EI2302 Analytical instruments Dept. of EIE
|
|
|
- Myrtle Charles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EI2302-ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS V SEMESTER (EIE & ICE) III YEAR UNIT I COLORIMETRY AND SPECTROPHOTOMETRY Part A 1. What is Spectrophotometer? Spectrophotometer are dispersive analyzers where a prism is used to separate the spectral components of the UV spectrum. 2. Name the main components of UV analyzer. The main components of UV analyzer are Source, Mono Chromator, Sample Cell, Detector, and Readout Device. 3. Give some example of radiation source used in UV region. Cadmium, Mercury and Zinc Vapour sources that are used in the UV region are emission line sources. 4. Name two sources used in NIR region. i. Tungsten filaments ii. Quartzhalide lampsf 5. What is the use of O-rings? Sealing of cell is accomplished with O-ring gaskets.viton, Ethylene-propylene and Kalrez are commonly used. 6. Name few detectors used in UV region. i. Silicon photo diode ii. Photo Diode array 7. Classify UV analyzer based on design. i. Single-beam analyzer ii. Split-beam analyzer iii. Dual beam- Single detector analyzer iv. Dual beam- Dual detector analyzer v. Flicker Photometer vi. Photodiode Analyzer vii. Retro reflector analyzer. 8. Define path length. The distance between the windows in the sample cell defines the path length. 9. What is the purpose of sample cell? The purpose of sample cell is to contain a representative sample from the process stream. 10. Write the principle used in scanning spectrophotometer. Scanning spectrophotometer are dispersive devices that normally utilize diffraction gratings to scan across a spectral regions. Scanning devices can be used for multiple component applications. 11. Give some applications of Photo diode array. i. Analysis of Hydrogen sulphide and sulphur dioxide in sulphur recovery ii.determination of octane number are two examples of PDA applications 12. Give some applications of scanning spectrophotometer. i. Measurement of multi component solvent mixture ii.determination of octane number for gasoline samples 13. Write the applications of atomic absorption Spectrophotometry. Mercury is conveniently analyzed by atomic absorption technique because the elemental vapour exists in atomic form under normal ambient conditions. 14. Write the features of single Beam configuration of IR Spectrophotometer. i. Less expensive. But power variations or temperature changes can cause zero and span drift and necessitates frequent re-zeroing. ii. Drift caused by dirt accumulation on the windows is not a problem as the instrument is automatically re-zeroed on each revolution of the chopper wheel. 15. What is FTIR spectrophotometer? FTIR spectrophotometer are dispersive devices that are being used for on-line analysis in the near infrared region. Instead of separating different wavelengths for measurement, the complete spectrum is encoded as an interferogram in a few seconds of measurement time, and the spectrum computed by fast Fourier transform. 16. What are the basic components of Infra-red Spectrometer. i.source of radiation, ii.monochromator for dispersing the radiation iii.detector which registers the residual intensity after selective absorption by the sample. 17. Write the detector used in Infrared radiation. Chettinad College of Engineering & Technology 1 ISO 9001:2008
2 i. Thermal detector ii. Photo conductive cells 18. Define wave number. Wave number is defined as the number of wavelengths per-centimeter and it is expressed as cm What are the advantages of double beam spectrophotometers 1)speed of operation 2)automatic compensation for variation in lamp output 3)solvent absorption at various 8 4)changes in detector sensitivity 5)spectra scan 20. Mention the application of Colorimeter. Essentially, a colorimeter is a scientific instrument that measures the amount of light passing through a solution relative to the amount that passes through a sample of pure solvent. Colorimeters have many applications in the fields of biology and chemistry 21. What are the applications of flame photometry? 1).Analyze wide variety of materials such as environmental biological fluids, solids, plant materials and industrial cement, ferrous metals, glasses etc, 2). It is used for determining sodium, potassium, Aluminum, Calcium, and Iron in soil. 22. List the advantages of Fourier transform spectrometer. 1. Signal to noise ratio is high 2. Retrieval of data is possible.3. Information could be obtained on all frequencies. 4. Processing speed of data is high. 5. High reliability and good sensitivity. 23. What are the disadvantages of Fourier transform spectrometer? 1. Cost is the major problem. 2. Maintenance of the instrument. 24. What is total internal reflection in spectrometry? (May 2013) is a sampling technique used in conjunction with infrared spectroscopy which enables samples to be examined directly in the solid or liquid state without further preparation. 25. State Beer-Lambert law. (May 2013) The Beer-Lambert law is the fundamental law for quantitative analysis by absorption spectroscopy. This law states A= abc where A = absorbance, a = Molar absorptivity, b = Sample path length, c = Concentration of absorbing species 26. Name the types of detectors used in IR spectrometry. (Nov 2013) i.bolometers ii.thermocouples iii.thermistors iv.golay cell v.pyroelectric transducer vi.photoconductivity cell Unit-I Part B 1. State and derive Beer s law from basic principles. Discuss the limitations of it. 2. With a schematic diagram explain the atomic emission spectroscopy. 3. Explain flame emission photometer with its instrumentation. 4. Explain mono-chromators and detectors. 5. Explain about photo multiplier tube. 6. Explain Fourier transform infra-red spectrometers. 7. Explain different radiation source in absorption spectrophotometry. 8. Explain the working principle of various radiation sources and detectors in IR Spectrophotometers. 9. With a neat diagram, explain the instrumentation setup of Atomic absorption spectroscopy (MAY 2013) 10. With a neat sketch, explain the instrumentation setup and working principle of IR spectrometer. (May 2013) 11. Draw and Explain the schematic diagram of a typical double beam spectrophotometer. (Nov 2013) 12. What are non-dispersive spectrophotometers? Explain in detail the FTIR spectrometer. Also specify the advantages of the FTIR spectrophotometer. (Nov 2013) UNIT II CHROMATOGRAPHY Part A 1. What is Chromatography? Chettinad College of Engineering & Technology 2 ISO 9001:2008
3 Chromatography describes a physical method of separation that is based on the difference in solubility ( or adsorption ) of substance between a mobile and stationary phase. 2. Define Chromatogram. The individual components register a series of signals which appear as successive peaks above a base line on the recorded curve is called Chromatogram. 3. What are the different components of Gas Chromatography? The basic parts of a gas chromatograph are i. carrier gas supply along with pressure regulator and flow monitor ii. Sample injection system, iii. Chromatographic column iv. Thermal compartment or thermostat v. Detection system, vi. The strip-chart recorder 4. Name the detectors used in liquid Chromatography. i. UV-Visible Spectrophotometric detectors ii. Fluroscence Detector iii. Refractive Index detectors, iv. Adsorption Detector v. Electrical Conductivity detector vi. Thermal Detector 5. Name some source carrier gas used in Gas Chromatography. Hydrogen, Helium, Nitrogen, Argon and CO2. 6. Write the limitations in FID. i. Does not respond to inert gas and inorganic compounds ii. The emerging compound get destroyed in the flame iii. The response to sample weight has to be separately determined for each component. 7. What are the different components of Liquid Chromatography? i. A High pressure pump system to force the liquid mobile phase through the column. ii. A gradient elusion or solvent programmer iii. The sample injection system iv. The column v. The detection system including display or recording devices. 8. Write the choice of a particular type of detector in Gas Chromatography. i. Detectors should have high sensitivity, to be sufficient enough to provide an adequate signal for all components with a small sample. ii. The response of the detector should be linear over the whole range iii. The detector should give good reproducibility iv. Detector should be insensitive to changes in the rate of flow of the carrier gas 9. Write the application of argon Ionization detector. Responds to most of the organic and Inorganic Compounds. 10. Write the methods used in sample injection system in liquid Chromatography. i. Syringe Injection method ii. Injection valve method. 11. What are the factors to be considered when a detector is interfaced with Liquid Chromatography? i.good sensitivity- to deal with low concentration of typical analyses. ii.the volume of the detector must be small to avoid additional band broadeninig due to extra column., iii.detector must be able to function in the presence of a large background signal and be able to null out this signal. 12. State the principle used in refractive Index detectors. Refractive Index detectors depends on Snell s law. It is based on refraction, reflection or interference of light beams. 13. Write the principle of adsorption detector. This detector depends on the measurement of the evolution of the heat of adsorption and heat uptake at desorption as the solutes in the effluent stream comes in contact with an adsorbent. 14. Write the factors affecting Gas flow rate. The rate of the gas flow depends upon column diameter. The flow rate is generally in the range ml/ minute. Very low and very high flow rate affect the efficiency adversely. 15. Define dead time and dead volume. Dead time is the time required for a molecule of mobile phase to pass through the column. Dead volume Vm is the volume of the mobile phase from the point of injection through the column to the detector. 16. Write advantages of HPLC over gas chromatography. i) Gas chromatography is in need of conversion of nonvolatile substances into volatile, such conversion is not needed in HPLC. ii)gas chromatography is not applicable to thermally unstable substances. but liquid chromatography can be applied to thermally unstable substances. Chettinad College of Engineering & Technology 3 ISO 9001:2008
