Fri. Oct. 13, Reading: For Today. Andrews-Hanna et al (GRAIL Procellarium region)
|
|
|
- Augusta Woods
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fri. Oct. 13, 2017 Reading: For Today Zuber et al Grail Lunar Gravity Andrews-Hanna et al (GRAIL Procellarium region) Reading: For Wed. Oct. 25 Wood Ch. 5 Atmospheres (on reserve) For Friday Oct. 27 Stevenson and Halliday 2014 "The origin of the moon" Phil. Trans. of the Royal Soc. 372: Hartmann 2014 "The giant impact hypothesis: past, present (and future?)" Phil. Trans. of the Royal Soc. 372: Crawford and Joy 2014 "Lunar exploration: opening a window into the history and evolution of the inner Solar System" Phil. Trans. of the Royal Soc. 372: No Class Oct. 16, 18, 20 Today: Cratering 1
2 Formation of an impact crater Crater caused by the explosion Impactor is melted, perhaps vaporized by the kinetic energy released Temporary transient crater is round Gravity causes walls to slump inward forming terraces Movement of material inward from all sides (trying to fill in the hole) may push up central peak in the middle. Final crater is typically ~10 times the size of the impactor 2 From the Astro 1050 text: Horizons by Seeds
3 Crater Fundamentals Primary craters are explosion processes Typical crater diameter 10 that of impactor Involves assumption about typical impact velocity Doesn t apply to secondary craters For small craters original form largely preserved Typical Depth/Diameter = 1/10 See Stöffler et al for more detailed scaling For larger craters gravity can heavily modify original form 3
4 Crater Mechanics Explosion caused by large kinetic energy of incoming body E = ½ mv2 V Vesc : due to infall plus original (solar) orbital velocity of body Vesc = 11.2 km/sec Earth Vesc = 2.4 km/sec Moon V esc = 2 GM = R 2G 4 3 πr 3 ρ R = 8πGρ R 3 so for similar type objects Vesc scales roughly with radius R Results insensitive to angle of incoming projectile Only important for grazing angles less that ~15 o from horizontal Understanding this was stumbling block to early acceptance of crater mechanism 4 From the Astro 1050 text: Horizons by Seeds
5 Crater Mechanics Detailed steps in crater formation 1) 2) 3) 4) Shock wave during collision converts kinetic energy to compression & heat Rarefraction wave releases compression and ejects material Ejecta falls on surrounding region Transient crater modified by gravity effects (slumping, rebound) Play: deep_impact_pumice_side.mpg From text by Christiansen and Hamblin Impact into pumice 4.5 km/sec, 500 frames per second from the Deep Impact Team 5
6 2-D calculations From Melosh 1989: Impact Cratering: A Geological Process As compression and rarefaction wave propagate horizontally, they produce an expanding cone of ejects seen in the next slide 6
7 Movie of impact 7
8 Calculations and Experiment Crater only hemispherical initially By definition the shock waves are barely able to eject material when the crater has expanded to maximum size. This last bit of ejected material can form an stratigraphically inverted flap just outside the rim. From Melosh Impact Cratering From Melosh 1989: Impact Cratering: A Geological Process 8
9 Presence of overturned layer From Melosh 1989: Impact Cratering: A Geological Process Stratigraphically inverted flap of material 9
10 Simple craters retain original shape From Melosh 1989: Impact Cratering: A Geological Process 10
11 Aside: Effect of regolith = weak upper layer (separate from size scaling effects described later) From Melosh1989: Impact Cratering: A Geological Process 11
12 Aside: Effect of regolith = weak upper layer (separate from size scaling effects later) In addition to the bench caused by the vertical layering note the presence of small blocks of rock thrown out from the underlying bedrock. From Melosh Impact Cratering From Melosh1989: Impact Cratering: A Geological Process 12
13 Depth-Diameter (H/D) Break Strength effect not regolith depth From Melosh1989: Impact Cratering: A Geological Process Transition from simple craters shown clearly by H/D ratio Linear with Depth/Diameter (H/D) ~ 1/5 for simple craters Transition at D ~ 20 km marks onset of major modifications Slumped walls, central peaks Both simple and complex craters exist near transition diameter Transition occurs where gravity effects overcome strength of material Diameter of transition scales with 1/g 13
14 Crater Morphology Size effects All transient craters roughly similar: bowl-shaped With small craters material strength of target preserves bowl-shape With larger craters gravity greater than material yield strength: Walls collapse due to slumping which forms terraces Isostatic rebound moves material upward and inward to fill in cavity Motion collides in center to form central peak on moderate size craters Central ring forms in slightly larger craters Multiple rings form in very large craters 14
15 Size / Morphology Correlation From Hartmann and Wood
16 Detailed Form From our text by Christiansen and Hamblin Distinguishing characteristics of craters Floor lower than surrounding base level Overturned strata at rim (not shown in above drawing) Breccia and fractures in crater dying out at depth Shocked minerals Ejecta blanket morphology Morphology of crater itself changes in characteristic way with size 16
17 Secondary Craters and Ejecta Blanket Secondary impacts from material thrown out of main crater Lower speed not pure explosion shape so not always round Often occur in groups or chains Affect crater count statistics 17
18 Ages from crater counts Ignoring complications, number of craters (of given size) per unit area should be proportional to age. Complications: For absolute ages, need to know cratering rate Need to distinguish primary from secondary craters Power law distribution of impactor object masses Lots of small impactors, fewer larger ones Saturation effects 18
19 Crater saturation 19 From Melosh1989: Impact Cratering: A Geological Process
20 Cratering Rates From Melosh1989: Impact Cratering: A Geological Process These plots assume a steep production power law N D-b (i.e. relatively few large impactors compared to small ones) The saturation curve has the form N D-2 where the 2 comes from the fact that Area (Diameter)2 so the number of craters you can fit in a given area must go down as D-2. 20
