Research Article Stochastic Analysis of a Two-Unit Cold Standby System Wherein Both Units May Become Operative Depending upon the Demand
|
|
|
- Gabriella Garrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering, Article ID , 13 pages Research Article Stochastic Analysis of a Two-Unit Cold Standby System Wherein Both Units May Become Operative Depending upon the Demand Reetu Malhotra 1 and Gulshan Taneja 2 1 DepartmentofAppliedSciences,ChitkaraUniversity,Rajpura,Punjab1441,India 2 Department of Mathematics, Maharshi Dayanand University, Rohtak, Haryana 1241, India Correspondence should be addressed to Reetu Malhotra; reetu.malhotra@chitkarauniversity.edu.in Received 16 June 214; Revised 13 October 214; Accepted 28 October 214; Published 1 December 214 Academic Editor: Yi-Hung Chen Copyright 214 R. Malhotra and G. Taneja. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. The present paper analyzes a two-unit cold standby system in both units may become operative depending upon the demand. Initially, one of the units is operative while the other is kept as cold standby. If the operative unit fails or the demand increases to the extent that one operative unit is not capable of meeting the demand, the standby unit becomes operative instantaneously. Thus, both units may become operative simultaneously to meet the increased demand. Availability in three types of upstates is as follows: (i when the demand is less than or equal to production manufactured by one unit; (ii when the demand is greater than whatever produced by one unit but less than or equal to production made by two units; and (iii when the demand is greater than the produces by two units. Other measures of the system effectiveness have also been obtained in general case as well as for a particular case. Techniques of semi-markov processes and regenerative processes have been used to obtain various measures of the system effectiveness. 1. Introduction In the literature of reliability, extensive studies have been madeondifferenttypesofone-unitortwo-unitstandby redundant systems owing to their frequent use in modern business and industrial systems. There are two major types of redundancy parallel and standby. In parallel redundancy, the redundant units form part of the system from the start, as in a standby system the redundant units do not form part of the system from the start (until they are needed. Standby units can be classified as cold, warm, or hot. Acold standby is completely inactive and since it is not hooked up, it cannot fail until it is replacing the primary unit. A warm standby hasadiminishedloadbecauseitisonlypartially energized. A hot standby is fully active in the system (although redundant. A lot of work has been done on reliability and cost analysis of various systems by various researchers including [1 17] who have analyzed these systems by considering variousconceptsliketheerlangianrepairtime,operatingand rest periods, hardware/software faults, congestion of calls, availability, two types of repair facility, human failure, regenerative point technique, priority repair discipline, instruction, accident, patience time, chances of nonavailability of expert repairman, one big unit and two small identical units with priority for operation/repair to big unit, patience time, partial failures, and optimized maintenance of the diesel system in locomotives. In all such studies, the demand was fixed. There may be situations demand may vary and hence it affects the operability of the units of a system. The concept of variation in demand has been studied by [18, 19]. This concept of variation in demand was considered for single unit systems, the system either is in working state on some demand orisputtoshutdownmodeonnodemand.however,the demand may be much more than whatever produced by a single unit system and hence there is need of having one additional unit to meet the demand. Study of the concept of variation in demand for the two-unit system thus becomes more important. Keeping the above observations in view, we, in the present paper, develop a reliability model for a two-unit standby system working in a cable manufacturing plant in cold
2 2 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering standby may become operative depending on demand. Information of such a system was gathered on visiting a cable manufacturing plant in H.P., India. It was observed that there were two units in the plant which were used to manufacture polyvinyl chloride (PVC wires as per the demand in the market. If the demand is less than whatever produced by one unit, only one unit is kept operative, as if demand is greater than the production from a single unit, both units are put to operative mode. Various measures of the system effectiveness are analyzed by making use of semi-markov processes and regenerative point techniques. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we develop the proposed semi-markov model and presented its description. In Section 3, we find the steady-state probabilities and mean sojourn times. Section 4 deals with the computation of steady-state measures, such as mean time to system failure (MTSF, availability in three types of upstates (i.e., when demand is less than or equal to production made by one unit; when demand is greater than production made by one unit, but less than or equal to production made by two units; when demand is greater than production made by two units, busy period of the repairman for repair, and expected number of visits by the repairman. In Section 5, cost-benefit hasbeenobtainedasageneralcase.onthebasisofthe data/information estimated from the cable manufacturing plant, a particular case has been discussed in Section 6 and various graphs have been plotted in Section 7. Final conclusions along with some future directions are presented in Section Model Description and Assumptions Figure 1 depicts the state transition model which we developed for a two-unit standby system working in a cable manufacturing plant in cold standby may become operative depending on demand. If one or both units are in working mode, then the system is in operative state. When both units are not working, that is, one is under repair and the other is waiting to be repaired, the system will stay in the failed state. Variousassumptionsforthemodelareasfollows. (1 The units are similar and statistically independent. (2 Demand cannot be decreased further, when at the most one unit is operative. (3 Each unit is new after repair. (4 If a unit is failed, standby unit takes over automatically. (5 The system becomes inoperable when both units fail in a two-unit system. (6 All the random variables are independent. (7 Switching is perfect and instantaneous. (8 Failure and repair time follow exponential and general time distribution, respectively. 3. Transition Probabilities and Mean Sojourn Times The transition diagram showing the various states of the system is shown as in Figure 1.Theepochsofentryintostates S, S 1, S 2, S 5, S 6,andS 7 are regeneration points and thus are regenerative states. States S 3, S 9,andS 1 are failed states. The transition probabilities are q 1 (t =γ 11 e (+γ 11t, q 2 (t =e (+γ 11t, q 1 (t =γ 12 e (+γ 12+γ 21 t, q 15 (t =γ 21 e (+γ 12+γ 21 t, q 16 (t =e (+γ 12+γ 21 t, q 2 (t =e (+γ 11t g (t, q 4 21 (t = (γ 11e (+γ 11t De (+γ 21t g(t, q 3 22 (t = (e (+γ 11t De γ 11t g(t, q 23 (t =e (+γ11t G (t, q (4,8 2,5 (t = (γ 11 e (+γ11t Dγ 21 e (+γ21t De t g(t, q (3,9 2,6 (t = (e (+γ 11t Dγ 11 e γ 11t De γ 21t g(t, q (4,9 2,6 (t = (γ 11 e (+γ 11t De (+γ 21t De γ 21t g(t, q (3,9,1 2,7 (t = (e (+γ 11t Dγ 11 e γ 11t Dγ 21 e γ 21t D1 g (t, q (4,8,1 2,7 (t = (γ 11 e (+γ 11t Dγ 21 e (+γ 21t De t D1 g (t, q (4,9,1 2,7 (t = (γ 11 e (+γ 11t De (+γ 21t Dγ 21 e γ 21t 1 g (t, q 4 29 (t = (γ 11e (+γ 11t De (+γ 21t G (t, q (4,8 2,1 (t = (γ 11e (+γ 11t Dγ 21 e (+γ 21t De t G (t, q 51 (t =γ 22 e (+γ 22t, q 57 (t =e (+γ 22t, q 61 (t =e (+γ 21t g (t, q 8 65 (t = (γ 21e (+γ 21t De t g(t, q 9 66 (t = (e (+γ 21t De γ 21t g(t, q (8,1 6,7 (t = (γ 21 e (+γ 21t De t D1 g (t, q (9,1 6,7 (t = (e (+γ 21t Dγ 21 e γ 21t D1 g (t, q 69 (t = (e (+γ 21t G (t,
3 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering 3 g(t γ 11 S 4 F R,Op p 1 <d p 2 S 9 F R,F W p 1 <d p 2 γ γ S S 1 S 5 Op, C Op, Op S Op, Op d p γ 12 p 1 <d p 2 1 d<p2 γ 22 g(t g(t g(t g(t S S 6 S 7 2 F F r,op r,op F r,op p 1 <d p 2 d>p2 d p 1 γ 21 g(t g(t g(t S 8 γ 11 S 3 F R,Op S 1 F F R,F d>p R,F W W 2 d>p d p 2 1 γ 21 γ 21 Regeneration point Operative state Failed state Figure 1: State transition diagram. q 8 6,1 (t = (γ 21e (+γ 21t De t G (t, q 75 (t =e t g (t, q 1 77 (t = (e t D1 g (t, q 7,1 (t =e t G (t. Clearly,forthemodeltobeaccurate,itisimportanttoestimate accurately the model parameters (i.e., mean sojourn times and the steady-state transition probabilities. The nonzero elements p ij = lim s q ij (s are obtained as γ p 1 = 11 ( + γ 11, p 2 = ( + γ 11, γ p 1 = 12 ( + γ 12 +γ 21, γ p 15 = 21 ( + γ 12 +γ 21, p 16 = ( + γ 12 +γ 21, p 2 =g (+γ 11, p 4 21 = γ 11 (γ 21 γ 11 (g (+γ 11 g (+γ 21, (1 p 3 22 =( g (+γ 11+g (γ 11, p 23 = ( + γ 11 (1 g (+γ 11, p (4,8 2,5 =γ 11 γ 21 ( g (+γ 11 (γ 11 γ 21 γ 11 g (+γ 21 (γ 11 γ 21 γ 21 + g ( (γ 11 γ 21, p (3,9 2,6 =γ 11 ( g (+γ 11 (+γ 11 γ 21 g (γ 21 ( + γ 11 γ 21 (γ 21 γ 11 p (4,9 + g (γ 11 (γ 21 γ 11, g ( + γ 2,6 =γ 11 ( 11 ( + γ 11 γ 21 (γ 21 γ 11 + g (+γ 21 (γ 21 γ 11 p (3,9,1 2,7 =γ 11 γ 21 g (γ + 21 (+γ 11 γ 21, g ( + γ ( 11 (+γ 11 (+γ 11 γ 21 g (γ 11 γ 11 (γ 21 γ 11 g (γ + 21 γ 21 (γ 21 γ 11 (+γ 11 γ 21
