Ūdens cietības ietekme uz ūdens elektrolīzes procesu, izmantojot titāna oksīda keramikas elektrodus
|
|
|
- Maximillian Gregory
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ūdens cietības ietekme uz ūdens elektrolīzes procesu, izmantojot titāna oksīda keramikas elektrodus Madars Reimanis 1, Jurijs Ozolins 2, Juris Malers 3, Lidija Ece 4, 1-4 Riga Technical University Kopsavilkums. Modernās ūdens apgādes inženiersistēmās aktuāla ir ūdens sagatavošana, īpašu uzmanību pievēršot ūdens mikrobioloģiskajam stāvoklim. Starp daudzajām metodēm, kuras izmanto ūdens dezinfekcijai, jāizdala ūdens elektroķīmiskā apstrāde. Elektrolīzes procesā var veidoties dezinficējošas vielas, kas iznīcina ūdenī esošos mikroorganismus, kā arī samazina to spēju vairoties. Darbā pētīta ūdens cietības ietekme uz ūdens elektrolīzes procesu, izmantojot titāna oksīda keramikas elektrodus. Augsta ūdens mineralizācija var veicināt blakus reakciju norisi uz elektrodu virsmas, kā arī nogulšņu veidošanos, kas samazina elektriskās strāvas plūsmu elektrolīzes šūnā. Elektrolīzes laikā, ja šķīdums satur kalcija un hidrogēnkarbonāta jonus, uz titāna oksīda keramikas elektrodiem un šķīdumā izgulsnējas CaCO 3 nogulsnes. Ūdens plūsmas turbulence un kalcija hidrogēnkarbonāta koncentrācijas pieaugums stimulē CaCO 3 izgulsnēšanos, kas skaidrojama ar masas apmaiņas procesu intensificēšanos pie elektrodu virsmas. Nogulšņu pieaugums uz katoda elektroda atkarībā no kalcija hidrogēnkarbonāta koncentrācijas izmaiņām pie dažādiem plūsmas režīmiem aprakstāms pēc lineāra vienādojuma. Darbā konstatēts, ka ūdens cietība var ietekmēt kopējo izdalītā hlora daudzumu elektrolīzes laikā, kas skaidrojama ar blakus reakcijām uz elektrodu virsmas, un izdalītā hlora blakus reakcijām. Cieta ūdens gadījumā hlora izdalīšanos var konstatēt tikai pēc pirmajām desmit procesa minūtēm. Atslēgas vārdi: titāna oksīda keramika, elektrolīzes, ūdens cietība, dezinfekcija. I. IEVADS Modernās ūdens apgādes inženiersistēmās aktuāla ir ūdens sagatavošana, īpašu uzmanību pievēršot ūdens mikrobioloģiskajam stāvoklim [1]. Starp daudzajām metodēm, kuras izmanto ūdens dezinfekcijai, jāizdala ūdens elektroķīmiskā apstrāde [2, 3]. Elektrolīzes (EL) procesā var veidoties dezinficējošas vielas, kas iznīcina ūdenī esošos mikroorganismus, kā arī samazina to spēju vairoties [4, 5, 6]. Procesa efektivitāti lielā mērā var ietekmēt pielietoto elektrodu materiālu spēja izdalīt no ūdenī esošajiem joniem pietiekamā daudzumā aktīvos savienojumus [7, 8, 9, 10]. Bez tradicionāli izmantotajiem elektrodu materiāliem pēdējos gados pastiprināta uzmanība ir pievērsta titāna oksīda keramikai. Augstās temperatūrās reducējošā ūdeņraža atmosfērā no TiO 2 iegūst nestehiometriska titāna oksīda keramiku [11, 12, 13], kas ir ķīmiski izturīga un elektrību vadoša. Elektrovadītspēja šādam materiālam ir salīdzināma ar grafīta vadītspēju. Darbā [14] pētīta elektrību vadoša titāna oksīda keramika ar pietiekamu mehānisku un ķīmisku izturību, kas iegūta, neizmantojot apstrādi reducējošā vidē. No šāda materiāla izgatavoti elektrodi var tikt izmantoti ūdens dezinfekcijai ar elektrolīzes metodi [15, 16, 17, 18], Dezinfekcijas efektivitāti elektrolīzes procesā lielā mērā var ietekmēt ūdens ķīmiskais sastāvs. Augsta ūdens mineralizācija var veicināt blakus reakciju norisi uz elektrodu virsmas, tai skaitā nogulšņu veidošanos, kas samazina elektriskās strāvas plūsmu elektrolīzes šūnā [19]. Ja elektrolizējamais ūdens satur Mg 2+, Ca 2+ un CO 3 2- jonus, uz elektrodiem veidojas nogulsnes [19]. Darba mērķis bija noskaidrot ūdens cietības un elektrolizējamā ūdens plūsmas režīma ietekmi uz nogulšņu veidošanās intensitāti un elektrolīzes procesā izdalītā hlora daudzumu. Lai paātrināti noteiktu šķīduma cietības ietekmi, elektrolīzes eksperiments tika veikts laboratorijas apstākļos, apstrādājot ar kalcija joniem piesātinātus modeļšķīdumus, izmantojot no vakuumā aktivētas titāna oksīda keramikas izgatavotus elektrodus [14]. II. MATERIĀLI UN METODES Modeļšķīdumu pagatavošana. Hlorīda jonu modeļšķīdumu ar koncentrāciju 1 mmol/l pagatavoja, izšķīdinot dejonizētā ūdenī KCl; izvēlētā maksimālā koncentrācija nepārsniedza dzeramajā ūdenī pieļaujamo hlora jonu koncentrāciju [20]. Kalcija jonu koncentrācija tika noteikta titrimetriski [21]. Nosakot Ca 2+ jonus paraugos, kas noskaloti ar skābi no elektrodiem, lai sasniegtu analīzei nepieciešamo vides ph, izmantoja palielinātu buferšķīduma daudzumu Kalcija hidrogēnkarbonāta šķīdumu pagatavoja, ūdens suspensiju, saturošu 4,5 mmol/l CaCO 3, piesātinot ar CO 2 gāzi. Piesātināšana turpinājās 2 dienas un ilgāk līdz eksperimenta sākuma brīdim, lai sasniegtu pilnīgu piesātinājumu. Dzidro šķīdumu tieši pirms izmantošanas dekantēja no trauka apakšā esošajām neizšķīdušajām CaCO 3 nogulšņu paliekām. Kopējo hlora koncentrāciju ūdenī noteica, izmantojot titrēšanas un kolorimetrijas metodes [22, 23]. Šķīduma sārmainība tika noteikta titrimetriski [24]. Nogulšņu mikrostruktūru pētīja ar skenējošo elektronu mikroskopu (SEM) Tescan Mira/LMM. Parauga kristālisko fāžu analīzei izmantoja rentgenstaru difraktometru (XRD) Pananalitical X pert PRO ar CuKa lampas starojumu 2 θ diapazonā no 10 līdz 70 o. Eksperimenta procedūra. Ūdens elektrolīzi veica speciāli izveidotā elektrolīzes šūnā ar tilpumu 0,5 L. Elektrolizējamā ūdens plūsmas režīmu modelēja traukā ar maisītāju; mainot maisītāja apgriezienu skaitu, noteica bezdimensionālo centrbēdzes Reinoldsa kritēriju: 2 n d Re, (1) c kur n apgriezienu skaits, s -1, ρ ūdens blīvums kg/m 3, d - maisītāja diametrs, m, μ - ūdens viskozitāte, Pa*s (skat. 1.att.). 66
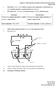
2 2012 / 25 1.att. Eksperimentālās iekārtas shēma: 1 termostats, 2 trauks ar elektrolizēto šķīdumu, 3 maisītājs, 4 līdzstrāvas avots, 5 sildītājs, 6 epoksīda sveķi, 7 titāna oksīda keramikas elektrodi, 8 strāvas vads Izveidotajā elektrolīzes iekārtā kā anods un katods tika izmantoti vienādi titāna oksīda keramikas elektrodi stienīša formā ar laukumu 12,4 cm 2. Par līdzstrāvas avotu izmantoja Rectifier HQ Power, PS5005 (0 50 V DC, 0 5 A). Elektrolīzes process tika veikts pie strāvas stipruma 0,05A (4,2 ma/cm 2 ), temperatūras 20 ± 2 C, ar kontrolētu maisīšanas režīmu 2 h. III. REZULTĀTI UN DISKUSIJA Elektrolīzes iekārtas darbības efektivitāti nosaka plūsmas režīms iekārtā, kas veicina jonu nokļūšanu pie elektrodu virsmas, pieliktais strāvas stiprums, kas nosaka dezinficējošo vielu izdalīšanās intensitāti, un ūdens ķīmiskais sastāvs, kas var izraisīt blakus reakcijas un nosēdumu veidošanos uz elektrodiem cieta ūdens gadījumā. Energoefektīvā elektrolīzes šūnā, kam raksturīga zema elektriskā pretestība, attālumi starp elektrodiem parasti ir mazi. Nogulsnes, kas veidojās uz elektrodiem, palielina šūnas elektrisko pretestību, un traucē ūdens plūsmai starp elektrodiem. Svarīgi noskaidrot, kā cietību veidojošie joni un plūsmas raksturs iespaido elektrodu apaugšanu, un kā šis process ietekmē dezinficējošo vielu veidošanās intensitāti. Nogulšņu veidošanās uz elektrodiem ir saistīta ar Ca 2+ un - HCO 3 jonu koncentrācijas samazināšanos elektrolizējamā ūdenī, kas var izsaukt sistēmas elektrovadītspējas izmaiņas. Kā redzams no 2. att., šķīduma elektrovadītspēja, pieaugot elektrolīzes laikam, samazinās. Krasāks samazinājums novērojams, apstrādājot šķīdumu ilgāk par min. Palielinoties elektrolīzes laikam, pieaug caurplūdušās strāvas lādiņš un tā izraisītās reakcijas uz elektrodu virsmas. Pieaugot plūsmas turbulencei, šie procesi pastiprinās. Elektrolīzes laikā pie elektrodiem izdalījušās gāzes var samazināt CO 2 šķīdību ūdenī, kas izsauc kalcija hidrogēnkarbonāta pāreju nešķīstošā CaCO 3 formā. Minēto apgalvojumu apstiprina šķīduma sārmainības samazināšanās un ph pieaugums elektrolīzes procesā (skat. 3.att.). Arī šajā gadījumā plūsmas turbulence izsauc šo lielumu straujākas izmaiņas. 