Exploring Climate Patterns Embedded in Global Climate Change Datasets
|
|
|
- Moses Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exploring Climate Patterns Embedded in Global Climate Change Datasets James Bothwell, May Yuan Department of Geography University of Oklahoma Norman, OK
2 Exploring Climate Patterns Embedded in Global Climate Change Datasets Abstract This paper aims to explore the analysis of climate patterns embedded in the Global Climate Data Sets generated by the Community Climate System Model (CCSM) for the 4 th Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Report for Climate Change (IPCC). A Geographic Information Systems (GIS) approach is taken to examine spatiotemporal correlates among climate processes and to draw insights into their relationships and responses to climate change scenarios. With foci on El Nino southern Oscillation (ENSO) events and precipitation anomalies, the research explores three CCSM cases from worst-case, average, and conservative CO2 emission scenarios, respectively. The scenarios used are A2: continental economic regions dominate with an economic focus (representing a worst case scenario), B1: a global economy with environmental focus (representing an average scenario), CC: CO2 levels are stable at the current level (representing the best case scenario). GIS methods were used to examine the spatial and temporal development of precipitation anomalies under these three scenarios. A GIS spatiotemporal object growth classification scheme is proposed and then developed further in this paper. Further research is proposed to further the development and use of the GIS spatiotemporal object growth classification scheme. Introduction Geographic Information Systems (GIS) offers a new methodological framework to study the interaction of atmospheric and oceanic processes. The El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) event is one such event with a global impact on weather patterns. On the other hand, the increase in CO2 can have significant influence on the ENSO patterns and intensity. The degree to which CO2 scenarios affect ENSO patterns in space and time is critical to the understanding of possible long term effects of CO2 driven climate change. GIS provides an integrated platform for spatial analysis of the range of future climates possible under the different Intergovernmental Report for Climate Change (IPCC) CO2 emission scenarios (Nakicenovic and Swart 2000). The model runs of the different scenarios offer important information in isolation. The correlations between different model scenarios and time periods are also a rich source of information on the potential impact of CO2 driven climate change (McCarthy, Canziani, Leary, Dokken and White 2001). Central to the GIS methods being developed is a temporal GIS framework with abilities to represent and analyze geographic dynamics. The research expands upon the processbased GIS approach (Yuan 2001, McIntosh and Yuan 2004) that incorporates representational and analytical needs to characterize spatiotemporal behavior and relationships of ENSO Sea Surface Temperature (SST) and global precipitation anomalies. Precipitation anomalies from years classified as El Nino event years are modeled as GIS data objects with spatial and temporal dimensions. The shape, growth, movement, internal structure, lifecycle and other spatiotemporal characteristics of the anomaly data objects were examined (Hornsby and Egenhofer 2002). In addition to object characterization, these measures serve as the basis for similarity queries and correlation analysis. Similarity query facilitates retrieval of anomaly events that exhibit similar spatiotemporal behaviors, such as similar El Nino events or similar precipitation anomalies in the three scenarios. An anomaly tree based on similarity measures can
3 suggest the effects of CO2 emission scenarios on the distributions of El Nino events and precipitation anomalies, respectively. Complementarily, correlation analysis relates El Nino events and precipitation anomalies to reveal their spatial and temporal correspondences in answering questions such as where, when and how precipitation anomalies echo El Nino events. The life cycle classification of the spatiotemporal anomalies portrayed in GIS can be envisioned as tubes in a two-dimensional space (x,y) with a one-dimensional time (t). Three types of life cycle classifications were initially envisioned; oscillatory, emergence and dissipative. Oscillatory exist during the entire time being represented but change shape and/or location. Emergent spatiotemporal anomalies initially do not exist and then appear during the time interval under study. Dissipative spatiotemporal anomalies exist at the initial time but dissipate during the time period under study. Oscillatory Emergent Dissipative Time Y X Figure 1: A tube model to represent three basic lifecycle types of spatiotemporal anomalies. The tube analogy allows examination of spatiotemporal anomalies with respect to location, spatial extent, internal structure and life cycle. Spatiotemporal anomaly locations define search areas to explore the forcing functions that drive the anomaly. Spatial extent and internal structure give indications of the strength of the forcing function driving the anomaly. Life cycle classification allows the grouping of spatiotemporal anomalies with similar forcing function behavior. The location, spatial extent, internal structure and life cycle information can be used to construct anomaly trees and to do correlation analysis. Methodology Data for this research was obtained from the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) GIS Initiative. The NCAR GIS Initiative provides Global Climate Data Sets
4 generated by the Community Climate System Model (CCSM) for the 4 th Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Report for Climate Change (IPCC). The CCSM data was available in monthly averages for both atmospheric and surface climate variables. Thirty years of monthly data for the variables of interest were used to generate climatological means. Linear regression was used to model the slow rise in background mean temperature that existed in the CCSM scenario models. El Nino events were determined by using average SST in the Nino 3.4 region: i.e. the area between 5S and 5N and between 170W and 120W. El Nino events were indicated when the monthly SST mean was greater than the climatological monthly mean for the Nino 3.4 region by more than 0.5C for the months of December, January and February (NOAA 2002). The CCSM model output years used were 2069 to The year 2099 was observed to have somewhat erratic values when compared to the other years. The climatological monthly mean for the Nino 3.4 region was generated by using a linear regression fit on thirty years of Nino 3.4 region SST data. Monthly specific precipitation data for scenario model runs with El Nino events were then used to generate monthly specific precipitation anomalies for the El Nino event years. For each scenario, model runs generate thirty years of monthly precipitation data based on which we calculated monthly climatological means for each data cell in the CCSM data grids. Similarly, we used the monthly climatological means to identify the monthly precipitation anomalies for the years of interest. The CCSM global model inherently has a large amount of inter-annual variability. Aggregation over decadal periods and over several model runs were used to filter out the inter-annual variability. El Nino precipitation data for all of a scenario s model runs were aggregated into three decadal periods. Each scenario has El Nino event precipitation anomaly data maps for the following decadal periods; , and ArcMap was used to generate GIS layers of the precipitation anomalies for the three decadal periods that differed from the mean precipitation anomaly for the year by more than two standard deviations. Over the three decadal periods, area with the monthly precipitation above the mean plus two standard deviations were separated into data layers of monthly deluge events. Furthermore, area with monthly precipitation below the mean minus two standard deviations were separated into data layers of monthly drought events. ArcScene was then used to visualize the spatial and temporal distribution of the monthly precipitation anomalies. Two different approaches were taken to analyze the spatiotemporal patterns embedded in the precipitation anomalies for El Nino years. The first approach was a color coded map of precipitation anomalies (Figure 2). The precipitation anomalies have an interesting spatiotemporal pattern off of the east coast of South America. During the decadal period of there is a deluge region with a drought region just to the south. Both regions have a large east west extant. During the decadal period of only a deluge region appears midway between the locations of the previous decadal period s anomalies. Finally in the final decal period there is no large anomaly off of the east coast at all. The overall pattern of spatial anomalies has no discernable spatiotemporal pattern.
