QUADRATIC DEPLETION MODEL FOR GADOLINIUM ISOTOPES IN CASMO-5
|
|
|
- Jerome Farmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advances in Nuclear Fuel Management IV (ANFM 2009) Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, USA, April 12-15, 2009, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2009) QUADRATIC DEPLETION MODEL FOR GADOLINIUM ISOTOPES IN CASMO-5 Deokjung Lee, Joel Rhodes, and Kord Smith Studsvik Scandpower 504 Shoup Ave, Suite 201, Idaho Falls, ID 83402, USA Deokjung.Lee, Joel.Rhodes, Keywords: CASMO-5, Gadolinium, Quadratic Depletion ABSTRACT The huge absorption cross sections of Gd-155 and Gd-157 cause strong spatial shielding effects in Gd-bearing pins. A quadratic depletion model has been implemented in CASMO-5 in order to address the issue of small depletion steps typically required for Gd-bearing fuel assemblies. In this model, the microscopic absorption reaction rates of gadolinium isotopes are assumed to be quadratic functions of the number density of Gd This quadratic function assumption models the variations of the spatial shielding effects over the depletion step and therefore improves the overall accuracy of depletion calculations. With this new model, a depletion step size four times larger than the step size for a conventional predictor-corrector method can be used for Gd-bearing assemblies without compromising accuracy. 1. INTRODUCTION CASMO-5 is the latest version of Studsvik s lattice physics code. 1 A summary of new features in CASMO-5 is as follows:! 586 group neutron data library based on ENDF/B-VII! 18 group gamma data library based on ENDF/B-VII! 586 energy group pincell calculation! More detailed geometries in method of characteristics (MOC) calculation, e.g., BWR cruciform control rods! Higher order P n scattering capability! Characteristics based Dancoff calculations! Multi-assembly calculation capability! Spent nuclear fuel data generation! Expanded depletion chains! U-238 upscatter model 2! Explicit energy release per fission model 3 ANS 2009, Topical Meeting ANFM 2009, p. 1/10
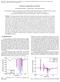
2 ! Quadratic depletion for gadolinium isotopes This paper presents the details of the quadratic depletion model for gadolinium isotopes. For the general depletion calculation of typical LWR lattices, CASMO uses a conventional predictor-corrector (PC) method with a depletion step size of 1.0 MWd/kgU. 4,5 However, for the depletion of Gd-bearing fuel assemblies, the default depletion step size between 2D MOC calculations is 0.5 MWd/kgU. In each step, CASMO-4 employs 4 substeps, each with a step size of MWd/kgU, in which CASMO-4 performs the resonance calculation, pincell calculation, and burnup calculation but omits the expensive 2D transport solution. With this substepping method, CASMO-4 permits a depletion step size two times larger than the conventional PC method. The newer CASMO-5 code employs a higher-order depletion method rather than multiple small substeps with a low order depletion. By assuming a quadratic shape of the microscopic reaction rates over the corrector step, CASMO-5 can avoid the cumbersome substepping and still improve the accuracy of the depletion calculation for the Gd-bearing assemblies. 2. QUADRATIC DEPLETION MODEL Considering only neutron capture, as can be done for gadolinium isotopes, a burnup equation for isotope, m, can be written as!" # $%&!% '( )*+ $,&- )*+ $,&.$,& / ( ) $,&- ) $,&.$,&, (1) where N m (t) is the number density of isotope, m, as a function of time, t, - ) $,& is the microscopic capture cross section of isotope, m, and.$,& is neutron flux. In the conventional PC method, the absorption reaction rate, - ) $,&.$,&, is assumed to be constant. This assumption is a good assumption for small depletion step sizes. Even for practically reasonable depletion step sizes, combined with two depletion calculations (predictor & corrector), the PC method gives accurate solutions for normal LWR assemblies in the absence of gadolinium. However, if gadolinium is present, the depletion step size must be reduced to maintain accuracy. A conventional PC method is applied to deplete a BWR GE14 assembly with 10x10 pins, shown in Fig. 1. Red pins represent 7% Gd 2 O 3 pins. Fig. 2 shows k-infinity through the depletion. Usually the step size of 1.0 MWd/kgU is sufficiently fine for typical LWR assemblies; however, it is apparent that the depletion step of 1.0 MWd/kgU is not fine enough for this Gd-bearing assembly. Eigenvalues at a burnup of 18.0 MWd/kgU are summarized in Table 1. It is easily noted that, in case of Gd-bearing assemblies, the PC method requires smaller depletion steps by a factor of 10 to retain comparable accuracy to non-gd assemblies. In order to investigate the need for fine depletion steps in Gd-bearing assemblies, the microscopic capture reaction rates of Gd-155 and Gd-157 are plotted in Fig. 3. The ANS 2009, Topical Meeting ANFM 2009, p. 2/10
3 shape is varying non-linear and the magnitude varies by several orders of magnitude over the depletion. This significant variation of the absorption reaction rates is caused by spatial shielding effects of gadolinium isotopes. Gd-155 and Gd-157 have huge capture cross sections in the thermal neutron energy range and burn out quickly as shown in Fig. 4. Unless very fine depletion steps are used (at least initially), it is difficult to obtain good accuracy with the conventional PC method. The spatial shielding effect is a function of the isotopic number density and therefore the capture reaction rates are plotted in Fig. 5 as a function of the number density of Gd-155 which has a large capture cross section and persists longer than Gd It can be easily noted that the reaction rates are smooth functions of Gd-155 number density and the dependency is non-linear. Fig. 1 GE14 Assembly with 17 Gd (7%) Pins ANS 2009, Topical Meeting ANFM 2009, p. 3/10
4 k!infinity Burnup"(MWd/kgU) PC,! PC,!0.125 PC,!0.25 PC,!0.5 PC,!1.0 Fig. 2 K-inf vs. Burnup for GE14 Assembly with 17 Gd pins Table 1. Impact of Gd Pins on Accuracy of GE14 Assembly Burnup Calculation (18.0 MWd/kgU) Step!Size! No!Gd! 17!Gd!Pins! (MWd/kgU)! k"inf! Diff!(pcm)! k"inf! Diff!(pcm)! ! ! "! ! "! 0.125! ! "1! ! "9! 0.25! ! "3! ! "41! 0.5! ! "6! ! "166! 1.0! ! "12! ! "684! ANS 2009, Topical Meeting ANFM 2009, p. 4/10
5 1.E+06 Reaction"Rate"per"Atom 1.E+05 1.E+04 1.E+03 Gd"155 Gd"157 1.E Burnup"(MWd/kgU) Fig. 3 Microscopic Capture Reaction Rates of Gd-155 and Gd-177 (vs. Burnup) 2.0E"04 1.8E"04 Number"Density"(#/barn!cm) 1.6E"04 1.4E"04 1.2E"04 1.0E"04 8.0E"05 6.0E"05 4.0E"05 2.0E"05 0.0E Gd"152 Gd"154 Gd"155 Gd"156 Gd"157 Gd"158 Gd"160 Burnup"(MWd/kgU) Fig. 4 Number Densities of Gadolinium Isotopes ANS 2009, Topical Meeting ANFM 2009, p. 5/10
