Fathi Abubrig, Mohamed Delfag, Suad M. Abuzariba
|
|
|
- Madlyn Farmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 World cademy of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Mathematical, Computational, Physical, Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol:8, No:, 4 The Effect of the Crystal Field Interaction on the Critical Temperatures and the Sublattice Magnetizations of a Mixed Spin-/ and Spin-5/ Ferrimagnetic System Fathi bubrig, Mohamed Delfag, Suad M. buzariba International Science Index, Physical and Mathematical Sciences Vol:8, No:, 4 waset.org/publication/ bstract The influence of the crystal field interactions on the mixed spin-/ and spin-5/ ferrimagnetic Ising system is considered by using the mean field theory based on ogoliubov inequality for the Gibbs free energy. The ground-state phase diagram is constructed, the phase diagrams of the second-order critical temperatures are obtained, and the thermal variation of the sublattice magnetizations is investigated in detail. We find some interesting phenomena for the sublattice magnetizations at particular values of the crystal field interactions. Keywords Crystal field, Ising system, Ferrimagnetic, magnetization, phase diagrams. I. INTRODUCTION HE Ising model, with high and mixed spins, is an Tinteresting subect of study because of its observed critical behaviors. The two sublattice mixed Ising ferrimagnetic systems have been of interest in the last two decades, for not only purely theoretical purposes but also because they have been proposed as possible systems to describe ferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic materials []. Moreover, the increasing interest in these systems is mainly related to the technological applications of these systems in the area of thermomagnetic recording []. Since the mixed spin Ising systems have less translational symmetry than their single spin counterparts, they exhibit many new phenomena which cannot be observed in the single-spin Ising systems and the study of these systems can be relevant for understanding of bimetallic molecular systems based magnetic materials []. One of the earliest and simplest of these models to be studied was the mixed spin Ising system consisting of spin-/ and spin-s (S > /) in a uniaxial crystal field. The model for different values of S (S > /) has been investigated by exact (on honeycomb lattice [4]-[6], as well as on ethe lattice [7], [8], mean field approximation [9], effective field theory with correlations []-[4], cluster variational theory [8], renormalization-group technique [5] and Monte-Carlo simulation [6]-[8]. The mixed- spin Ising systems consisting Fathi bubrig is with the Physics Department, Faculty of science, Elmergeb University, Zliten, Libya ( Dr_fathiomar@yahoo.com). Mohamed Delfag is with the Physics Department, Faculty of Education, Misurata University, Libya ( msdelfag@yahoo.com). Suad M buzariba is with the Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Misurata University ( suadabu@yahoo.com). of higher spins are not without interest. Indeed, the magnetic properties of mixed spin- and spin-/ Ising ferromagnetic system with different single-ion anisotropies have been investigated with the use of an effective field theory [8], [9], mean field theory [], a cluster variational method [] and Monte Carlo simulation []. Recently, the investigations have been extended to high order mixed spin ferrimagnetic systems (mixed spin-/ and spin- ferrimagnetic system and mixed spin-/ and spin-5/) in order to construct their phase diagrams in the temperatureanisotropy plane and to consider magnetic properties of these systems. obak and Delay investigated the effect of single-ion anisotropy on the phase diagram of the mixed spin-/ and spin- Ising system by the use of a mean-field theory based on the ogoliubov inequality for the free energy []. lbayrak [4] studied the critical behaviour of the mixed spin- and spin-5/ Ising ferrimagnetic system on ethe lattice and he also [5] examined the critical and the compensation temperatures of the mixed spin- and spin-5/ Ising ferrimagnetic system on ethe lattice by using the exact recursion equations. ayram Deviren et al. have used the effective field theory to study the magnetic properties of the ferrimagnetic mixed spin-/ and spin- Ising model with crystal field in a longitudinal magnetic field on a honeycomb and a square lattice [6]. In this paper, our aim is to consider a mixed spin-/ and spin-5/ ferrimagnetic system within the framework of the mean-field theory based on ogoliubov inequality for the Gibbs free energy, in order to investigate the influence of the crystal-field interaction on the critical temperatures and to find the change in the sublattice magnetizations of the system as a function of the temperature at a different values of the crystalfield interaction. This paper is organized as follows: Section II briefly presents the mixed spin Ising model and its mean-field solution. Section III gives the results and the discussions. In Section IV the conclusion is summarized. II. THE MODEL ND CLCULTION We consider a mixed Ising spin- and spin-5/ system consisting of two sublattices and, which are arranged alternately. The sublattice are occupied by spins S i, which International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 8() 4 54
2 World cademy of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Mathematical, Computational, Physical, Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol:8, No:, 4 International Science Index, Physical and Mathematical Sciences Vol:8, No:, 4 waset.org/publication/ take the spin values of ± /, ± /, while the sublattice are occupied by spins S, which take the spin values of. ± 5 /, ± /, ± /. In each site of the lattice, there is a single-ion anisotropy D in the sublattices and D in the sublattice ) acting in the spin-/ and spin-5/. The Hamiltonian of the system according to the mean-field theory is given by ( H = J S i S D S ) D ( S ), () i ( i, ) where the first summation is carried out only over nearestneighbor pairs of spins on different sublattices and J is the nearest-neighbour exchange interaction. The most direct way of deriving the mean-field theory is to use the variation principle for the Gibbs free energy, β = G( H) Φ G ( H ) + H H, () where G ( H ) is the true free energy of the model described by Hamiltonian given in (), G ( H ) is the model described by the trial Hamiltonian H which depends on variational parameters and denotes a thermal average over the ensemble defined by H. Now, depending on the choice of the trial Hamiltonian, one can construct approximate methods of different accuracy. However, owing to the complexity of the problem, we consider in this work the simple choice of H, namely H γ S + D ( S ) ],() = [ Si + D( Si ) ] [ γ i where γ and γ are the two variational parameters related to the molecular fields acting on the two different sublattices, respectively. y evaluating (), it is easy to obtain the expression of the free energy per site in MF, φ 5 5 g= = ln exp βd cosh βγ+ exp ( 4 βd) cosh βγ + exp ( 6 β D) cosh βγ N β ln exp βd cosh βγ + exp ( β D) cosh βγ + ( zjmm) 4 / k T 5 5 sinh exp ( 4 )sinh exp ( 6 ) sinh βγ + βd βγ + βγ β γ m = 5 cosh βγ + exp ( 4 βd ) cosh βγ + exp ( 6 βd ) cosh β γ m ( βγ ) + βd ( βγ) ( β γ ) + β D ( βγ ) sinh / exp( )sinh / = (6) cosh / exp ( ) cosh / where, N is the total number of sites of the lattice and z is the number of the nearest neighbors of every ion in the lattice m and m are the sublattice magnetizations per site which are defined by (5). Now, by minimizing the free energy (4) with respect to γ and γ, we obtain γ = zj m, γ = zj m. (7) The mean-field properties of the present model are then given by (4)-(7). Since (5)-(7) have in general several solutions for the pair ( m, m ), the stable phase will be the one which minimizes the free energy. When the system undergoes the second-order transition from an ordered state ( m, m ), to the paramagnetic state ( m =, m = ), this part of the phase diagram can be determined analytically. ecause the magnetizations m and m are very small in the neighborhood of second-order transition point, we can expand (4)-(6) to obtain a Landau-like expansion. In this way, critical and tricritical points are determined according to the following routine; ) Second-order transition lines when a= and b>; ) Tricritical points, if they are exist, when a=b=, and c >. (4) (5) International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 8() 4 544
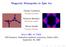
