Chapter 18: Aromatic Compounds
|
|
|
- Ambrose Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 hapter 18: Aromatic ompounds [Sections: 18.1, , 18.8] The Structure of Benzene skeletal condensed 1800's sausage Friedrich August Kekule Kekule's Dream 6 6 Kekule wakes up Some urious Things About Benzene?? R 2 2 l l faster l R l l the reactivity of benzene is MU less than what would be expected based on its skeletal structure alone it does T engage in the same type of reactions expected of alkenes
2 xs 2, Pt predict actual 120 kj/mol xs 2, Pt predicted xs 2, Pt E benzene is MU more stable (by about 150 kj/mol) than would be expected based on its skeletal structure alone! flashback to dienes A B E A small amount of stabilization by conjugation still behaves essentially like an alkene resonance in benzene E A A B individual resonance forms (kekule forms) suggest "alternating" bond lengths for the structure the hybrid form correctly predicts "non-alternating" bond lengths does T behave like an alkene!! hybrid form
3 hybrid form much more stable than either resonance form alone does not resemble either individual resonance form, but is a true mixture of both the surprising stability of benzene comes from the strong stabilization of the hybrid form by the equal contribution of two excellent resonance forms of equivalent energy the two contributing resonance forms (kekule forms) allow the electrons in the benzene pi system to be completely delocalized amongst 6 different carbon atoms! the special stabilization resulting from this electron delocalization due to resonance is called "aromaticity" all of the carbons of benzene are SP2 hybridized, thus the molecule is flat. In addition, the equal contribution of the two resonance forms means all of the bond lengths (1.4 A) and bond angles (120 ) are equilvalent 2 l l 2 Fe 3 thus, the lack of reactivity of benzene can be attributed to the reluctance of benzene to lose its aromatic stability if it were to react like a typical alkene via addition reactions! when forced, benzene WILL react with electrophiles, but the end result is a substitution reaction rather than addition because aromaticity is retained in substitution reactions
4 Is Benzene the nly Aromatic ompound? Properties of Aromatic ompounds 1. yclic array of uninterrupted SP 2 hybridized atoms 2. Fully planar structure 3. igh stability beyond what simple Lewis Dot structures would predict 4. Undergo substitution reactions (to retain aromaticity) rather than typical alkene addition reactions (in which case aromaticity would be lost) 5. All carbon-carbon bonds are of the same length (non-alternating bond lengths) other information bond lengths? alt? non-alt? type of reaction? substitution/ addition 2 2, Pt kj/mol 2, Pt predict = actual = ΔE = = stable than predicted! 2 ΔE = 2, Pt 2, Pt kj/mol predict = actual = 2, Pt 2, Pt kj/mol predict = actual = ΔE = = stable than predicted! Problems: 1,2
5 What Determines Whether a Planar yclic Polyene is Aromatic or ot? Flashback to atomic orbital electron configurations: Fluorine A = 9 1s 2 2s 2 2p x 2 2p y 2 2p z 1 eon A = 10 1s 2 2s 2 2p x 2 2p y 2 2p z 2 closed shell configurations lead to stable species unfilled (or open shell) configurations lead to unstable species all molecules have a set of molecular orbitals that are filled in the same manner as atomic orbitals for systems with pi bonds, the pi molecular orbitals can be viewed separately from the sigma molecular orbitals all planar cyclic polyenes have the same approximate distribution of pi molecular orbitals E When a proper number of electrons is contained in the pi system to completely fill all of the occupied molecular orbitals an aromatic system will result (if all other criteria for aromaticity are fulfilled). This occurs when there is an DD number of electron pairs in the pi system = uckel Rule (also fits the equation 4n+2). This is a general equation such that if a cyclic pi system contains a number of electrons that satisfies this equation, it will have the proper number of pi electrons to completely fill all of the occupied molecular orbitals for a planar cyclic aromatic molecule Erich uckel uckel satisfied? Aromatic? When an improper number of electrons is contained in the pi system such that singly-occupied molecular orbitals are created, the system will be especially unstable! such systems are termed anti-aromatic This occurs when there is an EVE number of electron pairs in the pi system = uckel Rule (also fits the equation 4n). This is a general equation such that if a cyclic pi system contains a number of electrons that satisfies this equation, it will have the improper number of pi electrons to completely fill all of the occupied molecular orbitals and an antiaromatic molecule may result
6 Properties of Aromatic ompounds 1. yclic array of uninterrupted SP 2 hybridized atoms 2. Fully planar structure 3. igh stability beyond what simple Lewis Dot structures would predict 4. Undergo substitution reactions (in order to retain aromaticity) rather than typical alkene addition reactions (in which case aromaticity would be lost) 5. All carbon-carbon bonds are of the same length 6. DD number of electron pairs in pi system (4n+2 pi electrons) 7. Properties of Anti-Aromatic ompounds 1. yclic array of uninterrupted SP 2 hybridized atoms 2. Fully planar structure 3. igh reactivity beyond what simple Lewis Dot structures would predict 4. Undergo typical alkene addition reactions (in order to LSE anti-aromaticity) 5. Alternating carbon-carbon bond lengths 6. EVE number of electron pairs in pi system (4n pi electrons) 7. there are not many cases of anti-aromatic compounds since such cyclic polyenes will adopt a non-planar conformation to avoid anti-aromaticity MR Effects circulation of the pi electrons in an aromatic system create a magnetic field that increases the effect of the external magnetic field and pushes resonance to higher PPM (i.e., deshields the protons) this is a diamagnetic ring current effect B 0 circulation of the pi electrons in an aromatic system create a magnetic field that decreases the effect of the external magnetic field and pushes resonance to lower PPM (i.e., deshields the protons) this is a paramagnetic ring current effect 7.3 ppm aromatic protons show up at higher PPM than typical alkene protons (deshielded) 6.5 non-aromatic cyclic compounds have typical alkene proton chemical shifts anti-aromatic protons show up at lower PPM than typical alkene protons (shielded) 9.3 ppm (deshielded) 3 ppm (shielded)
7 Aromatic eterocycles heterocycles are cyclic compounds that contain, or some other non- atom pyridine pyridine is essentially a benzene ring in which one of the carbons has been replaced by a nitrogen atom the pi system of pyridine is equivalent to that of benzene and contains a uckel number (6) of pi electrons the lone pair on the nitrogen is orthogonal to the pi system and cannot contribute to the pi electron count typical cyclic amine pyrrole a typical nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons will adopt SP3 hybridization (tetrahedral shape) pyrrole could T be aromatic if the nitrogen atom were SP3 hybridized additionally, pyrrole has two = bonds which contribute only 4 pi electrons by adopting SP2 hybridization at the nitrogen atom, pyrrole attains a cyclic array of SP2 hybridized the orbitals and also adds the two electrons from its lone pair to the pi system to give a uckel number (6) of pi electrons and becomes aromatic! typical cyclic ether (TF) furan a typical oxygen atom with two lone pairs of electrons will adopt SP3 hybridization furan could T be aromatic if the oxygen atom were SP3 hybridized additionally, furan has two = bonds which contribute only 4 pi electrons by adopting SP2 hybridization at the oxygen atom, furan attains a cyclic array of SP2 hybridized the orbitals and also adds the two electrons from one of its lone pair to the pi system to give a uckel number (6) of pi electrons and becomes aromatic!