4 4 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering p (4,8,1 2,7 =γ 11 γ 21 p (4,9,1 2,7 =γ 11 γ 21 p 4 29 = γ 11 (γ 21 γ γ 11 γ 21 ( + γ 11, g (+γ ( 11 γ 11 ( + γ 11 (γ 21 γ 11 g (+γ 21 γ 21 ( + γ 21 (γ 21 γ 11 g ( 1 + γ 11 γ 21 (+γ 11 (+γ 21, g (+γ ( 11 ( + γ 11 (+γ 11 γ 21 (γ 21 γ 11 g (+γ 21 (+γ 21 (γ 21 γ 11 g (γ 21 γ 21 ( + γ 11 γ γ 21 ( + γ 11 (+γ 21, ( (1 g (+γ 11 ( + γ 11 p (4,8 2,1 =γ 11γ 21 (1 g (+γ 21, ( + γ 21 ( (1 g (+γ 11 γ 11 ( + γ 11 (γ 11 γ 21 (1 g (+γ 21 γ 21 ( + γ 21 (γ 11 γ 21 + (1 g (, (γ 11 γ 21 p 51 = p 57 = γ 22 ( + γ 22, ( + γ 22, p 61 =g (+γ 21, p 8 65 =g (+γ 21+g (, p 9 66 = g (+γ 21+g (γ 21, p (8,1 =γ 21 ( g (+γ 21 γ 21 ( + γ 21 g ( (γ (+γ 21, p (9,1 =γ 21 ( g (+γ 21 g (γ (+γ 21 (γ 21 γ 21 ( + γ 21, p 69 = ( + γ 21 (1 g (+γ 21, p 8 6,1 =γ 21 ( (1 g ( + γ 21 γ 21 ( + γ 21 p 75 =g (, + p 1 77 =1 g (, p 7,1 =1 g (. (1 g (, (γ 21 By these transition probabilities, it can be verified that p 1 +p 2 =p 1 +p 15 +p 16 =p 2 +p p 23 +p (4,8 +p p(4,8 2,1 =1, p 2 +p p3 22 +p(4,8 +p (3,9 +p (4,9 +p (3,9,1 +p (4,8,1 +p (4,9,1 =1, p 51 +p 57 =p 61 +p p 69 +p 8 6,1 =p 61 +p p9 66 +p(8,1 +p (9,1 =1, p 75 +p 7,1 =p 75 +p 1 77 =1. The mean sojourn time (μ i instatei is μ 5 = μ = 1 ( + γ 11 ; μ 1 1 = ( + γ 11 +γ 21 ; μ 2 = ( + γ 11 (1 g (+γ 11, 1 ( + γ 22 ; μ 6 = ( + γ 21 (1 g (+γ 21 ; (2 (3 μ 7 = 1 (1 g (. (4 Analysis carried out in this paper depends only on the mean sojourn time and is independent of the actual sojourn time distributions for the semi-markov processes states. If we were to carry out a transient analysis of the semi-markov processes, this will no longer be true. The unconditional mean time taken by the system to transit for any state j when it is counted from epoch of entrance into state i is mathematically stated as m ij = tq ij (t dt = q ij (. (5
5 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering 5 Thus, +(q 69 (s +q 8 6,1 (s m 1 +m 2 =μ ; m 1 +m 15 +m 16 =μ 1, m 2 +m m 23 +m (4,8 +m m(4,8 2,1 =μ 7, m 2 +m m3 22 +m(4,8 +m (3,9 +m (4,9 +m (3,9,1 +m (4,8,1 +m (4,9,1 =k 1, m 51 +m 57 =μ 5, m 61 +m m 69 +m 8 6,1 =μ 7 =m 75 +m 7,1 m 61 +m m9 +m(8,1 +m (9,1 =k 1 =m 75 +m 1 77, (6 (q 1 (s q 16 (s (1 q 57 (s q 75 (s q 2 (s q 16 (s ( q 4 21 (s (1 q 57 (s q 75 (s q 51 (s q (4,8 (s q 7,1 (s (q 1 (s ( q 15 (s q 57 (s +q 2 (s q 16 (s q 57 (s q 8 65 (s k 1 = tg(tdt. 4. Measures of System Effectiveness 4.1.MeanTimetoSystemFailure.To determine the mean time to system failure (MTSF of the system, we regard the failed states as absorbing states. By probabilistic arguments, we obtain the following recursive relations for φ i (t, i =, 1, 2, 5, 6, 7 are given by φ (t =Q 1 (t φ 1 (t +Q 2 (t φ 2 (t, φ 1 (t =Q 1 (t φ (t +Q 15 (t φ 5 (t +Q 16 (t φ 6 (t, φ 2 (t =Q 2 (t φ (t +Q 4 21 (t φ 1 (t +Q 23 (t +Q (4,8 (t φ 5 (t +Q 4 29 (t +Q(4,8 2,1 (t, φ 5 (t =Q 51 (t φ 1 (t +Q 57 (t φ 7 (t, φ 6 (t =Q 61 (t φ 1 (t +Q 8 65 (t φ 5 (t +Q 69 (t +Q 8 6,1 (t, φ 7 (t =Q 75 (t φ 5 (t +Q 7,1 (t. Taking Laplace-Stieltjes Transform (L.S.T. of the relations given by (7 and solving them for Ls(φ (t,weobtain Ls (φ (t = N (s =q 2 (s (q 23 (s +q 9 24 (7 N (s D (s, (8 (s +q(4,8 2,1 (s (1 q 57 (s q 75 (s q 15 (s q 51 (s q 16 (s (q 51 (s q 8 65 (s +q 61 (s (1 q 57 (s q 75 (s ( q (4,8 (s q 57 (s q 15 (s q 4 21 (s q 57 (s q 16 (s q 57 (s D (s =(1 q 57 (s q 75 (s (q 4 21 (s q8 65 (s q 61 (s q (4,8 (s, (1 q 16 (s q 61 (s q 1 (s q 1 (s q 2 (s (q 1 (s q 4 21 (s +q 2 (s (1 q 16 (s q 61 (s q 51 (s ((1 q 2 (s q 2 (s (q 15 (s +q 16 (s q 8 65 (s +q 2 (s q 1 (s q (4,8 (s. Now, the reliability R(t of the system at time t is given as (9 R (t = Inverse Laplace transform of (1 Ls (φ (t. s (1 Now,themeantimetosystemfailure(MTSFwhenthe system starts from the state is MTSF = R (t dt = limr (s. s (11 Using L Hospital rule and putting the value of Ls(φ (t from (8,wehave MTSF = N D, (12
6 6 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering N=μ [(1 p 57 p 75 (p 16 (p 69 +p 8 6,1 +p 1 +p 7,1 (p 15 p 57 +p 16 p 57 p 5 68 ] +μ 1 [p 1 (1 p 57 p 75 +p 2 p 4 21 (1 p 57p 75 +p 51 p 2 p 48 ] +μ 5 [((1 p 2 p 2 (p 15 +p 16 p p 2p 1 p (4,8 (p 23 +p p(4,8 2,1 p 2 (p 15 +p 16 p (p 69 +p 8 6,1 p 2p 16 p 48 ] +μ 7 [p 2 ((1 p 57 p 75 (1 p 16 p 61 D=(1 p 57 p 75 p 51 (p 15 +p 16 p p 1 p 16 (1 p 57 p 75 p 2 p 16 ( p 4 21 (1 p 57p 75 p 51 p 48 +p 57 (p 1 (p 15 +p 16 p p 2 (p 48 +p4 21 p 15 (1 p 16 p 61 p 1 p 1 +p 16 (p 4 21 p8 65 p 61p 48 ], p 2 (p 1 p p 2 (1 p 16 p 61 p 51 ((1 p 2 p 2 (p 15 +p 16 p p 2p 1 p 48. ( Availability Analysis When Demand Is Less Than or Equal to Production Made by One Unit (d p 1. Letting i (t i =, 1, 2, 5, 6, 7 as the probability that the system is in upstate when demand is not less than production made by one unit at instant t giventhatitenteredthestateiat t=and using the arguments of the theory of the regeneration process, the availability i (t isseentosatisfythefollowingrecursive relations: +q (3,9,1 (t D 7 (t +q(4,8,1 (t D 7 (t +q (4,9,1 (t DA p1 7 (t, 5 (t =q 51 (t D 1 (t +q 57 (t D 7 (t, 6 (t =q 61 (t D 1 (t +q8 65 (t DAp 1 5 (t +q 9 66 DAp 1 6 +q (9,1 (t D 7 (t, (t +q(8,1 (t D 7 (t 7 (t =q 75 (t D 5 (t +q1 77 (t DAp 1 7 (t, (14 M (t = e (+γ 11t and M 2 (t =e (+γ 11t G (t +(γ 11 e (+γ 11t De (+γ 21t G (t D (γ 11 e (+γ 11t Dγ 21 e (+γ 21t De t G (t. (15 Taking Laplace transforms of above equations (14 and solving them for A (s,weget (s = N 1 (s D 1 (s, (16 N 1 (s =(M (s (1 q 3 22 (s+m 2 (s q 2 (s [(1 q 9 66 (s ((1 q 1 77 (s q 57 (s q 75 (s q 15 (s q 51 (s (1 q 1 77 (s +(1 q 1 77 (s ( q 16 (s (q 51 (s q 8 65 (s +q 61 (s q 75 (s q 16 (s ((q (8,1 (s +q (9,1 (s (t =M +q 1 (t D 1 (t +q 2 (t D 2 (t, 1 (t =q 1 (t D (t +q 15 (t D 5 (t +q 16 (t D 6 (t, 2 (t =M 2 (t +q 2 (t D (t +q4 21 (t DAp 1 1 (t +q 3 22 (t DAp 1 2 (t +q(4,8 (t D 5 (t +q (3,9 (t D 6 (t +q(4,9 (t D 6 (t +q 61 (s q 57 (s], D 1 (s = ((1 q 3 22 (s q 2 (s q 2 (s [(1 q 9 66 (s (1 q 1 77 (s q 57 (s q 75 (s q 15 (s q 51 (s (1 q 1 77 (s (17
7 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering 7 +(1 q 1 77 (s ( q 16 (s (q 51 (s q 8 65 (s +q 16 (s q 75 (s q 16 (s (q (8,1 (s +q (9,1 (s +q 61 (s q 57 (s]+q 1 (s [(1 q 9 66 (s ((1 q 1 77 (s q 57 (s q 75 (s (q 1 (s (1 q 3 22 (s+q 2 (s q 4 21 (s +q 2 (s (1 q 1 77 (s ((q 51 (s q 8 65 (s +q 61 (s +(q (3,9 (s +q (4,9 (s +(1 q 9 66 (sq(4,8 (s q 51 (s q 51 (s q 75 (s (q (8,1 (s +q (9,1 (s (q (3,9 (s +q (4,9 (s q 51 (s q 75 (s (1 q 9 66 (s (q (3,9,1 (s +q (4,8,1 (s +q (4,9,1 (s +q 61 (s q 57 (s q 75 (s (q (3,9 (s +q (4,9 (s]. In steady-state, the availability (18 of the system is given by = lim s (sap 1 (s = N 1 ( D 1 ( = N 1 D 1, (19 N 1 =(μ (1 p μ 2p 2 [(1 p 9 66 ((1 p 1 77 p 57p 75 p 15 p 51 (1 p (1 p 1 77 ( p 16 (p 51 p p 61 p 75 p 16 (p (8,1 +p (9,1 +p 61 p 57 ], D 1 = μ ((1 p 3 22 (1 p9 66 (1 p1 77 p 57p 75 p 1 μ 1 [(1 p 9 66 ((1 p1 77 p 57p 75 (p 1 (1 p p 2p p 2 (1 p 1 77 ((p 51 p p 61(p (3,9 +p (4,9 +(1 p 9 66 p48 p 51 p 51 p 75 ((p (8,1 +p (9,1 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 (1 p 9 66 (p (3,9,1 +p (4,8,1 +p (4,9,1 +p 61 p 57 p 75 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 ] +μ 2 (p 1 p 51 p 75 (1 p μ 5 ((1 p 3 22 p 2p 2 ( p 61 p 75 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 +p 1 p 75 (1 p 9 66 (p 1 (1 p p 2p p 75 (1 p p 16p 61 +k 1 (p 2 ((p 51 p p 61(p (3,9 +p (4,9 +(1 p 9 66 p48 p 51 +p 1 (1 p 9 66 (p 1 (1 p p 2p (p 57 (1 p 9 66 p 15p 51 +p 16 (p 51 p p 61 ((1 p 3 22 p 2p 2 +p 51 p 75 ((p (8,1 +p (9,1 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 +p 16 p 75 ((1 p 3 22 p 2p 2. ( Availability Analysis When Demand Is Greater Than the Production Made by One Unit and Less Than or Equal to Production Made by Two Units (p 1 <d p 2. Letting A p 2 i (t i =, 1, 2, 5, 6, 7 as the probability that the system is inupstatewhendemandisgreaterthantheproductionmade by one unit and less than or equal to production made by two units at instant t given that it entered the state i at t=and proceeding in the similar fashion as in 5.2, in steady-state, the availability A p 2 is given by A p 2 = lim s (sap 2 (s =N 2, (21 D 1 N 2 =μ 1 [(1 p 9 66 ((1 p1 77 p 57p 75 (p 1 (1 p p 2p p 2 (1 p 1 77 ((p 51 p p 61(p (3,9 +p (4,9 +(1 p 9 66 p48 p 51
8 8 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering p 51 p 75 ((p (8,1 +p (9,1 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 (1 p 9 66 (p (3,9,1 +p (4,8,1 +p (4,9,1 +p 61 p 57 p 75 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 ] +μ 7 [p 1 (1 p 3 22 (p 16 (1 p 1 77 p 57p 75 μ 7 [ p 2 (p (3,9,1 +p (4,8,1 +p (4,9,1 ((1 p 9 66 (1 p 15p 51 p 16 (p 51 p p 61 (p (8,1 +p (9,1 (p 1 p 16 (1 p 3 22 p 2 ((1 p 15 p 51 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 p 2 (p 16 (( p 4 21 (1 p1 77 p 57p 75 +p 51 (p 48 (1 p1 77 p 75 (p (3,9,1 +p (4,8,1 and D 1 is already specified. +p 16 (p p 51p (4,8 ], (24 +p 2 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 +p (4,9, Busy Period Analysis of the Repairman. The total fraction of the time for which the system is under repair of the repairman, in steady-state, is given by ((1 p 1 77 (1 p 15p 51 p 57 p 75 ], (22 B = lim s (sb (s = N 4 D 1, ( and D 1 is already specified Availability Analysis When Demand Is Greater Than Production Made by Two Units (d > p 2. Letting A d i (t i =, 1, 2, 5, 6, 7 as the probability that the system is in upstate when demand is greater than the production made by two units at instant t giventhatitenteredthestatei at t = and proceeding in the similar fashion as in Section 4.2, the availability A d in steady-state is given by A d = lim s (sad (s =N 3 D 1, (23 N 3 =p 1 (1 p 3 22 (p 15 (1 p p 16p 8 65 ( μ 5 p 16 p 75 (p (8,1 +p (9,1 +p 57 μ 7 p 2 (( p (4,8 (1 p 9 66 (p8 65 +p 15p 61 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 p 15 p 4 21 (1 p9 66 p 16 (p 4 21 p8 65 p 61p (4,8 ((1 p 1 77 μ 5 +p 57 μ 7 μ 5 p 2 [ (p (3,9,1 +p (4,8,1 +p (4,9,1 (p 75 (1 p 9 66 p 16p 61 p 75 p 75 (p (8,1 +p (9,1 ((p (3,9 +p (4,9 +p 16 p 4 21 ] N 4 =k 1 [p 2 ((1 p 9 66 ((1 p 1 77 p 57p 75 p 15 p 51 (1 p (1 p 1 77 ( p 16 (p 51 p p 61 p 75 p 16 ((p (8,1 +p (9,1 +p 61 p 57 +(p 1 (1 p 3 22 (p 16 (1 p 1 77 p 57p 75 p 2 (p 16 (( p 4 21 (1 p1 77 p 57p 75 +p 51 (p 48 (1 p1 77 p 75 (p (3,9,1 +p (4,8,1 +p 2 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 +p (4,9,1 ((1 p 1 77 (1 p 15p 51 p 1 (1 p 3 22 p 57 p 75 (p 15 (1 p p 16p 8 65 p 57 p 2 (( p (4,8 (1 p 9 66 (p p 15p 61 (p (3,9 +p (4,9
