Aromatics H H H H H H
|
|
|
- Suzanna Amice Payne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Aromatics
3 Some istory 1825 Michael Faraday isolates a new hydrocarbon from illuminating gas Eilhardt Mitscherlich isolates same substance and determines its empirical formula to be C n n. Compound comes to be called benzene August W. von ofmann isolates benzene from coal tar August Kekulé proposes structure of benzene.
4 Greatest Scientist in istory?? Michael Faraday ( )
5 What in the World is Benzene?? C 6 6 discovered by Michael Faraday in 1825 Synthesized in 1834 from benzoic acid Remarkable chemical stability Unsaturation number is very high but. Does not add Bromine Substitutiuon with Br 2 / FeBr 3 Not oxidized by Permanganate or ozone No reaction with strong Br (aq) No reaction with ydrogen on Pd..??????
6 Addition vs Substitution a Mystery Br + Br 2 Br Addition of Bromine to Cyclohexene + Br 2 FeBr 3 Br + Br Substitution of Bromine for ydrogen in Benzene C Br 2 C 6 5 Br + Br
7 of ydrogenation Name ethylene propene 1-butene cis-2-butene trans-2-butene 2-methyl-2-butene 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene Structural Formula C 2 =C 2 C 3 C=C 2 C 3 C 2 C=C 2 C 3 C=CC 3 C 3 C=CC 3 (C 3 ) 2 C=CC 3 (C 3 ) 2 C=C(C 3 ) 2 (kcal/mol)
8 A quantitative measure of the special stability of benzene
9 Friedrich August Kekulé ( )
10 Friedrich August von Kekule had a dream of whirling snakes, and the structure of benzene. e reported the dream in the following words in 1890, in a speech at a dinner commemorating his discovery that reportedly occurred during a reverie on a London bus. Again the atoms were gamboling before my eyes. This time the smaller groups kept modestly to the background. My mental eye, rendered more acute by repeated vision of this kind, could not distinguish larger structures, tures, of manifold conformation; long rows, sometimes more closely fitted together; all twining and twisting in snakelike motion. But look! What was that? One of the snakes had seized hold of its own n tail, and the form whirled mockingly before my eyes. As if by a flash of lighting I awoke... Let us learn to dream, gentlemen. Arthur Koestler (in "The Act of Creation") called this incident "probably the most important dream in history since Joseph's seven fat and seven lean cows.
11
12 QUESTION: Can you tell me more about this vision to which you have referred? KEKULÉ: Surely! Let me read to you the remarks I am about to make to the assembly today: During my stay in London I resided in Clapham Road...I frequently, however, spent my evenings with my friend ugo Mueller...We talked of many things but most often of our beloved chemistry. One fine summer evening I was returning by the last bus, riding outside as usual, through the deserted streets of the city...i fell into a reverie, and lo, the atoms were gamboling before my eyes. Whenever, hitherto, these diminutive beings had appeared to me, they had always been in motion. Now, however, I saw how, frequently, two smaller atoms united to form a pair: how a larger one embraced the two smaller ones; how still larger ones kept hold of three or even four of the smaller: whilst the whole kept whirling in a giddy dance. I saw how the larger ones formed a chain, dragging the smaller ones after them but only at the ends of the chains...the cry of the conductor: "Clapham Road," awakened me from my dreaming; but I spent a part of the night in putting on paper at least sketches of these dream forms.
13 Contributors to our understanding of the Structure of Benzene
14 Kekulé Formulation of Benzene Note bond lengths
15 Kekulé Formulation of Benzene Later, Kekulé revised his proposal by suggesting a rapid equilibrium between two equivalent structures.
16 Kekulé Formulation of Benzene owever, this proposal suggested isomers of the kind shown were possible. Yet, none were ever found. X X X X
17 All C C C C bond distances = 140 pm 140 pm 140 pm 146 pm 140 pm 140 pm 140 pm 140 pm 134 pm 140 pm is the average between the C C C C single bond distance and the double bond distance in 1,3- butadiene.
18 A Resonance Picture of Bonding in Benzene
19 Kekulé Formulation of Benzene Instead of Kekulé's suggestion of a rapid equilibrium between two structures:
20 Resonance Formulation of Benzene Pauling described the structure of benzene as a resonance hybrid of the two Lewis structures. Electrons are not localized in alternating single and double bonds, but are delocalized over all six ring carbons.