2.att. Šķīduma elektrovadītspējas izmaiņas atkarībā no elektrolīzes laika pie dažādiem plūsmas režīmiem: Re c = 0; X Re c = 288; Re c = 5760; + Re c = ; Re c = att. Šķīduma sārmainības un ph izmaiņas pēc elektrolīzes atkarībā no plūsmas režīma. Apstrādi veic 1h Otrs apstāklis, kas var izsaukt kalcija hidrogēnkarbonāta pāreju nešķīstošā CaCO 3 formā, veidojot uz elektrodu virsmas blīvas nogulsnes, ir elektrolīzes procesā pie katoda izdalītais ūdeņradis, kas samazina H + jonu koncentrāciju un palielina šķīduma bāziskumu. Izstrādājot elektrolīzes iekārtas ūdens dezinfekcijai, ir svarīgi noskaidrot apstākļus, kas ietekmē elektrodu apaugšanas ātrumu, kas, savukārt, var samazināt šķīduma plūsmu starp elektrodiem un līdz ar to iespējamo dezinfekcijas efektivitāti. Nogulšņu veidošanos uz elektrodiem modelēja, veicot Ca(HCO 3 ) 2 šķīduma elektrolīzi, mainot plūsmas režīmus. Nogulšņu pieaugumu uz katoda elektrolīzes laikā kvantitatīvi raksturoja, izšķīdinot tās sālsskābē un nosakot Ca 2+ jonu daudzumu tajā (skat. 4. att.). 4.att. Ca 2+ jonu daudzuma pieaugums uz elektrodiem atkarībā elektrolīzes laika pie dažādiem plūsmas režīmiem: Re c = 0; X Re c = 288; Re c = 5760; + Re c = ; Re c =
3 Kā redzams no 4. att., palielinoties elektrolīzes laikam, nogulšņu daudzums uz katoda pieaug, pie tam plūsmas turbulence veicina šo procesu. Acīmredzot intensīva elektrolizējamā šķīduma sajaukšanās veicina aprakstīto reakciju norisi. Pretēji eksperimentāli noteiktam Ca 2+ jonu daudzuma pieaugumam uz elektrodu virsmas, atlikušā kalcija jonu koncentrācija šķīdumā, pieaugot elektrolīzes laikam un plūsmas turbulencei, samazinās. procesā uz katoda elektroda nogulsnējies CaCO 3 veido izteiktu kalcīta kristālisko modifikāciju (skat. 6. att.). Paraugu XRD difraktogrammās novērojami CaCO 3 kalcīta kristāliskajai fāzei raksturīgie difrakcijas maksimumi. Nogulšņu veidošanās uz elektrodiem elektrolīzes procesā var ietekmēt izdalītā hlora daudzumu un līdz ar to arī dezinfekcijas efektivitāti. Ūdens cietības ietekmi uz izdalītā hlora daudzumu elektrolīzes procesā novērtēja, pievienojot kalcīta hidrogēnkarbonāta modeļšķīdumam 1 mmol/l KCl (skat. 7. att.). 5.att. Ca 2+ jonu daudzuma izmaiņas uz elektrodiem atkarībā no Ca 2+ jonu koncentrācijas izejas šķīdumā pie dažādiem plūsmas režīmiem: Re c =288; Re c = Apstrādi veic 1h Tā kā dabas ūdeņu cietība ir ļoti mainīga, bija svarīgi noskaidrot, kā kalcija jonu koncentrācija izejas šķīdumā iespaido nogulšņu veidošanos uz katoda elektrolīzes laikā. Pieaugot kalcija jonu koncentrācijai elektrolizējamā šķīdumā, nogulšņu veidošanās intensitāte uz elektroda virsmas palielinās (skat. 5. att.). Intensīva šķīduma sajaukšanās veicina šo procesu. Nogulšņu veidošanās intensitāte atkarībā no kalcija jonu koncentrācijas, pie dažādiem plūsmas režīmiem ir aprakstāma ar lineāru vienādojumu. Pievienojot kalcija hidrogēnkarbonāta modeļšķīdumam 1 mmol/l KCl, bija novērojamas analogas nogulšņu veidošanās likumsakarības elektrolīzes procesā; Cl - jonu klātbūtne CaCO 3 izgulsnēšanās kinētiku neietekmē. 7.att. Hlora izdalīšanās šķīdumā no apstrādes laika pie dažādām Ca 2+ jonu koncentrācijām: 0 mmol/l; 4.5 mmol/l Kā redzams, hlora izdalīšanās kinētika elektrolīzes procesā no šķīduma, kas nesatur kalcija jonus, un šķīduma, kas satur 4,5 mmol/l Ca 2+ (atbilst ļoti cietam šķīdumam), būtiski atšķiras. CaCO 3 + 2Cl 2 + H 2 O 2 HClO + CaCl 2 + CO 2 (2) Cieta ūdens gadījumā hlora izdalīšanos var konstatēt tikai pēc pirmajām desmit procesa minūtēm. Tas ir izskaidrojams ar dažādām blakus reakcijām uz elektroda virsmas, kurās var būt iesaistīts arī elektrolīzes procesā producētais hlors (skat. 2 vienādojumu). IV. SECINĀJUMI 1. Elektrolīzes laikā uz titāna oksīda keramikas elektrodiem un šķīdumā veidojas CaCO 3 nogulsnes, ja šķīdums satur kalcija un hidrogēnkarbonāta jonus. 2. Plūsmas turbulence un kalcija hidrogēnkarbonāta koncentrācija šķīdumā stimulē CaCO 3 izkrišanu nogulsnēs uz katoda elektroda un šķīdumā, kas skaidrojams ar masas apmaiņas palielināšanos pie elektrodu virsmas. 3. Ūdens cietība var ietekmēt kopējo izdalītā hlora daudzumu elektrolīzes laikā, kas skaidrojams ar blakus reakcijām uz elektrodu virsmas un izdalītā hlora blakus reakcijām. Cieta ūdens gadījumā hlora izdalīšanos var konstatēt tikai pēc pirmajām desmit procesa minūtēm. 6.att. Uz elektrodu virsmas elektrolīzes laikā izveidojušo nogulšņu SEM mikrofotogrāfija Radušos nogulšņu virsmas morfoloģiju un struktūru noteica, izmantojot rentgenstruktūranalīzi un skenējošo elektronu mikroskopiju (SEM). Kā redzams, elektrolīzes PATEICĪBA This work has been supported by the European Regional Development Fund within the project Development of innovative water procession technology using nanostructured ceramic, No. 2010/0257/2DP/ /10/APIA/VIAA/
4 2012 / 25 LITERATŪRAS SARAKSTS 1. G.E. Kapellos, T.S. Alexiou, A.C. Payatakes. Hierarchical simulator of biofilm growth and dynamics in granular porous materials. Advances in Water Resources. 2007, 30: M.I. Kerwicka, S.M. Reddy, A.H.L. Chamberlain, D.M. Holta. Electrochemical disinfection, an environmentally acceptable method of drinking water disinfection? Electrochimica Acta. 200, 50: A. Kraft, M. Blaschke, D. Kreysig, B. Sandt, F. Schröder, J. Rennau. Electrochemical water disinfection. Part II: Hypochlorite production from potable water, chlorine consumption and the problem of calcareous deposits. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1999, 29: W.K. Kwang, K. In-Take, I.P. Geun, H.L. Eil. Electrolytic decomposition of ammonia to nitrogen in a multi-cell-stacked electrolyzer with a self-phadjustment function. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry. 2006, 36: H.X. Shi, J.H. Qu, A.M. Wang, J.T. Ge. Degradation of microcystins in aqueous solution with in situ electrogenerated active chlorine. Chemosphere. 2005, 60: M.E.H. Bergmann, A.S. Koparal. Studies on electrochemical disinfectant production using anodes containing RuO 2. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry. 2005, 35: J. Jeong, C. Kim, J. Yoon. The effect of electrode material on the generation of oxidants and microbial inactivation in the electrochemical disinfection processes. water research: 2009, 43, Joonseon Jeogen, Choonsoo Kim, Jeyong Yoon. The effect of electrode material on the generation of oxidants and microbial inactivation in the electrochemical disinfection processes. Water Research, 2009, 43, C.A. Martinez-Huitle, E.Brillas. Electrochemical Alternatives for Drinking Water Disinfection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2008, 47, D. Ghernaout, M.W. Naceur, A. Aouabed. On the dependence of chlorine by-products generated species formation of the electrode material and applied charge during electrochemical water treatment. Desalination, 2011, 270, P.C.S. Hayfield. Development of a New Material monolithic Ti 4 O 7 Ebonex R Ceramic. RSC, UK, 2002, 97 p. 12. A.A. Gusev, E.G. Avvakumov, A.Zh. Medvedev, A.I. Masliy. Ceramic Electrodes Based on Magneli Phases of Titanium Oxides. Science of Sintering, 2007, 39, J.R. Smith, F.C. Walsh, R.L. Clarke. Electrodes based on Magneli phase titanium oxides: the properties and applications of EbonexR materials, 1998, 28 (10), A.Pavlova, L.Berzina-Cimdina, J.Locs, J.Barloti, V.Teters, Investigation of the electrical properties of vacuum annealed titanium oxide-containing ceramics, Processing and Application of Ceramics, 2009, 3 (4), L. Mezule, M. Reimanis, J. Malers, J. Ozolins, T. Juhna. Application of electrolysis with Ti n O 2n-1 ceramic electrodes for disinfection of drinking water. The Scientific Proceedings of Riga Technical University, Material science and applied chemistry. 