3 World cademy of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Mathematical, Computational, Physical, Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol:8, No:, 4 International Science Index, Physical and Mathematical Sciences Vol:8, No:, 4 waset.org/publication/ III. RESULTS ND DISCUSSIONS. Ground State Phase Diagram efore going into the detailed calculation of the phase diagram of the model at higher temperature, let us first investigate the ground state structure of the model at zero temperature analytically. The ground-state phase diagram is easily determined from Hamiltonian Equation () by comparing the ground-state energies of the different phases, then the ground state configuration is the one with the lowest energy and each of these configurations for the given system parameters correspond to the stable states of the model which are indicated in Fig.. t zero temperature, we find six phases with different values of { m, m, q, q}, namely the ordered ferrimagnetic phases. These ordered phases are separated by first ordered lines and the values of { m, m, q, q} for these phases are given as following: O =, O =, O =,, O = O =, O = where the parameters q and q q = S i and are defined by: q = S It should be mentioned that, in this mixed-spin-system, the ground- state phase diagram exhibit no disordered phases and that the ground state phase diagram is very important in classifying the different phase regions of the model for the phase diagrams at higher temperatures.. Finite Temperature Phase Diagrams In Figs. and, the second-order critical temperature lines which separate the ordered phases, i.e. ferrimagnetic phases, from the paramagnetic phase of the mixed spin-/ and the spin-5/ Ising ferrimagnetic system are depicted in the ( D J, k T J ) c and ( D, k T ) c planes for some selected values of D J for spin-5/ and D / z J for spin-/, respectively. -.5 D / Z D /Z Fig. Ground-state phase diagram of the mixed spin-/ and spin-5/ Ising ferrimagnetic system with the coordination number z and different single-ion anisotropies D / z J and D / z J The four phases: ordered O, O, O, O 4, O 5, O6 and there are no disordered phases in the ground-state phase diagram The second-order critical temperature lines are easily obtained by setting a= and b >. The first phase diagram is obtained on the ( D / z J, ktc / z J ) plane and presented in Fig.. This phase diagram shows the general characteristics of the model for given values of D J in the range 6. < D < 6.. In this figure, one can observe that this mixed spin system exhibits second-order critical temperature lines only and does not exhibit any tricritical points or first order critical temperature lines, indicating that this system has no first order phase transition. It is also obvious that the second-order lines corresponding to each value of D / z J present two straight portions at lower and higher temperatures for the low negative and high positive values of D J, respectively, meaning that the critical temperatures of the model become constant in these limits. These two straight portions of the second-order lines combine with each other with a gradually increasing part. t this part, the values of the second-order critical temperatures increase rapidly by increasing the values of D J, then, they start to increase slowly until they come to the highest saturated value at high positive values of D J. 4 International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 8() 4 545
4 World cademy of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Mathematical, Computational, Physical, Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol:8, No:, 4 k Tc/z 4 D /z = D /z k Tc/z 4 D /z = D /z International Science Index, Physical and Mathematical Sciences Vol:8, No:, 4 waset.org/publication/ Fig. Phase diagram in the ( D, T) plane for the mixed-spin Ising ferrimagnet with the coordination number z, when the value of D / z J is changed k Tc/zJ 4 D/zJ = -6-6 Fig. Phase diagram in the ( D, T) plane for the mixed-spin Ising ferrimagnet with the coordination number z, when the value of D / z J is changed On the other hand, at this part, the second-order critical temperatures values decrease rapidly by decreasing the values of D J, then they start to decrease slowly until they come to the lowest saturated value at low negative values of D J. The second phase diagram is obtained on the ( D, k T ). D/zJ c plane for selected values of D J in the range 6. < D J < 6. and is depicted in Fig.. From this figure, it is clear that the behavior of the second order critical temperature lines with D J for different values of D J is similar to their behavior with D J for different values of D J which is depicted in Fig.. Fig. 4 Phase diagram in the ( D, T ) plane for the mixed-spin Ising ferrimagnet with the coordination number z, when the value of D / z J = and D / z J =. The saturated values of the second-order critical temperatures are shown in this figure For the final illustrations, let us now turn our attention to the saturated values of the critical temperatures for high values and low values of D / z J and D / z J. s shown in Fig. 4, for high positive and negative values of D / z J and D / z J. When / z J and D / z J k, the saturated value of the critical temperatures is Tc J =. 75. When D / z J and D / z J, the saturated value of the critical temperatures is k T c / z J =. 5. When D D / z J and / z J D, the saturated value of the critical points is. T J =. 75. If k c D / z J and D / z J, the saturated value is T J =. 5 k c. C. Sublattice Magnetizations m and m. In this subsection, let us at first examine the temperature dependence of the sublattice magnetizations m and m for the system. The results are depicted in Figs Fig. 5 shows typical sublattice magnetization curves with D J =., and selected values of / z J D. In this case, all the sublattice magnetization curves have standard characteristic convex shape. Moreover, in the present system and for all the values of the crystal field interactions D J and D / z J, the present system exhibits second-order phase transitions only, consequently, the sublattice magnetizations decrease by increasing temperature from their International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 8() 4 546
5 World cademy of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Mathematical, Computational, Physical, Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol:8, No:, 4 International Science Index, Physical and Mathematical Sciences Vol:8, No:, 4 waset.org/publication/ saturation values at T = K and vanish continuously at the critical temperatures T c. y comparing the values of the sublattice magnetizations at zero temperature, for different values of D / z J and D / z J in Fig. 5 with the values of the sublattice magnetizations, corresponding to the different phases and to the boundary between the phases, at the ground-state phase diagram (Fig. ), we find that they are in an agreement and every sublattice magnetization has the same saturated value at T = K as in the ground state phase diagram. In Figs. 6 and 7, we turn our attention to the points which are located close to or at the boundaries between the phases in the ground-state phase diagram. In Fig. 6, when D / z J =. and D / z J =. 5 ( this point located in the ordered phase O and close to the boundary between the ordered phase O and the ordered phase O in the ground state phase diagram, where D / z J =. 75 ). In this case, the temperature dependences of m may exhibit a rather rapid decrease (damping) from its saturation value at T = K. The phenomena is further enhanced when the value of D J approaches the boundary. t D / z J =.75 (at the boundary) and for T = K, the saturation value of m is m =., which indicates that in the ground state the spin configuration of in the system S consists of the mixed state; in this state half of the spins on sublattice are equal to +5/ (or -5/) and the other half are equal to +/ (or -/). y further decreasing D, the ground state becomes O, with m = / at T = K. In this region, when D J =.4 (slightly below the boundary between the ordered phases O and O ) the thermal variation of m exhibits an interesting feature which is the initial rise (excitation) of m with the increase of temperature before decreasing to zero at the critical point. On the other hand, for all values of D / z J..4 m m k T/z Fig. 5 Thermal variation of the sublattice magnetizations m, m for, the mixed-spin Ising ferrimagnet with the coordination number z, when the value of D J is changed for fixed D J =. m m D /z =. -. D /z = D /z = k T/z Fig. 6 Thermal variation of the sublattice magnetizations m,, m for the mixed-spin Ising ferrimagnet with the coordination number z, when the value of D J is changed for fixed D J =. In Fig. 6 and for all these values of D the sublattice magnetization m may show normal behavior even though it is coupled to m. When D has the values.7,. 75 and.8 (close to and at the boundary between the orderedphases O and O 5 in the ground-state phase diagram), it is clear from Fig. 6 that the temperature dependences of m and m exhibit similar behaviors to the temperature dependences of m and m in the previous case. D /z =. International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 8() 4 547