9 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering 9 and D 1 (s is already specified. p 15 p 4 21 (1 p9 66 p 16 (p 4 21 p8 65 p 61p (4,8 p 57 ( p 2 (p (3,9,1 +p (4,8,1 +p (4,9,1 ((1 p 9 66 (1 p 15p 51 p 16 (p 51 p p 61 (p (8,1 +p (9,1 (p 1 p 16 (1 p 3 22 p 2 (1 p 15 p 51 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 +p 16 (p p 51p (4,8 ], ( 4.6. Expected Number of Visits by the Repairman. The expected number of visits per unit time by the repairman, in steady-state, is given by N 5 =p 2 (1 p 3 22 V = lim s (sv (s = N 5 D 1, ( [(1 p 9 66 ((1 p1 77 p 57p 75 p 15 p 51 (1 p (1 p 1 77 ( p 16 (p 51 p p 61 p 75 p 16 ((p (8,1 +p (9,1 +p 61 p 57 ] p 16 [(1 p 9 66 ((1 p1 77 p 57p 75 (p 1 (1 p p 2p p 2 (1 p 1 77 ((p 51 p p 61 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 +(1 p 9 66 p48 p 51 p 51 p 75 ((p (8,1 +p (9,1 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 (1 p 9 66 (p (3,9,1 +p (4,8,1 +p (4,9,1 +p 61 p 57 p 75 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 ] p 57 p 1 (1 p 3 22 (p 15 (1 p p 16p 8 65 ( p 16 p 75 (p (8,1 +p (9,1 p 2 (( p (4,8 (1 p 9 66 (p p 15p 61 (p (3,9 +p (4,9 p 15 p 4 21 (1 p9 66 p 16 (p 4 21 p8 65 p 61p (4,8 (1 p 1 77 p 2 ( (p (3,9,1 +p (4,8,1 +p (4,9,1 and D 1 is already specified. (p 75 (1 p 9 66 p 16p 61 p 75 p 75 (p (8,1 +p (9,1 5. Cost-Benefit Analysis ((p (3,9 +p (4,9 +p 16 p 4 21, (28 The expected profit can be calculated by expected total revenue in (, t] minus expected total repair in (, t] minus expected cost of visits by repairman in (, t].hencethetotal profit in (, t] is given by Profit P (t =(C (t +C 1A p 2 (t +C 2A d (t (29 C 3 B (t C 4 V (t. In steady-state, the expected profit per unit time incurred to the system is given by P (t P= lim ( =lim (s 2 P (s, t t s (3 Profit P=(C +C 1A p 2 +C 2A d C 3B C 4, C is revenue per unit uptime when demand is less than or equal to production made by one unit (d p 1, C 1 is revenue per unit uptime when demand is greater than theproductionmadebyoneunitandlessthanorequalto production made by two units (p 1 <d p 2, C 2 is revenue per unit uptime when demand is greater than the production made by two units (d >p 2, C 3 is cost per unit uptime for engaging the repairman for repair, and C 4 is cost per visit of the repairman. 6. Particular Case For the particular case, let us take g(t = αe αt and the values estimated from the system, that is, γ 11 =.235/hr, γ 12 =.7/hr, γ 21 =.4213/hr, γ 22 =.353/hr, α=1/hr, =.3/hr, C = INR 7, C 1 = INR 1, C 2 = INR 2, C 3 = INR 1, andc 4 = INR 4 (all costs are in Indian rupees.
10 1 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering Various measures of the system effectiveness are given by the following: (i mean time to system failure (MTSF = hrs; (ii steady-state availability when demand is less than or equal to production made by one unit (d p 1 ( =.2366; (iii steady-state availability when demand is greater than theproductionmadebyoneunitandlessthanor equal to production made by two units (p 1 <d p 2 (A p 2 = ; (iv steady-state availability when demand is greater than the production made by two units (d >p 2 (A d = ; (v busy period of the repairman for repair (B =.4613; (viexpectednumberofvisitsbytherepairman(v =.157; (vii profit incurred to the system = INR Graphical Analysis For the numerical results, let us take g(t = αe αt, α is repair rate. Data/information was gathered on failure and repair times from cable manufacturing system. On the basis of the gathered information, the following values are estimated: γ 11 =.235/hr, γ 21 =.4213/hr, γ 12 =.7/hr, γ 22 =.353/hr. (31 Various graphs have been plotted for the MTSF, the availability, and the profit with respect to rates/revenue per unit uptime for different values of rates/costs. Some have been shownhereandtheothershavenotbeenshowntoavoid space. The following interpretations can be made from the graphs. (i MTSF gets decreased with increase in the values of failureratebutincreasedwithincreaseinthevalues of repair rate. The values of other parameters per hour are taken as γ 11 =.235/hr, γ 21 =.4213/hr, γ 12 =.7/hr, γ 22 =.353/hr. (32 (ii The graph of availability ( when demand is less than or equal to whatever production given by a single unit (d p 1 versusfailurerate( fordifferent values of repair rate (α shows that it gets decreased monotonically with increase in the values of failure rate but increases with increase in the values of repair rate. Similar behavior has been shown for the availability (A p 2 when demand is greater than the production by one unit but less than or equal to production Profit (P (INR Profit (P versus failure rate ( for different values of repair rate (α α =.6/hr α = 1.1/hr α = 1.6/hr Failure rate ( (/hr Figure 2: Profit (P versus failure rate( for different values of repair rate (α. made by two units (p 1 < d p 2 andalsoforthe availability (A d when demand is greater than the production made by two units (d > p 2. The graphs revealed that the availabilities in three types of the upstates (, (Ap 2, (Ad are different in magnitude for the same values of parameters, α, γ 11, γ 12, γ 21, and γ 22. (iii Behavior of the profit with respect to failure rate/ revenue per unit uptime for different values of repair rate/cost of engaging the repairman has also been observed from the graphs. Some of these graphs are shown in Figures 2, 3, 4,and5.Thegraphsdepictthat theprofitgetsdecreasedwithincreaseinthevaluesof failurerateandalsowiththeincreaseincostofengaging/visiting the repairman but increases with increase in the values of repair rate/revenue per unit uptime. Cut-off points as to when the profit is positive or negative have been obtained from the graphs and are shown in Table Conclusion A two-unit cold standby system in cable manufacturing plant in both units may become operative depending upon the demand has been analyzed. A state transition model that describes the dynamic behavior of such a system is used as a basis for developing a stochastic model. In this paper, we have obtained several general probability distribution functions thatcanbeusedtodescribethesystembehavior.various measures of system effectiveness are estimated using semi- Markov processes and regenerative point techniques. These include the following: (i mean sojourn times; (ii steady-state probabilities; (iii mean time to system failure (MTSF; (iv availability in three types of upstates (i.e., when demand is less than or equal to production made by
11 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering 11 Table 1 Fixed parameter γ 11 =.235/hr, γ 12 =.7/hr, γ 21 =.4213/hr, γ 22 =.353/hr, C = INR 7, C 1 = INR 1, C 2 = INR 2, C 3 = INR 1, C 4 =INR4 γ 11 =.235/hr, γ 12 =.7/hr, γ 21 =.4213/hr, γ 22 =.353/hr, α=1/hr, =.3/hr, C 1 = INR 1, C 2 = INR 2, C 4 = INR 4 γ 11 =.235/hr, γ 12 =.7/hr, γ 21 =.4213/hr, γ 22 =.353/hr, α =1/hr, =.3/hr, C = INR 7, C 2 = INR 2, C 4 =INR 4 γ 11 =.235/hr, γ 12 =.7/hr, γ 21 =.4213/hr, γ 22 =.353/hr, α =1/hr, =.3/hr, C = INR 7, C 1 = INR 1, C 4 = INR 4 γ 11 =.235/hr, γ 12 =.7/hr, γ 21 =.4213/hr, γ 22 =.353/hr, α =1/hr, =.3/hr, C 1 = INR 1, C 2 = INR 2, C 3 =INR 1 γ 11 =.235/hr, γ 12 =.7/hr, γ 21 =.4213/hr, γ 22 =.353/hr, α = 1/hr, =.3/hr, C = INR 7, C 2 = INR 2, C 3 =INR1 γ 11 =.235/hr, γ 12 =.7/hr, γ 21 =.4213/hr, γ 22 =.353/hr, α =1/hr, =.3/hr, C = INR 7, C 1 = INR 1, C 3 = INR 1 Varied parameter Profit Positive Negative Zero (cut-off point α =.6/hr <.598 >.598 =.598 α = 1.1/hr, <.796 >.796 =.796 α = 1.6/hr <.943 >.943 =.943 C 3 =INR24 C > 395. C < 395. C =395. C 3 =INR C > 53. C < 58.2 C = 53. C 3 = INR C > 69. C < 69. C = 69. C 3 =INR18 C 1 > C 1 < C 1 = C 3 = INR 22 C 1 > C 1 < C 1 = C 3 = INR C 1 > C 1 < C 1 = C 3 =INR18 C 2 > C 2 < C 2 = C 3 = INR 22 C 2 > C 2 < C 2 = C 3 = INR C 2 > 5.82 C 2 < 5.82 C 2 =5.82 C 4 = INR 3 C > C < C = C 4 =INR31 C > 58.2 C < 58.2 C = 58.2 C 4 =INR32 C > C < C = C 4 = INR 3 C 1 > C 1 < C 1 =422.9 C 4 =INR32 C 1 > C 1 < C 1 = C 4 =INR34 C 1 > C 1 < C 1 =599.2 C 4 =INR18 C 2 > C 2 < C 2 = C 4 =INR24 C 2 > C 2 < C 2 = C 4 = INR 3 C 2 > C 2 < C 2 = Profit (P (INR Profit (P versus revenue per unit uptime (C for different values of cost (C Revenue per unit uptime (C (INR C 3 = INR 24 C 3 = INR C 3 = INR Figure 3: Profit (P versus revenue per unit uptime (C for different values of cost (C 3. one unit; when demand is greater than production made by one unit, but less than or equal to production made by two units; when demand is greater than production made by two units and other measures of the system effectiveness which have been obtained in general case as well as for a particular case; it can also be concluded that these steady-state availabilities have different values in magnitude for the same value of failure rate and repair rate; (v busy period of the repairman for repair; Profit (P (INR Profit (P versus revenue per unit uptime (C 1 for different values of cost (C Revenue per unit uptime (C 1 (INR C 4 = INR 3 C 4 = INR 32 C 4 = INR 34 Figure 4: Profit (P versus revenue per unit uptime (C 1 for different values of cost (C 4. (vi expected number of visits by the repairman; (vii profit incurred to the system; (viii various graphs which are plotted to provide a better understanding of the behaviour of the system, help to refine its stochastic description, and lead to better estimates of the model parameters; (ix graphs from which the behavior of mean time to system failure, different types of availability, and the