4 17. Define thin layer chromatography A method of separating two or more chemical compounds in a solution through their differential migrations across a thin layer of adsorbent spread over a glass or plastic plate. 18. What are the applications of HPLC? 1. It is applied in the process of isolation and purification of compounds. The information that is obtained from this includes identification, quantification and resolution of a compound. 2. Chemical separation can be accomplished using HPLC by utilizing the fact that certain compounds have different migration rates with respect to the particular column and mobile phase. The degree of separation is mostly determined by the choice of stationary and mobile phase. 19. What are the application of gas chromatography? Gas chromatography is applicable for the analysis of the solute in both qualitatively and quantitatively. 20. What do you mean by open tubular column? Capillary column are the open tubular column constructed from fused silica ( a very high purity glass).the length of the column from 30 to 300m and a diameter of 1mm or less. 21. Name the detectors used in Gas Chromatography.(May 2013) i. Katharometer or Thermal Conductivity detector ii. Flame Ionisation Detector iii. Differential flame Ionisation Detector iv. Electron Capture detector v. Argon Ionisation Detector vi Cross-Section Ionisation Detector 22. What is HPLC? (May 2013) High Pressure Liquid chromatography. The most widely used analytical separations technique. Utilizes a liquid mobile phase to separate components of mixture. uses high pressure to push solvent through the column. 23. What is Pyrolysis? (Nov 2013) Pyrolysis offers a technique for injection of certain types of materials which are low or non-volatile. This is a valuable technique for sample injection in rubber, plastics, polymers and adhesive industries. 24. Define retention time. (Nov 2013) Time required by the component in the sample to emerge is called retention time. 25. What are the properties of carrier gas? (Nov 2013) 1. The carrier gas must be chemically inert. That is otherwise it should not react with the sample or stationary phase. 2. It should be suitable for the detector employed and the type of sample analysed.3. It should give best column performance consistent with required speed of the analysis. 4. It should be free from the risk of fire. Unit-II Part B 1. Draw the schematic diagram of a gas chromatography and explain the different parts in Gas chromatography.(may 2013), (Nov 2013) 2. Describe a gas liquid chromatography with a schematic diagram. Explain how it works. 3. Give a typical chromatogram. Discuss some applications of gas liquid chromatography. 4. Explain in detail the following detectors used in Gas Chromatography. a).thermal conductivity detector b).flame ionization detector 5. With a neat schematic diagram discuss the separation principle of HPLC. (May 2013) 6. What are the requirements of HPLC pumping system and enumerate the application of HPLC. 7. Give in detail the classification of chromatography. Explain liquid chromatography. Chromatography 8. Explain various detectors used in liquid chromatography. 9. Explain about Refractive index detector and electrochemical detector 10. Explain with neat diagram about flame photometric detector, photo ionization detector and electron capture detector. UNIT III INDUSTRIAL GAS ANALYSER AND POLLUTION MONITORING INSTRUMENTS Part A 1. Classify gas analyzer based on principle. i. No interaction of intramolecular energy states, ii. With excitation of intramolecular energy states, iii.with chemical or electrochemical reaction 2. Explain paramagnetic property.give some example. Chettinad College of Engineering & Technology 4 ISO 9001:2008
5 It does not have strong magnetism as permanent magent but it is attracted into a magnetic field. Ex: O 2, NO, N O 2 3. Write the drawbacks of CO monitor. i. Sources must be balanced either electrically or mechanically. ii. Unbalanced chopper causes failure of chopper motor bearings iii. Difficult to maintain and expensive to replace 4. Define thermal conductivity of a gas. It is defined as the quantity of heat (calories) transferred in unit time (secs) in a gas between two surfaces 1 sq.cm in area and 1 cm apart with a temperature difference between the surface 1 deg C. 5. Write the advantage of using thermistor in thermal conductivity analyzer. i. It is sensitive to minute changes in temperature. ii. High negative temperature coefficient of resistance 6. Write the considerations in industrial process analyzer. i. Simple to design and easy to maintain, ii. Ability to withstand harsh plant environment (mechanical shocks, vibration, dust and weather). iii. Decreasing the analyzer sizes facilitates the installation and reduces the cost. iv. Reliability is important. 7. Write the methods used in electrochemical analyzer. i. Galvanic method ii. Polographic method iii. conduct metric method 8. Write the methods used for measurement of Nox in Industry. i. Infrared analysis ii. Ultraviolet Analysis iii. Chemiluminescent Analysis iv. ElectroChemical Analysis v. Gas Chromatography 9. Write the methods used for measurement of Nox in ambient gas. i. Coulometric analyzer ii. Calorometric analyzer 10. What are the different types of Hydrogen Sulfide Analyzer? i. Electrochemical diffusion ii. Solid state or gold film sensors iii. UV Photometric iv. Gas Chromatography 11. Why thermistors are used in thermal conductivity analyzer as a heat sensing elements? Thermistors possess the advantage of being extremely sensitive to relatively minute changes in temperature and have high negative temperature coefficients. The speed of response is also high. 12. What are the applications of thermal conductivity gas analyzer? a. It is used in the measurement of hydrogen in blast furnace gases b. In the determination of argon in Oxygen in the process of air decomposition c. In the determination of sulphur dioxide in roasting gases in the production of sulphuric acid. 13. How is nitrogen-di-oxide prepared by chemiluminescence? The nitric oxide reacts with ozone to form nitrogen-di-oxide with chemiluminescence. NO + O > NO 2 + hv (light 0.6-3μ) 14. What are the advantages of Hydrogen Sulfide analyzer? i. It do not require pumps or aspirators to pull in the sample ii. They are unaffected by wind or variations in relative humidity. 15. What are the applications of oxygen analyzer? i. It is used in the areas of oxygen absorption studies on plants and tissues. ii. It is used in food processing industries. iii. It is also used in respiratory studies. 16. What are the sources of error in oxygen analyzer? i. The filament temperature is affected by changes in the thermal conductivity of the carrier gas, ii. The cross tube must be horizontal to avoid an error due to gravitational chimney-flow effects, iii. Hydrocarbons and other combustible gases in the sample stream react on the heated filaments causes changes in temperature and therefore their resistance, which results in large error. 17. Explain the different analysis methods of Nitrogen Oxide. i. Infrared ii. Ultraviolet iii. Chemiluminescent iv. Colorimetric v. Electrochemical 18. What are the applications of Electrochemical and Infrared sensors? i. Electrochemical sensors are used for ambient air monitoring ii.infrared sensors are used for stack gas concentration 19. Explain the detection methods of Carbon Monoxide Analyzer. i. Non dispersive method ii. Mercury Vapour iii. Catalytic Oxidation iv. Electrochemical fuel cell 20. Explain the calibration methods used in NO2 analyzer. Chettinad College of Engineering & Technology 5 ISO 9001:2008
6 The calibration methods are Dynamic calibration & Static calibration. Dynamic calibration requires preparation of inert gas containing a known concentration of NO2. This may be accomplished by gas dilution techniques. Static calibration is carried out with standard solutions of nitrite. 21. Mention the uses of IR analyzer 1. It is used for single component analysis such as ethylene, CO, acetylene, methane etc, 2. Multiple component for cereal, meat and paper could also be analyzed 22. What is the need of carbon monoxide in flue gas? The carbon monoxide is colorless, odorless, poisonous gas that has an affinity for hemoglobin, which is 210 times that of oxygen. By combining with hemoglobin in the blood it inhibits the delivery of oxygen to the body s tissues, thereby causing asphyxia or shortness of breath. 23. Write the principle of smoke meter. (Nov 2013) Smoke meter is based on the principle of absorption / obscuration of light which is indicative of the quality of smoke. The light beam passes through a smoke cell and onto a silicon photo detector which is continuously senses the intensity of the light incident on it and converts it into a electrical signal which is further processed by precise signal handling circuits. 24. Brief the principle of dust monitor. (May 2013)(Nov 2013) Dust monitor works on the principle of passing a focused light beam through the duct or chimney on a photocell and the variations in the signal of the photocell circuit will be a measure of the variation of the obstruction of the light source dur to the smoke and dust in the gases. 25. What is thermal conductivity? (May 2013) A measure of the ability of a material to transfer heat. Given two surfaces on either side of a material with a temperature difference between them, the thermal conductivity is the heat energy transferred per unit time and per unit surface area, divided by the temperature difference. 26. What is the use of gold films in Hydrogen Sulfide analyzer? (Nov 2013) Gold films absorb hydrogen sulfide and register the concentration by a proportional change in their electrical resistance. It is available in ppb range and is not sensitive to interferences by SO 2, CO 2 or CO. Unit-III Part B 1. With a neat sketch, explain the construction and working principle of parametric oxygen analyzer. (May 2013) 2. With a block diagram, explain the method of measuring carbon monoxide using Non-dispersive Infrared Analyzer. (Nov 2013) 3. Explain how the NO 2 analyzer is used. (May 2013) 4. Explain how the H 2 S analyzer is used. 5. Explain how the dust and smoke analyzer is used. (May 2013) 6. Explain how the IR analyzer is used. 7. With a suitable diagram explain the construction and working principle of thermal conductivity analyzer. (Nov 2013) 8. What are the sources of air pollution and explain in detail? 9. What are the type s gas analyzers? Explain anyone with example. 10. Discuss the method of analysis based on ionization of gases. 11. With the instrumentation setups explain any one method to estimate sulphur-di-oxide present in air. 12. Explain the photometric method of measuring dust and smoke measurement in thermal power plant. 13. Why do we need temperature compensation in conductivity measurement? Describe a method of temperature compensation UNIT IV ph METER AND DISSOLVED COMPONENT ANALYZER Part A 1. What is a ph meter? It is used to measure ph which is the hydrogen ion concentration in a test solution. It is defined Chettinad College of Engineering & Technology 6 ISO 9001:2008
