Microseismic Aids In Fracturing Shale By Adam Baig, Sheri Bowman and Katie Jeziorski
|
|
|
- Osborne McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AUGUST 2014 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Microseismic Aids In Fracturing Shale By Adam Baig, Sheri Bowman and Katie Jeziorski KINGSTON, ONTARIO Adding to the complexity of hydraulic fracturing is that there are many options for completing a pad of wells. Examples include progressive fracturing of one well at a time, zipper frac programs that attempt to manage stress regimes in the reservoir by alternating treatment wells, and simulfrac methods, which treat two wells simultaneously. Completion techniques may use sliding-sleeve or plug-and-perforate methods to define separate treatment zones, while individual stages may employ unique treatment designs by varying factors such as fluid, proppant, perforation intervals, or hesitation periods. Often, these variations in completion styles attempt to stimulate different fracture sets within a network of pre-existing fractures in order to stimulate the largest volume of reservoir while minimizing cost. An important consideration during hydraulic fracture stimulation is how to best assess the effectiveness of various completion styles. While production decline curves and history matching are viewed as primary validation methods, these take years to realize fully. In the short term, it is important to receive reliable and rapid feedback on treatment success. Microseismic monitoring has become a routine method for identifying overall shale fracture characteristics such as fracture geometry, stage overlap, and estimated stimulated reservoir volume. Used in conjunction with injection/engineering data, microseismic results often are used to assess stimulation effectiveness in real time. Microseismic monitoring has become an attractive option for tracking hydraulic fracture stimulations because, unlike most other monitoring techniques, it provides information about fracture behavior away from the wellbore. However, in most cases, the potential for microseismic to develop an overall picture of fracture interactions within a reservoir is not fully exploited. Event Failure Mechanisms Microseismic event locations provide only a finite level of feedback on reservoir stimulation. They cannot reveal definitively whether each fracture generated will contribute to production. An example of this FIGURE 1 limitation is demonstrated by the fact that early estimates of stimulated reservoir volume (SRV), which encompassed merely the envelope of microseismic events, resulted in an overestimation of the SRV. Rather, evaluating event failure mechanisms is a key aspect to understanding how the treatment programs will improve the drainage characteristics of the reservoir. Each microseismic event can be viewed as the failure of a fracture plane (strike and dip) of a certain size that is, itself, part of a discrete fracture network (DFN) of new or pre-existing fractures. Therefore, microseismic event distributions can be used to reconstruct the DFN that is acti- Microseismic data increase resolution in the scale of interest between core/log/outcrop data and larger, sparsely populated faults obtained from 3-D seismic data. Image courtesy of Reine and Dunphy, GeoConvention, Reproduced for ESG Solutions with permission from The American Oil & Gas Reporter
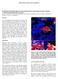
2 FIGURE vating in response to the stimulation program. Seismic moment tensor inversion (SMTI) can connect seismic observations of an event to the physical processes at the source that are causing the event, such as the event failure mechanism, principle strain axes, and potential failure plane orientations. Coupled with the dimensions of the failure planes, fracture orientations inferred from the moment tensor can generate an activated DFN model. Key inputs for geomechanical characterization of hydraulic fracturing using DFN models include fracture length, azimuth and intensity, aperture, and transmissibility. Image log measurements and well tests may provide feedback for the last two parameters. Microseismic monitoring can characterize the fracture distributions in the reservoir, including fracture orientations, intensity and fracture sizes, which generally follow a power law relationship. Assessing Fracture Size The power law of fracture size typically is assessed through core, outcrop and 3- D seismic measurements. Core data sample the smaller scales, consisting of fractures over a few centimeters in length, while outcrops may provide fracture information on the scale of meters. 3-D seismic attributes such as curvature features are limited by the resolution of the seismic 1.5 4,000 ft Passive seismic events detected during the stimulation of five horizontal treatment wells are colored and size-scaled by magnitude. imaging and typically can see features larger than 100 m. Considering these limitations, there clearly is a gap in the observable fracture lengths ranging in scale from meters to hundreds of meters. This gap is shown in Figure 1 as the scale of interest. Microseismic results can help fill in this missing information using a measurement of source radii of detected events. Typical size scales for microseismic events detected on a downhole array range from one to 20 meters. Using a hybrid or broadband system, this scale increases to provide feedback on events exhibiting radii in the hundreds of meters. Within naturally fractured formations, core data reveal that a variety of pre-existing fracture sets are found within a reservoir, often forming dense and interconnected networks. While some fractures are dominantly vertical, horizontal fractures related to bedding planes are present also, and all surfaces exhibit considerable roughness along their interfaces. Stimulations, therefore, will cause these differently oriented fractures to fail in different ways. Assessing fracture networks can become even more complicated when faults or geological structures are present. Fault activation stimulates considerably larger fracture lengths than typically seen in microseismic results. Inaccurate characterization of larger fracture lengths may influence dramatically the interpretation of stimulation and deformation within a reservoir. In our first case study, we discuss microseismic results from a multiwell hydraulic fracture program that activated multiple structures. Fault Activation ESG acquired and processed microseismic and induced seismicity data from five multistage horizontal hydraulic fracture stimulations targeting a North American shale play. Passive seismic data were collected from time-synchronized downhole and near-surface arrays using a patented approach that integrated traditional downhole microseismic with surface- and near-surface induced seismicity arrays to provide visibility for seismic events ranging from -4 to +4 in moment magnitudes (M). The surface array consisted of eight surface stations, each equipped with a 4.5-hertz geophone and a force balanced accelerometer (FBA). Typical microseismic networks are designed to detect and analyze smallscale microseismicity. In particular, hydraulic fracturing generates thousands of microseismic events with magnitudes in the range of M-4 to M0. However, the 15-Hz geophones typically used in these networks are not optimized to record the lower frequency signals associated with larger magnitude events ranging from M0 to M4. Incorporating near-surface arrays of lower frequency sensors, such as 4.5-Hz geophones and FBAs, will more accurately capture seismic signals for large magnitude events, effectively widening the range of magnitudes that can be evaluated accurately with a single passive seismic system. Microseismic results recorded during the multiwell stimulation program are provided in Figure 2, where larger magnitude events measuring above zero on the moment magnitude scale are indicated by larger red dots. A number of positive magnitude events represent fractures ranging in length from 30 to 150 meters, whereas the smaller magnitude microseismic events reflect fracture lengths from five to 30 meters. Large events were observed to separate into two clusters during the completion: Cluster A formed first near the toes of the wells. Cluster B formed later in the stimulation and further along the treatment wells. Because the large events are recorded across a broad number of surface stations
3 over a wide azimuthal distribution, we were able to determine the focal mechanisms for these events. Cluster 1 featured only five mechanisms; however, they all demonstrated a steeply dipping feature striking approximately east-west. Cluster 2 featured more gently dipping fractures exhibiting a southwest strike. Analyzing these results suggested that the local stress conditions rotated during the fracture stimulation program, such that different fracture sets were being activated. Assessing the fracture lengths suggests the fractures were bounded by the treatment formation. Although the events were large, they did not appear to activate features that crosscut the formation and breached the cap rock. FIGURE 4 Well 2 Well 1 Stage A Stage B Stage C 3 Perfs Stage A Stage D Stage B Stage E Stage C Stage D Stage E FIGURE 3 Well 1 Stage A Well 2 Stage A Well 1 Stage B Well 2 Stage B Well 1 Stage C Well 2 Stage C Well 1 Stage D Well 2 Stage D Well 1 Stage E Well 2 Stage E Well 2 Well 1 Hesitation Frac Evaluating Completions In a second example, microseismic monitoring was used to evaluate the success of various completion methods, including a hesitation approach to successfully stimulate multiple known fracture sets. Hesitation stimulation is an approach used by a number of producers that attempts to stimulate a complex, dendritic (branching) network of pre-existing fractures to enhance well productivity. The well is stimulated initially with fluids and proppants, after which it is shut in for a period, allowing for flow back before the well is stimulated a second time. The flow-back period is believed to relax the state of stress in the reservoir sufficiently to enable a secondary fracture set to become more optimally oriented for failure, ultimately enhancing well productivity. Advanced microseismic assessment based on SMTI analysis provided information about the orientations of the stimulated fracture sets. 0 4,000 ft The microseismic events shown here were detected for 10 stages of a multiwell hydraulic fracture stimulation in a North American shale play. Core Natural Fracture Core Drilling Induced Fracture This plan view of well locations includes rosette diagrams for the SMTI-derived fractures for each stage. In addition, the mapped natural and induced (secondary) fractures described by Gale, et al, (2007) also are shown on rosette diagrams. Unless indicated, each stage consisted of four perforations. North is toward the top of the figure. 3 Perfs A secondary goal of the program was to evaluate the effect of modifying injection pressures, slurry rates, perforation strategies, etc., on the resulting microseismicbased DFN. Both fracture intensity and fracture orientations were used to assess the complexity of the fracture network generated in response to the dynamic behavior of in situ stresses in the reservoir. Microseismic events generated during a multiwell, multistage hydraulic fracture stimulation in a North American shale play were monitored using a 24-level vertical geophone array and a 24-level whip array. The whip array is a unique sensor configuration where sensors are deployed in both the horizontal and vertical sections of an adjacent lateral well. Figure 3 illustrates the microseismic results for 10 of the stages. The fracture stimulation program evaluated a number of completion approaches. With the exception of stage E, all stages in well 1 were completed with at least four perforation clusters. A slightly more varied program was used for well 2, which employed either three or four perforation clusters, as well as a hesitation approach in two stages. Assessing the resulting orientations of the SMTI-derived fractures is summarized in rosette diagrams in Figure 4. Also included in Figure 4 are the fracture orientations mapped from a core taken just to the south of the study area.
