Alcohols. Ethanol Production. 182 minutes. 181 marks. Page 1 of 26
|
|
|
- Shannon Franklin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ..0 Alcohols Ethanol Production 8 minutes 8 marks Page of 6
2 M. Condition = two from yeast (anywhere in question) Air excluded or sterile / clean () Ignore references to pressure / temperature / aqueous / dark / high alcohol conc Temperature too low inactivates / deactivates enzymes or reaction too slow () Temperature too high destroys or denatures yeast / enzymes () Not kills enzymes; not deactivates here Advantage = sugar / glucose / carbohydrate is renewable resource / source () Advantage = production uses low level technology / cheap equipment () Ignore references to energy Do not allow contra-arguments about ethene C 6 6 C C + C balanced () C + C + balanced () Allow C 6 but penalise C once [8] M. (a) % =.6 % () If % not calculated only M available C () =. =. =. Ratio: : 0: ( C 0 ) () If arithmetic error in any result lose M If percentage composition calculation done zero (b) (i) Type of alcohol: Tertiary () Reason: No hydrogen atom on central carbon () Penalise missing bonds / incorrect bonds once per paper Page of 6
3 (c) (i) Aldehyde () Ignore named aldehydes or their structures, penalise wrong named compound C C C C + [] C C C C + () Balanced () C 0 is K as a reactant [] can be over arrow C 7 C not accepted for product, but C C C is K If use C or C compounds no marks in C.E of wrong alcohol (iii) Name Butanoic acid () Structure: C C C C () mark conseq. or as stated (d) Advantage: Fast reaction R pure product R continuous process R cheap on manpower R high yield, 00% alcohol () Disadvantage: igh technology R ethene from non renewable source R expensive equipment not just costly () Not answers based on fermentation (e) [8] M. (a) (i) addition of water / steam () Ignore to the reaction Page of 6
4 Advantage: low technology renewable feedstock / resource allowed for use in drinks, perfumes considered to be green () any one NT infinite or non-finite resource Disadvantage: slow low yield significant land use has to be distilled labour intensive any one Ignore yeast NT (unqualified) batch production NT impure product (b) (i) Structure of aldehyde Structure of carboxylic acid () () NT C C NT C C Penalise incorrect R group once Reagent: sodium (/ potassium) dichromate (VI) (VI not essential) () M Conditions: acidified or sulphuric acid () Can be with reagent M (heat under reflux) () M r correct formula for M and M M depends on M (but M correct from Cr 7, K Cr 7 etc M mark independent Credit KMn for M Ignore T and P for M (c) (i) () () (d) (i) Al or S or P () Name or formula Page of 6
5 For M the + can be on or if - used For M the arrow must go to the + or to oxygen Synchronous loss without carbocation loses carbocation structure mark; can still score ¾ i.e. penalise M [] M. (a) ethan(e)-,-diol R,-ethan(e)diol () antifreeze () R production of Terylene / polyester feedstock for polyester / PET NT surfactant NT plasticizer NT solvent NT de-icer (b) Reaction or steam () Reaction () NT air Ignore reaction Reaction () Reaction N () For Reaction ; credit dil S R S (aq) R Cl (aq) but NT steam and NT Na(aq) Page of 6
6 (c) Penalise M incorrect δ+ / δ Penalise δ on alkene (M) Penalise dots on bonds once Penalise M (structure) for use of wrong alkene Penalise M for use of Br (d) Water R aqueous solution R (aq) in equation () Yeast R enzyme/zymase R T C but T not below 0 C and allow warm N.B. yeast and T=60 con Ignore p Ignore anaerobic / oxygen Ignore time Ignore pressure M M C 6 6 C (or C C ) + C Allow C if balanced equation M R M needs the use of good English and correct chemistry to gain credit M M: The rate of fermentation is slower () R The rate of hydration is faster QoL R (The rate of) fermentation is slow and (the rate of) hydration is fast reference correctly to time rather than rate gains credit M: The product of fermentation is less pure or lower purity R The product of hydration is more pure or higher purity R The product of fermentation is impure and that of hydration is pure R Specific reference to 0 % versus 90 00% R correct reference to higher or lower yield [] Page 6 of 6
7 (r C 6 or C C ) (In equation, allow additional on both sides of the equation) M. (a) (i) C 6 6 C + C (r C C ) (Ignore state symbols in the equation) Fermentation (b) (i) C + C + C or carbon monoxide or C or carbon NLY (iii) C + N C + N R N N + R N + C N + C R C N 8C + ½N + 9 (c) Elimination (Penalise additional words such as electrophilic ) M structure of protonated alcohol (allow C C ) M arrow to show breakage of C bond on protonated alcohol M structure of carbocation (allow ) M arrow from correct C bond on carbocation (penalise sticks once only for structures M and M) (synchronous mechanism using correct structure required for M, loses M) Page 7 of 6
8 (d) C 6 C + (d) Silver R silver-based (NT silver oxide) M correct structure for epoxyethane (Allow C =C or C in the equation) (Credit the structure of epoxyethane independently) (Credit M provided has been used and the atoms balance, but the structure is poor e.g. C or C C but NT C C) [] M6. (a) M fermentation M dehydration or elimination (b) (i) yeast R zymase R an enzyme concentrated sulphuric or phosphoric acid (penalise aqueous or dilute as a contradiction) (c) (i) primary or sugar or glucose or ethanol is renewable R ethanol does not contain sulphur-containing impurities R ethanol produces less pollution or is less smoky or less C/C (the objective is a positive statement about ethanol) (penalise the idea that ethanol is an infinite source or vague statements that ethanol has less impurities) (penalise the idea that ethanol produces no pollution) (e) Addition (ignore self or chain as a preface to addition ) (penalise additional) [8] Page 8 of 6
9 (penalise C 6 once only in this question) M7. (a) (i) C 6 6 C + C ; Concentrated S R concentrated P R Al ; (penalise aqueous or dilute as a contradiction) C C + R C C = C + ; (b) (penalise C. C and C -C and C : C for ethene) Nickel R Ni R platinum R Pt R palladium R Pd; ydrogen R ; (c) (i) C 8 nly; C 9 7 nly; (empirical formula is not consequential on molecular formula) (An unsaturated compound) contains (at least) one double bond R Contains C=C; (must be a positive statement) Page 9 of 6
10 (iii) M: Bromine water R Br (aq) R Bromine R Br ; (penalise bromide water, but mark on) M: decolourised or goes colourless R from brown/red/orange/yellow to colourless; (Must be colourless not clear for M) (chemical error if no reagent or wrong reagent, loses both marks) (credit KMn for M, (purple) to colourless for M (if acidified) R (purple) to brown/brown precipitate (if alkaline or unspecified) (No credit for hydrogen or iodine as reagents) [0] Page 0 of 6
11 M8. (a) M: aqueous or solution in water or (aq) in the equation M: yeast or zymase (do not credit an enzyme unless qualified) M: anaerobic/absence of oxygen/absence of air or neutral p/p value 6 8 M: T in the range 0 0 C only M: fermentation (ignore references to pressure) (ignore uv light) M6: C 6 6 C C + C (ignore state symbols but penalise M if the state symbol in the equation contradicts) M7: C C + C + (credit use of C ) (penalise use of C 6 once only in M6 or M7) (b) M: dehydration is the elimination of water or removal of combined water or qualified loss of/removal of water e.g. from a compound/molecule/alcohol or removal of and in the ratio : from a compound/ molecule/alcohol (do not credit from a substance ) (do not credit removal of water molecules unless qualified from a compound/molecule etc.) M: Catalyst = concentrated S or concentrated/oily/syrupy phosphoric acid or aluminium oxide/ pumice/porous pot M: C C C=C + (credit use of C ) (penalise use of C 6 here unless already penalised in part(a). Possible credit as repeat error) (credit C and C =C for ethene, but penalise C C, C. C, C :C ) (ignore S if it appears on both sides of equation) Page of 6