6 1.E+05 Reaction"Rate"per"Atom 1.E+04 1.E+03 Gd"155 Gd"157 1.E+02 0.E+00 1.E"05 2.E"05 3.E"05 4.E"05 5.E"05 6.E"05 7.E"05 Number"Density"(Gd!155) Fig. 5 Microscopic Capture Reaction Rates of Gd-155 and Gd-177 (vs. Gd-155 Number Density) Recently, Yamamoto et al. proposed a projected predictor-corrector method in order to improve the accuracy of the depletion calculation of Gd-bearing assemblies. 6 Yamamoto s method is based on the assumption that the microscopic absorption reaction rate is a linear function of its number density. In this paper, a quadratic depletion (QD) method is presented, in which the microscopic capture reaction rates of gadolinium isotopes are assumed to be quadratic functions of Gd-155 number density. This QD method has been used for the last 5 years in CASMO-4E 7 and is now the default depletion model for gadolinium isotopes used in CASMO-5. The quadratic assumption can be written as: 0 ) 1- ). ' 2 ) 3( ) 3( 4 68 ), (2) where 0 ) is the reaction rate per atom of isotope m, 2 ) 97 ) 9::;<=::8 ) are coefficients of quadratic function, 3( 4 = ( 4 (t) -:( 4 (t n ), and m = 1,, 7 for Gd-152, Gd-154, Gd-155, Gd-156, Gd-157, Gd-158, and Gd-160. Three coefficients for each gadolinium isotopes can be determined using three sets of $0 ) 9 3( 4 &. For the corrector step from t n to t n+1 (where n is depletion step number), this data set is known at t n-1, t n, and t n+1. For t n+1, the predicted information from a conventional PC method is used, i.e., the QD method is applied to corrector step only. Once all the coefficients are determined, Eq. (2) is inserted into Eq. (1). Then one can solve Eq. (1) easily by numerical integration from t n to t n+1. In this QD method, the ANS 2009, Topical Meeting ANFM 2009, p. 6/10
7 predictor number densities and reaction rates are used just to determine the coefficients of the quadratic functions, and they are not necessarily accurate due to the fact that it still assumes constant microscopic reaction rates. However, the corrector step number densities from the quadratic depletion are very accurate as will be shown in the next section. Usually in the PC method (QD method too), only one flux calculation is performed with predictor step number densities to save calculation time. In this case, even though the corrector step number densities are accurate, the flux and eigenvalue solutions may not be as accurate as the corrector number densities. One way to overcome this deficiency is the post correction of the predictor number ( )9>?+ '( )9> B CDE:FG< H )9>?+ I J KL )9> M, (3) B ( )9> where the correction factor is defined as L )9> 'L )9>*+ K NOQ " S #9R I " S W #9RTU P V NOX " Y #9RI " S Z #9RTU, (4) where subscripts m, n are indexes for isotope and time step, respectively, superscripts p, c, u stand for predictor, corrector, and post-corrected. This post-correction is based on the approximation that the error in the number density ratio is constant over the depletion. After the post-correction, the flux calculation is performed with the corrected step number density, ( )9>?+. This post-correction is very important for the accuracy of QD method. Numerical tests show that more than 50% of the accuracy improvement comes from this post-correction. One key assumption for QD is that the reaction rates vary smoothly with depletion which makes it well suited for a constant condition depletion as is typically performed in a lattice physics code. 3. NUMERICAL RESULTS The QD method has been applied to a GE14 assembly with 17 Gd 2 O 3 pins. Postcorrection factors are plotted in Fig. 6. At the first depletion step, these factors are set to 1.0 and vary smoothly over the depletion. Once the number density reduces below 1.e-6 /barn-cm, then the factors are reset to 1.0. Eigenvalues are plotted as a function of burnup in Fig. 7. The case with a depletion step size MWd/kgU with the PC method is used as the reference. It is obvious that there is a huge improvement using QD compared to the standard PC method. ANS 2009, Topical Meeting ANFM 2009, p. 7/10
8 Fig. 8 shows the eigenvalue behavior at a burnup of 18 MWd/kgU as a function of depletion step size for PC and QD (with and without post-correction) methods. The QD method is insensitive to the depletion step size and, with a step size of 0.5 MWd/kgU, it shows an almost converged solution in terms of depletion step size. Post!correction"Factor Burnup"(MWd/kgU) Gd"152 Gd"154 Gd"155 Gd"156 Gd"157 Gd"158 Gd"160 Fig. 6 Post-correction Factors for Predictor Number Densities of Gadolinium Isotopes (GE14, QD, 0.5) k!infinity PC,! PC,!0.5 QD,!0.125 QD,!0.25 QD,!0.5 QD,! Burnup"(MWd/kgU) Fig. 7 k-infinity vs. Burnup for GE14 Assembly with 17 Gd Pins (QD method) ANS 2009, Topical Meeting ANFM 2009, p. 8/10
9 k!infinity Fig. 8 PC QD QD!without!post"correction Burnup"Step"Size"(MWd/kgU) k-infinity of GE14 Assembly with 17 Gd Pins at 18.0 MWd/kgU 4. CONCLUSION The root cause of the necessity of small depletion steps for Gd-bearing assembly has been identified as the strong spatial self-shielding of Gd-155 and Gd-157, and a quadratic depletion model has been proposed to overcome this difficulty and to increase the depletion step size without compromising the accuracy of depletion calculation. The newly proposed method has been implemented in CASMO-5 and test results show significant improvement in accuracy for larger depletion step sizes with a GE14 assembly containing Gd 2 O 3 pins. It was observed that QD method with the step size of 0.5 MWd/kgU produces very accurate results for Gd-bearing fuel assemblies. REFERENCES 1. J. D. RHODES, K. S. SMITH, D. LEE, CASMO-5 development and applications, PHYSOR 2006, Vancouver, Canada, (2006). 2. D. LEE, K. S. SMITH, and J. RHODES, The impact of U-238 resonance elastic scattering approximations on thermal reactor Doppler reactivity, PHYSOR 2008, Interlaken Switzerland, September (2008). 3. J. RHODES, K. S. SMITH, Z. XU, CASMO-5 energy release per fission model, PHYSOR 2008, Interlaken Switzerland, September (2008). 4. J. RHODES, et al., CASMO-4 Users Manual Rev. 4, SSP-01/400 Rev 4, Studsvik Scandpower (2004). ANS 2009, Topical Meeting ANFM 2009, p. 9/10
10 5. J. RHODES, et al., CASMO-5 Users Manual Rev. 0, SSP-07/431 Rev 0, Studsvik Scandpower (2004). 6. A. YAMAMOTO, et al., Projected Predictor-corrector Method for Burnup Calculations of Gd-bearing Fuel Assemblies, PHYSOR 2008, Interlaken, Switzerland, September (2008). 7. J. RHODES, et al., CASMO-4E, Extended Capability of CASMO-4, User s Manual, SSP01/401 Rev 2, Studsvik Scandpower (2004). ANS 2009, Topical Meeting ANFM 2009, p. 10/10
CASMO-5 Development and Applications. Abstract
 Organized and hosted by the Canadian Nuclear Society. Vancouver, BC, Canada. 2006 September 10-14 CASMO-5 Development and Applications Joel Rhodes *1, Kord Smith 1, and Deokjung Lee 1 1 Studsvik Scandpower
Organized and hosted by the Canadian Nuclear Society. Vancouver, BC, Canada. 2006 September 10-14 CASMO-5 Development and Applications Joel Rhodes *1, Kord Smith 1, and Deokjung Lee 1 1 Studsvik Scandpower
CASMO-5/5M Code and Library Status. J. Rhodes, K. Smith, D. Lee, Z. Xu, & N. Gheorghiu Arizona 2008
 CASMO-5/5M Code and Library Status J. Rhodes, K. Smith, D. Lee, Z. Xu, & N. Gheorghiu Arizona 2008 CASMO Methodolgy Evolution CASMO-3 Homo. transmission probability/external Gd depletion CASMO-4 up to
CASMO-5/5M Code and Library Status J. Rhodes, K. Smith, D. Lee, Z. Xu, & N. Gheorghiu Arizona 2008 CASMO Methodolgy Evolution CASMO-3 Homo. transmission probability/external Gd depletion CASMO-4 up to
Consistent Code-to-Code Comparison of Pin-cell Depletion Benchmark Suite
 Consistent Code-to-Code Comparison of Pin-cell Depletion Benchmark Suite September 27, 26 Jinsu Park, Deokjung Lee * COmputational Reactor Physics & Experiment lab Contents VERA depletion benchmark suite
Consistent Code-to-Code Comparison of Pin-cell Depletion Benchmark Suite September 27, 26 Jinsu Park, Deokjung Lee * COmputational Reactor Physics & Experiment lab Contents VERA depletion benchmark suite
Neutronic analysis of SFR lattices: Serpent vs. HELIOS-2
 Neutronic analysis of SFR lattices: Serpent vs. HELIOS-2 E. Fridman 1, R. Rachamin 1, C. Wemple 2 1 Helmholtz Zentrum Dresden Rossendorf 2 Studsvik Scandpower Inc. Text optional: Institutsname Prof. Dr.
Neutronic analysis of SFR lattices: Serpent vs. HELIOS-2 E. Fridman 1, R. Rachamin 1, C. Wemple 2 1 Helmholtz Zentrum Dresden Rossendorf 2 Studsvik Scandpower Inc. Text optional: Institutsname Prof. Dr.
