AUSTRALIAN MUSEUM SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS
|
|
|
- Mitchell Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AUSTRALIAN MUSEUM SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS Wells, J. W., Two new scleractinian corals from Australia. Records of the Australian Museum 25(11): , plates xvi xviii. [19 June 1962]. doi: /j ISSN Published by the Australian Museum, Sydney nature culture discover Australian Museum science is freely accessible online at 6 College Street, Sydney NSW 2010, Australia
2 VOL. XXV, No. 11 SYDNEY, 19th June, RECORDS of The Australian Museum (World List abbreviation: Ree. Anst. Mu ) Printed order of the Trustees Edited by the Director, J. W. EV ANS, Sc.D. Two New Scleractinian Corals ft"om Australia By JOHN W. WELLS Pages Plates XVI-XVIII Registered at the General Post Office, Sydney, for transmission by post as a periodical G 17388
3 239 TWO NEW SCLERACTINIAN CORALS FROM AUSTRALIA By John W. Wells CorneIl University, U.S.A. Plates XVI XVIII Manuscript received Several years ago two new species of the reef-building coral genus Coscinaraea were discovered nearly simultaneously in the extreme eastern and south-western parts of Australia. The writer is indebted to Mrs. Lois Marsh and Mr. E. P. Hodgkin, of the University of Western Australia, and Mr. R. W. George, of the Western Australian Museum, for a suite of specimens of C. marshae, and to Mr. K. E. W. Salter, of the University of Sydney, and Mr. F. A. McNeill, of the Australian Museum, for specimens, photographs, and other data on C. mcneilli, and to Dr. D. F. Squires, of the American Museum of Natural History, and Mr. E. de Villa, of Sydney, for photographs of the type of the latter species. The two new species described below occur at the extreme southern limits of hermatypic corals in eastern and south-western Australia. The most southerly occurrence of Coscinaraea known to this time is at Rundle Island (23 30 S.) on the Great Barrier Reefs (Wells, 155, p. 25, and chart), about 600 miles north of Sydney and where the winter minimum temperatures are about 1 r C. The genus has not been previously reported from north western or western Australia. In eastern Australia the writer (1955) has noted the occurrence of a few reef coral genera as far south as Sydney: Montipora, Cyphastrea, Turbinaria, Stylocoeniella and Plesiastrea. To this short list is now added Coscinaraea mcneilli n.sp., from Manly Cove and vicinity, in waters where the temperature range is from 12 C. in June to 24'5 C. in January. From Western Australia comes Coscinaraea marshae n. sp., represented by a number of specimens from Rottnest Island off Fremantle (320 S.) southward to Cape Naturaliste and Geographe Bay (330 30' S.). The winter minimum temperatures here are considerably higher and within the normal tropical range (about 18 c., according to E. P. Hodgkin) and the coral fauna is richer than that of approximately the same latitude at Sydney (340 S.). The following species, in addition to C. marshae, are found: Favites abdita (ElIis and Solander), F. magnisteliata (Milne-Edwards and Haime), Platygyra sp. cl. P. lamellina (Ehrenberg), Montipora sp. cl. M. multi/ormis Bernard, Turbinaria sp. cl. T. danae Bernarcl, Pocillopora damicornis (Linnaeus), Oulophyllia crispa (Lamarck), Goniastrea benhami Vaughan, Plesiastrea urvillei Milne Edwards and Haime, Tubastrea aurea (Quoy and Gaimard), T. diaphana (Dana), and Homophyllia australis Milne-Edwards and Haime. Notable is the absence here, as well as in the vicinity of Sydney, of species of the protean but more tropical genera Acropora and Porites. Plesiastrea urvillei and Homophyllia australis are exceptional in that their northern limit seems to be at or near Houtman's Abrohlos (29 30' S.) in the west, but they extend down and around the southern coast of Australia (type locality of H. australis is Port Lincoln, South Australia), the northern coast of Tasmania, and north probably as far as Moreton Bay, Queensland (27 30' S.). There is a specimen of H. australis in the Australian Museum (No ) labelled as coming from Lord Howe Island. This record needs verification. Family SIDERASTREIDAE Genus Coscinaraea Milne-Edwards and Haime, 1848 Crossland (1941) discussed the type species, Co monile (ForskaI), and its synonyms, and figured ForskaI's type specimen. The writer briefly considered most of the Recent species in 1954 (p. 446). C. monile and C. labyrinthica (Audouin) are confined to the Red Sea and Indian Ocean; C. ostreaeformis van der Horst (Wells, 1954, p. 446, pi. 155, f. 5, 6, and Matthai, 1948, pi. 8, figs (as C. monile» is a deep water form in the Indo-Pacific; and C. columna (Dana) and C. Jossata (Dana) have been found only in the Pacific. Coscinaraea mcneilli n. sp. Plate xvi, figs. 1-3 Corallum a broad expanded thamnasterioid plate attached basally or laterally to the substratum in the mode of a bracket fungus, up to 10 mm. thick. Lower surface non'epithecate, common wall solid and imperforate, covered with relatively broad, rounded, granulated, equal costae with narrow inters paces ; the fine costal granules or spinules are scattered over the costae rather than forming regular rows. Dimensions of holotype (a piece from a large colony): 9 x 16 cm. Colony-formation by circumoral budding, new centres grouped in roughly G
4 240 concentric rows separated by very low collines. Over parts of the calicular surface cohines appear to be absent. Calices shallow, 2-3 mm. in diameter, their centres 3-4 mm. apart. Septa numbering 15-20, of which extend to the columella, equal and thick midway between centres, thinning evenly towards the columella, imperforate, strongly spinulosely beaded laterally and marginally. Over the low walls and collines the septa number per centimeter. Columella small, trabecular, papillate at surface, not as sharply differentiated from inner coarse beads of septa as it is in most species of the genus. Corallite walls, except the basal wall, scarcely differentiated and represented by two or three vague vertical rows of synapticulae. This species groups with C. monile, C. columna and C. ostreaeformis-species in which collines are weakly developed. It differs clearly from the first of these in the smaller calices (7-9 mm. in C. monile) and growth-form, from C. columna by its larger calices in which nearly twice as many septa reach the columella, and from C. ostreaeformis by its deeper calices (calices may be protuberant in C. ostraeaformis) and proportionally finer septa. The bracket growth form is much like that of the quiet-water form of C. columna described by the writer from the Marshal! Islands (1954, pi. 179, f. 2). This growth-form is well shown in an underwater photograph (PI. XVI, f. 3), taken by E. de Villa, of the entire colony some 60 centimetres long from which the hojotype piece was broken. Material.