5 Figure 2: Month of May Anomalies for the IPCC Global Economy with Environmental Focus Scenario (CCSM El Nino Year Precipitation Anomalies for IPCC Scenario B1. Dark blue indicates deluge regions; Dark gold indicates drought regions; Medium blue indicates deluge regions; Medium gold indicates drought regions; Light blue indicates deluge regions; Light gold indicates drought regions.) The second technique for analyzing the spatiotemporal changes was to construct a layered map in ArcScene. The lower layers were from earlier decadal periods. The following two figures were from the Climate Change commitment scenario where CO2 is held constant at the current levels. The Pacific Ocean was the only area that shows consistent precipitation anomalies over the three decadal periods. Precipitation anomalies in areas other than the Pacific were independent of CO2 level as the CO2 level remains constant in this scenario.
6 Figure 3: Month of January Anomalies for the IPCC Climate Change Commitment Scenario (CCSM El Nino Year Precipitation Anomalies for IPCC Scenario CC. Dark blue indicates deluge regions; Medium blue indicates deluge regions; Light blue indicates deluge regions.) Figure 4: Month of January Anomalies for the IPCC Climate Change Commitment Scenario (CCSM El Nino Year Precipitation Anomalies for IPCC Scenario CC. Dark gold indicates drought regions; Medium gold indicates drought regions; Light gold indicates drought regions.)
7 GIS Analysis Results Spatiotemporal Patterns across Decadal Periods within a Single Scenario The Climate Change (CC) scenario displays a repeated spatiotemporal pattern in the Pacific Ocean in the equatorial region during the months of January across decadal periods when El Nino s are occurring. By GIS functions, we stacked the precipitation anomalies vertically along the time line to examine the spatial and temporal persistence of anomalies (Fig. 3 and 4). Precipitation anomaly spatiotemporal patterns are no longer discernable during the month of May in the CC scenario across the three decadal periods. (Fig. 5 and 6) The Pacific Ocean anomalies migrate spatially and change its area extent with time. The single progression in CC scenario drought and deluge regions is the drought region to the northeast of Australia. The CC scenario is the most stable of the scenarios as the CO2 level is constant. The failure to discern a spatiotemporal pattern indicates that the monthly variability removes any El Nino event spatiotemporal signature within four months or less Figure 5: Month of May Anomalies for the IPCC Climate Change Commitment Scenario (CCSM El Nino Year Precipitation Anomalies for IPCC Scenario CC. Dark gold indicates drought regions; Medium gold indicates drought regions; Light gold indicates drought regions.)
8 Figure 6: Month of May Anomalies for the IPCC Climate Change Commitment Scenario (CCSM El Nino Year Precipitation Anomalies for IPCC Scenario CC. Dark blue indicates deluge regions; Medium blue indicates deluge regions; Light blue indicates deluge regions.) Spatiotemporal Patterns across Decadal Periods across multiple Scenarios The Climate Change Commitment scenario, with static CO2 levels at the current level, shows a spatiotemporal pattern in the Pacific Ocean for the months of January during El Nino event years. (Fig. 3 and 4) The precipitation anomalies align along the time axis for all three decadal periods. The persistent spatial coverage and magnitude in certain area is expected as the CO2 level is constant for the CC scenario. The A2 and B1 scenario January precipitation anomalies are compared to discern spatiotemporal differences. However, the B1 scenarios showed the same spatiotemporal pattern as the CC scenario as B1 scenario results are compatible with results from the average CC scenario, therefore, the following discussions emphasize the comparison between results from A2 and averaged CC scenarios. The A2 precipitation anomalies, droughts and deluges, exhibited uncoupled behavior. A single El Nino occurred for the decadal period during five runs of the A2 model. This single event is not associated with any decadal precipitation anomalies due to significantly high variability in precipitation throughout the decade. In addition, A2 scenario assumes the largest increase in CO2 of the model scenarios. The ENSO events essentially disappear in this scenario by the year Accordingly, the droughts diminished in spatial extant and shifted between the two decadal periods in all locations in the A2 scenario with the exception of west of Mexico, over central Australia and southeast of Africa. In the west of Mexico and over central Australia, new drought regions emerged. Several drought regions north of Australia and in the Indian Ocean exhibit dissipative behavior. The drought region southeast of Africa appears to be growing. Deluges exhibit growth in two regions during the and decadal periods: the central Pacific and the west coast of North America. There is no
9 other discernable pattern in the spatiotemporal patterns of precipitation anomalies suggested in the A2 scenario. Figure 7: Month of January Anomalies for the IPCC Economic Focus Scenario (CCSM El Nino Year Precipitation Anomalies for IPCC Scenario A2. Dark gold indicates drought regions; Medium gold indicates drought regions.) Figure 8: Month of January Anomalies for the IPCC Economic Focus Scenario (CCSM El Nino Year Precipitation Anomalies for IPCC Scenario A2. Dark blue indicates deluge regions; Medium blue indicates deluge regions.)