21 Resonance Formulation of Benzene Circle-in in-a-ring notation stands for resonance description of benzene (hybrid of two Kekulé structures)
22 Unusual Stability of Benzene benzene is the best and most familiar example of a substance that possesses "special stability" or "aromaticity" aromaticity" Aromatic molecules have stability that is substantially greater for a molecule than would be expected on the basis of any of the Lewis structures written for it
23 Thermochemical Measures of Stability heat of hydrogenation: compare experimental value with "expected" value for hypothetical "cyclohexatriene" Pt = 208 kj [ kj / kcal ]
24 3 x cyclohexene 231 kj/mol 360 kj/mol 120 kj/mol 208 kj/mol
25 3 x cyclohexene 120 kj/mol "expected" heat of hydrogenation of benzene is 3 x heat of hydrogenation of cyclohexene 360 kj/mol
26 observed heat of hydrogenation is 152 kj/mol less than "expected" benzene is 152 kj/mol more stable than expected 152 kj/mol is the resonance energy of benzene 208 kj/mol?! 3 x cyclohexene 360 kj/mol
27 231 kj/mol hydrogenation of 1,3-cyclohexadiene (2 2 ) gives off more heat than hydrogenation of benzene (3 2 )!!! 208 kj/mol
28 Cyclic conjugation versus noncyclic conjugation 3 2 Pt heat of hydrogenation = 208 kj/mol 3 2 Pt heat of hydrogenation = 337 kj/mol
29 Resonance Energy of Benzene compared to localized 1,3,5-cyclohexatriene 152 kj/mol compared to 1,3,5-hexatriene 129 kj/mol exact value of resonance energy of benzene depends on what it is compared to, but regardless of model, benzene is more stable than expected by a substantial amount
30 Molecular Orbital View of Bonding in Benzene Dr. Anslyn will cover this in detail
31 Molecular Orbital Model of Bonding in Benzene igh electron density above and below plane of ring
32 Another Depiction of Benzene
33 Electron Density Map of Benzene
34 Benzene MOs
35 The Three Bonding π MOs of Benzene
36 Benzene MOs Antibonding orbitals Energy Bonding orbitals 6 p AOs combine to give 6 π MOs 3 MOs are bonding; 3 are antibonding
37 Benzene MOs Antibonding orbitals Energy Bonding orbitals All bonding MOs are filled No electrons in antibonding orbitals
38 The special stability of benzene results from the fact that these three bonding MOs are much lower in energy than the six uncombined 2p atomic orbitals.and the bonding orbitals are full
39 Frost Circles a Great Trick Inscribe a polygon of the same number of sides as the ring to be examined such that one of the vertices is at the bottom of the ring The relative energies of the MOs in the ring are given by where the vertices touch the circle The MOs below the horizontal line through the center of the ring are bonding MOs on the horizontal line are nonbonding MOs above the horizontal line are antibonding MOs
40
41 π-mos of Cyclobutadiene (square planar) Antibonding Cyclo- butadiene Bonding 4 π electrons; bonding orbital is filled; other 2 π electrons singly occupy two nonbonding orbitals
42 Structure of Cyclobutadiene structure of a stabilized derivative is characterized by alternating short bonds and long bonds (C 3 ) 3 C C(C 3 ) 3 (C 3 ) 3 C 151 pm 138 pm CO 2 C 3
43 π-mos of Cyclooctatetraene (square planar) Antibonding Cyclo- octatetraene Bonding 8 p orbitals give 8 π orbitals 3 orbitals are bonding, 3 are antibonding,, and 2 are nonbonding
44 π-mos of Cyclooctatetraene (square planar) Antibonding Cyclo- octatetraene Bonding 8 π electrons; 3 bonding orbitals are filled; 2 nonbonding orbitals are each half-filled filled
45 Structure of Cyclooctatetraene cyclooctatetraene is not planar has alternating long (146 pm) and short (133 pm) bonds
46 eats of ydrogenation to give cyclohexane (kj/mol) heat of hydrogenation of benzene is 152 kj/mol less than 3 times heat of hydrogenation of cyclohexene
47 eats of ydrogenation to give cyclooctane (kj/mol) heat of hydrogenation of cyclooctatetraene is more than 4 times the heat of hydrogenation of cyclooctene.no special stability here!
48 Requirements for Aromaticity cyclic conjugation is necessary, but not sufficient not aromatic aromatic not aromatic
49 Conclusion there must be some factor in addition to cyclic conjugation that determines whether a molecule is aromatic or not
50 ückel's Rule the additional factor that influences aromaticity is the number of π electrons
51 among planar, monocyclic, completely conjugated polyenes,, only those with 4n π electrons possess special stability (are aromatic) n 4n benzene! ückel's Rule
52 ückel's Rule for Aromaticity To be Aromatic a compound must : 1. be Cyclic 2. have one P orbital on each atom in the ring 3. be planar or nearly so to give orbital overlap 4. have a closed loop of 4n+2 pi electrons in the cyclic arrangement of p orbitals
53 ückel's Rule defines a condition for cyclic molecules in which the bonding molecular orbitals are filled and there are no electrons in non-bonding or antibonding orbitals.roughly analogous to the rare gas condition fpr atomic orbitals
54 π-mos of Benzene Antibonding Benzene 6 π electrons fill all of the bonding orbitals all π antibonding orbitals are empty Bonding
55 π-mos of Cyclobutadiene (square planar) Antibonding Cyclo- butadiene Bonding 4 π electrons; bonding orbital is filled; other 2 π electrons singly occupy two nonbonding orbitals
56 π-mos of Cyclooctatetraene (square planar) Antibonding Cyclo- octatetraene Bonding 8 π electrons; 3 bonding orbitals are filled; 2 nonbonding orbitals are each half-filled filled
57 π-electron Requirement for Aromaticity 4 π electrons 6 π electrons 8 π electrons not aromatic aromatic not aromatic
58 Completely Conjugated Polyenes 6 π electrons; completely conjugated 6 π electrons; not completely conjugated aromatic not aromatic
59 Annulenes Annulenes are planar, monocyclic, completely conjugated polyenes.. That is, they are the kind of hydrocarbons treated by ückel's rule.
60 [10]Annulene predicted to be aromatic by ückel's rule, but too much angle strain when planar and all double bonds are cis 10-sided regular polygon has angles of 144
61 [10]Annulene strain between these two hydrogens incorporating two trans double bonds into the ring relieves angle strain but introduces another kind of strain into the structure and causes the ring to be distorted from planarity
62 ow about [14]Annulene?? 14 π electrons satisfies ückel's rule There is some strain between hydrogens inside the ring
63 [16]Annulene?? 16 π electrons does not satisfy ückel's rule alternating short (134 pm) and long (146 pm) bonds not aromatic
64 [18]Annulene The protons resonate at -3.0 and at 9.3δ!!! 18 π electrons satisfies ückel's rule resonance energy = 418 kj/mol bond distances range between pm