-Holotype: Australian Museum No. G13638 (this is the specimen figured by Gillett and McNeill, 1959, p. 51, f. 41); paratype: A.M. No. G13639 (small piece of this in the U. S. National Museum). Occurrence: Sydney Harbour (Port Jackson), New South Wales. Holotype from Fairlight, a small bay near Manly, depth 25 feet, collected by E. de Villa, aqua-lung diver. Paratype from about same depth nearby off North Headland, collected by W. Gibson, aqua-lung diver. Coscinaraea marshae n, Sp. Plate xvii, figs. 1-4; plate xviii, figs. 1-3 Corallum open caliciform, attached centrally by a stout stalk. Old colonies expanded laminar, very thick centrally, with nearly even calicular surface. Common wan of lower surface solid, imperforate, about 2 mm. thick peripherally, non-epithecate, with sharp, equal, faintly beaded costae corresponding to all the marginal septa. Colony-formation by circumoral budding, resulting in short, irregular series in earlier stages, tending to become long, nearly continuous and concentric with the margin. Series 7-10 mm. wide, separated by high, rounded collines over which the septa dip steeply to the valley floors. Depth of valleys about 4 mm. Marginally the collines are asymmetric in profile, steeper on the outer side, giving the valleys an outward-looking aspect. One or two centimetres in from the margin, however, they are nearly symmetrical. Over the collines the septa are equal, numbering per centimetre. Calicular centres are 6-8 mm. apart, with lamellar or trabecular linkage. Septa of higher cycles unite irregularly with those of lower cycles so that about half (15-18) extend to and join the columella. Columella small, trabecular, with a few surface papillae, sunk in a shallow pit below the inner ends of the major septa. Corallite walls represented only by a few synapticulae (pi. XVIII, fig. 3). Dissepiments thin, convex. Compared with other species of the genus the septa are thin, and imperforate as in C. mcneilli. Living polyps yellow-brown to brown. At first glance the habit and aspect of this handsome species suggest Leptoseris, but the septal structures are those of Coscinaraea and other siderastreids. The serial nature of the calices groups it with the other more or less meandrine species, C. fossala and C. labyrinthica. In neither of these, however, do the series show anything approaching the more or less regularly concentric arrangement of C. marshae, in which the valleys are proportionally wider and more open; the septa, also, are much thinner and less perforate than in most other species, and generally narrower than the inters paces rather than two or three times as wide. This is the only species with a distinctly and consistently caliciform growth form. Although the caliciform corallum and mode of colony-formation are constant in the specimens examined, there is a wide variation in the development of the cohines and the spacing of the calicular centres. The holotype-diameter 17 cm., height 10 cm., concavity 3 5 mm. (pi. XVII, figs. 1, 2)-is at one end of the range, with highly developed, roughly concentric, high, narrow collines and centres 5 mm. apart. At the other end is a colony 24 cm. in diameter, 9 cm. high, with a nearly flat (concavity, 1 cm.) calicular surface, very low, relatively broad collines and centres spaced 6-8 mm., resembling C. mcneilli but with very thick corallum. A thin corallum 17 cm. in diameter and 6 cm. high (pi. XVIII, fig. 1) also has a nearly flat calicular surface, with low, relatively narrow collines developed on the inner side of the widely-spaced (5-15 mm.) calicular centres, especially near the margin where the aspect is much like that of Leptoseris or Mycedium. These three specimens would appear to be as many species, but they are interconnected by nine other specimens.
5 REC. AUST. MUS., VOL XXV. PLATE XVI. 3 G
6 REC. AUST, MUS., VOL. XXV. xxv. PLATE XVIL
7 REC AUST. MUS" VOL. XXV. PLATE XVIII.
8 241 Material.-Holotype: Western Australian Museum, No ; paratypes: W.A.M.: Nos , 59-59, , , , ; Australian Museum (1); U.S. National Museum (2). Occurrence: Western Australia at various localities between Fremantle and Geographe Bay; holotype and paratype No : Point Clune, Rottnest Island, depth 10 feet; paratypes Nos ,103-28: Cathedral Rocks, Rottnest I.; paratype 59-59: 1 5 miles off Dunsborough, Geographe Bay, depth 25 feet C H from a crevice in a rocky ledge "); paratype No : Eagle Bay, Cape Naturaliste, depth 30 feet (H in a rock crevice "); paratype No : Woodman Point near Fremantle; paratypes (2 specimens, one in Western Australian Museum, one in Australian Museum): Cathedral Rocks, Rottnest 1.; paratype (Dept. Zoology, Univ. Western Australia): Cape Vlaming, Rottnest I.; paratypes (2 specimens in U. S. National Museum): Rottnest I. REFERENCES Crossland, C. (1941). On Forskah collection of corals in the Zoological Museum, Copenhagen. Univ. Zool. Mus., Copenhagen, Skrifter 1: 63, 12 pis. GiIlett, K., and McNeill, F. A. (1959). The Great Barrier Reef and Adjacent Isles. Coral Press, Sydney. Matthai, G. (1948). On the mode of growth of the skeleton in fungid corals. Phi!. Truns., London, 233B : , pis Wells, J. W. (1954). Recent corals of the Marshall Islands, U. S. Geol. Survey Prof. Paper 261-L: , pis , figs, , 4 tables (1955). A survey of the distribution of reef coral genera in the Great Barrier Reef region. Repts. G. B. Reef Committee, 8: chart. EXPLANATION OF PLATES PLATE XVI Coscinaraea mcneilli n. Sp. Figs. 1,2: C. mcneilli, holotype (A.M. GI3638), calicular surface, x 1/2; calices, x 6. Photographs by courtesy of D. F. Squires. Fig. 3: C. mcneilli, entire colony from which holotype piece was taken, in situ, depth 25 feet, Fairlight, Sydney Harbour. Width, about 60 centimetres. Photograph by E. de Villa. PLATE xvn Coscinaraea marshae n. Sp. Figs. 1,2,3: C. marshae, ho1otype CW.A.M ): I. Calicular surface, x 1/2; 2. lateral aspect, x 1/2; 3. Calices, x 6. Fig. 4: C. marshae, paratype (W.A.M ): exterior of part of small colony, showing costate common wall, x 1. PLATE XVIII Coscinaraea marshae n. Sp. Fig. I: C. marshae, paratype (W.A.M ): Leptoseris-form, calicular surface, x 1/2. Fig. 2: C. marshae, paratype (W.A.M., Cathedral Rocks): young colony, Leptoseris-form, x 1/2. Fig. 3: C. mars/tae, paratype (W.A.M ): natural vertical section, lateral faces of septa, synapliculae, and endotheca, x 4. Sydney: V. C. N. Blight, Government Printer-1962
MEMOIRS NATIONAL MUSEUM OF VICTORIA MELBOURNE. (World List abbrev. Mern. n:lt. A~LI~. \'ict.) No. 27. Irrued 2nd Novembe~; 1966 MELBOURNE
 MEMOIRS NATIONAL MUSEUM OF VICTORIA MELBOURNE (World List abbrev. Mern. n:lt. A~LI~. \'ict.) No. 27 Irrued 2nd Novembe~; 1966 MELBOURNE MEM. NAT. MUS. VICT. 271966 PORT PHILLIP SURVEY 1957 1963 SCLERACTINIA.
MEMOIRS NATIONAL MUSEUM OF VICTORIA MELBOURNE (World List abbrev. Mern. n:lt. A~LI~. \'ict.) No. 27 Irrued 2nd Novembe~; 1966 MELBOURNE MEM. NAT. MUS. VICT. 271966 PORT PHILLIP SURVEY 1957 1963 SCLERACTINIA.