10 Concluding Remarks and Future Work As shown in Fig. 5 and 6, several deluge and drought regions suggested in the A2 scenario exhibit dissipation or emergence behavior. Further research will be required to determine if these regions are truly dissipative or emergent and to map out their life cycles. The presented work sets forward a GIS-based methodological framework to explore and compare spatial and temporal patterns associated with three climate change scenarios. An implementation of an algorithm for the spatiotemporal aggregation of the anomalies is required to mine such spatiotemporal regions from a large data set of the IPCC scenarios. Recognizing emergence and dissipation behavior in regions of anomalies and comparing their behavior will enable the investigation of underlying forcing functions that may have generated the spatiotemporal regions. In the presented analysis, the CCSM climate data suggest January precipitation anomalies during El Nino years until when CO2 reaches a threshold level and climate warming has occurred. Establishing this threshold value may provide new insights into the affect of climate change on the ENSO event. The A2 scenario exhibits this transition into an expected diminished ENSO regime (Timmerman 2005). With the proposed GIS approach, algorithms can be developed to identify periods of missing precipitation anomalies and extract correspondent CO2 levels for inspection. The proposed life cycle classification for spatiotemporal phenomena provides a new approach to examine spatiotemporal behavior of climate events. Still, the life cycle classification needs further development. Simple classification as emergent, dissipative or oscillating is not enough. A definition of the rate of growth, positive and negative, oscillatory amplitude and frequency is required to compare phenomena of like classification. Oscillatory and growth are not mutually exclusive classification. One possible approach to combining the two is shown below. Our study also suggests that precipitation anomalies persistent more than four months after the January El Nino are affected by the monthly variability, making it difficult to discern spatiotemporal relationships between the later month s precipitation anomalies and the January anomalies. Analyzing the spatiotemporal patterns of a climate variable of less spatial and temporal variability than precipitation may simplify anomaly identification. In light of the issue of spatiotemporal variability, we plan to investigate how climate zones defined by Koeppen and Thornthwaite climate classification schemes may vary in space and time among IPCC climate change scenarios. Long term climatological changes will have a large effect on the global distributions of flora and fauna and on human activities and adaptability. Mining of climatological data to determine the location of emergent and dissipative spatial events enables researchers to recognize spatiotemporal patterns, and based on which to hypothesize the forcing function or environmental variable behind the emergence or dissipation of the spatial event.
11 Dynamic Spatial Phenomena Life Index Algorithm time y Event local spatial maximums extent Event local spatial minimums Event local maximums spatial extent change Event local minimum spatial extent change Emergent or Dissipative Classification Emergent Blinker Steady State or Complex Oscillation x - - Dissipative References Hornsby, K. and M. Egenhofer (2002). Modeling Moving Objeccts over Multiple Granularities. Annals of Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence 36(1-2): McCarthy, J. J., Canziani, O. F., Leary, Dokken, D. J. and White, K. S. (2001). Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. IPCC. Available at McIntosh, J. and M. Yuan Assessing similarity of geographic processes and events. Transactions in GIS. 9(2): Nakicenovic, N. and Swart, R. (eds.) (2000). Special Report on Emissions Scenarios. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom. NOAA (2002) Warm (El Nino) southern Oscillation - (ENSO) Episodes in the Tropical Pacific NOAA. Available at
12 n Timmermann, A., et. al. (2005) ENSO Suppression due to Weakening of the North Atlantic Thermohaline Circulation. Journal of Climate 18 (16): Yuan, M. (2001). Representing Complex Geographic Phenomena with both Objectand Field- like Properties. Cartography and Geographic Information Science 28 (2): 83-96
Mozambique. General Climate. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
Climate Variability. Andy Hoell - Earth and Environmental Systems II 13 April 2011
 Climate Variability Andy Hoell - andrew_hoell@uml.edu Earth and Environmental Systems II 13 April 2011 The Earth System Earth is made of several components that individually change throughout time, interact
Climate Variability Andy Hoell - andrew_hoell@uml.edu Earth and Environmental Systems II 13 April 2011 The Earth System Earth is made of several components that individually change throughout time, interact
Suriname. General Climate. Recent Climate Trends. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. Temperature. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G.
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Suriname C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Suriname C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN
 MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN Abdul Rashid 1 Abstract: El-Nino is the dominant mod of inter- annual climate variability on a planetary scale. Its impact is associated worldwide
MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN Abdul Rashid 1 Abstract: El-Nino is the dominant mod of inter- annual climate variability on a planetary scale. Its impact is associated worldwide
Malawi. General Climate. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Malawi C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Malawi C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
Seasonal Climate Outlook for South Asia (June to September) Issued in May 2014
 Ministry of Earth Sciences Earth System Science Organization India Meteorological Department WMO Regional Climate Centre (Demonstration Phase) Pune, India Seasonal Climate Outlook for South Asia (June
Ministry of Earth Sciences Earth System Science Organization India Meteorological Department WMO Regional Climate Centre (Demonstration Phase) Pune, India Seasonal Climate Outlook for South Asia (June
St Lucia. General Climate. Recent Climate Trends. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. Temperature. Precipitation
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles St Lucia C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles St Lucia C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
Grenada. General Climate. Recent Climate Trends. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. Temperature. Precipitation
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
Climate Forecast Applications Network (CFAN)
 Forecast of 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Activity April 5, 2018 Summary CFAN s inaugural April seasonal forecast for Atlantic tropical cyclone activity is based on systematic interactions among ENSO, stratospheric
Forecast of 2018 Atlantic Hurricane Activity April 5, 2018 Summary CFAN s inaugural April seasonal forecast for Atlantic tropical cyclone activity is based on systematic interactions among ENSO, stratospheric
SHORT COMMUNICATION EXPLORING THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE NORTH ATLANTIC OSCILLATION AND RAINFALL PATTERNS IN BARBADOS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 6: 89 87 (6) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI:./joc. SHORT COMMUNICATION EXPLORING THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 6: 89 87 (6) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI:./joc. SHORT COMMUNICATION EXPLORING THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Research on Climate of Typhoons Affecting China
 Research on Climate of Typhoons Affecting China Xu Ming Shanghai Typhoon Institute November,25 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Typhoon disasters in China 3. Climatology and climate change of typhoon affecting
Research on Climate of Typhoons Affecting China Xu Ming Shanghai Typhoon Institute November,25 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Typhoon disasters in China 3. Climatology and climate change of typhoon affecting
Climate Prediction Center National Centers for Environmental Prediction
 NOAA s Climate Prediction Center Monthly and Seasonal Forecast Operations Wassila M. Thiaw Climate Prediction Center National Centers for Environmental Prediction Acknowlegement: Mathew Rosencrans, Arun
NOAA s Climate Prediction Center Monthly and Seasonal Forecast Operations Wassila M. Thiaw Climate Prediction Center National Centers for Environmental Prediction Acknowlegement: Mathew Rosencrans, Arun
Cape Verde. General Climate. Recent Climate. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. Temperature. Precipitation
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
Zambia. General Climate. Recent Climate Trends. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. Temperature. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G.
