From Electrons to Materials Properties
|
|
|
- Emmeline Mosley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 From Electrons to Materials Properties Density Functional Theory for Engineers and Materials Scientists Dr. Andreas Funk
2 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 Page 2 Chapter VI Potential Energy Surfaces
3 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 Page 3 Potential energy surfaces (PES s) Whenever we are dealing with the chemistry of a system we have to understand that any stable conformation of atoms is a minimum on the potential energy surface (PES). A PES is defined as a surface of co-dimension 1 to the atomic degrees of freedom, meaning that it is a scalar function of the atomic coordinates. Physically, it is a field of potential energy. As stable conformers are minima, reaction paths connect two or more minima in a way that the connecting path (the reaction path) always has the lowest energy possible. The point with highest energy on the reaction path, the transition state, is then a first-order saddle point. Hence, finding stable conformers is mathematically the task of finding minima, and finding transition states is identical to the task of finding first-order saddle points.
4 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 Page 4
5 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 Page 5 This means that whenever we are going to analyze our PES, we need to know at least the first derivatives of the (potential) energy, hence the gradients of the energy E (1) g = R n n In principle we can obtain these numerically, yet this is rather costly. Yet, there exists a theorem (the Hellmann-Feynman theorem), which allows us to obtain gradients analytically: (2) ψ H ψ R n = E ψ ψ = E ψ ψ = ψ H ψ = ψ H R n R n R n R n ψ This is quite helpful, as we can now simply obtain the derivatives of our Hamiltionian and apply the new operator to our converged wavefunctions. In principle, we can try something similar for second derivatives.
6 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 Page 6 Alternatively, we can approximate the Hessian (matrix of second derivatives) from the gradients. We define (3) δ = R (k+1) R (k) (4) γ = g (k+1) g (k) We initialize our Hessian as the unit matrix and update its inverse matrix whenever we change the positions of one or all atoms (5) G (k+1) 1 = G (k) γt G (k) 1 γ δ T γ δδ T δ T γ δγt G (k) 1 + G (k) 1 γδ T δ T γ
7 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 Page 7 Geometry Optimization Now as we have both, first and second derivatives, we can do some analysis. We have either an extremal point if the necessary condition (6) g = 0 is fulfilled. Furthermore, if the Hessian is positive definite we have a minimum and we have a transition state if one and only one eigenvalue of the Hessian is negative and all others are positive. We have found a global minimum if our energy value is lower than at any other point of the PES, and a local minimum otherwise (if we are in a minimum). In addition, we have found the true transition state if there is no lower first-order saddle point between the two minima it connects.
8 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 Page 8 Let us optimize a geometry. Obviously we can reach the closest minimum by simply following the gradient where it descends steepest. This is the simple equation (7) R (k+1) = R (k) g (k+1) Unfortunately we are lacking second derivatives, so we cannot say for sure what kind of extremal point we reached. In addition, this simple algorithm tends to oscillate. We can improve this applying a weighted gradient, where we weight by conjugate gradients, i.e. according to Fletcher and Reeves (8) R (k+1) = R (k) g(k+1)t g (k+1) g (k)t g (k) or as proposed by Polak and Ribière g (k+1) (9) R (k+1) = R (k) g(k+1)t g (k+1) g (k) g (k)t g (k) g (k+1)
9 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 Page 9 Beyond its vastly improved stability the conjugate gradients (CG) method has the advantage that it converges to a minimum within a maximum of k = N steps, where N is the dimension of the problem. Linear convergence is guaranteed. But maybe we can go with superlinear convergence. Let us take second derivatives, in a Newton-like method: (10) R (k+1) = R (k) G (k+1) 1 g (k+1) This is not only stable, it yields especially in proximity to the minimum superlinear convergence. Plus we automatically move towards a minimum, as the sign of the Hessian pushes us in the right direction. Furthermore we can select one eigenvalue of the Hessian to run into the opposite direction. This directly leads us to a transition state.
10 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 Page 10 Finally, we may want to optimize our cell parameters. This yields 6 additional degrees of freedom from the stress tensor (11) σ = σ xx τ xy τ xz τ yx σ yy τ yz τ zx τ zy σ zz We have reached a minimum if our PES is minimal under the constraints of the pressure tensor, i.e. when all forces are zero. This means that we derive forces on the cell, typically as sum of atomic forces. We can apply the aforementioned optimization algorithms to cell optimization as well, and we can optimize molecular geometries and cell parameters synchronously.
11 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 Page 11 Sometimes we want to keep some parts of our ensemble fixed. This yields constrained optimization, which is a widely used tool. There are many different constraints, i.e. fixed distances, added forces, fixed chemical potential etc. One example of constrained optimization are nudged elastic band (NEB) methods. Here, a series of geometrical interpolations, called images, between reactant and products structures are constructed and constrained by a spring force so they form a chain.