AUSTRALIAN MUSEUM SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS
 AUSTRALIAN MUSEUM SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS Miller, A. H., 1962. The history and significance of the fossil Casuarius lydekkeri. Records of the Australian Museum 25(10): 235 238. [19 June 1962]. doi:10.3853/j.0067-1975.25.1962.662
AUSTRALIAN MUSEUM SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS Miller, A. H., 1962. The history and significance of the fossil Casuarius lydekkeri. Records of the Australian Museum 25(10): 235 238. [19 June 1962]. doi:10.3853/j.0067-1975.25.1962.662
Corals of Rottnest Island
 Corals of Rottnest Island MScience Pty Ltd June 2012 Volume 1, Issue 1 MARINE RESEARCH Produced with the Assistance of the Rottnest Island Authority Cover picture courtesy of H. Shortland Jones * Several
Corals of Rottnest Island MScience Pty Ltd June 2012 Volume 1, Issue 1 MARINE RESEARCH Produced with the Assistance of the Rottnest Island Authority Cover picture courtesy of H. Shortland Jones * Several
ZOOLOGISCHE MEDEDELINGEN
 ZOOLOGISCHE MEDEDELINGEN UITGEGEVEN DOOR HET RIJKSMUSEUM VAN NATUURLIJKE HISTORIE TE LEIDEN (MINISTERIE VAN WELZIJN, VOLKSGEZONDHEID EN CULTUUR) Deel 61 no. 21 7 oktober 1987 ISSN 0024-0672 FUNGIA (VERRILLOFUNGIA)
ZOOLOGISCHE MEDEDELINGEN UITGEGEVEN DOOR HET RIJKSMUSEUM VAN NATUURLIJKE HISTORIE TE LEIDEN (MINISTERIE VAN WELZIJN, VOLKSGEZONDHEID EN CULTUUR) Deel 61 no. 21 7 oktober 1987 ISSN 0024-0672 FUNGIA (VERRILLOFUNGIA)
Paleontological Contributions
 Paleontological Contributions Number 13 A new rhizangiid genus from the Miocene of North America (Sclerangia n. gen.; Florida, USA) Rosemarie Christine Baron-Szabo and Stephen Douglas Cairns April 30,
Paleontological Contributions Number 13 A new rhizangiid genus from the Miocene of North America (Sclerangia n. gen.; Florida, USA) Rosemarie Christine Baron-Szabo and Stephen Douglas Cairns April 30,
(East Indies) Cyphastrea monticulifera Felix Upper" Miocene (East Borneo). Fungophyllia aspera Gertii, Lower' - Miocene (Borneo).
 Leidsche Deel XI, 1939 Geologische Mcdedcelingen Afl. 1, p. 62 67. Miocene corals from Flores (East Indies) BY J.H.F. U mbgrove Dr. Ph. H. Kuenen kindly entrusted me with a suite of corals collected by
Leidsche Deel XI, 1939 Geologische Mcdedcelingen Afl. 1, p. 62 67. Miocene corals from Flores (East Indies) BY J.H.F. U mbgrove Dr. Ph. H. Kuenen kindly entrusted me with a suite of corals collected by
OF PLANALVEOLITES POUGHTI
 CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE MUSEUM OF PALEONTOLOGY THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN VOL. XXI, No. 2, pp. 67-72 (1 pl.) MAP 10, 1967 PLANALVEOLITELLA, A NEW GENUS OF DEVONIAN TABULATE CORALS, WITH A REDESCRIPTION
CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE MUSEUM OF PALEONTOLOGY THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN VOL. XXI, No. 2, pp. 67-72 (1 pl.) MAP 10, 1967 PLANALVEOLITELLA, A NEW GENUS OF DEVONIAN TABULATE CORALS, WITH A REDESCRIPTION
Seas. A sea is a part of an ocean that is nearly surrounded by water. The Mediterranean, Arctic and Black Sea are really part of the Atlantic Ocean.
 Exploring the Ocean Since ancient times people have studied the ocean such as waters and ocean floor It provides food and services, and serves as a route for trade and travel The World s Oceans 71% of
Exploring the Ocean Since ancient times people have studied the ocean such as waters and ocean floor It provides food and services, and serves as a route for trade and travel The World s Oceans 71% of
Some Problems in Reef Coral Taxonomy 1
 Some Problems in Reef Coral Taxonomy 1 RICHARD H. RANDALL Marine Laboratory, University of Guam P.O. EK, Agana, Guam 96910 This paper is a brief presentation about some of the current problems in reef
Some Problems in Reef Coral Taxonomy 1 RICHARD H. RANDALL Marine Laboratory, University of Guam P.O. EK, Agana, Guam 96910 This paper is a brief presentation about some of the current problems in reef
AN ILLUSTRATED KEY TO THE BRITISH LITHOSTROTIONID CO.RALS
 ACT A Vol. 25 P A L A EON T 0 LOG I C A 1'80 POLONICA No. JOHN R. NUDDS AN ILLUSTRATED KEY TO THE BRITISH LITHOSTROTIONID CO.RALS NUDDS, J. R.: An illustrated. key to the British lithostrotionid corals.
ACT A Vol. 25 P A L A EON T 0 LOG I C A 1'80 POLONICA No. JOHN R. NUDDS AN ILLUSTRATED KEY TO THE BRITISH LITHOSTROTIONID CO.RALS NUDDS, J. R.: An illustrated. key to the British lithostrotionid corals.
Aspects of Pacific Coral Reefs
 Aspects of Pacific Coral Reefs John W. WELLS Department of Geology, Cornell University Introduction Coral reefs are the only major earth features determined by the complexly integrated operation of both
Aspects of Pacific Coral Reefs John W. WELLS Department of Geology, Cornell University Introduction Coral reefs are the only major earth features determined by the complexly integrated operation of both
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor
 Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
THE SCLERACTINIAN CORAL FAUNA OF RAKITU ISLAND, NORTH-EASTERN NEW ZEALAND. by F.J. Brook
 TANE 28,1982 THE SCLERACTINIAN CORAL FAUNA OF RAKITU ISLAND, NORTH-EASTERN NEW ZEALAND by F.J. Brook Department of Geology, University of Auckland, Private Bag, Auckland SUMMARY Four species of ahermatypic
TANE 28,1982 THE SCLERACTINIAN CORAL FAUNA OF RAKITU ISLAND, NORTH-EASTERN NEW ZEALAND by F.J. Brook Department of Geology, University of Auckland, Private Bag, Auckland SUMMARY Four species of ahermatypic
The Indian Ocean. Copyright 2010 LessonSnips
 The Indian Ocean One of the five major geographic divisions of the world s ocean, the Indian Ocean is located in the Eastern Hemisphere. The Indian Ocean is bounded by three continents: Africa to the west,
The Indian Ocean One of the five major geographic divisions of the world s ocean, the Indian Ocean is located in the Eastern Hemisphere. The Indian Ocean is bounded by three continents: Africa to the west,
Recent and Subfossil Corals of Moreton Bay, Queensland
 UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND PAPERS DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY Volume IV. (New Series) 19.55 Number 10 Recent and Subfossil Corals of Moreton Bay, Queensland By JOHN W. WELLS Cornell University Price: Three ShiUU.gs
UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND PAPERS DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY Volume IV. (New Series) 19.55 Number 10 Recent and Subfossil Corals of Moreton Bay, Queensland By JOHN W. WELLS Cornell University Price: Three ShiUU.gs
