Late Holocene changes in Atlantic Surface and Deep Water Circulation
|
|
|
- Steven Price
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Late Holocene changes in Atlantic Surface and Deep Water Circulation Peter B. demenocal Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Gerard C. Bond Lamont-Doherty Earth Obs. Tom Marchitto Univ. Colorado, Boulder Brad Linsley SUNY at Albany Tom Guilderson CAMS, Lawrence Livermore Nat. Lab)
2 Deep-sea sediment coring R/V Ewing (Columbia s research ship) Multicoring & Gravity corer
3 Ocean sediment tracers of Holocene climate change
4 Holocene Climate North Atlantic Bond et al., 1997
5 Holocene cooling events Century-scale cooling events Multicentury-scale cycles Widespread - N. Atlantic 1-2 C amplitude apparently paced by (small) solar irradiance changes From Bond et al., 2001
6 Pacemaker of Holocene climate variability appears to have been solar variability... Bond et al., 2001
7 Questions 1. Late Holocene changes in N. Atlantic surface and deep ocean circulation? 2. Late Holocene amplitudes and rates of change relative to historical record? 3. Links to solar variability? Links to the subtropics and ITCZ?
8 Coring with Gerard in the North Atlantic (1998) MC11 GGC13 MC10 GGC09
9 A focus on Intermediate Waters Historically very sensitive to surface climate changes. Responsive to NAO-related surface climate changes (LSW is cooler, fresher, thicker during NAO+) Large property changes over recent decades ( T ~0.8 C, S ~0.1 psu) Large, multidecadal trends. It s possible to resolve changes of this magnitude. Labrador Sea Water LSW at 1800m (courtesy Ruth Curry, WHOI)
10 Historical LSW property trends 3.8 GSA Temp ( C) Trend: 1 C/cent THET SALT Trend: 0.1 ppt/cent Year (AD) Salinity (psu) (OWS Bravo, J. Lazier)
11 Decadal property trends in Nordic Seas Freshening of Nordic Seas over last years To ~1.5 km depth Salinity Associated with amplifying NAO. Density Tracked down to 8 N OWS Mike: Norwegian Sea t = 28.0
12 Approach Coring transect along Laurentian Slope Cores within modern LSW Multicores assure modern sediments. Bottom water T & S: Benthic foraminiferal Mg/Ca and 18 O measurements. Surface water Temperature: Planktonic foraminiferal Mg/Ca, 18 O, % N. pachy (s.).
13 Core Locations: Laurentian Slope Two Intermediate-water sediment cores m (MC11, GGC13) m (MC10, GGC09) MC23 Approx yr sampling MC11 GGC13 MC10 GGC09 LSW at 1800m (courtesy Ruth Curry, WHOI)
14 Local Hydrography LSW GGC13 GGC09
15 Reconstructing Bottom Water Temperatures Benthic foraminiferal Mg/Ca data from Lear et al., 2002 data from Hall & Chan, 2004 This Study r 2 = 0.91 C. pachyderma Marchitto and demenocal, 2003 (G-cubed)
16 Age control MC11/GGC13 ~42 cm/ka MC10/GGC09 ~20 cm/ka AMS Dates: G. bulloides R = 90±25 yrs 2-sigma errors 1030m 1850m
17 Bottom Water Temperatures Marchitto and demenocal, 2003 (G-cubed) Reproducibility ±0.2 C
18 Estimating bottom water salinity changes calcite 18 O decreases with temperature seawater 18 O increases with salinity Lynch-Stieglitz et al. (1999) Assume Mg/Ca monitors bottom water temperature (1 ±0.1 C replicate precision) Calculate 18 O seawater from Mg/Ca and 18 O calcite Calculate bottom water salinity from 18 O seawater (1 ±0.1 ppt joint error)
19 Estimating paleo-lsw properties
20 Theta - Salinity plot: Historical vs. Paleo LSW historical data LSW past 4000 yr 2x greater temperature variability 6x greater salinity variability Lower density during cold (fresh) periods
21 Probable Mechanisms Deep water cooling events: Most likely deep convection changes (UNADW..). Colder periods also fresher, consistent with instrumental record (but larger) Greater variability at deep site (and stability of shallow site) may indicate changes in UNADW rather than LSW. Higher bottom current speeds during cool periods at Björn Drift (1630m; Hall et al., 2004).
22 Estimating bottom water temperature rates of change
23 Bottom Water Temperature: Rates of Change Late Holocene Historical record OWS Bravo (J. Lazier) 2 ±2.4 C/cent. LSW cooled by 0.6 C between Multidecadal Trend: 1 C/century cooling Past rates greater than historical trend. Late Holocene rates ~2x greater than historical trend.
24 Bottom Water Salinity: Rates of change Late Holocene Historical record Very rough estimates due to large errors (±0.1 ppt) and low resolution. ±0.6 ppt / century (2 ) LSW trend Multidecadal trend: -0.1 ppt / century Late Holocene rates (much?) greater than historical trend.
25 Surface Water records: Core Locations MC11 GGC13 MC10 GGC09
26 Lab. Sea 55 N Surface Water records: Laur. Slope 45 N 2-3 C centennial-scale cooling (Interannual range: ±1 C) Consistent long-term trends Regionally Synchronous Some correspondence with Bond s lithic events
27 N. Atlantic Surface and Deep waters
28 Links to the subtropics? Florida Straits surface ocean Venezuela Humidity/runoff
29 Some Observations North Atlantic intermediate waters cooled by 1-2 C and freshened during late Holocene cool events. North Atlantic Surface and Deep water changes were similar. Amplitudes were much larger than historical. In the subtropical Atlantic, surface waters became saltier during cool events and ITCZ shifted southward Analogies to LGM? (e.g. Chiang et al., 2003; Haug et al., 2001; Schmidt et al., 2004).
30 Were solar minima associated with cooler/expanded subpolar gyre, a more smaller/constrained subtropical gyre, and southward displacement of ITCZ?
