16.1 Hooke s Law: Stress and Strain Revisited
|
|
|
- Brenda Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 550 CHAPTER 16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES Introduction to Oscillatory Motion and Waves What do an ocean buoy, a child in a swing, the cone inside a speaker, a guitar, atoms in a crystal, the motion of chest cavities, and the beating of hearts all have in common? They all oscillate -that is, they move back and forth between two points. Many systems oscillate, and they have certain characteristics in common. All oscillations involve force and energy. You push a child in a swing to get the motion started. The energy of atoms vibrating in a crystal can be increased with heat. You put energy into a guitar string when you pluck it. Some oscillations create waves. A guitar creates sound waves. You can make water waves in a swimming pool by slapping the water with your hand. You can no doubt think of other types of waves. Some, such as water waves, are visible. Some, such as sound waves, are not. But every wave is a disturbance that moves from its source and carries energy. Other examples of waves include earthquakes and visible light. Even subatomic particles, such as electrons, can behave like waves. By studying oscillatory motion and waves, we shall find that a small number of underlying principles describe all of them and that wave phenomena are more common than you have ever imagined. We begin by studying the type of force that underlies the simplest oscillations and waves. We will then expand our exploration of oscillatory motion and waves to include concepts such as simple harmonic motion, uniform circular motion, and damped harmonic motion. Finally, we will explore what happens when two or more waves share the same space, in the phenomena known as superposition and interference Hooke s Law: Stress and Strain Revisited Figure 16.2 When displaced from its vertical equilibrium position, this plastic ruler oscillates back and forth because of the restoring force opposing displacement. When the ruler is on the left, there is a force to the right, and vice versa. Newton s first law implies that an object oscillating back and forth is experiencing forces. Without force, the object would move in a straight line at a constant speed rather than oscillate. Consider, for example, plucking a plastic ruler to the left as shown in Figure The deformation of the ruler creates a force in the opposite direction, known as a restoring force. Once released, the restoring force causes the ruler to move back toward its stable equilibrium position, where the net force on it is zero. However, by the time the ruler gets there, it gains momentum and continues to move to the right, producing the opposite deformation. It is then forced to the left, back through equilibrium, and the process is repeated until dissipative forces dampen the motion. These forces remove mechanical energy from the system, gradually reducing the motion until the ruler comes to rest. The simplest oscillations occur when the restoring force is directly proportional to displacement. When stress and strain were covered in Newton s Third Law of Motion, the name was given to this relationship between force and displacement was Hooke s law: F = kx. Here, F is the restoring force, x is the displacement from equilibrium or deformation, and k is a constant related to the difficulty in deforming the system. The minus sign indicates the restoring force is in the direction opposite to the displacement. (16.1) Figure 16.3 (a) The plastic ruler has been released, and the restoring force is returning the ruler to its equilibrium position. (b) The net force is zero at the equilibrium position, but the ruler has momentum and continues to move to the right. (c) The restoring force is in the opposite direction. It stops the ruler and moves it back toward equilibrium again. (d) Now the ruler has momentum to the left. (e) In the absence of damping (caused by frictional forces), the ruler reaches its original position. From there, the motion will repeat itself. The force constant k is related to the rigidity (or stiffness) of a system the larger the force constant, the greater the restoring force, and the stiffer the system. The units of k are newtons per meter (N/m). For example, k is directly related to Young s modulus when we stretch a string. Figure 16.4 shows a graph of the absolute value of the restoring force versus the displacement for a system that can be described by Hooke s law a simple spring in this case. The slope of the graph equals the force constant k in newtons per meter. A common physics laboratory exercise is to measure restoring forces created by springs, determine if they follow Hooke s law, and calculate their force constants if they do.
2 CHAPTER 16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES 551 Figure 16.4 (a) A graph of absolute value of the restoring force versus displacement is displayed. The fact that the graph is a straight line means that the system obeys Hooke s law. The slope of the graph is the force constant k. (b) The data in the graph were generated by measuring the displacement of a spring from equilibrium while supporting various weights. The restoring force equals the weight supported, if the mass is stationary. Example 16.1 How Stiff Are Car Springs? Figure 16.5 The mass of a car increases due to the introduction of a passenger. This affects the displacement of the car on its suspension system. (credit: exfordy on Flickr) What is the force constant for the suspension system of a car that settles 1.20 cm when an 80.0-kg person gets in? Strategy Consider the car to be in its equilibrium position x = 0 before the person gets in. The car then settles down 1.20 cm, which means it is displaced to a position x = m. At that point, the springs supply a restoring force F equal to the person s weight w = mg = 80.0 kg 9.80 m/s 2 = 784 N. We take this force to be F in Hooke s law. Knowing F and x, we can then solve the force constant k. Solution 1. Solve Hooke s law, F = kx, for k :
