Shinji Murai,* Fumitoshi Kakiuchi. Shinya Sekine, Yasuo Tanaka, Asayuki Kamatani, Motohiro Sonoda, and Naoto Chatani
|
|
|
- Lawrence Baldwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pure &App/. Chem., Vol. 66, No. 7, pp , Printed in Great Britain UPAC Catalytic C-H/olefin coupling Shinji Murai,* Fumitoshi Kakiuchi. Shinya Sekine, Yasuo Tanaka, Asayuki Kamatani, Motohiro Sonoda, and Naoto Chatani Department of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering, Osaka University, Suita, Osaka 565, Japan Abstract - Several ruthenium complexes have been found to catalyze the addition of the C-H bond of arenes to olefins. Phenyl methyl ketone undergoes addition at its ortho position across the double bond of trimethylvinylsilane in the presence of a catalytic amount of RuH2(CO)(PPh3)3 to give 1 : 1 and 1 : 2 coupling products. n the latter, the two ortho hydrogens have reacted. Similarly, 2-methylphenyl methyl ketone reacts with trimethylvinylsilane and triethoxyvinylsilane to give the corresponding 1 : 1 coupling products in virtually quantitative yields. The results represent a breakthrough in the chemistry of carbon-hydrogen bond cleavage by metal complexes. NTRODUCTON n this paper we disclose an efficient catalytic reaction that enables the addition of arenes to olefins. This discovery represents a breakthrough in the chemistry of C- H bond cleavage by metal complexes, a field that has been under intense study since 1963 when Kleiman and Dubeck reported a C-H bond cleavage of azobenzene by reaction with a nickel complex (eq 11.1 Q Q Chatt and Davidson subsequently observed in 1965 an oxidative addition to a C-H bond of naphthalene with a Ru(0) complex generated in situ by the reduction of a Ru(1) complex with sodium naphthalenide, as shown in eq
2 1528 S. MURAl eta/. The crystal structure of RuC12(PPh3)3 determined by La Placa and bers in 1965 showed that the ruthenium was in the center of an octahedron containing the five ligands; the last coordination site being occupied by an ortho-hydrogen of one of the PPh3 ligands.3 This observation clearly demonstrated that there can exist a nonclassical interaction between a bonded hydrogen atom and a transition metal. Prompted by' these observations, numerous studies have been carried out ever since. C-H bond cleavage by metals has now been established as a common phenomenon in stoichiometric eactions. Various interesting catalytic reactions s involving C-H bond cleavage have also been reported but with a limited degree of success from the view point of organic synthesis. More than fifty review articles in this field have a~peared.~ Notable advances in catalytic reactions reported recently are those of Jordan and Taylor (eq 3)s and Moore and co-workers (eq 41.6 n both cases, a new carboncarbon bond is formed from pyridines in exceptionally high yields. However, in the reaction 3 the use of hydrogen was necessary to obtain higher yield, which in turn resulted in consumption of the olefin by hydrogenation. n the latter (eq 4), a large excess amount of pyridine was used. (+H2) atrn 1 atm mmol CH2C2 23 "C, 25 h - quantitative (based on picoline)
3 Catalytic C-H/olefin coupling 1529 cat. Ru,(CO),, mmc + co rl, fn& + q&/ N' (4) OC, 16 h 15mL 4mmol 15Opsi (solvent) 65% (13: 1) (based on -hexene) RESULTS' A remarkable catalytic reaction involving C-H bond cleavage has been found. By this reaction the C-H bond at the ortho position of aromatic ketones can be added across the double bond of olefins. The catalytic C-H/olefin coupling begins with cyclometalation of an aromatic ketone with a Ru(0) complex followed by interception of the thus formed intermediate to give the addition product after reductive elimination (vide infra). The reaction of phenyl methyl ketone (1) with trimethylvinylsilane (2) has been found to proceed in the presence of a catalytic amount of ruthenium complexes (eq 5). For example, when a mixture of 1 (), 2 (), and RuHz(CO)(PPh3)3 (0.04 mmol) was vigorously refluxed in 3 ml of toluene for several minutes, a 1 : 1 coupling product 3 and a 1 : 2 coupling product 4 were obtained in 29% and 27% yields based on 1, respectively (eq 5). The yield of 4 was 54% based on 2. SiMe, 0"- & cat. RUH2(CO)(PPh3) mmol &+ (5) + esime, toluene 3 ml \ \ SiMe, SiMe, 1 2 reflux (bath temp 135 "C) 8 min 3 (29%) 4 (27%) (54% based on 2) Among the ruthenium complexes examined for their catalytic activities, RuH2(CO)(PPh3)3 and Ru(C0)2(PPh3)3 were the most effective in catalyzing the reaction of eq 5. Similar ruthenium complexes such as RuHz(PPh& and Ru (C 0) 3 (PPh3)2 were fairly effective, while RuHCl(C0) (PPh3)3, RuC12 (PPh3)3. RuC12(C0)2(PPh3)2, RuCl(OAc)(CO)(PPh3)2, and Rug(C0) 12 did not show any catalytic activity for the reaction 5 under the reaction conditions described above. Although the ruthenium complex RuCl(OAc)(CO)(PPh3)2 is known to react with phenyl methyl ketone to give an orthoruthenation product as the result of C-H bond cleavage (vide infra),* it is not effective as a catalyst for the above reaction.
