UNIT-10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
|
|
|
- Rolf Morrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Important terms and concepts: UNIT-10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES Alkyl halide or Haloalkane is the compound obtained by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of an alkane by same number of halogen atoms. Eg: CH3CI,CH3Br R-H+X 2 R-X+H-X For C4H9Br, four isomeric compounds are possible out of which one(sec-butyl bromide) can show enantiomerism. For C5H11Br, eight isomeric compounds are possible out of which three can exhibit enantiomerism. Alcohols can be converted into chlorides by reaction with (i)hcl/zncl2 (ii)pcl5 (iii)pcl3 (iv) SOCl2/Pyridine.The reaction with SOCl2/Pyridine is preferred because in this case side products are gaseous and can be expelled during distillation. Halogenation of alkenes in the presence of peroxides takes place through free radicals as intermediates and results in anti-markownikoff s product. For same alkyl group boiling points of alkyl halide are in the order:ri RBr RCl RF Among isomeric halides boiling point decreases with increase in branching in alkyl group. Alkyl halides are insoluble in water due to their inability to form hydrogen bonds with water. Allylic halide : CH2=CH-CH2X Benzylic halide : C6H5CH2Cl Vinylic halide : CH2=CH-Cl Order of reactivity of Alkyl halide in SN1 reaction: 3 0 > 2 0 > 1 0 Order of reactivity of Alkyl halide in SN2 reaction: 1 0 > Finkelstein reaction: R X + NaI R I + NaX Swart reaction : R X + AgF R F +Ag
2 Saytzeff srule: It states that during dehydro halogenations, the preferred product is that alkene which has greater number of alkyl groups attached to the doubly bonded carbon atoms. Alc.KOH CH 3 -CH 2 CH- CH 3 CH 3 CH= CH- CH 3 Br 81% More highly substituted Alkenes will be more stable Some important name reaction: 1. Wurtz reaction R X+2Na + X R Dry ether R-R+2NaX 2. Wurtz- fittig reaction R X+2Na + R Ar Dryether R-Ar+2NaX 3.Sandmeyer s reaction: ArNH2 + HNO2+HCl 273 K ArN2Cl Cu2X2+HX ArX +N2 CCl4 is used as fire extinguisher under the name Pyrene. CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS Q1. Why are halo alkanes more reactive than haloarenes?. Ans. In haloarenes, there is double bond character between carbon and halogen due to resonance effect which makes it less reactive. (ii)in benzene, carbon atom is sp2 hybridised which is shorter than sp3 present in halo alkanes. Hence C-Cl bond in aryl halides is shorter and stronger. Q2. Why do halo alkanes undergo nucleophillic substitution where as haloarenes undergo electophillic substitution. Ans. Due to more electro negative nature of halogen atom in halo alkanes carbon atom becomes slightly positive and is easily attacked by nucleophillic reagents. While in halo arenes due to resonance, carbon atom becomes slightly negative and attacked by electrophillic reagents.
3 Q3. When an alkyl halide is treated with ethanolic solution of KCN, the major product is alkylcyanide where as if alkyl halide is treated with AgCN, the major product is alkyl isocyanide. Ans. KCN is ionic they can attach through C or N but C-C bond is stronger than C-N bond. So RCN is major product. AgCN is covalent and so more electro negative N can attach to C and forms iso cyanides. Q4. Aryl halides cannot be prepared by the action of sodium halide on phenol in the presence H 2 SO 4. Why? Ans. Due to resonance the carbon-oxygen bond in phenol has partial double bond character and it is stronger than carbon oxygen single bond. Q5. Grignard reagent should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. Why? Ans. Grignard reagent reacts with H 2 O (moisture) to form alkanes, therefore they are prepared under anhydrous condition. Q6.Why is Sulphuric acid not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI? Ans. It is because HI formed will get oxidized to I 2 by concentrated Sulphuric acid which is an oxidizing agent. Q7. p-dichloro benzene has higher m.p.than those of ortho and m- isomers.? Ans. p-dichloro benzene is symmetrical, fits into crystal lattice more readily and has higher melting point. Q8. Although chlorine is an electron-with drawing group, it is ortho and para directing in electrophillic aromatic substitution reactions. Why? Ans. Chlorobenzene is resonance hybrid, there is ve charge at ortho and parapositions, electro phallic substitution reaction will takeplace at ortho and para position due to +R effect which dominating over the I effect
4 Q9.The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH lead to the formation of alcohols but in presence of alcoholic KOH alkenes are major products. Explain? Ans. In aqueous KOH, (OH-) is nucleo phile which replaces another nucleophile. R-X+KOH Where as in alcoholic KOH C 2 H 5 OH+KOH CH 3 CH 2 -Cl+alco.KOH R-OH+KX C 2 H 5 O- +K+ CH 2 =CH 2 +C 2 H 5 OH Q10. Explain why vinylchloride is unreactive in nucleophillic substitution reaction? Ans. Vinylchloride is unreactive in nucleophillic substitution reaction because of double bond character between C=C-Clbond which is difficult to break. Q11. Arrange the following compounds according to reactivity towards nucleophilic substitution reaction with CH 3 ONa- 4-nitro chlorobenzene, 2, 4 di nitro chlorobenzene, 2, 4, 6, tri nitro chlorobenzene Ans- 2, 4, 6, trinitro chlorobenzene>2, 4 di nitro chlorobenzene>4-nitro chlorobenzene Q12. Which compound will react faster in SN 2 reaction with OH-? Ans-(a)CH 3 Br and CH 3 I CH 3 I will react faster than CH 3 Br since I is a easily leaving group (b)(ch 3 ) 3 C-Cl or CH 3 Cl CH 3 Cl will react faster than 3 0 halide since (CH 3 ) 3 C has more steric