3 552 CHAPTER 16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES Substitute known values and solve k : Discussion k = F x. k = 784 N m = N/m. (16.2) (16.3) Note that F and x have opposite signs because they are in opposite directions the restoring force is up, and the displacement is down. Also, note that the car would oscillate up and down when the person got in if it were not for damping (due to frictional forces) provided by shock absorbers. Bouncing cars are a sure sign of bad shock absorbers. Energy in Hooke s Law of Deformation In order to produce a deformation, work must be done. That is, a force must be exerted through a distance, whether you pluck a guitar string or compress a car spring. If the only result is deformation, and no work goes into thermal, sound, or kinetic energy, then all the work is initially stored in the deformed object as some form of potential energy. The potential energy stored in a spring is PE el = 1 2 kx 2. Here, we generalize the idea to elastic potential energy for a deformation of any system that can be described by Hooke s law. Hence, PE el = 1 2 kx 2, (16.4) where PE el is the elastic potential energy stored in any deformed system that obeys Hooke s law and has a displacement x from equilibrium and a force constant k. It is possible to find the work done in deforming a system in order to find the energy stored. This work is performed by an applied force F app. The applied force is exactly opposite to the restoring force (action-reaction), and so F app = kx. Figure 16.6 shows a graph of the applied force versus deformation x for a system that can be described by Hooke s law. Work done on the system is force multiplied by distance, which equals the area under the curve or (1 / 2)kx 2 (Method A in the figure). Another way to determine the work is to note that the force increases linearly from 0 to kx, so that the average force is (1 / 2)kx, the distance moved is x, and thus W = F app d = [(1 / 2)kx](x) = (1 / 2)kx 2 (Method B in the figure). Figure 16.6 A graph of applied force versus distance for the deformation of a system that can be described by Hooke s law is displayed. The work done on the system equals the area under the graph or the area of the triangle, which is half its base multiplied by its height, or W = (1 / 2)kx 2. Example 16.2 Calculating Stored Energy: A Tranquilizer Gun Spring We can use a toy gun s spring mechanism to ask and answer two simple questions: (a) How much energy is stored in the spring of a tranquilizer gun that has a force constant of 50.0 N/m and is compressed m? (b) If you neglect friction and the mass of the spring, at what speed will a 2.00-g projectile be ejected from the gun?
4 CHAPTER 16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES 553 Figure 16.7 (a) In this image of the gun, the spring is uncompressed before being cocked. (b) The spring has been compressed a distance x, and the projectile is in place. (c) When released, the spring converts elastic potential energy PE el into kinetic energy. Strategy for a (a): The energy stored in the spring can be found directly from elastic potential energy equation, because k and x are given. Solution for a Entering the given values for k and x yields Strategy for b PE el = 1 2 kx 2 = 1 2 (50.0 N/m)(0.150 m)2 = N m = J Because there is no friction, the potential energy is converted entirely into kinetic energy. The expression for kinetic energy can be solved for the projectile s speed. Solution for b 1. Identify known quantities: 2. Solve for v : 3. Convert units: 23.7 m / s Discussion KE f = PE el or 1 / 2mv 2 = (1 / 2)kx 2 = PE el = J v = el 2PE 1 / 2 m = 2(0.563 J) kg 1 / 2 = 23.7 J/kg 1 / 2 (a) and (b): This projectile speed is impressive for a tranquilizer gun (more than 80 km/h). The numbers in this problem seem reasonable. The force needed to compress the spring is small enough for an adult to manage, and the energy imparted to the dart is small enough to limit the damage it might do. Yet, the speed of the dart is great enough for it to travel an acceptable distance. (16.5) (16.6) (16.7) Check your Understanding Envision holding the end of a ruler with one hand and deforming it with the other. When you let go, you can see the oscillations of the ruler. In what way could you modify this simple experiment to increase the rigidity of the system? Solution You could hold the ruler at its midpoint so that the part of the ruler that oscillates is half as long as in the original experiment. Check your Understanding If you apply a deforming force on an object and let it come to equilibrium, what happened to the work you did on the system? Solution It was stored in the object as potential energy.
5 582 CHAPTER 16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES Constructive interference occurs when two identical waves are superimposed in phase. Destructive interference occurs when two identical waves are superimposed exactly out of phase. A standing wave is one in which two waves superimpose to produce a wave that varies in amplitude but does not propagate. Nodes are points of no motion in standing waves. An antinode is the location of maximum amplitude of a standing wave. Waves on a string are resonant standing waves with a fundamental frequency and can occur at higher multiples of the fundamental, called overtones or harmonics. Beats occur when waves of similar frequencies f 1 and f 2 are superimposed. The resulting amplitude oscillates with a beat frequency given by Energy in Waves: Intensity Intensity is defined to be the power per unit area: I = P A and has units of W/m2. Conceptual Questions 16.1 Hooke s Law: Stress and Strain Revisited 1. Describe a system in which elastic potential energy is stored Simple Harmonic Motion: A Special Periodic Motion 2. What conditions must be met to produce simple harmonic motion? f B = f 1 f (a) If frequency is not constant for some oscillation, can the oscillation be simple harmonic motion? (b) Can you think of any examples of harmonic motion where the frequency may depend on the amplitude? 4. Give an example of a simple harmonic oscillator, specifically noting how its frequency is independent of amplitude. 5. Explain why you expect an object made of a stiff material to vibrate at a higher frequency than a similar object made of a spongy material. 6. As you pass a freight truck with a trailer on a highway, you notice that its trailer is bouncing up and down slowly. Is it more likely that the trailer is heavily loaded or nearly empty? Explain your answer. 7. Some people modify cars to be much closer to the ground than when manufactured. Should they install stiffer springs? Explain your answer The Simple Pendulum 8. Pendulum clocks are made to run at the correct rate by adjusting the pendulum s length. Suppose you move from one city to another where the acceleration due to gravity is slightly greater, taking your pendulum clock with you, will you have to lengthen or shorten the pendulum to keep the correct time, other factors remaining constant? Explain your answer Energy and the Simple Harmonic Oscillator 9. Explain in terms of energy how dissipative forces such as friction reduce the amplitude of a harmonic oscillator. Also explain how a driving mechanism can compensate. (A pendulum clock is such a system.) 16.7 Damped Harmonic Motion 10. Give an example of a damped harmonic oscillator. (They are more common than undamped or simple harmonic oscillators.) 