2009, 20: M. Reimanis, J. Malers, J. Ozolins. Preparation of water using Electrochemical Processes. International Journal of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, World Academy of research and publication Press. 2010, 1(1): M. Reimanis, L. Mezule, J. Malers, L. Berzina-Cimdina, T. Juhna, J. Ozolins. Preperation of water with electrolysis method using ceramic electrodes. In: IWA Specialist Conference Water and Wastewater Treatment Plants in Towns and Communities of the XXI Century: Technologies, Design and Operation, [electronic resource], Moscow, Russia on 2-4 June, 2010, Madars Reimanis, Jurijs Ozolins, Juris Malers, Janis Locs and Talis Juhna. Water disinfection using Ti n O 2n-1 electrodes nd International Conference on Environmental Engineering and Applications. International Proceedings of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, 2011, 17, A. Kraft, M. Stadelmann, M. Blaschke, D. Kreysig, B. Sandt, F.Schroder, J. Rennau. Electrochemical water disinfection Part I: Hypochlorite production from very dilute chloride solutions. J. Appl Electrochemistry. 1999, 29: Anonymous (1998) Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998 on the quality of water intended for human consumption, Official Journal of European Community 5(12). 21. Anonymous (1984) Water quality - Determination of the sum of calcium and magnesium - EDTA titrimetric method (1984), ISO 6059:1984, 22. Anonymous (1985) Water quality - Determination of free chlorine and total chlorine - Part 1: Titrimetric method using N, N-diethyl-1, 4- phenylenediamine (1985), ISO :1985, International Standard Organisation, Geneva, Switzerland. 23. Anonymous (1990) Water quality - Determination of free chlorine and total chlorine - Part 3: Iodometric titration method for the determination of total chlorine (1990). ISO :1990, 24. Anonymous (1994) Water quality - Determination of alkalinity - Part 1: Determination of total and composite alkalinity (1994). ISO :1994, Madars Reimanis, Mg.sc.ing., Researcher at Riga Technical University, Faculty of Materials Science and Applied Chemistry, Institute of General Chemical Engineering. He is the author of more than 30 scientific publications in the branch of water preparation chemistry, microbiology and technology. Over the last 5 years his research interests are related to electrochemical water treatment method improvement for microbiological contaminated water disinfection and treatment. Phone: madars.r@inbox.lv Juris Mālers, Dr.sc.ing.(1992), Asoc.Prof., Leading Researcher at Riga Technical University, Faculty of Materials Science and Applied Chemistry, Institute of General Chemistry Technology. He is the author and co-author of more than 75 publications in the branch of polymer technology and environmental engineering (soil and groundwater remediation, microbiological contamination of drinking water). He delivers such lecture courses as: Environmental Engineering; Contaminated Site Assessment; Contaminated Soil Treatment Technologies; Groundwater Treatment Technologies; Environmental Engineering (selected topics), for Bachelor s and Master s degree students. Phone: juris_malers@ktf.rtu.lv Jurijs Ozoliņš, Dr.sc.ing., Prof., Leading Researcher at Riga Technical University, Faculty of Materials Science and Applied Chemistry, Institute of General Chemical Technology. He is the author and co-author of more than 95 publications in the branch of polymer technology and environmental engineering (mass transfer processes, titanium oxide ceramic properties and use, microbiological contamination of drinking water). He delivers such lecture courses as: Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer, Unit Operation of Chemical Engineering, Heat Transfer Processes and Equipment, Special Processes and Equipment, Processes in the Material Technology. Phone: juris_oz@inbox.lv Lidija Ēce, Assistant Lecturer at Riga Technical University, Faculty of Materials Science and Applied Chemistry, Institute of General Chemical Engineering. Her current field of professional interests includes water electrolysis processes using titanium oxide ceramic electrodes. Phone: ecelidija@gmail.com Madars Reimanis, Jurijs Ozolins, Juris Malers, Lidija Ece. The Effect of Water Hardness on the Water Electrolysis Process Using Titanium Oxide Ceramic Electrodes Nowadays in water supply engineering systems, water preparation is very topical, especially paying attention to water biological condition. Among numerous methods used for water disinfection, electrochemical water treatment must be singled out. During the electrolysis process generation of specific disinfectants is possible, which are able to eliminate the microorganisms present in water, as well as decrease their ability to reproduce. 69
5 In the research, the influence of water hardness on water electrolysis has been investigated using titanium oxide ceramic electrodes. High water mineralization can facilitate by-reactions on the surface of electrodes, as well as the formation of sediments that reduces the current of electricity in the electrolytic cell. If the solution contains calcium and hydrocarbonate ions, then during the electrolysis process CaCO 3 sediments precipitate on the electrodes and in the solution. The turbulence of water flow and the increase of concentration of calcium hydrocarbonate facilitate the precipitation of CaCO 3, which can be explained with the intensification of mass exchange process at the surface of electrodes. The increase of sediments on cathode depending on the changes of calcium hydrocarbonate concentration at different flow conditions can be described with the help of a linear equation. It has been detected that water hardness can affect the total amount of produced chlorine during electrolysis, which can be explained by the by-reactions on the electrode surface and the produced chlorine by-reactions. In case of hard water, the production of chlorine can be detected only after the first ten minutes. Мадарс Реиманис, Юрий Озолинш, Юриc Малерс, Лидия Эце. Влияние жесткости воды на процесс электролиза воды с применением керамических электродов на основе окиси титана. В современных инженерных системах водоснабжения при подготовке воды особое внимание уделяется микробиологическому состоянию воды. Среди множества методов дезинфецирования воды надо выделить электрохимическую обработку воды. В процессе электролиза возникают дезинфицирующие вещества, уничтожающие в воде находящиеся микроорганизмы, а также снижают их способность размножаться. В работе исследовалось влияние жесткости воды на процесс электролиза с применением керамических электродов на основе окиси титана. Высокая минерализация воды может способствовать возникновению побочных реакций на поверхности электродов, возникновению осадка и уменьшению электрического тока в электролизной ячейке. Если раствор содержит ионы кальция и гидрогенкарбоната, то в процессе электролиза на поверхности керамических электродов и в растворе выделяется CaCO 3 в виде осадка. Увеличение турбулентности потока и повышенные концентрации гидрогенкарбоната кальция способствуют осаждению CaCO 3, что объясняется интенсификацией процессов массообмена у поверхности электродов. Прирост осадка на катоде в зависимости от концентрации гидрогенкарбоната кальция при разных режимах потока описывается уравнением прямой. Установлено, что жесткость воды влияет на выделение хлора в процессе электролиза, что объясняется побочными реакциями на поверхности электродов а также побочными реакциями выделенного хлора. В случае жесткой воды выделение хлора можно обнаружить только после первых десяти минут процесса электролиза. 70
Water disinfection using Ti n O 2n-1 electrodes
