IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice
|
|
|
- Daniella Young
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice 1. What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7 (s) and Cr 2O 3 (s)? 2. Which of the following is a redox reaction? 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl 3 (aq) 2Al (s) + 3MgCl 2 (aq) SiO 2 (s) + 2NaOH (aq) Na 2SiO 3 (aq) + H 2O (l) KCl (aq) + AgNO 3 (aq) AgCl (s) + KNO 3 (aq) 2NaHCO 3 (aq) Na 2CO 3 (aq) + CO 2 (g) + H 2O (l) 3. What is the reaction type and major product at the anode (positive electrode) when molten sodium chloride is electrolysed using platinum electrodes? 4. What is the order of decreasing reactivity of the metals (most reactive first)? Zn(s) + Sn 2+ (aq) Zn 2+ (aq) + Sn(s) Cu(s) + Zn 2+ (aq) No Reaction Sn(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) Sn 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) Ag(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) No Reaction Zn > Cu > Sn > Ag Sn > Zn > Ag > Cu Ag > Cu > Zn > Sn Zn > Sn > Cu > Ag 5. What is the oxidation half-equation in the redox reaction? 2S 2O 3 2 (aq) + I 2(aq) S 4O 6 2 (aq) + 2I (aq) I 2(aq) + 2e 2I (aq) 2I (aq) I 2(aq) + 2e 2S 2O 3 2 (aq) S 4O 6 2 (aq) + 2e S 4O 6 2 (aq) + 2e 2S 2O 3 2 (aq) 1
2 6. Which statements are correct for a voltaic cell? 7. Which of the following does not react with dilute HCl(aq)? Na 2CO 3 Cu Zn CuO 8. Which element is reduced in the following decomposition? (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7(s) N 2(g) + Cr 2O 3(s) + 4H 2O(g) N H Cr O 9. Which of the following is not a redox reaction? CH 4(g) + Cl 2(g) CH 3Cl(g) + HCl(g) C(s) + O 2(g) CO 2(g) 2CO(g) CO 2(g) + C(s) CH 3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) CH 3COONa(aq) + H 2O(l) 10. What occurs at the anode (positive electrode) during the electrolysis of molten strontium bromide? Formation of bromine and oxidation Formation of bromine and reduction Formation of strontium and oxidation Formation of strontium and reduction 11. Consider the following half-equations: I 2 (s) + 2e 2I (aq) E θ = V (brown) (colourless) MnO 4 (aq) + 8H + (aq) + 5e Mn 2+ (aq) + 4H 2O (l) E θ = V (purple) (colourless) Which statement is correct for the reaction between KMnO 4 (aq) and KI (aq) in acidic conditions? MnO 4 reduces I to I 2. I reduces MnO 4 to Mn 2+. The colour changes from brown to purple. MnO 4 is oxidized to Mn 2+. 2
3 12. What are the products when an aqueous solution of copper(ii) sulfate is electrolysed using inert graphite electrodes? 13. Which change represents oxidation? HClO 4 to HClO 3 N 2 to NH 3 N 2O to NO SO 4 2 to SO A reaction takes place when a rechargeable battery is used: Pb(s) + PbO 2(s) + 4H + (aq) + 2SO 4 2 (aq) 2PbSO 4(s) + 2H 2O(l) Which statements are correct? I. H + is reduced II. The oxidation state of Pb metal changes from 0 to +2 III. PbO 2 is the oxidising agent 15. Which statement is correct for the overall reaction in a voltaic cell? 2AgNO 3(aq) + Ni(s) 2Ag(s) + Ni(NO 3) 2(aq) E θ = V Electrons flow from Ag electrode to Ni electrode. Ni is oxidized to Ni 2+ at the cathode (negative electrode). Ag + is reduced to Ag at the anode (positive electrode). Ag has a more positive standard electrode potential value than Ni. 16. In the electrolysis of aqueous potassium nitrate, KNO 3(aq), using inert electrodes, 0.1 mol of a gas was formed at the cathode (negative electrode). Which is correct? 17. Which element is reduced in the following decomposition? (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7(s) N 2(g) + Cr 2O 3(s) + 4H 2O(g) N H Cr O 3
4 18. What is the standard half-cell potential of copper if the zero potential reference electrode is changed from the standard hydrogen electrode to a standard zinc electrode? What are the relative volumes of gas given off at E and F during electrolysis of the two cells in series? Assume all electrodes are inert. 1:1 1:2 2:1 5:2 20. Which compounds can be reduced? I. C 2H 4 II. CH 3COOH III. CH 3CHO 21. Which experimental methods could be used to observe the progress of the following reaction? Cr 2O 7 2-(aq) + 6I - (aq) + 14H + (aq) 2Cr 3+ (aq) + 3I 2(aq) + 7H 2O(l) I. Change in colour II. Change in mass III. Change in electrical conductivity 22. Which is a correct statement for the reaction below? 2MnO 4 -(aq) + 6H + (aq) + 5NO 2 -(aq) 2Mn 2+ (aq) + 5NO 3 -(aq) + 3H 2O(l) MnO 4 - is the reducing agent and the oxidation number of Mn increases. MnO 4 - is the oxidizing agent and the oxidation number of Mn decreases. NO 2 - is the reducing agent and the oxidation number of N decreases. NO 2 - is the oxidizing agent and the oxidation number of N increases. 4
5 23. Applying IUPAC rules, what is the name of MnO 2? Magnesium(II) oxide Manganese(II) oxide Magnesium(IV) oxide Manganese(IV) oxide 24. Which statement is correct for a voltaic but not for an electrolytic cell? An electrolyte is required. The anode is where oxidation occurs. Ions move in the electrolyte. Electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode. 25. A voltaic cell is constructed from zinc and copper half-cells. Zinc is more reactive than copper. Which statement is correct when this cell produces electricity? Electrons flow from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell. The concentration of Cu 2+ (aq) increases. Electrons flow through the salt bridge. Negative ions flow through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell. 26. Which are necessary conditions for the standard hydrogen electrode to have an E Θ of exactly zero? I. Temperature = 298 K II. [H + ]=1 moldm 3 III. [H2]=1 moldm Which statement is correct for a voltaic but not for an electrolytic cell? An electrolyte is required. The anode is where oxidation occurs. Ions move in the electrolyte. Electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode. 28. Which compound forms both hydrogen and oxygen at the electrodes when a concentrated aqueous solution is electrolyzed? KI NaCl H 2SO 4 AgNO 3 5
6 29. Which signs for both E θ cell and ΔG θ result in a spontaneous redox reaction occurring under standard conditions? 30. z mol of copper is deposited from CuSO 4 (aq) by a current, I, in time t. What is the amount of silver, in mol, deposited by electrolysis from AgNO 3 (aq) by a current,, in time 2t? z 2z 31. An iron rod is electroplated with silver. Which is a correct condition for this process? The silver electrode is the positive electrode. The iron rod is the positive electrode. The electrolyte is iron(ii) sulfate. Oxidation occurs at the negative electrode. 32. Which represents a redox reaction? 33. Which species can oxidize ethanol to ethanoic acid? Fe Acidified 34. Two half-cells are connected via a salt bridge to make a voltaic cell. Which statement about this cell is correct? Oxidation occurs at the positive electrode (cathode). It is also known as an electrolytic cell. Ions flow through the salt bridge. It requires a power supply to operate. 6
7 35. What are the oxidation states of each element in? 36. What is the coefficient for I when the following equation is balanced using the smallest possible whole numbers? A voltaic cell is made by connecting a copper half-cell,, to an iron half-cell. Which combination correctly identifies the positive electrode and the species being oxidized? 38. Which represents a redox reaction? 7
8 39. Two half-cells are connected via a salt bridge to make a voltaic cell. Which statement about this cell is correct? Oxidation occurs at the positive electrode (cathode). It is also known as an electrolytic cell. Ions flow through the salt bridge. It requires a power supply to operate. 40. Which signs are correct for a spontaneous redox reaction? 41. Consider the standard electrode potentials: What is the standard cell potential, in V, for the reaction? 42. Which is a redox reaction? 43. The standard electrode potentials for three reactions involving copper and copper ions are: Which statement is correct? ions are a better oxidizing agent than ions. Copper metal is a better reducing agent than ions. ions will spontaneously form copper metal and ions in solution. Copper metal can be spontaneously oxidized by ions to form ions. 8