6 World cademy of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Mathematical, Computational, Physical, Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol:8, No:, 4 International Science Index, Physical and Mathematical Sciences Vol:8, No:, 4 waset.org/publication/ m m Fig. 7 Thermal variation of the sublattice magnetizations m, m for, the mixed-spin Ising ferrimagnet with the coordination number z, when the value of D J is changed for fixed D J =. Fig. 7 shows the sublattice magnetization curves as a function of temperature for several values of D / z J, when / z J =.. In this case, the selection of D D /z = D /z = k T D / z J corresponds to the crossover from the O to the O phase. When D J =., the sublattice magnetization may show normal behavior. When D =. (slightly above the boundary between the ordered phase O and the ordered phase O, where D / z J =. ) the magnetization curve m may exhibit a rather rapid decrease from its saturation value ( m = / ) at T = K, while for the value of D / z J =.5 (slightly below that boundary), there is a rapid increase of m from the saturation value ( m = / ) with the increase in T. When the value of D / z J =. 5, the saturation value of the sublattice magnetization m at T = K is ( m =. ). It indicates that at this point, the spin configuration of S in the ground state consists of the mixed state; half of the spins on the sublattice are equal to -/ (or +/ as well) and the other half are equal to -/ (or +/ as well). It is also seen from Fig. 7 that when D / z J =., the sublattice magnetization m decreases normally from its saturation value ( m = / ) to vanish at the critical temperature T c. On the other hand, for all values of D / z J the sublattice magnetization m may show normal behavior, even though it is coupled to m.. m IV. CONCLUSIONS In this work, we have studied The effect of the crystal field interactions on the critical temperatures and the sublattice magnetizations of a mixed spin-/ and spin-5/ ferrimagnetic system by using the mean-field theory based on ogoliubov inequality for the Gibbs free energy. Some new results on the phase diagrams and the sublattice magnetization curves have been obtained. We obtain six ordered Phases in the ground state phase diagram. We have found that the ground-state phase diagram for this system does not exhibit disordered phases. The finite temperature phase diagrams exhibit only second-order critical temperature lines. We found that for the values of the crystal field interactions close to the boundaries between the phases in the ground state phase diagram, the sublattice magnetization curves for this system may exhibit a rapid increase or decrease in their values by increasing the temperature before the sublattice magnetizations vanish at the critical points. REFERENCES [] Drillon M, Coronado E, eltran D, Georges R. Classical treatment of a heisenberg linear chain with spin alternation; application to the MnNi(EDT) 6H O complex. Chem Phys, 98, 79: [] M. Mansuripur, Magnetization Reversal, Coercivity, and the Process of Thermomagnetic Recording in Thin Films of morphous Rare Earth Transition Metal lloys, Journal of pplied Physics, Vol. 6, No. 4, 987, pp [] O. Kahn, in: E. Coronado, et al., (Eds.), Molecular Magnetism: From Molecular ssemblies to the Devices, Kluwer cademic Publishers, Dordrecht, 996. [4] L. L. Goncaloves, Uniaxial nisotropy Effects in the Ising Model: n Exactly Soluble Model, Physica Scripta, Vol., No., 986, p. 9. [5]. Dakhama and N. enayad, On the Existence of Compensation Temperature in d Mixed-Spin Ising Ferri magnets: n Exactly Solvable Model, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol., No. -,, pp [6] N. R. da Silva and S. R. Salinas, Mixed-Spin Ising Model on eth Lattice, Physical Review, Vol. 44, No., 99, pp [7] J. W. Tucker, The Ferrimagnetic Mixed Spin-/ and Spin- Sing System, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 95, No., 999, pp. [8] T. Kaneyoshi and J. C. Chen, Mean-Field nalysis of a Ferrimagnetic Mixed Spin System, Journal of Magnet ism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 98, No. -, 99, pp. -4. [9] T. Kaneyoshi, Curie Temperatures and Tricritical Points in Mixed Ising Ferromagnetic Systems, The Physical Society of Japan, Vol. 56, 987, pp doi:.4/jpsj [] T. Kaneyoshi, Phase Transition of the Mixed Spin System with a Random Crystal Field, Physica, Vol. 5, No., 988, pp [] T. Kaneyoshi, M. Jascur and P. Tomczak, The Ferri magnetic Mixed Spin-/ and Spin-/ Ising System, Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, Vol. 4, No. 49, 99, pp. L65-L658. [] T. Kaneyoshi, Tricritical ehavior of a Mixed Spin-/ and Spin- Ising System, Physica, Vol. 5, No. 4, 994, pp []. obak and M. Jurcisin, Discussion of Critical ehaviour in a Mixed-Spin Ising Model, Physica, Vol. 4, No. -4, 997, pp [4] S. G.. Quadros and S. R. Salinas, Renormalization Group Calculations for a Mixed-Spin Ising Model, Physica : Statistical Mechanics and Its pplications, Vol. 6, No. -4, 994, pp [5] G. M. Zhang, Ch.Z. Yang, "Monte Carlo Study of the Two-Dimensional Quadratic Ising Ferromagnet with Spins S = / and S = and with Crystal-Field Interactions, Physical Review, Vol. 48, No., 99, pp [6] G. M. uendia and M.. Novotny, Numerical Study of a Mixed Ising Ferrimagnetic System, Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, Vol. 9, No. 7, 997, pp International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 8() 4 548
7 World cademy of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Mathematical, Computational, Physical, Electrical and Computer Engineering Vol:8, No:, 4 International Science Index, Physical and Mathematical Sciences Vol:8, No:, 4 waset.org/publication/ [7] G. M. uendia and J.. Liendo, Monte Carlo Simulation of a Mixed Spin-/ and Spin-/ Ising Ferrimagnetic System, Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, Vol. 9, No. 5, 997, pp [8] obak, The Effect of nisotropies on the Magnetic Pro perties of a Mixed Spin- and Spin-/ Ising Ferrimag netic System, Physica, Vol. 58, No. -, 998, pp [9]. obak, O. F. bubrig and D. Horvath, n Effective-Field Study of the Mixed Spin- and Spin-/ Ising Ferrimagnetic System, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 46, No. -,, pp [] O. F. bubrig, D. Horváth,. obák and M. Jaščur, Mean-field solution of the mixed spin- and spin-/ Ising system with different single-ion anisotropies, Physica 96 () [] J. W. Tucker, Mixed Spin- and Spin-/ lume-capel Ising Ferromagnet, Journal of Magnetism and Mgnetic Materials, Vol. 7, No.,, pp [] Y. Nakamura and J. W. Tucker. Monte Carlo study of a mixed spin- and spin-/ Ising system ferromagnet. IEEE Trans. Magn., 8:46 48,. []. obak, The Effect of nisotropies on the Magnetic Properties of a Mixed Spin- and Spin-/ Ising Ferri magnetic System, Physica, Vol. 58, No. -, 998, pp [4] E. lbayrak, Mixed-Spin- and Spin-5/ lume-emery Griffiths Model, Physica : Statistical Mechanics and Its pplications, Vol. 75, No., 7, pp [5] M. Keskin and M. Ertas, Existence of a Dynamic Compensation Temperature of a Mixed Spin- and Spin-5/ Ising Ferrimagnetic System in an Oscillating Field, Physical Review E, Vol. 8, No. 6, 9. [6]. Deviren, E. Kantar and M. Keskin, Magnetic Proper ties of a Mixed Spin-/ and Spin- Ising Ferrimagnetic System within the Effective- Field Theory, Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 56, No. 6,, pp International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation 8() 4 549
A theoretical investigation for low-dimensional molecular-based magnetic materials
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) 3003 3017. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)87508-5 A theoretical investigation for low-dimensional molecular-based magnetic materials T Kaneyoshi and Y Nakamura
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) 3003 3017. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)87508-5 A theoretical investigation for low-dimensional molecular-based magnetic materials T Kaneyoshi and Y Nakamura
Bond Dilution Effects on Bethe Lattice the Spin-1 Blume Capel Model
 Commun. Theor. Phys. 68 (2017) 361 365 Vol. 68, No. 3, September 1, 2017 Bond Dilution Effects on Bethe Lattice the Spin-1 Blume Capel Model Erhan Albayrak Erciyes University, Department of Physics, 38039,
Commun. Theor. Phys. 68 (2017) 361 365 Vol. 68, No. 3, September 1, 2017 Bond Dilution Effects on Bethe Lattice the Spin-1 Blume Capel Model Erhan Albayrak Erciyes University, Department of Physics, 38039,
The mixed-spins 1/2 and 3/2 Blume Capel model with a random crystal field
 The mixed-spins 1/2 and 3/2 Blume Capel model with a random crystal field Erhan Albayrak Erciyes University, Department of Physics, 38039, Kayseri, Turkey (Received 25 August 2011; revised manuscript received
The mixed-spins 1/2 and 3/2 Blume Capel model with a random crystal field Erhan Albayrak Erciyes University, Department of Physics, 38039, Kayseri, Turkey (Received 25 August 2011; revised manuscript received
Critical Properties of Mixed Ising Spin System with Different Trimodal Transverse Fields in the Presence of Single-Ion Anisotropy
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 45 (2006) pp. 111 116 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 45, No. 6, June 15, 2006 Critical Properties of Mixed Ising Spin System with Different Trimodal Transverse
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 45 (2006) pp. 111 116 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 45, No. 6, June 15, 2006 Critical Properties of Mixed Ising Spin System with Different Trimodal Transverse
Renormalization Group for the Two-Dimensional Ising Model
 Chapter 8 Renormalization Group for the Two-Dimensional Ising Model The two-dimensional (2D) Ising model is arguably the most important in statistical physics. This special status is due to Lars Onsager
Chapter 8 Renormalization Group for the Two-Dimensional Ising Model The two-dimensional (2D) Ising model is arguably the most important in statistical physics. This special status is due to Lars Onsager
WORLD SCIENTIFIC (2014)
 WORLD SCIENTIFIC (2014) LIST OF PROBLEMS Chapter 1: Magnetism of Free Electrons and Atoms 1. Orbital and spin moments of an electron: Using the theory of angular momentum, calculate the orbital
WORLD SCIENTIFIC (2014) LIST OF PROBLEMS Chapter 1: Magnetism of Free Electrons and Atoms 1. Orbital and spin moments of an electron: Using the theory of angular momentum, calculate the orbital
Ferromagnetism. Iron, nickel, and cobalt are ferromagnetic.