21 Different types of Frequency Plots From Head et al Global Distribution of Large Lunar Craters The left cumulative histogram shows the number of all craters of diameter greater than a specified D: (N with diameter D). Other types are differential showing the number of craters in a given size diameter bin: (dn/dd) The cumulative plots can be obtained by integrating the incremental plots and (for power law distributions) look similar. The index (exponent) just changes by 1 when you integrate. On the right another variant called an R plot is shown: It is the incremental plot divided by (normalized by) an expected D-3 power law so R = D3 dn/dd It gives a horizontal line when the actual curve agrees with that expected D -3 shape 21
22 Effects of resurfacing From Hartmann and Wood 1971 Observed crater counts can show a relative deficiency of small craters the opposite of what would be predicted from the previous argument. That can be explained by resurfacing, which obliterates small (but not large) craters 22
23 Ages and Depths of resurfacing From Hartmann and Wood 1971 Crater counts for diameters below the break give the age of the resurfacing The diameter of the break (when multiplied by the depth-todiameter ratio of the craters) gives the depth of resurfacing 23
A geologic process An erosional force A chronological tool An influence on biology
 Impact Cratering: Physics and Chronology A geologic process An erosional force A chronological tool An influence on biology Impact features are common All solar system bodies with solid surfaces show evidence
Impact Cratering: Physics and Chronology A geologic process An erosional force A chronological tool An influence on biology Impact features are common All solar system bodies with solid surfaces show evidence
Astr 1050 Fri., Feb. 24, 2017
 Astr 1050 Fri., Feb. 24, 2017 Chapter 7 & 8: Overview & Formation of the Solar System Reading: Chapters 7 on Solar System Chapter 8: Earth & Terrestrial Planets Reminders: New homework on MA up this afternoon,
Astr 1050 Fri., Feb. 24, 2017 Chapter 7 & 8: Overview & Formation of the Solar System Reading: Chapters 7 on Solar System Chapter 8: Earth & Terrestrial Planets Reminders: New homework on MA up this afternoon,
Introduction. Background
 Introduction In introducing our research on mars we have asked the question: Is there a correlation between the width of an impact crater and the depth of that crater? This will lead to answering the question:
Introduction In introducing our research on mars we have asked the question: Is there a correlation between the width of an impact crater and the depth of that crater? This will lead to answering the question:
When Asteroids Collide
 Constructing the Solar System: A Smashing Success When Asteroids Collide Thomas M. Davison Department of the Geophysical Sciences Compton Lecture Series Autumn 2012 T. M. Davison Constructing the Solar
Constructing the Solar System: A Smashing Success When Asteroids Collide Thomas M. Davison Department of the Geophysical Sciences Compton Lecture Series Autumn 2012 T. M. Davison Constructing the Solar
Moon Formation. Capture Hypothesis Many Hypothesis Fission Hypothesis Double Impact Hypothesis Giant Impact Hypothesis
 Moon Formation Capture Hypothesis Many Hypothesis Fission Hypothesis Double Impact Hypothesis Giant Impact Hypothesis Capture Hypothesis Earth seized a pre-formed moon Disproved when lunar samples showed
Moon Formation Capture Hypothesis Many Hypothesis Fission Hypothesis Double Impact Hypothesis Giant Impact Hypothesis Capture Hypothesis Earth seized a pre-formed moon Disproved when lunar samples showed
5. Crater Rim Uplift and Crater Wall Collapse
 5. Crater Rim Uplift and Crater Wall Collapse The basic processes involved in crater rim uplift are understood, but there is a lot of evidence at the crater that has not been fully explored and may eventually
5. Crater Rim Uplift and Crater Wall Collapse The basic processes involved in crater rim uplift are understood, but there is a lot of evidence at the crater that has not been fully explored and may eventually
The Moon. Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon
 The Moon Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon Earth Moon Semi-major Axis 1 A.U. 384 x 10 3 km Inclination 0 Orbital period 1.000 tropical year 27.32
The Moon Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon Earth Moon Semi-major Axis 1 A.U. 384 x 10 3 km Inclination 0 Orbital period 1.000 tropical year 27.32
Lunar Crater Activity - Teacher Pages
 Adapted from: http://www.nasa.gov/pdf/180572main_etm.impact.craters.pdf I took the activity and simplified it so that there was just one independent variable: the drop height, and one dependent variable:
Adapted from: http://www.nasa.gov/pdf/180572main_etm.impact.craters.pdf I took the activity and simplified it so that there was just one independent variable: the drop height, and one dependent variable:
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON
 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University Of London Observatory PHAS1510 Certicate in Astronomy 1213.01 PHAS1510-03: Impact Craters on the Moon, Mars and Mercury Name: An experienced student should aim to complete
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University Of London Observatory PHAS1510 Certicate in Astronomy 1213.01 PHAS1510-03: Impact Craters on the Moon, Mars and Mercury Name: An experienced student should aim to complete
Lecture 15 Crater counting on Mars (Matt Smith, ESS)
 Tuesday, 24 February Lecture 15 Crater counting on Mars (Matt Smith, ESS) Reading assignment: Ch. 8.1-8.5 Radar Basics (p.626 648) Ch 8.20 - Passive microwave (p. 709-714) Next lecture Forest remote sensing,
Tuesday, 24 February Lecture 15 Crater counting on Mars (Matt Smith, ESS) Reading assignment: Ch. 8.1-8.5 Radar Basics (p.626 648) Ch 8.20 - Passive microwave (p. 709-714) Next lecture Forest remote sensing,
Analysis of impact craters on Mercury s surface
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 11, 124 c SAIt 2007 Memorie della Supplementi Analysis of impact craters on Mercury s surface E. Martellato 1, G. Cremonese 1, F. Marzari 2, M. Massironi 3, M.T. Capria 4 (1) INAF
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 11, 124 c SAIt 2007 Memorie della Supplementi Analysis of impact craters on Mercury s surface E. Martellato 1, G. Cremonese 1, F. Marzari 2, M. Massironi 3, M.T. Capria 4 (1) INAF
I. Introduction: II. Background:
 I. Introduction: Is there a difference between the size of the crater and the ejecta blanket? This question could lead to many different discoveries. When you think about the thousands of craters on mars,
I. Introduction: Is there a difference between the size of the crater and the ejecta blanket? This question could lead to many different discoveries. When you think about the thousands of craters on mars,
Assignment 2. Due March 4, 2019