 211 2nd International Conference on Environmental Engineering and Applications IPCBEE vol.17 (211) (211) IACSIT Press, Singapore Water disinfection using Ti n O 2n-1 electrodes Madars Reimanis 1, Jurijs
211 2nd International Conference on Environmental Engineering and Applications IPCBEE vol.17 (211) (211) IACSIT Press, Singapore Water disinfection using Ti n O 2n-1 electrodes Madars Reimanis 1, Jurijs
Latvian Journal of Chemistry, No 4, 2012, DRINKING WATER DISINFECTION WITH ELECTROLYSIS
 Latvian Journal of Chemistry, No 4, 2012, 296 304 DOI: 10.2478/v10161-012-0016-9 296 DRINKING WATER DISINFECTION WITH ELECTROLYSIS M. Reimanis 1, L. Mezule, J. Ozolins 1, J. Malers 1, T. Juhna 2 1 Riga
Latvian Journal of Chemistry, No 4, 2012, 296 304 DOI: 10.2478/v10161-012-0016-9 296 DRINKING WATER DISINFECTION WITH ELECTROLYSIS M. Reimanis 1, L. Mezule, J. Ozolins 1, J. Malers 1, T. Juhna 2 1 Riga
LATVIAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS AND TECHNICAL SCIENCES 2010, N /v EVALUATION OF ATMOSPHERIC LUCIDITY AND DIFFUSED RADIATION
 LATVIAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS AND TECHNICAL SCIENCES 21, N 6 1.2478/v147-1-29-7 EVALUATION OF ATMOSPHERIC LUCIDITY AND DIFFUSED RADIATION I. Pelece 1, M. Vanags 2, L. Migla 2,3 1 Latvian University of Agriculture,
LATVIAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS AND TECHNICAL SCIENCES 21, N 6 1.2478/v147-1-29-7 EVALUATION OF ATMOSPHERIC LUCIDITY AND DIFFUSED RADIATION I. Pelece 1, M. Vanags 2, L. Migla 2,3 1 Latvian University of Agriculture,
Reuse of Produced Water for Electrolytic Oxidant Production: Challenges and Solutions
 Reuse of Produced Water for Electrolytic Oxidant Production: Challenges and Solutions Produced Water Produced water is extracted from wells at a rate far greater than hydrocarbon extraction ~8 bblproduced
Reuse of Produced Water for Electrolytic Oxidant Production: Challenges and Solutions Produced Water Produced water is extracted from wells at a rate far greater than hydrocarbon extraction ~8 bblproduced
The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. covalent ionic non-metallic
 1 The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. (a) (i) Choose a word from the box to complete the sentence. covalent ionic non-metallic Electrolysis takes place when electricity
1 The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. (a) (i) Choose a word from the box to complete the sentence. covalent ionic non-metallic Electrolysis takes place when electricity
PROPERTIES OF ISOLATED LIGNIN FROM MODEL WASTEWATER
 ISSN 1691-5402 ISBN 978-9984-44-070-5 Environment. Technology. Resources Proceedings of the 8th International Scientific and Practical Conference. Volume 1 Rēzeknes Augstskola, Rēzekne, RA Izdevniecība,
ISSN 1691-5402 ISBN 978-9984-44-070-5 Environment. Technology. Resources Proceedings of the 8th International Scientific and Practical Conference. Volume 1 Rēzeknes Augstskola, Rēzekne, RA Izdevniecība,
Preparation of Hydrogen Peroxide by Electrochemical Method
 Preparation of Hydrogen Peroxide by Electrochemical Method Ri Kwang Il, Kim Dok Sung, Pak Chol Min, YongSon Hong * Faculty of Chemistry, Kim Il Sung University, D.P.R.K Corresponding author.* E-mail address:
Preparation of Hydrogen Peroxide by Electrochemical Method Ri Kwang Il, Kim Dok Sung, Pak Chol Min, YongSon Hong * Faculty of Chemistry, Kim Il Sung University, D.P.R.K Corresponding author.* E-mail address:
Projekts Materiālu mehānisko mikro nano- mēroga īpašības un to ietekme uz cilvēka drošību. Izbraukuma seminārs
 Valsts pētījumu programma Inovatīvi materiāli un viedās tehnoloģijas vides drošumam Projekts Materiālu mehānisko mikro nano- mēroga īpašības un to ietekme uz cilvēka drošību Izbraukuma seminārs 2016. 03.03.
Valsts pētījumu programma Inovatīvi materiāli un viedās tehnoloģijas vides drošumam Projekts Materiālu mehānisko mikro nano- mēroga īpašības un to ietekme uz cilvēka drošību Izbraukuma seminārs 2016. 03.03.
Solar desalination coupled with water remediation and molecular hydrogen production: A novel solar water-energy nexus
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 17 Supporting Information Solar desalination coupled with water remediation and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 17 Supporting Information Solar desalination coupled with water remediation and
Technology offer: Wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation (EC)
 Technology offer: Wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation (EC) Technology offer Wastewater treatment by Electrocoagulation (EC) Reference: TO-ECOAG SUMMARY The Department of Physical Chemistry (Applied
Technology offer: Wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation (EC) Technology offer Wastewater treatment by Electrocoagulation (EC) Reference: TO-ECOAG SUMMARY The Department of Physical Chemistry (Applied
Chemical Oxidation and Reduction
 Chemical Oxidation and Reduction Benno Rahardyan FTSL-ITB Taken from : PIERO M. ARMENANTE NJIT What is oxidation? Simply put: The adding of an oxygen atom You are changing the composition of a molecule
Chemical Oxidation and Reduction Benno Rahardyan FTSL-ITB Taken from : PIERO M. ARMENANTE NJIT What is oxidation? Simply put: The adding of an oxygen atom You are changing the composition of a molecule
Science: Double Award (Modular) Paper 2 Higher Tier [G8205] 1 hour 30 minutes.
![Science: Double Award (Modular) Paper 2 Higher Tier [G8205] 1 hour 30 minutes. Science: Double Award (Modular) Paper 2 Higher Tier [G8205] 1 hour 30 minutes.](/thumbs/81/82622722.jpg) 71 Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2011 Science: Double Award (Modular) Paper 2 Higher Tier [G8205] FRIDAY 27 MAY, MORNING TIME 1 hour 30 minutes. INSTRUCTIONS
71 Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2011 Science: Double Award (Modular) Paper 2 Higher Tier [G8205] FRIDAY 27 MAY, MORNING TIME 1 hour 30 minutes. INSTRUCTIONS
Effect of Chloride Anions on the Synthesis and. Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Silver Nanocoral
 Supporting Information Effect of Chloride Anions on the Synthesis and Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Silver Nanocoral Electrodes for CO 2 Electroreduction Polyansky* Yu-Chi Hsieh, Sanjaya D. Senanayake,
Supporting Information Effect of Chloride Anions on the Synthesis and Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Silver Nanocoral Electrodes for CO 2 Electroreduction Polyansky* Yu-Chi Hsieh, Sanjaya D. Senanayake,
Porous silicon as base material of MEMS-compatible fuel cell components
 Porous silicon as base material of MEMS-compatible fuel cell components José Geraldo Alves Brito Neto Tokyo University of Science - Faculty of Science and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering
Porous silicon as base material of MEMS-compatible fuel cell components José Geraldo Alves Brito Neto Tokyo University of Science - Faculty of Science and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering
A Study on Brine Resource Utilization in Desalination Plants. Chen-Yu CHANG 1,*, Chiung-Ta WU 2, Yi-Ying LI 2 and Yung-Hsu HSIEH 2
 2017 2nd International Conference on Environmental Science and Engineering (ESE 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-474-5 A Study on Brine Resource Utilization in Desalination Plants Chen-Yu CHANG 1,*, Chiung-Ta WU
2017 2nd International Conference on Environmental Science and Engineering (ESE 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-474-5 A Study on Brine Resource Utilization in Desalination Plants Chen-Yu CHANG 1,*, Chiung-Ta WU
Olimpiāžu uzdevumus, rezultātus un citu informāciju Tu vari atrast mūsu Interneta mājas lapā Lai veicas!