4 1530 S. MURAl eta/. To avoid complexity, 2-methylphenyl methyl ketone (6) was examined as the ketone component to prevent formation of the 1 : 2 coupling product. The catalytic reaction of 5 with two equivalents of 2 gave the coupling product 6 almost quantitatively (eq mmol cat. RUH2(CO)(PPh3) mmol L toluene 3 ml reflux (bath temp 135 "C) 2h 6 (97%) We were interested in the difference in the reaction time required for consumption of the aromatic ketones in the reactions 5 and 6. Particularly, the rate of formation of 4 seemed to be much greater than 6. The results of experiments described below imply that coordination of the carbonyl group of the ketone to the ruthenium is important. Two competitive reactions were carried out as shown in eqs 7 and esime,, cat. RuH,(CO)(PPh,), 2 1 mrnol 0.04 rnmol * 10 min SiMe, & + & & + ~ SiMe, \ SiMe, SiMe, (7) total (0.3) (0.19 rnmol) (0.09 mrnol) based on 2 32% 38% 9 Yo (79%) based on 1 16% 9.5% - (25.5%) based on % (4.5%)
5 Catalytic C-H/oleiin coupling min 3 5 SiMe3 4 6 total (0.25 mmol) (0.40 mmol) based on 2 25% 40 /o ' (65%) based on % - (12.5%) based on 5-20% (20%) Under the reaction conditions shown above, a mixture of 1 and 5 reacted with an insufficient amount of the olefin 2 to give three products, 3, 4, and 6 (eq 7). Yields based on each starting material are shown in the eq 7. The 1 : 2 coupling product 4 seemed to be produced by further reaction of the 1 : 1 coupling product 3, but this is only partly true as will be described below. Similarly a mixture of equal amounts of 3 (the plausible intermediate for the formation of 4) and 5 reacted with an insufficient amount of 2 to afford 4 and 6 in the yields given in eq 8. The relative rate of consumption of 1, 5, and 3 are estimated to be 9 : 1.6 : 1, as calculated from the consumption of % in eq 7, 5 4.5% in eq 7, 5 20% in eq 8, and % in eq 8. These relative rates indicate that introduction of an alkyl group to the phenyl ring retards significantly the rate of the catalytic reaction. Of note is the formation of an unexpectedly large amount of 4 in reaction 7. Assuming that all of 4 is formed via 3 in reaction 7, the yield of 4 in eq 7 should not exceed 2.8% (= 4.5 X (12.5/20)) as estimated from the relative rates of formation of 4 and 6 in eq 8. Actually, however, the yield of 4 in eq 7 is 9.5% and the above assumption is obviously not correct. At least 6.7% yield (= ) of 4 in eq 7 must have been produced by a route not involving 3. We suggest that the major portion of the product 4 is formed from 1 without decomplexation of the carbonyl group of 3 from ruthenium throughout the reaction. This leads to estimation that at least 71% (= (6.7/9.5) X 100) of 4 is formed by the route not involving "free 3" and 29% of 4 from once liberated "free 3", in reaction 7. The course of the catalytic reaction is depicted in Scheme.
6 1532 S. MURAl eta/. Scheme NO H-Ru-0 SiMe3 \ o For simplicity, possible equilibria are not included in Scheme. Coordination of the carbonyl oxygen (1 to 7) is important to direct the ruthenium metal close to the C-H bond to be cleaved. Thus formed ruthenium hydride complex 8 undergoes olefin coordination and migratory insertion followed by reductive elimination to afford 9, i.e., 3*Ru complex. Decomplexation affords 3. On the other hand, carboncarbon bond rotation (9 + 10) directs the ruthenium metal close to the other ortho C-H bond. Cleavage of this second C-H bond results in the formation of intermediate 11. The cyclometalated complex 11 reacts with a second molecule of vinylsilane to afford the 1 : 2 coupling product 4. nterestingly, the above results indicate that decomplexation of the ketone ligand from the metal is competitive with C-H bond cleavage. n other words, in the present reaction the rate of C-H bond cleavage is of the order of that for decomplexation of a ketone ligand. As described above, the reaction of mono-alkylphenyl ketone, 4 or 5, was much slower than unsubstituted one 1. This can be attributed to the steric repulsion between the ketonic methyl group and the alkyl group in the phenyl ring in the form such as 10 or 11. The mechanism of the present reaction is far from clear at the present time. That shown in Scheme neglects many important steps. Much work remains to be done to solve the intriguing questions raised by the present discovery. t is noteworthy that cyclometalated complexes such as 12,8 13,g and 1410 structurally similar to 8 have been reported.
7 Catalytic C-H/olefin coupling 1533 OBu The vinylsilane 2 was less than ideal in the present reaction since its boiling point (bp 55 "C) is much lower than the reaction temperature. The use of a higher boiling vinylsilane 15 (bp 160 "C) gave the most impressive result even when equimolecular amounts of reactants were used (eq 9). The reaction was so clean that the initial GLC peaks of reactants, 5 and 15 disappeared after two hours and only a single new GLC peak for the 1 : 1 couping product 16 appeared (93% GLC yield). The reaction is operationally simple: mix the reagents and reflux. solation procedures are also straightforward. Evaporation of the solvent and bulb-to-bulb distillation allowed isolation of the pure product 16 (- 90% yield) that gave correct elemental analysis data. 0"- \ 5 fisi(oet)3 15 cat. RUH2(CO)(PPh3) mmol + toluene 3 ml reflux (bath temp 135 "C) 2h 0 16 (93%) OUTLOOK We are extending the present discovery in various directions. The new catalytic reaction can be applied to various carbonyl compounds and to various olefins. The results7 indicate that catalytic reactions involving C-H bond cleavage by transition metals are now reaching the level required for practical organic synthesis with respect to efficiency, selectivity, and generality, for the first time since the initial discoveries made thirty years ago.1-4 n addition, the concept of interception of cyclometalated intermediates will become a powerful methodology for the development of new catalytic reactions. These results will be reported in due course.
8 1534 S. MURAl eta/. REFERENCES J. P. Kleiman and M. Dubeck, J. Am Chern. Soc. 85, 1544 (1963). J. Chatt and J. M. Davidson, J. Chem SOC. 843 (1965). S. J. La Placa and J. A. bers, norg. Chem 4, 778 (1965). For example. (a) G. W. Parshall, Acc. Chern. Res. 4, 113 (1975);(b) D. E. Webster, Adv. Organornet. Chem 15, 147 (1977). (c). Omae, Chern. Rev. 79, 287 (1979); (d) S. Komiya, A. Yamamoto and T. Yamamoto, Yuki Gosei Kagaku Kyokai Shi 38, 633 (1980); (e) E. L. Muetterties, Chem Soc. Rev. 1, 283 (1982); (0 H. Yamazaki and P. Hong, J. Mol. Catal. 21, 133 (1983); (g) R. G. Bergman, Science 223, 902 (1984); (h) M. L. H. Green and D. O'Hare, Pure Appl. Chern. 57, 1897 (1985); (i) R. H. Crabtree, Chem. Rev. 85, 245 (1985); (j) G. R. Newkome, W. E. Puckett, V. K. Gupta and G. E. Kiefer, Chem Rev. 86, 451 (1986); (k) A. Miyashita, Shokubai 29, 373 (1987); (1) Y. Moro-oka and H. Suzuki, Shokubai 30, 234 (1988);(m) M. Tanaka, Yuki Gosei Kagaku Kyokai Shi 46, 832 (1988); (n) Y. Fujiwara, Kagaku 43, 461 (1988); (0). P. Rothwell, Acc. Chern. Res. 21, 153 (1988); (p) M. Tanaka, CHEMTECH 59 (1989); (9) W. D. Jones and F. J. Feher, Acc. Chem. Res. 22, 91 (1989); (r) A. D. Ryabov, Chem. Rev. 90, 403 (1990); (s) M. Pfeffer, Pure Appl. Chern. 64, 335 (1992); (t) R. G. Bergman, Adv. Chern. Ser. 230, 211 (1992). R. F. Jordan and D. F. Taylor, J. Am Chem Soc. 111, 778 (1989). E. J. Moore, W. R. Pretzer, J. T. O'Connell, J. Harris, L. LaBounty, L. Chou and S. S. Grimmer, J. Am Chem SOC. 114, 5888 (1992). All of our results are unpublished as of September M. F. McGuiggan and L. H. Pignolet, norg. Chem. 21, 2523 (1982). R. J. McKinney, G. Firestein and H. D. Kaesz, norg. Chem. 14, 2057 (1975). (a) S. Komiya and A. Yamamoto, Chem Lett. 475 (1975); (b) S. Komiya T. to, M. Cowie, A. Yamamoto and J. A. bers, J. Am. Chem Soc. 98, 3874 (1976).