5 hindrance Q13. Arrange in order of boiling points. (a)bromo benzene, Bromoform, chloro methane, Dibromo-methane (b)1-chloro propane, Iso propyle chloride,1-chlorobutane. Ans. (a)chloro methane<bromo benzene<dibromo-methane<, Bromoform (b), Iso propyl chloride<1-chloropropane<1-chlorobutane (As branching increases, boiling point decreases) Q14. Predict the reactivity in SN 1 (a) C 6 H 5 CH 2 Br, C 6 H 5 CH(C 6 H 5 )Br, C 6 H 5 CH(CH 3 )Br, C 6 H 5 C(CH 3 )(C 6 H 5 )Br Ans. 3 0 >2 0 >1 0 (SN 1 ) C 6 H 5 C(CH 3 )(C 6 H 5 )Br >C 6 H 5 (C 6 H 5 )Br > C 6 H 5 CH(CH 3 )Br >C 6 H 5 CH 2 Br (3 0 ) (2 0 ) (2 0 ) (1 0 ) VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION[1MARKS] 1. Write the IUPAC name of : CH2=CHCH2Br - ( All India 2011) 2. An alkyl halide having molecular formula C 4 H 9 Cl is optically active. What is its structure? 3. Why is vinyl chloride less reactive than ethyl chloride? 4.Write the structural isomers of C 3 H 6 Cl 2 which can exihibit enantiomerism? 5. Write down the structure of the following compounds; (a)1-chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane (b)1,4-dibronebut-2-ene (c)4-terbutyl-3-iodoheptane (d)1-bromo-4-secbutyl-2-methylbenzene 6. A hydro carbon C 5 H 12s does not react with chlorine in dark but it gives a single mono chloro compound in bright sunlight. Identify the compound. 7. Why is sulphuric acid not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI? 8. Out of C 6 H 5 CH 2 Cl &C 6 H 5 CH(Cl)C 6 H 5 which is more easily hydrolysed with aq.koh & why? 9. What is meant by the following terms: (1)chirality (2)enantiomerism (3)Ambident nucleophiles.
6 10. Chloroform is stored in dark coloured & sealed bottle. Why? Short answer type questions 1. Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds? A) ClCH 2 C= CCH 2 Br b) (CCl 3 )3CCl C)CH 3 CH(Cl)CH(Br)CH 3 2. How would you carry out the following conversions? ( All India 2008) (i) Ethyl magnesium chloride to propanol. (ii) Benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol. 3. What is significance of 12 in Freon 12? 4. Predict the product of the following reaction CH2=CH-CH3 + HBr +Peroxide 5. Write the reaction involved in: (A) Sandmeyers reaction (B) Swarts reaction (C) Finkelstein reaction (D) Fittigs reaction 6. Rearrange the following in order of increasing ease of dehydrohalogenations CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 Cl, CH 3 CHClCH 3, CH 3 C-Cl(CH 3 )2 1. Account for the following: ( C.B.S.E. 2013) (i)the C Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than that in CH3 Cl? (ii)chloroform is stored in closed dark brown bottles. 8. Give the uses of (a)ccl 4 (b)iodoform 9. Propose the mechanism of the following reaction: CH 3 -CH 2 -Br+CH 3 OH CH 3 -CH 2 -OCH 3 +HBr 10.Suggest a possible mechanism for the following reaction: (C.B.S.E. DELHI 2009) n-bubr + KCN n- BuCN 11. How will you bring the following conversion? (a)propene to Propyne (b)toluene to Benzyl Alcohol(c) Aniline to Phenyl iso cyanide 12. What happen when;
7 (a)n-butyl chloride is treated with alc.koh. (b) ethyl chloride is treated with aq.koh. (c)methyl chloride is treated with KCN. 13. How can we produce nitro benzene from phenol? Ans.(I)First convert phenol to benzene by heating with Zn dust. (II) Nitration of benzene with conc.nitric acid in presence of conc.sulphuric acid. 14. Alcohols react with halogen acids to form haloalkanes but phenol does not form halo benzene. Explain. Ans. The C-O bond in phenol acquires partial double bond character due to resonance. Hence it is not Cleaved by X- ions to form halobenzenes. But in alcohols a pure single bond C O bond is maintained and can be cleaved by X ions. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS Q1) How do you convert the following? (i)propenetopropan-1-ol (ii)1-bromopropaneto2-bromopropane (iii)toluenetobenzylalcohol (iv)benzeneto4-bromonitrobenzene (v)benzylalcoholto2-phenylethanoicacid 1. CH3-CH=CH2+HBr Peroxide CH3CH2CH2Br aq.koh CH3CH2CH2OH 2.
8 Q2) How are the following conversions carried out? (i)ethanol to propane nitrile (ii)aniline to chloro benzene (iii)2-chloro butane to 3, 4-dimethyl hexane (iv)2-methyl-1-propene to 2-chloro-2-methylpropane (v)ethyl chloride to propanoic acid 1. 2.
9 Q3) How are the following conversions carried out? (i) But-1-ene to n-butyliodide (ii) 2-Chloropropane to1-propanol (iii) Iso propyl alcohol to iodoform (iv) Chloro benzene to p-nitrophenol (v) 2-Bromopropane to 1-bromopropane
10
11 5.. Q4.How will you carry out the followingconversions? (i)chloro ethane to butane (ii)benzene to diphenyl 1. 2.
HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
 Unit - 10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES 1. Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds. Br CH = CH C CH (vi) (vii) (ix) (CCl 3 ) 3 CCl 103 XII Chemistry 2. Write the structure of following halogen compounds
Unit - 10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES 1. Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds. Br CH = CH C CH (vi) (vii) (ix) (CCl 3 ) 3 CCl 103 XII Chemistry 2. Write the structure of following halogen compounds
Chapter 10- Halo Alkanes and Halo arenes LEVEL-1 QUESTIONS
 Chapter 10- Halo Alkanes and Halo arenes LEVEL-1 QUESTIONS 1. Out of PCl5 and SOCl2 which one is better reagent for conversion of alcohol to alkylchloride. Why? Answer: SOCl2.Because all the biproducts
Chapter 10- Halo Alkanes and Halo arenes LEVEL-1 QUESTIONS 1. Out of PCl5 and SOCl2 which one is better reagent for conversion of alcohol to alkylchloride. Why? Answer: SOCl2.Because all the biproducts
Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes
 alo Alkanes and alo Arenes Short Answer Questions: **1. Write the isomers of the compound having formula C 4 9 Br? Sol. There are five isomers of C 4 9 Br. These are: 2-bromobutane is expected to exhibit
alo Alkanes and alo Arenes Short Answer Questions: **1. Write the isomers of the compound having formula C 4 9 Br? Sol. There are five isomers of C 4 9 Br. These are: 2-bromobutane is expected to exhibit
DAV CENTENARY PUBLIC SCHOOL, PASCHIM ENCLAVE, NEW DELHI-87
 (iv) benzene 1 Chloromethyl 3 (2, 2 dimethylpropyl) Q1 Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system. (CH 3 ) 3 CCH 2 CH(Br)C 6 H 5 CH 3 C(C 2 H 5 ) 2 CH 2 Br CH 3 CH=CHC(Br)(CH 3 ) 2 (iv) o-br-c
(iv) benzene 1 Chloromethyl 3 (2, 2 dimethylpropyl) Q1 Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system. (CH 3 ) 3 CCH 2 CH(Br)C 6 H 5 CH 3 C(C 2 H 5 ) 2 CH 2 Br CH 3 CH=CHC(Br)(CH 3 ) 2 (iv) o-br-c
Chapter: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
 Characteristics of halo compounds. Chapter: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question 1 Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:(ch 3 ) 3 CCH 2 Br The IUPAC name of the given structure is 2, 2-Dimethylbromopropane.
Characteristics of halo compounds. Chapter: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question 1 Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:(ch 3 ) 3 CCH 2 Br The IUPAC name of the given structure is 2, 2-Dimethylbromopropane.
REASONING QUESTIONS FROM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH. 1 & 2)
 REASONING QUESTIONS FROM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH. 1 & 2) 1.) Why do haloalkenes under go nucleophillic substitution whereas haloarenes under go electophillic substitution. Ans. Due to more electro negative
REASONING QUESTIONS FROM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH. 1 & 2) 1.) Why do haloalkenes under go nucleophillic substitution whereas haloarenes under go electophillic substitution. Ans. Due to more electro negative
a. (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH(Cl)CH 3 b. CH 3 CH 2 CH(CH 3 )CH(C 2 H 5 )Cl c. CH 3 CH 2 C(CH 3 ) 2 CH 2 I d. (CH 3 ) 3 CCH 2 CH(Br)C 6 H 5.
 1. Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides: a. (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH(Cl)CH 3 b. CH 3 CH 2 CH(CH 3 )CH(C
1. Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides: a. (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH(Cl)CH 3 b. CH 3 CH 2 CH(CH 3 )CH(C
UNIT.10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
 UNIT.10 ALOALKANES AND ALOARENES ONE MARKS QUESTIONS 1. What are haloalkanes? aloalkane is a derivative obtained by replacing hydrogen atom of alkane by halogen atom. 2. What is the hybridization of the
UNIT.10 ALOALKANES AND ALOARENES ONE MARKS QUESTIONS 1. What are haloalkanes? aloalkane is a derivative obtained by replacing hydrogen atom of alkane by halogen atom. 2. What is the hybridization of the
CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
 CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Nature of C-X bond in alkyl halides: X is more electronegative than carbon. So, the C-X bond is polarized with C having
CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Nature of C-X bond in alkyl halides: X is more electronegative than carbon. So, the C-X bond is polarized with C having
 Question 10.1: Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides: (i) (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH(Cl)CH 3 CH 3 CH 2
Question 10.1: Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides: (i) (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH(Cl)CH 3 CH 3 CH 2
 1 Class XII Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 1. Nature of C-X bond in alkyl halides: X is more electronegative than carbon. So, the C-X bond is polarized with C having a partial positive
1 Class XII Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 1. Nature of C-X bond in alkyl halides: X is more electronegative than carbon. So, the C-X bond is polarized with C having a partial positive
AJNISH GUPTA & BHARTI GUPTA
 Performance Booster Organic Chemistry For Board Examinations By AJNISH GUPTA & BHARTI GUPTA Professor of Organic Chemistry Copyright 2015 by Ajnish Gupta All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Performance Booster Organic Chemistry For Board Examinations By AJNISH GUPTA & BHARTI GUPTA Professor of Organic Chemistry Copyright 2015 by Ajnish Gupta All rights reserved. No part of this publication
DAV CENTENARY PUBLIC SCHOOL, PASCHIM ENCLAVE, NEW DELHI - 87
 HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
CHAPTER HYDROCARBONS. Chapterwise Previous year Qs. (a) Na (b) HCl in H2O (c) KOH in C2H5OH (d) Zn in alcohol. Ans: (c)
 122 CHAPTER HYDROCARBONS 1. Acetylenic hydrogens are acidic because [1989] Sigma electron density of C Hbond in acetylene is nearer to carbon, which has 50% s- character Acetylene has only open hydrogen
