Class 21: Anisotropy and Periodic Potential in a Solid
|
|
|
- Howard Osborne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Class 21: Anisotropy and Periodic Potential in a Solid In the progress made so far in trying to build a model for the properties displayed by materials, an underlying theme is that we wish to build the simplest model that we can get away with. This is the reason we examined the Drude model, which is very simple, but still makes good predictions. However, we have been able to identify its limitations as well. It is worth noting that in the approach we have taken so far, we typically start by assuming that the system follows specific rules and then build equations consistent with these rules. In this process, the equations are typically correct within the context of the rules assumed, and hence when the predictions do not turn out to be accurate, it is not the equations, but the rules themselves, that need to be reexamined. In other words, the rules chosen for the system, are themselves not appropriate for the system, and hence need to be modified. It is in this vein that the Drude-Sommerfeld model, differs from the Classical Drude model. The Drude Sommerfeld model relinquishes the assumption of classical behavior of the electrons and imposes the assumption of quantum mechanical behavior of electrons, thereby changing the rules for the system. The new rules result in improved predictions. In the further refinements that we will make as we proceed, the overall approach will be the same. Limitations of models that we will try to overcome will come about due to changes or modifications in the rules we will expect the system to obey, and hence equations that will result, will differ. We note that the Drude-Somerfeld model is still a free electron model. There is no variation in the potential experienced by electrons in the solid as they traverse the extent of the solid. The justification for this assumption is that all of the negative charges in the solid, from the free electron cloud, will be neutralized by all of the positive charges in the solid, from the ionic cores, since the solid is charge neutral. Therefore the free electron model is not unreasonable at first glance. However, it is also true, that while the overall material is charge neutral, the positive and negative charges are not distributed uniformly across the extent of the solid, when examined at an atomic level. The ionic cores occupy specific locations within the solid, and their influence is more strongly prevalent in the vicinity of their locations. Therefore, when an electron moves through the solid, although the solid is charge neutral from an overall perspective, the potential the electron experiences is a very strong function of its position i.e., a flat uniform potential is far from reality. Having recognized that the flat potential model is too simplistic, it is also of interest to identify specific aspects of material properties that the Drude-Sommerfeld model may not be in a position to address. Perhaps the most prominent aspect of material properties that cannot be addressed by the Drude-Sommerfeld model in its present form is the anisotropy, or dependence on direction, in properties displayed by most materials. Let us briefly examine how anisotropy manifests itself in material properties, and why we may not always notice it, even though the material is inherently anisotropic.
2 Consider the samples shown in Figure 21.1 below: Figure21.1: a) A single crystal; b) A polycrystal with large crystal sizes; c) A polycrystal with very small crystal sizes. The lines and shading within the crystals are representative of crystal planes. The direction of the lines is representative of the orientation of the crystal planes. In a single crystal, shown in Figure 21.1a, the atoms are in perfect crystallographic order from one end of the sample to the other. Therefore each direction in the sample that is a single crystal, represents a specific order of atoms and atomic planes. Therefore, a single crystal sample typically shows strong directionality, or anisotropy, in its properties. The sample properties represent inherent material properties.
3 In a polycrystal with large crystal sizes as shown in Figure 21.1b, assuming that the crystals are randomly oriented, there is an increased chance that the sample properties are averaged versions of the material properties across a few different directions. The same sample direction will likely be different crystallographic directions in each of the crystals. Therefore the overall property displayed in a given direction by the sample, will have contributions from different crystallographic directions from each of the crystals making up the sample. In a polycrystal with very small crystal sizes as shown in Figure 21.1c, assuming that the crystals are randomly oriented, the sample properties will necessarily be averaged versions of the material properties across many different crystallographic directions. This averaging is a direct result of the fact that a given direction in the sample, will have contributions from a very large number of crystallographic directions corresponding to the many randomly oriented crystals making up the sample. So while Figure 21.1a results in the display of material properties during measurements, Figures 21.1b and 21.1c progressively result in the display of sample properties rather than the inherent material properties during measurements. While the sample properties do originate from the inherent material properties, averaging of the properties due to the polycrystalline nature of the samples, masks details of the directionality of the inherent material properties. The sample may be isotropic while the material itself is anisotropic. A classic example of a material that shows significant anisotropy, is graphite. Figure 21.2 below shows the layered structure of graphite.
4 Figure 21.2: The layered structure of graphite. Graphite displays poor electronic conductivity perpendicular to the sheets of carbon atoms, and excellent electronic conductivity parallel to the sheets of carbon atoms. Graphite has excellent electronic conductivity parallel to the sheets of graphite, and very poor conductivity perpendicular to the sheets. There is nothing in the Drude-Sommerfeld model to suggest anisotropy. The model assumes a uniform field within the material and ignores the ionic arrangements. The model has therefore effectively enforced isotropy. The model assumes isotropy, therefore the results are isotropic. Therefore there is a need to develop a better picture of the potential an electron experiences as it travels through the solid. In other words we need to incorporate into the model the dependence of potential on the position of the electron. Let us first consider a single ionic core and examine the potential the electron experiences as it moves from infinity, towards the ionic core. The energy, or potential, due to the coulombic force
5 of attraction between the negatively charged electron and the positively charged ionic core is given by the expression: Where is the permittivity of free space, is the charge of the electron, and is the distance between the electron and the ionic core. The electron will experience the above potential as a function of position, regardless of the direction from which it approaches the ionic core. For simplicities sake a one dimensional example is taken and the potential experienced by the electron as a function of position, as it approaches the ionic core from the positive x direction and the negative x direction, is shown in Figure 21.3 below. Figure 21.3: A one dimensional example of potential experienced by an electron, as a function of position with respect to an ionic core. In reality, if the electron gets extremely close to the ionic core, it will start interacting with the electron cloud around the ionic core and a repulsive force will result. For the purposes of the present discussion, this repulsive interaction is being ignored based on the idea that only free electrons are being examined and hence they can be expected to not get very close to any particular ionic core. If we extend the above analysis to a one dimensional lattice, with regularly spaced ionic cores, we can expect the interaction of the electron with each of the ionic cores to be identical to that
6 described above for the single ionic core. Figure 21.4a shows the interaction of the electron with each individual ionic core, neglecting the influence of the remaining ionic cores on the electron. Figure 21.4: The potential experienced by an electron, as a function of position with respect to a one dimensional lattice of uniformly spaced ionic cores; a) interaction with each ionic core, ignoring the impact of the other ionic cores; b) interaction with the lattice as a whole In reality, since the ionic cores are relatively close to each other, as the electron moves from left to right in the figure above, it will begin to experience the presence of each succeeding ionic core, before it has fully escaped from the influence of the preceding ionic core. The interaction of the electron with the one dimensional lattice as a whole is shown in Figure 21.4b above.