11. How would a car bounce after a bump under each of these conditions? overdamping underdamping critical damping 12. Most harmonic oscillators are damped and, if undriven, eventually come to a stop. How is this observation related to the second law of thermodynamics? 16.8 Forced Oscillations and Resonance 13. Why are soldiers in general ordered to route step (walk out of step) across a bridge? 16.9 Waves 14. Give one example of a transverse wave and another of a longitudinal wave, being careful to note the relative directions of the disturbance and wave propagation in each. 15. What is the difference between propagation speed and the frequency of a wave? Does one or both affect wavelength? If so, how? Superposition and Interference 16. Speakers in stereo systems have two color-coded terminals to indicate how to hook up the wires. If the wires are reversed, the speaker moves in a direction opposite that of a properly connected speaker. Explain why it is important to have both speakers connected the same way Energy in Waves: Intensity
6 584 CHAPTER 16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES Problems & Exercises 16.1 Hooke s Law: Stress and Strain Revisited 1. Fish are hung on a spring scale to determine their mass (most fishermen feel no obligation to truthfully report the mass). (a) What is the force constant of the spring in such a scale if it the spring stretches 8.00 cm for a 10.0 kg load? (b) What is the mass of a fish that stretches the spring 5.50 cm? (c) How far apart are the half-kilogram marks on the scale? 2. It is weigh-in time for the local under-85-kg rugby team. The bathroom scale used to assess eligibility can be described by Hooke s law and is depressed 0.75 cm by its maximum load of 120 kg. (a) What is the spring s effective spring constant? (b) A player stands on the scales and depresses it by 0.48 cm. Is he eligible to play on this under-85 kg team? 3. One type of BB gun uses a spring-driven plunger to blow the BB from its barrel. (a) Calculate the force constant of its plunger s spring if you must compress it m to drive the kg plunger to a top speed of 20.0 m/s. (b) What force must be exerted to compress the spring? 4. (a) The springs of a pickup truck act like a single spring with a force constant of N/m. By how much will the truck be depressed by its maximum load of 1000 kg? (b) If the pickup truck has four identical springs, what is the force constant of each? 5. When an 80.0-kg man stands on a pogo stick, the spring is compressed m. (a) What is the force constant of the spring? (b) Will the spring be compressed more when he hops down the road? 6. A spring has a length of m when a kg mass hangs from it, and a length of m when a 1.95-kg mass hangs from it. (a) What is the force constant of the spring? (b) What is the unloaded length of the spring? 15. A kg mass suspended from a spring oscillates with a period of 1.50 s. How much mass must be added to the object to change the period to 2.00 s? 16. By how much leeway (both percentage and mass) would you have in the selection of the mass of the object in the previous problem if you did not wish the new period to be greater than 2.01 s or less than 1.99 s? 17. Suppose you attach the object with mass m to a vertical spring originally at rest, and let it bounce up and down. You release the object from rest at the spring s original rest length. (a) Show that the spring exerts an upward force of 2.00 mg on the object at its lowest point. (b) If the spring has a force constant of 10.0 N/m and a 0.25-kg-mass object is set in motion as described, find the amplitude of the oscillations. (c) Find the maximum velocity. 18. A diver on a diving board is undergoing simple harmonic motion. Her mass is 55.0 kg and the period of her motion is s. The next diver is a male whose period of simple harmonic oscillation is 1.05 s. What is his mass if the mass of the board is negligible? 19. Suppose a diving board with no one on it bounces up and down in a simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 4.00 Hz. The board has an effective mass of 10.0 kg. What is the frequency of the simple harmonic motion of a 75.0-kg diver on the board? Period and Frequency in Oscillations 7. What is the period of 60.0 Hz electrical power? 8. If your heart rate is 150 beats per minute during strenuous exercise, what is the time per beat in units of seconds? 9. Find the frequency of a tuning fork that takes s to complete one oscillation. 10. A stroboscope is set to flash every s. What is the frequency of the flashes? 11. A tire has a tread pattern with a crevice every 2.00 cm. Each crevice makes a single vibration as the tire moves. What is the frequency of these vibrations if the car moves at 30.0 m/s? 12. Engineering Application Each piston of an engine makes a sharp sound every other revolution of the engine. (a) How fast is a race car going if its eight-cylinder engine emits a sound of frequency 750 Hz, given that the engine makes 2000 revolutions per kilometer? (b) At how many revolutions per minute is the engine rotating? 16.3 Simple Harmonic Motion: A Special Periodic Motion 13. A type of cuckoo clock keeps time by having a mass bouncing on a spring, usually something cute like a cherub in a chair. What force constant is needed to produce a period of s for a kg mass? 14. If the spring constant of a simple harmonic oscillator is doubled, by what factor will the mass of the system need to change in order for the frequency of the motion to remain the same? Figure This child s toy relies on springs to keep infants entertained. (credit: By Humboldthead, Flickr) The device pictured in Figure entertains infants while keeping them from wandering. The child bounces in a harness suspended from a door frame by a spring constant. (a) If the spring stretches m while supporting an 8.0-kg child, what is its spring constant? (b) What is the time for one complete bounce of this child? (c) What is the child s maximum velocity if the amplitude of her bounce is m? 21. A 90.0-kg skydiver hanging from a parachute bounces up and down with a period of 1.50 s. What is the new period of oscillation when a second skydiver, whose mass is 60.0 kg, hangs from the legs of the first, as seen in Figure
Hooke's Law: Stress and Strain Revisited *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42240 1 Hooke's Law: Stress and Strain Revisited * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain
OpenStax-CNX module: m42240 1 Hooke's Law: Stress and Strain Revisited * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain
Simple Harmonic Motion: A Special Periodic Motion
 Simple Harmonic Motion: A Special Periodic Motion Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The oscillations of a system in which the net force can be described by Hooke s law are of special importance, because they are very