12 12 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering Profit (P (INR Profit (P versus revenue per unit uptime (C 2 for different values of cost (C Revenue per unit uptime (C 2 (INR C 3 = INR 18 C 3 = INR 22 C 3 = INR Figure 5: Profit (P versus revenue per unit uptime (C 2 for different values of cost (C 3. profit can be depicted with respect to failure rate/ repair rate/cost for engaging repairman/revenue per unituptime/costpervisitoftherepairmanthathave been plotted; (x various cut-off points for the profit of the system whichhelptodecideabouthowmuchshouldbethe maximum tolerable value of the failure rate of the system and how much the cost price of the product (cable wires manufactured by the system should be soldtogetatleastthatvalueofrevenueperunit uptime so as to get positive profit; (xi the lower limits for the revenue per unit uptime for positive profit that have been obtained which may be quite useful for the system manufacturers, engineers, and the system analysts; (xii the upper limit for the cost per visit as well as for engaging the repairman which has been obtained. The above conclusions have been drawn on the basis of a particular case and the data collected. However, our model can be used by anyone using such system and can draw the conclusions in the similar fashion by putting those values of parameters, which exist for his/her system, in the general expressions obtained by us for the model. Further, we are focusing on developing some more realistic models (e.g., hot standby system related to the given system. Cost-benefit analysis for the system will be carried out to increase the uptime of the system and to reduce the cost involved in system. Nomenclature Symbols for the Various States : Operativestateforthesystem :Failedstateforthesystem D: Symbol for demand p 1 : Symbol for production by single unit p 2 : Symbol for production by two units. Notations : Failure rate of the operative unit γ 11 : Rate of increase of demand when demand is greater than the production made by one unit and less than or equal to production made by two units (p 1 <d p 2 γ 12 : Rateofdecreaseofdemandsoasto become less than or equal to production made by one unit (d p 1 γ 21 : Rate of further increase of demand when demand is greater than the production made by two units (d > p 2 γ 22 : Rate of decrease of demand when demand is greater than the production made by one unit and less than or equal to production made by two units (p 1 <d p 2 i (t: Probability that the system is in upstate when demand is less than or equal to production made by one unit (d p 1 at instant t giventhatitenteredthestatei at t= A p 2 i (t: Probability that the system is in upstate when demand is greater than the production made by one unit and less than orequaltoproductionmadebytwounits (p 1 <d p 2 at instant t given that it entered the state i at t= A d i (t: Probability that the system is in upstate when demand is greater than production made by two units (d > p 2 at instant t giventhatitenteredthestatei at t= B i (t: Probability that the repairman is busy to repair the failed unit at instant t given that it entered the state i at t= M i (t: Probability that the system, initially up in the regenerative state i,isupattimet without passing through any other regenerative state m ij : Contributiontomeansojourntimein regenerative state i before transitingto regenerative state j withoutvisitingany other state μ i : Mean sojourn time in regenerative state i before transiting to any other state : Symbol for derivative : Symbol for Laplace transforms Ls: Symbol for Laplace Stieltjes transforms D: Symbol for Laplace convolution : Symbol for Stieltjes convolution q ij (t, Q ij (t: p.d.f. and c.d.f of the first passage time from a regenerative state i to a regenerative state j or to a failed state j without visiting any other regenerative state in (, t] g(t, G(t: p.d.f. and c.d.f of repair rate at instant t.
13 Journal of Quality and Reliability Engineering 13 States of System C S : Op (d p 1 : Unitisincoldstandbystate Unitisinoperativestatewhen demand is less than or equal to production made by one unit Op (p 1 <d p 2 :Unitisinoperativestatewhen demand is greater than the production made by one unit and less than or equal to production made by two units Op (d > p 2 : F r : F R : F w : Conflict of Interests Unitisinoperativestatewhen demand is greater than production made by two units Failed unit under repair Repair of failed unit continuing from previous state Failed unit waiting for repair. The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper. References [1] P. Chandrasekhar, R. Natarajan, and V. S. Yadavalli, A study on a two unit standby system with Erlangian repair time, Asia- Pacific Journal of Operational Research,vol.21,no.3,pp.1 7, 24. [2] A.Goyal,G.Taneja,andD.V.Singh, Reliabilityandprofitevaluation of a 2-unit cold standby system working in a sugar mill with operating and rest periods, Caledonian Journal of Engineering,vol.5,pp.1 5,29. [3] R. Kumar and S. Kapoor, Cost-benefit analysis of a reliability model for a base transceiver system considering hardware/software faults and congestion of calls, International Journal of Science and Technology,vol.4,no.6,pp.13 23,212. [4] R. Kumar and M. Kumar, Performance and cost-benefit analysis of a hardware software system considering hardware based software interaction failures and different types of recovery, International Journal of Computer Applications, vol.53,no.17, pp. 32,212. [5] B. B. Madan, K. Goševa-Popstojanova, K. Vaidyanathan, and K. S. Trivedi, A method for modeling and quantifying the security attributes of intrusion tolerant systems, Performance Evaluation,vol.56,no.1 4,pp.1 186,24. [6] H. Mine and H. Kawai, Repair priority effect on avail ability of two-unit system, IEEE Transactions on Reliability, vol.28,no. 4, pp. 3 3, [7] K. Murari and V. Goyal, Reliability system with two types of repair facilities, Microelectronics Reliability, vol. 23, no. 6, pp , [8] D. Pandey and M. Jacob, Cost analysis, availability and MTTF of a three state standby complex system under common cause and human failures, Microelectronics Reliability, vol. 35, no. 1, pp.91 95,1995. [9] B. Parashar and G. Taneja, Reliability and profit evaluation of a PLC hot standby system based on a master-slave concept and two types of repair facilities, IEEE Transactions on Reliability, vol. 56, no. 3, pp , 27. [1] S. M. Rizwan, V. Khurana, and G. Taneja, Reliability analysis of a hot standby industrial system, International Journal of Modelling and Simulation,vol.3,no.3,pp ,21. [11] B. S. Siwach, R. P. Singh, and G. Taneja, Reliability and profit evaluation of a two-unit cold standby system with instructions and accidents, Pure and Applied Mathematika Sciences,vol.53, no. 1-2, pp , 21. [12] S. K. Srinivasan and M. N. Gopalan, Probabilistic analysis of atwo-unitsystemwithawarmstandbyandasinglerepair facility, Operations Research,vol.21,pp ,1973. [13] G. Taneja, A. Goyal, and D. V. Singh, Reliability and cost-benefit analysis of a system comprising one big unit and two small identical units with priority for operation/repair to big unit, Mathematical Sciences,vol.5,no.3,pp ,211. [14] G. Taneja and V. Naveen, Comparative study of two reliability models with patience time and chances of non-availability of expert repairman, PureandAppliedMathematikaSciences,vol. 57, no. 1-2, pp , 23. [15] R. K. Tuteja, R. T. Arora, and G. Taneja, Analysis of a two-unit system with partial failures and three types of repairs, Reliability Engineering & System Safety, vol.33,no.2,pp , [16] K. S. Trivedi, Probability and Statistics with Reliability, Queuing, and Computer Science Application, JohnWiley&Sons,New York, NY, USA, 2nd edition, 21. [17] Z.Zhag,W.Gao,Y.Zhou,andZ.Zhiqiang, Reliabilitymodeling and maintenance optimization of the Diesel system in Locomotives, Maintenance and Reliability, vol. 14, no. 4, pp , 212. [18] R. Malhotra and G. Taneja, Reliability and availability analysis of a single unit system with varying demand, Mathematical Journal of Interdisciplinary Sciences,vol.2,no.1,pp.77 88,213. [19] G. Taneja and R. Malhotra, Cost-benefit analysis of a single unit system with scheduled maintenance and variation in demand, Journal of Mathematics and Statistics,vol.9,no.3,pp , 213.