BURNUP CALCULATION CAPABILITY IN THE PSG2 / SERPENT MONTE CARLO REACTOR PHYSICS CODE
 International Conference on Mathematics, Computational Methods & Reactor Physics (M&C 29) Saratoga Springs, New York, May 3-7, 29, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (29) BURNUP CALCULATION
International Conference on Mathematics, Computational Methods & Reactor Physics (M&C 29) Saratoga Springs, New York, May 3-7, 29, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (29) BURNUP CALCULATION
PWR CONTROL ROD EJECTION ANALYSIS WITH THE MOC CODE DECART
 PWR CONTROL ROD EJECTION ANALYSIS WITH THE MOC CODE DECART Mathieu Hursin and Thomas Downar University of California Berkeley, USA mhursin@nuc.berkeley.edu,downar@nuc.berkeley.edu ABSTRACT During the past
PWR CONTROL ROD EJECTION ANALYSIS WITH THE MOC CODE DECART Mathieu Hursin and Thomas Downar University of California Berkeley, USA mhursin@nuc.berkeley.edu,downar@nuc.berkeley.edu ABSTRACT During the past
Research Article Calculations for a BWR Lattice with Adjacent Gadolinium Pins Using the Monte Carlo Cell Code Serpent v.1.1.7
 Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Volume 2, Article ID 65946, 4 pages doi:.55/2/65946 Research Article Calculations for a BWR Lattice with Adjacent Gadolinium Pins Using the Monte Carlo Cell
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations Volume 2, Article ID 65946, 4 pages doi:.55/2/65946 Research Article Calculations for a BWR Lattice with Adjacent Gadolinium Pins Using the Monte Carlo Cell
AEGIS: AN ADVANCED LATTICE PHYSICS CODE FOR LIGHT WATER REACTOR ANALYSES
 AEGIS: AN ADVANCED LATTICE PHYSICS CODE FOR LIGHT WATER REACTOR ANALYSES AKIO YAMAMOTO *, 1, TOMOHIRO ENDO 1, MASATO TABUCHI 2, NAOKI SUGIMURA 2, TADASHI USHIO 2, MASAAKI MORI 2, MASAHIRO TATSUMI 3 and
AEGIS: AN ADVANCED LATTICE PHYSICS CODE FOR LIGHT WATER REACTOR ANALYSES AKIO YAMAMOTO *, 1, TOMOHIRO ENDO 1, MASATO TABUCHI 2, NAOKI SUGIMURA 2, TADASHI USHIO 2, MASAAKI MORI 2, MASAHIRO TATSUMI 3 and
Systems Analysis of the Nuclear Fuel Cycle CASMO-4 1. CASMO-4
 1. CASMO-4 1.1 INTRODUCTION 1.1.1 General The CASMO-4 code is a multi-group two-dimensional transport code developed by Studsvik, which is entirely written in FORTRAN 77. It is used for burnup calculations
1. CASMO-4 1.1 INTRODUCTION 1.1.1 General The CASMO-4 code is a multi-group two-dimensional transport code developed by Studsvik, which is entirely written in FORTRAN 77. It is used for burnup calculations
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF WWER-440 REACTOR CORE WITH PARCS/HELIOS AND PARCS/SERPENT CODES
 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF WWER-440 REACTOR CORE WITH PARCS/HELIOS AND PARCS/SERPENT CODES S. Bznuni, A. Amirjanyan, N. Baghdasaryan Nuclear and Radiation Safety Center Yerevan, Armenia Email: s.bznuni@nrsc.am
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF WWER-440 REACTOR CORE WITH PARCS/HELIOS AND PARCS/SERPENT CODES S. Bznuni, A. Amirjanyan, N. Baghdasaryan Nuclear and Radiation Safety Center Yerevan, Armenia Email: s.bznuni@nrsc.am
A PWR ASSEMBLY COMPUTATIONAL SCHEME BASED ON THE DRAGON V4 LATTICE CODE
 Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (M&C + SNA 2007) Monterey, California, April 15-19, 2007, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2007) A PWR ASSEMBLY COMPUTATIONAL SCHEME BASED
Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (M&C + SNA 2007) Monterey, California, April 15-19, 2007, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2007) A PWR ASSEMBLY COMPUTATIONAL SCHEME BASED
VALIDATION OF VISWAM SQUARE LATTICE MODULE WITH MOX PIN CELL BENCHMARK
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series C, Vol. 77, Iss. 4, 2015 ISSN 2286-3540 VALIDATION OF VISWAM SQUARE LATTICE MODULE WITH MOX PIN CELL BENCHMARK Arvind MATHUR 1, Suhail Ahmad KHAN 2, V. JAGANNATHAN 3, L. THILAGAM
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series C, Vol. 77, Iss. 4, 2015 ISSN 2286-3540 VALIDATION OF VISWAM SQUARE LATTICE MODULE WITH MOX PIN CELL BENCHMARK Arvind MATHUR 1, Suhail Ahmad KHAN 2, V. JAGANNATHAN 3, L. THILAGAM
The Effect of Burnup on Reactivity for VVER-1000 with MOXGD and UGD Fuel Assemblies Using MCNPX Code
 Journal of Nuclear and Particle Physics 2016, 6(3): 61-71 DOI: 10.5923/j.jnpp.20160603.03 The Effect of Burnup on Reactivity for VVER-1000 with MOXGD and UGD Fuel Assemblies Using MCNPX Code Heba K. Louis
Journal of Nuclear and Particle Physics 2016, 6(3): 61-71 DOI: 10.5923/j.jnpp.20160603.03 The Effect of Burnup on Reactivity for VVER-1000 with MOXGD and UGD Fuel Assemblies Using MCNPX Code Heba K. Louis
Resonance self-shielding methodology of new neutron transport code STREAM
 Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology ISSN: 0022-3131 (Print) 1881-1248 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnst20 Resonance self-shielding methodology of new neutron transport
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology ISSN: 0022-3131 (Print) 1881-1248 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnst20 Resonance self-shielding methodology of new neutron transport
REACTOR PHYSICS ASPECTS OF PLUTONIUM RECYCLING IN PWRs
 REACTOR PHYSICS ASPECTS OF PLUTONIUM RECYCLING IN s Present address: J.L. Kloosterman Interfaculty Reactor Institute Delft University of Technology Mekelweg 15, NL-2629 JB Delft, the Netherlands Fax: ++31
REACTOR PHYSICS ASPECTS OF PLUTONIUM RECYCLING IN s Present address: J.L. Kloosterman Interfaculty Reactor Institute Delft University of Technology Mekelweg 15, NL-2629 JB Delft, the Netherlands Fax: ++31
NEUTRON PHYSICAL ANALYSIS OF SIX ENERGETIC FAST REACTORS
 NEUTRON PHYSICAL ANALYSIS OF SIX ENERGETIC FAST REACTORS Peter Vertes Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Centre for Energy Research ABSTRACT Numerous fast reactor constructions have been appeared world-wide
NEUTRON PHYSICAL ANALYSIS OF SIX ENERGETIC FAST REACTORS Peter Vertes Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Centre for Energy Research ABSTRACT Numerous fast reactor constructions have been appeared world-wide
Treatment of Implicit Effects with XSUSA.