 Latvijas 47. Nacionālā ķīmijas olimpiāde 2006. gada 28. martā Teorētiskie uzdevumi. Cienījamais olimpieti! Latvijas 47. Nacionālās ķīmijas olimpiādes Rīcības komiteja apsveic Tevi ar panākumiem rajona
Latvijas 47. Nacionālā ķīmijas olimpiāde 2006. gada 28. martā Teorētiskie uzdevumi. Cienījamais olimpieti! Latvijas 47. Nacionālās ķīmijas olimpiādes Rīcības komiteja apsveic Tevi ar panākumiem rajona
Electro2catalytic oxidation of phenol on Sb2doped SnO 2 2coated Titanium foams electrodes
 25 8 2005 8 Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae Vol. 25,No. 8 Aug., 2005,,,. [J ].,2005,25 (8) :1015-1020 LIU Haiping, LI Ning, ZHOU Derui, et al. Electro2catalytic oxidation of phenol on Sb2doped SnO 2 2coated
25 8 2005 8 Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae Vol. 25,No. 8 Aug., 2005,,,. [J ].,2005,25 (8) :1015-1020 LIU Haiping, LI Ning, ZHOU Derui, et al. Electro2catalytic oxidation of phenol on Sb2doped SnO 2 2coated
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17
 Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
MOLES AND EQUATIONS. Answer all questions. Max 51 marks. Mark../51...% Grade. Paddington Academy 1
 MOLES AND EQUATIONS Answer all questions Max 51 marks Name.. Mark../51...% Grade Paddington Academy 1 1. In the sixteenth century, a large deposit of graphite was discovered in the Lake District. People
MOLES AND EQUATIONS Answer all questions Max 51 marks Name.. Mark../51...% Grade Paddington Academy 1 1. In the sixteenth century, a large deposit of graphite was discovered in the Lake District. People
BASU. Healthcare. Knowledge brings the greatest benefit
 BASU Healthcare Knowledge brings the greatest benefit Knowledge brings the greatest benefit BASU is a privately owned company in Austria. We design and manufacture high quality products using simple reagents.
BASU Healthcare Knowledge brings the greatest benefit Knowledge brings the greatest benefit BASU is a privately owned company in Austria. We design and manufacture high quality products using simple reagents.
Chemistry 112 Name Practice Exam 3C Section
 Chemistry 112 Name Practice Exam 3C Section email IMPORTANT: On the scantron (answer sheet), you MUST clearly fill your name, your student number, section number, and test form (white cover = test form
Chemistry 112 Name Practice Exam 3C Section email IMPORTANT: On the scantron (answer sheet), you MUST clearly fill your name, your student number, section number, and test form (white cover = test form
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 032/1 CHEMISTRY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates) Time: 3 Hours Thursday, 06 th November
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 032/1 CHEMISTRY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates) Time: 3 Hours Thursday, 06 th November
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015
 Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
AP Questions: Electrochemistry
 AP Questions: Electrochemistry I 2 + 2 S 2O 2-3 2 I - + S 4O 2-6 How many moles of I 2 was produced during the electrolysis? The hydrogen gas produced at the cathode during the electrolysis was collected
AP Questions: Electrochemistry I 2 + 2 S 2O 2-3 2 I - + S 4O 2-6 How many moles of I 2 was produced during the electrolysis? The hydrogen gas produced at the cathode during the electrolysis was collected
Nanostrukturēta dzelzs oksīdu fotoanodu sintēze un īpašības, impulsa elektrolīzes un fotoelektrolīzes mehānismi
 RĪGAS TEHNISKĀ UNIVERSITĀTE Materiālzinātnes un Lietišķās Ķīmijas fakultāte Tehniskās Fizikas institūts Mārtiņš Vanags Doktora studiju programmas Materiālzinātnes doktorants Nanostrukturēta dzelzs oksīdu
RĪGAS TEHNISKĀ UNIVERSITĀTE Materiālzinātnes un Lietišķās Ķīmijas fakultāte Tehniskās Fizikas institūts Mārtiņš Vanags Doktora studiju programmas Materiālzinātnes doktorants Nanostrukturēta dzelzs oksīdu
Guangfu Li, PhD. Room 230H, Science and Engineering Building 2
 Curriculum Vitae Education Room 230H, Science and Engineering Building 2 Thermal and Electrochemical Energy Laboratory University of California, Merced, CA, 95343 Phone: 209-7772351 Email: gli27@ucmerced.edu
Curriculum Vitae Education Room 230H, Science and Engineering Building 2 Thermal and Electrochemical Energy Laboratory University of California, Merced, CA, 95343 Phone: 209-7772351 Email: gli27@ucmerced.edu
(c) dilute solution of glucose (d) chloroform 12 Which one of the following represents the same net reaction as the electrolysis of aqueous H2SO4
 1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
ICSE Board. Class X Chemistry. Board Paper Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80
 ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2013 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2013 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
Instrumental Chemical Analysis. Dr. Abdul Muttaleb Jaber Professor Faculty of Pharmacy Philadelphia University Fall 2012/2013
 0510212 Instrumental Chemical Analysis Dr. Abdul Muttaleb Jaber Professor Faculty of Pharmacy Philadelphia University Fall 2012/2013 Chapter 1 Electroanalytical Methods Electroanalytical Chemistry Electroanalytical
0510212 Instrumental Chemical Analysis Dr. Abdul Muttaleb Jaber Professor Faculty of Pharmacy Philadelphia University Fall 2012/2013 Chapter 1 Electroanalytical Methods Electroanalytical Chemistry Electroanalytical
CHEM N-12 November In the electrolytic production of Al, what mass of Al can be deposited in 2.00 hours by a current of 1.8 A?
 CHEM161 014-N-1 November 014 In the electrolytic production of Al, what mass of Al can be deposited in.00 hours by a current of 1.8 A? What products would you expect at the anode and the cathode on electrolysis
CHEM161 014-N-1 November 014 In the electrolytic production of Al, what mass of Al can be deposited in.00 hours by a current of 1.8 A? What products would you expect at the anode and the cathode on electrolysis
GOZO COLLEGE BOYS SECONDARY SCHOOL
 GOZO COLLEGE BOYS SECONDARY SCHOOL Embracing Diversity Half Yearly Exams 2013-2014 FORM 4 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min Name: Class: Useful Data: One Faraday is equivalent to 96500 C. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 H 1
GOZO COLLEGE BOYS SECONDARY SCHOOL Embracing Diversity Half Yearly Exams 2013-2014 FORM 4 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min Name: Class: Useful Data: One Faraday is equivalent to 96500 C. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 H 1
Inmaculada Rodríguez Ramos Nanostructured catalysts for sustainable chemical processes
 Inmaculada Rodríguez Ramos Nanostructured catalysts for sustainable chemical processes Instituto de Catálisis y Petroleoquímica (ICP) Institute of Catalysis and Petroleochemistry http://www.icp.csic.es
Inmaculada Rodríguez Ramos Nanostructured catalysts for sustainable chemical processes Instituto de Catálisis y Petroleoquímica (ICP) Institute of Catalysis and Petroleochemistry http://www.icp.csic.es
Electrochemistry. Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts
 Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts What do I need to know about electrochemistry? Electrochemistry Learning Outcomes: Candidates should be able to: a) Describe
Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts What do I need to know about electrochemistry? Electrochemistry Learning Outcomes: Candidates should be able to: a) Describe
Effect of the mixing velocity and the active chlorine concentration in anolyte on the indirect electrochemical oxidation of the Acid Red35 dye.
 Journal of Materials and Environmental Sciences ISSN : 2028-2508 Copyright 2017, University of Mohammed Premier Oujda Morocco JMES, 2017 Volume 8, Issue 8, Page 2769-2780 http://www.jmaterenvironsci.com/
Journal of Materials and Environmental Sciences ISSN : 2028-2508 Copyright 2017, University of Mohammed Premier Oujda Morocco JMES, 2017 Volume 8, Issue 8, Page 2769-2780 http://www.jmaterenvironsci.com/
Personalised Learning Checklists Edexcel Combined: Chemistry Paper 1
 Edexcel (combined) Chemistry Topics (1SC0) from 2016 - Paper 1 (Topic 1 parts a&b) Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe how the Dalton model of an atom has changed over time because of the discovery
Edexcel (combined) Chemistry Topics (1SC0) from 2016 - Paper 1 (Topic 1 parts a&b) Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe how the Dalton model of an atom has changed over time because of the discovery
Supporting Information. Free-Standing 3D Porous N-Doped Graphene Aerogel Supported. Platinum Nanocluster for Efficient Hydrogen Production from
 Supporting Information Free-Standing 3D Porous N-Doped Graphene Aerogel Supported Platinum Nanocluster for Efficient Hydrogen Production from Ammonia Electrolysis Yufei Zhou, Guoquan Zhang *, Mingchuan
Supporting Information Free-Standing 3D Porous N-Doped Graphene Aerogel Supported Platinum Nanocluster for Efficient Hydrogen Production from Ammonia Electrolysis Yufei Zhou, Guoquan Zhang *, Mingchuan
7/26/2018 3:17 PM Approved (Changed Course) WWTR 122 Course Outline as of Fall 2017
 7/26/2018 3:17 PM Approved (Changed Course) WWTR 122 Course Outline as of Fall 2017 CATALOG INFORMATION Dept and Nbr: WWTR 122 Title: CHEM FOR WATER TECH Full Title: Chemistry for Water and Wastewater
7/26/2018 3:17 PM Approved (Changed Course) WWTR 122 Course Outline as of Fall 2017 CATALOG INFORMATION Dept and Nbr: WWTR 122 Title: CHEM FOR WATER TECH Full Title: Chemistry for Water and Wastewater
Electrolysis. Question Paper. Cambridge International Examinations. Score: /48. Percentage: /100
 Electrolysis Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations Electrolysis Question Paper Time llowed: 58 minutes Score: /48 Percentage: /100 1 queous
Electrolysis Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations Electrolysis Question Paper Time llowed: 58 minutes Score: /48 Percentage: /100 1 queous
on-line analyzer systems for safety and control of chlorine production plants by Chris Du Bois by Thibaut Bettini Buenos Aires Argentina Nov.