12 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 Page 12 Optimizing the images now yields the minima for the two final images, but all images in between are experiencing a harmonic force by both neighbors. This means that they cannot proceed to their closest minimum, as in this case the additional force from the constraint rises quadratically. This optimizes them (ideally) so that all images are on the minimum energy path (MEP), hence the reaction path. The images highest in energy can serve as an approximation to the transition state. Why do we need a transition state? According to transition state theory (TST) we can obtain the rate constant from it as (12) k = k BT h or, more precise exp ETS E init k B T (13) k = k BT h i i 3N init υ i 3N 1 TS υ exp ETS E init i k B T
13 From Electrons to Materials Properties: DFT for Engineers and Materials Scientists Funk Fachgebiet Werkstoffe des Bauwesens und Bauchemie Mar-17, 2016 Page 13 Optimization of your batch script (UCI HPC) #!/bin/bash #$ -N test #$ -q free32i #$ -pe one-node-mpi 32 #$ -R y #$ -m beas module load espresso/5.3.0 export StartDir=$PWD export WorkDir=/scratch/$JOB_ID mkdir $WorkDir cp * $WorkDir cd $WorkDir mpirun -np $CORES pw.x -i pyrope.in > pyrope.out cp -r * $StartDir rm -rf $WorkDir
TECHNIQUES TO LOCATE A TRANSITION STATE
 32 III. TECHNIQUES TO LOCATE A TRANSITION STATE In addition to the location of minima, the calculation of transition states and reaction pathways is an interesting task for Quantum Chemistry (QC). The
32 III. TECHNIQUES TO LOCATE A TRANSITION STATE In addition to the location of minima, the calculation of transition states and reaction pathways is an interesting task for Quantum Chemistry (QC). The
A DARK GREY P O N T, with a Switch Tail, and a small Star on the Forehead. Any
 Y Y Y X X «/ YY Y Y ««Y x ) & \ & & } # Y \#$& / Y Y X» \\ / X X X x & Y Y X «q «z \x» = q Y # % \ & [ & Z \ & { + % ) / / «q zy» / & / / / & x x X / % % ) Y x X Y $ Z % Y Y x x } / % «] «] # z» & Y X»
Y Y Y X X «/ YY Y Y ««Y x ) & \ & & } # Y \#$& / Y Y X» \\ / X X X x & Y Y X «q «z \x» = q Y # % \ & [ & Z \ & { + % ) / / «q zy» / & / / / & x x X / % % ) Y x X Y $ Z % Y Y x x } / % «] «] # z» & Y X»
22 Path Optimisation Methods
 22 Path Optimisation Methods 204 22 Path Optimisation Methods Many interesting chemical and physical processes involve transitions from one state to another. Typical examples are migration paths for defects
22 Path Optimisation Methods 204 22 Path Optimisation Methods Many interesting chemical and physical processes involve transitions from one state to another. Typical examples are migration paths for defects
Introduction to Geometry Optimization. Computational Chemistry lab 2009
 Introduction to Geometry Optimization Computational Chemistry lab 9 Determination of the molecule configuration H H Diatomic molecule determine the interatomic distance H O H Triatomic molecule determine
Introduction to Geometry Optimization Computational Chemistry lab 9 Determination of the molecule configuration H H Diatomic molecule determine the interatomic distance H O H Triatomic molecule determine
Geometry Optimisation
 Geometry Optimisation Matt Probert Condensed Matter Dynamics Group Department of Physics, University of York, UK http://www.cmt.york.ac.uk/cmd http://www.castep.org Motivation Overview of Talk Background
Geometry Optimisation Matt Probert Condensed Matter Dynamics Group Department of Physics, University of York, UK http://www.cmt.york.ac.uk/cmd http://www.castep.org Motivation Overview of Talk Background
Numerical Optimization Professor Horst Cerjak, Horst Bischof, Thomas Pock Mat Vis-Gra SS09
 Numerical Optimization 1 Working Horse in Computer Vision Variational Methods Shape Analysis Machine Learning Markov Random Fields Geometry Common denominator: optimization problems 2 Overview of Methods
Numerical Optimization 1 Working Horse in Computer Vision Variational Methods Shape Analysis Machine Learning Markov Random Fields Geometry Common denominator: optimization problems 2 Overview of Methods
Chapter 10 Conjugate Direction Methods
 Chapter 10 Conjugate Direction Methods An Introduction to Optimization Spring, 2012 1 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/4/13 Introduction Conjugate direction methods can be viewed as being intermediate between the method
Chapter 10 Conjugate Direction Methods An Introduction to Optimization Spring, 2012 1 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/4/13 Introduction Conjugate direction methods can be viewed as being intermediate between the method
Unconstrained optimization
 Chapter 4 Unconstrained optimization An unconstrained optimization problem takes the form min x Rnf(x) (4.1) for a target functional (also called objective function) f : R n R. In this chapter and throughout
Chapter 4 Unconstrained optimization An unconstrained optimization problem takes the form min x Rnf(x) (4.1) for a target functional (also called objective function) f : R n R. In this chapter and throughout
Unit IV State of stress in Three Dimensions
 Unit IV State of stress in Three Dimensions State of stress in Three Dimensions References Punmia B.C.,"Theory of Structures" (SMTS) Vol II, Laxmi Publishing Pvt Ltd, New Delhi 2004. Rattan.S.S., "Strength
Unit IV State of stress in Three Dimensions State of stress in Three Dimensions References Punmia B.C.,"Theory of Structures" (SMTS) Vol II, Laxmi Publishing Pvt Ltd, New Delhi 2004. Rattan.S.S., "Strength
Applications of Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors
 Applications of Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors Louie L. Yaw Walla Walla University Engineering Department For Linear Algebra Class November 17, 214 Outline 1 The eigenvalue/eigenvector problem 2 Principal
Applications of Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors Louie L. Yaw Walla Walla University Engineering Department For Linear Algebra Class November 17, 214 Outline 1 The eigenvalue/eigenvector problem 2 Principal
12. Stresses and Strains
 12. Stresses and Strains Finite Element Method Differential Equation Weak Formulation Approximating Functions Weighted Residuals FEM - Formulation Classification of Problems Scalar Vector 1-D T(x) u(x)
12. Stresses and Strains Finite Element Method Differential Equation Weak Formulation Approximating Functions Weighted Residuals FEM - Formulation Classification of Problems Scalar Vector 1-D T(x) u(x)
Lagrange Multipliers
 Optimization with Constraints As long as algebra and geometry have been separated, their progress have been slow and their uses limited; but when these two sciences have been united, they have lent each
Optimization with Constraints As long as algebra and geometry have been separated, their progress have been slow and their uses limited; but when these two sciences have been united, they have lent each
Chapter 4. Unconstrained optimization
 Chapter 4. Unconstrained optimization Version: 28-10-2012 Material: (for details see) Chapter 11 in [FKS] (pp.251-276) A reference e.g. L.11.2 refers to the corresponding Lemma in the book [FKS] PDF-file
Chapter 4. Unconstrained optimization Version: 28-10-2012 Material: (for details see) Chapter 11 in [FKS] (pp.251-276) A reference e.g. L.11.2 refers to the corresponding Lemma in the book [FKS] PDF-file
LOWELL WEEKLY JOURNAL
 Y -» $ 5 Y 7 Y Y -Y- Q x Q» 75»»/ q } # ]»\ - - $ { Q» / X x»»- 3 q $ 9 ) Y q - 5 5 3 3 3 7 Q q - - Q _»»/Q Y - 9 - - - )- [ X 7» -» - )»? / /? Q Y»» # X Q» - -?» Q ) Q \ Q - - - 3? 7» -? #»»» 7 - / Q
Y -» $ 5 Y 7 Y Y -Y- Q x Q» 75»»/ q } # ]»\ - - $ { Q» / X x»»- 3 q $ 9 ) Y q - 5 5 3 3 3 7 Q q - - Q _»»/Q Y - 9 - - - )- [ X 7» -» - )»? / /? Q Y»» # X Q» - -?» Q ) Q \ Q - - - 3? 7» -? #»»» 7 - / Q
Chapter 9: Differential Analysis
 9-1 Introduction 9-2 Conservation of Mass 9-3 The Stream Function 9-4 Conservation of Linear Momentum 9-5 Navier Stokes Equation 9-6 Differential Analysis Problems Recall 9-1 Introduction (1) Chap 5: Control
9-1 Introduction 9-2 Conservation of Mass 9-3 The Stream Function 9-4 Conservation of Linear Momentum 9-5 Navier Stokes Equation 9-6 Differential Analysis Problems Recall 9-1 Introduction (1) Chap 5: Control
Deep Learning. Authors: I. Goodfellow, Y. Bengio, A. Courville. Chapter 4: Numerical Computation. Lecture slides edited by C. Yim. C.