8 Summary for aromatic heterocycles aromaticity is not restricted to all-carbon molecules as long as all of the requirements for aromaticity are fulfilled (uninterrupted cyclic array of SP2 hybridized atoms, planar structure, 4n+2 pi electrons) any molecule may exhibit aromaticity atoms with lone pairs may only contribute E of the lone pairs into the pi system to satisfy the 4n+2 rule ow can I tell if a heteroatom will donate its lone pair to a pi system? a heteroatom will only adopt SP2 hybridization and donate a lone pair if it makes the system aromatic if the heteroatom is already part of a double bond, it cannot donate any lone pairs (the lone pairs will be orthogonal to the pi system) if an atom has two lone pairs, it can only contribute E pair into the pi system some guy purine critical component of nucleic acids are the rings which nitrogens contribute lone pairs? Fused Benzenes benzene naphthalene anthracene benzopyrene liver enzymes Problems: 3, 5, 10
9 harged Aromatic ompounds Flashback to atomic orbital electron configurations: Lithium Li A = 3, # electrons =3 1s 2 2s 1 Li + A = 3, # electrons = 2 1s 2 Fluorine, F A = 9, # electrons = 9 1s 2 2s 2 2p x 2 2p y 2 2p z 1 Fluoride, F A = 9, # electrons = 10 1s 2 2s 2 2p x 2 2p y 2 2p z 2 unstable open-shell atoms could be made stable by adding (to form anions) or subtracting (to form cations) electrons to provide ions with complete outer shells aromatic anions and cations can also be formed if the 4n+2 uckel number of pi electrons results anti-aromatic anions and cations cal be formed if the 4n number of pi electrons results Anionic (negatively charged) Pi Systems - 2 electrons + 2 electrons cyclooctatetraene Effect of aromaticity on acidity Flashback pka ~ 3 3 pka ~ stabilization of the conjugate base of a molecule by electronegativity or resonance strongly enhances acidity bond is more acidic than because is more electronegative than and can therefore stabilize the negative charge better resonance can increase acidity by stabilizing the negative charge via delocalization 2 2 pka ~
10 acidity of cyclopentadiene pka ~ hybrid form acidity of cycloheptatriene cyclopentadiene is unusually acidic for a - bond! remember: acidic compounds have stabilized conjugate bases! its acidity can be traced to the strong stabilization of the resulting negative charge because the resulting pi system has an aromatic number of pi electrons (6 pi electrons)! thus, deprotonation of cyclopentadience changes the molecule from something that is T aromatic to a molecule that IS aromatic! because the anion is so stable, it is easily formed via deprotonation and the - bond is observed to be unusually acidic pka ~ hybrid form resonance considerations alone suggest it should be very easy to deprotonate cycloheptatriene since the negative charge is highly delocalized, unlike cyclopentadiene, however, cycloheptatriene is T unusually acidic addition of two electrons to the pi system yields 8 pi electrons, which is T a uckel number thus, deprotonation of cycloheptatriene (a non-aromatic molecule) does T provide aromatic stabilization and it is therefore does not exhibit an acidic - bond
11 ationic (positively charged) Pi Systems 100X faster resonance stabilization of the allylic carbocation results in faster reaction since the allylic carbocation is easier to form than the localized 2 carbocation hybrid form usually carbocations stabilized by resonance forms are very stable and easily formed thus, resonance alone suggests it should be very easy to lose the leaving group since the resulting carbocation is stabilized via delocatlization of the positive charge. however, loss of the and formation of the carbocation creates an anti-aromatic pi system! thus, the refuses to act as a leaving group to avoid going from a molecule that is T aromatic to a molecule that is ATI-ARMATI and therefore strongly destabilized! hybrid form the cycloheptatrienyl carbocation (tropylium cation) is exceptionally stable (and therefore easily formed) because it contains a uckel number (6) of pi electrons, making it an aromatic compound! thus, the leaving group is easily lost to form this strongly stabilized aromatic carbocation Problems: 2,6,7,9
12/27/2010. Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds
 Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives Benzene is the parent name for some monosubstituted benzenes; the substituent name is added as a prefix Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds For other monosubstituted benzenes,
Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives Benzene is the parent name for some monosubstituted benzenes; the substituent name is added as a prefix Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds For other monosubstituted benzenes,
Benzene and Aromaticity
 Benzene and Aromaticity Why this Chapter? Reactivity of substituted aromatic compounds is tied to their structure Aromatic compounds provide a sensitive probe for studying relationship between structure
Benzene and Aromaticity Why this Chapter? Reactivity of substituted aromatic compounds is tied to their structure Aromatic compounds provide a sensitive probe for studying relationship between structure
Benzene a remarkable compound. Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds. Some proposed structures for C 6 H 6. Dimethyl substituted benzenes are called xylenes
 Benzene a remarkable compound Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds Discovered by Faraday 1825 Formula C 6 H 6 Highly unsaturated, but remarkably stable Whole new class of benzene derivatives called aromatic compounds
Benzene a remarkable compound Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds Discovered by Faraday 1825 Formula C 6 H 6 Highly unsaturated, but remarkably stable Whole new class of benzene derivatives called aromatic compounds