Simple Harmonic Motion: A Special Periodic Motion Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The oscillations of a system in which the net force can be described by Hooke s law are of special importance, because they are very
Simple Harmonic Motion: A Special Periodic Motion
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42242 1 Simple Harmonic Motion: A Special Periodic Motion OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract
OpenStax-CNX module: m42242 1 Simple Harmonic Motion: A Special Periodic Motion OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract
16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES
 Chapter 16 Oscillatory Motion and Waves 603 16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES Figure 16.1 There are at least four types of waves in this picture only the water waves are evident. There are also sound waves,
Chapter 16 Oscillatory Motion and Waves 603 16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES Figure 16.1 There are at least four types of waves in this picture only the water waves are evident. There are also sound waves,
16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES
 CHAPTER 16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES 549 16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES Figure 16.1 There are at least four types of waves in this picture only the water waves are evident. There are also sound waves,
CHAPTER 16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES 549 16 OSCILLATORY MOTION AND WAVES Figure 16.1 There are at least four types of waves in this picture only the water waves are evident. There are also sound waves,
College Physics. This document is attributed to: Dr. Paul Peter Urone and Dr. Roger Hinrichs. Chapter 16. Oscillatory Motion and Waves
 College Physics This document is attributed to: Dr. Paul Peter Urone and Dr. Roger Hinrichs Chapter 16. Oscillatory Motion and Waves OPEN ASSEMBLY EDITION OPEN ASSEMBLY editions of Open Textbooks have
College Physics This document is attributed to: Dr. Paul Peter Urone and Dr. Roger Hinrichs Chapter 16. Oscillatory Motion and Waves OPEN ASSEMBLY EDITION OPEN ASSEMBLY editions of Open Textbooks have
Simple Harmonic Motion *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m54154 1 Simple Harmonic Motion * OpenStax HS Physics This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 : By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m54154 1 Simple Harmonic Motion * OpenStax HS Physics This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 : By the end of this section,
Chapter 16: Oscillatory Motion and Waves. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
 Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
700 Chapter 16 Oscillatory Motion and Waves
 700 Chapter 16 Oscillatory Motion and Waves Check Your Understanding A famous magic trick involves a performer singing a note toward a crystal glass until the glass shatters. Explain why the trick works
700 Chapter 16 Oscillatory Motion and Waves Check Your Understanding A famous magic trick involves a performer singing a note toward a crystal glass until the glass shatters. Explain why the trick works
Chapter 12 Vibrations and Waves Simple Harmonic Motion page
 Chapter 2 Vibrations and Waves 2- Simple Harmonic Motion page 438-45 Hooke s Law Periodic motion the object has a repeated motion that follows the same path, the object swings to and fro. Examples: a pendulum
Chapter 2 Vibrations and Waves 2- Simple Harmonic Motion page 438-45 Hooke s Law Periodic motion the object has a repeated motion that follows the same path, the object swings to and fro. Examples: a pendulum
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
 CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Chapter 13, Vibrations and Waves. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to compress it only m. What is the spring constant of the spring?
 CHAPTER 13 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to compress it only 0.010 m. What is the spring constant of the spring? a. 125 000 N/m b. 15 000 N/m c. 15 N/m d. 1.5 N/m 2. A 0.20-kg object is attached
CHAPTER 13 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to compress it only 0.010 m. What is the spring constant of the spring? a. 125 000 N/m b. 15 000 N/m c. 15 N/m d. 1.5 N/m 2. A 0.20-kg object is attached
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984
 Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Chapter 13. Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition. Next Week!
 Chapter 13 Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition Next Week! Review Physics 2A: Springs, Pendula & Circular Motion Elastic Systems F = kx Small Vibrations
Chapter 13 Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition Next Week! Review Physics 2A: Springs, Pendula & Circular Motion Elastic Systems F = kx Small Vibrations
Chapter 16 Lectures. Oscillatory Motion and Waves
 Chapter 16 Lectures January-06-18 5:48 PM Oscillatory Motion and Waves Oscillations are back-and-forth motions. Sometimes the word vibration is used in place of oscillation; for our purposes, we can consider
Chapter 16 Lectures January-06-18 5:48 PM Oscillatory Motion and Waves Oscillations are back-and-forth motions. Sometimes the word vibration is used in place of oscillation; for our purposes, we can consider
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. The student is expected to:
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. Chapter 11. Preview. Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
2016 AP Physics Unit 6 Oscillations and Waves.notebook December 09, 2016
 AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
Work. Work and Energy Examples. Energy. To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or:
 Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Simple Harmonic Motion Test Tuesday 11/7
 Simple Harmonic Motion Test Tuesday 11/7 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 1 If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is
Simple Harmonic Motion Test Tuesday 11/7 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 1 If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is
Outline. Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves
 Outline Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves Hooke s Law Force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the equilibrium
Outline Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves Hooke s Law Force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the equilibrium
1. a) A flag waving in the breeze flaps once each s. What is the period and frequency of the flapping flag?
 PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
Lectures Chapter 10 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition)
 PH 201-4A spring 2007 Simple Harmonic Motion Lectures 24-25 Chapter 10 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 The Ideal Spring Springs are objects that exhibit elastic behavior. It will return back
PH 201-4A spring 2007 Simple Harmonic Motion Lectures 24-25 Chapter 10 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 The Ideal Spring Springs are objects that exhibit elastic behavior. It will return back
PHYSICS 1 Simple Harmonic Motion
 Advanced Placement PHYSICS 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Student 014-015 What I Absolutely Have to Know to Survive the AP* Exam Whenever the acceleration of an object is proportional to its displacement and
Advanced Placement PHYSICS 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Student 014-015 What I Absolutely Have to Know to Survive the AP* Exam Whenever the acceleration of an object is proportional to its displacement and
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA G.F. ABELA JUNIOR COLLEGE
 UNIVERSITY OF MALTA G.F. ABELA JUNIOR COLLEGE FIRST YEAR END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATION SUBJECT: PHYSICS DATE: JUNE 2010 LEVEL: INTERMEDIATE TIME: 09.00h to 12.00h Show ALL working Write units where appropriate
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA G.F. ABELA JUNIOR COLLEGE FIRST YEAR END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATION SUBJECT: PHYSICS DATE: JUNE 2010 LEVEL: INTERMEDIATE TIME: 09.00h to 12.00h Show ALL working Write units where appropriate
CHAPTER 7: OSCILLATORY MOTION REQUIRES A SET OF CONDITIONS
 CHAPTER 7: OSCILLATORY MOTION REQUIRES A SET OF CONDITIONS 7.1 Period and Frequency Anything that vibrates or repeats its motion regularly is said to have oscillatory motion (sometimes called harmonic
CHAPTER 7: OSCILLATORY MOTION REQUIRES A SET OF CONDITIONS 7.1 Period and Frequency Anything that vibrates or repeats its motion regularly is said to have oscillatory motion (sometimes called harmonic
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille. Chapter Thirteen. Vibrations and Waves
 Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Thirteen Vibrations and Waves Periodic Motion and Waves Periodic motion is one of the most important kinds of physical behavior Will include a closer look at Hooke
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Thirteen Vibrations and Waves Periodic Motion and Waves Periodic motion is one of the most important kinds of physical behavior Will include a closer look at Hooke
Oscillation the vibration of an object. Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter
 Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Chapter 14: Periodic motion
 Chapter 14: Periodic motion Describing oscillations Simple harmonic motion Energy of simple harmonic motion Applications of simple harmonic motion Simple pendulum & physical pendulum Damped oscillations
Chapter 14: Periodic motion Describing oscillations Simple harmonic motion Energy of simple harmonic motion Applications of simple harmonic motion Simple pendulum & physical pendulum Damped oscillations
Test, Lesson 7 Waves - Answer Key Page 1
 Test, Lesson 7 Waves - Answer Key Page 1 1. Match the proper units with the following: W. wavelength 1. nm F. frequency 2. /sec V. velocity 3. m 4. ms -1 5. Hz 6. m/sec (A) W: 1, 3 F: 2, 4, 5 V: 6 (B)
Test, Lesson 7 Waves - Answer Key Page 1 1. Match the proper units with the following: W. wavelength 1. nm F. frequency 2. /sec V. velocity 3. m 4. ms -1 5. Hz 6. m/sec (A) W: 1, 3 F: 2, 4, 5 V: 6 (B)
Harmonic Oscillator. Mass-Spring Oscillator Resonance The Pendulum. Physics 109 Experiment Number 12
 Harmonic Oscillator Mass-Spring Oscillator Resonance The Pendulum Physics 109 Experiment Number 12 Outline Simple harmonic motion The vertical mass-spring system Driven oscillations and resonance The pendulum
Harmonic Oscillator Mass-Spring Oscillator Resonance The Pendulum Physics 109 Experiment Number 12 Outline Simple harmonic motion The vertical mass-spring system Driven oscillations and resonance The pendulum
AP Physics 1 Multiple Choice Questions - Chapter 9
 1 If an object of mass m attached to a light spring is replaced by one of mass 9m, the frequency of the vibrating system changes by what multiplicative factor? a 1/9 b 1/3 c 3 d 9 e 6 2 A mass of 0.40
1 If an object of mass m attached to a light spring is replaced by one of mass 9m, the frequency of the vibrating system changes by what multiplicative factor? a 1/9 b 1/3 c 3 d 9 e 6 2 A mass of 0.40
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations
 Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Chapter 10: Simple Harmonic Motion
 Chapter 10: Simple Harmonic Motion Oscillations are back-and forth motions. Sometimes the word vibration is used in place of oscillation; for our purposes, we can consider the two words to represent the
Chapter 10: Simple Harmonic Motion Oscillations are back-and forth motions. Sometimes the word vibration is used in place of oscillation; for our purposes, we can consider the two words to represent the
Unit 2: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
 Unit 2: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) THE MOST COMMON FORM OF MOTION FALL 2015 Objectives: Define SHM specifically and give an example. Write and apply formulas for finding the frequency f, period T, w
Unit 2: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) THE MOST COMMON FORM OF MOTION FALL 2015 Objectives: Define SHM specifically and give an example. Write and apply formulas for finding the frequency f, period T, w
AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to
Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to
Chapter 14 Oscillations
 Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Chapter 15. Oscillatory Motion
 Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion Part 2 Oscillations and Mechanical Waves Periodic motion is the repeating motion of an object in which it continues to return to a given position after a fixed time interval.
