Fuel Cells Jong Hak Kim Chemical Engineering Yonsei University
|
|
|
- Alaina Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 에너지소재특론 Fuel Cells Jong Hak Kim Chemical Engineering Yonsei University
2 Fuel Cells Electrochemical cell which can continuously convert the chemical energy of a fuel and an oxidant to electrical energy PEMFC (Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell) H 2, CH 3 OH/ H 2 O H+ DMFC (Direct Methanol Fuel Cell)
3 Fuel Cell vs. Battery Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA) Li x C 6 /Electrolyte/CoO 2 Chemical E Electrical E Continuous generation of electricity. No need for electrical charging. Chemical E Electrical E Discontinuous generation of electricity. Need for electrical charging.
4 Direct Fuel Cell Classifications of fuel cells - Operating T: Low(<100 C), intermediate( ), high(>500 C) - Type of fuels: natural gas, hydrogen, organics (hydrocarbons, alcohols), nitrogen compounds (ammonia, hydrazine) - Nature of electrolytes: aqueous, molten salts, solid electrolyte (ceramic), polymer electrolyte Indirect Fuel Cell - Organics to hydrogen (or other fuels) by reformer or catalyst - Enzymatic decomposition of biomaterials to hydrogen Long-term direction - New fuels & new fuel cell systems - New organics, Biochemicals, etc.
5 Characteristics of fuel cells i) High efficiency and reliability - convert up to 90% of the energy in fuel into electric power & heat (high electrical conversion efficiency: 46% for PAFC, 60% for MCFC) - fewer moving parts higher reliability ii) Environmental performance - improving air quality: lower pollutant emission (SO 2, NO x, CO 2, ash etc) - reduce water consumption & waste water discharge - quiet, no noise - no used battery problem iii) Unique operating characteristics - economic benefits & technologies research - potential markets of fuel cell systems - power plant, electrical vehicle, portable electronics
6 Thermodynamics Basic Principles G = H - T S, G 0 = - RT lnk K ; equilibrium constant, G < 0 a reaction can occur G = - nfe Kinetics - Overvoltage or Polarization: ohmic, activation, concentration < Polarization curves of H 2 -O 2 cell > Activation - slow electrode RXN Ohmic - resistance of electrolyte Concentration - difference btn. surface & bulk
7 Electrode Mechanism H 2 -O 2 fuel cell - In acid electrolyte anode: H 2 2H + + 2e - cathode: 1/2O 2 + 2H + + 2e - H 2 O Total: H 2 + 1/2O 2 H 2 O E 0 = V E 0 = V E 0 = V - In alkaline electrolyte anode: H 2 + 2OH - 2H 2 O + 2e - cathode: 1/2O 2 + H 2 O + 2e - 2OH - Total: H 2 + 1/2O 2 H 2 O E 0 = V E 0 = V E 0 = V
8 Overall mechanism H 2 2H - + 2e - ½O 2 + H 2 O + 2e - 2OH - 2H + + 2OH - 2H 2 O 1) Hydrogen enters the pores of anode and reaches the reaction zone, where gas, electrolyte and conducting material meet. 2) Hydrogen diffuses to the active site of catalyst and ionized. 3) H + react with OH - of the electrolyte to form water. 4) Two electrons are available to the electrical circuit. Cathode provides OH - by 1/2O 2 + H 2 O + 2e - 2OH -
9 Anode Process - Potential of hydrogen anode is constant: easier interpretation in acid solution; 1/2H 2,ads + H 2 O H 3 O + + e - in alkaline electrolyte; 1/2H 2 + OH - H 2 O + e - Mechanisms 1) Adsorption of H 2 on the electrode surface H 2 H 2,solv H 2,ads 2) Hydration & Ionization of H 2,ads a) Dissociation of H 2 with subsequent ionization/hydration H 2,ads 2H + ads (Tafel reaction) H + ads + OH - H 2 O + e - (alkaline) H + ads + H 2 O H 3 O + + e - (acid)
10 b) Hydration & Ionization in one step (Heyrovsky-Volmer mechanism) H 2,ads + OH - H ads H 2 O + e - H + ads + H 2 O + e - (alkaline) H 2,ads + H 2 O H ads H 3 O + + e - H + ads + H 3 O + + e - (acid) 3) Desorption of products (H 3 O +, H 2 O) and transport into electrolyte - Hg, Ag: no H 2 chemisorption & no oxidation - Pt, Ir, Rh, Pd, Au: chemisorption & oxidation Reaction process on three phase border of H 2 -electrode
11 Cathodic Process - Number of possible mechanisms of cathodic reaction e.g., forming intermediate hydrogen peroxide Actual potential ( V) < Theoretical (1.23 V) due to the formation of hydrogen peroxide O 2 + H 2 O + 2e - HO 2- + OH - E 0 = V 2HO 2- H 2 O 2 + O 2 Nernst equation: concentration dependence of O 2 /H 2 O 2 E = E 0 RT/nF log Q E = E log [(a OH- a HO2- )/(p O2 a H2O )] ~ 10-8 mol/l of H 2 O ~ 240 mv potential drop - Active catalyst (Pt, Pd) reduces the concentration to mol/l
12 Porous gas diffusion electrode Gas Diffusion Electrode - provide a large reaction zone area with a minimum of mass transport hindrance for the access of reactants and removal of products e.g., smooth Pt: μa, porous electrode: A - Three phase zone: reactant, electrolyte and catalyst meet, large area can be achieved by metal powder (100 m 2 /g) or carbon (1000 m 2 /g) - Hydrophobic gas diffusion electrodes: fine carbon powder bonded with polymer, e.g., polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) - hydrophobic gas diffusion layer + electrolyte wettable thin layer keeping the pores free and facilitating gas access to the reaction sites
13 Bipolar Plates Monopolar: edge collection of current, high conductivity, size up to 400 cm 2, no serious problem with one cell failure Bipolar: current collector, large size, low conductivity materials
14 Electrocatalysts - Acceleration of electrode reaction by a substance which is not consumed in the overall reaction - H 2 2H + + 2e - The highest activity in Pt, Pd, Ni
15 Requirements for high catalytic activity - large, accessible surface (porosity) - fine distribution - adsorbability on the surface - desorption property of product - weakened bond in the adsorbed partner Low T H 2 -O 2 fuel cell - hydrogen electrode (Pt, Pd) - oxygen electrode (Pt, Pd, special carbons, porphyrines, Ni etc) Nobel metal catalysts - poisoned by impurities (CO, S, etc) non-noble metal catalysts
16 Fuel Cell efficiency Carnot efficiency : theoretical efficiency of heat engine η = (T 1 T 2 )/T 1 the efficiency can be unity 1) if T 2 is at absolute zero or 2) if T 1 becomes a very high value - maximum Carnot efficiency: % - actual efficiencies ~ ½ of maximum efficiency Thermodynamic efficiency η th = G/ H = 1 - T S/ H - typically ~ 90% (H 2 + 1/2O 2 H 2 O, 83%) - over 100% if the entropy of products > reactants (C + 1/2O 2 CO, 124%) Electrochemical efficiency: η el = - nfe K / G = E K /E 0
17 Fuel cell systems Classifications; T, P, fuels, electrolytes
18 Typical Electrochemical Reactions in Fuel Cells Fuel Cell Anode Reaction Cathode Reaction Alkaline Fuel Cells H 2 + 2(OH) - 2H 2 O + 2e - ½O 2 + H 2 O + 2e - 2(OH) - Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells H 2 2H + + 2e - ½O 2 + 2H + + 2e - H 2 O H 2 2H + + 2e - ½O 2 + 2H + + 2e - H 2 O H 2 + CO 3 2- H 2 O + CO 2 + 2e - ½O 2 + CO 2 + 2e - CO 3 2- Solid Oxide Fuel Cells H 2 + O 2- H 2 O + 2e - ½O 2 + 2e - O 2-
19 Advantages - no corrosive liquid in the cell - simple to fabricate the cell - low operating temperature - able to withstand large pressure differences - minimal material corrosion problems - long lifetime Polymer electrolyte membrane FC (PEMFC) Proton exchange membrane FC Disadvantages - expensive fluorinated polymer electrolyte & high cell costs - water-management in the membrane - noble metal catalysts needed - poor CO tolerance - difficulty in thermally integrating with a reformer
20 Membranes - the electrolyte to provide ionic communication btn. electrodes - a separator for two reactant gases Water management - Dehydration of membrane reduces conductivity - Excess of water can lead to flooding of the electrodes poor cell performance to drain or supply water by capillary action, humidifying the reactants, flow design, temperature rising (increase water vapor).