 Assignment 2 Due March 4, 2019 Show all work and turn in answers on separate pages, not on these pages. Circle your final answers for clarity. Be sure to show/explain all of your reasoning and that your
Assignment 2 Due March 4, 2019 Show all work and turn in answers on separate pages, not on these pages. Circle your final answers for clarity. Be sure to show/explain all of your reasoning and that your
Impact Cratering. David A. Hardy MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM
 Impact Cratering David A. Hardy MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM Impact cratering overview: What we will learn about impact craters today: Causes of impacts - meteorites! Impact craters in our solar system Formation
Impact Cratering David A. Hardy MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM Impact cratering overview: What we will learn about impact craters today: Causes of impacts - meteorites! Impact craters in our solar system Formation
6. Crater Rim Uplift and Crater Wall Collapse
 6. Crater Rim Uplift and Crater Wall Collapse The basic processes involved in crater rim uplift are understood, but there is a lot of evidence at the crater that has not been fully explored and may eventually
6. Crater Rim Uplift and Crater Wall Collapse The basic processes involved in crater rim uplift are understood, but there is a lot of evidence at the crater that has not been fully explored and may eventually
crater density: number of craters per unit area on a surface
 Reading for this week: Chap. 9, Sect. 9.4-9.5, Chap. 10, Sect. 10.1-10.5 Homework 6: due in recitation Friday/Monday (Oct. 13, 16) Midterm grade estimates posted on Blackboard this week Astro 120 Fall
Reading for this week: Chap. 9, Sect. 9.4-9.5, Chap. 10, Sect. 10.1-10.5 Homework 6: due in recitation Friday/Monday (Oct. 13, 16) Midterm grade estimates posted on Blackboard this week Astro 120 Fall
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1828 Projectile Remnants in Central Peaks of Lunar Impact Craters Authors: Z. Yue 1, 2, B. C. Johnson 3, D. A. Minton 2, H. J. Melosh 2,3 *, K. Di 1, W. Hu 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1828 Projectile Remnants in Central Peaks of Lunar Impact Craters Authors: Z. Yue 1, 2, B. C. Johnson 3, D. A. Minton 2, H. J. Melosh 2,3 *, K. Di 1, W. Hu 1,
The Earth's Moon. The Earth's Moon, in many ways, is prototypical of a substantial fraction of the objects in the Solar System.
 1 The Earth's Moon The Earth's Moon, in many ways, is prototypical of a substantial fraction of the objects in the Solar System. Like many other moons and planets it exhibits a heavily cratered surface
1 The Earth's Moon The Earth's Moon, in many ways, is prototypical of a substantial fraction of the objects in the Solar System. Like many other moons and planets it exhibits a heavily cratered surface
EART160 Planetary Sciences. Francis Nimmo
 EART160 Planetary Sciences Francis Nimmo Last Week - Volcanism How and why are melts generated? Increase in mantle potential temperature; or Reduction in solidus temperature (e.g. water); or Thinning of
EART160 Planetary Sciences Francis Nimmo Last Week - Volcanism How and why are melts generated? Increase in mantle potential temperature; or Reduction in solidus temperature (e.g. water); or Thinning of
Assignment 4. Due TBD
 Assignment 4 Due TBD Show all work and turn in answers on separate pages, not on these pages. Circle your final answers for clarity. Be sure to show/explain all of your reasoning and that your work is
Assignment 4 Due TBD Show all work and turn in answers on separate pages, not on these pages. Circle your final answers for clarity. Be sure to show/explain all of your reasoning and that your work is
Impact Craters Teacher Page Purpose
 1 of 5 2008-05-01 12:15 PM Hawai'i Space Grant College, Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology, University of Hawai'i, 1996 Background Impact Craters Teacher Page Purpose To determine the factors
1 of 5 2008-05-01 12:15 PM Hawai'i Space Grant College, Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology, University of Hawai'i, 1996 Background Impact Craters Teacher Page Purpose To determine the factors
Lunar Cratering and Surface Composition
 Lunar Cratering and Surface Composition Earth vs. Moon On Earth, the combined actions of wind and water erode our planet s surface and reshape its appearance almost daily Most of the ancient history of
Lunar Cratering and Surface Composition Earth vs. Moon On Earth, the combined actions of wind and water erode our planet s surface and reshape its appearance almost daily Most of the ancient history of
Purpose: To determine the factors affecting the appearance of impact craters and ejecta.
 Title: Impact Craters Subject: Science Grade Level: 4 th - 8th Purpose: To determine the factors affecting the appearance of impact craters and ejecta. Materials 1 pan Lunar surface material Tempera paint,
Title: Impact Craters Subject: Science Grade Level: 4 th - 8th Purpose: To determine the factors affecting the appearance of impact craters and ejecta. Materials 1 pan Lunar surface material Tempera paint,
Practice Test for Midterm Exam
 A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
Teachersʼ Guide. Creating Craters. Down to Earth KS3
 Teachersʼ Guide Creating Craters Creating Craters! Creating Craters - Teachersʼ Guide - 2 Overview This lesson allows pupils to create impact craters in layered dry materials. Pupils can perform controlled
Teachersʼ Guide Creating Craters Creating Craters! Creating Craters - Teachersʼ Guide - 2 Overview This lesson allows pupils to create impact craters in layered dry materials. Pupils can perform controlled
Calculating Damage from Asteroid Impacts. H. J. Melosh Purdue University Planetary Defense Conference April 18, 2013
 Calculating Damage from Asteroid Impacts H. J. Melosh Purdue University Planetary Defense Conference April 18, 2013 Impact Effects can be divided into two basic categories: Local or Regional: Global: Thermal
Calculating Damage from Asteroid Impacts H. J. Melosh Purdue University Planetary Defense Conference April 18, 2013 Impact Effects can be divided into two basic categories: Local or Regional: Global: Thermal
On estimating contributions of basin ejecta to regolith deposits at lunar sites
 Meteoritics & Planetary Science 38, Nr 1, 13 33 (23) Abstract available online at http://meteoritics.org On estimating contributions of basin ejecta to regolith deposits at lunar sites Larry A. HASKIN
Meteoritics & Planetary Science 38, Nr 1, 13 33 (23) Abstract available online at http://meteoritics.org On estimating contributions of basin ejecta to regolith deposits at lunar sites Larry A. HASKIN
IMPACT-INDUCED MELTING OF NEAR-SURFACE WATER ICE ON MARS