 Ferromagnetism Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Ferromagnetism elow a critical temperature (called the Curie temperature) a magnetization spontaneously appears in a ferromagnet
Ferromagnetism Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Ferromagnetism elow a critical temperature (called the Curie temperature) a magnetization spontaneously appears in a ferromagnet
Complex Systems Methods 9. Critical Phenomena: The Renormalization Group
 Complex Systems Methods 9. Critical Phenomena: The Renormalization Group Eckehard Olbrich e.olbrich@gmx.de http://personal-homepages.mis.mpg.de/olbrich/complex systems.html Potsdam WS 2007/08 Olbrich (Leipzig)
Complex Systems Methods 9. Critical Phenomena: The Renormalization Group Eckehard Olbrich e.olbrich@gmx.de http://personal-homepages.mis.mpg.de/olbrich/complex systems.html Potsdam WS 2007/08 Olbrich (Leipzig)
MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF THIN FILM WITH S = 1. ISOTHERMAL SUSCEPTIBILITY AND MAGNETIC SPECIFIC HEAT
 Vol. 92 (1997) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 3 MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF THIN FILM WITH S = 1. ISOTHERMAL SUSCEPTIBILITY AND MAGNETIC SPECIFIC HEAT Μ. GZIK AND T. BALCERZAK Solid State Physics Department, University
Vol. 92 (1997) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 3 MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF THIN FILM WITH S = 1. ISOTHERMAL SUSCEPTIBILITY AND MAGNETIC SPECIFIC HEAT Μ. GZIK AND T. BALCERZAK Solid State Physics Department, University
A Monte Carlo Study of the Order-Disorder Layering Transitions in the Blume-Capel Model
 A Monte Carlo Study of the Order-Disorder Layering Transitions in the Blume-Capel Model L. Bahmad, A. Benyoussef and H. Ez-Zahraouy* Laboratoire de Magnétisme et de la Physique des Hautes Energies Université
A Monte Carlo Study of the Order-Disorder Layering Transitions in the Blume-Capel Model L. Bahmad, A. Benyoussef and H. Ez-Zahraouy* Laboratoire de Magnétisme et de la Physique des Hautes Energies Université
Multilayer Transitions in Mixed Spin-3/2 and 1/2 Blume Capel Model with RKKY Interaction
 Vol. 120 2011 ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 3 Multilayer Transitions in Mixed Spin-3/2 and 1/2 Blume Capel Model with RKKY Interaction F. El Hallani, H. Ez-Zahraouy, A. Benyoussef and L. Bahmad LMPHE, Department
Vol. 120 2011 ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 3 Multilayer Transitions in Mixed Spin-3/2 and 1/2 Blume Capel Model with RKKY Interaction F. El Hallani, H. Ez-Zahraouy, A. Benyoussef and L. Bahmad LMPHE, Department
Metropolis Monte Carlo simulation of the Ising Model
 Metropolis Monte Carlo simulation of the Ising Model Krishna Shrinivas (CH10B026) Swaroop Ramaswamy (CH10B068) May 10, 2013 Modelling and Simulation of Particulate Processes (CH5012) Introduction The Ising
Metropolis Monte Carlo simulation of the Ising Model Krishna Shrinivas (CH10B026) Swaroop Ramaswamy (CH10B068) May 10, 2013 Modelling and Simulation of Particulate Processes (CH5012) Introduction The Ising
Decimation Technique on Sierpinski Gasket in External Magnetic Field
 Egypt.. Solids, Vol. (), No. (), (009 ) 5 Decimation Technique on Sierpinski Gasket in External Magnetic Field Khalid Bannora, G. Ismail and M. Abu Zeid ) Mathematics Department, Faculty of Science, Zagazig
Egypt.. Solids, Vol. (), No. (), (009 ) 5 Decimation Technique on Sierpinski Gasket in External Magnetic Field Khalid Bannora, G. Ismail and M. Abu Zeid ) Mathematics Department, Faculty of Science, Zagazig
Magnetism at finite temperature: molecular field, phase transitions
 Magnetism at finite temperature: molecular field, phase transitions -The Heisenberg model in molecular field approximation: ferro, antiferromagnetism. Ordering temperature; thermodynamics - Mean field
Magnetism at finite temperature: molecular field, phase transitions -The Heisenberg model in molecular field approximation: ferro, antiferromagnetism. Ordering temperature; thermodynamics - Mean field
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 14 Mar 2006
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 14 Mar 2006 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 14 Mar 2006](/thumbs/78/78595771.jpg) Condensed Matter Physics, 2?, Vol.?, No?, pp. 1?? arxiv:cond-mat/63377v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 14 Mar 26 1. Introduction The effect of uniaxial crystal-field anisotropy on magnetic properties of the superexchange
Condensed Matter Physics, 2?, Vol.?, No?, pp. 1?? arxiv:cond-mat/63377v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 14 Mar 26 1. Introduction The effect of uniaxial crystal-field anisotropy on magnetic properties of the superexchange
S j H o = gµ o H o. j=1
 LECTURE 17 Ferromagnetism (Refs.: Sections 10.6-10.7 of Reif; Book by J. S. Smart, Effective Field Theories of Magnetism) Consider a solid consisting of N identical atoms arranged in a regular lattice.
LECTURE 17 Ferromagnetism (Refs.: Sections 10.6-10.7 of Reif; Book by J. S. Smart, Effective Field Theories of Magnetism) Consider a solid consisting of N identical atoms arranged in a regular lattice.
Concentration of magnetic transitions in dilute magnetic materials
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Concentration of magnetic transitions in dilute magnetic materials To cite this article: V I Beloon et al 04 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 490 065 Recent citations
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Concentration of magnetic transitions in dilute magnetic materials To cite this article: V I Beloon et al 04 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 490 065 Recent citations
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Feb 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Feb 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 16 Feb 2010](/thumbs/92/110261903.jpg) An introduced effective-field theory study of spin-1 transverse Ising model with crystal field anisotropy in a longitudinal magnetic field Yusuf Yüksel and Hama Polat Department of Physics, Doku Eylül
An introduced effective-field theory study of spin-1 transverse Ising model with crystal field anisotropy in a longitudinal magnetic field Yusuf Yüksel and Hama Polat Department of Physics, Doku Eylül
Finite-temperature magnetism of ultrathin lms and nanoclusters PhD Thesis Booklet. Levente Rózsa Supervisor: László Udvardi
 Finite-temperature magnetism of ultrathin lms and nanoclusters PhD Thesis Booklet Levente Rózsa Supervisor: László Udvardi BME 2016 Background of the research Magnetic materials continue to play an ever
Finite-temperature magnetism of ultrathin lms and nanoclusters PhD Thesis Booklet Levente Rózsa Supervisor: László Udvardi BME 2016 Background of the research Magnetic materials continue to play an ever
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 18 Mar 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 18 Mar 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 18 Mar 1998](/thumbs/81/84367854.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/9803220v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 18 Mar 1998 Mean-Field Study of the Degenerate Blume-Emery-Griffiths Model in a Random Crystal Field 1 N. S. Branco a,2 and Luciano Bachmann b a Universidade
arxiv:cond-mat/9803220v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 18 Mar 1998 Mean-Field Study of the Degenerate Blume-Emery-Griffiths Model in a Random Crystal Field 1 N. S. Branco a,2 and Luciano Bachmann b a Universidade
The Phase Transition of the 2D-Ising Model
 The Phase Transition of the 2D-Ising Model Lilian Witthauer and Manuel Dieterle Summer Term 2007 Contents 1 2D-Ising Model 2 1.1 Calculation of the Physical Quantities............... 2 2 Location of the
The Phase Transition of the 2D-Ising Model Lilian Witthauer and Manuel Dieterle Summer Term 2007 Contents 1 2D-Ising Model 2 1.1 Calculation of the Physical Quantities............... 2 2 Location of the
shows the difference between observed (black) and calculated patterns (red). Vertical ticks indicate
 Intensity (arb. unit) a 5 K No disorder Mn-Pt disorder 5 K Mn-Ga disorder 5 K b 5 K Observed Calculated Difference Bragg positions 24 28 32 2 4 6 8 2 4 2θ (degree) 2θ (degree) Supplementary Figure. Powder
Intensity (arb. unit) a 5 K No disorder Mn-Pt disorder 5 K Mn-Ga disorder 5 K b 5 K Observed Calculated Difference Bragg positions 24 28 32 2 4 6 8 2 4 2θ (degree) 2θ (degree) Supplementary Figure. Powder
Phase Transitions of Random Binary Magnetic Square Lattice Ising Systems
 I. Q. Sikakana Department of Physics and Non-Destructive Testing, Vaal University of Technology, Vanderbijlpark, 1900, South Africa e-mail: ike@vut.ac.za Abstract Binary magnetic square lattice Ising system
I. Q. Sikakana Department of Physics and Non-Destructive Testing, Vaal University of Technology, Vanderbijlpark, 1900, South Africa e-mail: ike@vut.ac.za Abstract Binary magnetic square lattice Ising system
Luigi Paolasini
 Luigi Paolasini paolasini@esrf.fr LECTURE 5: MAGNETIC STRUCTURES - Mean field theory and magnetic order - Classification of magnetic structures - Collinear and non-collinear magnetic structures. - Magnetic
Luigi Paolasini paolasini@esrf.fr LECTURE 5: MAGNETIC STRUCTURES - Mean field theory and magnetic order - Classification of magnetic structures - Collinear and non-collinear magnetic structures. - Magnetic
Partition function of nearest neighbour Ising models: Some new insights
 J Chem Sci, Vol, o 5, September 9, pp 595 599 Indian Academy of Sciences Partition function of nearest neighbour Ising models: Some new insights G ADHII and M V SAGARAARAYAA* Department of Chemistry, Indian
J Chem Sci, Vol, o 5, September 9, pp 595 599 Indian Academy of Sciences Partition function of nearest neighbour Ising models: Some new insights G ADHII and M V SAGARAARAYAA* Department of Chemistry, Indian
M. A. Gusmão IF-UFRGS
 M. A. Gusmão IF-UFRGS - 217 1 FIP164-217/2 Text 9 Mean-field approximation - II Heisenberg Hamiltonian in wave-vector space As we saw in Text 8, the uniform susceptibility does not diverge in the case
M. A. Gusmão IF-UFRGS - 217 1 FIP164-217/2 Text 9 Mean-field approximation - II Heisenberg Hamiltonian in wave-vector space As we saw in Text 8, the uniform susceptibility does not diverge in the case
'etion 4. Surfaces and -interface. Chapter 1 Statistical Mechanics of SurfcSytman Quantum -Correlated Systems. Chapter 2 Synchrotron X-Ray Studies o
 'etion 4 Surfaces and -interface Chapter 1 Statistical Mechanics of SurfcSytman Quantum -Correlated Systems Chapter 2 Synchrotron X-Ray Studies o ufc iodrn Chapter 3 Chemical Reaction Dynamics tsrae Chapter
'etion 4 Surfaces and -interface Chapter 1 Statistical Mechanics of SurfcSytman Quantum -Correlated Systems Chapter 2 Synchrotron X-Ray Studies o ufc iodrn Chapter 3 Chemical Reaction Dynamics tsrae Chapter
Evaluation of Wang-Landau Monte Carlo Simulations
 2012 4th International Conference on Computer Modeling and Simulation (ICCMS 2012) IPCSIT vol.22 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Evaluation of Wang-Landau Monte Carlo Simulations Seung-Yeon Kim School
2012 4th International Conference on Computer Modeling and Simulation (ICCMS 2012) IPCSIT vol.22 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Evaluation of Wang-Landau Monte Carlo Simulations Seung-Yeon Kim School
A Monte Carlo Implementation of the Ising Model in Python
 A Monte Carlo Implementation of the Ising Model in Python Alexey Khorev alexey.s.khorev@gmail.com 2017.08.29 Contents 1 Theory 1 1.1 Introduction...................................... 1 1.2 Model.........................................