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Zambia C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Zambia C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
ENSO and April SAT in MSA. This link is critical for our regression analysis where ENSO and
 Supplementary Discussion The Link between El Niño and MSA April SATs: Our study finds a robust relationship between ENSO and April SAT in MSA. This link is critical for our regression analysis where ENSO
Supplementary Discussion The Link between El Niño and MSA April SATs: Our study finds a robust relationship between ENSO and April SAT in MSA. This link is critical for our regression analysis where ENSO
How Patterns Far Away Can Influence Our Weather. Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK
 Teleconnections How Patterns Far Away Can Influence Our Weather Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK Teleconnections Connectedness of large-scale weather patterns across the world If you poke
Teleconnections How Patterns Far Away Can Influence Our Weather Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK Teleconnections Connectedness of large-scale weather patterns across the world If you poke
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
THE INFLUENCE OF CLIMATE TELECONNECTIONS ON WINTER TEMPERATURES IN WESTERN NEW YORK INTRODUCTION
 Middle States Geographer, 2014, 47: 60-67 THE INFLUENCE OF CLIMATE TELECONNECTIONS ON WINTER TEMPERATURES IN WESTERN NEW YORK Frederick J. Bloom and Stephen J. Vermette Department of Geography and Planning
Middle States Geographer, 2014, 47: 60-67 THE INFLUENCE OF CLIMATE TELECONNECTIONS ON WINTER TEMPERATURES IN WESTERN NEW YORK Frederick J. Bloom and Stephen J. Vermette Department of Geography and Planning
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Antigua and Barbuda. General Climate. Recent Climate Trends. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. Temperature
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Antigua and Barbuda C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Antigua and Barbuda C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research
Cuba. General Climate. Recent Climate Trends. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. Temperature. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G.
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Cuba C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Cuba C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING. GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13
 ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13 Agenda for February 3 Assignment 3: Due on Friday Lecture Outline Numerical modelling Long-range forecasts Oscillations
ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13 Agenda for February 3 Assignment 3: Due on Friday Lecture Outline Numerical modelling Long-range forecasts Oscillations
Seasonal Climate Watch January to May 2016
 Seasonal Climate Watch January to May 2016 Date: Dec 17, 2015 1. Advisory Most models are showing the continuation of a strong El-Niño episode towards the latesummer season with the expectation to start
Seasonal Climate Watch January to May 2016 Date: Dec 17, 2015 1. Advisory Most models are showing the continuation of a strong El-Niño episode towards the latesummer season with the expectation to start
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall?
 Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
Lecture 8: Natural Climate Variability
 Lecture 8: Natural Climate Variability Extratropics: PNA, NAO, AM (aka. AO), SAM Tropics: MJO Coupled A-O Variability: ENSO Decadal Variability: PDO, AMO Unforced vs. Forced Variability We often distinguish
Lecture 8: Natural Climate Variability Extratropics: PNA, NAO, AM (aka. AO), SAM Tropics: MJO Coupled A-O Variability: ENSO Decadal Variability: PDO, AMO Unforced vs. Forced Variability We often distinguish
EL NIÑO/LA NIÑA UPDATE
 World Meteorological Organization EL NIÑO/LA NIÑA UPDATE Current Situation and Outlook A mature and strong El Niño is now present in the tropical Pacific Ocean. The majority of international climate outlook
World Meteorological Organization EL NIÑO/LA NIÑA UPDATE Current Situation and Outlook A mature and strong El Niño is now present in the tropical Pacific Ocean. The majority of international climate outlook
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 11 November 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 11 November 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 11 November 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Assessment of the Impact of El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Events on Rainfall Amount in South-Western Nigeria
 2016 Pearl Research Journals Journal of Physical Science and Environmental Studies Vol. 2 (2), pp. 23-29, August, 2016 ISSN 2467-8775 Full Length Research Paper http://pearlresearchjournals.org/journals/jpses/index.html
2016 Pearl Research Journals Journal of Physical Science and Environmental Studies Vol. 2 (2), pp. 23-29, August, 2016 ISSN 2467-8775 Full Length Research Paper http://pearlresearchjournals.org/journals/jpses/index.html
The Climate System and Climate Models. Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado
 The Climate System and Climate Models Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado The climate system includes all components of the physical earth system that affect weather
The Climate System and Climate Models Gerald A. Meehl National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado The climate system includes all components of the physical earth system that affect weather
Climate Outlook for December 2015 May 2016
 The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for December 2015 May 2016 BUSAN, 25 November 2015 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for December 2015 to May 2016 (DJFMAM) at the APEC Climate Center (APCC),
The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for December 2015 May 2016 BUSAN, 25 November 2015 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for December 2015 to May 2016 (DJFMAM) at the APEC Climate Center (APCC),
El Niño: How it works, how we observe it. William Kessler and the TAO group NOAA / Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory
 El Niño: How it works, how we observe it William Kessler and the TAO group NOAA / Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory The normal situation in the tropical Pacific: a coupled ocean-atmosphere system
El Niño: How it works, how we observe it William Kessler and the TAO group NOAA / Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory The normal situation in the tropical Pacific: a coupled ocean-atmosphere system
Evaluating a Genesis Potential Index with Community Climate System Model Version 3 (CCSM3) By: Kieran Bhatia
 Evaluating a Genesis Potential Index with Community Climate System Model Version 3 (CCSM3) By: Kieran Bhatia I. Introduction To assess the impact of large-scale environmental conditions on tropical cyclone
Evaluating a Genesis Potential Index with Community Climate System Model Version 3 (CCSM3) By: Kieran Bhatia I. Introduction To assess the impact of large-scale environmental conditions on tropical cyclone
Stefan Liess University of Minnesota Saurabh Agrawal, Snigdhansu Chatterjee, Vipin Kumar University of Minnesota
 Introducing and Finding Tripoles: A Connection Between Central Asia and the Tropical Pacific Stefan Liess University of Minnesota liess@umn.edu Saurabh Agrawal, Snigdhansu Chatterjee, Vipin Kumar University
Introducing and Finding Tripoles: A Connection Between Central Asia and the Tropical Pacific Stefan Liess University of Minnesota liess@umn.edu Saurabh Agrawal, Snigdhansu Chatterjee, Vipin Kumar University
The New Normal or Was It?