17.24 To name the compounds use the directions from Answer 17.3.
 Benzene and Aromatic Compounds 7 7 7.2 If benzene could be described by a single Kekulé structure, only one product would form in Reaction [], but there would be four (not three) dibromobenzenes (A ),
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds 7 7 7.2 If benzene could be described by a single Kekulé structure, only one product would form in Reaction [], but there would be four (not three) dibromobenzenes (A ),
16.4 Cyclobutadiene. .. H c)
 16.4 CYCLOBUTADIEE 649 arranged about zero energy, it is necessary for one degenerate pair, 4 nb and 5 nb, to be located at zero energy. MOs at zero energy are termed nonbonding.) If the total number of
16.4 CYCLOBUTADIEE 649 arranged about zero energy, it is necessary for one degenerate pair, 4 nb and 5 nb, to be located at zero energy. MOs at zero energy are termed nonbonding.) If the total number of
CHEM 263 Notes Oct 1, Beta-carotene (depicted below) is responsible for the orange-red colour in carrots.
 EM 263 otes ct 1, 2013 onjugated Dienes and olour ontinued Beta-carotene (depicted below) is responsible for the orange-red colour in carrots. In the below example, astaxanthin, a blue-green pigment in
EM 263 otes ct 1, 2013 onjugated Dienes and olour ontinued Beta-carotene (depicted below) is responsible for the orange-red colour in carrots. In the below example, astaxanthin, a blue-green pigment in
2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes
 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reactions of Isolated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Mechanism Double Bonds can have Different Reactivities
2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reactions of Isolated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Mechanism Double Bonds can have Different Reactivities
Organic Chemistry, 7 L. G. Wade, Jr. 2010, Prentice Hall
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH AROMATICITY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: AROMATICTY INTRODUCTION Aromatic compounds display an unusual stability for their high level of electron density. Their high level of unsaturation should make them extremely
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: AROMATICTY INTRODUCTION Aromatic compounds display an unusual stability for their high level of electron density. Their high level of unsaturation should make them extremely
Lecture 10. More Aromatics. February 15, Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 10 More Aromatics February 15, 2018 ückel's Rule for Aromaticity To be Aromatic a compound must : 1. be Cyclic 2. have one P orbital on each atom in the ring 3. be planar or nearly so to give orbital
Lecture 10 More Aromatics February 15, 2018 ückel's Rule for Aromaticity To be Aromatic a compound must : 1. be Cyclic 2. have one P orbital on each atom in the ring 3. be planar or nearly so to give orbital
Frost Circles a Great Trick
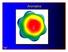 Aromatics Frost Circles a Great Trick Inscribe a polygon of the same number of sides as the ring to be examined such that one of the vertices is at the bottom of the ring The relative energies of the MOs
Aromatics Frost Circles a Great Trick Inscribe a polygon of the same number of sides as the ring to be examined such that one of the vertices is at the bottom of the ring The relative energies of the MOs
4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY
 4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY During the early 1800's, a group of compounds of natural origin became collectively known as aromatic compounds. As several of these compounds
4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY During the early 1800's, a group of compounds of natural origin became collectively known as aromatic compounds. As several of these compounds
Solution problem 22: Non-Benzoid Aromatic Sytems
 Solution problem 22: on-enzoid Aromatic Sytems 22.1 & 22.2 Each double bond and each heteroatom (, ) with lone pairs donates 2 π- electrons as well as a negative charge. oron or a positive charge does
Solution problem 22: on-enzoid Aromatic Sytems 22.1 & 22.2 Each double bond and each heteroatom (, ) with lone pairs donates 2 π- electrons as well as a negative charge. oron or a positive charge does
Aromatic Substitution Chemistry (Part of Chapter 2 and Chapter 11)
 Aromatic Substitution hemistry (Part of hapter 2 and hapter 11) Aliphatic ompounds: Aromatic ompounds: pentane 2-pentene 2-pentyne Aromatic compounds have closed loops of electrons that give rise to an
Aromatic Substitution hemistry (Part of hapter 2 and hapter 11) Aliphatic ompounds: Aromatic ompounds: pentane 2-pentene 2-pentyne Aromatic compounds have closed loops of electrons that give rise to an
Aromatic Compounds. A number of these compounds had a distinct odor. Hence these compounds were called aromatic
 Aromatic Compounds Early in the history of organic chemistry (late 18 th, early 19 th century) chemists discovered a class of compounds which were unusually stable A number of these compounds had a distinct
Aromatic Compounds Early in the history of organic chemistry (late 18 th, early 19 th century) chemists discovered a class of compounds which were unusually stable A number of these compounds had a distinct
Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds. Discovery of Benzene
 Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C: ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C: ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
12.1 AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 12 Arenes and Aromaticity estradiol 12.1 AROMATIC COMPOUNDS O O O O C 3 C 3 O O safrole (oil of sassafras) O methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen) O vanillin (vanilla) C 3 N C 3 C 3 CC 2 ibuprofen C C
12 Arenes and Aromaticity estradiol 12.1 AROMATIC COMPOUNDS O O O O C 3 C 3 O O safrole (oil of sassafras) O methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen) O vanillin (vanilla) C 3 N C 3 C 3 CC 2 ibuprofen C C
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURES Dr Ali El-Agamey. Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURES 11-12 Dr Ali El-Agamey Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Amines 2010, Prentice Hall Reactions N,N-Disubstituted amides 2 o amine
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURES 11-12 Dr Ali El-Agamey Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Amines 2010, Prentice Hall Reactions N,N-Disubstituted amides 2 o amine
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes
 Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Chapter Tell whether the following compounds are ortho-, meta-, or para-disubstituted: (a) M-chlorotoluene (b) NO 2
 Chapter 15 15.1 Tell whether the following compounds are ortho-, meta-, or para-disubstituted: (a) Cl C 3 M-chlorotoluene (b) 2 P-bromonitrobenzene (c) S 3 -hydroxybenzenesulfonid acid 15.2 Give IUPAC
Chapter 15 15.1 Tell whether the following compounds are ortho-, meta-, or para-disubstituted: (a) Cl C 3 M-chlorotoluene (b) 2 P-bromonitrobenzene (c) S 3 -hydroxybenzenesulfonid acid 15.2 Give IUPAC
Reaction mechanisms offer us insights into how reactions work / how molecules react with one another.