31
32 Intermediate water summary This system appears to have been very responsive. Upper NADW cooled by 1-2 C during late Holocene cool events. Amplitudes and rates of change were many times greater than historical observations. Most probably due to changes in deep convection linked to surface climate changes
Gulf Stream Temperature, Salinity, and Transport during the Last Millennium
 Gulf Stream Temperature, Salinity, and Transport during the Last Millennium David Lund - University of Michigan Part I - Geostrophic estimation of Gulf Stream flow - Gulf Stream strength varied by ~10%
Gulf Stream Temperature, Salinity, and Transport during the Last Millennium David Lund - University of Michigan Part I - Geostrophic estimation of Gulf Stream flow - Gulf Stream strength varied by ~10%
Deep Ocean Circulation & implications for Earth s climate
 Deep Ocean Circulation & implications for Earth s climate I. Ocean Layers and circulation types 1) Ocean Layers Ocean is strongly Stratified Consists of distinct LAYERS controlled by density takes huge
Deep Ocean Circulation & implications for Earth s climate I. Ocean Layers and circulation types 1) Ocean Layers Ocean is strongly Stratified Consists of distinct LAYERS controlled by density takes huge
G 3. AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society
 Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 4, Number 12 6 December 2003 1100, doi:10.1029/2003gc000598 ISSN: 1525-2027 Late Holocene
Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 4, Number 12 6 December 2003 1100, doi:10.1029/2003gc000598 ISSN: 1525-2027 Late Holocene
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE
 SEPTEMBER 2008 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 2097 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On the Temporally Varying Northward Penetration of Mediterranean Overflow Water and Eastward Penetration of Labrador
SEPTEMBER 2008 N O T E S A N D C O R R E S P O N D E N C E 2097 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE On the Temporally Varying Northward Penetration of Mediterranean Overflow Water and Eastward Penetration of Labrador
Geoffrey (Jake) Gebbie Research Associate, Harvard University Visiting Scientist, MIT
 Our basic understanding of past ocean circulation Geoffrey (Jake) Gebbie Research Associate, Harvard University Visiting Scientist, MIT ACDC Summer School, 5 June 2009 The view down a borehole (Helen Freeman,
Our basic understanding of past ocean circulation Geoffrey (Jake) Gebbie Research Associate, Harvard University Visiting Scientist, MIT ACDC Summer School, 5 June 2009 The view down a borehole (Helen Freeman,
Selected Presentation from the INSTAAR Monday Noon Seminar Series.
 Selected Presentation from the INSTAAR Monday Noon Seminar Series. Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research, University of Colorado at Boulder. http://instaar.colorado.edu http://instaar.colorado.edu/other/seminar_mon_presentations
Selected Presentation from the INSTAAR Monday Noon Seminar Series. Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research, University of Colorado at Boulder. http://instaar.colorado.edu http://instaar.colorado.edu/other/seminar_mon_presentations
Centennial-scale Climate Change from Decadally-paced Explosive Volcanism
 Centennial-scale Climate Change from Decadally-paced Explosive Volcanism Yafang Zhong and Gifford Miller INSTAAR, University of Colorado at Boulder, USA Bette Otto-Bliesner, Caspar Ammann, Marika Holland,
Centennial-scale Climate Change from Decadally-paced Explosive Volcanism Yafang Zhong and Gifford Miller INSTAAR, University of Colorado at Boulder, USA Bette Otto-Bliesner, Caspar Ammann, Marika Holland,
Holocene Oscillations in the Temperature and Salinity of the Surface Subpolar North Atlantic
 Holocene Oscillations in the Temperature and Salinity of the Surface Subpolar North Atlantic David J.R. Thornalley 1,2, Harry Elderfield 1 & I. Nick McCave 1 1. The Godwin Laboratory for Palaeoclimate
Holocene Oscillations in the Temperature and Salinity of the Surface Subpolar North Atlantic David J.R. Thornalley 1,2, Harry Elderfield 1 & I. Nick McCave 1 1. The Godwin Laboratory for Palaeoclimate
Surface Circulation Ocean current Surface Currents:
 All Write Round Robin G1. What makes up the ocean water? G2. What is the source of the salt found in ocean water? G3. How does the water temperature affect the density of ocean water? G4. How does the
All Write Round Robin G1. What makes up the ocean water? G2. What is the source of the salt found in ocean water? G3. How does the water temperature affect the density of ocean water? G4. How does the
National Oceanography Centre. Research & Consultancy Report No. 36
 National Oceanography Centre Research & Consultancy Report No. 36 State of the eastern North Atlantic subpolar gyre: The Extended Ellett Line Programme Annual Report No. 1 N P Holliday 1, S Cunningham
National Oceanography Centre Research & Consultancy Report No. 36 State of the eastern North Atlantic subpolar gyre: The Extended Ellett Line Programme Annual Report No. 1 N P Holliday 1, S Cunningham
Nordic recipes: constraining the ocean s northern overturning
 WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Nordic recipes: constraining the ocean s northern overturning Tor Eldevik, Jan Even Ø. Nilsen, et al. nersc.no/~torel/ Nordic recipes Observed sources and variability of Nordic seas
WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Nordic recipes: constraining the ocean s northern overturning Tor Eldevik, Jan Even Ø. Nilsen, et al. nersc.no/~torel/ Nordic recipes Observed sources and variability of Nordic seas
IPCC AR5 WG1 - Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Nandini Ramesh
 IPCC AR5 WG1 - Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis Nandini Ramesh Seminar in Atmospheric Science 21 st February, 2014 1. Introduc,on The ocean exchanges heat, freshwater, and C with the atmosphere.
IPCC AR5 WG1 - Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis Nandini Ramesh Seminar in Atmospheric Science 21 st February, 2014 1. Introduc,on The ocean exchanges heat, freshwater, and C with the atmosphere.
MAR 110 LECTURE #10 The Oceanic Conveyor Belt Oceanic Thermohaline Circulation
 1 MAR 110 LECTURE #10 The Oceanic Conveyor Belt Oceanic Thermohaline Circulation Ocean Climate Temperature Zones The pattern of approximately parallel oceanic surface isotherms (lines of constant temperature)
1 MAR 110 LECTURE #10 The Oceanic Conveyor Belt Oceanic Thermohaline Circulation Ocean Climate Temperature Zones The pattern of approximately parallel oceanic surface isotherms (lines of constant temperature)
Homework 5: Background Ocean Water Properties & Stratification
 14 August 2008 MAR 110 HW5: Ocean Properties 1 Homework 5: Background Ocean Water Properties & Stratification The ocean is a heterogeneous mixture of water types - each with its own temperature, salinity,
14 August 2008 MAR 110 HW5: Ocean Properties 1 Homework 5: Background Ocean Water Properties & Stratification The ocean is a heterogeneous mixture of water types - each with its own temperature, salinity,
Assessing how North Atlantic ocean overturning has varied over the last 50 years
 Assessing how North Atlantic ocean overturning has varied over the last 50 years Vassil Roussenov 1, Ric Williams 1, M. Susan Lozier 2 and Doug Smith 3 1. School of Environmental Sciences, University of
Assessing how North Atlantic ocean overturning has varied over the last 50 years Vassil Roussenov 1, Ric Williams 1, M. Susan Lozier 2 and Doug Smith 3 1. School of Environmental Sciences, University of
Muted change in Atlantic overturning circulation over some glacial-aged Heinrich events
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2045 Muted change in Atlantic overturning circulation over some glacial-aged Heinrich events Jean Lynch-Stieglitz 1, Matthew W. Schmidt 2, L. Gene Henry 1,7,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2045 Muted change in Atlantic overturning circulation over some glacial-aged Heinrich events Jean Lynch-Stieglitz 1, Matthew W. Schmidt 2, L. Gene Henry 1,7,
Chapter 4. Understanding the Weather. Weather is short-term and caused by various air and ocean circulations
 Video: Meteorologist Paul Douglas April 2013 Understanding the Weather Weather is short-term and caused by various air and ocean circulations There are natural climate cycle that cause large climate changes
Video: Meteorologist Paul Douglas April 2013 Understanding the Weather Weather is short-term and caused by various air and ocean circulations There are natural climate cycle that cause large climate changes
1. Introduction 2. Ocean circulation a) Temperature, salinity, density b) Thermohaline circulation c) Wind-driven surface currents d) Circulation and
 1. Introduction 2. Ocean circulation a) Temperature, salinity, density b) Thermohaline circulation c) Wind-driven surface currents d) Circulation and climate change e) Oceanic water residence times 3.