21 Electrodes: gas diffusion electrodes - porous carbon cloth with catalyst (Pt or supported Pt) - how to reduce Pt loading : smaller nanoparticles, changes in electrode structure, Pt on surface only, supported Pt - Cyclic voltammetry: 10-20% Pt was active for hydrogen/oxygen adsorption/desorption Cyclic Voltammograms (a) uncatalyzed (b) 10wt% Pt/C (c) 20wt% Pt/C
22 Catalysts and Substrates Ionomer ion containing polymer, polyelectrolyte copolymer nonionic and ionic repeat unit
23 Gas diffusion layer : current collecting, water removing, physical support, fuel diffusion Catalyst layer: electrode (anode, cathode) Membrane: electrolyte
24 Polymer Membrane: NAFION - Thickness : 50~175μm, equivalent weight : 1,100 meq/g - High oxygen solubility, high proton conductivity, low density, high chemical and thermal stability, high water solubility - H 2 SO 4 solution as pretreatment Problem - Low water content => low proton conductivity High content => flooding in electrode => inefficient reaction - Methanol crossover in DMFC - High cost
25 Production Company for Membrane US : Du Pont (Nafion), Dow Chemical (XUS), W.L. Gore & Associate (Gore-Select) Canada : Ballard Advanced Materials (BAM3G) Japan : Asahi Chemical (Aciplex), Asahi Glass (Flemion), Chlorine Engineer (Product c ), German : Hoechst Membranes Equivalent weight (g/mol SO 3- ) Thickness, Dry (um) Water content(%) Conductivity (S/cm) XUS Aciplex-S Nafion Gore-Select Flemion , 80 Gore-Select: Fine mesh PTFE support impregnated with Nafion
26 Conducting Mechanisms Grotthus mechanism vs vehicle mechanism Polar ionic groups - tend to cluster together - away from nonpolar backbones Reversible crosslinker - when heated, ionic groups loose their attraction - chains move around freely
27 Sulfonated Aromatic Polymers Poly(styrene) (PS) Poly(ether ether ketone) (PEEK) Poly(benz imidazole) (PBI) Polysulfone (PSf) Poly(ether sulfone) (PES) Poly(phenylene sulfide) (PPS)
28 Performance of PEMFC Effect of Temperature T resistance of electrolyte cell performance Effect of cathodic reactant : composition & pressure P, O 2 increase of MT cell performance
29 Performance of PEMFC Effect of CO in the fuel gas reduce CO content (selective oxidation of CO to CO 2 by passing with small oxygen or air through a small reactor containing Pt) CO-tolerant Pt catalysts
30 Acid-Base Complex PBI/H 3 PO 4 High thermal and mechanical stability PBI/H 3 PO 4 : 0.04 S/cm at 140 o C and 10 % RH Nafion: < 0.01 S/cm at 140 o C and 10 % RH
31 Nanocomposite membranes Addition of Nanofiller - Clay (montmorillonite (MMT)) - Zeolite (NaA) - Metal Oxide (SiO 2 / TiO 2 / Al 2 O 3 / ZrO 2 ) - Heteropolyacid (phosphotungstic acid)
32 Block/Graft Copolymer Electrolytes H + H + conducting H + H + Advantages - Formation of ion conducting channels by microphase separation - Hindering of swelling by surrounding nonsulfonated phase - Lowering of MeOH permeability - High mechanical stability Microphase separation nonconducting High ionic conductivity Good mechanical property
Oxygen Reduction Reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Oxygen Reduction Reaction Oxygen is the most common oxidant for most fuel cell cathodes simply
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Oxygen Reduction Reaction Oxygen is the most common oxidant for most fuel cell cathodes simply
Advanced Analytical Chemistry Lecture 12. Chem 4631
 Advanced Analytical Chemistry Lecture 12 Chem 4631 What is a fuel cell? An electro-chemical energy conversion device A factory that takes fuel as input and produces electricity as output. O 2 (g) H 2 (g)
Advanced Analytical Chemistry Lecture 12 Chem 4631 What is a fuel cell? An electro-chemical energy conversion device A factory that takes fuel as input and produces electricity as output. O 2 (g) H 2 (g)
Cross Section of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
 PEMFC Electrodes 1 Cross Section of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Anode Cathode 2 Typical PEMFC Electrodes: - Anode Hydrogen Oxidation - Pt Ru / C - Cathode Oxygen reduction - Pt / C Pt is alloyed
PEMFC Electrodes 1 Cross Section of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Anode Cathode 2 Typical PEMFC Electrodes: - Anode Hydrogen Oxidation - Pt Ru / C - Cathode Oxygen reduction - Pt / C Pt is alloyed
Fuel Cells in Energy Technology. Tutorial 5 / SS solutions. Prof. W. Schindler, Jassen Brumbarov / Celine Rüdiger
 Fuel Cells in Energy Technology Tutorial 5 / SS 2013 - solutions Prof. W. Schindler, Jassen Brumbarov / Celine Rüdiger 05.06.2013 Homework 3: What hydrogen flow rate (g/hour) is required to generate 1
Fuel Cells in Energy Technology Tutorial 5 / SS 2013 - solutions Prof. W. Schindler, Jassen Brumbarov / Celine Rüdiger 05.06.2013 Homework 3: What hydrogen flow rate (g/hour) is required to generate 1
Batteries (Electrochemical Power Sources)
 Batteries (Electrochemical Power Sources) 1. Primary (single-discharge) batteries. => finite quantity of the reactants 2. Secondary or rechargeable batteries => regeneration of the original reactants by
Batteries (Electrochemical Power Sources) 1. Primary (single-discharge) batteries. => finite quantity of the reactants 2. Secondary or rechargeable batteries => regeneration of the original reactants by
Direct Energy Conversion: Fuel Cells
 Direct Energy Conversion: Fuel Cells References and Sources: Direct Energy Conversion by Stanley W. Angrist, Allyn and Beacon, 1982. Fuel Cell Systems, Explained by James Larminie and Andrew Dicks, Wiley,
Direct Energy Conversion: Fuel Cells References and Sources: Direct Energy Conversion by Stanley W. Angrist, Allyn and Beacon, 1982. Fuel Cell Systems, Explained by James Larminie and Andrew Dicks, Wiley,
ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND IMPROVEMENT OF PERFORMANCE OF A PROTON EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (PEM) FUEL CELL IN MOBILE APPLICATIONS
 Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 015, vol.0, No., pp.319-38 DOI: 10.1515/ijame-015-001 ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND IMPROVEMENT OF PERFORMANCE OF A PROTON EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (PEM) FUEL CELL
Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 015, vol.0, No., pp.319-38 DOI: 10.1515/ijame-015-001 ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND IMPROVEMENT OF PERFORMANCE OF A PROTON EXCHANGE MEMBRANE (PEM) FUEL CELL
Ion and Electron Transport Jong Hak Kim Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Yonsei University
 에너지소재특론 Ion and Electron Transport Jong Hak Kim Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Yonsei University Polymer Electrolytes (PEs) Newest solid ionics: generation, storage, distribution - Applications to
에너지소재특론 Ion and Electron Transport Jong Hak Kim Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Yonsei University Polymer Electrolytes (PEs) Newest solid ionics: generation, storage, distribution - Applications to
January 21, 2004 Fuel Cell Engineering Course CHEG 320 Taught at UTC Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells
 January 21, 2004 Fuel Cell Engineering Course CHEG 320 Taught at UTC Fuel Cells Fuel Cells Instructor James M. Fenton, Professor, Chemical Engineering University of Connecticut Teaching Assistants: 1.
January 21, 2004 Fuel Cell Engineering Course CHEG 320 Taught at UTC Fuel Cells Fuel Cells Instructor James M. Fenton, Professor, Chemical Engineering University of Connecticut Teaching Assistants: 1.
Basic overall reaction for hydrogen powering
 Fuel Cell Basics Basic overall reaction for hydrogen powering 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O Hydrogen produces electrons, protons, heat and water PEMFC Anode reaction: H 2 2H + + 2e Cathode reaction: (½)O 2 + 2H +
Fuel Cell Basics Basic overall reaction for hydrogen powering 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O Hydrogen produces electrons, protons, heat and water PEMFC Anode reaction: H 2 2H + + 2e Cathode reaction: (½)O 2 + 2H +
Prof. Mario L. Ferrari
 Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems Dr. Ing. Mario L. Ferrari Thermochemical Power Group (TPG) - DiMSET University of Genoa, Italy Lesson II Lesson II: fuel cells (electrochemistry)
Sustainable Energy Mod.1: Fuel Cells & Distributed Generation Systems Dr. Ing. Mario L. Ferrari Thermochemical Power Group (TPG) - DiMSET University of Genoa, Italy Lesson II Lesson II: fuel cells (electrochemistry)
Electrolytes for Fuel Cells
 Electrolytes for Fuel Cells Tom Zawodzinski Materials Science and Technology Division Los Alamos National Laboratory Air-Breather Fuel Cell Stack Systems Laptop Demo DCH/Enable Prototype Small Battery
Electrolytes for Fuel Cells Tom Zawodzinski Materials Science and Technology Division Los Alamos National Laboratory Air-Breather Fuel Cell Stack Systems Laptop Demo DCH/Enable Prototype Small Battery
FUEL CELLS: INTRODUCTION
 FUEL CELLS: INTRODUCTION M. OLIVIER marjorie.olivier@fpms.ac.be 19/5/8 A SIMPLE FUEL CELL Two electrochemical half reactions : H 1 O H + + H + e + + e H O These reactions are spatially separated: Electrons:
FUEL CELLS: INTRODUCTION M. OLIVIER marjorie.olivier@fpms.ac.be 19/5/8 A SIMPLE FUEL CELL Two electrochemical half reactions : H 1 O H + + H + e + + e H O These reactions are spatially separated: Electrons:
Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example)
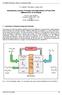 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil -4 December 00 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil 00 Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example) Prof. Dr. Wolf Vielstich University of
3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil -4 December 00 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil 00 Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example) Prof. Dr. Wolf Vielstich University of
Basic overall reaction for hydrogen powering
 Fuel Cell Basics Basic overall reaction for hydrogen powering 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O Hydrogen produces electrons, protons, heat and water PEMFC Anode reaction: H 2 2H + + 2e Cathode reaction: (½)O 2 + 2H +
Fuel Cell Basics Basic overall reaction for hydrogen powering 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O Hydrogen produces electrons, protons, heat and water PEMFC Anode reaction: H 2 2H + + 2e Cathode reaction: (½)O 2 + 2H +
Development of Bifunctional Electrodes for Closed-loop Fuel Cell Applications. Pfaffenwaldring 6, Stuttgart, Germany
 Development of Bifunctional Electrodes for Closed-loop Fuel Cell Applications S. Altmann a,b, T. Kaz b, K. A. Friedrich a,b a Institute of Thermodynamics and Thermal Engineering, University Stuttgart,
Development of Bifunctional Electrodes for Closed-loop Fuel Cell Applications S. Altmann a,b, T. Kaz b, K. A. Friedrich a,b a Institute of Thermodynamics and Thermal Engineering, University Stuttgart,
possesses negative potential & undergoes oxidation preferably act as ANODE
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Introduction: Electrochemistry is the area of Chemistry dealing with the interconversion of electrical energy and chemical energy. There are many applications of this in every day life.
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Introduction: Electrochemistry is the area of Chemistry dealing with the interconversion of electrical energy and chemical energy. There are many applications of this in every day life.