Palladium-Catalyzed Alkylation of sp2 and sp3 C-H Bonds with Methylboroxine and Alkylboronic Acids: Two Distinct C-H Activation Pathways
 Palladium-Catalyzed Alkylation of sp2 and sp3 C-H Bonds with Methylboroxine and Alkylboronic Acids: Two Distinct C-H Activation Pathways Xiao Cheng, Charles Goodhue, and Jin-Quan Yu Brandeis University
Palladium-Catalyzed Alkylation of sp2 and sp3 C-H Bonds with Methylboroxine and Alkylboronic Acids: Two Distinct C-H Activation Pathways Xiao Cheng, Charles Goodhue, and Jin-Quan Yu Brandeis University
ACTIVATION OF C H BONDS BY LOW-VALENT METAL COMPLEXES ( THE ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY )
 CHAPTER IV ACTIVATION OF C H BONDS BY LOW-VALENT METAL COMPLEXES ( THE ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY ) n the end of the 1960s the leading specialist in homogeneous catalysis Jack Halpern wrote [1]: to develop
CHAPTER IV ACTIVATION OF C H BONDS BY LOW-VALENT METAL COMPLEXES ( THE ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY ) n the end of the 1960s the leading specialist in homogeneous catalysis Jack Halpern wrote [1]: to develop
Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage (C-C Activation) Group Meeting Timothy Chang
 Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage (C-C Activation) Group Meeting 01-15-2008 Timothy Chang Outlines - Fundamental considerations, C-H versus C-C activation - Orbital interactions -
Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage (C-C Activation) Group Meeting 01-15-2008 Timothy Chang Outlines - Fundamental considerations, C-H versus C-C activation - Orbital interactions -
Please inquire for pricing and availability of listed products to our local sales representatives.
 lease inquire for pricing and availability of listed products to our local sales representatives. 1 C- Bond Activation Reaction Recently, there have been a large number of reports on C- bond activation
lease inquire for pricing and availability of listed products to our local sales representatives. 1 C- Bond Activation Reaction Recently, there have been a large number of reports on C- bond activation
Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) H Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group
 Literature eport Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group eporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Yue Ji Date: 2016-04-05 Yu, J.-Q. et al. Science 2016, 351, 252-256. Scripps esearch
Literature eport Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group eporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Yue Ji Date: 2016-04-05 Yu, J.-Q. et al. Science 2016, 351, 252-256. Scripps esearch
Rhenium-Catalyzed Synthesis of Multisubstituted Aromatic Compounds via C-C Single-Bond Cleavage
 henium-catalyzed Synthesis of Multisubstituted Aromatic Compounds via C-C Single-Bond Cleavage Kuninobu, Y.; Takata,.; Kawata, A.; Takai, K. rg. Lett. ASAP Et 5 6 cat. [ebr(c) 3 (thf)] 2 5 6 Current Literature
henium-catalyzed Synthesis of Multisubstituted Aromatic Compounds via C-C Single-Bond Cleavage Kuninobu, Y.; Takata,.; Kawata, A.; Takai, K. rg. Lett. ASAP Et 5 6 cat. [ebr(c) 3 (thf)] 2 5 6 Current Literature
C H activation of aliphatic amines without unnecessary mask M2 Takaya Togo
 C H activation of aliphatic amines without unnecessary mask 2017.11.25 M2 Takaya Togo 1 Outline 1.Introduction 2.Free amines as DG Discovery of new activation mode Mechanistic studies Application of the
C H activation of aliphatic amines without unnecessary mask 2017.11.25 M2 Takaya Togo 1 Outline 1.Introduction 2.Free amines as DG Discovery of new activation mode Mechanistic studies Application of the
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation
 Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions
 Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions A Primer on MO Theory σ-bonding in Organotransition Metal Complexes M-C Bond Energies in Organotransition Metal Complexes Thermodynamic Predictions
Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions A Primer on MO Theory σ-bonding in Organotransition Metal Complexes M-C Bond Energies in Organotransition Metal Complexes Thermodynamic Predictions
(Neither an oxidation or reduction: Addition or loss of H +, H 2 O, HX).
 eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
Chapter 10: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
 Chapter 10: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives The back of the white willow tree (Salix alba) is a source of salicylic acid which is used to make aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) The functional group
Chapter 10: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives The back of the white willow tree (Salix alba) is a source of salicylic acid which is used to make aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) The functional group
b.p.=100 C b.p.=65 C b.p.=-25 C µ=1.69 D µ=2.0 D µ=1.3 D
 Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Functionalization of terminal olefins via H migratory insertion /reductive elimination sequence Hydrogenation
 M.C. White, Chem 153 verview -282- Week of ovember 11, 2002 Functionalization of terminal olefins via migratory insertion /reductive elimination sequence ydrogenation ML n E ydrosilylation Si 3 Si 3 ML
M.C. White, Chem 153 verview -282- Week of ovember 11, 2002 Functionalization of terminal olefins via migratory insertion /reductive elimination sequence ydrogenation ML n E ydrosilylation Si 3 Si 3 ML
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols
 Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols 45 -Alcohols have the general formula R-OH and are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group, -OH. -Phenols have a hydroxyl group attached directly to an
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols 45 -Alcohols have the general formula R-OH and are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group, -OH. -Phenols have a hydroxyl group attached directly to an
14-1 Reactions Involving Gain or Loss of Ligands Reactions Involving Modification of Ligands
 Organometallic Reaction and Catalysis 14-1 Reactions Involving Gain or Loss of Ligands 14-2 Reactions Involving Modification of Ligands 14-3 Organometallic Catalysts 14-4 Heterogeneous Catalysts Inorganic
Organometallic Reaction and Catalysis 14-1 Reactions Involving Gain or Loss of Ligands 14-2 Reactions Involving Modification of Ligands 14-3 Organometallic Catalysts 14-4 Heterogeneous Catalysts Inorganic
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Ethers. Synthesis of Ethers. Chemical Properties of Ethers
 Page 1 of 6 like alcohols are organic derivatives of water, but lack the labile -OH group. As a result, ethers, except for epoxides, are usually not very reactive and are often used as solvents for organic
Page 1 of 6 like alcohols are organic derivatives of water, but lack the labile -OH group. As a result, ethers, except for epoxides, are usually not very reactive and are often used as solvents for organic
Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Relative Reactivity of carbonyls: Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes
 Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Weak nucleophiles, such as water, alcohols, and amines, require acid or base catalysis to undergo addition to carbonyl compounds Relative Reactivity
Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Weak nucleophiles, such as water, alcohols, and amines, require acid or base catalysis to undergo addition to carbonyl compounds Relative Reactivity
Atovaquone: An Antipneumocystic Agent
 Atovaquone: An Antipneumocystic Agent Atovaquone is a pharmaceutical compound marketed in the United States under different combinations to prevent and treat pneumocystosis and malaria. In a report from
Atovaquone: An Antipneumocystic Agent Atovaquone is a pharmaceutical compound marketed in the United States under different combinations to prevent and treat pneumocystosis and malaria. In a report from
18-Electron Rule: Myth or Reality? An NBO Perspective
 18-Electron Rule: Myth or Reality? An NBO Perspective Eric CLOT UMR 5253 - CNRS, UM2, ENSCM, UM1 Interaction Experiment/Theory Experimental Chemists have Questions Where are the Nucleophilic and Electrophilic
18-Electron Rule: Myth or Reality? An NBO Perspective Eric CLOT UMR 5253 - CNRS, UM2, ENSCM, UM1 Interaction Experiment/Theory Experimental Chemists have Questions Where are the Nucleophilic and Electrophilic
sp 3 C-H Alkylation with Olefins Yan Xu Dec. 3, 2014
 sp 3 C-H Alkylation with Olefins, Yan Xu Dec. 3, 2014 1) sp 3 C-H Alkylation via Directed C-H activation 2) Hydroaminoalkylation (still via C-H activation) 3) Hydrohydroxyalkylation (via radical chemistry)
sp 3 C-H Alkylation with Olefins, Yan Xu Dec. 3, 2014 1) sp 3 C-H Alkylation via Directed C-H activation 2) Hydroaminoalkylation (still via C-H activation) 3) Hydrohydroxyalkylation (via radical chemistry)
Hydrogen-Mediated C-C Bond Formation
 EPFL - ISIC - LSPN Hydrogen-Mediated C-C Bond Formation History and selected examples The Research of Prof. Michael Krische (University of Texas at Austin) LSPN Group Seminar Mathias Mamboury Table of
EPFL - ISIC - LSPN Hydrogen-Mediated C-C Bond Formation History and selected examples The Research of Prof. Michael Krische (University of Texas at Austin) LSPN Group Seminar Mathias Mamboury Table of
CO 2 and CO activation
 2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. It is possible that in the next several decades we may have to shift toward other carbon
2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. It is possible that in the next several decades we may have to shift toward other carbon
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006
 Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chemistry Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers
 Chemistry 235 - Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers A GEERAL CEMISTRY answers are given from 1-20: no reaction C 3 CC 3 Ph C C C C C 3 Et 2 2 2 B. REACTIS AD REAGETS [32 MARKS] 2. A single substance
Chemistry 235 - Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers A GEERAL CEMISTRY answers are given from 1-20: no reaction C 3 CC 3 Ph C C C C C 3 Et 2 2 2 B. REACTIS AD REAGETS [32 MARKS] 2. A single substance
Palladium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Benzylic Alkylation Reactions
 Palladium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Benzylic Alkylation Reactions Reporter: Hong-Qiang Shen Checker: Cong Liu Date: 2016/07/12 Masahiro Miura et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6973. Masahiro Miura Osaka
Palladium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Benzylic Alkylation Reactions Reporter: Hong-Qiang Shen Checker: Cong Liu Date: 2016/07/12 Masahiro Miura et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6973. Masahiro Miura Osaka
Direct, Catalytic Hydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated Olefins with N-Alkyl Arylamines
 Current Literature - May 12, 2007 Direct, Catalytic ydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated lefins with -Alkyl ylamines ' '' Ta[ 2 ] 5 (4-8 mol%), 160-165 o C 24-67h 66-95% ' '' S. B. erzon and J. F. artwig,
Current Literature - May 12, 2007 Direct, Catalytic ydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated lefins with -Alkyl ylamines ' '' Ta[ 2 ] 5 (4-8 mol%), 160-165 o C 24-67h 66-95% ' '' S. B. erzon and J. F. artwig,
-catalyzed reactions utilizing isocyanides as a C 1
 Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 78, No. 2, pp. 275 280, 2006. doi:10.1351/pac200678020275 2006 IUPAC GaCl 3 -catalyzed reactions utilizing isocyanides as a C 1 source* Mamoru Tobisu, Masayuki Oshita, Sachiko Yoshioka,
Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 78, No. 2, pp. 275 280, 2006. doi:10.1351/pac200678020275 2006 IUPAC GaCl 3 -catalyzed reactions utilizing isocyanides as a C 1 source* Mamoru Tobisu, Masayuki Oshita, Sachiko Yoshioka,
Catellani Reaction (Pd-Catalyzed Sequential Reaction) Todd Luo
 Catellani Reaction (Pd-Catalyzed Sequential Reaction) Todd Luo 2014.1.6 1 Content Introduction Progress of Catellani Reaction o-alkylation and Applications o-arylation and Applications Conclusion and Outlook
Catellani Reaction (Pd-Catalyzed Sequential Reaction) Todd Luo 2014.1.6 1 Content Introduction Progress of Catellani Reaction o-alkylation and Applications o-arylation and Applications Conclusion and Outlook
CHEM 153 PRACTICE TEST #1 ANSWER KEY
 CEM 153 PACTICE TEST #1 ASWE KEY Provide a mechanism for the following transformation, indicating the electron count and oxidation state of each organometallic intermediate: u 3 (C) 12 (5 mol%) TF, 135
CEM 153 PACTICE TEST #1 ASWE KEY Provide a mechanism for the following transformation, indicating the electron count and oxidation state of each organometallic intermediate: u 3 (C) 12 (5 mol%) TF, 135
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ruthenium-Catalyzed Oxidative Annulation and Hydroarylation of Chromene-3- carboxamides with Alkynes via Double C-H Functionalization R. N. Prasad Tulichala, Mallepalli Shankar and
Supporting Information Ruthenium-Catalyzed Oxidative Annulation and Hydroarylation of Chromene-3- carboxamides with Alkynes via Double C-H Functionalization R. N. Prasad Tulichala, Mallepalli Shankar and
Nickel-Catalyzed Three-Component [3+2+2] Cocyclization of Ethyl Cyclopropylideneacetate and Alkynes
![Nickel-Catalyzed Three-Component [3+2+2] Cocyclization of Ethyl Cyclopropylideneacetate and Alkynes Nickel-Catalyzed Three-Component [3+2+2] Cocyclization of Ethyl Cyclopropylideneacetate and Alkynes](/thumbs/77/74720708.jpg) Nickel-Catalyzed Three-Component [3+2+2] Cocyclization of Ethyl Cyclopropylideneacetate and Alkynes Selective Synthesis of Multisubstituted Cycloheptadienes 1 2 Cat. Ni 0 1 2 Komagawa, S.; Saito, S. Angew.