 Treatment of Implicit Effects with Friederike Bostelmann 1,2, Andreas Pautz 2, Winfried Zwermann 1 1 Gesellschaft für Anlagen- und Reaktorsicherheit (GRS) ggmbh, Boltzmannstraße 14, 85748 Garching, Germany
Treatment of Implicit Effects with Friederike Bostelmann 1,2, Andreas Pautz 2, Winfried Zwermann 1 1 Gesellschaft für Anlagen- und Reaktorsicherheit (GRS) ggmbh, Boltzmannstraße 14, 85748 Garching, Germany
Challenges in Prismatic HTR Reactor Physics
 Challenges in Prismatic HTR Reactor Physics Javier Ortensi R&D Scientist - Idaho National Laboratory www.inl.gov Advanced Reactor Concepts Workshop, PHYSOR 2012 April 15, 2012 Outline HTR reactor physics
Challenges in Prismatic HTR Reactor Physics Javier Ortensi R&D Scientist - Idaho National Laboratory www.inl.gov Advanced Reactor Concepts Workshop, PHYSOR 2012 April 15, 2012 Outline HTR reactor physics
REACTOR PHYSICS CALCULATIONS ON MOX FUEL IN BOILING WATER REACTORS (BWRs)
 REACTOR PHYSICS CALCULATIONS ON MOX FUEL IN BOILING ATER REACTORS (BRs) Christophe Demazière Chalmers University of Technology Department of Reactor Physics SE-42 96 Gothenburg Sweden Abstract The loading
REACTOR PHYSICS CALCULATIONS ON MOX FUEL IN BOILING ATER REACTORS (BRs) Christophe Demazière Chalmers University of Technology Department of Reactor Physics SE-42 96 Gothenburg Sweden Abstract The loading
Testing the EPRI Reactivity Depletion Decrement Uncertainty Methods
 Testing the EPRI Reactivity Depletion Decrement Uncertainty Methods by Elliot M. Sykora B.S. Physics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (0) Submitted to the Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering
Testing the EPRI Reactivity Depletion Decrement Uncertainty Methods by Elliot M. Sykora B.S. Physics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (0) Submitted to the Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering
On-the-fly Doppler Broadening in Serpent
 On-the-fly Doppler Broadening in Serpent 1st International Serpent User Group Meeting 16.9.2011, Dresden Tuomas Viitanen VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Outline Fuel temperatures in neutronics
On-the-fly Doppler Broadening in Serpent 1st International Serpent User Group Meeting 16.9.2011, Dresden Tuomas Viitanen VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Outline Fuel temperatures in neutronics
Neutronics of MAX phase materials
 Neutronics of MAX phase materials Christopher Grove, Daniel Shepherd, Mike Thomas, Paul Little National Nuclear Laboratory, Preston Laboratory, Springfields, UK Abstract This paper examines the neutron
Neutronics of MAX phase materials Christopher Grove, Daniel Shepherd, Mike Thomas, Paul Little National Nuclear Laboratory, Preston Laboratory, Springfields, UK Abstract This paper examines the neutron
Chapter 7 & 8 Control Rods Fission Product Poisons. Ryan Schow
 Chapter 7 & 8 Control Rods Fission Product Poisons Ryan Schow Ch. 7 OBJECTIVES 1. Define rod shadow and describe its causes and effects. 2. Sketch typical differential and integral rod worth curves and
Chapter 7 & 8 Control Rods Fission Product Poisons Ryan Schow Ch. 7 OBJECTIVES 1. Define rod shadow and describe its causes and effects. 2. Sketch typical differential and integral rod worth curves and
Kord Smith Art DiGiovine Dan Hagrman Scott Palmtag. Studsvik Scandpower. CASMO User s Group May 2003
 Kord Smith Art DiGiovine Dan Hagrman Scott Palmtag CASMO User s Group May 2003 TFU-related data is required input for: -CASMO-4 - SIMULATE-3 - SIMULATE-3K and SIMULATE-3R (implicit in XIMAGE and GARDEL)
Kord Smith Art DiGiovine Dan Hagrman Scott Palmtag CASMO User s Group May 2003 TFU-related data is required input for: -CASMO-4 - SIMULATE-3 - SIMULATE-3K and SIMULATE-3R (implicit in XIMAGE and GARDEL)
Energy Dependence of Neutron Flux
 Energy Dependence of Neutron Flux B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Contents We start the discussion of the energy
Energy Dependence of Neutron Flux B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Contents We start the discussion of the energy
Cross Section Generation Strategy for High Conversion Light Water Reactors Bryan Herman and Eugene Shwageraus
 Cross Section Generation Strategy for High Conversion Light Water Reactors Bryan Herman and Eugene Shwageraus 1 Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts
Cross Section Generation Strategy for High Conversion Light Water Reactors Bryan Herman and Eugene Shwageraus 1 Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts
Lecture 27 Reactor Kinetics-III
 Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following In this lecture we will understand some general concepts on control. We will learn about reactivity coefficients and their general nature. Finally,
Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following In this lecture we will understand some general concepts on control. We will learn about reactivity coefficients and their general nature. Finally,
Effect of WIMSD4 libraries on Bushehr VVER-1000 Core Fuel Burn-up
 International Conference Nuccllearr Enerrgy fforr New Eurrope 2009 Bled / Slovenia / September 14-17 ABSTRACT Effect of WIMSD4 libraries on Bushehr VVER-1000 Core Fuel Burn-up Ali Pazirandeh and Elham
International Conference Nuccllearr Enerrgy fforr New Eurrope 2009 Bled / Slovenia / September 14-17 ABSTRACT Effect of WIMSD4 libraries on Bushehr VVER-1000 Core Fuel Burn-up Ali Pazirandeh and Elham
Use of Monte Carlo and Deterministic Codes for Calculation of Plutonium Radial Distribution in a Fuel Cell
 Use of Monte Carlo and Deterministic Codes for Calculation of Plutonium Radial Distribution in a Fuel Cell Dušan Ćalić, Marjan Kromar, Andrej Trkov Jožef Stefan Institute Jamova 39, SI-1000 Ljubljana,
Use of Monte Carlo and Deterministic Codes for Calculation of Plutonium Radial Distribution in a Fuel Cell Dušan Ćalić, Marjan Kromar, Andrej Trkov Jožef Stefan Institute Jamova 39, SI-1000 Ljubljana,
Continuous Energy Neutron Transport
 Continuous Energy Neutron Transport Kevin Clarno Mark Williams, Mark DeHart, and Zhaopeng Zhong A&M Labfest - Workshop IV on Parallel Transport May 10-11, 2005 College Station, TX clarnokt@ornl.gov (865)
Continuous Energy Neutron Transport Kevin Clarno Mark Williams, Mark DeHart, and Zhaopeng Zhong A&M Labfest - Workshop IV on Parallel Transport May 10-11, 2005 College Station, TX clarnokt@ornl.gov (865)
USE OF LATTICE CODE DRAGON IN REACTOR CALUCLATIONS
 USE OF LATTICE CODE DRAGON IN REACTOR CALUCLATIONS ABSTRACT Dušan Ćalić ZEL-EN razvojni center Hočevarjev trg 1 Slovenia-SI8270, Krško, Slovenia dusan.calic@zel-en.si Andrej Trkov, Marjan Kromar J. Stefan
USE OF LATTICE CODE DRAGON IN REACTOR CALUCLATIONS ABSTRACT Dušan Ćalić ZEL-EN razvojni center Hočevarjev trg 1 Slovenia-SI8270, Krško, Slovenia dusan.calic@zel-en.si Andrej Trkov, Marjan Kromar J. Stefan
Assessment of the MCNP-ACAB code system for burnup credit analyses
 Assessment of the MCNP-ACAB code system for burnup credit analyses N. García-Herranz, O. Cabellos, J. Sanz UPM - UNED International Workshop on Advances in Applications of Burnup Credit for Spent Fuel
Assessment of the MCNP-ACAB code system for burnup credit analyses N. García-Herranz, O. Cabellos, J. Sanz UPM - UNED International Workshop on Advances in Applications of Burnup Credit for Spent Fuel
Study of Burnup Reactivity and Isotopic Inventories in REBUS Program
 Study of Burnup Reactivity and Isotopic Inventories in REBUS Program T. Yamamoto 1, Y. Ando 1, K. Sakurada 2, Y. Hayashi 2, and K. Azekura 3 1 Japan Nuclear Energy Safety Organization (JNES) 2 Toshiba
Study of Burnup Reactivity and Isotopic Inventories in REBUS Program T. Yamamoto 1, Y. Ando 1, K. Sakurada 2, Y. Hayashi 2, and K. Azekura 3 1 Japan Nuclear Energy Safety Organization (JNES) 2 Toshiba
Diffusion coefficients and critical spectrum methods in Serpent
 Diffusion coefficients and critical spectrum methods in Serpent Serpent User Group Meeting 2018 May 30, 2018 Espoo, Finland A. Rintala VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Ltd Overview Some diffusion
Diffusion coefficients and critical spectrum methods in Serpent Serpent User Group Meeting 2018 May 30, 2018 Espoo, Finland A. Rintala VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Ltd Overview Some diffusion
Reactivity Coefficients
 Reactivity Coefficients B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Reactivity Changes In studying kinetics, we have seen
Reactivity Coefficients B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Reactivity Changes In studying kinetics, we have seen
Core Physics Second Part How We Calculate LWRs
 Core Physics Second Part How We Calculate LWRs Dr. E. E. Pilat MIT NSED CANES Center for Advanced Nuclear Energy Systems Method of Attack Important nuclides Course of calc Point calc(pd + N) ϕ dn/dt N
Core Physics Second Part How We Calculate LWRs Dr. E. E. Pilat MIT NSED CANES Center for Advanced Nuclear Energy Systems Method of Attack Important nuclides Course of calc Point calc(pd + N) ϕ dn/dt N
Chapter 2 Nuclear Reactor Calculations
 Chapter 2 Nuclear Reactor Calculations Keisuke Okumura, Yoshiaki Oka, and Yuki Ishiwatari Abstract The most fundamental evaluation quantity of the nuclear design calculation is the effective multiplication
Chapter 2 Nuclear Reactor Calculations Keisuke Okumura, Yoshiaki Oka, and Yuki Ishiwatari Abstract The most fundamental evaluation quantity of the nuclear design calculation is the effective multiplication
Nuclear Reactor Physics I Final Exam Solutions
