipartimento di Matematica, Universitá di Milano via Saldini 50, 0133 Milano (Italy) 19.11.14 1 Introduction The aim of this note is to present an
Lecture 9 Examples and Problems
 Lecture 9 Examples and Problems Counting microstates of combined systems Volume exchange between systems Definition of Entropy and its role in equilibrium The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of
Lecture 9 Examples and Problems Counting microstates of combined systems Volume exchange between systems Definition of Entropy and its role in equilibrium The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of
Dynamic and Thermodynamic Stability of Black Holes and Black Branes
 Dynamic and Thermodynamic Stability of Black Holes and Black Branes Robert M. Wald with Stefan Hollands arxiv:1201.0463 Commun. Math. Phys. 321, 629 (2013) (see also K. Prabhu and R.M. Wald, Commun. Math.
Dynamic and Thermodynamic Stability of Black Holes and Black Branes Robert M. Wald with Stefan Hollands arxiv:1201.0463 Commun. Math. Phys. 321, 629 (2013) (see also K. Prabhu and R.M. Wald, Commun. Math.
Grand Canonical Formalism
 Grand Canonical Formalism Grand Canonical Ensebmle For the gases of ideal Bosons and Fermions each single-particle mode behaves almost like an independent subsystem, with the only reservation that the
Grand Canonical Formalism Grand Canonical Ensebmle For the gases of ideal Bosons and Fermions each single-particle mode behaves almost like an independent subsystem, with the only reservation that the
Hydrodynamics. Stefan Flörchinger (Heidelberg) Heidelberg, 3 May 2010
 Hydrodynamics Stefan Flörchinger (Heidelberg) Heidelberg, 3 May 2010 What is Hydrodynamics? Describes the evolution of physical systems (classical or quantum particles, fluids or fields) close to thermal
Hydrodynamics Stefan Flörchinger (Heidelberg) Heidelberg, 3 May 2010 What is Hydrodynamics? Describes the evolution of physical systems (classical or quantum particles, fluids or fields) close to thermal
arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 12 Sep 2018
![arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 12 Sep 2018 arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 12 Sep 2018](/thumbs/93/111792566.jpg) The gravity of light-waves arxiv:1809.04309v1 [gr-qc] 1 Sep 018 J.W. van Holten Nikhef, Amsterdam and Leiden University Netherlands Abstract Light waves carry along their own gravitational field; for simple
The gravity of light-waves arxiv:1809.04309v1 [gr-qc] 1 Sep 018 J.W. van Holten Nikhef, Amsterdam and Leiden University Netherlands Abstract Light waves carry along their own gravitational field; for simple
Outline 1. Introduction 1.1. Historical Overview 1.2. The Theory 2. The Relativistic String 2.1. Set Up 2.2. The Relativistic Point Particle 2.3. The
 Classical String Theory Proseminar in Theoretical Physics David Reutter ETH Zürich April 15, 2013 Outline 1. Introduction 1.1. Historical Overview 1.2. The Theory 2. The Relativistic String 2.1. Set Up
Classical String Theory Proseminar in Theoretical Physics David Reutter ETH Zürich April 15, 2013 Outline 1. Introduction 1.1. Historical Overview 1.2. The Theory 2. The Relativistic String 2.1. Set Up
Modified Equations for Variational Integrators
 Modified Equations for Variational Integrators Mats Vermeeren Technische Universität Berlin Groningen December 18, 2018 Mats Vermeeren (TU Berlin) Modified equations for variational integrators December
Modified Equations for Variational Integrators Mats Vermeeren Technische Universität Berlin Groningen December 18, 2018 Mats Vermeeren (TU Berlin) Modified equations for variational integrators December
Solutions to Problems in Goldstein, Classical Mechanics, Second Edition. Chapter 9
 Solutions to Problems in Goldstein, Classical Mechanics, Second Edition Homer Reid October 29, 2002 Chater 9 Problem 9. One of the attemts at combining the two sets of Hamilton s equations into one tries
Solutions to Problems in Goldstein, Classical Mechanics, Second Edition Homer Reid October 29, 2002 Chater 9 Problem 9. One of the attemts at combining the two sets of Hamilton s equations into one tries
