PFG-NMR ON DOUBLE EMULSIONS: A DETAILED LOOK INTO MOLECULAR PROCESSES
|
|
|
- Abner Cooper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 First published in: Magnetic Resonance in Food Science. An Exciting Future. Ed.: J.-P. Renou ISBN PFG-NMR ON DOUBLE EMULSIONS: A DETAILED LOOK INTO MOLECULAR PROCESSES R. Bernewitz 1, X. Guan 1, G. Guthausen 1, F. Wolf 2 and H. P. Schuchmann 2 KIT, D Karlsruhe, Germany 1 SRG10-2, Institute for Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics 2 Institute of Process Engineering in Life Sciences, Section I: Food Process Engineering 1 INTRODUCTION Single emulsions are of high interest in different fields and therefore well investigated. They provide more advantages when an emulsion is part of another emulsion, as double- or multiple emulsion. Multiple emulsions, as novel food systems, reduce the amount of fat in food or encapsulate active substances. They are not only of interest for food, but also for pharmaceutical or cosmetic products. As in case of single emulsions, multi-modality and droplet size distribution (DSD) of multiple emulsions are important parameters for product quality and physical properties (e.g. viscosity and shelf life). These parameters are also important to gain insight into mechanisms taking place in the second step of the two-step production of double emulsions, which still is not understood in detail. Currently, common measurement techniques for the determination of DSD and its modality of single emulsions are Laser light scattering, Laser diffraction, Ultra sonic attenuation and PFG-NMR. However, acoustic and optical methods do not work properly or not even at all, when aiming for information about structure properties of the inner emulsions. Additionally, results on the outer emulsion are not reliable anymore when using the optical methods, due to multiple diffraction inside the double emulsion. PFG-NMR is a well established method to determine the droplet size distribution of single emulsions. It is known to work non-destructive with a small workload and a high selectivity. In this context, high selectivity means, that the optical properties of the media do not play a role. Using 1 H-NMR for example, only molecules containing hydrogen can be detected. These molecules can be differentiated by their specific chemical shift in high resolution NMR, or by relaxation filters as applied in low filed NMR. Therefore, the PFG-NMR method is in principle suitable to determine structural parameters like DSD in double emulsions. However, the current restrictions have to be exploited, and new models have to be created to analyze the signal decays measured on double emulsions. Molecular processes like diffusion phenomena, relaxation and spectral properties have to be understood in order to obtain a correct interpretation of the data and quantitative meaningful double emulsion s DSD. EVA-STAR (Elektronisches Volltextarchiv Scientific Articles Repository)
2 2 METHOD AND RESULTS 2.1 Methods Preparation of W 1 /O/W 2 Double Emulsions. The double emulsions were produced in a two-step process: First, the inner emulsion was produced, using a tooth rim dispersing device. The inner emulsion consisted of water W 1 with 0.5% gelatine and vegetable oil with 10% PGPR90. In the second step, the inner emulsion was further emulsified by a colloid mill with water W 2 containing 2% LEO-10 and, recipe depended, 0.6% Xanthan. The typical range of mean oil droplets size is d 50,3 = 14 µm, and of W 1 droplets d 50,3 = 6 µm. In this work, double emulsions of the type W 1 /O/W 2 with a disperse phase ratio of 15%/35%/50% (Figure 1a)) were investigated by PFG-STE NMR experiments (Figure 1b)) and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) PFG-STE NMR on W 1 /O/W 2 Double Emulsions. The NMR experiments were performed on a Bruker Avance 200 SWB. The parameters of the PFG-STE sequence are summarized in Table 1. The sequence is known to be a suitable method to measure molecular diffusion phenomena. In comparison to a PFG-SE Hahn-Echo experiment, it allows longer diffusion times due to the T 2 -bypass after the second gradient pulse so that the diffusion time is restricted by T 1. PFG-NMR measures the displacement of molecules during. In pure substances, the diffusion of molecules is described by random movement, with a final displacement r( ), 1-3 In confining geometries, like in an emulsion s droplets, the mean free path differs from the one observed at free self-diffusion. Therefore, molecules exposed to restricted diffusion exhibit a different PFG-NMR signal. Summarizing, molecules in confined geometries show a different diffusion behaviour than molecules in the pure substance. NMR data of single emulsions are most commonly evaluated with the model of Murday and Cotts / von Neuman (MC) 3, 4. This model is valid for single emulsions of water and oil, containing spherical droplets with a mean diameter d 50,3 > 1 µm, assuming the Gaussian phase approximation. The question is, if data of double emulsions are modelled correctly by this model. Figure 1 a) Scheme of a W 1 /O/W 2 double emulsion b) PFG-STE NMR sequence.
3 Table 1 Parameters and their values of NMR experiments on a Bruker Avance 200 Symbol Parameter Typical Value(s) Gradient pulse duration 4 ms Diffusion time 50, 100, 150, 200, 300, 500 ms P 90 rf-pulse length 10 µs at 0 db 1 First rf-pulse delay ms D 1 Repetition time 8 s g Amplitude of magnetic gradient 3.54 mt/m 5.99 T/m linear in 32 steps; 3.54 mt/m 22 mt/m (W 2 ) G Amplitude of spoiler gradient 0.2 T/m Duration of spoiler gradient 5 ms Rise time for gradient 100 µs Time for gradient stabilisation 2 ms NS Number of scans 2 DS Number of dummy scans 2 Larmor-Frequency MHz Spectral width Hz Number of complex data points CLSM on W 1 /O/W 2 Double Emulsions. The double emulsions were additionally investigated by a CLSM in order to compare NMR results to a more direct method. To obtain a contrast between the three phases the oil phase was dyed with Rhodamine-B. CLSM was used because of its 2.5D-capability. This allows a scan of the sample slice by slice. 2.2 Results NMR Signal Attenuation of Double Emulsions. The spectra of a double emulsion, measured with = 0.3 s, exhibit specific resonances of water (at 4.6 ppm) and oil (Figure 2a)). The investigated double emulsion W 1 /O/W 2 was prepared as described in with the speciality that W 2 didn t contain Xanthan. The spectrum amplitudes depend on the gradient amplitude as it is expected for signal from diffusing molecules. In Figure 2b) the logarithmic signal attenuation of the double emulsion is shown together with the logarithmic signal attenuations of W 1 and W 1 /O single emulsion, which were retained during the production process. The pure water phase W 1 only shows a signal near g = 0 T/m (Figure 2 b), ). This is due to free self-diffusion of water molecules in W 1. The diffusion coefficient is in accordance with the water self diffusion at the measurement temperature of 22 C. The NMR data of the single emulsion, shown in figure 2b), was modelled with the MCmodel. Assuming a log-normal distribution function for the DSD, it revealed a median d 50,3 3.5 µm with a width of σ 0.5 of the corresponding Gaussian distribution. By a Coulter Counter LS230 laser diffraction device, the median of the single emulsion s DSD was determined to d 50,3 2 µm. Comparing both results, the difference of d 50,3 is within the mean standard deviation specified on the Coulter Counter.
4 W 1 /O W 1 /O/W 2 W 1 Figure 2 a) Spectrum of a W 1 /O/W 2 double emulsion as a function of g. b) Logarithmic signal attenuation of pure inner water phase W 1, the W 1 /O single emulsion after first emulsion step and the double emulsion. However, the signal attenuation of the double emulsion differs significantly from the attenuation of the single emulsion. Modelling of the data with the MC-model leads to d 50,3 7 µm with a width of σ Assuming a complete preservation of the simple emulsion s properties this DSD is physically meaningless. In the analysis, the whole water signal was considered and lead to the wrong DSD. But there are possible reasons for the failure of the data modelling: Also fractions of W 2 following the laws of restricted diffusion could have influenced the signal attenuation. Diffusion between the two water phases could occur, which leads to an imprecise separation of the signal of the two water phases. This means, diffusion takes place through the oil phase, which is called molecular exchange in our context. The bounds of the oil droplets function as a thin membrane in this picture. This phenomenon is also described for different inhomogeneous systems Influence of restriction on water diffusion in W 2. In Figure 3, the signal attenuations of O/W single emulsions are shown as a function of the disperse phase concentration. The emulsions were measured via PFG-STE-NMR at 200 MHz with = 0.05 s. The disperse phase ratio was varied from 0% to 50%. 0% means pure continuous phase, consisting of water with 2% Leo10 and 0.2% Xanthan.
