SRF-Seminars Jacek Sekutowicz
|
|
|
- Randell Lloyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SRF-Seminars Jacek Sekutowicz 1/32
2 5. SUPERCONDUCTING PHOTO-INJECTORS 2/32
3 SRF Photo-Injectors; Topics 1. Introduction 2. Projects; Specs and measured data 3. Cathodes 4. RF-performance of sc-cavities 5. RF-focusing 6. ε growth compensation with DC- and RF-magnetic field 7. Nb-Pb gun 8. Conclusions 3/32
4 SRF Injectors Acknowledgements BNL: AES: FZR: DESY: IHIP: INFN: JLAB: INS: SUNY: UNI-ŁÓDŹ: SLAC: A. Burrill, I. Ben-Zvi, R. Calaga, T. Rao, J. Smedley T. Favale, A. Todd, J. Rathke D. Janssen, J. Teichert D. Kostin, B. Krause, A. Matheisen, W.-D. Möller, R. Lange J. Hao, K. Zhao M. Ferrario P. Kneisel J. Langner, P. Strzyżewski R. Lefferts, A. Lipski K. Szałowski K. Ko, Z. Li. 4/32
5 1. Introduction SRF Injectors Motivation to develop SRF electron guns: Operation in CW mode with high acc. gradient on photo-cathode. Low power dissipation and excellent thermal stability. What is technically challenging: Integration of non-superconducting cathodes into the sc environment. Lower QE of superconducting cathodes than alkali cathodes. Emittance growth compensation with magnetic field is more difficult and needs novel approaches. 5/32
6 1. Introduction SRF Injectors FZR (since 1998) IHIP PU (since 2001) f =1.3 GHz Cs 2 Te E RF f =1.3 GHz Cs 2 Te E DC Courtesy of Dietmar Janssen Courtesy of Hao Jiankui BNL (since 2002) BNL/AES (since 2004) f =1.3 GHz f = MHz Nb E RF Alkali+ E RF Courtesy of Triveni Rao Courtesy of Alan Todd 6/32
7 2. Four projects: Spec/Measured SRF Injectors E [MeV] ΔE [kev] q/bunch [nc] Bunches/s [10 6 ] I b [ma] q [nc] BESSY S: 5 S:? S: 2.5 S: S: S: 2.5 FZR S: 9.5 S: 5 S: S: 13 S: 1.0 S: FZR S: 9.5 S: S: 1.0 S: 1 S: 1.0 S: 1.0 M: 0.85 M: 8.5 M: M: 26 M: 0.52 M: S: 2.61 S: 30 S: S: 17 S: 1.0 S: M: 0.58 M: 35 M: M: 81 M: 0.08 M: Cavities have been built mainly for measurements of QE of cold Nb S: 2.0 S: 62 S: 1.33 S: 352 S: 704 S: 500 S: 1000 S: 1.33 M: ( - ) M: ( - ) M: ( - ) M: ( - ) M: ( - ) M: ( - ) 7/32
8 3. Cathodes: Spec / Measured SRF Injectors Emitter/T < λ Ph at operation E pulse / P laser [µj] / [W] Cathode Life Time Spot size [mm] E cath [MV/m] Cs 2 Te / 78 K S BESSY : 0.01/262 S FZR : 0.01/262 S: 1.19/0.03 S: 0.5 / 0.5 >50 days S: Ø 3.0 S: 25 M: 0.003/260 M: 0.06/1.5 M: Ø 2.0 M: 22 S: 0.01 / 266 S: 0.015/1.2 S: Ø 5.6 Cs 2 Te /273 K ~100 days M: 2.7 M: 0.01/ 266 M: 0.010/0.8 M: Ø 6.0 Nb / 2-4 K 10-5 / /0.15 (?) 4x1.5 M: 48 S: Alkali /? S: Alkali+D/? S: 0.05 / 527 S: 5 / / /0.2? S: Ø 2.0 S: 40 8/32
9 4. Cavities: Measured RF-performance SRF Injectors FZR IHIP-Peking 4 K-test E peak =22 MV/m 4.2 K- test 10 Eacc= 5 MV/m 2 K-test 5 10 E peak =46 MV/m 1.E+11 Qo T=1.99K BNL/AES Test at JLab E+11 Q0 AES: MHz not yet fabricated but MHz is very similar Test at JLab E+10 1.E+10 1.E Epeak [MV/m] 1.E Epeak [MV/ m ] 9/32
10 4. Cavities: Next Steps SRF Injectors FZR Test cavity (RRR=40) received BCP in Sept High RRR=300 cavity will be treated and tested at DESY soon BNL/AES 1.3 GHz QWC will be added for cathode with diamond: IHIP-Peking University DC+1.5-cell 3.5-cell Eacc [MV/m] 15 V-DC [kv] 100 I beam [ma] 1 Energy [MeV] 4.9 Energy spread [%] 2.27 Emittance (rms) [µrad] 3.4 BNL/AES MHz RF Design will be finished in 2005? ε=1.99 [µrad] ΔE/E= 3.8% 10/32
11 5. E-field Focusing; Recessed cathode SRF Injectors 60 MV/m Cathode shifted by 3 mm only 60 MV/m 20 MV/m r 0 z 57 MV/m r 0 z Ez(r,+1mm) Er(r,+1mm) Ez(r,+1mm) Er(r,+1mm) Ez, Er [MV/m] Ez, Er [MV/m] r [mm] r [mm] 11/32
12 5. E-field Focusing; Recessed cathode SRF Injectors Since position of the cathode is a very sensitive knob Cathode longitudinal position tuner as proposed by RFZ 12/32
13 5. E-field Focusing; Inclined back wall SRF Injectors FZR: 1.3 GHz 1.5-cells and 3.5-cells have recessed cathode and inclined back wall BNL/AES: 1.3 GHz and MHz will have recessed cathode and inclined back wall Without RF focusing With RF focusing ε n µrad] Recess [mm] With RF focusing ε n [µrad] 1.99 Recess [mm] 3 D. Janssen, V. Volkov, NIM A452(2000)34 R. Calaga, Proceed. SRF2005,Cornell 13/32
14 6. Emittance compensation with H-field: SRF Injectors Exposing a sc cavity to H-field may cause degradation in the performance. 1. One can put solenoid and the sc-cavity at different locations split injector (M. Ferrario, J.B. Rosenzweig): ε n [µrad] 6 q = 1nC r spot = 1.5mm t pulse = 20ps ε th = 0.45µrad E cath = 60 MV/m E cry = 13.5 MV/m σ r [mm] ε n I = 50 A E = 120 MeV ε n = 0.6 µrad σ r 0 z [m] 16 Sc-cavity Solenoid; 0.3 T 14/32
15 6. Emittance compensation with H-field: SRF Injectors Example: 1 mm thick µ-metal shield 2K 4K Solenoid (0.3 T) Cathode (20 µt) Nb stainless steel 410 mm (optimum 360 mm) 15/32
16 6. Emittance compensation with H-field: SRF Injectors 2. One can use solenoidal modes of (TE0xx) for the ε compensation (D. Janssen) 1.3 GHz TM010; E field 3.8 GHz TE011; B field ~ 350mm TE 021 ε n for 1 nc [µrad] ε n minimum at z [m] 4.25 B TE on axis [T] Surf. B max = [B 2 TM + B2 TE ]0.5 [T] The low emittance results from: RF-focusing and B RF compensation and weakly depends on the phase of the solenoidal mode. D. Janssen et al, Proc. of FEL /32
17 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: DESY, BNL, INFN, SUNY, JLab, INS SRF Injectors Motivation is to build cw operating RF-source of ~0.5-1 ma class for an XFEL facility. An all superconducting RF-gun follows the all niobium RF-gun of BNL QE = λ =266 nm In 2003 we proposed to investigate quantum efficiency of Pb (TTF Meeting, Frascati, June 2003, Phys. Rev. ST-AB, vol. 8, January 2005) Lead is commonly used superconductor for accelerating cavities: T c = 7.2 K, B c = 70 mt 17/32
18 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: Quantum Efficiency of Lead at 300 K SRF Injectors QE measured at 300K using setup at BNL (J. Smedley, T. Rao) Light sources: ArF- laser: 193 nm, KrF-laser: 248 nm, 4-th harmonic Nd: YAG laser : 266 nm Deuterium light source with monochromator (2 nm bandwidth): nm QE Pb: vacuum-deposited Pb: bulk Pb: electro-plated Nb: bulk Pb: arc-deposited Pb: magnetron-deposited 248 nm 240 nm 230 nm 210 nm 213 nm 220 nm 200 nm 193 nm 190 nm 0.55% Measured also at ~100 K Ep [ev] 18/32
19 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: Quantum Efficiency of Lead at 300 K SRF Injectors Surface Uniformity (Courtesy J. Smedley) Arc Deposited Sputtered Vacuum Deposited Solid 10 μm All cathodes laser cleaned with 0.2 mj/mm2 of 248nm light 19/32
20 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: Quantum Efficiency of Lead SRF Injectors Preparation Nb used as substrate Four deposition methods: Electroplating Vacuum deposition (evaporation) Sputtering Vacuum Arc deposition Solid lead, mechanically polished In situ laser cleaning KrF Excimer (248 nm), 12 ns pulse, ~0.2 mj/mm 2 20/32
21 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: Quantum Efficiency of Lead SRF Injectors Lead Surface Finish and Damage Threshold (Courtesy J. Smedley) (Electroplated Lead) Prior to Laser Cleaning 0.11 mj/mm mj/mm mj/mm mj/mm mj/mm 2 21/32
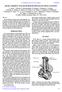