65 What about??
Lecture 8 MOs and Benzene H H H H
 Lecture 8 MOs and Benzene b February 11, 2016 First Midterm Exam When: Wednesday, 2/17 When: 7-9 PM (please do not be late) Where: WEL 3.502 enter from Inner Campus Drive What: Covers material through
Lecture 8 MOs and Benzene b February 11, 2016 First Midterm Exam When: Wednesday, 2/17 When: 7-9 PM (please do not be late) Where: WEL 3.502 enter from Inner Campus Drive What: Covers material through
Happy Valentines Day
 Lecture 8 MOs and Benzene appy Valentines Day February 14, 2019 First Midterm Exam When: Wednesday, 2/20 When: 7-9 PM (please do not be late) Where: Painter 3.02!!! What: Covers material through Thursday
Lecture 8 MOs and Benzene appy Valentines Day February 14, 2019 First Midterm Exam When: Wednesday, 2/20 When: 7-9 PM (please do not be late) Where: Painter 3.02!!! What: Covers material through Thursday
Lecture 9. Chemistry! Chemistry 328N. February 20, 2018
 Lecture 9 Chemistry! February 20, 2018 Some istory Michael Faraday 1791-1867 British physicist and chemist, best known for his discoveries of electromagnetic induction and of the laws of electrolysis.
Lecture 9 Chemistry! February 20, 2018 Some istory Michael Faraday 1791-1867 British physicist and chemist, best known for his discoveries of electromagnetic induction and of the laws of electrolysis.
12/27/2010. Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds
 Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives Benzene is the parent name for some monosubstituted benzenes; the substituent name is added as a prefix Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds For other monosubstituted benzenes,
Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives Benzene is the parent name for some monosubstituted benzenes; the substituent name is added as a prefix Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds For other monosubstituted benzenes,
Frost Circles a Great Trick
 Aromatics Frost Circles a Great Trick Inscribe a polygon of the same number of sides as the ring to be examined such that one of the vertices is at the bottom of the ring The relative energies of the MOs
Aromatics Frost Circles a Great Trick Inscribe a polygon of the same number of sides as the ring to be examined such that one of the vertices is at the bottom of the ring The relative energies of the MOs
Chapter 16. Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
Benzene. Named benzene by Eilhardt Mitscherlich in < Molecular formula: C 6 H 6. < Representative of the aromatic hydrocarbon family:
 Benzene < Discovered in 1825 by Michael Faraday: e called it bicarburet of hydrogen. Named benzene by Eilhardt Mitscherlich in 1833. < Molecular formula: C 6 6 < Representative of the aromatic hydrocarbon
Benzene < Discovered in 1825 by Michael Faraday: e called it bicarburet of hydrogen. Named benzene by Eilhardt Mitscherlich in 1833. < Molecular formula: C 6 6 < Representative of the aromatic hydrocarbon
Benzene a remarkable compound. Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds. Some proposed structures for C 6 H 6. Dimethyl substituted benzenes are called xylenes
 Benzene a remarkable compound Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds Discovered by Faraday 1825 Formula C 6 H 6 Highly unsaturated, but remarkably stable Whole new class of benzene derivatives called aromatic compounds
Benzene a remarkable compound Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds Discovered by Faraday 1825 Formula C 6 H 6 Highly unsaturated, but remarkably stable Whole new class of benzene derivatives called aromatic compounds
12.1 AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 12 Arenes and Aromaticity estradiol 12.1 AROMATIC COMPOUNDS O O O O C 3 C 3 O O safrole (oil of sassafras) O methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen) O vanillin (vanilla) C 3 N C 3 C 3 CC 2 ibuprofen C C
12 Arenes and Aromaticity estradiol 12.1 AROMATIC COMPOUNDS O O O O C 3 C 3 O O safrole (oil of sassafras) O methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen) O vanillin (vanilla) C 3 N C 3 C 3 CC 2 ibuprofen C C
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURES Dr Ali El-Agamey. Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURES 11-12 Dr Ali El-Agamey Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Amines 2010, Prentice Hall Reactions N,N-Disubstituted amides 2 o amine
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURES 11-12 Dr Ali El-Agamey Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Amines 2010, Prentice Hall Reactions N,N-Disubstituted amides 2 o amine
Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds. Discovery of Benzene
 Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C: ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C: ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
Organic Chemistry, 7 L. G. Wade, Jr. 2010, Prentice Hall
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized
Aromatic Compounds I
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 1 Aromatic Compounds I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 16 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 1 Aromatic Compounds I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 16 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
Lecture 24 Organic Chemistry 1
 CEM 232 Organic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 24 Organic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop April 6, 2010 1 Which shorthand orbital diagram best represents the LUMO of a dienophile in a Diels-Alder
CEM 232 Organic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 24 Organic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop April 6, 2010 1 Which shorthand orbital diagram best represents the LUMO of a dienophile in a Diels-Alder
Introduction to Aromaticity
 Introduction to Aromaticity Historical Timeline: 1 Spotlight on Benzene: 2 Early 19 th century chemists derive benzene formula (C 6 H 6 ) and molecular mass (78). Carbon to hydrogen ratio of 1:1 suggests
Introduction to Aromaticity Historical Timeline: 1 Spotlight on Benzene: 2 Early 19 th century chemists derive benzene formula (C 6 H 6 ) and molecular mass (78). Carbon to hydrogen ratio of 1:1 suggests
Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds. Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde
 Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde Sources of Benzene Benzene, C 6 H 6, is the parent hydrocarbon of the especially stable compounds known
Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde Sources of Benzene Benzene, C 6 H 6, is the parent hydrocarbon of the especially stable compounds known