14 International Journal of Rotating Machinery Engineering Journal of The Scientific World Journal International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks Journal of Sensors Journal of Control Science and Engineering Advances in Civil Engineering Submit your manuscripts at Journal of Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering Robotics VLSI Design Advances in OptoElectronics International Journal of Navigation and Observation Chemical Engineering Active and Passive Electronic Components Antennas and Propagation Aerospace Engineering International Journal of International Journal of International Journal of Modelling & Simulation in Engineering Shock and Vibration Advances in Acoustics and Vibration
Reliability and Economic Analysis of a Power Generating System Comprising One Gas and One Steam Turbine with Random Inspection
 J Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Original Research Paper Reliability and Economic Analysis of a Power Generating System Comprising One Gas and One Steam Turbine with Random Inspection alip Singh
J Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Original Research Paper Reliability and Economic Analysis of a Power Generating System Comprising One Gas and One Steam Turbine with Random Inspection alip Singh
Stochastic Analysis of a Two-Unit Cold Standby System with Arbitrary Distributions for Life, Repair and Waiting Times
 International Journal of Performability Engineering Vol. 11, No. 3, May 2015, pp. 293-299. RAMS Consultants Printed in India Stochastic Analysis of a Two-Unit Cold Standby System with Arbitrary Distributions
International Journal of Performability Engineering Vol. 11, No. 3, May 2015, pp. 293-299. RAMS Consultants Printed in India Stochastic Analysis of a Two-Unit Cold Standby System with Arbitrary Distributions
Comparative study of two reliability models on a two -unit hot standby system with unannounced failures
 IJREAS VOLUME 5, ISSUE 8 (August, 205) (ISS 2249-3905) International Journal of Research in Engineering and Applied Sciences (IMPACT FACTOR 5.98) Comparative study of two reliability models on a two -unit
IJREAS VOLUME 5, ISSUE 8 (August, 205) (ISS 2249-3905) International Journal of Research in Engineering and Applied Sciences (IMPACT FACTOR 5.98) Comparative study of two reliability models on a two -unit
Stochastic Modelling of a Computer System with Software Redundancy and Priority to Hardware Repair
 Stochastic Modelling of a Computer System with Software Redundancy and Priority to Hardware Repair Abstract V.J. Munday* Department of Statistics, Ramjas College, University of Delhi, Delhi 110007 (India)
Stochastic Modelling of a Computer System with Software Redundancy and Priority to Hardware Repair Abstract V.J. Munday* Department of Statistics, Ramjas College, University of Delhi, Delhi 110007 (India)
Probabilistic Analysis of a Desalination Plant with Major and Minor Failures and Shutdown During Winter Season
 Probabilistic Analysis of a Desalination Plant with Major and Minor Failures and Shutdown During Winter Season Padmavathi N Department of Mathematics & Statistics Caledonian college of Engineering Muscat,
Probabilistic Analysis of a Desalination Plant with Major and Minor Failures and Shutdown During Winter Season Padmavathi N Department of Mathematics & Statistics Caledonian college of Engineering Muscat,
Comparative Analysis of Two-Unit Hot Standby Hardware-Software Systems with Impact of Imperfect Fault Coverages
 International Journal of Statistics and Systems ISSN 0973-2675 Volume 12, Number 4 (2017), pp. 705-719 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Comparative Analysis of Two-Unit Hot Standby
International Journal of Statistics and Systems ISSN 0973-2675 Volume 12, Number 4 (2017), pp. 705-719 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Comparative Analysis of Two-Unit Hot Standby
Stochastic and Cost-Benefit Analysis of Two Unit Hot Standby Database System
 International Journal of Performability Engineering, Vol. 13, No. 1, January 2017, pp. 63-72 Totem Publisher, Inc., 4625 Stargazer Dr., Plano, Printed in U.S.A. Stochastic and Cost-Benefit Analysis of
International Journal of Performability Engineering, Vol. 13, No. 1, January 2017, pp. 63-72 Totem Publisher, Inc., 4625 Stargazer Dr., Plano, Printed in U.S.A. Stochastic and Cost-Benefit Analysis of
STOCHASTIC MODELLING OF A COMPUTER SYSTEM WITH HARDWARE REDUNDANCY SUBJECT TO MAXIMUM REPAIR TIME
 STOCHASTIC MODELLING OF A COMPUTER SYSTEM WITH HARDWARE REDUNDANCY SUBJECT TO MAXIMUM REPAIR TIME V.J. Munday* Department of Statistics, M.D. University, Rohtak-124001 (India) Email: vjmunday@rediffmail.com
STOCHASTIC MODELLING OF A COMPUTER SYSTEM WITH HARDWARE REDUNDANCY SUBJECT TO MAXIMUM REPAIR TIME V.J. Munday* Department of Statistics, M.D. University, Rohtak-124001 (India) Email: vjmunday@rediffmail.com
OPTIMIZATION OF COST MAINTENANCE AND REPLACEMENT FOR ONE-UNIT SYSTEM RELIABILITY MODEL WITH POST REPAIR
 Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 23 Sanjay Gupta and Suresh Kumar Gupta, 23 Research Paper ISSN 2278 49 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 2, No. 4, October 23 23 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved OPTIMIZATION OF COST MAINTENANCE
Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 23 Sanjay Gupta and Suresh Kumar Gupta, 23 Research Paper ISSN 2278 49 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 2, No. 4, October 23 23 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved OPTIMIZATION OF COST MAINTENANCE
Reliability Analysis of a Single Machine Subsystem of a Cable Plant with Six Maintenance Categories
 International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 973-4562 Volume 12, Number 8 (217) pp. 1752-1757 Reliability Analysis of a Single Machine Subsystem of a Cable Plant with Six Maintenance Categories
International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 973-4562 Volume 12, Number 8 (217) pp. 1752-1757 Reliability Analysis of a Single Machine Subsystem of a Cable Plant with Six Maintenance Categories
Reliability Analysis of Two-Unit Warm Standby System Subject to Hardware and Human Error Failures
 Reliability Analysis of Two-Unit Warm Standby System Subject to Hardware and Human Error Failures Pravindra Singh 1, Pankaj Kumar 2 & Anil Kumar 3 1 C. C. S. University, Meerut,U.P 2 J.N.V.U Jodhpur &
Reliability Analysis of Two-Unit Warm Standby System Subject to Hardware and Human Error Failures Pravindra Singh 1, Pankaj Kumar 2 & Anil Kumar 3 1 C. C. S. University, Meerut,U.P 2 J.N.V.U Jodhpur &
Cost-Benefit Analysis of a System of Non-identical Units under Preventive Maintenance and Replacement Subject to Priority for Operation
 International Journal of Statistics and Systems ISSN 973-2675 Volume 11, Number 1 (216), pp. 37-46 esearch India ublications http://www.ripublication.com Cost-Benefit Analysis of a System of Non-identical
International Journal of Statistics and Systems ISSN 973-2675 Volume 11, Number 1 (216), pp. 37-46 esearch India ublications http://www.ripublication.com Cost-Benefit Analysis of a System of Non-identical
Reliability Analysis of a Fuel Supply System in Automobile Engine
 ISBN 978-93-84468-19-4 Proceedings of International Conference on Transportation and Civil Engineering (ICTCE'15) London, March 21-22, 2015, pp. 1-11 Reliability Analysis of a Fuel Supply System in Automobile
ISBN 978-93-84468-19-4 Proceedings of International Conference on Transportation and Civil Engineering (ICTCE'15) London, March 21-22, 2015, pp. 1-11 Reliability Analysis of a Fuel Supply System in Automobile
COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS OF A SYSTEM OF NON- IDENTICAL UNITS UNDER PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE AND REPLACEMENT
 Journal of Reliability and Statistical Studies; ISSN (Print): 0974-8024, (Online): 2229-5666 Vol. 9, Issue 2 (2016): 17-27 COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS OF A SYSTEM OF NON- IDENTICAL UNITS UNDER PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
Journal of Reliability and Statistical Studies; ISSN (Print): 0974-8024, (Online): 2229-5666 Vol. 9, Issue 2 (2016): 17-27 COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS OF A SYSTEM OF NON- IDENTICAL UNITS UNDER PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
RELIABILITY ANALYSIS OF A FUEL SUPPLY SYSTEM IN AN AUTOMOBILE ENGINE
 International J. of Math. Sci. & Engg. Appls. (IJMSEA) ISSN 973-9424, Vol. 9 No. III (September, 215), pp. 125-139 RELIABILITY ANALYSIS OF A FUEL SUPPLY SYSTEM IN AN AUTOMOBILE ENGINE R. K. AGNIHOTRI 1,
International J. of Math. Sci. & Engg. Appls. (IJMSEA) ISSN 973-9424, Vol. 9 No. III (September, 215), pp. 125-139 RELIABILITY ANALYSIS OF A FUEL SUPPLY SYSTEM IN AN AUTOMOBILE ENGINE R. K. AGNIHOTRI 1,
3-Unit System Comprising Two Types of Units with First Come First Served Repair Pattern Except When Both Types of Units are Waiting for Repair
 Journal of Mathematics and Statistics 6 (3): 36-30, 00 ISSN 49-3644 00 Science Publications 3-Unit System Comrising Two Tyes of Units with First Come First Served Reair Pattern Excet When Both Tyes of
Journal of Mathematics and Statistics 6 (3): 36-30, 00 ISSN 49-3644 00 Science Publications 3-Unit System Comrising Two Tyes of Units with First Come First Served Reair Pattern Excet When Both Tyes of
A Comparative Study of Profit Analysis of Two Reliability Models on a 2-unit PLC System
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 4, Aril-2013 400 A Comarative Study of Profit Analysis of Two Reliability Models on a 2-unit PLC System Dr. Bhuender Parashar,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 4, Aril-2013 400 A Comarative Study of Profit Analysis of Two Reliability Models on a 2-unit PLC System Dr. Bhuender Parashar,
Stochastic Modeling of a Computer System with Software Redundancy
 Volume-5, Issue-, February-205 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 295-302 Stochastic Modeling of a Computer System with Software Redundancy V.J. Munday, S.C. Malik
Volume-5, Issue-, February-205 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 295-302 Stochastic Modeling of a Computer System with Software Redundancy V.J. Munday, S.C. Malik
Stochastic Analysis of a Cold Standby System with Server Failure
 International Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention (IJMSI) E-ISSN: 2321 4767 P-ISSN: 2321-4759 Volume 4 Issue 6 August. 2016 PP-18-22 Stochastic Analysis of a Cold Standby System with Server
International Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention (IJMSI) E-ISSN: 2321 4767 P-ISSN: 2321-4759 Volume 4 Issue 6 August. 2016 PP-18-22 Stochastic Analysis of a Cold Standby System with Server
Reliability Analysis of a Seven Unit Desalination Plant with Shutdown during Winter Season and Repair/Maintenance on FCFS Basis
 International Journal of Perforability Engineering Vol. 9, No. 5, Septeber 2013, pp. 523-528. RAMS Consultants Printed in India Reliability Analysis of a Seven Unit Desalination Plant with Shutdown during
International Journal of Perforability Engineering Vol. 9, No. 5, Septeber 2013, pp. 523-528. RAMS Consultants Printed in India Reliability Analysis of a Seven Unit Desalination Plant with Shutdown during
Stochastic Modeling of Repairable Redundant System Comprising One Big Unit and Three Small Dissimilar Units
 American Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, (4): 74-88 DOI:.59/j.ajcam.4.6 Stochastic Modeling of Repairable Redundant System Comprising One Big Unit and Three Small Dissimilar Units Ibrahim
American Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, (4): 74-88 DOI:.59/j.ajcam.4.6 Stochastic Modeling of Repairable Redundant System Comprising One Big Unit and Three Small Dissimilar Units Ibrahim
Stochastic analysis of edible oil refinery industry
 2018; 3(1): 0412 ISSN: 24561452 Maths 2018; 3(1): 0412 2018 Stats & Maths www.mathsjournal.com Received: 08102017 Accepted: 11112017 Sunita Thori Research Scholar, J.J.T. University, Jhunjhnu, Rajasthan,
2018; 3(1): 0412 ISSN: 24561452 Maths 2018; 3(1): 0412 2018 Stats & Maths www.mathsjournal.com Received: 08102017 Accepted: 11112017 Sunita Thori Research Scholar, J.J.T. University, Jhunjhnu, Rajasthan,
Reliability Analysis of a Two Dissimilar Unit Cold Standby System with Three Modes Using Kolmogorov Forward Equation Method
 Available online at http://www.ajol.info/index.php/njbas/index Nigerian Journal of Basic and Applied Science (September, 03), (3): 97-06 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/0.434/njbas.vi3.5 ISSN 0794-5698 Reliability