7 The steep fall in potential close to each ionic core, is called a potential well. As seen from Figure 21.4 above, the potential inside a solid is not constant or flat. It is therefore necessary to build enough detail into the model to incorporate the potential experienced by an electron as a function of position in the one dimensional lattice. However, it turns out that while it is important to capture the reality of potential wells in the model, it is not necessary to immediately focus on the exact shape of the curve associated with the formation of the potential well. It will be adequate if we can make a reasonable approximation of the potential landscape experienced by an electron in the solid. The approximation we make should capture enough detail of the reality of the situation while minimizing the associated complexity. Figure 21.5 below represents an approximation of the potential landscape experienced by an electron in a one dimensional solid. Figure 21.5: An approximation of the potential landscape experienced by an electron, moving along the x-direction, due to the presence of a one dimensional solid which is also aligned along the x-direction. The primary features of the above approximation are as follows: When the electron is very far from the one dimensional solid, it experiences zero potential due to lack of interaction with the solid. This is true on either side of this hypothetical one dimensional solid. This situation represents the electron having completely escaped from the solid, such as in the case of a photo electron. Such an electron is a truly free electron.
8 As the electron gets closer to the solid, it experiences a slight drop in potential due to its interaction with the overall solid. This situation represents the electron being confined to the solid, but not attached to any specific ionic core. Such electrons are nearly free electrons, and are the electrons that participate in the electronic conductivity process since they are free to roam through the solid. The free electron gas of the Drude model also referred to these nearly free electrons only. When the electron gets very close to an ionic core, it experiences a very sharp drop in potential. The electrons trapped in this deep potential well represent bound electrons. These are electrons which are confined to each individual ionic core. In a typical metallic solid, these represent the majority of the electrons, but they do not contribute to the electronic conductivity of the solid since they are unable to move through the solid. In the approximation above, the curves corresponding to the actual potential experienced by the electron, have been approximated to straight lines. This approximation results in the potential wells becoming square potential wells (in view of their rectangular shape), and makes subsequent calculations simpler. It will be necessary to judge at a later stage if this approximation is reasonable. In the next class we will examine more features of the above picture and see how it relates to parameters we have discussed so far such as the Fermi energy and the work function of the solid.
ATOMIC BONDING Atomic Bonding
 ATOMIC BONDING Atomic Bonding Primary Bonds Secondary Bonds Ionic Covalent Metallic van der Waals 1. IONIC BONDING q 11 Na & 17 Cl These two ions are attracted to eachother by the electrostatic force developed
ATOMIC BONDING Atomic Bonding Primary Bonds Secondary Bonds Ionic Covalent Metallic van der Waals 1. IONIC BONDING q 11 Na & 17 Cl These two ions are attracted to eachother by the electrostatic force developed
Mid 1800s. 1930s. Prediction of new materials using computers (Late 1990s) Quantum Mechanics. Newtonian Mechanics
 Structure of an atom: Agreed upon by experimentalists and theoreticians. Today s knowledge of an atom comes from meetings like 1 Mid 1800s 1930s From F = m x a Newtonian Mechanics to E=ħxω Quantum Mechanics
Structure of an atom: Agreed upon by experimentalists and theoreticians. Today s knowledge of an atom comes from meetings like 1 Mid 1800s 1930s From F = m x a Newtonian Mechanics to E=ħxω Quantum Mechanics
Sommerfeld-Drude model. Ground state of ideal electron gas
 Sommerfeld-Drude model Recap of Drude model: 1. Treated electrons as free particles moving in a constant potential background. 2. Treated electrons as identical and distinguishable. 3. Applied classical
Sommerfeld-Drude model Recap of Drude model: 1. Treated electrons as free particles moving in a constant potential background. 2. Treated electrons as identical and distinguishable. 3. Applied classical
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 10 The Free Electron Theory of Metals - Electrical Conductivity (Refer Slide Time: 00:20)
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 10 The Free Electron Theory of Metals - Electrical Conductivity (Refer Slide Time: 00:20)
, (1) e i = ˆσ 1 h ii. c 2016, Jeffrey S. Simonoff 1
 Regression diagnostics As is true of all statistical methodologies, linear regression analysis can be a very effective way to model data, as along as the assumptions being made are true. For the regression
Regression diagnostics As is true of all statistical methodologies, linear regression analysis can be a very effective way to model data, as along as the assumptions being made are true. For the regression
with a proper choice of the potential U(r). Clearly, we should include the potential of the ions, U ion (r):.
 The Hartree Equations So far we have ignored the effects of electron-electron (e-e) interactions by working in the independent electron approximation. In this lecture, we shall discuss how this effect
The Hartree Equations So far we have ignored the effects of electron-electron (e-e) interactions by working in the independent electron approximation. In this lecture, we shall discuss how this effect
ELECTROSTATICS. kq q SUPERPOSITION
 ELECTROSTATICS As seen in class, we observe both attractive and repulsive forces. This requires at least two kinds of charge. Although more is possible we choose the simplest explanation consistent with
ELECTROSTATICS As seen in class, we observe both attractive and repulsive forces. This requires at least two kinds of charge. Although more is possible we choose the simplest explanation consistent with
ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS
 CHATER 18 ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS CONCETUAL QUESTIONS 1. REASONING AND SOLUTION In Figure 18.9, the grounding wire is removed first, followed by the rod, and the sphere is left with a positive
CHATER 18 ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS CONCETUAL QUESTIONS 1. REASONING AND SOLUTION In Figure 18.9, the grounding wire is removed first, followed by the rod, and the sphere is left with a positive
Solid State Physics FREE ELECTRON MODEL. Lecture 14. A.H. Harker. Physics and Astronomy UCL
 Solid State Physics FREE ELECTRON MODEL Lecture 14 A.H. Harker Physics and Astronomy UCL 6 The Free Electron Model 6.1 Basic Assumptions In the free electron model, we assume that the valence electrons
Solid State Physics FREE ELECTRON MODEL Lecture 14 A.H. Harker Physics and Astronomy UCL 6 The Free Electron Model 6.1 Basic Assumptions In the free electron model, we assume that the valence electrons
Class 27: Reciprocal Space 1: Introduction to Reciprocal Space
 Class 27: Reciprocal Space 1: Introduction to Reciprocal Space Many properties of solid materials stem from the fact that they have periodic internal structures. Electronic properties are no exception.