 The New Normal or Was It? by Chuck Coffey The recent drought has caused many to reflect upon the past and wonder what is in store for the future. Just a couple of years ago, few agricultural producers
The New Normal or Was It? by Chuck Coffey The recent drought has caused many to reflect upon the past and wonder what is in store for the future. Just a couple of years ago, few agricultural producers
2015 Record breaking temperature anomalies
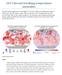 2015 Record breaking temperature anomalies June 2015 global temperature was the highest in 136 (since 1880) years reaching an average of 0.88 C above the 20 th century average. This is an increase of 0.12
2015 Record breaking temperature anomalies June 2015 global temperature was the highest in 136 (since 1880) years reaching an average of 0.88 C above the 20 th century average. This is an increase of 0.12
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 24 September 2012
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 24 September 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 24 September 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño
lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry
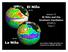 lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry SPATIAL STRUCTURE OF ENSO In 1899, the Indian monsoon failed, leading to drought
lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry SPATIAL STRUCTURE OF ENSO In 1899, the Indian monsoon failed, leading to drought
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 30 October 2017
 ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 30 October 2017 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 30 October 2017 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
Seasonal Outlook for Summer Season (12/05/ MJJ)
 Seasonal Outlook for Summer Season (12/05/2010 - MJJ) Ι. SEASONAL FORECASTS for MAY JUNE JULY FROM GLOBAL CIRCULATION MODELS... 2 I.1. Oceanic Forecast... 2 I.1.a Sea Surface Temperature (SST)... 2 I.1.b
Seasonal Outlook for Summer Season (12/05/2010 - MJJ) Ι. SEASONAL FORECASTS for MAY JUNE JULY FROM GLOBAL CIRCULATION MODELS... 2 I.1. Oceanic Forecast... 2 I.1.a Sea Surface Temperature (SST)... 2 I.1.b
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Cat Response
 2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
Name: Climate Date: EI Niño Conditions
 Name: Date: Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the maps and the passage below. The maps show differences in trade wind strength, ocean current direction, and water temperature associated with air-pressure
Name: Date: Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the maps and the passage below. The maps show differences in trade wind strength, ocean current direction, and water temperature associated with air-pressure
Climate Outlook for October 2017 March 2018
 The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for October 2017 March 2018 BUSAN, 25 September 2017 The synthesis of the latest model forecasts for October 2017 to March 2018 (ONDJFM) from the APEC Climate Center
The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for October 2017 March 2018 BUSAN, 25 September 2017 The synthesis of the latest model forecasts for October 2017 to March 2018 (ONDJFM) from the APEC Climate Center
June 1989 T. Nitta and S. Yamada 375. Recent Warming of Tropical Sea Surface Temperature and Its. Relationship to the Northern Hemisphere Circulation
 June 1989 T. Nitta and S. Yamada 375 Recent Warming of Tropical Sea Surface Temperature and Its Relationship to the Northern Hemisphere Circulation By Tsuyoshi Nitta and Shingo Yamada Long-Range Forecast
June 1989 T. Nitta and S. Yamada 375 Recent Warming of Tropical Sea Surface Temperature and Its Relationship to the Northern Hemisphere Circulation By Tsuyoshi Nitta and Shingo Yamada Long-Range Forecast
Weather Outlook: 2015 Growing Season
 Weather Outlook: 2015 Growing Season Leon F. Osborne Chester Fritz Distinguished Professor Regional Weather Information Center University of North Dakota Grand Forks, North Dakota Why Should We Be Concerned?
Weather Outlook: 2015 Growing Season Leon F. Osborne Chester Fritz Distinguished Professor Regional Weather Information Center University of North Dakota Grand Forks, North Dakota Why Should We Be Concerned?
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Event Response
 PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
1.Decadal prediction ( ) 2. Longer term (to 2100 and beyond)
 Coordinated climate change experiments (formulated by WGCM and AIMES) to be run for assessment in IPCC AR5 Two classes of models to address two time frames and two sets of science questions: 1.Decadal
Coordinated climate change experiments (formulated by WGCM and AIMES) to be run for assessment in IPCC AR5 Two classes of models to address two time frames and two sets of science questions: 1.Decadal
The U. S. Winter Outlook
 The 2018-2019 U. S. Winter Outlook Michael Halpert Deputy Director Climate Prediction Center Mike.Halpert@noaa.gov http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov Outline About the Seasonal Outlook Review of 2017-18 U. S.
The 2018-2019 U. S. Winter Outlook Michael Halpert Deputy Director Climate Prediction Center Mike.Halpert@noaa.gov http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov Outline About the Seasonal Outlook Review of 2017-18 U. S.
Projected Impacts of Climate Change in Southern California and the Western U.S.