 .11 Nuclear Reactor Physics I Final Exam Solutions Author: Lulu Li Professor: Kord Smith May 5, 01 Prof. Smith wants to stress a couple of concepts that get people confused: Square cylinder means a cylinder
.11 Nuclear Reactor Physics I Final Exam Solutions Author: Lulu Li Professor: Kord Smith May 5, 01 Prof. Smith wants to stress a couple of concepts that get people confused: Square cylinder means a cylinder
PHYS-E0562 Ydinenergiatekniikan jatkokurssi Lecture 5 Burnup calculation
 PHYS-E0562 Ydinenergiatekniikan jatkokurssi Lecture 5 Burnup calculation Jaakko Leppänen (Lecturer), Ville Valtavirta (Assistant) Department of Applied Physics Aalto University, School of Science Jaakko.Leppanen@aalto.fi
PHYS-E0562 Ydinenergiatekniikan jatkokurssi Lecture 5 Burnup calculation Jaakko Leppänen (Lecturer), Ville Valtavirta (Assistant) Department of Applied Physics Aalto University, School of Science Jaakko.Leppanen@aalto.fi
CALCULATION OF TEMPERATURE REACTIVITY COEFFICIENTS IN KRITZ-2 CRITICAL EXPERIMENTS USING WIMS ABSTRACT
 CALCULATION OF TEMPERATURE REACTIVITY COEFFICIENTS IN KRITZ-2 CRITICAL EXPERIMENTS USING WIMS D J Powney AEA Technology, Nuclear Science, Winfrith Technology Centre, Dorchester, Dorset DT2 8DH United Kingdom
CALCULATION OF TEMPERATURE REACTIVITY COEFFICIENTS IN KRITZ-2 CRITICAL EXPERIMENTS USING WIMS D J Powney AEA Technology, Nuclear Science, Winfrith Technology Centre, Dorchester, Dorset DT2 8DH United Kingdom
Development of depletion models for radionuclide inventory, decay heat and source term estimation in discharged fuel
 Development of depletion models for radionuclide inventory, decay heat and source term estimation in discharged fuel S. Caruso, A. Shama, M. M. Gutierrez National Cooperative for the Disposal of Radioactive
Development of depletion models for radionuclide inventory, decay heat and source term estimation in discharged fuel S. Caruso, A. Shama, M. M. Gutierrez National Cooperative for the Disposal of Radioactive
Improved time integration methods for burnup calculations with Monte Carlo neutronics
 Improved time integration methods for burnup calculations with Monte Carlo neutronics Aarno Isotalo 13.4.2010 Burnup calculations Solving time development of reactor core parameters Nuclide inventory,
Improved time integration methods for burnup calculations with Monte Carlo neutronics Aarno Isotalo 13.4.2010 Burnup calculations Solving time development of reactor core parameters Nuclide inventory,
Critical Experiment Analyses by CHAPLET-3D Code in Two- and Three-Dimensional Core Models
 Journal of NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, Vol. 42, No. 1, p. 101 108 (January 2005) TECHNICAL REPORT Critical Experiment Analyses by CHAPLET-3D Code in Two- and Three-Dimensional Core Models Shinya KOSAKA
Journal of NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, Vol. 42, No. 1, p. 101 108 (January 2005) TECHNICAL REPORT Critical Experiment Analyses by CHAPLET-3D Code in Two- and Three-Dimensional Core Models Shinya KOSAKA
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF ALLEGRO MOX CORE. Bratislava, Iľkovičova 3, Bratislava, Slovakia
 SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF ALLEGRO MOX CORE Jakub Lüley 1, Ján Haščík 1, Vladimír Slugeň 1, Vladimír Nečas 1 1 Institute of Nuclear and Physical Engineering, Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava,
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF ALLEGRO MOX CORE Jakub Lüley 1, Ján Haščík 1, Vladimír Slugeň 1, Vladimír Nečas 1 1 Institute of Nuclear and Physical Engineering, Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava,
Impact of Photon Transport on Power Distribution
 Impact of Photon Transport on Power Distribution LIEGEARD Clément, CALLOO Ansar, MARLEAU Guy, GIRARDI Enrico Électricité de France, R&D, Simulation neutronique techniques de l information et calcul scientifique
Impact of Photon Transport on Power Distribution LIEGEARD Clément, CALLOO Ansar, MARLEAU Guy, GIRARDI Enrico Électricité de France, R&D, Simulation neutronique techniques de l information et calcul scientifique
Study of Predictor-corrector methods. for Monte Carlo Burnup Codes. Dan Kotlyar Dr. Eugene Shwageraus. Supervisor
 Serpent International Users Group Meeting Madrid, Spain, September 19-21, 2012 Study of Predictor-corrector methods for Monte Carlo Burnup Codes By Supervisor Dan Kotlyar Dr. Eugene Shwageraus Introduction
Serpent International Users Group Meeting Madrid, Spain, September 19-21, 2012 Study of Predictor-corrector methods for Monte Carlo Burnup Codes By Supervisor Dan Kotlyar Dr. Eugene Shwageraus Introduction
TRANSMUTATION OF CESIUM-135 WITH FAST REACTORS
 TRANSMUTATION OF CESIUM-3 WITH FAST REACTORS Shigeo Ohki and Naoyuki Takaki O-arai Engineering Center Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) 42, Narita-cho, O-arai-machi, Higashi-Ibaraki-gun,
TRANSMUTATION OF CESIUM-3 WITH FAST REACTORS Shigeo Ohki and Naoyuki Takaki O-arai Engineering Center Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) 42, Narita-cho, O-arai-machi, Higashi-Ibaraki-gun,
COVARIANCE DATA FOR 233 U IN THE RESOLVED RESONANCE REGION FOR CRITICALITY SAFETY APPLICATIONS
 Mathematics and Computation, Supercomputing, Reactor Physics and Nuclear and Biological Applications Palais des Papes, Avignon, France, September 12-15, 2005, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange
Mathematics and Computation, Supercomputing, Reactor Physics and Nuclear and Biological Applications Palais des Papes, Avignon, France, September 12-15, 2005, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange
Assessment of the neutron and gamma sources of the spent BWR fuel
 October 2000 Assessment of the neutron and gamma sources of the spent BWR fuel Interim report on Task FIN JNT A 101 of the Finnish support programme to IAEA Safeguards Aapo Tanskanen VTT Energy In STUK
October 2000 Assessment of the neutron and gamma sources of the spent BWR fuel Interim report on Task FIN JNT A 101 of the Finnish support programme to IAEA Safeguards Aapo Tanskanen VTT Energy In STUK
Requests on Nuclear Data in the Backend Field through PIE Analysis
 Requests on Nuclear Data in the Backend Field through PIE Analysis Yoshihira Ando 1), Yasushi Ohkawachi 2) 1) TOSHIBA Corporation Power System & Services Company Power & Industrial Systems Research & Development
Requests on Nuclear Data in the Backend Field through PIE Analysis Yoshihira Ando 1), Yasushi Ohkawachi 2) 1) TOSHIBA Corporation Power System & Services Company Power & Industrial Systems Research & Development
EVALUATION OF PWR AND BWR CALCULATIONAL BENCHMARKS FROM NUREG/CR-6115 USING THE TRANSFX NUCLEAR ANALYSIS SOFTWARE
 ANS MC2015 - Joint International Conference on Mathematics and Computation (M&C), Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (SNA) and the Monte Carlo (MC) Method Nashville, Tennessee April 19 23, 2015, on
ANS MC2015 - Joint International Conference on Mathematics and Computation (M&C), Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (SNA) and the Monte Carlo (MC) Method Nashville, Tennessee April 19 23, 2015, on
THE NEXT GENERATION WIMS LATTICE CODE : WIMS9
 THE NEXT GENERATION WIMS LATTICE CODE : WIMS9 T D Newton and J L Hutton Serco Assurance Winfrith Technology Centre Dorchester Dorset DT2 8ZE United Kingdom tim.newton@sercoassurance.com ABSTRACT The WIMS8
THE NEXT GENERATION WIMS LATTICE CODE : WIMS9 T D Newton and J L Hutton Serco Assurance Winfrith Technology Centre Dorchester Dorset DT2 8ZE United Kingdom tim.newton@sercoassurance.com ABSTRACT The WIMS8
TMS On-the-fly Temperature Treatment in Serpent
 TMS On-the-fly Temperature Treatment in Serpent Tuomas Viitanen & Jaakko Leppänen Serpent User Group Meeting, Cambridge, UK September 17 19, 2014 Effects of thermal motion on neutron transport On reaction
TMS On-the-fly Temperature Treatment in Serpent Tuomas Viitanen & Jaakko Leppänen Serpent User Group Meeting, Cambridge, UK September 17 19, 2014 Effects of thermal motion on neutron transport On reaction
in U. S. Department of Energy Nuclear Criticality Technology and Safety Project 1995 Annual Meeting SanDiego, CA
 T. LESSONS LEARNED FROM APPLYING VIM TO FAST REACTOR CRITICAL EXPERIMENTS by R. W. Schaefer, R. D. McKnight and P. J. Collins Argonne National Laboratory P. 0. Box 2528 Idaho Falls, ID 83404-2528 Summary
T. LESSONS LEARNED FROM APPLYING VIM TO FAST REACTOR CRITICAL EXPERIMENTS by R. W. Schaefer, R. D. McKnight and P. J. Collins Argonne National Laboratory P. 0. Box 2528 Idaho Falls, ID 83404-2528 Summary
WHY A CRITICALITY EXCURSION WAS POSSIBLE IN THE FUKUSHIMA SPENT FUEL POOLS
 PHYSOR 014 The Role of Reactor Physics Toward a Sustainable Future The Westin Miyako, Kyoto, Japan, September 8 October 3, 014, on CD-ROM (014) WHY CRITICLITY EXCURSION WS POSSIBLE IN THE FUKUSHIM SPENT
PHYSOR 014 The Role of Reactor Physics Toward a Sustainable Future The Westin Miyako, Kyoto, Japan, September 8 October 3, 014, on CD-ROM (014) WHY CRITICLITY EXCURSION WS POSSIBLE IN THE FUKUSHIM SPENT
Fundamentals of Nuclear Reactor Physics
 Fundamentals of Nuclear Reactor Physics E. E. Lewis Professor of Mechanical Engineering McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science Northwestern University AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW
Fundamentals of Nuclear Reactor Physics E. E. Lewis Professor of Mechanical Engineering McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science Northwestern University AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW
but mostly as the result of the beta decay of its precursor 135 I (which has a half-life of hours).