22 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: Quantum Efficiency of Lead at 300 K SRF Injectors The best QE was demonstrated by arc-deposited samples prepared at INS-Swierk. Courtesy P. Strzyzewski, A. Soltan INS, Swierk. Magnetic field distribution in the Aksenov-type magnetic filter and in the T-type magnetic filter; 1 cathode, 2 anode, 3 focusing coil, 4 filter inlet, 5 filter exit, 6 high-current cable, 7 ion collector position, 8 plasma stream, 9 - correcting coil. Calculated magnetic filed strengths: - near-cathode region 16 mt - magnetic duct region mt 22/32
23 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: Quantum Efficiency of Lead at 170 K SRF Injectors Effect of Temperature and Vacuum on QE (Courtesy J: Smedley) Arc Deposited Cathode 200 nm Vacuum (warm) Vacuum (-170C) = 8 ntorr = 6 ntorr Vacuum (warm) Vacuum (-170C) = 1.3 μtorr = 0.2 μtorr 23/32
24 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: RF-design SRF Injectors High RRR Nb cavity small emitting Pb spot Parameter Unit π-mode frequency [MHz] mode frequency [MHz] Cell-to-cell coupling Active length 1.6 λ/2 [m] Nominal E cath at cathode [MV/m] 60 Energy stored at nominal E cath [J] 20 Nominal beam energy [MeV] 6 15 B [mt] 0 6 mt << B c r [mm] B-field on the cathode at 60 MV/m 24/32
25 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: RF-design SRF Injectors HOM damping scheme: - FPC is not sufficient - 1 or 2 HOM couplers must be attached Mode f [MHz] (R/Q) Monopole: Beam Tube [Ω] Dipole: TE111-1a [Ω/cm 2 ] Dipole: TE111-1b [Ω/cm 2 ] Dipole: Beam Tube-a [Ω/cm 2 ] Dipole: Beam Tube-b [Ω/cm 2 ] Dipole: TM110-1a [Ω/cm 2 ] Dipole: TM110-1b [Ω/cm 2 ] Dipole: TM110-2a [Ω/cm 2 ] Dipole: TM110-2b [Ω/cm 2 ] Monopole: TM [Ω] Almost no damping Good damping 25/32
26 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: RF-design SRF Injectors Modeling of the FPC and HOM coupler region (D. Kostin) 26/32
27 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: RF-performance of test cavities SRF Injectors JLab (P. Kneisel) ; 1.42 GHz good for test of various coatings DESY; 1.3 GHz good for test of the final coating Nb plug without and with Pb coating: D=10mm, h=10µm 1.E+10 1.E+11 Qo 1.E+10 1.E+09 Qo 1.E+08 With lead No lead Epeak [MV/m] 1.E+09 1.E+08 Input Antenna Matched Input Antenna Undercoupled Epeak [MV/m] 27/32
28 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: Two questions SRF Injectors 1. Relaxation time of Cooper pairs after the illumination How does intrinsic Q changes when laser illuminates the Pb cathode? An example: QE = 213nm q = 1 nc requires 3.4 µj/pulse. Nb at 2K Ø~3.4 mm Pb Photon penetration depth is ~10 nm N Cooper pairs = µj Nγ = All CPs in the 10 nm layer are broken. The layer is in the normalconducting state after the laser pulse. F= 60 MeV/m T rf /4=200ps later the diffusion and recombination processes of quasiparticles in the Pb layer start. 28/32
29 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: Two questions SRF Injectors The relaxation time to the thermal equilibrium Nb Pb teff, ns T, K This has to be verified experimentally. 29/32
30 7. Nb-Pb RF-gun: Two questions SRF Injectors 2. Thermal emittance? Pb work function is ~ 4.25 ev Estimation of the thermal emittance: ε TH = r 2 3 for : λ ph = 213nm (5.8 spot radius r = 1.7 mm Schottky at 60 MV/m E k = = 1.27 µrad! mc mc 2 If experiment with 1.5-cells confirms this estimation we will reduce r to ~1 mm and charge to ~0.4 nc, to get ε TH = 0.7µrad HOMDYN (M. Ferrario) B Q r 2 ε 2 σ t r 2 σ t I = 18 A ε n = 0.76 µrad 30/32
31 8. Conclusions SRF Injectors There is visible progress in the SRF- gun projects: Two SRF-guns generated electron beam FZR (2002) and IHIP (2003). But still some years of R&D are needed to reach spec in the performance. Ad 1. Spec vs. Measurements: The FZR gun and IHIP gun have demonstrated almost emittance spec but with much lower charge. Ad 2. Cathodes: IHIP Cs 2 Te cathode has demonstrated QE=0.01 and 100 days lifetime what is almost the spec. Nb cathode showed lower QE at cold than expected but vacuum during the cool down was not as good as it should be. Deposition of the Pb cathode on Nb wall is challenging. Thermal emittance of Pb may cause some limitation in the emitted charge/bunch. Intrinsic Q and recovery time of broken Cooper pairs (Nb, Pb cathode) need experimental verification. 31/32
32 8. Conclusions SRF Injectors Ad 3. New emittance compensation: The compensation by means of the solenoidal mode is interesting and should be demonstrated experimentally. All these questions show that coming years will be very exciting for the community involved in the SRF-gun R&D programs. 32/32
Superconducting RF Photoinjectors
 Superconducting RF Photoinjectors Jacek Sekutowicz, DESY Introduction Projects; Specs and measured data Cathodes RF-performance of sc-cavities RF-focusing _ growth compensation with DC- and RF-magnetic
Superconducting RF Photoinjectors Jacek Sekutowicz, DESY Introduction Projects; Specs and measured data Cathodes RF-performance of sc-cavities RF-focusing _ growth compensation with DC- and RF-magnetic
Overview of FEL injectors
 Overview of FEL injectors Massimo Ferrario INFN - LNF VISA-DUV-HGHG 4GLS FLASH-XFEL LEUTL BESSY PAL LCLS Arc en Ciel FERMI SCSS LEG SPARX SDUV 1 SASE FEL Electron Beam Requirement: High Brightness B n
Overview of FEL injectors Massimo Ferrario INFN - LNF VISA-DUV-HGHG 4GLS FLASH-XFEL LEUTL BESSY PAL LCLS Arc en Ciel FERMI SCSS LEG SPARX SDUV 1 SASE FEL Electron Beam Requirement: High Brightness B n
The New Superconducting RF Photoinjector a High-Average Current & High-Brightness Gun
 The New Superconducting RF Photoinjector a High-Average Current & High-Brightness Gun Jochen Teichert for the BESSY-DESY-FZD-MBI collaboration and the ELBE crew High-Power Workshop, UCLA, Los Angeles 14
The New Superconducting RF Photoinjector a High-Average Current & High-Brightness Gun Jochen Teichert for the BESSY-DESY-FZD-MBI collaboration and the ELBE crew High-Power Workshop, UCLA, Los Angeles 14
ICFA ERL Workshop Jefferson Laboratory March 19-23, 2005 Working Group 1 summary Ilan Ben-Zvi & Ivan Bazarov
 ICFA ERL Workshop Jefferson Laboratory March 19-23, 2005 Working Group 1 summary Ilan Ben-Zvi & Ivan Bazarov Sincere thanks to all WG1 participants: Largest group, very active participation. This summary
ICFA ERL Workshop Jefferson Laboratory March 19-23, 2005 Working Group 1 summary Ilan Ben-Zvi & Ivan Bazarov Sincere thanks to all WG1 participants: Largest group, very active participation. This summary
Review of proposals of ERL injector cryomodules. S. Belomestnykh
 Review of proposals of ERL injector cryomodules S. Belomestnykh ERL 2005 JLab, March 22, 2005 Introduction In this presentation we will review injector cryomodule designs either already existing or under
Review of proposals of ERL injector cryomodules S. Belomestnykh ERL 2005 JLab, March 22, 2005 Introduction In this presentation we will review injector cryomodule designs either already existing or under
Modeling of the secondary electron emission in rf photocathode guns
