BIOLOGICAL IMPACT ON WEATHERING OF GRANITOIDS IN THE HIGH TATRA MTS.
|
|
|
- Lindsey Caldwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOLOGICAL IMPACT ON WEATHERING OF GRANITOIDS IN THE HIGH TATRA MTS. M. MICHALIK 1 and W. WILCZYŃSKA MICHALIK 2 1 Institute of Geological Sciences, Jagiellonian University, ul. Olenadry 2a, Kraków, Poland; michalik@geos.ing.uj.edu.pl; 2 Institute of Geography, Pedagogical University, ul. Podchorążych 2, Kraków, Poland; wmichali@ap.krakow.pl Abstract: Influence of lichen encrustation on weathering of granitoids from the High Tatra Mts. was studied. Presence of lichen promotes biomechanical and biochemical processes of weathering. Biomechanical processes are caused by penetration of hyphae into minerals. Their intensity is related to the composition of minerals. Biomechanical processes result in fragmentation of the rock. Fragmentation can be stimulated by swelling of hyphae inside minerals in relation to ambient humidity and freeze-thaw processes. Biochemical processes are influenced by the activity of lichen acids, dissolved respiratory CO 2, and retention of moisture in the superficial layer of the rock. Increasing degree of fragmentation of the rock and decreasing average fragments size enhance biochemical processes rate because of increase of reaction surface. Biochemical processes cause migration of elements. Lowering of K content in biotite accompanied by increase of Al and Ca content is observed. Fe and Ti are often concentrated near altered biotite. Accumulation of element in lichen thalli is variable and partly related to the chemical composition of minerals (e.g. Ba in vicinity of K-feldspar). It is difficult to evaluate the protective role of lichen in granite weathering processes. Detached rock fragments are bound beneath lichen thallus but the fragmentation is enhanced by the development of lichens. INTRODUCTION Increase of weathering rate of silicate rock under lichen encrustation is commonly suggested however, protective role of lichens is postulated also. Brady et al. (1999) and McCaroll and Viles (1995) determined that intensity of weathering under lichens is 2-18 times or times higher than in the abiotic case. The crustose lichens can enhance
2 weathering by biomechanical action (biogeophysical weathering) and by biochemical processes (biogeochemical weathering) (Adamo & Violante, 2000, Chen et al., 2000). According to Lee and Parsons (1999), Rhizocarpon geographicum on granite binds mineral fragments and prevent rocks from entering soils. Lichen acts also as thermal insulation inhibiting mechanical disaggregation by freeze-thaw. Silica-rich layer formed during biochemical interaction between lichen and granite plays also a protective role covering mineral surfaces and closing of intragranular pores (Lee and Parsons 1999). MATERIALS Granite boulders covered by lichens (Rhizocarpon geographicum, Umbilicaria cylindrica, Lecanora intricata, L. Polytropa, Protoparmelia badia) from moraine at the Hala Gąsienicowa were collected. Granite samples from the Kościelec ridge were coated by encrustation of Rhizocarpon gepographicum and Orphiniospora moriopsis. Rocks studied represent so-called marginal zone type granite and are characterized by different textural types (medium-, coarse- very coarse-grained rocks). Mineral composition is relatively simple. Quartz and plagioclase (of oligoclase composition) are accompanied by K-feldspar, biotite and scarce muscovite. The amount of K-feldspar and muscovite increases in very coarsegrained rocks of pegmatite appearance. METHODS Observations of superficial layer of the rocks were performed using JEOL JSM 5410 and HITACHI S4700 scanning electron microscopes. Contact zones lichen crust-rock and several millimetres thick outermost layer of the rock were studied. Both rough surfaces and polished preparations were observed after carbon coating. Chemical composition of components of studied samples was determined using energy dispersive spectrometres (EDS) VOYAGER 3100 and VANTAGE (manufactured by NORAN). Optical microscopy (transmitting and reflected light) was used also. RESULTS A bleached layer (from 0.5 to 1.0 mm thick) or diffused rusty brown zone (up to several mm thick) can be observed beneath lichen layer. The occurrence of bleached or rusty layer can be related to the mineral composition of granite (e.g. abundance of biotite and other iron-containing minerals) or to the assemblage of lichens. More detailed observations are needed for establishment of these relationships.