 8. Effects of 135Xe The xenon isotope 135 Xe plays an important role in any power reactor. It has a very large absorption cross section for thermal neutrons and represents therefore a considerable load
8. Effects of 135Xe The xenon isotope 135 Xe plays an important role in any power reactor. It has a very large absorption cross section for thermal neutrons and represents therefore a considerable load
Fuel BurnupCalculations and Uncertainties
 Fuel BurnupCalculations and Uncertainties Outline Review lattice physics methods Different approaches to burnup predictions Linkage to fuel safety criteria Sources of uncertainty Survey of available codes
Fuel BurnupCalculations and Uncertainties Outline Review lattice physics methods Different approaches to burnup predictions Linkage to fuel safety criteria Sources of uncertainty Survey of available codes
Measurements of Neutron Capture Cross Sections for 237, 238 Np
 Measurements of Neutron Capture Cross Sections for 237, 238 Np H. Harada 1), H. Sakane 1), S. Nakamura 1), K. Furutaka 1), J. Hori 2), T. Fujii 2), H. Yamana 2) 1) Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute,
Measurements of Neutron Capture Cross Sections for 237, 238 Np H. Harada 1), H. Sakane 1), S. Nakamura 1), K. Furutaka 1), J. Hori 2), T. Fujii 2), H. Yamana 2) 1) Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute,
Spatially Dependent Self-Shielding Method with Temperature Distribution for the Two-Dimensional
 Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology ISSN: 0022-3131 (Print) 1881-1248 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnst20 Spatially Dependent Self-Shielding Method with Temperature Distribution
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology ISSN: 0022-3131 (Print) 1881-1248 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnst20 Spatially Dependent Self-Shielding Method with Temperature Distribution
Parametric Study of Control Rod Exposure for PWR Burnup Credit Criticality Safety Analyses
 35281 NCSD Conference Paper #2 7/17/01 3:58:06 PM Computational Physics and Engineering Division (10) Parametric Study of Control Rod Exposure for PWR Burnup Credit Criticality Safety Analyses Charlotta
35281 NCSD Conference Paper #2 7/17/01 3:58:06 PM Computational Physics and Engineering Division (10) Parametric Study of Control Rod Exposure for PWR Burnup Credit Criticality Safety Analyses Charlotta
A PERTURBATION ANALYSIS SCHEME IN WIMS USING TRANSPORT THEORY FLUX SOLUTIONS
 A PERTURBATION ANALYSIS SCHEME IN WIMS USING TRANSPORT THEORY FLUX SOLUTIONS J G Hosking, T D Newton, B A Lindley, P J Smith and R P Hiles Amec Foster Wheeler Dorchester, Dorset, UK glynn.hosking@amecfw.com
A PERTURBATION ANALYSIS SCHEME IN WIMS USING TRANSPORT THEORY FLUX SOLUTIONS J G Hosking, T D Newton, B A Lindley, P J Smith and R P Hiles Amec Foster Wheeler Dorchester, Dorset, UK glynn.hosking@amecfw.com
Target accuracy of MA nuclear data and progress in validation by post irradiation experiments with the fast reactor JOYO
 Target accuracy of MA nuclear data and progress in validation by post irradiation experiments with the fast reactor JOYO Shigeo OHKI, Kenji YOKOYAMA, Kazuyuki NUMATA *, and Tomoyuki JIN * Oarai Engineering
Target accuracy of MA nuclear data and progress in validation by post irradiation experiments with the fast reactor JOYO Shigeo OHKI, Kenji YOKOYAMA, Kazuyuki NUMATA *, and Tomoyuki JIN * Oarai Engineering
Purdue University, 400 Central Drive, West Lafayette, IN, 47907, b
 Jeju, Korea, April 16-2, 217, on USB (217) Extension of MC 2-3 for Generation of Multiroup Cross Sections in Thermal Enery Rane B. K. Jeon a, W. S. Yan a, Y. S. Jun a,b and C. H. Lee b a Purdue University,
Jeju, Korea, April 16-2, 217, on USB (217) Extension of MC 2-3 for Generation of Multiroup Cross Sections in Thermal Enery Rane B. K. Jeon a, W. S. Yan a, Y. S. Jun a,b and C. H. Lee b a Purdue University,
Xenon Effects. B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec.
 enon Effects B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Contents We study the importance of e-135 in the operation of
enon Effects B. Rouben McMaster University Course EP 4D03/6D03 Nuclear Reactor Analysis (Reactor Physics) 2015 Sept.-Dec. 2015 September 1 Contents We study the importance of e-135 in the operation of
IMPACT OF THE FISSION YIELD COVARIANCE DATA IN BURN-UP CALCULATIONS
 IMPACT OF THE FISSION YIELD COVARIANCE DATA IN BRN-P CALCLATIONS O. Cabellos, D. Piedra, Carlos J. Diez Department of Nuclear Engineering, niversidad Politécnica de Madrid, Spain E-mail: oscar.cabellos@upm.es
IMPACT OF THE FISSION YIELD COVARIANCE DATA IN BRN-P CALCLATIONS O. Cabellos, D. Piedra, Carlos J. Diez Department of Nuclear Engineering, niversidad Politécnica de Madrid, Spain E-mail: oscar.cabellos@upm.es
A COMPARISON OF PEBBLE MIXING AND DEPLETION ALGORITHMS USED IN PEBBLE-BED REACTOR EQUILIBRIUM CYCLE SIMULATION
 International Conference on Mathematics, Computational Methods & Reactor Physics (M&C 2009) Saratoga Springs, New York, May 3-7, 2009, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2009) A COMPARISON
International Conference on Mathematics, Computational Methods & Reactor Physics (M&C 2009) Saratoga Springs, New York, May 3-7, 2009, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2009) A COMPARISON
Nuclear Fission. 1/v Fast neutrons. U thermal cross sections σ fission 584 b. σ scattering 9 b. σ radiative capture 97 b.