1. Name at least one place that the mid-atlantic Ridge is exposed above sea level.
 Interpreting Tectonic and Bathymetric Maps. The purpose of this lab is to provide experience interpreting the bathymetry of the seafloor in terms of tectonic and geologic settings and processes. Use the
Interpreting Tectonic and Bathymetric Maps. The purpose of this lab is to provide experience interpreting the bathymetry of the seafloor in terms of tectonic and geologic settings and processes. Use the
A MEGASECOPTERON FROM UPPER CARBONIFEROUS BY F. M. CARPENTER. In I962 Professor F. Stockmans, of the Institut Royal des Sciences STRATA IN SPAIN
 A MEGASECOPTERON FROM UPPER CARBONIFEROUS STRATA IN SPAIN BY F. M. CARPENTER Harvard University In I962 Professor F. Stockmans, of the Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de. Belgique, kindly sent me
A MEGASECOPTERON FROM UPPER CARBONIFEROUS STRATA IN SPAIN BY F. M. CARPENTER Harvard University In I962 Professor F. Stockmans, of the Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de. Belgique, kindly sent me
Unit 9: CORAL GROWTH. Coral Reef. Ecology Curriculum
 Unit 9: CORAL GROWTH Coral Reef Ecology Curriculum This unit is part of the Coral Reef Ecology Curriculum that was developed by the Education Department of the Khaled bin Sultan Living Oceans Foundation.
Unit 9: CORAL GROWTH Coral Reef Ecology Curriculum This unit is part of the Coral Reef Ecology Curriculum that was developed by the Education Department of the Khaled bin Sultan Living Oceans Foundation.
1. Draw a line from each ocean listed below to its location on the map. 2. Label the Pacific Ring of Fire on the map above.
 1. Draw a line from each ocean listed below to its location on the map. Atlantic Ocean Pacific Ocean Indian Ocean Arctic Ocean 2. Label the Pacific Ring of Fire on the map above. 3. Find Fairbanks on the
1. Draw a line from each ocean listed below to its location on the map. Atlantic Ocean Pacific Ocean Indian Ocean Arctic Ocean 2. Label the Pacific Ring of Fire on the map above. 3. Find Fairbanks on the
Downloaded from
 I II III IV V VI Define the following terms:- a) Orbitb) Meteoroids c) Celestial bodies GEOGRAPHY ASSIGNMENTS The Earth In The Solar System d) Satellite e) Comets Give one word answers:- a) Blue planet
I II III IV V VI Define the following terms:- a) Orbitb) Meteoroids c) Celestial bodies GEOGRAPHY ASSIGNMENTS The Earth In The Solar System d) Satellite e) Comets Give one word answers:- a) Blue planet
Department of Botany, University of Dhaka, Dhaka 1000, Bangladesh. Key words: Seaweeds, Marine algae, Kallymenia spp., St. Martin's Is.
 Bangladesh J. Bot. 37(2): 173-178, 2008 (December) MARINE ALGAE OF THE ST. MARTIN S ISLAND, BANGLADESH. VI. NEW RECORDS OF SPECIES OF THE GENUS KALLYMENIA J. AG. (RHODOPHYTA) ABDUL AZIZ, A.K.M. NURUL ISLAM
Bangladesh J. Bot. 37(2): 173-178, 2008 (December) MARINE ALGAE OF THE ST. MARTIN S ISLAND, BANGLADESH. VI. NEW RECORDS OF SPECIES OF THE GENUS KALLYMENIA J. AG. (RHODOPHYTA) ABDUL AZIZ, A.K.M. NURUL ISLAM
Laboratory #7: Plate Tectonics
 Materials Needed: 1. Pencil 2. Colored Pencils 3. Metric/Standard Ruler 4. Calculator 5. Tracing Paper Laboratory #7: Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics The Earth is composed of layers. At the center is a
Materials Needed: 1. Pencil 2. Colored Pencils 3. Metric/Standard Ruler 4. Calculator 5. Tracing Paper Laboratory #7: Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics The Earth is composed of layers. At the center is a
The Sea Floor. Chapter 2
 The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
AUSTRALIAN MUSEUM SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS
 AUSTRALIAN MUSEUM SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS McCarthy, Frederick D., 1943. Trimmed pebble implements of Kartan type from ancient kitchen-middens at Clybucca, New South Wales. Records of the Australian Museum
AUSTRALIAN MUSEUM SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS McCarthy, Frederick D., 1943. Trimmed pebble implements of Kartan type from ancient kitchen-middens at Clybucca, New South Wales. Records of the Australian Museum
8.1 Attachment 1: Ambient Weather Conditions at Jervoise Bay, Cockburn Sound
 8.1 Attachment 1: Ambient Weather Conditions at Jervoise Bay, Cockburn Sound Cockburn Sound is 20km south of the Perth-Fremantle area and has two features that are unique along Perth s metropolitan coast
8.1 Attachment 1: Ambient Weather Conditions at Jervoise Bay, Cockburn Sound Cockburn Sound is 20km south of the Perth-Fremantle area and has two features that are unique along Perth s metropolitan coast
Understanding Projections
 GEOGRAPHY SKILLS 1 Understanding Projections The earth is a sphere and is best shown as a globe. For books and posters, though, the earth has to be represented as a flat object. To do this, mapmakers create
GEOGRAPHY SKILLS 1 Understanding Projections The earth is a sphere and is best shown as a globe. For books and posters, though, the earth has to be represented as a flat object. To do this, mapmakers create
The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are
 11.1 Ocean Basins The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are w the Pacific w the Atlantic w the Indian w the Southern w the Arctic The
11.1 Ocean Basins The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are w the Pacific w the Atlantic w the Indian w the Southern w the Arctic The
The Puzzling Plates Part I. Follow the steps below while taking notes in your science notebook.
 Procedure Follow the steps below while taking notes in your science notebook. 1. On the table is a pile of cardboard puzzle pieces. Work with your team to assemble the puzzle. The edges of the completed
Procedure Follow the steps below while taking notes in your science notebook. 1. On the table is a pile of cardboard puzzle pieces. Work with your team to assemble the puzzle. The edges of the completed
The structure of the Earth and how its motion creates the seasons. The landforms of the earth and the forces that shape the land.
 The structure of the Earth and how its motion creates the seasons. The landforms of the earth and the forces that shape the land. The role of wind and water in creating climate. The different climate and
The structure of the Earth and how its motion creates the seasons. The landforms of the earth and the forces that shape the land. The role of wind and water in creating climate. The different climate and
New observations on Scleractinian corals from Indonesia: 3. Species belonging to the Merulinidae with new records of Merulina and Boninastrea
 New observations on Scleractinian corals from Indonesia: 3. Species belonging to the Merulinidae with new records of Merulina and Boninastrea M.B. Best & Suharsono Best, M.B. & Suharsono. New observations
New observations on Scleractinian corals from Indonesia: 3. Species belonging to the Merulinidae with new records of Merulina and Boninastrea M.B. Best & Suharsono Best, M.B. & Suharsono. New observations
Crustal Boundaries. As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries they interact in various ways. Convergent Transform Divergent
 Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *5317218974* GEOGRAPHY 0460/22 Paper 2 February/March 2018 Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *5317218974* GEOGRAPHY 0460/22 Paper 2 February/March 2018 Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
ON THE SPECIES OF SARMATIUM DANA, R. SERÈNE and C. L. SOH National Museum, Singapore
 ON THE SPECIES OF SARMATIUM DANA, 1851 (DECAPODA, BRACHYURA) BY R. SERÈNE and C. L. SOH National Museum, Singapore Dana (1851) established the genus Sarmatium for the single species S. crassum Dana, 1851.