122 CHAPTER HYDROCARBONS 1. Acetylenic hydrogens are acidic because [1989] Sigma electron density of C Hbond in acetylene is nearer to carbon, which has 50% s- character Acetylene has only open hydrogen
Indian School Muscat. Chemistry IIT - JEE
 Indian School Muscat Chemistry IIT - JEE HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES 1. Which one of the following is not formed when a mixture of methyl bromide and bromobenzene is heated with sodium metal in the presence
Indian School Muscat Chemistry IIT - JEE HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES 1. Which one of the following is not formed when a mixture of methyl bromide and bromobenzene is heated with sodium metal in the presence
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE (AUTONOMOUS) ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE ROAD, CUDDALORE CH101T ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (SEMESTER-I)
 UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
C 3 H 6 ClBr represent a saturated alkyl halide. The following structural isomers are possible for the given compound. Among the above 5 structural is
 Q. No. 1 In CH 3 CH 2 Br, % of Br is 80 73 70 7 Molecular mass of CH 3 CH 2 Br = 109 At Wt. of Br = 80 80 % of Br is = 100 = 73.3 109 Q. No. 2 Which of the following is primary halide Isopropyl iodide
Q. No. 1 In CH 3 CH 2 Br, % of Br is 80 73 70 7 Molecular mass of CH 3 CH 2 Br = 109 At Wt. of Br = 80 80 % of Br is = 100 = 73.3 109 Q. No. 2 Which of the following is primary halide Isopropyl iodide
Class XI Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Chemistry
 Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Aryl Halides. Structure
 Aryl Halides Structure Aryl halides are compounds containing halogen attached directly to an aromatic ring. They have the general formula ArX, where Ar is phenyl, substituted phenyl. X= F,Cl,Br,I An aryl
Aryl Halides Structure Aryl halides are compounds containing halogen attached directly to an aromatic ring. They have the general formula ArX, where Ar is phenyl, substituted phenyl. X= F,Cl,Br,I An aryl
MUNISH KAKAR s INSTITUTE OF CHEMISTRY
 REACTONS & PREPARATON OF HALOGENATED COMPDS. WS#3 Q1. Reagent for preparing a chloroalkane from an alcohol is (a) SOCl 2 (b) HCl/ZnCl 2 (c) PCl 3 (d) All of these Q2. n the addition of H to propene in
REACTONS & PREPARATON OF HALOGENATED COMPDS. WS#3 Q1. Reagent for preparing a chloroalkane from an alcohol is (a) SOCl 2 (b) HCl/ZnCl 2 (c) PCl 3 (d) All of these Q2. n the addition of H to propene in
Organic Chemistry Worksheets
 Highlight the single longest, continuous carbon-carbon chain. Note the alkyl branches that are connected to the root chain. Count the carbons in the root chain, starting from the end closest to the alkyl
Highlight the single longest, continuous carbon-carbon chain. Note the alkyl branches that are connected to the root chain. Count the carbons in the root chain, starting from the end closest to the alkyl
1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES. Vikasana - CET 2012
 CET OBJECTIVE QUESTION ON 1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES 1.The inductive effect a. Implies the atoms ability to cause
CET OBJECTIVE QUESTION ON 1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES 1.The inductive effect a. Implies the atoms ability to cause
HSSLiVE.IN HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES These are compounds containing halogen atoms attached to an alkyl or aryl group. The general representation of haloalkanes is R-X and that of haloarenes is Ar-X [where X = F,
HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES These are compounds containing halogen atoms attached to an alkyl or aryl group. The general representation of haloalkanes is R-X and that of haloarenes is Ar-X [where X = F,
Page (Extra space) (4) Benzene can be converted into amine U by the two-step synthesis shown below.
 Q1. The hydrocarbons benzene and cyclohexene are both unsaturated compounds. Benzene normally undergoes substitution reactions, but cyclohexene normally undergoes addition reactions. (a) The molecule cyclohexatriene
Q1. The hydrocarbons benzene and cyclohexene are both unsaturated compounds. Benzene normally undergoes substitution reactions, but cyclohexene normally undergoes addition reactions. (a) The molecule cyclohexatriene
A4 Alcohols form H-bonds with water due to the presence of OH group. However, hydrocarbons cannot form H-bonds with water.
 Q1 p-dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. and lower solubility than those of o- and m-isomers. Discuss. A4 Alcohols form H-bonds with water due to the presence of OH group. However, hydrocarbons cannot form
Q1 p-dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. and lower solubility than those of o- and m-isomers. Discuss. A4 Alcohols form H-bonds with water due to the presence of OH group. However, hydrocarbons cannot form
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
TOPIC 13 ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES a) (i) UV light / temperatures > 500 ºC (ii) CH 4 (g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl(g) + HCl(g) Cl(g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl 2 (l) + HCl(g) Cl 2 (l) + Cl 2 (g) CHCl 3 (l) + HCl(g) CHCl 3 (l) + Cl 2 (g)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES a) (i) UV light / temperatures > 500 ºC (ii) CH 4 (g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl(g) + HCl(g) Cl(g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl 2 (l) + HCl(g) Cl 2 (l) + Cl 2 (g) CHCl 3 (l) + HCl(g) CHCl 3 (l) + Cl 2 (g)
Chemistry 2.5 AS WORKBOOK. Working to Excellence Working to Excellence
 Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Dr. Anand Gupta Mr Mahesh Kapil
 Dr. Anand Gupta Mr Mahesh Kapil 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Preparation of Haloalkanes From Alkanes Alkenes Alcohols Carboxylic Acids (Hundsdicker Reaction) Halide
Dr. Anand Gupta Mr Mahesh Kapil 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Preparation of Haloalkanes From Alkanes Alkenes Alcohols Carboxylic Acids (Hundsdicker Reaction) Halide
The C-X bond gets longerand weakergoing down the periodic table.