7 as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration. ph= - log[h+] 2. Give the ph of water, acid, base. Water ph=7, Acid ph<7, Base ph>7 3. What are the different electrodes used for ph measurement? Hydrogen electrode, Glass electrode, Calomel electrode, Combination electrode. 4. What is the principle of a ph meter? The measurement of hydrogen ion concentration in a test solution is made by measuring the potential developed in an electrochemical cell. The electrochemical Ph cell consists of a measuring electrode and a reference electrode both immersed in the solution under test. The two electrodes are connected for measuring the instantaneous emf between the two electrodes. The measuring electrodes are ph sensitive and the potential is proportional to the ph value of the solution and the reference electrode always develops a constant electrical potential,the potential of the measuring electrode may be written as E = Eo RT/F log C; E = Eo RT/F ph ph= ph value deviation from 7 C = hydrogen ion concentration 5. Define Sampling System. The key to any continuous analysis is the sample transport system. Figure shows simple method of continuous sensing used for variable such as ph, conductivity, dissolved oxygen and water temperature. 6. What is the use of Conductivity Meter? It measures the ability of the solution to carry electric current (conductivity of an electrolyte). If a potential is applied to the electrode immersed in the solution, ions are accelerated towards the electrode. 7. Define Cell constant. Cell constant is given by Cell constant =L/A where, L= length A =area Cell constant can be determined by the measuring the value of resistance of a solution of known specific conductance. 8. Write the methods of measuring ph. i. Direct reading type ii. Null detector type 9. Define equivalent conductance. Conductance =A/pl = K(a/l) K=1/p = Specific conductance Equivalent conductance: The ability of indiv9dual ions to conduct current is expressed as equivalent conductance. It is the conductance of a solution containing 1 gram equivalent of an electrolyte per cubic cm of a solution. This is represented as ^ Relationship between K and ^ ^ = 1000 K/C 10. Write the use of sodium analyzer. i. To determine sodium ion concentration in boiler water ii.used for industrial water pollution monitoring iii.monitors and carries over detections of condenser leaks and the exhaustion of water treatment plant cation exchange unit. Ion selective electrode is the most powerful tool for specific analysis. It is used to determine the specific constituents like cyanide, fluoride, ammonia in a sample. 11. Write the methods of measuring oxygen. 1) Physical: a) Paramagnetic property of oxygen b) Thermal conductivity for quantitative determination 2) Chemical: a) Potentiometry b) Catalytic combustion 12. Write the principle of silica analyzer. A silica analyzer works on the calorometric principle. Ammonium molybdate solution (ph=7), sulphuric acid and a reducing solution are added to a metered volume of a sample through separate measuring cylinders to eliminate the precipitation of molybdic acid. 13. Define moisture. It is defined as the amount of water vapour absorbed by a solid or adsorbed by a liquid. 14. Define ionic concentration and ionic activity. Ionic activity: measures the number of free ions in the solution. Ionic concentration: measures the free and bonded ions. Chettinad College of Engineering & Technology 7 ISO 9001:2008
8 15. What is buffer solution? It may be defined as the solution whose ph remains nearly a constant despite the addition of a substantial quantity of acid or base. Buffers are employed for the standardization of a ph cell. 16. Write the advantage of direct reading type instruments. 1) simplicity of operation 2) speed of measurement 17. Why are glass electrodes preferred? Glass electrodes are preferred because of their following characteristics i. Low melting point ii. High hygroscopicity iii. High electrical conductivity 18. What are the considerations in diagramming a ph meter. 1) Internal resistance of glass electrode is very high. 2) Current should neither be drawn by the ph meter from the solution nor any current should flow on the electrode which might result in the polarization of the electrode. Such polarized electrodes give erroneous reading of ph values. 3) Meter should have a provision for compensating the charge in the ph reading due to temperature change. 19. Write the applications of ph measurement. i. Tanning industries ii. Chemical industries iii. Distillation plants 20. Give the characterizes of glass electrode? i.sensitivity is above 95% ii. Fast response iii. Low melting point iv. Relatively high electrical conductivity v. High horoscopy. 21. What are the advantages of hydrogen electrode 1. It is standard reference electrode with which the potentials of electrodes are calculated. 2. The results are highly accurate.3.it gives no salt error 4.The error due to electrical leakage is negligible. 22. What are called bio-sensors? A bio-sensor is a device that uses biological material to monitor the presence of various chemicals in a substance or it can also be defined as it is a device for the detection of an analyze that combines a biological component with a physiochemical detector component. 23. Define P H of a solution. (May 2013) It is defined as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration. ph= - log[h+] 24. List the demerits of glass electrode.(may 2013) 1) Measuring solutions containing particulate can damage the glass membrane and 2) the glass membrane is easily broken. 25. List the different types of electrodes used in PH measurement? (Nov 2013) Glass electrode, platinum electrode 26. What is the use of blank in silica analyzer? (Nov 2013) Blank calibration uses a method different from zero silica content water content. Generally the blank is set by measuring the gap between absorbance of the normal measurement and that using a double volume of molybdate reagent. Unit IV Part B 1. Describe how a conductivity cell is used. Give the applications of conductivity measurement of a liquid. Explain how the oxygen analyzer is used. 2. Describe the construction of a ph electrode. Draw the electronic circuit diagram for measuring ph of a liquid and explain its working. 3. Discuss how ph values are measured. Explain the role of calomel electrodes in this measurement. 4. Briefly explain about dissolved oxygen analyzer. 5. Discuss in detail the principle, characteristics of electrodes used in ph meters. 6. Describe with a neat sketch, the principle of operation of water purity meter. 7. Discuss the method of measuring electrical conductivity of a liquid. Also describe the techniques for determining the purity of water. 8. Discuss how ph of a solution is measured using glass electrode and reference electrode with Chettinad College of Engineering & Technology 8 ISO 9001:2008
9 necessary diagrams. 9. Explain about sodium analyzer in detail. (May 2013) 10. Explain about silica analyzer 11. Explain different types of ion selective electrodes. (Nov 2013) 12. List the types of electrodes used for ph measurement. Explain the construction details of Digital ph meter. Also specify the need of reference electrode for ph measurement. 13. Describe a method of measuring dissolved oxygen content in the boiler feed water. Why dissolved oxygen content is monitored in feed water? Also specify the cause of dissolved oxygen content in feed water. (May 2013) 14. Explain the working principles of biosensors with a conceptual diagram. Also specify the various parameters to be measured using Biosensor. (Nov 2013) UNIT V ELECTRO MAGNETIC RESONANCE AND MICROSCOPIC TECHNIQUES Part A 1. Define state of resonance. When a nucleus is placed in a system where it absorbs energy, it becomes excited. It then loses energy to return to the unexcited state. It absorbs energy and again enters an excited state. This nucleus which alternately becomes excited and unexcited is said to be in a state of resonance. 2. Define Chemical shift. The shift in the positions of NMR signals ( compared with a standard reference) resulting from the shielding and deshielding by electrons are referred to as Chemical shift. 3. Write a method for measuring the Chemical shift. To measure the magnitudes of chemical shifts of different kinds of protons, there must be some standard signal with respect to which the measurement can be made.for this purpose,tetramethylsilane(tms),(ch3)4si is used as the reference or standard compound.it gives only one signal which serves as fixed reference. 4. What are the factors that influence chemical shift? The main factors which influence the chemical shift are ; i. Inductive effect ii. Anisotropic effect iii. Hydrogen bonding 5. What is Spin-Spin coupling? The interaction between the spins of the neighboring nuclei in a molecule may cause the splitting of the lines in the NMR spectrum. This is known as spin-spin coupling which occurs through bonds by means of a slight unpairing of the bonding electrons. 6. Give some applications of NMR spectroscopy. i.structural Diagnosis ii.quantitaive analysis used to determine the molar ratio of the components in a mixture. iii Hydrogen Bonding Used to study the hydrogen bonding in metal chelates as well as in organic compounds iv.structural determination v.intra molecular conversion vi.keto-enol Tautomerism vii.intermolecular Exchange reaction viii.elemental analysis- used for the determination of the total concentration of a given kind of magnetic nucleus in a sample. 7. Write the limitation of NMR spectroscopy. The limitations of NMR spectroscopy are : i. Lack of sensitivity. The minimum sample size is about 0.1 ml having minimum concentration of about 1% ii. In some compounds, two different types of hydrogen atoms resonate at similar resonance frequencies. This results in an overlap of spectra and makes such spectra difficult to interpret. iii.only liquids can be studied by NMR spectroscopy, although polymers, when preheated with various solvents, frequently become fluids which can be treated as liquids 8. Define mass spectrum. The compound under investigation is bombarded with a beam of electrons which produce an ionic molecule or ionic fragments of the original species. The resulting assortment of Chettinad College of Engineering & Technology 9 ISO 9001:2008