4 FIGURE 5 Seismic Moment (Nm) 1.00E E E E E E E E E E E E E + 04 Surface Array Events (M>0) Downhole Array Events (M>0) SD 10 MPa SD 1 MPa SD 0.1 MPa SD 0.01 MPa SD MPa Two groupings were identified within these core fractures: those referred to as natural fractures developed during paleo-stress conditions, and those induced by core drilling (secondary fractures) are responding to the current stress regime. In general, the natural fractures trend NW-SE, whereas the induced fractures are to the NE-SW. In most stages in well 1, the fractures resembled those of the mapped natural fracture network. In contrast, stages with three perforation clusters succeeded in generating increased fracture complexity, activating both the natural fracture network and initiating secondary fractures. The hesitation regime also appears to increase the level of fracture complexity resulting from a local reorientation of the stress field. Self-Similar Scaling The power law shown in Figure 1 gives the impression that the frequency of fractures follows a uniform power law over a range of fracture scales. Such behavior is indicative of self-similar scaling processes. In other words, the behavior E E E E E E + 03 This image plots log source radius versus moment for two datasets. Green data represent larger magnitude events recorded from a near-surface regional seismic network, while the yellow data represent smaller microseismic events recorded with a downhole array. Although there is some scatter, each dataset appears to follow a self-similar distribution. However, the two datasets are not self-similar, since they each release different levels of stress of the reservoirs at the smaller scales is a scaled down version of the response of the larger features. In the context of microseismic events, this implies there is a given relationship between the moment magnitude of the event and the size of the fracture that it is activating, described by a constant release of stress (stress drop). However, over the FIGURE 6 Moment (Nm) Ds = 10 MPa Ds = 1 MPa Ds = 100 kpa Ds = 10 kpa Ds = 1 kpa range of the scales of fractures present in the reservoir, there may be different processes to which the microseismicity is responding (fluid-induced versus stresstriggered), as well as lithological controls on the fracture sizes present (large scale fractures may be bound by lithology). Understanding these relationships gives additional insight into the behavior of the reservoir and the triggering processes responsible for controlling the seismicity. In Figure 5, the relationships between moment and source radius are plotted against lines of constant stress drop for two datasets. Green data represent larger magnitude events recorded from a nearsurface regional seismic network, while the yellow data represent smaller microseismic events recorded with a downhole array. Each dataset appears to follow a selfsimilar distribution, as shown by their tendency to follow lines of constant stress drop, albeit with a significant degree of scatter. The two datasets seem to fall along lines of constant stress drop, but the larger events may have a slightly higher stress drop, indicating that there are potentially higher stresses driving these failures. This difference in overall stress release supports the interpretation that the higher-magnitude events are responding to a stress transfer process on nearby faults, whereas the smaller magnitude events all are associated with a stage of a hydraulic fracture treatment, and their lower stress drops are more characteristic of the fluid-induced events typically seen in these injections. Horn River Data The same analysis was performed In these scaling plots for two stages during a hydraulic fracture treatment, the red line indicates that there is a critical fracture length, beyond which it takes significantly more energy to activate a fracture, contrasting the observation of self-similar scaling. Moment (Nm) Ds = 10 MPa Ds = 1 MPa Ds = 100 kpa Ds = 10 kpa Ds = 1 kpa
5 using two groups of downhole microseismic data acquired from separate stages of a hydraulic fracture stimulation in the Horn River Basin (Figure 6). There appears to be a fracture radius (around eight m) that is a firm but not absolutely hard limit on the observed fracture sizes. The effect of this barrier is to locally divert the self-similar scaling relationship. For these fracture sizes, there is an increase in moment for events of equal radius, indicating that in this case, the microseismic response shows some deviation from the consistent power law behavior. In this case, above the fracture limit of eight meters, the formation requires significantly more energy to activate a fracture of the same size. Here, we suggest that lithological controls play a role in determining fracture sizes (fractures bound to certain lithological units need to have a higher energy to transition out of that unit into adjacent units), and in yielding larger fracture sizes. This lithological constraint to the scaling relationship and power law relationship is an important feature to be incorporated into any geomechanical DFN to ensure accurate modeling of the reservoir. The stimulation of naturally fractured shale formations was used to emphasize how different fracture sets of different sizes are activated by different completion programs and in varying lithologies. SMTI-derived fracture planes can be used to define the distribution of the size scales of fractures in the form of a power law, providing direct input to help constrain and validate reservoir models. ADAM BAIG Adam Baig is a seismologist with ESG Solutions, managing research and development for its global energy services division. He joined the company in 2008, and has led its efforts to understand the dynamics of hydraulic fracturing and other injection processes through the seismicity associated with moment tensor inversion of signals to reveal underlying fracture sets and the dynamic in situ stress/strain conditions. Baig obtained a B.S. and an M.S. in geophysics from the University of Alberta, and a Ph.D. in geosciences from Princeton University, studying diffraction and scattering effects on seismic wave propagation. SHERI BOWMAN Sheri Bowman is the manager of analytics and technical sales at ESG Solutions. She joined ESG in 2007 as a geophysicist and has held positions of geophysical analyst, project manager, and manager of data services. Bowman holds dual bachelors in applied math and mechanical engineering, and geological sciences from Queen s University in Ontario. KATIE JEZIORSKI Katie Jeziorski is an engineer at ESG Solutions, and has spent the past five years in various technical and marketing roles. She currently holds the position of technical marketing coordinator. Her primary focus has been examining the integration of microseismics with fracture engineering and geomechanics to create a higher level of understanding about the applications of microseismics in unconventional oil and gas production. Jeziorski holds an M.S. in engineering from Queen s University in Ontario.