 Modeling of the secondary electron emission in rf photocathode guns J.-H. Han, DESY Zeuthen 8 June 2004 Joint Uni. Hamburg and DESY Accelerator Physics Seminar Contents 1. Necessity of secondary electron
Modeling of the secondary electron emission in rf photocathode guns J.-H. Han, DESY Zeuthen 8 June 2004 Joint Uni. Hamburg and DESY Accelerator Physics Seminar Contents 1. Necessity of secondary electron
Overview of Energy Recovery Linacs
 Overview of Energy Recovery Linacs Ivan Bazarov Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source Talk Outline: Historical Perspective Parameter Space Operational ERLs & Funded Projects Challenges ERL Concept: conventional
Overview of Energy Recovery Linacs Ivan Bazarov Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source Talk Outline: Historical Perspective Parameter Space Operational ERLs & Funded Projects Challenges ERL Concept: conventional
Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site
 1 Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site Sakhorn Rimjaem (on behalf of the PITZ team) Motivation Photo Injector Test Facility at
1 Diagnostic Systems for Characterizing Electron Sources at the Photo Injector Test Facility at DESY, Zeuthen site Sakhorn Rimjaem (on behalf of the PITZ team) Motivation Photo Injector Test Facility at
AREAL Test Facility for Advanced Accelerator and Radiation Sources Concepts
 2 nd European Advanced Accelerator Concepts AREAL Test Facility for Advanced Accelerator and Radiation Sources Concepts V. Tsakanov CANDLE SRI 13-19 Sep 2015, La Biodola, Isola d'elba Introduction 2nd
2 nd European Advanced Accelerator Concepts AREAL Test Facility for Advanced Accelerator and Radiation Sources Concepts V. Tsakanov CANDLE SRI 13-19 Sep 2015, La Biodola, Isola d'elba Introduction 2nd
Introduction to the benchmark problem
 Introduction to the benchmark problem M. Krasilnikov (DESY) Working group 4: Low emittance electron guns 37th ICFA Beam Dynamics Workshop Future Light Sources 15 19 May 6 DESY, Hamburg, Germany Outline
Introduction to the benchmark problem M. Krasilnikov (DESY) Working group 4: Low emittance electron guns 37th ICFA Beam Dynamics Workshop Future Light Sources 15 19 May 6 DESY, Hamburg, Germany Outline
Design of an RF Photo-Gun (PHIN)
 Design of an RF Photo-Gun (PHIN) R. Roux 1, G. Bienvenu 1, C. Prevost 1, B. Mercier 1 1) CNRS-IN2P3-LAL, Orsay, France Abstract In this note we show the results of the RF simulations performed with a 2-D
Design of an RF Photo-Gun (PHIN) R. Roux 1, G. Bienvenu 1, C. Prevost 1, B. Mercier 1 1) CNRS-IN2P3-LAL, Orsay, France Abstract In this note we show the results of the RF simulations performed with a 2-D
THE LCLS-II INJECTOR DESIGN*
 THE LCLS-II INJECTOR DESIGN* J.F. Schmerge #, A. Brachmann, D. Dowell, A. Fry, R.K. Li, Z. Li, T. Raubenheimer, T. Vecchione, F. Zhou, SLAC, Menlo Park, CA 94025, USA A. Bartnik, I. Bazarov, B. Dunham,
THE LCLS-II INJECTOR DESIGN* J.F. Schmerge #, A. Brachmann, D. Dowell, A. Fry, R.K. Li, Z. Li, T. Raubenheimer, T. Vecchione, F. Zhou, SLAC, Menlo Park, CA 94025, USA A. Bartnik, I. Bazarov, B. Dunham,
SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE*
 SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE* E. Panofski #, A. Jankowiak, T. Kamps, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, Berlin, Germany P.N. Lu, J. Teichert, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf,
SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE* E. Panofski #, A. Jankowiak, T. Kamps, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, Berlin, Germany P.N. Lu, J. Teichert, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf,
Photoinjector design for the LCLS
 SLAC-PUB-8962 LCLS-TN-01-05 Revised November 2001 Photoinjector design for the LCLS P.R. Bolton a, J.E. Clendenin a, D.H. Dowell a, M. Ferrario b, A.S. Fisher a, S.M. Gierman a, R.E. Kirby a, P. Krejcik
SLAC-PUB-8962 LCLS-TN-01-05 Revised November 2001 Photoinjector design for the LCLS P.R. Bolton a, J.E. Clendenin a, D.H. Dowell a, M. Ferrario b, A.S. Fisher a, S.M. Gierman a, R.E. Kirby a, P. Krejcik
Diamond secondary emitter status & plans. Ilan Ben-Zvi Collider-Accelerator Department Brookhaven National Laboratory
 Diamond secondary emitter status & plans Ilan Ben-Zvi Collider-Accelerator Department Brookhaven National Laboratory What is desired in a cathode of a CW, high brightness injector? Timing by a laser short
Diamond secondary emitter status & plans Ilan Ben-Zvi Collider-Accelerator Department Brookhaven National Laboratory What is desired in a cathode of a CW, high brightness injector? Timing by a laser short
OVERVIEW OF FEL INJECTORS
 OVERVIEW OF FEL INJECTORS M. Ferrario, INFN-LNF, Frascati, Italy Abstract Future light sources based on high gain free electron lasers, require the production, acceleration and transport up to the undulator
OVERVIEW OF FEL INJECTORS M. Ferrario, INFN-LNF, Frascati, Italy Abstract Future light sources based on high gain free electron lasers, require the production, acceleration and transport up to the undulator
Novel, Hybrid RF Injector as a High-average. Dinh Nguyen. Lloyd Young
 Novel, Hybrid RF Injector as a High-average average-current Electron Source Dinh Nguyen Los Alamos National Laboratory Lloyd Young TechSource Energy Recovery Linac Workshop Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator
Novel, Hybrid RF Injector as a High-average average-current Electron Source Dinh Nguyen Los Alamos National Laboratory Lloyd Young TechSource Energy Recovery Linac Workshop Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator
LCLS Injector Prototyping at the GTF
 LCLS Injector Prototyping at at the GTF John John Schmerge, SLAC SLAC November 3, 3, 23 23 GTF GTF Description Summary of of Previous Measurements Longitudinal Emittance Transverse Emittance Active LCLS
LCLS Injector Prototyping at at the GTF John John Schmerge, SLAC SLAC November 3, 3, 23 23 GTF GTF Description Summary of of Previous Measurements Longitudinal Emittance Transverse Emittance Active LCLS
Reduction of thermal emittance of rf guns *
 SLAC-PUB-884 LCLS TN 99-8 October 1999 Reduction of thermal emittance of rf guns * J. E. Clendenin, T. Kotseroglou, G. A. Mulhollan, D. T. Palmer, and J. F. Schmerge Stanford Linear Accelerator Center,
SLAC-PUB-884 LCLS TN 99-8 October 1999 Reduction of thermal emittance of rf guns * J. E. Clendenin, T. Kotseroglou, G. A. Mulhollan, D. T. Palmer, and J. F. Schmerge Stanford Linear Accelerator Center,
New Electron Source for Energy Recovery Linacs
 New Electron Source for Energy Recovery Linacs Ivan Bazarov 20m Cornell s photoinjector: world s brightest electron source 1 Outline Uses of high brightness electron beams Physics of brightness High brightness
New Electron Source for Energy Recovery Linacs Ivan Bazarov 20m Cornell s photoinjector: world s brightest electron source 1 Outline Uses of high brightness electron beams Physics of brightness High brightness
Status of linear collider designs:
 Status of linear collider designs: Electron and positron sources Design overview, principal open issues G. Dugan March 11, 2002 Electron sourcesfor 500 GeV CM machines Parameter TESLA NLC CLIC Cycle rate