1. Introduction 2. Ocean circulation a) Temperature, salinity, density b) Thermohaline circulation c) Wind-driven surface currents d) Circulation and climate change e) Oceanic water residence times 3.
Deep Sea Coral Evidence for the state of the Southern Ocean Biological Pump (and Circulation) During the Last Glacial Period and Deglaciation
 Deep Sea Coral Evidence for the state of the Southern Ocean Biological Pump (and Circulation) During the Last Glacial Period and Deglaciation Sophie Hines, Caltech Andrea Burke, St. Andrews Laura Robinson,
Deep Sea Coral Evidence for the state of the Southern Ocean Biological Pump (and Circulation) During the Last Glacial Period and Deglaciation Sophie Hines, Caltech Andrea Burke, St. Andrews Laura Robinson,
EXPORT PATHWAYS FROM THE SUBPOLAR NORTH ATLANTIC OCEAN
 CRUISE REPORT EXPORT PATHWAYS FROM THE SUBPOLAR NORTH ATLANTIC OCEAN R/V Oceanus Cruise OC 395-2 July 9-23, 2003 1. Introduction and Objectives The importance of the pathways of the ocean s meridional
CRUISE REPORT EXPORT PATHWAYS FROM THE SUBPOLAR NORTH ATLANTIC OCEAN R/V Oceanus Cruise OC 395-2 July 9-23, 2003 1. Introduction and Objectives The importance of the pathways of the ocean s meridional
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
Paleo-VITALS team overview
 Paleo-VITALS team overview The team : Anne de Vernal & Claude Hillaire-Marcel, Geotop UQAM Evan Edinger, MUN; Markus Kienast, Dalhousie; Roger François, UBC + Collaborators : Martin Frank, Simone Kasemann,
Paleo-VITALS team overview The team : Anne de Vernal & Claude Hillaire-Marcel, Geotop UQAM Evan Edinger, MUN; Markus Kienast, Dalhousie; Roger François, UBC + Collaborators : Martin Frank, Simone Kasemann,
Tracers. 1. Conservative tracers. 2. Non-conservative tracers. Temperature, salinity, SiO 2, Nd, 18 O. dissolved oxygen, phosphate, nitrate
 Tracers 1. Conservative tracers Temperature, salinity, SiO 2, Nd, 18 O 2. Non-conservative tracers dissolved oxygen, phosphate, nitrate Temperature itself is a tracer but other tracers (like oxygen isotopes)
Tracers 1. Conservative tracers Temperature, salinity, SiO 2, Nd, 18 O 2. Non-conservative tracers dissolved oxygen, phosphate, nitrate Temperature itself is a tracer but other tracers (like oxygen isotopes)
A twenty year reversal in water mass trends in the subtropical North Atlantic
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L12608, doi:10.1029/2007gl029957, 2007 A twenty year reversal in water mass trends in the subtropical North Atlantic S. J. Leadbetter,
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L12608, doi:10.1029/2007gl029957, 2007 A twenty year reversal in water mass trends in the subtropical North Atlantic S. J. Leadbetter,
SIO 210 Final examination Answer Key for all questions except Daisyworld. Wednesday, December 10, PM Name:
 SIO 210 Final examination Answer Key for all questions except Daisyworld. Wednesday, December 10, 2008 3-6 PM Name: This is a closed book exam. You may use a calculator. There are two parts: Talley (weighted
SIO 210 Final examination Answer Key for all questions except Daisyworld. Wednesday, December 10, 2008 3-6 PM Name: This is a closed book exam. You may use a calculator. There are two parts: Talley (weighted
AMOC Impacts on Climate
 AMOC Impacts on Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA, Princeton, NJ, USA Paleo-AMOC Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA May 24, 2016 Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Kuklbrodt et al. 2007 McManus et al.,
AMOC Impacts on Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA, Princeton, NJ, USA Paleo-AMOC Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA May 24, 2016 Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Kuklbrodt et al. 2007 McManus et al.,
How de-coupling cloud radiative feedbacks strengthens the AMOC
 How de-coupling cloud radiative feedbacks strengthens the AMOC Elizabeth Maroon1, Eleanor Middlemas2, Jennifer Kay1, Brian Medeiros3 1CIRES, University of Colorado Boulder, 2University of Miami, 3National
How de-coupling cloud radiative feedbacks strengthens the AMOC Elizabeth Maroon1, Eleanor Middlemas2, Jennifer Kay1, Brian Medeiros3 1CIRES, University of Colorado Boulder, 2University of Miami, 3National
Glacial water mass geometry and the distribution of D 13 Cof2CO 2 in the western Atlantic Ocean
 PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 20,, doi:10.1029/2004pa001021, 2005 Glacial water mass geometry and the distribution of D 13 Cof2CO 2 in the western Atlantic Ocean W. B. Curry and D. W. Oppo Department of Geology
PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 20,, doi:10.1029/2004pa001021, 2005 Glacial water mass geometry and the distribution of D 13 Cof2CO 2 in the western Atlantic Ocean W. B. Curry and D. W. Oppo Department of Geology
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY
 MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
OCN/ATM/ESS 587. Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics.