 in 13 th APS Topical Conference on Shock-Compression of Condensed Matter 2003, edited by M. D. Furnish, Y. M. Gupta, and J. W. Forbes, pp. 1484-1487, Amer. Inst. Phys., New York, 2004 IMPACT-INDUCED MELTING
in 13 th APS Topical Conference on Shock-Compression of Condensed Matter 2003, edited by M. D. Furnish, Y. M. Gupta, and J. W. Forbes, pp. 1484-1487, Amer. Inst. Phys., New York, 2004 IMPACT-INDUCED MELTING
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
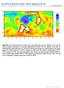 doi:10.1038/nature12280 Figure S1. The map shows the crater density (for craters larger than 25 km in diameter, N(25), per 10 6 km 2 ) on Mercury calculated in a moving neighborhood of radius 500 km, updated
doi:10.1038/nature12280 Figure S1. The map shows the crater density (for craters larger than 25 km in diameter, N(25), per 10 6 km 2 ) on Mercury calculated in a moving neighborhood of radius 500 km, updated
Mercury = Hermes Mythology. Planet Mercury, Element, Mercredi God of Commerce, Messenger God, guide to Hades Winged sandals and staff
 Mercury = Hermes Mythology Planet Mercury, Element, Mercredi God of Commerce, Messenger God, guide to Hades Winged sandals and staff Mercury s Orbit Mercury never seen more than 28 from the sun Revolves/orbits
Mercury = Hermes Mythology Planet Mercury, Element, Mercredi God of Commerce, Messenger God, guide to Hades Winged sandals and staff Mercury s Orbit Mercury never seen more than 28 from the sun Revolves/orbits
Fig. 2 Fig. 2: Nadir view from above the north pole of Phobos. Stickney Crater is tilted 13.4 west-to-east from an alignment with the geometric center
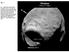 Fig. 1 Fig. 1: Phobos shown from the nadir viewpoint of ~30 W, ~0 N. The very low escape velocity from Phobos causes the majority of ejecta from the D ~9 km Stickney Crater to be inserted into orbits around
Fig. 1 Fig. 1: Phobos shown from the nadir viewpoint of ~30 W, ~0 N. The very low escape velocity from Phobos causes the majority of ejecta from the D ~9 km Stickney Crater to be inserted into orbits around
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 9 CRATERED WORLDS PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 9 CRATERED WORLDS PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 9.1 Apollo 11 Astronaut Edwin Buzz Aldrin on the Surface of the Moon. Because there is no atmosphere, ocean, or geological activity
ASTRONOMY Chapter 9 CRATERED WORLDS PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 9.1 Apollo 11 Astronaut Edwin Buzz Aldrin on the Surface of the Moon. Because there is no atmosphere, ocean, or geological activity
Finding Impact Craters with Landsat
 Name Finding Impact Craters with Landsat Known Effects of Impact Events When an object from space hits the Earth, here is what can happen. There's a huge explosion. The impact makes a big hole or crater
Name Finding Impact Craters with Landsat Known Effects of Impact Events When an object from space hits the Earth, here is what can happen. There's a huge explosion. The impact makes a big hole or crater
 http://www.lpi.usra.edu/nlsi/education/hsresearch/crateringlab/ Page 1 of 1 Impact Cratering Lab The Impact Cratering Lab exercises found on this website introduce a geologic process that has had major
http://www.lpi.usra.edu/nlsi/education/hsresearch/crateringlab/ Page 1 of 1 Impact Cratering Lab The Impact Cratering Lab exercises found on this website introduce a geologic process that has had major
Where do they come from?
 Exploring Meteorite Mysteries Lesson 7 Crater Hunters Objectives Students will: observe impact craters on Earth and other solar system bodies. discuss geologic forces that have removed most of the evidence
Exploring Meteorite Mysteries Lesson 7 Crater Hunters Objectives Students will: observe impact craters on Earth and other solar system bodies. discuss geologic forces that have removed most of the evidence
Determining a Correlation Between Ejecta Radius and Crater Diameter for Differing Lunar Materials
 Determining a Correlation Between Ejecta Radius and Crater Diameter for Differing Lunar Materials Chenango Forks Team 1 Taylor Powers Ariel Roys Andrew Collyer Bradley Oliver Hailey Brace Abstract There
Determining a Correlation Between Ejecta Radius and Crater Diameter for Differing Lunar Materials Chenango Forks Team 1 Taylor Powers Ariel Roys Andrew Collyer Bradley Oliver Hailey Brace Abstract There
What is the Moon? A natural satellite One of more than 96 moons in our Solar System The only moon of the planet Earth
 The Moon What is the Moon? A natural satellite One of more than 96 moons in our Solar System The only moon of the planet Earth Location, location, location! About 384,000 km (240,000 miles) from Earth
The Moon What is the Moon? A natural satellite One of more than 96 moons in our Solar System The only moon of the planet Earth Location, location, location! About 384,000 km (240,000 miles) from Earth
PLANETARY CRATERING MECHANICS
 Papers Presented To The SYMPOSIUM ON PLANETARY CRATERING MECHANICS LUNAR SCIENCE INSTITUTE TOPICAL CONFERENCE HOSTED BY THE U. S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY, GEOLOGIC DIVISION BRANCH OF ASTROGEOLOGIC STUDIES FLAGSTAFF,
Papers Presented To The SYMPOSIUM ON PLANETARY CRATERING MECHANICS LUNAR SCIENCE INSTITUTE TOPICAL CONFERENCE HOSTED BY THE U. S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY, GEOLOGIC DIVISION BRANCH OF ASTROGEOLOGIC STUDIES FLAGSTAFF,
Center of Mass & Linear Momentum
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
Impact Age Dating. ASTRO 202 Lecture Thursday, February 14, Review. What is relative age dating? What is relative age dating?
 Review Impact Age Dating ASTRO 202 Lecture Thursday, February 14, 2008 Carbon-14, Potassium-Argon isotopic age determination: (1) Parent decays to daughter at some predictable rate (2) How much now? (3)
Review Impact Age Dating ASTRO 202 Lecture Thursday, February 14, 2008 Carbon-14, Potassium-Argon isotopic age determination: (1) Parent decays to daughter at some predictable rate (2) How much now? (3)
CRATER COMPARISONS Investigating Impact Craters on Earth and Other Planetary Worlds
 CRATER COMPARISONS Investigating Impact Craters on Earth and Other Planetary Worlds PART 1: OBSERVATIONS AND PRELIMINARY QUESTIONS The images below are of impact craters from different planetary worlds
CRATER COMPARISONS Investigating Impact Craters on Earth and Other Planetary Worlds PART 1: OBSERVATIONS AND PRELIMINARY QUESTIONS The images below are of impact craters from different planetary worlds
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 00 (2012) 1??