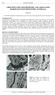
3 The lichen layer is tightly attached to the rock substrate. Numerous mineral fragments (up to few µm in size) are dispersed in the lichen thallus (Fig. 1, 2). The number of mineral fragments increase towards the rock surface. In local engulfment polygrained aggregate dozen of µm thick are present between rock surface and lichen crust. In the outer part of lichen encrustation variable concentrations of Al, Si, K, Ca, Fe, S, and P were noted (beside C) using SEM-EDS method. Irregular rounded forms very rich in Al were found inside thalli. The relatively coarse grained texture of granite allows determination of interactions of lichen crust with separate minerals. Quartz. The boundary between quartz grain and lichen encrustation is sharp. In several points small quartz fragments detached from the background are present in lichen thalli. Feldspar. Hyphae of lichens penetrate feldspar grains. Penetrations are usually cleavage controlled. Locally cleavage planes are broadened and hyphae can be seen inside (Fig. 3). Numerous pits related to lichen penetration are present on feldspar sections. The depth of penetration is variable; it often reaches 4 mm. Lichen hyphae can be also penetrate inside weakened zones in feldspar related to sericitization (Fig. 3). Lichen thallus on feldspar contains irregular grain material of various chemical composition. Point chemical analyses indicate concentration of Ba, Al, Si, Ca (Fig. 4). Biotite. Interactions between biotite and lichens are complex. Lichen penetrates deep into biotite crystals along cleavage (Fig. 5). The depth of penetration is related to the orientation of biotite. Biotite situated perpendicularly to the rock surface is penetrated significantly more deep than biotite oriented parallel to the surface. In extreme case lens-like remains of split biotite flakes are present inside lichen thallus. Significant chemical changes in biotite composition are related to the development of lichen community. Lowering of K content and increase of content Fe, Ti and Ca is typical of biotite flakes (Fig. 6, 7, 8). The content of Al is often also higher than in non-altered biotite. In lichen thallus in close vicinity of biotite Cl, Fe, Ti, Al and Si can be strongly concentrated (Fig. 8). Variable content of S can be also noted in lichen thalli. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS Presence of lichen on the surface of granite promotes both biomechanical processes (biogeophysical weathering) and biochemical processes (biogeochemical weathering). Biomechanical processes are caused by penetration of hyphae and their intensity is related to the type of rock forming minerals (biotite>feldspar>quartz). Biomechanical processes result in fragmentation of the rock. Fragmentation can be stimulated by swelling
4 and contraction of hyphae inside minerals related to ambient humidity and freeze-thaw processes. Expansion and contraction of thallus is also important among physical processes (Adamo & Violante 2000; Chen et al., 2000). Biochemical processes are influenced by the activity of oxalic acid and so-called lichen acids (Chen et al., 2000). Dissolution of respiratory CO 2 in water contained in lichen thalli generates carbonic acid (Chen et al., 2000). The retention of moisture in the superficial layer of the rock by lichen layer enhances biochemical processes also. The net result of biochemical processes is related also to the reaction surface which increases with increasing degree of fragmentation and decreasing average fragments size. Biochemical processes cause migration of elements from minerals and accumulation in the thallus. Lowering of K content in biotite accompanied by increase of Al and Ca. Similar chemical changes in biotite were noted by Wierzchos and Ascaso (1996, 1998) and attributed to transformation of biotite to biotite/vermiculite interstatified mineral formation (Wierzchos & Ascaso 1998). Ti and Fe accumulations near transformed biotite are often observed. Accumulation of element in lichen thalli is variable and partly related to the chemical composition of minerals (e.g. Ba in vicinity of K-feldspar). Biotite is most subject to biochemical weathering processes among studied minerals. This phenomenon was noted in laboratory studies (Song & Huang 1988 vide Chen et al., 2000). The protective role of lichen in granite weathering processes is difficult for evaluation. Binding of detached fragments beneath lichen thallus is clearly visible but it should be remembered that fragmentation is, at least partly, related to the development of lichens. The presence of S in lichen encrustation can be related to adsorption of components of atmospheric pollution or but relatively low S content is typical of lichen from unpolluted areas. Acknowledgements. Authors would like to express their gratitude to Professor Dr J. Kiszka for determination of lichen encrusting studied rocks. References ADAMO P., VIOLANTE P., 2000: Weathering of rocks and neogenesis of minerals associated with lichen activity. Applied Clay Sci., 16, BRADY P. V., DORN R. I., BRAZEL A. J., CLARK J., MOORE R. B., GLIDEWELL T., 1999: Direct measurement of the combined effect of lichen, rainfall, and temperature on silicate weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 63, CHEN J., BLUME VH.-P., BEYER L., 2000: Weathering of rocks induced by lichen colonization a review. Catena, 39,
5 LEE M. R., PARSONS I., 1999: Biomechanical and biochemical weathering of lichen-encrusted granite: textural controls on organic-mineral interactions and deposition of silica-rich layers. Chemical Geology, 161, McCAROLL D., VILES H. A., 1995: Rock weathering by the lichen Lecidea auriculata in an arctic alpine environment. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 20, WIERZCHOS J., ASCASO C., 1996: Morphological and chemical features of bioweathered granitic biotite induced by lichen activity. Clays and Clay Minerals, 44, WIERZCHOS J., ASCASO C., 1996: Mineralogical transformation of bioweathered granitic biotite, studied by HRTEM: evidence for a new pathway in lichen activity. Clays and Clay Minerals, 46, WILCZYŃSKA-MICHALIK W., MICHALIK M., 2000: Impact of lichens on rock weathering; results of preliminary study of the Tatra granites. Pol. Tow. Mineral. Prace Spec., 17, Fig. 1. Fragmented rock beneath lichen thallus (left). Numerous small grains accumulated near rock surface. Fig. 2. Quartz, feldspar and biotite grains beneath lichen thallus. Biotite (Bt) penetrated and disrupted by hyphae (upper right corner). Fig. 3. Cleavage and sericitization zones penetrated by hyphae. Fig. 4. Contact between lichen and sericitized biotite. Hyphae visible in holes related to sericitization. Variable concentrations of different elements in lichen. Point 3-1 high concentration of Al, Ba, Si; point 3-2 high concentration of Al and Si (Al>Si); medium concentration of Na and Ca; point 3-3 high concentration of Si; medium concentration of Ca and Al. Fig. 5. Biotite (Bt) beneath lichen thallus. Deep penetrations in biotite cleavage. Fig. 6. Remains of biotite in lichen thallus. Grains (probably of secondary accumulation) of various composition. Point 5-1 high concentration of Al, Si and Fe; medium concentration of Ti and Ca; point 5-2 high concentration of Ti; lower amount of Al and Si. Fig. 7. Lichen thallus with orientation inherited after biotite. Points 6-1 and 6-2 remains of biotite flakes domination of Si; high concentration of Al, Fe, Ti; medium concentration of Mg and Ca, very low content of K; point 6-3 Si, Al, and Cl beside C. Fig. 8. Remains of biotite flakes dispersed in lichen thallus. Point 10-1 biotite of relatively non-changed chemical composition, point 10-2 thallus between biotite flakes high concentration of Al and Si; Fe, Ca and S are present also.