 Projected Impacts of Climate Change in Southern California and the Western U.S. Sam Iacobellis and Dan Cayan Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego Sponsors: NOAA RISA
Projected Impacts of Climate Change in Southern California and the Western U.S. Sam Iacobellis and Dan Cayan Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego Sponsors: NOAA RISA
June 1993 T. Nitta and J. Yoshimura 367. Trends and Interannual and Interdecadal Variations of. Global Land Surface Air Temperature
 June 1993 T. Nitta and J. Yoshimura 367 Trends and Interannual and Interdecadal Variations of Global Land Surface Air Temperature By Tsuyoshi Nitta Center for Climate System Research, University of Tokyo,
June 1993 T. Nitta and J. Yoshimura 367 Trends and Interannual and Interdecadal Variations of Global Land Surface Air Temperature By Tsuyoshi Nitta Center for Climate System Research, University of Tokyo,
Climate Outlook for March August 2018
 The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for March August 2018 BUSAN, 26 February 2018 The synthesis of the latest model forecasts for March to August 2018 (MAMJJA) from the APEC Climate Center (APCC),
The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for March August 2018 BUSAN, 26 February 2018 The synthesis of the latest model forecasts for March to August 2018 (MAMJJA) from the APEC Climate Center (APCC),
Climate Outlook through 2100 South Florida Ecological Services Office Vero Beach, FL January 13, 2015
 Climate Outlook through 2100 South Florida Ecological Services Office Vero Beach, FL January 13, 2015 Short Term Drought Map: Short-term (
Climate Outlook through 2100 South Florida Ecological Services Office Vero Beach, FL January 13, 2015 Short Term Drought Map: Short-term (
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 9 November 2015
 ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 9 November 2015 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 9 November 2015 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest
 Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest Don Wuebbles Zachary Zobel Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois, Urbana November 11, 2015 Date Name of Meeting 1 Arctic
Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest Don Wuebbles Zachary Zobel Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois, Urbana November 11, 2015 Date Name of Meeting 1 Arctic
Summer 2018 Southern Company Temperature/Precipitation Forecast
 Scott A. Yuknis High impact weather forecasts, climate assessment and prediction. 14 Boatwright s Loop Plymouth, MA 02360 Phone/Fax 508.927.4610 Cell: 508.813.3499 ClimateImpact@comcast.net Climate Impact
Scott A. Yuknis High impact weather forecasts, climate assessment and prediction. 14 Boatwright s Loop Plymouth, MA 02360 Phone/Fax 508.927.4610 Cell: 508.813.3499 ClimateImpact@comcast.net Climate Impact
A Study of the Uncertainty in Future Caribbean Climate Using the PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 A Study of the Uncertainty in Future Caribbean Climate Using the PRECIS Regional Climate Model by Abel Centella and Arnoldo Bezanilla Institute of Meteorology, Cuba & Kenrick R. Leslie Caribbean Community
A Study of the Uncertainty in Future Caribbean Climate Using the PRECIS Regional Climate Model by Abel Centella and Arnoldo Bezanilla Institute of Meteorology, Cuba & Kenrick R. Leslie Caribbean Community
KUALA LUMPUR MONSOON ACTIVITY CENT
 T KUALA LUMPUR MONSOON ACTIVITY CENT 2 ALAYSIAN METEOROLOGICAL http://www.met.gov.my DEPARTMENT MINISTRY OF SCIENCE. TECHNOLOGY AND INNOVATIO Introduction Atmospheric and oceanic conditions over the tropical
T KUALA LUMPUR MONSOON ACTIVITY CENT 2 ALAYSIAN METEOROLOGICAL http://www.met.gov.my DEPARTMENT MINISTRY OF SCIENCE. TECHNOLOGY AND INNOVATIO Introduction Atmospheric and oceanic conditions over the tropical
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP July 26, 2004
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP July 26, 2004 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic NiZo Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP July 26, 2004 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic NiZo Index
11/24/09 OCN/ATM/ESS The Pacific Decadal Oscillation. What is the PDO? Causes of PDO Skepticism Other variability associated with PDO
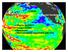 11/24/09 OCN/ATM/ESS 587.. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation What is the PDO? Causes of PDO Skepticism Other variability associated with PDO The Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO). (+) ( ) EOF 1 of SST (+)
11/24/09 OCN/ATM/ESS 587.. The Pacific Decadal Oscillation What is the PDO? Causes of PDO Skepticism Other variability associated with PDO The Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO). (+) ( ) EOF 1 of SST (+)
WINTER FORECAST NY Metro
 2015-2016 WINTER FORECAST NY Metro Weather @NY_WX DISCLAIMER: Seasonal forecasting is difficult and this is my first attempt at a Winter Forecast. I ve looked at all factors and put them together to create
2015-2016 WINTER FORECAST NY Metro Weather @NY_WX DISCLAIMER: Seasonal forecasting is difficult and this is my first attempt at a Winter Forecast. I ve looked at all factors and put them together to create
SEASONAL RAINFALL FORECAST FOR ZIMBABWE. 28 August 2017 THE ZIMBABWE NATIONAL CLIMATE OUTLOOK FORUM
 2017-18 SEASONAL RAINFALL FORECAST FOR ZIMBABWE METEOROLOGICAL SERVICES DEPARTMENT 28 August 2017 THE ZIMBABWE NATIONAL CLIMATE OUTLOOK FORUM Introduction The Meteorological Services Department of Zimbabwe
2017-18 SEASONAL RAINFALL FORECAST FOR ZIMBABWE METEOROLOGICAL SERVICES DEPARTMENT 28 August 2017 THE ZIMBABWE NATIONAL CLIMATE OUTLOOK FORUM Introduction The Meteorological Services Department of Zimbabwe
Percentage of normal rainfall for April 2018 Departure from average air temperature for April 2018
 New Zealand Climate Update No 227, May 2018 Current climate April 2018 Overall, April 2018 was characterised by lower pressure than normal over and to the southeast of New Zealand. Unlike the first three
New Zealand Climate Update No 227, May 2018 Current climate April 2018 Overall, April 2018 was characterised by lower pressure than normal over and to the southeast of New Zealand. Unlike the first three
the 2 past three decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
Second-Order Draft Chapter 10 IPCC WG1 Fourth Assessment Report
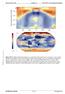 Second-Order Draft Chapter IPCC WG Fourth Assessment Report Figure... Multi model mean changes in a) zonal mean cloud fraction (in %), shown as a cross section though the atmosphere, and b) total cloud
Second-Order Draft Chapter IPCC WG Fourth Assessment Report Figure... Multi model mean changes in a) zonal mean cloud fraction (in %), shown as a cross section though the atmosphere, and b) total cloud
Global Temperature Is Continuing to Rise: A Primer on Climate Baseline Instability. G. Bothun and S. Ostrander Dept of Physics, University of Oregon
 Global Temperature Is Continuing to Rise: A Primer on Climate Baseline Instability G. Bothun and S. Ostrander Dept of Physics, University of Oregon The issue of whether or not humans are inducing significant
Global Temperature Is Continuing to Rise: A Primer on Climate Baseline Instability G. Bothun and S. Ostrander Dept of Physics, University of Oregon The issue of whether or not humans are inducing significant
Chapter outline. Reference 12/13/2016
 Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION There is now unequivocal evidence from direct observations of a warming of the climate system (IPCC, 2007). Despite remaining uncertainties, it is now clear that the upward trend
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION There is now unequivocal evidence from direct observations of a warming of the climate system (IPCC, 2007). Despite remaining uncertainties, it is now clear that the upward trend
Chapter 1 Climate in 2016
 Chapter 1 Climate in 2016 1.1 Global climate summary Extremely high temperatures were frequently observed in many regions of the world, and in particular continued for most of the year in various places
Chapter 1 Climate in 2016 1.1 Global climate summary Extremely high temperatures were frequently observed in many regions of the world, and in particular continued for most of the year in various places
 Page 1 of 5 Home research global climate enso effects Research Effects of El Niño on world weather Precipitation Temperature Tropical Cyclones El Niño affects the weather in large parts of the world. The
Page 1 of 5 Home research global climate enso effects Research Effects of El Niño on world weather Precipitation Temperature Tropical Cyclones El Niño affects the weather in large parts of the world. The