 Chapter 4: Numerical Computation Deep Learning Authors: I. Goodfellow, Y. Bengio, A. Courville Lecture slides edited by 1 Chapter 4: Numerical Computation 4.1 Overflow and Underflow 4.2 Poor Conditioning
Chapter 4: Numerical Computation Deep Learning Authors: I. Goodfellow, Y. Bengio, A. Courville Lecture slides edited by 1 Chapter 4: Numerical Computation 4.1 Overflow and Underflow 4.2 Poor Conditioning
Computer Applications in Engineering and Construction Programming Assignment #9 Principle Stresses and Flow Nets in Geotechnical Design
 CVEN 302-501 Computer Applications in Engineering and Construction Programming Assignment #9 Principle Stresses and Flow Nets in Geotechnical Design Date distributed : 12/2/2015 Date due : 12/9/2015 at
CVEN 302-501 Computer Applications in Engineering and Construction Programming Assignment #9 Principle Stresses and Flow Nets in Geotechnical Design Date distributed : 12/2/2015 Date due : 12/9/2015 at
Vasil Khalidov & Miles Hansard. C.M. Bishop s PRML: Chapter 5; Neural Networks
 C.M. Bishop s PRML: Chapter 5; Neural Networks Introduction The aim is, as before, to find useful decompositions of the target variable; t(x) = y(x, w) + ɛ(x) (3.7) t(x n ) and x n are the observations,
C.M. Bishop s PRML: Chapter 5; Neural Networks Introduction The aim is, as before, to find useful decompositions of the target variable; t(x) = y(x, w) + ɛ(x) (3.7) t(x n ) and x n are the observations,
Chapter 9: Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow
 of Fluid Flow Objectives 1. Understand how the differential equations of mass and momentum conservation are derived. 2. Calculate the stream function and pressure field, and plot streamlines for a known
of Fluid Flow Objectives 1. Understand how the differential equations of mass and momentum conservation are derived. 2. Calculate the stream function and pressure field, and plot streamlines for a known
Topological insulator part I: Phenomena
 Phys60.nb 5 Topological insulator part I: Phenomena (Part II and Part III discusses how to understand a topological insluator based band-structure theory and gauge theory) (Part IV discusses more complicated
Phys60.nb 5 Topological insulator part I: Phenomena (Part II and Part III discusses how to understand a topological insluator based band-structure theory and gauge theory) (Part IV discusses more complicated
Numerical Optimization of Partial Differential Equations
 Numerical Optimization of Partial Differential Equations Part I: basic optimization concepts in R n Bartosz Protas Department of Mathematics & Statistics McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
Numerical Optimization of Partial Differential Equations Part I: basic optimization concepts in R n Bartosz Protas Department of Mathematics & Statistics McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
Neatest and Promptest Manner. E d i t u r ami rul)lihher. FOIt THE CIIILDIIES'. Trifles.
 » ~ $ ) 7 x X ) / ( 8 2 X 39 ««x» ««! «! / x? \» «({? «» q «(? (?? x! «? 8? ( z x x q? ) «q q q ) x z x 69 7( X X ( 3»«! ( ~«x ««x ) (» «8 4 X «4 «4 «8 X «x «(» X) ()»» «X «97 X X X 4 ( 86) x) ( ) z z
» ~ $ ) 7 x X ) / ( 8 2 X 39 ««x» ««! «! / x? \» «({? «» q «(? (?? x! «? 8? ( z x x q? ) «q q q ) x z x 69 7( X X ( 3»«! ( ~«x ««x ) (» «8 4 X «4 «4 «8 X «x «(» X) ()»» «X «97 X X X 4 ( 86) x) ( ) z z
Figure 1: Transition State, Saddle Point, Reaction Pathway
 Computational Chemistry Workshops West Ridge Research Building-UAF Campus 9:00am-4:00pm, Room 009 Electronic Structure - July 19-21, 2016 Molecular Dynamics - July 26-28, 2016 Potential Energy Surfaces
Computational Chemistry Workshops West Ridge Research Building-UAF Campus 9:00am-4:00pm, Room 009 Electronic Structure - July 19-21, 2016 Molecular Dynamics - July 26-28, 2016 Potential Energy Surfaces
Stress, Strain, Mohr s Circle
 Stress, Strain, Mohr s Circle The fundamental quantities in solid mechanics are stresses and strains. In accordance with the continuum mechanics assumption, the molecular structure of materials is neglected
Stress, Strain, Mohr s Circle The fundamental quantities in solid mechanics are stresses and strains. In accordance with the continuum mechanics assumption, the molecular structure of materials is neglected
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering
 Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Solution of Matrix Eigenvalue Problem
 Outlines October 12, 2004 Outlines Part I: Review of Previous Lecture Part II: Review of Previous Lecture Outlines Part I: Review of Previous Lecture Part II: Standard Matrix Eigenvalue Problem Other Forms
Outlines October 12, 2004 Outlines Part I: Review of Previous Lecture Part II: Review of Previous Lecture Outlines Part I: Review of Previous Lecture Part II: Standard Matrix Eigenvalue Problem Other Forms
MAE 323: Lecture 1. Review
 This review is divided into two parts. The first part is a mini-review of statics and solid mechanics. The second part is a review of matrix/vector fundamentals. The first part is given as an refresher
This review is divided into two parts. The first part is a mini-review of statics and solid mechanics. The second part is a review of matrix/vector fundamentals. The first part is given as an refresher
Lecture 8 Optimization
 4/9/015 Lecture 8 Optimization EE 4386/5301 Computational Methods in EE Spring 015 Optimization 1 Outline Introduction 1D Optimization Parabolic interpolation Golden section search Newton s method Multidimensional
4/9/015 Lecture 8 Optimization EE 4386/5301 Computational Methods in EE Spring 015 Optimization 1 Outline Introduction 1D Optimization Parabolic interpolation Golden section search Newton s method Multidimensional
Math 263 Assignment #4 Solutions. 0 = f 1 (x,y,z) = 2x 1 0 = f 2 (x,y,z) = z 2 0 = f 3 (x,y,z) = y 1
 Math 263 Assignment #4 Solutions 1. Find and classify the critical points of each of the following functions: (a) f(x,y,z) = x 2 + yz x 2y z + 7 (c) f(x,y) = e x2 y 2 (1 e x2 ) (b) f(x,y) = (x + y) 3 (x
Math 263 Assignment #4 Solutions 1. Find and classify the critical points of each of the following functions: (a) f(x,y,z) = x 2 + yz x 2y z + 7 (c) f(x,y) = e x2 y 2 (1 e x2 ) (b) f(x,y) = (x + y) 3 (x
Nonlinear Optimization: What s important?
