N-Oxy Radical Chemistry
|
|
|
- Joel Parks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 N-Oxy Radical Chemistry - Toward Application for Efficient Catalysis - Literature Seminar Shogo HASHIZUME (D1) (Mon.) 1
2 Today s Contents 1. Fundamentals of N-Oxy Radical Species 2. Aminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 3. Imidoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 4. Iminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 5. Perspectives For exploration of novel & efficient N-oxy radical catalysis 2
3 Today s Contents 1. Fundamentals of N-Oxy Radical Species 2. Aminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 3. Imidoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 4. Iminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 5. Perspectives For exploration of novel & efficient N-oxy radical catalysis 3
4 Why N-OHs Generate Radicals?? Radical = Subvalent compounds one less bond than principle of general valency 1. Fundamentals Hicks, R. G. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, Radical states is generally reactive and difficult to generate But, some radicals are stable to isolate or generatable although transient. Due to - Delocalization of unpaired electron by conjugation - Steric shielding of unpaired electron Stability of N-oxy radical owes much to delocalization of the unpaired electron over N-O bond. 4
5 What Makes N-Oxy Radical Stable?? Factors to stabilize the radical state: 1. Fundamentals 1. Enough conjugation with N s lone pair - Conformational advantage for conjugation - Varied stabilities depending on N s electron density Conjugation is not reduced by steric freedom 5
6 What Makes N-Oxy Radical Stable?? Factors to stabilize the radical state: 1. Fundamentals 2. Structure NOT to cause self-decomposition - More one-electron oxidation to afford nitrone - Radicalic dimerization N-O radical having a-proton is unstable 6
7 Considering Bond-Dissociation-Energy (BDE) 1. Fundamentals Bond-Dissociation-Energy (BDE) = Enthalpy change when a bond is cleaved by homolysis Useful representation of generation & stability of radical BDEs of some compounds Blanksby, S. J.; Ellison, G. B. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 255; and reviews on N-oxy radical 7
8 Classification of N-Oxy Radicals 1. Fundamentals 1. Aminoxyl Radical 2. Imidoxyl/Amidoxyl Radical 3. Iminoxyl Radical 8
9 Aminoxyl Radicals 1. Fundamentals Bulky/sterically restricted aminoxyl radicals are generally stable & isolable. TEMPO Lebedev, Nazarnovskii (1960) Di-tert-butylnitroxyl Hoffmann, Hnderson (1960) One more oxidation of TEMPO affords oxoammonium cation. Disproportionation occurs under acidic conditions. 9
10 Imidoxyl/Amidoxyl Radicals 1. Fundamentals PINO radical: Not isolated but detected in situ generation a N = 4.36 G : smaller than other N-O g = : larger than other N-O These values indicate strong decrease of spin density on nitrogen small increase of spin density on oxygen EWG on N increases BDE = unstable radical state due to decrease of conjugation Recupero, F. et al. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107,
11 Imidoxyl/Amidoxyl Radicals 1. Fundamentals PINO radical cause self-decomposition due to its non-persistency (especially high temp.) PINO often cause H-abstraction because of its unstability. 11
12 Iminoxyl Radicals - First identified iminoxyl radicals 1. Fundamentals Thomas, J. R. JACS 1964, 86, Suggesting generation of oxime radical - Large nitrogen coupling constant The unpaired e - on N is not in pure 2p z orbital. (=Having s-radical characteristics?) - cis/trans isomers detected (Fig.1a) Isomerization by conjudation occurs 12
13 Iminoxyl Radicals - Isolated stable iminoxyl radicals 1. Fundamentals Ingold, K. U. et al. JACS 1971, 93, First example of isolated iminoxyl radical - Carorimetric studies on iminoxyl radicals Mahoney, L. R.; Ingold, K. U. et al. JACS 1973, 95, Isolablity of stable oxime radical is due to its low BDE. 13
14 What Stabilizes Iminoxyl Radicals?? 1. Fundamentals Bordwell, F. G.; Zhang, S.-H. et al. JACS 1995, 117, Decreasing BDE parallels increasing the steric hinderance. Bulkier alkyl group increase relief of steric strain by loss of H-atom The steric hinderance effects 14