 Chapter 10: Organohalides Organic molecules containing halogen atoms (X) bonded to carbon are useful compounds in synthesis and on their own. 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides The C-X bond gets longerand
Chapter 10: Organohalides Organic molecules containing halogen atoms (X) bonded to carbon are useful compounds in synthesis and on their own. 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides The C-X bond gets longerand
3.2.8 Haloalkanes. Nucleophilic Substitution. 267 minutes. 264 marks. Page 1 of 36
 3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide.
 Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
Alkenes. Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents
 Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane?
 1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? The formation of ethane is due to the side reaction in termination step by the combination of two CH 3 free radicals. 2.
1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? The formation of ethane is due to the side reaction in termination step by the combination of two CH 3 free radicals. 2.
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION
 REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
3.2.8 Haloalkanes. Elimination. 148 minutes. 145 marks. Page 1 of 22
 3.2.8 Haloalkanes Elimination 148 minutes 145 marks Page 1 of 22 Q1. Reaction of 2-bromobutane with potassium hydroxide can produce two types of product depending on the solvent used. In aqueous solution,
3.2.8 Haloalkanes Elimination 148 minutes 145 marks Page 1 of 22 Q1. Reaction of 2-bromobutane with potassium hydroxide can produce two types of product depending on the solvent used. In aqueous solution,
Class Revision on Intro to Organic, Alkanes and Alkenes
 Class Revision on Intro to Organic, Alkanes and Alkenes 2015 Term 1 Week 1 169 min 110 marks ~ Section A: Multiple Choice Questions Circle the best answer 1. What is the correct name of this compound?
Class Revision on Intro to Organic, Alkanes and Alkenes 2015 Term 1 Week 1 169 min 110 marks ~ Section A: Multiple Choice Questions Circle the best answer 1. What is the correct name of this compound?
Arrange the following alkene in increasing order of their enthalpy of hydrogenation ( )
 Q.1. Which of the statements is correct? (I) Melting point of alkane increases with increase of C atoms and with increase in branching. (II) Boiling point of alkane increases with increase of C atoms but
Q.1. Which of the statements is correct? (I) Melting point of alkane increases with increase of C atoms and with increase in branching. (II) Boiling point of alkane increases with increase of C atoms but
Two stereoisomers of but-2-ene are formed when 2-bromobutane reacts with ethanolic potassium hydroxide
 Q1. (a) Name and outline a mechanism for the reaction of 2-bromo-2-methylpropane with ethanolic potassium hydroxide to form the alkene 2-methylpropene, (CH 3) 2C=CH 2 Name of mechanism... Mechanism (4)
Q1. (a) Name and outline a mechanism for the reaction of 2-bromo-2-methylpropane with ethanolic potassium hydroxide to form the alkene 2-methylpropene, (CH 3) 2C=CH 2 Name of mechanism... Mechanism (4)
C. CH CH COH CH CCH. 6. Which substance(s) could be formed during the incomplete combustion of a hydrocarbon?
 1. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? O O A. CH 3CH 2 CH B. CH 3CCH3 C. CH 3CH 2 COH D. CH COCH 2. What product results from the reaction of CH 2 ==CH 2 with Br 2? A. CHBrCHBr B. CH 2 CHBr C.
1. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? O O A. CH 3CH 2 CH B. CH 3CCH3 C. CH 3CH 2 COH D. CH COCH 2. What product results from the reaction of CH 2 ==CH 2 with Br 2? A. CHBrCHBr B. CH 2 CHBr C.
Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms]
![Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms] Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms]](/thumbs/89/100347388.jpg) Program Name B.Sc. (Chemistry) B.Sc. - Part I Paper Code CH- 02 (Organic chemistry) Section A (Very Short Answer Questions 2 Each Question Carries 2 Marks Part -1 1. Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital
Program Name B.Sc. (Chemistry) B.Sc. - Part I Paper Code CH- 02 (Organic chemistry) Section A (Very Short Answer Questions 2 Each Question Carries 2 Marks Part -1 1. Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital
Ethers & Epoxides. Chapter 5. Dr. Seham ALTERARY. Chem 340-2nd semester
 Ethers & Epoxides Chapter 5 Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chapter s out line Ethers Definition; General formula; Classification and Types Nomenclature - Common Names. - IUPAC Naming. Physical Properties General methods
Ethers & Epoxides Chapter 5 Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chapter s out line Ethers Definition; General formula; Classification and Types Nomenclature - Common Names. - IUPAC Naming. Physical Properties General methods
Q. No. 4 Chlorination of toluene in the presence of light and heat followed by treatment with aqueous NaOH gives o cresol p cresol 2, 4 dihydroxy tolu
 Q. No. 1 Glycerine has One primary and two secondary OH groups One secondary and two primary OH groups Three primary OH groups Three secondary OH groups Q. No. 2 The structural formula of cyclohexanol
Q. No. 1 Glycerine has One primary and two secondary OH groups One secondary and two primary OH groups Three primary OH groups Three secondary OH groups Q. No. 2 The structural formula of cyclohexanol
Molecular Models and Isomerism
 Name Lab Day Molecular Models and Isomerism Introduction: When two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of their atoms, the various individual compounds
Name Lab Day Molecular Models and Isomerism Introduction: When two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of their atoms, the various individual compounds
Organic Chemistry. REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling
 Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES. Vikasana - CET 2012
 CET OBJECTIVE QUESTION ON 1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES 1.The inductive effect a. Implies the atoms ability to cause
CET OBJECTIVE QUESTION ON 1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES 1.The inductive effect a. Implies the atoms ability to cause
Name: Unit 3 Packet: Activation Energy, Free Radical Chain Reactions, Alkane Preparations, S N 2, E 2
 Name: Unit 3 Packet: Activation Energy, Free Radical Chain Reactions, Alkane Preparations, S N 2, E 2 Key Terms For Unit 3 Free Radical Chain Reaction Homolytic Cleavage Free Radical Initiation Propagation
Name: Unit 3 Packet: Activation Energy, Free Radical Chain Reactions, Alkane Preparations, S N 2, E 2 Key Terms For Unit 3 Free Radical Chain Reaction Homolytic Cleavage Free Radical Initiation Propagation
AMINES. 3. Secondary When two hydrogen atoms are replaced by two alkyl or aryl groups.