12 (c) M: large(r) to small(er) molecules/hydrocarbons/compounds or high(er) M r alkanes to low(er) M r alkanes (+ alkenes) (+ ) M: breakage/homolysis/splitting of C C/carbon chain/carbon skeleton (do not credit breaking C bonds alone, but ignore if accompanied by C C) M: reactive intermediate is (free/alkyl) radical or radical mechanism (do not credit free radical substitution and penalise M as a contradiction if mentioned with free radical intermediates) M: any T (or range) in the range 00 to 900 C or high temperature (ignore pressure ) M: C C C C (R C 0 ) C=C + C C (R C 6 ) or C C C C (R C 0 ) C=C + (credit C and C =C for ethene, but penalise C C, C.C, C :C and note possible RE from part(b)) [] M9. (a) Ag or silver or silver-based or silver on an alumina base epoxyethane (penalise specific silver compounds) Page of 6
13 (b) electrophilic addition M: curly arrow from C=C bond towards/alongside the side of atom on -S (penalise M if arrow to S R to formal charge on of - bond) (ignore partial charges on and of S, but penalise if these are incorrect on the atom being attacked) (credit M and M if correct curly arrow to + provided the anion is present) M: curly arrow from bond towards/alongside the side of the atom on S (credit the arrow even if there are partial or formal charges on and but the structure of S is correct) M: correct structure of the carbocation (penalise use of sticks in this structure) M: curly arrow from lone pair on an individual oxygen atom of (correct formula for) hydrogensulphate ion towards/alongside C atom bearing the positive charge (insist that the an ion has the correct formula with a lone pair of electrons and a negative charge) (c) (i) ethanal correct structure for ethanal (aldehyde functional group must be drawn out) oxidation or redox [0] Page of 6
14 M0. (a) Three conditions in any order for M to M M yeast or zymase M 0 C T C M anaerobic/no oxygen/no air R neutral p M C 6 6 C + C R C 6 6 C + C (b) M Carbon-neutral Mark independently Penalise bacteria and phosphoric acid using the list principle Ignore reference to aqueous or water (i.e. not part of the list principle) r other multiples Ignore biofuel M M 6 (mol/molecules) C /carbon dioxide taken in/used/used up (to form glucose or in photosynthesis) 6 (mol/molecules) C /carbon dioxide given out due to (mol/molecules) C /carbon dioxide from fermentation/ Process and (mol/molecules) C /carbon dioxide from combustion/process It is NT sufficient in M and M for equations alone without commentary or annotation or calculation (c) M (could be scored by a correct mathematical expression) (Sum of) bonds broken (Sum of) bonds made/formed = Δ R (Σ) B reactants (Σ) B products = Δ (where B = bond enthalpy/bond energy) For M there must be a correct mathematical expression using Δ or enthalpy change M Reactants = (+) 79 R Products = ( ) 70 Page of 6
15 M verall = 0 (kj mol ) (This is worth marks) Award full marks for correct answer. Ignore units. M is for either value underlined M is NT consequential on M Award mark NLY for +0 Candidates may use a cycle and gain full marks. M Mean bond enthalpies are not specific for this reaction R they are average values from many different compounds/molecules Do not forget to award this mark (d) M q = m c ΔT (this mark for correct mathematical formula) M M M = 6688 (J) R (kj) R 6.69 (kj) R 6.7 (kj) 0.6g is 0.0 mol therefore Δ = 669 kj mol R 670 kjmol R kj mol Award M, M and M for correct answer to the calculation Penalise M NLY if correct answer but sign is incorrect In M, do not penalise incorrect cases in the formula If m = 0.6 or m = 00.6 R if ΔT = 8, CE and penalise M and M If c =.8 (leads to 7696) penalise M NLY and mark on for M = R 770 Ignore incorrect units in M Incomplete combustion Do not forget to award this mark. Mark independently [] M. (a) to neutralise stomach acidity R as an antacid R eases indigestion/heartburn Ignore milk of magnesia Credit suitable reference to indigestion/laxative/relief of constipation Page of 6
16 (b) (i) an electron acceptor R (readily) gains/accepts/receives electron(s) NT an electron pair acceptor Ignore removes/takes away/attracts electrons Br NLY Ignore bromine Apply the list principle (iii) S e S + R S e S + Ignore state symbols Ignore absence of negative charge on electron r multiples of equations (c) (i) (acid) catalyst R catalyses (the reaction) R to speed up the reaction/increase the rate (of reaction) Ignore provides + ions Accept phonetic spelling M must show an arrow from the double bond towards the atom of the bond R on a compound with molecular formula for S (or accept S here) M could be to an + ion and M an independent bond break on a compound with molecular formula for S or S Page 6 of 6
17 M M M must show the breaking of the bond. must show an arrow from the lone pair of electrons on the correct oxygen of the negatively charged ion towards the positively charged carbon atom. is for the structure of the carbocation. NB The arrows here are double-headed M Ignore partial charges unless wrong M NT S (iii) For M, credit as shown or : S NLY with the negative charge anywhere on this ion R correctly drawn out with the negative charge placed correctly on oxygen Max marks for wrong reactant Do not penalise the use of sticks Primary R (alcohol) (iv) Displayed formula for ethanoic acid, C C All the bonds must be drawn out and this includes the bond Ignore bond angles. [] Page 7 of 6
18 M. (a) M C 6 6 C C + C (C ) Mark independently For M and M ignore state symbols and credit multiples For M and M penalise C 6 once only M fermentation M C C + C + (C ) M A specified process e.g. planting / harvesting / transport / extracting sugar / distilling ethanol solution / fertiliser production etc. M The specified process uses / burns (fossil) fuel that releases C For M, releases / increases carbon emissions is insufficient as an alternative to releases C Page 8 of 6
19 (b) M sodium or potassium hydroxide / Na / K Mark on to M from hydroxide ion M depends on correct M Ignore if K/ warm / heat / reflux and aqueous or (aq) or water For M ignore dilute For M penalise T > 00 C M nucleophilic substitution Acidified K/Na or S with K/Na loses M and M For M, both words required NB The arrows here are double-headed M must show an arrow from the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom of the negatively charged hydroxide ion to the C atom. Penalise M if covalent Na / K is used Penalise one mark from M or M if half-headed arrows are used M must show the movement of a pair of electrons from the C Br bond to the Br atom. Mark M independently provided it is from their original molecule. Penalise M for formal charge on C of the C Br or incorrect partial charges on C Br Penalise once only for a line and two dots to show a bond. For M and M, award full marks for an S N mechanism For M and M, maximum of marks if wrong reactant is used. Penalise M if an extra arrow is drawn from the Br of the C Br bond to, for example, K + span> Do not penalise the use of sticks M6 ne statement from The yield is (very) low / not a high yield R elimination occurs / ethene formed The rate of reaction slow Bromoethane has to be manufactured / made first Bromoethane is expensive For M6 ignore references to other costs and expenses 6 Page 9 of 6