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
The Production of Sediment. Contents. Weathering. Chapters 1, 3
 The Production of Sediment Chapters 1, 3 Contents Weathering Physical, chemical, biogeochemical processes Rates Products Carbon cycle and global change Erosion/Soils Sediment Texture Weathering General
The Production of Sediment Chapters 1, 3 Contents Weathering Physical, chemical, biogeochemical processes Rates Products Carbon cycle and global change Erosion/Soils Sediment Texture Weathering General
The Lithosphere. Definition
 10/14/2014 www.komar.de The Lithosphere Ben Sullivan, Assistant Professor NRES 765, Biogeochemistry October 14th, 2014 Contact: bsullivan@cabnr.unr.edu Definition io9.com tedquarters.net Lithos = rocky;
10/14/2014 www.komar.de The Lithosphere Ben Sullivan, Assistant Professor NRES 765, Biogeochemistry October 14th, 2014 Contact: bsullivan@cabnr.unr.edu Definition io9.com tedquarters.net Lithos = rocky;
9/4/2015. Feldspars White, pink, variable Clays White perfect Quartz Colourless, white, red, None
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Chapter 3.0: Weathering & soils Chapter 4.0: Geological
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Chapter 3.0: Weathering & soils Chapter 4.0: Geological
The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rocks and minerals at or near Earth s surface.
 The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rocks and minerals at or near Earth s surface. The material that is chemically and mechanically weathered to yield sediment and soil. Regolith consisting
The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rocks and minerals at or near Earth s surface. The material that is chemically and mechanically weathered to yield sediment and soil. Regolith consisting
WEATHERING. Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions 10/22/2012
 WEATHERING Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions Igneous rocks form at high temperatures; at the Earth s surface they are chemically unstable and will begin to disintegrate and decompose in a process
WEATHERING Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions Igneous rocks form at high temperatures; at the Earth s surface they are chemically unstable and will begin to disintegrate and decompose in a process
PETROGRAPHIC CHARACTERIZATION OF PAINTED ENEOLITHIC CERAMICS
 European Journal of Science and Theology, April 2013, Vol.9, No.2, 243-248 PETROGRAPHIC CHARACTERIZATION OF PAINTED ENEOLITHIC CERAMICS Daniela-Afrodita Boldea and Mirela Praisler * Dunarea de Jos University
European Journal of Science and Theology, April 2013, Vol.9, No.2, 243-248 PETROGRAPHIC CHARACTERIZATION OF PAINTED ENEOLITHIC CERAMICS Daniela-Afrodita Boldea and Mirela Praisler * Dunarea de Jos University
Weathering: the disintegration, or breakdown of rock material
 Weathering: the disintegration, or breakdown of rock material Mechanical Weathering: no change in chemical composition--just disintegration into smaller pieces Chemical Weathering: breakdown as a result
Weathering: the disintegration, or breakdown of rock material Mechanical Weathering: no change in chemical composition--just disintegration into smaller pieces Chemical Weathering: breakdown as a result
23/9/2013 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY. Chapter 2: Rock classification:
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
1/31/2013. Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes. Weathering Mechanisms. Wind abrasion forming Ventifacts
 Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes Weathering Mechanisms Physical
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes Weathering Mechanisms Physical
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy. Thanks to Rob Viens for slides
 Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
ENVI.2030L Rock Identification
 ENVI.2030L Rock Identification Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety of rocks - aggregates
ENVI.2030L Rock Identification Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety of rocks - aggregates
EARTH SCIENCE. Geology, the Environment and the Universe. Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks
 EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
GEOL FORENSIC GEOLOGY ROCK IDENTIFICATION
 GEOL.2150 - FORENSIC GEOLOGY ROCK IDENTIFICATION Name I. Introduction There are three basic types of rocks - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic: Igneous. Igneous rocks have solidified from molten matter
GEOL.2150 - FORENSIC GEOLOGY ROCK IDENTIFICATION Name I. Introduction There are three basic types of rocks - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic: Igneous. Igneous rocks have solidified from molten matter
LAB 2: SILICATE MINERALS
 GEOLOGY 640: Geology through Global Arts and Artifacts LAB 2: SILICATE MINERALS FRAMEWORK SILICATES The framework silicates quartz and feldspar are the most common minerals in Earth s crust. Quartz (SiO
GEOLOGY 640: Geology through Global Arts and Artifacts LAB 2: SILICATE MINERALS FRAMEWORK SILICATES The framework silicates quartz and feldspar are the most common minerals in Earth s crust. Quartz (SiO
Rocks and the Rock Cycle notes from the textbook, integrated with original contributions
 Rocks and the Rock Cycle notes from the textbook, integrated with original contributions Alessandro Grippo, Ph.D. Gneiss (a metamorphic rock) from Catalina Island, California Alessandro Grippo review Rocks
Rocks and the Rock Cycle notes from the textbook, integrated with original contributions Alessandro Grippo, Ph.D. Gneiss (a metamorphic rock) from Catalina Island, California Alessandro Grippo review Rocks
LAB 2 IDENTIFYING MATERIALS FOR MAKING SOILS: ROCK AND PARENT MATERIALS
 LAB 2 IDENTIFYING MATERIALS FOR MAKING SOILS: ROCK AND PARENT MATERIALS Learning outcomes The student is able to: 1. understand and identify rocks 2. understand and identify parent materials 3. recognize
LAB 2 IDENTIFYING MATERIALS FOR MAKING SOILS: ROCK AND PARENT MATERIALS Learning outcomes The student is able to: 1. understand and identify rocks 2. understand and identify parent materials 3. recognize
Geology for Engineers Rocks
 89.325 Geology for Engineers Rocks Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety of rocks -
89.325 Geology for Engineers Rocks Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety of rocks -
Arsenic and Other Trace Elements in Groundwater in the Southern San Joaquin Valley of California
 Arsenic and Other Trace Elements in Groundwater in the Southern San Joaquin Valley of California Dirk Baron Geological Sciences California State University, Bakersfield Trace Element Maximum Contaminant
Arsenic and Other Trace Elements in Groundwater in the Southern San Joaquin Valley of California Dirk Baron Geological Sciences California State University, Bakersfield Trace Element Maximum Contaminant
Why study Weathering?