10 charged particles is then separated according to their masses. The spectrum produced is known as mass spectrum. 9. Define time of flight. All ions leave the acceleration field with different velocities depending on their masses. With magnetic focusing, the ions gets separated by changing their directions. However, if these ions are allowed to travel in a straight line through a magnetic field free region, they will take different times to travel a given distance. The measurement of this time of flight FORM the basis for the nonmagnetic separator. 10. What are the different types of mass spectrometer? i. Magnetic Deflection mass spectrometer ii. Time of flight mass spectrometer iii. Double focusing mass spectrometer iv. Quadrupole mass spectrometer 11. What are the different components of a mass spectrometer? i. Inlet Sample System ii. Ion Sources iii. Electrostatic Accelerating System iv. Ion detectors and Recording of mass spectrograph, v. Vacuum System 12. Write the components of electron spectroscopy. i. A source of radiation to excite the sample. ii. An electron energy analyzer. iii. An electron detector. iv. Read out system. v. High vacuum system. 13. Give some applications of mass spectrometry. i. Molecular mass can be accurately determined by the mass spectrometry. ii. It is used to determine the amount of component of a complicated mixture. iii. Method for the detection of impurities. iv. Polymers can be characterized by mass spectrometry. v. Molecular formulae can be determined from the mass spectrum either partially or exactly. 14. What are the types of NMR spectrometer. i. Minimal type NMR spectrometer ii. Multipurpose NMR spectrometer iii. Wideline NMR spectrometer 15. Write the advantages and disadvantages of time of flight mass spectrometer. Advantages It is simple and ruggedness. It can handle unlimited mass range. Disadvantage Limited resolution and sensitivity. 16. What are the types of detectors in mass spectrometer? i. Electron multiplier ii. Faraday cup collector iii. Photographic plates 17. What are the two common designs of Double focusing mass spectrometer? i. Nier - Johnson design ii Mattauch - Herzog geometry 18. What is the basic principle of NMR? A radically different type of interaction between matter and electromagnetic forces can be observed by subjecting a substance simultaneously to two magnetic fields, one stationary and other varying at some radio frequency. At particular combinations of fields energy is observed by the sample and the absorption can be observed as a change in signal developed by a radio frequency detector and amplifier. The energy absorption can be related to the magnetic dipolar nature of spinning nuclei. 19. What is the advantage of ESR Spectroscopy? It is used to detect 1)Volume (300 ml) and concentration ( mm) often low 2)Recording spectrum can be done quickly (usually no more than min) 3)Spectrum is only of paramagnetic species 4)Spectrum is often simple to interpret 5)Spectrum often can be recorded in vivo 20. Write down the principle of Mass Spectrometry. (May 2013) In Mass Spectrometer the sample to be analyzed is first bombarded with electron beam to produce ions. These ions are then sorted out by accelerating them through electric and magnetic fields according to their mass /charge ratio. Mass spectrometer separates the ions on the basis of their mass to charge ratio. But most of the ions are singly charged, so the ratio is equal to the mass of the ions. A record of the number of different kinds of ions is called the mass spectrum. 21. Brief the principle of scanning electron microscope. (May 2013) A normal scanning electron microscope operates at a high vacuum. The basic principle is that a beam of electrons is generated by a suitable source, typically a tungsten filament or a field Chettinad College of Engineering & Technology 10 ISO 9001:2008
11 emission gun. The electron beam is accelerated through a high voltage (e.g.: 20 kv) and pass through a system of apertures and electromagnetic lenses to produce a thin beam of electrons., then the beam scans the surface of the specimen by means of scan coils (like the spot in a cathode-ray tube "old-style" television).electrons are emitted from the specimen by the action of the scanning beam and collected by a suitably-positioned detector. 22. Write the principle of Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) spectrometer. (Nov 2013) Electron Spin Resonance involves detecting the detection of a physical phenomenon of absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the microwave region by paramagnetic species that are subjected tomagnetic field. 23. What is Nuclear magnetic resonance? (Nov 2013) The nuclei of atoms in a molecule on absorbing RF radiation may change their direction of spin.the analytical field involved with the interaction between the nuclei and rf radiation is called Nuclear magnetic resonance. (NMR ) Unit V Part B 1. Draw the block diagram of an NMR spectrometer. Explain the function of each part and explain how it is used to obtain NMR spectra. How are these spectra useful? (May 2013) 2. What are Mass spectrometers? Describe magnetic deflection mass spectrometers. (May 2013) 3. Explain time of flight and quadrupole mass spectrometers. 4. Describe the working of double beam mass spectrometer and give its applications. 5. Explain the instrumentation and applications of Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM). 6. Describe how various samples are analyzed using NMR spectrometer with neat diagram. 7. Explain the construction and working principle of Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) spectrometer with neat diagram. 8. Explain the construction and working of Radio frequency spectrometer with neat diagram. 9. Explain the various components of a mass spectrometer. 10. Explain in detail the construction and working principle of single focusing mass spectrophotometers. (Nov 2013) 11. In NMR spectroscopy mention the advantages of using a magnet with as great a field strength as possible. Also explain the difference between a continuous wave and fourier transform NMR. 12. With neat sketch explain the construction and working principle of mass spectrometer. 13. What are the basic components of electron Spectroscopy? Also explain the working principle of Electron spectroscopy with a neat block diagram. (Nov 2013) Chettinad College of Engineering & Technology 11 ISO 9001:2008
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR-603203 EI 2302 ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS QUESTION BANK UNIT I COLORIMETRY AND SPECTROPHOTOMETRY Part A 1. State Lambert
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR-603203 EI 2302 ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS QUESTION BANK UNIT I COLORIMETRY AND SPECTROPHOTOMETRY Part A 1. State Lambert
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6501 Analytical Instruments Regulation 2013 Academic
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6501 Analytical Instruments Regulation 2013 Academic
Atmospheric Analysis Gases. Sampling and analysis of gaseous compounds
 Atmospheric Analysis Gases Sampling and analysis of gaseous compounds Introduction - External environment (ambient air) ; global warming, acid rain, introduction of pollutants, etc - Internal environment
Atmospheric Analysis Gases Sampling and analysis of gaseous compounds Introduction - External environment (ambient air) ; global warming, acid rain, introduction of pollutants, etc - Internal environment
Questions on Instrumental Methods of Analysis
 Questions on Instrumental Methods of Analysis 1. Which one of the following techniques can be used for the detection in a liquid chromatograph? a. Ultraviolet absorbance or refractive index measurement.
Questions on Instrumental Methods of Analysis 1. Which one of the following techniques can be used for the detection in a liquid chromatograph? a. Ultraviolet absorbance or refractive index measurement.
Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry
 Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures into their components in order to analyze, identify, purify, and/or quantify
Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures into their components in order to analyze, identify, purify, and/or quantify
2401 Gas (liquid) Chromatography
 2401 Gas (liquid) Chromatography Chromatography Scheme Gas chromatography - specifically gas-liquid chromatography - involves a sample being vaporized and injected onto the head of the chromatographic
2401 Gas (liquid) Chromatography Chromatography Scheme Gas chromatography - specifically gas-liquid chromatography - involves a sample being vaporized and injected onto the head of the chromatographic
Gas chromatography. Advantages of GC. Disadvantages of GC
 Advantages of GC Gas chromatography Fast analysis, typically minutes Effi cient, providing high resolution Sensitive, easily detecting ppm and often ppb Nondestructive, making possible on - line coupling;
Advantages of GC Gas chromatography Fast analysis, typically minutes Effi cient, providing high resolution Sensitive, easily detecting ppm and often ppb Nondestructive, making possible on - line coupling;
Harris: Quantitative Chemical Analysis, Eight Edition CHAPTER 23: GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
 Harris: Quantitative Chemical Analysis, Eight Edition CHAPTER 23: GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Chapter 23. Gas Chromatography What did they eat in the year 1,000? GC of Cholesterol and other lipids extracted from
Harris: Quantitative Chemical Analysis, Eight Edition CHAPTER 23: GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Chapter 23. Gas Chromatography What did they eat in the year 1,000? GC of Cholesterol and other lipids extracted from
Chapter 31 Gas Chromatography. Carrier Gas System
 Chapter 31 Gas Chromatography GAS-LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY In gas chromatography, the components of a vaporized sample are fractionated as a consequence of being partitioned between a mobile gaseous phase
Chapter 31 Gas Chromatography GAS-LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY In gas chromatography, the components of a vaporized sample are fractionated as a consequence of being partitioned between a mobile gaseous phase
Reference literature. (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters )
 September 17, 2018 Reference literature (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters 13-14 ) Reference.: https://slideplayer.com/slide/8354408/ Spectroscopy Usual Wavelength Type of Quantum
September 17, 2018 Reference literature (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters 13-14 ) Reference.: https://slideplayer.com/slide/8354408/ Spectroscopy Usual Wavelength Type of Quantum
Spectroscopy. Page 1 of 8 L.Pillay (2012)
 Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiation is widely used in analytical chemistry. The identification and quantification of samples using electromagnetic radiation (light) is called spectroscopy. Light has
Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiation is widely used in analytical chemistry. The identification and quantification of samples using electromagnetic radiation (light) is called spectroscopy. Light has
Chromatography. Gas Chromatography
 Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
White Paper. Overview: NDIR Definition:
 Title: NDIR Technology Overview, Compliance, and Comparison to Other Generally Available Gas Measurement Technologies TSN Number: 06 File:\\MII- SRV1\Metron\Bridge_Analyzers\Customer_Service_Documentation\White_Papers\06
Title: NDIR Technology Overview, Compliance, and Comparison to Other Generally Available Gas Measurement Technologies TSN Number: 06 File:\\MII- SRV1\Metron\Bridge_Analyzers\Customer_Service_Documentation\White_Papers\06
Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section: 5 Gas Chromatography (GC) Prof. Tarek A. Fayed
 Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section: 5 Gas Chromatography (GC) Prof. Tarek A. Fayed Gas Chromatography (GC) In gas chromatography, the sample is vaporized and injected onto the head of a chromatographic
Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section: 5 Gas Chromatography (GC) Prof. Tarek A. Fayed Gas Chromatography (GC) In gas chromatography, the sample is vaporized and injected onto the head of a chromatographic
25 Instruments for Optical Spectrometry
 25 Instruments for Optical Spectrometry 25A INSTRUMENT COMPONENTS (1) source of radiant energy (2) wavelength selector (3) sample container (4) detector (5) signal processor and readout (a) (b) (c) Fig.