20 (c) M concentrated phosphoric acid / conc. P R concentrated sulfuric acid / conc. S Answers in any order Ignore reference to support medium in M M hydration or (electrophilic) addition For M and M any two from Do not apply the list principle to these three chosen criteria in M and M Excess ethene R Excess steam / water / R remove the ethanol as it forms R recycle the ethene Specified Pressure 0 atm P 00 atm R 000 kpa P 0000 kpa R MPa P 0 MPa ightemperature unless they give a value that is not in the ranges given here; R 00 C T 600 C R 70 K T 870 K Accept a reference to low temperature if they specify a correct temperature range or a correct temperature in the range [] Page 0 of 6
21 M. (a) M Safety (in Process ) Sodium hydroxide / alkali is corrosive / harmful / caustic or sodium hydroxide is alkali(ne) Ignore references to chromium compounds R Bromine compounds are toxic / poisonous Carbon-neutral alone is insufficient for M M Environmental Ignore references to greenhouse gases Process could be used as a carbon sink / for carbon capture R uses waste / recycled C / C from the factory / C from the bioethanol (or biofuel) production R reduces or limits the amount of C released / given out (into the atmosphere) R Process uses renewable glucose / renewable resource(s) Page of 6
22 (b) (i) M nucleophilic substitution For M, both words required M must show an arrow from the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom of the negatively charged hydroxide ion to the C atom. Penalise M if covalent Na / K is used Penalise one mark from M or M if half-headed arrows are used M must show the movement of a pair of electrons from the C Br bond to the Br atom. Mark M independently provided it is from the original molecule Penalise M for formal charge on C of the C Br or incorrect partial charges on C Br Penalise once only for a line and two dots to show a bond. For M and M award full marks for an S N mechanism For M and M, maximum of marks for the mechanism if wrong reactant is used. Penalise M if an extra arrow is drawn from the Br of the C Br bond to, for example, K + Accept the correct use of sticks NB The arrows here are double-headed M B M C M A (c) M fermentation Mark M to M independently Three conditions in any order for M to M Penalise bacteria and phosphoric acid using the list principle M (enzymes from) yeast or zymase M C T C R 98 K T K Ignore reference to aqueous or water, closed container, pressure, lack of oxygen, concentration of ethanol and batch process (i.e. not part of the list principle) M anaerobic / no oxygen / no air R neutral p Page of 6
23 (d) M primary R (alcohol) Mark independently M acidified potassium or sodium dichromate For M, it must be a whole reagent and/or correct formulae R S / K Cr 7 R + / K Cr 7 Do not penalise incorrect attempt at formula if name is correct or vice versa Accept phonetic spelling If oxidation state given in name, it must be correct. For M accept acidified potassium manganate(vii) R correct combination of formula and name M C C C C + [] CC C C + For M structures must be correct and not molecular formula [] M. (a) (i) C Atoms in any order Accept a clear indication that C 6 6 yields C as the answer No peak / no absorption / no C= in the range 680 to 70 (cm ) (suggesting no evidence of C=) Allow the words dip, spike, low transmittance and trough as alternatives for absorption Ignore references to other wavenumbers (b) M C 6 6 C C + C Penalise (C ) 6 Allow multiples of the equation in M Either order M (enzymes from) yeast or zymase M C T C R 98 K T K For M and M Ignore aqueous Ignore anaerobic / absence of oxygen Ignore controlled p Ignore warm Page of 6
24 (c) (i) Displayed formula for C C All bonds must be drawn out, but ignore bond angles e Ignore state symbols Negative charge on electron not essential Accept multiples Accept electrons subtracted from RS (iii) C C + C C e (C 6 or C ) Ignore state symbols Negative charge on electron not essential Accept multiples Accept electrons subtracted from LS (iv) M Acidified potassium or sodium dichromate For M, it must be a whole reagent and / or correct formulae R S / K Cr 7 R + / K Cr 7 etc. Do not penalise incorrect attempt at formula if name is correct or vice versa R correct combination of formula and name If oxidation state given in name, it must be correct, but mark on from an incorrect attempt at a correct reagent. M (requires an attempt at M) orange to green Credit acidified potassium chromate(vi) / S + K Cr Possible alternative M (acidified) potassium manganate(vii) R KMn / S M purple to colourless ther alternatives will be accepted but M is dependent on M in every case M requires an attempt at a correct reagent for M Ignore reference to states Page of 6
25 (d) (i) An activity which has no net / overall (annual) carbon emissions to the atmosphere / air The idea that the carbon / C given out equals the carbon / C that was taken in from the atmosphere / air R An activity which has no net / overall (annual) greenhouse gas emissions to the atmosphere / air. Answer must refer to the atmosphere or air R (iii) There is no change in the total amount of carbon dioxide / carbon /greenhouse gas present in the atmosphere / air Renewable / sustainable NLY Ignore references to global warming or greenhouse gases Any one statement about this process from Subject to weather / climate Ignore batch R Depletes food supply R the land use for (specified) food R Requires use of / uses more fossil fuels R Not carbon-neutral R C produced during a named process (eg harvest, transport etc.) R Slow process / slow rate of reaction / takes a long time (to grow crops) R This route leads to the production of a mixture of water and ethanol / impure ethanol that requires separation / further processing [] Page of 6
26 Page 6 of 6
Alkenes and Alcohols Answers
 Alkenes and Alcohols Answers Chemistry - AQA GCE Mark Scheme 200 June series Q Part Sub Part Marking Guidance Mark Comments 8 a Three conditions in any order for M to M3 4 Mark independently M M2 M3 yeast
Alkenes and Alcohols Answers Chemistry - AQA GCE Mark Scheme 200 June series Q Part Sub Part Marking Guidance Mark Comments 8 a Three conditions in any order for M to M3 4 Mark independently M M2 M3 yeast
Deduce the empirical and molecular formulas of the carboxylic acid formed. Empirical formula =... Molecular formula =... (4)
 Glucose can decompose in the presence of microorganisms to form a range of products. One of these is a carboxylic acid (M r = 88.0) containing 40.9% carbon and 4.5% hydrogen by mass. (a) Deduce the empirical
Glucose can decompose in the presence of microorganisms to form a range of products. One of these is a carboxylic acid (M r = 88.0) containing 40.9% carbon and 4.5% hydrogen by mass. (a) Deduce the empirical
M1.B [1] M2.B [1] OR H PO 4. M1 (1) heat (1) M2 OR 150 C C Condition mark linked to correct reagent but award M2 if H 2.
![M1.B [1] M2.B [1] OR H PO 4. M1 (1) heat (1) M2 OR 150 C C Condition mark linked to correct reagent but award M2 if H 2. M1.B [1] M2.B [1] OR H PO 4. M1 (1) heat (1) M2 OR 150 C C Condition mark linked to correct reagent but award M2 if H 2.](/thumbs/87/97087846.jpg) Penalise reagent and condition if dilute H S 4 / H P 4 4 M.B [] M.B [] M. (a) Reaction : NaH KH () M alcohol (ic) ethanol (ic)() M ignore heat Condition mark linked to correct reagent but award M if H
Penalise reagent and condition if dilute H S 4 / H P 4 4 M.B [] M.B [] M. (a) Reaction : NaH KH () M alcohol (ic) ethanol (ic)() M ignore heat Condition mark linked to correct reagent but award M if H
Chapter 16. Answers to examination-style questions. Answers Marks Examiner s tips. 1 (a) (i) C 6 H 12 O 6 2C 2 H 5 OH + 2CO 2 (ii) fermentation
 Chapter 6 (a) (i) C 6 O 6 C 5 O + CO (ii) fermentation (b) (i) C 5 O + 3O CO + 3 O (ii) CO or carbon monoxide or C or carbon (a) (i) potassium (or sodium) dichromate(vi) or correct formula or potassium
Chapter 6 (a) (i) C 6 O 6 C 5 O + CO (ii) fermentation (b) (i) C 5 O + 3O CO + 3 O (ii) CO or carbon monoxide or C or carbon (a) (i) potassium (or sodium) dichromate(vi) or correct formula or potassium