Status of linear collider designs: Electron and positron sources Design overview, principal open issues G. Dugan March 11, 2002 Electron sourcesfor 500 GeV CM machines Parameter TESLA NLC CLIC Cycle rate
Experimental Optimization of Electron Beams for Generating THz CTR and CDR with PITZ
 Experimental Optimization of Electron Beams for Generating THz CTR and CDR with PITZ Introduction Outline Optimization of Electron Beams Calculations of CTR/CDR Pulse Energy Summary & Outlook Prach Boonpornprasert
Experimental Optimization of Electron Beams for Generating THz CTR and CDR with PITZ Introduction Outline Optimization of Electron Beams Calculations of CTR/CDR Pulse Energy Summary & Outlook Prach Boonpornprasert
Motivation of emission studies at PITZ
 Motivation of emission studies at PITZ PITZ activities to understand the discrepancies between measurements and simulations in: Transverse phase space Optimum machine parameters Auxiliary measurements
Motivation of emission studies at PITZ PITZ activities to understand the discrepancies between measurements and simulations in: Transverse phase space Optimum machine parameters Auxiliary measurements
Jlab FEL Photoemission DC Guns
 Jlab FEL Photoemission DC Guns Fay Hannon On behalf of the FEL team FLS 2010, 2 nd March 2 Operational Guns 1. FEL Gun 60m Gun Test Stand (GTS) 2. Backup gun, test stand with beam characterization beamline
Jlab FEL Photoemission DC Guns Fay Hannon On behalf of the FEL team FLS 2010, 2 nd March 2 Operational Guns 1. FEL Gun 60m Gun Test Stand (GTS) 2. Backup gun, test stand with beam characterization beamline
AREAL. Test Facility for Advanced Accelerator and Radiation Sources Concepts. Part.1 Introduction. V. Tsakanov CANDLE SRI
 AREAL Test Facility for Advanced Accelerator and Radiation Sources Concepts Part.1 Introduction V. Tsakanov CANDLE SRI 01 October 2015 2 nd European Advanced Accelerator Concepts 13-19 Sep 2015, Isola
AREAL Test Facility for Advanced Accelerator and Radiation Sources Concepts Part.1 Introduction V. Tsakanov CANDLE SRI 01 October 2015 2 nd European Advanced Accelerator Concepts 13-19 Sep 2015, Isola
Low Energy RHIC electron Cooling (LEReC)
 Low Energy RHIC electron Cooling (LEReC) LEReC overview: project goal and cooling approach Alexei Fedotov MEIC Collaboration Meeting 30 31 LEReC Project Mission/Purpose The purpose of the LEReC is to provide
Low Energy RHIC electron Cooling (LEReC) LEReC overview: project goal and cooling approach Alexei Fedotov MEIC Collaboration Meeting 30 31 LEReC Project Mission/Purpose The purpose of the LEReC is to provide
E E L C E T C R T O R N O N SO S U O R U C R E C S E S A N A D N D INJ N EC E T C O T R O S
 ELECTRON SOURCES AND INJECTORS Fernando Sannibale Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory 1 ELECTRON SOURCES AND INJECTORS Lecture 1: The role of electron sources and injectors in light source Requirements
ELECTRON SOURCES AND INJECTORS Fernando Sannibale Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory 1 ELECTRON SOURCES AND INJECTORS Lecture 1: The role of electron sources and injectors in light source Requirements
Issues of Electron Cooling
 Issues of Electron Cooling Yaroslav Derbenev derbenev@jlab.org JLEIC Spring 2016 Collaboration Meeting JLab, March 29-31, 2016 Outline Friction force Magnetized cooling Misalignment impact Cooling rates
Issues of Electron Cooling Yaroslav Derbenev derbenev@jlab.org JLEIC Spring 2016 Collaboration Meeting JLab, March 29-31, 2016 Outline Friction force Magnetized cooling Misalignment impact Cooling rates
Linac Driven Free Electron Lasers (III)
 Linac Driven Free Electron Lasers (III) Massimo.Ferrario@lnf.infn.it SASE FEL Electron Beam Requirements: High Brightness B n ( ) 1+ K 2 2 " MIN r #$ % &B! B n 2 n K 2 minimum radiation wavelength energy
Linac Driven Free Electron Lasers (III) Massimo.Ferrario@lnf.infn.it SASE FEL Electron Beam Requirements: High Brightness B n ( ) 1+ K 2 2 " MIN r #$ % &B! B n 2 n K 2 minimum radiation wavelength energy
Dark Current at Injector. Jang-Hui Han 27 November 2006 XFEL Beam Dynamics Meeting
 Dark Current at Injector Jang-Hui Han 27 November 2006 XFEL Beam Dynamics Meeting Considerations for the guns Ultra-low slice emittance of electron beams higher gradient at the gun cavity solenoid field
Dark Current at Injector Jang-Hui Han 27 November 2006 XFEL Beam Dynamics Meeting Considerations for the guns Ultra-low slice emittance of electron beams higher gradient at the gun cavity solenoid field
Introduction. Thermoionic gun vs RF photo gun Magnetic compression vs Velocity bunching. Probe beam design options
 Introduction Following the 19/05/04 meeting at CERN about the "CTF3 accelerated programme", a possible french contribution has been envisaged to the 200 MeV Probe Beam Linac Two machine options were suggested,
Introduction Following the 19/05/04 meeting at CERN about the "CTF3 accelerated programme", a possible french contribution has been envisaged to the 200 MeV Probe Beam Linac Two machine options were suggested,
Superconducting Superstructure for the TESLA Collider
 Date: 14-04-1998 Superconducting Superstructure for the TESLA Collider J. Sekutowicz*, M. Ferrario#, C. Tang* physics/9804015 14 Apr 1998 * DESY, MHF-SL, Hamburg, (Germany) - # INFN, Frascati, (Italy)
Date: 14-04-1998 Superconducting Superstructure for the TESLA Collider J. Sekutowicz*, M. Ferrario#, C. Tang* physics/9804015 14 Apr 1998 * DESY, MHF-SL, Hamburg, (Germany) - # INFN, Frascati, (Italy)
Photo Injector Test facility at DESY, Zeuthen site
 Photo Injector Test facility at DESY, Zeuthen site PITZ EXPERIENCE ON THE EXPERIMENTAL OPTIMIZATION OF THE RF PHOTO INJECTOR FOR THE EUROPEAN XFEL Mikhail Krasilnikov (DESY) for the PITZ Team FEL 2013
Photo Injector Test facility at DESY, Zeuthen site PITZ EXPERIENCE ON THE EXPERIMENTAL OPTIMIZATION OF THE RF PHOTO INJECTOR FOR THE EUROPEAN XFEL Mikhail Krasilnikov (DESY) for the PITZ Team FEL 2013
Experimental Measurements of the ORION Photoinjector Drive Laser Oscillator Subsystem
 Experimental Measurements of the ORION Photoinjector Drive Laser Oscillator Subsystem D.T Palmer and R. Akre Laser Issues for Electron RF Photoinjectors October 23-25, 2002 Stanford Linear Accelerator
Experimental Measurements of the ORION Photoinjector Drive Laser Oscillator Subsystem D.T Palmer and R. Akre Laser Issues for Electron RF Photoinjectors October 23-25, 2002 Stanford Linear Accelerator
Beam dynamics studies for PITZ using a 3D full-wave Lienard-Wiechert PP code
 Beam dynamics studies for PITZ using a 3D full-wave Lienard-Wiechert PP code Y. Chen, E. Gjonaj, H. De Gersem, T. Weiland TEMF, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Germany DESY-TEMF Collaboration Meeting
Beam dynamics studies for PITZ using a 3D full-wave Lienard-Wiechert PP code Y. Chen, E. Gjonaj, H. De Gersem, T. Weiland TEMF, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Germany DESY-TEMF Collaboration Meeting
A Polarized Electron PWT Photoinjector for the ILC
 2005 ALCPG & ILC Workshops Snowmass, U.S.A. A Polarized Electron PWT Photoinjector for the ILC David Yu, Yan Luo, Alexei Smirnov, DULY Research Inc., Rancho Palos Verdes, CA 90275 Ivan Bazarov, Cornell