 AMINES Amine may be regarded as derivative of ammonia formed by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by corresponding number of alkyl or aryl group CLASSIFICATION 1. Ammonia 2. Primary amine 3. Secondary
AMINES Amine may be regarded as derivative of ammonia formed by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by corresponding number of alkyl or aryl group CLASSIFICATION 1. Ammonia 2. Primary amine 3. Secondary
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
 ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a a saturated C (sp3) They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a a saturated C (sp3) They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to
Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 13: Amines Top concepts
 Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 13: Amines Top concepts 1. Amines are regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl group 2. Classification
Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 13: Amines Top concepts 1. Amines are regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl group 2. Classification
Chapter 3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry
 Chapter 3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry Functional Group: Be able to identify and name any of the functional groups listed on Table 3.1, pages 76-77. Summary of important functional
Chapter 3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry Functional Group: Be able to identify and name any of the functional groups listed on Table 3.1, pages 76-77. Summary of important functional
Class XII - Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Chapter-wise Problems
 Class XII - Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Chapter-wise Problems I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic medium and in the presence of Hg
Class XII - Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Chapter-wise Problems I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic medium and in the presence of Hg
Haloalkanes. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers for C 5 H 11 Br
 Haloalkanes The basics: The functional group is a halogen atom: F, Cl, Br or I General formula C n H 2n+1 X Use the prefixes: fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers
Haloalkanes The basics: The functional group is a halogen atom: F, Cl, Br or I General formula C n H 2n+1 X Use the prefixes: fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers
IB Topics 10, 20 & 21 MC Practice
 IB Topics 10, 20 & 21 MC Practice 1. What is the major product of the reaction between HCl and but-2-ene? 1,2-dichlorobutane 2,3-dichlorobutane 1-chlorobutane 2-chlorobutane 2. Which compound can be oxidized
IB Topics 10, 20 & 21 MC Practice 1. What is the major product of the reaction between HCl and but-2-ene? 1,2-dichlorobutane 2,3-dichlorobutane 1-chlorobutane 2-chlorobutane 2. Which compound can be oxidized
ORGANIC MOLECULES (LIVE) 10 APRIL 2015 Section A: Summary Notes and Examples Naming and Functional Groups
 ORGANIC MOLECULES (LIVE) 10 APRIL 2015 Section A: Summary Notes and Examples Naming and Functional Groups Important Features of Carbon There are different allotropes (same element, same phase, different
ORGANIC MOLECULES (LIVE) 10 APRIL 2015 Section A: Summary Notes and Examples Naming and Functional Groups Important Features of Carbon There are different allotropes (same element, same phase, different
Alcohol, Phenols & Ethers
 Alcohol, Phenols & Ethers 1) Conc. H 2 S 4 Heated with excess of C 2 H 5 at 140 o c to form CH 2 b) CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 d) CH 2 = CH 2 2) In the following series of chemical reactions identify Z C 3 H
Alcohol, Phenols & Ethers 1) Conc. H 2 S 4 Heated with excess of C 2 H 5 at 140 o c to form CH 2 b) CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 d) CH 2 = CH 2 2) In the following series of chemical reactions identify Z C 3 H
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
When 2-bromopentane reacts with ethanolic KOH, two structurally isomeric alkenes are formed.
 Q1. Organic reaction mechanisms help chemists to understand how the reactions of organic compounds occur. The following conversions illustrate a number of different types of reaction mechanism. (a) When
Q1. Organic reaction mechanisms help chemists to understand how the reactions of organic compounds occur. The following conversions illustrate a number of different types of reaction mechanism. (a) When
3 free radical is most stable. Q.5. A + Cl 2 hv monochloro product To maximize the yield of monochloro product in the above reaction? Cl 2 must be add
 Q.1. I II III IV IV III II I I III II IV IV II III I I II III IV The decreasing order of the anti knocking value of octane number of the following is: (I) CH 4 (II) C 2 H 6 (III) C 3 H 8 (IV) C 4 H 10
Q.1. I II III IV IV III II I I III II IV IV II III I I II III IV The decreasing order of the anti knocking value of octane number of the following is: (I) CH 4 (II) C 2 H 6 (III) C 3 H 8 (IV) C 4 H 10
Test Date: (Sunday) Test Time: 1:00 pm to 2:00 pm Test Venue: Lajpat Bhawan, Madhya Marg, Sector 15-B, Chandigarh
 Test ate: 1.09.015 (Sunday) Test Time: 1:00 pm to :00 pm Test Venue: Lajpat hawan, Madhya Marg, Sector 15-, handigarh r. Sangeeta Khanna Ph. 1 EMISTRY OING IRLE G:\+ Grand test-4 L-1.doc r. Sangeeta Khanna
Test ate: 1.09.015 (Sunday) Test Time: 1:00 pm to :00 pm Test Venue: Lajpat hawan, Madhya Marg, Sector 15-, handigarh r. Sangeeta Khanna Ph. 1 EMISTRY OING IRLE G:\+ Grand test-4 L-1.doc r. Sangeeta Khanna
Functional Groups. Functional groups: special groups of atoms attached to a hydrocarbon skeleton; the most common sites of chemical reactivity.
 Functional Groups Functional groups: special groups of atoms attached to a hydrocarbon skeleton; the most common sites of chemical reactivity. Organic halides: a hydrogen is replaced by a halogen fluoro-,
Functional Groups Functional groups: special groups of atoms attached to a hydrocarbon skeleton; the most common sites of chemical reactivity. Organic halides: a hydrogen is replaced by a halogen fluoro-,
What is the major product of the following reaction?