Comparison of Microseismic Results in Complex Geologies Reveals the Effect of Local Stresses on Fracture Propagation
 Comparison of Microseismic Results in Complex Geologies Reveals the Effect of Local Stresses on Fracture Propagation Mike Preiksaitis, Sheri Bowman, Ted Urbancic ESG Canada Inc. Summary Understanding the
Comparison of Microseismic Results in Complex Geologies Reveals the Effect of Local Stresses on Fracture Propagation Mike Preiksaitis, Sheri Bowman, Ted Urbancic ESG Canada Inc. Summary Understanding the
Abstracts ESG Solutions
 Abstracts ESG Solutions 2015-2016 For more information, please contact Melissa Hoy, Technical Marketing Coordinator at melissa.hoy@esgsolutions.com Visit us online at www.esgsolutions.com Abstract #1 Fracture
Abstracts ESG Solutions 2015-2016 For more information, please contact Melissa Hoy, Technical Marketing Coordinator at melissa.hoy@esgsolutions.com Visit us online at www.esgsolutions.com Abstract #1 Fracture
Microseismic Monitoring Shale Gas Plays: Advances in the Understanding of Hydraulic Fracturing 20 MAR 16 HANNAH CHITTENDEN
 Microseismic Monitoring Shale Gas Plays: Advances in the Understanding of Hydraulic Fracturing 20 MAR 16 HANNAH CHITTENDEN Introduction Early days: Microseismic monitoring has been around since the early
Microseismic Monitoring Shale Gas Plays: Advances in the Understanding of Hydraulic Fracturing 20 MAR 16 HANNAH CHITTENDEN Introduction Early days: Microseismic monitoring has been around since the early
Microseismic Geomechanical Modelling of Asymmetric Upper Montney Hydraulic Fractures
 Microseismic Geomechanical Modelling of Asymmetric Upper Montney Hydraulic Fractures Drew Chorney, Byungtark Lee, Shawn Maxwell (IMaGE) Summary Geomechanical modelling is a powerful tool to quantitatively
Microseismic Geomechanical Modelling of Asymmetric Upper Montney Hydraulic Fractures Drew Chorney, Byungtark Lee, Shawn Maxwell (IMaGE) Summary Geomechanical modelling is a powerful tool to quantitatively
An Open Air Museum. Success breeds Success. Depth Imaging; Microseismics; Dip analysis. The King of Giant Fields WESTERN NEWFOUNDLAND:
 VOL. 7, NO. 4 2010 GEOSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EXPLAINED GEO EXPRO VOL. 7, NO. 4 2010 Success breeds Success geoexpro.com Country Profile: Senegal Ocean Bottom Node Seismic WESTERN NEWFOUNDLAND: An Open Air
VOL. 7, NO. 4 2010 GEOSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EXPLAINED GEO EXPRO VOL. 7, NO. 4 2010 Success breeds Success geoexpro.com Country Profile: Senegal Ocean Bottom Node Seismic WESTERN NEWFOUNDLAND: An Open Air
Summary. Introduction
 1540160 Using Microseismicity to Understand Subsurface Fracture Systems and Increase the Effectiveness of Completions: Eagle Ford Shale, TX John P. Detring 1 and Sherilyn Williams-Stroud 2 1. Analysis,
1540160 Using Microseismicity to Understand Subsurface Fracture Systems and Increase the Effectiveness of Completions: Eagle Ford Shale, TX John P. Detring 1 and Sherilyn Williams-Stroud 2 1. Analysis,
Fracture Geometry from Microseismic. Norm Warpinski
 Fracture Geometry from Microseismic Norm Warpinski Pinnacle A Halliburton Service Hydraulic Fracturing: Models Versus Reality Conceptually, fracturing is a simple process Elastic behavior Planar fractures
Fracture Geometry from Microseismic Norm Warpinski Pinnacle A Halliburton Service Hydraulic Fracturing: Models Versus Reality Conceptually, fracturing is a simple process Elastic behavior Planar fractures
Focal Mechanism Analysis of a Multi-lateral Completion in the Horn River Basin
 Focal Mechanism Analysis of a Multi-lateral Completion in the Horn River Basin Paige Snelling*, Cameron Wilson, MicroSeismic Inc., Calgary, AB, Canada psnelling@microseismic.com Neil Taylor, Michael de
Focal Mechanism Analysis of a Multi-lateral Completion in the Horn River Basin Paige Snelling*, Cameron Wilson, MicroSeismic Inc., Calgary, AB, Canada psnelling@microseismic.com Neil Taylor, Michael de
Extending the magnitude range of seismic reservoir monitoring by Utilizing Hybrid Surface Downhole Seismic Networks
 Extending the magnitude range of seismic reservoir monitoring by Utilizing Hybrid Surface Downhole Seismic Networks Gisela Viegas*, ESG, Kingston, Ontario, Canada Gisela.Fernandes@esgsolutions.com and
Extending the magnitude range of seismic reservoir monitoring by Utilizing Hybrid Surface Downhole Seismic Networks Gisela Viegas*, ESG, Kingston, Ontario, Canada Gisela.Fernandes@esgsolutions.com and
Duvernay Fracturing: From Microseismic Monitoring to Unconventional Fracture Model Construction
 Duvernay Fracturing: From Microseismic Monitoring to Unconventional Fracture Model Construction Martin Haege, Alexey Zhmodik, Drazenko Boskovic, Venkateshwaran Ramanathan, Tina Hoffart, Qiuguo Li, and
Duvernay Fracturing: From Microseismic Monitoring to Unconventional Fracture Model Construction Martin Haege, Alexey Zhmodik, Drazenko Boskovic, Venkateshwaran Ramanathan, Tina Hoffart, Qiuguo Li, and
F021 Detetection of Mechanical Failure During Hyraulic Fracturing Through Passive Seismic Microseismic Monitoring
 F021 Detetection of Mechanical Failure During Hyraulic Fracturing Through Passive Seismic Microseismic Monitoring A. De La Pena* (Microseismic Inc.), L. Eisner (Microseismic Inc.), M.P. Thornton (Microseismic
F021 Detetection of Mechanical Failure During Hyraulic Fracturing Through Passive Seismic Microseismic Monitoring A. De La Pena* (Microseismic Inc.), L. Eisner (Microseismic Inc.), M.P. Thornton (Microseismic
Microseismic data illuminate fractures in the Montney
 Spectraseis White Paper August 16, 2012 2013 Spectraseis Microseismic data illuminate fractures in the Montney Brad Birkelo and Konrad Cieslik, Spectraseis High-quality data reveal fracture orientation
Spectraseis White Paper August 16, 2012 2013 Spectraseis Microseismic data illuminate fractures in the Montney Brad Birkelo and Konrad Cieslik, Spectraseis High-quality data reveal fracture orientation
Microseismicity applications in hydraulic fracturing monitoring
 Available online atwww.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2016, 8 (4):13-19 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Microseismicity
Available online atwww.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2016, 8 (4):13-19 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Microseismicity
What Can Microseismic Tell Us About Hydraulic Fracturing?
 What Can Microseismic Tell Us About Hydraulic Fracturing? Shawn Maxwell May 2015 Microseismic Geomechanics: Increased understanding; reduced risk 1 Outline Microseismic Introduction Microseismic in Unconventional
What Can Microseismic Tell Us About Hydraulic Fracturing? Shawn Maxwell May 2015 Microseismic Geomechanics: Increased understanding; reduced risk 1 Outline Microseismic Introduction Microseismic in Unconventional
Modeling Optimizes Asset Performance By Chad Baillie
 MARCH 2016 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Modeling Optimizes Asset Performance By Chad Baillie MISSOURI CITY, TX. As more well and completion data
MARCH 2016 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Modeling Optimizes Asset Performance By Chad Baillie MISSOURI CITY, TX. As more well and completion data
stress direction are less stable during both drilling and production stages (Zhang et al., 2006). Summary
 Inversion and attribute-assisted hydraulically-induced microseismic fracture prediction: A North Texas Barnett Shale case study Xavier E. Refunjol *, Katie M. Keranen, and Kurt J. Marfurt, The University
Inversion and attribute-assisted hydraulically-induced microseismic fracture prediction: A North Texas Barnett Shale case study Xavier E. Refunjol *, Katie M. Keranen, and Kurt J. Marfurt, The University
Low-frequency tremor signals from a hydraulic fracture treatment in northeast British Columbia, Canada
 Low-frequency tremor signals from a hydraulic fracture treatment in northeast British Columbia, Canada David W. Eaton*, Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada eatond@ucalgary.ca
Low-frequency tremor signals from a hydraulic fracture treatment in northeast British Columbia, Canada David W. Eaton*, Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada eatond@ucalgary.ca
Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs
 Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs Lindsey N. Meighan, Ted Urbancic and Adam Baig ESG, Kingston, Ontario Summary
Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs Lindsey N. Meighan, Ted Urbancic and Adam Baig ESG, Kingston, Ontario Summary
This paper was prepared for presentation at the Unconventional Resources Technology Conference held in San Antonio, Texas, USA, 1-3 August 2016.