15 Today s Contents 1. Fundamentals of N-Oxy Radical Species 2. Aminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 3. Imidoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 4. Iminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 5. Perspectives For exploration of novel & efficient N-oxy radical catalysis 15
16 Aminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions TEMPO : most popular aminoxyl radical 2. Aminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions Stability of the radical state = easy to be oxidized Useful mediator for redox reaction?? Main topic = Alcohol oxidation 2-1. Copper-TEMPO catalysis 2-2. Ruthenium-TEMPO catalysis 2-3. Metal-free catalysis 16
17 2-0. Early Works of TEMPO Oxidation Early Works on TEMPO-Mediated Oxidation - With stoichiometric oxoammonium cation Golubev, V. A. et al. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR, Chem. Ser. 1965, 14, With stoichiometric TEMPO Bobbitt, J. M. et al. JOC 1991, 56, Oxidation proceed by in situ disproportionation of TEMPO (TEMPO is known to disproportionate at acidic ph.) Sheldon, R. A. et al. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346,
18 Mechanism of TEMPO-Mediated Oxidation?? Considerable mechanism Hammet study 2-0. Early Works of TEMPO Oxidation Semmelhack et al. TL 1986, 27, Only slight positive charge at benzylic carbon in RDS Path b unfavorable Cyclopropyl carbinol Path a unfavorable Via intermediate 4 Path c favorable?? Which is actual mechanism?? 18
19 Mechanism of TEMPO-Mediated Oxidation?? Considerable mechanism Hammet study 2-0. Early Works of TEMPO Oxidation Semmelhack et al. TL 1986, 27, Only slight positive charge at benzylic carbon in RDS Path b unfavorable Cyclopropyl carbinol Path a unfavorable Via intermediate 4 Path c favorable?? Possible pathway (Although cannot rule out d) 19
20 2-1. Cu-TEMPO Catalysis Copper-TEMPO Catalysis with O 2 - Cu(II)-phen.-tBu 2 nitroxide catalysis Brackman W.; Gaasbeek, C. J. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1966, 85, 257. Mechanism proposed by them Oxidation proceeds by cooperation of Cu(II) and N-O radical?? 20
21 2-1. Cu-TEMPO Catalysis Copper-TEMPO Catalysis with O 2 - Cu(I)-TEMPO catalysis Semmelhack, M. F. et al. JACS 1984, 106, Mechanism proposed by them Actual oxidant?? 21
22 What s The Correct Mechanism?? - Mechanistic study 2-1. Cu-TEMPO Catalysis Sheldon, R. A. et al. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, Cu(I) is oxidized by TEMPO - Cu(I)-catalyzed reaction using stoichiometric TEMPO 22
23 What s The Correct Mechanism?? 2-1. Cu-TEMPO Catalysis - Mechanistic study - KIE and Hammet correlation study Sheldon, R. A. et al. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, Similar to GO/GO-mimics rather than oxoammonium salt 23
24 What s The Correct Mechanism?? - Plausible mechanism Cu(II)-TEMPO 2-1. Cu-TEMPO Catalysis Sheldon, R. A. et al. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, Cu(I)-TEMPOH Key step occurs via alkoxycopper(ii)-tempo complex 24
25 Selective Copper-TEMPO Oxidation 2-1. Cu-TEMPO Catalysis Sheldon, R. A. et al. Chem. Commun. 2003, Rationalization of the selectivity Remarkable selectivity for primary over secondary 25
26 2-2. Ru-TEMPO Catalysis Ruthenium-TEMPO Catalysis with O 2 Sheldon, R. A. et al. JACS 2001, 123, Plat. Metals Rev. 2001, 45, 15. Although these substrates are unreactive (deactivating catalyst by chelating??) 26
27 Mechanism of Ruthenium-TEMPO Catalysis - Mechanistic study 2-2. Ru-TEMPO Catalysis Sheldon, R. A. et al. JACS 2001, 123, Reaction proceeds even in inert atmosphere with stoichiometric TEMPO KIEs are same in the absence/presence of O 2 Under stoichiometric TEMPO & inert atmosphere condition The same active species with/without oxygen Dehydrogenation by RuCl 2 (PPh 3 ) 3 and TEMPO regenerates RuX 2 from RuH 2?? 27
28 Mechanism of Ruthenium-TEMPO Catalysis - Mechanistic study RuH 2 reacts with TEMPO (observed in situ IR) 2-2. Ru-TEMPO Catalysis Sheldon, R. A. et al. JACS 2001, 123, *Ru-H vibration of RuH 2 (PPh 3 ) 3 at 2150 cm -1 Conclusive mechanism 28