Fuel Cell Activities in MME Waterloo
 Fuel Cell Activities in MME Waterloo Xianguo Li and Roydon Fraser Fuel Cells and Green Energy Research Group Department of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario,
Fuel Cell Activities in MME Waterloo Xianguo Li and Roydon Fraser Fuel Cells and Green Energy Research Group Department of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario,
Porous silicon as base material of MEMS-compatible fuel cell components
 Porous silicon as base material of MEMS-compatible fuel cell components José Geraldo Alves Brito Neto Tokyo University of Science - Faculty of Science and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering
Porous silicon as base material of MEMS-compatible fuel cell components José Geraldo Alves Brito Neto Tokyo University of Science - Faculty of Science and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering
Modeling of Liquid Water Distribution at Cathode Gas Flow Channels in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell - PEMFC
 Modeling of Liquid Water Distribution at Cathode Gas Flow Channels in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell - PEMFC Sandro Skoda 1*, Eric Robalinho 2, André L. R. Paulino 1, Edgar F. Cunha 1, Marcelo Linardi
Modeling of Liquid Water Distribution at Cathode Gas Flow Channels in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell - PEMFC Sandro Skoda 1*, Eric Robalinho 2, André L. R. Paulino 1, Edgar F. Cunha 1, Marcelo Linardi
Introduction Fuel Cells Repetition
 Introduction Fuel Cells Repetition Fuel cell applications PEMFC PowerCell AB, (S1-S3) PEMFC,1-100 kw Toyota Mirai a Fuel Cell Car A look inside The hydrogen tank 1. Inside Layer of polymer closest to the
Introduction Fuel Cells Repetition Fuel cell applications PEMFC PowerCell AB, (S1-S3) PEMFC,1-100 kw Toyota Mirai a Fuel Cell Car A look inside The hydrogen tank 1. Inside Layer of polymer closest to the
Current and Temperature Distributions in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
 Current and Temperature Distributions in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell by Ibrahim Alaefour A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree
Current and Temperature Distributions in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell by Ibrahim Alaefour A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree
Figure 1. Schematic of Scriber Associates Model 850C fuel cell system.
 Objective of the fuel cell experiments: To familiarize the working principles and performance characteristics of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Experimental Procedures Instrumentation A Scriber Associates
Objective of the fuel cell experiments: To familiarize the working principles and performance characteristics of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Experimental Procedures Instrumentation A Scriber Associates
The Curious Case of Au Nanoparticles
 The Curious Case of Au Nanoparticles Industrial reactions performed by metals 1 Low Au reactivity Predictions are typically based on d-band model Hold well for polycrystalline materials Coinage metals
The Curious Case of Au Nanoparticles Industrial reactions performed by metals 1 Low Au reactivity Predictions are typically based on d-band model Hold well for polycrystalline materials Coinage metals
CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials. Compiled by. Dr. A.O. Oladebeye
 CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials Compiled by Dr. A.O. Oladebeye Department of Chemistry University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, Nigeria Electrochemical Cell Electrochemical
CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials Compiled by Dr. A.O. Oladebeye Department of Chemistry University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, Nigeria Electrochemical Cell Electrochemical
Highly Durable MEA for PEMFC Under High Temperature and Low Humidity Conditions. Eiji Endoh a. Yokohama, JAPAN
 10.1149/1.2356118, copyright The Electrochemical Society Highly Durable MEA for PEMFC Under High Temperature and Low Humidity Conditions Eiji Endoh a a Research Center, Asahi Glass Co., Ltd. 1150 Hazawacho,
10.1149/1.2356118, copyright The Electrochemical Society Highly Durable MEA for PEMFC Under High Temperature and Low Humidity Conditions Eiji Endoh a a Research Center, Asahi Glass Co., Ltd. 1150 Hazawacho,
Stoichiometry: Chemical Calculations. Chapter 3-4
 Chapters 3-4 Stoichiometry: Chemical Calculations Slide 1 of 48 Molecular Masses And Formula Masses Molecular Masses Molecular mass is the sum of the masses of the atoms represented in a molecular formula.
Chapters 3-4 Stoichiometry: Chemical Calculations Slide 1 of 48 Molecular Masses And Formula Masses Molecular Masses Molecular mass is the sum of the masses of the atoms represented in a molecular formula.
FACTORS INFLUENCING ELECTROCHEMICAL PROPERTIES AND PERFORMANCE OF HYDROCARBON BASED IONOMER PEMFC CATALYST LAYERS
 FACTORS INFLUENCING ELECTROCHEMICAL PROPERTIES AND PERFORMANCE OF HYDROCARBON BASED IONOMER PEMFC CATALYST LAYERS by Toby Duncan Astill B.Sc. (Hons), University of Victoria, 2003 THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL
FACTORS INFLUENCING ELECTROCHEMICAL PROPERTIES AND PERFORMANCE OF HYDROCARBON BASED IONOMER PEMFC CATALYST LAYERS by Toby Duncan Astill B.Sc. (Hons), University of Victoria, 2003 THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL
FINITE ELEMENT METHOD MODELLING OF A HIGH TEMPERATURE PEM FUEL CELL
 CONDENSED MATTER FINITE ELEMENT METHOD MODELLING OF A HIGH TEMPERATURE PEM FUEL CELL V. IONESCU 1 1 Department of Physics and Electronics, Ovidius University, Constanta, 900527, Romania, E-mail: ionescu.vio@gmail.com
CONDENSED MATTER FINITE ELEMENT METHOD MODELLING OF A HIGH TEMPERATURE PEM FUEL CELL V. IONESCU 1 1 Department of Physics and Electronics, Ovidius University, Constanta, 900527, Romania, E-mail: ionescu.vio@gmail.com
Hydrocarbon Fuel Cell Membranes Containing Perfluorosulfonic Acid Group
 Hydrocarbon Fuel Cell Membranes Containing Perfluorosulfonic Acid Group Ying Chang and Chulsung Bae Department of Chemistry & Chemical Biology Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY 12180 Collaborators
Hydrocarbon Fuel Cell Membranes Containing Perfluorosulfonic Acid Group Ying Chang and Chulsung Bae Department of Chemistry & Chemical Biology Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY 12180 Collaborators
Fernando O. Raineri. Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby).