 URTeC: 2444366 Using Depletion-Zone Microseismicity to Understand Producing Volumes Jonathan P. McKenna*, Michael H. Grealy, Michael S. Blaz and Nathan M. Toohey, MicroSeismic, Inc. Copyright 2016, Unconventional
URTeC: 2444366 Using Depletion-Zone Microseismicity to Understand Producing Volumes Jonathan P. McKenna*, Michael H. Grealy, Michael S. Blaz and Nathan M. Toohey, MicroSeismic, Inc. Copyright 2016, Unconventional
This paper was prepared for presentation at the Unconventional Resources Technology Conference held in Denver, Colorado, USA, August 2014.
 URTeC 1922263 Utilizing Ant-tracking to Identify Slowly Slipping Faults in the Barnett Shale Noha Sameh Farghal* and Mark D. Zoback, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA Copyright 2014, Unconventional
URTeC 1922263 Utilizing Ant-tracking to Identify Slowly Slipping Faults in the Barnett Shale Noha Sameh Farghal* and Mark D. Zoback, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA Copyright 2014, Unconventional
Microdeformation: combining direct fracture height measurement with microseismic response Natalia Verkhovtseva, Greg Stanley
 Microdeformation: combining direct fracture height measurement with microseismic response Natalia Verkhovtseva, Greg Stanley Principal Geophysicist Pinnacle a Halliburton service Outline Introduction Microseismic
Microdeformation: combining direct fracture height measurement with microseismic response Natalia Verkhovtseva, Greg Stanley Principal Geophysicist Pinnacle a Halliburton service Outline Introduction Microseismic
Monitoring induced microseismic events usually
 SPECIAL M i c r SECTION: o s e i s m M i ci c r o s e i s m i c Beyond the dots in the box: microseismicity-constrained fracture models for reservoir simulation Leo Eisner, Sherilyn Williams-Stroud, Andrew
SPECIAL M i c r SECTION: o s e i s m M i ci c r o s e i s m i c Beyond the dots in the box: microseismicity-constrained fracture models for reservoir simulation Leo Eisner, Sherilyn Williams-Stroud, Andrew
Microseismic monitoring is a valuable
 SPECIAL SECTION: M i c r o s e i s m i c moment tensors: A path to understanding frac growth ADAM BAIG and TED URBANCIC, Engineering Seismology Group Canada monitoring is a valuable tool in understanding
SPECIAL SECTION: M i c r o s e i s m i c moment tensors: A path to understanding frac growth ADAM BAIG and TED URBANCIC, Engineering Seismology Group Canada monitoring is a valuable tool in understanding
Passive seismic monitoring in unconventional oil and gas
 Passive seismic monitoring in unconventional oil and gas Michael Kendall, James Verdon, Alan Baird, Anna Stork and Philip Usher Bristol University Microseismicity Projects (BUMPS) Microseismicity and
Passive seismic monitoring in unconventional oil and gas Michael Kendall, James Verdon, Alan Baird, Anna Stork and Philip Usher Bristol University Microseismicity Projects (BUMPS) Microseismicity and
Call for Papers. Hydraulic Fracturing Special Issue
 Call for Papers Hydraulic Fracturing Special Issue Hydraulic fracturing of ultra-low and low permeability reservoirs has become the hottest energy-related topic within the oil and gas community as well
Call for Papers Hydraulic Fracturing Special Issue Hydraulic fracturing of ultra-low and low permeability reservoirs has become the hottest energy-related topic within the oil and gas community as well
DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODELLING OF HYDRAULIC FRACTURING IN A STRUCTURALLY CONTROLLED AREA OF THE MONTNEY FORMATION, BC
 DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODELLING OF HYDRAULIC FRACTURING IN A STRUCTURALLY CONTROLLED AREA OF THE MONTNEY FORMATION, BC Steve Rogers Golder Associates Ltd Pat McLellan McLellan Energy Advisors Inc Gordon
DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODELLING OF HYDRAULIC FRACTURING IN A STRUCTURALLY CONTROLLED AREA OF THE MONTNEY FORMATION, BC Steve Rogers Golder Associates Ltd Pat McLellan McLellan Energy Advisors Inc Gordon
Use of S-wave attenuation from perforation shots to map the growth of the stimulated reservoir volume in the Marcellus gas shale
 Use of S-wave attenuation from perforation shots to map the growth of the stimulated reservoir volume in the Marcellus gas shale Yunhui Tan 1, Chengping Chai 1, and Terry Engelder 1 Downloaded 10/07/14
Use of S-wave attenuation from perforation shots to map the growth of the stimulated reservoir volume in the Marcellus gas shale Yunhui Tan 1, Chengping Chai 1, and Terry Engelder 1 Downloaded 10/07/14
MITIGATE RISK, ENHANCE RECOVERY Seismically-Constrained Multivariate Analysis Optimizes Development, Increases EUR in Unconventional Plays
 White Paper MITIGATE RISK, ENHANCE RECOVERY Seismically-Constrained Multivariate Analysis Optimizes Development, Increases EUR in Unconventional Plays SM Seismically-Constrained Multivariate Analysis Optimizes
White Paper MITIGATE RISK, ENHANCE RECOVERY Seismically-Constrained Multivariate Analysis Optimizes Development, Increases EUR in Unconventional Plays SM Seismically-Constrained Multivariate Analysis Optimizes
Characterization of Induced Seismicity in a Petroleum Reservoir: A Case Study
 Characterization of Induced Seismicity in a Petroleum Reservoir: A Case Study Edmond Sze, M. Nafi Toksöz, and Daniel R. Burns Earth Resources Laboratory Dept. of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences
Characterization of Induced Seismicity in a Petroleum Reservoir: A Case Study Edmond Sze, M. Nafi Toksöz, and Daniel R. Burns Earth Resources Laboratory Dept. of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences
Calculation of Focal mechanism for Composite Microseismic Events
 Calculation of Focal mechanism for Composite Microseismic Events Hongliang Zhang, David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Summary It is often difficult to obtain a reliable single-event
Calculation of Focal mechanism for Composite Microseismic Events Hongliang Zhang, David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Summary It is often difficult to obtain a reliable single-event
A Better Modeling Approach for Hydraulic Fractures in Unconventional Reservoirs
 A Better Modeling Approach for Hydraulic Fractures in Unconventional Reservoirs OUTLINE Numerical Simulation: Comparison of Conventional and NEW Approaches NEW Approach as a Modeling Tool (understanding
A Better Modeling Approach for Hydraulic Fractures in Unconventional Reservoirs OUTLINE Numerical Simulation: Comparison of Conventional and NEW Approaches NEW Approach as a Modeling Tool (understanding
A Better Modeling Approach for Hydraulic Fractures in Unconventional Reservoirs
 A Better Modeling Approach for Hydraulic Fractures in Unconventional Reservoirs OUTLINE Numerical Simulation: Comparison of Conventional and NEW Approaches NEW Approach as a Modeling Tool (understanding
A Better Modeling Approach for Hydraulic Fractures in Unconventional Reservoirs OUTLINE Numerical Simulation: Comparison of Conventional and NEW Approaches NEW Approach as a Modeling Tool (understanding
Gas Shale Hydraulic Fracturing, Enhancement. Ahmad Ghassemi
 Gas Shale Hydraulic Fracturing, Stimulated Volume and Permeability Enhancement Ahmad Ghassemi Tight Gas A reservoir that cannot produce gas in economic quantities without massive fracture stimulation treatments
Gas Shale Hydraulic Fracturing, Stimulated Volume and Permeability Enhancement Ahmad Ghassemi Tight Gas A reservoir that cannot produce gas in economic quantities without massive fracture stimulation treatments
Geomechanics for reservoir and beyond Examples of faults impact on fluid migration. Laurent Langhi Team Leader August 2014
 Geomechanics for reservoir and beyond Examples of faults impact on fluid migration Laurent Langhi Team Leader August 2014 Reservoir Geomechanics It is critical to understand the mechanical behaviour of
Geomechanics for reservoir and beyond Examples of faults impact on fluid migration Laurent Langhi Team Leader August 2014 Reservoir Geomechanics It is critical to understand the mechanical behaviour of