5 Figure 3 Signal attenuation of O/W emulsions with different disperse phase ratios φ. The logarithmic signal attenuation of the pure continuous phase is a linear function of q², which was expected because of free self-diffusion. The curvature of ln(s/s 0 ) increases with growing disperse phase ratio, because of increasing non-spherical restriction of the water molecules between the oil droplets. However, taking the small range of q² into account, the influence of this effect is marginal. Regarding the range of q² of common PFG-NMR experiments (Figure 2b), the effect can be neglected for W 1 diffusional behaviour. Concluding, the outer phases in single emulsions as well as the outermost phase in double emulsions have to be considered as following restricted diffusion even at very small disperse phase concentrations Diffusion Phenomena between W 1 and W 2 in W 1 /O/W 2. In several publications, the possibility of molecular exchange in double emulsions is discussed In some publications 8-10, a molecular exchange model was applied, which originally was found to be applicable in case of cellular systems 5-7. There is, however, some controversy whether such effects are observed or other phenomena are responsible for the experimental results. One argument against the exchange hypothesis is that the solubility of the two substances is low and they tend to separate when mixed. To find out if and on which time scale diffusion between W 1 and W 2 takes place 11, the idea was to add a small amount of Xanthan to W 2. Xanthan is a common thickener, also used in food industry. It increases the viscosity and consequently decreases the mobility of molecules. In Figure 4a) NMR data obtained from a double emulsion with Xanthan in W 2 is shown. In comparison to a double emulsion without Xanthan (Figure 2a)), a sudden drop occurs after the first gradient step. This difference could be explained by decreased exchange between W 1 and W 2. To verify this suspicion, another experiment was performed, using driven diffusion effects. Right before the NMR experiment, the W 1 /O/W 2 double emulsions with Xanthan in W 2 were diluted with additional 50% W 2, containing different amounts of sugar (1%, 5%,
6 15%). To avoid further large energy input, the additional phase was added by hand while stirring with a glass stick. As shown in (Figure 4 b)-d)), the signals at g > 0 T/m disappear with increasing sugar concentration. By adding sugar, the equilibrium of exchange was influenced, and driven diffusion from W 1 to W 2 took place. The process continues on a short time scale until a new equilibrium between the two phases is established. Regarding this fact, the conclusion is that, despite of Xanthan in the outer water phase, molecular exchange between W 1 and W 2 occurs. However, the exchange rate is that low that it is negligible on the time scale of the NMR experiments. This observation is proofed by pictures made with a CLSM, shown in Figure 5. Here, a double emulsion with Xanthan in W 2 was recorded before adding additional W 2, containing 15% sugar. The process was observed online while adding the phase. During the disappearance of W 1 it was observed in the CLSM experiments that the W 1 -droplets near the interface of the oil droplets tow 2 tend to move fast along the boundary of the oil droplet. In contrast to that, the W 1 -droplets in the centre of the oil droplets seem not to be influenced by the sugar in the outer water phase and do not move on a short time scale. The impression is that the exchange processes start from the interface of the oil droplets to W 2, but no evidence is found that complete W 1 -droplets break the oil droplet s interface. A rearrangement of the remaining W 1 droplets toward the droplet s boundary occurs on a longer time scale as the system aims for concentration equilibrium. This process can be observed until the W 1 -droplets disappeared completely. Figure 4 NMR spectra of a) a WOW double emulsion wit Xanthan in W 2, b) the same emulsion with additional W 2 containing 1% sugar, c) 5% sugar, d) 15% sugar.
7 Figure 5 CLSM pictures of a) a W 1 /O/W 2 double emulsion with Xanthan in W 2 before adding additional W 2 with 15% sugar. b) a W 1 /O/W 2 double emulsion with Xanthan in W 2 after adding additional W 2 with 15% sugar Two Compartment Model. With the knowledge from these experiments, it is possible to separate the NMR signals of W 1 and W 2 in a W 1 /O/W 2 emulsion with Xanthan in W 2. A two compartment model is applicable. The two water phases can be regarded as independent and completely separate on the experimental time scale on which the exchange is negligible. The total water signal is observed near g = 0 T/m. At higher gradient amplitudes, W 2 is negligible or even not measurable. To eliminate the signal of outer water, the measured points over q² can be cut at the second gradient step. Discarding the signal near g = 0 T/m, the signal of W 1 can now be processed with the MC-model. Therefore, the inner water phase of double emulsions of the type W 1 /O/W 2 can be characterised, and its DSD is found to be consistent with other measuring techniques.
8 3 CONCLUSIONS PFG-NMR is a suitable method to characterise W 1 /O/W 2 double emulsions with respect to DSD and molecular exchange phenomena. Due to the molecular exchange between both water phases, a characterisation with the common models as the MC-model is not generally possible. With Xanthan in W 2 of W 1 /O/W 2 double emulsions, a two compartment model is applicable. The water phases can be regarded as independent. Thereby, the separated signal of the inner water phase can be evaluated by the MC-model applicable and known from investigations of single emulsions. In case of other W 1 /O/W 2 recipes, the exchange model can successfully be applied, revealing the DSD of the inner emulsions. Acknowledgements The Shared Research Group 10-2 received financial support by the Concept for the future of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology within the framework of the German Excellence Initiative. Additional support was given the DFG, which are also highly appreciated. We would like to thank K. Sachsenheimer for help during the NMR experiments and Lydia Schütz for emulsion preparation. Special thanks to Azad Emin for help with the CLSM experiments. References 1 P. T. Callaghan, Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance microscopy, Clarendon Press, Oxford, M. L. Johns and K. G. Hollingsworth, Progress in NMR Spectroscopy, 2007, 50, J. S. Murday, R. M. Cotts, J. Chem. Phys., 1968, 48, C. H. Neuman, J. Chem. Phys., 1974, 60, J. Pfeuffer, U. Flögel, D. Leibfritz, NMR Biomed., 1998, 11, J. Pfeuffer, U. Flögel, D. Leibfritz, NMR Biomed., 1998, 11, W. S. Price, A.V. Barzykin, K. Hayamizu, M. Tachiya, Biophys. J., 1998, 74, B. Balinov, O. Weman, J.C. Ravey, J. Phys. Chem., 1994, 98, J. P. Hindmarsh, J. Su, J. Flanagan, H. Singh, Langmuir 2005, 21, F. Wolf, L. Hecht, H. P. Schuchmann, E. H. Hardy, G. Guthausen, Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol., 2009, 111, X. Guan, K. Hailu, G. Guthausen, F. Wolf, R. Bernewitz, H. P. Schuchmann, Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol., 2010, 112, G. Muschiolik, I. Scherze, P. Preissler, J. Weiss et al., Multiple emulsions preparation and stability, 13th World Congress of Food Science & Technology Food is Life, 2006,
Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopy
 Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopy Paul T. Callaghan Department of Physics and Biophysics Massey University New Zealand CLARENDON PRESS OXFORD CONTENTS 1 PRINCIPLES OF IMAGING 1 1.1 Introduction
Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopy Paul T. Callaghan Department of Physics and Biophysics Massey University New Zealand CLARENDON PRESS OXFORD CONTENTS 1 PRINCIPLES OF IMAGING 1 1.1 Introduction
Suppression of Static Magnetic Field in Diffusion Measurements of Heterogeneous Materials
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 1, 2009 81 Suppression of Static Magnetic Field in Diffusion Measurements of Heterogeneous Materials Eva Gescheidtova 1 and Karel Bartusek 2 1 Faculty of Electrical Engineering
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 1, 2009 81 Suppression of Static Magnetic Field in Diffusion Measurements of Heterogeneous Materials Eva Gescheidtova 1 and Karel Bartusek 2 1 Faculty of Electrical Engineering
Supplementary Information. (Communication Ref.: B802671H)
 upplementary Information (Communication Ref.: B80671H) Phosphoesterase activity of [Mo 7 O 4 ] 6- cluster: diffusion ordered NMR spectroscopy as a tool for obtaining insights into the reactivity of polyoxometalates
upplementary Information (Communication Ref.: B80671H) Phosphoesterase activity of [Mo 7 O 4 ] 6- cluster: diffusion ordered NMR spectroscopy as a tool for obtaining insights into the reactivity of polyoxometalates
Gas Transport in Aluminosilicate Nanotubes by Diffusion NMR
 The Open-Access Journal for the Basic Principles of Diffusion Theory, Experiment and Application Gas Transport in Aluminosilicate Nanotubes by Diffusion NMR Muslim Dvoyashkin,3, Ryan Wood, Clifford R.