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 00 (2012) 1?? Journal Logo The onset of the lunar cataclysm as recorded in its ancient crater populations Simone Marchi a,b, William F. Bottke b, David A. Kring c, Alessandro
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 00 (2012) 1?? Journal Logo The onset of the lunar cataclysm as recorded in its ancient crater populations Simone Marchi a,b, William F. Bottke b, David A. Kring c, Alessandro
Wed. Oct. 04, Makeup lecture time? Will Friday noon work for everyone? No class Oct. 16, 18, 20?
 Wed. Oct. 04, 2017 Reading: For Friday: Bugiolacchi et al. 2008 Laurence et al. 1998" Makeup lecture time? Will Friday noon work for everyone? No class Oct. 16, 18, 20? Today: Finish Lunar overview (from
Wed. Oct. 04, 2017 Reading: For Friday: Bugiolacchi et al. 2008 Laurence et al. 1998" Makeup lecture time? Will Friday noon work for everyone? No class Oct. 16, 18, 20? Today: Finish Lunar overview (from
The Coriolis effect. Why does the cloud spin? The Solar Nebula. Origin of the Solar System. Gravitational Collapse
 Origin of the Solar System Our theory must explain the data 1. Large bodies in the Solar System have orderly motions. 2. There are two types of planets. small, rocky terrestrial planets large, hydrogen-rich
Origin of the Solar System Our theory must explain the data 1. Large bodies in the Solar System have orderly motions. 2. There are two types of planets. small, rocky terrestrial planets large, hydrogen-rich
1 Describe the structure of the moon 2. Describe its surface features 3. Summarize the hypothesis of moon formation
 Loulousis 1 Describe the structure of the moon 2. Describe its surface features 3. Summarize the hypothesis of moon formation moon -a body that revolves around a planet and that has less mass than the
Loulousis 1 Describe the structure of the moon 2. Describe its surface features 3. Summarize the hypothesis of moon formation moon -a body that revolves around a planet and that has less mass than the
Today: Collect homework Hand out new homework Exam Friday Sept. 20. Carrick Eggleston begins lectures on Wednesday
 Geol 2000 Mon. Sep. 09, 2013 Today: Collect homework Hand out new homework Exam Friday Sept. 20 Review session THIS Friday Sept. 13 10AM? Geol. 216? (Discuss with class if this time works for students.
Geol 2000 Mon. Sep. 09, 2013 Today: Collect homework Hand out new homework Exam Friday Sept. 20 Review session THIS Friday Sept. 13 10AM? Geol. 216? (Discuss with class if this time works for students.
7-6 Inelastic Collisions
 7-6 Inelastic Collisions With inelastic collisions, some of the initial kinetic energy is lost to thermal or potential energy. It may also be gained during explosions, as there is the addition of chemical
7-6 Inelastic Collisions With inelastic collisions, some of the initial kinetic energy is lost to thermal or potential energy. It may also be gained during explosions, as there is the addition of chemical
This Week. 1/15/2015 Physics 214 Spring
 This Week Gravity: Dropping and throwing objects From Baseballs to satellites What causes motion. All changes involve motion Extinction of the dinosaurs 1/15/2015 Physics 214 Spring 2015 1 One dimensional
This Week Gravity: Dropping and throwing objects From Baseballs to satellites What causes motion. All changes involve motion Extinction of the dinosaurs 1/15/2015 Physics 214 Spring 2015 1 One dimensional
Numerical Modeling of Crater Formation by Meteorite Impact and Nuclear Explosion
 Numerical Modeling of Crater Formation by Meteorite Impact and Nuclear Explosion Charles L. Mader Abstract The NOBEL code for modeling compressible fluid dynamics is used to model the formation of the
Numerical Modeling of Crater Formation by Meteorite Impact and Nuclear Explosion Charles L. Mader Abstract The NOBEL code for modeling compressible fluid dynamics is used to model the formation of the
The Moon. Tides. Tides. Mass = 7.4 x 1025 g = MEarth. = 0.27 REarth. (Earth 5.5 g/cm3) Gravity = 1/6 that of Earth
 The Moon Mass = 7.4 x 1025 g = 0.012 MEarth Radius = 1738 km = 0.27 REarth Density = 3.3 g/cm3 (Earth 5.5 g/cm3) Gravity = 1/6 that of Earth Dark side of the moon We always see the same face of the Moon.
The Moon Mass = 7.4 x 1025 g = 0.012 MEarth Radius = 1738 km = 0.27 REarth Density = 3.3 g/cm3 (Earth 5.5 g/cm3) Gravity = 1/6 that of Earth Dark side of the moon We always see the same face of the Moon.