 Nuclear Fission 1/v Fast neutrons should be moderated. 235 U thermal cross sections σ fission 584 b. σ scattering 9 b. σ radiative capture 97 b. Fission Barriers 1 Nuclear Fission Q for 235 U + n 236 U
Nuclear Fission 1/v Fast neutrons should be moderated. 235 U thermal cross sections σ fission 584 b. σ scattering 9 b. σ radiative capture 97 b. Fission Barriers 1 Nuclear Fission Q for 235 U + n 236 U
MOx Benchmark Calculations by Deterministic and Monte Carlo Codes
 MOx Benchmark Calculations by Deterministic and Monte Carlo Codes G.Kotev, M. Pecchia C. Parisi, F. D Auria San Piero a Grado Nuclear Research Group (GRNSPG), University of Pisa via Diotisalvi 2, 56122
MOx Benchmark Calculations by Deterministic and Monte Carlo Codes G.Kotev, M. Pecchia C. Parisi, F. D Auria San Piero a Grado Nuclear Research Group (GRNSPG), University of Pisa via Diotisalvi 2, 56122
New Capabilities for the Chebyshev Rational Approximation method (CRAM)
 New Capabilities for the Chebyshev Rational Approximation method (CRAM) A. Isotaloa,b W. Wieselquista M. Pusac aoak Ridge National Laboratory PO Box 2008, Oak Ridge, TN 37831-6172, USA baalto University
New Capabilities for the Chebyshev Rational Approximation method (CRAM) A. Isotaloa,b W. Wieselquista M. Pusac aoak Ridge National Laboratory PO Box 2008, Oak Ridge, TN 37831-6172, USA baalto University
Radioactivity III: Measurement of Half Life.
 PHY 192 Half Life Spring 2010 1 Radioactivity III: Measurement of Half Life. Introduction This experiment will once again use the apparatus of the first experiment, this time to measure radiation intensity
PHY 192 Half Life Spring 2010 1 Radioactivity III: Measurement of Half Life. Introduction This experiment will once again use the apparatus of the first experiment, this time to measure radiation intensity
Chapter 5: Applications Fission simulations
 Chapter 5: Applications Fission simulations 1 Using fission in FISPACT-II FISPACT-II is distributed with a variety of fission yields and decay data, just as incident particle cross sections, etc. Fission
Chapter 5: Applications Fission simulations 1 Using fission in FISPACT-II FISPACT-II is distributed with a variety of fission yields and decay data, just as incident particle cross sections, etc. Fission
17 Neutron Life Cycle
 17 Neutron Life Cycle A typical neutron, from birth as a prompt fission neutron to absorption in the fuel, survives for about 0.001 s (the neutron lifetime) in a CANDU. During this short lifetime, it travels
17 Neutron Life Cycle A typical neutron, from birth as a prompt fission neutron to absorption in the fuel, survives for about 0.001 s (the neutron lifetime) in a CANDU. During this short lifetime, it travels
Lectures on Applied Reactor Technology and Nuclear Power Safety. Lecture No 1. Title: Neutron Life Cycle
 Lectures on Nuclear Power Safety Lecture No 1 Title: Neutron Life Cycle Department of Energy Technology KTH Spring 2005 Slide No 1 Outline of the Lecture Infinite Multiplication Factor, k Four Factor Formula
Lectures on Nuclear Power Safety Lecture No 1 Title: Neutron Life Cycle Department of Energy Technology KTH Spring 2005 Slide No 1 Outline of the Lecture Infinite Multiplication Factor, k Four Factor Formula
Improvements of Isotopic Ratios Prediction through Takahama-3 Chemical Assays with the JEFF3.0 Nuclear Data Library
 PHYSOR 2004 -The Physics of Fuel Cycles and Advanced Nuclear Systems: Global Developments Chicago, Illinois, April 25-29, 2004, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, Lagrange Park, IL. (2004) Improvements
PHYSOR 2004 -The Physics of Fuel Cycles and Advanced Nuclear Systems: Global Developments Chicago, Illinois, April 25-29, 2004, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, Lagrange Park, IL. (2004) Improvements
HTR Spherical Super Lattice Model For Equilibrium Fuel Cycle Analysis. Gray S. Chang. September 12-15, 2005
 INEEL/CON-05-02655, Revision 3 PREPRINT HTR Spherical Super Lattice Model For Equilibrium Fuel Cycle Analysis Gray S. Chang September 12-15, 2005 Mathematics And Computation, Supercomputing, Reactor Physics
INEEL/CON-05-02655, Revision 3 PREPRINT HTR Spherical Super Lattice Model For Equilibrium Fuel Cycle Analysis Gray S. Chang September 12-15, 2005 Mathematics And Computation, Supercomputing, Reactor Physics
Chem 481 Lecture Material 4/22/09
 Chem 481 Lecture Material 4/22/09 Nuclear Reactors Poisons The neutron population in an operating reactor is controlled by the use of poisons in the form of control rods. A poison is any substance that
Chem 481 Lecture Material 4/22/09 Nuclear Reactors Poisons The neutron population in an operating reactor is controlled by the use of poisons in the form of control rods. A poison is any substance that
Uncertainty quantification using SCALE 6.2 package and GPT techniques implemented in Serpent 2
 6th International Serpent User Group Meeting Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy September 26 th -30 th, 2016 Uncertainty quantification using SCALE 6.2 package and GPT techniques implemented in Serpent
6th International Serpent User Group Meeting Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy September 26 th -30 th, 2016 Uncertainty quantification using SCALE 6.2 package and GPT techniques implemented in Serpent
Comparison of PWR burnup calculations with SCALE 5.0/TRITON other burnup codes and experimental results. Abstract
 Comparison of PWR burnup calculations with SCALE 5.0/TRITON other burnup codes and experimental results Ph.Oberle, C.H.M.Broeders, R.Dagan Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Institut for Reactor Safety Hermann-von-Helmholtz-Platz-1,
Comparison of PWR burnup calculations with SCALE 5.0/TRITON other burnup codes and experimental results Ph.Oberle, C.H.M.Broeders, R.Dagan Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Institut for Reactor Safety Hermann-von-Helmholtz-Platz-1,
THORIUM SELF-SUFFICIENT FUEL CYCLE OF CANDU POWER REACTOR
 International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe 2005 Bled, Slovenia, September 5-8, 2005 ABSTRACT THORIUM SELF-SUFFICIENT FUEL CYCLE OF CANDU POWER REACTOR Boris Bergelson, Alexander Gerasimov Institute
International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe 2005 Bled, Slovenia, September 5-8, 2005 ABSTRACT THORIUM SELF-SUFFICIENT FUEL CYCLE OF CANDU POWER REACTOR Boris Bergelson, Alexander Gerasimov Institute
A Deterministic against Monte-Carlo Depletion Calculation Benchmark for JHR Core Configurations. A. Chambon, P. Vinai, C.
 A Deterministic against Monte-Carlo Depletion Calculation Benchmark for JHR Core Configurations A. Chambon, P. Vinai, C. Demazière Chalmers University of Technology, Department of Physics, SE-412 96 Gothenburg,
A Deterministic against Monte-Carlo Depletion Calculation Benchmark for JHR Core Configurations A. Chambon, P. Vinai, C. Demazière Chalmers University of Technology, Department of Physics, SE-412 96 Gothenburg,
Development of Multigroup Cross Section Generation Code MC 2-3 for Fast Reactor Analysis
 Development o Multigroup Cross Section Generation Code MC 2-3 or Fast Reactor Analysis International Conerence on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles December 7-11, 2009 Kyoto, Japan Changho Lee and
Development o Multigroup Cross Section Generation Code MC 2-3 or Fast Reactor Analysis International Conerence on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles December 7-11, 2009 Kyoto, Japan Changho Lee and
QUALIFICATION OF THE APOLLO 2 ASSEMBLY CODE USING PWR-UO 2 ISOTOPIC ASSAYS.
 QUALIFICATION OF THE APOLLO 2 ASSEMBLY CODE USING PWR-UO 2 ISOTOPIC ASSAYS. THE IMPORTANCE OF IRRADIATION HISTORY AND THERMO-MECHANICS ON FUEL INVENTORY PREDICTION Christine Chabert, Alain Santamarina,
QUALIFICATION OF THE APOLLO 2 ASSEMBLY CODE USING PWR-UO 2 ISOTOPIC ASSAYS. THE IMPORTANCE OF IRRADIATION HISTORY AND THERMO-MECHANICS ON FUEL INVENTORY PREDICTION Christine Chabert, Alain Santamarina,
VI. Chain Reaction. Two basic requirements must be filled in order to produce power in a reactor:
 VI. Chain Reaction VI.1. Basic of Chain Reaction Two basic requirements must be filled in order to produce power in a reactor: The fission rate should be high. This rate must be continuously maintained.
VI. Chain Reaction VI.1. Basic of Chain Reaction Two basic requirements must be filled in order to produce power in a reactor: The fission rate should be high. This rate must be continuously maintained.