Locating Events using Borehole Microseismic Monitoring by Inclusion of Particle Motion Analysis
 Locating Events using Borehole Microseismic Monitoring by Inclusion of Particle Motion Analysis Balikpapan, October 5th-8th, 2015 REXHA VERDHORA RY Geophysical Engineering Institut Teknologi Bandung ANDRI
Locating Events using Borehole Microseismic Monitoring by Inclusion of Particle Motion Analysis Balikpapan, October 5th-8th, 2015 REXHA VERDHORA RY Geophysical Engineering Institut Teknologi Bandung ANDRI
Yusuke Mukuhira. Integration of Induced Seismicity and Geomechanics For Better Understanding of Reservoir Physics
 Integration of Induced Seismicity and Geomechanics For Better Understanding of Reservoir Physics Yusuke Mukuhira Postdoctoral Fellow (JSPS research fellow) Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary
Integration of Induced Seismicity and Geomechanics For Better Understanding of Reservoir Physics Yusuke Mukuhira Postdoctoral Fellow (JSPS research fellow) Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary
Demystifying Tight-gas Reservoirs using Multi-scale Seismic Data
 Demystifying Tight-gas Reservoirs using Multi-scale Seismic Data Overview Murray Roth* Transform Software and Services, Inc., Littleton, CO murray@transformsw.com Tom Davis Colorado School of Mines, Golden,
Demystifying Tight-gas Reservoirs using Multi-scale Seismic Data Overview Murray Roth* Transform Software and Services, Inc., Littleton, CO murray@transformsw.com Tom Davis Colorado School of Mines, Golden,
Seismic techniques for imaging fractures, cracks and faults in the Earth. Michael Kendall
 Seismic techniques for imaging fractures, cracks and faults in the Earth Michael Kendall Issues and Challanges Geometry (aspect ratio, size, orientation, density) Non-uniqueness (e.g., single set of aligned
Seismic techniques for imaging fractures, cracks and faults in the Earth Michael Kendall Issues and Challanges Geometry (aspect ratio, size, orientation, density) Non-uniqueness (e.g., single set of aligned
2015 Training Course Offerings
 2015 Training Course Offerings OilField Geomechanics offers a wide-range of the geomechanics-related training including: 1) Geomechanics for Unconventional Plays; 2) Basic Geomechanics for the Oilfield;
2015 Training Course Offerings OilField Geomechanics offers a wide-range of the geomechanics-related training including: 1) Geomechanics for Unconventional Plays; 2) Basic Geomechanics for the Oilfield;
This paper was prepared for presentation at the Unconventional Resources Technology Conference held in San Antonio, Texas, USA, 1-3 August 2016.
 URTeC: 2461621 Determining Maximum Horizontal Stress With Microseismic Focal Mechanisms Case Studies in the Marcellus, Eagle Ford, Wolfcamp Alireza Agharazi*, MicroSeismic Inc. Copyright 2016, Unconventional
URTeC: 2461621 Determining Maximum Horizontal Stress With Microseismic Focal Mechanisms Case Studies in the Marcellus, Eagle Ford, Wolfcamp Alireza Agharazi*, MicroSeismic Inc. Copyright 2016, Unconventional
Microseismic Monitoring of a Multi-Stage Frac In the Bakken Formation, SE Saskatchewan
 Microseismic Monitoring of a Multi-Stage Frac In the Bakken Formation, SE Saskatchewan Summary Rob Kendall* Petrobank Energy and Resources Ltd., Calgary. Alberta kendall@petrobank.com Downhole microseismic
Microseismic Monitoring of a Multi-Stage Frac In the Bakken Formation, SE Saskatchewan Summary Rob Kendall* Petrobank Energy and Resources Ltd., Calgary. Alberta kendall@petrobank.com Downhole microseismic
Induced microseismic fracture prediction
 Predicting hydraulically-induced microseismic fractures from seismic inversion volumes: A North Texas Barnett Shale case study Xavier E. Refunjol*, University of Oklahoma, Joël Le Calvez, Schlumberger,
Predicting hydraulically-induced microseismic fractures from seismic inversion volumes: A North Texas Barnett Shale case study Xavier E. Refunjol*, University of Oklahoma, Joël Le Calvez, Schlumberger,
Full-Azimuth 3-D Characterizes Shales
 JULY 2013 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Full-Azimuth 3-D Characterizes Shales By Duane Dopkin, Joanne Wang and Shiv Pujan Singh HOUSTON Shale
JULY 2013 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Full-Azimuth 3-D Characterizes Shales By Duane Dopkin, Joanne Wang and Shiv Pujan Singh HOUSTON Shale
Magnitude, scaling, and spectral signature of tensile microseisms
 Magnitude, scaling, and spectral signature of tensile microseisms David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Summary The spatial dimensions and rupture characteristics of microseismic
Magnitude, scaling, and spectral signature of tensile microseisms David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Summary The spatial dimensions and rupture characteristics of microseismic
and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Optimising Resource Plays An integrated GeoPrediction Approach
 Optimising Resource Plays An integrated GeoPrediction Approach Edward Hoskin, Stephen O Connor, Scott Mildren, Michel Kemper, Cristian Malaver, Jeremy Gallop and Sam Green Ikon Science Ltd. Summary A mechanical
Optimising Resource Plays An integrated GeoPrediction Approach Edward Hoskin, Stephen O Connor, Scott Mildren, Michel Kemper, Cristian Malaver, Jeremy Gallop and Sam Green Ikon Science Ltd. Summary A mechanical
Halliburton Engineering for Success in Developing Shale Assets
 Halliburton Engineering for Success in Developing Shale Assets Nov 30, 2010 Shale is a Very Broad Name Used to Describe a Large Category of Rock In conventional petroleum geology shale is thought of as
Halliburton Engineering for Success in Developing Shale Assets Nov 30, 2010 Shale is a Very Broad Name Used to Describe a Large Category of Rock In conventional petroleum geology shale is thought of as
URTeC: Abstract
 URTeC: 2902950 Can Seismic Inversion Be Used for Geomechanics? A Casing Deformation Example Jeremy J. Meyer 1*, Jeremy Gallop 1, Alvin Chen 1, Scott Reynolds 1, Scott Mildren 1 ; 1. Ikon Science Copyright
URTeC: 2902950 Can Seismic Inversion Be Used for Geomechanics? A Casing Deformation Example Jeremy J. Meyer 1*, Jeremy Gallop 1, Alvin Chen 1, Scott Reynolds 1, Scott Mildren 1 ; 1. Ikon Science Copyright
Microseismic Monitoring for Unconventional Resource Development
 Microseismic Monitoring for Unconventional Resource Development Peter M. Duncan MicroSeismic, Inc., Houston USA, 1300 W Sam Houston Pkwy S., Suite 200,Houston TX USA 77042 Abstract Microseismic monitoring
Microseismic Monitoring for Unconventional Resource Development Peter M. Duncan MicroSeismic, Inc., Houston USA, 1300 W Sam Houston Pkwy S., Suite 200,Houston TX USA 77042 Abstract Microseismic monitoring
Hoadley Microseismic Experiment: Reprocessing and characterization of long-duration tremor signals
 Hoadley Microseismic Experiment: Reprocessing and characterization of long-duration tremor signals Enrico Caffagni and David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Summary Downhole seismic
Hoadley Microseismic Experiment: Reprocessing and characterization of long-duration tremor signals Enrico Caffagni and David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Summary Downhole seismic
Maximize the potential of seismic data in shale exploration and production Examples from the Barnett shale and the Eagle Ford shale
 Maximize the potential of seismic data in shale exploration and production Examples from the Barnett shale and the Eagle Ford shale Joanne Wang, Paradigm Duane Dopkin, Paradigm Summary To improve the success
Maximize the potential of seismic data in shale exploration and production Examples from the Barnett shale and the Eagle Ford shale Joanne Wang, Paradigm Duane Dopkin, Paradigm Summary To improve the success
Scientific approach applied to multi-well pad development in Eagle Ford shale