Available online at http://www.ajol.info/index.php/njbas/index Nigerian Journal of Basic and Applied Science (September, 03), (3): 97-06 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/0.434/njbas.vi3.5 ISSN 0794-5698 Reliability
Markov Chain Profit Modelling and Evaluation between Two Dissimilar Systems under Two Types of Failures
 Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. SSN: 9-966 Vol., ssue (December 06), pp. 89-50 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An nternational Journal (AAM) Markov Chain Profit Modelling and
Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. SSN: 9-966 Vol., ssue (December 06), pp. 89-50 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An nternational Journal (AAM) Markov Chain Profit Modelling and
COMPARATIVE RELIABILITY ANALYSIS OF FIVE REDUNDANT NETWORK FLOW SYSTEMS
 I. Yusuf - COMARATIVE RELIABILITY ANALYSIS OF FIVE REDUNDANT NETWORK FLOW SYSTEMS RT&A # (35) (Vol.9), December COMARATIVE RELIABILITY ANALYSIS OF FIVE REDUNDANT NETWORK FLOW SYSTEMS I. Yusuf Department
I. Yusuf - COMARATIVE RELIABILITY ANALYSIS OF FIVE REDUNDANT NETWORK FLOW SYSTEMS RT&A # (35) (Vol.9), December COMARATIVE RELIABILITY ANALYSIS OF FIVE REDUNDANT NETWORK FLOW SYSTEMS I. Yusuf Department
Research Article Doppler Velocity Estimation of Overlapping Linear-Period-Modulated Ultrasonic Waves Based on an Expectation-Maximization Algorithm
 Advances in Acoustics and Vibration, Article ID 9876, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55//9876 Research Article Doppler Velocity Estimation of Overlapping Linear-Period-Modulated Ultrasonic Waves Based on an
Advances in Acoustics and Vibration, Article ID 9876, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55//9876 Research Article Doppler Velocity Estimation of Overlapping Linear-Period-Modulated Ultrasonic Waves Based on an
STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF A TWO UNIT SYSTEM WITH VACATION FOR THE REPAIR FACILITY AFTER m REPAIRS
 139 ORiON, Vol. 16, No. 2, pp139148 ISSN 0259191X STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF A TWO UNIT SYSTEM WITH VACATION FOR THE REPAIR FACILITY AFTER m REPAIRS V.S.S. YADAVALLI & M. BOTHA University of South Africa Department
139 ORiON, Vol. 16, No. 2, pp139148 ISSN 0259191X STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF A TWO UNIT SYSTEM WITH VACATION FOR THE REPAIR FACILITY AFTER m REPAIRS V.S.S. YADAVALLI & M. BOTHA University of South Africa Department
Asymptotic Confidence Limits for a Repairable System with Standbys Subject to Switching Failures
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (11): 84-847, 007 ISSN 1546-99 007 Science Publications Asymptotic Confidence Limits for a Repairable System with Stbys Subject to Switching Failures 1 Jau-Chuan
American Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (11): 84-847, 007 ISSN 1546-99 007 Science Publications Asymptotic Confidence Limits for a Repairable System with Stbys Subject to Switching Failures 1 Jau-Chuan
Research Article Weather Forecasting Using Sliding Window Algorithm
 ISRN Signal Processing Volume 23, Article ID 5654, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/23/5654 Research Article Weather Forecasting Using Sliding Window Algorithm Piyush Kapoor and Sarabjeet Singh Bedi 2 KvantumInc.,Gurgaon22,India
ISRN Signal Processing Volume 23, Article ID 5654, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/23/5654 Research Article Weather Forecasting Using Sliding Window Algorithm Piyush Kapoor and Sarabjeet Singh Bedi 2 KvantumInc.,Gurgaon22,India
Research Article Research on Dynamic Reliability of a Jet Pipe Servo Valve Based on Generalized Stochastic Petri Nets
 Aerospace Engineering Volume 2015, Article ID 171642, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.55/2015/171642 Research Article Research on Dynamic Reliability of a Jet Pipe Servo Valve Based on Generalized Stochastic
Aerospace Engineering Volume 2015, Article ID 171642, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.55/2015/171642 Research Article Research on Dynamic Reliability of a Jet Pipe Servo Valve Based on Generalized Stochastic
Probabilistic Analysis of a Computer System with Inspection and Priority for Repair Activities of H/W over Replacement of S/W
 International Journal of Comuter Alications (975 8887) Volume 44 o. Aril Probabilistic Analysis of a Comuter ystem with Insection and Priority for Reair Activities of /W over Relacement of /W Jyoti Anand
International Journal of Comuter Alications (975 8887) Volume 44 o. Aril Probabilistic Analysis of a Comuter ystem with Insection and Priority for Reair Activities of /W over Relacement of /W Jyoti Anand
Research Article Travel-Time Difference Extracting in Experimental Study of Rayleigh Wave Acoustoelastic Effect
 ISRN Mechanical Engineering, Article ID 3492, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/3492 Research Article Travel-Time Difference Extracting in Experimental Study of Rayleigh Wave Acoustoelastic Effect Hu Eryi
ISRN Mechanical Engineering, Article ID 3492, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/3492 Research Article Travel-Time Difference Extracting in Experimental Study of Rayleigh Wave Acoustoelastic Effect Hu Eryi
Research Article The Microphone Feedback Analogy for Chatter in Machining
 Shock and Vibration Volume 215, Article ID 976819, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/976819 Research Article The Microphone Feedback Analogy for Chatter in Machining Tony Schmitz UniversityofNorthCarolinaatCharlotte,Charlotte,NC28223,USA
Shock and Vibration Volume 215, Article ID 976819, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/976819 Research Article The Microphone Feedback Analogy for Chatter in Machining Tony Schmitz UniversityofNorthCarolinaatCharlotte,Charlotte,NC28223,USA
Stochastic outlook of two non-identical unit parallel system with priority in repair
 STATISTICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Stochastic outlook of two non-identical unit parallel system with priority in repair Pramendra Singh Pundir 1, Rohit Patawa 1 and Puneet Kumar Gupta 1 * Received: 24 August
STATISTICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Stochastic outlook of two non-identical unit parallel system with priority in repair Pramendra Singh Pundir 1, Rohit Patawa 1 and Puneet Kumar Gupta 1 * Received: 24 August
Research Article A Deterministic Inventory Model of Deteriorating Items with Two Rates of Production, Shortages, and Variable Production Cycle
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 011, Article ID 657464, 16 pages doi:10.540/011/657464 Research Article A Deterministic Inventory Model of Deteriorating Items with
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 011, Article ID 657464, 16 pages doi:10.540/011/657464 Research Article A Deterministic Inventory Model of Deteriorating Items with
Research Article Partial Pole Placement in LMI Region
 Control Science and Engineering Article ID 84128 5 pages http://dxdoiorg/11155/214/84128 Research Article Partial Pole Placement in LMI Region Liuli Ou 1 Shaobo Han 2 Yongji Wang 1 Shuai Dong 1 and Lei
Control Science and Engineering Article ID 84128 5 pages http://dxdoiorg/11155/214/84128 Research Article Partial Pole Placement in LMI Region Liuli Ou 1 Shaobo Han 2 Yongji Wang 1 Shuai Dong 1 and Lei
Research Article The Application of Baum-Welch Algorithm in Multistep Attack
 e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 374260, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/374260 Research Article The Application of Baum-Welch Algorithm in Multistep Attack Yanxue Zhang, 1 Dongmei Zhao, 2
e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 374260, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/374260 Research Article The Application of Baum-Welch Algorithm in Multistep Attack Yanxue Zhang, 1 Dongmei Zhao, 2
Markov Reliability and Availability Analysis. Markov Processes
 Markov Reliability and Availability Analysis Firma convenzione Politecnico Part II: Continuous di Milano e Time Veneranda Discrete Fabbrica State del Duomo di Milano Markov Processes Aula Magna Rettorato
Markov Reliability and Availability Analysis Firma convenzione Politecnico Part II: Continuous di Milano e Time Veneranda Discrete Fabbrica State del Duomo di Milano Markov Processes Aula Magna Rettorato
International Journal on Mechanical Engineering and Robotics (IJMER)
 Cost- Benefit Analysis of Two Similar Cold Standby Satellite System subject to Failure due to leak in the Russian cryogenic engine and Failure caused by an anomaly on the Fuel Booster Turbo Pump (FBTP)
Cost- Benefit Analysis of Two Similar Cold Standby Satellite System subject to Failure due to leak in the Russian cryogenic engine and Failure caused by an anomaly on the Fuel Booster Turbo Pump (FBTP)
Research Letter An Algorithm to Generate Representations of System Identification Errors
 Research Letters in Signal Processing Volume 008, Article ID 5991, 4 pages doi:10.1155/008/5991 Research Letter An Algorithm to Generate Representations of System Identification Errors Wancheng Zhang and
Research Letters in Signal Processing Volume 008, Article ID 5991, 4 pages doi:10.1155/008/5991 Research Letter An Algorithm to Generate Representations of System Identification Errors Wancheng Zhang and
Research Article SGC Tests for Influence of Material Composition on Compaction Characteristic of Asphalt Mixtures
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 735640, 10 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/735640 Research Article SGC Tests for Influence of Material Composition on Compaction Characteristic
The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 735640, 10 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/735640 Research Article SGC Tests for Influence of Material Composition on Compaction Characteristic
Research Article A New Type of Magnetic Actuator Capable of Wall-Climbing Movement Using Inertia Force
 Engineering Volume 14, Article ID 93178, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/14/93178 Research Article A New Type of Magnetic Actuator Capable of Wall-Climbing Movement Using Inertia Force H. Yaguchi, S.
Engineering Volume 14, Article ID 93178, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/14/93178 Research Article A New Type of Magnetic Actuator Capable of Wall-Climbing Movement Using Inertia Force H. Yaguchi, S.
Research Article A Mathematical Images Group Model to Estimate the Sound Level in a Close-Fitting Enclosure
 Advances in Acoustics and Vibration, Article ID 284362, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/284362 Research Article A Mathematical Images Group Model to Estimate the Sound Level in a Close-Fitting Enclosure
Advances in Acoustics and Vibration, Article ID 284362, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/284362 Research Article A Mathematical Images Group Model to Estimate the Sound Level in a Close-Fitting Enclosure
Research Article Simplified Robotics Joint-Space Trajectory Generation with a via Point Using a Single Polynomial
 Robotics Volume, Article ID 75958, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55//75958 Research Article Simplified Robotics Joint-Space Trajectory Generation with a via Point Using a Single Polynomial Robert L. Williams
Robotics Volume, Article ID 75958, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55//75958 Research Article Simplified Robotics Joint-Space Trajectory Generation with a via Point Using a Single Polynomial Robert L. Williams
Research Article Two Mathematical Models for Generation of Crowned Tooth Surface
 e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 6409, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/204/6409 Research Article Two Mathematical Models for Generation of Crowned Tooth Surface Laszlo Kelemen and Jozsef Szente University
e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 6409, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/204/6409 Research Article Two Mathematical Models for Generation of Crowned Tooth Surface Laszlo Kelemen and Jozsef Szente University
ANALYSIS FOR A PARALLEL REPAIRABLE SYSTEM WITH DIFFERENT FAILURE MODES
 Journal of Reliability and Statistical Studies; ISSN (Print): 0974-8024, (Online):2229-5666, Vol. 5, Issue 1 (2012): 95-106 ANALYSIS FOR A PARALLEL REPAIRABLE SYSTEM WITH DIFFERENT FAILURE MODES M. A.
Journal of Reliability and Statistical Studies; ISSN (Print): 0974-8024, (Online):2229-5666, Vol. 5, Issue 1 (2012): 95-106 ANALYSIS FOR A PARALLEL REPAIRABLE SYSTEM WITH DIFFERENT FAILURE MODES M. A.