Class 27: Reciprocal Space 1: Introduction to Reciprocal Space Many properties of solid materials stem from the fact that they have periodic internal structures. Electronic properties are no exception.
Class 24: Density of States
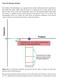 Class 24: Density of States The solution to the Schrödinger wave equation showed us that confinement leads to quantization. The smaller the region within which the electron is confined, the more widely
Class 24: Density of States The solution to the Schrödinger wave equation showed us that confinement leads to quantization. The smaller the region within which the electron is confined, the more widely
Coulomb s Law. Phys102 Lecture 2. Key Points. Coulomb s Law The electric field (E is a vector!) References
 Phys102 Lecture 2 Phys102 Lecture 2-1 Coulomb s Law Key Points Coulomb s Law The electric field (E is a vector!) References SFU Ed: 21-5,6,7,8,9,10. 6 th Ed: 16-6,7,8,9,+. Phys102 Lecture 2 Phys102 Lecture
Phys102 Lecture 2 Phys102 Lecture 2-1 Coulomb s Law Key Points Coulomb s Law The electric field (E is a vector!) References SFU Ed: 21-5,6,7,8,9,10. 6 th Ed: 16-6,7,8,9,+. Phys102 Lecture 2 Phys102 Lecture
Electromagnetism II. Instructor: Andrei Sirenko Spring 2013 Thursdays 1 pm 4 pm. Spring 2013, NJIT 1
 Electromagnetism II Instructor: Andrei Sirenko sirenko@njit.edu Spring 013 Thursdays 1 pm 4 pm Spring 013, NJIT 1 PROBLEMS for CH. 6 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/phys433/phys433eandm013.htm Can obtain
Electromagnetism II Instructor: Andrei Sirenko sirenko@njit.edu Spring 013 Thursdays 1 pm 4 pm Spring 013, NJIT 1 PROBLEMS for CH. 6 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/phys433/phys433eandm013.htm Can obtain
Unit III Free Electron Theory Engineering Physics
 . Introduction The electron theory of metals aims to explain the structure and properties of solids through their electronic structure. The electron theory is applicable to all solids i.e., both metals
. Introduction The electron theory of metals aims to explain the structure and properties of solids through their electronic structure. The electron theory is applicable to all solids i.e., both metals
Potential & Potential Energy
 Potential & Potential Energy Lecture 10: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Electrostatic Boundary Conditions : We had seen that electric field has a discontinuity
Potential & Potential Energy Lecture 10: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Electrostatic Boundary Conditions : We had seen that electric field has a discontinuity
Coulombs Law and Electric Field Intensity
 Coulombs Law and Electric Field Intensity 2.1 Coulomb s law Coulomb stated that the force between two very small objects separated in a vacuum or free space by a distance, which is large compared to their
Coulombs Law and Electric Field Intensity 2.1 Coulomb s law Coulomb stated that the force between two very small objects separated in a vacuum or free space by a distance, which is large compared to their
Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 21 Central Potential and Central Force Ready now to take up the idea
Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 21 Central Potential and Central Force Ready now to take up the idea
Atomic Structure. Niels Bohr Nature, March 24, 1921
 1 of 5 4/26/2013 12:47 AM Atomic Structure Niels Bohr Nature, March 24, 1921 In a letter to NATURE of November 25 last Dr. Norman Campbell discusses the problem of the possible consistency of the assumptions
1 of 5 4/26/2013 12:47 AM Atomic Structure Niels Bohr Nature, March 24, 1921 In a letter to NATURE of November 25 last Dr. Norman Campbell discusses the problem of the possible consistency of the assumptions
Electrostatics. Typeset by FoilTEX 1
 Electrostatics Typeset by FoilTEX 1 Question 1 A plastic rod is rubbed and touched to a small metal ball. After this the rod is observed to repel the ball. Which of the following is correct? 1. The force
Electrostatics Typeset by FoilTEX 1 Question 1 A plastic rod is rubbed and touched to a small metal ball. After this the rod is observed to repel the ball. Which of the following is correct? 1. The force
Chapter 6 Free Electron Fermi Gas
 Chapter 6 Free Electron Fermi Gas Free electron model: The valence electrons of the constituent atoms become conduction electrons and move about freely through the volume of the metal. The simplest metals
Chapter 6 Free Electron Fermi Gas Free electron model: The valence electrons of the constituent atoms become conduction electrons and move about freely through the volume of the metal. The simplest metals
Condensed matter theory Lecture notes and problem sets 2012/2013
 Condensed matter theory Lecture notes and problem sets 2012/2013 Dmitri Ivanov Recommended books and lecture notes: [AM] N. W. Ashcroft and N. D. Mermin, Solid State Physics. [Mar] M. P. Marder, Condensed
Condensed matter theory Lecture notes and problem sets 2012/2013 Dmitri Ivanov Recommended books and lecture notes: [AM] N. W. Ashcroft and N. D. Mermin, Solid State Physics. [Mar] M. P. Marder, Condensed
Quantum Percolation: Electrons in a Maze. Brianna Dillon-Thomas, PhD 2016
 Quantum Percolation: Electrons in a Maze Brianna Dillon-Thomas, PhD 2016 Physicists, especially theoretical physicists, love to make models of the world to help us understand it. We weigh various effects
Quantum Percolation: Electrons in a Maze Brianna Dillon-Thomas, PhD 2016 Physicists, especially theoretical physicists, love to make models of the world to help us understand it. We weigh various effects
Chapter 1 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields
 Chapter 1 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields 1 Units of Chapter 1 Electric Charge Insulators and Conductors Coulomb s Law The Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric Fields Generated by simple distributions
Chapter 1 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields 1 Units of Chapter 1 Electric Charge Insulators and Conductors Coulomb s Law The Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric Fields Generated by simple distributions
2 The Electric Field: Description and Effect
 Chapter 2 The lectric Field: Description and ffect 2 The lectric Field: Description and ffect An electric field is an invisible entity 1 which exists in the region around a charged particle. It is caused
Chapter 2 The lectric Field: Description and ffect 2 The lectric Field: Description and ffect An electric field is an invisible entity 1 which exists in the region around a charged particle. It is caused
Ohm s Law. R = L ρ, (2)
 Ohm s Law Ohm s Law which is perhaps the best known law in all of Physics applies to most conducting bodies regardless if they conduct electricity well or poorly, or even so poorly they are called insulators.