 Introduction 1) Lewis Structures 2) Representing Organic Structures 3) Geometry and Hybridization 4) Electronegativities and Dipoles 5) Resonance Structures (a) Drawing Them (b) Rules for Resonance 6)
Introduction 1) Lewis Structures 2) Representing Organic Structures 3) Geometry and Hybridization 4) Electronegativities and Dipoles 5) Resonance Structures (a) Drawing Them (b) Rules for Resonance 6)
Aromatic Compounds I
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 1 Aromatic Compounds I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 16 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 1 Aromatic Compounds I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 16 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds
 1 Background Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas
1 Background Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas
Chapter 2. Molecular Representations
 hapter 2. Molecular Representations 3 () 3 ( 3 ) 2 3 3 3 8 Lewis (Kekule) structure ondensed and par6ally condensed structure Skeletal (bond- line) structure Molecular formula Amoxicillin a widely prescribed
hapter 2. Molecular Representations 3 () 3 ( 3 ) 2 3 3 3 8 Lewis (Kekule) structure ondensed and par6ally condensed structure Skeletal (bond- line) structure Molecular formula Amoxicillin a widely prescribed
Module III: Aromatic Hydrocarbons (6 hrs)
 Module III: Aromatic Hydrocarbons (6 hrs) Nomenclature and isomerism in substituted benzene. Structure and stability of benzene: Kekule, resonance and molecular orbital description. Mechanism of aromatic
Module III: Aromatic Hydrocarbons (6 hrs) Nomenclature and isomerism in substituted benzene. Structure and stability of benzene: Kekule, resonance and molecular orbital description. Mechanism of aromatic
Benzene and aromaticity
 aromaticity The word "benzene" derives historically from "gum benzoin", sometimes called "benjamin" (i.e., benzoin resin), an aromatic resin known to European pharmacists and perfumers since the 15th century
aromaticity The word "benzene" derives historically from "gum benzoin", sometimes called "benjamin" (i.e., benzoin resin), an aromatic resin known to European pharmacists and perfumers since the 15th century
15.7 INTRODUCTION TO AROMATIC COMPOUNDS 716 CHAPTER 15 DIENES, RESONANCE, AND AROMATICITY
 716 APTER 15 DIENES, RESONANE, AND AROMATIITY PROBLEMS 15.27 In each of the following sets, show by the curved-arrow or fishhook notation how each resonance structure is derived from the other one, and
716 APTER 15 DIENES, RESONANE, AND AROMATIITY PROBLEMS 15.27 In each of the following sets, show by the curved-arrow or fishhook notation how each resonance structure is derived from the other one, and
Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity
 Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity Solutions to In-Text Problems 15.2 The delocalization energy is the energy
Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity Solutions to In-Text Problems 15.2 The delocalization energy is the energy
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 Introduction to rganic hemistry 59 Introduction to rganic hemistry andout 3 - chanism u u http://burton.chem.ox.ac.uk/teaching.html rganic hemistry J. layden,. Greeves, S. Warren Stereochemistry at a Glance
Introduction to rganic hemistry 59 Introduction to rganic hemistry andout 3 - chanism u u http://burton.chem.ox.ac.uk/teaching.html rganic hemistry J. layden,. Greeves, S. Warren Stereochemistry at a Glance
Resonance and M.O. View of Butadiene. Super-Conjugated or Aromatic p e - Systems
 Resonance and M.. View of Butadiene The different resonance forms of butadiene suggest p bonding character between the two central carbon atoms. 2 2 2 2 carbanion 2 2 carbocation The M.. view of butadiene
Resonance and M.. View of Butadiene The different resonance forms of butadiene suggest p bonding character between the two central carbon atoms. 2 2 2 2 carbanion 2 2 carbocation The M.. view of butadiene
Solutions a) 4-bromo-2-methylphenol b) 2-hydroxy-5-bromotoluene c) 4-bromo-1-hydroxy-2-methylbenzene OMe OH
 CAPTER 18 413 R R Solutions 18.1. 3-isopropylbenzaldehyde or meta-isopropylbenzaldehyde 2-bromotoluene or ortho-bromotoluene c) 2,4-dinitrophenol d) 2-ethyl-1,4-diisopropylbenzene f) 2,6-dibromo-4-chloro-3-ethyl-5-isopropylphenol
CAPTER 18 413 R R Solutions 18.1. 3-isopropylbenzaldehyde or meta-isopropylbenzaldehyde 2-bromotoluene or ortho-bromotoluene c) 2,4-dinitrophenol d) 2-ethyl-1,4-diisopropylbenzene f) 2,6-dibromo-4-chloro-3-ethyl-5-isopropylphenol
Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories
 Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories Ionic Radii Ions, just like atoms, follow a periodic trend in their radii. The metal ions in a given period are smaller than the non-metal ions in the same
Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories Ionic Radii Ions, just like atoms, follow a periodic trend in their radii. The metal ions in a given period are smaller than the non-metal ions in the same
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds. Chapter 15 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Chapter 15 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Background Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Four degrees of unsaturation. It
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Chapter 15 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Background Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Four degrees of unsaturation. It
5. (6 pts) Show how the following compound can be synthesized from the indicated starting material:
 Exam 2 Name CHEM 212 1. (36 pts) Complete the following chemical reactions showing all major organic products; illustrate proper stereochemistry where appropriate. If no reaction occurs, indicate NR :
Exam 2 Name CHEM 212 1. (36 pts) Complete the following chemical reactions showing all major organic products; illustrate proper stereochemistry where appropriate. If no reaction occurs, indicate NR :
CHEM 263 Notes Sep 27, Equivalent resonance forms gives stability to a compound.