 Fernando O. Raineri Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby). P1) What is the reduction potential of the hydrogen electrode g bar H O aq Pt(s) H,1 2 3 when the aqueous solution
Fernando O. Raineri Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby). P1) What is the reduction potential of the hydrogen electrode g bar H O aq Pt(s) H,1 2 3 when the aqueous solution
Structural and Electronic properties of platinum nanoparticles studied by diffraction and absorption spectroscopy
 The 4 th SUNBEAM Workshop Structural and Electronic properties of platinum nanoparticles studied by in situ x-ray x diffraction and in situ x-ray x absorption spectroscopy Hideto Imai Fundamental and Environmental
The 4 th SUNBEAM Workshop Structural and Electronic properties of platinum nanoparticles studied by in situ x-ray x diffraction and in situ x-ray x absorption spectroscopy Hideto Imai Fundamental and Environmental
Optimization of platinum nanoparticles for proton exchange membrane fuel cells using pulse electrochemical deposition
 Optimization of platinum nanoparticles for proton exchange membrane fuel cells using pulse electrochemical deposition Ryan Lindeborg, AJ Swoboda Harvard College 16, Princeton College 15 Jonathan Burk,
Optimization of platinum nanoparticles for proton exchange membrane fuel cells using pulse electrochemical deposition Ryan Lindeborg, AJ Swoboda Harvard College 16, Princeton College 15 Jonathan Burk,
Modeling the Behaviour of a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane within a Fuel Cell Using COMSOL
 Modeling the Behaviour of a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane within a Fuel Cell Using COMSOL S. Beharry 1 1 University of the West Indies, St. Augustine, Trinidad and Tobago Abstract: In recent years, scientists
Modeling the Behaviour of a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane within a Fuel Cell Using COMSOL S. Beharry 1 1 University of the West Indies, St. Augustine, Trinidad and Tobago Abstract: In recent years, scientists
Modeling as a tool for understanding the MEA. Henrik Ekström Utö Summer School, June 22 nd 2010
 Modeling as a tool for understanding the MEA Henrik Ekström Utö Summer School, June 22 nd 2010 COMSOL Multiphysics and Electrochemistry Modeling The software is based on the finite element method A number
Modeling as a tool for understanding the MEA Henrik Ekström Utö Summer School, June 22 nd 2010 COMSOL Multiphysics and Electrochemistry Modeling The software is based on the finite element method A number
Student Achievement. Chemistry 12
 Student Achievement Chemistry 12 Key Elements: Reaction Kinetics Estimated Time: 14 16 hours By the end of this course, students will be able to explain the significance of reaction rates, demonstrate
Student Achievement Chemistry 12 Key Elements: Reaction Kinetics Estimated Time: 14 16 hours By the end of this course, students will be able to explain the significance of reaction rates, demonstrate
Fuel Cells Activation polarization
 Fuel Cells The principle of fuel cells Oxygen and hydrogen, when mixed together in the presence of enough activation energy have a natural tendency to react and form water, because the Gibbs free energy
Fuel Cells The principle of fuel cells Oxygen and hydrogen, when mixed together in the presence of enough activation energy have a natural tendency to react and form water, because the Gibbs free energy
Materials for Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage. Truls Norby 1.1
 Materials for Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage Truls Norby 1.1 Preface This text is being written in the first round to serve as curriculum for parts of the course MEF3200/MEF4200 Energy Materials
Materials for Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage Truls Norby 1.1 Preface This text is being written in the first round to serve as curriculum for parts of the course MEF3200/MEF4200 Energy Materials
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. College of Engineering COMPUTATIONAL EXPLORATION OF HIGH POWER OPERATION IN POROUS FLOW
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Engineering COMPUTATIONAL EXPLORATION OF HIGH POWER OPERATION IN POROUS FLOW FIELD POLYMER ELECTROLYTE FUEL CELLS WITH A VALIDATED MODEL
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School College of Engineering COMPUTATIONAL EXPLORATION OF HIGH POWER OPERATION IN POROUS FLOW FIELD POLYMER ELECTROLYTE FUEL CELLS WITH A VALIDATED MODEL
17.1 Redox Chemistry Revisited
 Chapter Outline 17.1 Redox Chemistry Revisited 17.2 Electrochemical Cells 17.3 Standard Potentials 17.4 Chemical Energy and Electrical Work 17.5 A Reference Point: The Standard Hydrogen Electrode 17.6
Chapter Outline 17.1 Redox Chemistry Revisited 17.2 Electrochemical Cells 17.3 Standard Potentials 17.4 Chemical Energy and Electrical Work 17.5 A Reference Point: The Standard Hydrogen Electrode 17.6
Improved Fuel Transport Selectivity in Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. Kyle Tyler Clark. A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the
 Improved Fuel Transport Selectivity in Polymer Electrolyte Membranes By Kyle Tyler Clark A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Engineering
Improved Fuel Transport Selectivity in Polymer Electrolyte Membranes By Kyle Tyler Clark A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Engineering
Activity. Modeling the Fuel Cell Reaction. Overview. Advance Preparation. Background Information
 4 Activity 1-2 class sessions Modeling the uel Cell Reaction 2011 Regents of the University of California Overview n order to understand the chemistry of fuel cells, students are introduced to oxidation-reduction
4 Activity 1-2 class sessions Modeling the uel Cell Reaction 2011 Regents of the University of California Overview n order to understand the chemistry of fuel cells, students are introduced to oxidation-reduction
Introduction to Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC)
 Introduction to Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Basics Electrochemistry Microstructure Effects Stacks Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) CATHODE: (La,Sr)(Mn)O 3 (LSM) LSM-YSZ ELECTROLYTE: ANODE: Y-doped ZrO 2 (YSZ) Ni-YSZ
Introduction to Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Basics Electrochemistry Microstructure Effects Stacks Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) CATHODE: (La,Sr)(Mn)O 3 (LSM) LSM-YSZ ELECTROLYTE: ANODE: Y-doped ZrO 2 (YSZ) Ni-YSZ
DMFC Models and Applications - A Literature Survey, Part I
 Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management Bali, Indonesia, January 7 9, 2014 DMFC Models and Applications - A Literature Survey, Part I S. Patrabansh,
Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management Bali, Indonesia, January 7 9, 2014 DMFC Models and Applications - A Literature Survey, Part I S. Patrabansh,
Facile and Gram-scale Synthesis of Metal-free Catalysts: Toward Realistic Applications for Fuel Cells
 Supplementary Information Facile and Gram-scale Synthesis of Metal-free Catalysts: Toward Realistic Applications for Fuel Cells Ok-Hee Kim 1, Yong-Hun Cho 2, Dong Young Chung 3,4, Minjeong Kim 3,4, Ji
Supplementary Information Facile and Gram-scale Synthesis of Metal-free Catalysts: Toward Realistic Applications for Fuel Cells Ok-Hee Kim 1, Yong-Hun Cho 2, Dong Young Chung 3,4, Minjeong Kim 3,4, Ji
Modeling of Electrochemical Cells: HYD Lecture 04. Overview of transport processes in PEMs