 OCN/ATM/ESS 587 Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics. Equation of state for seawater General T/S properties of the upper ocean Heat balance of the upper ocean Upper ocean circulation Deep circulation
OCN/ATM/ESS 587 Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics. Equation of state for seawater General T/S properties of the upper ocean Heat balance of the upper ocean Upper ocean circulation Deep circulation
Ocean Dynamics Call for Papers for a Topical Collection on Multi-scale Modeling of Coastal, Shelf and Global Ocean Dynamics
 Ocean Dynamics Call for Papers for a Topical Collection on Multi-scale Modeling of Coastal, Shelf and Global Ocean Dynamics Ocean Dynamic manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) P. Scholz et al.
Ocean Dynamics Call for Papers for a Topical Collection on Multi-scale Modeling of Coastal, Shelf and Global Ocean Dynamics Ocean Dynamic manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) P. Scholz et al.
The role of salinity in the decadal variability of the North Atlantic meridional overturning circulation
 The role of salinity in the decadal variability of the North Atlantic meridional overturning circulation Claude Frankignoul LOCEAN / IPSL, Université Pierre et Marie Curie - Paris 6, case 100, 4 place
The role of salinity in the decadal variability of the North Atlantic meridional overturning circulation Claude Frankignoul LOCEAN / IPSL, Université Pierre et Marie Curie - Paris 6, case 100, 4 place
Supplementary Figure S1: Separated benthic 18 O data over 5 Myr. (a) Benthic LR04 benthic 18 O stack 16 ( ) in black with seawater 18 O ( w ) in blue
 Supplementary Figure S1: Separated benthic 18 O data over 5 Myr. (a) Benthic LR04 benthic 18 O stack 16 ( ) in black with seawater 18 O ( w ) in blue and temperature contribution ( T ) in green. (b) Surface-air
Supplementary Figure S1: Separated benthic 18 O data over 5 Myr. (a) Benthic LR04 benthic 18 O stack 16 ( ) in black with seawater 18 O ( w ) in blue and temperature contribution ( T ) in green. (b) Surface-air
North Atlantic climate and deep-ocean flow speed changes during the last 230 years
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L13614, doi:10.1029/2007gl030285, 2007 North Atlantic climate and deep-ocean flow speed changes during the last 230 years K. P. Boessenkool, 1 I. R. Hall, 1 H. Elderfield,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L13614, doi:10.1029/2007gl030285, 2007 North Atlantic climate and deep-ocean flow speed changes during the last 230 years K. P. Boessenkool, 1 I. R. Hall, 1 H. Elderfield,
60 W GREENLAND 70 N IRELAND 50 N. North Atlantic.
 NEWFOUNDLAND L A B R A D O R GREENLAND North Atlantic Current 70 N 60 E North Atlantic s Transformation Pipeline Chills and Redistributes Subtropical Water But It s Not A Smooth Process And It Mightily
NEWFOUNDLAND L A B R A D O R GREENLAND North Atlantic Current 70 N 60 E North Atlantic s Transformation Pipeline Chills and Redistributes Subtropical Water But It s Not A Smooth Process And It Mightily
Heat and Freshwater Transport through the Central Labrador Sea*
 606 J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L O C E A N O G R A P H Y VOLUME 36 Heat and Freshwater Transport through the Central Labrador Sea* F. STRANEO Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic
606 J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L O C E A N O G R A P H Y VOLUME 36 Heat and Freshwater Transport through the Central Labrador Sea* F. STRANEO Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic
Natural Climate Variability: Short Term
 Natural Climate Variability: Short Term Natural Climate Change Today: Natural Climate Change-1: Overview of processes, with focus on short to medium timescales Natural Climate Change 1) Systems Revisited:
Natural Climate Variability: Short Term Natural Climate Change Today: Natural Climate Change-1: Overview of processes, with focus on short to medium timescales Natural Climate Change 1) Systems Revisited:
Radiocarbon and stable isotope constraints on Last Glacial Maximum and Younger Dryas ventilation in the western North Atlantic
 PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 19,, doi:10.1029/2004pa001029, 2004 Radiocarbon and stable isotope constraints on Last Glacial Maximum and Younger Dryas ventilation in the western North Atlantic Lloyd D. Keigwin
PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 19,, doi:10.1029/2004pa001029, 2004 Radiocarbon and stable isotope constraints on Last Glacial Maximum and Younger Dryas ventilation in the western North Atlantic Lloyd D. Keigwin
Temperature and salinity fluctuations in the Norwegian Sea in relation to wind
 ICES Annual Science Conference 1999 Theme session L: Nordic Seas Exchanges ICES C.M. 19991L:03 Temperature and salinity fluctuations in the Norwegian Sea in relation to wind by Kjell Arne Mork and Lars
ICES Annual Science Conference 1999 Theme session L: Nordic Seas Exchanges ICES C.M. 19991L:03 Temperature and salinity fluctuations in the Norwegian Sea in relation to wind by Kjell Arne Mork and Lars
Seawater Chemistry and Chemical Oceanography. The Universal Solvent. Sphere of Hydration
 Seawater Chemistry and Chemical Oceanography The Universal Solvent Polarity of molecule makes water very effective at hydrating even weakly charged ions Sphere of Hydration Polarity of water molecules
Seawater Chemistry and Chemical Oceanography The Universal Solvent Polarity of molecule makes water very effective at hydrating even weakly charged ions Sphere of Hydration Polarity of water molecules
Clathromorphum (a calcified ALGA!) meets requirements for climate archive
 Clathromorphum (a calcified ALGA!) meets requirements for climate archive Exhibit high temporal climate recording resolution Multicentury-scale lifespan Abundant in Arctic and Subarctic Accurately records
Clathromorphum (a calcified ALGA!) meets requirements for climate archive Exhibit high temporal climate recording resolution Multicentury-scale lifespan Abundant in Arctic and Subarctic Accurately records
Arctic Ocean simulation in the CCSM4
 Arctic Ocean simulation in the CCSM4 Alexandra Jahn National Center for Atmospheric Sciences, Boulder, USA Collaborators: K. Sterling, M.M. Holland, J. Kay, J.A. Maslanik, C.M. Bitz, D.A. Bailey, J. Stroeve,
Arctic Ocean simulation in the CCSM4 Alexandra Jahn National Center for Atmospheric Sciences, Boulder, USA Collaborators: K. Sterling, M.M. Holland, J. Kay, J.A. Maslanik, C.M. Bitz, D.A. Bailey, J. Stroeve,
Upper Ocean Circulation
 Upper Ocean Circulation C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth 1 MAR555 Lecture 4: The Upper Oceanic Circulation The Oceanic Circulation
Upper Ocean Circulation C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth 1 MAR555 Lecture 4: The Upper Oceanic Circulation The Oceanic Circulation
Oceanography Vol.21, No.1
 S p e c i a l I s s u e O n S a l i n i t y Evolution of North Atlantic Water Masses Inferred from Labrador Sea Salinity Series Abstr act The Labrador Sea is the coldest and freshest basin of the North