2005 ALCPG & ILC Workshops Snowmass, U.S.A. A Polarized Electron PWT Photoinjector for the ILC David Yu, Yan Luo, Alexei Smirnov, DULY Research Inc., Rancho Palos Verdes, CA 90275 Ivan Bazarov, Cornell
Towards a Low Emittance X-ray FEL at PSI
 Towards a Low Emittance X-ray FEL at PSI A. Adelmann, A. Anghel, R.J. Bakker, M. Dehler, R. Ganter, C. Gough, S. Ivkovic, F. Jenni, C. Kraus, S.C. Leemann, A. Oppelt, F. Le Pimpec, K. Li, P. Ming, B. Oswald,
Towards a Low Emittance X-ray FEL at PSI A. Adelmann, A. Anghel, R.J. Bakker, M. Dehler, R. Ganter, C. Gough, S. Ivkovic, F. Jenni, C. Kraus, S.C. Leemann, A. Oppelt, F. Le Pimpec, K. Li, P. Ming, B. Oswald,
Cornell Injector Performance
 Cornell Injector Performance Adam Bartnik 1 Cornell Injector Performance as an ERL injector 2 Cornell Injector Performance as an ERL injector as an FEL injector (e.g. LCLS-II) as an injector for EIC applications
Cornell Injector Performance Adam Bartnik 1 Cornell Injector Performance as an ERL injector 2 Cornell Injector Performance as an ERL injector as an FEL injector (e.g. LCLS-II) as an injector for EIC applications
RF Gun Photo-Emission Model for Metal Cathodes Including Time Dependent Emission
 RF Gun Photo-Emission Model for Metal Cathodes Including Time Dependent Emission SLAC-PUB-117 February 6 (A) J. F. SCHMERGE, J. E. CLENDENIN, D. H. DOWELL, AND S. M. GIERMAN SLAC, Stanford University,
RF Gun Photo-Emission Model for Metal Cathodes Including Time Dependent Emission SLAC-PUB-117 February 6 (A) J. F. SCHMERGE, J. E. CLENDENIN, D. H. DOWELL, AND S. M. GIERMAN SLAC, Stanford University,
Optimum beam creation in photoinjectors using spacecharge expansion II: experiment
 Optimum beam creation in photoinjectors using spacecharge expansion II: experiment J. Rosenzweig, A. Cook, M. Dunning, R.J. England, G. Travish, UCLA P. Musumeci, C. Vicario, D. Filippetto, M. Ferrario,
Optimum beam creation in photoinjectors using spacecharge expansion II: experiment J. Rosenzweig, A. Cook, M. Dunning, R.J. England, G. Travish, UCLA P. Musumeci, C. Vicario, D. Filippetto, M. Ferrario,
Using IMPACT T to perform an optimization of a DC gun system Including merger
 Using IMPACT T to perform an optimization of a DC gun system Including merger Xiaowei Dong and Michael Borland Argonne National Laboratory Presented at ERL09 workshop June 10th, 2009 Introduction An energy
Using IMPACT T to perform an optimization of a DC gun system Including merger Xiaowei Dong and Michael Borland Argonne National Laboratory Presented at ERL09 workshop June 10th, 2009 Introduction An energy
Alignment requirement for the SRF cavities of the LCLS-II injector LCLSII-TN /16/2014
 Alignment requirement for the SRF cavities of the LCLS-II injector LCLS-II TN-14-16 12/16/2014 R. K. Li, C. Papadopoulos, T. O. Raubenheimer, J. F. Schmerge, and F. Zhou December 16, 2014 LCLSII-TN-14-16
Alignment requirement for the SRF cavities of the LCLS-II injector LCLS-II TN-14-16 12/16/2014 R. K. Li, C. Papadopoulos, T. O. Raubenheimer, J. F. Schmerge, and F. Zhou December 16, 2014 LCLSII-TN-14-16
Present status of 200keV polarized electron gun at Nagoya University
 Present status of 200keV polarized electron gun at Nagoya University Nagoya University Masahiro Yamamoto, N. Yamamoto, T. Nakanishi, S. Okumi, F. Furuta, M. Miyamoto, M. Kuwahara, K. Naniwa, K. Yasui KEK
Present status of 200keV polarized electron gun at Nagoya University Nagoya University Masahiro Yamamoto, N. Yamamoto, T. Nakanishi, S. Okumi, F. Furuta, M. Miyamoto, M. Kuwahara, K. Naniwa, K. Yasui KEK
Emittance and Quantum Efficiency Measurements from a 1.6 cell S- Band Photocathode RF Gun with Mg Cathode *
 LCLS-TN-4-3 SLAC PUB 763 September, 4 Emittance and Quantum Efficiency Measurements from a.6 cell S- Band Photocathode RF Gun with Mg Cathode * J.F. Schmerge, J.M. Castro, J.E. Clendenin, D.H. Dowell,
LCLS-TN-4-3 SLAC PUB 763 September, 4 Emittance and Quantum Efficiency Measurements from a.6 cell S- Band Photocathode RF Gun with Mg Cathode * J.F. Schmerge, J.M. Castro, J.E. Clendenin, D.H. Dowell,
FACET-II Design Update
 FACET-II Design Update October 17-19, 2016, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Glen White FACET-II CD-2/3A Director s Review, August 9, 2016 Planning for FACET-II as a Community Resource FACET-II Photo
FACET-II Design Update October 17-19, 2016, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Glen White FACET-II CD-2/3A Director s Review, August 9, 2016 Planning for FACET-II as a Community Resource FACET-II Photo
ASTRA simulations of the slice longitudinal momentum spread along the beamline for PITZ
 ASTRA simulations of the slice longitudinal momentum spread along the beamline for PITZ Orlova Ksenia Lomonosov Moscow State University GSP-, Leninskie Gory, Moscow, 11999, Russian Federation Email: ks13orl@list.ru
ASTRA simulations of the slice longitudinal momentum spread along the beamline for PITZ Orlova Ksenia Lomonosov Moscow State University GSP-, Leninskie Gory, Moscow, 11999, Russian Federation Email: ks13orl@list.ru
BERLinPro. An ERL Demonstration facility at the HELMHOLTZ ZENTRUM BERLIN
 BERLinPro An ERL Demonstration facility at the HELMHOLTZ ZENTRUM BERLIN BERLinPro: ERL demonstration facility to prepare the ground for a few GeV ERL @ Berlin-Adlershof Goal: 100MeV, 100mA beam Small emittance,
BERLinPro An ERL Demonstration facility at the HELMHOLTZ ZENTRUM BERLIN BERLinPro: ERL demonstration facility to prepare the ground for a few GeV ERL @ Berlin-Adlershof Goal: 100MeV, 100mA beam Small emittance,
THz Electron Gun Development. Emilio Nanni 3/30/2016
 THz Electron Gun Development Emilio Nanni 3/30/2016 Outline Motivation Experimental Demonstration of THz Acceleration THz Generation Accelerating Structure and Results Moving Forward Parametric THz Amplifiers
THz Electron Gun Development Emilio Nanni 3/30/2016 Outline Motivation Experimental Demonstration of THz Acceleration THz Generation Accelerating Structure and Results Moving Forward Parametric THz Amplifiers
HIGH CURRENT AND HIGH BRIGHTNESS ELECTRON SOURCES
 HIGH CURRENT AND HIGH BRIGHTNESS ELECTRON SOURCES F. Loehl, I. Bazarov, S. Belomestnykh, M. Billing, E. Chojnacki, Z. Conway, J. Dobbins, B. Dunham, R. Ehrlich, M. Forster, S. M. Gruner, C. Gulliford,
HIGH CURRENT AND HIGH BRIGHTNESS ELECTRON SOURCES F. Loehl, I. Bazarov, S. Belomestnykh, M. Billing, E. Chojnacki, Z. Conway, J. Dobbins, B. Dunham, R. Ehrlich, M. Forster, S. M. Gruner, C. Gulliford,
WG2 on ERL light sources CHESS & LEPP
 Charge: WG2 on ERL light sources Address and try to answer a list of critical questions for ERL light sources. Session leaders can approach each question by means of (a) (Very) short presentations (b)
Charge: WG2 on ERL light sources Address and try to answer a list of critical questions for ERL light sources. Session leaders can approach each question by means of (a) (Very) short presentations (b)
Spoke and other TEM-class superconducting cavities. J.L. Muñoz, ESS-Bilbao Academy-Industry Matching Event CIEMAT, Madrid, 27.May.