 Why study Weathering? Weathering process of disintegrating solid rock & producing loose debris To understand geol process (like hydrologic systems) and how landscapes evolve (topo maps, landforms) Weathering
Why study Weathering? Weathering process of disintegrating solid rock & producing loose debris To understand geol process (like hydrologic systems) and how landscapes evolve (topo maps, landforms) Weathering
EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
Wednesday, October 10 th
 Wednesday, October 10 th Page 13a (left side) / Place Lab on table Objective: We will describe the different types of weathering and erosion and identify evidence of each type. Warm-up: 1. What is weathering?
Wednesday, October 10 th Page 13a (left side) / Place Lab on table Objective: We will describe the different types of weathering and erosion and identify evidence of each type. Warm-up: 1. What is weathering?
INTRODUCTION ROCK COLOR
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS Instructions: Some rocks that you would be working with may have sharp edges and corners, therefore, be careful when working with them! When you are
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS Instructions: Some rocks that you would be working with may have sharp edges and corners, therefore, be careful when working with them! When you are
GROUNDWATER GEOCHEMISTRY AND ASSOCIATED HARDPANS IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA
 254 GROUNDWATER GEOCHEMISTRY AND ASSOCIATED HARDPANS IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA Sam Lee CRC LEME, Department of Applied Geology, Curtin University of Technology, Bentley, Western Australia, 6485 INTRODUCTION
254 GROUNDWATER GEOCHEMISTRY AND ASSOCIATED HARDPANS IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA Sam Lee CRC LEME, Department of Applied Geology, Curtin University of Technology, Bentley, Western Australia, 6485 INTRODUCTION
Practice Questions for Lecture 5 Geology 1200
 Practice Questions for Lecture 5 Geology 1200 Use these questions to test your knowledge of Lecture5. The exams will be similar in format, except that they will deal with more than one chapter, and will
Practice Questions for Lecture 5 Geology 1200 Use these questions to test your knowledge of Lecture5. The exams will be similar in format, except that they will deal with more than one chapter, and will
Weathering. Weathering: is the process which breaks rocks into smaller bits. A. Physical or mechanical weathering
 Weathering Weathering: is the process which breaks rocks into smaller bits. Types of Weathering: A. Physical or mechanical weathering B. Chemical weathering C. Biological weathering 1 Mechanical or Physical
Weathering Weathering: is the process which breaks rocks into smaller bits. Types of Weathering: A. Physical or mechanical weathering B. Chemical weathering C. Biological weathering 1 Mechanical or Physical
Soil Mechanics/Geotechnical Engineering I Prof. Dilip Kumar Baidya Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Soil Mechanics/Geotechnical Engineering I Prof. Dilip Kumar Baidya Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 01 Rock Cycle Good morning. I welcome you to this
Soil Mechanics/Geotechnical Engineering I Prof. Dilip Kumar Baidya Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 01 Rock Cycle Good morning. I welcome you to this
A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals.
 Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals
 Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral.
Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral.
Igneous Rocks. Sedimentary Rocks. Metamorphic Rocks
 Name: Date: Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from the solidification of magma either below (intrusive igneous rocks) or above (extrusive igneous rocks) the Earth s surface. For example, the igneous rock
Name: Date: Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from the solidification of magma either below (intrusive igneous rocks) or above (extrusive igneous rocks) the Earth s surface. For example, the igneous rock
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Speciation of Individual Mineral Particles of Micrometer Size by the Combined Use of ATR-FT-IR Imaging and Quantitative ED-EPMA Techniques
 Speciation of Individual Mineral Particles of Micrometer Size by the ombined Use of ATR-FT-IR Imaging and Quantitative ED-EPMA Techniques Md Abdul Malek, Hae-Jin Jung, JiYeon Ryu, BoHwa Kim, Young-hul
Speciation of Individual Mineral Particles of Micrometer Size by the ombined Use of ATR-FT-IR Imaging and Quantitative ED-EPMA Techniques Md Abdul Malek, Hae-Jin Jung, JiYeon Ryu, BoHwa Kim, Young-hul
Hand specimen descriptions of igneous rocks
 Hand specimen descriptions of igneous rocks Basically, hand specimen descriptions should tell someone looking at a rock everything they need to know to recognize it in the field. Descriptions should be
Hand specimen descriptions of igneous rocks Basically, hand specimen descriptions should tell someone looking at a rock everything they need to know to recognize it in the field. Descriptions should be
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100
 Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Introduction to Weathering
 Name: Date: Period: Unit 9: Earth s Destructive Forces A. Kinds of Weathering Introduction to Weathering Distinguish between two major processes that change the Earth surface. Identify two types of weathering.
Name: Date: Period: Unit 9: Earth s Destructive Forces A. Kinds of Weathering Introduction to Weathering Distinguish between two major processes that change the Earth surface. Identify two types of weathering.
ESS 439 Lab 2 Examine Optical Properties of Minerals
 ESS 439 Lab 2 Examine Optical Properties of Minerals The optical properties depend on the manner that visible light is transmitted through the crystal, and thus are dependent on mineral s Crystal Structure
ESS 439 Lab 2 Examine Optical Properties of Minerals The optical properties depend on the manner that visible light is transmitted through the crystal, and thus are dependent on mineral s Crystal Structure
Weathering and Clast Production Geol 113
 Weathering and Clast Production Geol 113 Goals: To understand the production of clasts from the weathering of rocks. Materials: rock and sediment samples from the two localities, sediment grain size chart,
Weathering and Clast Production Geol 113 Goals: To understand the production of clasts from the weathering of rocks. Materials: rock and sediment samples from the two localities, sediment grain size chart,
What Do You See? Learning Outcomes Goals Learning Outcomes Think About It Identify classify In what kinds of environments do igneous rocks form?