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion Part 2 Oscillations and Mechanical Waves Periodic motion is the repeating motion of an object in which it continues to return to a given position after a fixed time interval.
C. points X and Y only. D. points O, X and Y only. (Total 1 mark)
 Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
The maximum kinetic energy is directly proportional to the frequency. The time for one oscillation is directly proportional to the frequency.
 Q1.For a body performing simple harmonic motion, which one of the following statements is correct? The maximum kinetic energy is directly proportional to the frequency. The time for one oscillation is
Q1.For a body performing simple harmonic motion, which one of the following statements is correct? The maximum kinetic energy is directly proportional to the frequency. The time for one oscillation is
Chapter 16: Oscillations
 Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
PHYS 1114, Lecture 33, April 10 Contents:
 PHYS 1114, Lecture 33, April 10 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, and has been replaced by the common exam Tuesday, April 11, 5:30 PM. A review and Q&A session is scheduled instead during class
PHYS 1114, Lecture 33, April 10 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, and has been replaced by the common exam Tuesday, April 11, 5:30 PM. A review and Q&A session is scheduled instead during class
Simple Harmonic Motion Investigating a Mass Oscillating on a Spring
 17 Investigating a Mass Oscillating on a Spring A spring that is hanging vertically from a support with no mass at the end of the spring has a length L (called its rest length). When a mass is added to
17 Investigating a Mass Oscillating on a Spring A spring that is hanging vertically from a support with no mass at the end of the spring has a length L (called its rest length). When a mass is added to
Chapter 13. Simple Harmonic Motion
 Chapter 13 Simple Harmonic Motion Hooke s Law F s = - k x F s is the spring force k is the spring constant It is a measure of the stiffness of the spring A large k indicates a stiff spring and a small
Chapter 13 Simple Harmonic Motion Hooke s Law F s = - k x F s is the spring force k is the spring constant It is a measure of the stiffness of the spring A large k indicates a stiff spring and a small
Grade XI. Physics Exam Preparation Booklet. Chapter-wise Important Questions. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Mass on a Horizontal Spring
 Course- B.Sc. Applied Physical Science (Computer Science) Year- IInd, Sem- IVth Subject Physics Paper- XIVth, Electromagnetic Theory Lecture No. 22, Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction Hello friends in
Course- B.Sc. Applied Physical Science (Computer Science) Year- IInd, Sem- IVth Subject Physics Paper- XIVth, Electromagnetic Theory Lecture No. 22, Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction Hello friends in
NARAYANA JUNIOR COLLEGE
 SR IIT ALL STREAMS ADV MODEL DPT-6 Date: 18/04/2016 One (or) More Than One Answer Type: PHYSICS 31. A particle is executing SHM between points -X m and X m, as shown in figure-i. The velocity V(t) of the
SR IIT ALL STREAMS ADV MODEL DPT-6 Date: 18/04/2016 One (or) More Than One Answer Type: PHYSICS 31. A particle is executing SHM between points -X m and X m, as shown in figure-i. The velocity V(t) of the
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to investigate simple harmonic motion. We will determine the elastic spring constant of a spring first and then study small vertical oscillations
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to investigate simple harmonic motion. We will determine the elastic spring constant of a spring first and then study small vertical oscillations
HOMEWORK ANSWERS. Lesson 4.1: Simple Harmonic Motion
 DEVIL PHYSICS HOMEWORK ANSWERS Tsokos, Chapter 3 Test Lesson 4.1: Simple Harmonic Motion 1. Objectives. By the end of this class you should be able to: a) Understand that in simple harmonic motion there
DEVIL PHYSICS HOMEWORK ANSWERS Tsokos, Chapter 3 Test Lesson 4.1: Simple Harmonic Motion 1. Objectives. By the end of this class you should be able to: a) Understand that in simple harmonic motion there
9.1 Harmonic Motion. Motion in cycles. linear motion - motion that goes from one place to another without repeating.
 9.1 Harmonic Motion A bicyclist pedaling past you on the street moves in linear motion. Linear motion gets us from one place to another (Figure 9.1A). This chapter is about another kind of motion called
9.1 Harmonic Motion A bicyclist pedaling past you on the street moves in linear motion. Linear motion gets us from one place to another (Figure 9.1A). This chapter is about another kind of motion called
Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 Equilibrium and Elasticity Suggested Videos for Chapter 8 Prelecture Videos Static Equilibrium Elasticity Video Tutor Solutions Equilibrium and Elasticity Class Videos Center
Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 Equilibrium and Elasticity Suggested Videos for Chapter 8 Prelecture Videos Static Equilibrium Elasticity Video Tutor Solutions Equilibrium and Elasticity Class Videos Center
OSCILLATIONS ABOUT EQUILIBRIUM
 OSCILLATIONS ABOUT EQUILIBRIUM Chapter 13 Units of Chapter 13 Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring
OSCILLATIONS ABOUT EQUILIBRIUM Chapter 13 Units of Chapter 13 Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring
CHAPTER 11 TEST REVIEW
 AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
SPRING 2003 Final Exam, Part A
 Physics 151 SPRING 2003 Final Exam, Part A Roster No.: Score: 17 pts. possible Exam time limit: 2 hours. You may use calculators and both sides of 2 sheets of notes, handwritten only. Closed book; no collaboration.
