Solution manual of Simulation with Arena 6th Edition by W. David Kelton, Randall Sadowski and Nancy Zupick
|
|
|
- Benjamin Singleton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Solution manual of Simulation with Arena 6th Edition by W. David Kelton, Randall Sadowski and Nancy Zupick Link download full: Exercise 2-1 Solution file from Kelton/Sadowski/Zupick, Simulation With Arena, 6th edition, McGraw-Hill, 2015 Define S(t) = the total number of parts in the system (in queue plus in service) at time t, let S denote the area under S(t) up to the event time at a row in the table, and S* be the maximum value of S(t) observed up to the event time in the row. Table 2-2 is then augmented as follows (the new cells are shaded):
2 Just-Finished Event Variables Attributes Statistical Accumulators Event Calendar Entity No. Time t Event Type Arrival Times: Q(t) B(t) S(t) (In Queue) In Service TS* Time, P N WQ WQ* TS Q Q* B S S* [Entity No., Type] [1, 0.00, Arr] 0.00 Init () [2, 1.73, Arr] Arr () [1, 2.90, Dep] [1, 2.90, Dep] Arr (1.73) [3, 3.08, Arr] [3, 3.08, Arr] Dep () [2, 4.66, Dep] [4, 3.79, Arr] Arr (3.08) [2, 4.66, Dep] [5, 4.41, Arr] Arr (3.79, 3.08) [2, 4.66, Dep] [2, 4.66, Dep] Arr (4.41, 3.79, 3.08) [6, 18.69, Arr] [3, 8.05, Dep] Dep (4.41, 3.79) [6, 18.69, Arr] [4, 12.57, Dep] Dep (4.41) [6, 18.69, Arr]
3 [5, 17.03, Dep] This file was downloaded from the Solutions area of the website Dep () [6, 18.69, Arr] for the 6th ed. of "Simulation With Arena" by Kelton, Sadowski, and [6, 18.69, Arr] Zupick, McGraw-Hill, Dep () [7, 19.39, Arr] Arr () Arr (19.39) [8, 34.91, Arr] End (19.39) [8, 34.91, Arr]
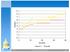
4 The time-average number in system is 34.12/20 = and the maximum number in system is 4. Here s a crude plot of S(t): Exercise 2-3 Solution file from Kelton/Sadowski/Zupick, Simulation With Arena, 6th edition, McGraw-Hill, Zupick, McGraw-Hill, Depict this future-service-time attribute by representing the parts in service and in queue by a (vertical) two-vector with the first (top) entry s being the arrival time, as already done, and the second (bottom) entry s being the service requirement, as taken from Table 2-1. Also, keep the queue ranked in decreasing order of the service-requirement attribute. The resulting hand-simulation table looks like this (the shaded entries indicate differences from Table 2-2 that were caused by moving from the FIFO to the SPT queue discipline):
5 Just-Finished Event Variables Attributes Statistical Accumulators Event Calendar Entity Time Event Arrival Times: No. t Type Q(t) B(t) (In Queue) In Serv ice P N WQ WQ* TS TS* Q Q* B [Entity No., Time, Type] [1, 0.00, Arr] 0.00 Init 0 0 () () [2, 1.73, Arr] Arr 0 1 () [1, 2.90, Dep] () 2.90 [1, 2.90, Dep] Arr 1 1 (1.73) [3, 3.08, Arr] (1.76) 2.90 [3, 3.08, Arr] Dep 0 1 () [2, 4.66, Dep] () 1.76 [4, 3.79, Arr] Arr 1 1 (3.08) [2, 4.66, Dep] (3.39) 1.76 [5, 4.41, Arr] Arr 2 1 (3.79, 3.08) [2, 4.66, Dep] (4.52, 3.39) 1.76 [2, 4.66, Dep] Arr 3 1 (3.79, 4.41, 3.08) [6, 18.69, Arr] ( 4.52, 4.46, 3.39) 1.76
6 [3, 8.05, Dep] Dep 2 1 (3.79, 4.41) [6, 18.69, Arr] ( 4.52, ) Dep 1 1 (3.79) (4.52) [5, [6, [, 12.51, Dep], 18.69Arr], 20.00End] Dep 0 1 () ) [4, 17.03, Dep] [6, 18.69, Arr] [6, 18.69, Arr] Dep 0 0 () () [7, 19.39, Arr] Arr 0 1 () () Arr 1 1 (19.39) (2.07) [8, 34.91, Arr] End 1 1 (19.39) (2.07) [8, 34.91, Arr] The first time this rule has an effect is in the order of the queue after the Arrival of entity 5 at time 4.41, whose service time (4.46) is less than the service time (4.52) of entity 4, which is already in queue; entity 5 jumps ahead of entity 4 at this point. The final output performance measures, corresponding to Table 2-3, are:
7 Performance Measure Total production Average waiting time in queue Maximum waiting time in queue Value Result from Table 2-3 Change 5 parts 5 parts No change 2.52 minutes per part (6 p arts) 2.53 minutes per part (6 parts) Decreased 8.72 minutes 8.16 minutes Increased Average total time in system 6.43 minutes per part (5 arts) 6.44 minutes per part (5 parts) Decreased Maximum total time in system minutes minutes Increased Time-average number of parts in queue Maximum number of parts in queue Drill-press utilization 0.92 (dimensionless proportion) 0.79 part 0.79 part No change 3 parts 3 parts No change 0.92 (dimensionless proportion) No change The effect of SPT rather than FIFO is for the average waiting time in queue and the average total time in system to go down (get better), while the maximum of these two measures went up (got worse), since the large jobs get stuck at the back of the queue for a long time. Thus, whether this is better depends on the performance measure It would also be possible to put entities into the queue at the end and then do a search on the service-requirement attribute to decide which entity to remove; this would be somewhat more computation, though, since inserting the entity in the right place will generally require searching less than the whole queue, while picking the minimum-service-requirement entity out of an unordered queue will always require searching the entire queue to be sure we get the minimum.