 Modeling of Electrochemical Cells: Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells HYD7007 01 Lecture 04. Overview of transport processes in PEMs Dept. of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Yonsei University Spring,
Modeling of Electrochemical Cells: Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells HYD7007 01 Lecture 04. Overview of transport processes in PEMs Dept. of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering Yonsei University Spring,
8. Draw Lewis structures and determine molecular geometry based on VSEPR Theory
 Chemistry Grade 12 Outcomes 1 Quantum Chemistry and Atomic Structure Unit I 1. Perform calculations on wavelength, frequency and energy. 2. Have an understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum. 3. Relate
Chemistry Grade 12 Outcomes 1 Quantum Chemistry and Atomic Structure Unit I 1. Perform calculations on wavelength, frequency and energy. 2. Have an understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum. 3. Relate
Review A Perspective on Low-Temperature Water Electrolysis Challenges in Alkaline and Acidic Technology
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 13 (2018) 1173 1226, doi: 10.20964/2018.02.26 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Review A Perspective on Low-Temperature Water Electrolysis
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 13 (2018) 1173 1226, doi: 10.20964/2018.02.26 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Review A Perspective on Low-Temperature Water Electrolysis
Q1. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
 Q1. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution? A1. Conductivity of a solution is the conductance of ions present in a unit volume of the solution. On dilution the number of ions per
Q1. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution? A1. Conductivity of a solution is the conductance of ions present in a unit volume of the solution. On dilution the number of ions per
PFSA Aquivion membranes: general features and degradation mechanisms. Luca Merlo*, C. Oldani, M. Apostolo, V. Arcella Solvay Specialty Polymers SPA
 PFSA Aquivion membranes: general features and degradation mechanisms Luca Merlo*, C. Oldani, M. Apostolo, V. Arcella Solvay Specialty Polymers SPA Agenda PFSA ionomers Aquivion general features PFSA degradation
PFSA Aquivion membranes: general features and degradation mechanisms Luca Merlo*, C. Oldani, M. Apostolo, V. Arcella Solvay Specialty Polymers SPA Agenda PFSA ionomers Aquivion general features PFSA degradation
Ugur Pasaogullari, Chao-Yang Wang Electrochemical Engine Center The Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA, 16802
 Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells using Fluent Ugur Pasaogullari, Chao-Yang Wang Electrochemical Engine Center The Pennsylvania State University University Park,
Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells using Fluent Ugur Pasaogullari, Chao-Yang Wang Electrochemical Engine Center The Pennsylvania State University University Park,
Graphene-based Electrodes for Electrochemical Energy Conversion
 Graphene-based Electrodes for Electrochemical Energy Conversion September 23, 2014 AVS North California Chapter Prof. Min Hwan Lee School of Engineering Graphene for electrochemical devices Properties
Graphene-based Electrodes for Electrochemical Energy Conversion September 23, 2014 AVS North California Chapter Prof. Min Hwan Lee School of Engineering Graphene for electrochemical devices Properties
Hydrogen production by electrolysis. Ann Cornell, Department of Chemical Engineering, KTH
 Hydrogen production by electrolysis Ann Cornell, Department of Chemical Engineering, KTH amco@kth.se Sources for hydrogen International Energy Agency. Technology Roadmap Hydrogen and Fuel Cells, 2015
Hydrogen production by electrolysis Ann Cornell, Department of Chemical Engineering, KTH amco@kth.se Sources for hydrogen International Energy Agency. Technology Roadmap Hydrogen and Fuel Cells, 2015
CHEM J-14 June 2014
 CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems
 BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems Catalysis of environmental reactions Dr. Zifei Liu Catalysis and catalysts Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation
BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems Catalysis of environmental reactions Dr. Zifei Liu Catalysis and catalysts Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation
ELECTROCHEMISTRY OXIDATION-REDUCTION
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
Chemistry: The Central Science. Chapter 20: Electrochemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 20: Electrochemistry Redox reaction power batteries Electrochemistry is the study of the relationships between electricity and chemical reactions o It includes the
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 20: Electrochemistry Redox reaction power batteries Electrochemistry is the study of the relationships between electricity and chemical reactions o It includes the
Nguyen Viet Long, Cao Minh Thi, Masayuki Nogami and Michitaka Ohtaki
 Chapter 11 Novel Pt and Pd Based Core-Shell Catalysts with Critical New Issues of Heat Treatment, Stability and Durability for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells and Direct Methanol Fuel Cells Nguyen
Chapter 11 Novel Pt and Pd Based Core-Shell Catalysts with Critical New Issues of Heat Treatment, Stability and Durability for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells and Direct Methanol Fuel Cells Nguyen
Figure 1. Contact mode AFM (A) and the corresponding scanning Kelvin probe image (B) of Pt-TiN surface.
 Synopsis Synopsis of the thesis entitled Titanium Nitride-ased Electrode Materials for Oxidation of Small Molecules: pplications in Electrochemical Energy Systems submitted by Muhammed Musthafa O. T under
Synopsis Synopsis of the thesis entitled Titanium Nitride-ased Electrode Materials for Oxidation of Small Molecules: pplications in Electrochemical Energy Systems submitted by Muhammed Musthafa O. T under
Topic: APPLIED ELECTROCHEMISTRY. Q.1 What is polarization? Explain the various type of polarization.
 Topic: APPLIED ELECTROCHEMISTRY T.Y.B.Sc Q.1 What is polarization? Explain the various type of polarization. Ans. The phenomenon of reverse e.m.f. brought about by the presence of product of electrolysis
Topic: APPLIED ELECTROCHEMISTRY T.Y.B.Sc Q.1 What is polarization? Explain the various type of polarization. Ans. The phenomenon of reverse e.m.f. brought about by the presence of product of electrolysis
Review of temperature distribution in cathode of PEMFC
 Project Report 2008 MVK 160 Heat and Mass Transport May 08, 2008, Lund, Sweden Review of temperature distribution in cathode of PEMFC Munir Ahmed Khan Department of Energy Sciences, Lund Institute of Technology,
Project Report 2008 MVK 160 Heat and Mass Transport May 08, 2008, Lund, Sweden Review of temperature distribution in cathode of PEMFC Munir Ahmed Khan Department of Energy Sciences, Lund Institute of Technology,
N Goalby chemrevise.org
 Redox Equilibria Electrochemical cells This type of cell can be called a Voltaic cell or Galvanic cell. Voltaic cells convert energy from spontaneous, exothermic chemical processes to electrical energy.
Redox Equilibria Electrochemical cells This type of cell can be called a Voltaic cell or Galvanic cell. Voltaic cells convert energy from spontaneous, exothermic chemical processes to electrical energy.