 CEM 263 otes Sep 27, 2016 Aromatic Compounds Continued Aromaticity Equivalent resonance forms gives stability to a compound. resonance 1,2-dibromobenzene Aromatic compounds are especially stable. For benzene,
CEM 263 otes Sep 27, 2016 Aromatic Compounds Continued Aromaticity Equivalent resonance forms gives stability to a compound. resonance 1,2-dibromobenzene Aromatic compounds are especially stable. For benzene,
Chapter 8. Acidity, Basicity and pk a
 Chapter 8 Acidity, Basicity and pk a p182 In this reaction water is acting as a base, according to our definition above, by accepting a proton from HCl which in turn is acting as an acid by donating a
Chapter 8 Acidity, Basicity and pk a p182 In this reaction water is acting as a base, according to our definition above, by accepting a proton from HCl which in turn is acting as an acid by donating a
The now-banned diet drug fen-phen is a mixture of two synthetic substituted benzene: fenfluramine and phentermine.
 The now-banned diet drug fen-phen is a mixture of two synthetic substituted benzene: fenfluramine and phentermine. Chemists have synthesized compounds with structures similar to adrenaline, producing amphetamine.
The now-banned diet drug fen-phen is a mixture of two synthetic substituted benzene: fenfluramine and phentermine. Chemists have synthesized compounds with structures similar to adrenaline, producing amphetamine.
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
Exam (6 pts) Show which starting materials are used to produce the following Diels-Alder products:
 Exam 1 Name CHEM 212 1. (18 pts) Complete the following chemical reactions showing all major organic products; illustrate proper stereochemistry where appropriate. If no reaction occurs, indicate NR :
Exam 1 Name CHEM 212 1. (18 pts) Complete the following chemical reactions showing all major organic products; illustrate proper stereochemistry where appropriate. If no reaction occurs, indicate NR :
SIX MEMBERED AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES
 SIX MEMBERED AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES Ṇ. Pyridine Pyridine is aromatic as there are six delocalized electrons in the ring. Six-membered heterocycles are more closely related to benzene as they are aromatic
SIX MEMBERED AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES Ṇ. Pyridine Pyridine is aromatic as there are six delocalized electrons in the ring. Six-membered heterocycles are more closely related to benzene as they are aromatic
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
11/5/ Conjugated Dienes. Conjugated Dienes. Conjugated Dienes. Heats of Hydrogenation
 8.12 Sites of unsaturation Many compounds have numerous sites of unsaturation If sites are well separated in molecule they react independently If sites are close together they may interact with one another
8.12 Sites of unsaturation Many compounds have numerous sites of unsaturation If sites are well separated in molecule they react independently If sites are close together they may interact with one another
Chemistry Exam 1. The Periodic Table
 ame: Last First MI Chemistry 234-002 Exam 1 Spring 2017 Dr. J. sbourn Instructions: The first 18 questions of this exam should be answered on the provided Scantron. You must use a pencil for filling in
ame: Last First MI Chemistry 234-002 Exam 1 Spring 2017 Dr. J. sbourn Instructions: The first 18 questions of this exam should be answered on the provided Scantron. You must use a pencil for filling in
CHEM 303 Organic Chemistry II Problem Set II Chapter 13 Answers
 CEM 303 rganic Chemistry II Problem Set II Chapter 13 Answers 1) Explain the reason for the different chemical reactivity of cyclopentadiene and cycloheptatriene toward bromine. 2 + 2 + oth no doubt start
CEM 303 rganic Chemistry II Problem Set II Chapter 13 Answers 1) Explain the reason for the different chemical reactivity of cyclopentadiene and cycloheptatriene toward bromine. 2 + 2 + oth no doubt start
NO 2 O NH 2. Br Br. Br CF 3
 1. Rank the following compounds in the trend requested. (15 points each) a. Rank by energy of the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUM). The molecule with the LUM that is lowest in energy is 1, while
1. Rank the following compounds in the trend requested. (15 points each) a. Rank by energy of the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUM). The molecule with the LUM that is lowest in energy is 1, while
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Chapter 15 Benzene and Aromaticity
 Chapter 15 Benzene and Aromaticity Aromatic Compounds Aromatic Originally used to describe fragrant substances Refers to a class of compounds that meets Hückel criteria for aromaticity 2 Aromatic Compounds
Chapter 15 Benzene and Aromaticity Aromatic Compounds Aromatic Originally used to describe fragrant substances Refers to a class of compounds that meets Hückel criteria for aromaticity 2 Aromatic Compounds
Synthesis Using Aromatic Materials
 Chapter 10 Synthesis Using Aromatic Materials ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION AND DIRECTED ORTHO METALATION Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 10.2 p Bonds Acting as Nucleophiles Copyright
Chapter 10 Synthesis Using Aromatic Materials ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION AND DIRECTED ORTHO METALATION Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 10.2 p Bonds Acting as Nucleophiles Copyright
Loudon Chapter 15 Review: Dienes and Aromaticity Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 1/28/2019
 This chapter looks at the behavior of carbon-carbon double bonds when several of them are in the same molecule. There are several possible ways they can be grouped. Conjugated dienes have a continuous
This chapter looks at the behavior of carbon-carbon double bonds when several of them are in the same molecule. There are several possible ways they can be grouped. Conjugated dienes have a continuous
PAPER No. 5:Organic Chemistry-2(Reaction Mechanism-1) MODULE No. 6: Generation, Structure, Stability and Reactivity of Carbocations
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5: Organic Chemistry-II (Reaction Mechanism-1) Generation, Structure, Stability and Reactivity of Carbocations CHE_P5_M6 TABLE
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5: Organic Chemistry-II (Reaction Mechanism-1) Generation, Structure, Stability and Reactivity of Carbocations CHE_P5_M6 TABLE
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
25.3 THE CHEMISTRY OF FURAN, PYRROLE, AND THIOPHENE