More on Input Distributions
 More on Input Distributions Importance of Using the Correct Distribution Replacing a distribution with its mean Arrivals Waiting line Processing order System Service mean interarrival time = 1 minute mean
More on Input Distributions Importance of Using the Correct Distribution Replacing a distribution with its mean Arrivals Waiting line Processing order System Service mean interarrival time = 1 minute mean
Stochastic Models of Manufacturing Systems
 Stochastic Models of Manufacturing Systems Ivo Adan Systems 2/49 Continuous systems State changes continuously in time (e.g., in chemical applications) Discrete systems State is observed at fixed regular
Stochastic Models of Manufacturing Systems Ivo Adan Systems 2/49 Continuous systems State changes continuously in time (e.g., in chemical applications) Discrete systems State is observed at fixed regular
EE 368. Weeks 3 (Notes)
 EE 368 Weeks 3 (Notes) 1 State of a Queuing System State: Set of parameters that describe the condition of the system at a point in time. Why do we need it? Average size of Queue Average waiting time How
EE 368 Weeks 3 (Notes) 1 State of a Queuing System State: Set of parameters that describe the condition of the system at a point in time. Why do we need it? Average size of Queue Average waiting time How
Section 1.2: A Single Server Queue
 Section 12: A Single Server Queue Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course c 2006 Pearson Ed, Inc 0-13-142917-5 Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course Section 12: A Single Server Queue 1/ 30 Section
Section 12: A Single Server Queue Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course c 2006 Pearson Ed, Inc 0-13-142917-5 Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course Section 12: A Single Server Queue 1/ 30 Section
Exercises Solutions. Automation IEA, LTH. Chapter 2 Manufacturing and process systems. Chapter 5 Discrete manufacturing problems
 Exercises Solutions Note, that we have not formulated the answers for all the review questions. You will find the answers for many questions by reading and reflecting about the text in the book. Chapter
Exercises Solutions Note, that we have not formulated the answers for all the review questions. You will find the answers for many questions by reading and reflecting about the text in the book. Chapter
Queuing Theory. Using the Math. Management Science
 Queuing Theory Using the Math 1 Markov Processes (Chains) A process consisting of a countable sequence of stages, that can be judged at each stage to fall into future states independent of how the process
Queuing Theory Using the Math 1 Markov Processes (Chains) A process consisting of a countable sequence of stages, that can be judged at each stage to fall into future states independent of how the process
Row Reduction and Echelon Forms
 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms 1 / 29 Key Concepts row echelon form, reduced row echelon form pivot position, pivot, pivot column basic variable, free variable general solution, parametric solution existence
Row Reduction and Echelon Forms 1 / 29 Key Concepts row echelon form, reduced row echelon form pivot position, pivot, pivot column basic variable, free variable general solution, parametric solution existence
Queueing Theory. VK Room: M Last updated: October 17, 2013.
 Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
CS418 Operating Systems
 CS418 Operating Systems Lecture 14 Queuing Analysis Textbook: Operating Systems by William Stallings 1 1. Why Queuing Analysis? If the system environment changes (like the number of users is doubled),
CS418 Operating Systems Lecture 14 Queuing Analysis Textbook: Operating Systems by William Stallings 1 1. Why Queuing Analysis? If the system environment changes (like the number of users is doubled),
of 8 28/11/ :25
 Paul's Online Math Notes Home Content Chapter/Section Downloads Misc Links Site Help Contact Me Differential Equations (Notes) / First Order DE`s / Modeling with First Order DE's [Notes] Differential Equations
Paul's Online Math Notes Home Content Chapter/Section Downloads Misc Links Site Help Contact Me Differential Equations (Notes) / First Order DE`s / Modeling with First Order DE's [Notes] Differential Equations
Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems
 Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems John Shortle George Mason University February 28, 2018 Outline Why stochastic models matter M/M/1 queue Little s law Priority
Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems John Shortle George Mason University February 28, 2018 Outline Why stochastic models matter M/M/1 queue Little s law Priority
Finite Math Section 4_1 Solutions and Hints
 Finite Math Section 4_1 Solutions and Hints by Brent M. Dingle for the book: Finite Mathematics, 7 th Edition by S. T. Tan. DO NOT PRINT THIS OUT AND TURN IT IN!!!!!!!! This is designed to assist you in
Finite Math Section 4_1 Solutions and Hints by Brent M. Dingle for the book: Finite Mathematics, 7 th Edition by S. T. Tan. DO NOT PRINT THIS OUT AND TURN IT IN!!!!!!!! This is designed to assist you in
Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues
 Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues 1 Examples of reversible processes 11 Birth-death processes We define two non-negative sequences birth and death rates denoted by {λ n : n N 0 } and {µ n : n
Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues 1 Examples of reversible processes 11 Birth-death processes We define two non-negative sequences birth and death rates denoted by {λ n : n N 0 } and {µ n : n
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling
 NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
Classification of Queuing Models
 Classification of Queuing Models Generally Queuing models may be completely specified in the following symbol form:(a/b/c):(d/e)where a = Probability law for the arrival(or inter arrival)time, b = Probability