The Open-Access Journal for the Basic Principles of Diffusion Theory, Experiment and Application Gas Transport in Aluminosilicate Nanotubes by Diffusion NMR Muslim Dvoyashkin,3, Ryan Wood, Clifford R.
CONTENTS. 2 CLASSICAL DESCRIPTION 2.1 The resonance phenomenon 2.2 The vector picture for pulse EPR experiments 2.3 Relaxation and the Bloch equations
 CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgements Symbols Abbreviations 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Scope of pulse EPR 1.2 A short history of pulse EPR 1.3 Examples of Applications 2 CLASSICAL DESCRIPTION 2.1 The resonance phenomenon
CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgements Symbols Abbreviations 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Scope of pulse EPR 1.2 A short history of pulse EPR 1.3 Examples of Applications 2 CLASSICAL DESCRIPTION 2.1 The resonance phenomenon
NMR/MRI examination (8N080 / 3F240)
 NMR/MRI examination (8N080 / 3F240) Remarks: 1. This test consists of 3 problems with at total of 26 sub-questions. 2. Questions are in English. You are allowed to answer them in English or Dutch. 3. Please
NMR/MRI examination (8N080 / 3F240) Remarks: 1. This test consists of 3 problems with at total of 26 sub-questions. 2. Questions are in English. You are allowed to answer them in English or Dutch. 3. Please
SUPORTING INFORMATION The Cathodic Voltammetric Behavior of Pillar[5]quinone in Nonaqueous Media. Symmetry Effects on the Electron Uptake Sequence.
![SUPORTING INFORMATION The Cathodic Voltammetric Behavior of Pillar[5]quinone in Nonaqueous Media. Symmetry Effects on the Electron Uptake Sequence. SUPORTING INFORMATION The Cathodic Voltammetric Behavior of Pillar[5]quinone in Nonaqueous Media. Symmetry Effects on the Electron Uptake Sequence.](/thumbs/93/113498494.jpg) SUPORTING INFORMATION The Cathodic Voltammetric Behavior of Pillar[5]quinone in Nonaqueous Media. Symmetry Effects on the Electron Uptake Sequence. Beijun Cheng and Angel E. Kaifer* Department of Chemistry
SUPORTING INFORMATION The Cathodic Voltammetric Behavior of Pillar[5]quinone in Nonaqueous Media. Symmetry Effects on the Electron Uptake Sequence. Beijun Cheng and Angel E. Kaifer* Department of Chemistry
3 rd Food Emulsions Short Course November 13 th & 14 th, 2008 University of Massachusetts. David Julian McClements University of Massachusetts
 3 rd Food Emulsions Short Course November 13 th & 14 th, 2008 University of Massachusetts David Julian McClements University of Massachusetts Program Objectives Review Basic Principles of Emulsion Science
3 rd Food Emulsions Short Course November 13 th & 14 th, 2008 University of Massachusetts David Julian McClements University of Massachusetts Program Objectives Review Basic Principles of Emulsion Science
Supporting Information Elucidating Lithium-Ion and Proton Dynamics in Anti- Perovskite Solid Electrolytes
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Elucidating Lithium-Ion and Proton Dynamics in Anti-
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Elucidating Lithium-Ion and Proton Dynamics in Anti-
A spoiler recovery method for rapid diffusion measurements
 The Open-Access Journal for the Basic Principles of Diffusion Theory, Experiment and Application A spoiler recovery method for rapid diffusion measurements Geir Humborstad Sørland 1, Henrik Walbye Anthonsen
The Open-Access Journal for the Basic Principles of Diffusion Theory, Experiment and Application A spoiler recovery method for rapid diffusion measurements Geir Humborstad Sørland 1, Henrik Walbye Anthonsen
Monte Carlo Simulation of Long-Range Self-Diffusion in Model Porous Membranes and Catalysts
 Monte Carlo Simulation of Long-Range Self-Diffusion in Model Porous Membranes and Catalysts Brian DeCost and Dr. Sergey Vasenkov College of Engineering, University of Florida Industrial processes involving
Monte Carlo Simulation of Long-Range Self-Diffusion in Model Porous Membranes and Catalysts Brian DeCost and Dr. Sergey Vasenkov College of Engineering, University of Florida Industrial processes involving
Explorative Study of NMR Drilling Fluids Measurement
 ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 15, 2007 Explorative Study of NMR Drilling Fluids Measurement Rizal Rismanto, Claas van der Zwaag University of Stavanger, Dep. of Petroleum Technology,
ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 15, 2007 Explorative Study of NMR Drilling Fluids Measurement Rizal Rismanto, Claas van der Zwaag University of Stavanger, Dep. of Petroleum Technology,
On Accurate Measurements of Diffusion Coefficients by PGSE NMR Methods (Version 2) Kikuko Hayamizu
 February 15, 2012 On Accurate Measurements of Diffusion Coefficients by PGSE NMR Methods (Version 2) -Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids- Kikuko Hayamizu Diffusion coeffients of molecules, ions and particles
February 15, 2012 On Accurate Measurements of Diffusion Coefficients by PGSE NMR Methods (Version 2) -Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids- Kikuko Hayamizu Diffusion coeffients of molecules, ions and particles
NMR and MRI : an introduction
 Intensive Programme 2011 Design, Synthesis and Validation of Imaging Probes NMR and MRI : an introduction Walter Dastrù Università di Torino walter.dastru@unito.it \ Introduction Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Intensive Programme 2011 Design, Synthesis and Validation of Imaging Probes NMR and MRI : an introduction Walter Dastrù Università di Torino walter.dastru@unito.it \ Introduction Magnetic Resonance Imaging
PROBING THE CONNECTIVITY BETWEEN PORES IN ROCK CORE SAMPLES
 SCA2007-42 1/6 PROBING THE CONNECTIVITY BETWEEN PORES IN ROCK CORE SAMPLES Geir Humborstad Sørland 1,3, Ketil Djurhuus 3, Hege Christin Widerøe 2, Jan R. Lien 3, Arne Skauge 3, 1 Anvendt Teknologi AS,
SCA2007-42 1/6 PROBING THE CONNECTIVITY BETWEEN PORES IN ROCK CORE SAMPLES Geir Humborstad Sørland 1,3, Ketil Djurhuus 3, Hege Christin Widerøe 2, Jan R. Lien 3, Arne Skauge 3, 1 Anvendt Teknologi AS,
NMR Imaging in porous media
 NMR Imaging in porous media What does NMR give us. Chemical structure. Molecular structure. Interactions between atoms and molecules. Incoherent dynamics (fluctuation, rotation, diffusion). Coherent flow
NMR Imaging in porous media What does NMR give us. Chemical structure. Molecular structure. Interactions between atoms and molecules. Incoherent dynamics (fluctuation, rotation, diffusion). Coherent flow
Non contact measurement of viscoelastic properties of biopolymers
 Non contact measurement of viscoelastic properties of biopolymers Christelle Tisserand, Anton Kotzev, Mathias Fleury, Laurent Brunel, Pascal Bru, Gérard Meunier Formulaction, 10 impasse Borde Basse, 31240
Non contact measurement of viscoelastic properties of biopolymers Christelle Tisserand, Anton Kotzev, Mathias Fleury, Laurent Brunel, Pascal Bru, Gérard Meunier Formulaction, 10 impasse Borde Basse, 31240
A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging. Outline
 A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging Outline General Goals Linear Imaging Systems An Example, The Pin Hole Camera Radiations and Their Interactions with Matter Coherent vs. Incoherent Imaging Length
A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging Outline General Goals Linear Imaging Systems An Example, The Pin Hole Camera Radiations and Their Interactions with Matter Coherent vs. Incoherent Imaging Length
Supplementary Information: Three-dimensional quantum photonic elements based on single nitrogen vacancy-centres in laser-written microstructures
 Supplementary Information: Three-dimensional quantum photonic elements based on single nitrogen vacancy-centres in laser-written microstructures Andreas W. Schell, 1, a) Johannes Kaschke, 2 Joachim Fischer,
Supplementary Information: Three-dimensional quantum photonic elements based on single nitrogen vacancy-centres in laser-written microstructures Andreas W. Schell, 1, a) Johannes Kaschke, 2 Joachim Fischer,
Scholar: M. Azad Emin. Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Ing. Heike P. Schuchmann
 Final report of project 2819: Emulsification of triglyceride phases in cereal matrices via high-speed extrusion process for the stabilization of lipophilic bioactive components in starch-based products
Final report of project 2819: Emulsification of triglyceride phases in cereal matrices via high-speed extrusion process for the stabilization of lipophilic bioactive components in starch-based products
Technical University of Denmark
 Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 11 pages Written test, 9 December 2010 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: none. "Weighting": All problems weight equally.
Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 11 pages Written test, 9 December 2010 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: none. "Weighting": All problems weight equally.
Relaxation times in nuclear magnetic resonance
 Relaxation times in TEP Related topics Nuclear spins, atomic nuclei with a magnetic moment, precession movement of the nuclear spins, Landau-Lifshitz equation, Bloch equation, magnetisation, resonance
Relaxation times in TEP Related topics Nuclear spins, atomic nuclei with a magnetic moment, precession movement of the nuclear spins, Landau-Lifshitz equation, Bloch equation, magnetisation, resonance
Soft matters end use properties analysis thanks to Microrheology
 Soft matters end use properties analysis thanks to Microrheology Formulaction, 10 impasse Borde Basse, 31240 L Union, France, www.formulaction.com Abstract. We present a new technique of passive microrheology
Soft matters end use properties analysis thanks to Microrheology Formulaction, 10 impasse Borde Basse, 31240 L Union, France, www.formulaction.com Abstract. We present a new technique of passive microrheology
LAB 3: Confocal Microscope Imaging of single-emitter fluorescence. LAB 4: Hanbury Brown and Twiss setup. Photon antibunching. Roshita Ramkhalawon
 LAB 3: Confocal Microscope Imaging of single-emitter fluorescence LAB 4: Hanbury Brown and Twiss setup. Photon antibunching Roshita Ramkhalawon PHY 434 Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Rochester
LAB 3: Confocal Microscope Imaging of single-emitter fluorescence LAB 4: Hanbury Brown and Twiss setup. Photon antibunching Roshita Ramkhalawon PHY 434 Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Rochester
THE INFLUENCE OF XANTHAN AND CREAMING AND FLOCCULATION OF AN OIL-IN-WATER EMULSION CONTAINING SOY PROTEIN
 Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering ISSN 0104-6632 Printed in Brazil Vol. 19, No. 04, pp. 411-417, October - December 2002 THE INFLUENCE OF XANTHAN AND λ-carrageenan ON THE CREAMING AND FLOCCULATION
Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering ISSN 0104-6632 Printed in Brazil Vol. 19, No. 04, pp. 411-417, October - December 2002 THE INFLUENCE OF XANTHAN AND λ-carrageenan ON THE CREAMING AND FLOCCULATION
Supplements to : Isotropic stress reduces cell proliferation in tumor spheroids
 Supplements to : Isotropic stress reduces cell proliferation in tumor spheroids Fabien Montel 1, Morgan Delarue 1,4, Jens Elgeti 1, Danijela Vignjevic 2, Giovanni Cappello 1, Jacques Prost 1,3 1 UMR 168,
Supplements to : Isotropic stress reduces cell proliferation in tumor spheroids Fabien Montel 1, Morgan Delarue 1,4, Jens Elgeti 1, Danijela Vignjevic 2, Giovanni Cappello 1, Jacques Prost 1,3 1 UMR 168,
NMRis the most valuable spectroscopic technique for organic chemists because it maps the carbon-hydrogen framework of a molecule.
 Chapter 13: Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy NMRis the most valuable spectroscopic technique for organic chemists because it maps the carbon-hydrogen framework of a molecule. 13.2 The nature of
Chapter 13: Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy NMRis the most valuable spectroscopic technique for organic chemists because it maps the carbon-hydrogen framework of a molecule. 13.2 The nature of
Mechanically Induced Pyrogallol[4]arene Hexamer Assembly in the Solid State Extends the Scope of Molecular Encapsulation
![Mechanically Induced Pyrogallol[4]arene Hexamer Assembly in the Solid State Extends the Scope of Molecular Encapsulation Mechanically Induced Pyrogallol[4]arene Hexamer Assembly in the Solid State Extends the Scope of Molecular Encapsulation](/thumbs/82/86976534.jpg) Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information for: Mechanically Induced Pyrogallol[4]arene Hexamer
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information for: Mechanically Induced Pyrogallol[4]arene Hexamer
Diffusion measurements with the pulsed gradient nonlinear spin echo method
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 1 MARCH 000 Diffusion measurements with the pulsed gradient nonlinear spin echo method Ioan Ardelean a) and Rainer Kimmich Universität Ulm, Sektion Kernresonanzspektroskopie,
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 1 MARCH 000 Diffusion measurements with the pulsed gradient nonlinear spin echo method Ioan Ardelean a) and Rainer Kimmich Universität Ulm, Sektion Kernresonanzspektroskopie,
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ADDITIONAL CHARACTERIZATION OF NANODIAMOND SOLUTIONS AND THE OVERHAUSER EFFECT
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ADDITIONAL CHARACTERIZATION OF NANODIAMOND SOLUTIONS AND THE OVERHAUSER EFFECT Nanodiamond (ND) solutions were prepared using high power probe sonication and analyzed by dynamic
1 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ADDITIONAL CHARACTERIZATION OF NANODIAMOND SOLUTIONS AND THE OVERHAUSER EFFECT Nanodiamond (ND) solutions were prepared using high power probe sonication and analyzed by dynamic
EL-GY 6813/BE-GY 6203 Medical Imaging, Fall 2016 Final Exam
 EL-GY 6813/BE-GY 6203 Medical Imaging, Fall 2016 Final Exam (closed book, 1 sheets of notes double sided allowed, no calculator or other electronic devices allowed) 1. Ultrasound Physics (15 pt) A) (9
EL-GY 6813/BE-GY 6203 Medical Imaging, Fall 2016 Final Exam (closed book, 1 sheets of notes double sided allowed, no calculator or other electronic devices allowed) 1. Ultrasound Physics (15 pt) A) (9
Spectroscopy of Polymers
 Spectroscopy of Polymers Jack L. Koenig Case Western Reserve University WOMACS Professional Reference Book American Chemical Society, Washington, DC 1992 Contents Preface m xiii Theory of Polymer Characterization
Spectroscopy of Polymers Jack L. Koenig Case Western Reserve University WOMACS Professional Reference Book American Chemical Society, Washington, DC 1992 Contents Preface m xiii Theory of Polymer Characterization
Physikalische Chemie IV (Magnetische Resonanz) HS Solution Set 2. Hand out: Hand in:
 Solution Set Hand out:.. Hand in:.. Repetition. The magnetization moves adiabatically during the application of an r.f. pulse if it is always aligned along the effective field axis. This behaviour is observed
Solution Set Hand out:.. Hand in:.. Repetition. The magnetization moves adiabatically during the application of an r.f. pulse if it is always aligned along the effective field axis. This behaviour is observed
NMR Spectroscopy: A Quantum Phenomena
 NMR Spectroscopy: A Quantum Phenomena Pascale Legault Département de Biochimie Université de Montréal Outline 1) Energy Diagrams and Vector Diagrams 2) Simple 1D Spectra 3) Beyond Simple 1D Spectra 4)
NMR Spectroscopy: A Quantum Phenomena Pascale Legault Département de Biochimie Université de Montréal Outline 1) Energy Diagrams and Vector Diagrams 2) Simple 1D Spectra 3) Beyond Simple 1D Spectra 4)
Final exam questions ED
 Final exam questions ED 2015-2016 1. Radiation a) Properties and types of radiation b) Physical parameters of radiation 2. Law of attenuation of radiation a) Experimental interpretation of the law b) Forms
Final exam questions ED 2015-2016 1. Radiation a) Properties and types of radiation b) Physical parameters of radiation 2. Law of attenuation of radiation a) Experimental interpretation of the law b) Forms
STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR OF NIOBIUM PHOSPHATE VITROCERAMICS IN SIMULATED BODY FLUID
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials Vol. 7, No. 6, December 2005, p. 2839-2843 STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR OF NIOBIUM PHOSPHATE VITROCERAMICS IN SIMULATED BODY FLUID S. Simon *, V. R. F. Turcu,
Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials Vol. 7, No. 6, December 2005, p. 2839-2843 STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR OF NIOBIUM PHOSPHATE VITROCERAMICS IN SIMULATED BODY FLUID S. Simon *, V. R. F. Turcu,
Doppler echocardiography & Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Doppler echocardiography. History: - Langevin developed sonar.