CHEMISTRY - CLUTCH CH.18 - ELECTROCHEMISTRY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Chemists use some important terminology to describe the movement of electrons. In reactions we have the movement of electrons from one reactant
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Chemists use some important terminology to describe the movement of electrons. In reactions we have the movement of electrons from one reactant
Appendix A Electric Vehicle PEM Fuel Cell Stack Parameters
 Appendix A Electric Vehicle PEM Fuel Cell Stack Parameters A.1 Return Manifold Polynomial Fitting Table A.1 Return manifold polynomial fitting Parameter Value Return manifold parameter p 0 0.001248 kg/s
Appendix A Electric Vehicle PEM Fuel Cell Stack Parameters A.1 Return Manifold Polynomial Fitting Table A.1 Return manifold polynomial fitting Parameter Value Return manifold parameter p 0 0.001248 kg/s
Proportions to find moles Correctly organized Example. Problem
 Reactions continued And chemical review!! Steps to find grams in chemical Balance the equation to get molar ratios Find molar mass of the substances in question Find moles of the one given in grams Set
Reactions continued And chemical review!! Steps to find grams in chemical Balance the equation to get molar ratios Find molar mass of the substances in question Find moles of the one given in grams Set
ADVANCED OXYGEN REDUCTION REACTION CATALYSTS/MATERIAL FOR DIRECT METHANOL FUEL CELL (DMFC) APPLICATION. Rapelang Gloria Motsoeneng
 ADVANCED OXYGEN REDUCTION REACTION CATALYSTS/MATERIAL FOR DIRECT METHANOL FUEL CELL (DMFC) APPLICATION BY Rapelang Gloria Motsoeneng Student Number: 2766546 A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements
ADVANCED OXYGEN REDUCTION REACTION CATALYSTS/MATERIAL FOR DIRECT METHANOL FUEL CELL (DMFC) APPLICATION BY Rapelang Gloria Motsoeneng Student Number: 2766546 A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements
POLITECNICO DI MILANO
 POLITECNICO DI MILANO Facoltà di Ingegneria Industriale POLITECNICO DI MILANO Department Corso di Laurea of Energy in Doctoral Ingegneria Program in Energy and Nuclear Science and Technology DMFC MODELING:
POLITECNICO DI MILANO Facoltà di Ingegneria Industriale POLITECNICO DI MILANO Department Corso di Laurea of Energy in Doctoral Ingegneria Program in Energy and Nuclear Science and Technology DMFC MODELING:
Master of Applied Science
 A Three-Dimensional Computational Model of PEM Fuel Cell with Serpentine Gas Channels by Phong Thanh Nguyen B.E.Sc., University of Western Ontario, 2001 A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the
A Three-Dimensional Computational Model of PEM Fuel Cell with Serpentine Gas Channels by Phong Thanh Nguyen B.E.Sc., University of Western Ontario, 2001 A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the
Development and Application of a Chemical Degradation Model for Reinforced Electrolyte Membranes in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells
 Development and Application of a Chemical Degradation Model for Reinforced Electrolyte Membranes in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells by Sumit Kundu A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo
Development and Application of a Chemical Degradation Model for Reinforced Electrolyte Membranes in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells by Sumit Kundu A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS ON 36cm 2 PEM FUEL CELL FOR PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT
 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS ON 36cm 2 PEM FUEL CELL FOR PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT Lakshminarayanan V 1, Karthikeyan P 2, D. S. Kiran Kumar 1 and SMK Dhilip Kumar 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, KGiSL Institute
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS ON 36cm 2 PEM FUEL CELL FOR PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT Lakshminarayanan V 1, Karthikeyan P 2, D. S. Kiran Kumar 1 and SMK Dhilip Kumar 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, KGiSL Institute
Rate of reaction refers to the amount of reactant used up or product created, per unit time. We can therefore define the rate of a reaction as:
 Rates of Reaction Rate of reaction refers to the amount of reactant used up or product created, per unit time. We can therefore define the rate of a reaction as: Rate = change in concentration units: mol
Rates of Reaction Rate of reaction refers to the amount of reactant used up or product created, per unit time. We can therefore define the rate of a reaction as: Rate = change in concentration units: mol
ELECTROCHEMISTRY I. The science concerned with the study of electron transfer across phase boundary
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY I The science concerned with the study of electron transfer across phase boundary Electrode: Is a conducting material immersed in a media. Electrode potential: Is the potential difference
ELECTROCHEMISTRY I The science concerned with the study of electron transfer across phase boundary Electrode: Is a conducting material immersed in a media. Electrode potential: Is the potential difference
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Chapter 14
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Chapter 14 Basic Concepts: Overview of Electrochemical Process at Constant T, P (14-1) ΔG = ΔG o + RT ln Q = w elec (maximum) = qe = ItE (exp) (E intensive parameter, q extensive) = nfe
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Chapter 14 Basic Concepts: Overview of Electrochemical Process at Constant T, P (14-1) ΔG = ΔG o + RT ln Q = w elec (maximum) = qe = ItE (exp) (E intensive parameter, q extensive) = nfe
Chapter 7 Electrochemistry
 Chapter 7 Electrochemistry Outside class reading Levine: pp. 417 14.4 Galvanic cells: pp. 423 14.5 types of reversible electrodes 7.6.1 Basic concepts of electrochemical apparatus (1) Electrochemical apparatus
Chapter 7 Electrochemistry Outside class reading Levine: pp. 417 14.4 Galvanic cells: pp. 423 14.5 types of reversible electrodes 7.6.1 Basic concepts of electrochemical apparatus (1) Electrochemical apparatus
Introduction to electrochemistry
 Introduction to electrochemistry Oxidation reduction reactions involve energy changes. Because these reactions involve electronic transfer, the net release or net absorption of energy can occur in the
Introduction to electrochemistry Oxidation reduction reactions involve energy changes. Because these reactions involve electronic transfer, the net release or net absorption of energy can occur in the
CARBON. Electrochemical ond Physicochemicol Properties KIM KINOSHITA. Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Berkeley, California
 CARBON Electrochemical ond Physicochemicol Properties KIM KINOSHITA Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Berkeley, California A Wiley-Interscience Publicotion JOHN WILEY & SONS New York / Chichester / Brisbane
CARBON Electrochemical ond Physicochemicol Properties KIM KINOSHITA Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Berkeley, California A Wiley-Interscience Publicotion JOHN WILEY & SONS New York / Chichester / Brisbane
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Chapter 18 problems (with solutions)
 Chapter 18 problems (with solutions) 1) Assign oxidation numbers for the following species (for review see section 9.4) a) H2SO3 H = +1 S = +4 O = -2 b) Ca(ClO3)2 Ca = +2 Cl = +5 O = -2 c) C2H4 C = -2
Chapter 18 problems (with solutions) 1) Assign oxidation numbers for the following species (for review see section 9.4) a) H2SO3 H = +1 S = +4 O = -2 b) Ca(ClO3)2 Ca = +2 Cl = +5 O = -2 c) C2H4 C = -2
AQA Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Chemical Kinetics. What quantities do we study regarding chemical reactions? 15 Chemical Kinetics
 Chemical Kinetics Chemical kinetics: the study of reaction rate, a quantity conditions affecting it, the molecular events during a chemical reaction (mechanism), and presence of other components (catalysis).
Chemical Kinetics Chemical kinetics: the study of reaction rate, a quantity conditions affecting it, the molecular events during a chemical reaction (mechanism), and presence of other components (catalysis).