Alcohols. Ethanol Production. 182 minutes. 181 marks. Page 1 of 25
 3..10 Alcohols Ethanol Production 18 minutes 181 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Ethanol is produced commercially by fermentation of aqueous glucose, C 6 H 1 O 6 State two conditions, other than temperature, which
3..10 Alcohols Ethanol Production 18 minutes 181 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Ethanol is produced commercially by fermentation of aqueous glucose, C 6 H 1 O 6 State two conditions, other than temperature, which
Alcohols. Nomenclature. 57 minutes. 57 marks. Page 1 of 9
 ..0 Alcohols Nomenclature 57 minutes 57 marks Page of 9 M. (a) % O =.6 % () If % O not calculated only M available C O () = 5. =.5 =.5 Ratio: : 0: ( C 0 O) () If arithmetic error in any result lose M If
..0 Alcohols Nomenclature 57 minutes 57 marks Page of 9 M. (a) % O =.6 % () If % O not calculated only M available C O () = 5. =.5 =.5 Ratio: : 0: ( C 0 O) () If arithmetic error in any result lose M If
3.5 Alcohols H H C C. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 H H. Bond angles in Alcohols. Boiling points. Different types of alcohols H 2 C CH 2 CH 2
 3.5 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
3.5 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
3.2.9 Alkenes. Polymerisation. 152 minutes. 149 marks. Page 1 of 22
 ..9 Alkenes Polymerisation 5 minutes 49 marks Page of M. Oxygen or air () Can score from the equation Silver catalyst () Linked to process: e.g. Consequence of leaks etc. () Hazard = flammable or explosive
..9 Alkenes Polymerisation 5 minutes 49 marks Page of M. Oxygen or air () Can score from the equation Silver catalyst () Linked to process: e.g. Consequence of leaks etc. () Hazard = flammable or explosive
10.2 ALCOHOLS EXTRA QUESTIONS. Reaction excess conc, H SO 180 C
 10.2 ALOOLS EXTRA QUESTIONS 1. onsider the reaction scheme below which starts from butanone. N Reaction 1 3 2 3 3 2 3 O Reaction 2 O A 3 O B 2 3 excess conc, SO 180 2 4 but 1 ene and but 2 ene (a) When
10.2 ALOOLS EXTRA QUESTIONS 1. onsider the reaction scheme below which starts from butanone. N Reaction 1 3 2 3 3 2 3 O Reaction 2 O A 3 O B 2 3 excess conc, SO 180 2 4 but 1 ene and but 2 ene (a) When
Page 2. M1.(a) P 3,3 dimethylbut 1 ene OR accept 3,3 dimethylbutene Ignore absence of commas, hyphens and gaps Require correct spelling Q OR
 M.(a) P 3,3 dimethylbut ene OR accept 3,3 dimethylbutene Ignore absence of commas, hyphens and gaps Require correct spelling Q OR 3 chloro 2,2 dimethylbutane accept 2 chloro 3,3 dimethylbutane In Q, chloro
M.(a) P 3,3 dimethylbut ene OR accept 3,3 dimethylbutene Ignore absence of commas, hyphens and gaps Require correct spelling Q OR 3 chloro 2,2 dimethylbutane accept 2 chloro 3,3 dimethylbutane In Q, chloro
3.2.9 Alkenes. Addition Reactions. 271 minutes. 268 marks. Page 1 of 39
 ..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 7 minutes 68 marks Page of 9 M. (a) Electrophile: e pair / lone pair acceptor or e deficient species or e seeking species () For species accept atom, molecule, ion NOT +
..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 7 minutes 68 marks Page of 9 M. (a) Electrophile: e pair / lone pair acceptor or e deficient species or e seeking species () For species accept atom, molecule, ion NOT +
Unit 2. Answers to examination-style questions. Answers Marks Examiner s tips. 1 (a) heat energy change at constant pressure
 (a) heat energy change at constant pressure This is in the spec but not so well known. Learn it. (b) N 2 (g) + ½O 2 (g) N 2 O(g) (c) (i) D = (bonds broken) (bonds made) = ½(945) + (3/2)(59) 3(278) = 23
(a) heat energy change at constant pressure This is in the spec but not so well known. Learn it. (b) N 2 (g) + ½O 2 (g) N 2 O(g) (c) (i) D = (bonds broken) (bonds made) = ½(945) + (3/2)(59) 3(278) = 23
Question number 1 (a) Statement. Answer Notes Marks. 1 mark for each line correct. Fractional distillation. Cracking. Crude oil is heated
 (a) Statement Crude oil is heated Fractional distillation ( ) Cracking mark for each line correct 5 A catalyst may be used Alkenes are formed Decomposition reactions occur Fuels are obtained (b) i i ii
(a) Statement Crude oil is heated Fractional distillation ( ) Cracking mark for each line correct 5 A catalyst may be used Alkenes are formed Decomposition reactions occur Fuels are obtained (b) i i ii
Q.1 Which of the structures is/are classified as phenols?
 Alcohols 1 ALOOLS Aliphatic Aromatic general formula n 2n+1 O - provided there are no rings named as substituted alkanes by removing the final -e and adding -ol for isomers the position of the O is given
Alcohols 1 ALOOLS Aliphatic Aromatic general formula n 2n+1 O - provided there are no rings named as substituted alkanes by removing the final -e and adding -ol for isomers the position of the O is given
A mass spectrometer can be used to distinguish between samples of butane and propanal. The table shows some precise relative atomic mass values.
 Butane and propanal are compounds with M r = 58.0, calculated using data from your Periodic Table. (a) A mass spectrometer can be used to distinguish between samples of butane and propanal. The table shows
Butane and propanal are compounds with M r = 58.0, calculated using data from your Periodic Table. (a) A mass spectrometer can be used to distinguish between samples of butane and propanal. The table shows
2.8 EXTRA QUESTIONS MS. (iii) C 6 H 5 CHCl 2 / C 6 H 5 CCl 3 / C 6 H 5 CHCHC 6 H 5 / other correct possible answer (1) 1
 .8 EXTRA QUESTIONS MS 1. (i) l l / ½ l l 1 (ii) l 6 5 6 5 l 6 5 l l 6 5 l (iii) 6 5 l / 6 5 l / 6 5 6 5 / other correct possible answer 1 [4]. (a) (i) (free)radical substitution 1 (both words required
.8 EXTRA QUESTIONS MS 1. (i) l l / ½ l l 1 (ii) l 6 5 6 5 l 6 5 l l 6 5 l (iii) 6 5 l / 6 5 l / 6 5 6 5 / other correct possible answer 1 [4]. (a) (i) (free)radical substitution 1 (both words required
3.2.9 Alkenes. Addition Reactions. 271 minutes. 268 marks. Page 1 of 35
 ..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
Version 1.0: 1006 abc. General Certificate of Education examination - June series
 Version.0: 006 abc General Certificate of Education Chemistry 542 CHM3/W Introduction to Organic Chemistry Mark Scheme 2006 examination - June series Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
Version.0: 006 abc General Certificate of Education Chemistry 542 CHM3/W Introduction to Organic Chemistry Mark Scheme 2006 examination - June series Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY
 WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY enthalpy change of reaction, enthalpy change of combustion and standard molar enthalpy change of formation, Δ fh ϴ Hess s law and energy cycles concept
WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY enthalpy change of reaction, enthalpy change of combustion and standard molar enthalpy change of formation, Δ fh ϴ Hess s law and energy cycles concept
Name/CG: 2012 Term 2 Organic Chemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question
 Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Organic Chemistry Review: Topic 10 & Topic 20
 Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Cherry Hill Tuition A Level Chemistry OCR (A) Paper 9 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE CHEMISTRY A Chains, Energy and Resources F322 * OCE / 1 9 2 3 4* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE CHEMISTRY A Chains, Energy and Resources F322 * OCE / 1 9 2 3 4* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry
Organic Chemistry. Alkanes are hydrocarbons in which the carbon atoms are joined by single covalent bonds.