 Originally appeared in World Oil JULY 2017 issue, pgs 53-57. Posted with permission. SHALETECH REPORT / INNOVATIONS AND TECHNIQUES Scientific approach applied to multi-well pad development in Eagle Ford
Originally appeared in World Oil JULY 2017 issue, pgs 53-57. Posted with permission. SHALETECH REPORT / INNOVATIONS AND TECHNIQUES Scientific approach applied to multi-well pad development in Eagle Ford
MAXIMIZING THE RESERVOIR ACCESS WITH COMPLETION OPTIMIZATION AND EFFECTIVENESS. Luciano Fucello, NCS Multistage Fabio Chiarandini, Gaffney & Cline
 MAXIMIZING THE RESERVOIR ACCESS WITH COMPLETION OPTIMIZATION AND EFFECTIVENESS Luciano Fucello, NCS Multistage Fabio Chiarandini, Gaffney & Cline AGENDA: Completion effectiveness Intro Case Study Completion
MAXIMIZING THE RESERVOIR ACCESS WITH COMPLETION OPTIMIZATION AND EFFECTIVENESS Luciano Fucello, NCS Multistage Fabio Chiarandini, Gaffney & Cline AGENDA: Completion effectiveness Intro Case Study Completion
J.V. Herwanger* (Ikon Science), A. Bottrill (Ikon Science) & P. Popov (Ikon Science)
 29829. One 4D geomechanical model and its many applications J.V. Herwanger* (Ikon Science), A. Bottrill (Ikon Science) & P. Popov (Ikon Science) Main objectives (i) Field case study demonstrating application
29829. One 4D geomechanical model and its many applications J.V. Herwanger* (Ikon Science), A. Bottrill (Ikon Science) & P. Popov (Ikon Science) Main objectives (i) Field case study demonstrating application
Search and Discovery Article # (2009) Posted July 25, Abstract
 AV Fracture Imaging Pilot esigned to Compare Various Microseismic Monitoring Techniques* idier rapeau 1, Francis Cerda 1, Laszlo Maurel 2, Pablo Ferguson 2, Raul Sanchez 2, Christophe Maisons 3, Emmanuel
AV Fracture Imaging Pilot esigned to Compare Various Microseismic Monitoring Techniques* idier rapeau 1, Francis Cerda 1, Laszlo Maurel 2, Pablo Ferguson 2, Raul Sanchez 2, Christophe Maisons 3, Emmanuel
swisstopo, Swiss Geological Survey, Wabern, Switzerland, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Earth & Environmental Sciences Area, Berkeley, USA
 Aseismic fault slip and leakage preceding an earthquake induced during an in-situ fault reactivation experiment in the Opalinus Clay, Mont Terri rock laboratory, Switzerland Christophe Nussbaum 1, Yves
Aseismic fault slip and leakage preceding an earthquake induced during an in-situ fault reactivation experiment in the Opalinus Clay, Mont Terri rock laboratory, Switzerland Christophe Nussbaum 1, Yves
Considerations for Infill Well Development in Low Permeability Reservoirs
 Considerations for Infill Well Development in Low Permeability Reservoirs George Waters Technical Manager Unconventional Completions September 9, 2014 Topics Continuous Improvement in Field Development
Considerations for Infill Well Development in Low Permeability Reservoirs George Waters Technical Manager Unconventional Completions September 9, 2014 Topics Continuous Improvement in Field Development
Shale Gas; Wellbore Positioning Challenges
 Shale Gas; Wellbore Positioning Challenges Pete Clark, Directional Drilling Advisor ISCWSA, Copenhagen, 3/4/11 Shale Gas; Wellbore Positioning Challenges Why is it important to us? Emerging trend in drilling
Shale Gas; Wellbore Positioning Challenges Pete Clark, Directional Drilling Advisor ISCWSA, Copenhagen, 3/4/11 Shale Gas; Wellbore Positioning Challenges Why is it important to us? Emerging trend in drilling
Identifying fault activation during hydraulic stimulation in the Barnett shale: source mechanisms, b
 Identifying fault activation during hydraulic stimulation in the Barnett shale: source mechanisms, b values, and energy release analyses of microseismicity Scott Wessels*, Michael Kratz, Alejandro De La
Identifying fault activation during hydraulic stimulation in the Barnett shale: source mechanisms, b values, and energy release analyses of microseismicity Scott Wessels*, Michael Kratz, Alejandro De La
Identifying faults and fractures using source mechanism inversion, b values, and energy release rates
 Identifying faults and fractures using source mechanism inversion, b values, and energy release rates Abstract: Identifying and differentiating between fracture stimulation and fault activation is critical
Identifying faults and fractures using source mechanism inversion, b values, and energy release rates Abstract: Identifying and differentiating between fracture stimulation and fault activation is critical
Stress Shadows Explained: What It Is, What It Isn t, And Why You Should Care
 Stress Shadows Explained: What It Is, What It Isn t, And Why You Should Care Introduction Much is now made about Stress Shadows (SSs) and its impact on hydraulic fracturing. In fact, many (most?) of the
Stress Shadows Explained: What It Is, What It Isn t, And Why You Should Care Introduction Much is now made about Stress Shadows (SSs) and its impact on hydraulic fracturing. In fact, many (most?) of the
Identifying faults and fractures in unconventional reservoirs through microseismic monitoring
 first break volume 29, July 2011 special topic Identifying faults and fractures in unconventional reservoirs through microseismic monitoring Scott A. Wessels, * Alejandro De La Peña, Michael Kratz, Sherilyn
first break volume 29, July 2011 special topic Identifying faults and fractures in unconventional reservoirs through microseismic monitoring Scott A. Wessels, * Alejandro De La Peña, Michael Kratz, Sherilyn
SHALE GAS AND HYDRAULIC FRACTURING
 SHALE GAS AND HYDRAULIC FRACTURING JAMES VERDON FRONTIERS IN EARTH SCIENCES (EASC M0016) WEDNESDAY 29.11.2011 Tight gas reservoirs have permeability of 0.1mD or less difficult to produce at economic rates.
SHALE GAS AND HYDRAULIC FRACTURING JAMES VERDON FRONTIERS IN EARTH SCIENCES (EASC M0016) WEDNESDAY 29.11.2011 Tight gas reservoirs have permeability of 0.1mD or less difficult to produce at economic rates.
New 3-D Seismic Vector Attribute Explains Hydraulic Fracture Behavior
 MRCH 2014 The etter usiness Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry New 3-D Seismic Vector ttribute Explains Hydraulic Fracture ehavior y Martin Haege Shawn Maxwell Lars Sonneland
MRCH 2014 The etter usiness Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry New 3-D Seismic Vector ttribute Explains Hydraulic Fracture ehavior y Martin Haege Shawn Maxwell Lars Sonneland
Heterogeneity Type Porosity. Connected Conductive Spot. Fracture Connected. Conductive Spot. Isolated Conductive Spot. Matrix.
 Porosity Histogram Porosity Contribution 1.3.3.3 Connected 9.8 ohm.m U R D 9 18 7. 5.25 4.38 3.5 2.63 1.75 48 Heterogeneity Distribution Image Orientation, L U 27 36.4.3 X,X72.5 Depth, ft.3 1 Isolated.3
Porosity Histogram Porosity Contribution 1.3.3.3 Connected 9.8 ohm.m U R D 9 18 7. 5.25 4.38 3.5 2.63 1.75 48 Heterogeneity Distribution Image Orientation, L U 27 36.4.3 X,X72.5 Depth, ft.3 1 Isolated.3
FRACTURE CHARACTERIZATION FROM CORE TO DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODEL DOUG BEARINGER, CHELSEY HILLIER
 FRACTURE CHARACTERIZATION FROM CORE TO DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODEL DOUG BEARINGER, CHELSEY HILLIER SHALE CHALLENGES Simple models versus observations of complex fracture networks A good earth model
FRACTURE CHARACTERIZATION FROM CORE TO DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODEL DOUG BEARINGER, CHELSEY HILLIER SHALE CHALLENGES Simple models versus observations of complex fracture networks A good earth model
Chapter 6. Conclusions. 6.1 Conclusions and perspectives
 Chapter 6 Conclusions 6.1 Conclusions and perspectives In this thesis an approach is presented for the in-situ characterization of rocks in terms of the distribution of hydraulic parameters (called SBRC
Chapter 6 Conclusions 6.1 Conclusions and perspectives In this thesis an approach is presented for the in-situ characterization of rocks in terms of the distribution of hydraulic parameters (called SBRC
Project Geology RPSEA. GTI Project Technology. February 15, is a low. Similar to. Marcellus Gas Shale. area follows.