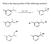 What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
MOSTLY ALCOHOLS. Question 2, 2017 The structure of a molecule of an organic compound, threonine, is shown below.
 MOSTLY ALCOHOLS Modified Question 1, 2017 A chemistry class was learning about the chemistry of haloalkanes. They were researching the effect of heat and concentrated potassium hydroxide in ethanol, conc.
MOSTLY ALCOHOLS Modified Question 1, 2017 A chemistry class was learning about the chemistry of haloalkanes. They were researching the effect of heat and concentrated potassium hydroxide in ethanol, conc.
Downloaded from
 1 Class XII Chemistry Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols And Ethers Top concepts: 1. Structure of alcohols, phenols and ethers: 2. Preparation of alcohols: 3. Preparation of phenols: 2 4. Physical properties of
1 Class XII Chemistry Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols And Ethers Top concepts: 1. Structure of alcohols, phenols and ethers: 2. Preparation of alcohols: 3. Preparation of phenols: 2 4. Physical properties of
Straight. C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized. Butane, C 4 H 10 H 3 C
 Hydrocarbons Straight Chain Alkanes aren t Straight C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized Butane, C 4 H 10 Structural Shorthand Explicit hydrogens (those required to complete carbon s valence) are usually left
Hydrocarbons Straight Chain Alkanes aren t Straight C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized Butane, C 4 H 10 Structural Shorthand Explicit hydrogens (those required to complete carbon s valence) are usually left
Organic Chemistry. Chapter 10
 Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 10.1 Homologous Series Overview We Are Here Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds. From the very simple: methane To the very complex:
Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 10.1 Homologous Series Overview We Are Here Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds. From the very simple: methane To the very complex:
 Unit - 11 ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS 1. Write IUPAC names of the following compounds : (ix) C 6 H 5 OC 3 H 7 (x) O Cl 2. Write the structures of the compounds whose names are given below : (i) 3, 5-dimethoxyhexane-1,
Unit - 11 ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS 1. Write IUPAC names of the following compounds : (ix) C 6 H 5 OC 3 H 7 (x) O Cl 2. Write the structures of the compounds whose names are given below : (i) 3, 5-dimethoxyhexane-1,
CHEMISTRY PAPER-1 PART I. Answer all questions.
 CHEMISTRY PAPER-1 (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper They must NOT start writing during this time) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CHEMISTRY PAPER-1 (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper They must NOT start writing during this time) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ALKYL HALIDE & ARYL HALIDE
 QUESTION BANK--1 ALKYL ALIDE & ARYL ALIDE LEVEL I 1. SN1reaction of alkyl halides lead to (a) Retention of configuration (c) Inversion of configuration 2. The reaction 3 + O 3O + is (a) SN2 (c) SE1 (b)
QUESTION BANK--1 ALKYL ALIDE & ARYL ALIDE LEVEL I 1. SN1reaction of alkyl halides lead to (a) Retention of configuration (c) Inversion of configuration 2. The reaction 3 + O 3O + is (a) SN2 (c) SE1 (b)
Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline
 Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Slide 2 Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of and its compounds. The major sources of carbon are the fossil fuels: petroleum, natural gas,
Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Slide 2 Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of and its compounds. The major sources of carbon are the fossil fuels: petroleum, natural gas,
SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1. The credit for synthesizing first organic compound in the laboratory went to a) Berzelius b) Wohler c) Kolbe d) Berthelot Ans : b) Wohler [Note : (i) N H 4 Cl+KCNO NH 4 CNO
SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1. The credit for synthesizing first organic compound in the laboratory went to a) Berzelius b) Wohler c) Kolbe d) Berthelot Ans : b) Wohler [Note : (i) N H 4 Cl+KCNO NH 4 CNO
Organic Chemistry. Unit 10
 Organic Chemistry Unit 10 Halides Primary Carbons Secondary Carbons Tertiary Carbons IMPORTANCE?? REACTIONS!! Benzene C6H6 Aromatic functional group - C6H5 (IUPAC name - phenyl) Substitution Reactions
Organic Chemistry Unit 10 Halides Primary Carbons Secondary Carbons Tertiary Carbons IMPORTANCE?? REACTIONS!! Benzene C6H6 Aromatic functional group - C6H5 (IUPAC name - phenyl) Substitution Reactions
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry Specimen Paper for first teaching
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry Specimen Paper for first teaching
Organic Chemistry. Why are these compounds called Organic. What is a Hydrocarbon? Questions: P167 Read
 Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X. Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): R + X X 2.
 Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES. 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction....
 EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction. C 6 H 5 3 + Cl 2 C 6 H 5 2 Cl + HCl Write an equation for the initiation
EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction. C 6 H 5 3 + Cl 2 C 6 H 5 2 Cl + HCl Write an equation for the initiation
 Top concepts Chapter: Amines 1. Amines are regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl group 2. Classification of amines: 3. Preparation
Top concepts Chapter: Amines 1. Amines are regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl group 2. Classification of amines: 3. Preparation
Ch 16 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Ch 16 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Mechanism - Aromatic rings typically undergo substitution, where an H is replaced with an electrophile (E+). - The rings do not typically undergo addition across
Ch 16 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Mechanism - Aromatic rings typically undergo substitution, where an H is replaced with an electrophile (E+). - The rings do not typically undergo addition across
Organic Chemistry, 7 L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter , Prentice Hall
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although h benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although h benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic
DAV CENTENARY PUBLIC SCHOOL, PASCHIM ENCLAVE, NEW DELHI-87
 Q 1 Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system. (iii) (iv) (v) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) Answer 1 3-Chloromethyl-2-isopropylpentan-1-ol 2, 5-Dimethylhexane-1, 3-diol (iii) 3-Bromocyclohexanol
Q 1 Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system. (iii) (iv) (v) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) Answer 1 3-Chloromethyl-2-isopropylpentan-1-ol 2, 5-Dimethylhexane-1, 3-diol (iii) 3-Bromocyclohexanol
3.2.9 Alkenes. Addition Reactions. 271 minutes. 268 marks. Page 1 of 35
 ..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
Benzylamine reacts with nitrous acid to form unstable diazonium salt, which in turn gives alcohol with the evolution of nitrogen gas.