 6 CAPTER 5 TE CEMITRY F TE ARMATIC ETERCYCE B. Acidity of Pyrrole and Indole Pyrrole and indole are weak acids. + B _ etc. + B 4 _ (a base) _ (5.9) Further Exploration 5. Relative Acidities of,-cyclopentadiene
6 CAPTER 5 TE CEMITRY F TE ARMATIC ETERCYCE B. Acidity of Pyrrole and Indole Pyrrole and indole are weak acids. + B _ etc. + B 4 _ (a base) _ (5.9) Further Exploration 5. Relative Acidities of,-cyclopentadiene
Chapter 17. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy
 Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Lecture Topics: I. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Suggested solutions for Chapter 29
 s for Chapter 29 29 PRBLEM 1 or each of the following reactions (a) state what kind of substitution is suggested and (b) suggest what product might be formed if monosubstitution occured. Br 2 3 2 S 4 S
s for Chapter 29 29 PRBLEM 1 or each of the following reactions (a) state what kind of substitution is suggested and (b) suggest what product might be formed if monosubstitution occured. Br 2 3 2 S 4 S
240 Chem. Aromatic Compounds. Chapter 6
 240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
Chapter 7: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 7: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Electronegativity and Bond Polarity Lewis Structures Orbital Overlap Hybrid Orbitals The Shapes of Molecules (VSEPR Model) Molecular
Chapter 7: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Electronegativity and Bond Polarity Lewis Structures Orbital Overlap Hybrid Orbitals The Shapes of Molecules (VSEPR Model) Molecular
1. In most stable molecules, all the atoms will have filled valence shells. Vigabatrin -
 Your goal should be to understand, not memorize, the material presented in your organic chemistry course. The following principles should be learned as you begin your study of organic chemistry, then used
Your goal should be to understand, not memorize, the material presented in your organic chemistry course. The following principles should be learned as you begin your study of organic chemistry, then used
CHEMISTRY Topic #3: Addition Reactions of Conjugated Dienes Spring 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay
 CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #3: Addition Reactions of Conjugated Dienes Spring 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay Different Kinds of Dienes When a molecule contains multiple π-bonds, their reactivity is dictated in part by
CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #3: Addition Reactions of Conjugated Dienes Spring 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay Different Kinds of Dienes When a molecule contains multiple π-bonds, their reactivity is dictated in part by
Acid/Base stuff Beauchamp 1
 cid/base stuff Beauchamp 1 Problems You should be able to match a pk a value with its acid in each group below and explain the differences. You should be able to draw an arrow-pushing mechanism with general
cid/base stuff Beauchamp 1 Problems You should be able to match a pk a value with its acid in each group below and explain the differences. You should be able to draw an arrow-pushing mechanism with general
Chapter 2 Molecular Representations
 hapter 2 Molecular Representations Structural Formulas and ondensed Structures Because organic compounds are molecular in nature, the additional information conveyed in structural formulas is sometimes
hapter 2 Molecular Representations Structural Formulas and ondensed Structures Because organic compounds are molecular in nature, the additional information conveyed in structural formulas is sometimes
Answers To Chapter 1 In-Chapter Problems.
 Answers To Chapter In-Chapter Problems... The resonance structure on the right is better because every atom has its octet... C + C C C C C C C C C C C the second structure is hopelessly strained Chapter..
Answers To Chapter In-Chapter Problems... The resonance structure on the right is better because every atom has its octet... C + C C C C C C C C C C C the second structure is hopelessly strained Chapter..
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Elimination. S N 2 in synthesis. S N 2 and E2. Kinetics. Mechanism bimolecular
 bimolecular B: limination B * 1 Kinetics 2 ate determining step involves both reactants rate = k [base] [-] Second order kinetics 2 B + 2 = limination, 2 nd order 2 3 2 4 Zaitsev s ule In some cases a
bimolecular B: limination B * 1 Kinetics 2 ate determining step involves both reactants rate = k [base] [-] Second order kinetics 2 B + 2 = limination, 2 nd order 2 3 2 4 Zaitsev s ule In some cases a
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Aromatic compounds do not react like other alkenes. With an appropriate catalyst, however, benzene will react
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Aromatic compounds do not react like other alkenes 2 Fe 3 2 Does not form A major part of the problem for this reaction is the product has lost all aromatic stabilization,
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Aromatic compounds do not react like other alkenes 2 Fe 3 2 Does not form A major part of the problem for this reaction is the product has lost all aromatic stabilization,
CHEM 3013 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I LECTURE NOTES
 M 3013 OAI MIST I LTU OTS 1 APT 1 1. Atomic orbitals a. eisenberg Uncertainty Principle The exact position of an electron cannot be specified; only the probability that it occupies a certain position of
M 3013 OAI MIST I LTU OTS 1 APT 1 1. Atomic orbitals a. eisenberg Uncertainty Principle The exact position of an electron cannot be specified; only the probability that it occupies a certain position of
Answers To Chapter 1 Problems.
 Answers To Chapter Problems.. (a) Both and in amides have lone pairs that can react with electrophiles. When the reacts with an electrophile +, a product is obtained for which two good resonance structures
Answers To Chapter Problems.. (a) Both and in amides have lone pairs that can react with electrophiles. When the reacts with an electrophile +, a product is obtained for which two good resonance structures
Chapter 13 Reactions of Arenes Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 . 13 hapter 13 eactions of Arenes lectrophilic Aromatic ubstitution lectrophiles add to aromatic rings in a fashion somewhat similar to the addition of electrophiles to alkenes. ecall: 3 4 Y 1 4 2 1 δ
. 13 hapter 13 eactions of Arenes lectrophilic Aromatic ubstitution lectrophiles add to aromatic rings in a fashion somewhat similar to the addition of electrophiles to alkenes. ecall: 3 4 Y 1 4 2 1 δ
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. Meaning of Organic?