 Marcellus Gas Shale Project RPSEA Project 9122-04 GTI Project 211000 Technology Status Assessment February 15, 20111 Background The Marcellus Shale, stretching across Pennsylvania, Westt Virginia, Ohio,
Marcellus Gas Shale Project RPSEA Project 9122-04 GTI Project 211000 Technology Status Assessment February 15, 20111 Background The Marcellus Shale, stretching across Pennsylvania, Westt Virginia, Ohio,
Shale Capacity Key In Shale Modeling
 SEPTEMBER 213 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Shale Capacity Key In Shale Modeling By Ahmed Ouenes HOUSTON After more than a decade of successful
SEPTEMBER 213 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Shale Capacity Key In Shale Modeling By Ahmed Ouenes HOUSTON After more than a decade of successful
Integrated Approach to Drilling Project in Unconventional Reservoir Using Reservoir Simulation
 Integrated Approach to Drilling Project in Unconventional Reservoir Using Reservoir Simulation Jerzy Stopa 1,*, Rafał Wiśniowski 1, Paweł Wojnarowski 1, Damian Janiga 1, and Krzysztof Skrzypaszek 1 1 AGH
Integrated Approach to Drilling Project in Unconventional Reservoir Using Reservoir Simulation Jerzy Stopa 1,*, Rafał Wiśniowski 1, Paweł Wojnarowski 1, Damian Janiga 1, and Krzysztof Skrzypaszek 1 1 AGH
Practical Geomechanics
 www.bakerhughes.com Practical Geomechanics Baker Hughes - RDS Geomechanics Services 2015 Baker Hughes Incorporated. All rights reserved Copyright By accepting these materials you agree that all materials
www.bakerhughes.com Practical Geomechanics Baker Hughes - RDS Geomechanics Services 2015 Baker Hughes Incorporated. All rights reserved Copyright By accepting these materials you agree that all materials
Geomechanical Analysis of Hydraulic Fracturing Induced Seismicity at Duvernay Field in Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin
 Geomechanical Analysis of Hydraulic Fracturing Induced Seismicity at Duvernay Field in Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin Suvrat P Lele 1, Timothy Tyrrell 2, Ganeswara R Dasari 1, William A Symington 1
Geomechanical Analysis of Hydraulic Fracturing Induced Seismicity at Duvernay Field in Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin Suvrat P Lele 1, Timothy Tyrrell 2, Ganeswara R Dasari 1, William A Symington 1
Effect Of The In-Situ Stress Field On Casing Failure *
 Effect Of The In-Situ Stress Field On Casing Failure * Tang Bo Southwest Petroleum Institute, People's Republic of China Lian Zhanghua Southwest Petroleum Institute, People's Republic of China Abstract
Effect Of The In-Situ Stress Field On Casing Failure * Tang Bo Southwest Petroleum Institute, People's Republic of China Lian Zhanghua Southwest Petroleum Institute, People's Republic of China Abstract
Analytical Stress Modeling for Mine related Microseismicity
 Analytical Stress Modeling for Mine related Microseismicity Himanshu Barthwal and Mirko van der Baan University of Alberta Summary Microseismicity is recorded in an underground mine by a network of 7 boreholes
Analytical Stress Modeling for Mine related Microseismicity Himanshu Barthwal and Mirko van der Baan University of Alberta Summary Microseismicity is recorded in an underground mine by a network of 7 boreholes
ractical Geomechanics for Oil & Gas Industry
 P ractical Geomechanics for Oil & Gas Industry Practical Geomechanics for Oil and Gas Industry The integrity of the wellbore plays an important role in petroleum operations including drilling, completion
P ractical Geomechanics for Oil & Gas Industry Practical Geomechanics for Oil and Gas Industry The integrity of the wellbore plays an important role in petroleum operations including drilling, completion
Role of lithological layering on spatial variation of natural and induced fractures in hydraulic fracture stimulation
 Role of lithological layering on spatial variation of natural and induced fractures in hydraulic fracture stimulation Vincent Roche *, Department of Physics, University of Alberta, Edmonton roche@ualberta.ca
Role of lithological layering on spatial variation of natural and induced fractures in hydraulic fracture stimulation Vincent Roche *, Department of Physics, University of Alberta, Edmonton roche@ualberta.ca
Risk Evaluation. Todd Shipman PhD, Alberta Geological Survey/Alberta Energy Regulator November 17 th,2017 Induced Seismicity Workshop, Yellowknife NWT
 Risk Evaluation Todd Shipman PhD, Alberta Geological Survey/Alberta Energy Regulator November 17 th,2017 Induced Seismicity Workshop, Yellowknife NWT Risk Management Approach to Induced Seismicity Establishing
Risk Evaluation Todd Shipman PhD, Alberta Geological Survey/Alberta Energy Regulator November 17 th,2017 Induced Seismicity Workshop, Yellowknife NWT Risk Management Approach to Induced Seismicity Establishing
Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story
 Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story Petr Kolinsky 1, Leo Eisner 1, Vladimir Grechka 2, Dana Jurick 3, Peter Duncan 1 Summary Shear
Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story Petr Kolinsky 1, Leo Eisner 1, Vladimir Grechka 2, Dana Jurick 3, Peter Duncan 1 Summary Shear
Predrill Passive Method Images Fracs
 JANUARY 2014 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Predrill Passive Method Images Fracs Ambient fracture imaging using passive arrays captures detailed
JANUARY 2014 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Predrill Passive Method Images Fracs Ambient fracture imaging using passive arrays captures detailed
Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock
 Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock Bradford H. Hager Director, Earth Resources Laboratory and Cecil and Ida Green Professor Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock Bradford H. Hager Director, Earth Resources Laboratory and Cecil and Ida Green Professor Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
Integrated Fracture Identification with Z-VSP and Borehole Images: A study from Cambay Basin
 P-124 Integrated Fracture Identification with Z-VSP and Borehole Images: A study from Cambay Basin Sattwati Dey, Jubilant Energy; Chandramani Shrivastva, Schlumberger; Sreemanti Gijare*, Schlumberger;
P-124 Integrated Fracture Identification with Z-VSP and Borehole Images: A study from Cambay Basin Sattwati Dey, Jubilant Energy; Chandramani Shrivastva, Schlumberger; Sreemanti Gijare*, Schlumberger;
Estimating energy balance for hydraulic fracture stimulations: Lessons Learned from Basel
 Estimating energy balance for hydraulic fracture stimulations: Lessons Learned from Basel David W. Eaton*, Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada eatond@ucalgary.ca and Neda Boroumand,
Estimating energy balance for hydraulic fracture stimulations: Lessons Learned from Basel David W. Eaton*, Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada eatond@ucalgary.ca and Neda Boroumand,
RESULTS OF STIMULATION TREATMENTS AT THE GEOTHERMAL RESEARCH WELLS IN GROß SCHÖNEBECK/GERMANY
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Third Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 8-3, 8 SGP-TR-185 RESULTS OF STIMULATION TREATMENTS AT THE GEOTHERMAL RESEARCH
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Third Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 8-3, 8 SGP-TR-185 RESULTS OF STIMULATION TREATMENTS AT THE GEOTHERMAL RESEARCH
3D velocity model with complex geology and voids for microseismic location and mechanism
 Deep Mining 2014 A.A. Editor and B. Editor (eds) 2014 Australian Centre for Geomechanics, Sudbury, ISBN 978-0-9870937-9-0 3D velocity model with complex geology and voids for microseismic location and
Deep Mining 2014 A.A. Editor and B. Editor (eds) 2014 Australian Centre for Geomechanics, Sudbury, ISBN 978-0-9870937-9-0 3D velocity model with complex geology and voids for microseismic location and
DETAILED IMAGE OF FRACTURES ACTIVATED BY A FLUID INJECTION IN A PRODUCING INDONESIAN GEOTHERMAL FIELD
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 9-11, 2009 SGP-TR-187 DETAILED IMAGE OF FRACTURES ACTIVATED BY A FLUID INJECTION
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 9-11, 2009 SGP-TR-187 DETAILED IMAGE OF FRACTURES ACTIVATED BY A FLUID INJECTION
Instructional Objectives
 GE 6477 DISCONTINUOUS ROCK 8. Fracture Detection Dr. Norbert H. Maerz Missouri University of Science and Technology (573) 341-6714 norbert@mst.edu Instructional Objectives 1. List the advantages and disadvantages
GE 6477 DISCONTINUOUS ROCK 8. Fracture Detection Dr. Norbert H. Maerz Missouri University of Science and Technology (573) 341-6714 norbert@mst.edu Instructional Objectives 1. List the advantages and disadvantages
Kinematic inversion of pre-existing faults by wastewater injection-related induced seismicity: the Val d Agri oil field case study (Italy)
 Kinematic inversion of pre-existing faults by wastewater injection-related induced seismicity: the Val d Agri oil field case study (Italy) Buttinelli M., Improta L., Bagh S., Chiarabba C. 1/10 The Val
Kinematic inversion of pre-existing faults by wastewater injection-related induced seismicity: the Val d Agri oil field case study (Italy) Buttinelli M., Improta L., Bagh S., Chiarabba C. 1/10 The Val
Research Themes in Stimulation Geomechanics. How do we optimize slickwater frac ing?