 Nonlinear Optimization: What s important? Julian Hall 10th May 2012 Convexity: convex problems A local minimizer is a global minimizer A solution of f (x) = 0 (stationary point) is a minimizer A global
Nonlinear Optimization: What s important? Julian Hall 10th May 2012 Convexity: convex problems A local minimizer is a global minimizer A solution of f (x) = 0 (stationary point) is a minimizer A global
Stress/Strain. Outline. Lecture 1. Stress. Strain. Plane Stress and Plane Strain. Materials. ME EN 372 Andrew Ning
 Stress/Strain Lecture 1 ME EN 372 Andrew Ning aning@byu.edu Outline Stress Strain Plane Stress and Plane Strain Materials otes and News [I had leftover time and so was also able to go through Section 3.1
Stress/Strain Lecture 1 ME EN 372 Andrew Ning aning@byu.edu Outline Stress Strain Plane Stress and Plane Strain Materials otes and News [I had leftover time and so was also able to go through Section 3.1
Tensor Visualization. CSC 7443: Scientific Information Visualization
 Tensor Visualization Tensor data A tensor is a multivariate quantity Scalar is a tensor of rank zero s = s(x,y,z) Vector is a tensor of rank one v = (v x,v y,v z ) For a symmetric tensor of rank 2, its
Tensor Visualization Tensor data A tensor is a multivariate quantity Scalar is a tensor of rank zero s = s(x,y,z) Vector is a tensor of rank one v = (v x,v y,v z ) For a symmetric tensor of rank 2, its
Unconstrained Multivariate Optimization
 Unconstrained Multivariate Optimization Multivariate optimization means optimization of a scalar function of a several variables: and has the general form: y = () min ( ) where () is a nonlinear scalar-valued
Unconstrained Multivariate Optimization Multivariate optimization means optimization of a scalar function of a several variables: and has the general form: y = () min ( ) where () is a nonlinear scalar-valued
Two Posts to Fill On School Board
 Y Y 9 86 4 4 qz 86 x : ( ) z 7 854 Y x 4 z z x x 4 87 88 Y 5 x q x 8 Y 8 x x : 6 ; : 5 x ; 4 ( z ; ( ) ) x ; z 94 ; x 3 3 3 5 94 ; ; ; ; 3 x : 5 89 q ; ; x ; x ; ; x : ; ; ; ; ; ; 87 47% : () : / : 83
Y Y 9 86 4 4 qz 86 x : ( ) z 7 854 Y x 4 z z x x 4 87 88 Y 5 x q x 8 Y 8 x x : 6 ; : 5 x ; 4 ( z ; ( ) ) x ; z 94 ; x 3 3 3 5 94 ; ; ; ; 3 x : 5 89 q ; ; x ; x ; ; x : ; ; ; ; ; ; 87 47% : () : / : 83
DIPOLES III. q const. The voltage produced by such a charge distribution is given by. r r'
 DIPOLES III We now consider a particularly important charge configuration a dipole. This consists of two equal but opposite charges separated by a small distance. We define the dipole moment as p lim q
DIPOLES III We now consider a particularly important charge configuration a dipole. This consists of two equal but opposite charges separated by a small distance. We define the dipole moment as p lim q
LOWELL JOURNAL. MUST APOLOGIZE. such communication with the shore as Is m i Boimhle, noewwary and proper for the comfort
 - 7 7 Z 8 q ) V x - X > q - < Y Y X V - z - - - - V - V - q \ - q q < -- V - - - x - - V q > x - x q - x q - x - - - 7 -» - - - - 6 q x - > - - x - - - x- - - q q - V - x - - ( Y q Y7 - >»> - x Y - ] [
- 7 7 Z 8 q ) V x - X > q - < Y Y X V - z - - - - V - V - q \ - q q < -- V - - - x - - V q > x - x q - x q - x - - - 7 -» - - - - 6 q x - > - - x - - - x- - - q q - V - x - - ( Y q Y7 - >»> - x Y - ] [
Exploring the energy landscape
 Exploring the energy landscape ChE210D Today's lecture: what are general features of the potential energy surface and how can we locate and characterize minima on it Derivatives of the potential energy
Exploring the energy landscape ChE210D Today's lecture: what are general features of the potential energy surface and how can we locate and characterize minima on it Derivatives of the potential energy
MECH 5312 Solid Mechanics II. Dr. Calvin M. Stewart Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at El Paso
 MECH 5312 Solid Mechanics II Dr. Calvin M. Stewart Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at El Paso Table of Contents Preliminary Math Concept of Stress Stress Components Equilibrium
MECH 5312 Solid Mechanics II Dr. Calvin M. Stewart Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at El Paso Table of Contents Preliminary Math Concept of Stress Stress Components Equilibrium
Steepest descent algorithm. Conjugate gradient training algorithm. Steepest descent algorithm. Remember previous examples
 Conjugate gradient training algorithm Steepest descent algorithm So far: Heuristic improvements to gradient descent (momentum Steepest descent training algorithm Can we do better? Definitions: weight vector
Conjugate gradient training algorithm Steepest descent algorithm So far: Heuristic improvements to gradient descent (momentum Steepest descent training algorithm Can we do better? Definitions: weight vector
Module #3. Transformation of stresses in 3-D READING LIST. DIETER: Ch. 2, pp Ch. 3 in Roesler Ch. 2 in McClintock and Argon Ch.