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Meaning of Organic? Initially scientists believed there was a special force in living organisms -this was assumed the unique component of organic material In 1828 Wöhler synthesized urea
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Meaning of Organic? Initially scientists believed there was a special force in living organisms -this was assumed the unique component of organic material In 1828 Wöhler synthesized urea
CHEMISTRY MIDTERM # 2 ANSWER KEY July 10, 2002
 EMISTRY 314-81 MIDTERM # 2 ANSWER KEY July 10, 2002 Statistics: Average: 47 pts (67%); ighest: 69 pts (99%); Lowest: 26 pts (37%) Number of students performing at or above average: 12 (46%) 1. (7 pts)
EMISTRY 314-81 MIDTERM # 2 ANSWER KEY July 10, 2002 Statistics: Average: 47 pts (67%); ighest: 69 pts (99%); Lowest: 26 pts (37%) Number of students performing at or above average: 12 (46%) 1. (7 pts)
1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?.
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
Carbon and Its Compounds
 Chapter 1 Carbon and Its Compounds Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 1.2 Organic Molecules from the Inside Out I: The Modelling of Atoms Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 2 s orbitals:
Chapter 1 Carbon and Its Compounds Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 1.2 Organic Molecules from the Inside Out I: The Modelling of Atoms Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 2 s orbitals:
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model.
 Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model. Determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar based
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model. Determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar based
Constructing a MO of NH 3. Nitrogen AO symmetries are
 Constructing a MO of NH 3 Nitrogen AO symmetries are To develop a MO scheme for NH 3 assume that only the 2s and2p orbitals of nitrogen interact with the hydrogen 1s orbitals (i.e., the nitrogen 1s orbital
Constructing a MO of NH 3 Nitrogen AO symmetries are To develop a MO scheme for NH 3 assume that only the 2s and2p orbitals of nitrogen interact with the hydrogen 1s orbitals (i.e., the nitrogen 1s orbital
Introduction to Aromaticity
 Introduction to Aromaticity Historical Timeline: 1 Spotlight on Benzene: 2 Early 19 th century chemists derive benzene formula (C 6 H 6 ) and molecular mass (78). Carbon to hydrogen ratio of 1:1 suggests
Introduction to Aromaticity Historical Timeline: 1 Spotlight on Benzene: 2 Early 19 th century chemists derive benzene formula (C 6 H 6 ) and molecular mass (78). Carbon to hydrogen ratio of 1:1 suggests
Reactions. Reactions. Elimination. 2. Elimination Often competes with nucleophilic substitution. 2. Elimination Alkyl halide is treated with a base
 eactions 1 eactions 2 2. limination Alkyl halide is treated with a base B: 2. limination ften competes with nucleophilic substitution LIMINATIN Nu: SUBSTITUTIN Nu Bimolecular B: limination B * * 3 Kinetics
eactions 1 eactions 2 2. limination Alkyl halide is treated with a base B: 2. limination ften competes with nucleophilic substitution LIMINATIN Nu: SUBSTITUTIN Nu Bimolecular B: limination B * * 3 Kinetics
Chemistry. for the life and medical sciences. Mitch Fry and Elizabeth Page. second edition
 hemistry for the life and medical sciences Mitch Fry and Elizabeth Page second edition ontents Preface to the second edition Preface to the first edition about the authors ix x xi 1 elements, atoms and
hemistry for the life and medical sciences Mitch Fry and Elizabeth Page second edition ontents Preface to the second edition Preface to the first edition about the authors ix x xi 1 elements, atoms and
Pyrrole reaction. Assis.Prof.Dr.Mohammed Hassan Lecture 4
 Pyrrole reaction Assis.Prof.Dr.Mohammed assan Lecture 4 Acidic properties of pyrrole Due to participation of lone pair in aromaticity), pyrrole has exceptionally strong acidic properties It can react with
Pyrrole reaction Assis.Prof.Dr.Mohammed assan Lecture 4 Acidic properties of pyrrole Due to participation of lone pair in aromaticity), pyrrole has exceptionally strong acidic properties It can react with
2. A triple Diels-Alder reaction followed by a triple retro Diels Alder reaction give this interesting product:
 Lecture 8 October 6, 2011 Last time we talked a lot about highly reactive dienes, especially those developed by the group of Sam Danishefsky. One more example of an interesting diene is isobenzofuran:
Lecture 8 October 6, 2011 Last time we talked a lot about highly reactive dienes, especially those developed by the group of Sam Danishefsky. One more example of an interesting diene is isobenzofuran:
CURVED ARROW FORMALISM
 . ELETR DELALZAT AD RESAE LEARG BJETVES To introduce the concept of electron delocalization from the perspective of molecular orbitals, to understand the relationship between electron delocalization and
. ELETR DELALZAT AD RESAE LEARG BJETVES To introduce the concept of electron delocalization from the perspective of molecular orbitals, to understand the relationship between electron delocalization and
Chapter 22: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3. Nitrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic
 hapter 22: Amines. rganic derivatives of ammonia, 3. itrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic 22.1: Amines omenclature. (please read) sp 3 Amines are classified
hapter 22: Amines. rganic derivatives of ammonia, 3. itrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic 22.1: Amines omenclature. (please read) sp 3 Amines are classified
Organic Chemistry. Second Edition. Chapter 18 Aromatic Compounds. David Klein. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e
 Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 18 Aromatic Compounds Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 18.1 Introduction to Aromatic Compounds
Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 18 Aromatic Compounds Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 18.1 Introduction to Aromatic Compounds
CHEM Aromatic Chemistry. LECTURE 1 - Aromaticity
 1 CHEM40003 Aromatic Chemistry LECTURE 1 - Aromaticity Alan C. Spivey a.c.spivey@imperial.ac.uk May 2018 2 Format and scope of presentation Aromaticity: Historical perspective (Kekulé) Characteristics,
1 CHEM40003 Aromatic Chemistry LECTURE 1 - Aromaticity Alan C. Spivey a.c.spivey@imperial.ac.uk May 2018 2 Format and scope of presentation Aromaticity: Historical perspective (Kekulé) Characteristics,
Version 188 Exam 2 mccord (51600) 1
 Version 188 Exam 2 mccord (51600) 1 This print-out should have 35 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. l I l l 001 3.0 points
Version 188 Exam 2 mccord (51600) 1 This print-out should have 35 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. l I l l 001 3.0 points
3) The delocalized π system in benzene is formed by a cyclic overlap of 6 orbitals. A) s B) p C) sp D) sp2 E) sp3
 Chapter 8 Questions 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? A) All of the carbon atoms are sp hybridized. B) It has delocalized electrons. C) The carbon-carbon bond lengths are
Chapter 8 Questions 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? A) All of the carbon atoms are sp hybridized. B) It has delocalized electrons. C) The carbon-carbon bond lengths are
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH
 C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE The Ionic Bond Formation of Ions The
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE The Ionic Bond Formation of Ions The
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam
 AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for
Chapter 01 Covalent Bonding and Shapes of Molecules. Atomic Structure. Chapter 01 Topics. Structure. Atomic Structure. Subatomic Particles
 hapter 01 ovalent Bonding and Shapes of Molecules EM 240: Fall 2016 Prof. Greg ook hapter 01 Topics Mostly a review of general chemistry Atomic Structure Lewis Models and Bonding Bonding and Shapes of
hapter 01 ovalent Bonding and Shapes of Molecules EM 240: Fall 2016 Prof. Greg ook hapter 01 Topics Mostly a review of general chemistry Atomic Structure Lewis Models and Bonding Bonding and Shapes of
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 hapter 8 Basic oncepts of hemical Bonding An Important Principle in hemistry The microscopic structure defines the properties of matter at our mesoscopic level. Ex. Graphite and Diamond (both are pure
hapter 8 Basic oncepts of hemical Bonding An Important Principle in hemistry The microscopic structure defines the properties of matter at our mesoscopic level. Ex. Graphite and Diamond (both are pure
CHAPTER 9 COVALENT BONDING: ORBITALS 323
 APTER 9 OVALET BODIG: ORBITALS 323 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 2 3 O * * 2 o; most of the carbons are not in the same plane since a majority of carbon atoms exhibit a tetrahedral structure (19.5 bond angles).