 1 Doppler echocardiography & Magnetic Resonance Imaging History: - Langevin developed sonar. - 1940s development of pulse-echo. - 1950s development of mode A and B. - 1957 development of continuous wave
1 Doppler echocardiography & Magnetic Resonance Imaging History: - Langevin developed sonar. - 1940s development of pulse-echo. - 1950s development of mode A and B. - 1957 development of continuous wave
K ex. Conformational equilibrium. equilibrium K B
 Effects of Chemical Exchange on NMR Spectra Chemical exchange refers to any yprocess in which a nucleus exchanges between two or more environments in which its NMR parameters (e.g. chemical shift, scalar
Effects of Chemical Exchange on NMR Spectra Chemical exchange refers to any yprocess in which a nucleus exchanges between two or more environments in which its NMR parameters (e.g. chemical shift, scalar
A method for imaging and spectroscopy. using γ-rays and magnetic resonance
 A method for imaging and spectroscopy using γ-rays and magnetic resonance Y. Zheng et al. Nature 537, 19775 (Sep 2016) Parker Brue PHY 492 Abstract Background: Magnetic resonance imaging and Nuclear imaging
A method for imaging and spectroscopy using γ-rays and magnetic resonance Y. Zheng et al. Nature 537, 19775 (Sep 2016) Parker Brue PHY 492 Abstract Background: Magnetic resonance imaging and Nuclear imaging
Introduction to Relaxation Theory James Keeler
 EUROMAR Zürich, 24 Introduction to Relaxation Theory James Keeler University of Cambridge Department of Chemistry What is relaxation? Why might it be interesting? relaxation is the process which drives
EUROMAR Zürich, 24 Introduction to Relaxation Theory James Keeler University of Cambridge Department of Chemistry What is relaxation? Why might it be interesting? relaxation is the process which drives
MRI Physics I: Spins, Excitation, Relaxation
 MRI Physics I: Spins, Excitation, Relaxation Douglas C. Noll Biomedical Engineering University of Michigan Michigan Functional MRI Laboratory Outline Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI Physics I: Spins, Excitation, Relaxation Douglas C. Noll Biomedical Engineering University of Michigan Michigan Functional MRI Laboratory Outline Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Nonlinear Optics. Single-Molecule Microscopy Group. Physical Optics Maria Dienerowitz.
 Single-Molecule Microscopy Group Nonlinear Optics Physical Optics 21-06-2017 Maria Dienerowitz maria.dienerowitz@med.uni-jena.de www.single-molecule-microscopy.uniklinikum-jena.de Contents Introduction
Single-Molecule Microscopy Group Nonlinear Optics Physical Optics 21-06-2017 Maria Dienerowitz maria.dienerowitz@med.uni-jena.de www.single-molecule-microscopy.uniklinikum-jena.de Contents Introduction
NMR of liquid 3 Не in clay pores at 1.5 K
 NMR of liquid 3 Не in clay pores at 1.5 K Gazizulin R.R. 1, Klochkov A.V. 1, Kuzmin V.V. 1, Safiullin K.R. 1, Tagirov M.S. 1, Yudin A.N. 1, Izotov V.G. 2, Sitdikova L.M. 2 1 Physics Faculty, Kazan (Volga
NMR of liquid 3 Не in clay pores at 1.5 K Gazizulin R.R. 1, Klochkov A.V. 1, Kuzmin V.V. 1, Safiullin K.R. 1, Tagirov M.S. 1, Yudin A.N. 1, Izotov V.G. 2, Sitdikova L.M. 2 1 Physics Faculty, Kazan (Volga
Surface Modification of PTMS Particles with Organosilanes: TEOS-, VTMS-, and MTMS-Modified Particles
 Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 31, 117 121, 2004 c 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The United States. Surface Modification of PTMS Particles with Organosilanes: TEOS-, VTMS-,
Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 31, 117 121, 2004 c 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The United States. Surface Modification of PTMS Particles with Organosilanes: TEOS-, VTMS-,
A novel sputtering technique: Inductively Coupled Impulse Sputtering (ICIS)
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering A novel sputtering technique: Inductively Coupled Impulse Sputtering (ICIS) To cite this article: D A L Loch and A P Ehiasarian 2012 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering A novel sputtering technique: Inductively Coupled Impulse Sputtering (ICIS) To cite this article: D A L Loch and A P Ehiasarian 2012 IOP Conf. Ser.:
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure. X-ray diffraction pattern of CH 3 NH 3 PbI 3 film. Strong reflections of the () family of planes is characteristics of the preferred orientation of the perovskite
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure. X-ray diffraction pattern of CH 3 NH 3 PbI 3 film. Strong reflections of the () family of planes is characteristics of the preferred orientation of the perovskite
Elec Eng 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials
 Elec Eng 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials Page 1 of 12 Day Class Instructor: Dr. I. C. BRUCE Duration of Examination: 3 Hours McMaster University Final Examination December 5, 2008 This examination
Elec Eng 3BA3: Structure of Biological Materials Page 1 of 12 Day Class Instructor: Dr. I. C. BRUCE Duration of Examination: 3 Hours McMaster University Final Examination December 5, 2008 This examination
Rapid, Efficient Phase Pure Synthesis of Ca 2 AlNO 3 Layered Double Hydroxide
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Rapid, Efficient Phase Pure Synthesis of Ca 2 AlNO
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Rapid, Efficient Phase Pure Synthesis of Ca 2 AlNO
Introduction to MRI. Spin & Magnetic Moments. Relaxation (T1, T2) Spin Echoes. 2DFT Imaging. K-space & Spatial Resolution.
 Introduction to MRI Spin & Magnetic Moments Relaxation (T1, T2) Spin Echoes 2DFT Imaging Selective excitation, phase & frequency encoding K-space & Spatial Resolution Contrast (T1, T2) Acknowledgement:
Introduction to MRI Spin & Magnetic Moments Relaxation (T1, T2) Spin Echoes 2DFT Imaging Selective excitation, phase & frequency encoding K-space & Spatial Resolution Contrast (T1, T2) Acknowledgement:
Fundamental MRI Principles Module Two
 Fundamental MRI Principles Module Two 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance There are three main subatomic particles: protons neutrons electrons positively charged no significant charge negatively charged Protons
Fundamental MRI Principles Module Two 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance There are three main subatomic particles: protons neutrons electrons positively charged no significant charge negatively charged Protons
Sharper low power STED nanoscopy by time gating
 Nature Methods Sharper low power nanoscopy by time gating G. Vicidomini,3, G. Moneron,3, K. Y. Han,3, V. Westphal, H. Ta, M. Reuss, J. Engelhardt, C. Eggeling, S. W. Hell, Max Planc nstitute for Biophysical
Nature Methods Sharper low power nanoscopy by time gating G. Vicidomini,3, G. Moneron,3, K. Y. Han,3, V. Westphal, H. Ta, M. Reuss, J. Engelhardt, C. Eggeling, S. W. Hell, Max Planc nstitute for Biophysical
Fatigue Testing of Materials by UV Pulsed Laser Irradiation
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN TS DEPARTMENT EDMS Nr. 5292 CERN-TS-24-4(MME) CLIC Note 615 Fatigue Testing of Materials by UV Pulsed Laser Irradiation S. Calatroni, H. Neupert, M. Taborelli
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN TS DEPARTMENT EDMS Nr. 5292 CERN-TS-24-4(MME) CLIC Note 615 Fatigue Testing of Materials by UV Pulsed Laser Irradiation S. Calatroni, H. Neupert, M. Taborelli
Apparative Methoden in der Physikalischen Chemie DIFFUSION MEASUREMENTS BY NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (NMR) 1 Introduction.