 Spoke and other TEM-class superconducting cavities J.L. Muñoz, ESS-Bilbao Academy-Industry Matching Event CIEMAT, Madrid, 27.May.2013 Outline Introduction Basic design of TEM cavities Cavity design issues
Spoke and other TEM-class superconducting cavities J.L. Muñoz, ESS-Bilbao Academy-Industry Matching Event CIEMAT, Madrid, 27.May.2013 Outline Introduction Basic design of TEM cavities Cavity design issues
High average current photo injector (PHIN) for the CLIC Test Facility at CERN
 High average current photo injector (PHIN) for the CLIC Test Facility at CERN CLIC and CTF3 motivation Photo injectors, PHIN Emittance measurements Long pulse operation, time resolved measurements Cathode
High average current photo injector (PHIN) for the CLIC Test Facility at CERN CLIC and CTF3 motivation Photo injectors, PHIN Emittance measurements Long pulse operation, time resolved measurements Cathode
Coherent Electron Cooling
 Proof-of-Principle of Principle Experiment for FEL-based Coherent Electron Cooling G. Wang Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY, USA Collaboration of BNL, Jlab and Tech-X Vladimir N. Litvinenko (PI),
Proof-of-Principle of Principle Experiment for FEL-based Coherent Electron Cooling G. Wang Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY, USA Collaboration of BNL, Jlab and Tech-X Vladimir N. Litvinenko (PI),
Tools of Particle Physics I Accelerators
 Tools of Particle Physics I Accelerators W.S. Graves July, 2011 MIT W.S. Graves July, 2011 1.Introduction to Accelerator Physics 2.Three Big Machines Large Hadron Collider (LHC) International Linear Collider
Tools of Particle Physics I Accelerators W.S. Graves July, 2011 MIT W.S. Graves July, 2011 1.Introduction to Accelerator Physics 2.Three Big Machines Large Hadron Collider (LHC) International Linear Collider
A Polarized Electron PWT Photoinjector for the ILC
 2005 ALCPG & ILC Workshops Snowmass, U.S.A. A Polarized Electron PWT Photoinjector for the ILC David Yu, Yan Luo, Alexei Smirnov, DULY Research Inc., Rancho Palos Verdes, CA 90275 Ivan Bazarov, Cornell
2005 ALCPG & ILC Workshops Snowmass, U.S.A. A Polarized Electron PWT Photoinjector for the ILC David Yu, Yan Luo, Alexei Smirnov, DULY Research Inc., Rancho Palos Verdes, CA 90275 Ivan Bazarov, Cornell
ANALYSIS OF HIGH ORDER MODES IN 1.3 GHZ CW SRF ELECTRON LINAC FOR A LIGHT SOURCE
 ANALYSIS OF HIGH ORDER MODES IN 1.3 GHZ CW SRF ELECTRON LINAC FOR A LIGHT SOURCE A. Sukhanov, A. Vostrikov, V. Yakovlev, Fermilab, Batavia, IL 60510, USA Abstract Design of a Light Source (LS) based on
ANALYSIS OF HIGH ORDER MODES IN 1.3 GHZ CW SRF ELECTRON LINAC FOR A LIGHT SOURCE A. Sukhanov, A. Vostrikov, V. Yakovlev, Fermilab, Batavia, IL 60510, USA Abstract Design of a Light Source (LS) based on
Dark current at the Euro-XFEL
 Dark current at the Euro-XFEL Jang-Hui Han DESY, MPY Observations at PITZ and FLASH Estimation for the European XFEL Ideas to reduce dark current at the gun DC at FLASH RF gun M1 M2 M3 M4 M5 M6 M7 6 undulator
Dark current at the Euro-XFEL Jang-Hui Han DESY, MPY Observations at PITZ and FLASH Estimation for the European XFEL Ideas to reduce dark current at the gun DC at FLASH RF gun M1 M2 M3 M4 M5 M6 M7 6 undulator
Accelerator Design of High Luminosity Electron-Hadron Collider erhic
 Accelerator Design of High Luminosity Electron-Hadron Collider erhic V. PTITSYN ON BEHALF OF ERHIC DESIGN TEAM: E. ASCHENAUER, M. BAI, J. BEEBE-WANG, S. BELOMESTNYKH, I. BEN-ZVI, M. BLASKIEWICZ, R. CALAGA,
Accelerator Design of High Luminosity Electron-Hadron Collider erhic V. PTITSYN ON BEHALF OF ERHIC DESIGN TEAM: E. ASCHENAUER, M. BAI, J. BEEBE-WANG, S. BELOMESTNYKH, I. BEN-ZVI, M. BLASKIEWICZ, R. CALAGA,
Modeling Electron Emission From Diamond-Amplified Cathodes
 Modeling Electron Emission From Diamond-Amplified Cathodes D. A. Dimitrov Tech-X Corporation, Boulder, CO I. Ben-Zvi, T. Rao, J. Smedley, E. Wang, X. Chang Brookhaven National Lab, NY This work is funded
Modeling Electron Emission From Diamond-Amplified Cathodes D. A. Dimitrov Tech-X Corporation, Boulder, CO I. Ben-Zvi, T. Rao, J. Smedley, E. Wang, X. Chang Brookhaven National Lab, NY This work is funded
Development of Cs 2 Te photocathode RF gun system for compact THz SASE-FEL
 Development of Cs 2 Te photocathode RF gun system for compact THz SASE-FEL R. Kuroda, H. Ogawa, N. Sei, H. Toyokawa, K. Yagi-Watanabe, M. Yasumoto, M. Koike, K. Yamada, T. Yanagida*, T. Nakajyo*, F. Sakai*
Development of Cs 2 Te photocathode RF gun system for compact THz SASE-FEL R. Kuroda, H. Ogawa, N. Sei, H. Toyokawa, K. Yagi-Watanabe, M. Yasumoto, M. Koike, K. Yamada, T. Yanagida*, T. Nakajyo*, F. Sakai*
Applications of High Brightness Beams: Energy Recovered Linacs
 Applications of High Brightness Beams: Energy Recovered Linacs G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Schematic Representation of Accelerator Types RF Installation Beam injector and dump Beamline Ring Linac Recirculating
Applications of High Brightness Beams: Energy Recovered Linacs G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Schematic Representation of Accelerator Types RF Installation Beam injector and dump Beamline Ring Linac Recirculating
PAL LINAC UPGRADE FOR A 1-3 Å XFEL
 PAL LINAC UPGRADE FOR A 1-3 Å XFEL J. S. Oh, W. Namkung, Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, POSTECH, Pohang 790-784, Korea Y. Kim, Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, D-603 Hamburg, Germany Abstract With
PAL LINAC UPGRADE FOR A 1-3 Å XFEL J. S. Oh, W. Namkung, Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, POSTECH, Pohang 790-784, Korea Y. Kim, Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, D-603 Hamburg, Germany Abstract With
CsK 2 Sb PHOTOCATHODE DEVELOPMENT FOR. Martin Schmeißer, Julius Kühn, Thorsten Kamps, Andreas Jankowiak Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin
 CsK 2 Sb PHOTOCATHODE DEVELOPMENT FOR Martin Schmeißer, Julius Kühn, Thorsten Kamps, Andreas Jankowiak Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin 1 PHOTOCATHODES Photoinjector for berlinpro Aim: 0.5 mm mrad emittance from
CsK 2 Sb PHOTOCATHODE DEVELOPMENT FOR Martin Schmeißer, Julius Kühn, Thorsten Kamps, Andreas Jankowiak Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin 1 PHOTOCATHODES Photoinjector for berlinpro Aim: 0.5 mm mrad emittance from
Recent Status of Polarized Electron Sources at Nagoya University
 Recent Status of Polarized Electron Sources at Nagoya University M. Kuwahara, N. Yamamoto, F. Furuta, T. Nakanishi, S. Okumi, M. Yamamoto, M. Kuriki *, T. Ujihara ** and K. Takeda ** Graduate School of
Recent Status of Polarized Electron Sources at Nagoya University M. Kuwahara, N. Yamamoto, F. Furuta, T. Nakanishi, S. Okumi, M. Yamamoto, M. Kuriki *, T. Ujihara ** and K. Takeda ** Graduate School of
THE ERL HIGH-ENERGY COOLER FOR RHIC*
 THE ERL HIGH-ENERGY COOLER FOR RHIC* I. Ben-Zvi** for the electron cooling team***, C-AD, BNL, Upton, NY, USA Abstract Electron cooling [1] entered a new era with the July 2005 cooling of the Tevatron
THE ERL HIGH-ENERGY COOLER FOR RHIC* I. Ben-Zvi** for the electron cooling team***, C-AD, BNL, Upton, NY, USA Abstract Electron cooling [1] entered a new era with the July 2005 cooling of the Tevatron