Ohm s Law Ohm s Law which is perhaps the best known law in all of Physics applies to most conducting bodies regardless if they conduct electricity well or poorly, or even so poorly they are called insulators.
Modeling of Anisotropic Polymers during Extrusion
 Modeling of Anisotropic Polymers during Extrusion Modified on Friday, 01 May 2015 10:38 PM by mpieler Categorized as: Paper of the Month Modeling of Anisotropic Polymers during Extrusion Arash Ahmadzadegan,
Modeling of Anisotropic Polymers during Extrusion Modified on Friday, 01 May 2015 10:38 PM by mpieler Categorized as: Paper of the Month Modeling of Anisotropic Polymers during Extrusion Arash Ahmadzadegan,
Lesson 5 Representing Fields Geometrically
 Lesson 5 Representing Fields Geometrically Lawrence B. Rees 27. You may make a single copy of this document for personal use without written permission. 5. Introduction In Lesson 3 we introduced the idea
Lesson 5 Representing Fields Geometrically Lawrence B. Rees 27. You may make a single copy of this document for personal use without written permission. 5. Introduction In Lesson 3 we introduced the idea
Chapter 9: Statistical Mechanics
 Chapter 9: Statistical Mechanics Chapter 9: Statistical Mechanics...111 9.1 Introduction...111 9.2 Statistical Mechanics...113 9.2.1 The Hamiltonian...113 9.2.2 Phase Space...114 9.2.3 Trajectories and
Chapter 9: Statistical Mechanics Chapter 9: Statistical Mechanics...111 9.1 Introduction...111 9.2 Statistical Mechanics...113 9.2.1 The Hamiltonian...113 9.2.2 Phase Space...114 9.2.3 Trajectories and
THE HELIUM ATOM: AN INTUITIVE APPROACH
 MISN-0-247 THE HELIUM ATOM: AN INTUITIVE APPROACH THE HELIUM ATOM: AN INTUITIVE APPROACH by E. H. Carlson 1. Introduction.............................................. 1 2. The Size of the Atom....................................
MISN-0-247 THE HELIUM ATOM: AN INTUITIVE APPROACH THE HELIUM ATOM: AN INTUITIVE APPROACH by E. H. Carlson 1. Introduction.............................................. 1 2. The Size of the Atom....................................
Everything starts with atomic structure and bonding
 Everything starts with atomic structure and bonding not all energy values can be possessed by electrons; e- have discrete energy values we call energy levels or states. The energy values are quantized
Everything starts with atomic structure and bonding not all energy values can be possessed by electrons; e- have discrete energy values we call energy levels or states. The energy values are quantized
Physical Properties Explained (hopefully)
 Physical Properties Explained (hopefully) Melting and Boiling Points: in order to melt or boil a compound, the solid form of the compound must be broken up into small particles what these particles are,
Physical Properties Explained (hopefully) Melting and Boiling Points: in order to melt or boil a compound, the solid form of the compound must be broken up into small particles what these particles are,
Chapter 14: Electric Fields and Matter
 Chapter 14: Electric Fields and Matter We extend the concepts of charge and electric fields due to point particles (and dipoles) to macroscopic objects In terms of their response to electric fields, we
Chapter 14: Electric Fields and Matter We extend the concepts of charge and electric fields due to point particles (and dipoles) to macroscopic objects In terms of their response to electric fields, we
Ch. 12 Section 1: Introduction to Chemical Bonding
 Name Period Date Chemical Bonding & Intermolecular Forces (Chapter 12, 13 &14) Fill-in the blanks during the PowerPoint presentation in class. Ch. 12 Section 1: Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical
Name Period Date Chemical Bonding & Intermolecular Forces (Chapter 12, 13 &14) Fill-in the blanks during the PowerPoint presentation in class. Ch. 12 Section 1: Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical
(D) Blv/R Counterclockwise
 1. There is a counterclockwise current I in a circular loop of wire situated in an external magnetic field directed out of the page as shown above. The effect of the forces that act on this current is
1. There is a counterclockwise current I in a circular loop of wire situated in an external magnetic field directed out of the page as shown above. The effect of the forces that act on this current is
PHYS102 - Gauss s Law.
 PHYS102 - Gauss s Law. Dr. Suess February 2, 2007 PRS Questions 2 Question #1.............................................................................. 2 Answer to Question #1......................................................................
PHYS102 - Gauss s Law. Dr. Suess February 2, 2007 PRS Questions 2 Question #1.............................................................................. 2 Answer to Question #1......................................................................
Physics 22: Homework 1
 Physics 22: Homework 1 The following problems encompass the topics of charge, as well as electrostatic forces, torques, and fields. 1. What is the total charge of all the electrons in 1.2 mol of diatomic
Physics 22: Homework 1 The following problems encompass the topics of charge, as well as electrostatic forces, torques, and fields. 1. What is the total charge of all the electrons in 1.2 mol of diatomic
Figure I. A. Look at the atomic sizes shown in the table and describe all the trends that you see in the space below.