9 44. The same quantity of electricity is passed through separate dilute aqueous solutions of sulfuric acid and copper(ii) sulfate using platinum electrodes under the same conditions. Which statement is correct? The same volume of oxygen is obtained in both cases. The same volume of hydrogen is obtained in both cases. The amount of copper deposited at the negative electrode in the copper(ii) sulfate solution is half the amount of hydrogen gas formed at the negative electrode in the sulfuric acid solution. The ph of both solutions increases as the electrolysis proceeds. 45. Which species of vanadium has a different oxidation number from the rest? 46. Which statement is correct for the following reaction? is the oxidizing agent and it undergoes reduction. is the reducing agent and it undergoes oxidation. is the oxidizing agent and it undergoes oxidation. is the reducing agent and it undergoes reduction. 47. Which statement about an electrolytic cell is correct? Chemical energy is converted to electrical energy. Electrons move through the electrolyte. The cathode is the negative electrode. The negative ions move towards the negative electrode. 48. At which side of the equation are electrons, ions and needed to complete the half-equation? 49. What are the correct names for and, using oxidation numbers? Potassium permanganate and potassium dichromate Potassium manganate(iv) and potassium chromate(vii) Potassium permanganate(iv) and potassium dichromate(vii) Potassium manganate(vii) and potassium dichromate(vi) 9
10 50. At which electrodes does oxidation occur in a voltaic cell and in an electrolytic cell? 51. What are the correct oxidation numbers of chromium in and manganese in? 52. Zinc is more reactive than copper. In this voltaic cell, which species is reduced and in which direction do negative ions flow in the salt bridge? 53. Which process occurs when a molten salt is electrolysed? The metal ion is oxidized and deposited on the negative electrode (cathode). The metal ion is reduced and deposited on the negative electrode (cathode). The metal ion is oxidized and deposited on the positive electrode (anode). The metal ion is reduced and deposited on the positive electrode (anode). 10
11 54. Which species are produced at each electrode during the electrolysis of molten lead(ii) bromide,? 55. Consider the following standard electrode potentials. Which species will reduce H Fe (aq) Sn (aq) Sn(s) Fe (aq) (aq) to H (g) under standard conditions? 56. A number of molten metal chlorides are electrolysed, using the same current for the same length of time. Which metal will be produced in the greatest amount, in mol? Mg Al K Ca 57. The overall equation of a voltaic cell is: The standard electrode potential for, is. What is the standard electrode potential for the silver half-cell,, in V? 58. Which species are the oxidizing and reducing agents in the following reaction? 11
12 59. Which components are used to make the standard hydrogen electrode? 60. What is the cell potential, in V, of the reaction below? 61. What is the name of? Cobalt(II) phosphite Cobalt(II) phosphate Cobalt(III) phosphite Cobalt(III) phosphate 62. Consider the following reaction. Which statement is correct? is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation. is the reducing agent because the oxidation number of nitrogen changes from to. Sn is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes reduction. Sn is the reducing agent because the oxidation number of tin changes from 0 to. 63. Which statements are correct for the electrolysis of molten lead(ii) bromide,? I. is reduced at the negative electrode (cathode). II. is oxidized at the positive electrode (anode). III. Bubbles of a brown gas are observed at the negative electrode (cathode). 64. Which statement is correct about a reducing agent? It is reduced by gaining electrons. It is oxidized by gaining electrons. It is oxidized by losing electrons. It is reduced by losing electrons. 12
13 65. What is the correct increasing order of reactivity of the metals X, Y and Z based on the following information? 66. Which statement describes a reducing agent? It is reduced and gains electrons. It is reduced and loses electrons. It is oxidized and gains electrons. It is oxidized and loses electrons. 67. Which is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? 68. The overall reaction in the voltaic cell below is: Which statement is correct for the nickel half-cell? Nickel is the positive electrode (cathode) and is reduced. Nickel is the negative electrode (anode) and is reduced. Nickel is the positive electrode (cathode) and is oxidized. Nickel is the negative electrode (anode) and is oxidized. 13
14 69. In the electrolytic cell shown, at which electrode will chlorine form, and what is the process taking place there? 70. Consider the following reaction. Which statement is correct? is the oxidizing agent and the oxidation number of chromium changes from +3 to +6. is the reducing agent and undergoes reduction. is the oxidizing agent and the oxidation number of chlorine changes from +1 to 0. is the reducing agent and the oxidation number of chlorine changes from 1 to Consider the following two standard electrode potentials at 298 K. What is the equation and cell potential for the spontaneous reaction that occurs? 72. What happens during the electrolysis of concentrated aqueous potassium chloride? I. Reduction takes place at the negative electrode (cathode). II. Hydrogen gas is evolved at the negative electrode (cathode). III. The ph of the electrolyte increases. 73. An aqueous solution of a metal salt is electrolysed. Which factor will have no effect on the mass of the metal deposited on the negative electrode (cathode), if all other variables remain constant? Size of metal ion Relative atomic mass of metal Current Charge on metal ion 14
15 74. Which are correct statements about a voltaic cell? I. A spontaneous redox reaction occurs which converts chemical energy to electrical energy. II. Oxidation occurs at the negative electrode (anode). III. Electricity is conducted by the movement of electrons through the salt bridge. 75. The standard electrode potentials of some half-reactions are given below. Which of the following reactions will occur spontaneously? Iodine reduces to Iodine reduces to Iodine oxidizes to Iodine oxidizes to 76. Which statement is correct for electroplating an object with gold? The object must be the negative electrode (cathode). The negative electrode (cathode) must be gold. The object must be the positive electrode (anode). The gold electrode must be pure. 77. Which compound contains nitrogen with an oxidation number of +3? NH 4Cl HNO 3 N 2O 4 KNO A voltaic cell is made by connecting zinc and lead half-cells. The overall equation for the reaction occurring in the cell is shown below. Which statements are correct when the cell produces electricity? I. The zinc is oxidized. II. Electrons move from zinc to lead in the external circuit. III. The mass of the lead electrode increases. 79. Which process occurs during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? Oxidation occurs at the positive electrode (anode). Electrons move through the electrolyte. Sodium ions move through the electrolyte to the positive electrode (anode). Chloride ions move through the electrolyte and are reduced at the negative electrode (cathode). 15