 HOMEWORK From Dieter -3, -4, 3-7 Module #3 Transformation of stresses in 3-D READING LIST DIETER: Ch., pp. 7-36 Ch. 3 in Roesler Ch. in McClintock and Argon Ch. 7 in Edelglass The Stress Tensor z z x O
HOMEWORK From Dieter -3, -4, 3-7 Module #3 Transformation of stresses in 3-D READING LIST DIETER: Ch., pp. 7-36 Ch. 3 in Roesler Ch. in McClintock and Argon Ch. 7 in Edelglass The Stress Tensor z z x O
Multiplication of Polynomials
 Summary 391 Chapter 5 SUMMARY Section 5.1 A polynomial in x is defined by a finite sum of terms of the form ax n, where a is a real number and n is a whole number. a is the coefficient of the term. n is
Summary 391 Chapter 5 SUMMARY Section 5.1 A polynomial in x is defined by a finite sum of terms of the form ax n, where a is a real number and n is a whole number. a is the coefficient of the term. n is
Crystal Relaxation, Elasticity, and Lattice Dynamics
 http://exciting-code.org Crystal Relaxation, Elasticity, and Lattice Dynamics Pasquale Pavone Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin http://exciting-code.org PART I: Structure Optimization Pasquale Pavone Humboldt-Universität
http://exciting-code.org Crystal Relaxation, Elasticity, and Lattice Dynamics Pasquale Pavone Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin http://exciting-code.org PART I: Structure Optimization Pasquale Pavone Humboldt-Universität
1 Newton s Method. Suppose we want to solve: x R. At x = x, f (x) can be approximated by:
 Newton s Method Suppose we want to solve: (P:) min f (x) At x = x, f (x) can be approximated by: n x R. f (x) h(x) := f ( x)+ f ( x) T (x x)+ (x x) t H ( x)(x x), 2 which is the quadratic Taylor expansion
Newton s Method Suppose we want to solve: (P:) min f (x) At x = x, f (x) can be approximated by: n x R. f (x) h(x) := f ( x)+ f ( x) T (x x)+ (x x) t H ( x)(x x), 2 which is the quadratic Taylor expansion
Nonlinear Programming
 Nonlinear Programming Kees Roos e-mail: C.Roos@ewi.tudelft.nl URL: http://www.isa.ewi.tudelft.nl/ roos LNMB Course De Uithof, Utrecht February 6 - May 8, A.D. 2006 Optimization Group 1 Outline for week
Nonlinear Programming Kees Roos e-mail: C.Roos@ewi.tudelft.nl URL: http://www.isa.ewi.tudelft.nl/ roos LNMB Course De Uithof, Utrecht February 6 - May 8, A.D. 2006 Optimization Group 1 Outline for week
Chapter 5. The Differential Forms of the Fundamental Laws
 Chapter 5 The Differential Forms of the Fundamental Laws 1 5.1 Introduction Two primary methods in deriving the differential forms of fundamental laws: Gauss s Theorem: Allows area integrals of the equations
Chapter 5 The Differential Forms of the Fundamental Laws 1 5.1 Introduction Two primary methods in deriving the differential forms of fundamental laws: Gauss s Theorem: Allows area integrals of the equations
Quantum-ESPRESSO. Rare Events and Nudged Elastic Band
 Quantum-ESPRESSO Rare Events and Nudged Elastic Band Rare Events the characteristic time scale of this transition process is t jump t vib e E A K B T Van t-hoff - Arrhenius (1890) Rare Events the characteristic
Quantum-ESPRESSO Rare Events and Nudged Elastic Band Rare Events the characteristic time scale of this transition process is t jump t vib e E A K B T Van t-hoff - Arrhenius (1890) Rare Events the characteristic
Programming, numerics and optimization
 Programming, numerics and optimization Lecture C-3: Unconstrained optimization II Łukasz Jankowski ljank@ippt.pan.pl Institute of Fundamental Technological Research Room 4.32, Phone +22.8261281 ext. 428
Programming, numerics and optimization Lecture C-3: Unconstrained optimization II Łukasz Jankowski ljank@ippt.pan.pl Institute of Fundamental Technological Research Room 4.32, Phone +22.8261281 ext. 428
ECE580 Exam 1 October 4, Please do not write on the back of the exam pages. Extra paper is available from the instructor.
 ECE580 Exam 1 October 4, 2012 1 Name: Solution Score: /100 You must show ALL of your work for full credit. This exam is closed-book. Calculators may NOT be used. Please leave fractions as fractions, etc.
ECE580 Exam 1 October 4, 2012 1 Name: Solution Score: /100 You must show ALL of your work for full credit. This exam is closed-book. Calculators may NOT be used. Please leave fractions as fractions, etc.
Let f(x) = x, but the domain of f is the interval 0 x 1. Note
 I.g Maximum and Minimum. Lagrange Multipliers Recall: Suppose we are given y = f(x). We recall that the maximum/minimum points occur at the following points: (1) where f = 0; (2) where f does not exist;
I.g Maximum and Minimum. Lagrange Multipliers Recall: Suppose we are given y = f(x). We recall that the maximum/minimum points occur at the following points: (1) where f = 0; (2) where f does not exist;
' Liberty and Umou Ono and Inseparablo "
 3 5? #< q 8 2 / / ) 9 ) 2 ) > < _ / ] > ) 2 ) ) 5 > x > [ < > < ) > _ ] ]? <
3 5? #< q 8 2 / / ) 9 ) 2 ) > < _ / ] > ) 2 ) ) 5 > x > [ < > < ) > _ ] ]? <
NDT&E Methods: UT. VJ Technologies CAVITY INSPECTION. Nondestructive Testing & Evaluation TPU Lecture Course 2015/16.
 CAVITY INSPECTION NDT&E Methods: UT VJ Technologies NDT&E Methods: UT 6. NDT&E: Introduction to Methods 6.1. Ultrasonic Testing: Basics of Elasto-Dynamics 6.2. Principles of Measurement 6.3. The Pulse-Echo
CAVITY INSPECTION NDT&E Methods: UT VJ Technologies NDT&E Methods: UT 6. NDT&E: Introduction to Methods 6.1. Ultrasonic Testing: Basics of Elasto-Dynamics 6.2. Principles of Measurement 6.3. The Pulse-Echo
Nonlinear Optimization for Optimal Control
 Nonlinear Optimization for Optimal Control Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS Many slides and figures adapted from Stephen Boyd [optional] Boyd and Vandenberghe, Convex Optimization, Chapters 9 11 [optional]
Nonlinear Optimization for Optimal Control Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS Many slides and figures adapted from Stephen Boyd [optional] Boyd and Vandenberghe, Convex Optimization, Chapters 9 11 [optional]
Optimization and Calculus
 Optimization and Calculus To begin, there is a close relationship between finding the roots to a function and optimizing a function. In the former case, we solve for x. In the latter, we solve: g(x) =
Optimization and Calculus To begin, there is a close relationship between finding the roots to a function and optimizing a function. In the former case, we solve for x. In the latter, we solve: g(x) =