 Benzylamine reacts with nitrous acid to form unstable diazonium salt, which in turn gives alcohol with the evolution of nitrogen gas. On the other hand, aniline reacts with HNO2 at a low temperature to
Benzylamine reacts with nitrous acid to form unstable diazonium salt, which in turn gives alcohol with the evolution of nitrogen gas. On the other hand, aniline reacts with HNO2 at a low temperature to
Downloaded from
 Name reactions in pairs 1# Carbylamine Reaction (PN-393) and Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction (PN- 386) 2# Sandmeyer Reaction (PN- 397) and Gatterman Reaction (PN-397) 3# Cannizzaro Reaction (PN-
Name reactions in pairs 1# Carbylamine Reaction (PN-393) and Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction (PN- 386) 2# Sandmeyer Reaction (PN- 397) and Gatterman Reaction (PN-397) 3# Cannizzaro Reaction (PN-
CHAPTER 16 - CHEMISTRY OF BENZENE: ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION
 CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
12/27/2010. Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
HALOALKANES, HALOARENES
 HALOALKANES, HALOARENES 1- Important terms and concept R-H +X 2 R-X + H-X (i) Halogen derivative of alkenes called halo alkenes e.g. R- CH 3 (ii)halogen derivative of arenes called halo arenes e.g. R-
HALOALKANES, HALOARENES 1- Important terms and concept R-H +X 2 R-X + H-X (i) Halogen derivative of alkenes called halo alkenes e.g. R- CH 3 (ii)halogen derivative of arenes called halo arenes e.g. R-
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Unit 13-NITROGEN CONTAINING ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
 Unit 13-NITROGEN CONTAINING ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Two marks: 1. Name the product obtained when a nitrile is reduced by H 2 /Ni,. Give the equation. H 2 /Ni, Primary amine: RCN RCH 2 NH 2. 2. How is nitrobenzene
Unit 13-NITROGEN CONTAINING ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Two marks: 1. Name the product obtained when a nitrile is reduced by H 2 /Ni,. Give the equation. H 2 /Ni, Primary amine: RCN RCH 2 NH 2. 2. How is nitrobenzene
Organic Chemistry. A. Introduction
 Organic Chemistry A. Introduction 1. Organic chemistry is defined as the chemistry of CARBON compounds. There are a huge number of organic compounds. This results from the fact that carbon forms chains
Organic Chemistry A. Introduction 1. Organic chemistry is defined as the chemistry of CARBON compounds. There are a huge number of organic compounds. This results from the fact that carbon forms chains
ORGANIC COMPOUND CONTAINING HALOGENS
 Einstein Classes, Unit o. 102, 10, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road ew Delhi 110 018, Ph. : 91262905, 8527112111 COH 1 ORGAIC COMPOUD COTAIIG HALOGES Einstein Classes, Unit o.
Einstein Classes, Unit o. 102, 10, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road ew Delhi 110 018, Ph. : 91262905, 8527112111 COH 1 ORGAIC COMPOUD COTAIIG HALOGES Einstein Classes, Unit o.
BENZENE & AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BENZENE & AROMATIC COMPOUNDS Dr. Zainab M Almarhoon 2 Learning Objectives By the end of chapter four the students will: Understand the resonance description of structure of benzene Understand the hybridization
BENZENE & AROMATIC COMPOUNDS Dr. Zainab M Almarhoon 2 Learning Objectives By the end of chapter four the students will: Understand the resonance description of structure of benzene Understand the hybridization
Physical Properties: Structure:
 Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
Class XII Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers Chemistry. Question 11.1: Write IUPAC names of the following compounds: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi)
 Question 11.1: Write IUPAC names of the following compounds: (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) Page 1 of 37 (ix) (x) (xi) (xii) 2, 2, 4-Trimethylpentan-3-ol 5-Ethylheptane-2, 4-diol (iii) Butane-2, 3-diol
Question 11.1: Write IUPAC names of the following compounds: (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) Page 1 of 37 (ix) (x) (xi) (xii) 2, 2, 4-Trimethylpentan-3-ol 5-Ethylheptane-2, 4-diol (iii) Butane-2, 3-diol
10. Alkyl Halides. What Is an Alkyl Halide. An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen
 10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
William H. Brown & Christopher Foote
 William H. Brown & Christopher Foote Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:permissions Department, Harcourt Brace & Company, 6277 Sea Harbor Drive, Orlando,
William H. Brown & Christopher Foote Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:permissions Department, Harcourt Brace & Company, 6277 Sea Harbor Drive, Orlando,
Organic Chemistry. February 18, 2014
 Organic Chemistry February 18, 2014 What does organic mean? Organic Describes products Grown through natural biological process Without synthetic materials In the 18 th century Produced by a living system
Organic Chemistry February 18, 2014 What does organic mean? Organic Describes products Grown through natural biological process Without synthetic materials In the 18 th century Produced by a living system
Lecture Topics: I. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes
 Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons generally fall into 2 general groupings, aliphatic hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons. Aliphatic hydrocarbons contain chains and rings of hydrocarbons,
Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons generally fall into 2 general groupings, aliphatic hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons. Aliphatic hydrocarbons contain chains and rings of hydrocarbons,
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 203/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry
 E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