Synthesis of Highly Ion-Conductive Polymers for Fuel Cells (for H + and OH )
 Synthesis of Highly Ion-Conductive Polymers for Fuel Cells (for H + and OH ) Chulsung Bae Department of Chemistry & Chemical Biology Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Collaborators: Michael A. Hickner (Penn
Synthesis of Highly Ion-Conductive Polymers for Fuel Cells (for H + and OH ) Chulsung Bae Department of Chemistry & Chemical Biology Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Collaborators: Michael A. Hickner (Penn
Electrochemical System
 Electrochemical System Topic Outcomes Week Topic Topic Outcomes 8-10 Electrochemical systems It is expected that students are able to: Electrochemical system and its thermodynamics Chemical reactions in
Electrochemical System Topic Outcomes Week Topic Topic Outcomes 8-10 Electrochemical systems It is expected that students are able to: Electrochemical system and its thermodynamics Chemical reactions in
Principles and Applications of Electrochemistry
 Principles and Applications of Electrochemistry Fourth edition D. R. CROW Professor of Electrochemistry and Dean of Research University of Wolverhampton BLACKIE ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman
Principles and Applications of Electrochemistry Fourth edition D. R. CROW Professor of Electrochemistry and Dean of Research University of Wolverhampton BLACKIE ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman
Basic Concepts in Electrochemistry
 Basic Concepts in Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemical Cell Electrons Current + - Voltage Source ANODE Current CATHODE 2 Fuel Cell Electrons (2 e) Current - + Electrical Load ANODE Current CATHODE H 2 2H
Basic Concepts in Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemical Cell Electrons Current + - Voltage Source ANODE Current CATHODE 2 Fuel Cell Electrons (2 e) Current - + Electrical Load ANODE Current CATHODE H 2 2H
Graphene-based Air Electrodes for Solid Oxide Electrochemical Cells
 Graphene-based Air Electrodes for Solid Oxide Electrochemical Cells April 18, 2014 Prof. Min Hwan Lee School of Engineering Graphene for electrochemical devices Properties Applications Electron conducting
Graphene-based Air Electrodes for Solid Oxide Electrochemical Cells April 18, 2014 Prof. Min Hwan Lee School of Engineering Graphene for electrochemical devices Properties Applications Electron conducting
Estimation of approximate activation energy loss and mass transfer coefficient from a polarization curve of a polymer electrolyte fuel cell
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 29(9), 1158-1162 (2012) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-012-0006-3 INVITED REVIEW PAPER Estimation of approximate activation energy loss and mass transfer coefficient from a polarization curve
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 29(9), 1158-1162 (2012) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-012-0006-3 INVITED REVIEW PAPER Estimation of approximate activation energy loss and mass transfer coefficient from a polarization curve
CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL
 *P15* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2008 CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in all These must include at least two questions from Section A All questions carry
*P15* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2008 CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in all These must include at least two questions from Section A All questions carry
High-Performance Blend Membranes Composed of An Amphoteric Copolymer Containing Supramolecular Nanosieves for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells
 Electonic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chemical Communications High-Performance Blend Membranes Composed of An Amphoteric Copolymer Containing Supramolecular Nanosieves for Direct Methanol Fuel
Electonic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chemical Communications High-Performance Blend Membranes Composed of An Amphoteric Copolymer Containing Supramolecular Nanosieves for Direct Methanol Fuel
Electrochemical reaction
 Electrochemical reaction electrochemistry electrochem. reaction mechanism electrode potential Faradays law electrode reaction kinetics 1 Electrochemistry in industry Chlor-Alkali galvano industry production
Electrochemical reaction electrochemistry electrochem. reaction mechanism electrode potential Faradays law electrode reaction kinetics 1 Electrochemistry in industry Chlor-Alkali galvano industry production
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Cells
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Electrochemistry. Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts
 Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts What do I need to know about electrochemistry? Electrochemistry Learning Outcomes: Candidates should be able to: a) Describe
Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts What do I need to know about electrochemistry? Electrochemistry Learning Outcomes: Candidates should be able to: a) Describe
FUEL CELLS in energy technology (4)
 Fuel Cells 1 FUEL CELLS in energy technology (4) Werner Schindler Department of Physics Nonequilibrium Chemical Physics TU Munich summer term 213 Fuel Cells 2 Nernst equation and its application to fuel
Fuel Cells 1 FUEL CELLS in energy technology (4) Werner Schindler Department of Physics Nonequilibrium Chemical Physics TU Munich summer term 213 Fuel Cells 2 Nernst equation and its application to fuel
Effect of Phosphotungstic Acid in Electrodes on PEMFC Performance at Elevated. Temperature and Low Humidity. A thesis presented to.
 1 Effect of Phosphotungstic Acid in Electrodes on PEMFC Performance at Elevated Temperature and Low Humidity A thesis presented to the faculty of the Russ College of Engineering and Technology of Ohio
1 Effect of Phosphotungstic Acid in Electrodes on PEMFC Performance at Elevated Temperature and Low Humidity A thesis presented to the faculty of the Russ College of Engineering and Technology of Ohio
Combined Science: Trilogy
 Co-teaching GCSE Chemistry and GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy This high level co-teaching guide will help you plan your route through the course. You ll be able to see what common themes and topics span
Co-teaching GCSE Chemistry and GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy This high level co-teaching guide will help you plan your route through the course. You ll be able to see what common themes and topics span
4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes. Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3. C2.1.1a Structure and bonding
 Summary of changes This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our previous GCSE Chemistry (4402) to the new specification (8462). Our new specifications
Summary of changes This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our previous GCSE Chemistry (4402) to the new specification (8462). Our new specifications
Reactions continued. And chemical review!!
 Reactions continued And chemical review!! Steps to find grams in chemical reaction Balance the equation to get molar ratios Find molar mass of the substances in question Find moles of the one given in
Reactions continued And chemical review!! Steps to find grams in chemical reaction Balance the equation to get molar ratios Find molar mass of the substances in question Find moles of the one given in
Analysis of the Catalyst Layer of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells
 33 Research Report Analysis of the Catalyst Layer of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells Takahisa Suzuki Hajime Murata Tatsuya Hatanaka Yu Morimoto Comprehensive techniques for diagnosing the catalyst layer
33 Research Report Analysis of the Catalyst Layer of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells Takahisa Suzuki Hajime Murata Tatsuya Hatanaka Yu Morimoto Comprehensive techniques for diagnosing the catalyst layer
An Introduction to Chemical Kinetics
 An Introduction to Chemical Kinetics Michel Soustelle WWILEY Table of Contents Preface xvii PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMICAL KINETICS 1 Chapter 1. Chemical Reaction and Kinetic Quantities 3 1.1. The
An Introduction to Chemical Kinetics Michel Soustelle WWILEY Table of Contents Preface xvii PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMICAL KINETICS 1 Chapter 1. Chemical Reaction and Kinetic Quantities 3 1.1. The
Modelling fuel cells in start-up and reactant starvation conditions
 Modelling fuel cells in start-up and reactant starvation conditions Brian Wetton Radu Bradean Keith Promislow Jean St Pierre Mathematics Department University of British Columbia www.math.ubc.ca/ wetton
Modelling fuel cells in start-up and reactant starvation conditions Brian Wetton Radu Bradean Keith Promislow Jean St Pierre Mathematics Department University of British Columbia www.math.ubc.ca/ wetton
Electrochemistry. Review oxidation reactions and how to assign oxidation numbers (Ch 4 Chemical Reactions).
 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction: Review oxidation reactions and how to assign oxidation numbers (Ch 4 Chemical Reactions). Half Reactions Method for Balancing Redox Equations: Acidic solutions: 1.
Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction: Review oxidation reactions and how to assign oxidation numbers (Ch 4 Chemical Reactions). Half Reactions Method for Balancing Redox Equations: Acidic solutions: 1.