F-Praktikum Physikalisches Institut (PI) Stark korrelierte Elektronen und Spins. Report
 F-Praktikum Physikalisches Institut (PI) Stark korrelierte Elektronen und Spins Report Experiment Schallausbreitung in Kristallen (Sound Propagation in Crystals) Intsar Bangwi Physics bachelor 5. term
F-Praktikum Physikalisches Institut (PI) Stark korrelierte Elektronen und Spins Report Experiment Schallausbreitung in Kristallen (Sound Propagation in Crystals) Intsar Bangwi Physics bachelor 5. term
Classical Mechanics. Luis Anchordoqui
 1 Rigid Body Motion Inertia Tensor Rotational Kinetic Energy Principal Axes of Rotation Steiner s Theorem Euler s Equations for a Rigid Body Eulerian Angles Review of Fundamental Equations 2 Rigid body
1 Rigid Body Motion Inertia Tensor Rotational Kinetic Energy Principal Axes of Rotation Steiner s Theorem Euler s Equations for a Rigid Body Eulerian Angles Review of Fundamental Equations 2 Rigid body
OPER 627: Nonlinear Optimization Lecture 14: Mid-term Review
 OPER 627: Nonlinear Optimization Lecture 14: Mid-term Review Department of Statistical Sciences and Operations Research Virginia Commonwealth University Oct 16, 2013 (Lecture 14) Nonlinear Optimization
OPER 627: Nonlinear Optimization Lecture 14: Mid-term Review Department of Statistical Sciences and Operations Research Virginia Commonwealth University Oct 16, 2013 (Lecture 14) Nonlinear Optimization
FALL 2018 MATH 4211/6211 Optimization Homework 4
 FALL 2018 MATH 4211/6211 Optimization Homework 4 This homework assignment is open to textbook, reference books, slides, and online resources, excluding any direct solution to the problem (such as solution
FALL 2018 MATH 4211/6211 Optimization Homework 4 This homework assignment is open to textbook, reference books, slides, and online resources, excluding any direct solution to the problem (such as solution
3D Elasticity Theory
 3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
Section 14.8 Maxima & minima of functions of two variables. Learning outcomes. After completing this section, you will inshaallah be able to
 Section 14.8 Maxima & minima of functions of two variables 14.8 1 Learning outcomes After completing this section, you will inshaallah be able to 1. explain what is meant by relative maxima or relative
Section 14.8 Maxima & minima of functions of two variables 14.8 1 Learning outcomes After completing this section, you will inshaallah be able to 1. explain what is meant by relative maxima or relative
Geometry Optimization
 Geometry Optimization Matt Probert Condensed Matter Dynamics Group Department of Physics, University of York, U.K. http://www-users.york.ac.uk/~mijp1 Overview of lecture n Background Theory n Hellman-Feynman
Geometry Optimization Matt Probert Condensed Matter Dynamics Group Department of Physics, University of York, U.K. http://www-users.york.ac.uk/~mijp1 Overview of lecture n Background Theory n Hellman-Feynman
TUTORIAL 8: PHONONS, LATTICE EXPANSION, AND BAND-GAP RENORMALIZATION
 TUTORIAL 8: PHONONS, LATTICE EXPANSION, AND BAND-GAP RENORMALIZATION 1 INVESTIGATED SYSTEM: Silicon, diamond structure Electronic and 0K properties see W. Huhn, Tutorial 2, Wednesday August 2 2 THE HARMONIC
TUTORIAL 8: PHONONS, LATTICE EXPANSION, AND BAND-GAP RENORMALIZATION 1 INVESTIGATED SYSTEM: Silicon, diamond structure Electronic and 0K properties see W. Huhn, Tutorial 2, Wednesday August 2 2 THE HARMONIC
Motivation: We have already seen an example of a system of nonlinear equations when we studied Gaussian integration (p.8 of integration notes)
 AMSC/CMSC 460 Computational Methods, Fall 2007 UNIT 5: Nonlinear Equations Dianne P. O Leary c 2001, 2002, 2007 Solving Nonlinear Equations and Optimization Problems Read Chapter 8. Skip Section 8.1.1.
AMSC/CMSC 460 Computational Methods, Fall 2007 UNIT 5: Nonlinear Equations Dianne P. O Leary c 2001, 2002, 2007 Solving Nonlinear Equations and Optimization Problems Read Chapter 8. Skip Section 8.1.1.
MANY BILLS OF CONCERN TO PUBLIC
 - 6 8 9-6 8 9 6 9 XXX 4 > -? - 8 9 x 4 z ) - -! x - x - - X - - - - - x 00 - - - - - x z - - - x x - x - - - - - ) x - - - - - - 0 > - 000-90 - - 4 0 x 00 - -? z 8 & x - - 8? > 9 - - - - 64 49 9 x - -
- 6 8 9-6 8 9 6 9 XXX 4 > -? - 8 9 x 4 z ) - -! x - x - - X - - - - - x 00 - - - - - x z - - - x x - x - - - - - ) x - - - - - - 0 > - 000-90 - - 4 0 x 00 - -? z 8 & x - - 8? > 9 - - - - 64 49 9 x - -
13, Applications of molecular symmetry and group theory
 Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Chemistry 13, Applications of molecular symmetry and group theory 27, Group theory and vibrational spectroscopy: Part-IV(Selection rules for IR
Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Chemistry 13, Applications of molecular symmetry and group theory 27, Group theory and vibrational spectroscopy: Part-IV(Selection rules for IR
Continuum mechanism: Stress and strain
 Continuum mechanics deals with the relation between forces (stress, σ) and deformation (strain, ε), or deformation rate (strain rate, ε). Solid materials, rigid, usually deform elastically, that is the
Continuum mechanics deals with the relation between forces (stress, σ) and deformation (strain, ε), or deformation rate (strain rate, ε). Solid materials, rigid, usually deform elastically, that is the
Maxima and Minima. Marius Ionescu. November 5, Marius Ionescu () Maxima and Minima November 5, / 7
 Maxima and Minima Marius Ionescu November 5, 2012 Marius Ionescu () Maxima and Minima November 5, 2012 1 / 7 Second Derivative Test Fact Suppose the second partial derivatives of f are continuous on a
Maxima and Minima Marius Ionescu November 5, 2012 Marius Ionescu () Maxima and Minima November 5, 2012 1 / 7 Second Derivative Test Fact Suppose the second partial derivatives of f are continuous on a
Electricity and Magne/sm II
 8.1 Electricity and Magne/sm II Griffiths Chapter 8 Conserva/on Laws Clicker Ques/ons 8.2 The work energy theorem states: W = This theorem is valid f " F net! dl = 1 2 mv 2 f # 1 2 mv i2 i A. only for
8.1 Electricity and Magne/sm II Griffiths Chapter 8 Conserva/on Laws Clicker Ques/ons 8.2 The work energy theorem states: W = This theorem is valid f " F net! dl = 1 2 mv 2 f # 1 2 mv i2 i A. only for