16 80. What is the name of? Copper(I) sulfide Copper(I) sulfate Copper(II) sulfide Copper(II) sulfate 81. Consider the following reaction: Which statement is correct? is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation. is the reducing agent because it undergoes oxidation. is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation. is the reducing agent because it undergoes oxidation. 82. What occurs during the operation of a voltaic cell based on the following overall reaction? 83. Consider the following standard electrode potentials: What is the value of the cell potential, in V, for the spontaneous reaction that occurs when the two halfcells are connected together? Two electrolytic cells are connected in series and the same current passes through each cell. The first cell contains silver electrodes in silver nitrate solution. The second cell contains copper electrodes in copper(ii) sulfate solution. In one experiment 1.00 g of silver is deposited in the first cell. What mass of copper, in g, is deposited in the second cell? 16
17 85. What is the correct decreasing order of reactivity of the metals X, Y and Z based on the following equations? X Y Z Y Z X Z Y X Y X Z 86. What is produced at the positive electrode (anode) and negative electrode (cathode) during the electrolysis of molten lithium chloride and molten lead bromide? 87. Which of the following redox reactions take place? I. II. III. 88. Which species could be reduced to form? NO 89. Consider the overall reaction taking place in a voltaic cell. What is the role of zinc in the cell? The positive electrode and the oxidizing agent. The positive electrode and the reducing agent. The negative electrode and the oxidizing agent. The negative electrode and the reducing agent. 17
18 90. What happens to the manganese in the following reaction? It is oxidized and its oxidation number increases. It is oxidized and its oxidation number decreases. It is reduced and its oxidation number increases. It is reduced and its oxidation number decreases. 1. B 2. A 3. B 4. D 5. C 6. B 7. B 8. C 9. D 10. A 11. B 12. C 13. C 14. C 15. D 16. B 17. C 18. D 19. B 20. D 21. B 22. B 23. D 24. D 25. D 26. A 27. D 28. C 29. D 30. D 31. A 32. A 33. D 34. C 35. A 36. D 37. A 38. A 39. C 40. A 41. B 42. C 43. C 44. A 45. D 46. A 47. C 48. A 49. D 50. C 51. B 52. A 53. B 54. D 55. C 56. C 57. C 58. D 59. A 60. B 61. B 62. D 63. A 64. C 65. A 66. D 67. B 68. D 69. D 70. C 71. B 72. D 73. A 74. A 75. D 76. A 77. D 78. D 79. A 80. A 81. B 82. C 83. D 84. C 85. D 86. D 87. A 88. B 89. D 90. D 18
Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction
 Name Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction 1. What are the oxidation numbers of the elements in sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4? Hydrogen Sulfur Oxygen A. +1 +6 2 B. +1 +4 2 C. +2 +1 +4 D. +2 +6 8 2. Consider
Name Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction 1. What are the oxidation numbers of the elements in sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4? Hydrogen Sulfur Oxygen A. +1 +6 2 B. +1 +4 2 C. +2 +1 +4 D. +2 +6 8 2. Consider
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17
 Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number
 General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
Danyal Education (Contact: ) A commitment to teach and nurture
 Chemistry of Reactions: Redox (#) Candidates should be able to: a) define oxidation and reduction (redox) in terms of oxygen/hydrogen gain/loss b) define redox in terms of electron transfer and changes
Chemistry of Reactions: Redox (#) Candidates should be able to: a) define oxidation and reduction (redox) in terms of oxygen/hydrogen gain/loss b) define redox in terms of electron transfer and changes
Redox Reactions, Chemical Cells and Electrolysis
 Topic 5 Redox Reactions, Chemical Cells and Electrolysis Part A Unit-based exercise Unit 19 Chemical cells in daily life Fill in the blanks 1 chemical; electrical 2 electrolyte 3 voltmeter; multimeter
Topic 5 Redox Reactions, Chemical Cells and Electrolysis Part A Unit-based exercise Unit 19 Chemical cells in daily life Fill in the blanks 1 chemical; electrical 2 electrolyte 3 voltmeter; multimeter
Chem II. Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq)
 Redox Review Chem II 1. What is the sum of the oxidation numbers of the atoms in the compound CO2? A) 0 B) 2 C) 4 D) +4 2. In which substance does phosphorus have a +3 oxidation state? A) P4O10 B) PCl5
Redox Review Chem II 1. What is the sum of the oxidation numbers of the atoms in the compound CO2? A) 0 B) 2 C) 4 D) +4 2. In which substance does phosphorus have a +3 oxidation state? A) P4O10 B) PCl5
Oxidation numbers are charges on each atom. Oxidation-Reduction. Oxidation Numbers. Electrochemical Reactions. Oxidation and Reduction
 Oxidation-Reduction Oxidation numbers are charges on each atom. 1 2 Electrochemical Reactions Oxidation Numbers In electrochemical reactions, electrons are transferred from one species to another. In order
Oxidation-Reduction Oxidation numbers are charges on each atom. 1 2 Electrochemical Reactions Oxidation Numbers In electrochemical reactions, electrons are transferred from one species to another. In order
Redox. Question Paper. Cambridge International Examinations Chemical Reactions. Score: /43. Percentage: /100
 Redox Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub-Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations hemical Reactions Redox Question Paper Time llowed: 52 minutes Score: /43 Percentage:
Redox Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub-Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations hemical Reactions Redox Question Paper Time llowed: 52 minutes Score: /43 Percentage:
Chem!stry. Assignment on Redox
 Chem!stry Name: ( ) Class: Date: / / Assignment on Redox Question 1: Which one of the following elements is the most powerful reducing agent? A Aluminium B Copper C Lead D Potassium Question 2: Which of
Chem!stry Name: ( ) Class: Date: / / Assignment on Redox Question 1: Which one of the following elements is the most powerful reducing agent? A Aluminium B Copper C Lead D Potassium Question 2: Which of
Regents review Electrochemistry(redox)
 2011-2012 1. Chlorine has an oxidation state of +3 in the compound A) HClO B) HClO2 C) HClO3 D) HClO4 2. What is the oxidation number of iodine in KIO4? A) +1 B) 1 C) +7 D) 7 3. What is the oxidation number
2011-2012 1. Chlorine has an oxidation state of +3 in the compound A) HClO B) HClO2 C) HClO3 D) HClO4 2. What is the oxidation number of iodine in KIO4? A) +1 B) 1 C) +7 D) 7 3. What is the oxidation number
(c) In marble, we assign calcium ion an oxidation number of +2, and oxygen a value of 2. We can determine the value of carbon in CaCO 3 as follows:
 Example Exercise 17.1 Calculating Oxidation Numbers for Carbon Calculate the oxidation number for carbon in each of the following compounds: (a) diamond, C (b) dry ice, CO 2 (c) marble, CaCO 3 (d) baking
Example Exercise 17.1 Calculating Oxidation Numbers for Carbon Calculate the oxidation number for carbon in each of the following compounds: (a) diamond, C (b) dry ice, CO 2 (c) marble, CaCO 3 (d) baking
Unit 13 Electrochemistry Review
 1. What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in NaNO2? A) +1 B) +2 C) +3 D) +4 2. Given the reaction that occurs in an electrochemical cell: Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) During this reaction, the
1. What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in NaNO2? A) +1 B) +2 C) +3 D) +4 2. Given the reaction that occurs in an electrochemical cell: Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) During this reaction, the
9.1 Exercises. HClO
 Topic 9 Oxidation and Reduction Answers 9.1 Exercises 1. Define oxidation and reduction in terms of a) electron transfer Oxidation is the loss of electrons from an atom, ion or molecule. Reduction is the
Topic 9 Oxidation and Reduction Answers 9.1 Exercises 1. Define oxidation and reduction in terms of a) electron transfer Oxidation is the loss of electrons from an atom, ion or molecule. Reduction is the
Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes
 Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes Chemical Activity (or Chemical Reactivity) is the measure of the reactivity of elements. If an element has high activity, then it means that the element is willing to
Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes Chemical Activity (or Chemical Reactivity) is the measure of the reactivity of elements. If an element has high activity, then it means that the element is willing to
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW. C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3. A. Fe B. CO
 CHAPTER 5 REVIEW 1. The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 What is the reducing agent in this process? A. Fe B. CO C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW 1. The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 What is the reducing agent in this process? A. Fe B. CO C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3
SCHOOL YEAR CH- 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE: 12
 SCHOOL YEAR 2017-18 NAME: CH- 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE: 12 TEST A Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. During oxidation, one or more electrons
SCHOOL YEAR 2017-18 NAME: CH- 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE: 12 TEST A Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. During oxidation, one or more electrons
(for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes)
 www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 20.4-3 In a voltaic cell electrons flow from the anode to the cathode. Value 2. chem10b 20.1-35 How many grams
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 20.4-3 In a voltaic cell electrons flow from the anode to the cathode. Value 2. chem10b 20.1-35 How many grams
CHEM N-12 November In the electrolytic production of Al, what mass of Al can be deposited in 2.00 hours by a current of 1.8 A?
 CHEM161 014-N-1 November 014 In the electrolytic production of Al, what mass of Al can be deposited in.00 hours by a current of 1.8 A? What products would you expect at the anode and the cathode on electrolysis
CHEM161 014-N-1 November 014 In the electrolytic production of Al, what mass of Al can be deposited in.00 hours by a current of 1.8 A? What products would you expect at the anode and the cathode on electrolysis
Chemical Equation Calculations
 Mole Relationships Chemical Equation Calculations 1. How many moles of chlorine gas react with 1 mol of hydrogen gas according to the balanced chemical equation? (a) 1 mol (b) 2 mol (c) 3 mol (d) 4 mol
Mole Relationships Chemical Equation Calculations 1. How many moles of chlorine gas react with 1 mol of hydrogen gas according to the balanced chemical equation? (a) 1 mol (b) 2 mol (c) 3 mol (d) 4 mol
Page 1 Name: 2Al 3+ (aq) + 3Mg(s) 3Mg 2+ (aq) + 2Al(s) Fe 2 O 3 + 2Al Al 2 O 3 + 2Fe
 9666-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of chromium in the chromate ion, CrO 2-4? A) +8 B) +3 C) +2 D) +6 2) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in Na 2 S 2 O 3? A) +6 B) +4 C) +2 D) -1
9666-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of chromium in the chromate ion, CrO 2-4? A) +8 B) +3 C) +2 D) +6 2) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in Na 2 S 2 O 3? A) +6 B) +4 C) +2 D) -1
9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction
 9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 - Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron loss and gain Oxidation The loss of electrons from a substance. This may happen through the gain
9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 - Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron loss and gain Oxidation The loss of electrons from a substance. This may happen through the gain
A voltaic cell using the following reaction is in operation: 2 Ag + (lm) + Cd(s) 2 Ag(s) + Cd 2+ (l M)
 0. Cu (s) + 2Ag + Cu 2+ + 2Ag (s) If the equilibrium constant for the reaction above is 3.7x10 15, which of the following correctly describes the standard voltage, E o and the standard free energy change,
0. Cu (s) + 2Ag + Cu 2+ + 2Ag (s) If the equilibrium constant for the reaction above is 3.7x10 15, which of the following correctly describes the standard voltage, E o and the standard free energy change,
Moles, Mass, and Limiting Reactants
 Moles, Mass, and Limiting Reactants Interpreting a Chemical Equation 1. How many moles of chlorine gas react with 1 mol of hydrogen gas according to the balanced chemical equation? (a) 1 mol (b) 2 mol
Moles, Mass, and Limiting Reactants Interpreting a Chemical Equation 1. How many moles of chlorine gas react with 1 mol of hydrogen gas according to the balanced chemical equation? (a) 1 mol (b) 2 mol
ELECTROCHEMISTRY. these are systems involving oxidation or reduction there are several types METALS IN CONTACT WITH SOLUTIONS OF THEIR IONS
 Electrochemistry 1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY REDOX Reduction gain of electrons Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e > Cu(s) Oxidation removal of electrons Zn(s) > Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e HALF CELLS these are systems involving oxidation or
Electrochemistry 1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY REDOX Reduction gain of electrons Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e > Cu(s) Oxidation removal of electrons Zn(s) > Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e HALF CELLS these are systems involving oxidation or
(c) dilute solution of glucose (d) chloroform 12 Which one of the following represents the same net reaction as the electrolysis of aqueous H2SO4
 1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
REDOX test practice. 2 Cr(s) + 3 Sn 2+ (aq) 2 Cr 3+ (aq) + 3 Sn(s)
 1. Which polyatomic ion has a charge of 3? A) chromate ion B) oxalate ion C) phosphate ion D) thiocyanate ion 2. What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in NaNO2? A) +1 B) +2 C) +3 D) +4 3. What are the
1. Which polyatomic ion has a charge of 3? A) chromate ion B) oxalate ion C) phosphate ion D) thiocyanate ion 2. What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in NaNO2? A) +1 B) +2 C) +3 D) +4 3. What are the
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Introduction to Electrochemistry
 ADVANCED PLACEMENT CHEMISTRY Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Introduction to Electrochemistry Students will be able to: identify oxidation and reduction of chemical species; identify oxidants and reductants
ADVANCED PLACEMENT CHEMISTRY Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Introduction to Electrochemistry Students will be able to: identify oxidation and reduction of chemical species; identify oxidants and reductants
Electrolysis. Question Paper. Cambridge International Examinations. Score: /48. Percentage: /100
 Electrolysis Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations Electrolysis Question Paper Time llowed: 58 minutes Score: /48 Percentage: /100 1 queous
Electrolysis Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations Electrolysis Question Paper Time llowed: 58 minutes Score: /48 Percentage: /100 1 queous
CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems
 1. When the redox equation CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems MnO 4 (aq) + H + (aq) + H 3 AsO 3 (aq) Mn 2+ (aq) + H 3 AsO 4 (aq) + H 2 O(l) is properly balanced, the coefficients will
1. When the redox equation CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems MnO 4 (aq) + H + (aq) + H 3 AsO 3 (aq) Mn 2+ (aq) + H 3 AsO 4 (aq) + H 2 O(l) is properly balanced, the coefficients will
REDOX AND ELECTROCHEMISTRY
 SOUTH HIGH SCHOOL REDOX AND ELECTROCHEMISTRY Regents Chemistry Dr. Lombardo NAME Content Objectives REDOX & ELECTROCHEMISTRY What will students know and be able to do by the end of this instructional unit?