ON THE SPECIES OF SARMATIUM DANA, 1851 (DECAPODA, BRACHYURA) BY R. SERÈNE and C. L. SOH National Museum, Singapore Dana (1851) established the genus Sarmatium for the single species S. crassum Dana, 1851.
THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN ORDOVICIAN STREPTELASMID RUGOSE CORALS FROM MICHIGAN
 CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE MUSEUM OF PALEONTOLOGY THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN VOL. XVIII, No. 2, pp. 23-31 (2 pls.) MARCH 20, 1963 ORDOVICIAN STREPTELASMID RUGOSE CORALS FROM MICHIGAN BY ERWIN C. STUMM FROM
CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE MUSEUM OF PALEONTOLOGY THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN VOL. XVIII, No. 2, pp. 23-31 (2 pls.) MARCH 20, 1963 ORDOVICIAN STREPTELASMID RUGOSE CORALS FROM MICHIGAN BY ERWIN C. STUMM FROM
60% water. Big Bang: 14,000 millions years ago The Earth originated about 4,500 millions years ago its orbit allows water to exist in a liquid state!
 Ch2. The Sea Floor #1 Why geology of the oceans? Marine habitats are directly shaped by geological processes The form of the coastlines The depth of the water Type of bottom (muddy, sandy, rocky) #2 Geological
Ch2. The Sea Floor #1 Why geology of the oceans? Marine habitats are directly shaped by geological processes The form of the coastlines The depth of the water Type of bottom (muddy, sandy, rocky) #2 Geological
Lab # - Ocean Bottom Topography. Background Information:
 Name Lab Grade /10 Date Period Lab # - Ocean Bottom Topography Background Information: Ocean depth varies markedly from one location to another. Over large areas water depth is less than 200m (650 ft);
Name Lab Grade /10 Date Period Lab # - Ocean Bottom Topography Background Information: Ocean depth varies markedly from one location to another. Over large areas water depth is less than 200m (650 ft);
NEW DATA ON CHEUDONURA AMOENA BERGH, 1905 (OPISTHOBRANCHIA: CEPHALASPIDEA: AGLAJIDAE).
 The Beagle, Records of the Museums and Art. Galleries of the Nonhern Territory, 1995 12:9-18 NEW DATA ON CHEUDONURA AMOENA BERGH, 1905 (OPISTHOBRANCHIA: CEPHALASPIDEA: AGLAJIDAE). R. C. Wll..LANI AND R.
The Beagle, Records of the Museums and Art. Galleries of the Nonhern Territory, 1995 12:9-18 NEW DATA ON CHEUDONURA AMOENA BERGH, 1905 (OPISTHOBRANCHIA: CEPHALASPIDEA: AGLAJIDAE). R. C. Wll..LANI AND R.
specimen location on label country dating on label original NHM identification
 Appendix Table 1. Registration numbers and specimen label data associated with the Natural History Museum (NHM) fossils used in this paper. The original locality, age and identification information are
Appendix Table 1. Registration numbers and specimen label data associated with the Natural History Museum (NHM) fossils used in this paper. The original locality, age and identification information are
Chapter 6, Part Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great.
 Social Studies 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great. 2. The Earth is years old and is composed
Social Studies 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great. 2. The Earth is years old and is composed
Tuesday 10 June 2014 Afternoon
 Tuesday 10 June 2014 Afternoon A2 GCE GEOLOGY F795/01 Evolution of Life, Earth and Climate *1242977619* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required: Electronic
Tuesday 10 June 2014 Afternoon A2 GCE GEOLOGY F795/01 Evolution of Life, Earth and Climate *1242977619* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required: Electronic
What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley
 1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
Coral interactions and community structure: an analysis of spatial pattern
 Vol. 11: 265-271,1983 MARINE ECOOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. I Published March 24 Coral interactions and community structure: an analysis of spatial pattern R. H. Bradbury1 and P. C. Young2
Vol. 11: 265-271,1983 MARINE ECOOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. I Published March 24 Coral interactions and community structure: an analysis of spatial pattern R. H. Bradbury1 and P. C. Young2
2 Earth s Changing Continents
 CHAPTER 9 SECTION The History of Life on Earth 2 Earth s Changing Continents California Science Standards 7.4.a, 7.4.e, 7.4.f BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 9 SECTION The History of Life on Earth 2 Earth s Changing Continents California Science Standards 7.4.a, 7.4.e, 7.4.f BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
Small area of the ocean that is partially surrounded by land. The Ocean Basins. Three Major Oceans. Three Major Oceans. What is a SEA?
 The Ocean Basins How Deep is the Ocean? 1 2 Three Major Oceans Three Major Oceans Pacific Atlantic the shallowest ocean (3.3km average depth) Indian second shallowest ocean (3.8km average depth) Pacific
The Ocean Basins How Deep is the Ocean? 1 2 Three Major Oceans Three Major Oceans Pacific Atlantic the shallowest ocean (3.3km average depth) Indian second shallowest ocean (3.8km average depth) Pacific
3. The diagram below shows how scientists think some of Earth's continents were joined together in the geologic past.
 1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
Our Dynamic Earth Unit Unit 5
 EARTH SCIENCE REGENTS - SOTO Our Dynamic Earth Unit Unit 5 Mr. Soto - Key 1/1/2013 Our Dynamic Earth Vocabulary List 1 Directions: Define each vocabulary word provided below. You may have to use your Earth
EARTH SCIENCE REGENTS - SOTO Our Dynamic Earth Unit Unit 5 Mr. Soto - Key 1/1/2013 Our Dynamic Earth Vocabulary List 1 Directions: Define each vocabulary word provided below. You may have to use your Earth
Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory
 Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory What is Plate Tectonics? - 7 large tectonic plates and many smaller ones that break up the lithosphere - Plates are brittle and float on asthenosphere and glide past
Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory What is Plate Tectonics? - 7 large tectonic plates and many smaller ones that break up the lithosphere - Plates are brittle and float on asthenosphere and glide past
A FOSSIL CRAB FROM THE LAKES ENTRANCE OIL SHAFT, GIPPSLAND, VICTORIA
 gtopt JtoAtty 0f WitUxm. -..., ' -: / '.. v - - ^.. ' ' * A FOSSIL CRAB FROM THE LAKES ENTRANCE OIL SHAFT, GIPPSLAND, VICTORIA BY.'. " ; IRENE CRESPIN, R. A. Read 6** June, 1946 ' Reprinted from Proo.
gtopt JtoAtty 0f WitUxm. -..., ' -: / '.. v - - ^.. ' ' * A FOSSIL CRAB FROM THE LAKES ENTRANCE OIL SHAFT, GIPPSLAND, VICTORIA BY.'. " ; IRENE CRESPIN, R. A. Read 6** June, 1946 ' Reprinted from Proo.