by: Mohammad El-Moniem Soleha
 Reliability and Availability Characteristics of A Two-Dissimilar-Unit Cold Standby System With three Modes by Using Linear First Order Differential Equations by: Mohammad El-Moniem Soleha ABSTRACT : This
Reliability and Availability Characteristics of A Two-Dissimilar-Unit Cold Standby System With three Modes by Using Linear First Order Differential Equations by: Mohammad El-Moniem Soleha ABSTRACT : This
Analysis of a Machine Repair System with Warm Spares and N-Policy Vacations
 The 7th International Symposium on Operations Research and Its Applications (ISORA 08) ijiang, China, October 31 Novemver 3, 2008 Copyright 2008 ORSC & APORC, pp. 190 198 Analysis of a Machine Repair System
The 7th International Symposium on Operations Research and Its Applications (ISORA 08) ijiang, China, October 31 Novemver 3, 2008 Copyright 2008 ORSC & APORC, pp. 190 198 Analysis of a Machine Repair System
Review Paper Machine Repair Problem with Spares and N-Policy Vacation
 Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-2502 Res.J.Recent Sci. Review Paper Machine Repair Problem with Spares and N-Policy Vacation Abstract Sharma D.C. School of Mathematics Statistics and Computational
Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-2502 Res.J.Recent Sci. Review Paper Machine Repair Problem with Spares and N-Policy Vacation Abstract Sharma D.C. School of Mathematics Statistics and Computational
Research Article Experimental Parametric Identification of a Flexible Beam Using Piezoelectric Sensors and Actuators
 Shock and Vibration, Article ID 71814, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/71814 Research Article Experimental Parametric Identification of a Flexible Beam Using Piezoelectric Sensors and Actuators Sajad
Shock and Vibration, Article ID 71814, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/71814 Research Article Experimental Parametric Identification of a Flexible Beam Using Piezoelectric Sensors and Actuators Sajad
Research Article Propagation Characteristics of Oblique Incident Terahertz Wave in Nonuniform Dusty Plasma
 Antennas and Propagation Volume 216, Article ID 945473, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/945473 Research Article Propagation Characteristics of Oblique Incident Terahert Wave in Nonuniform Dusty Plasma
Antennas and Propagation Volume 216, Article ID 945473, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/945473 Research Article Propagation Characteristics of Oblique Incident Terahert Wave in Nonuniform Dusty Plasma
Research Article Influence of the Parameterization in the Interval Solution of Elastic Beams
 Structures Volume 04, Article ID 3953, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/04/3953 Research Article Influence of the Parameterization in the Interval Solution of Elastic Beams Stefano Gabriele and Valerio Varano
Structures Volume 04, Article ID 3953, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/04/3953 Research Article Influence of the Parameterization in the Interval Solution of Elastic Beams Stefano Gabriele and Valerio Varano
Availability Analysis of Refining System of a Sugar Plant Using Markov Process
 Availability Analysis of Refining System of a Sugar Plant Using Markov Process Er. Aman 1, Dr. V.K. Mahna 2, Dr. Rajiv Khanduja 3 1 Research Scholar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, M.R.I.U., Faridabad,Haryana,
Availability Analysis of Refining System of a Sugar Plant Using Markov Process Er. Aman 1, Dr. V.K. Mahna 2, Dr. Rajiv Khanduja 3 1 Research Scholar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, M.R.I.U., Faridabad,Haryana,
Analysis for Parallel Repairable System with Degradation Facility
 American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics 212, 2(4): 7-74 DOI: 1.5923/j.ajms.21224.2 Analysis for Parallel Repairable System with Degradation Facility M. A. El-Damcese *, N. S. Temraz Department of
American Journal of Mathematics and Statistics 212, 2(4): 7-74 DOI: 1.5923/j.ajms.21224.2 Analysis for Parallel Repairable System with Degradation Facility M. A. El-Damcese *, N. S. Temraz Department of
Performance analysis of a juice packaging plant using BFT
 Malaya Journal of Matematik, Vol. S, No., -, 08 https://doi.org/0./mjm0s0/08 Performance analysis of a juice packaging plant using BFT Nitin Kumar Sharm *, Sachin Kumar and Neelam Sharm Abstract In this
Malaya Journal of Matematik, Vol. S, No., -, 08 https://doi.org/0./mjm0s0/08 Performance analysis of a juice packaging plant using BFT Nitin Kumar Sharm *, Sachin Kumar and Neelam Sharm Abstract In this
Unique Journal of Engineering and Advanced Sciences Available online: Research Article
 ISSN 2348-375X Unique Journal of Engineering and Advanced Sciences Available online: www.ujconline.net Research Article COST- BENEFIT ANALYSIS OF TWO DISSIMILAR WARM STANDBY SPACE SHUTTLE SYSTEM SUBJECT
ISSN 2348-375X Unique Journal of Engineering and Advanced Sciences Available online: www.ujconline.net Research Article COST- BENEFIT ANALYSIS OF TWO DISSIMILAR WARM STANDBY SPACE SHUTTLE SYSTEM SUBJECT
Research Article On the Security of a Novel Probabilistic Signature Based on Bilinear Square Diffie-Hellman Problem and Its Extension
 e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 345686, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/345686 Research Article On the Security of a Novel Probabilistic Signature Based on Bilinear Square Diffie-Hellman
e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 345686, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/345686 Research Article On the Security of a Novel Probabilistic Signature Based on Bilinear Square Diffie-Hellman
Comparison between four dissimilar solar panel configurations
 J Ind Eng Int () 49 48 DOI./s49--9-8 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparison between four dissimilar solar panel configurations K. Suleiman U. A. Ali, Ibrahim Yusuf A. D. Koko S. I. Bala Received 9 December 4 / Accepted
J Ind Eng Int () 49 48 DOI./s49--9-8 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparison between four dissimilar solar panel configurations K. Suleiman U. A. Ali, Ibrahim Yusuf A. D. Koko S. I. Bala Received 9 December 4 / Accepted
Dependable Computer Systems
 Dependable Computer Systems Part 3: Fault-Tolerance and Modelling Contents Reliability: Basic Mathematical Model Example Failure Rate Functions Probabilistic Structural-Based Modeling: Part 1 Maintenance
Dependable Computer Systems Part 3: Fault-Tolerance and Modelling Contents Reliability: Basic Mathematical Model Example Failure Rate Functions Probabilistic Structural-Based Modeling: Part 1 Maintenance
Research Article Numerical Study of Flutter of a Two-Dimensional Aeroelastic System
 ISRN Mechanical Volume 213, Article ID 127123, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/127123 Research Article Numerical Study of Flutter of a Two-Dimensional Aeroelastic System Riccy Kurniawan Department
ISRN Mechanical Volume 213, Article ID 127123, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/127123 Research Article Numerical Study of Flutter of a Two-Dimensional Aeroelastic System Riccy Kurniawan Department
Chapter 5. System Reliability and Reliability Prediction.
 Chapter 5. System Reliability and Reliability Prediction. Problems & Solutions. Problem 1. Estimate the individual part failure rate given a base failure rate of 0.0333 failure/hour, a quality factor of
Chapter 5. System Reliability and Reliability Prediction. Problems & Solutions. Problem 1. Estimate the individual part failure rate given a base failure rate of 0.0333 failure/hour, a quality factor of
Terminology and Concepts
 Terminology and Concepts Prof. Naga Kandasamy 1 Goals of Fault Tolerance Dependability is an umbrella term encompassing the concepts of reliability, availability, performability, safety, and testability.
Terminology and Concepts Prof. Naga Kandasamy 1 Goals of Fault Tolerance Dependability is an umbrella term encompassing the concepts of reliability, availability, performability, safety, and testability.
Fault Tolerance. Dealing with Faults
 Fault Tolerance Real-time computing systems must be fault-tolerant: they must be able to continue operating despite the failure of a limited subset of their hardware or software. They must also allow graceful
Fault Tolerance Real-time computing systems must be fault-tolerant: they must be able to continue operating despite the failure of a limited subset of their hardware or software. They must also allow graceful
Research Article Characterization and Modelling of LeBlanc Hydrodynamic Stabilizer: A Novel Approach for Steady and Transient State Models
 Modelling and Simulation in Engineering Volume 215, Article ID 729582, 11 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/729582 Research Article Characterization and Modelling of LeBlanc Hydrodynamic Stabilizer: A
Modelling and Simulation in Engineering Volume 215, Article ID 729582, 11 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/729582 Research Article Characterization and Modelling of LeBlanc Hydrodynamic Stabilizer: A
Research Article Estimation of Population Mean in Chain Ratio-Type Estimator under Systematic Sampling
 Probability and Statistics Volume 2015 Article ID 2837 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/2837 Research Article Estimation of Population Mean in Chain Ratio-Type Estimator under Systematic Sampling
Probability and Statistics Volume 2015 Article ID 2837 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/2837 Research Article Estimation of Population Mean in Chain Ratio-Type Estimator under Systematic Sampling
Availability Optimization for Coal Handling System using Genetic Algorithm
 International Journal of Performability Engineering Vol. 9, o. 1, January 21, pp. 19-1. RAMS Consultants Printed in India Availability Optimization for Coal Handling System using Genetic Algorithm SAJAY
International Journal of Performability Engineering Vol. 9, o. 1, January 21, pp. 19-1. RAMS Consultants Printed in India Availability Optimization for Coal Handling System using Genetic Algorithm SAJAY
STOCHASTIC REPAIR AND REPLACEMENT OF A STANDBY SYSTEM
 Journal of Mathematics and Statistics 0 (3): 384-389, 04 ISSN: 549-3644 04 doi:0.3844/jmssp.04.384.389 Published Online 0 (3) 04 (http://www.thescipub.com/jmss.toc) STOCHASTIC REPAIR AND REPLACEMENT OF
Journal of Mathematics and Statistics 0 (3): 384-389, 04 ISSN: 549-3644 04 doi:0.3844/jmssp.04.384.389 Published Online 0 (3) 04 (http://www.thescipub.com/jmss.toc) STOCHASTIC REPAIR AND REPLACEMENT OF
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Availability. M(t) = 1 - e -mt
 Availability Availability - A(t) the probability that the system is operating correctly and is available to perform its functions at the instant of time t More general concept than reliability: failure
Availability Availability - A(t) the probability that the system is operating correctly and is available to perform its functions at the instant of time t More general concept than reliability: failure
Reliability evaluation of a repairable system under fuzziness
 ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 12 (2016) No. 1, pp. 48-58 Reliability evaluation of a repairable system under fuzziness Kalika Patrai 1, Indu Uprety 2 1 Department
ISSN 1 746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 12 (2016) No. 1, pp. 48-58 Reliability evaluation of a repairable system under fuzziness Kalika Patrai 1, Indu Uprety 2 1 Department
Research Article Calculation for Primary Combustion Characteristics of Boron-Based Fuel-Rich Propellant Based on BP Neural Network
 Combustion Volume 2012, Article ID 635190, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/635190 Research Article Calculation for Primary Combustion Characteristics of Boron-Based Fuel-Rich Propellant Based on BP Neural Network
Combustion Volume 2012, Article ID 635190, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/635190 Research Article Calculation for Primary Combustion Characteristics of Boron-Based Fuel-Rich Propellant Based on BP Neural Network
STEADY-STATE BEHAVIOR OF AN M/M/1 QUEUE IN RANDOM ENVIRONMENT SUBJECT TO SYSTEM FAILURES AND REPAIRS. S. Sophia 1, B. Praba 2
 International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 101 No. 2 2015, 267-279 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.12732/ijpam.v101i2.11
International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 101 No. 2 2015, 267-279 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.12732/ijpam.v101i2.11
Research Article Band Structure Engineering in 2D Photonic Crystal Waveguide with Rhombic Cross-Section Elements
 Advances in Optical Technologies Volume 214, Article ID 78142, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1155/214/78142 Research Article Band Structure Engineering in 2D Photonic Crystal Waveguide with Rhombic Cross-Section
Advances in Optical Technologies Volume 214, Article ID 78142, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1155/214/78142 Research Article Band Structure Engineering in 2D Photonic Crystal Waveguide with Rhombic Cross-Section
Contents Preface The Exponential Distribution and the Poisson Process Introduction to Renewal Theory
 Contents Preface... v 1 The Exponential Distribution and the Poisson Process... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 The Density, the Distribution, the Tail, and the Hazard Functions... 2 1.2.1 The Hazard Function