 Section 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Identify and classify
Section 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Identify and classify
Soils and Soil Minerals. Remember, most things can be too little or too much.
 Soils and Soil Minerals Remember, most things can be too little or too much. 1 2 3 Source of essential elements CO 2, O 2 from atmosphere H 2 0, O 2, minerals from soil NH 4, SO 4 can volatilize and be
Soils and Soil Minerals Remember, most things can be too little or too much. 1 2 3 Source of essential elements CO 2, O 2 from atmosphere H 2 0, O 2, minerals from soil NH 4, SO 4 can volatilize and be
Chapter 6 9/25/2012. Weathering, Erosion and Soils. Introduction. How Are Earth Materials Altered? Introduction. How Are Earth Materials Altered?
 Chapter 6 Introduction Rocks and minerals are disintegrated and decomposed by the processes of mechanical and chemical weathering. Weathering, Erosion and Soils This breakdown occurs because the parent
Chapter 6 Introduction Rocks and minerals are disintegrated and decomposed by the processes of mechanical and chemical weathering. Weathering, Erosion and Soils This breakdown occurs because the parent
Geology 229 Engineering Geology. Lecture 6. Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5)
 Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 6 Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5) Outline of this Lecture 1. Rock types and rock cycle 2. Geological and engineering
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 6 Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5) Outline of this Lecture 1. Rock types and rock cycle 2. Geological and engineering
Sedimentary Geology. Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1
 Sedimentary Geology Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1 Sedimentology vs. Stratigraphy Sedimentology is the study of the origin and classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks Mostly the physical and chemical
Sedimentary Geology Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1 Sedimentology vs. Stratigraphy Sedimentology is the study of the origin and classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks Mostly the physical and chemical
Geology, Alteration and. Petrogenesis
 The Mutooroo Copper Deposit: Geology, Alteration and Petrogenesis Graham S. Teale Consultant t Andrew T. Price Havilah Resources NL The speaker would like to thank Havilah Resources NL for the opportunity
The Mutooroo Copper Deposit: Geology, Alteration and Petrogenesis Graham S. Teale Consultant t Andrew T. Price Havilah Resources NL The speaker would like to thank Havilah Resources NL for the opportunity
WEATHERING DEFINITION:
 WEATHERING WEATHERING DEFINITION: Breaking down of rock to form soil. Rock is continually broken down into smaller and smaller particles, resulting in the formation of soil. Discuss the importance of soil
WEATHERING WEATHERING DEFINITION: Breaking down of rock to form soil. Rock is continually broken down into smaller and smaller particles, resulting in the formation of soil. Discuss the importance of soil
Name Class Date. In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements.
 CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Quartz Cementation in Mudrocks: How Common Is It?
 Quartz Cementation in Mudrocks: How Common Is It? Kitty L. Milliken Barnett Shale SE/CL image Woodford Shale SE/CL image Cements are Pore-filling Precipitates Specific definition differs with research
Quartz Cementation in Mudrocks: How Common Is It? Kitty L. Milliken Barnett Shale SE/CL image Woodford Shale SE/CL image Cements are Pore-filling Precipitates Specific definition differs with research
Rocks. Rocks are composed of 1 or more minerals. Rocks are classified based on how they formed (origin). 3 classes of rocks:
 ROCKS Rocks If a mineral is a naturally occurring homogeneous solid, inorganically formed, with a definite chemical composi:on and a crystalline structure then what is a rock? Rocks Rocks are composed
ROCKS Rocks If a mineral is a naturally occurring homogeneous solid, inorganically formed, with a definite chemical composi:on and a crystalline structure then what is a rock? Rocks Rocks are composed
Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community
 Ch 1 Bedrock Geology 9/17/04 12:48 PM Page 14 Activity 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community Goals In this activity you will: Identify several igneous rocks using a rock chart. Describe
Ch 1 Bedrock Geology 9/17/04 12:48 PM Page 14 Activity 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community Goals In this activity you will: Identify several igneous rocks using a rock chart. Describe
Mechanical Weathering
 Weathering is the disintegration and decomposition of material at or near the surface. Erosion is the incorporation and transportation of material by a mobile agent, usually water, wind, or ice. Geologists
Weathering is the disintegration and decomposition of material at or near the surface. Erosion is the incorporation and transportation of material by a mobile agent, usually water, wind, or ice. Geologists
Chapter 6. Weathering, Erosion, and Soil
 Chapter 6 Weathering, Erosion, and Soil Introduction Rocks and minerals disintegrate and decompose by the processes of physical and chemical weathering. This breakdown occurs because the parent material
Chapter 6 Weathering, Erosion, and Soil Introduction Rocks and minerals disintegrate and decompose by the processes of physical and chemical weathering. This breakdown occurs because the parent material
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Mechanisms
 Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes WEATHERING CHAPTER 7 Weathering
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes WEATHERING CHAPTER 7 Weathering
Weathering, Soil, & Mass Movements. Chapter 5
 Weathering, Soil, & Mass Movements Chapter 5 5.1 Weathering Weathering: the breaking down and changing of rocks at or near the Earth s surface. Basic part of the rock cycle. 2 main types: 1. Mechanical
Weathering, Soil, & Mass Movements Chapter 5 5.1 Weathering Weathering: the breaking down and changing of rocks at or near the Earth s surface. Basic part of the rock cycle. 2 main types: 1. Mechanical
A Technique for Microscopical Soil Examinations
 A Technique for Microscopical Soil Examinations Skip Palenik Microtrace LLC Elgin, IL USA www.microtracescientific.com Edmond Locard Preliminary Separation Color (dry) Sieving Low Power Microscopy Seeds,
A Technique for Microscopical Soil Examinations Skip Palenik Microtrace LLC Elgin, IL USA www.microtracescientific.com Edmond Locard Preliminary Separation Color (dry) Sieving Low Power Microscopy Seeds,
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Lecture 5 Sedimentary rocks Recap+ continued. and Metamorphic rocks!