Wed. Aug. 30, 2017 Reading:
 Wed. Aug. 30, 2017 Reading: Reading for Fri.: Wood Ch. 1 (solar system overview) Reading for Wed. Wed. Wood Ch. 6 & 8 (Asteroids & Meteorites, Solar Nebula) Reading for Fri. Sept. 8. Rozel et al. (link
Wed. Aug. 30, 2017 Reading: Reading for Fri.: Wood Ch. 1 (solar system overview) Reading for Wed. Wed. Wood Ch. 6 & 8 (Asteroids & Meteorites, Solar Nebula) Reading for Fri. Sept. 8. Rozel et al. (link
9. Moon, Mercury, Venus
 9. Moon, Mercury, Venus All the heavier elements were manufactured by stars later, either by thermonuclear fusion reactions deep in their interiors or by the violent explosions that mark the end of massive
9. Moon, Mercury, Venus All the heavier elements were manufactured by stars later, either by thermonuclear fusion reactions deep in their interiors or by the violent explosions that mark the end of massive
LECTURE 13- PROBLEMS. Chapter 1-9,13 Professor Noronha-Hostler Professor Montalvo
 LECTURE 13- PROBLEMS Chapter 1-9,13 Professor Noronha-Hostler Professor Montalvo FARADAY LECTURES! Physics Lecture Hall Friday Dec. 7 Demos: 6pm Show: 7-8:30pm Saturday Dec. 8 Demos: 2pm Show: 3-4:30pm
LECTURE 13- PROBLEMS Chapter 1-9,13 Professor Noronha-Hostler Professor Montalvo FARADAY LECTURES! Physics Lecture Hall Friday Dec. 7 Demos: 6pm Show: 7-8:30pm Saturday Dec. 8 Demos: 2pm Show: 3-4:30pm
Differentiation of planetary interiors. Rocky Planets Interiors and surface geophysics
 Differentiation of planetary interiors Rocky Planets Interiors and surface geophysics Process of separation of internal planetary layers that takes place as a result of the physical and chemical properties
Differentiation of planetary interiors Rocky Planets Interiors and surface geophysics Process of separation of internal planetary layers that takes place as a result of the physical and chemical properties
18.1 Earth and Its Moon Earth s shape and orbit Earth s shape Earth s orbit around the Sun
 18.1 Earth and Its Moon Revolving around Earth at a distance of 384,400 kilometers is our only moon. Since the invention of spacecraft, our knowledge of Earth and the Moon has grown tremendously. In fact,
18.1 Earth and Its Moon Revolving around Earth at a distance of 384,400 kilometers is our only moon. Since the invention of spacecraft, our knowledge of Earth and the Moon has grown tremendously. In fact,
Interpreting the Hotchkiss structure: A possible meteorite impact feature in northwestern Alberta
 : A possible meteorite impact feature in northwestern Alberta Michael J. Mazur and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT The Hotchkiss structure in NW Alberta is an enigmatic feature whose appearance on seismic data
: A possible meteorite impact feature in northwestern Alberta Michael J. Mazur and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT The Hotchkiss structure in NW Alberta is an enigmatic feature whose appearance on seismic data
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Collision Theory Challenge Problems Solutions
 Collision Theory Challenge Problems Solutions Problem 1 Estimate the energy loss in a completely inelastic collision between two identical cars that collide head-on traveling at highway speeds! Solution:
Collision Theory Challenge Problems Solutions Problem 1 Estimate the energy loss in a completely inelastic collision between two identical cars that collide head-on traveling at highway speeds! Solution:
Unit 4 Lesson 3 Mountain Building. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Stressed Out How can tectonic plate motion cause deformation? The movement of tectonic plates causes stress on rock structures. Stress is the amount of force per unit area that is placed on an object.
Stressed Out How can tectonic plate motion cause deformation? The movement of tectonic plates causes stress on rock structures. Stress is the amount of force per unit area that is placed on an object.
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements. Next midterm 3/1!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Next midterm 3/1! 1 Previously Solar flux decreases as radiation spreads out away from the Sun Planets are exposed to some small amount of the total solar radiation A
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Next midterm 3/1! 1 Previously Solar flux decreases as radiation spreads out away from the Sun Planets are exposed to some small amount of the total solar radiation A
Outline. Hawking radiation and the LHC. Black Hole Firewall. Singularities. Wormholes
 Outline Hawking radiation and the LHC Black Hole Firewall Singularities Wormholes What happens at the end of evaporation? Eventually, energy of photon emitted would be larger than mass-energy of black
Outline Hawking radiation and the LHC Black Hole Firewall Singularities Wormholes What happens at the end of evaporation? Eventually, energy of photon emitted would be larger than mass-energy of black
Terrestrial World Surfaces
 1 Terrestrial World Surfaces Solid rocky surfaces shaped (to varying degrees) by: Impact cratering Volcanism Tectonics (gross movement of surface by interior forces) Erosion (by impacts or by weather)
1 Terrestrial World Surfaces Solid rocky surfaces shaped (to varying degrees) by: Impact cratering Volcanism Tectonics (gross movement of surface by interior forces) Erosion (by impacts or by weather)
Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)
![Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a) Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)](/thumbs/83/87594074.jpg) Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Astro 210 Lecture 19 October 8, 2010
 Astro 210 Lecture 19 October 8, 2010 Announcements Remember me? HW 5 due HW 6 available, due in class next Friday Night Observing continues next week Last time: The Moon Q: from Earth we only see one side
Astro 210 Lecture 19 October 8, 2010 Announcements Remember me? HW 5 due HW 6 available, due in class next Friday Night Observing continues next week Last time: The Moon Q: from Earth we only see one side
10. Our Barren Moon. Moon Data (Table 10-1) Moon Data: Numbers. Moon Data: Special Features 1. The Moon As Seen From Earth
 10. Our Barren Moon Lunar plains & craters Manned lunar exploration The lunar interior The Moon s geologic history The formation of the Moon Moon Data (Table 10-1) Moon Data: Numbers Diameter: 3,476.km
10. Our Barren Moon Lunar plains & craters Manned lunar exploration The lunar interior The Moon s geologic history The formation of the Moon Moon Data (Table 10-1) Moon Data: Numbers Diameter: 3,476.km
Theory and equations for Craters from Impacts and Explosions. Keith A. Holsapple
 Theory and equations or Craters rom Impacts and Explosions Keith A. Holsapple 1. Dimensionless Forms As the primary example, the volume V o a crater ormed by a given impact can be expected to depend on
Theory and equations or Craters rom Impacts and Explosions Keith A. Holsapple 1. Dimensionless Forms As the primary example, the volume V o a crater ormed by a given impact can be expected to depend on
Dynamics Examples. Robin Hughes and Anson Cheung. 28 th June, 2010
 Dynamics Examples Robin Hughes and Anson Cheung 28 th June, 2010 1 Newton s Laws Figure 1: 3 connected blocks Figure 2: Masses on a trolley 1. Two blocks of mass m 1 = 1kg and m 2 = 2kg on a frictionless
Dynamics Examples Robin Hughes and Anson Cheung 28 th June, 2010 1 Newton s Laws Figure 1: 3 connected blocks Figure 2: Masses on a trolley 1. Two blocks of mass m 1 = 1kg and m 2 = 2kg on a frictionless
Astronomy 1 Fall Reminder: When/where does your observing session meet? [See from your TA.]
![Astronomy 1 Fall Reminder: When/where does your observing session meet? [See from your TA.] Astronomy 1 Fall Reminder: When/where does your observing session meet? [See from your TA.]](/thumbs/90/103712995.jpg) Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Reminder: When/where does your observing session meet? [See email from your TA.] Lecture 9, October 25, 2016 Previously on Astro-1 What is the Moon made of? How did the Moon form?