1.3 Reactions of Hydrocarbons
 1.3 Reactions of ydrocarbons All hydrocarbons readily burn in air to give carbon dioxide and water, with the release of large amounts of energy (Figure 1); this chemical reaction accounts for the extensive
1.3 Reactions of ydrocarbons All hydrocarbons readily burn in air to give carbon dioxide and water, with the release of large amounts of energy (Figure 1); this chemical reaction accounts for the extensive
3) The delocalized π system in benzene is formed by a cyclic overlap of 6 orbitals. A) s B) p C) sp D) sp2 E) sp3
 Chapter 8 Questions 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? A) All of the carbon atoms are sp hybridized. B) It has delocalized electrons. C) The carbon-carbon bond lengths are
Chapter 8 Questions 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? A) All of the carbon atoms are sp hybridized. B) It has delocalized electrons. C) The carbon-carbon bond lengths are
Benzene and aromaticity
 aromaticity The word "benzene" derives historically from "gum benzoin", sometimes called "benjamin" (i.e., benzoin resin), an aromatic resin known to European pharmacists and perfumers since the 15th century
aromaticity The word "benzene" derives historically from "gum benzoin", sometimes called "benjamin" (i.e., benzoin resin), an aromatic resin known to European pharmacists and perfumers since the 15th century
Organic Chemistry. Second Edition. Chapter 18 Aromatic Compounds. David Klein. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e
 Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 18 Aromatic Compounds Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 18.1 Introduction to Aromatic Compounds
Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 18 Aromatic Compounds Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 18.1 Introduction to Aromatic Compounds
Lecture 10. More Aromatics. February 15, Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 10 More Aromatics February 15, 2018 ückel's Rule for Aromaticity To be Aromatic a compound must : 1. be Cyclic 2. have one P orbital on each atom in the ring 3. be planar or nearly so to give orbital
Lecture 10 More Aromatics February 15, 2018 ückel's Rule for Aromaticity To be Aromatic a compound must : 1. be Cyclic 2. have one P orbital on each atom in the ring 3. be planar or nearly so to give orbital
SiO 2 CO 2 MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 7/20/2009. Two forms of carbon; graphite and diamond. Quartz grows in beautiful, regular crystals
 MOLECULAR STRUCTURE A computer representation of K 3 C 60, a superconducting substance formed by reacting potassium with buckminster fullerine (C 60 ) Source: Photo Researchers, Inc. Copyright oughton
MOLECULAR STRUCTURE A computer representation of K 3 C 60, a superconducting substance formed by reacting potassium with buckminster fullerine (C 60 ) Source: Photo Researchers, Inc. Copyright oughton
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Exam. Name. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? 1) A) All of the carbon
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? 1) A) All of the carbon
CHEM 263 Notes Oct 1, Beta-carotene (depicted below) is responsible for the orange-red colour in carrots.
 EM 263 otes ct 1, 2013 onjugated Dienes and olour ontinued Beta-carotene (depicted below) is responsible for the orange-red colour in carrots. In the below example, astaxanthin, a blue-green pigment in
EM 263 otes ct 1, 2013 onjugated Dienes and olour ontinued Beta-carotene (depicted below) is responsible for the orange-red colour in carrots. In the below example, astaxanthin, a blue-green pigment in
Chemistry 263 Quiz 1/Exam 1 Practice Spring 2018
 Chemistry 263 Quiz 1/Exam 1 Practice Spring 2018 The following practice contains 36 questions covering chapters 14, 15, and 16 in Loudon and Parise s rganic Chemistry, 6 th edition. Quiz 1 will contain
Chemistry 263 Quiz 1/Exam 1 Practice Spring 2018 The following practice contains 36 questions covering chapters 14, 15, and 16 in Loudon and Parise s rganic Chemistry, 6 th edition. Quiz 1 will contain
Benzene and Aromaticity
 Benzene and Aromaticity Why this Chapter? Reactivity of substituted aromatic compounds is tied to their structure Aromatic compounds provide a sensitive probe for studying relationship between structure
Benzene and Aromaticity Why this Chapter? Reactivity of substituted aromatic compounds is tied to their structure Aromatic compounds provide a sensitive probe for studying relationship between structure
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
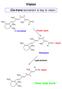 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes
 Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Aromatic Compounds. A number of these compounds had a distinct odor. Hence these compounds were called aromatic
 Aromatic Compounds Early in the history of organic chemistry (late 18 th, early 19 th century) chemists discovered a class of compounds which were unusually stable A number of these compounds had a distinct
Aromatic Compounds Early in the history of organic chemistry (late 18 th, early 19 th century) chemists discovered a class of compounds which were unusually stable A number of these compounds had a distinct
CHEM Aromatic Chemistry. LECTURE 1 - Aromaticity
 1 CHEM40003 Aromatic Chemistry LECTURE 1 - Aromaticity Alan C. Spivey a.c.spivey@imperial.ac.uk May 2018 2 Format and scope of presentation Aromaticity: Historical perspective (Kekulé) Characteristics,
1 CHEM40003 Aromatic Chemistry LECTURE 1 - Aromaticity Alan C. Spivey a.c.spivey@imperial.ac.uk May 2018 2 Format and scope of presentation Aromaticity: Historical perspective (Kekulé) Characteristics,
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH AROMATICITY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: AROMATICTY INTRODUCTION Aromatic compounds display an unusual stability for their high level of electron density. Their high level of unsaturation should make them extremely
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: AROMATICTY INTRODUCTION Aromatic compounds display an unusual stability for their high level of electron density. Their high level of unsaturation should make them extremely
Chemistry 3351: Organic Chemistry Thursday: Sept. 7:00pm 9:00/1 st Exam. Name: (please print)
 Chemistry 3351: Organic Chemistry Thursday: Sept. 23 @ 7:00pm 9:00/1 st Exam 1 Name: (please print) Page Possible Points Score 2 9 3 9 4 8 5 10 6 10 7 4 8 9 9 10 10 10 11 10 12 10 13 10 TOTAL 109 2 1.