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (May 2017)
 UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (May 2017) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions in April 2017 1.1 Inter monsoon conditions, characterised by afternoon showers and winds that are generally
UPDATE OF REGIONAL WEATHER AND SMOKE HAZE (May 2017) 1. Review of Regional Weather Conditions in April 2017 1.1 Inter monsoon conditions, characterised by afternoon showers and winds that are generally
Characteristics of Global Precipitable Water Revealed by COSMIC Measurements
 Characteristics of Global Precipitable Water Revealed by COSMIC Measurements Ching-Yuang Huang 1,2, Wen-Hsin Teng 1, Shu-Peng Ho 3, Ying-Hwa Kuo 3, and Xin-Jia Zhou 3 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
Characteristics of Global Precipitable Water Revealed by COSMIC Measurements Ching-Yuang Huang 1,2, Wen-Hsin Teng 1, Shu-Peng Ho 3, Ying-Hwa Kuo 3, and Xin-Jia Zhou 3 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
El Niño Seasonal Weather Impacts from the OLR Event Perspective
 Science and Technology Infusion Climate Bulletin NOAA s National Weather Service 41 st NOAA Annual Climate Diagnostics and Prediction Workshop Orono, ME, 3-6 October 2016 2015-16 El Niño Seasonal Weather
Science and Technology Infusion Climate Bulletin NOAA s National Weather Service 41 st NOAA Annual Climate Diagnostics and Prediction Workshop Orono, ME, 3-6 October 2016 2015-16 El Niño Seasonal Weather
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter 2016-17 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University December 5, 2016 Well after an October that felt more like November, we just finished a November that
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter 2016-17 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University December 5, 2016 Well after an October that felt more like November, we just finished a November that
Appearance of solar activity signals in Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) phenomena and monsoon climate pattern over Indonesia
 Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2007) 35, 575 579 Appearance of solar activity signals in Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) phenomena and monsoon climate pattern over Indonesia Jalu Tejo Nugroho National Institute of
Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2007) 35, 575 579 Appearance of solar activity signals in Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) phenomena and monsoon climate pattern over Indonesia Jalu Tejo Nugroho National Institute of
A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS:
 2.6 A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS: 2000-2007 James V. Rudolph*, K. Friedrich, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Colorado at Boulder,
2.6 A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS: 2000-2007 James V. Rudolph*, K. Friedrich, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Colorado at Boulder,
J8.4 TRENDS OF U.S. SNOWFALL AND SNOW COVER IN A WARMING WORLD,
 J8.4 TRENDS OF U.S. SNOWFALL AND SNOW COVER IN A WARMING WORLD, 1948-2008 Richard R. Heim Jr. * NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina 1. Introduction The Intergovernmental Panel
J8.4 TRENDS OF U.S. SNOWFALL AND SNOW COVER IN A WARMING WORLD, 1948-2008 Richard R. Heim Jr. * NOAA National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina 1. Introduction The Intergovernmental Panel
Extreme rainfall events over southern Africa: influence of Atlantic SST on rainfall variability
 Extreme rainfall events over southern Africa: influence of Atlantic SST on rainfall variability Charles Williams 1 Dominic Kniveton 2 Russell Layberry 3 1 The Walker Institute, University of Reading, UK
Extreme rainfall events over southern Africa: influence of Atlantic SST on rainfall variability Charles Williams 1 Dominic Kniveton 2 Russell Layberry 3 1 The Walker Institute, University of Reading, UK
Highlight: Support for a dry climate increasing.
 Scott A. Yuknis High impact weather forecasts, climate assessment and prediction. 14 Boatwright s Loop Plymouth, MA 02360 Phone/Fax 508.927.4610 Cell: 508.813.3499 ClimateImpact@comcast.net Climate Impact
Scott A. Yuknis High impact weather forecasts, climate assessment and prediction. 14 Boatwright s Loop Plymouth, MA 02360 Phone/Fax 508.927.4610 Cell: 508.813.3499 ClimateImpact@comcast.net Climate Impact
Global Climate Patterns and Their Impacts on North American Weather
 Global Climate Patterns and Their Impacts on North American Weather By Julie Malmberg and Jessica Lowrey, Western Water Assessment Introduction This article provides a broad overview of various climate
Global Climate Patterns and Their Impacts on North American Weather By Julie Malmberg and Jessica Lowrey, Western Water Assessment Introduction This article provides a broad overview of various climate
RISK ASSESSMENT COMMUNITY PROFILE NATURAL HAZARDS COMMUNITY RISK PROFILES. Page 13 of 524
 RISK ASSESSMENT COMMUNITY PROFILE NATURAL HAZARDS COMMUNITY RISK PROFILES Page 13 of 524 Introduction The Risk Assessment identifies and characterizes Tillamook County s natural hazards and describes how
RISK ASSESSMENT COMMUNITY PROFILE NATURAL HAZARDS COMMUNITY RISK PROFILES Page 13 of 524 Introduction The Risk Assessment identifies and characterizes Tillamook County s natural hazards and describes how
Thai Meteorological Department, Ministry of Digital Economy and Society
 Thai Meteorological Department, Ministry of Digital Economy and Society Three-month Climate Outlook For November 2017 January 2018 Issued on 31 October 2017 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Thai Meteorological Department, Ministry of Digital Economy and Society Three-month Climate Outlook For November 2017 January 2018 Issued on 31 October 2017 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Understanding Global Environmental Trends and Projections. Ants Leetmaa Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Princeton, NJ 08542
 Understanding Global Environmental Trends and Projections Ants Leetmaa Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Princeton, NJ 08542 Climate Scenarios Used for Attribution Studies of Climate Variability and
Understanding Global Environmental Trends and Projections Ants Leetmaa Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Princeton, NJ 08542 Climate Scenarios Used for Attribution Studies of Climate Variability and
Climate Outlook for March August 2017
 The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for March August 2017 BUSAN, 24 February 2017 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for March to August 2017 (MAMJJA) at the APEC Climate Center (APCC), located
The APEC CLIMATE CENTER Climate Outlook for March August 2017 BUSAN, 24 February 2017 Synthesis of the latest model forecasts for March to August 2017 (MAMJJA) at the APEC Climate Center (APCC), located
Global Climate Systems
 Global Climate Systems I. Earth s Climate A. Past Climate B. Present Climate and Classification 1. Climate components 2. Classification 3. Köppen Climate Classification 4. El Nino III. Global Climate Change
Global Climate Systems I. Earth s Climate A. Past Climate B. Present Climate and Classification 1. Climate components 2. Classification 3. Köppen Climate Classification 4. El Nino III. Global Climate Change
Please be ready for today by:
 Please be ready for today by: 1. HW out for a stamp 2. Paper and pencil/pen for notes 3. Be ready to discuss what you know about El Nino after you view the video clip What is El Nino? El Nino Basics El
Please be ready for today by: 1. HW out for a stamp 2. Paper and pencil/pen for notes 3. Be ready to discuss what you know about El Nino after you view the video clip What is El Nino? El Nino Basics El
Interannual Variability of the South Atlantic High and rainfall in Southeastern South America during summer months
 Interannual Variability of the South Atlantic High and rainfall in Southeastern South America during summer months Inés Camilloni 1, 2, Moira Doyle 1 and Vicente Barros 1, 3 1 Dto. Ciencias de la Atmósfera
Interannual Variability of the South Atlantic High and rainfall in Southeastern South America during summer months Inés Camilloni 1, 2, Moira Doyle 1 and Vicente Barros 1, 3 1 Dto. Ciencias de la Atmósfera
Semiblind Source Separation of Climate Data Detects El Niño as the Component with the Highest Interannual Variability
 Semiblind Source Separation of Climate Data Detects El Niño as the Component with the Highest Interannual Variability Alexander Ilin Neural Networks Research Centre Helsinki University of Technology P.O.