 Question: How do we use the model of the electronic structure of the atom to understand periodic trends of the elements? I. Data Collection Using a web browser access the following address: http://www.chem.iastate.edu/group/greenbowe/sections/projectfolder/flashfiles/matters/periodictbl2.html
Question: How do we use the model of the electronic structure of the atom to understand periodic trends of the elements? I. Data Collection Using a web browser access the following address: http://www.chem.iastate.edu/group/greenbowe/sections/projectfolder/flashfiles/matters/periodictbl2.html
Electric Field Intensity
 Electric Field Intensity Every charged object creates an electric field of force in the space around it. Any other charged object in that space will experience a force of attraction or repulsion from the
Electric Field Intensity Every charged object creates an electric field of force in the space around it. Any other charged object in that space will experience a force of attraction or repulsion from the
Welcome to the Solid State
 Max Planck Institut für Mathematik Bonn 19 October 2015 The What 1700s 1900s Since 2005 Electrical forms of matter: conductors & insulators superconductors (& semimetals & semiconductors) topological insulators...
Max Planck Institut für Mathematik Bonn 19 October 2015 The What 1700s 1900s Since 2005 Electrical forms of matter: conductors & insulators superconductors (& semimetals & semiconductors) topological insulators...
LAST NAME FIRST NAME DATE
 LAST NAME FIRST NAME DATE CJ - Assignment 1 18.1 The Origin of Electricity 18.2 Charged Objects & the Electric Force 18.3 Conductors & Insulators 18.4 Charging by Contact & by Induction Conceptual Question
LAST NAME FIRST NAME DATE CJ - Assignment 1 18.1 The Origin of Electricity 18.2 Charged Objects & the Electric Force 18.3 Conductors & Insulators 18.4 Charging by Contact & by Induction Conceptual Question
Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 1.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Introduction to
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 1.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Introduction to
Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules
 Chem 220 Notes Page 1 Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules I. Types of Chemical Bonds A. Why do atoms forms bonds? Atoms want to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas atom (noble
Chem 220 Notes Page 1 Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules I. Types of Chemical Bonds A. Why do atoms forms bonds? Atoms want to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas atom (noble
Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding
 Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding Chapter Outline Review of Atomic Structure Atomic Bonding Atomic Structure Atoms are the smallest structural units of all solids, liquids & gases. Atom: The smallest
Atomic Structure & Interatomic Bonding Chapter Outline Review of Atomic Structure Atomic Bonding Atomic Structure Atoms are the smallest structural units of all solids, liquids & gases. Atom: The smallest
8 Wavefunctions - Schrödinger s Equation
 8 Wavefunctions - Schrödinger s Equation So far we have considered only free particles - i.e. particles whose energy consists entirely of its kinetic energy. In general, however, a particle moves under
8 Wavefunctions - Schrödinger s Equation So far we have considered only free particles - i.e. particles whose energy consists entirely of its kinetic energy. In general, however, a particle moves under
3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry. Lecture Notes No. 6a BONDING AND SURFACES
 3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 6a BONDING AND SURFACES 1. INTRODUCTION Surfaces have increasing importance in technology today. Surfaces become more important as the size
3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 6a BONDING AND SURFACES 1. INTRODUCTION Surfaces have increasing importance in technology today. Surfaces become more important as the size
AP Physics C. Electricity - Term 3
 AP Physics C Electricity - Term 3 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the
AP Physics C Electricity - Term 3 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the
PHYS 2426 Brooks INTRODUCTION. Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli
 PHYS 2426 Brooks INTRODUCTION http://iws.ccccd.edu/mbrooks Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli Chapter 21 Electric Charge and Electric Field Static Electricity;
PHYS 2426 Brooks INTRODUCTION http://iws.ccccd.edu/mbrooks Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli Chapter 21 Electric Charge and Electric Field Static Electricity;
Semester 2 Physics (SF 026) Lecture: BP 3 by Yew Sze Fiona Website:
 Semester 2 Physics (SF 026) Lecture: BP 3 by Yew Sze Ling @ Fiona Website: http://yslphysics.weebly.com/ Chapter 1: Electrostatics The study of electric charges at rest, the forces between them and the
Semester 2 Physics (SF 026) Lecture: BP 3 by Yew Sze Ling @ Fiona Website: http://yslphysics.weebly.com/ Chapter 1: Electrostatics The study of electric charges at rest, the forces between them and the
The broad topic of physical metallurgy provides a basis that links the structure of materials with their properties, focusing primarily on metals.
 Physical Metallurgy The broad topic of physical metallurgy provides a basis that links the structure of materials with their properties, focusing primarily on metals. Crystal Binding In our discussions
Physical Metallurgy The broad topic of physical metallurgy provides a basis that links the structure of materials with their properties, focusing primarily on metals. Crystal Binding In our discussions
Chapter 21 Electric Charge and Electric Field
 Chapter 21 Electric Charge and Electric Field 21-1 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation Objects can be charged by rubbing 21-1 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation
Chapter 21 Electric Charge and Electric Field 21-1 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation Objects can be charged by rubbing 21-1 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation
Physics 2 for Students of Mechanical Engineering
 Homework #4 203-1-1721 Physics 2 for Students of Mechanical Engineering Part A 2. Derive an expression for the work required by an external agent to put the four charges together as indicated in Fig. 28-28
Homework #4 203-1-1721 Physics 2 for Students of Mechanical Engineering Part A 2. Derive an expression for the work required by an external agent to put the four charges together as indicated in Fig. 28-28
E x p e r i m e n t a l l y, t w o k i n d s o f o r d e r h a v e b e e n d e t e c t e d
 The Order Disorder Transformation The nature of ordering: - T h e r e are many types of order in s o lid m aterials,as t h e s p atial o rd e r o f the at o ms i n a p ure c r ys t a l.the t e r m o r
The Order Disorder Transformation The nature of ordering: - T h e r e are many types of order in s o lid m aterials,as t h e s p atial o rd e r o f the at o ms i n a p ure c r ys t a l.the t e r m o r
Physics 107 Final Exam December 13, Your Name: Questions
 Physics 107 Final Exam December 13, 1993 Your Name: Questions 1. 11. 21. 31. 41. 2. 12. 22. 32. 42. 3. 13. 23. 33. 43. 4. 14. 24. 34. 44. 5. 15. 25. 35. 45. 6. 16. 26. 36. 46. 7. 17. 27. 37. 47. 8. 18.
Physics 107 Final Exam December 13, 1993 Your Name: Questions 1. 11. 21. 31. 41. 2. 12. 22. 32. 42. 3. 13. 23. 33. 43. 4. 14. 24. 34. 44. 5. 15. 25. 35. 45. 6. 16. 26. 36. 46. 7. 17. 27. 37. 47. 8. 18.