A Monte Carlo Implementation of the Ising Model in Python Alexey Khorev alexey.s.khorev@gmail.com 2017.08.29 Contents 1 Theory 1 1.1 Introduction...................................... 1 1.2 Model.........................................
Critical Behavior I: Phenomenology, Universality & Scaling
 Critical Behavior I: Phenomenology, Universality & Scaling H. W. Diehl Fachbereich Physik, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Campus Essen 1 Goals recall basic facts about (static equilibrium) critical behavior
Critical Behavior I: Phenomenology, Universality & Scaling H. W. Diehl Fachbereich Physik, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Campus Essen 1 Goals recall basic facts about (static equilibrium) critical behavior
Renormalization Group analysis of 2D Ising model
 Renormalization Group analysis of D Ising model Amir Bar January 7, 013 1 Introduction In this tutorial we will see explicitly how RG can be used to probe the phase diagram of d > 1 systems, focusing as
Renormalization Group analysis of D Ising model Amir Bar January 7, 013 1 Introduction In this tutorial we will see explicitly how RG can be used to probe the phase diagram of d > 1 systems, focusing as
Surface effects in frustrated magnetic materials: phase transition and spin resistivity
 Surface effects in frustrated magnetic materials: phase transition and spin resistivity H T Diep (lptm, ucp) in collaboration with Yann Magnin, V. T. Ngo, K. Akabli Plan: I. Introduction II. Surface spin-waves,
Surface effects in frustrated magnetic materials: phase transition and spin resistivity H T Diep (lptm, ucp) in collaboration with Yann Magnin, V. T. Ngo, K. Akabli Plan: I. Introduction II. Surface spin-waves,
J ij S i S j B i S i (1)
 LECTURE 18 The Ising Model (References: Kerson Huang, Statistical Mechanics, Wiley and Sons (1963) and Colin Thompson, Mathematical Statistical Mechanics, Princeton Univ. Press (1972)). One of the simplest
LECTURE 18 The Ising Model (References: Kerson Huang, Statistical Mechanics, Wiley and Sons (1963) and Colin Thompson, Mathematical Statistical Mechanics, Princeton Univ. Press (1972)). One of the simplest
Thickness Dependence of Magnetic Hysteresis of Ising Films in Nano-thickness Range
 CMU. J.Nat.Sci. Special Issue on Nanotechnology (2008) Vol. 7(1) 203 Thickness Dependence of Magnetic Hysteresis of Ising Films in Nano-thickness Range Atchara Punya 1*, Pitak Laoratanakul 2, Rattikorn
CMU. J.Nat.Sci. Special Issue on Nanotechnology (2008) Vol. 7(1) 203 Thickness Dependence of Magnetic Hysteresis of Ising Films in Nano-thickness Range Atchara Punya 1*, Pitak Laoratanakul 2, Rattikorn
8.334: Statistical Mechanics II Problem Set # 4 Due: 4/9/14 Transfer Matrices & Position space renormalization
 8.334: Statistical Mechanics II Problem Set # 4 Due: 4/9/14 Transfer Matrices & Position space renormalization This problem set is partly intended to introduce the transfer matrix method, which is used
8.334: Statistical Mechanics II Problem Set # 4 Due: 4/9/14 Transfer Matrices & Position space renormalization This problem set is partly intended to introduce the transfer matrix method, which is used
Magnetic properties of spherical fcc clusters with radial surface anisotropy
 Magnetic properties of spherical fcc clusters with radial surface anisotropy D. A. Dimitrov and G. M. Wysin Department of Physics Kansas State University Manhattan, KS 66506-2601 (December 6, 1994) We
Magnetic properties of spherical fcc clusters with radial surface anisotropy D. A. Dimitrov and G. M. Wysin Department of Physics Kansas State University Manhattan, KS 66506-2601 (December 6, 1994) We
Spontaneous magnetization of the square 2D Ising lattice with nearest- and weak next-nearest-neighbour interactions
 Phase Transitions Vol. 82, No. 2, February 2009, 191 196 Spontaneous magnetization of the square 2D Ising lattice with nearest- and weak next-nearest-neighbour interactions H.J.W. Zandvliet a * and C.
Phase Transitions Vol. 82, No. 2, February 2009, 191 196 Spontaneous magnetization of the square 2D Ising lattice with nearest- and weak next-nearest-neighbour interactions H.J.W. Zandvliet a * and C.
Phase transitions and finite-size scaling
 Phase transitions and finite-size scaling Critical slowing down and cluster methods. Theory of phase transitions/ RNG Finite-size scaling Detailed treatment: Lectures on Phase Transitions and the Renormalization
Phase transitions and finite-size scaling Critical slowing down and cluster methods. Theory of phase transitions/ RNG Finite-size scaling Detailed treatment: Lectures on Phase Transitions and the Renormalization
Renormalization Group Study of a One Dimensional Generalised Alternating Superlattice at Half - Filling
 International Journal of Pure and pplied Physics. ISSN 0973-1776 Volume 13, Number 3 (2017), pp. 271-277 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Renormalization Group Study of a One Dimensional
International Journal of Pure and pplied Physics. ISSN 0973-1776 Volume 13, Number 3 (2017), pp. 271-277 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Renormalization Group Study of a One Dimensional
Triangular Ising model with nearestand
 Chapter 3 Triangular Ising model with nearestand next-nearest-neighbor couplings in a field We study the Ising model on the triangular lattice with nearest-neighbor couplings K nn, next-nearest-neighbor
Chapter 3 Triangular Ising model with nearestand next-nearest-neighbor couplings in a field We study the Ising model on the triangular lattice with nearest-neighbor couplings K nn, next-nearest-neighbor
Chapter 6 Antiferromagnetism and Other Magnetic Ordeer
 Chapter 6 Antiferromagnetism and Other Magnetic Ordeer 6.1 Mean Field Theory of Antiferromagnetism 6.2 Ferrimagnets 6.3 Frustration 6.4 Amorphous Magnets 6.5 Spin Glasses 6.6 Magnetic Model Compounds TCD
Chapter 6 Antiferromagnetism and Other Magnetic Ordeer 6.1 Mean Field Theory of Antiferromagnetism 6.2 Ferrimagnets 6.3 Frustration 6.4 Amorphous Magnets 6.5 Spin Glasses 6.6 Magnetic Model Compounds TCD
Antiferromagnetic Textures
 Antiferromagnetic Textures This image cannot currently be displayed. ULRICH K. RÖSSLE IFW DRESDEN SPICE Workshop Antiferromagnetic Spintronics 26.-30/09/2016 Schloss Waldthausen u.roessler@ifw-dresden.de
Antiferromagnetic Textures This image cannot currently be displayed. ULRICH K. RÖSSLE IFW DRESDEN SPICE Workshop Antiferromagnetic Spintronics 26.-30/09/2016 Schloss Waldthausen u.roessler@ifw-dresden.de
5.1 Mean-Field Treatments of the Ising Model
 Chapter 5 Mean-Field Theory 5.1 Mean-Field Treatments of the Ising Model In this Section, we are discussing various approaches to obtain a mean-field solution to the Ising model. In fact, several of the
Chapter 5 Mean-Field Theory 5.1 Mean-Field Treatments of the Ising Model In this Section, we are discussing various approaches to obtain a mean-field solution to the Ising model. In fact, several of the
Frustrated diamond lattice antiferromagnets
 Frustrated diamond lattice antiferromagnets ason Alicea (Caltech) Doron Bergman (Yale) Leon Balents (UCSB) Emanuel Gull (ETH Zurich) Simon Trebst (Station Q) Bergman et al., Nature Physics 3, 487 (007).