 Research Themes in Stimulation Geomechanics How do stress, fractures and rock properties affect the success of stimulation? How do pressure and stress (and formation properties) evolve during stimulation?
Research Themes in Stimulation Geomechanics How do stress, fractures and rock properties affect the success of stimulation? How do pressure and stress (and formation properties) evolve during stimulation?
Stimulated Fractured Reservoir DFN Models Calibrated with Microseismic Source Mechanisms
 ARMA 10-520 Stimulated Fractured Reservoir DFN Models Calibrated with Microseismic Source Mechanisms Williams-Stroud, S. C. and Eisner, L. MicroSeismic, Inc., Houston, TX, USA Copyright 2010 ARMA, American
ARMA 10-520 Stimulated Fractured Reservoir DFN Models Calibrated with Microseismic Source Mechanisms Williams-Stroud, S. C. and Eisner, L. MicroSeismic, Inc., Houston, TX, USA Copyright 2010 ARMA, American
Finite element modelling of fault stress triggering due to hydraulic fracturing
 Finite element modelling of fault stress triggering due to hydraulic fracturing Arsalan, Sattari and David, Eaton University of Calgary, Geoscience Department Summary In this study we aim to model fault
Finite element modelling of fault stress triggering due to hydraulic fracturing Arsalan, Sattari and David, Eaton University of Calgary, Geoscience Department Summary In this study we aim to model fault
Optimizing Vaca Muerta Development
 Optimizing Vaca Muerta Development What can be applied from seismic experiences in the Eagle Ford and other unconventional plays? Wednesday, September 19, 2012 4:50 PM Murray Roth, President Transform
Optimizing Vaca Muerta Development What can be applied from seismic experiences in the Eagle Ford and other unconventional plays? Wednesday, September 19, 2012 4:50 PM Murray Roth, President Transform
FRACTURE REORIENTATION IN HORIZONTAL WELL WITH MULTISTAGE HYDRAULIC FRACTURING
 SPE Workshop OILFIELD GEOMECHANICS Slide 1 FRACTURE REORIENTATION IN HORIZONTAL WELL WITH MULTISTAGE HYDRAULIC FRACTURING A. Pimenov, R. Kanevskaya Ltd. BashNIPIneft March 27-28, 2017 Moscow, Russia Slide
SPE Workshop OILFIELD GEOMECHANICS Slide 1 FRACTURE REORIENTATION IN HORIZONTAL WELL WITH MULTISTAGE HYDRAULIC FRACTURING A. Pimenov, R. Kanevskaya Ltd. BashNIPIneft March 27-28, 2017 Moscow, Russia Slide
Toward interpretation of intermediate microseismic b-values
 Toward interpretation of intermediate microseismic b-values Abdolnaser Yousefzadeh, Qi Li, Schulich School of Engineering, University of Calgary, Claudio Virues, CNOOC- Nexen, and Roberto Aguilera, Schulich
Toward interpretation of intermediate microseismic b-values Abdolnaser Yousefzadeh, Qi Li, Schulich School of Engineering, University of Calgary, Claudio Virues, CNOOC- Nexen, and Roberto Aguilera, Schulich
SPE DISTINGUISHED LECTURER SERIES is funded principally through a grant of the SPE FOUNDATION
 SPE DISTINGUISHED LECTURER SERIES is funded principally through a grant of the SPE FOUNDATION The Society gratefully acknowledges those companies that support the program by allowing their professionals
SPE DISTINGUISHED LECTURER SERIES is funded principally through a grant of the SPE FOUNDATION The Society gratefully acknowledges those companies that support the program by allowing their professionals
Unconventional Natural Gas A Brief Review for Instituto Petroquimica Argentina
 October 5, 2010 Unconventional Natural Gas A Brief Review for Instituto Petroquimica Argentina William L. Tittle Principal and Director of Strategy Americas and Asia Raul Arias Alvarez Senior Consultant
October 5, 2010 Unconventional Natural Gas A Brief Review for Instituto Petroquimica Argentina William L. Tittle Principal and Director of Strategy Americas and Asia Raul Arias Alvarez Senior Consultant
Case study 2: Using seismic reflection to design a mine
 Case study 2: Using seismic reflection to design a mine Rob Knipe, Graham Stuart * and Stephen Freeman Rock Deformation Research & School of Earth and Environment * University of Leeds Seismic Reflection
Case study 2: Using seismic reflection to design a mine Rob Knipe, Graham Stuart * and Stephen Freeman Rock Deformation Research & School of Earth and Environment * University of Leeds Seismic Reflection
Hostile downhole conditions present complex challenges
 Haynesville Shale Hostile downhole conditions present complex challenges Solving challenges. conservative estimates show 168 trillion cubic feet of natural gas Haynesville formation The Haynesville shale
Haynesville Shale Hostile downhole conditions present complex challenges Solving challenges. conservative estimates show 168 trillion cubic feet of natural gas Haynesville formation The Haynesville shale
Identified a possible new offset location where the customer is currently exploring drill options.
 GroundMetrics was hired to conduct a Full-Field Resistivity Survey for an oil and gas producer that needed to make crucial decisions to drive profitability at the location. The results saved them hundreds
GroundMetrics was hired to conduct a Full-Field Resistivity Survey for an oil and gas producer that needed to make crucial decisions to drive profitability at the location. The results saved them hundreds
An Analytic Approach to Sweetspot Mapping in the Eagle Ford Unconventional Play
 An Analytic Approach to Sweetspot Mapping in the Eagle Ford Unconventional Play Murray Roth*, Transform Software and Services, Denver, Colorado, Murray@transformsw.com Michael Roth, Transform Software
An Analytic Approach to Sweetspot Mapping in the Eagle Ford Unconventional Play Murray Roth*, Transform Software and Services, Denver, Colorado, Murray@transformsw.com Michael Roth, Transform Software
3.4 Fuzzy Logic Fuzzy Set Theory Approximate Reasoning Fuzzy Inference Evolutionary Optimization...
 Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 The Shale Revolution... 2 1.2 Traditional Modeling... 4 1.3 A Paradigm Shift... 4 2 Modeling Production from Shale... 7 2.1 Reservoir Modeling of Shale... 9 2.2 System
Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 The Shale Revolution... 2 1.2 Traditional Modeling... 4 1.3 A Paradigm Shift... 4 2 Modeling Production from Shale... 7 2.1 Reservoir Modeling of Shale... 9 2.2 System