 Organic Chemistry Organic compounds: The branch of chemistry which deals with the study of carbon compounds is called organic chemistry. Catenation: The carbon atom has a property to undergo self linking
Organic Chemistry Organic compounds: The branch of chemistry which deals with the study of carbon compounds is called organic chemistry. Catenation: The carbon atom has a property to undergo self linking
Answer Marks Guidance
 Question number (a) molecular formula: C 4 H 8 Answer Marks Guidance empirical formula: CH 2 This is a revision of earlier chapters. (b) (i) name of mechanism: electrophilic addition Remember that reactions
Question number (a) molecular formula: C 4 H 8 Answer Marks Guidance empirical formula: CH 2 This is a revision of earlier chapters. (b) (i) name of mechanism: electrophilic addition Remember that reactions
M1. (a) Functional group (isomerism) 1
 M. (a) Functional group (isomerism) (b) M Tollens (reagent) (Credit ammoniacal silver nitrate a description of making Tollens ) (Ignore either AgNO or [Ag(NH ) 2 + ] or the silver mirror test on their
M. (a) Functional group (isomerism) (b) M Tollens (reagent) (Credit ammoniacal silver nitrate a description of making Tollens ) (Ignore either AgNO or [Ag(NH ) 2 + ] or the silver mirror test on their
Electrophilic substitution Both words needed Ignore minor misspellings 1
 M.(a) Electrophilic substitution Both words needed Ignore minor misspellings (b) (i) Sn / HCl OR H 2 / Ni OR H 2 / Pt OR Fe / HCl OR Zn / HCl OR SnCl 2 / HCl Ignore conc or dil with HCl, Allow (dil) H
M.(a) Electrophilic substitution Both words needed Ignore minor misspellings (b) (i) Sn / HCl OR H 2 / Ni OR H 2 / Pt OR Fe / HCl OR Zn / HCl OR SnCl 2 / HCl Ignore conc or dil with HCl, Allow (dil) H
Bond C=O C H C O O H. Use the enthalpy change for the reaction and data from the table to calculate a value for the H H bond enthalpy.
 Many chemical processes release waste products into the atmosphere. Scientists are developing new solid catalysts to convert more efficiently these emissions into useful products, such as fuels. One example
Many chemical processes release waste products into the atmosphere. Scientists are developing new solid catalysts to convert more efficiently these emissions into useful products, such as fuels. One example
F322 Chains, Energy and Resources
 F322 Chains, Energy and Resources 1 (a) C n 2n+2 1 ALLOW C n 2(n+1) IGNORE size of subscripts (b) (i) C 8 18 + 8½O 2 8CO + 9 2 O 1 ALLOW any correct multiples IGNORE state symbols (ii) limited supply of
F322 Chains, Energy and Resources 1 (a) C n 2n+2 1 ALLOW C n 2(n+1) IGNORE size of subscripts (b) (i) C 8 18 + 8½O 2 8CO + 9 2 O 1 ALLOW any correct multiples IGNORE state symbols (ii) limited supply of
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level. Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis
 OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
2.9 ALKENES EXTRA QUESTIONS MS. (b) Addition 1 (ignore self or chain as a preface to addition ) (penalise additional)
 2.9 ALKENES EXTRA QUESTIONS MS 1. (a) 2 6 2 4 2 1 (b) Addition 1 (ignore self or chain as a preface to addition ) (penalise additional) 2. Electrophilic addition 1 M1: curly arrow from = bond towards/alongside
2.9 ALKENES EXTRA QUESTIONS MS 1. (a) 2 6 2 4 2 1 (b) Addition 1 (ignore self or chain as a preface to addition ) (penalise additional) 2. Electrophilic addition 1 M1: curly arrow from = bond towards/alongside
Q1. Which one of the following is not a correct general formula for the non-cyclic compounds listed?
 C Step 4 : concentrated H SO 4 (Total 1 mark) Q1. Which one of the following is not a correct general formula for the non-cyclic compounds listed? A B alcohols C n H n+ O aldehydes C n H n+1 O C esters
C Step 4 : concentrated H SO 4 (Total 1 mark) Q1. Which one of the following is not a correct general formula for the non-cyclic compounds listed? A B alcohols C n H n+ O aldehydes C n H n+1 O C esters
Le Lycee Mauricien. Proposed Syllabus Chemistry (5070) - Form 5
 Le Lycee Mauricien Proposed Syllabus 2017 Chemistry (5070) - Form 5 First Term 1. Metals Properties of metals - Physical properties of metals - Structure of alloys and uses Reactivity Series - Place metals
Le Lycee Mauricien Proposed Syllabus 2017 Chemistry (5070) - Form 5 First Term 1. Metals Properties of metals - Physical properties of metals - Structure of alloys and uses Reactivity Series - Place metals
AS Organic Chemistry Revision. Part 1
 AS Organic Chemistry Revision. Part 1 2.2 Nomenclature and isomerism in organic compounds 2.2.1 understand the terms empirical, molecular and structural formulae, homologous series and functional groups;
AS Organic Chemistry Revision. Part 1 2.2 Nomenclature and isomerism in organic compounds 2.2.1 understand the terms empirical, molecular and structural formulae, homologous series and functional groups;
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 0620 CHEMISTRY
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 0620 CHEMISTRY 0620/31 Paper 3 (Extended Theory), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 0620 CHEMISTRY 0620/31 Paper 3 (Extended Theory), maximum
Chapter 10 Organic Reactions
 Chapter 0 Organic Reactions Name: Class: Date: Time: 85 minutes Marks: 85 marks Comments: Page of 32 This question is about organic compounds. (a) Ethanol burns in air. Use the correct answer from the
Chapter 0 Organic Reactions Name: Class: Date: Time: 85 minutes Marks: 85 marks Comments: Page of 32 This question is about organic compounds. (a) Ethanol burns in air. Use the correct answer from the
Alkanes and Alkenes. The Alkanes
 Alkanes and Alkenes The Alkanes Alkanes are hydrocarbons (i.e. compounds of carbon and hydrogen only). They are called saturated hydrocarbons because they contain no double bonds, and so cannot undergo
Alkanes and Alkenes The Alkanes Alkanes are hydrocarbons (i.e. compounds of carbon and hydrogen only). They are called saturated hydrocarbons because they contain no double bonds, and so cannot undergo
Question number 1 (a) (i) Answer Accept Reject Marks polyethene / polythene / polyethylene. poly(ethene) cracking M1 - bar labelled 9.
 (a) (i) (b) (i) poly(ethene) cracking M - bar labelled 9 Answer Accept Reject Marks polyethene / polythene / polyethylene M2 - drawn to correct height (boiling point/it) increases as of carbon atoms increases
(a) (i) (b) (i) poly(ethene) cracking M - bar labelled 9 Answer Accept Reject Marks polyethene / polythene / polyethylene M2 - drawn to correct height (boiling point/it) increases as of carbon atoms increases
Fractional Distillation
 ..6. Fractional Distillation minutes 09 marks Page of 4 M. (a) Missing fraction = naphtha (allow naphtha from list if not quoted separately) () Order = mineral oil (lubricating oil), gas oil (diesel),
..6. Fractional Distillation minutes 09 marks Page of 4 M. (a) Missing fraction = naphtha (allow naphtha from list if not quoted separately) () Order = mineral oil (lubricating oil), gas oil (diesel),
3.2.1 Energetics. Hess's Law. 183 minutes. 181 marks. Page 1 of 21
 .. Energetics Hess's Law 8 minutes 8 marks Page of M. (a) (Enthalpy change) when mol () of a compound is formed from its constituent elements () in their standard states () Allow energy or heat, Ignore
.. Energetics Hess's Law 8 minutes 8 marks Page of M. (a) (Enthalpy change) when mol () of a compound is formed from its constituent elements () in their standard states () Allow energy or heat, Ignore
DO NOT ALLOW any reference to spatial/space
 Question Answer Mark Guidance 1 (a) (i) (compounds or molecules having the) same molecular 1 ALLOW different structure OR different displayed formula but different structural formulae formula OR different
Question Answer Mark Guidance 1 (a) (i) (compounds or molecules having the) same molecular 1 ALLOW different structure OR different displayed formula but different structural formulae formula OR different
5070 CHEMISTRY. 5070/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 75
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 5070 CHEMISTRY 5070/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an aid to
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 5070 CHEMISTRY 5070/22 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an aid to
Acceptable Answers Reject Mark. The sulfur trioxide can accept a pair of electrons An electron 1
 (a)(i sulfuric acid / fuming H SO 4 / oleum / H S O 7 Conc. (for fuming) Fuming dilute sulfuric acid Just sulfuric acid Just H SO 4 (a)(ii) Sulfur is δ+ and on at least one oxygen δ- Full + or charge(s)
(a)(i sulfuric acid / fuming H SO 4 / oleum / H S O 7 Conc. (for fuming) Fuming dilute sulfuric acid Just sulfuric acid Just H SO 4 (a)(ii) Sulfur is δ+ and on at least one oxygen δ- Full + or charge(s)
3.2.1 Energetics. Enthalpy Change. 263 minutes. 259 marks. Page 1 of 33
 .. Energetics Enthalpy Change 6 minutes 59 marks Page of M. (a) (Enthalpy change) when mol () of a compound is formed from its constituent elements () in their standard states () Allow energy or heat,
.. Energetics Enthalpy Change 6 minutes 59 marks Page of M. (a) (Enthalpy change) when mol () of a compound is formed from its constituent elements () in their standard states () Allow energy or heat,
Question Answer Mark Guidance 1 (a)
 Question Answer Mark Guidance 1 (a) 1 ALLW correct structural R displayed R skeletal 3 3 formula R mixture of the above 3 D NT ALLW molecular formula Br Br ALLW dichloro or diiodo compound instead of the
Question Answer Mark Guidance 1 (a) 1 ALLW correct structural R displayed R skeletal 3 3 formula R mixture of the above 3 D NT ALLW molecular formula Br Br ALLW dichloro or diiodo compound instead of the
1 Compound Q decolourises bromine water. Compound Q has two carbon atoms in each molecule. Which statement about compound Q is correct?