Classification of Queuing Models Generally Queuing models may be completely specified in the following symbol form:(a/b/c):(d/e)where a = Probability law for the arrival(or inter arrival)time, b = Probability
BY DEBORAH BARRETT - LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION (4TH EDITION) ( ) [HARDCOVER] BY DEBORAH BARRETT
![BY DEBORAH BARRETT - LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION (4TH EDITION) ( ) [HARDCOVER] BY DEBORAH BARRETT BY DEBORAH BARRETT - LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION (4TH EDITION) ( ) [HARDCOVER] BY DEBORAH BARRETT](/thumbs/90/102824673.jpg) Read Online and Download Ebook BY DEBORAH BARRETT - LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION (4TH EDITION) (2013-09- 04) [HARDCOVER] BY DEBORAH BARRETT DOWNLOAD EBOOK : BY DEBORAH BARRETT - LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION Click
Read Online and Download Ebook BY DEBORAH BARRETT - LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION (4TH EDITION) (2013-09- 04) [HARDCOVER] BY DEBORAH BARRETT DOWNLOAD EBOOK : BY DEBORAH BARRETT - LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION Click
Quiz Queue II. III. ( ) ( ) =1.3333
 Quiz Queue UMJ, a mail-order company, receives calls to place orders at an average of 7.5 minutes intervals. UMJ hires one operator and can handle each call in about every 5 minutes on average. The inter-arrival
Quiz Queue UMJ, a mail-order company, receives calls to place orders at an average of 7.5 minutes intervals. UMJ hires one operator and can handle each call in about every 5 minutes on average. The inter-arrival
M/G/1 and Priority Queueing
 M/G/1 and Priority Queueing Richard T. B. Ma School of Computing National University of Singapore CS 5229: Advanced Compute Networks Outline PASTA M/G/1 Workload and FIFO Delay Pollaczek Khinchine Formula
M/G/1 and Priority Queueing Richard T. B. Ma School of Computing National University of Singapore CS 5229: Advanced Compute Networks Outline PASTA M/G/1 Workload and FIFO Delay Pollaczek Khinchine Formula
Lecture No. # 07 Linear System Part 4
 Advanced Matrix Theory And Linear Algebra For Engineers Prof. Vittal Rao Department of Electronics Design And Technology Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 07 Linear System Part 4 You
Advanced Matrix Theory And Linear Algebra For Engineers Prof. Vittal Rao Department of Electronics Design And Technology Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 07 Linear System Part 4 You
A 3D PRINTED SUNDIAL
 A 3D PRINTED SUNDIAL The objective was to 3d print a sundial correct for latitude. The selection of multiple colors involves extra steps, and this was not considered here. Simon Wheaton-Smith June 26,
A 3D PRINTED SUNDIAL The objective was to 3d print a sundial correct for latitude. The selection of multiple colors involves extra steps, and this was not considered here. Simon Wheaton-Smith June 26,
Generating Random Variates II and Examples
 Generating Random Variates II and Examples Holger Füßler Holger Füßler Universität Mannheim Summer 2004 Side note: TexPoint» TexPoint is a Powerpoint add-in that enables the easy use of Latex symbols and
Generating Random Variates II and Examples Holger Füßler Holger Füßler Universität Mannheim Summer 2004 Side note: TexPoint» TexPoint is a Powerpoint add-in that enables the easy use of Latex symbols and
Performance-based Dynamic Scheduling of Hybrid Real-time Applications on a Cluster of Heterogeneous Workstations 1
 Performance-based Dynamic Scheduling of Hybrid Real-time Applications on a Cluster of Heterogeneous Worstations 1 Ligang He, Stephen A. Jarvis, Daniel P. Spooner and Graham R. Nudd Department of Computer
Performance-based Dynamic Scheduling of Hybrid Real-time Applications on a Cluster of Heterogeneous Worstations 1 Ligang He, Stephen A. Jarvis, Daniel P. Spooner and Graham R. Nudd Department of Computer
(I.D) Solving Linear Systems via Row-Reduction
 (I.D) Solving Linear Systems via Row-Reduction Turning to the promised algorithmic approach to Gaussian elimination, we say an m n matrix M is in reduced-row echelon form if: the first nonzero entry of
(I.D) Solving Linear Systems via Row-Reduction Turning to the promised algorithmic approach to Gaussian elimination, we say an m n matrix M is in reduced-row echelon form if: the first nonzero entry of
Lecture 3i Complex Systems of Equations (pages )
 Lecture 3i Complex Systems of Equations (pages 47-48) Now that we have covered the fundamentals of the complex numbers, we want to move on to study the vector space properties of the complex numbers. As
Lecture 3i Complex Systems of Equations (pages 47-48) Now that we have covered the fundamentals of the complex numbers, we want to move on to study the vector space properties of the complex numbers. As
1 Continuous-time chains, finite state space
 Université Paris Diderot 208 Markov chains Exercises 3 Continuous-time chains, finite state space Exercise Consider a continuous-time taking values in {, 2, 3}, with generator 2 2. 2 2 0. Draw the diagramm
Université Paris Diderot 208 Markov chains Exercises 3 Continuous-time chains, finite state space Exercise Consider a continuous-time taking values in {, 2, 3}, with generator 2 2. 2 2 0. Draw the diagramm
ISyE 6644 Fall 2016 Test #1 Solutions
 1 NAME ISyE 6644 Fall 2016 Test #1 Solutions This test is 85 minutes. You re allowed one cheat sheet. Good luck! 1. Suppose X has p.d.f. f(x) = 3x 2, 0 < x < 1. Find E[3X + 2]. Solution: E[X] = 1 0 x 3x2
1 NAME ISyE 6644 Fall 2016 Test #1 Solutions This test is 85 minutes. You re allowed one cheat sheet. Good luck! 1. Suppose X has p.d.f. f(x) = 3x 2, 0 < x < 1. Find E[3X + 2]. Solution: E[X] = 1 0 x 3x2
Che-Wei Chang Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Chang Gung University
 Che-Wei Chang chewei@mail.cgu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Chang Gung University } 2017/11/15 Midterm } 2017/11/22 Final Project Announcement 2 1. Introduction 2.
Che-Wei Chang chewei@mail.cgu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Chang Gung University } 2017/11/15 Midterm } 2017/11/22 Final Project Announcement 2 1. Introduction 2.