S p e c i a l I s s u e O n S a l i n i t y Evolution of North Atlantic Water Masses Inferred from Labrador Sea Salinity Series Abstr act The Labrador Sea is the coldest and freshest basin of the North
Recent changes in the North Atlantic circulation
 Recent changes in the North Atlantic circulation Thierry Huck Laboratoire de Physique des Océans (UMR6523 CNRS IFREMER IRD UBO) UBO-UFR Sciences F308, 6 avenue Le Gorgeu, CS 93837,
Recent changes in the North Atlantic circulation Thierry Huck Laboratoire de Physique des Océans (UMR6523 CNRS IFREMER IRD UBO) UBO-UFR Sciences F308, 6 avenue Le Gorgeu, CS 93837,
The North Atlantic Ocean s Role In Abrupt Climate Change A Scientific Strategy
 The North Atlantic Ocean s Role In Abrupt Climate Change A Scientific Strategy Developed by the Ocean and Climate Change Institute WOODS HOLE OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTITUTION 1 As most of the world gradually
The North Atlantic Ocean s Role In Abrupt Climate Change A Scientific Strategy Developed by the Ocean and Climate Change Institute WOODS HOLE OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTITUTION 1 As most of the world gradually
Rates and Mechanisms of Water Mass Transformation in the Labrador Sea as Inferred from Tracer Observations*
 666 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY VOLUME 2 Rates and Mechanisms of Water Mass Transformation in the Labrador Sea as Inferred from Tracer Observations* SAMAR KHATIWALA, PETER SCHLOSSER, AND MARTIN VISBECK
666 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY VOLUME 2 Rates and Mechanisms of Water Mass Transformation in the Labrador Sea as Inferred from Tracer Observations* SAMAR KHATIWALA, PETER SCHLOSSER, AND MARTIN VISBECK
Earth/Environmental Science Oceanography
 Earth/Environmental Science Oceanography Name Part I. Modeling Deep Ocean Currents LAB: Ocean Circulation and Climate DIRECTIONS DO NOT RINSE the container between solutions! A. Effect of Temperature 1.
Earth/Environmental Science Oceanography Name Part I. Modeling Deep Ocean Currents LAB: Ocean Circulation and Climate DIRECTIONS DO NOT RINSE the container between solutions! A. Effect of Temperature 1.
What We ve Learned from the AMOC Modeling Efforts about AMOC Processes and its Role in Weather and Climate
 What We ve Learned from the AMOC Modeling Efforts about AMOC Processes and its Role in Weather and Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA POS/PSMI Joint Breakout Session 2017 US CLIVAR Summit Baltimore, August 9,
What We ve Learned from the AMOC Modeling Efforts about AMOC Processes and its Role in Weather and Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA POS/PSMI Joint Breakout Session 2017 US CLIVAR Summit Baltimore, August 9,
Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation. Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B
 Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B The observed mean circulation Lateral structure of the surface circulation Vertical structure of the circulation
Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B The observed mean circulation Lateral structure of the surface circulation Vertical structure of the circulation
FRESH WATER AS AN ESSENTIAL CLIMATE VARIABLE
 FRESH WATER AS AN ESSENTIAL CLIMATE VARIABLE IN THE ARCTIC CLIMATE SYSTEM Dmitry Dukhovskoy Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies, Florida State University, USA Andrey Proshutinsky Woods Hole
FRESH WATER AS AN ESSENTIAL CLIMATE VARIABLE IN THE ARCTIC CLIMATE SYSTEM Dmitry Dukhovskoy Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies, Florida State University, USA Andrey Proshutinsky Woods Hole
Salinity distribution in the Oceans
 Salinity distribution in the Oceans Average practical salinity of open ocean waters 34.72 http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c542/ 1/58 Salinity distribution in the Oceans Factors that control seawater salinity:
Salinity distribution in the Oceans Average practical salinity of open ocean waters 34.72 http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c542/ 1/58 Salinity distribution in the Oceans Factors that control seawater salinity:
Applying Basin-Scale HyCOM Hindcasts in Providing Open Boundary Conditions for Nested High-Resolution Coastal Circulation Modeling
 Applying Basin-Scale HyCOM Hindcasts in Providing Open Boundary Conditions for Nested High-Resolution Coastal Circulation Modeling Ruoying He Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution December 7, 2005 Cape
Applying Basin-Scale HyCOM Hindcasts in Providing Open Boundary Conditions for Nested High-Resolution Coastal Circulation Modeling Ruoying He Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution December 7, 2005 Cape
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1639 Importance of density-compensated temperature change for deep North Atlantic Ocean heat uptake C. Mauritzen 1,2, A. Melsom 1, R. T. Sutton 3 1 Norwegian
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1639 Importance of density-compensated temperature change for deep North Atlantic Ocean heat uptake C. Mauritzen 1,2, A. Melsom 1, R. T. Sutton 3 1 Norwegian
θ-s structure of the North Atlantic circulation and the associated heat/freshwater transports
 θ-s structure of the North Atlantic circulation and the associated heat/freshwater transports Xiaobiao Xu 1, Peter Rhines 2, and Eric Chassignet 1 1 Florida State University; 2 University of Washington
θ-s structure of the North Atlantic circulation and the associated heat/freshwater transports Xiaobiao Xu 1, Peter Rhines 2, and Eric Chassignet 1 1 Florida State University; 2 University of Washington
An Arctic Perspective on Climate Change
 An Arctic Perspective on Climate Change 23 Oct 2012 Gifford Miller (and many others) University of Colorado Boulder The Earth is warming How do we know? Temperature Anomaly ( C) It s a fact Global Land
An Arctic Perspective on Climate Change 23 Oct 2012 Gifford Miller (and many others) University of Colorado Boulder The Earth is warming How do we know? Temperature Anomaly ( C) It s a fact Global Land
Typical Arctic profiles. How to form halocline water? 2012 Changing Arctic Ocean 506E/497E - Lecture 7 - Woodgate
 Schematic Surface and Atlantic Circulation Typical Arctic profiles MIXED LAYER Usually thin (no wind stirring) PACIFIC WATER High nutrients Shallow (
Schematic Surface and Atlantic Circulation Typical Arctic profiles MIXED LAYER Usually thin (no wind stirring) PACIFIC WATER High nutrients Shallow (
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. College of Earth and Mineral Sciences
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Earth and Mineral Sciences SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURE VARIABILITY OVER THE LAST 2000 YEARS IN THE NORTH ATLANTIC OCEAN AND ITS IMPLICATIONS
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Earth and Mineral Sciences SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURE VARIABILITY OVER THE LAST 2000 YEARS IN THE NORTH ATLANTIC OCEAN AND ITS IMPLICATIONS