Rainfall declines over Queensland from and links to the Subtropical Ridge and the SAM
 Rainfall declines over Queensland from 1951-2007 and links to the Subtropical Ridge and the SAM D A Cottrill 1 and J Ribbe 2 1 Bureau of Meteorology, 700 Collins St, Docklands, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
Rainfall declines over Queensland from 1951-2007 and links to the Subtropical Ridge and the SAM D A Cottrill 1 and J Ribbe 2 1 Bureau of Meteorology, 700 Collins St, Docklands, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
Map Elements & The 5 Oceans
 Map Elements & The 5 Oceans Latitude and Longitude Longitude lines run north and south. Latitude lines run east and west. The lines measure distances in degrees. Latitude Longitude Where is 0 degrees?
Map Elements & The 5 Oceans Latitude and Longitude Longitude lines run north and south. Latitude lines run east and west. The lines measure distances in degrees. Latitude Longitude Where is 0 degrees?
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Coral Reefs. Reef Corals
 Coral Reefs Highly diverse rivals tropical rain forest Biogenic habitat habitat made by living organisms Are found in areas of warm clear water that is also typically nutrient poor Are increasingly threatened
Coral Reefs Highly diverse rivals tropical rain forest Biogenic habitat habitat made by living organisms Are found in areas of warm clear water that is also typically nutrient poor Are increasingly threatened
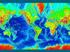
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE!
 ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
CALLISPHENUS GRACILIS, N. GEN., N. SP. A FOSSIL ALGA FROM THE WENLOCK OF THE OSLO REGION
 CALLISPHENUS GRACILIS, N. GEN., N. SP. A FOSSIL ALGA FROM THE WENLOCK OF THE OSLO REGION BY OVE HØEG WITH 2 PLATES The specimen described below was found in August, 191 O, on the small island of Kommersøy
CALLISPHENUS GRACILIS, N. GEN., N. SP. A FOSSIL ALGA FROM THE WENLOCK OF THE OSLO REGION BY OVE HØEG WITH 2 PLATES The specimen described below was found in August, 191 O, on the small island of Kommersøy
Australia and New Zealand: Powerpoint
 Australia and New Zealand: Powerpoint Physical Geography Australia and New Zealand are between the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Australia s seasons are opposite of the United States due to their location.
Australia and New Zealand: Powerpoint Physical Geography Australia and New Zealand are between the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Australia s seasons are opposite of the United States due to their location.
Four New Records of Two Genera Balanophyllia and Cladopsammia (Anthozoa: Hexacorallia: Scleractinia: Dendrophylliidae) from Korea
 Short communication Anim. Syst. Evol. Divers. Vol. 30, No. 3: 183-190, July 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.5635/ased.2014.30.3.183 Four New Records of Two Genera Balanophyllia and Cladopsammia (Anthozoa: Hexacorallia:
Short communication Anim. Syst. Evol. Divers. Vol. 30, No. 3: 183-190, July 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.5635/ased.2014.30.3.183 Four New Records of Two Genera Balanophyllia and Cladopsammia (Anthozoa: Hexacorallia:
Studying the Ocean Using Live Data
 Studying the Ocean Using Live Data Overview The Argo buoy project is a major oceanographic study that harnesses the power of automated unmanned buoys traveling the world s oceans (http://www.argo.ucsd.edu/).
Studying the Ocean Using Live Data Overview The Argo buoy project is a major oceanographic study that harnesses the power of automated unmanned buoys traveling the world s oceans (http://www.argo.ucsd.edu/).
The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and
 Earth s Structure The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and
Earth s Structure The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and
Reef Corals. Coral Reefs. Coral Nutrition. Zooxanthallae
 Coral Reefs Highly diverse rivals tropical rain forest Biogenic habitat habitat made by living organisms Are found in areas of warm clear water that is also typically nutrient poor Are increasingly threatened
Coral Reefs Highly diverse rivals tropical rain forest Biogenic habitat habitat made by living organisms Are found in areas of warm clear water that is also typically nutrient poor Are increasingly threatened
Hiroyuki Tachikawa. Introduction
 47 39 50 2011 4 15 Mem. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Tokyo, (47): 39 50, April 15, 2011 Review of the Japanese Species of Alatotrochus and Sphenotrochus (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Scleractinia: Turbinoliidae), with
47 39 50 2011 4 15 Mem. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Tokyo, (47): 39 50, April 15, 2011 Review of the Japanese Species of Alatotrochus and Sphenotrochus (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Scleractinia: Turbinoliidae), with
Copyright 2016 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 SI Quiz 14: Wk of Nov. 28 Copyright 2016 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Question #1 Two hundred and twenty-five million years ago, all of today's continents were part of a single continent known as Pangaea.
SI Quiz 14: Wk of Nov. 28 Copyright 2016 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Question #1 Two hundred and twenty-five million years ago, all of today's continents were part of a single continent known as Pangaea.
News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake
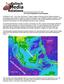 News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake PASADENA, Calif. - Kerry Sieh, the Robert P. Sharp Professor of Geology at the California Institute of Technology and a member of Caltech's
News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake PASADENA, Calif. - Kerry Sieh, the Robert P. Sharp Professor of Geology at the California Institute of Technology and a member of Caltech's
Discusssion / Activity 1 Suggested Answers. INSPECTION COPY for schools only
 Earth Structure Discusssion / Activity 1 Suggested Answers 1. Clearly label the diagram to show the main layers of the Earth. 2. What is the lithosphere? The lithosphere is the crust, plus a thin part
Earth Structure Discusssion / Activity 1 Suggested Answers 1. Clearly label the diagram to show the main layers of the Earth. 2. What is the lithosphere? The lithosphere is the crust, plus a thin part
UNVERSITY OF MICHIGAN THREE NEW SPECIES OF THE CYSTID GENUS LIPSANOCYSTIS FROM THE MIDDLE DEVONIAN TRAVERSE GROUP OF MICHIGAN
 CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE MUSEUM OF PALEONTOLOGY UNVERSITY OF MICHIGAN VOL. XII, No. 6, pp. 97-103 (2 pls.) APRIL 8, 1955 THREE NEW SPECIES OF THE CYSTID GENUS LIPSANOCYSTIS FROM THE MIDDLE DEVONIAN TRAVERSE
CONTRIBUTIONS FROM THE MUSEUM OF PALEONTOLOGY UNVERSITY OF MICHIGAN VOL. XII, No. 6, pp. 97-103 (2 pls.) APRIL 8, 1955 THREE NEW SPECIES OF THE CYSTID GENUS LIPSANOCYSTIS FROM THE MIDDLE DEVONIAN TRAVERSE
Cyphastrea kausti sp. n. (Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Scleractinia), a new species of reef coral from the Red Sea
 ZooKeys 496: 1 13 (2015) doi: 10.3897/zookeys.496.9433 http://zookeys.pensoft.net Cyphastrea kausti sp. n. (Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Scleractinia)... 1 RESEARCH ARTICLE A peer-reviewed open-access journal Launched
ZooKeys 496: 1 13 (2015) doi: 10.3897/zookeys.496.9433 http://zookeys.pensoft.net Cyphastrea kausti sp. n. (Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Scleractinia)... 1 RESEARCH ARTICLE A peer-reviewed open-access journal Launched
5. Gravity. 5.1 Geoid Variations. The Australian Continent: A Geophysical Synthesis Gravity
 34 The Australian Continent: A Geophysical Synthesis Gravity 5. Gravity Gravity data map subtle changes in the Earth s gravitational field caused by variations in the density of the underlying materials.