 Lecture 5 Sedimentary rocks Recap+ continued and Metamorphic rocks! Metamorphism Process that leads to changes in: Mineralogy Texture Sometimes chemical composition Metamorphic rocks are produced from
Lecture 5 Sedimentary rocks Recap+ continued and Metamorphic rocks! Metamorphism Process that leads to changes in: Mineralogy Texture Sometimes chemical composition Metamorphic rocks are produced from
LAB 5: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS
 EESC 2100: Mineralogy LAB 5: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS Part 1: Minerals in Granitic Rocks Learning Objectives: Students will be able to identify the most common minerals in granitoids Students will
EESC 2100: Mineralogy LAB 5: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS Part 1: Minerals in Granitic Rocks Learning Objectives: Students will be able to identify the most common minerals in granitoids Students will
GEOLOGY 333 LAB 5. Light Mechanics
 GEOLOGY 333 LAB 5 OPTICAL MICROSCOPY & MINERALS IN THIN SECTION Light Mechanics Light Waves: Visible light travels in waves, which have measurable wavelengths, frequencies, and velocities Wavelength (
GEOLOGY 333 LAB 5 OPTICAL MICROSCOPY & MINERALS IN THIN SECTION Light Mechanics Light Waves: Visible light travels in waves, which have measurable wavelengths, frequencies, and velocities Wavelength (
What factors affect the angle of a slope?
 Climate Rock type and Structure What factors affect the angle of a slope? Aspect Fast mass movements Slides: Slides are movements along the SLIP PLANE, i.e. a line of weakness in the rock or soil structure.
Climate Rock type and Structure What factors affect the angle of a slope? Aspect Fast mass movements Slides: Slides are movements along the SLIP PLANE, i.e. a line of weakness in the rock or soil structure.
About Earth Materials
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 3: EARTH MATERIALS Minerals and Rocks 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company About Earth Materials All Earth materials are composed of atoms bound
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 3: EARTH MATERIALS Minerals and Rocks 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company About Earth Materials All Earth materials are composed of atoms bound
Ecoregions Glossary. 7.8B: Changes To Texas Land Earth and Space
 Ecoregions Glossary Ecoregions The term ecoregions was developed by combining the terms ecology and region. Ecology is the study of the interrelationship of organisms and their environments. The term,
Ecoregions Glossary Ecoregions The term ecoregions was developed by combining the terms ecology and region. Ecology is the study of the interrelationship of organisms and their environments. The term,
GOLD DISTRIBUTION THROUGH THE REGOLITH PROFILE: EXAMPLES FROM THE WHITE DAM PROSPECT, OLARY, SOUTH AUSTRALIA
 GOLD DISTRIBUTION THROUGH THE REGOLITH PROFILE: EXAMPLES FROM THE WHITE DAM PROSPECT, OLARY, SOUTH AUSTRALIA Robert C. Dart, David J. Chittleborough and Karin M. Barovich CRC LEME, School of Earth and
GOLD DISTRIBUTION THROUGH THE REGOLITH PROFILE: EXAMPLES FROM THE WHITE DAM PROSPECT, OLARY, SOUTH AUSTRALIA Robert C. Dart, David J. Chittleborough and Karin M. Barovich CRC LEME, School of Earth and
Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Weathering and Soil
 Chapter 6 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Weathering and Soil Tarbuck and Lutgens Weathering Weathering involves the physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rock
Chapter 6 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Weathering and Soil Tarbuck and Lutgens Weathering Weathering involves the physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rock
Igneous, Metamorphic & Sedimentary. Chapter 5 & Chapter 6
 Igneous, Metamorphic & Sedimentary Chapter 5 & Chapter 6 Section 5.1 What are Igneous Rocks? Compare and contrast intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks. Describe the composition of magma Discuss the factors
Igneous, Metamorphic & Sedimentary Chapter 5 & Chapter 6 Section 5.1 What are Igneous Rocks? Compare and contrast intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks. Describe the composition of magma Discuss the factors
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment
 Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Copyright SOIL STRUCTURE and CLAY MINERALS
 SOIL STRUCTURE and CLAY MINERALS Soil Structure Structure of a soil may be defined as the mode of arrangement of soil grains relative to each other and the forces acting between them to hold them in their
SOIL STRUCTURE and CLAY MINERALS Soil Structure Structure of a soil may be defined as the mode of arrangement of soil grains relative to each other and the forces acting between them to hold them in their
CHAPTER 3.3: METAMORPHIC ROCKS
 CHAPTER 3.3: METAMORPHIC ROCKS Introduction Metamorphism - the process of changes in texture and mineralogy of pre-existing rock due to changes in temperature and/or pressure. Metamorphic means change
CHAPTER 3.3: METAMORPHIC ROCKS Introduction Metamorphism - the process of changes in texture and mineralogy of pre-existing rock due to changes in temperature and/or pressure. Metamorphic means change
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes
 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Name. GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks
 Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety
Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give an endless variety
Sedimentary Rocks, Stratigraphy, and Geologic Time
 Sedimentary Rocks, Stratigraphy, and Geologic Time A rock is any naturally formed, nonliving, coherent aggregate mass of solid matter that constitutes part of a planet, asteroid, moon, or other planetary
Sedimentary Rocks, Stratigraphy, and Geologic Time A rock is any naturally formed, nonliving, coherent aggregate mass of solid matter that constitutes part of a planet, asteroid, moon, or other planetary
Chapter 5: Weathering and Soils. Fig. 5.14
 Chapter 5: Weathering and Soils Fig. 5.14 OBJECTIVES Recognize that weathering breaks down minerals and rocks and occurs as a result of both mechanical and chemical processes. Explain the processes that
Chapter 5: Weathering and Soils Fig. 5.14 OBJECTIVES Recognize that weathering breaks down minerals and rocks and occurs as a result of both mechanical and chemical processes. Explain the processes that
Student Name: College: Grade:
 Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology Laboratory IGNEOUS MINERALS AND ROCKS IDENTIFICATION - INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE: In this lab you will learn to identify igneous rocks in hand samples from their
Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology Laboratory IGNEOUS MINERALS AND ROCKS IDENTIFICATION - INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE: In this lab you will learn to identify igneous rocks in hand samples from their
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition
 Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 16: WEATHERING, EROSION, AND MASS WASTING Interface Between Climate and Tectonics Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors,
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 16: WEATHERING, EROSION, AND MASS WASTING Interface Between Climate and Tectonics Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors,
Rocks & Minerals. Lesson 1 Properties of Minerals. What is a mineral? What is a mineral?