25 Instruments for Optical Spectrometry 25A INSTRUMENT COMPONENTS (1) source of radiant energy (2) wavelength selector (3) sample container (4) detector (5) signal processor and readout (a) (b) (c) Fig.
Cork Institute of Technology. Summer 2005 Instrumental Analysis (Time: 3 Hours) Section A
 Cork Institute of Technology Higher Certificate in Science in Applied Biology Award (National Certificate in Science in Applied Biology Award) Answer FIVE questions; answer Section A, TWO questions from
Cork Institute of Technology Higher Certificate in Science in Applied Biology Award (National Certificate in Science in Applied Biology Award) Answer FIVE questions; answer Section A, TWO questions from
Gas Chromatography. Chromatography Laboratory Course. Dr. Christian Jungnickel Chromatography Course GC September 2005
 Gas Chromatography Chromatography Laboratory Course The laboratory course experiments General Aim: Gain general experience using a GC Constant Injection technique Temperature variations Qualitative and
Gas Chromatography Chromatography Laboratory Course The laboratory course experiments General Aim: Gain general experience using a GC Constant Injection technique Temperature variations Qualitative and
Spectroscopy and Chromatography
 Spectroscopy and Chromatography Introduction Visible light is one very small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The different properties of the various types of radiation depend upon their wavelength.
Spectroscopy and Chromatography Introduction Visible light is one very small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The different properties of the various types of radiation depend upon their wavelength.
Atomization. In Flame Emission
 FLAME SPECTROSCOPY The concentration of an element in a solution is determined by measuring the absorption, emission or fluorescence of electromagnetic by its monatomic particles in gaseous state in the
FLAME SPECTROSCOPY The concentration of an element in a solution is determined by measuring the absorption, emission or fluorescence of electromagnetic by its monatomic particles in gaseous state in the
CH0302 Process Instrumentation. Lecture 9 Composition Analysis
 CH0302 Process Instrumentation Lecture 9 Composition Analysis Department of Chemical Engineering School of Bioengineering SRM University Kattankulathur 603203 4/3/15 Chemical Engineering 1 Industrial significance
CH0302 Process Instrumentation Lecture 9 Composition Analysis Department of Chemical Engineering School of Bioengineering SRM University Kattankulathur 603203 4/3/15 Chemical Engineering 1 Industrial significance
Luminescence transitions. Fluorescence spectroscopy
 Luminescence transitions Fluorescence spectroscopy Advantages: High sensitivity (single molecule detection!) Measuring increment in signal against a dark (zero) background Emission is proportional to excitation
Luminescence transitions Fluorescence spectroscopy Advantages: High sensitivity (single molecule detection!) Measuring increment in signal against a dark (zero) background Emission is proportional to excitation
2101 Atomic Spectroscopy
 2101 Atomic Spectroscopy Atomic identification Atomic spectroscopy refers to the absorption and emission of ultraviolet to visible light by atoms and monoatomic ions. It is best used to analyze metals.
2101 Atomic Spectroscopy Atomic identification Atomic spectroscopy refers to the absorption and emission of ultraviolet to visible light by atoms and monoatomic ions. It is best used to analyze metals.
3 - Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
 3 - Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Introduction Atomic-absorption (AA) spectroscopy uses the absorption of light to measure the concentration of gas-phase atoms. Since samples are usually liquids or solids,
3 - Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Introduction Atomic-absorption (AA) spectroscopy uses the absorption of light to measure the concentration of gas-phase atoms. Since samples are usually liquids or solids,
Sub-category: Physics and Principles of Measurement Topic: Monitoring anesthetic gases and vapours Date: January 15-17, 2016 Language: English
 Course n : Course 3 Title: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE Sub-category: Physics and Principles of Measurement Topic: Monitoring anesthetic gases
Course n : Course 3 Title: RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY, PHYSICS AND PATHOLOGY IN RELATION TO ANAESTHESIA AND INTENSIVE CARE Sub-category: Physics and Principles of Measurement Topic: Monitoring anesthetic gases
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Presentation by, Mrs. Sangita J. Chandratre Department of Microbiology M. J. college, Jalgaon
 Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry Presentation by, Mrs. Sangita J. Chandratre Department of Microbiology M. J. college, Jalgaon Defination In analytical chemistry, Atomic absorption spectroscopy is a
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry Presentation by, Mrs. Sangita J. Chandratre Department of Microbiology M. J. college, Jalgaon Defination In analytical chemistry, Atomic absorption spectroscopy is a
Chapter 27: Gas Chromatography
 Chapter 27: Gas Chromatography Gas Chromatography Mobile phase (carrier gas): gas (He, N 2, H 2 ) - do not interact with analytes - only transport the analyte through the column Analyte: volatile liquid
Chapter 27: Gas Chromatography Gas Chromatography Mobile phase (carrier gas): gas (He, N 2, H 2 ) - do not interact with analytes - only transport the analyte through the column Analyte: volatile liquid
3) In CE separation is based on what two properties of the solutes? (3 pts)
 Final Exam Chem 311 Fall 2002 December 16 Name 1) (3 pts) In GC separation is based on the following two properties of the solutes a) polarity and size b) vapor pressure and molecular weight c) vapor pressure
Final Exam Chem 311 Fall 2002 December 16 Name 1) (3 pts) In GC separation is based on the following two properties of the solutes a) polarity and size b) vapor pressure and molecular weight c) vapor pressure
Fundamentals of Mass Spectrometry. Fundamentals of Mass Spectrometry. Learning Objective. Proteomics
 Mass spectrometry (MS) is the technique for protein identification and analysis by production of charged molecular species in vacuum, and their separation by magnetic and electric fields based on mass
Mass spectrometry (MS) is the technique for protein identification and analysis by production of charged molecular species in vacuum, and their separation by magnetic and electric fields based on mass
Sampling. Information is helpful in implementing control measures for reducing pollutant concentration to acceptable levels
 Types of pollutant sampling and measurement: Air quality monitoring: Sampling and measurement of air pollutants generally known, as air quality monitoring. It is an integral component of any air pollution
Types of pollutant sampling and measurement: Air quality monitoring: Sampling and measurement of air pollutants generally known, as air quality monitoring. It is an integral component of any air pollution
Course: M.Sc (Chemistry) Analytical Chemistry Unit: III
 Course: M.Sc (Chemistry) Analytical Chemistry Unit: III Syllabus: Principle of spectrophotometry Types of spectrophotometer Applications - Dissociation constants of an indicator simultaneous spectrophotometric
Course: M.Sc (Chemistry) Analytical Chemistry Unit: III Syllabus: Principle of spectrophotometry Types of spectrophotometer Applications - Dissociation constants of an indicator simultaneous spectrophotometric
Ch 313 FINAL EXAM OUTLINE Spring 2010
 Ch 313 FINAL EXAM OUTLINE Spring 2010 NOTE: Use this outline at your own risk sometimes a topic is omitted that you are still responsible for. It is meant to be a study aid and is not meant to be a replacement
Ch 313 FINAL EXAM OUTLINE Spring 2010 NOTE: Use this outline at your own risk sometimes a topic is omitted that you are still responsible for. It is meant to be a study aid and is not meant to be a replacement
Gas Chromatography. Presented By Mr. Venkateswarlu Mpharm KTPC
 Gas Chromatography Gas Chromatography Presented By Mr. Venkateswarlu Mpharm KTPC What is Gas Chromatography? It is also known as Gas-Liquid Chromatography (GLC) GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Separation of gaseous
Gas Chromatography Gas Chromatography Presented By Mr. Venkateswarlu Mpharm KTPC What is Gas Chromatography? It is also known as Gas-Liquid Chromatography (GLC) GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY Separation of gaseous
Analytical techniques: Environmental samples. Lecture 2 Universidade do Algarve
 Analytical techniques: Environmental samples Lecture 2 Universidade do Algarve Terms, definitions & applications Difference between technique and method: Analytical technique: Fundamental scientific application
Analytical techniques: Environmental samples Lecture 2 Universidade do Algarve Terms, definitions & applications Difference between technique and method: Analytical technique: Fundamental scientific application
Chapter 13 An Introduction to Ultraviolet/Visible Molecular Absorption Spectrometry
 Chapter 13 An Introduction to Ultraviolet/Visible Molecular Absorption Spectrometry 13A Measurement Of Transmittance and Absorbance Absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet and visible radiation
Chapter 13 An Introduction to Ultraviolet/Visible Molecular Absorption Spectrometry 13A Measurement Of Transmittance and Absorbance Absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet and visible radiation
Emission spectrum of H
 Atomic Spectroscopy Atomic spectroscopy measures the spectra of elements in their atomic/ionized states. Atomic spectrometry, exploits quantized electronic transitions characteristic of each individual
Atomic Spectroscopy Atomic spectroscopy measures the spectra of elements in their atomic/ionized states. Atomic spectrometry, exploits quantized electronic transitions characteristic of each individual
(DCHE 21) M.Sc. (Final) DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER Second Year. Chemistry. Paper V ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY. PART A (4 10 = 40 marks)
 (DCHE 21) M.Sc. (Final) DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 2010. Second Year Chemistry Paper V ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY Time : Three hours Maximum : 100 marks PART A (4 10 = 40 marks) Answer any FOUR questions.