Chemistry for the gifted and talented 19
 19 Student worksheet: CDROM index 10SW Discussion of answers: CDROM index 10DA Topics How models are used in science, refining a model, geometry and coordination number and bond angles. Level Very able
19 Student worksheet: CDROM index 10SW Discussion of answers: CDROM index 10DA Topics How models are used in science, refining a model, geometry and coordination number and bond angles. Level Very able
COVALENT BONDING CHEMICAL BONDING I: LEWIS MODEL. Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Chapter 16 Electric Charge and Electric Field
 Chapter 16 Electric Charge and Electric Field 16.1 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation Objects can be charged by rubbing 16.1 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation
Chapter 16 Electric Charge and Electric Field 16.1 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation Objects can be charged by rubbing 16.1 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation
Solids. properties & structure
 Solids properties & structure Determining Crystal Structure crystalline solids have a very regular geometric arrangement of their particles the arrangement of the particles and distances between them is
Solids properties & structure Determining Crystal Structure crystalline solids have a very regular geometric arrangement of their particles the arrangement of the particles and distances between them is
Radiometry. Nuno Vasconcelos UCSD
 Radiometry Nuno Vasconcelos UCSD Light Last class: geometry of image formation pinhole camera: point (x,y,z) in 3D scene projected into image pixel of coordinates (x, y ) according to the perspective projection
Radiometry Nuno Vasconcelos UCSD Light Last class: geometry of image formation pinhole camera: point (x,y,z) in 3D scene projected into image pixel of coordinates (x, y ) according to the perspective projection
Bohmian Quantum Mechanics and the Finite Square Potential Barrier
 Bohmian Quantum Mechanics and the Finite Square Potential Barrier Matthew Gorski Physics Department, The College of Wooster, Wooster, Ohio 44691, USA (Dated: May 6, 2008) This project studies Bohmian quantum
Bohmian Quantum Mechanics and the Finite Square Potential Barrier Matthew Gorski Physics Department, The College of Wooster, Wooster, Ohio 44691, USA (Dated: May 6, 2008) This project studies Bohmian quantum
Section 10 Metals: Electron Dynamics and Fermi Surfaces
 Electron dynamics Section 10 Metals: Electron Dynamics and Fermi Surfaces The next important subject we address is electron dynamics in metals. Our consideration will be based on a semiclassical model.
Electron dynamics Section 10 Metals: Electron Dynamics and Fermi Surfaces The next important subject we address is electron dynamics in metals. Our consideration will be based on a semiclassical model.
PH2200 Practice Final Exam Summer 2003
 INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name and student identification number on the answer sheet. 2. Please cover your answer sheet at all times. 3. This is a closed book exam. You may use the PH2200 formula sheet
INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name and student identification number on the answer sheet. 2. Please cover your answer sheet at all times. 3. This is a closed book exam. You may use the PH2200 formula sheet
Review of Gordon Belot, Geometric Possibility Oxford: Oxford UP, 2011
 Review of Gordon Belot, Geometric Possibility Oxford: Oxford UP, 2011 (The Philosophical Review 122 (2013): 522 525) Jill North This is a neat little book (138 pages without appendices, under 200 with).
Review of Gordon Belot, Geometric Possibility Oxford: Oxford UP, 2011 (The Philosophical Review 122 (2013): 522 525) Jill North This is a neat little book (138 pages without appendices, under 200 with).
Atoms, Molecules and Solids (selected topics)
 Atoms, Molecules and Solids (selected topics) Part I: Electronic configurations and transitions Transitions between atomic states (Hydrogen atom) Transition probabilities are different depending on the
Atoms, Molecules and Solids (selected topics) Part I: Electronic configurations and transitions Transitions between atomic states (Hydrogen atom) Transition probabilities are different depending on the
A Simple Model s Best Hope: A Brief Introduction to Universality
 A Simple Model s Best Hope: A Brief Introduction to Universality Benjamin Good Swarthmore College (Dated: May 5, 2008) For certain classes of systems operating at a critical point, the concept of universality
A Simple Model s Best Hope: A Brief Introduction to Universality Benjamin Good Swarthmore College (Dated: May 5, 2008) For certain classes of systems operating at a critical point, the concept of universality
Introduction to Thermodynamic States Gases
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Thermodynamic States Gases We begin our study in thermodynamics with a survey of the properties of gases. Gases are one of the first things students study in general chemistry.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Thermodynamic States Gases We begin our study in thermodynamics with a survey of the properties of gases. Gases are one of the first things students study in general chemistry.
Angular Momentum Quantization: Physical Manifestations and Chemical Consequences
 Angular Momentum Quantization: Physical Manifestations and Chemical Consequences Michael Fowler, University of Virginia 7/7/07 The Stern-Gerlach Experiment We ve established that for the hydrogen atom,
Angular Momentum Quantization: Physical Manifestations and Chemical Consequences Michael Fowler, University of Virginia 7/7/07 The Stern-Gerlach Experiment We ve established that for the hydrogen atom,
This is a brief overview of some of the very basic and classic laws of physics and how magnetic energy theory fits into those laws.