Nickel-Catalyzed Three-Component [3+2+2] Cocyclization of Ethyl Cyclopropylideneacetate and Alkynes Selective Synthesis of Multisubstituted Cycloheptadienes 1 2 Cat. Ni 0 1 2 Komagawa, S.; Saito, S. Angew.
Additions to Metal-Alkene and -Alkyne Complexes
 Additions to tal-alkene and -Alkyne Complexes ecal that alkenes, alkynes and other π-systems can be excellent ligands for transition metals. As a consequence of this binding, the nature of the π-system
Additions to tal-alkene and -Alkyne Complexes ecal that alkenes, alkynes and other π-systems can be excellent ligands for transition metals. As a consequence of this binding, the nature of the π-system
CO 2 and CO activation
 2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. Itispossiblethatinthenextseveraldecadeswemayhavetoshifttowardothercarbonsources for these
2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. Itispossiblethatinthenextseveraldecadeswemayhavetoshifttowardothercarbonsources for these
Copper-Catalyzed Reaction of Alkyl Halides with Cyclopentadienylmagnesium Reagent
 Copper-Catalyzed eaction of Alkyl Halides with Cyclopentadienylmagnesium eagent Mg 1) cat. Cu(Tf) 2 i Pr 2, 25 o C, 3 h 2) H 2, Pt 2 Masahiro Sai, Hidenori Someya, Hideki Yorimitsu, and Koichiro shima
Copper-Catalyzed eaction of Alkyl Halides with Cyclopentadienylmagnesium eagent Mg 1) cat. Cu(Tf) 2 i Pr 2, 25 o C, 3 h 2) H 2, Pt 2 Masahiro Sai, Hidenori Someya, Hideki Yorimitsu, and Koichiro shima
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds
 Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols
Chapter 17. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
Student Manual for Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation Using a Copper(I)/TEMPO Catalyst System
 Student Manual for Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation Using a Copper(I)/TEMPO Catalyst System icholas J. Hill, Jessica M. Hoover and Shannon S. Stahl* Department of Chemistry, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1101
Student Manual for Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation Using a Copper(I)/TEMPO Catalyst System icholas J. Hill, Jessica M. Hoover and Shannon S. Stahl* Department of Chemistry, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1101
Direct Oxidative Heck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans
 Direct xidative eck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans by Zhang,.; Ferreira, E. M.; Stoltz, B. M. Angewandte
Direct xidative eck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans by Zhang,.; Ferreira, E. M.; Stoltz, B. M. Angewandte
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALKENES AND REACTIONS OF ALKENES
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKENES and ALKYNES Alkenes/Alkynes are named by adding the suffix modifier (- /- ) to the end of the root. Alkenes/alkynes receive in numbering alkanes Location is assigned
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKENES and ALKYNES Alkenes/Alkynes are named by adding the suffix modifier (- /- ) to the end of the root. Alkenes/alkynes receive in numbering alkanes Location is assigned
Investigation of the Role and Form. Formation. Michael Enright
 Investigation of the Role and Form of Silver Catalysts in C N Bond Formation Michael Enright Ripon College Importance Carbon Nitrogen Bonds Medicine Biological compounds Make C N bonds whenever we want
Investigation of the Role and Form of Silver Catalysts in C N Bond Formation Michael Enright Ripon College Importance Carbon Nitrogen Bonds Medicine Biological compounds Make C N bonds whenever we want
6 Synthesis of Alcohols
 6 Synthesis of Alcohols 6.1 Synthesis of Saturated Alcohols Hydroboration-oxidation is now a standard method for anti-markovnikov s cishydration [1] of alkenes from the less hindered side of the double
6 Synthesis of Alcohols 6.1 Synthesis of Saturated Alcohols Hydroboration-oxidation is now a standard method for anti-markovnikov s cishydration [1] of alkenes from the less hindered side of the double
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections:
 Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections: 9.14-9.19 Aldehydes and ketones are found in many fragrant odors of many fruits, fine perfumes, hormones etc. some examples are listed below. Aldehydes
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections: 9.14-9.19 Aldehydes and ketones are found in many fragrant odors of many fruits, fine perfumes, hormones etc. some examples are listed below. Aldehydes
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
6,6 -Dihydroxy terpyridine: A proton-responsive bifunctional ligand and its application in catalytic transfer hydrogenation of ketones
 Electronic Supplementary Information for: 6,6 -Dihydroxy terpyridine: A proton-responsive bifunctional ligand and its application in catalytic transfer hydrogenation of ketones Cameron M. Moore a and Nathaniel
Electronic Supplementary Information for: 6,6 -Dihydroxy terpyridine: A proton-responsive bifunctional ligand and its application in catalytic transfer hydrogenation of ketones Cameron M. Moore a and Nathaniel
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Description
 CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
JF Annual Paper II 2002 Model Answers
 JF Annual Paper II 2002 Model Answers Q1. yclohexane conformation chair more stable than the boat conformation (not answer d). For substituted cyclohexanes axial position is less stable than equatorial
JF Annual Paper II 2002 Model Answers Q1. yclohexane conformation chair more stable than the boat conformation (not answer d). For substituted cyclohexanes axial position is less stable than equatorial
CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer Instructor: Paul J. Bracher. Quiz # 3. Monday, July 21 st, :30 a.m.
 CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Quiz # 3 Solutions Key Page 1 of 9 CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Quiz # 3 Monday, July 21 st,
CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Quiz # 3 Solutions Key Page 1 of 9 CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Quiz # 3 Monday, July 21 st,
Wilkinson s other (ruthenium) catalyst
 Wilkinson s other (ruthenium) catalyst Cl 3 ; 2 h 3, reflux 3h h 3 Cl h 3 h Cl 3 Good catalyst especially for 2 1-alkenes 2, base toluene Cl h 3 h 3 h 3 Et 3 Cl h 3 Cl h 3 h 3 R h 3 h 3 Cl h 3 R RC 2 C
Wilkinson s other (ruthenium) catalyst Cl 3 ; 2 h 3, reflux 3h h 3 Cl h 3 h Cl 3 Good catalyst especially for 2 1-alkenes 2, base toluene Cl h 3 h 3 h 3 Et 3 Cl h 3 Cl h 3 h 3 R h 3 h 3 Cl h 3 R RC 2 C
H Organometallic Catalysis in Industry
 H Organometallic Catalysis in Industry Some terminology: Catalytic cycles: a circular path meant to show productive reactions, in order, that lead from the catalytically active species and its reaction
H Organometallic Catalysis in Industry Some terminology: Catalytic cycles: a circular path meant to show productive reactions, in order, that lead from the catalytically active species and its reaction
Thermolysis of polyazapentadienes. Part The 1,1-dialkyl- 5- aryl-1,3,5-triazapentadiene problem
 Thermolysis of polyazapentadienes. Part 12. 1 The 1,1-dialkyl- 5- aryl-1,3,5-triazapentadiene problem amish Mcab* and M. Elizabeth-Ann Murray Department of Chemistry, The University of Edinburgh, West
Thermolysis of polyazapentadienes. Part 12. 1 The 1,1-dialkyl- 5- aryl-1,3,5-triazapentadiene problem amish Mcab* and M. Elizabeth-Ann Murray Department of Chemistry, The University of Edinburgh, West
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
CHMA2000 EXPT 7: The Physical and Chemical Properties of Alcohols
 CHMA2000 EXPT 7: The Physical and Chemical Properties of Alcohols Objectives: At the end of this experiment you should be able to: 1. Understand the physical and chemical properties of alcohols 2. Understand
CHMA2000 EXPT 7: The Physical and Chemical Properties of Alcohols Objectives: At the end of this experiment you should be able to: 1. Understand the physical and chemical properties of alcohols 2. Understand
Background Information
 ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
Kinetic Isotope Effects
 1 Experiment 31 Kinetic Isotope Effects Isotopic substitution is a useful technique for the probing of reaction mechanisms. The change of an isotope may affect the reaction rate in a number of ways, providing
1 Experiment 31 Kinetic Isotope Effects Isotopic substitution is a useful technique for the probing of reaction mechanisms. The change of an isotope may affect the reaction rate in a number of ways, providing
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION
 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols by various reactions Structure of the Carbonyl
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols by various reactions Structure of the Carbonyl
Aldol Condensation Notes
 Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the laboratory manual. Aldol Condensation Notes History and Application Condensation reactions are molecular transformations that join together
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the laboratory manual. Aldol Condensation Notes History and Application Condensation reactions are molecular transformations that join together
An Aldol Condensation to synthesize Chalcones. By: Blake Burger FFR#3
 An Aldol Condensation to synthesize Chalcones By: Blake Burger FFR#3 Burger, 2 Introduction A chalcone is a molecule formed by two core functional groups: an aromatic ketone and an enone. Chalcones are
An Aldol Condensation to synthesize Chalcones By: Blake Burger FFR#3 Burger, 2 Introduction A chalcone is a molecule formed by two core functional groups: an aromatic ketone and an enone. Chalcones are
Aromatic Compounds II
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
Synthesis of Amines Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction II. Reductive Amination
 Synthesis of Amines I. Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction Amines can be alkylated in SN2 fashion by alkyl halides; primary halides are best for this purpose. This is not a practical reaction for formation
Synthesis of Amines I. Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction Amines can be alkylated in SN2 fashion by alkyl halides; primary halides are best for this purpose. This is not a practical reaction for formation
CH 3 TMG, DMF N H 3 CO 2 S. (PPh 3 ) 2 Pd 0
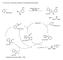 1. (a) rovide a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I S 2 C 3 C 3 ( 3 ) 2 2, CuI C 3 TMG, DMF 3 C 2 S TMG = Me 2 Me 2 ICu ( 3 ) 2 0 I S 2 C 3 S 2 C 3 Cu I 3 3 3 C 2 S I 3 3 3 C 2 S 3
1. (a) rovide a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I S 2 C 3 C 3 ( 3 ) 2 2, CuI C 3 TMG, DMF 3 C 2 S TMG = Me 2 Me 2 ICu ( 3 ) 2 0 I S 2 C 3 S 2 C 3 Cu I 3 3 3 C 2 S I 3 3 3 C 2 S 3
Synthesis of Tetraphenylcyclopentadienone. Becky Ortiz
 Synthesis of Tetraphenylcyclopentadienone Becky Ortiz Introduction An aldol reaction is a reaction in which aldehydes or ketones undergo a base- catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction to form a beta-
Synthesis of Tetraphenylcyclopentadienone Becky Ortiz Introduction An aldol reaction is a reaction in which aldehydes or ketones undergo a base- catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction to form a beta-
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation
 Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation Chiral dioxirane strategy: R 3 + 1 xone, ph 10.5, K 2 C 3, H 2, C R 3 formed in situ catalyst (10-20 mol%) is prepared from D-fructose, and its enantiomer from L-sorbose oxone,
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation Chiral dioxirane strategy: R 3 + 1 xone, ph 10.5, K 2 C 3, H 2, C R 3 formed in situ catalyst (10-20 mol%) is prepared from D-fructose, and its enantiomer from L-sorbose oxone,
Alcohols Oxidation by oxygen O 2 in presence of vanadoheteropolyacid (H 5 PMo 10 V 2 O 40 ) as green catalyst
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.2, No.3, pp 1666-1672, July-Sept 2010 Alcohols Oxidation by oxygen O 2 in presence of vanadoheteropolyacid (H 5 PMo 10
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.2, No.3, pp 1666-1672, July-Sept 2010 Alcohols Oxidation by oxygen O 2 in presence of vanadoheteropolyacid (H 5 PMo 10
Methyl Migration to Coordinated CO
 Methyl Migration to ordinated EFEENCES EXPEIMENT 6 Meisler, G.L., Tarr, D.A. Inorganic Chemistry, 3 rd Ed., Prentice all, Upper Saddle iver, N, 2004, Chapters 13 and 14. SAFETY EMMENDATINS Cyclopentadienyl
Methyl Migration to ordinated EFEENCES EXPEIMENT 6 Meisler, G.L., Tarr, D.A. Inorganic Chemistry, 3 rd Ed., Prentice all, Upper Saddle iver, N, 2004, Chapters 13 and 14. SAFETY EMMENDATINS Cyclopentadienyl
Experiment 2 Solvent-free Aldol Condensation between 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde and 1-indanone
 Experiment 2 Solvent-free Aldol Condensation between 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde and 1-indanone Chemical Concepts Carbonyl chemistry, base catalyzed aldol reaction, melting point, recrystallization Green
Experiment 2 Solvent-free Aldol Condensation between 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde and 1-indanone Chemical Concepts Carbonyl chemistry, base catalyzed aldol reaction, melting point, recrystallization Green
Experiment 3. Condensation Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes: The Aldol Condensation Reaction.