34 The Australian Continent: A Geophysical Synthesis Gravity 5. Gravity Gravity data map subtle changes in the Earth s gravitational field caused by variations in the density of the underlying materials.
Unit 1: Geography. For additional information, refer to this website: 1 G e o g r a p h y
 Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
61. On Some Simple Corals from the Neogene of,lava. (Comm. by H. YABE, M.I.A., July 12, 1941.)
 No. 7.] 269 61. On Some Simple Corals from the Neogene of,lava. By Hisakatsu YABE and Motoki EGUCHI. (Comm. by H. YABE, M.I.A., July 12, 1941.) The present material forms a part of Messrs. Y. Chitani and
No. 7.] 269 61. On Some Simple Corals from the Neogene of,lava. By Hisakatsu YABE and Motoki EGUCHI. (Comm. by H. YABE, M.I.A., July 12, 1941.) The present material forms a part of Messrs. Y. Chitani and
faster moving water compared to suspension feeders that are in contact with slower moving
 Samantha Bund 7-12-05 Marine Adaptations Exploratory 1 Orange Cup Coral Size Distribution Introduction: Sessile suspension feeders such as Anthozoans rely on moving water to capture food and nutrients,
Samantha Bund 7-12-05 Marine Adaptations Exploratory 1 Orange Cup Coral Size Distribution Introduction: Sessile suspension feeders such as Anthozoans rely on moving water to capture food and nutrients,
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 10 - Whole Lotta Shakin' Goin' On
 General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 10 - Whole Lotta Shakin' Goin' On Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 10 - Whole Lotta Shakin' Goin' On Name Not attempting to answer questions on expeditions will result in point deductions on course workbook (two or more blank
Bleaching interpretation/alert
 Global coral bleaching response and resilience testing programme, September 7, 2007 p 1 of 6 Pilot early warning for regional bleaching warning network WESTERN INDIAN OCEAN DATE OF THIS ALERT: 10 April
Global coral bleaching response and resilience testing programme, September 7, 2007 p 1 of 6 Pilot early warning for regional bleaching warning network WESTERN INDIAN OCEAN DATE OF THIS ALERT: 10 April
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor
 Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Matching. Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. 1. hydrothermal vents A. convergent
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Matching. Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. 1. hydrothermal vents A. convergent
Moreton Bay and Key Geographic Concepts Worksheet
 Moreton Bay and Key Geographic Concepts Worksheet The Australian Curriculum: Geography draws on seven key geographic concepts: place scale space environment change interconnection sustainability They are
Moreton Bay and Key Geographic Concepts Worksheet The Australian Curriculum: Geography draws on seven key geographic concepts: place scale space environment change interconnection sustainability They are
Full file at
 Essentials of Oceanography, 10e (Trujillo/Keller) Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. A)
Essentials of Oceanography, 10e (Trujillo/Keller) Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. A)
Note on an Amoeba-like Parasite from Clavellina.
 AN AMOEBA-LIKE PARASITE FROM CLAVEM/INA. 413 Note on an Amoeba-like Parasite from Clavellina. By.... Julian S. Huxley, Fellow of New College and Senior Demonstrator in the Department of Comparative Anatomy,
AN AMOEBA-LIKE PARASITE FROM CLAVEM/INA. 413 Note on an Amoeba-like Parasite from Clavellina. By.... Julian S. Huxley, Fellow of New College and Senior Demonstrator in the Department of Comparative Anatomy,
Unit 4 - Water. Earth s Interior. Earth s Interior. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Crust. Mantle. Core.
 Unit 4 - Water How did the oceans form? What special adaptations do saltwater organisms have? Where does our water come from? How do humans affect the Earth s water? Crust Rigid outer shell of Earth Oceanic
Unit 4 - Water How did the oceans form? What special adaptations do saltwater organisms have? Where does our water come from? How do humans affect the Earth s water? Crust Rigid outer shell of Earth Oceanic
Supplemental Slides. Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Junction of Land & Water. Sea Level Variations. Shore vs. Coast. Sea Level Variations
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA DEPARTMENT OF NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT. RECORD No. 1964/160. BUREAU OF Inv:AL It. ireoropn GECCIKICAL LIMY
 ic14.41-(1(-0 eopy 3 COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA DEPARTMENT OF NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT BUREAU OF MINERAL RESOURCES, GEOLOGY AND GEOPHYSICS RECORD No. 1964/160 BUREAU OF Inv:AL It. ireoropn GECCIKICAL LIMY EeL^S.*.
ic14.41-(1(-0 eopy 3 COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA DEPARTMENT OF NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT BUREAU OF MINERAL RESOURCES, GEOLOGY AND GEOPHYSICS RECORD No. 1964/160 BUREAU OF Inv:AL It. ireoropn GECCIKICAL LIMY EeL^S.*.
Rock Carvings in Hong Kong and the New Territories S. G. DAVIS, SHIRLEE EDELSTEIN, LAN TAU ISLAND
 Rock Carvings in Hong Kong and the New Territories Received 26 September 1973 S. G. DAVIS, SHIRLEE EDELSTEIN, AND MADELEINE H. TANG LAN TAU ISLAND WHEN the Shek Pik district on Lantau Island (Fig. 1) was
Rock Carvings in Hong Kong and the New Territories Received 26 September 1973 S. G. DAVIS, SHIRLEE EDELSTEIN, AND MADELEINE H. TANG LAN TAU ISLAND WHEN the Shek Pik district on Lantau Island (Fig. 1) was
Plate Tectonics. Structure of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
Tamal Mondal, C. Raghunathan and K. Venkataraman. Zoological Survey of India, Prani Vigyan Bhavan, M- Block, New Alipore, Kolkata , India
 World Journal of Zoology 9 (4): 281-290, 2014 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2014.9.4.86207 Continental Shelf of North, Middle and South Button Island National Parks of
World Journal of Zoology 9 (4): 281-290, 2014 ISSN 1817-3098 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjz.2014.9.4.86207 Continental Shelf of North, Middle and South Button Island National Parks of
Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity?