Bidiagonal pairs, Tridiagonal pairs, Lie algebras, and Quantum Groups
 Bidiagonal pairs, Tridiagonal pairs, Lie algebras, and Quantum Groups Darren Funk-Neubauer Department of Mathematics and Physics Colorado State University - Pueblo Pueblo, Colorado, USA darren.funkneubauer@colostate-pueblo.edu
Bidiagonal pairs, Tridiagonal pairs, Lie algebras, and Quantum Groups Darren Funk-Neubauer Department of Mathematics and Physics Colorado State University - Pueblo Pueblo, Colorado, USA darren.funkneubauer@colostate-pueblo.edu
OWELL WEEKLY JOURNAL
 Y \»< - } Y Y Y & #»»» q ] q»»»>) & - - - } ) x ( - { Y» & ( x - (» & )< - Y X - & Q Q» 3 - x Q Y 6 \Y > Y Y X 3 3-9 33 x - - / - -»- --
Y \»< - } Y Y Y & #»»» q ] q»»»>) & - - - } ) x ( - { Y» & ( x - (» & )< - Y X - & Q Q» 3 - x Q Y 6 \Y > Y Y X 3 3-9 33 x - - / - -»- --
Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Stress and Strain
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Stress and Strain
CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations Lecture 7.1. in situ Stresses I (Das, Ch. 8)
 CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations Lecture 7.1 in situ Stresses I (Das, Ch. 8) Class Outline Stress tensor, stress units Effective stress, Stresses in saturated soil without seepage Stresses in saturated
CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations Lecture 7.1 in situ Stresses I (Das, Ch. 8) Class Outline Stress tensor, stress units Effective stress, Stresses in saturated soil without seepage Stresses in saturated
Topic 8c Multi Variable Optimization
 Course Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utep.edu Topic 8c Multi Variable Optimization EE 4386/5301 Computational Methods in EE Outline Mathematical Preliminaries
Course Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utep.edu Topic 8c Multi Variable Optimization EE 4386/5301 Computational Methods in EE Outline Mathematical Preliminaries
Advanced Spectroscopy. Dr. P. Hunt Rm 167 (Chemistry) web-site:
 Advanced Spectroscopy Dr. P. Hunt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 167 (Chemistry) web-site: http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt Maths! Coordinate transformations rotations! example 18.1 p501 whole chapter on Matrices
Advanced Spectroscopy Dr. P. Hunt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 167 (Chemistry) web-site: http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt Maths! Coordinate transformations rotations! example 18.1 p501 whole chapter on Matrices
The Conjugate Gradient Method
 The Conjugate Gradient Method Lecture 5, Continuous Optimisation Oxford University Computing Laboratory, HT 2006 Notes by Dr Raphael Hauser (hauser@comlab.ox.ac.uk) The notion of complexity (per iteration)
The Conjugate Gradient Method Lecture 5, Continuous Optimisation Oxford University Computing Laboratory, HT 2006 Notes by Dr Raphael Hauser (hauser@comlab.ox.ac.uk) The notion of complexity (per iteration)
14.7: Maxima and Minima
 14.7: Maxima and Minima Marius Ionescu October 29, 2012 Marius Ionescu () 14.7: Maxima and Minima October 29, 2012 1 / 13 Local Maximum and Local Minimum Denition Marius Ionescu () 14.7: Maxima and Minima
14.7: Maxima and Minima Marius Ionescu October 29, 2012 Marius Ionescu () 14.7: Maxima and Minima October 29, 2012 1 / 13 Local Maximum and Local Minimum Denition Marius Ionescu () 14.7: Maxima and Minima
Static unconstrained optimization
 Static unconstrained optimization 2 In unconstrained optimization an objective function is minimized without any additional restriction on the decision variables, i.e. min f(x) x X ad (2.) with X ad R
Static unconstrained optimization 2 In unconstrained optimization an objective function is minimized without any additional restriction on the decision variables, i.e. min f(x) x X ad (2.) with X ad R
Ordinary Least Squares and its applications
 Ordinary Least Squares and its applications Dr. Mauro Zucchelli University Of Verona December 5, 2016 Dr. Mauro Zucchelli Ordinary Least Squares and its applications December 5, 2016 1 / 48 Contents 1
Ordinary Least Squares and its applications Dr. Mauro Zucchelli University Of Verona December 5, 2016 Dr. Mauro Zucchelli Ordinary Least Squares and its applications December 5, 2016 1 / 48 Contents 1
THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 123,
 THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 23, 2240 2005 Efficient methods for finding transition states in chemical reactions: Comparison of improved dimer method and partitioned rational function optimization method
THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 23, 2240 2005 Efficient methods for finding transition states in chemical reactions: Comparison of improved dimer method and partitioned rational function optimization method
TUTORIAL 6: PHONONS, LATTICE EXPANSION, AND BAND-GAP RENORMALIZATION
 Hands-On Tutorial Workshop, July 29 th 2014 TUTORIAL 6: PHONONS, LATTICE EXPANSION, AND BAND-GAP RENORMALIZATION Christian Carbogno & Manuel Schöttler Fritz-Haber-Institut der Max-Planck-Gesellschaft,
Hands-On Tutorial Workshop, July 29 th 2014 TUTORIAL 6: PHONONS, LATTICE EXPANSION, AND BAND-GAP RENORMALIZATION Christian Carbogno & Manuel Schöttler Fritz-Haber-Institut der Max-Planck-Gesellschaft,
19. Principal Stresses
 19. Principal Stresses I Main Topics A Cauchy s formula B Principal stresses (eigenvectors and eigenvalues) C Example 10/24/18 GG303 1 19. Principal Stresses hkp://hvo.wr.usgs.gov/kilauea/update/images.html
19. Principal Stresses I Main Topics A Cauchy s formula B Principal stresses (eigenvectors and eigenvalues) C Example 10/24/18 GG303 1 19. Principal Stresses hkp://hvo.wr.usgs.gov/kilauea/update/images.html
Wave and Elasticity Equations
 1 Wave and lasticity quations Now let us consider the vibrating string problem which is modeled by the one-dimensional wave equation. Suppose that a taut string is suspended by its extremes at the points
1 Wave and lasticity quations Now let us consider the vibrating string problem which is modeled by the one-dimensional wave equation. Suppose that a taut string is suspended by its extremes at the points
2x (x 2 + y 2 + 1) 2 2y. (x 2 + y 2 + 1) 4. 4xy. (1, 1)(x 1) + (1, 1)(y + 1) (1, 1)(x 1)(y + 1) 81 x y y + 7.