Frustrated diamond lattice antiferromagnets ason Alicea (Caltech) Doron Bergman (Yale) Leon Balents (UCSB) Emanuel Gull (ETH Zurich) Simon Trebst (Station Q) Bergman et al., Nature Physics 3, 487 (007).
Exchange bias in core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: experimental results and numerical simulations
 Exchange bias in core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: experimental results and numerical simulations Xavier Batlle, A. Labarta, Ò. Iglesias, M. García del Muro and M. Kovylina Goup of Magnetic Nanomaterials
Exchange bias in core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: experimental results and numerical simulations Xavier Batlle, A. Labarta, Ò. Iglesias, M. García del Muro and M. Kovylina Goup of Magnetic Nanomaterials
Magnetization and quadrupolar plateaus in the one-dimensional antiferromagnetic spin-3/2 and spin-2 Blume Capel model
 Original Paper phys. stat. sol. (b) 243, No. 12, 2901 2912 (2006) / DOI 10.1002/pssb.200541252 Magnetization and quadrupolar plateaus in the one-dimensional antiferromagnetic spin-3/2 and spin-2 Blume
Original Paper phys. stat. sol. (b) 243, No. 12, 2901 2912 (2006) / DOI 10.1002/pssb.200541252 Magnetization and quadrupolar plateaus in the one-dimensional antiferromagnetic spin-3/2 and spin-2 Blume
Finite-size analysis via the critical energy -subspace method in the Ising models
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 23, No. 4, 25 Finite-size analysis via the critical energy -subspace method in the Ising models A. C. MAAKIS *, I. A. HADJIAGAPIOU, S. S. MARTINOS, N. G. FYTAS Faculty of
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 23, No. 4, 25 Finite-size analysis via the critical energy -subspace method in the Ising models A. C. MAAKIS *, I. A. HADJIAGAPIOU, S. S. MARTINOS, N. G. FYTAS Faculty of
Statistical description of magnetic domains in the Ising model
 arxiv:0804.3522v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Apr 2008 Statistical description of magnetic domains in the Ising model K. Lukierska-Walasek Institute of Physics University of Zielona Góra ul. Z. Szafrana 4a,
arxiv:0804.3522v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Apr 2008 Statistical description of magnetic domains in the Ising model K. Lukierska-Walasek Institute of Physics University of Zielona Góra ul. Z. Szafrana 4a,
Numerical Analysis of 2-D Ising Model. Ishita Agarwal Masters in Physics (University of Bonn) 17 th March 2011
 Numerical Analysis of 2-D Ising Model By Ishita Agarwal Masters in Physics (University of Bonn) 17 th March 2011 Contents Abstract Acknowledgment Introduction Computational techniques Numerical Analysis
Numerical Analysis of 2-D Ising Model By Ishita Agarwal Masters in Physics (University of Bonn) 17 th March 2011 Contents Abstract Acknowledgment Introduction Computational techniques Numerical Analysis
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 1 Dec 1999
 Impurity relaxation mechanism for dynamic magnetization reversal in a single domain grain Vladimir L. Safonov and H. Neal Bertram Center for Magnetic Recording Research, University of California San arxiv:cond-mat/9912014v1
Impurity relaxation mechanism for dynamic magnetization reversal in a single domain grain Vladimir L. Safonov and H. Neal Bertram Center for Magnetic Recording Research, University of California San arxiv:cond-mat/9912014v1
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 18 Mar 2003
 Hysteresis loop of a nanoscopic magnetic array A. Kaczanowski, K. Malarz and K. Ku lakowski arxiv:cond-mat/3333v1 18 Mar 23 Department of Applied Computer Science, Faculty of Physics and Nuclear Techniques,
Hysteresis loop of a nanoscopic magnetic array A. Kaczanowski, K. Malarz and K. Ku lakowski arxiv:cond-mat/3333v1 18 Mar 23 Department of Applied Computer Science, Faculty of Physics and Nuclear Techniques,
Monte Carlo Simulation of the Ising Model. Abstract
 Monte Carlo Simulation of the Ising Model Saryu Jindal 1 1 Department of Chemical Engineering and Material Sciences, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 (Dated: June 9, 2007) Abstract This paper
Monte Carlo Simulation of the Ising Model Saryu Jindal 1 1 Department of Chemical Engineering and Material Sciences, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 (Dated: June 9, 2007) Abstract This paper
Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics. Landau Theory of Second Order Phase Transitions. Order Parameter
 Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics Landau Theory of Second Order Phase Transitions Order Parameter Second order phase transitions occur when a new state of reduced symmetry develops continuously from
Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics Landau Theory of Second Order Phase Transitions Order Parameter Second order phase transitions occur when a new state of reduced symmetry develops continuously from
Phase Transition & Approximate Partition Function In Ising Model and Percolation In Two Dimension: Specifically For Square Lattices
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) ISS: 2278-4861. Volume 2, Issue 3 (ov. - Dec. 2012), PP 31-37 Phase Transition & Approximate Partition Function In Ising Model and Percolation In Two Dimension:
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) ISS: 2278-4861. Volume 2, Issue 3 (ov. - Dec. 2012), PP 31-37 Phase Transition & Approximate Partition Function In Ising Model and Percolation In Two Dimension:
Phase Transitions in Condensed Matter Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking and Universality. Hans-Henning Klauss. Institut für Festkörperphysik TU Dresden
 Phase Transitions in Condensed Matter Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking and Universality Hans-Henning Klauss Institut für Festkörperphysik TU Dresden 1 References [1] Stephen Blundell, Magnetism in Condensed
Phase Transitions in Condensed Matter Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking and Universality Hans-Henning Klauss Institut für Festkörperphysik TU Dresden 1 References [1] Stephen Blundell, Magnetism in Condensed
Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
8.334: Statistical Mechanics II Spring 2014 Test 2 Review Problems
 8.334: Statistical Mechanics II Spring 014 Test Review Problems The test is closed book, but if you wish you may bring a one-sided sheet of formulas. The intent of this sheet is as a reminder of important
8.334: Statistical Mechanics II Spring 014 Test Review Problems The test is closed book, but if you wish you may bring a one-sided sheet of formulas. The intent of this sheet is as a reminder of important
Study of the Magnetic Properties of a Lieb Core-Shell Nano-Structure: Monte Carlo Simulations
 Study of the Magnetic Properties of a Lieb Core-Shell Nano-Structure: Monte Carlo Simulations S. Aouini, S. Ziti, H. Labrim,* and L. Bahmad,* Laboratoire de la Matière Condensée et Sciences Interdisciplinaires
Study of the Magnetic Properties of a Lieb Core-Shell Nano-Structure: Monte Carlo Simulations S. Aouini, S. Ziti, H. Labrim,* and L. Bahmad,* Laboratoire de la Matière Condensée et Sciences Interdisciplinaires
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Apr 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Apr 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Apr 1998](/thumbs/80/81746456.jpg) Nonequilibrium Phase Transition in the Kinetic Ising model: Dynamical symmetry breaking by randomly varying magnetic field arxiv:cond-mat/979v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Apr 998 Muktish Acharyya Institute
Nonequilibrium Phase Transition in the Kinetic Ising model: Dynamical symmetry breaking by randomly varying magnetic field arxiv:cond-mat/979v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Apr 998 Muktish Acharyya Institute
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 20 Feb 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 20 Feb 2018 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 20 Feb 2018](/thumbs/83/88223467.jpg) Spin-1/2 anisotropic Heisenberg antiferromagnet with Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction via mean-field approximation arxiv:1802.07172v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 20 Feb 2018 Walter E. F. Parente Universidade
Spin-1/2 anisotropic Heisenberg antiferromagnet with Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction via mean-field approximation arxiv:1802.07172v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 20 Feb 2018 Walter E. F. Parente Universidade
Quantum spin systems - models and computational methods
 Summer School on Computational Statistical Physics August 4-11, 2010, NCCU, Taipei, Taiwan Quantum spin systems - models and computational methods Anders W. Sandvik, Boston University Lecture outline Introduction
Summer School on Computational Statistical Physics August 4-11, 2010, NCCU, Taipei, Taiwan Quantum spin systems - models and computational methods Anders W. Sandvik, Boston University Lecture outline Introduction
Mean-field theory. Alessandro Vindigni. ETH October 29, Laboratorium für Festkörperphysik, ETH Zürich
 Alessandro Vindigni Laboratorium für Festkörperphysik, ETH Zürich ETH October 29, 2012 Lecture plan N-body problem Lecture plan 1. Atomic magnetism (Pescia) 2. Magnetism in solids (Pescia) 3. Magnetic
Alessandro Vindigni Laboratorium für Festkörperphysik, ETH Zürich ETH October 29, 2012 Lecture plan N-body problem Lecture plan 1. Atomic magnetism (Pescia) 2. Magnetism in solids (Pescia) 3. Magnetic
Study on Magnetic Properties of Vermiculite Intercalation compounds
 Study on Magnetic Properties of Vermiculite Intercalation compounds M. Suzuki and I.S. Suzuki Department of Physics, State University of New York at Binghamton (October, ) I. INTRODUCTION In recent years
Study on Magnetic Properties of Vermiculite Intercalation compounds M. Suzuki and I.S. Suzuki Department of Physics, State University of New York at Binghamton (October, ) I. INTRODUCTION In recent years
Quantum annealing for problems with ground-state degeneracy
 Proceedings of the International Workshop on Statistical-Mechanical Informatics September 14 17, 2008, Sendai, Japan Quantum annealing for problems with ground-state degeneracy Yoshiki Matsuda 1, Hidetoshi
Proceedings of the International Workshop on Statistical-Mechanical Informatics September 14 17, 2008, Sendai, Japan Quantum annealing for problems with ground-state degeneracy Yoshiki Matsuda 1, Hidetoshi
S i J <ij> h mf = h + Jzm (4) and m, the magnetisation per spin, is just the mean value of any given spin. S i = S k k (5) N.