 Rocks & Minerals What is a mineral? A mineral must have 5 specific characteristics to be considered a mineral a. b. c. d. e. Naturally occurring - formed by natural processes. Solid - must have a definite
Rocks & Minerals What is a mineral? A mineral must have 5 specific characteristics to be considered a mineral a. b. c. d. e. Naturally occurring - formed by natural processes. Solid - must have a definite
Petrographic Investigation of Two Float Samples from the Goldstake Property, Northern Ontario. Prepared for: Mr. Robert Dillman
 Petrographic Investigation of Two Float Samples from the Goldstake Property, Northern Ontario Prepared for: Mr. Robert Dillman by Jim Renaud Renaud Geological Consulting Ltd. 21272 Denfield Road London,
Petrographic Investigation of Two Float Samples from the Goldstake Property, Northern Ontario Prepared for: Mr. Robert Dillman by Jim Renaud Renaud Geological Consulting Ltd. 21272 Denfield Road London,
Physical Geology 101 Laboratory MINERALS II Silicate and Carbonate Rock-Forming Minerals
 Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology 101 Laboratory MINERALS II Silicate and Carbonate Rock-Forming Minerals I. INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lab is you will improve your mineral identification
Student Name: College: Grade: Physical Geology 101 Laboratory MINERALS II Silicate and Carbonate Rock-Forming Minerals I. INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lab is you will improve your mineral identification
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks
 Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Topics that will be discussed
 Topics that will be discussed The Rock Cycle Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock The Rock Cycle -Rocks The parent material for all rocks is MAGMA. What is MAGMA? -Rock forming Minerals Are:
Topics that will be discussed The Rock Cycle Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock The Rock Cycle -Rocks The parent material for all rocks is MAGMA. What is MAGMA? -Rock forming Minerals Are:
Examining Minerals and Rocks
 Examining Minerals and Rocks What is a mineral? A mineral is homogenous, naturally occurring substance formed through geological processes that has a characteristic chemical composition, a highly ordered
Examining Minerals and Rocks What is a mineral? A mineral is homogenous, naturally occurring substance formed through geological processes that has a characteristic chemical composition, a highly ordered
Instructor: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 8 INTRODUCTION TO ROCKS AND THE ROCK CYCLE
 DATE DUE: Name: Instructor: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 8 INTRODUCTION TO ROCKS AND THE ROCK CYCLE Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer Provide specific and detailed
DATE DUE: Name: Instructor: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 8 INTRODUCTION TO ROCKS AND THE ROCK CYCLE Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer Provide specific and detailed
muscovite PART 4 SHEET SILICATES
 muscovite PART 4 SHEET SILICATES SHEET SILICATES = PHYLLOSILICATES Phyllon = leaf Large group of mineral including many common minerals: muscovite, biotite, serpentine, chlorite, talc, clay minerals Structure:
muscovite PART 4 SHEET SILICATES SHEET SILICATES = PHYLLOSILICATES Phyllon = leaf Large group of mineral including many common minerals: muscovite, biotite, serpentine, chlorite, talc, clay minerals Structure:
305 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND MINERALS
 DATE DUE: Name: Instructor: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND MINERALS Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC VOCABULARY where APPLICABLE!
DATE DUE: Name: Instructor: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND MINERALS Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC VOCABULARY where APPLICABLE!
The Nucleus. Protons. Positive electrical charge The number of protons in the nucleus determines the atomic number
 Matter Atoms The smallest unit of an element that retain its properties Small nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons The nucleus contains protons and neutrons The Nucleus Protons Positive electrical
Matter Atoms The smallest unit of an element that retain its properties Small nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons The nucleus contains protons and neutrons The Nucleus Protons Positive electrical
Bradbury Mountain, Pownal, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities August, 2008 Bradbury Mountain, Pownal, Maine 43 o 53 56.56 N, 70 o 10 45.11 W Text by Henry N. Berry IV, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Introduction
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities August, 2008 Bradbury Mountain, Pownal, Maine 43 o 53 56.56 N, 70 o 10 45.11 W Text by Henry N. Berry IV, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Introduction
Earth and Space Science. Semester 2 Review, Part 2
 Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Review, Part 2 2015 Chemical Weathering -The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes. Examples that cause chemical weathering include the action of water
Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Review, Part 2 2015 Chemical Weathering -The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes. Examples that cause chemical weathering include the action of water
Block: Igneous Rocks. From this list, select the terms which answer the following questions.