A multi-proxy study of planktonic foraminifera to identify past millennialscale. climate variability in the East Asian Monsoon and the Western Pacific
 This pdf file consists of all pages containing figures within: A multi-proxy study of planktonic foraminifera to identify past millennialscale climate variability in the East Asian Monsoon and the Western
This pdf file consists of all pages containing figures within: A multi-proxy study of planktonic foraminifera to identify past millennialscale climate variability in the East Asian Monsoon and the Western
Lecture 1. Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions. Pressure gradient + force force
 Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
Influence of volcanic eruptions. on the bi-decadal variability in. the North Atlantic
 EPIDOM Evaluation of Interannual to decennial predictability starting from observations and models Influence of volcanic eruptions on the bi-decadal variability in the North Atlantic Didier Swingedouw,
EPIDOM Evaluation of Interannual to decennial predictability starting from observations and models Influence of volcanic eruptions on the bi-decadal variability in the North Atlantic Didier Swingedouw,
size fraction for elemental measurement. Samples for Mg/Ca were cleaned using the full
 DR2008246 SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE MATERIALS Methods 51GGC and 36GGC. Samples were taken for elemental and isotopic analyses at 2 (51GGC) and 4 (36GGC) cm intervals giving a time resolution of 200 to 300 years
DR2008246 SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE MATERIALS Methods 51GGC and 36GGC. Samples were taken for elemental and isotopic analyses at 2 (51GGC) and 4 (36GGC) cm intervals giving a time resolution of 200 to 300 years
Capabilities of Ocean Mixed Layer Models
 Capabilities of Ocean Mixed Layer Models W.G. Large National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder Co, USA 1. Introduction The capabilities expected in today s state of the art models of the ocean s
Capabilities of Ocean Mixed Layer Models W.G. Large National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder Co, USA 1. Introduction The capabilities expected in today s state of the art models of the ocean s
Recent Variability in Western Boundary Currents on the Atlantic Slope from Moored Measurements and Altimetry
 Fisheries and Oceans Canada Pêches et Océans Canada Canada Recent Variability in Western Boundary Currents on the Atlantic Slope from Moored Measurements and Altimetry John Loder 1, Yuri Geshelin 1, Igor
Fisheries and Oceans Canada Pêches et Océans Canada Canada Recent Variability in Western Boundary Currents on the Atlantic Slope from Moored Measurements and Altimetry John Loder 1, Yuri Geshelin 1, Igor
G 3. Meridional overturning circulation in the South Atlantic at the last glacial maximum
 Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 7, Number 10 3 October 2006 Q10N03, doi:10.1029/2005gc001226 ISSN: 1525-2027 Click
Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 7, Number 10 3 October 2006 Q10N03, doi:10.1029/2005gc001226 ISSN: 1525-2027 Click
PROXY EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF GLOBAL TELECONNECTIONS IN MIDDLE EAST HYDROCLIMATE VARIABILITY
 PROXY EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF GLOBAL TELECONNECTIONS IN MIDDLE EAST HYDROCLIMATE VARIABILITY Yochanan Kushnir, Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory Mordchai Stein, Geological Survey of Israel! Paper published
PROXY EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF GLOBAL TELECONNECTIONS IN MIDDLE EAST HYDROCLIMATE VARIABILITY Yochanan Kushnir, Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory Mordchai Stein, Geological Survey of Israel! Paper published
Sensitivity Analysis of Sea Level Rise Simulation To the Ocean Open Boundary Specification Using the 2017 CH3D-ICM
 Sensitivity Analysis of Sea Level Rise Simulation To the Ocean Open Boundary Specification Using the 2017 CH3D-ICM STAC WQSTM Peer Review July 7, 2017 Lew Linker, Ping Wang, Richard Tian, and the CBPO
Sensitivity Analysis of Sea Level Rise Simulation To the Ocean Open Boundary Specification Using the 2017 CH3D-ICM STAC WQSTM Peer Review July 7, 2017 Lew Linker, Ping Wang, Richard Tian, and the CBPO
isopycnal outcrop w < 0 (downwelling), v < 0 L.I. V. P.
 Ocean 423 Vertical circulation 1 When we are thinking about how the density, temperature and salinity structure is set in the ocean, there are different processes at work depending on where in the water
Ocean 423 Vertical circulation 1 When we are thinking about how the density, temperature and salinity structure is set in the ocean, there are different processes at work depending on where in the water
Anticipated changes in the Nordic Seas marine climate: Scenarios for 2020, 2050, and 2080.
 Anticipated changes in the Nordic Seas marine climate: Scenarios for 2020, 2050, and 2080. By Tore Furevik 1, Helge Drange 2, and Asgeir Sorteberg 1,3 1 Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen 2 Nansen
Anticipated changes in the Nordic Seas marine climate: Scenarios for 2020, 2050, and 2080. By Tore Furevik 1, Helge Drange 2, and Asgeir Sorteberg 1,3 1 Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen 2 Nansen
Continental Hydrology, Rapid Climate Change, and the Intensity of the Atlantic MOC: Insights from Paleoclimatology
 Continental Hydrology, Rapid Climate Change, and the Intensity of the Atlantic MOC: Insights from Paleoclimatology W.R. Peltier Department of Physics University of Toronto WOCE derived N-S salinity section
Continental Hydrology, Rapid Climate Change, and the Intensity of the Atlantic MOC: Insights from Paleoclimatology W.R. Peltier Department of Physics University of Toronto WOCE derived N-S salinity section
The Influence of Subpolar Gyre Dynamics on Centennial to Millennial Scale Holocene Climate Variability in the High-Latitude North Atlantic
 University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Geological Sciences Graduate Theses & Dissertations Geological Sciences Summer 7-27-2014 The Influence of Subpolar Gyre Dynamics on Centennial to Millennial Scale
University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Geological Sciences Graduate Theses & Dissertations Geological Sciences Summer 7-27-2014 The Influence of Subpolar Gyre Dynamics on Centennial to Millennial Scale
ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT
 ATOC 1060-002 OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 22 (Chp 15, Chp 14 Pages 288-290) Objectives of Today s Class Chp 15 Global Warming, Part 1: Recent and Future Climate: Recent climate: The Holocene Climate
ATOC 1060-002 OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 22 (Chp 15, Chp 14 Pages 288-290) Objectives of Today s Class Chp 15 Global Warming, Part 1: Recent and Future Climate: Recent climate: The Holocene Climate
We re living in the Ice Age!