Chemistry 3351: Organic Chemistry Thursday: Sept. 23 @ 7:00pm 9:00/1 st Exam 1 Name: (please print) Page Possible Points Score 2 9 3 9 4 8 5 10 6 10 7 4 8 9 9 10 10 10 11 10 12 10 13 10 TOTAL 109 2 1.
Chapter 18: Aromatic Compounds
 hapter 18: Aromatic ompounds [Sections: 18.1, 18.3-18.5, 18.8] The Structure of Benzene skeletal condensed 1800's sausage 3 2 2 3 3 3 3 Friedrich August Kekule 1829-1896 Kekule's Dream 6 6 Kekule wakes
hapter 18: Aromatic ompounds [Sections: 18.1, 18.3-18.5, 18.8] The Structure of Benzene skeletal condensed 1800's sausage 3 2 2 3 3 3 3 Friedrich August Kekule 1829-1896 Kekule's Dream 6 6 Kekule wakes
Chem 263 Sept 22, Beta-carotene (depicted below) is the orange-red colour in carrots. β-carotene
 hem 263 Sept 22, 2009 onjugated Dienes and olour ontinued Beta-carotene (depicted below) is the orange-red colour in carrots. Xanthophylls β-carotene Xanthophylls are oxygenated carotene molecules. Zeaxanthin,
hem 263 Sept 22, 2009 onjugated Dienes and olour ontinued Beta-carotene (depicted below) is the orange-red colour in carrots. Xanthophylls β-carotene Xanthophylls are oxygenated carotene molecules. Zeaxanthin,
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems 13.1 Introduction Allyl radical C 2 C C 2 C C C Allyl cation C 2 C C 2 C C C 1,3-Butadiene C 2 C C C 2 C C C C Molecules with delocalized π bonds are called conjugated unsaturated
Conjugated Unsaturated Systems 13.1 Introduction Allyl radical C 2 C C 2 C C C Allyl cation C 2 C C 2 C C C 1,3-Butadiene C 2 C C C 2 C C C C Molecules with delocalized π bonds are called conjugated unsaturated
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes
 Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy
 Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY
 4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY During the early 1800's, a group of compounds of natural origin became collectively known as aromatic compounds. As several of these compounds
4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY During the early 1800's, a group of compounds of natural origin became collectively known as aromatic compounds. As several of these compounds
The Hückel Approximation
 The ückel Approximation 1 In this exercise you will use a program called ückel to look at the π molecular orbitals in conjugated molecules. The program calculates the energies and shapes of π (pi) molecular
The ückel Approximation 1 In this exercise you will use a program called ückel to look at the π molecular orbitals in conjugated molecules. The program calculates the energies and shapes of π (pi) molecular
240 Chem. Aromatic Compounds. Chapter 6
 240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Aromatic Substitution Chemistry (Part of Chapter 2 and Chapter 11)
 Aromatic Substitution hemistry (Part of hapter 2 and hapter 11) Aliphatic ompounds: Aromatic ompounds: pentane 2-pentene 2-pentyne Aromatic compounds have closed loops of electrons that give rise to an
Aromatic Substitution hemistry (Part of hapter 2 and hapter 11) Aliphatic ompounds: Aromatic ompounds: pentane 2-pentene 2-pentyne Aromatic compounds have closed loops of electrons that give rise to an
The Hückel Approximation Consider a conjugated molecule i.e. a molecule with alternating double and single bonds, as shown in Figure 1.
 The Hückel Approximation In this exercise you will use a program called Hückel to look at the p molecular orbitals in conjugated molecules. The program calculates the energies and shapes of p (pi) molecular
The Hückel Approximation In this exercise you will use a program called Hückel to look at the p molecular orbitals in conjugated molecules. The program calculates the energies and shapes of p (pi) molecular
16.4 Cyclobutadiene. .. H c)
 16.4 CYCLOBUTADIEE 649 arranged about zero energy, it is necessary for one degenerate pair, 4 nb and 5 nb, to be located at zero energy. MOs at zero energy are termed nonbonding.) If the total number of
16.4 CYCLOBUTADIEE 649 arranged about zero energy, it is necessary for one degenerate pair, 4 nb and 5 nb, to be located at zero energy. MOs at zero energy are termed nonbonding.) If the total number of
followed by H 2, Ni 2 B (P-2)
 Chemistry 263 omework 1 Part 2 Spring 2018 Out: 04/04/18 Due: 04/13/18 1 Value: A very generous 9 points 2 All questions are valued at ½ point per question unless otherwise noted. Name: KEY 1. Which of
Chemistry 263 omework 1 Part 2 Spring 2018 Out: 04/04/18 Due: 04/13/18 1 Value: A very generous 9 points 2 All questions are valued at ½ point per question unless otherwise noted. Name: KEY 1. Which of
Homework for Chapter 17 Chem 2320
 Homework for Chapter 17 Chem 2320 I. Cumulated, isolated, and conjugated dienes Name 1. Draw structures which fit the following descriptions. Use correct geometry! a conjugated diene with the formula C
Homework for Chapter 17 Chem 2320 I. Cumulated, isolated, and conjugated dienes Name 1. Draw structures which fit the following descriptions. Use correct geometry! a conjugated diene with the formula C
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories. Lecture Presentation. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Chapter 27 Pericyclic Reactions
 Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 27 Pericyclic Reactions Solutions to In-Text Problems 27.1 (b) This is a sigmatropic reaction; two electrons are
Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 27 Pericyclic Reactions Solutions to In-Text Problems 27.1 (b) This is a sigmatropic reaction; two electrons are
Carbon Compounds. Electronegativity. Chemical Bonding Part 1c. Bond Polarity. Bond Polarity
 Electronegativity Carbon Compounds Electronegativity is a relative measure on the pull of electrons by an atom in a bond. Most bonds fall somewhere in between and these bonds are considered polar. Chemical
Electronegativity Carbon Compounds Electronegativity is a relative measure on the pull of electrons by an atom in a bond. Most bonds fall somewhere in between and these bonds are considered polar. Chemical
18.1 Intro to Aromatic Compounds
 18.1 Intro to Aromatic Compounds AROMATIC compounds or ARENES include benzene and benzene derivatives. Aromatic compounds are quite common. Many aromatic compounds were originally isolated from fragrant
18.1 Intro to Aromatic Compounds AROMATIC compounds or ARENES include benzene and benzene derivatives. Aromatic compounds are quite common. Many aromatic compounds were originally isolated from fragrant
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model.
 Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model. Determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar based
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model. Determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar based
ADDITION OF HYDROGEN HALIDES TO CONJUGATED DIENES A. 1,2- and 1,4-Additions 700 CHAPTER 15 DIENES, RESONANCE, AND AROMATICITY
 700 CAPTER 15 DIENES, RESONANCE, AND AROMATICITY 15.18 Give the structures of the starting materials that would yield each of the compounds below in Diels Alder reactions. Pay careful attention to stereochemistry,
700 CAPTER 15 DIENES, RESONANCE, AND AROMATICITY 15.18 Give the structures of the starting materials that would yield each of the compounds below in Diels Alder reactions. Pay careful attention to stereochemistry,
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA
 CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
Chem101 General Chemistry. Lecture 11 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 hem101 General hemistry Lecture 11 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated ydrocarbons ontain one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. University of Wisconsin-Eau laire hem101 - Lecture 11 2 Unsaturated
hem101 General hemistry Lecture 11 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated ydrocarbons ontain one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. University of Wisconsin-Eau laire hem101 - Lecture 11 2 Unsaturated
Chemistry Lecture Notes
 Molecular orbital theory Valence bond theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding. Useful for predicting shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations
Molecular orbital theory Valence bond theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding. Useful for predicting shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations
Columbia University 92CORG14.DOC CHEM S3443D Summer 1992 Professor Grace B. Borowitz Exam No. 4 July 2, 1992
 olumbia University 92RG14.D EM S3443D Summer 1992 Professor Grace B. Borowitz Exam No. 4 July 2, 1992 Name: Grade: Please use a non-red pen. Answer questions in the provided space. If you write any answers
olumbia University 92RG14.D EM S3443D Summer 1992 Professor Grace B. Borowitz Exam No. 4 July 2, 1992 Name: Grade: Please use a non-red pen. Answer questions in the provided space. If you write any answers
Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity
 Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity Solutions to In-Text Problems 15.2 The delocalization energy is the energy
Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity Solutions to In-Text Problems 15.2 The delocalization energy is the energy
Benzene and its Isomers
 Gopalpur Nagendrappa Benzene and its Isomers How many Structures can we raw for C 6? Gopalpur Nagendrappa Gopalpur Nagendrappa teaches organic chemistry at Bangalore University. His work includes organic
Gopalpur Nagendrappa Benzene and its Isomers How many Structures can we raw for C 6? Gopalpur Nagendrappa Gopalpur Nagendrappa teaches organic chemistry at Bangalore University. His work includes organic
Pericyclic Reactions and Organic Photochemistry S. Sankararaman Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Pericyclic Reactions and Organic Photochemistry S. Sankararaman Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module No. #01 Lecture No. #03 Pericyclic reactions Introduction to Electrocyclic
Pericyclic Reactions and Organic Photochemistry S. Sankararaman Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module No. #01 Lecture No. #03 Pericyclic reactions Introduction to Electrocyclic
15.7 INTRODUCTION TO AROMATIC COMPOUNDS 716 CHAPTER 15 DIENES, RESONANCE, AND AROMATICITY
 716 APTER 15 DIENES, RESONANE, AND AROMATIITY PROBLEMS 15.27 In each of the following sets, show by the curved-arrow or fishhook notation how each resonance structure is derived from the other one, and
716 APTER 15 DIENES, RESONANE, AND AROMATIITY PROBLEMS 15.27 In each of the following sets, show by the curved-arrow or fishhook notation how each resonance structure is derived from the other one, and
Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems. Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems Alkenes and Alkynes Problems adapted from Chemistry - The Central Science, 3 rd edition. 24.2 Consider the hydrocarbon drawn below. (a) What is the hybridisation
Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems Alkenes and Alkynes Problems adapted from Chemistry - The Central Science, 3 rd edition. 24.2 Consider the hydrocarbon drawn below. (a) What is the hybridisation
Chapter 01 Structure Determines Properties part 2
 Chapter 01 Structure Determines Properties part 2 CEM 341: Spring 2012 Prof. Greg Cook Resonance Section 1.8 Resonance Some molecules may have more than one correct Lewis structure These are NT isomers.
Chapter 01 Structure Determines Properties part 2 CEM 341: Spring 2012 Prof. Greg Cook Resonance Section 1.8 Resonance Some molecules may have more than one correct Lewis structure These are NT isomers.