 Statistical Physics Section 10: Mean-Field heory of the Ising Model Unfortunately one cannot solve exactly the Ising model or many other interesting models) on a three dimensional lattice. herefore one
Statistical Physics Section 10: Mean-Field heory of the Ising Model Unfortunately one cannot solve exactly the Ising model or many other interesting models) on a three dimensional lattice. herefore one
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 May 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 May 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 May 2010](/thumbs/94/118952645.jpg) arxiv:1005.0565v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 May 2010 Critical Slowing Down along the Dynamic Phase Boundary in Ising meanfield dynamics Muktish Acharyya Department of Physics, Presidency College 86/1 College
arxiv:1005.0565v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 May 2010 Critical Slowing Down along the Dynamic Phase Boundary in Ising meanfield dynamics Muktish Acharyya Department of Physics, Presidency College 86/1 College
Quantum Phase Transitions
 Quantum Phase Transitions Subir Sachdev Department of Physics Yale University P.O. Box 208120, New Haven, CT 06520-8120 USA E-mail: subir.sachdev@yale.edu May 19, 2004 To appear in Encyclopedia of Mathematical
Quantum Phase Transitions Subir Sachdev Department of Physics Yale University P.O. Box 208120, New Haven, CT 06520-8120 USA E-mail: subir.sachdev@yale.edu May 19, 2004 To appear in Encyclopedia of Mathematical
VI. Series Expansions
 VI. Series Expansions VI.A Low-temperature expansions Lattice models can also be studied by series expansions. Such expansions start with certain exactly solvable limits, and typically represent perturbations
VI. Series Expansions VI.A Low-temperature expansions Lattice models can also be studied by series expansions. Such expansions start with certain exactly solvable limits, and typically represent perturbations
Magnetism in Condensed Matter
 Magnetism in Condensed Matter STEPHEN BLUNDELL Department of Physics University of Oxford OXFORD 'UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Magnetic moments 1 1 1.1.1 Magnetic moments and angular momentum
Magnetism in Condensed Matter STEPHEN BLUNDELL Department of Physics University of Oxford OXFORD 'UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Magnetic moments 1 1 1.1.1 Magnetic moments and angular momentum
Renormalization of Tensor Network States. Partial order and finite temperature phase transition in the Potts model on irregular lattice
 Renormalization of Tensor Network States Partial order and finite temperature phase transition in the Potts model on irregular lattice Tao Xiang Institute of Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences Background:
Renormalization of Tensor Network States Partial order and finite temperature phase transition in the Potts model on irregular lattice Tao Xiang Institute of Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences Background:
Paramagnetic phases of Kagome lattice quantum Ising models p.1/16
 Paramagnetic phases of Kagome lattice quantum Ising models Predrag Nikolić In collaboration with T. Senthil Massachusetts Institute of Technology Paramagnetic phases of Kagome lattice quantum Ising models
Paramagnetic phases of Kagome lattice quantum Ising models Predrag Nikolić In collaboration with T. Senthil Massachusetts Institute of Technology Paramagnetic phases of Kagome lattice quantum Ising models
Magnetic monopoles in spin ice
 Magnetic monopoles in spin ice Claudio Castelnovo Oxford University Roderich Moessner MPI-PKS Dresden Shivaji Sondhi Princeton University Nature 451, 42 (2008) The fundamental question astroparticle physics
Magnetic monopoles in spin ice Claudio Castelnovo Oxford University Roderich Moessner MPI-PKS Dresden Shivaji Sondhi Princeton University Nature 451, 42 (2008) The fundamental question astroparticle physics
Principles of Equilibrium Statistical Mechanics
 Debashish Chowdhury, Dietrich Stauffer Principles of Equilibrium Statistical Mechanics WILEY-VCH Weinheim New York Chichester Brisbane Singapore Toronto Table of Contents Part I: THERMOSTATICS 1 1 BASIC
Debashish Chowdhury, Dietrich Stauffer Principles of Equilibrium Statistical Mechanics WILEY-VCH Weinheim New York Chichester Brisbane Singapore Toronto Table of Contents Part I: THERMOSTATICS 1 1 BASIC
Preface Introduction to the electron liquid
 Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
Critical Dynamics of Two-Replica Cluster Algorithms
 University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Jonathan Machta 2001 Critical Dynamics of Two-Replica Cluster Algorithms X. N. Li Jonathan Machta, University of Massachusetts Amherst Available
University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Jonathan Machta 2001 Critical Dynamics of Two-Replica Cluster Algorithms X. N. Li Jonathan Machta, University of Massachusetts Amherst Available
Phase transitions and critical phenomena
 Phase transitions and critical phenomena Classification of phase transitions. Discontinous (st order) transitions Summary week -5 st derivatives of thermodynamic potentials jump discontinously, e.g. (
Phase transitions and critical phenomena Classification of phase transitions. Discontinous (st order) transitions Summary week -5 st derivatives of thermodynamic potentials jump discontinously, e.g. (
Mean-Field Analysis of the Ising Hysteresis Relaxation Time
 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2009; 36(3) 263 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2009; 36(3) : 263-275 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper Mean-Field Analysis of the Ising Hysteresis Relaxation Time
Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2009; 36(3) 263 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2009; 36(3) : 263-275 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper Mean-Field Analysis of the Ising Hysteresis Relaxation Time
Magnetic Properties of 2D Nano-Islands Subject to Anisotropy and Transverse Fields: EFT Ising Model
 Modern Applied Science; Vol. 7, No. 9; 013 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-185 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Magnetic Properties of D Nano-Islands Subject to Anisotropy and Transverse
Modern Applied Science; Vol. 7, No. 9; 013 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-185 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Magnetic Properties of D Nano-Islands Subject to Anisotropy and Transverse
Magnetic Monopoles in Spin Ice
 Magnetic Monopoles in Spin Ice Claudio Castelnovo University of Oxford Roderich Moessner Max Planck Institut Shivaji Sondhi Princeton University Nature 451, 42 (2008) ISIS Seminars, Rutherford Appleton
Magnetic Monopoles in Spin Ice Claudio Castelnovo University of Oxford Roderich Moessner Max Planck Institut Shivaji Sondhi Princeton University Nature 451, 42 (2008) ISIS Seminars, Rutherford Appleton
Local persistense and blocking in the two dimensional Blume-Capel Model arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 Apr 2004.