 Chapter 18. Coping with the Weather: Causes and Consequences of Naturally Induce Climate Change 지구시스템의이해 We re living in the Ice Age! 1 Phanerozoic Climate 서늘해지고 더웠고 따뜻했고 3 Climate Rollercoaster 4 2 Time
Chapter 18. Coping with the Weather: Causes and Consequences of Naturally Induce Climate Change 지구시스템의이해 We re living in the Ice Age! 1 Phanerozoic Climate 서늘해지고 더웠고 따뜻했고 3 Climate Rollercoaster 4 2 Time
Ocean & climate: an introduction and paleoceanographic perspective
 Ocean & climate: an introduction and paleoceanographic perspective Edouard BARD Chaire de l évolution du climat et de l'océan du Collège de France CEREGE, UMR CNRS, AMU, IRD, CdF Aix-en-Provence The ocean
Ocean & climate: an introduction and paleoceanographic perspective Edouard BARD Chaire de l évolution du climat et de l'océan du Collège de France CEREGE, UMR CNRS, AMU, IRD, CdF Aix-en-Provence The ocean
DROUGHT IN AMERICA DURING THE PAST MILLENNIUM
 DROUGHT IN AMERICA DURING THE PAST MILLENNIUM Mark Cane Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University With Ed Cook, Richard Seager, Amy Clement and Michael Mann Photo: Rose Werner The New York
DROUGHT IN AMERICA DURING THE PAST MILLENNIUM Mark Cane Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University With Ed Cook, Richard Seager, Amy Clement and Michael Mann Photo: Rose Werner The New York
A 1600-year history of the Labrador Current off Nova Scotia
 Climate Dynamics (2003) 21: 53 62 DOI 10.1007/s00382-003-0316-6 L. D. Keigwin Æ J. P. Sachs Æ Y. Rosenthal A 1600-year history of the Labrador Current off Nova Scotia Received: 11 June 2002 / Accepted:
Climate Dynamics (2003) 21: 53 62 DOI 10.1007/s00382-003-0316-6 L. D. Keigwin Æ J. P. Sachs Æ Y. Rosenthal A 1600-year history of the Labrador Current off Nova Scotia Received: 11 June 2002 / Accepted:
Sea surface temperature and salinity variability at Bermuda during the end of the Little Ice Age
 PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 23,, doi:10.1029/2007pa001532, 2008 Sea surface temperature and salinity variability at Bermuda during the end of the Little Ice Age Nathalie F. Goodkin, 1,2 Konrad A. Hughen, 3
PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 23,, doi:10.1029/2007pa001532, 2008 Sea surface temperature and salinity variability at Bermuda during the end of the Little Ice Age Nathalie F. Goodkin, 1,2 Konrad A. Hughen, 3
Land Bridge for migration of mammals and people? Arctic Change Woodgate Paleo role of Bering Strait
 Paleo role of Bering Strait Stabilizer for World Climate? (DeBoer & Nof, 2004) - if Bering Strait is open, excess freshwater in the Atlantic (from, for example, ice sheet collapse) can vent through the
Paleo role of Bering Strait Stabilizer for World Climate? (DeBoer & Nof, 2004) - if Bering Strait is open, excess freshwater in the Atlantic (from, for example, ice sheet collapse) can vent through the
Response of the Atlantic Thermohaline Circulation to Increased Atmospheric CO 2 in a Coupled Model
 4267 Response of the Atlantic Thermohaline Circulation to Increased Atmospheric CO 2 in a Coupled Model AIXUE HU, GERALD A. MEEHL, WARREN M. WASHINGTON, AND AIGUO DAI National Center for Atmospheric Research,*
4267 Response of the Atlantic Thermohaline Circulation to Increased Atmospheric CO 2 in a Coupled Model AIXUE HU, GERALD A. MEEHL, WARREN M. WASHINGTON, AND AIGUO DAI National Center for Atmospheric Research,*
Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation as seen in models, observations and paleo data
 WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation as seen in models, observations and paleo data Odd Helge Otterå, et al., oddho@nersc.no G.C. Rieber Climate Institute, NERSC, Bergen Bjerknes Centre
WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation as seen in models, observations and paleo data Odd Helge Otterå, et al., oddho@nersc.no G.C. Rieber Climate Institute, NERSC, Bergen Bjerknes Centre
Climate sensitivity of coupled models with differing ocean components
 Climate sensitivity of coupled models with differing ocean components Alex Megann, Adam Blaker and Adrian New National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK LOM Workshop, Miami, February 2011 Overview Introduction
Climate sensitivity of coupled models with differing ocean components Alex Megann, Adam Blaker and Adrian New National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK LOM Workshop, Miami, February 2011 Overview Introduction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
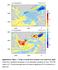 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Ocean Mixing and Climate Change
 Ocean Mixing and Climate Change Factors inducing seawater mixing Different densities Wind stirring Internal waves breaking Tidal Bottom topography Biogenic Mixing (??) In general, any motion favoring turbulent
Ocean Mixing and Climate Change Factors inducing seawater mixing Different densities Wind stirring Internal waves breaking Tidal Bottom topography Biogenic Mixing (??) In general, any motion favoring turbulent
Agulhas Leakage in the CCSM4. Wilbert Weijer (LANL, Los Alamos) Erik van Sebille (UNSW, Sydney)
 Agulhas Leakage in the CCSM4 Wilbert Weijer (LANL, Los Alamos) Erik van Sebille (UNSW, Sydney) Slide 1 Agulhas Leakage Exchange of water between South Indian and Atlantic Oceans Takes part in Supergyre
Agulhas Leakage in the CCSM4 Wilbert Weijer (LANL, Los Alamos) Erik van Sebille (UNSW, Sydney) Slide 1 Agulhas Leakage Exchange of water between South Indian and Atlantic Oceans Takes part in Supergyre
Last Glacial Maximum ocean thermohaline circulation: PMIP2 model intercomparisons and data constraints
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L12706, doi:10.1029/2007gl029475, 2007 Last Glacial Maximum ocean thermohaline circulation: PMIP2 model intercomparisons and data constraints
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L12706, doi:10.1029/2007gl029475, 2007 Last Glacial Maximum ocean thermohaline circulation: PMIP2 model intercomparisons and data constraints
Thermohaline Processes in the Ocean
 Chapter 11 Thermohaline Processes in the Ocean Heating and freshening at the ocean surface produce a buoyancy flux that can result in density gradients in the upper ocean. Depending on the scale of the
Chapter 11 Thermohaline Processes in the Ocean Heating and freshening at the ocean surface produce a buoyancy flux that can result in density gradients in the upper ocean. Depending on the scale of the
Multi-decadal simulation of Atlantic Ocean climate variability driven by realistic high-frequency atmospheric reanalysis
 Multi-decadal simulation of Atlantic Ocean climate variability driven by realistic high-frequency atmospheric reanalysis Z. Garraffo, G.Halliwell, L. Smith, G. Peng, E. Chassignet Discussions with B. Molinari,