 This is a brief overview of some of the very basic and classic laws of physics and how magnetic energy theory fits into those laws. There are changes coming to our planet and solar system and after these
This is a brief overview of some of the very basic and classic laws of physics and how magnetic energy theory fits into those laws. There are changes coming to our planet and solar system and after these
ECE 535 Notes for Lecture # 3
 ECE 535 Notes for Lecture # 3 Class Outline: Quantum Refresher Sommerfeld Model Part 1 Quantum Refresher 1 But the Drude theory has some problems He was nominated 84 times for the Nobel Prize but never
ECE 535 Notes for Lecture # 3 Class Outline: Quantum Refresher Sommerfeld Model Part 1 Quantum Refresher 1 But the Drude theory has some problems He was nominated 84 times for the Nobel Prize but never
Electric Flux and Gauss Law
 Electric Flux and Gauss Law Gauss Law can be used to find the electric field of complex charge distribution. Easier than treating it as a collection of point charge and using superposition To use Gauss
Electric Flux and Gauss Law Gauss Law can be used to find the electric field of complex charge distribution. Easier than treating it as a collection of point charge and using superposition To use Gauss
International Physics Course Entrance Examination Questions
 International Physics Course Entrance Examination Questions (May 2010) Please answer the four questions from Problem 1 to Problem 4. You can use as many answer sheets you need. Your name, question numbers
International Physics Course Entrance Examination Questions (May 2010) Please answer the four questions from Problem 1 to Problem 4. You can use as many answer sheets you need. Your name, question numbers
Surfaces, Interfaces, and Layered Devices
 Surfaces, Interfaces, and Layered Devices Building blocks for nanodevices! W. Pauli: God made solids, but surfaces were the work of Devil. Surfaces and Interfaces 1 Interface between a crystal and vacuum
Surfaces, Interfaces, and Layered Devices Building blocks for nanodevices! W. Pauli: God made solids, but surfaces were the work of Devil. Surfaces and Interfaces 1 Interface between a crystal and vacuum
CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE. From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum
 CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum 1997 65 CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE 4.0. Introduction In Chapter
CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum 1997 65 CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE 4.0. Introduction In Chapter
Vibrations and Rotations of Diatomic Molecules
 Chapter 6 Vibrations and Rotations of Diatomic Molecules With the electronic part of the problem treated in the previous chapter, the nuclear motion shall occupy our attention in this one. In many ways
Chapter 6 Vibrations and Rotations of Diatomic Molecules With the electronic part of the problem treated in the previous chapter, the nuclear motion shall occupy our attention in this one. In many ways
A Derivation of Space and Time
 Volume 15 (2019) PROGRESS IN PHYSICS Issue 2 (July) A Derivation of Space and Time Paul Bernard White ORCID: 0000-0002-2681-3670. E-mail: pbwx@att.net Four simple postulates are presented, from which we
Volume 15 (2019) PROGRESS IN PHYSICS Issue 2 (July) A Derivation of Space and Time Paul Bernard White ORCID: 0000-0002-2681-3670. E-mail: pbwx@att.net Four simple postulates are presented, from which we
33 Electric Fields and Potential. An electric field is a storehouse of energy.
 An electric field is a storehouse of energy. The space around a concentration of electric charge is different from how it would be if the charge were not there. If you walk by the charged dome of an electrostatic
An electric field is a storehouse of energy. The space around a concentration of electric charge is different from how it would be if the charge were not there. If you walk by the charged dome of an electrostatic
Chemical Background for Spring 2010 BIO 311C Brand Part II
 Chemical Background for Spring 2010 BIO 311C Brand Part II Discussion Period 2: Jan. 29 & Feb 1 Functional Groups of Organic Molecules Many large biological molecules have several or many different functions,
Chemical Background for Spring 2010 BIO 311C Brand Part II Discussion Period 2: Jan. 29 & Feb 1 Functional Groups of Organic Molecules Many large biological molecules have several or many different functions,
Bonding in solids The interaction of electrons in neighboring atoms of a solid serves the very important function of holding the crystal together.
 Bonding in solids The interaction of electrons in neighboring atoms of a solid serves the very important function of holding the crystal together. For example Nacl In the Nacl lattice, each Na atom is
Bonding in solids The interaction of electrons in neighboring atoms of a solid serves the very important function of holding the crystal together. For example Nacl In the Nacl lattice, each Na atom is
AP Physics C. Magnetism - Term 4
 AP Physics C Magnetism - Term 4 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the world
AP Physics C Magnetism - Term 4 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the world
4/4/2013. Covalent Bonds a bond that results in the sharing of electron pairs between two atoms.
 A chemical bond is a mutual electrical attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Why bond? As independent particles, atoms have a high potential
A chemical bond is a mutual electrical attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Why bond? As independent particles, atoms have a high potential
+ 1. which gives the expected number of Fermions in energy state ɛ. The expected number of Fermions in energy range ɛ to ɛ + dɛ is then dn = n s g s
 Chapter 8 Fermi Systems 8.1 The Perfect Fermi Gas In this chapter, we study a gas of non-interacting, elementary Fermi particles. Since the particles are non-interacting, the potential energy is zero,
Chapter 8 Fermi Systems 8.1 The Perfect Fermi Gas In this chapter, we study a gas of non-interacting, elementary Fermi particles. Since the particles are non-interacting, the potential energy is zero,
EXPERIMENTAL PROJECT Rigid Pendulum Experiment
 EXPERIMENTAL PROJECT 2012-2013 Rigid Pendulum Experiment INTRODUCTION The simple pendulum is familiar idea to many students as they will have seen a small mass swinging from side to side at the end of
EXPERIMENTAL PROJECT 2012-2013 Rigid Pendulum Experiment INTRODUCTION The simple pendulum is familiar idea to many students as they will have seen a small mass swinging from side to side at the end of
MATH 320, WEEK 2: Slope Fields, Uniqueness of Solutions, Initial Value Problems, Separable Equations
 MATH 320, WEEK 2: Slope Fields, Uniqueness of Solutions, Initial Value Problems, Separable Equations 1 Slope Fields We have seen what a differential equation is (relationship with a function and its derivatives),
MATH 320, WEEK 2: Slope Fields, Uniqueness of Solutions, Initial Value Problems, Separable Equations 1 Slope Fields We have seen what a differential equation is (relationship with a function and its derivatives),
AP Physics C - E & M
 AP Physics C - E & M Gauss's Law 2017-07-08 www.njctl.org Electric Flux Gauss's Law Sphere Table of Contents: Gauss's Law Click on the topic to go to that section. Infinite Rod of Charge Infinite Plane
AP Physics C - E & M Gauss's Law 2017-07-08 www.njctl.org Electric Flux Gauss's Law Sphere Table of Contents: Gauss's Law Click on the topic to go to that section. Infinite Rod of Charge Infinite Plane
PHY222 Lab 2 - Electric Fields Mapping the Potential Curves and Field Lines of an Electric Dipole
 Print Your Name PHY222 Lab 2 - Electric Fields Mapping the Potential Curves and Field Lines of an Electric Dipole Print Your Partners' Names Instructions January 23, 2015 Before lab, read the Introduction,
Print Your Name PHY222 Lab 2 - Electric Fields Mapping the Potential Curves and Field Lines of an Electric Dipole Print Your Partners' Names Instructions January 23, 2015 Before lab, read the Introduction,
Tunneling. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Tunneling Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Protons and neutrons are bound inside nuclei, that means energy must be supplied to break them away. The situation is analogous to a marble in a bowl that can roll around
Tunneling Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Protons and neutrons are bound inside nuclei, that means energy must be supplied to break them away. The situation is analogous to a marble in a bowl that can roll around
II. Equilibrium Thermodynamics Lecture 7: Statistical Thermodynamics
 II. Equilibrium Thermodynamics Lecture 7: Statistical Thermodynamics Notes by ChangHoon Lim (and MZB) Open circuit voltage of galvanic cell is To understand compositional effects on, we need to consider
II. Equilibrium Thermodynamics Lecture 7: Statistical Thermodynamics Notes by ChangHoon Lim (and MZB) Open circuit voltage of galvanic cell is To understand compositional effects on, we need to consider
Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Big Ideas in Unit 6 How do atoms form chemical bonds? How does the type of a chemical bond influence a compounds physical and
Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Big Ideas in Unit 6 How do atoms form chemical bonds? How does the type of a chemical bond influence a compounds physical and
Chapter 18 Electrostatics Electric Forces and Fields
 Chapter 18 Electrostatics Electric Forces and Fields Electrical charges that does not flow through an object, but sit stationary on the surface of an object. Usually it is isolated on the surface, but
Chapter 18 Electrostatics Electric Forces and Fields Electrical charges that does not flow through an object, but sit stationary on the surface of an object. Usually it is isolated on the surface, but
We have considered how Coulombic attractions and repulsions help to organize electrons in atoms and ions.