 Apparative Methoden in der Physikalischen Chemie DIFFUSION MEASUREMENTS BY NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (NMR) 12th March 2008 Before reading the following script it is recommended first obtain basic knowledge
Apparative Methoden in der Physikalischen Chemie DIFFUSION MEASUREMENTS BY NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (NMR) 12th March 2008 Before reading the following script it is recommended first obtain basic knowledge
4 Spin-echo, Spin-echo Double Resonance (SEDOR) and Rotational-echo Double Resonance (REDOR) applied on polymer blends
 4 Spin-echo, Spin-echo ouble Resonance (SEOR and Rotational-echo ouble Resonance (REOR applied on polymer blends The next logical step after analyzing and concluding upon the results of proton transversal
4 Spin-echo, Spin-echo ouble Resonance (SEOR and Rotational-echo ouble Resonance (REOR applied on polymer blends The next logical step after analyzing and concluding upon the results of proton transversal
NMR course at the FMP: NMR of organic compounds and small biomolecules - II -
 NMR course at the FMP: NMR of organic compounds and small biomolecules - II - 16.03.2009 The program 2/76 CW vs. FT NMR What is a pulse? Vectormodel Water-flip-back 3/76 CW vs. FT CW vs. FT 4/76 Two methods
NMR course at the FMP: NMR of organic compounds and small biomolecules - II - 16.03.2009 The program 2/76 CW vs. FT NMR What is a pulse? Vectormodel Water-flip-back 3/76 CW vs. FT CW vs. FT 4/76 Two methods
N E W S L E T T E R F R O M TO S H V I N A N A LY T I C A L P V T. LT D.
 N E W S L E T T E R F R O M TO S H V I N A N A LY T I C A L P V T. LT D. AUGUST 204 TABLE OF CONTENTS Evaluation of Light Intensity Graph and Particle Size Distribution of Mixture Particle Application
N E W S L E T T E R F R O M TO S H V I N A N A LY T I C A L P V T. LT D. AUGUST 204 TABLE OF CONTENTS Evaluation of Light Intensity Graph and Particle Size Distribution of Mixture Particle Application
Introduction to Dynamic Light Scattering for Particle Size Determination
 www.horiba.com/us/particle Jeffrey Bodycomb, Ph.D. Introduction to Dynamic Light Scattering for Particle Size Determination 2016 HORIBA, Ltd. All rights reserved. 1 Sizing Techniques 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10
www.horiba.com/us/particle Jeffrey Bodycomb, Ph.D. Introduction to Dynamic Light Scattering for Particle Size Determination 2016 HORIBA, Ltd. All rights reserved. 1 Sizing Techniques 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10
Chapter 1 Pulsed Field Gradient NMR Sequences
 Chapter 1 Pulsed Field Gradient NMR Sequences Abstract The mechanism via which an NMR signal is generated and how diffusion can be measured from solving the equation of motion of the nuclear spins is described.
Chapter 1 Pulsed Field Gradient NMR Sequences Abstract The mechanism via which an NMR signal is generated and how diffusion can be measured from solving the equation of motion of the nuclear spins is described.
Unilateral NMR of Activated Carbon
 Unilateral NMR of Activated Carbon Stuart Brewer 2, Hans Adriaensen 1, Martin Bencsik 1, Glen McHale 1 and Martin W Smith 2 [1]: Nottingham Trent University (NTU), UK [2]: Defence Science and Technology
Unilateral NMR of Activated Carbon Stuart Brewer 2, Hans Adriaensen 1, Martin Bencsik 1, Glen McHale 1 and Martin W Smith 2 [1]: Nottingham Trent University (NTU), UK [2]: Defence Science and Technology
Biophysical Chemistry: NMR Spectroscopy
 Relaxation & Multidimensional Spectrocopy Vrije Universiteit Brussel 9th December 2011 Outline 1 Relaxation 2 Principles 3 Outline 1 Relaxation 2 Principles 3 Establishment of Thermal Equilibrium As previously
Relaxation & Multidimensional Spectrocopy Vrije Universiteit Brussel 9th December 2011 Outline 1 Relaxation 2 Principles 3 Outline 1 Relaxation 2 Principles 3 Establishment of Thermal Equilibrium As previously
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION I-2 MEDICAL IMAGING Reading Activity Answers IB Assessment Statements Option I-2, Medical Imaging: X-Rays I.2.1. I.2.2. I.2.3. Define
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION I-2 MEDICAL IMAGING Reading Activity Answers IB Assessment Statements Option I-2, Medical Imaging: X-Rays I.2.1. I.2.2. I.2.3. Define
Natural abundance solid-state 95 Mo MAS NMR of MoS 2 reveals precise 95 Mo anisotropic parameters from its central and satellite transitions
 Electronic Supplementary Information for: Natural abundance solid-state 95 Mo MAS NMR of MoS 2 reveals precise 95 Mo anisotropic parameters from its central and satellite transitions Hans J. Jakobsen,*
Electronic Supplementary Information for: Natural abundance solid-state 95 Mo MAS NMR of MoS 2 reveals precise 95 Mo anisotropic parameters from its central and satellite transitions Hans J. Jakobsen,*
Measurement of Water Droplets in Water-in-Oil Emulsions Using Low Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance for Gas Hydrate Slurry Application
 Canadian Journal of Chemistry Measurement of Water Droplets in Water-in-Oil Emulsions Using Low Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance for Gas Hydrate Slurry Application Journal: Canadian Journal of Chemistry
Canadian Journal of Chemistry Measurement of Water Droplets in Water-in-Oil Emulsions Using Low Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance for Gas Hydrate Slurry Application Journal: Canadian Journal of Chemistry
Insights on Interfacial Structure, Dynamics and. Proton Transfer from Ultrafast Vibrational Sum. Frequency Generation Spectroscopy of the
 Insights on Interfacial Structure, Dynamics and Proton Transfer from Ultrafast Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy of the Alumina(0001)/Water Interface Aashish Tuladhar, Stefan M. Piontek,
Insights on Interfacial Structure, Dynamics and Proton Transfer from Ultrafast Vibrational Sum Frequency Generation Spectroscopy of the Alumina(0001)/Water Interface Aashish Tuladhar, Stefan M. Piontek,
Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 Spectroscopy in Inorganic Chemistry Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy spin deuterium 2 helium 3 The neutron has 2 quarks with a -e/3 charge and one quark with a +2e/3 charge resulting in a total
Spectroscopy in Inorganic Chemistry Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy spin deuterium 2 helium 3 The neutron has 2 quarks with a -e/3 charge and one quark with a +2e/3 charge resulting in a total
Technical University of Denmark
 Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 10 pages Written test, 12 December 2012 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: None. Pocket calculator not allowed "Weighting":
Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 10 pages Written test, 12 December 2012 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: None. Pocket calculator not allowed "Weighting":
Solid state 13 Cand 1 H MAS NMR investigations of C 60 (ferrocene-d 10 ) 2 complex
 Spectroscopy 17 (2003) 39 44 39 IOS Press Solid state 13 Cand 1 H MAS NMR investigations of C 60 (ferrocene-d 10 ) 2 complex E. Shabanova, K. Schaumburg and F.S. Kamounah CISMI, Department of Chemistry,
Spectroscopy 17 (2003) 39 44 39 IOS Press Solid state 13 Cand 1 H MAS NMR investigations of C 60 (ferrocene-d 10 ) 2 complex E. Shabanova, K. Schaumburg and F.S. Kamounah CISMI, Department of Chemistry,
Chapter 7. Pickering Stabilisation ABSTRACT
 Chapter 7 Pickering Stabilisation ABSTRACT In this chapter we investigate the interfacial properties of Pickering emulsions. Based upon findings that indicate these emulsions to be thermodynamically stable,
Chapter 7 Pickering Stabilisation ABSTRACT In this chapter we investigate the interfacial properties of Pickering emulsions. Based upon findings that indicate these emulsions to be thermodynamically stable,
Modelling Dynamical Fluorescent Micro Thermal Imaging of the Heat Diffusion in the La 5 Ca 9 Cu 24 O 41 Spin Ladder Compound.