Multi-decadal simulation of Atlantic Ocean climate variability driven by realistic high-frequency atmospheric reanalysis Z. Garraffo, G.Halliwell, L. Smith, G. Peng, E. Chassignet Discussions with B. Molinari,
Rates of North Atlantic Deep Water formation calculated from chloro#uorocarbon inventories
 Deep-Sea Research I 48 (2001) 189}215 Rates of North Atlantic Deep Water formation calculated from chloro#uorocarbon inventories William M. Smethie Jr. *, Rana A. Fine Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
Deep-Sea Research I 48 (2001) 189}215 Rates of North Atlantic Deep Water formation calculated from chloro#uorocarbon inventories William M. Smethie Jr. *, Rana A. Fine Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
PMIP3/CMIP5 Last Millennium Model Simulation Effort
 PMIP3/CMIP5 Last Millennium Model Simulation Effort Bette Otto-Bliesner and Steven Phipps National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado University of New South Wales, Sydney Outline Background
PMIP3/CMIP5 Last Millennium Model Simulation Effort Bette Otto-Bliesner and Steven Phipps National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado University of New South Wales, Sydney Outline Background
CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations
 CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations Dan Marsh, Mike Mills, Natalia Calvo, Marika Holland, Cécile Hannay WAWG meeting, Boulder, February 2011 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science
CESM1-WACCM: Comparison with CCSM4/ CESM CMIP5 simulations Dan Marsh, Mike Mills, Natalia Calvo, Marika Holland, Cécile Hannay WAWG meeting, Boulder, February 2011 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science
Advancing decadal-scale climate prediction in the North Atlantic Sector Noel Keenlyside
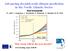 Advancing decadal-scale climate prediction in the North Atlantic Sector Noel Keenlyside M. Latif, J. Jungclaus, L. Kornblueh, E. Roeckner, V. Semenov & W. Park IPCC, 2007 How warm will be the next decade?
Advancing decadal-scale climate prediction in the North Atlantic Sector Noel Keenlyside M. Latif, J. Jungclaus, L. Kornblueh, E. Roeckner, V. Semenov & W. Park IPCC, 2007 How warm will be the next decade?
Paired benthic foraminiferal Cd/Ca and Zn/Ca evidence for a greatly increased presence of Southern Ocean Water in the glacial North Atlantic
 PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 17, NO. 3, 1038, 10.1029/2000PA000598, 2002 Paired benthic foraminiferal Cd/Ca and Zn/Ca evidence for a greatly increased presence of Southern Ocean Water in the glacial North Atlantic
PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 17, NO. 3, 1038, 10.1029/2000PA000598, 2002 Paired benthic foraminiferal Cd/Ca and Zn/Ca evidence for a greatly increased presence of Southern Ocean Water in the glacial North Atlantic
Thermohaline and wind-driven circulation
 Thermohaline and wind-driven circulation Annalisa Bracco Georgia Institute of Technology School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences NCAR ASP Colloquium: Carbon climate connections in the Earth System Tracer
Thermohaline and wind-driven circulation Annalisa Bracco Georgia Institute of Technology School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences NCAR ASP Colloquium: Carbon climate connections in the Earth System Tracer
Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research. Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes
 Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes Acknowledgments Anders Levermann Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact
Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes Acknowledgments Anders Levermann Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact
MONTHLY TEMPERATURE, SALINITY AND TRANSPORT VARIABILITY OF THE BERING STRAIT THROUGHFLOW
 MONTHLY TEMPERATURE, SALINITY AND TRANSPORT VARIABILITY OF THE BERING STRAIT THROUGHFLOW Rebecca A. Woodgate, Knut Aagaard, Polar Science Center, Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington, Seattle,
MONTHLY TEMPERATURE, SALINITY AND TRANSPORT VARIABILITY OF THE BERING STRAIT THROUGHFLOW Rebecca A. Woodgate, Knut Aagaard, Polar Science Center, Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington, Seattle,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SI #1 Sample preparation and analyses New planktonic and benthic foraminiferal radiocarbon ages were generated for late glacial and deglacial intervals from two shallow cores (Table S1). Core RR53 JPC
SI #1 Sample preparation and analyses New planktonic and benthic foraminiferal radiocarbon ages were generated for late glacial and deglacial intervals from two shallow cores (Table S1). Core RR53 JPC
REVISING THE BERING STRAIT FRESHWATER FLUX INTO THE ARCTIC OCEAN
 REVISING THE BERING STRAIT FRESHWATER FLUX INTO THE ARCTIC OCEAN Rebecca A. Woodgate and Knut Aagaard, Polar Science Center, Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington, Corresponding Author:
REVISING THE BERING STRAIT FRESHWATER FLUX INTO THE ARCTIC OCEAN Rebecca A. Woodgate and Knut Aagaard, Polar Science Center, Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington, Corresponding Author:
An analysis of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) in an Atmosphere-Ocean General Circulation Model
 An analysis of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) in an Atmosphere-Ocean General Circulation Model Virginie Guemas, David Salas-Mélia Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques (CNRM)
An analysis of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) in an Atmosphere-Ocean General Circulation Model Virginie Guemas, David Salas-Mélia Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques (CNRM)
Rapid Climate Change: Heinrich/Bolling- Allerod Events and the Thermohaline Circulation. By: Andy Lesage April 13, 2010 Atmos.
 Rapid Climate Change: Heinrich/Bolling- Allerod Events and the Thermohaline Circulation By: Andy Lesage April 13, 2010 Atmos. 6030 Outline Background Heinrich Event I/Bolling-Allerod Transition (Liu et
Rapid Climate Change: Heinrich/Bolling- Allerod Events and the Thermohaline Circulation By: Andy Lesage April 13, 2010 Atmos. 6030 Outline Background Heinrich Event I/Bolling-Allerod Transition (Liu et
Decadal-timescale changes of the Atlantic overturning circulation and climate in a coupled climate model with a hybrid-coordinate ocean component
 Clim Dyn (22) 39:2 42 DOI.7/s382-2-432-y Decadal-timescale changes of the Atlantic overturning circulation and climate in a coupled climate model with a hybrid-coordinate ocean component A. Persechino
Clim Dyn (22) 39:2 42 DOI.7/s382-2-432-y Decadal-timescale changes of the Atlantic overturning circulation and climate in a coupled climate model with a hybrid-coordinate ocean component A. Persechino