MATH 3330 INFORMATION SHEET FOR TEST 3 SPRING Test 3 will be in PKH 113 in class time, Tues April 21
 MATH INFORMATION SHEET FOR TEST SPRING Test will be in PKH in class time, Tues April See above for date, time and location of Test It will last 7 minutes and is worth % of your course grade The material
MATH INFORMATION SHEET FOR TEST SPRING Test will be in PKH in class time, Tues April See above for date, time and location of Test It will last 7 minutes and is worth % of your course grade The material
S. T. Enns Paul Rogers. Dept. of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering University of Calgary Calgary, AB., T2N-1N4, CANADA
 Proceedings of the 2008 Winter Simulation Conference S. J. Mason, R. R. Hill, L. Mönch, O. Rose, T. Jefferson, J. W. Fowler eds. CLARIFYING CONWIP VERSUS PUSH SYSTEM BEHAVIOR USING SIMULATION S. T. Enns
Proceedings of the 2008 Winter Simulation Conference S. J. Mason, R. R. Hill, L. Mönch, O. Rose, T. Jefferson, J. W. Fowler eds. CLARIFYING CONWIP VERSUS PUSH SYSTEM BEHAVIOR USING SIMULATION S. T. Enns
A STAFFING ALGORITHM FOR CALL CENTERS WITH SKILL-BASED ROUTING: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 A STAFFING ALGORITHM FOR CALL CENTERS WITH SKILL-BASED ROUTING: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL by Rodney B. Wallace IBM and The George Washington University rodney.wallace@us.ibm.com Ward Whitt Columbia University
A STAFFING ALGORITHM FOR CALL CENTERS WITH SKILL-BASED ROUTING: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL by Rodney B. Wallace IBM and The George Washington University rodney.wallace@us.ibm.com Ward Whitt Columbia University
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems
 Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Control and Dynamical Systems
 CDS 101 1. Åström and Murray, Exercise 1.3 2. Åström and Murray, Exercise 1.4 3. Åström and Murray, Exercise 2.6, parts (a) and (b) CDS 110a 1. Åström and Murray, Exercise 1.4 2. Åström and Murray, Exercise
CDS 101 1. Åström and Murray, Exercise 1.3 2. Åström and Murray, Exercise 1.4 3. Åström and Murray, Exercise 2.6, parts (a) and (b) CDS 110a 1. Åström and Murray, Exercise 1.4 2. Åström and Murray, Exercise
CS 550 Operating Systems Spring CPU scheduling I
 1 CS 550 Operating Systems Spring 2018 CPU scheduling I Process Lifecycle Ready Process is ready to execute, but not yet executing Its waiting in the scheduling queue for the CPU scheduler to pick it up.
1 CS 550 Operating Systems Spring 2018 CPU scheduling I Process Lifecycle Ready Process is ready to execute, but not yet executing Its waiting in the scheduling queue for the CPU scheduler to pick it up.
The Queue Inference Engine and the Psychology of Queueing. ESD.86 Spring 2007 Richard C. Larson
 The Queue Inference Engine and the Psychology of Queueing ESD.86 Spring 2007 Richard C. Larson Part 1 The Queue Inference Engine QIE Queue Inference Engine (QIE) Boston area ATMs: reams of data Standard
The Queue Inference Engine and the Psychology of Queueing ESD.86 Spring 2007 Richard C. Larson Part 1 The Queue Inference Engine QIE Queue Inference Engine (QIE) Boston area ATMs: reams of data Standard
6-2 Matrix Multiplication, Inverses and Determinants
 Find AB and BA, if possible. 1. A = A = ; A is a 1 2 matrix and B is a 2 2 matrix. Because the number of columns of A is equal to the number of rows of B, AB exists. To find the first entry of AB, find
Find AB and BA, if possible. 1. A = A = ; A is a 1 2 matrix and B is a 2 2 matrix. Because the number of columns of A is equal to the number of rows of B, AB exists. To find the first entry of AB, find
MSA 640 Homework #2 Due September 17, points total / 20 points per question Show all work leading to your answers
 Name MSA 640 Homework #2 Due September 17, 2010 100 points total / 20 points per question Show all work leading to your answers 1. The annual demand for a particular type of valve is 3,500 units. The cost
Name MSA 640 Homework #2 Due September 17, 2010 100 points total / 20 points per question Show all work leading to your answers 1. The annual demand for a particular type of valve is 3,500 units. The cost
Chapter 6 Queueing Models. Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation
 Chapter 6 Queueing Models Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queueing models. A simple but typical queueing model: Queueing
Chapter 6 Queueing Models Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queueing models. A simple but typical queueing model: Queueing
NCES: MA.N.1.1; MA.A.2; MBC.A.1.2
 Unit 1-Functions, Equations and Systems Name Lesson 1- Direct and Indirect Variation-Investigation 1 Date NCES: MA.N.1.1; MA.A.2; MBC.A.1.2 Block NCSCS: Algebra I 1.03; Algebra II 1.05 (Developed by PHS
Unit 1-Functions, Equations and Systems Name Lesson 1- Direct and Indirect Variation-Investigation 1 Date NCES: MA.N.1.1; MA.A.2; MBC.A.1.2 Block NCSCS: Algebra I 1.03; Algebra II 1.05 (Developed by PHS