17.24 To name the compounds use the directions from Answer 17.3.
 Benzene and Aromatic Compounds 7 7 7.2 If benzene could be described by a single Kekulé structure, only one product would form in Reaction [], but there would be four (not three) dibromobenzenes (A ),
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds 7 7 7.2 If benzene could be described by a single Kekulé structure, only one product would form in Reaction [], but there would be four (not three) dibromobenzenes (A ),
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds
 1 Background Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas
1 Background Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas
Organic Chemistry 1 Lecture 5
 CEM 232 Organic Chemistry I Illinois at Chicago Organic Chemistry 1 Lecture 5 Instructor: Prof. Duncan Wardrop Time/Day: T & R, 12:30-1:45 p.m. January 26, 2010 1 Self Test Question Which of the following
CEM 232 Organic Chemistry I Illinois at Chicago Organic Chemistry 1 Lecture 5 Instructor: Prof. Duncan Wardrop Time/Day: T & R, 12:30-1:45 p.m. January 26, 2010 1 Self Test Question Which of the following
Loudon Chapter 15 Review: Dienes and Aromaticity Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 1/28/2019
 This chapter looks at the behavior of carbon-carbon double bonds when several of them are in the same molecule. There are several possible ways they can be grouped. Conjugated dienes have a continuous
This chapter looks at the behavior of carbon-carbon double bonds when several of them are in the same molecule. There are several possible ways they can be grouped. Conjugated dienes have a continuous
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chem 263 Sept 29, 2016 lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzene appears to be a remarkably stable (36 kcal/mole more) and unreactive compared to alkenes, such as cyclohexene or ethylene, or even alkanes,
Chem 263 Sept 29, 2016 lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzene appears to be a remarkably stable (36 kcal/mole more) and unreactive compared to alkenes, such as cyclohexene or ethylene, or even alkanes,
Chapter 6 H 2 H 3 C C H CH 3 C H H 2 C C CH 3. (b) =2 H 2 C C C H H C H CH 2 C CH 3 H 3 C C C CH 3. (c) =2
 hapter 6 6.1 alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the following hydrocarbons: 8 14 ; 5 6 (c) 12 20 (d) 20 32 (e) 40 56 =2 =3 (c) =3 (d) =5 (e) =13 6.2 alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the
hapter 6 6.1 alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the following hydrocarbons: 8 14 ; 5 6 (c) 12 20 (d) 20 32 (e) 40 56 =2 =3 (c) =3 (d) =5 (e) =13 6.2 alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the
Name: Class: Date: 3. How many lone pairs of electrons are assigned to the carbon atom in carbon monoxide? a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3
 Class: Date: Midterm 3, Fall 2009 Record your name on the top of this exam and on the scantron form. Record the test ID letter in the top right box of the scantron form. Record all of your answers on the
Class: Date: Midterm 3, Fall 2009 Record your name on the top of this exam and on the scantron form. Record the test ID letter in the top right box of the scantron form. Record all of your answers on the
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
Chapter 13. Conjugated Unsaturated Systems. +,., - Allyl. What is a conjugated system? AllylicChlorination (High Temperature)
 What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
- H. Predicts linear structure. Above are all σ bonds
 arbon sp hybrids: : Acetylene and the Triple bond 2 2 is - - Form sp on each leaving 2p x, 2p y unused - sp sp + + sp sp - Predicts linear structure. Above are all σ bonds --- Uses up 2 valence e - for
arbon sp hybrids: : Acetylene and the Triple bond 2 2 is - - Form sp on each leaving 2p x, 2p y unused - sp sp + + sp sp - Predicts linear structure. Above are all σ bonds --- Uses up 2 valence e - for
CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling
 CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling The Use of Computational Chemistry to Support Experimental Organic Chemistry Day 1 all calculation data obtained from Gaussian09 using B3LYP/6-31G(d) unless otherwise noted.
CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling The Use of Computational Chemistry to Support Experimental Organic Chemistry Day 1 all calculation data obtained from Gaussian09 using B3LYP/6-31G(d) unless otherwise noted.
Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes
 Section 21.1 Introduction to Hydrocarbons Section 1 Objectives: Explain the terms organic compound and organic chemistry. Section 21.2 Alkanes Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes
Section 21.1 Introduction to Hydrocarbons Section 1 Objectives: Explain the terms organic compound and organic chemistry. Section 21.2 Alkanes Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes
2.1A: Another look at the H 2 molecule: bonding and antibonding sigma molecular orbitals
 Ashley Robison My Preferences Site Tools Popular pages MindTouch User Guide FAQ Sign Out If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it
Ashley Robison My Preferences Site Tools Popular pages MindTouch User Guide FAQ Sign Out If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it
Chemistry 11. Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons
 Chemistry 11 Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons 2 1. Unsaturated hydrocarbons So far, we have studied the hydrocarbons in which atoms are connected exclusively by
Chemistry 11 Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons 2 1. Unsaturated hydrocarbons So far, we have studied the hydrocarbons in which atoms are connected exclusively by
NAME: SPRING 2015 MIDTERM
 page 1 pts NAME: SPRING 2015 MIDTERM hemistry 231 Professor: Dr. Gergens take-home portion (DUE at the beginning of the period, 4/6) Do your best on this take-home portion of your mid-term. I may grade
page 1 pts NAME: SPRING 2015 MIDTERM hemistry 231 Professor: Dr. Gergens take-home portion (DUE at the beginning of the period, 4/6) Do your best on this take-home portion of your mid-term. I may grade
There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): 1. Isolated: (two or more single bonds between them)
 1 Chapter 15: Conjugation and Reactions of Dienes I. Introduction to Conjugation There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): 1. Isolated: (two or more
1 Chapter 15: Conjugation and Reactions of Dienes I. Introduction to Conjugation There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): 1. Isolated: (two or more
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Chapter 13
 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Chapter 9. and Bonding Theories
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The
Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The
hand and delocalization on the other, can be instructively exemplified and extended
 Text Related to Segment 8.0 00 Claude E. Wintner The ideas developed up to this point, concerning stereochemistry on the one hand and delocalization on the other, can be instructively exemplified and extended
Text Related to Segment 8.0 00 Claude E. Wintner The ideas developed up to this point, concerning stereochemistry on the one hand and delocalization on the other, can be instructively exemplified and extended
Chapter 27: Structure and Bonding
 Chapter 27: Structure and Bonding 1 Atomic Orbitals: Wave functions that represent the probability of finding electrons in a specific region of space s, p, d, f orbitals In organic chemistry, need to concentrate
Chapter 27: Structure and Bonding 1 Atomic Orbitals: Wave functions that represent the probability of finding electrons in a specific region of space s, p, d, f orbitals In organic chemistry, need to concentrate
Constitutional Isomers and Conformations of Alkanes & Cycloalkanes
 Discovering Molecular Models #1: Constitutional Isomers Conformations of Alkanes & Cycloalkanes There are no additional tutorial or laboratory notes. Read bring your course notes, as they provide all of
Discovering Molecular Models #1: Constitutional Isomers Conformations of Alkanes & Cycloalkanes There are no additional tutorial or laboratory notes. Read bring your course notes, as they provide all of
Constitutional Isomers and Conformations of Alkanes & Cycloalkanes
 Discovering Molecular Models #1: Constitutional Isomers Conformations of Alkanes & Cycloalkanes There are no additional tutorial or laboratory notes. Read bring your course notes, as they provide all of
Discovering Molecular Models #1: Constitutional Isomers Conformations of Alkanes & Cycloalkanes There are no additional tutorial or laboratory notes. Read bring your course notes, as they provide all of