(DCHE 21) M.Sc. (Final) DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 2010. Second Year Chemistry Paper V ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY Time : Three hours Maximum : 100 marks PART A (4 10 = 40 marks) Answer any FOUR questions.
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 34. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 34 From molecular to elemental analysis there are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry Mass spectrometry X-ray spectrometry
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 34 From molecular to elemental analysis there are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry Mass spectrometry X-ray spectrometry
2001 Spectrometers. Instrument Machinery. Movies from this presentation can be access at
 2001 Spectrometers Instrument Machinery Movies from this presentation can be access at http://www.shsu.edu/~chm_tgc/sounds/sound.html Chp20: 1 Optical Instruments Instrument Components Components of various
2001 Spectrometers Instrument Machinery Movies from this presentation can be access at http://www.shsu.edu/~chm_tgc/sounds/sound.html Chp20: 1 Optical Instruments Instrument Components Components of various
EMISSION SPECTROSCOPY
 IFM The Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology LAB 57 EMISSION SPECTROSCOPY NAME PERSONAL NUMBER DATE APPROVED I. OBJECTIVES - Understand the principle of atomic emission spectra. - Know how to acquire
IFM The Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology LAB 57 EMISSION SPECTROSCOPY NAME PERSONAL NUMBER DATE APPROVED I. OBJECTIVES - Understand the principle of atomic emission spectra. - Know how to acquire
Because light behaves like a wave, we can describe it in one of two ways by its wavelength or by its frequency.
 Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Chem 321 Name Answer Key D. Miller
 1. For a reversed-phase chromatography experiment, it is noted that the retention time of an analyte decreases as the percent of acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) increases in a CH 3 CN/H 2 O mobile phase. Explain
1. For a reversed-phase chromatography experiment, it is noted that the retention time of an analyte decreases as the percent of acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) increases in a CH 3 CN/H 2 O mobile phase. Explain
High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
 High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a form of column chromatography that pumps a sample mixture or analyte in a solvent (known as the
High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a form of column chromatography that pumps a sample mixture or analyte in a solvent (known as the
Compact Knowledge: Absorbance Spectrophotometry. Flexible. Reliable. Personal.
 L A B O R A T O R Y C O M P E T E N C E Compact Knowledge: Absorbance Spectrophotometry Flexible. Reliable. Personal. The interaction of light with molecules is an essential and well accepted technique
L A B O R A T O R Y C O M P E T E N C E Compact Knowledge: Absorbance Spectrophotometry Flexible. Reliable. Personal. The interaction of light with molecules is an essential and well accepted technique
CHAPTER A2 LASER DESORPTION IONIZATION AND MALDI
 Back to Basics Section A: Ionization Processes CHAPTER A2 LASER DESORPTION IONIZATION AND MALDI TABLE OF CONTENTS Quick Guide...27 Summary...29 The Ionization Process...31 Other Considerations on Laser
Back to Basics Section A: Ionization Processes CHAPTER A2 LASER DESORPTION IONIZATION AND MALDI TABLE OF CONTENTS Quick Guide...27 Summary...29 The Ionization Process...31 Other Considerations on Laser
AQA Chemistry (Combined Science) Specification Checklists. Name: Teacher:
 AQA Chemistry (Combined Science) Specification Checklists Name: Teacher: Paper 1-4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic
AQA Chemistry (Combined Science) Specification Checklists Name: Teacher: Paper 1-4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic
Process Analyzer and Sampling Systems
 Process Analyzer and Sampling Systems Course Price 3050 Course Description Analytical instruments used for online chemical analysis of process streams or plant environments are generally called Process
Process Analyzer and Sampling Systems Course Price 3050 Course Description Analytical instruments used for online chemical analysis of process streams or plant environments are generally called Process
Research Equipment in the UCA Chemistry Department
 Research Equipment in the UCA Chemistry Department Varian 220 Atomic Absorption Spectrometer Atomic Absorption spectroscopy is used to measure the amount of a metal ion present in a solution. It is particularly
Research Equipment in the UCA Chemistry Department Varian 220 Atomic Absorption Spectrometer Atomic Absorption spectroscopy is used to measure the amount of a metal ion present in a solution. It is particularly
Volumetric Analysis. Quantitative analysis answers the second question
 Volumetric Analysis Volumetric analysis is a form of quantitative analysis involving the measuring of volumes of reacting solutions, it involves the use of titrations. When buying food we often have two
Volumetric Analysis Volumetric analysis is a form of quantitative analysis involving the measuring of volumes of reacting solutions, it involves the use of titrations. When buying food we often have two
Gas Chromatography CHEM Dr. Reem M. Alghanmi st term
 Gas Chromatography CHEM 313-5 Dr. Reem M. Alghanmi 2017 1 st term 17.7 Gas Chromatography Introduction There are two types of gas chromatography: Gas-solid (adsorption) chromatography. Gas-liquid (partition)
Gas Chromatography CHEM 313-5 Dr. Reem M. Alghanmi 2017 1 st term 17.7 Gas Chromatography Introduction There are two types of gas chromatography: Gas-solid (adsorption) chromatography. Gas-liquid (partition)
CHROMATOGRAPHY. The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments.
 CHROMATOGRAPHY The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments. THEORY OF CHROMATOGRAPHY: Separation of two sample components in
CHROMATOGRAPHY The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments. THEORY OF CHROMATOGRAPHY: Separation of two sample components in
FLAME PHOTOMETRY AIM INTRODUCTION
 FLAME PHOTOMETRY AIM INTRODUCTION Atomic spectroscopy is based on the absorption, emission or fluorescence process of light by atoms or elementary ions. Information for atomic scale is obtained in two
FLAME PHOTOMETRY AIM INTRODUCTION Atomic spectroscopy is based on the absorption, emission or fluorescence process of light by atoms or elementary ions. Information for atomic scale is obtained in two
Matter mass space atoms solid, a liquid, a gas, or plasm elements compounds mixtures atoms Compounds chemically combined Mixtures not chemically
 SOL PS.2 THE NATURE OF MATTER Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. Matter can exist as a solid, a liquid, a gas, or plasma. Matter
SOL PS.2 THE NATURE OF MATTER Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. Matter can exist as a solid, a liquid, a gas, or plasma. Matter
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis
 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis Hansen, Steen ISBN-13: 9780470661222 Table of Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 1.1 Applications and Definitions 1 1.2 The
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis Hansen, Steen ISBN-13: 9780470661222 Table of Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 1.1 Applications and Definitions 1 1.2 The
Absorption spectrometry summary
 Absorption spectrometry summary Rehearsal: Properties of light (electromagnetic radiation), dual nature light matter interactions (reflection, transmission, absorption, scattering) Absorption phenomena,
Absorption spectrometry summary Rehearsal: Properties of light (electromagnetic radiation), dual nature light matter interactions (reflection, transmission, absorption, scattering) Absorption phenomena,
Gas Chromatography (GC)
 Gas Chromatography (GC) Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11541 Saudi Arabia Office: AA53
Gas Chromatography (GC) Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11541 Saudi Arabia Office: AA53
Lecture- 08 Emission and absorption spectra
 Atomic and Molecular Absorption Spectrometry for Pollution Monitoring Dr. J R Mudakavi Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture- 08 Emission and absorption spectra
Atomic and Molecular Absorption Spectrometry for Pollution Monitoring Dr. J R Mudakavi Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture- 08 Emission and absorption spectra
10/2/2008. hc λ. νλ =c. proportional to frequency. Energy is inversely proportional to wavelength And is directly proportional to wavenumber
 CH217 Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry Module Leader: Dr. Alison Willows Electromagnetic spectrum Properties of electromagnetic radiation Many properties of electromagnetic radiation can be described
CH217 Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry Module Leader: Dr. Alison Willows Electromagnetic spectrum Properties of electromagnetic radiation Many properties of electromagnetic radiation can be described
1901 Application of Spectrophotometry
 1901 Application of Spectrophotometry Chemical Analysis Problem: 1 Application of Spectroscopy Organic Compounds Organic compounds with single bonds absorb in the UV region because electrons from single
1901 Application of Spectrophotometry Chemical Analysis Problem: 1 Application of Spectroscopy Organic Compounds Organic compounds with single bonds absorb in the UV region because electrons from single
Liquid storage: Holds the solvent which is going to act as the mobile phase. Pump: Pushes the solvent through to the column at high pressure.