A. Incorrect! This inequality is a disjunction and has a solution set shaded outside the boundary points.
 Problem Solving Drill 11: Absolute Value Inequalities Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which inequality has the solution set shown in the graph? Question #01 (A) x + 6 > 1 (B) x + 6 < 1 (C) x + 6 1 (D)
Problem Solving Drill 11: Absolute Value Inequalities Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which inequality has the solution set shown in the graph? Question #01 (A) x + 6 > 1 (B) x + 6 < 1 (C) x + 6 1 (D)
7.5 Operations with Matrices. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 7.5 Operations with Matrices Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Decide whether two matrices are equal. Add and subtract matrices and multiply matrices by scalars. Multiply
7.5 Operations with Matrices Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Decide whether two matrices are equal. Add and subtract matrices and multiply matrices by scalars. Multiply
Chapter 3: Markov Processes First hitting times
 Chapter 3: Markov Processes First hitting times L. Breuer University of Kent, UK November 3, 2010 Example: M/M/c/c queue Arrivals: Poisson process with rate λ > 0 Example: M/M/c/c queue Arrivals: Poisson
Chapter 3: Markov Processes First hitting times L. Breuer University of Kent, UK November 3, 2010 Example: M/M/c/c queue Arrivals: Poisson process with rate λ > 0 Example: M/M/c/c queue Arrivals: Poisson
MEDIAN CONFIDENCE INTERVALS -GROUPING DATAINTO BATCHES AND COMPARISON WITH OTHER TECHNIQUES
 MEDIAN CONFIDENCE INTERVALS -GROUPING DATAINTO BATCHES AND COMPARISON WITH OTHER TECHNIQUES Johann Christoph Strelen Rheinische Friedrich Wilhelms Universität Bonn Römerstr. 164, 53117 Bonn, Germany E-mail:
MEDIAN CONFIDENCE INTERVALS -GROUPING DATAINTO BATCHES AND COMPARISON WITH OTHER TECHNIQUES Johann Christoph Strelen Rheinische Friedrich Wilhelms Universität Bonn Römerstr. 164, 53117 Bonn, Germany E-mail:
ISyE 2030 Practice Test 2
 1 NAME ISyE 2030 Practice Test 2 Summer 2005 This test is open notes, open books. You have exactly 75 minutes. 1. Short-Answer Questions (a) TRUE or FALSE? If arrivals occur according to a Poisson process
1 NAME ISyE 2030 Practice Test 2 Summer 2005 This test is open notes, open books. You have exactly 75 minutes. 1. Short-Answer Questions (a) TRUE or FALSE? If arrivals occur according to a Poisson process
SOLUTIONS MANUAL COLLEGE PHYSICS GIAMBATTISTA RICHARDSON
 SOLUTIONS MANUAL COLLEGE PHYSICS GIAMBATTISTA RICHARDSON Download Free PDF Full Version here! GIAMBATTISTA COLLEGE PHYSICS 4TH EDITION AMAZON Amazon college physics alan giambattista betty richardson student
SOLUTIONS MANUAL COLLEGE PHYSICS GIAMBATTISTA RICHARDSON Download Free PDF Full Version here! GIAMBATTISTA COLLEGE PHYSICS 4TH EDITION AMAZON Amazon college physics alan giambattista betty richardson student
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS
 BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
CPU Scheduling Exercises
 CPU Scheduling Exercises NOTE: All time in these exercises are in msec. Processes P 1, P 2, P 3 arrive at the same time, but enter the job queue in the order presented in the table. Time quantum = 3 msec
CPU Scheduling Exercises NOTE: All time in these exercises are in msec. Processes P 1, P 2, P 3 arrive at the same time, but enter the job queue in the order presented in the table. Time quantum = 3 msec
Verification and Validation. CS1538: Introduction to Simulations
 Verification and Validation CS1538: Introduction to Simulations Steps in a Simulation Study Problem & Objective Formulation Model Conceptualization Data Collection Model translation, Verification, Validation
Verification and Validation CS1538: Introduction to Simulations Steps in a Simulation Study Problem & Objective Formulation Model Conceptualization Data Collection Model translation, Verification, Validation
Richard C. Larson. March 5, Photo courtesy of Johnathan Boeke.
 ESD.86 Markov Processes and their Application to Queueing Richard C. Larson March 5, 2007 Photo courtesy of Johnathan Boeke. http://www.flickr.com/photos/boeke/134030512/ Outline Spatial Poisson Processes,
ESD.86 Markov Processes and their Application to Queueing Richard C. Larson March 5, 2007 Photo courtesy of Johnathan Boeke. http://www.flickr.com/photos/boeke/134030512/ Outline Spatial Poisson Processes,
QueueTraffic and queuing theory
 QueueTraffic and queuing theory + Queues in everyday life You have certainly been in a queue somewhere. Where? How were they different? At ticket vending machines, cash desks, at the doctors, at printers,
QueueTraffic and queuing theory + Queues in everyday life You have certainly been in a queue somewhere. Where? How were they different? At ticket vending machines, cash desks, at the doctors, at printers,
Photo: US National Archives
 ESD.86. Markov Processes and their Application to Queueing II Richard C. Larson March 7, 2007 Photo: US National Archives Outline Little s Law, one more time PASTA treat Markov Birth and Death Queueing
ESD.86. Markov Processes and their Application to Queueing II Richard C. Larson March 7, 2007 Photo: US National Archives Outline Little s Law, one more time PASTA treat Markov Birth and Death Queueing
Unit 3 Day 4. Solving Equations with Rational Exponents and Radicals
 Unit Day 4 Solving Equations with Rational Exponents and Radicals Day 4 Warm Up You know a lot about inverses in mathematics we use them every time we solve equations. Write down the inverse operation
Unit Day 4 Solving Equations with Rational Exponents and Radicals Day 4 Warm Up You know a lot about inverses in mathematics we use them every time we solve equations. Write down the inverse operation
A Note on the Event Horizon for a Processor Sharing Queue
 A Note on the Event Horizon for a Processor Sharing Queue Robert C. Hampshire Heinz School of Public Policy and Management Carnegie Mellon University hamp@andrew.cmu.edu William A. Massey Department of
A Note on the Event Horizon for a Processor Sharing Queue Robert C. Hampshire Heinz School of Public Policy and Management Carnegie Mellon University hamp@andrew.cmu.edu William A. Massey Department of
Kenneth Krane Solutions Manual
 Kenneth Krane Solutions Manual If you are looking for a book Kenneth krane solutions manual in pdf format, then you've come to right website. We presented the full variant of this ebook in doc, epub, PDF,
Kenneth Krane Solutions Manual If you are looking for a book Kenneth krane solutions manual in pdf format, then you've come to right website. We presented the full variant of this ebook in doc, epub, PDF,
SuperCELL Data Programmer and ACTiSys IR Programmer User s Guide
 SuperCELL Data Programmer and ACTiSys IR Programmer User s Guide This page is intentionally left blank. SuperCELL Data Programmer and ACTiSys IR Programmer User s Guide The ACTiSys IR Programmer and SuperCELL
SuperCELL Data Programmer and ACTiSys IR Programmer User s Guide This page is intentionally left blank. SuperCELL Data Programmer and ACTiSys IR Programmer User s Guide The ACTiSys IR Programmer and SuperCELL
Analysis of Software Artifacts
 Analysis of Software Artifacts System Performance I Shu-Ngai Yeung (with edits by Jeannette Wing) Department of Statistics Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 2001 by Carnegie Mellon University
Analysis of Software Artifacts System Performance I Shu-Ngai Yeung (with edits by Jeannette Wing) Department of Statistics Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 2001 by Carnegie Mellon University
Module 5: CPU Scheduling