ASTRA BASED SWARM OPTIMIZATIONS OF THE BERLinPro INJECTOR
 ASTRA BASED SWARM OPTIMIZATIONS OF THE BERLinPro INJECTOR M. Abo-Bakr FRAAC4 Michael Abo-Bakr 2012 ICAP Warnemünde 1 Content: Introduction ERL s Introduction BERLinPro Motivation Computational Aspects
ASTRA BASED SWARM OPTIMIZATIONS OF THE BERLinPro INJECTOR M. Abo-Bakr FRAAC4 Michael Abo-Bakr 2012 ICAP Warnemünde 1 Content: Introduction ERL s Introduction BERLinPro Motivation Computational Aspects
ILC Particle Sources -Electron and PositronMasao KURIKI (Hiroshima University)
 ILC Particle Sources -Electron and PositronMasao KURIKI (Hiroshima University) Introduction Electron Polarization is important for ILC. NEA GaAs is practically the only solution. Positron polarization
ILC Particle Sources -Electron and PositronMasao KURIKI (Hiroshima University) Introduction Electron Polarization is important for ILC. NEA GaAs is practically the only solution. Positron polarization
Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility. May 19, 2014
 Perspectives on Superconducting RF A workshop incelebration ofthe careerofpeter Kneisel Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility May 19, 2014 1 Pioneers of SRF How SRF made it out of the laboratory
Perspectives on Superconducting RF A workshop incelebration ofthe careerofpeter Kneisel Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility May 19, 2014 1 Pioneers of SRF How SRF made it out of the laboratory
$)ODW%HDP(OHFWURQ6RXUFHIRU/LQHDU&ROOLGHUV
 $)ODW%HDP(OHFWURQ6RXUFHIRU/LQHDU&ROOLGHUV R. Brinkmann, Ya. Derbenev and K. Flöttmann, DESY April 1999 $EVWUDFW We discuss the possibility of generating a low-emittance flat (ε y
$)ODW%HDP(OHFWURQ6RXUFHIRU/LQHDU&ROOLGHUV R. Brinkmann, Ya. Derbenev and K. Flöttmann, DESY April 1999 $EVWUDFW We discuss the possibility of generating a low-emittance flat (ε y
Simulations of the IR/THz Options at PITZ (High-gain FEL and CTR)
 Case Study of IR/THz source for Pump-Probe Experiment at the European XFEL Simulations of the IR/THz Options at PITZ (High-gain FEL and CTR) Introduction Outline Simulations of High-gain FEL (SASE) Simulation
Case Study of IR/THz source for Pump-Probe Experiment at the European XFEL Simulations of the IR/THz Options at PITZ (High-gain FEL and CTR) Introduction Outline Simulations of High-gain FEL (SASE) Simulation
Development of Pulsed High Gradient Photoelectron Gun
 Development of Pulsed High Gradient Photoelectron Gun Paul Scherrer Institut, 4MeV test stand Presented by Martin Paraliev Slide 1/25 Motivation X-ray Free Electron Lasers (XFEL) are important for future
Development of Pulsed High Gradient Photoelectron Gun Paul Scherrer Institut, 4MeV test stand Presented by Martin Paraliev Slide 1/25 Motivation X-ray Free Electron Lasers (XFEL) are important for future
Georg Hoffstaetter Cornell Physics Dept. / CLASSE Cornell s ERL team
 1 R&D toward an ERL Georg Hoffstaetter Cornell Physics Dept. / Cornell s ERL team DC-gun R&D CW linac R&D SRF injector R&D Undulator R&D 2 Cornell history: The ERL principle Energy recovery needs continuously
1 R&D toward an ERL Georg Hoffstaetter Cornell Physics Dept. / Cornell s ERL team DC-gun R&D CW linac R&D SRF injector R&D Undulator R&D 2 Cornell history: The ERL principle Energy recovery needs continuously
6 Injector TECHNICAL SYNOPSIS
 6 Injector TECHNICAL SYNOPSIS The injector for the LCLS is required to produce a single 15-MeV bunch of charge 1. nc and 1 A peak current at a repetition rate of 12 Hz with a normalized rms transverse
6 Injector TECHNICAL SYNOPSIS The injector for the LCLS is required to produce a single 15-MeV bunch of charge 1. nc and 1 A peak current at a repetition rate of 12 Hz with a normalized rms transverse
The CeB6 Electron Gun for the Soft-X-ray FEL Project at SPring-8
 May 25, 2004 DESY, Hamburg, Germany The CeB6 Electron Gun for the Soft-X-ray FEL Project at SPring-8 K. Togawa SPring-8 / RIKEN Harima Institute T. Shintake, H. Baba, T. Inagaki, T. Tanaka SPring-8 / RIKEN
May 25, 2004 DESY, Hamburg, Germany The CeB6 Electron Gun for the Soft-X-ray FEL Project at SPring-8 K. Togawa SPring-8 / RIKEN Harima Institute T. Shintake, H. Baba, T. Inagaki, T. Tanaka SPring-8 / RIKEN
TTF and VUV-FEL Injector Commissioning
 TESLA Collaboration Meeting Sep. 6-8, 2004 Orsay TTF and VUV-FEL Injector Commissioning Siegfried Schreiber, Klaus Floettmann DESY Brief description of the injector Basic measurements Preliminary results
TESLA Collaboration Meeting Sep. 6-8, 2004 Orsay TTF and VUV-FEL Injector Commissioning Siegfried Schreiber, Klaus Floettmann DESY Brief description of the injector Basic measurements Preliminary results
Investigations on the electron bunch distribution in the longitudinal phase space at a laser driven RF-electron source for the European X-FEL
 Juliane Rönsch Universität Hamburg / DESY Investigations on the electron bunch distribution in the longitudinal phase space at a laser driven RF-electron source for the European X-FEL 5/27/2009 1 Contents
Juliane Rönsch Universität Hamburg / DESY Investigations on the electron bunch distribution in the longitudinal phase space at a laser driven RF-electron source for the European X-FEL 5/27/2009 1 Contents
DIAGNOSTIC TEST-BEAM-LINE FOR THE MESA INJECTOR
 DIAGNOSTIC TEST-BEAM-LINE FOR THE MESA INJECTOR I.Alexander,K.Aulenbacher,V.Bechthold,B.Ledroit,C.Matejcek InstitutfürKernphysik,JohannesGutenberg-Universität,D-55099Mainz,Germany Abstract With the test-beam-line
DIAGNOSTIC TEST-BEAM-LINE FOR THE MESA INJECTOR I.Alexander,K.Aulenbacher,V.Bechthold,B.Ledroit,C.Matejcek InstitutfürKernphysik,JohannesGutenberg-Universität,D-55099Mainz,Germany Abstract With the test-beam-line
Beam Breakup, Feynman and Complex Zeros
 Beam Breakup, Feynman and Complex Zeros Ivan Bazarov brown bag seminar, 16 Jan 04 Ivan Bazarov, BBU, feynman and complex zeros, Brown Bag seminar, 16 January 2004 1 Outline BBU: code-writing and simulation
Beam Breakup, Feynman and Complex Zeros Ivan Bazarov brown bag seminar, 16 Jan 04 Ivan Bazarov, BBU, feynman and complex zeros, Brown Bag seminar, 16 January 2004 1 Outline BBU: code-writing and simulation
High Gradient Tests of Dielectric Wakefield Accelerating Structures
 High Gradient Tests of Dielectric Wakefield Accelerating Structures John G. Power, Sergey Antipov, Manoel Conde, Felipe Franchini, Wei Gai, Feng Gao, Chunguang Jing, Richard Konecny, Wanming Liu, Jidong
High Gradient Tests of Dielectric Wakefield Accelerating Structures John G. Power, Sergey Antipov, Manoel Conde, Felipe Franchini, Wei Gai, Feng Gao, Chunguang Jing, Richard Konecny, Wanming Liu, Jidong
THERMAL EMITTANCE MEASUREMENTS AT THE SwissFEL INJECTOR TEST FACILITY
 THERMAL EMITTANCE MEASUREMENTS AT THE SwissFEL INJECTOR TEST FACILITY E. Prat, S. Bettoni, H. H. Braun, M. C. Divall, R. Ganter, T. Schietinger, A. Trisorio, C. Vicario PSI, Villigen, Switzerland C. P.
THERMAL EMITTANCE MEASUREMENTS AT THE SwissFEL INJECTOR TEST FACILITY E. Prat, S. Bettoni, H. H. Braun, M. C. Divall, R. Ganter, T. Schietinger, A. Trisorio, C. Vicario PSI, Villigen, Switzerland C. P.