 1 ompound Q decolourises bromine water. ompound Q has two carbon atoms in each molecule. Which statement about compound Q is correct? It contains carbon-hydrogen double bonds. It has six hydrogen atoms
1 ompound Q decolourises bromine water. ompound Q has two carbon atoms in each molecule. Which statement about compound Q is correct? It contains carbon-hydrogen double bonds. It has six hydrogen atoms
Southfields Academy A-Level Chemistry Entrance Exam Revision booklet
 Southfields Academy A-Level Chemistry Entrance Exam Revision booklet This booklet is for students who got a grade 6 in the GCSE mathematics exam. In order to be accepted on to the Chemistry A-level course
Southfields Academy A-Level Chemistry Entrance Exam Revision booklet This booklet is for students who got a grade 6 in the GCSE mathematics exam. In order to be accepted on to the Chemistry A-level course
OCR AS Chemistry A H032 for first assessment in Complete Tutor Notes. Section: Boomer Publications
 R AS hemistry A 032 for first assessment in 2016 omplete Tutor Notes www.boomerchemistry.com Section: 4.2.1 Alcohols 4.2.2 aloalkanes 2015 Boomer Publications page 145 page 152 40 Alcohols Page 155 Ethanol
R AS hemistry A 032 for first assessment in 2016 omplete Tutor Notes www.boomerchemistry.com Section: 4.2.1 Alcohols 4.2.2 aloalkanes 2015 Boomer Publications page 145 page 152 40 Alcohols Page 155 Ethanol
M1.(a) (i) 2Cl Cl 2 + 2e Ignore state symbols Credit loss of electrons from LHS Credit multiples Do not penalise absence of charge on electron 1
 M.(a) (i) 2Cl Cl 2 + 2e Credit loss of electrons from LHS Credit multiples Do not penalise absence of charge on electron (ii) (iii) +7 7 VII +VII Allow Mn +7 and 7+ MnO 4 + 8H + + 5e Mn 2+ + 4H 2 O Credit
M.(a) (i) 2Cl Cl 2 + 2e Credit loss of electrons from LHS Credit multiples Do not penalise absence of charge on electron (ii) (iii) +7 7 VII +VII Allow Mn +7 and 7+ MnO 4 + 8H + + 5e Mn 2+ + 4H 2 O Credit
Module 2A Alcohols and halogenoalkanes
 Module 2A Alcohols and halogenoalkanes Making ethanol Ethanol is made in 1 of 2 ways: 1) Hydration of ethene: This is a reversible reaction and only about 5% of ethene is converted to ethanol. Unreacted
Module 2A Alcohols and halogenoalkanes Making ethanol Ethanol is made in 1 of 2 ways: 1) Hydration of ethene: This is a reversible reaction and only about 5% of ethene is converted to ethanol. Unreacted
3.2.1 Energetics. Enthalpy Change. 263 minutes. 259 marks. Page 1 of 41
 ..1 Energetics Enthalpy Change 6 minutes 59 marks Page 1 of 41 Q1. (a) Define the term standard molar enthalpy of formation, ΔH f. (b) State Hess s law. (c) Propanone, CO, burns in oxygen as shown by the
..1 Energetics Enthalpy Change 6 minutes 59 marks Page 1 of 41 Q1. (a) Define the term standard molar enthalpy of formation, ΔH f. (b) State Hess s law. (c) Propanone, CO, burns in oxygen as shown by the
Page 2. (polyethene) any four from:
 M.(a) (ethene) (polyethene) (b) any four from: poly(ethene) produced by addition polymerisation whereas polyester by condensation polymerisation poly(ethene) produced from one monomer wheareas polyester
M.(a) (ethene) (polyethene) (b) any four from: poly(ethene) produced by addition polymerisation whereas polyester by condensation polymerisation poly(ethene) produced from one monomer wheareas polyester
Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL
 Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Understandings: A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ
Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Understandings: A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ
Synthesis and Sustainable Chemistry
 Synthesis and Sustainable Chemistry Considering % yield and % Atom Economy: high % yield means very efficient conversion from reactants to products increasing % yield means more efficient use of starting
Synthesis and Sustainable Chemistry Considering % yield and % Atom Economy: high % yield means very efficient conversion from reactants to products increasing % yield means more efficient use of starting
3.2.8 Haloalkanes. Nucleophilic Substitution. 267 minutes. 264 marks. Page 1 of 36
 3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
UNIT 2 REVISION CHECKLIST. a) understand that reactions are either exothermic or endothermic and apply the sign convention
 UNIT 2 REVISION CHECKLIST Topic 2.1 Energetics a) understand that reactions are either exothermic or endothermic and apply the sign convention b) define the term enthalpy change, recall what standard conditions
UNIT 2 REVISION CHECKLIST Topic 2.1 Energetics a) understand that reactions are either exothermic or endothermic and apply the sign convention b) define the term enthalpy change, recall what standard conditions
Marking Guidance Mark Comments
 Energetics Answers Chemistry - AQA GCE Mark Scheme 200 June series Q Part Sub Part Marking Guidance Mark Comments a i M drawn curve starts at reactants and ends at products M2 curve peak is below the one
Energetics Answers Chemistry - AQA GCE Mark Scheme 200 June series Q Part Sub Part Marking Guidance Mark Comments a i M drawn curve starts at reactants and ends at products M2 curve peak is below the one
Atoms, Elements, Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures. Compounds and Mixtures. Atoms and the Periodic Table. Atoms and the.