 Module 5: CPU Scheduling Basic Concepts Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms Multiple-Processor Scheduling Real-Time Scheduling Algorithm Evaluation 5.1 Basic Concepts Maximum CPU utilization obtained
Module 5: CPU Scheduling Basic Concepts Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms Multiple-Processor Scheduling Real-Time Scheduling Algorithm Evaluation 5.1 Basic Concepts Maximum CPU utilization obtained
Lecture 3: Gaussian Elimination, continued. Lecture 3: Gaussian Elimination, continued
 Definition The process of solving a system of linear equations by converting the system to an augmented matrix is called Gaussian Elimination. The general strategy is as follows: Convert the system of
Definition The process of solving a system of linear equations by converting the system to an augmented matrix is called Gaussian Elimination. The general strategy is as follows: Convert the system of
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3. Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, Announcements
 Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
CPU scheduling. CPU Scheduling
 EECS 3221 Operating System Fundamentals No.4 CPU scheduling Prof. Hui Jiang Dept of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, York University CPU Scheduling CPU scheduling is the basis of multiprogramming
EECS 3221 Operating System Fundamentals No.4 CPU scheduling Prof. Hui Jiang Dept of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, York University CPU Scheduling CPU scheduling is the basis of multiprogramming
Row Reducing Matrices
 A Presentation on Procedures Used to Work with Matrices Prepared by David Morín MEnTe Program East Los Angeles College Topics Introduction Row Operations Row Echelon Form Reduced Row Echelon Form Check
A Presentation on Procedures Used to Work with Matrices Prepared by David Morín MEnTe Program East Los Angeles College Topics Introduction Row Operations Row Echelon Form Reduced Row Echelon Form Check
Matrix Theory and Differential Equations Homework 6 Solutions, 10/5/6
 Matrix Theory and Differential Equations Homework 6 Solutions, 0/5/6 Question Find the general solution of the matrix system: x 3y + 5z 8t 5 x + 4y z + t Express your answer in the form of a particulaolution
Matrix Theory and Differential Equations Homework 6 Solutions, 0/5/6 Question Find the general solution of the matrix system: x 3y + 5z 8t 5 x + 4y z + t Express your answer in the form of a particulaolution
Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling
 Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Basic Concepts Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms Multiple-Processor Scheduling Real-Time Scheduling Algorithm Evaluation 6.1 Basic Concepts Maximum CPU utilization obtained
Chapter 6: CPU Scheduling Basic Concepts Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms Multiple-Processor Scheduling Real-Time Scheduling Algorithm Evaluation 6.1 Basic Concepts Maximum CPU utilization obtained
Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations
 What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
EFFICIENT COMPUTATION OF PROBABILITIES OF EVENTS DESCRIBED BY ORDER STATISTICS AND APPLICATION TO A PROBLEM OFQUEUES
 EFFICIENT COMPUTATION OF PROBABILITIES OF EVENTS DESCRIBED BY ORDER STATISTICS AND APPLICATION TO A PROBLEM OFQUEUES Lee K. Jones and Richard C. Larson OR 249-91 May 1991 Efficient Computation of Probabilities
EFFICIENT COMPUTATION OF PROBABILITIES OF EVENTS DESCRIBED BY ORDER STATISTICS AND APPLICATION TO A PROBLEM OFQUEUES Lee K. Jones and Richard C. Larson OR 249-91 May 1991 Efficient Computation of Probabilities
IOE 202: lectures 11 and 12 outline
 IOE 202: lectures 11 and 12 outline Announcements Last time... Queueing models intro Performance characteristics of a queueing system Steady state analysis of an M/M/1 queueing system Other queueing systems,
IOE 202: lectures 11 and 12 outline Announcements Last time... Queueing models intro Performance characteristics of a queueing system Steady state analysis of an M/M/1 queueing system Other queueing systems,
ISLAMIC PATTERNS: AN ANALYTICAL AND COSMOLOGICAL APPROACH BY KEITH CRITCHLOW
 Read Online and Download Ebook ISLAMIC PATTERNS: AN ANALYTICAL AND COSMOLOGICAL APPROACH BY KEITH CRITCHLOW DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ISLAMIC PATTERNS: AN ANALYTICAL AND Click link bellow and free register to download
Read Online and Download Ebook ISLAMIC PATTERNS: AN ANALYTICAL AND COSMOLOGICAL APPROACH BY KEITH CRITCHLOW DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ISLAMIC PATTERNS: AN ANALYTICAL AND Click link bellow and free register to download
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2008 The Kaprekar Routine Emy Jones University of
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2008 The Kaprekar Routine Emy Jones University of
1 Markov decision processes
 2.997 Decision-Making in Large-Scale Systems February 4 MI, Spring 2004 Handout #1 Lecture Note 1 1 Markov decision processes In this class we will study discrete-time stochastic systems. We can describe
2.997 Decision-Making in Large-Scale Systems February 4 MI, Spring 2004 Handout #1 Lecture Note 1 1 Markov decision processes In this class we will study discrete-time stochastic systems. We can describe
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.1. Tutorial illustrating new options for grouping with metabolism
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.1 Tutorial illustrating new options for grouping with metabolism Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims The exercise Workflow 2 Background Grouping with metabolism is a procedure
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.1 Tutorial illustrating new options for grouping with metabolism Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims The exercise Workflow 2 Background Grouping with metabolism is a procedure
Signalized Intersection Delay Models
 Chapter 35 Signalized Intersection Delay Models 35.1 Introduction Signalized intersections are the important points or nodes within a system of highways and streets. To describe some measure of effectiveness
Chapter 35 Signalized Intersection Delay Models 35.1 Introduction Signalized intersections are the important points or nodes within a system of highways and streets. To describe some measure of effectiveness
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems
 Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
General Gibbs Minimization as an Approach to Equilibrium
 General Gibbs Minimization as an Approach to Equilibrium Most of us have used the equilibrium constant approach to find equilibrium compositions for simple systems. This requires you to hypothesize equilibrium
General Gibbs Minimization as an Approach to Equilibrium Most of us have used the equilibrium constant approach to find equilibrium compositions for simple systems. This requires you to hypothesize equilibrium
2/5/07 CSE 30341: Operating Systems Principles
 page 1 Shortest-Job-First (SJR) Scheduling Associate with each process the length of its next CPU burst. Use these lengths to schedule the process with the shortest time Two schemes: nonpreemptive once
page 1 Shortest-Job-First (SJR) Scheduling Associate with each process the length of its next CPU burst. Use these lengths to schedule the process with the shortest time Two schemes: nonpreemptive once
Simulation of Process Scheduling Algorithms
 Simulation of Process Scheduling Algorithms Project Report Instructor: Dr. Raimund Ege Submitted by: Sonal Sood Pramod Barthwal Index 1. Introduction 2. Proposal 3. Background 3.1 What is a Process 4.