APTER 9 OVALET BODIG: ORBITALS 323 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 2 3 O * * 2 o; most of the carbons are not in the same plane since a majority of carbon atoms exhibit a tetrahedral structure (19.5 bond angles).
Chapter 1: Structure Determines Properties 1.1: Atoms, Electrons, and Orbitals
 hapter 1: Structure Determines Properties 1.1: Atoms, Electrons, and rbitals Molecules are made up of atoms Atoms- protons- (+)-charge, mass = 1.676 X 10-7 kg neutrons- no charge, mass = 1.6750 X 10-7
hapter 1: Structure Determines Properties 1.1: Atoms, Electrons, and rbitals Molecules are made up of atoms Atoms- protons- (+)-charge, mass = 1.676 X 10-7 kg neutrons- no charge, mass = 1.6750 X 10-7
Chapter 3. Orbitals and Bonding
 Chapter 3. Orbitals and Bonding What to master Assigning Electrons to Atomic Orbitals Constructing Bonding and Antibonding Molecular Orbitals with Simple MO Theory Understanding Sigma and Pi Bonds Identifying
Chapter 3. Orbitals and Bonding What to master Assigning Electrons to Atomic Orbitals Constructing Bonding and Antibonding Molecular Orbitals with Simple MO Theory Understanding Sigma and Pi Bonds Identifying
Organic Chemistry CHM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Structure & Shape of Organic Molecules - Chapter 1 (Wade)
 rganic hemistry M 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, al Poly Pomona Structure & Shape of rganic Molecules - hapter 1 (Wade) rganic (living things, chemistry of carbon) Examples of rganic ompounds: Inorganic (rocks,
rganic hemistry M 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, al Poly Pomona Structure & Shape of rganic Molecules - hapter 1 (Wade) rganic (living things, chemistry of carbon) Examples of rganic ompounds: Inorganic (rocks,
antidisestablishmenttarianism an-ti-dis-es-tab-lish-ment-ta-ri-an-ism
 What do you do when you encounter a very long, difficult word? 1 antidisestablishmenttarianism break it up into syllables: an-ti-dis-es-tab-lish-ment-ta-ri-an-ism meaning: antidisestablishmenttarianism
What do you do when you encounter a very long, difficult word? 1 antidisestablishmenttarianism break it up into syllables: an-ti-dis-es-tab-lish-ment-ta-ri-an-ism meaning: antidisestablishmenttarianism
Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds 5.1 Structure of Benzene: The Kekule Proposal Mid-1800s, benzene was known to have the molecular formula C 6 6. Benzene reacts with 2 in the presence of iron to give substitution
Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds 5.1 Structure of Benzene: The Kekule Proposal Mid-1800s, benzene was known to have the molecular formula C 6 6. Benzene reacts with 2 in the presence of iron to give substitution
Valence electrons octet rule. Lewis structure Lewis structures
 Lewis Dot Diagrams Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. An element with a full octet of valence electrons has a stable configuration. The tendency of bonded atoms
Lewis Dot Diagrams Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. An element with a full octet of valence electrons has a stable configuration. The tendency of bonded atoms
CHEMISTRY 31 Name: KEY Exam #1 100 pts 1. (6 pts) Provide the complete IUPAC name for each of the following compounds:
 CEMISTRY 31 ame: KEY Exam #1 100 pts 1. (6 pts) Provide the complete IUPAC name for each of the following compounds: (1S,3S)-1-bromo-3-butylcyclopentane 3,4-diethyl-2,2-dimethyloctane 1-cyclopropyl-2-methylcyclobutane
CEMISTRY 31 ame: KEY Exam #1 100 pts 1. (6 pts) Provide the complete IUPAC name for each of the following compounds: (1S,3S)-1-bromo-3-butylcyclopentane 3,4-diethyl-2,2-dimethyloctane 1-cyclopropyl-2-methylcyclobutane
Organic Chemistry Lecture I. Dr. John D. Spence
 HEMISTRY 3 Organic hemistry Lecture I Dr. John D. Spence jdspence@scu.edu jspence@csus.eduedu http://www.csus.edu/indiv/s/spencej What is Organic hemistry? 780 s hemistry of compounds from living organisms
HEMISTRY 3 Organic hemistry Lecture I Dr. John D. Spence jdspence@scu.edu jspence@csus.eduedu http://www.csus.edu/indiv/s/spencej What is Organic hemistry? 780 s hemistry of compounds from living organisms