Physics 151 SPRING 2003 Final Exam, Part A Roster No.: Score: 17 pts. possible Exam time limit: 2 hours. You may use calculators and both sides of 2 sheets of notes, handwritten only. Closed book; no collaboration.
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test
 AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. baby bouncer consisting of a harness and elastic ropes is suspended from a doorway. When a baby of mass 10 kg is placed in the harness, the ropes stretch by 0.25 m. When the
PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. baby bouncer consisting of a harness and elastic ropes is suspended from a doorway. When a baby of mass 10 kg is placed in the harness, the ropes stretch by 0.25 m. When the
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems
 Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
DO NOT OPEN THE EXAMINATION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD BY THE SUPERVISOR TO BEGIN PHYSICS FINAL EXAMINATION June General Instructions
 Name: Teacher: DO NOT OPEN THE EXAMINATION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD BY THE SUPERVISOR TO BEGIN PHYSICS 2204 FINAL EXAMINATION June 2012 Value: 80 marks General Instructions This examination consists of
Name: Teacher: DO NOT OPEN THE EXAMINATION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD BY THE SUPERVISOR TO BEGIN PHYSICS 2204 FINAL EXAMINATION June 2012 Value: 80 marks General Instructions This examination consists of
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY
 CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS (e) When the force is perpendicular to the displacement, as in C, there is no work When the force points in the same direction as the displacement,
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS (e) When the force is perpendicular to the displacement, as in C, there is no work When the force points in the same direction as the displacement,
5. A car moves with a constant speed in a clockwise direction around a circular path of radius r, as represented in the diagram above.
 1. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is 20. Newtons. If the mass of each object were doubled, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the objects would be A) 5.0 N B)
1. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is 20. Newtons. If the mass of each object were doubled, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the objects would be A) 5.0 N B)
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. When a spring is compressed 10 cm, compared to its
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. When a spring is compressed 10 cm, compared to its
Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion
 Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Wave Motion Waves Motion of an Object Attached to a Spring The Pendulum Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Sinusoidal Wave Function
Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Wave Motion Waves Motion of an Object Attached to a Spring The Pendulum Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Sinusoidal Wave Function
Chapter 14 Oscillations
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Chapter Goal: To understand systems that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. Slide 14-2 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-3 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-4 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-5
Chapter 14 Oscillations Chapter Goal: To understand systems that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. Slide 14-2 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-3 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-4 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-5
Exam 3 Review. Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations A stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations.
 Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
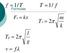 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
Good Vibes: Introduction to Oscillations
 Chapter 14 Solutions Good Vibes: Introduction to Oscillations Description: Several conceptual and qualitative questions related to main characteristics of simple harmonic motion: amplitude, displacement,
Chapter 14 Solutions Good Vibes: Introduction to Oscillations Description: Several conceptual and qualitative questions related to main characteristics of simple harmonic motion: amplitude, displacement,
Physics lab Hooke s Law and Pendulums
 Name: Date: Physics lab Hooke s Law and Pendulums Part A: Hooke s Law Introduction Hooke s Law explains the relationship between the force exerted on a spring, the stretch of the string, and the spring
Name: Date: Physics lab Hooke s Law and Pendulums Part A: Hooke s Law Introduction Hooke s Law explains the relationship between the force exerted on a spring, the stretch of the string, and the spring
WAVES & SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 PROJECT WAVES & SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION EVERY WAVE, REGARDLESS OF HOW HIGH AND FORCEFUL IT CRESTS, MUST EVENTUALLY COLLAPSE WITHIN ITSELF. - STEFAN ZWEIG What s a Wave? A wave is a wiggle in time and space
PROJECT WAVES & SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION EVERY WAVE, REGARDLESS OF HOW HIGH AND FORCEFUL IT CRESTS, MUST EVENTUALLY COLLAPSE WITHIN ITSELF. - STEFAN ZWEIG What s a Wave? A wave is a wiggle in time and space
Oscillatory Motion SHM
 Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion SHM Dr. Armen Kocharian Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion SHM Dr. Armen Kocharian Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A
Chapter 15. simple harmonic motion
 Chapter 15 Simple Harmonic Motion GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms, and use it
Chapter 15 Simple Harmonic Motion GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms, and use it
3) When a rigid body rotates about a fixed axis all the points in the body have the same centripetal acceleration. FALSE
 PHYSICS 1401 Exam 3 Review Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) When a rigid body rotates about a fixed axis all the points in the body have the same
PHYSICS 1401 Exam 3 Review Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) When a rigid body rotates about a fixed axis all the points in the body have the same
Physics General Physics. Lecture 24 Oscillating Systems. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 24 Oscillating Systems Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 2 Oscillating Motion We have studied linear motion objects moving in straight lines at either constant
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 24 Oscillating Systems Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 2 Oscillating Motion We have studied linear motion objects moving in straight lines at either constant
Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2)
 Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2) What to study: Quiz 6 Homework problems for Chapters 15 & 16 Material indicated in the following review slides Other Specific things:
Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2) What to study: Quiz 6 Homework problems for Chapters 15 & 16 Material indicated in the following review slides Other Specific things:
1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is:
 1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is: 2) The bob of simple Pendulum is a spherical hallow ball filled with water. A plugged hole near
1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is: 2) The bob of simple Pendulum is a spherical hallow ball filled with water. A plugged hole near
Periodic Motion. Periodic motion is motion of an object that. regularly repeats
 Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A special kind of periodic motion occurs in mechanical systems
Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A special kind of periodic motion occurs in mechanical systems