 Geology 12 Name: Mix and Match: Igneous Rocks Refer to the following list. Block: porphyritic volatiles mafic glassy magma mixing concordant discontinuous reaction series igneous vesicular partial melting
Geology 12 Name: Mix and Match: Igneous Rocks Refer to the following list. Block: porphyritic volatiles mafic glassy magma mixing concordant discontinuous reaction series igneous vesicular partial melting
Weathering and Erosion
 Weathering and Erosion Weathering the disintegration and decomposition of material at the surface Erosion the transportation of weathered material by water, wind, or ice Weathering Two kinds of weathering
Weathering and Erosion Weathering the disintegration and decomposition of material at the surface Erosion the transportation of weathered material by water, wind, or ice Weathering Two kinds of weathering
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e and s Chapter 5 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Jennifer Cole Northeastern University Earth
Essentials of Geology, 11e and s Chapter 5 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Jennifer Cole Northeastern University Earth
WEATHERING AND MASS MOVEMENTS. 1. Introduction 2. Physical/mechanical weathering 3. Chemical weathering 4. Mass movement processes
 WEATHERING AND MASS MOVEMENTS 1. Introduction 2. Physical/mechanical weathering 3. Chemical weathering 4. Mass movement processes Mean annual temperature ( C) Hot Cold TEMP. -10 0 10 20 Strong chemical
WEATHERING AND MASS MOVEMENTS 1. Introduction 2. Physical/mechanical weathering 3. Chemical weathering 4. Mass movement processes Mean annual temperature ( C) Hot Cold TEMP. -10 0 10 20 Strong chemical
Chapter 8 Lecture. Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology. Twelfth Edition. Metamorphism. Rocks. Tarbuck and Lutgens Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Twelfth Edition Metamorphism and dmetamorphic Rocks Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 8 Metamorphic Rocks What Is Metamorphism? Metamorphism means
Chapter 8 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Twelfth Edition Metamorphism and dmetamorphic Rocks Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 8 Metamorphic Rocks What Is Metamorphism? Metamorphism means
WEATHERING. Weathering breakdown of rock materials Erosion transport of broken-down materials
 WEATHERING the interacting physical, chemical & biological processes that progressively alter the original lithologic character of rocks to produce secondary minerals (e.g. clays) & unconsolidated regolith
WEATHERING the interacting physical, chemical & biological processes that progressively alter the original lithologic character of rocks to produce secondary minerals (e.g. clays) & unconsolidated regolith
UV-V-NIR Reflectance Spectroscopy
 UV-V-NIR Reflectance Spectroscopy Methods and Results A. Nathues Naturally-occurring inorganic substances with a definite and predictable chemical composition and physical properties Major groups: Silicates
UV-V-NIR Reflectance Spectroscopy Methods and Results A. Nathues Naturally-occurring inorganic substances with a definite and predictable chemical composition and physical properties Major groups: Silicates
2. REPLACEMENT OF PRIMARY PLAGIOCLASE BY SECONDARY K-FELDSPAR AND MYRMEKITE
 1 ISSN 1526-5757 2. REPLACEMENT OF PRIMARY PLAGIOCLASE BY SECONDARY K-FELDSPAR AND MYRMEKITE Lorence G. Collins email: lorencec@sysmatrix.net November 21, 1996; revised February 17, 1997 The following
1 ISSN 1526-5757 2. REPLACEMENT OF PRIMARY PLAGIOCLASE BY SECONDARY K-FELDSPAR AND MYRMEKITE Lorence G. Collins email: lorencec@sysmatrix.net November 21, 1996; revised February 17, 1997 The following
GEOL Lab 11 (Metamorphic Rocks in Hand Sample and Thin Section)
 GEOL 333 - Lab 11 (Metamorphic Rocks in Hand Sample and Thin Section) Introduction - Metamorphic rock forms from any pre-existing rock that undergoes changes due to intense heat and pressure without melting.
GEOL 333 - Lab 11 (Metamorphic Rocks in Hand Sample and Thin Section) Introduction - Metamorphic rock forms from any pre-existing rock that undergoes changes due to intense heat and pressure without melting.
305 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND MINERALS
 DATE DUE: Name: Instructor: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND MINERALS Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC VOCABULARY where APPLICABLE!
DATE DUE: Name: Instructor: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND MINERALS Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC VOCABULARY where APPLICABLE!
IGNEOUS ROCKS. SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks?
 Date Period Name IGNEOUS ROCKS SECTION.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Date Period Name IGNEOUS ROCKS SECTION.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Wikipedia.org BUILDING STONES. Chapter 4. Materials of Construction-Building Stones 1
 Wikipedia.org BUILDING STONES Chapter 4 Materials of Construction-Building Stones 1 What is Stone? Stone is a concretion of mineral matter. Used either as a; Construction material, Manufacture of other
Wikipedia.org BUILDING STONES Chapter 4 Materials of Construction-Building Stones 1 What is Stone? Stone is a concretion of mineral matter. Used either as a; Construction material, Manufacture of other
Rocks Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3
 Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3 I. Environmental significance II. Definition III. 3 major classes IV. The Rock Cycle V. Secondary classification VI. Additional sub-classes
Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3 I. Environmental significance II. Definition III. 3 major classes IV. The Rock Cycle V. Secondary classification VI. Additional sub-classes
Rocks Environmental Significance. Rocks Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3. Rocks Definition of a rock
 Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3 Environmental Significance I. Environmental significance II. Definition III. 3 major classes IV. The Rock Cycle V. Secondary classification
Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3 Environmental Significance I. Environmental significance II. Definition III. 3 major classes IV. The Rock Cycle V. Secondary classification
Atoms, Molecules and Minerals
 Atoms, Molecules and Minerals Atoms Matter The smallest unit of an element that retain its properties Molecules - a small orderly group of atoms that possess specific properties - H 2 O Small nucleus surrounded
Atoms, Molecules and Minerals Atoms Matter The smallest unit of an element that retain its properties Molecules - a small orderly group of atoms that possess specific properties - H 2 O Small nucleus surrounded