 on-line analyzer systems for safety and control of chlorine production plants by Chris Du Bois Exc. VP Systems Integration Div. AppliTek by Thibaut Bettini Project Engineer AppliTek Buenos Aires Argentina
on-line analyzer systems for safety and control of chlorine production plants by Chris Du Bois Exc. VP Systems Integration Div. AppliTek by Thibaut Bettini Project Engineer AppliTek Buenos Aires Argentina
Laws Of Chloride - Ions Oxidation On Various Electrodes and Green Electrochemical Method of Higher α-olefins Processing
 10.1149/1.3300057 The lectrochemical Society Laws Of Chloride - Ions Oxidation On Various lectrodes and Green lectrochemical Method of Higher α-olefins Processing Yu. H. Budnikova, S. A. Krasnov, I. M.
10.1149/1.3300057 The lectrochemical Society Laws Of Chloride - Ions Oxidation On Various lectrodes and Green lectrochemical Method of Higher α-olefins Processing Yu. H. Budnikova, S. A. Krasnov, I. M.
CHEMICAL OXIDATION. The use of oxidizing agents without the need of microorganisms for the reactions to proceed
 CHEMICAL OXIDATION The use of oxidizing agents without the need of microorganisms for the reactions to proceed oxidizing agents : O 3, H 2 O 2, Cl 2 or HOCl or O 2 etc catalysts : ph, transition metals,
CHEMICAL OXIDATION The use of oxidizing agents without the need of microorganisms for the reactions to proceed oxidizing agents : O 3, H 2 O 2, Cl 2 or HOCl or O 2 etc catalysts : ph, transition metals,
*GSD22* *16GSD2201* Double Award Science: Chemistry. Unit C1 Higher Tier THURSDAY 14 MAY 2015, MORNING [GSD22] *GSD22* TIME 1 hour.
![*GSD22* *16GSD2201* Double Award Science: Chemistry. Unit C1 Higher Tier THURSDAY 14 MAY 2015, MORNING [GSD22] *GSD22* TIME 1 hour. *GSD22* *16GSD2201* Double Award Science: Chemistry. Unit C1 Higher Tier THURSDAY 14 MAY 2015, MORNING [GSD22] *GSD22* TIME 1 hour.](/thumbs/83/88610647.jpg) Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 2015 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C1 Higher Tier [GSD22] *GSD22* *GSD22* THURSDAY 14 MAY 2015, MORNING TIME 1 hour.
Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 2015 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C1 Higher Tier [GSD22] *GSD22* *GSD22* THURSDAY 14 MAY 2015, MORNING TIME 1 hour.
11.3. Electrolytic Cells. Electrolysis of Molten Salts. 524 MHR Unit 5 Electrochemistry
 11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
FĀŽU PĀREJAS Sn x S y PLĀNAJĀS KĀRTIŅĀS UN TO ĪPAŠĪBAS
 RĪGAS TEHNISKĀ UNIVERSITĀTE Materiālzinātnes un lietišķās ķīmijas fakultāte Silikātu materiālu institūts Līga Grase Doktora studiju programmas Materiālzinātne doktorante FĀŽU PĀREJAS Sn x S y PLĀNAJĀS
RĪGAS TEHNISKĀ UNIVERSITĀTE Materiālzinātnes un lietišķās ķīmijas fakultāte Silikātu materiālu institūts Līga Grase Doktora studiju programmas Materiālzinātne doktorante FĀŽU PĀREJAS Sn x S y PLĀNAJĀS
Treatment of Reactive Blue 69 solution by electro-fenton process using carbon nanotubes based cathode
 2011 International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry IPCBEE vol.24 (2011) (2011)IACSIT Press, Singapoore Treatment of Reactive Blue 69 solution by electro-fenton process using carbon nanotubes
2011 International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry IPCBEE vol.24 (2011) (2011)IACSIT Press, Singapoore Treatment of Reactive Blue 69 solution by electro-fenton process using carbon nanotubes
Chapter 3 Electrochemical methods of Analysis-Potentiometry
 Chapter 3 Electrochemical methods of Analysis-Potentiometry Electroanalytical chemistry Contents Introduction Galvanic and electrolytic cells Salt bridge Electrode potential and cell potential Indicator
Chapter 3 Electrochemical methods of Analysis-Potentiometry Electroanalytical chemistry Contents Introduction Galvanic and electrolytic cells Salt bridge Electrode potential and cell potential Indicator
Photosynthesis Characteristics of Festulolium and Lolium Boucheanum Sward Fotosintētiskās darbības rādītāji Festulolium un Lolium boucheanum zelmenī
 Photosynthesis Characteristics of Festulolium and Lolium Boucheanum Sward Fotosintētiskās darbības rādītāji Festulolium un Lolium boucheanum zelmenī Iveta Gūtmane, Aleksandrs Adamovičs Institute of Agrobiotechnology,
Photosynthesis Characteristics of Festulolium and Lolium Boucheanum Sward Fotosintētiskās darbības rādītāji Festulolium un Lolium boucheanum zelmenī Iveta Gūtmane, Aleksandrs Adamovičs Institute of Agrobiotechnology,
ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING. Chemical Engineering department
 ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING Chemical Engineering department WATER TREATMENT Many aquifers and isolated surface waters are of high water quality and may be pumped from the supply and transmission network
ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING Chemical Engineering department WATER TREATMENT Many aquifers and isolated surface waters are of high water quality and may be pumped from the supply and transmission network
Voltammetric Comparison of the Electrochemical Oxidation of Toluene on Monolithic and Reticulated Glassy Carbon Electrodes in Aqueous Medium
 Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2010, 28(6), 397-404 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201006397 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Voltammetric Comparison of the Electrochemical Oxidation of Toluene on Monolithic
Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2010, 28(6), 397-404 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201006397 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Voltammetric Comparison of the Electrochemical Oxidation of Toluene on Monolithic
CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems
 1. When the redox equation CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems MnO 4 (aq) + H + (aq) + H 3 AsO 3 (aq) Mn 2+ (aq) + H 3 AsO 4 (aq) + H 2 O(l) is properly balanced, the coefficients will
1. When the redox equation CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems MnO 4 (aq) + H + (aq) + H 3 AsO 3 (aq) Mn 2+ (aq) + H 3 AsO 4 (aq) + H 2 O(l) is properly balanced, the coefficients will
Tatiana Sadyrbaeva, Riga Technical University
 ISSN 1407-7353 print / 2255-8713 online Material Science and Applied Chemistry Separation of Cobalt(II) and Nickel(II) by Liquid Membranes during Electrodialysis Tatiana Sadyrbaeva, Riga Technical University
ISSN 1407-7353 print / 2255-8713 online Material Science and Applied Chemistry Separation of Cobalt(II) and Nickel(II) by Liquid Membranes during Electrodialysis Tatiana Sadyrbaeva, Riga Technical University
Influence of the type of activator and emulsifier on heterogeneously initiated polymerization of styrene
 nfluence of the type of activator and emulsifier on heterogeneously initiated polymerization of styrene V. CHRÁSTOVÁ, P. CTOVCKÝ, D. MKULÁŠOVA, and J. SCHENKMAYER Department of Chemical Technology of Plastics
nfluence of the type of activator and emulsifier on heterogeneously initiated polymerization of styrene V. CHRÁSTOVÁ, P. CTOVCKÝ, D. MKULÁŠOVA, and J. SCHENKMAYER Department of Chemical Technology of Plastics
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 032/1 CHEMISTRY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates) TIME: 3 Hours Tuesday afternoon 09/10/2007
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 032/1 CHEMISTRY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates) TIME: 3 Hours Tuesday afternoon 09/10/2007
F321: Atoms, Bonds and Groups Moles and Equations
 F321: Atoms, Bonds and Groups Moles and Equations 108 Marks 1. (a) A student carries out a titration to find the concentration of some sulfuric acid. The student finds that 25.00 cm 3 of 0.0880 mol dm
F321: Atoms, Bonds and Groups Moles and Equations 108 Marks 1. (a) A student carries out a titration to find the concentration of some sulfuric acid. The student finds that 25.00 cm 3 of 0.0880 mol dm
Name Date Class ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS
 21.1 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Section Review Objectives Use the activity series to identify which metal in a pair is more easily oxidized Identify the source of electrical energy in a voltaic cell Describe