 Modelling Dynamical Fluorescent Micro Thermal Imaging of the Heat Diffusion in the La 5 Ca 9 Cu 4 O 41 Spin Ladder Compound. E.I. Khadikova* 1, M.Montagnese, F. de Haan 1, P.H.M. van Loosdrecht 1,. 1 Zernike
Modelling Dynamical Fluorescent Micro Thermal Imaging of the Heat Diffusion in the La 5 Ca 9 Cu 4 O 41 Spin Ladder Compound. E.I. Khadikova* 1, M.Montagnese, F. de Haan 1, P.H.M. van Loosdrecht 1,. 1 Zernike
NMR Studies of 3 He Impurities in 4 He in the Proposed Supersolid Phase
 Journal of Low Temperature Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) NMR Studies of 3 He Impurities in 4 He in the Proposed Supersolid Phase S. S. Kim 1 C. Huan 1 L. Yin 1 J. S. Xia 1 D.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) NMR Studies of 3 He Impurities in 4 He in the Proposed Supersolid Phase S. S. Kim 1 C. Huan 1 L. Yin 1 J. S. Xia 1 D.
NMR and Core Analysis
 NMR and Core Analysis Technical Datasheet Introduction Most people involved in core analysis know that NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) has been part of the available suite of well logging measurements
NMR and Core Analysis Technical Datasheet Introduction Most people involved in core analysis know that NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) has been part of the available suite of well logging measurements
NMR, the vector model and the relaxation
 NMR, the vector model and the relaxation Reading/Books: One and two dimensional NMR spectroscopy, VCH, Friebolin Spin Dynamics, Basics of NMR, Wiley, Levitt Molecular Quantum Mechanics, Oxford Univ. Press,
NMR, the vector model and the relaxation Reading/Books: One and two dimensional NMR spectroscopy, VCH, Friebolin Spin Dynamics, Basics of NMR, Wiley, Levitt Molecular Quantum Mechanics, Oxford Univ. Press,
An Analytical Model of Water Diffusion and Exchange in White Matter from Diffusion MRI and Its Application in Measuring Axon Radii
 An Analytical Model of Water Diffusion and Exchange in White Matter from Diffusion MRI and Its Application in Measuring Axon Radii Wenjin Zhou, Student Member, IEEE, and David H. Laidlaw, Senior Member,
An Analytical Model of Water Diffusion and Exchange in White Matter from Diffusion MRI and Its Application in Measuring Axon Radii Wenjin Zhou, Student Member, IEEE, and David H. Laidlaw, Senior Member,
Chem 325 NMR Intro. The Electromagnetic Spectrum. Physical properties, chemical properties, formulas Shedding real light on molecular structure:
 Physical properties, chemical properties, formulas Shedding real light on molecular structure: Wavelength Frequency ν Wavelength λ Frequency ν Velocity c = 2.998 10 8 m s -1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Physical properties, chemical properties, formulas Shedding real light on molecular structure: Wavelength Frequency ν Wavelength λ Frequency ν Velocity c = 2.998 10 8 m s -1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Confocal Microscopy Imaging of Single Emitter Fluorescence and Hanbury Brown and Twiss Photon Antibunching Setup
 1 Confocal Microscopy Imaging of Single Emitter Fluorescence and Hanbury Brown and Twiss Photon Antibunching Setup Abstract Jacob Begis The purpose of this lab was to prove that a source of light can be
1 Confocal Microscopy Imaging of Single Emitter Fluorescence and Hanbury Brown and Twiss Photon Antibunching Setup Abstract Jacob Begis The purpose of this lab was to prove that a source of light can be
MEDIUM RESOLUTION NMR AT 20 MHz: POSSIBILITIES AND CHALLENGES
 First published in: Magnetic Resonance in Food Science. An Exciting Future. Ed.: J.-P. Renou. 2011. ISBN 978-1-84973-233-8 MEDIUM RESOLUTION NMR AT 20 MHz: POSSIBILITIES AND CHALLENGES M. Cudaj 1,2, T.
First published in: Magnetic Resonance in Food Science. An Exciting Future. Ed.: J.-P. Renou. 2011. ISBN 978-1-84973-233-8 MEDIUM RESOLUTION NMR AT 20 MHz: POSSIBILITIES AND CHALLENGES M. Cudaj 1,2, T.
Holographic Characterization of Agglomerates in CMP Slurries
 Holographic Characterization of Agglomerates in CMP Slurries Total Holographic Characterization (THC) Comparison of THC to other technologies Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Scanning Electron Microscopy
Holographic Characterization of Agglomerates in CMP Slurries Total Holographic Characterization (THC) Comparison of THC to other technologies Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Scanning Electron Microscopy
Diffusion during Plasma Formation
 Chapter 6 Diffusion during Plasma Formation Interesting processes occur in the plasma formation stage of the Basil discharge. This early stage has particular interest because the highest plasma densities
Chapter 6 Diffusion during Plasma Formation Interesting processes occur in the plasma formation stage of the Basil discharge. This early stage has particular interest because the highest plasma densities
Nonlinear Optics. Single-Molecule Microscopy Group. Physical Optics Maria Dienerowitz.
 Single-Molecule Microscopy Group Nonlinear Optics Physical Optics 21-06-2017 Maria Dienerowitz maria.dienerowitz@med.uni-jena.de www.single-molecule-microscopy.uniklinikum-jena.de Contents Introduction
Single-Molecule Microscopy Group Nonlinear Optics Physical Optics 21-06-2017 Maria Dienerowitz maria.dienerowitz@med.uni-jena.de www.single-molecule-microscopy.uniklinikum-jena.de Contents Introduction
Classical behavior of magnetic dipole vector. P. J. Grandinetti
 Classical behavior of magnetic dipole vector Z μ Y X Z μ Y X Quantum behavior of magnetic dipole vector Random sample of spin 1/2 nuclei measure μ z μ z = + γ h/2 group μ z = γ h/2 group Quantum behavior
Classical behavior of magnetic dipole vector Z μ Y X Z μ Y X Quantum behavior of magnetic dipole vector Random sample of spin 1/2 nuclei measure μ z μ z = + γ h/2 group μ z = γ h/2 group Quantum behavior
CHEM / BCMB 4190/6190/8189. Introductory NMR. Lecture 10
 CHEM / BCMB 490/690/889 Introductory NMR Lecture 0 - - CHEM 490/690 Spin-Echo The spin-echo pulse sequence: 90 - τ - 80 - τ(echo) Spins echoes are widely used as part of larger pulse sequence to refocus
CHEM / BCMB 490/690/889 Introductory NMR Lecture 0 - - CHEM 490/690 Spin-Echo The spin-echo pulse sequence: 90 - τ - 80 - τ(echo) Spins echoes are widely used as part of larger pulse sequence to refocus
Interpreting Your PSA Results
 Interpreting Your PSA Results Decoding the Acronyms and Finding Insights Ian Treviranus ian.treviranus@horiba.com www.horiba.com/us/particle Outline The Basics Define Parameters Choose Parameters Interpret
Interpreting Your PSA Results Decoding the Acronyms and Finding Insights Ian Treviranus ian.treviranus@horiba.com www.horiba.com/us/particle Outline The Basics Define Parameters Choose Parameters Interpret
Chapter 8 Magnetic Resonance
 Chapter 8 Magnetic Resonance 9.1 Electron paramagnetic resonance 9.2 Ferromagnetic resonance 9.3 Nuclear magnetic resonance 9.4 Other resonance methods TCD March 2007 1 A resonance experiment involves
Chapter 8 Magnetic Resonance 9.1 Electron paramagnetic resonance 9.2 Ferromagnetic resonance 9.3 Nuclear magnetic resonance 9.4 Other resonance methods TCD March 2007 1 A resonance experiment involves
A fast method for the measurement of long spin lattice relaxation times by single scan inversion recovery experiment
 Chemical Physics Letters 383 (2004) 99 103 www.elsevier.com/locate/cplett A fast method for the measurement of long spin lattice relaxation times by single scan inversion recovery experiment Rangeet Bhattacharyya
Chemical Physics Letters 383 (2004) 99 103 www.elsevier.com/locate/cplett A fast method for the measurement of long spin lattice relaxation times by single scan inversion recovery experiment Rangeet Bhattacharyya
1 Introduction Why the Interpretive Approach? (Niall W. G. Young).
 1 Introduction Why the Interpretive Approach? (Niall W. G. Young). 1.1 Rheology What is in it for me? 1.1.1 Case study. 2 Viscosity and Oscillatory Rheology (Taghi Miri). 2.1 Introduction. 2.2 Food rheology.