29 Metal-Free N-Oxy Radical Catalysis 2-3. Metal-Free Catalysis - TEMPO + stoichiometric oxidant Many reports - The first non-metal aerobic oxidation catalyzed by TEMPO all catalytic amount Liang, X.- M.; Hu, X.-Q. et al. JACS 2004, 126, But multiple components = Difficult application for complex molecule?? 29
30 Metal-Free N-Oxy Radical Catalysis - Novel N-oxy radical AZADO for high efficiency TEMPO: inefficient for hindered secondary alcohol 2-3. Metal-Free Catalysis Iwabuchi, Y. et al. JACS 2006, 128, Concept of their catalyst design: AZADO exhibits great reactivity for alcohol oxidation 30
31 Metal-Free N-Oxy Radical Catalysis - Novel N-oxy radical AZADO for high efficiency And various hindered alcohols can be oxidized Metal-Free Catalysis Iwabuchi, Y. et al. JACS 2006, 128,
32 Metal-Free N-Oxy Radical Catalysis - Aerobic version with more efficient catalyst Introduction of F at C 5 position 2-3. Metal-Free Catalysis Iwabuchi, Y. et al. JACS 2011, 133, Also wide substrate scope including hindered alcohol 32
33 Metal-Free N-Oxy Radical Catalysis - Aerobic version with more efficient catalyst Proposed mechanism 2-3. Metal-Free Catalysis Iwabuchi, Y. et al. JACS 2011, 133, I think oxoammonium cation is generated through disproportionation (Because solvent is AcOH) 33
34 Today s Contents 1. Fundamentals of N-Oxy Radical Species 2. Aminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 3. Imidoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 4. Iminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 5. Perspectives For exploration of novel & efficient N-oxy radical catalysis 34
35 Imidoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 3. Imidoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions Imidoxyl radical : High BDE makes the radical state unstable Enables radicalic cleaveage of various C-H bonds Reactions introduced today: 3-1. Alkane oxidation to alcohols/carboxylic acids 3-2. Ethers/Acetals oxidation 3-3. Application to C-C bond formation 35
36 Early Works on NHPI-Mediated Reactions 3-0. Early Works - Coupling between ethers and DEAD Grochowski, E. et al. Synthesis 1977, 718. Initiation occurred by homolysis of N=N bond? - Electrochemical oxidation of alcohols Masui, M. et al. Chem. Commun. 1983,
37 3-1. Alkane Oxidation Alkane C(sp 3 )-H Oxidation Focusing on Prof. Ishii s Work Key person: Prof. Ishii Alkane oxidation using O 2 Green oxidation of bulk chemicals?? (Adv. Synth. Catal. 2001, 343, 393.) 37
38 3-1. Alkane Oxidation Alkane C(sp 3 )-H Oxidation Focusing on Prof. Ishii s Work - Oxidation catalyzed by NHPI Ishii, Y. et al. JOC 1995, 60, But conversions of simple alkanes are low - Co-NHPI combined catalysis Ishii, Y. et al. JOC 1996, 61, With broad substrate scope of simple alkane 38
39 3-1. Alkane Oxidation Alkane C(sp 3 )-H Oxidation Focusing on Prof. Ishii s Work - Co-NHPI catalysis at room temp. Ishii, Y. et al. JOC 1997, 62, First example of catalytic aerobic oxidation of toluene at rt. - THICA catalysis Ishii, Y. et al. JOC 2003, 68, THICA allows low cat. loading due to stability of its radical (PINO is subject to the decomposition) 39
40 3. Imidoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions What s The Mechanism of NHPI Catalysis?? - O 2 uptake experiment Ishii, Y. et al. JOC 1996, 61, Co II + NHPI - ESR measurement Co III + NHPI Co II is the active catalyst?? (Co III somehow reduced in situ.) Ishii, Y. et al. JOC 1997, 62, PINO s ESR spectra Co II accelerates generation of PINO 40
41 3. Imidoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions What s The Mechanism of NHPI Catalysis?? - General mechanism of free radical chain aerobic oxidation Co II acts as the initiator?? Key to efficient catalytic cycle: 1. Increase of the propagation rate 2. Decreasing of the termination rate NHPI mediates radical propagation cycle??
42 3. Imidoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions What s The Mechanism of NHPI Catalysis?? - Plausible mechanism (for toluene oxidation) Ishii, Y. et al. JOC 1997, 62, initiation But some questionable points remain How is alcohol product generated?? Reduction by Co II?? propagation Peroxide really oxidized by Co III?? Not via formation of aldehyde?? etc.