 Name: Date: TEACHER VERSION: Suggested Student Responses Included Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity? Introduction The circulation
Name: Date: TEACHER VERSION: Suggested Student Responses Included Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity? Introduction The circulation
Growth and Asexual Reproduction of the Starfish Nepanthia belcheri (Perrier)
 Growth and Asexual Reproduction of the Starfish Nepanthia belcheri (Perrier) RON KENNyl ABSTRACT: Nepanthia belcheri (Perrier) attains a longest arm radius of mm during the first growing period, 8 mm in
Growth and Asexual Reproduction of the Starfish Nepanthia belcheri (Perrier) RON KENNyl ABSTRACT: Nepanthia belcheri (Perrier) attains a longest arm radius of mm during the first growing period, 8 mm in
Drifting Continents and Spreading Seas. The Road To Plate Tectonics
 Drifting Continents and Spreading Seas The Road To Plate Tectonics Alfred Wegener and the Continental Drift hypothesis: Up until the early 1900s, long-held tradition in the earth sciences stated that continents
Drifting Continents and Spreading Seas The Road To Plate Tectonics Alfred Wegener and the Continental Drift hypothesis: Up until the early 1900s, long-held tradition in the earth sciences stated that continents
Black Point & Bihler Point
 Black Point & Bihler Point Conglomerate Photo: looking north toward end of Black Point (south of post 1) All of the rocks in this photo are conglomerate. Both Black Point and Bihler Point are formed from
Black Point & Bihler Point Conglomerate Photo: looking north toward end of Black Point (south of post 1) All of the rocks in this photo are conglomerate. Both Black Point and Bihler Point are formed from
Excursion guide NW Skåne, NGEA 01, 2018 PART 3. ASSIGNMENTS
 Excursion guide NW Skåne, NGEA 01, 2018 PART 3. ASSIGNMENTS by Associate Prof. Jonas Åkerman 1 Cover photo; The NW exposed coastline at Josefinelust with coarse beach boulders (Sw. malar ), gneiss is the
Excursion guide NW Skåne, NGEA 01, 2018 PART 3. ASSIGNMENTS by Associate Prof. Jonas Åkerman 1 Cover photo; The NW exposed coastline at Josefinelust with coarse beach boulders (Sw. malar ), gneiss is the
Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/8 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/8 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 7 No School 8 E 9 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Continental Drift Notes
clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 4 5 Dates: 9/8 9/12 Unit: Plate Tectonics Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 7 No School 8 E 9 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Continental Drift Notes
Unit: 4 Plate Tectonics LT 4.1 Earth s Interior: I can draw and interpret models of the interior of the earth.
 Unit: 4 Plate Tectonics LT 4.1 Earth s Interior: I can draw and interpret models of the interior of the earth. 1. Can you draw the 3-layer model and the 5-layer model of the Earth? #1 Yes I can: 2. Can
Unit: 4 Plate Tectonics LT 4.1 Earth s Interior: I can draw and interpret models of the interior of the earth. 1. Can you draw the 3-layer model and the 5-layer model of the Earth? #1 Yes I can: 2. Can
The Ocean Floor Chapter 14. Essentials of Geology, 8e. Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College
 The Ocean Floor Chapter 14 Essentials of Geology, 8e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the water planet 71% of Earth s surface
The Ocean Floor Chapter 14 Essentials of Geology, 8e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred to as the water planet 71% of Earth s surface
Short communication. Haloclasty on the bed of the Lake Gairdner salina, South Australia
 Cadernos Lab. Xeolóxico de Laxe Coruña. 2008. Vol. 33, pp. 59-63 ISSN: 0213-4497 Short communication Haloclasty on the bed of the Lake Gairdner salina, South Australia TWIDALE, C. R. 1 and BOURNE, J. A.
Cadernos Lab. Xeolóxico de Laxe Coruña. 2008. Vol. 33, pp. 59-63 ISSN: 0213-4497 Short communication Haloclasty on the bed of the Lake Gairdner salina, South Australia TWIDALE, C. R. 1 and BOURNE, J. A.
 Page 1 of 9 Name: Base your answer to the question on the diagram below. The arrows show the direction in which sediment is being transported along the shoreline. A barrier beach has formed, creating a
Page 1 of 9 Name: Base your answer to the question on the diagram below. The arrows show the direction in which sediment is being transported along the shoreline. A barrier beach has formed, creating a
22.4 Plate Tectonics. Africa
 The Red Sea between Africa and the Arabian peninsula in Asia marks a region where two pieces of the lithosphere are slowly moving apart. Over the next 100 million years, the Red Sea could become an ocean.
The Red Sea between Africa and the Arabian peninsula in Asia marks a region where two pieces of the lithosphere are slowly moving apart. Over the next 100 million years, the Red Sea could become an ocean.
In order to study Plate Tectonics, we must first
 TB Chapter 13 In order to study Plate Tectonics, we must first reorganize our layering system for the Earth: Old System 4 layers Crust (rigid) id) (rigid) Mantle (putty like) (semi rigid) Outer core (liquid)
TB Chapter 13 In order to study Plate Tectonics, we must first reorganize our layering system for the Earth: Old System 4 layers Crust (rigid) id) (rigid) Mantle (putty like) (semi rigid) Outer core (liquid)
Produced by Canadian Ice Service of. 2 December Seasonal Outlook Gulf of St Lawrence and East Newfoundland Waters Winter
 Environment Canada Environnement Canada Produced by Canadian Ice Service of Environment Canada 2 December 2010 Seasonal Outlook Gulf of St Lawrence and East Newfoundland Waters Winter 2010-2011 2010 Canadian
Environment Canada Environnement Canada Produced by Canadian Ice Service of Environment Canada 2 December 2010 Seasonal Outlook Gulf of St Lawrence and East Newfoundland Waters Winter 2010-2011 2010 Canadian
CHAPTER 2 THE WAY THE EARTH WORKS: EXAMINING PLATE TECTONICS
 CHAPTER 2 THE WAY THE EARTH WORKS: EXAMINING PLATE TECTONICS Coverage of plate tectonics is required early in introductory Geology as context for the mineralogy, petrology, structure, internal processes,
CHAPTER 2 THE WAY THE EARTH WORKS: EXAMINING PLATE TECTONICS Coverage of plate tectonics is required early in introductory Geology as context for the mineralogy, petrology, structure, internal processes,
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators
 Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators Table of Contents Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Benchmarks Chapter 1 The Practice of Science...................... 11
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators Table of Contents Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Benchmarks Chapter 1 The Practice of Science...................... 11
The World of Geography Pre-Test/Study Guide Chapter 1 Test
 Read each statement or question. On the lines below write the letter of the best answer. 1. Geographers look at the Earth 5. What are the two specific A. by studying cities first. measurements of Earth
Read each statement or question. On the lines below write the letter of the best answer. 1. Geographers look at the Earth 5. What are the two specific A. by studying cities first. measurements of Earth
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
FIRST GRADE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES UNIVERSE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FIRST GRADE UNIVERSE WEEK 1. PRE: Describing the Universe. LAB: Comparing and contrasting bodies that reflect light. POST: Exploring
Introduction to Geography
 Introduction to Geography ropic of Cancer 3½ N Arctic Circle 90 N Prime Meridian 0 Arctic Ocean Mississippi R. Appalachian Mts. Europe Rocky Mountains N. America Atlantic Gulf of Ocean Mexico Caribbean
Introduction to Geography ropic of Cancer 3½ N Arctic Circle 90 N Prime Meridian 0 Arctic Ocean Mississippi R. Appalachian Mts. Europe Rocky Mountains N. America Atlantic Gulf of Ocean Mexico Caribbean