 High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a much more sensitive and useful technique than paper and thin layer chromatography. The instrument used for HPLC is called a high performance liquid chromatograph.
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a much more sensitive and useful technique than paper and thin layer chromatography. The instrument used for HPLC is called a high performance liquid chromatograph.
Sampling for Gases and Vapors
 Sampling for Gases and Vapors EOH 466B Evaluating the Occupational Environment Spring 2008 Gases and Vapors Gases: don't exist in liquid state at STP e.g.: nitrous oxides, ozone, carbon monoxide Vapors:
Sampling for Gases and Vapors EOH 466B Evaluating the Occupational Environment Spring 2008 Gases and Vapors Gases: don't exist in liquid state at STP e.g.: nitrous oxides, ozone, carbon monoxide Vapors:
Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications
 Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications Bedanta Kr. Deka, D. Thakuria, H. Bora and S. Banerjee # Department of Physicis, B. Borooah College, Ulubari,
Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications Bedanta Kr. Deka, D. Thakuria, H. Bora and S. Banerjee # Department of Physicis, B. Borooah College, Ulubari,
1 WHAT IS SPECTROSCOPY?
 1 WHAT IS SPECTROSCOPY? 1.1 The Nature Of Electromagnetic Radiation Anyone who has been sunburnt will know that light packs a punch: in scientific terms, it contains considerable amounts of energy. All
1 WHAT IS SPECTROSCOPY? 1.1 The Nature Of Electromagnetic Radiation Anyone who has been sunburnt will know that light packs a punch: in scientific terms, it contains considerable amounts of energy. All
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices
 Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 17 Clinical Systems Today Week in PBS&D Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation Spectrophotometry Autoanalyzers Chromatology - Gas Chromatgraphs (Mass) Spectroscopy
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 17 Clinical Systems Today Week in PBS&D Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation Spectrophotometry Autoanalyzers Chromatology - Gas Chromatgraphs (Mass) Spectroscopy
M.Sc. (Final) DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER Second Year Chemistry Paper V ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY. PART A (4 10 = 40 marks)
 (DCHE 21) M.Sc. (Final) DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 2009. Second Year Chemistry Paper V ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY Time : Three hours Maximum : 100 marks PART A (4 10 = 40 marks) Answer any FOUR questions.
(DCHE 21) M.Sc. (Final) DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 2009. Second Year Chemistry Paper V ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY Time : Three hours Maximum : 100 marks PART A (4 10 = 40 marks) Answer any FOUR questions.
a. An emission line as close as possible to the analyte resonance line
 Practice Problem Set 5 Atomic Emission Spectroscopy 10-1 What is an internal standard and why is it used? An internal standard is a substance added to samples, blank, and standards. The ratio of the signal
Practice Problem Set 5 Atomic Emission Spectroscopy 10-1 What is an internal standard and why is it used? An internal standard is a substance added to samples, blank, and standards. The ratio of the signal
GC Instruments. GC Instruments - Sample Introduction
 GC Instruments 1 Fairly simple instrumentation Maintaining constant average pressure is important! Pressure controls flow rate T influences retention (k ) Flow rate monitoring Changing flow rate changes
GC Instruments 1 Fairly simple instrumentation Maintaining constant average pressure is important! Pressure controls flow rate T influences retention (k ) Flow rate monitoring Changing flow rate changes
Gas Chromatography (GC)! Environmental Organic Chemistry CEE-PUBH Analysis Topic 5
 Gas Chromatography (GC)! Environmental Organic Chemistry CEE-PUBH 5730-6730 Analysis Topic 5 Chromatography! Group of separation techniques based on partitioning (mobile phase/stationary phase). Two immiscible
Gas Chromatography (GC)! Environmental Organic Chemistry CEE-PUBH 5730-6730 Analysis Topic 5 Chromatography! Group of separation techniques based on partitioning (mobile phase/stationary phase). Two immiscible
高等食品分析 (Advanced Food Analysis) I. SPECTROSCOPIC METHODS *Instrumental methods: 1. Spectroscopic methods (spectroscopy): a) Electromagnetic radiation
 *Instrumental methods: 1. Spectroscopic methods (spectroscopy): a) Electromagnetic radiation (EMR): γ-ray emission X-Ray absorption, emission, fluorescence and diffraction Vacuum ultraviolet (UV) absorption
*Instrumental methods: 1. Spectroscopic methods (spectroscopy): a) Electromagnetic radiation (EMR): γ-ray emission X-Ray absorption, emission, fluorescence and diffraction Vacuum ultraviolet (UV) absorption
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR NOMENCLATURE OF MASS SPECTROMETRY
 international UNION OF PURE AND APPLIED CHEMISTRY ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY DIVISION COMMISSION ON ANALYTICAL NOMENCLATURE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR NOMENCLATURE OF MASS SPECTROMETRY RULES APPROVED 1973 LONDON BUTTER
international UNION OF PURE AND APPLIED CHEMISTRY ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY DIVISION COMMISSION ON ANALYTICAL NOMENCLATURE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR NOMENCLATURE OF MASS SPECTROMETRY RULES APPROVED 1973 LONDON BUTTER
PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION OF CHROMATOGRAPHY. Dr. P. Jayachandra Reddy Mpharm PhD Principal & professor KTPC
 PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION OF CHROMATOGRAPHY Dr. P. Jayachandra Reddy Mpharm PhD Principal & professor KTPC CHROMATOGRAPHY Laboratory technique for the Separation of mixtures Chroma -"color" and graphein
PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION OF CHROMATOGRAPHY Dr. P. Jayachandra Reddy Mpharm PhD Principal & professor KTPC CHROMATOGRAPHY Laboratory technique for the Separation of mixtures Chroma -"color" and graphein
 HPLC Workshop 16 June 2009 What does this do? Chromatography Theory Review Several chromatographic techniques Even though each method utilizes different techniques to separate compounds, the principles
HPLC Workshop 16 June 2009 What does this do? Chromatography Theory Review Several chromatographic techniques Even though each method utilizes different techniques to separate compounds, the principles
Far UV Absorbance Detector
 Far UV Absorbance Detector Theory Most organic and inorganic species absorb strongly in the far UV. Notable exceptions are the inert gases, helium and nitrogen which absorb very weakly in this region.
Far UV Absorbance Detector Theory Most organic and inorganic species absorb strongly in the far UV. Notable exceptions are the inert gases, helium and nitrogen which absorb very weakly in this region.
The Theory of HPLC. Quantitative and Qualitative HPLC
 The Theory of HPLC Quantitative and Qualitative HPLC i Wherever you see this symbol, it is important to access the on-line course as there is interactive material that cannot be fully shown in this reference
The Theory of HPLC Quantitative and Qualitative HPLC i Wherever you see this symbol, it is important to access the on-line course as there is interactive material that cannot be fully shown in this reference
Chromatography Lab # 4
 Chromatography Lab # 4 Chromatography is a method for separating mixtures based on differences in the speed at which they migrate over or through a stationary phase which means that a complex mixture will
Chromatography Lab # 4 Chromatography is a method for separating mixtures based on differences in the speed at which they migrate over or through a stationary phase which means that a complex mixture will
Harris: Quantitative Chemical Analysis, Eight Edition
 Harris: Quantitative Chemical Analysis, Eight Edition CHAPTER 21: MASS SPECTROMETRY CHAPTER 21: Opener 21.0 Mass Spectrometry Mass Spectrometry provides information about 1) The elemental composition of
Harris: Quantitative Chemical Analysis, Eight Edition CHAPTER 21: MASS SPECTROMETRY CHAPTER 21: Opener 21.0 Mass Spectrometry Mass Spectrometry provides information about 1) The elemental composition of
Chemistry 311: Instrumentation Analysis Topic 2: Atomic Spectroscopy. Chemistry 311: Instrumentation Analysis Topic 2: Atomic Spectroscopy
 Topic 1: Atomic Spectroscopy Text: Chapter 12,13 & 14 Rouessac (~2 weeks) 1.0 Review basic concepts in Spectroscopy 2.0 Atomic Absorption and Graphite Furnace Instruments 3.0 Inductively Coupled Plasmas
Topic 1: Atomic Spectroscopy Text: Chapter 12,13 & 14 Rouessac (~2 weeks) 1.0 Review basic concepts in Spectroscopy 2.0 Atomic Absorption and Graphite Furnace Instruments 3.0 Inductively Coupled Plasmas
Gaseous CEMS technology
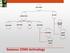 GAS CEMS EXTRACTIVE IN-SITU COLD DRY HOT WET DRY DILUTION PROBE/ POINT IN-STACK CROSS STACK OUT OF STACK Gaseous CEMS technology Probe (at stack) Heated filter Heated sample line Condenser Pump Analyzers
GAS CEMS EXTRACTIVE IN-SITU COLD DRY HOT WET DRY DILUTION PROBE/ POINT IN-STACK CROSS STACK OUT OF STACK Gaseous CEMS technology Probe (at stack) Heated filter Heated sample line Condenser Pump Analyzers
ii) Describe the various types of detectors used in IR spectroscopy.