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Reminder: When/where does your observing session meet? [See email from your TA.] Lecture 9, October 25, 2016 Previously on Astro-1 What is the Moon made of? How did the Moon form?
Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
1/3/12. Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System. Ancient Measurements. Earth s Size and Shape. Ancient Measurements. Ancient Measurements
 // Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
// Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
Lab #11. Impact Craters
 Lab #11 Impact Craters Introduction It is clear from the surface features of geologically old planets (the Moon, Mercury) and some of the unusual phenomena in the solar system (Earth s large moon, the
Lab #11 Impact Craters Introduction It is clear from the surface features of geologically old planets (the Moon, Mercury) and some of the unusual phenomena in the solar system (Earth s large moon, the
EXAM 3 MECHANICS 40% of the final grade
 EXAM 3 MECHANICS 40% of the final grade Winter 2018 Name: Each multiple-choice question is worth 2 marks. 1. The mass of the two wheels shown in the diagram is the same. A force of 1 N is exerted on the
EXAM 3 MECHANICS 40% of the final grade Winter 2018 Name: Each multiple-choice question is worth 2 marks. 1. The mass of the two wheels shown in the diagram is the same. A force of 1 N is exerted on the
Formation of the Earth and Solar System
 Formation of the Earth and Solar System a. Supernova and formation of primordial dust cloud. NEBULAR HYPOTHESIS b. Condensation of primordial dust. Forms disk-shaped nubular cloud rotating counterclockwise.
Formation of the Earth and Solar System a. Supernova and formation of primordial dust cloud. NEBULAR HYPOTHESIS b. Condensation of primordial dust. Forms disk-shaped nubular cloud rotating counterclockwise.
Teacher Background. Impact! Down to Earth KS 3&4
 Teacher Background Impact! Impact! - Teacher Background- 2 Meteorites What Are They, and Where Do They Come From? Meteorites are rocks from space that have passed through the atmosphere and landed on the
Teacher Background Impact! Impact! - Teacher Background- 2 Meteorites What Are They, and Where Do They Come From? Meteorites are rocks from space that have passed through the atmosphere and landed on the
Atom Model and Relativity
 Atom Model and Relativity Kimmo Rouvari September 8, 203 Abstract What is the theoretical explanation for fine structure? What is the mechanism behind relativity? These questions have bothered numerous
Atom Model and Relativity Kimmo Rouvari September 8, 203 Abstract What is the theoretical explanation for fine structure? What is the mechanism behind relativity? These questions have bothered numerous
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam
 South Pasadena AP Physics PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam FORMULAS Name Period Date / / d = vt d = v o t + ½ at 2 d = v o + v 2 t v = v o + at v 2 = v 2 o + 2ad v = v x 2 + v y 2 = tan 1 v y v v x = v cos
South Pasadena AP Physics PRACTICE TEST for Midterm Exam FORMULAS Name Period Date / / d = vt d = v o t + ½ at 2 d = v o + v 2 t v = v o + at v 2 = v 2 o + 2ad v = v x 2 + v y 2 = tan 1 v y v v x = v cos
2. The site mentions that a potential asteroid impact can change its Torino scale value. Give two reasons why such a change may occur.
 Astronomy 101 Name(s): Lab 7: Impacts! On June 30, 1908, a low-density 80-meter diameter asteroid entered the atmosphere above Tunguska, Siberia and generated a shock wave that flattened millions of trees
Astronomy 101 Name(s): Lab 7: Impacts! On June 30, 1908, a low-density 80-meter diameter asteroid entered the atmosphere above Tunguska, Siberia and generated a shock wave that flattened millions of trees
Safety goggles must be worn whenever the slingshot is in use!
 Name Impact Cratering Lab Class Purpose To learn about the mechanics of impact cratering, the concept of kinetic energy, and to recognize the landforms associated with impact cratering. Materials This
Name Impact Cratering Lab Class Purpose To learn about the mechanics of impact cratering, the concept of kinetic energy, and to recognize the landforms associated with impact cratering. Materials This
Formation of the Solar System Chapter 8
 Formation of the Solar System Chapter 8 To understand the formation of the solar system one has to apply concepts such as: Conservation of angular momentum Conservation of energy The theory of the formation
Formation of the Solar System Chapter 8 To understand the formation of the solar system one has to apply concepts such as: Conservation of angular momentum Conservation of energy The theory of the formation
TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID: GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom
 TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID:1542715 GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geology part 1 Page 1 of 6 Student: Class: Date: 1. The picture below shows
TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID:1542715 GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geology part 1 Page 1 of 6 Student: Class: Date: 1. The picture below shows
Craters of The Moon. Evan Sheridan, Tom Power, Chris Kervick March 4th 2013
 Craters of The Moon Evan Sheridan, Tom Power, Chris Kervick 11367741 March 4th 2013 Abstract Various properties of craters found on the moon were investigated. For a various number of craters both the
Craters of The Moon Evan Sheridan, Tom Power, Chris Kervick 11367741 March 4th 2013 Abstract Various properties of craters found on the moon were investigated. For a various number of craters both the
Craters of The Moon. David-Alexander Robinson ; Daniel Tanner; Jack Denning th November Abstract 2. 2 Introduction & Theory 2
 Craters of The Moon David-Alexander Robinson ; Daniel Tanner; Jack Denning 08332461 12th November 2009 Contents 1 Abstract 2 2 Introduction & Theory 2 3 Experimental Method 3 3.1 Depht of Craters.........................
Craters of The Moon David-Alexander Robinson ; Daniel Tanner; Jack Denning 08332461 12th November 2009 Contents 1 Abstract 2 2 Introduction & Theory 2 3 Experimental Method 3 3.1 Depht of Craters.........................
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity How do we describe motion? Precise definitions to describe motion: Speed: Rate at which object moves speed = distance time
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity How do we describe motion? Precise definitions to describe motion: Speed: Rate at which object moves speed = distance time
Name ID Section. 1. One mile is equal to 1609 m; 1 hour is equal to 3600 s. The highway speed limit of 65 mph is equivalent to the speed of:
 The exam is closed book and closed notes. There are 30 multiple choice questions. Make sure you put your name, section, and ID number on the SCANTRON form. The answers for the multiple choice Questions
The exam is closed book and closed notes. There are 30 multiple choice questions. Make sure you put your name, section, and ID number on the SCANTRON form. The answers for the multiple choice Questions
Cratering Pre-Lab. 1.) How are craters produced? 2.) How do you expect the size of a crater to depend on the kinetic energy of an impactor?