Simulation of Process Scheduling Algorithms Project Report Instructor: Dr. Raimund Ege Submitted by: Sonal Sood Pramod Barthwal Index 1. Introduction 2. Proposal 3. Background 3.1 What is a Process 4.
A TANDEM QUEUEING SYSTEM WITH APPLICATIONS TO PRICING STRATEGY. Wai-Ki Ching. Tang Li. Sin-Man Choi. Issic K.C. Leung
 Manuscript submitted to AIMS Journals Volume X, Number 0X, XX 00X Website: http://aimsciences.org pp. X XX A TANDEM QUEUEING SYSTEM WITH APPLICATIONS TO PRICING STRATEGY WAI-KI CHING SIN-MAN CHOI TANG
Manuscript submitted to AIMS Journals Volume X, Number 0X, XX 00X Website: http://aimsciences.org pp. X XX A TANDEM QUEUEING SYSTEM WITH APPLICATIONS TO PRICING STRATEGY WAI-KI CHING SIN-MAN CHOI TANG
Computer Engineering II Solution to Exercise Sheet Chapter 12
 Distributed Computing FS 07 Prof. R. Wattenhofer Computer Engineering II Solution to Exercise Sheet Chapter Quiz Questions a) Yes, by using states that consist of the current and the previous value in
Distributed Computing FS 07 Prof. R. Wattenhofer Computer Engineering II Solution to Exercise Sheet Chapter Quiz Questions a) Yes, by using states that consist of the current and the previous value in
Session-Based Queueing Systems
 Session-Based Queueing Systems Modelling, Simulation, and Approximation Jeroen Horters Supervisor VU: Sandjai Bhulai Executive Summary Companies often offer services that require multiple steps on the
Session-Based Queueing Systems Modelling, Simulation, and Approximation Jeroen Horters Supervisor VU: Sandjai Bhulai Executive Summary Companies often offer services that require multiple steps on the
The Multiple Traveling Salesman Problem with Time Windows: Bounds for the Minimum Number of Vehicles
 The Multiple Traveling Salesman Problem with Time Windows: Bounds for the Minimum Number of Vehicles Snežana Mitrović-Minić Ramesh Krishnamurti School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby,
The Multiple Traveling Salesman Problem with Time Windows: Bounds for the Minimum Number of Vehicles Snežana Mitrović-Minić Ramesh Krishnamurti School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby,
Introduction to the Simplex Algorithm Active Learning Module 3
 Introduction to the Simplex Algorithm Active Learning Module 3 J. René Villalobos and Gary L. Hogg Arizona State University Paul M. Griffin Georgia Institute of Technology Background Material Almost any
Introduction to the Simplex Algorithm Active Learning Module 3 J. René Villalobos and Gary L. Hogg Arizona State University Paul M. Griffin Georgia Institute of Technology Background Material Almost any
Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models
 Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr April 2, 2014 Introduction Introduction Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical
Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr April 2, 2014 Introduction Introduction Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical
CPSC 531 Systems Modeling and Simulation FINAL EXAM
 CPSC 531 Systems Modeling and Simulation FINAL EXAM Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Professor: Carey Williamson December 21, 2017 This is a CLOSED BOOK exam. Textbooks, notes, laptops,
CPSC 531 Systems Modeling and Simulation FINAL EXAM Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Professor: Carey Williamson December 21, 2017 This is a CLOSED BOOK exam. Textbooks, notes, laptops,
0.0.1 Section 1.2: Row Reduction and Echelon Forms Echelon form (or row echelon form): 1. All nonzero rows are above any rows of all zeros.
 0.0.1 Section 1.2: Row Reduction and Echelon Forms Echelon form (or row echelon form): 1. All nonzero rows are above any rows of all zeros. 2. Each leading entry (i.e. left most nonzero entry) of a row
0.0.1 Section 1.2: Row Reduction and Echelon Forms Echelon form (or row echelon form): 1. All nonzero rows are above any rows of all zeros. 2. Each leading entry (i.e. left most nonzero entry) of a row
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination
 Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
Twin paradox and Einstein mistake
 Twin paradox and Einstein mistake a mathematical approach Based on the book: Logic in the Universe Victor Orsini The Michelson-Morley experiment showed inadvertently that the speed of light is constant.
Twin paradox and Einstein mistake a mathematical approach Based on the book: Logic in the Universe Victor Orsini The Michelson-Morley experiment showed inadvertently that the speed of light is constant.