 (DCHE 21) ASSIGNMENT - 1, DEC - 2014. PAPER - V : ANALYTICAL 1) Describe a method for the determination of manganese in complex matrices. 2) Describe the instrumentation and working principles of IR. 3)
(DCHE 21) ASSIGNMENT - 1, DEC - 2014. PAPER - V : ANALYTICAL 1) Describe a method for the determination of manganese in complex matrices. 2) Describe the instrumentation and working principles of IR. 3)
AQA Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods
 Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods General Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation (EM) Wave Properties of EM Quantum Mechanical Properties of EM Quantitative Aspects of Spectrochemical
Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods General Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation (EM) Wave Properties of EM Quantum Mechanical Properties of EM Quantitative Aspects of Spectrochemical
(DCHE21) ASSIGNMENT - 1 M.Sc. (Second) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2019 Second Year CHEMISTRY Analytical Chemistry MAXIMUM : 30 MARKS ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS
 ASSIGNMENT - 1 Analytical Chemistry (DCHE21) Q1) State and explain Beer s Law mention its limitations. Q2) Write the basic instrumentation, principle and applications of nephelometry. Q3) Define Fluorescence
ASSIGNMENT - 1 Analytical Chemistry (DCHE21) Q1) State and explain Beer s Law mention its limitations. Q2) Write the basic instrumentation, principle and applications of nephelometry. Q3) Define Fluorescence
Gas Chromatography. Introduction
 Gas Chromatography Introduction 1.) Gas Chromatography Mobile phase (carrier gas) is a gas - Usually N 2, He, Ar and maybe H 2 - Mobile phase in liquid chromatography is a liquid Requires analyte to be
Gas Chromatography Introduction 1.) Gas Chromatography Mobile phase (carrier gas) is a gas - Usually N 2, He, Ar and maybe H 2 - Mobile phase in liquid chromatography is a liquid Requires analyte to be
Secondary Ion Mass Spectroscopy (SIMS)
 Secondary Ion Mass Spectroscopy (SIMS) Analyzing Inorganic Solids * = under special conditions ** = semiconductors only + = limited number of elements or groups Analyzing Organic Solids * = under special
Secondary Ion Mass Spectroscopy (SIMS) Analyzing Inorganic Solids * = under special conditions ** = semiconductors only + = limited number of elements or groups Analyzing Organic Solids * = under special
Lecture 15: Introduction to mass spectrometry-i
 Lecture 15: Introduction to mass spectrometry-i Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that measures the mass/charge ratio of charged particles in vacuum. Mass spectrometry can determine masse/charge
Lecture 15: Introduction to mass spectrometry-i Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that measures the mass/charge ratio of charged particles in vacuum. Mass spectrometry can determine masse/charge
Chromatography and other Separation Methods
 Chromatography and other Separation Methods Probably the most powerful class of modern analytical methods for analyzing mixture of components---and even for detecting a single component in a complex mixture!
Chromatography and other Separation Methods Probably the most powerful class of modern analytical methods for analyzing mixture of components---and even for detecting a single component in a complex mixture!
Spectroscopy: Introduction. Required reading Chapter 18 (pages ) Chapter 20 (pages )
 Spectroscopy: Introduction Required reading Chapter 18 (pages 378-397) Chapter 20 (pages 424-449) Spectrophotometry is any procedure that uses light to measure chemical concentrations Properties of Light
Spectroscopy: Introduction Required reading Chapter 18 (pages 378-397) Chapter 20 (pages 424-449) Spectrophotometry is any procedure that uses light to measure chemical concentrations Properties of Light
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Reprinted from February Hydrocarbon
 February2012 When speed matters Loek van Eijck, Yokogawa, The Netherlands, questions whether rapid analysis of gases and liquids can be better achieved through use of a gas chromatograph or near infrared
February2012 When speed matters Loek van Eijck, Yokogawa, The Netherlands, questions whether rapid analysis of gases and liquids can be better achieved through use of a gas chromatograph or near infrared
UNIT 4 Part 2 Measurements of Environmental Air Pollution Parameters j
 UNIT 4 Part 2 Measurements of Environmental Air Pollution Parameters j 1 Environmental Air Pollution The addition of any harmful material (having harmful effects on our lives) to our atmosphere is called
UNIT 4 Part 2 Measurements of Environmental Air Pollution Parameters j 1 Environmental Air Pollution The addition of any harmful material (having harmful effects on our lives) to our atmosphere is called
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan
 YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
Section 7. Temperature Measurement
 Section 7 Temperature Measurement 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 1 Working Definition Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules that make of a substance. After time,
Section 7 Temperature Measurement 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 1 Working Definition Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules that make of a substance. After time,
Chapter 12 Mass Spectrometry and Infrared Spectroscopy
 Organic Chemistry, 6 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 12 Mass Spectrometry and Infrared Spectroscopy Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District 2006, Prentice
Organic Chemistry, 6 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 12 Mass Spectrometry and Infrared Spectroscopy Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District 2006, Prentice
Physical Science DCI Progression Chart
 DCI Progression Chart PS1: Matter and Its Interactions Grade Bands PS1.A Structure & Properties of Matter Grades K-2 Grades 3-5 Grades 6-8 Grades 9-12 Second Grade * Different kinds of matter exist and
DCI Progression Chart PS1: Matter and Its Interactions Grade Bands PS1.A Structure & Properties of Matter Grades K-2 Grades 3-5 Grades 6-8 Grades 9-12 Second Grade * Different kinds of matter exist and
Spectrophotometry. Dr. Shareef SHAIK ASST. PROFESSOR Pharmacology
 Spectrophotometry Dr. Shareef SHAIK ASST. PROFESSOR Pharmacology Content Introduction Beer-Lambert law Instrument Applications Introduction 3 Body fluids such as blood, csf and urine contain organic and
Spectrophotometry Dr. Shareef SHAIK ASST. PROFESSOR Pharmacology Content Introduction Beer-Lambert law Instrument Applications Introduction 3 Body fluids such as blood, csf and urine contain organic and
Chapter 1. Chromatography. Abdul Muttaleb Jaber
 Chapter 1 Chromatography Abdul Muttaleb Jaber What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a physico-chemical process that belongs to fractionation methods same as distillation, crystallization or fractionated
Chapter 1 Chromatography Abdul Muttaleb Jaber What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a physico-chemical process that belongs to fractionation methods same as distillation, crystallization or fractionated
CHEM*3440. Photon Energy Units. Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation. Chemical Instrumentation. Spectroscopic Experimental Concept.
 Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation is light. Different energy light interacts with different motions in molecules. CHEM*344 Chemical Instrumentation Topic 7 Spectrometry Radiofrequency
Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation is light. Different energy light interacts with different motions in molecules. CHEM*344 Chemical Instrumentation Topic 7 Spectrometry Radiofrequency
Principles of Gas- Chromatography (GC)
 Principles of Gas- Chromatography (GC) Mohammed N. Sabir January 2017 10-Jan-17 1 GC is a chromatographic technique utilizes gas as the mobile phase which is usually an inert gas (Hydrogen, Helium, Nitrogen
Principles of Gas- Chromatography (GC) Mohammed N. Sabir January 2017 10-Jan-17 1 GC is a chromatographic technique utilizes gas as the mobile phase which is usually an inert gas (Hydrogen, Helium, Nitrogen
Physical Separations and Chromatography
 Lab #5A & B: Physical Separations and Chromatography Individual Objectives: At the end of these experiments you should be able to: Ø Distinguish between Rf and tr; chromatograph and chromatogram; adsorption
Lab #5A & B: Physical Separations and Chromatography Individual Objectives: At the end of these experiments you should be able to: Ø Distinguish between Rf and tr; chromatograph and chromatogram; adsorption
Electron Spin Resonance, Basic principle of NMR, Application of NMR in the study of Biomolecules, NMR imaging and in vivo NMR spectromicroscopy
 Electron Spin Resonance, Basic principle of NMR, Application of NMR in the study of Biomolecules, NMR imaging and in vivo NMR spectromicroscopy Mitesh Shrestha Electron Spin Resonance Electron paramagnetic
Electron Spin Resonance, Basic principle of NMR, Application of NMR in the study of Biomolecules, NMR imaging and in vivo NMR spectromicroscopy Mitesh Shrestha Electron Spin Resonance Electron paramagnetic
FTIR measurement of NH 3, HCN, SO 2, H 2 S and COS in pulverized lignite oxy-fuel flames Daniel Fleig, Stefan Hjärtstam and Daniel Kühnemuth
 FTIR measurement of NH 3, HCN, SO 2, H 2 S and COS in pulverized lignite oxy-fuel flames Daniel Fleig, Stefan Hjärtstam and Daniel Kühnemuth Abstract Nitrogen and sulphur compounds are investigated in
FTIR measurement of NH 3, HCN, SO 2, H 2 S and COS in pulverized lignite oxy-fuel flames Daniel Fleig, Stefan Hjärtstam and Daniel Kühnemuth Abstract Nitrogen and sulphur compounds are investigated in