SOUTH HIGH SCHOOL REDOX AND ELECTROCHEMISTRY Regents Chemistry Dr. Lombardo NAME Content Objectives REDOX & ELECTROCHEMISTRY What will students know and be able to do by the end of this instructional unit?
ELECTROCHEMISTRY. these are systems involving oxidation or reduction there are several types METALS IN CONTACT WITH SOLUTIONS OF THEIR IONS
 Electrochemistry 1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY REDOX Reduction gain of electrons Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e > Cu(s) Oxidation removal of electrons Zn(s) > Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e HALF CELLS these are systems involving oxidation or
Electrochemistry 1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY REDOX Reduction gain of electrons Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e > Cu(s) Oxidation removal of electrons Zn(s) > Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e HALF CELLS these are systems involving oxidation or
Unit 8 Redox 8-1. At the end of this unit, you ll be able to
 8-1 Unit 8 Redox At the end of this unit, you ll be able to Define and identify oxidation reactions Define and identify reduction reactions Assign oxidation numbers to elements in a compound Write and
8-1 Unit 8 Redox At the end of this unit, you ll be able to Define and identify oxidation reactions Define and identify reduction reactions Assign oxidation numbers to elements in a compound Write and
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION
 OXIDATION AND REDUCTION IMPORTANT FACTS: IMPORTANT DEFINATIONS Many chemical reactions involve the addition of oxygen or hydrogen to the reactants. The reaction in which oxygen is added is called oxidation
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION IMPORTANT FACTS: IMPORTANT DEFINATIONS Many chemical reactions involve the addition of oxygen or hydrogen to the reactants. The reaction in which oxygen is added is called oxidation
DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR.
 Practice Test 20.1 (va pg 1 of 5) This is practice - Do NOT cheat yourself of finding out what you are capable of doing. Be sure you follow the testing conditions outlined below. DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR.
Practice Test 20.1 (va pg 1 of 5) This is practice - Do NOT cheat yourself of finding out what you are capable of doing. Be sure you follow the testing conditions outlined below. DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR.
Chemistry 102 Chapter 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS
 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
ELECTROCHEMISTRY OXIDATION-REDUCTION
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
AP Chemistry: Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Answers
 AP Chemistry: Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Answers 14. Questions 14-17 The spontaneous reaction that occurs when the cell in the picture operates is as follows: 2Ag + + Cd (s) à 2 Ag (s) + Cd 2+ (A)
AP Chemistry: Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Answers 14. Questions 14-17 The spontaneous reaction that occurs when the cell in the picture operates is as follows: 2Ag + + Cd (s) à 2 Ag (s) + Cd 2+ (A)
Find the oxidation numbers of each element in a reaction and see which ones have changed.
 Find the oxidation numbers of each element in a reaction and see which ones have changed. Rules for oxidation numbers: An element that is not in a compound has an oxidation number of zero (0) Group 1 Metals
Find the oxidation numbers of each element in a reaction and see which ones have changed. Rules for oxidation numbers: An element that is not in a compound has an oxidation number of zero (0) Group 1 Metals
11/3/09. Aqueous Solubility of Compounds. Aqueous Solubility of Ionic Compounds. Aqueous Solubility of Ionic Compounds
 Aqueous Solubility of Compounds Not all compounds dissolve in water. Solubility varies from compound to compound. Chapter 5: Chemical Reactions Soluble ionic compounds dissociate. Ions are solvated Most
Aqueous Solubility of Compounds Not all compounds dissolve in water. Solubility varies from compound to compound. Chapter 5: Chemical Reactions Soluble ionic compounds dissociate. Ions are solvated Most
Worked solutions. Chapter 9. Exercises O 3
 Worked solutions Chapter 9 Exercises 1 The numbers are assigned following the strategy on page 408. In most of these it is best to assign the values for [2] and H [+1] first, and then assign values to
Worked solutions Chapter 9 Exercises 1 The numbers are assigned following the strategy on page 408. In most of these it is best to assign the values for [2] and H [+1] first, and then assign values to
Chapter 16 Redox Reactions
 Chapter 16 Redox Reactions p.1/7 16.1 Defining Oxidation and Reduction In terms of addition/removal of oxygen Consider the following reaction 1. Mg changed to MgO because Mg is oxidized by CuO. 2. CuO
Chapter 16 Redox Reactions p.1/7 16.1 Defining Oxidation and Reduction In terms of addition/removal of oxygen Consider the following reaction 1. Mg changed to MgO because Mg is oxidized by CuO. 2. CuO
(i) Voltameter consist of a vessel, two electrodes and electrolytic solution.
 Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry which deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical changes taking place in redox reactions i.e., how chemical energy produced
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry which deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical changes taking place in redox reactions i.e., how chemical energy produced
Electrochemistry. Galvanic Cell. Page 1. Applications of Redox
 Electrochemistry Applications of Redox Review Oxidation reduction reactions involve a transfer of electrons. OIL- RIG Oxidation Involves Loss Reduction Involves Gain LEO-GER Lose Electrons Oxidation Gain
Electrochemistry Applications of Redox Review Oxidation reduction reactions involve a transfer of electrons. OIL- RIG Oxidation Involves Loss Reduction Involves Gain LEO-GER Lose Electrons Oxidation Gain
Reactions in aqueous solutions Redox reactions
 Reactions in aqueous solutions Redox reactions Redox reactions In precipitation reactions, cations and anions come together to form an insoluble ionic compound. In neutralization reactions, H + ions and
Reactions in aqueous solutions Redox reactions Redox reactions In precipitation reactions, cations and anions come together to form an insoluble ionic compound. In neutralization reactions, H + ions and
Name: Regents Chemistry Date:
 Name: Date: 1. The reaction CuO + CO CO 2 + Cu is an example of (A) reduction, only (B) oxidation, only (C) both oxidation and reduction (D) neither oxidation nor reduction 6. In which compound does chlorine
Name: Date: 1. The reaction CuO + CO CO 2 + Cu is an example of (A) reduction, only (B) oxidation, only (C) both oxidation and reduction (D) neither oxidation nor reduction 6. In which compound does chlorine
Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions
 Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions 19-1 Oxidation and Reduction I. Oxidation States A. The oxidation rules (as summarized by Mr. Allan) 1. In compounds, hydrogen has an oxidation # of +1. In compounds,
Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions 19-1 Oxidation and Reduction I. Oxidation States A. The oxidation rules (as summarized by Mr. Allan) 1. In compounds, hydrogen has an oxidation # of +1. In compounds,
Chapter 17. Oxidation-Reduction. Cu (s) + 2AgNO 3(aq) 2Ag (s) + Cu(NO 3 ) 2(aq) pale blue solution. colorless solution. silver crystals.
 Chapter 17 Oxidation-Reduction Cu (s) + 2AgNO 3(aq) 2Ag (s) + Cu(NO 3 ) 2(aq) copper wire colorless solution silver crystals pale blue solution Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry 10e John
Chapter 17 Oxidation-Reduction Cu (s) + 2AgNO 3(aq) 2Ag (s) + Cu(NO 3 ) 2(aq) copper wire colorless solution silver crystals pale blue solution Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry 10e John
Electrochemistry. A. Na B. Ba C. S D. N E. Al. 2. What is the oxidation state of Xe in XeO 4? A +8 B +6 C +4 D +2 E 0
 Electrochemistry 1. Element M reacts with oxygen to from an oxide with the formula MO. When MO is dissolved in water, the resulting solution is basic. Element M is most likely: A. Na B. Ba C. S D. N E.
Electrochemistry 1. Element M reacts with oxygen to from an oxide with the formula MO. When MO is dissolved in water, the resulting solution is basic. Element M is most likely: A. Na B. Ba C. S D. N E.
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species.
 Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
Definition 1 An element or compound is oxidized when it gains oxygen atoms
 Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 5.3 REDOX EQUILIBRIA BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
 AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 5.3 REDOX EQUILIBRIA BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS 1. (a) Define the term oxidising agent in terms of electrons.... 2. Use the data in the table below, where appropriate,
AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 5.3 REDOX EQUILIBRIA BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS 1. (a) Define the term oxidising agent in terms of electrons.... 2. Use the data in the table below, where appropriate,
C4 Quick Revision Questions
 C4 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 Write the equation which shows the formation of iron oxide Answer 1... of 50 4Fe + 3O 2 2Fe 2 O 3 Question
C4 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 Write the equation which shows the formation of iron oxide Answer 1... of 50 4Fe + 3O 2 2Fe 2 O 3 Question
YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min
 YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Useful data: Q = It. Faraday Constant = 96,500 C mol -1. Use the Periodic table, given below, where necessary. Marks Grid [For Examiners use only] Question
YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Useful data: Q = It. Faraday Constant = 96,500 C mol -1. Use the Periodic table, given below, where necessary. Marks Grid [For Examiners use only] Question
REDOX EQUILIBRIA AND FEASIBILITY OF A REACTION
 REDOX EQUILIBRIA AND FEASIBILITY OF A REACTION Oxidizing agent Reducing agent Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Electron transfer reactions Electrons transferred from one substance to another Change in oxidation
REDOX EQUILIBRIA AND FEASIBILITY OF A REACTION Oxidizing agent Reducing agent Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Electron transfer reactions Electrons transferred from one substance to another Change in oxidation
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox)
 Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Electrochemistry involves the study of the conversions between chemical and electrical energy. Voltaic (galvanic) cells use chemical reactions to produce an electric current.
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Electrochemistry involves the study of the conversions between chemical and electrical energy. Voltaic (galvanic) cells use chemical reactions to produce an electric current.
Assignment #1: Redox Reaction Skill Drills
 Assignment #1: Redox Reaction Skill Drills Skill #1 Assigning Oxidation Numbers (Text Reference: p. 639 641) All elements have an oxidation number of 0. In compounds, oxidation numbers add up to 0. o Group
Assignment #1: Redox Reaction Skill Drills Skill #1 Assigning Oxidation Numbers (Text Reference: p. 639 641) All elements have an oxidation number of 0. In compounds, oxidation numbers add up to 0. o Group
1.11 Electrochemistry
 1.11 Electrochemistry Recap from 1.7: Oxidation and Reduction: Oxidation and Reduction: Oxidation and reduction reactions can be identified by looking at the reaction in terms of electron transfer: Definitions:
1.11 Electrochemistry Recap from 1.7: Oxidation and Reduction: Oxidation and Reduction: Oxidation and reduction reactions can be identified by looking at the reaction in terms of electron transfer: Definitions:
AP Questions: Electrochemistry
 AP Questions: Electrochemistry I 2 + 2 S 2O 2-3 2 I - + S 4O 2-6 How many moles of I 2 was produced during the electrolysis? The hydrogen gas produced at the cathode during the electrolysis was collected
AP Questions: Electrochemistry I 2 + 2 S 2O 2-3 2 I - + S 4O 2-6 How many moles of I 2 was produced during the electrolysis? The hydrogen gas produced at the cathode during the electrolysis was collected
Electrochemistry Worksheets
 Electrochemistry Worksheets Donald Calbreath, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive
Electrochemistry Worksheets Donald Calbreath, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive
Practice Packet Unit 13: Electrochemistry (RedOx)
 Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Practice Packet Unit 13: Electrochemistry (RedOx) Redox and Batteries? Ain t nobody got time for that!!! 1 Lesson 1: Oxidation States Oxidation numbers are very important
Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Practice Packet Unit 13: Electrochemistry (RedOx) Redox and Batteries? Ain t nobody got time for that!!! 1 Lesson 1: Oxidation States Oxidation numbers are very important
Definition: the process by which one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances. Another name for a chemical change.
 Chemical Reactions I. What is a chemical reaction? Definition: the process by which one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances. Another name for a chemical change. A. How can you
Chemical Reactions I. What is a chemical reaction? Definition: the process by which one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances. Another name for a chemical change. A. How can you
Moles, Mass, and Limiting Reactants
 Moles, Mass, and Limiting Reactants Answers follow at end Interpreting a Chemical Equation) 1. How many moles of chlorine gas react with 1 mol of hydrogen gas according tothe balanced chemical equation?
Moles, Mass, and Limiting Reactants Answers follow at end Interpreting a Chemical Equation) 1. How many moles of chlorine gas react with 1 mol of hydrogen gas according tothe balanced chemical equation?