1 Introduction Why the Interpretive Approach? (Niall W. G. Young). 1.1 Rheology What is in it for me? 1.1.1 Case study. 2 Viscosity and Oscillatory Rheology (Taghi Miri). 2.1 Introduction. 2.2 Food rheology.
EXCITATION OF GÖRTLER-INSTABILITY MODES IN CONCAVE-WALL BOUNDARY LAYER BY LONGITUDINAL FREESTREAM VORTICES
 ICMAR 2014 EXCITATION OF GÖRTLER-INSTABILITY MODES IN CONCAVE-WALL BOUNDARY LAYER BY LONGITUDINAL FREESTREAM VORTICES Introduction A.V. Ivanov, Y.S. Kachanov, D.A. Mischenko Khristianovich Institute of
ICMAR 2014 EXCITATION OF GÖRTLER-INSTABILITY MODES IN CONCAVE-WALL BOUNDARY LAYER BY LONGITUDINAL FREESTREAM VORTICES Introduction A.V. Ivanov, Y.S. Kachanov, D.A. Mischenko Khristianovich Institute of
Supplementary Information Access to side- chain carbon information in deuterated solids under ultra- fast MAS through non- rotor- synchronized mixing
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Supplementary Information Access to side- chain carbon information in deuterated solids under ultra-
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Supplementary Information Access to side- chain carbon information in deuterated solids under ultra-
Thermal and nonlinear optical studies of newly synthesized EDOT based bent-core and hockey-stick like liquid crystals
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 Electronic supplementary information:
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 Electronic supplementary information:
Linear and nonlinear spectroscopy
 Linear and nonlinear spectroscopy We ve seen that we can determine molecular frequencies and dephasing rates (for electronic, vibrational, or spin degrees of freedom) from frequency-domain or timedomain
Linear and nonlinear spectroscopy We ve seen that we can determine molecular frequencies and dephasing rates (for electronic, vibrational, or spin degrees of freedom) from frequency-domain or timedomain
Laserunterstützte magnetische Resonanz
 Laserunterstützte magnetische Resonanz http://e3.physik.uni-dortmund.de Dieter Suter Magnetische Resonanz Prinzip Die MR mißt Übergänge zwischen unterschiedlichen Spin-Zuständen. Diese werden durch ein
Laserunterstützte magnetische Resonanz http://e3.physik.uni-dortmund.de Dieter Suter Magnetische Resonanz Prinzip Die MR mißt Übergänge zwischen unterschiedlichen Spin-Zuständen. Diese werden durch ein
PII S X(98) FLOW AND TRANSPORT STUDIES IN (NON)CONSOLIDATED POROUS (BIO)SYSTEMS CONSISTING OF SOLID OR POROUS BEADS BY PFG NMR
 PII S0730-725X(98)00052-6 Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol. 16, Nos. 5/6, pp. 569 573, 1998 1998 Elsevier Science Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. 0730-725X/98 $19.00.00 Contributed Paper FLOW
PII S0730-725X(98)00052-6 Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol. 16, Nos. 5/6, pp. 569 573, 1998 1998 Elsevier Science Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. 0730-725X/98 $19.00.00 Contributed Paper FLOW
ULTRASONIC SPECTROSCOPY. Rajeesha.S and Mounika.G
 ULTRASONIC SPECTROSCOPY * Kamepalli Sujana, 1 Dr. Prameela Rani.A, Bramara Sandhya.P, Rajeesha.S and Mounika.G * Pharmaceutical Analysis division, Acharya Nagarjuna University College of Pharmaceutical
ULTRASONIC SPECTROSCOPY * Kamepalli Sujana, 1 Dr. Prameela Rani.A, Bramara Sandhya.P, Rajeesha.S and Mounika.G * Pharmaceutical Analysis division, Acharya Nagarjuna University College of Pharmaceutical
Measuring Spin-Lattice Relaxation Time
 WJP, PHY381 (2009) Wabash Journal of Physics v4.0, p.1 Measuring Spin-Lattice Relaxation Time L.W. Lupinski, R. Paudel, and M.J. Madsen Department of Physics, Wabash College, Crawfordsville, IN 47933 (Dated:
WJP, PHY381 (2009) Wabash Journal of Physics v4.0, p.1 Measuring Spin-Lattice Relaxation Time L.W. Lupinski, R. Paudel, and M.J. Madsen Department of Physics, Wabash College, Crawfordsville, IN 47933 (Dated:
Micro-encapsulation using an oil-in-water-in-air "Dry Water Emulsion"
 Micro-encapsulation using an oil-in-water-in-air "Dry Water Emulsion" Benjamin O. Carter, Jonathan V. M. Weaver, Weixing Wang, David G. Spiller, Dave J. Adams, and Andrew I. Cooper Supporting Information
Micro-encapsulation using an oil-in-water-in-air "Dry Water Emulsion" Benjamin O. Carter, Jonathan V. M. Weaver, Weixing Wang, David G. Spiller, Dave J. Adams, and Andrew I. Cooper Supporting Information
Fluorescence Spectroscopy
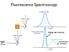 Fluorescence Spectroscopy Raleigh light scattering light all freqs Fluorescence emission Raleigh Scattering 10 nm Raleigh light scattering Fluorescence emission 400 nm Scattering - TWO particle 10 nm Particle
Fluorescence Spectroscopy Raleigh light scattering light all freqs Fluorescence emission Raleigh Scattering 10 nm Raleigh light scattering Fluorescence emission 400 nm Scattering - TWO particle 10 nm Particle
Asian Journal of Chemistry; Vol. 25, No. 4 (2013),
 Asian Journal of Chemistry; Vol. 25, No. 4 (213), 214-218 http://dx.doi.org/1.14233/ajchem.213.13346 Observation of Triplet Traces Obtained with Inversion Recovery Method in Both Residual Water- and H
Asian Journal of Chemistry; Vol. 25, No. 4 (213), 214-218 http://dx.doi.org/1.14233/ajchem.213.13346 Observation of Triplet Traces Obtained with Inversion Recovery Method in Both Residual Water- and H
The physics US and MRI. Prof. Peter Bogner
 The physics US and MRI Prof. Peter Bogner Sound waves mechanical disturbance, a pressure wave moves along longitudinal wave compression rarefaction zones c = nl, (c: velocity, n: frequency, l: wavelength
The physics US and MRI Prof. Peter Bogner Sound waves mechanical disturbance, a pressure wave moves along longitudinal wave compression rarefaction zones c = nl, (c: velocity, n: frequency, l: wavelength
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
 CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background
 The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background Abstract The CMP slurry monitor uses electroacoustic and ultrasonic attenuation measurements to determine the size and zeta potential of slurry particles. The article
The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background Abstract The CMP slurry monitor uses electroacoustic and ultrasonic attenuation measurements to determine the size and zeta potential of slurry particles. The article
Vibrational Spectroscopies. C-874 University of Delaware
 Vibrational Spectroscopies C-874 University of Delaware Vibrational Spectroscopies..everything that living things do can be understood in terms of the jigglings and wigglings of atoms.. R. P. Feymann Vibrational
Vibrational Spectroscopies C-874 University of Delaware Vibrational Spectroscopies..everything that living things do can be understood in terms of the jigglings and wigglings of atoms.. R. P. Feymann Vibrational