 Cratering Pre-Lab 1.) How are craters produced? 2.) How do you expect the size of a crater to depend on the kinetic energy of an impactor? 3.) What are the units of kinetic energy that you will use in
Cratering Pre-Lab 1.) How are craters produced? 2.) How do you expect the size of a crater to depend on the kinetic energy of an impactor? 3.) What are the units of kinetic energy that you will use in
Problem Set 3: Crater Counting
 Problem Set 3: Crater Counting Introduction Impact craters are the dominant landforms on most of the solid surfaces in our solar system. These impact craters have formed on the surfaces over the 4.6 billion
Problem Set 3: Crater Counting Introduction Impact craters are the dominant landforms on most of the solid surfaces in our solar system. These impact craters have formed on the surfaces over the 4.6 billion
Today. The Little Things. Comets. Dwarf Planets. Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then.
 Today The Little Things Comets Dwarf Planets Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then. 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Comets Fig 9.5 FROST LINE
Today The Little Things Comets Dwarf Planets Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then. 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Comets Fig 9.5 FROST LINE
Make sure that you are able to operate with vectors rapidly and accurately. Practice now will pay off in the rest of the course.
 Ch3 Page 1 Chapter 3: Vectors and Motion in Two Dimensions Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM Vectors are useful for describing physical quantities that have both magnitude and direction, such as position,
Ch3 Page 1 Chapter 3: Vectors and Motion in Two Dimensions Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM Vectors are useful for describing physical quantities that have both magnitude and direction, such as position,
Exam 2: Equation Summary
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Physics Fall Term 2012 Exam 2: Equation Summary Newton s Second Law: Force, Mass, Acceleration: Newton s Third Law: Center of Mass: Velocity
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Physics Fall Term 2012 Exam 2: Equation Summary Newton s Second Law: Force, Mass, Acceleration: Newton s Third Law: Center of Mass: Velocity
Venus - Overview. Exploration of Venus. Admin. 9/26/17. Second planet from Sun Earth s sister planet
 Admin. 9/26/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.35pm (end of period 5 and period 6), start
Admin. 9/26/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.35pm (end of period 5 and period 6), start
Unit 3 Lesson 2 Gravity and the Solar System. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Florida Benchmarks SC.8.N.1.4 Explain how hypotheses are valuable if they lead to further investigations, even if they turn out not to be supported by the data. SC.8.N.1.5 Analyze the methods used to develop
Florida Benchmarks SC.8.N.1.4 Explain how hypotheses are valuable if they lead to further investigations, even if they turn out not to be supported by the data. SC.8.N.1.5 Analyze the methods used to develop
Liquids CHAPTER 13 FLUIDS FLUIDS. Gases. Density! Bulk modulus! Compressibility. To begin with... some important definitions...
 CHAPTER 13 FLUIDS FLUIDS Liquids Gases Density! Bulk modulus! Compressibility Pressure in a fluid! Hydraulic lift! Hydrostatic paradox Measurement of pressure! Manometers and barometers Buoyancy and Archimedes
CHAPTER 13 FLUIDS FLUIDS Liquids Gases Density! Bulk modulus! Compressibility Pressure in a fluid! Hydraulic lift! Hydrostatic paradox Measurement of pressure! Manometers and barometers Buoyancy and Archimedes
The Moon: Internal Structure & Magma Ocean
 The Moon: Internal Structure & Magma Ocean 1 Lunar Magma Ocean & Lunar Interior 2 Two possible views of the Moon s interior: The Moon: Internal Structure 3 Like Earth, the Moon is a differentiated body.
The Moon: Internal Structure & Magma Ocean 1 Lunar Magma Ocean & Lunar Interior 2 Two possible views of the Moon s interior: The Moon: Internal Structure 3 Like Earth, the Moon is a differentiated body.
Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4
 Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 8 1. Which of the following processes is not important in shaping the surface of terrestrial planets? a) Impact cratering b) Tectonism
Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 8 1. Which of the following processes is not important in shaping the surface of terrestrial planets? a) Impact cratering b) Tectonism
The seismic expression and hydrocarbon potential of meteorite impact craters: Current research
 Meteorite impact craters: Current research The seismic expression and hydrocarbon potential of meteorite impact craters: Current research Michael J. Mazur and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT Nearly one quarter
Meteorite impact craters: Current research The seismic expression and hydrocarbon potential of meteorite impact craters: Current research Michael J. Mazur and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT Nearly one quarter
Tectonics. Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust
 Tectonics Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust Planetary History Planets formed HOT Denser materials fall to center Planet cools by conduction, convection, radiation to space
Tectonics Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust Planetary History Planets formed HOT Denser materials fall to center Planet cools by conduction, convection, radiation to space
Chapter 4: Dynamics. Newton s Laws
 Chapter 4: Dynamics Newton s Laws What if we all jumped at once? Newton s 1st Law Objects with mass have Inertia: the tendency to stay at rest (or moving!) The more mass an object has, the more difficult
Chapter 4: Dynamics Newton s Laws What if we all jumped at once? Newton s 1st Law Objects with mass have Inertia: the tendency to stay at rest (or moving!) The more mass an object has, the more difficult
The Sun and Planets Lecture Notes 5. The Moon
 The Sun and Planets Lecture Notes 5. Spring Semester 2019 Prof Dr Ravit Helled The Moon Definitions Escape Velocity Escape velocity is the minimum speed needed for an object to escape a massive body. The
The Sun and Planets Lecture Notes 5. Spring Semester 2019 Prof Dr Ravit Helled The Moon Definitions Escape Velocity Escape velocity is the minimum speed needed for an object to escape a massive body. The
GLY August, Ms. Nelda Breedt. Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth.
 Meteorite Impacts Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology 2 Meteorite Impacts Meteorite Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth. Meteoroid Before hitting the
Meteorite Impacts Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology 2 Meteorite Impacts Meteorite Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth. Meteoroid Before hitting the