Contents Preface... v 1 The Exponential Distribution and the Poisson Process... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 The Density, the Distribution, the Tail, and the Hazard Functions... 2 1.2.1 The Hazard Function
Research Article A Generalized Class of Exponential Type Estimators for Population Mean under Systematic Sampling Using Two Auxiliary Variables
 Probability and Statistics Volume 2016, Article ID 2374837, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2374837 Research Article A Generalized Class of Exponential Type Estimators for Population Mean under
Probability and Statistics Volume 2016, Article ID 2374837, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2374837 Research Article A Generalized Class of Exponential Type Estimators for Population Mean under
Reliable Computing I
 Instructor: Mehdi Tahoori Reliable Computing I Lecture 5: Reliability Evaluation INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING (ITEC) CHAIR FOR DEPENDABLE NANO COMPUTING (CDNC) National Research Center of the Helmholtz
Instructor: Mehdi Tahoori Reliable Computing I Lecture 5: Reliability Evaluation INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING (ITEC) CHAIR FOR DEPENDABLE NANO COMPUTING (CDNC) National Research Center of the Helmholtz
Research Article A Generalization of a Class of Matrices: Analytic Inverse and Determinant
 Advances in Numerical Analysis Volume 2011, Article ID 593548, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/593548 Research Article A Generalization of a Class of Matrices: Analytic Inverse and Determinant F. N. Valvi Department
Advances in Numerical Analysis Volume 2011, Article ID 593548, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/593548 Research Article A Generalization of a Class of Matrices: Analytic Inverse and Determinant F. N. Valvi Department
Research Article On the Charting Procedures: T 2 Chart and DD-Diagram
 Quality, Statistics, and Reliability Volume 2, Article ID 83764, 8 pages doi:.55/2/83764 Research Article On the Charting Procedures: T 2 Chart and DD-Diagram Mekki Hajlaoui Faculté des Sciences Economiques
Quality, Statistics, and Reliability Volume 2, Article ID 83764, 8 pages doi:.55/2/83764 Research Article On the Charting Procedures: T 2 Chart and DD-Diagram Mekki Hajlaoui Faculté des Sciences Economiques
Research Article Forward and Reverse Movements of a Linear Positioning Stage Based on the Parasitic Motion Principle
 Advances in Mechanical Engineering, Article ID 45256, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/45256 Research Article Forward and Reverse Movements of a Linear Positioning Stage Based on the Parasitic Motion
Advances in Mechanical Engineering, Article ID 45256, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/45256 Research Article Forward and Reverse Movements of a Linear Positioning Stage Based on the Parasitic Motion
Batch Arrival Queuing Models with Periodic Review
 Batch Arrival Queuing Models with Periodic Review R. Sivaraman Ph.D. Research Scholar in Mathematics Sri Satya Sai University of Technology and Medical Sciences Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh National Awardee
Batch Arrival Queuing Models with Periodic Review R. Sivaraman Ph.D. Research Scholar in Mathematics Sri Satya Sai University of Technology and Medical Sciences Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh National Awardee
Research Article Comprehensive Fractal Description of Porosity of Coal of Different Ranks
 e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 498, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/4/498 Research Article Comprehensive Fractal Description of Porosity of Coal of Different Ranks Jiangang Ren, Guocheng Zhang,,
e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 498, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/4/498 Research Article Comprehensive Fractal Description of Porosity of Coal of Different Ranks Jiangang Ren, Guocheng Zhang,,
Research Article Emissivity Measurement of Semitransparent Textiles
 Advances in Optical Technologies Volume 2012, Article ID 373926, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/373926 Research Article Emissivity Measurement of Semitransparent Textiles P. Bison, A. Bortolin, G. Cadelano,
Advances in Optical Technologies Volume 2012, Article ID 373926, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/373926 Research Article Emissivity Measurement of Semitransparent Textiles P. Bison, A. Bortolin, G. Cadelano,
Research Article A Partial Backlogging Inventory Model for Deteriorating Items with Fluctuating Selling Price and Purchasing Cost
 Advances in Operations Research Volume 2012, Article ID 385371, 15 pages doi:10.1155/2012/385371 Research Article A Partial Backlogging Inventory Model for Deteriorating Items with Fluctuating Selling
Advances in Operations Research Volume 2012, Article ID 385371, 15 pages doi:10.1155/2012/385371 Research Article A Partial Backlogging Inventory Model for Deteriorating Items with Fluctuating Selling
Quantitative evaluation of Dependability
 Quantitative evaluation of Dependability 1 Quantitative evaluation of Dependability Faults are the cause of errors and failures. Does the arrival time of faults fit a probability distribution? If so, what
Quantitative evaluation of Dependability 1 Quantitative evaluation of Dependability Faults are the cause of errors and failures. Does the arrival time of faults fit a probability distribution? If so, what
Multi-State Availability Modeling in Practice
 Multi-State Availability Modeling in Practice Kishor S. Trivedi, Dong Seong Kim, Xiaoyan Yin Depart ment of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708 USA kst@ee.duke.edu, {dk76,
Multi-State Availability Modeling in Practice Kishor S. Trivedi, Dong Seong Kim, Xiaoyan Yin Depart ment of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708 USA kst@ee.duke.edu, {dk76,
Research Article Study on Zero-Doppler Centroid Control for GEO SAR Ground Observation
 Antennas and Propagation Article ID 549269 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/549269 Research Article Study on Zero-Doppler Centroid Control for GEO SAR Ground Observation Yicheng Jiang Bin Hu Yun Zhang
Antennas and Propagation Article ID 549269 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/549269 Research Article Study on Zero-Doppler Centroid Control for GEO SAR Ground Observation Yicheng Jiang Bin Hu Yun Zhang
MODELLING AND ESTIMATION STUDY OF COMPLEX RELIABILITY SYSTEMS
 MODELLING AND ESTIMATION STUDY OF COMPLEX RELIABILITY SYSTEMS By SHAGUFTA ABBAS Submitted in accordance with the requirements For the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Industrial Systems Faculty of Engineering,
MODELLING AND ESTIMATION STUDY OF COMPLEX RELIABILITY SYSTEMS By SHAGUFTA ABBAS Submitted in accordance with the requirements For the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Industrial Systems Faculty of Engineering,
Research Article Trapped-Mode Resonance Regime of Thin Microwave Electromagnetic Arrays with Two Concentric Rings in Unit Cell
 Microwave Science and Technology Volume 2, Article ID 3688, 6 pages doi:.55/2/3688 Research Article Trapped-Mode Resonance Regime of Thin Microwave Electromagnetic Arrays with Two Concentric Rings in Unit
Microwave Science and Technology Volume 2, Article ID 3688, 6 pages doi:.55/2/3688 Research Article Trapped-Mode Resonance Regime of Thin Microwave Electromagnetic Arrays with Two Concentric Rings in Unit
Research Article On Counting and Embedding a Subclass of Height-Balanced Trees
 Modelling and Simulation in Engineering, Article ID 748941, 5 pages http://dxdoiorg/101155/2014/748941 Research Article On Counting and Embedding a Subclass of Height-Balanced Trees Indhumathi Raman School
Modelling and Simulation in Engineering, Article ID 748941, 5 pages http://dxdoiorg/101155/2014/748941 Research Article On Counting and Embedding a Subclass of Height-Balanced Trees Indhumathi Raman School
Dependable Systems. ! Dependability Attributes. Dr. Peter Tröger. Sources:
 Dependable Systems! Dependability Attributes Dr. Peter Tröger! Sources:! J.C. Laprie. Dependability: Basic Concepts and Terminology Eusgeld, Irene et al.: Dependability Metrics. 4909. Springer Publishing,
Dependable Systems! Dependability Attributes Dr. Peter Tröger! Sources:! J.C. Laprie. Dependability: Basic Concepts and Terminology Eusgeld, Irene et al.: Dependability Metrics. 4909. Springer Publishing,
RELIABILITY OF REPAIRABLE k out of n: F SYSTEM HAVING DISCRETE REPAIR AND FAILURE TIMES DISTRIBUTIONS
 www.arpapre.com/volume/vol29iue1/ijrras_29_1_01.pdf RELIABILITY OF REPAIRABLE k out of n: F SYSTEM HAVING DISCRETE REPAIR AND FAILURE TIMES DISTRIBUTIONS Sevcan Demir Atalay 1,* & Özge Elmataş Gültekin
www.arpapre.com/volume/vol29iue1/ijrras_29_1_01.pdf RELIABILITY OF REPAIRABLE k out of n: F SYSTEM HAVING DISCRETE REPAIR AND FAILURE TIMES DISTRIBUTIONS Sevcan Demir Atalay 1,* & Özge Elmataş Gültekin
9. Reliability theory
 Material based on original slides by Tuomas Tirronen ELEC-C720 Modeling and analysis of communication networks Contents Introduction Structural system models Reliability of structures of independent repairable
Material based on original slides by Tuomas Tirronen ELEC-C720 Modeling and analysis of communication networks Contents Introduction Structural system models Reliability of structures of independent repairable
Reliability analysis of a linear consecutive 2-out-of-3 system in the presence of supporting device and repairable service station
 International Journal of Operations Research International Journal of Operations Research Vol. 3, o., 3 4 (6) Reliability analysis of a linear consecutive -out-of-3 system in the presence of supporting
International Journal of Operations Research International Journal of Operations Research Vol. 3, o., 3 4 (6) Reliability analysis of a linear consecutive -out-of-3 system in the presence of supporting
STOCHASTIC MODELS FOR RELIABILITY, AVAILABILITY, AND MAINTAINABILITY
 STOCHASTIC MODELS FOR RELIABILITY, AVAILABILITY, AND MAINTAINABILITY Ph.D. Assistant Professor Industrial and Systems Engineering Auburn University RAM IX Summit November 2 nd 2016 Outline Introduction
STOCHASTIC MODELS FOR RELIABILITY, AVAILABILITY, AND MAINTAINABILITY Ph.D. Assistant Professor Industrial and Systems Engineering Auburn University RAM IX Summit November 2 nd 2016 Outline Introduction
Reliability and Availability Analysis of Uncaser System in A Brewary Plant
 IJRMET Vo l. 2, Is s u e 2, Ma y - Oc t 2012 ISSN : 2249-5762 (Online ISSN : 2249-5770 (Print Reliability and Availability Analysis of Uncaser System in A Brewary Plant 1 Sunil Kadiyan, 2 Dr. R. K. Garg,
IJRMET Vo l. 2, Is s u e 2, Ma y - Oc t 2012 ISSN : 2249-5762 (Online ISSN : 2249-5770 (Print Reliability and Availability Analysis of Uncaser System in A Brewary Plant 1 Sunil Kadiyan, 2 Dr. R. K. Garg,
Real-time Systems: Scheduling Periodic Tasks
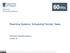 Real-time Systems: Scheduling Periodic Tasks Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 15 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view a copy of
Real-time Systems: Scheduling Periodic Tasks Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 15 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view a copy of
International Journal on Mechanical Engineering and Robotics (IJMER)
 Cost-Benefit Analysis of Two Similar Warm Standby system subject to India losing component and failure caused by an anomaly on the Fuel Booster Turbo Pump (FBTP) of the third stage Ashok Kumar Saini Assoc.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Two Similar Warm Standby system subject to India losing component and failure caused by an anomaly on the Fuel Booster Turbo Pump (FBTP) of the third stage Ashok Kumar Saini Assoc.
A Markov model for estimating the remaining life of electrical insulation in distribution transformer
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH 2010, Science Huβ, http://www.scihub.org/ajsir ISSN: 2153-649X doi:10.5251/ajsir.2010.1.3.539.548 A Markov model for estimating the remaining life
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH 2010, Science Huβ, http://www.scihub.org/ajsir ISSN: 2153-649X doi:10.5251/ajsir.2010.1.3.539.548 A Markov model for estimating the remaining life
Cost Analtsis for a Nuclear Power Plant with Standby Redundant Reactor Vessel
 Research Journal of Mathematics and Statistics 2(3): 91-96, 2010 ISSN: 2040-7505 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2010 Submitted Date: March 09, 2010 Accepted Date: April 30, 2010 Published Date: September
Research Journal of Mathematics and Statistics 2(3): 91-96, 2010 ISSN: 2040-7505 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2010 Submitted Date: March 09, 2010 Accepted Date: April 30, 2010 Published Date: September
Research Article Efficient Estimators Using Auxiliary Variable under Second Order Approximation in Simple Random Sampling and Two-Phase Sampling
 Advances in Statistics, Article ID 974604, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/204/974604 Research Article Efficient Estimators Using Auxiliary Variable under Second Order Approximation in Simple Random Sampling
Advances in Statistics, Article ID 974604, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/204/974604 Research Article Efficient Estimators Using Auxiliary Variable under Second Order Approximation in Simple Random Sampling