Lesson 14: Reactivity Variations and Control
 Lesson 14: Reactivity Variations and Control Reactivity Variations External, Internal Short-term Variations Reactivity Feedbacks Reactivity Coefficients and Safety Medium-term Variations Xe 135 Poisoning
Lesson 14: Reactivity Variations and Control Reactivity Variations External, Internal Short-term Variations Reactivity Feedbacks Reactivity Coefficients and Safety Medium-term Variations Xe 135 Poisoning
Delayed neutrons in nuclear fission chain reaction
 Delayed neutrons in nuclear fission chain reaction 1 Critical state Temporal flow Loss by leakage Loss by Absorption If the number of neutrons (the number of fission reactions) is practically constant
Delayed neutrons in nuclear fission chain reaction 1 Critical state Temporal flow Loss by leakage Loss by Absorption If the number of neutrons (the number of fission reactions) is practically constant
Simple benchmark for evaluating self-shielding models
 Simple benchmark for evaluating self-shielding models The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher
Simple benchmark for evaluating self-shielding models The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF SCALE NUCLEAR ANALYSIS METHODS FOR HIGH TEMPERATURE GAS-COOLED REACTORS
 DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF SCALE NUCLEAR ANALYSIS METHODS FOR HIGH TEMPERATURE GAS-COOLED REACTORS Jess Gehin, Matthew Jessee, Mark Williams, Deokjung Lee, Sedat Goluoglu, Germina Ilas, Dan Ilas, Steve
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF SCALE NUCLEAR ANALYSIS METHODS FOR HIGH TEMPERATURE GAS-COOLED REACTORS Jess Gehin, Matthew Jessee, Mark Williams, Deokjung Lee, Sedat Goluoglu, Germina Ilas, Dan Ilas, Steve
«CALCULATION OF ISOTOPE BURN-UP AND CHANGE IN EFFICIENCY OF ABSORBING ELEMENTS OF WWER-1000 CONTROL AND PROTECTION SYSTEM DURING BURN-UP».
 «CALCULATION OF ISOTOPE BURN-UP AND CHANGE IN EFFICIENCY OF ABSORBING ELEMENTS OF WWER-1000 CONTROL AND PROTECTION SYSTEM DURING BURN-UP». O.A. Timofeeva, K.U. Kurakin FSUE EDO «GIDROPRESS», Podolsk, Russia
«CALCULATION OF ISOTOPE BURN-UP AND CHANGE IN EFFICIENCY OF ABSORBING ELEMENTS OF WWER-1000 CONTROL AND PROTECTION SYSTEM DURING BURN-UP». O.A. Timofeeva, K.U. Kurakin FSUE EDO «GIDROPRESS», Podolsk, Russia
Serpent Monte Carlo Neutron Transport Code
 Serpent Monte Carlo Neutron Transport Code NEA Expert Group on Advanced Monte Carlo Techniques, Meeting September 17 2012 Jaakko Leppänen / Tuomas Viitanen VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Outline
Serpent Monte Carlo Neutron Transport Code NEA Expert Group on Advanced Monte Carlo Techniques, Meeting September 17 2012 Jaakko Leppänen / Tuomas Viitanen VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Outline
Working Party on Pu-MOX fuel physics and innovative fuel cycles (WPPR)
 R&D Needs in Nuclear Science 6-8th November, 2002 OECD/NEA, Paris Working Party on Pu-MOX fuel physics and innovative fuel cycles (WPPR) Hideki Takano Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, Japan Introduction(1)
R&D Needs in Nuclear Science 6-8th November, 2002 OECD/NEA, Paris Working Party on Pu-MOX fuel physics and innovative fuel cycles (WPPR) Hideki Takano Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, Japan Introduction(1)
FULL CORE POWER AND ISOTOPIC OSCILLATIONS WITH VARIOUS DEPLETION SCHEMES
 FULL CORE POWER AND ISOTOPIC OSCILLATIONS WITH VARIOUS DEPLETION SCHEMES A N D R E W J O H N S O N C O M P U TAT I O N A L R E A C T O R E N G I N E E R I N G OUTLINE Governing depletion equations Summary
FULL CORE POWER AND ISOTOPIC OSCILLATIONS WITH VARIOUS DEPLETION SCHEMES A N D R E W J O H N S O N C O M P U TAT I O N A L R E A C T O R E N G I N E E R I N G OUTLINE Governing depletion equations Summary
DOPPLER COEFFICIENT OF REACTIVITY BENCHMARK CALCULATIONS FOR DIFFERENT ENRICHMENTS OF UO 2
 Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (M&C + SNA 2007) Monterey, California, April 15-19, 2007, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2007) DOPPLER COEFFICIENT OF REACTIVITY BENCHMARK
Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (M&C + SNA 2007) Monterey, California, April 15-19, 2007, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2007) DOPPLER COEFFICIENT OF REACTIVITY BENCHMARK
A New MCNPX PTRAC Coincidence Capture File Capability: A Tool for Neutron Detector Design
 Abstract A New MCNPX PTRAC Coincidence Capture File Capability: A Tool for Neutron Detector Design L. G. Evans, M.A. Schear, J. S. Hendricks, M.T. Swinhoe, S.J. Tobin and S. Croft Los Alamos National Laboratory
Abstract A New MCNPX PTRAC Coincidence Capture File Capability: A Tool for Neutron Detector Design L. G. Evans, M.A. Schear, J. S. Hendricks, M.T. Swinhoe, S.J. Tobin and S. Croft Los Alamos National Laboratory
ENT OF THE RATIO OF FISSIONS IN U TO FISSIONS OF. IN U USING 1.60 MEV GAMMA RAYS THE FISSION PRODUCT La 14 0 MEASUREM
 NYO - 10210 MITNE- 36 MEASUREM TO FISSIONS OF ENT OF THE RATIO OF FISSIONS IN U 238 IN U 2 3 5 USING 1.60 MEV GAMMA RAYS THE FISSION PRODUCT La 14 0 by J. R. Wolberg T.J. Thompson I. Kaplan August 19,
NYO - 10210 MITNE- 36 MEASUREM TO FISSIONS OF ENT OF THE RATIO OF FISSIONS IN U 238 IN U 2 3 5 USING 1.60 MEV GAMMA RAYS THE FISSION PRODUCT La 14 0 by J. R. Wolberg T.J. Thompson I. Kaplan August 19,
MONK Under-sampling bias calculations for benchmark S2 - Initial results. Presented by PAUL SMITH EGAMCT Meeting, Paris 6 th July 2016
 MONK Under-sampling bias calculations for benchmark S2 - Initial results Presented by PAUL SMITH EGAMCT Meeting, Paris 6 th July 2016 Acknowledgement Team work the work was performed by the following ANSWERS
MONK Under-sampling bias calculations for benchmark S2 - Initial results Presented by PAUL SMITH EGAMCT Meeting, Paris 6 th July 2016 Acknowledgement Team work the work was performed by the following ANSWERS
DETERMINATION OF THE EQUILIBRIUM COMPOSITION OF CORES WITH CONTINUOUS FUEL FEED AND REMOVAL USING MOCUP
 Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (M&C + SNA 2007) Monterey, California, April 15-19, 2007, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2007) DETERMINATION OF THE EQUILIBRIUM COMPOSITION
Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (M&C + SNA 2007) Monterey, California, April 15-19, 2007, on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2007) DETERMINATION OF THE EQUILIBRIUM COMPOSITION
Available online at ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 71 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 71 (2015 ) 97 105 The Fourth International Symposium on Innovative Nuclear Energy Systems, INES-4 High-Safety Fast Reactor Core Concepts
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 71 (2015 ) 97 105 The Fourth International Symposium on Innovative Nuclear Energy Systems, INES-4 High-Safety Fast Reactor Core Concepts
Considerations for Measurements in Support of Thermal Scattering Data Evaluations. Ayman I. Hawari
 OECD/NEA Meeting: WPEC SG42 Thermal Scattering Kernel S(a,b): Measurement, Evaluation and Application May 13 14, 2017 Paris, France Considerations for Measurements in Support of Thermal Scattering Data
OECD/NEA Meeting: WPEC SG42 Thermal Scattering Kernel S(a,b): Measurement, Evaluation and Application May 13 14, 2017 Paris, France Considerations for Measurements in Support of Thermal Scattering Data
Figure 22.1 Unflattened Flux Distribution
 22 Neutron Flux Control If nothing were done to flatten the flux in our reactors, it would look something like Figure 22.1. The flux would be a maximum in the efuel of the reactor (where neutrons are moving
22 Neutron Flux Control If nothing were done to flatten the flux in our reactors, it would look something like Figure 22.1. The flux would be a maximum in the efuel of the reactor (where neutrons are moving