 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components
Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components
GCE. Chemistry A. Mark Scheme for June Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F322: Chains, Energy and Resources
 Cherry ill Tuition A Level Chemistry OCR (A) Paper 12. Mark Scheme ` GCE Chemistry A Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Mark Scheme for June 2011 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
Cherry ill Tuition A Level Chemistry OCR (A) Paper 12. Mark Scheme ` GCE Chemistry A Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Mark Scheme for June 2011 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
GCSE Chemistry. Module C7 Further Chemistry: What you should know. Name: Science Group: Teacher:
 GCSE Chemistry Module C7 Further Chemistry: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: R.A.G. each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this A = Amber: I partly
GCSE Chemistry Module C7 Further Chemistry: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: R.A.G. each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this A = Amber: I partly
4.4, 4.5 HW MS 1. (a) nucleophilic addition 1 M2. (b) (i) 2-hydroxybutanenitrile 1 (ii) 2 H 3C O H
 4.4, 4.5 W MS 1. (a) nucleophilic addition 1 M N N M1 M M4 4 (b) (i) -hydroxybutanenitrile 1 (ii) N (allow 1 for amide even if not 4 7 N, i.e. RN ) (if not amide, allow one for any isomer of 4 7 N which
4.4, 4.5 W MS 1. (a) nucleophilic addition 1 M N N M1 M M4 4 (b) (i) -hydroxybutanenitrile 1 (ii) N (allow 1 for amide even if not 4 7 N, i.e. RN ) (if not amide, allow one for any isomer of 4 7 N which
must show C=C Penalise sticks once per pair 1 H 10 Penalise sticks once per pair 1 or CH 3 C 2 Penalise sticks once per pair 1
 M. (a) A allow CH COCH B must show C=C Penalise sticks once per pair (b) C CH CH CH CH CH D NOT cyclopentane which is only C 5 H 0 Penalise sticks once per pair (c) E CH CH COOCH Allow C H 5 CO CH F CH
M. (a) A allow CH COCH B must show C=C Penalise sticks once per pair (b) C CH CH CH CH CH D NOT cyclopentane which is only C 5 H 0 Penalise sticks once per pair (c) E CH CH COOCH Allow C H 5 CO CH F CH
Organic Chemistry. Chapter 10
 Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 10.1 Homologous Series Overview We Are Here Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds. From the very simple: methane To the very complex:
Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 10.1 Homologous Series Overview We Are Here Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds. From the very simple: methane To the very complex:
OCR Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
2 Answer all the questions. 1 Nitrogen monoxide is formed when nitrogen and oxygen from the air combine. (g) + O 2
 2 Answer all the questions. 1 Nitrogen monoxide is formed when nitrogen and oxygen from the air combine. N 2 (g) + 2 (g) 2N(g) equation 1.1 Under normal atmospheric conditions, a further reaction occurs
2 Answer all the questions. 1 Nitrogen monoxide is formed when nitrogen and oxygen from the air combine. N 2 (g) + 2 (g) 2N(g) equation 1.1 Under normal atmospheric conditions, a further reaction occurs
Wednesday 16 January 2013 Morning
 Wednesday 16 January 2013 Morning AS GCE CEMISTRY A F322/01 Chains, Energy and Resources *F314440113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry A (inserted)
Wednesday 16 January 2013 Morning AS GCE CEMISTRY A F322/01 Chains, Energy and Resources *F314440113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry A (inserted)
OCR Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Collision Theory. Mark Scheme 2. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision
 Collision Theory Mark Scheme Level A Level Subject Chemistry Exam Board AQA Module 3. Physical Chemistry Topic 3..5 Kinetics Sub-Topic 3..5. Collision Theory Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 5 minutes
Collision Theory Mark Scheme Level A Level Subject Chemistry Exam Board AQA Module 3. Physical Chemistry Topic 3..5 Kinetics Sub-Topic 3..5. Collision Theory Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 5 minutes
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO
 SIR MIELANGEL REFAL SIXT FRM Annual Exam 2015 Subject: hemistry ADV 2 nd Time: 3 hours ANSWER ANY 6 QUESTINS. All questions carry equal marks. You are reminded of the importance of clear presentation in
SIR MIELANGEL REFAL SIXT FRM Annual Exam 2015 Subject: hemistry ADV 2 nd Time: 3 hours ANSWER ANY 6 QUESTINS. All questions carry equal marks. You are reminded of the importance of clear presentation in
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
... (1) Draw the structure of the organic product, B, formed when A is oxidised in the reaction with acidified potassium dichromate(vi).
 Alcohol A (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH(OH)CH 3 undergoes reactions separately with acidified potassium dichromate(vi) and with concentrated sulfuric acid. (a) Deduce the IUPAC name for alcohol A. () (b) Draw the structure
Alcohol A (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH(OH)CH 3 undergoes reactions separately with acidified potassium dichromate(vi) and with concentrated sulfuric acid. (a) Deduce the IUPAC name for alcohol A. () (b) Draw the structure
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 5070 CHEMISTRY. 5070/02 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 75
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 5070 CHEMISTRY 5070/02 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 5070 CHEMISTRY 5070/02 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published
CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Energy, Rate and Chemistry of Carbon Compounds
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A Level 2410U20-1 NEW AS S16-2410U20-1 CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Energy, Rate and Chemistry of Carbon Compounds P.M. FRIDAY, 10 June 2016 1 hour 30 minutes
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A Level 2410U20-1 NEW AS S16-2410U20-1 CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Energy, Rate and Chemistry of Carbon Compounds P.M. FRIDAY, 10 June 2016 1 hour 30 minutes
2004 Chemistry. Higher. Finalised Marking Instructions
 2004 Chemistry Higher Finalised Marking Instructions Higher Chemistry General information for markers The general comments given below should be considered during all marking. Marks should not be deducted
2004 Chemistry Higher Finalised Marking Instructions Higher Chemistry General information for markers The general comments given below should be considered during all marking. Marks should not be deducted
2 CH 2 O (-) Na (+) This equation scores (2) marks. CH 2 OHCH 2 O (-) Na (+)
 (a) Na + O (-) Na (+) O (-) Na (+) O (-) Na (+) + This equation scores () marks Accept multiples and ( ) and ( O (-) Na (+) ) Organic product (harges not needed) Na (+) O (-) Na (+) O (-) Reject bond from
(a) Na + O (-) Na (+) O (-) Na (+) O (-) Na (+) + This equation scores () marks Accept multiples and ( ) and ( O (-) Na (+) ) Organic product (harges not needed) Na (+) O (-) Na (+) O (-) Reject bond from
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Atomic Structure Recall the different charges of the particles that make up an atom. Describe why atoms have no overall charge. Use the periodic table to identify
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Atomic Structure Recall the different charges of the particles that make up an atom. Describe why atoms have no overall charge. Use the periodic table to identify
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
dihalogenoalkane H 2, Nickel Catalyst KOH alcoholic HBr, HCl Br Cl Elimination KOH aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution
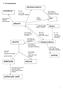 7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
Question Answer Mark Guidance 1 (a) Method 1: 100% OR (only) one product OR no waste 2 product OR addition (reaction)
 1 (a) Method 1: 100% OR (only) one product OR no waste 2 product OR addition (reaction) ALLOW co-product or by-product for waste product Method 2: < 100% AND two products OR (also) produces NaBr OR (There
1 (a) Method 1: 100% OR (only) one product OR no waste 2 product OR addition (reaction) ALLOW co-product or by-product for waste product Method 2: < 100% AND two products OR (also) produces NaBr OR (There
(b) (1) C 10 H 22 C 3 H 6 + C 7 H 16 1 (ii) correctly drawn structure of methylpropene 1 (insist on clearly drawn C-C and C=C bonds)
 1. (a) (i) fractional distillation or fractionation 1 (ii) C 9 H 20 only 1 (iii) C 11 H 24 + 17O 2 11CO 2 + 12H 2 O 1 (iv) C 11 H 24 + 6O 2 11C + 12H 2 O 1 (b) (1) C 10 H 22 C H 6 + C 7 H 16 1 (ii) correctly
1. (a) (i) fractional distillation or fractionation 1 (ii) C 9 H 20 only 1 (iii) C 11 H 24 + 17O 2 11CO 2 + 12H 2 O 1 (iv) C 11 H 24 + 6O 2 11C + 12H 2 O 1 (b) (1) C 10 H 22 C H 6 + C 7 H 16 1 (ii) correctly
M1. (a) Yellow (solution) 1. Orange solution 1 SO 4. Yellow / purple (solution) Allow orange / brown (solution) 1. Brown precipitate / solid 1 + 3H 2