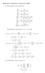 Homework 8 Solutions, November 007. (1 We calculate some derivatives: f x = f y = x (x + y + 1 y (x + y + 1 x = (x + y + 1 4x (x + y + 1 4 y = (x + y + 1 4y (x + y + 1 4 x y = 4xy (x + y + 1 4 Substituting
Homework 8 Solutions, November 007. (1 We calculate some derivatives: f x = f y = x (x + y + 1 y (x + y + 1 x = (x + y + 1 4x (x + y + 1 4 y = (x + y + 1 4y (x + y + 1 4 x y = 4xy (x + y + 1 4 Substituting
REVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS
 REVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS DONU ARAPURA 1. Limits and continuity To simplify the statements, we will often stick to two variables, but everything holds with any number of variables. Let f(x, y) be
REVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS DONU ARAPURA 1. Limits and continuity To simplify the statements, we will often stick to two variables, but everything holds with any number of variables. Let f(x, y) be
January 29, Non-linear conjugate gradient method(s): Fletcher Reeves Polak Ribière January 29, 2014 Hestenes Stiefel 1 / 13
 Non-linear conjugate gradient method(s): Fletcher Reeves Polak Ribière Hestenes Stiefel January 29, 2014 Non-linear conjugate gradient method(s): Fletcher Reeves Polak Ribière January 29, 2014 Hestenes
Non-linear conjugate gradient method(s): Fletcher Reeves Polak Ribière Hestenes Stiefel January 29, 2014 Non-linear conjugate gradient method(s): Fletcher Reeves Polak Ribière January 29, 2014 Hestenes
Gradient Descent Methods
 Lab 18 Gradient Descent Methods Lab Objective: Many optimization methods fall under the umbrella of descent algorithms. The idea is to choose an initial guess, identify a direction from this point along
Lab 18 Gradient Descent Methods Lab Objective: Many optimization methods fall under the umbrella of descent algorithms. The idea is to choose an initial guess, identify a direction from this point along
Chemistry 431. NC State University. Lecture 17. Vibrational Spectroscopy
 Chemistry 43 Lecture 7 Vibrational Spectroscopy NC State University The Dipole Moment Expansion The permanent dipole moment of a molecule oscillates about an equilibrium value as the molecule vibrates.
Chemistry 43 Lecture 7 Vibrational Spectroscopy NC State University The Dipole Moment Expansion The permanent dipole moment of a molecule oscillates about an equilibrium value as the molecule vibrates.
Section 2.4: Add and Subtract Rational Expressions
 CHAPTER Section.: Add and Subtract Rational Expressions Section.: Add and Subtract Rational Expressions Objective: Add and subtract rational expressions with like and different denominators. You will recall
CHAPTER Section.: Add and Subtract Rational Expressions Section.: Add and Subtract Rational Expressions Objective: Add and subtract rational expressions with like and different denominators. You will recall
HIGHER-ORDER THEORIES
 HIGHER-ORDER THEORIES THIRD-ORDER SHEAR DEFORMATION PLATE THEORY LAYERWISE LAMINATE THEORY J.N. Reddy 1 Third-Order Shear Deformation Plate Theory Assumed Displacement Field µ u(x y z t) u 0 (x y t) +
HIGHER-ORDER THEORIES THIRD-ORDER SHEAR DEFORMATION PLATE THEORY LAYERWISE LAMINATE THEORY J.N. Reddy 1 Third-Order Shear Deformation Plate Theory Assumed Displacement Field µ u(x y z t) u 0 (x y t) +
Basic Equations of Elasticity
 A Basic Equations of Elasticity A.1 STRESS The state of stress at any point in a loaded bo is defined completely in terms of the nine components of stress: σ xx,σ yy,σ zz,σ xy,σ yx,σ yz,σ zy,σ zx,andσ
A Basic Equations of Elasticity A.1 STRESS The state of stress at any point in a loaded bo is defined completely in terms of the nine components of stress: σ xx,σ yy,σ zz,σ xy,σ yx,σ yz,σ zy,σ zx,andσ
Chapter 2 Governing Equations
 Chapter Governing Equations Abstract In this chapter fundamental governing equations for propagation of a harmonic disturbance on the surface of an elastic half-space is presented. The elastic media is
Chapter Governing Equations Abstract In this chapter fundamental governing equations for propagation of a harmonic disturbance on the surface of an elastic half-space is presented. The elastic media is
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
11 th International Computational Accelerator Physics Conference (ICAP) 2012
 Eigenmode Computation For Ferrite-Loaded Cavity Resonators Klaus Klopfer*, Wolfgang Ackermann, Thomas Weiland Institut für Theorie Elektromagnetischer Felder, TU Darmstadt 11 th International Computational
Eigenmode Computation For Ferrite-Loaded Cavity Resonators Klaus Klopfer*, Wolfgang Ackermann, Thomas Weiland Institut für Theorie Elektromagnetischer Felder, TU Darmstadt 11 th International Computational
Transition states and reaction paths
 Transition states and reaction paths Lab 4 Theoretical background Transition state A transition structure is the molecular configuration that separates reactants and products. In a system with a single
Transition states and reaction paths Lab 4 Theoretical background Transition state A transition structure is the molecular configuration that separates reactants and products. In a system with a single
Course 2BA1: Hilary Term 2007 Section 8: Quaternions and Rotations
 Course BA1: Hilary Term 007 Section 8: Quaternions and Rotations David R. Wilkins Copyright c David R. Wilkins 005 Contents 8 Quaternions and Rotations 1 8.1 Quaternions............................ 1 8.
Course BA1: Hilary Term 007 Section 8: Quaternions and Rotations David R. Wilkins Copyright c David R. Wilkins 005 Contents 8 Quaternions and Rotations 1 8.1 Quaternions............................ 1 8.
AE/ME 339. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) K. M. Isaac. Momentum equation. Computational Fluid Dynamics (AE/ME 339) MAEEM Dept.
 AE/ME 339 Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) 9//005 Topic7_NS_ F0 1 Momentum equation 9//005 Topic7_NS_ F0 1 Consider the moving fluid element model shown in Figure.b Basis is Newton s nd Law which says
AE/ME 339 Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) 9//005 Topic7_NS_ F0 1 Momentum equation 9//005 Topic7_NS_ F0 1 Consider the moving fluid element model shown in Figure.b Basis is Newton s nd Law which says
Rubber Elasticity (Indented text follows Strobl, other follows Doi)
 Rubber Elasticity (Indented text follows Strobl, other follows Doi) Elasticity of A Single Chain: The spring constant associated with a single polymer chain is of importance in a wide range of situations
Rubber Elasticity (Indented text follows Strobl, other follows Doi) Elasticity of A Single Chain: The spring constant associated with a single polymer chain is of importance in a wide range of situations
Neural Network Training
 Neural Network Training Sargur Srihari Topics in Network Training 0. Neural network parameters Probabilistic problem formulation Specifying the activation and error functions for Regression Binary classification
Neural Network Training Sargur Srihari Topics in Network Training 0. Neural network parameters Probabilistic problem formulation Specifying the activation and error functions for Regression Binary classification
Physics 403. Segev BenZvi. Numerical Methods, Maximum Likelihood, and Least Squares. Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester
 Physics 403 Numerical Methods, Maximum Likelihood, and Least Squares Segev BenZvi Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester Table of Contents 1 Review of Last Class Quadratic Approximation
Physics 403 Numerical Methods, Maximum Likelihood, and Least Squares Segev BenZvi Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester Table of Contents 1 Review of Last Class Quadratic Approximation
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST

 «4 [< «
«4 [< «