 Experiment 3. Condensation Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes: The Aldol Condensation Reaction. References: Brown & Foote, Chapters 16, 19, 23 INTRODUCTION: This experiment continues the saga of carbon-carbon
Experiment 3. Condensation Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes: The Aldol Condensation Reaction. References: Brown & Foote, Chapters 16, 19, 23 INTRODUCTION: This experiment continues the saga of carbon-carbon
Palladium-catalyzed cross-addition of triisopropylsilylacetylene to unactivated alkynes*
 Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 80, No. 5, pp. 1161 1166, 2008. doi:10.1351/pac200880051161 2008 IUPAC Palladium-catalyzed cross-addition of triisopropylsilylacetylene to unactivated alkynes* Naofumi Tsukada, Satoshi
Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 80, No. 5, pp. 1161 1166, 2008. doi:10.1351/pac200880051161 2008 IUPAC Palladium-catalyzed cross-addition of triisopropylsilylacetylene to unactivated alkynes* Naofumi Tsukada, Satoshi
Novel Synthesis of 5-Substituted-Tetrazoles
 ovel Synthesis of 5-Substituted-Tetrazoles The AMPAC-GaTech Partnership fosters research aimed at opening and developing new avenues and compounds that fit the American Pacific Corporation (AMPAC) s potential
ovel Synthesis of 5-Substituted-Tetrazoles The AMPAC-GaTech Partnership fosters research aimed at opening and developing new avenues and compounds that fit the American Pacific Corporation (AMPAC) s potential
Melamine trisulfonic acid catalyzed regioselective nitration of aromatic compounds under solvent-free conditions
 J. Iranian Chem. Res. 5 (3) (2012) 155-159 ISSN 2008-1030 lamine trisulfonic acid catalyzed regioselective nitration of aromatic compounds under solvent-free conditions Jalal Albadi *,a, Farhad Shirini
J. Iranian Chem. Res. 5 (3) (2012) 155-159 ISSN 2008-1030 lamine trisulfonic acid catalyzed regioselective nitration of aromatic compounds under solvent-free conditions Jalal Albadi *,a, Farhad Shirini
Espacenet Claims: US (A)
 Espacenet - Claims http://worldwide.espacenet.com/publicationdetails/claims?cc=us&... 1 di 1 03/07/2012 17:00 Espacenet Claims: US5278333 (A) 1994-01-11 Process for the alpha-monoalkylation of arylacetonitriles,
Espacenet - Claims http://worldwide.espacenet.com/publicationdetails/claims?cc=us&... 1 di 1 03/07/2012 17:00 Espacenet Claims: US5278333 (A) 1994-01-11 Process for the alpha-monoalkylation of arylacetonitriles,
12/27/2010. Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones
 Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones 9.1 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al The aldehyde functional group is always carbon
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones 9.1 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al The aldehyde functional group is always carbon
C-H Activation Reactions of Ruthenium N-Heterocyclic Carbene. Complexes: Application in a Catalytic Tandem Reaction Involving C-C
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION C-H Activation Reactions of Ruthenium N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes: Application in a Catalytic Tandem Reaction Involving C-C Bond Formation from Alcohols Suzanne Burling, Belinda
SUPPORTING INFORMATION C-H Activation Reactions of Ruthenium N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes: Application in a Catalytic Tandem Reaction Involving C-C Bond Formation from Alcohols Suzanne Burling, Belinda
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
The Synthesis of Triphenylmethano. will synthesize Triphenylmethanol, a white crystalline aromatic
 HEM 333L rganic hemistry Laboratory Revision 2.0 The Synthesis of Triphenylmethano ol In this laboratory exercise we will synthesize Triphenylmethanol, a white crystalline aromatic compound. Triphenylmethanol
HEM 333L rganic hemistry Laboratory Revision 2.0 The Synthesis of Triphenylmethano ol In this laboratory exercise we will synthesize Triphenylmethanol, a white crystalline aromatic compound. Triphenylmethanol
Highly Efficient, Convergent, and Enantioselective Synthesis of Phthioceranic Acid
 Highly Efficient, Convergent, and Enantioselective Synthesis of Phthioceranic Acid Shiqing Xu, Akimichi Oda, Thomas Bobinski, Haijun Li, Yohei Matsueda, and Ei-ichi Negishi Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015,
Highly Efficient, Convergent, and Enantioselective Synthesis of Phthioceranic Acid Shiqing Xu, Akimichi Oda, Thomas Bobinski, Haijun Li, Yohei Matsueda, and Ei-ichi Negishi Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015,
Reversible Interaction between Substrate and Ligand
 Reversible Interaction between Substrate and Ligand 2010.6.9.YoheiShimizu(D3) is is is Ser 271 P Lys 229-2 3 P Zn 2+ Tyr P 3 2- + 3 Lys 107 P 3 2- class 1 aldolase class 2 aldolase Glu 185 Asp 211 C 2
Reversible Interaction between Substrate and Ligand 2010.6.9.YoheiShimizu(D3) is is is Ser 271 P Lys 229-2 3 P Zn 2+ Tyr P 3 2- + 3 Lys 107 P 3 2- class 1 aldolase class 2 aldolase Glu 185 Asp 211 C 2
Benzenes & Aromatic Compounds
 Benzenes & Aromatic Compounds 1 Structure of Benzene H H C C C H C 6 H 6 H C C C H H A cyclic conjugate molecule Benzene is a colourless odourless liquid, boiling at 80 o C and melting at 5 o C. It is
Benzenes & Aromatic Compounds 1 Structure of Benzene H H C C C H C 6 H 6 H C C C H H A cyclic conjugate molecule Benzene is a colourless odourless liquid, boiling at 80 o C and melting at 5 o C. It is
A Simple Introduction of the Mizoroki-Heck Reaction
 A Simple Introduction of the Mizoroki-Heck Reaction Reporter: Supervisor: Zhe Niu Prof. Yang Prof. Chen Prof. Tang 2016/2/3 Content Introduction Intermolecular Mizoroki-Heck Reaction Intramolecular Mizoroki-Heck
A Simple Introduction of the Mizoroki-Heck Reaction Reporter: Supervisor: Zhe Niu Prof. Yang Prof. Chen Prof. Tang 2016/2/3 Content Introduction Intermolecular Mizoroki-Heck Reaction Intramolecular Mizoroki-Heck
Metal-catalyzed asymmetric hetero-diels-alder reactions of unactivated dienes with glyoxylates
 Pure & Appl. Chern., Vol. 70, No. 5, pp. 11 17-1 122, 1998. Printed in Great Britain. (0 1998 IUPAC Metal-catalyzed asymmetric hetero-diels-alder reactions of unactivated dienes with glyoxylates Mogens
Pure & Appl. Chern., Vol. 70, No. 5, pp. 11 17-1 122, 1998. Printed in Great Britain. (0 1998 IUPAC Metal-catalyzed asymmetric hetero-diels-alder reactions of unactivated dienes with glyoxylates Mogens
Communications is available online at: This article is related to the Nobel Prize in chemis. Instructions for use
 Title The Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reaction of P Author(s)Miyaura, N.; Yanagi, T.; Suzuki, A. CitationSynthetic Communications, 11(7): 513-519 Issue Date 1981 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/44302
Title The Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reaction of P Author(s)Miyaura, N.; Yanagi, T.; Suzuki, A. CitationSynthetic Communications, 11(7): 513-519 Issue Date 1981 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/44302
Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium
 Literature report Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium Compounds Reporter: Zhang-Pei Chen Checker: Mu-Wang Chen Date: 02/07/2013 Feringa, B.L.et al. Feringa, B. L. et al. Nature Chem. 2013,
Literature report Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium Compounds Reporter: Zhang-Pei Chen Checker: Mu-Wang Chen Date: 02/07/2013 Feringa, B.L.et al. Feringa, B. L. et al. Nature Chem. 2013,