Geometry Optimization of DC and SRF Guns to Maximize Beam Brightness
 Geometry Optimization of and SRF Guns to Maximize Beam Brightness M.N. Lakshmanan and I.V. Bazarov, CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA T. Miyajima, Photon Factory, KEK, Tsukuba, Japan Abstract
Geometry Optimization of and SRF Guns to Maximize Beam Brightness M.N. Lakshmanan and I.V. Bazarov, CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA T. Miyajima, Photon Factory, KEK, Tsukuba, Japan Abstract
Beam. RF antenna. RF cable
 Status of LEP2 J. Wenninger, SL Operation for the SL division LEPC September 1998 Outline Optics and RF for 1998 Beam current limitations Injection and ramp Performance at high energy Conclusions LEPC/15-09-98
Status of LEP2 J. Wenninger, SL Operation for the SL division LEPC September 1998 Outline Optics and RF for 1998 Beam current limitations Injection and ramp Performance at high energy Conclusions LEPC/15-09-98
Needle cathodes for high-brightness beams. Chase Boulware Jonathan Jarvis Heather Andrews Charlie Brau
 Needle cathodes for high-brightness beams Chase Boulware Jonathan Jarvis Heather Andrews Charlie Brau Outline of the talk What is brightness? Definition Sources Why is brightness important? Light sources
Needle cathodes for high-brightness beams Chase Boulware Jonathan Jarvis Heather Andrews Charlie Brau Outline of the talk What is brightness? Definition Sources Why is brightness important? Light sources
Fermilab HG cavity and coupler R&D
 Fermilab HG cavity and coupler R&D Motivation HOM calculations Nikolay Solyak Fermilab Outline Main Coupler and HOM dumping Multipactor Lorentz Forces Single bunch beam dynamics Summary Nikolay Solyak
Fermilab HG cavity and coupler R&D Motivation HOM calculations Nikolay Solyak Fermilab Outline Main Coupler and HOM dumping Multipactor Lorentz Forces Single bunch beam dynamics Summary Nikolay Solyak
X-band Photoinjector Beam Dynamics
 X-band Photoinjector Beam Dynamics Feng Zhou SLAC Other contributors: C. Adolphsen, Y. Ding, Z. Li, T. Raubenheimer, and A. Vlieks, Thank Ji Qiang (LBL) for help of using ImpactT code ICFA FLS2010, SLAC,
X-band Photoinjector Beam Dynamics Feng Zhou SLAC Other contributors: C. Adolphsen, Y. Ding, Z. Li, T. Raubenheimer, and A. Vlieks, Thank Ji Qiang (LBL) for help of using ImpactT code ICFA FLS2010, SLAC,
Elliptical Cavities: Proven SRF Option
 Elliptical Cavities: Proven SRF Option Terry L. Grimm Michigan State University July 2005 Outline Multi-cell elliptical cavities Demonstrated for β > 0.4 Future trends Multi-spoke cavities Limited experimental
Elliptical Cavities: Proven SRF Option Terry L. Grimm Michigan State University July 2005 Outline Multi-cell elliptical cavities Demonstrated for β > 0.4 Future trends Multi-spoke cavities Limited experimental
Linac optimisation for the New Light Source
 Linac optimisation for the New Light Source NLS source requirements Electron beam requirements for seeded cascade harmonic generation LINAC optimisation (2BC vs 3 BC) CSR issues energy chirp issues jitter
Linac optimisation for the New Light Source NLS source requirements Electron beam requirements for seeded cascade harmonic generation LINAC optimisation (2BC vs 3 BC) CSR issues energy chirp issues jitter
High gradient, high average power structure development at UCLA and Univ. Rome in X-X. band
 High gradient, high average power structure development at UCLA and Univ. Rome in X-X and S-S band May 23-25, 25, 2007 US High Gradient Research Collaboration Workshop Atsushi Fukasawa, James Rosenzweig,
High gradient, high average power structure development at UCLA and Univ. Rome in X-X and S-S band May 23-25, 25, 2007 US High Gradient Research Collaboration Workshop Atsushi Fukasawa, James Rosenzweig,
Simulations for photoinjectors C.Limborg
 Simulations for photoinjectors C.Limborg 1- GTF Simulations Parmela modeling improvements Comparison to experimental results: 2ps & 4ps Sensitivity study Plans for future simulations 2- LCLS Injector Simulations
Simulations for photoinjectors C.Limborg 1- GTF Simulations Parmela modeling improvements Comparison to experimental results: 2ps & 4ps Sensitivity study Plans for future simulations 2- LCLS Injector Simulations
Potential use of erhic s ERL for FELs and light sources ERL: Main-stream GeV e - Up-gradable to 20 + GeV e -
 Potential use of erhic s ERL for FELs and light sources Place for doubling energy linac ERL: Main-stream - 5-10 GeV e - Up-gradable to 20 + GeV e - RHIC Electron cooling Vladimir N. Litvinenko and Ilan
Potential use of erhic s ERL for FELs and light sources Place for doubling energy linac ERL: Main-stream - 5-10 GeV e - Up-gradable to 20 + GeV e - RHIC Electron cooling Vladimir N. Litvinenko and Ilan
Center for the Advancement of Natural Discoveries using Light Emission AREAL. Facility Status and Highlights. V. Tsakanov. 12 July 2016, DESY, Hamburg
 Center for the Advancement of Natural Discoveries using Light Emission AREAL Facility Status and Highlights V. Tsakanov 12 July 2016, DESY, Hamburg Contents Introduction CANDLE First Stage AREAL Figure
Center for the Advancement of Natural Discoveries using Light Emission AREAL Facility Status and Highlights V. Tsakanov 12 July 2016, DESY, Hamburg Contents Introduction CANDLE First Stage AREAL Figure
On the future plan of KEK for ILC(International Linear Collider) Junji Urakawa(KEK) Contents
 On the future plan of KEK for ILC(International Linear Collider) Junji Urakawa(KEK) 2004.10.24 Contents 0. Outline until now. Review of SC-LC(TESLA) and R&D items. R&D Items at ATF. R&D plans for Superconducting
On the future plan of KEK for ILC(International Linear Collider) Junji Urakawa(KEK) 2004.10.24 Contents 0. Outline until now. Review of SC-LC(TESLA) and R&D items. R&D Items at ATF. R&D plans for Superconducting
Lecture 5: Photoinjector Technology. J. Rosenzweig UCLA Dept. of Physics & Astronomy USPAS, 7/1/04
 Lecture 5: Photoinjector Technology J. Rosenzweig UCLA Dept. of Physics & Astronomy USPAS, 7/1/04 Technologies Magnetostatic devices Computational modeling Map generation RF cavities 2 cell devices Multicell
Lecture 5: Photoinjector Technology J. Rosenzweig UCLA Dept. of Physics & Astronomy USPAS, 7/1/04 Technologies Magnetostatic devices Computational modeling Map generation RF cavities 2 cell devices Multicell
ELIC Design. Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators. Jefferson Lab. Second Electron-Ion Collider Workshop Jefferson Lab March 15-17, 2004
 ELIC Design Ya. Derbenev, K. Beard, S. Chattopadhyay, J. Delayen, J. Grames, A. Hutton, G. Krafft, R. Li, L. Merminga, M. Poelker, E. Pozdeyev, B. Yunn, Y. Zhang Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators
ELIC Design Ya. Derbenev, K. Beard, S. Chattopadhyay, J. Delayen, J. Grames, A. Hutton, G. Krafft, R. Li, L. Merminga, M. Poelker, E. Pozdeyev, B. Yunn, Y. Zhang Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators
LOLA: Past, present and future operation
 LOLA: Past, present and future operation FLASH Seminar 1/2/29 Christopher Gerth, DESY 8/5/29 FLASH Seminar Christopher Gerth 1 Outline Past Present Future 8/5/29 FLASH Seminar Christopher Gerth 2 Past
LOLA: Past, present and future operation FLASH Seminar 1/2/29 Christopher Gerth, DESY 8/5/29 FLASH Seminar Christopher Gerth 1 Outline Past Present Future 8/5/29 FLASH Seminar Christopher Gerth 2 Past
A Multi-beamlet Injector for Heavy Ion Fusion: Experiments and Modeling
 A Multi-beamlet Injector for Heavy Ion Fusion: Experiments and Modeling G.A. Westenskow, D.P. Grote; LLNL J.W. Kwan, F. Bieniosek; LBNL PAC07 - FRYAB01 Albuquerque, New Mexico June 29, 2007 This work has
A Multi-beamlet Injector for Heavy Ion Fusion: Experiments and Modeling G.A. Westenskow, D.P. Grote; LLNL J.W. Kwan, F. Bieniosek; LBNL PAC07 - FRYAB01 Albuquerque, New Mexico June 29, 2007 This work has
Tomographic transverse phase space measurements at PITZ.
 Tomographic transverse phase space measurements at PITZ. > Photo-Injector Test facility at DESY in Zeuthen - PITZ > Tomography in beam diagnostics > Hardware > Measurements & evaluation Georgios Kourkafas,
Tomographic transverse phase space measurements at PITZ. > Photo-Injector Test facility at DESY in Zeuthen - PITZ > Tomography in beam diagnostics > Hardware > Measurements & evaluation Georgios Kourkafas,
Field Emission and Channeling Radiation for High-Spectral-Brilliance X-ray Sources
 Field Emission and Channeling Radiation for High-Spectral-Brilliance X-ray Sources Charles Brau, Bo Choi, William Gabella, Anthony Hmelo, John Kozub, Borislav Ivanov, Jonathan Jarvis, Marcus Mendenhall
Field Emission and Channeling Radiation for High-Spectral-Brilliance X-ray Sources Charles Brau, Bo Choi, William Gabella, Anthony Hmelo, John Kozub, Borislav Ivanov, Jonathan Jarvis, Marcus Mendenhall
The technology decision took place The ITRP made clear
 Lutz.Lilje@desy.de The technology decision took place The ITRP made clear It s not a design choice TESLA design to be revisited International Collaboration needed NOW! SRF technology is considered more
Lutz.Lilje@desy.de The technology decision took place The ITRP made clear It s not a design choice TESLA design to be revisited International Collaboration needed NOW! SRF technology is considered more
SwissFEL INJECTOR DESIGN: AN AUTOMATIC PROCEDURE
 Proceedings of FEL03, New York, NY, USA SwissFEL INJECTOR DESIGN: AN AUTOMATIC PROCEDURE S. Bettoni, M. Pedrozzi, S. Reiche, PSI, Villigen, Switzerland Abstract The first section of FEL injectors driven
Proceedings of FEL03, New York, NY, USA SwissFEL INJECTOR DESIGN: AN AUTOMATIC PROCEDURE S. Bettoni, M. Pedrozzi, S. Reiche, PSI, Villigen, Switzerland Abstract The first section of FEL injectors driven