Electrodes are normally made out of inert (unreactive) materials. Graphite and platinum are common electrode materials.
 Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
3. Solids cannot conduct electricity because the ions cannot move freely 4. Electrolytic cell
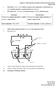 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
CHEM J-14 June 2014
 CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
7. Which equation represents an oxidation-reduction reaction?
 1. Which polyatomic ion has a charge of 3? 1) chromate ion 2) oxalate ion 3) phosphate ion 4) thiocyanate ion 2. An oxidation-reduction reaction involves the 1) sharing of electrons 2) sharing of protons
1. Which polyatomic ion has a charge of 3? 1) chromate ion 2) oxalate ion 3) phosphate ion 4) thiocyanate ion 2. An oxidation-reduction reaction involves the 1) sharing of electrons 2) sharing of protons
Chapter 7. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
 Chapter 7 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chapter Map Oxidation Historically oxidation meant reacting with oxygen. 2Zn(s) + O 2 (g) 2ZnO(s) Zn Zn 2+ + 2e or 2Zn 2Zn 2+ + 4e O + 2e O 2 or O 2 + 4e 2O 2 Oxidation
Chapter 7 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chapter Map Oxidation Historically oxidation meant reacting with oxygen. 2Zn(s) + O 2 (g) 2ZnO(s) Zn Zn 2+ + 2e or 2Zn 2Zn 2+ + 4e O + 2e O 2 or O 2 + 4e 2O 2 Oxidation
Chapter 9 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop
 Chapter 9 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Chapter Map Oxidation Historically, oxidation meant reacting with oxygen. 2Zn(s) + O 2 (g) 2ZnO(s) Zn Zn 2+ + 2e or 2Zn
Chapter 9 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Chapter Map Oxidation Historically, oxidation meant reacting with oxygen. 2Zn(s) + O 2 (g) 2ZnO(s) Zn Zn 2+ + 2e or 2Zn
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking
 INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Sixth Edition by Charles H. Corwin Oxidation and Reduction by Christopher Hamaker 1 Oxidation Reduction Reactions Oxidation reduction reactions are
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Sixth Edition by Charles H. Corwin Oxidation and Reduction by Christopher Hamaker 1 Oxidation Reduction Reactions Oxidation reduction reactions are
An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction involves the transfer of electrons (e - ). Sodium transfers its electrons to chlorine
 Oxidation-Reduction An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction involves the transfer of electrons (e - ). Sodium transfers its electrons to chlorine 2 Chemists need a way to keep track of what happens in
Oxidation-Reduction An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction involves the transfer of electrons (e - ). Sodium transfers its electrons to chlorine 2 Chemists need a way to keep track of what happens in
Oxidation numbers are used to identify the path of electrons in redox reactions. Each element in the compound must be assigned an oxidation number.
 Packet 9: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Many reactions are oxidation-reduction reactions A.k.a redox Reaction where one atom loses electrons and another atom gains electrons Atoms that lose electrons are
Packet 9: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Many reactions are oxidation-reduction reactions A.k.a redox Reaction where one atom loses electrons and another atom gains electrons Atoms that lose electrons are
Practice Packet: Oxidation Reduction. Regents Chemistry: Mrs. Mintz. Practice Packet. Chapter 14: Oxidation Reduction & Electrochemistry
 Practice Packet: Oxidation Reduction Regents Chemistry: Mrs. Mintz Practice Packet Chapter 14: Oxidation Reduction & Electrochemistry 1 Assigning Oxidation Numbers Objective: How do we assign atoms the
Practice Packet: Oxidation Reduction Regents Chemistry: Mrs. Mintz Practice Packet Chapter 14: Oxidation Reduction & Electrochemistry 1 Assigning Oxidation Numbers Objective: How do we assign atoms the
2. What are the oxidation numbers of the underlined elements in each of the following
 1. Assign oxidation number to the underlined elements in each of the following species (a) NaH 2 PO 4 (b) NaHSO 4 (c) H 4_ P 2 O 7 (d) K 2 MnO 4 (e) CaO 2 (f) NaBH 4 (g) H 2 S 2 O 7 (h) KAl(SO 4 ) 2.12H
1. Assign oxidation number to the underlined elements in each of the following species (a) NaH 2 PO 4 (b) NaHSO 4 (c) H 4_ P 2 O 7 (d) K 2 MnO 4 (e) CaO 2 (f) NaBH 4 (g) H 2 S 2 O 7 (h) KAl(SO 4 ) 2.12H
GIRLS JUNIOR LYCEUM L-IMRIEĦEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017
 1 GIRLS JUNIOR LYCEUM L-IMRIEĦEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017 FORM: 4 CHEMISTRY Time: 1hr30min Name: Class: One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday One mole of any gas occupies
1 GIRLS JUNIOR LYCEUM L-IMRIEĦEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017 FORM: 4 CHEMISTRY Time: 1hr30min Name: Class: One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday One mole of any gas occupies
Electrochemistry. Chapter 18. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Electrochemical processes are oxidation-reduction reactions in which: the energy
Electrochemistry Chapter 18 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Electrochemical processes are oxidation-reduction reactions in which: the energy
5.0 Electricity and Chemistry
 5.0 Electricity and hemistry Question Paper Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic Electricity and hemistry Sub-Topic 5.0 Electricity and hemistry ooklet
5.0 Electricity and hemistry Question Paper Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic Electricity and hemistry Sub-Topic 5.0 Electricity and hemistry ooklet
Qualitative Analysis Part Two Anions & Gases
 Qualitative Analysis Part Two Anions & Gases Qualitative Tests for Anions Which anions must I know the tests for? Describe tests to identify the following anions: Carbonate CO 3 2 (by the addition of dilute
Qualitative Analysis Part Two Anions & Gases Qualitative Tests for Anions Which anions must I know the tests for? Describe tests to identify the following anions: Carbonate CO 3 2 (by the addition of dilute
Reaction Writing Sheet #1 Key
 Reaction Writing Sheet #1 Key Write and balance each of the following reactions and indicate the reaction type(s) present: 1. zinc + sulfur zinc sulfide 8 Zn (s) + S 8 (s) 8 ZnS (s) synthesis 2. potassium
Reaction Writing Sheet #1 Key Write and balance each of the following reactions and indicate the reaction type(s) present: 1. zinc + sulfur zinc sulfide 8 Zn (s) + S 8 (s) 8 ZnS (s) synthesis 2. potassium
Unit 12 Redox and Electrochemistry
 Unit 12 Redox and Electrochemistry Review of Terminology for Redox Reactions OXIDATION loss of electron(s) by a species; increase in oxidation number. REDUCTION gain of electron(s); decrease in oxidation