 CHEM 2060 Lecture 10: Electrostatics L10-1 Electrostatics of Atoms & Molecules We have considered how Coulombic attractions and repulsions help to organize electrons in atoms and ions. We now look at Coulombic
CHEM 2060 Lecture 10: Electrostatics L10-1 Electrostatics of Atoms & Molecules We have considered how Coulombic attractions and repulsions help to organize electrons in atoms and ions. We now look at Coulombic
1 Review of semiconductor materials and physics
 Part One Devices 1 Review of semiconductor materials and physics 1.1 Executive summary Semiconductor devices are fabricated using specific materials that offer the desired physical properties. There are
Part One Devices 1 Review of semiconductor materials and physics 1.1 Executive summary Semiconductor devices are fabricated using specific materials that offer the desired physical properties. There are
Chapter 23 Term083 Term082
 Chapter 23 Term083 Q6. Consider two large oppositely charged parallel metal plates, placed close to each other. The plates are square with sides L and carry charges Q and Q. The magnitude of the electric
Chapter 23 Term083 Q6. Consider two large oppositely charged parallel metal plates, placed close to each other. The plates are square with sides L and carry charges Q and Q. The magnitude of the electric
Monopole polarization of C 60 fullerene shell
 Monopole polarization of C 6 fullerene shell M. Ya. Amusia 1, and A. S. Baltenkov 3 1 Racah Institute of Physics, the Hebrew University, Jerusalem, 9194 Israel Ioffe Physical-Technical Institute, St. Petersburg,
Monopole polarization of C 6 fullerene shell M. Ya. Amusia 1, and A. S. Baltenkov 3 1 Racah Institute of Physics, the Hebrew University, Jerusalem, 9194 Israel Ioffe Physical-Technical Institute, St. Petersburg,
e 2m e c I, (7.1) = g e β B I(I +1), (7.2) = erg/gauss. (7.3)
 Chemistry 126 Molecular Spectra & Molecular Structure Week # 7 Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy, Supplement Like the hydrogen nucleus, an unpaired electron in a sample has a spin of I=1/2. The magnetic
Chemistry 126 Molecular Spectra & Molecular Structure Week # 7 Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy, Supplement Like the hydrogen nucleus, an unpaired electron in a sample has a spin of I=1/2. The magnetic
1.1 The Fundamental Chemistry of life
 1.1 The Fundamental Chemistry of life Matter makes up everything in the universe, including all living organisms. Matter is composed of elements, a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler
1.1 The Fundamental Chemistry of life Matter makes up everything in the universe, including all living organisms. Matter is composed of elements, a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler
Electric Fields and Equipotentials
 OBJECTIVE Electric Fields and Equipotentials To study and describe the two-dimensional electric field. To map the location of the equipotential surfaces around charged electrodes. To study the relationship
OBJECTIVE Electric Fields and Equipotentials To study and describe the two-dimensional electric field. To map the location of the equipotential surfaces around charged electrodes. To study the relationship
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule For Lewis structures of covalent compounds least electronegative
 Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Treatment of Error in Experimental Measurements
 in Experimental Measurements All measurements contain error. An experiment is truly incomplete without an evaluation of the amount of error in the results. In this course, you will learn to use some common
in Experimental Measurements All measurements contain error. An experiment is truly incomplete without an evaluation of the amount of error in the results. In this course, you will learn to use some common
Bonding in Molecules Covalent Bonding
 Bonding in Molecules Covalent Bonding The term covalent implies sharing of electrons between atoms. Valence electrons and valence shell orbitals - nly valence electrons are used for bonding: ns, np, nd
Bonding in Molecules Covalent Bonding The term covalent implies sharing of electrons between atoms. Valence electrons and valence shell orbitals - nly valence electrons are used for bonding: ns, np, nd
Lecture 7: Extrinsic semiconductors - Fermi level
 Lecture 7: Extrinsic semiconductors - Fermi level Contents 1 Dopant materials 1 2 E F in extrinsic semiconductors 5 3 Temperature dependence of carrier concentration 6 3.1 Low temperature regime (T < T
Lecture 7: Extrinsic semiconductors - Fermi level Contents 1 Dopant materials 1 2 E F in extrinsic semiconductors 5 3 Temperature dependence of carrier concentration 6 3.1 Low temperature regime (T < T
Physics 342 Lecture 30. Solids. Lecture 30. Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I
 Physics 342 Lecture 30 Solids Lecture 30 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, April 18th, 2008 We can consider simple models of solids these highlight some special techniques. 30.1 An Electron in a
Physics 342 Lecture 30 Solids Lecture 30 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, April 18th, 2008 We can consider simple models of solids these highlight some special techniques. 30.1 An Electron in a