Semiblind Source Separation of Climate Data Detects El Niño as the Component with the Highest Interannual Variability Alexander Ilin Neural Networks Research Centre Helsinki University of Technology P.O.
Drought Impacts in the Southern Great Plains. Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK
 Drought Impacts in the Southern Great Plains Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK Causes of Drought: Large-Scale, Stationary High Pressure Air rotates clockwise around high pressure steers storms
Drought Impacts in the Southern Great Plains Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK Causes of Drought: Large-Scale, Stationary High Pressure Air rotates clockwise around high pressure steers storms
EL NINO-SOUTHERN OSCILLATION (ENSO): RECENT EVOLUTION AND POSSIBILITIES FOR LONG RANGE FLOW FORECASTING IN THE BRAHMAPUTRA-JAMUNA RIVER
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 8, No 3, pp 79-85, 2006 Copyright 2006 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved EL NINO-SOUTHERN OSCILLATION (ENSO): RECENT EVOLUTION AND POSSIBILITIES FOR LONG RANGE
Global NEST Journal, Vol 8, No 3, pp 79-85, 2006 Copyright 2006 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved EL NINO-SOUTHERN OSCILLATION (ENSO): RECENT EVOLUTION AND POSSIBILITIES FOR LONG RANGE
Atmospheric circulation analysis for seasonal forecasting
 Training Seminar on Application of Seasonal Forecast GPV Data to Seasonal Forecast Products 18 21 January 2011 Tokyo, Japan Atmospheric circulation analysis for seasonal forecasting Shotaro Tanaka Climate
Training Seminar on Application of Seasonal Forecast GPV Data to Seasonal Forecast Products 18 21 January 2011 Tokyo, Japan Atmospheric circulation analysis for seasonal forecasting Shotaro Tanaka Climate
Future population exposure to US heat extremes
 Outline SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2631 Future population exposure to US heat extremes Jones, O Neill, McDaniel, McGinnis, Mearns & Tebaldi This Supplementary Information contains additional
Outline SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2631 Future population exposure to US heat extremes Jones, O Neill, McDaniel, McGinnis, Mearns & Tebaldi This Supplementary Information contains additional
Impact of sea surface temperatures on African climate. Alessandra Giannini
 Impact of sea surface temperatures on African climate Alessandra Giannini alesall@iri.columbia.edu Outline: Intro/Motivation: demand-driven science, use of seasonal climate prediction, adaptation to climate
Impact of sea surface temperatures on African climate Alessandra Giannini alesall@iri.columbia.edu Outline: Intro/Motivation: demand-driven science, use of seasonal climate prediction, adaptation to climate
Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific
 Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific Wei Mei 1 Shang-Ping Xie 1, Ming Zhao 2 & Yuqing Wang 3 Climate Variability and Change and Paleoclimate Working
Forced and internal variability of tropical cyclone track density in the western North Pacific Wei Mei 1 Shang-Ping Xie 1, Ming Zhao 2 & Yuqing Wang 3 Climate Variability and Change and Paleoclimate Working
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
Separation of a Signal of Interest from a Seasonal Effect in Geophysical Data: I. El Niño/La Niña Phenomenon
 International Journal of Geosciences, 2011, 2, **-** Published Online November 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijg) Separation of a Signal of Interest from a Seasonal Effect in Geophysical Data: I.
International Journal of Geosciences, 2011, 2, **-** Published Online November 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijg) Separation of a Signal of Interest from a Seasonal Effect in Geophysical Data: I.
NOAA/OAR Observing Systems
 NOAA/OAR Observing Systems Dr. Christopher L. Sabine Director NOAA s Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory Workshop on Hydroclimate Monitoring Systems and Measurement Needs June, 2014 Global Ocean Observing
NOAA/OAR Observing Systems Dr. Christopher L. Sabine Director NOAA s Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory Workshop on Hydroclimate Monitoring Systems and Measurement Needs June, 2014 Global Ocean Observing
Christopher L. Castro Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Arizona
 Spatiotemporal Variability and Covariability of Temperature, Precipitation, Soil Moisture, and Vegetation in North America for Regional Climate Model Applications Christopher L. Castro Department of Atmospheric
Spatiotemporal Variability and Covariability of Temperature, Precipitation, Soil Moisture, and Vegetation in North America for Regional Climate Model Applications Christopher L. Castro Department of Atmospheric
Climate and the Atmosphere
 Climate and Biomes Climate Objectives: Understand how weather is affected by: 1. Variations in the amount of incoming solar radiation 2. The earth s annual path around the sun 3. The earth s daily rotation
Climate and Biomes Climate Objectives: Understand how weather is affected by: 1. Variations in the amount of incoming solar radiation 2. The earth s annual path around the sun 3. The earth s daily rotation