7. Arrange the molecular orbitals in order of increasing energy and add the electrons.
 Molecular Orbital Theory I. Introduction. A. Ideas. 1. Start with nuclei at their equilibrium positions. 2. onstruct a set of orbitals that cover the complete nuclear framework, called molecular orbitals
Molecular Orbital Theory I. Introduction. A. Ideas. 1. Start with nuclei at their equilibrium positions. 2. onstruct a set of orbitals that cover the complete nuclear framework, called molecular orbitals
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chem 263 ct. 8, 2013 lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzene appears to be a remarkably stable and unreactive compared to alkenes, such as cyclohexene or ethylene, or even alkanes, such as cyclohexane
Chem 263 ct. 8, 2013 lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzene appears to be a remarkably stable and unreactive compared to alkenes, such as cyclohexene or ethylene, or even alkanes, such as cyclohexane
Naming Aromatic Compounds (Benzene as the Parent)
 aming Aromatic Compounds (Benzene as the Parent) If the the alkyl chain is smaller than the ring use the ring as the parent Monosubstituted benzenes are named the same way as other hydrocarbons using benzene
aming Aromatic Compounds (Benzene as the Parent) If the the alkyl chain is smaller than the ring use the ring as the parent Monosubstituted benzenes are named the same way as other hydrocarbons using benzene
Chapter 9. and Bonding Theories. Molecular Shapes. What Determines the Shape of a Molecule? 3/8/2013
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice-Hall,
Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice-Hall,
Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Key Words Conjugated Diene Resonance Structures Dienophiles Concerted Reaction Pericyclic Reaction Cycloaddition Reaction Bridged Bicyclic Compound Cyclic
Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Key Words Conjugated Diene Resonance Structures Dienophiles Concerted Reaction Pericyclic Reaction Cycloaddition Reaction Bridged Bicyclic Compound Cyclic
Practice Hour Examination # 1-1
 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Monday,
CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Monday,
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 Introduction to rganic hemistry 59 Introduction to rganic hemistry andout 3 - chanism u u http://burton.chem.ox.ac.uk/teaching.html rganic hemistry J. layden,. Greeves, S. Warren Stereochemistry at a Glance
Introduction to rganic hemistry 59 Introduction to rganic hemistry andout 3 - chanism u u http://burton.chem.ox.ac.uk/teaching.html rganic hemistry J. layden,. Greeves, S. Warren Stereochemistry at a Glance
The Chemical principles of Coloration
 Chapter 2-3 Introduction The Chemical principles of Coloration A single atoms consists of a central core or nucleus which contains numbers of positively charged particles(protons) and uncharged particles(neutrons)
Chapter 2-3 Introduction The Chemical principles of Coloration A single atoms consists of a central core or nucleus which contains numbers of positively charged particles(protons) and uncharged particles(neutrons)
CHEMISTRY CHAPTER- HYDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions
 CEMISTRY CAPTER- YDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions 1. What type of structural isomerism is shown by alkanes? 2. Which metal is used in Wurtz reaction? 3. What happens when isopropyl bromide is subjected
CEMISTRY CAPTER- YDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions 1. What type of structural isomerism is shown by alkanes? 2. Which metal is used in Wurtz reaction? 3. What happens when isopropyl bromide is subjected
Chapter 2 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules. Advanced Bonding: Review
 hapter 2 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules hemistry 231 Organic hemistry I Fall 2007 Advanced Bonding: Review Atomic Quantum Mechanics cannot explain how molecules like 4 form: Valence Bond
hapter 2 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules hemistry 231 Organic hemistry I Fall 2007 Advanced Bonding: Review Atomic Quantum Mechanics cannot explain how molecules like 4 form: Valence Bond
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change CHAPTER 21 Table Of Contents Section Section Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes Section Section 21.5 Aromatic Hydrocarbons Explainthe terms organic compound
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change CHAPTER 21 Table Of Contents Section Section Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes Section Section 21.5 Aromatic Hydrocarbons Explainthe terms organic compound
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity (which atoms are physically connected). By noting the number of bonding and nonbonding electron
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity (which atoms are physically connected). By noting the number of bonding and nonbonding electron