 M. (a) Yellow (solution) range solution Cr + H + Cr 7 + H Allow equation with H S (b) Yellow / purple (solution) Allow orange / brown (solution) Brown precipitate / solid [Fe(H ) 6 ] + + H Fe(H ) (H) +
M. (a) Yellow (solution) range solution Cr + H + Cr 7 + H Allow equation with H S (b) Yellow / purple (solution) Allow orange / brown (solution) Brown precipitate / solid [Fe(H ) 6 ] + + H Fe(H ) (H) +
1 What is the formula of poly(but-1-ene)? H H H H n A C C C C H H H CH 2 CH 3 B C C H H C C C CH 3 CH 3 H H H H CH 3 H D C C C
 1 What is the formula of poly(but-1-ene)? n 2 3 n 3 3 n 3 n 2 Which of the following molecules is formed on adding bromine water to ethene? ethanol ethane-1,2-diol bromoethane 2-bromoethanol 3 section
1 What is the formula of poly(but-1-ene)? n 2 3 n 3 3 n 3 n 2 Which of the following molecules is formed on adding bromine water to ethene? ethanol ethane-1,2-diol bromoethane 2-bromoethanol 3 section
Wednesday 23 May 2012 Afternoon
 herry ill Tuition A Level hemistry OR (A) Paper 14 Wednesday 23 May 2012 Afternoon AS GE EMISTRY A F322 hains, Energy and Resources *F314620612* andidates answer on the Question Paper. OR supplied materials:
herry ill Tuition A Level hemistry OR (A) Paper 14 Wednesday 23 May 2012 Afternoon AS GE EMISTRY A F322 hains, Energy and Resources *F314620612* andidates answer on the Question Paper. OR supplied materials:
Final. Mark Scheme. Chemistry CHEM4. (Specification 2420) Unit 4: Kinetics, Equilibria and Organic Chemistry
 ERRY ILL TUITI AQA EMISTRY A2 PAPER 30 MARK SEME Question : /A Question 2: /A Question 3: /A General ertificate of Education (A-level) June 203 hemistry EM4 (Specification 2420) Unit 4: Kinetics, Equilibria
ERRY ILL TUITI AQA EMISTRY A2 PAPER 30 MARK SEME Question : /A Question 2: /A Question 3: /A General ertificate of Education (A-level) June 203 hemistry EM4 (Specification 2420) Unit 4: Kinetics, Equilibria
CHEM2. (JAN13CHEM201) WMP/Jan13/CHEM2. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January Unit 2 Chemistry in Action
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January 2013 Question 1 2
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January 2013 Question 1 2
14.5 Alkenes. Question Paper. Subject Chemistry (0620) Cambridge International Examinations (CIE) Organic Chemistry A* A B C D E U
 Save My Exams! The ome of Revision For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ 14.5 lkenes Question Paper Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620) Exam oard ambridge International
Save My Exams! The ome of Revision For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ 14.5 lkenes Question Paper Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620) Exam oard ambridge International
Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction?
 Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of -bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A Electrophilic addition B Electrophilic substitution
Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of -bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A Electrophilic addition B Electrophilic substitution
Candidate Style Answer
 Candidate Style Answer Chemistry A Unit F322 Chains, Energy and Resources Medium banded response This Support Material booklet is designed to accompany the OCR GCE Chemistry A Specimen Paper F322 for teaching
Candidate Style Answer Chemistry A Unit F322 Chains, Energy and Resources Medium banded response This Support Material booklet is designed to accompany the OCR GCE Chemistry A Specimen Paper F322 for teaching
1 What is used in the production of ethanol from ethene? hydrogen and oxygen. oxygen only. steam. yeast
 What is used in the production of ethanol from ethene? hydrogen and oxygen oxygen only steam yeast 2 Which term describes the formation of ethanol from glucose? cracking distillation polymerisation 3 Which
What is used in the production of ethanol from ethene? hydrogen and oxygen oxygen only steam yeast 2 Which term describes the formation of ethanol from glucose? cracking distillation polymerisation 3 Which
Paper Atomic structure and the periodic table
 Paper 1 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in
Paper 1 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in
It belongs to a homologous series with general formula C n H 2n+1 O
 1 Propene can be made by the dehydration of propan-2-ol. What is the percentage yield when 30 g of propene (M r = 42.0) are formed from 50 g of propan-2-ol (M r = 60.0)? 60% 67% 81% 86% 2 Which statement
1 Propene can be made by the dehydration of propan-2-ol. What is the percentage yield when 30 g of propene (M r = 42.0) are formed from 50 g of propan-2-ol (M r = 60.0)? 60% 67% 81% 86% 2 Which statement
International Advanced Level Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 2: Application of Core Principles of Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 2: Application of Core Principles of Chemistry Friday
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 2: Application of Core Principles of Chemistry Friday
CHERRY HILL TUITION EDEXCEL CHEMISTRY A2 PAPER 32 MARK SCHEME. ±½ a square
 Chemistry Advanced Level Paper 3 (9CH0/03) 1(a)(i) suitable scale and axes labelled including units (1) all points plotted correctly (1) line of best fit (1) Plotted points use at least half the available
Chemistry Advanced Level Paper 3 (9CH0/03) 1(a)(i) suitable scale and axes labelled including units (1) all points plotted correctly (1) line of best fit (1) Plotted points use at least half the available
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE CHEMISTRY A Chains, Energy and Resources F322 * OCE / 1 9 2 3 4* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE CHEMISTRY A Chains, Energy and Resources F322 * OCE / 1 9 2 3 4* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry
1 (a) Give the general formula for the homologous series of alkenes. (1) (b) What is meant by the term unsaturated as applied to alkenes?
 1 (a) Give the general formula for the homologous series of alkenes. (b) What is meant by the term unsaturated as applied to alkenes? (c) Name the alkene below using E-Z nomenclature. H 3 C H C C CH 2
1 (a) Give the general formula for the homologous series of alkenes. (b) What is meant by the term unsaturated as applied to alkenes? (c) Name the alkene below using E-Z nomenclature. H 3 C H C C CH 2
TOPIC 13 ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES a) (i) UV light / temperatures > 500 ºC (ii) CH 4 (g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl(g) + HCl(g) Cl(g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl 2 (l) + HCl(g) Cl 2 (l) + Cl 2 (g) CHCl 3 (l) + HCl(g) CHCl 3 (l) + Cl 2 (g)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES a) (i) UV light / temperatures > 500 ºC (ii) CH 4 (g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl(g) + HCl(g) Cl(g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl 2 (l) + HCl(g) Cl 2 (l) + Cl 2 (g) CHCl 3 (l) + HCl(g) CHCl 3 (l) + Cl 2 (g)
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Chemistry Paper 2
 AQA Chemistry (8462) from 2016 Topics C4.6 The rate and extent of chemical change Calculate the rate of a chemical reaction over time, using either the quantity of reactant used or the quantity of product
AQA Chemistry (8462) from 2016 Topics C4.6 The rate and extent of chemical change Calculate the rate of a chemical reaction over time, using either the quantity of reactant used or the quantity of product
6.5 Alcohols H H H H. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1. Bond angles in Alcohols. Different types of alcohols H 2 C CH 2 CH 2
 6.5 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
6.5 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
Explain what is meant by the term fraction as applied to fractional distillation. The fractions from petroleum contain alkane hydrocarbons.
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY AS REVISION QUESTIONS Q1. Petroleum is separated into fractions by fractional distillation.the petrol fraction (C 4 to C 12 ) is burned in internal combustion engines and the naphthafraction
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY AS REVISION QUESTIONS Q1. Petroleum is separated into fractions by fractional distillation.the petrol fraction (C 4 to C 12 ) is burned in internal combustion engines and the naphthafraction
Chemistry 2.5 AS WORKBOOK. Working to Excellence Working to Excellence
 Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Name: Class: Redox revision questions. 50 minutes. Time: Marks: 50. Comments: Page 1 of 17
 Name: Class: Redox revision questions Time: 50 minutes Marks: 50 Comments: Page of 7 Aqueous C 2 O ions react with MnO ions in acidic solution according to the equation 5 C 2 O + 2MnO + 6H + 2Mn 2+ + 0CO
Name: Class: Redox revision questions Time: 50 minutes Marks: 50 Comments: Page of 7 Aqueous C 2 O ions react with MnO ions in acidic solution according to the equation 5 C 2 O + 2MnO + 6H + 2Mn 2+ + 0CO