Unit 12 Redox and Electrochemistry Review of Terminology for Redox Reactions OXIDATION loss of electron(s) by a species; increase in oxidation number. REDUCTION gain of electron(s); decrease in oxidation
Lesson on Electrolysis
 Lesson on Electrolysis This lesson package includes a lesson plan, a worksheet for students, and teachers notes on the worksheet. Activity Lesson 1 (50 min-2 Period lesson) Teacher explains (page 1 to
Lesson on Electrolysis This lesson package includes a lesson plan, a worksheet for students, and teachers notes on the worksheet. Activity Lesson 1 (50 min-2 Period lesson) Teacher explains (page 1 to
Electrolysis. Introduction. Electrolysis APPENDIX. The key ideas required to understand this section are:
 Electrolysis APPENDIX 7 1 Introduction The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Redox reactions 100 Writings and balancing redox equations 104 Standard electrode potentials
Electrolysis APPENDIX 7 1 Introduction The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Redox reactions 100 Writings and balancing redox equations 104 Standard electrode potentials
Unit 4. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Unit 4 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 39. Changing a subscript in a correctly written chemical formula a. changes the number of moles represented
Unit 4 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 39. Changing a subscript in a correctly written chemical formula a. changes the number of moles represented
Colours in common redox reactions
 Colours in common redox reactions Fe 3+ Cr 2 O 7 MnO 4 - Cl 2 Br 2 I 2 Fe 2+ Cr 3+ Mn 2+ Cl - Br - I - Oxidation of metals Cu Fe Zn Mg Na Cu 2+ Fe 2+ Zn 2+ Mg 2+ Na + CHEM 2.7 Assessment For A: link one
Colours in common redox reactions Fe 3+ Cr 2 O 7 MnO 4 - Cl 2 Br 2 I 2 Fe 2+ Cr 3+ Mn 2+ Cl - Br - I - Oxidation of metals Cu Fe Zn Mg Na Cu 2+ Fe 2+ Zn 2+ Mg 2+ Na + CHEM 2.7 Assessment For A: link one
Homework 11. Electrochemical Potential, Free Energy, and Applications
 HW11 Electrochemical Poten!al, Free Energy, and Applica!ons Homework 11 Electrochemical Potential, Free Energy, and Applications Question 1 What is the E for Zn(s) Zn (aq) Ce (aq) Ce (aq) + cell + 4+ 3+
HW11 Electrochemical Poten!al, Free Energy, and Applica!ons Homework 11 Electrochemical Potential, Free Energy, and Applications Question 1 What is the E for Zn(s) Zn (aq) Ce (aq) Ce (aq) + cell + 4+ 3+
Topic 19 Redox 19.1 Standard Electrode Potentials. IB Chemistry T09D04
 Topic 19 Redox 19.1 Standard Electrode Potentials IB Chemistry T09D04 19.1 Standard Electrode Potentials 19.1.1 Describe the standard hydrogen electrode. (2) 19.1.2 Define the term standard electrode potential,
Topic 19 Redox 19.1 Standard Electrode Potentials IB Chemistry T09D04 19.1 Standard Electrode Potentials 19.1.1 Describe the standard hydrogen electrode. (2) 19.1.2 Define the term standard electrode potential,
Redox and Voltaic Cells
 Name: Redox and Voltaic Cells Period: 1. Which half-reaction equation represents the reduction of an iron(ii) ion? 1) Fe 2+ Fe 3+ + e 2) Fe 2+ + 2e Fe 1) 1 to +2 2) 1 to 2 3) Fe 3+ + e Fe 2+ 4) Fe Fe 2+
Name: Redox and Voltaic Cells Period: 1. Which half-reaction equation represents the reduction of an iron(ii) ion? 1) Fe 2+ Fe 3+ + e 2) Fe 2+ + 2e Fe 1) 1 to +2 2) 1 to 2 3) Fe 3+ + e Fe 2+ 4) Fe Fe 2+
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry. Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry. Notes.
 Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
Electrochemical Cells
 Electrochemical Cells There are two types: Galvanic and Electrolytic Galvanic Cell: a cell in which a is used to produce electrical energy, i.e., Chemical energy is transformed into Electrical energy.
Electrochemical Cells There are two types: Galvanic and Electrolytic Galvanic Cell: a cell in which a is used to produce electrical energy, i.e., Chemical energy is transformed into Electrical energy.
5072 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH SPA) BASIC TECHNIQUES 5067 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH PRACTICAL EXAM) BASIC TECHNIQUES
 5072 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH SPA) BASIC TECHNIQUES 5067 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH PRACTICAL EXAM) BASIC TECHNIQUES LEARNING OUTCOMES a) Be able to write formulae of simple compounds b) Be able to write
5072 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH SPA) BASIC TECHNIQUES 5067 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH PRACTICAL EXAM) BASIC TECHNIQUES LEARNING OUTCOMES a) Be able to write formulae of simple compounds b) Be able to write
Unit 4: Chemical Changes (Higher Content)
 Metals react with oxygen to produce metal oxides. E.g. Copper + Oxygen > Copper Oxide The reactions are oxidation reactions because the metals gain oxygen. Reactivity of Metals Metal Extraction Metals
Metals react with oxygen to produce metal oxides. E.g. Copper + Oxygen > Copper Oxide The reactions are oxidation reactions because the metals gain oxygen. Reactivity of Metals Metal Extraction Metals
UHS Tutoring. (4) Redox Reactions (02)
 UHS Tutoring (4) Redox Reactions (02) 8739 1844 www.uhsinternational.com UHS Tutoring 4. Oxidationreduction reactions are increasingly important as a source of energy Students learn to: A. Explain the
UHS Tutoring (4) Redox Reactions (02) 8739 1844 www.uhsinternational.com UHS Tutoring 4. Oxidationreduction reactions are increasingly important as a source of energy Students learn to: A. Explain the
Redox and Voltaic Cells
 Name: Redox and Voltaic Cells Period: 1. Which half-reaction equation represents the reduction of an iron(ii) ion? 1) Fe 2+ Fe 3+ + e 2) Fe 2+ + 2e Fe 1) 1 to +2 2) 1 to 2 3) Fe 3+ + e Fe 2+ 4) Fe Fe 2+
Name: Redox and Voltaic Cells Period: 1. Which half-reaction equation represents the reduction of an iron(ii) ion? 1) Fe 2+ Fe 3+ + e 2) Fe 2+ + 2e Fe 1) 1 to +2 2) 1 to 2 3) Fe 3+ + e Fe 2+ 4) Fe Fe 2+
Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry
 Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 9th Edition George W.J. Kenney, Jr, Professor of Chemistry Last Update: 11July2009 Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 9th Edition George W.J. Kenney, Jr, Professor of Chemistry Last Update: 11July2009 Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Name AP Chemistry September 30, 2013
 Name AP Chemistry September 30, 2013 AP Chemistry Exam Part I: 40 Questions, 40 minutes, Multiple Choice, No Calculator Allowed Bubble the correct answer on the blue side of your scantron for each of the
Name AP Chemistry September 30, 2013 AP Chemistry Exam Part I: 40 Questions, 40 minutes, Multiple Choice, No Calculator Allowed Bubble the correct answer on the blue side of your scantron for each of the
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Cells
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