21.1 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Section Review Objectives Use the activity series to identify which metal in a pair is more easily oxidized Identify the source of electrical energy in a voltaic cell Describe
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC TEXT REFERENCE. Electrochemistry. Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18. Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1
 Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Current efficiency of synthesis magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles via. electrodeposition
 3rd International Conference on Material, Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering (IC3ME 015) Current efficiency of synthesis magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles via electrodeposition XinZhong. Deng 1 ;
3rd International Conference on Material, Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering (IC3ME 015) Current efficiency of synthesis magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles via electrodeposition XinZhong. Deng 1 ;
Mercury, membrane or diaphragm
 Mercury, membrane or diaphragm Introduction The chloro-alkali industry is a major branch of the chemical industry. Its primary products are chlorine, sodium hydroxide and hydrogen which are produced from
Mercury, membrane or diaphragm Introduction The chloro-alkali industry is a major branch of the chemical industry. Its primary products are chlorine, sodium hydroxide and hydrogen which are produced from
3. Solids cannot conduct electricity because the ions cannot move freely 4. Electrolytic cell
 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chem 1120 Pretest 3 Sprin 2015
 Name: Class: Date: Chem 1120 Pretest 3 Sprin 2015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Chapter 19 Values The following equilibrium constants will
Name: Class: Date: Chem 1120 Pretest 3 Sprin 2015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Chapter 19 Values The following equilibrium constants will
Angel International SchoolManipay
 Grade OL Angel International SchoolManipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2016 Chemistry Duration: 3 Hours 1. Which property is common to calcium, potassium and sodium? a) Their atoms all lose two electrons
Grade OL Angel International SchoolManipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2016 Chemistry Duration: 3 Hours 1. Which property is common to calcium, potassium and sodium? a) Their atoms all lose two electrons
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0134775130* CHEMISTRY 5070/41 Paper 4 Alternative to Practical October/November 2016 1 hour Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0134775130* CHEMISTRY 5070/41 Paper 4 Alternative to Practical October/November 2016 1 hour Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
Electrochemical Cells
 CH302 LaBrake and Vanden Bout Electrochemical Cells Experimental Observations of Electrochemical Cells 1. Consider the voltaic cell that contains standard Co 2+ /Co and Au 3+ /Au electrodes. The following
CH302 LaBrake and Vanden Bout Electrochemical Cells Experimental Observations of Electrochemical Cells 1. Consider the voltaic cell that contains standard Co 2+ /Co and Au 3+ /Au electrodes. The following
DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES
 1 Exam 9 Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES For Marking guide contact and consultations: Dr. Bbosa Science 0776 802709. Answer all question in part I and six
1 Exam 9 Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES For Marking guide contact and consultations: Dr. Bbosa Science 0776 802709. Answer all question in part I and six
REMEDIATION OF SALT IMPACTED GROUNDWATER WITH ELECTROKINETICS. Paper by: Sean Kelly, Rick Churko, Sean Frisky, Anjum Mullick, Stuart Torr.
 REMEDIATION OF SALT IMPACTED GROUNDWATER WITH ELECTROKINETICS. Paper by: Sean Kelly, Rick Churko, Sean Frisky, Anjum Mullick, Stuart Torr. Alberta Transportation is supporting leading research in the use
REMEDIATION OF SALT IMPACTED GROUNDWATER WITH ELECTROKINETICS. Paper by: Sean Kelly, Rick Churko, Sean Frisky, Anjum Mullick, Stuart Torr. Alberta Transportation is supporting leading research in the use
Lesson on Electrolysis
 Lesson on Electrolysis This lesson package includes a lesson plan, a worksheet for students, and teachers notes on the worksheet. Activity Lesson 1 (50 min-2 Period lesson) Teacher explains (page 1 to
Lesson on Electrolysis This lesson package includes a lesson plan, a worksheet for students, and teachers notes on the worksheet. Activity Lesson 1 (50 min-2 Period lesson) Teacher explains (page 1 to
Page 1 Name: 2Al 3+ (aq) + 3Mg(s) 3Mg 2+ (aq) + 2Al(s) Fe 2 O 3 + 2Al Al 2 O 3 + 2Fe
 9666-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of chromium in the chromate ion, CrO 2-4? A) +8 B) +3 C) +2 D) +6 2) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in Na 2 S 2 O 3? A) +6 B) +4 C) +2 D) -1
9666-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of chromium in the chromate ion, CrO 2-4? A) +8 B) +3 C) +2 D) +6 2) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in Na 2 S 2 O 3? A) +6 B) +4 C) +2 D) -1
Chemistry Teach Yourself Series Topic 5: Electrolysis
 Chemistry Teach Yourself Series Topic 5: Electrolysis A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au TSSM 2013 Page 1 of 6 Contents Electrolysis...
Chemistry Teach Yourself Series Topic 5: Electrolysis A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au TSSM 2013 Page 1 of 6 Contents Electrolysis...
Production of Sodium Hypochlorite or Mixed Oxidant using Rhodium/Rhodium Oxide Mixed Modified Electrode
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 6(6): 4-5, ISSN 99-878 Production of Sodium Hypochlorite or Mixed Oxidant using Rhodium/Rhodium Oxide Mixed Modified Electrode H.H. Shaarawy and M.S. Shalaby
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 6(6): 4-5, ISSN 99-878 Production of Sodium Hypochlorite or Mixed Oxidant using Rhodium/Rhodium Oxide Mixed Modified Electrode H.H. Shaarawy and M.S. Shalaby
4. LATVIJAS UNIVERSITĀTES ĶĪMIJAS FAKULTĀTES JAUNO ĶĪMIĶU KONKURSA 3.KĀRTAS UZDEVUMI
 WWW.BIOSAN.LV 4. LATVIJAS UNIVERSITĀTES ĶĪMIJAS FAKULTĀTES JAUNO ĶĪMIĶU KONKURSA 3.KĀRTAS UZDEVUMI Atrisināt tālāk dotos sešus uzdevumus un atbildes ierakstīt MS Word atbilžu datnē, ko kā pievienoto dokumentu
WWW.BIOSAN.LV 4. LATVIJAS UNIVERSITĀTES ĶĪMIJAS FAKULTĀTES JAUNO ĶĪMIĶU KONKURSA 3.KĀRTAS UZDEVUMI Atrisināt tālāk dotos sešus uzdevumus un atbildes ierakstīt MS Word atbilžu datnē, ko kā pievienoto dokumentu
Reactive-transport modelling of electrokinetic extraction of heavy metals from marine sediments
 EREM63 Reactive-transport modelling of electrokinetic extraction of heavy metals from marine sediments Matteo Masi a, *, Alessio Ceccarini b, Renato Iannelli a a University of Pisa, Department of Energy,
EREM63 Reactive-transport modelling of electrokinetic extraction of heavy metals from marine sediments Matteo Masi a, *, Alessio Ceccarini b, Renato Iannelli a a University of Pisa, Department of Energy,
Copper electrodeposition in presence and absence of EDTA using reticulated vitreous carbon electrode
 Copper electrodeposition in presence and absence of EDTA using reticulated vitreous carbon electrode P. H. Britto a, L. A. M. Ruotolo a,b a Department of Chemical Engineering, Federal University of São
Copper electrodeposition in presence and absence of EDTA using reticulated vitreous carbon electrode P. H. Britto a, L. A. M. Ruotolo a,b a Department of Chemical Engineering, Federal University of São
Chemistry 112 Name Exam III Form A Section April 2,
 Chemistry 112 Name Exam III Form A Section April 2, 2013 email IMPORTANT: On the scantron (answer sheet), you MUST clearly fill your name, your student number, section number, and test form (white cover
Chemistry 112 Name Exam III Form A Section April 2, 2013 email IMPORTANT: On the scantron (answer sheet), you MUST clearly fill your name, your student number, section number, and test form (white cover
The test can be performed on the following devices. In addition, the required cuvette and the absorption range of the photometer are indicated.