![Local persistense and blocking in the two dimensional Blume-Capel Model arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 Apr 2004. Local persistense and blocking in the two dimensional Blume-Capel Model arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 Apr 2004.](/thumbs/90/103880677.jpg) Local persistense and blocking in the two dimensional Blume-Capel Model arxiv:cond-mat/0404082v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 Apr 2004 Roberto da Silva Departamento de Informática Teórica, Instituto de Informática,
Local persistense and blocking in the two dimensional Blume-Capel Model arxiv:cond-mat/0404082v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 Apr 2004 Roberto da Silva Departamento de Informática Teórica, Instituto de Informática,
Temperature dependence of the electron spin resonance linewidth in magnetic insulators
 Temperature dependence of the electron spin resonance linewidth in magnetic insulators M. Acikgoz 1 and D. L. Huber 2, a 1 Bahcesehir University, Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Besiktas,
Temperature dependence of the electron spin resonance linewidth in magnetic insulators M. Acikgoz 1 and D. L. Huber 2, a 1 Bahcesehir University, Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Besiktas,
Luigi Paolasini
 Luigi Paolasini paolasini@esrf.fr LECTURE 7: Magnetic excitations - Phase transitions and the Landau mean-field theory. - Heisenberg and Ising models. - Magnetic excitations. External parameter, as for
Luigi Paolasini paolasini@esrf.fr LECTURE 7: Magnetic excitations - Phase transitions and the Landau mean-field theory. - Heisenberg and Ising models. - Magnetic excitations. External parameter, as for
Calculations of the Partition Function Zeros for the Ising Ferromagnet on 6 x 6 Square Lattice with Periodic Boundary Conditions
 Calculations of the Partition Function Zeros for the Ising Ferromagnet on 6 x 6 Square Lattice with Periodic Boundary Conditions Seung-Yeon Kim School of Liberal Arts and Sciences, Korea National University
Calculations of the Partition Function Zeros for the Ising Ferromagnet on 6 x 6 Square Lattice with Periodic Boundary Conditions Seung-Yeon Kim School of Liberal Arts and Sciences, Korea National University
Structure and Curie temperature of Y 2 Fe 17 x Cr x
 Vol. 46 No. 4 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series G) August 2003 Structure and Curie temperature of Y 2 Fe 17 x Cr x HAO Shiqiang ( ) 1 & CHEN Nanxian ( ) 1,2 1. Department of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing
Vol. 46 No. 4 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series G) August 2003 Structure and Curie temperature of Y 2 Fe 17 x Cr x HAO Shiqiang ( ) 1 & CHEN Nanxian ( ) 1,2 1. Department of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing
Problem set for the course Skálázás és renormálás a statisztikus fizikában, 2014
 1 Problem set for the course Skálázás és renormálás a statisztikus fizikában, 014 Rules: You can choose at wish from problems having the same main number (i.e. from a given section), but you can collect
1 Problem set for the course Skálázás és renormálás a statisztikus fizikában, 014 Rules: You can choose at wish from problems having the same main number (i.e. from a given section), but you can collect
Examination paper for TFY4245 Faststoff-fysikk, videregående kurs
 Side 1 av 7 Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY445 Faststoff-fysikk, videregående kurs Academic contact during examination: Ragnvald Mathiesen Phone: 976913 Examination date: 08.06.017 Examination
Side 1 av 7 Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY445 Faststoff-fysikk, videregående kurs Academic contact during examination: Ragnvald Mathiesen Phone: 976913 Examination date: 08.06.017 Examination
PHASE TRANSITIONS AND CRITICAL PHENOMENA
 INTRODUCTION TO PHASE TRANSITIONS AND CRITICAL PHENOMENA BY H. EUGENE STANLEY Boston University OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS New York Oxford CONTENTS NOTATION GUIDE xv PART I INTRODUCTION 1. WHAT ARE THE CRITICAL
INTRODUCTION TO PHASE TRANSITIONS AND CRITICAL PHENOMENA BY H. EUGENE STANLEY Boston University OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS New York Oxford CONTENTS NOTATION GUIDE xv PART I INTRODUCTION 1. WHAT ARE THE CRITICAL
Magnetic ordering, magnetic anisotropy and the mean-field theory
 Magnetic ordering, magnetic anisotropy and the mean-field theory Alexandra Kalashnikova kalashnikova@mail.ioffe.ru Ferromagnets Mean-field approximation Curie temperature and critical exponents Magnetic
Magnetic ordering, magnetic anisotropy and the mean-field theory Alexandra Kalashnikova kalashnikova@mail.ioffe.ru Ferromagnets Mean-field approximation Curie temperature and critical exponents Magnetic
Scaling Theory. Roger Herrigel Advisor: Helmut Katzgraber
 Scaling Theory Roger Herrigel Advisor: Helmut Katzgraber 7.4.2007 Outline The scaling hypothesis Critical exponents The scaling hypothesis Derivation of the scaling relations Heuristic explanation Kadanoff
Scaling Theory Roger Herrigel Advisor: Helmut Katzgraber 7.4.2007 Outline The scaling hypothesis Critical exponents The scaling hypothesis Derivation of the scaling relations Heuristic explanation Kadanoff
Optimized statistical ensembles for slowly equilibrating classical and quantum systems
 Optimized statistical ensembles for slowly equilibrating classical and quantum systems IPAM, January 2009 Simon Trebst Microsoft Station Q University of California, Santa Barbara Collaborators: David Huse,
Optimized statistical ensembles for slowly equilibrating classical and quantum systems IPAM, January 2009 Simon Trebst Microsoft Station Q University of California, Santa Barbara Collaborators: David Huse,
3.320 Lecture 18 (4/12/05)
 3.320 Lecture 18 (4/12/05) Monte Carlo Simulation II and free energies Figure by MIT OCW. General Statistical Mechanics References D. Chandler, Introduction to Modern Statistical Mechanics D.A. McQuarrie,
3.320 Lecture 18 (4/12/05) Monte Carlo Simulation II and free energies Figure by MIT OCW. General Statistical Mechanics References D. Chandler, Introduction to Modern Statistical Mechanics D.A. McQuarrie,
First-Principles Calculation of Exchange Interactions
 Chapter 2 First-Principles Calculation of Exchange Interactions Before introducing the first-principles methods for the calculation of exchange interactions in magnetic systems we will briefly review two
Chapter 2 First-Principles Calculation of Exchange Interactions Before introducing the first-principles methods for the calculation of exchange interactions in magnetic systems we will briefly review two
复习题. 2 Calculate the intensity of magnetic field in the air gap of the magnetic circuit shown in the figure. Use the values N=200,
 复习题 1 Calculate the magnetic moment of a sphere of radius R made from a magnetic material with magnetic susceptibility, when it is magnetized by an external magnetic field H. How is the value of the moment
复习题 1 Calculate the magnetic moment of a sphere of radius R made from a magnetic material with magnetic susceptibility, when it is magnetized by an external magnetic field H. How is the value of the moment
The Magnetic Properties of Superparamagnetic Particles by a Monte Carlo Method
 The Magnetic Properties of Superparamagnetic Particles by a Monte Carlo Method D. A. Dimitrov and G. M. Wysin Department of Physics Kansas State University Manhattan, KS 6656-261 (June 19, 1996) We develop
The Magnetic Properties of Superparamagnetic Particles by a Monte Carlo Method D. A. Dimitrov and G. M. Wysin Department of Physics Kansas State University Manhattan, KS 6656-261 (June 19, 1996) We develop
Geometry, topology and frustration: the physics of spin ice
 Geometry, topology and frustration: the physics of spin ice Roderich Moessner CNRS and LPT-ENS 9 March 25, Magdeburg Overview Spin ice: experimental discovery and basic model Spin ice in a field dimensional
Geometry, topology and frustration: the physics of spin ice Roderich Moessner CNRS and LPT-ENS 9 March 25, Magdeburg Overview Spin ice: experimental discovery and basic model Spin ice in a field dimensional
Electron Correlation
 Series in Modern Condensed Matter Physics Vol. 5 Lecture Notes an Electron Correlation and Magnetism Patrik Fazekas Research Institute for Solid State Physics & Optics, Budapest lb World Scientific h Singapore
Series in Modern Condensed Matter Physics Vol. 5 Lecture Notes an Electron Correlation and Magnetism Patrik Fazekas Research Institute for Solid State Physics & Optics, Budapest lb World Scientific h Singapore
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field
 Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Phase Transitions and Critical Behavior:
 II Phase Transitions and Critical Behavior: A. Phenomenology (ibid., Chapter 10) B. mean field theory (ibid., Chapter 11) C. Failure of MFT D. Phenomenology Again (ibid., Chapter 12) // Windsor Lectures
II Phase Transitions and Critical Behavior: A. Phenomenology (ibid., Chapter 10) B. mean field theory (ibid., Chapter 11) C. Failure of MFT D. Phenomenology Again (ibid., Chapter 12) // Windsor Lectures
Lectures 16: Phase Transitions
 Lectures 16: Phase Transitions Continuous Phase transitions Aims: Mean-field theory: Order parameter. Order-disorder transitions. Examples: β-brass (CuZn), Ferromagnetic transition in zero field. Universality.
Lectures 16: Phase Transitions Continuous Phase transitions Aims: Mean-field theory: Order parameter. Order-disorder transitions. Examples: β-brass (CuZn), Ferromagnetic transition in zero field. Universality.
Transition Elements. pranjoto utomo
 Transition Elements pranjoto utomo Definition What is transition metal? One of which forms one or more stable ions which have incompletely filled d orbitals. 30Zn? Definition Zink is not transition elements
Transition Elements pranjoto utomo Definition What is transition metal? One of which forms one or more stable ions which have incompletely filled d orbitals. 30Zn? Definition Zink is not transition elements