1. For which of the following motions of an object must the acceleration always be zero?
 1. For which of the following motions of an object must the acceleration always be zero? I. Any motion in a straight line II. Simple harmonic motion III. Any motion in a circle I only II only III that
1. For which of the following motions of an object must the acceleration always be zero? I. Any motion in a straight line II. Simple harmonic motion III. Any motion in a circle I only II only III that
4. What is the speed (in cm s - 1 ) of the tip of the minute hand?
 Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 MECHANICS: SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION QUESTIONS SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (2016;3) A toy bumble bee hangs on a spring suspended from the ceiling in the laboratory. Tom pulls the bumble bee down 10.0 cm below
MECHANICS: SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION QUESTIONS SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (2016;3) A toy bumble bee hangs on a spring suspended from the ceiling in the laboratory. Tom pulls the bumble bee down 10.0 cm below
Baccalieu Collegiate. Physics Course Outline
 Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
PHYSICS. Chapter 15 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 15 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 15 Oscillations IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about systems that oscillate in simple harmonic
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 15 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 15 Oscillations IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about systems that oscillate in simple harmonic
Contents. Lehman College Department of Physics and Astronomy. Lab manual for PHY 141 Sound, speech and music 1 PENDULUM EXPERIMENT 3
 Lehman College Department of Physics and Astronomy Lab manual for PHY 141 Sound, speech and music Contents 1 PENDULUM EXPERIMENT 3 2 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION 9 3 STANDING WAVES ON STRINGS 15 4 STANDING WAVES
Lehman College Department of Physics and Astronomy Lab manual for PHY 141 Sound, speech and music Contents 1 PENDULUM EXPERIMENT 3 2 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION 9 3 STANDING WAVES ON STRINGS 15 4 STANDING WAVES
AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations 1975B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is drawn aside through
AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations 1975B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is drawn aside through
AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound 1. 1977-5 (Mechanical Waves/Sound) Two loudspeakers, S 1 and S 2 a distance d apart as shown in the diagram below left, vibrate in
AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound 1. 1977-5 (Mechanical Waves/Sound) Two loudspeakers, S 1 and S 2 a distance d apart as shown in the diagram below left, vibrate in
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves. The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position.
 Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations Elastic Deformations Hooke s Law Stress and
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations Elastic Deformations Hooke s Law Stress and
Energy and the Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42244 Energy and the Simple Harmonic Oscillator OpenStax College his wor is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Determine
OpenStax-CNX module: m42244 Energy and the Simple Harmonic Oscillator OpenStax College his wor is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Determine
Second Semester Review
 Second Semester Review Name Section 4.2 1. Define energy What is energy? Explain if it is scalar or vector in nature. 2. Explain what factors affect the speed of a rollercoaster. Whether a rollercoaster
Second Semester Review Name Section 4.2 1. Define energy What is energy? Explain if it is scalar or vector in nature. 2. Explain what factors affect the speed of a rollercoaster. Whether a rollercoaster
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form D
 Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form D Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form D Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form B
 Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form B Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form B Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form C
 Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form C Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form C Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form A
 Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form A Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form A Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
3) 4) Which car has the greatest acceleration during the time interval 10. seconds to 15 seconds? 1) A 2) B 3) C 4) D
 1. A cart travels with a constant nonzero acceleration along a straight line. Which graph best represents the relationship between the distance the cart travels and time of travel? 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. On a
1. A cart travels with a constant nonzero acceleration along a straight line. Which graph best represents the relationship between the distance the cart travels and time of travel? 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. On a
Lecture 30. Chapter 21 Examine two wave superposition (-ωt and +ωt) Examine two wave superposition (-ω 1 t and -ω 2 t)
 To do : Lecture 30 Chapter 21 Examine two wave superposition (-ωt and +ωt) Examine two wave superposition (-ω 1 t and -ω 2 t) Review for final (Location: CHEM 1351, 7:45 am ) Tomorrow: Review session,
To do : Lecture 30 Chapter 21 Examine two wave superposition (-ωt and +ωt) Examine two wave superposition (-ω 1 t and -ω 2 t) Review for final (Location: CHEM 1351, 7:45 am ) Tomorrow: Review session,
Test 3 Preparation Questions
 Test 3 Preparation Questions A1. Which statement is true concerning an object executing simple harmonic motion? (A) Its velocity is never zero. (B) Its acceleration is never zero. (C) Its velocity and
Test 3 Preparation Questions A1. Which statement is true concerning an object executing simple harmonic motion? (A) Its velocity is never zero. (B) Its acceleration is never zero. (C) Its velocity and
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension
 Lecture Outline Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Chapter 16: Waves in One Dimension Chapter Goal: To study the kinematic and dynamics of wave motion, i.e., the transport of energy through a
Lecture Outline Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Chapter 16: Waves in One Dimension Chapter Goal: To study the kinematic and dynamics of wave motion, i.e., the transport of energy through a