 Chlorine L a) 0.02-4.0 mg/l Cl 2 DPD 101 CL6 Instrument specific information The test can be performed on the following devices. In addition, the required cuvette and the absorption range of the photometer
Chlorine L a) 0.02-4.0 mg/l Cl 2 DPD 101 CL6 Instrument specific information The test can be performed on the following devices. In addition, the required cuvette and the absorption range of the photometer
KENYA NATIONAL EXAMINATION COUNCIL REVISION MOCK EXAMS 2016 TOP NATIONAL SCHOOLS KAPSABET BOYS CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 TIME: 2 HOURS
 KENYA NATIONAL EXAMINATION COUNCIL REVISION MOCK EXAMS 2016 TOP NATIONAL SCHOOLS KAPSABET BOYS CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 TIME: 2 HOURS SCHOOLS NET KENYA Osiligi House, Opposite KCB, Ground Floor Off Magadi Road,
KENYA NATIONAL EXAMINATION COUNCIL REVISION MOCK EXAMS 2016 TOP NATIONAL SCHOOLS KAPSABET BOYS CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 TIME: 2 HOURS SCHOOLS NET KENYA Osiligi House, Opposite KCB, Ground Floor Off Magadi Road,
Definition 1 An element or compound is oxidized when it gains oxygen atoms
 Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION. Instructions
 THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 032/1 CHEMISTRY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates) th TIME: 3 Hours Tuesday 7 October
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA NATIONAL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION 032/1 CHEMISTRY 1 (For Both School and Private Candidates) th TIME: 3 Hours Tuesday 7 October
9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction
 9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 - Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron loss and gain Oxidation The loss of electrons from a substance. This may happen through the gain
9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 - Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron loss and gain Oxidation The loss of electrons from a substance. This may happen through the gain
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Supporting Information. Dechlorination of trichloroacetic acid using a noble metal-free
 Supporting Information Dechlorination of trichloroacetic acid using a noble metal-free graphene-cu foam electrode via direct cathodic reduction and atomic H* Ran Mao a, b, Ning Li a, b, Huachun Lan a,
Supporting Information Dechlorination of trichloroacetic acid using a noble metal-free graphene-cu foam electrode via direct cathodic reduction and atomic H* Ran Mao a, b, Ning Li a, b, Huachun Lan a,
SPECIMEN. Candidate Number
 Advanced Subsidiary GCE CHEMISTRY A F321 QP Unit F321: Atoms, Bonds and Groups Specimen Paper Candidates answer on the question paper. Additional Materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry (Inserted) Scientific
Advanced Subsidiary GCE CHEMISTRY A F321 QP Unit F321: Atoms, Bonds and Groups Specimen Paper Candidates answer on the question paper. Additional Materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry (Inserted) Scientific
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Chemistry
 Grade 09 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Chemistry Duration: 2.30 Hours Index No:- Part -1 1) Select most suitable answers and underline them. 1) The diagram shows
Grade 09 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Chemistry Duration: 2.30 Hours Index No:- Part -1 1) Select most suitable answers and underline them. 1) The diagram shows
Reactions in Aqueous Solution
 Reading Assignments: Reactions in Aqueous Solution Chapter 4 Chapter 4 in R. Chang, Chemistry, 9 th Ed., McGraw-Hill, 2006. or previous editions. Or related topics in other textbooks. Consultation outside
Reading Assignments: Reactions in Aqueous Solution Chapter 4 Chapter 4 in R. Chang, Chemistry, 9 th Ed., McGraw-Hill, 2006. or previous editions. Or related topics in other textbooks. Consultation outside
Elements in the Periodic Table show a periodic trend in atomic radius. In your answer you should use appropriate technical terms, spelled correctly.
 1 The Periodic Table is arranged in periods and groups (a) Elements in the Periodic Table show a periodic trend in atomic radius State and explain the trend in atomic radius from Li to F In your answer
1 The Periodic Table is arranged in periods and groups (a) Elements in the Periodic Table show a periodic trend in atomic radius State and explain the trend in atomic radius from Li to F In your answer
MC 17 C - 6 SECTION - I
 SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Question 1. (a) Name the gas in each of the following : An alkaline gas which gives dense white fumes with hydrogen chloride.
SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Question 1. (a) Name the gas in each of the following : An alkaline gas which gives dense white fumes with hydrogen chloride.
IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice
 IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice 1. What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7 (s) and Cr 2O 3 (s)? 2. Which of the following is a redox reaction? 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl 3 (aq) 2Al
IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice 1. What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7 (s) and Cr 2O 3 (s)? 2. Which of the following is a redox reaction? 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl 3 (aq) 2Al
CE 370. Disinfection. Location in the Treatment Plant. After the water has been filtered, it is disinfected. Disinfection follows filtration.
 CE 70 Disinfection 1 Location in the Treatment Plant After the water has been filtered, it is disinfected. Disinfection follows filtration. 1 Overview of the Process The purpose of disinfecting drinking
CE 70 Disinfection 1 Location in the Treatment Plant After the water has been filtered, it is disinfected. Disinfection follows filtration. 1 Overview of the Process The purpose of disinfecting drinking
Chem 321 Lecture 16 - Potentiometry 10/22/13
 Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 16 - Potentiometry 10/22/13 In lab you will use an ion-selective electrode to determine the amount of fluoride in an unknown solution. In this approach, as
Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 16 - Potentiometry 10/22/13 In lab you will use an ion-selective electrode to determine the amount of fluoride in an unknown solution. In this approach, as
International Journal of Chemical Sciences
 International Journal of Chemical Sciences Research Vol 16 Iss 2 Synthesizing Graphene Oxide as a Working Electrode for Decreasing ph with Alkaline Water Electrolysis Pirim Setiarso and Aldwin Amireza
International Journal of Chemical Sciences Research Vol 16 Iss 2 Synthesizing Graphene Oxide as a Working Electrode for Decreasing ph with Alkaline Water Electrolysis Pirim Setiarso and Aldwin Amireza
ELECTROCHEMISTRY. these are systems involving oxidation or reduction there are several types METALS IN CONTACT WITH SOLUTIONS OF THEIR IONS
 Electrochemistry 1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY REDOX Reduction gain of electrons Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e > Cu(s) Oxidation removal of electrons Zn(s) > Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e HALF CELLS these are systems involving oxidation or
Electrochemistry 1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY REDOX Reduction gain of electrons Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e > Cu(s) Oxidation removal of electrons Zn(s) > Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e HALF CELLS these are systems involving oxidation or
TIME 1 hour 30 minutes, plus your additional time allowance.
 Centre Number 71 Candidate Number ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education 2012 Chemistry Assessment Unit AS 1 assessing Basic Concepts in Physical and Inorganic Chemistry [AC112] WEDNESDAY
Centre Number 71 Candidate Number ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education 2012 Chemistry Assessment Unit AS 1 assessing Basic Concepts in Physical and Inorganic Chemistry [AC112] WEDNESDAY
Kentaro INOUE. Introduction. Measurement principle (membrane polarographic method)
 FFeature Article Article Performance of the Dissolved Oxygen Monitor Used in the Semiconductor Wet Process; Low Concentration Monitoring, High Temperature, Small Amount of Sampling Volume, Chemical Resistance
FFeature Article Article Performance of the Dissolved Oxygen Monitor Used in the Semiconductor Wet Process; Low Concentration Monitoring, High Temperature, Small Amount of Sampling Volume, Chemical Resistance
(c) Na is deposited at the cathode (d) Na appears at the anode
 year chemiry n0tes new CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY MCQS Q.1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy
year chemiry n0tes new CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY MCQS Q.1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy
Chemistry 30 Review Test 3 Redox and Electrochemistry /55
 Chemistry 30 Review Test 3 Redox and Electrochemistry /55 Part I Multiple choice / Numerical Response Answer the following multiple choice questions on the scantron sheet. Answer the numerical response
Chemistry 30 Review Test 3 Redox and Electrochemistry /55 Part I Multiple choice / Numerical Response Answer the following multiple choice questions on the scantron sheet. Answer the numerical response
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ARTICLE NUMBER: 16185 DOI: 10.1038/NENERGY.2016.185 Photocatalytic hydrogen generation from hydriodic acid using methylammonium
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ARTICLE NUMBER: 16185 DOI: 10.1038/NENERGY.2016.185 Photocatalytic hydrogen generation from hydriodic acid using methylammonium
GIRLS JUNIOR LYCEUM L-IMRIEĦEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017
 1 GIRLS JUNIOR LYCEUM L-IMRIEĦEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017 FORM: 4 CHEMISTRY Time: 1hr30min Name: Class: One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday One mole of any gas occupies
1 GIRLS JUNIOR LYCEUM L-IMRIEĦEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017 FORM: 4 CHEMISTRY Time: 1hr30min Name: Class: One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday One mole of any gas occupies
In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium salt to produce potassium
 Q1. This question is about potassium. (a) Humphrey Davy was a professor of chemistry. In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium
Q1. This question is about potassium. (a) Humphrey Davy was a professor of chemistry. In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0673865816* CHEMISTRY 5070/42 Paper 4 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0673865816* CHEMISTRY 5070/42 Paper 4 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional
Chemical measurements QuestionIT
 Chemical measurements QuestionIT 1. What is the law of conservation of mass? Mass of reactants = mass products. 2. Why might some reactions appear to show a change in mass? A reactant or a product is a
Chemical measurements QuestionIT 1. What is the law of conservation of mass? Mass of reactants = mass products. 2. Why might some reactions appear to show a change in mass? A reactant or a product is a
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species.
 Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