Operations and Supply Chain Management Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Operations and Supply Chain Management Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 27 Flow Shop Scheduling - Heuristics - Palmer, Campbell Dudek
Operations and Supply Chain Management Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 27 Flow Shop Scheduling - Heuristics - Palmer, Campbell Dudek
Section 3.3: Discrete-Event Simulation Examples
 Section 33: Discrete-Event Simulation Examples Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course c 2006 Pearson Ed, Inc 0-13-142917-5 Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course Section 33: Discrete-Event Simulation
Section 33: Discrete-Event Simulation Examples Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course c 2006 Pearson Ed, Inc 0-13-142917-5 Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course Section 33: Discrete-Event Simulation
Networking = Plumbing. Queueing Analysis: I. Last Lecture. Lecture Outline. Jeremiah Deng. 29 July 2013
 Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Catalyst The Pearson Custom Library For Chemistry Answer Key Teacher S Edition
 Catalyst The Pearson Custom Library For Chemistry Answer Key Teacher S Edition We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing
Catalyst The Pearson Custom Library For Chemistry Answer Key Teacher S Edition We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing
Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics By Ferdinand Beer;E. Russell Johnston Jr.;William Clausen
 Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics By Ferdinand Beer;E. Russell Johnston Jr.;William Clausen If looking for a book Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics by Ferdinand Beer;E. Russell Johnston Jr.;William
Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics By Ferdinand Beer;E. Russell Johnston Jr.;William Clausen If looking for a book Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics by Ferdinand Beer;E. Russell Johnston Jr.;William
Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems (STORE)
 Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems (STORE) Introduction Basic Lesson 3: Using Microsoft Excel to Analyze Weather Data: Topography and Temperature This lesson uses NCDC data to compare
Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems (STORE) Introduction Basic Lesson 3: Using Microsoft Excel to Analyze Weather Data: Topography and Temperature This lesson uses NCDC data to compare
CE351 Transportation Systems: Planning and Design
 CE351 Transportation Systems: Planning and Design TOPIC: Level of Service (LOS) at Traffic Signals 1 Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement
CE351 Transportation Systems: Planning and Design TOPIC: Level of Service (LOS) at Traffic Signals 1 Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement
Physics 116A Solutions to Homework Set #5 Winter Boas, problem Use an augmented matrix to solve the following equation
 Physics 6A Solutions to Homework Set # Winter 202. Boas, problem 3.2 4. Use an augmented matrix to solve the following equation 2x + 3y z = 2 x + 2y z = 4 4x + 7y 3z = ( We can write this as a 3 x 4 matrix
Physics 6A Solutions to Homework Set # Winter 202. Boas, problem 3.2 4. Use an augmented matrix to solve the following equation 2x + 3y z = 2 x + 2y z = 4 4x + 7y 3z = ( We can write this as a 3 x 4 matrix
Thermodynamics (Classical) for Biological Systems Prof. G. K. Suraishkumar Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Thermodynamics (Classical) for Biological Systems Prof. G. K. Suraishkumar Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module No. # 04 Thermodynamics of Solutions Lecture No. # 25
Thermodynamics (Classical) for Biological Systems Prof. G. K. Suraishkumar Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module No. # 04 Thermodynamics of Solutions Lecture No. # 25
Cofactors and Laplace s expansion theorem
 Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 5: Determinants Section 3 Cofactors and Laplace s expansion theorem What you need to know already: What a determinant is. How to use Gauss-Jordan elimination to
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 5: Determinants Section 3 Cofactors and Laplace s expansion theorem What you need to know already: What a determinant is. How to use Gauss-Jordan elimination to
UNIT 2 MEAN, MEDIAN AND MODE
 Central Tendencies and Dispersion UNIT 2 MEAN, MEDIAN AND MODE Me Structure 2.0 Introduction 2.1 Objectives 2.2 Symbols Used in Calculation of Measures of Central Tendency 2.3 The Arithmetic Mean 2.3.1
Central Tendencies and Dispersion UNIT 2 MEAN, MEDIAN AND MODE Me Structure 2.0 Introduction 2.1 Objectives 2.2 Symbols Used in Calculation of Measures of Central Tendency 2.3 The Arithmetic Mean 2.3.1
Computer simulation of radioactive decay
 Computer simulation of radioactive decay y now you should have worked your way through the introduction to Maple, as well as the introduction to data analysis using Excel Now we will explore radioactive
Computer simulation of radioactive decay y now you should have worked your way through the introduction to Maple, as well as the introduction to data analysis using Excel Now we will explore radioactive
Last Minute Optics: A Concise Review Of Optics, Refraction And Contact Lenses By Constance E. West MD, David G. Hunter PhD MD
 Last Minute Optics: A Concise Review Of Optics, Refraction And By Constance E. West MD, David G. Hunter PhD MD The First Rule (Joe Pike series) ebook: Robert Crais: Amazon.de: Kindle-Shop. Amazon.de Prime
Last Minute Optics: A Concise Review Of Optics, Refraction And By Constance E. West MD, David G. Hunter PhD MD The First Rule (Joe Pike series) ebook: Robert Crais: Amazon.de: Kindle-Shop. Amazon.de Prime
IEOR 6711, HMWK 5, Professor Sigman
 IEOR 6711, HMWK 5, Professor Sigman 1. Semi-Markov processes: Consider an irreducible positive recurrent discrete-time Markov chain {X n } with transition matrix P (P i,j ), i, j S, and finite state space.
IEOR 6711, HMWK 5, Professor Sigman 1. Semi-Markov processes: Consider an irreducible positive recurrent discrete-time Markov chain {X n } with transition matrix P (P i,j ), i, j S, and finite state space.
MODEL ANSWERS TO THE THIRD HOMEWORK
 MODEL ANSWERS TO THE THIRD HOMEWORK 1 (i) We apply Gaussian elimination to A First note that the second row is a multiple of the first row So we need to swap the second and third rows 1 3 2 1 2 6 5 7 3
MODEL ANSWERS TO THE THIRD HOMEWORK 1 (i) We apply Gaussian elimination to A First note that the second row is a multiple of the first row So we need to swap the second and third rows 1 3 2 1 2 6 5 7 3
v WMS Tutorials GIS Module Importing, displaying, and converting shapefiles Required Components Time minutes
 v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Importing, displaying, and converting shapefiles Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to import GIS data, visualize it, and convert it into WMS coverage data that could be
v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Importing, displaying, and converting shapefiles Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to import GIS data, visualize it, and convert it into WMS coverage data that could be