1. Study the reaction scheme below, then answer the questions that follow.
 1. Study the reaction scheme below, then answer the questions that follow. (a) (i) Butanal contains a carbonyl group. State a chemical test for a carbonyl group and describe the result of the test. Test...
1. Study the reaction scheme below, then answer the questions that follow. (a) (i) Butanal contains a carbonyl group. State a chemical test for a carbonyl group and describe the result of the test. Test...
Synthesis of Tethered Chromium Carbene Complexes
 SYNTHESIS OF TETHERED CHROMIUM CARBENE COMPLEXES 375 Synthesis of Tethered Chromium Carbene Complexes Nicole S. Lueck Faculty Sponsor: Curtis Czerwinski, Department of Chemistry ABSTRACT Hydroxycarbene
SYNTHESIS OF TETHERED CHROMIUM CARBENE COMPLEXES 375 Synthesis of Tethered Chromium Carbene Complexes Nicole S. Lueck Faculty Sponsor: Curtis Czerwinski, Department of Chemistry ABSTRACT Hydroxycarbene
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 12, This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models. This test contains 11 pages
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 12, 2012 Your name: This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 11 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 24 3. / 26 4. / 30
CEM 203 Final Exam December 12, 2012 Your name: This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 11 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 24 3. / 26 4. / 30
Page 1 of 9. Sessional Examination (November 2017) Max Marks: 20 Date: Time: One Hour. Model Answers
 Page 1 of 9 Sessional Examination (November 2017) Class: B. Pharm-II yr (III sem) Subject: Pharma Org. Chem-II Max Marks: 20 Date: 14.11.2017 Time: One Hour Model Answers Q. 1. Solve the following (ANY
Page 1 of 9 Sessional Examination (November 2017) Class: B. Pharm-II yr (III sem) Subject: Pharma Org. Chem-II Max Marks: 20 Date: 14.11.2017 Time: One Hour Model Answers Q. 1. Solve the following (ANY
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 6 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Oxidation States Easy for inorganic salts: CrO 4 2- reduced to Cr 2 O 3. KMnO 4 reduced to MnO 2. Oxidation: Gain of O,
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 6 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Oxidation States Easy for inorganic salts: CrO 4 2- reduced to Cr 2 O 3. KMnO 4 reduced to MnO 2. Oxidation: Gain of O,
Experiment 12: Grignard Synthesis of Triphenylmethanol
 1 Experiment 12: Grignard Synthesis of Triphenylmethanol Reactions that form carbon-carbon bonds are among the most useful to the synthetic organic chemist. In 1912, Victor Grignard received the Nobel
1 Experiment 12: Grignard Synthesis of Triphenylmethanol Reactions that form carbon-carbon bonds are among the most useful to the synthetic organic chemist. In 1912, Victor Grignard received the Nobel
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds The π electrons of
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds The π electrons of
CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key
 CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key 1.) Fill in the appropriate reaction arrow. The starting material is on the left, the product is on the right. Use. Simple Ring Size. 5 and 6 are favored. 3 is not. That s it.
CHEM 345 Problem Set 07 Key 1.) Fill in the appropriate reaction arrow. The starting material is on the left, the product is on the right. Use. Simple Ring Size. 5 and 6 are favored. 3 is not. That s it.
Title. Author(s)Ishiyama, Tatsuo; Oohashi, Zengo; Ahiko, Taka-aki; M. CitationChemistry Letters, 8: Issue Date Doc URL.
 Title Nucleophilic Borylation of Benzyl Halides with Bis(p Author(s)Ishiyama, Tatsuo; Oohashi, Zengo; Ahiko, Taka-aki; M CitationChemistry Letters, 8: 7-781 Issue Date 2002-08-05 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/56196
Title Nucleophilic Borylation of Benzyl Halides with Bis(p Author(s)Ishiyama, Tatsuo; Oohashi, Zengo; Ahiko, Taka-aki; M CitationChemistry Letters, 8: 7-781 Issue Date 2002-08-05 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/56196
Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Esters from Ketones. Alkyl Group as a Leaving Group.
 Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Esters from Ketones. Alkyl Group as a Leaving Group. akatani, Y.; Koizumi, Y.; Yamasaki, R.; Saito, S. rg. Lett. 2008, 10, 2067-2070. An Annulation Reaction for the Synthesis
Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Esters from Ketones. Alkyl Group as a Leaving Group. akatani, Y.; Koizumi, Y.; Yamasaki, R.; Saito, S. rg. Lett. 2008, 10, 2067-2070. An Annulation Reaction for the Synthesis
Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~ 20
 Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
17 Alcohols H H C C. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 H H. Bond angles in Alcohols. Boiling points. Different types of alcohols H 2 C CH 2 CH 2
 17 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
17 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
The Mechanism of Rhenium Catalyzed Olefination of Aldehydes. Nathan Werner Denmark Group Meeting July 22 nd, 2008
 The Mechanism of Rhenium Catalyzed Olefination of Aldehydes Nathan Werner Denmark Group Meeting July 22 nd, 2008 Introduction First Use of Phosphanes to Olefinate Carbonyls: oxaphosphetane Advantages:
The Mechanism of Rhenium Catalyzed Olefination of Aldehydes Nathan Werner Denmark Group Meeting July 22 nd, 2008 Introduction First Use of Phosphanes to Olefinate Carbonyls: oxaphosphetane Advantages:
Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Experiment 8: Chlorination of 1-Chlorobutane
 1 Experiment 8: Chlorination of 1-Chlorobutane Alkanes contain only nonpolar carbon-hydrogen and carbon-carbon single bonds, which makes them unreactive toward most acidic and basic reagents. They can,
1 Experiment 8: Chlorination of 1-Chlorobutane Alkanes contain only nonpolar carbon-hydrogen and carbon-carbon single bonds, which makes them unreactive toward most acidic and basic reagents. They can,