43 Ethers/Acetals Oxidation 3-2. Ethers/Acetals Oxidation BDE of a-c-h bond of ethers/acetals is weak (xx kcal/mol) Facile radicalic C-H cleavage by PINO Masui, M. et al. JCS, Chem. Commun. 1985, Karimi. B. et al. Synthesis 2003, Oxidation affords cation equivalent 43
44 Application for C-C Bond Formation - Radicalic C-C bond formation 3-3. Application for C-C Bond Formation Trap the formed carbon radical by carbon electrophile (e.g. Michael acceptor) before trapped by oxygen Radicalic C-C bond formation?? Ishii, Y. et al. Chem. Commun. 2000, 613; Chem. Commun. 2000, 2457; JOC 2001, 66,
45 Application for C-C Bond Formation 3-3. Application for C-C Bond Formation - Cross-dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) Li, C.-J. et al. Synlett 2009, 138. Li, C.-J. et al. TL 2010, 51, Reaction proceeds via formation of cation intermediate?? 45
46 Today s Contents 1. Fundamentals of N-Oxy Radical Species 2. Aminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 3. Imidoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 4. Iminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 5. Perspectives For exploration of novel & efficient N-oxy radical catalysis 46
47 Iminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 4. Iminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions - Amine oxidation with stoichiometric iminoxyl radical Mendenhall, G. D. et al. JOC 1985, 50, Phenol oxidation with stoichiometric iminoxyl radical Mendenhall, G. D. et al. JOC 1986, 51, No reports on use of iminoxyl radical as catalyst. Why?? 47
48 Today s Contents 1. Fundamentals of N-Oxy Radical Species 2. Aminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 3. Imidoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 4. Iminoxyl Radical-Mediated Reactions 5. Perspectives For exploration of novel & efficient N-oxy radical catalysis 48
49 Toward C-H Bond Functionalization 5. Perspectives Inner-sphere C-H functionalization Outer-sphere C-H functionalization Advantages - Many catalysis & reaction mode - Selectivity Disadvantages - Harsh conditions - Directing group - Noble metal catalysts - Only unhindered C-H bond Advantages - Cheap metal/organocatalysts - Applicable for hindered C-H bond Disadvantages - Harsh conditions - Selectivity - Only limited examples Can we realize efficient outer-sphere C-H functionalization by overcoming current disadvantages?? 49
50 How to Overcome Disadvantages?? 5. Perspectives For utilization of N-oxy radical toward outer-sphere C-H functionalization - Harsh condition is often necessary - Chemoselectivity between several C-Hs New N-oxy radical having more suitable BDE New catalyst design based on strict strategy (e.g. BDE theory) is important?? 50
51 Future Potentiality 1 Sequential C-H Oxidation 5. Perspectives In highly oxidized, complex molecule synthesis Concept: Introduction of FGs at the late stage is ideal. Each C-H has each BDE Selectively cleaved by N-O catalyst having similar BDE in kinetically controlled reaction?? Related work: White, M. C. et al. Science, 2007, 318,
52 5. Perspectives Future Potentiality 2 Photoredox N-Oxy Radical Catalyst Activation of unreactive C-H bonds = thermodinamically unfavorable process This is the cause of need of harsh conditions?? Concept: Can we use photoenergy as energy source?? Ref.) Mr.Kojima s lit. seminar (2012) 52
53 References (Reviews) What s new in stable radical chemisty? Hicks, R. G. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, Organocatalytic Oxidations Mediated by Nitroxyl Radicals Sheldon, R. A. et al. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, Free Radical Functionalization of Organic Compounds Catalyzed by N-Hydroxyphtalimide Recupero, F. et al. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107,
O H Hydrogen bonding promotes H-atom transfer from C H bonds for C-alkylation of alcohols
 ydrogen bonding promotes -atom transfer from C bonds for C-alkylation of alcohols Jenna L. Jeffrey, Jack A. Terrett, David W. C. MacMillan Science 2015, 349, 1532-1536 Raffaele Colombo 9/26/2015 Raffaele
ydrogen bonding promotes -atom transfer from C bonds for C-alkylation of alcohols Jenna L. Jeffrey, Jack A. Terrett, David W. C. MacMillan Science 2015, 349, 1532-1536 Raffaele Colombo 9/26/2015 Raffaele
Hybridization of Nickel Catalysis and Photoredox Catalysis. Literature seminar#1 B4 Hiromu Fuse 2017/02/04(Sat)
 Hybridization of Nickel Catalysis and Photoredox Catalysis Literature seminar#1 B4 Hiromu Fuse 2017/02/04(Sat) Introduction Novel cross coupling was reported! Highly selective sp 3 C-H functionalization!
Hybridization of Nickel Catalysis and Photoredox Catalysis Literature seminar#1 B4 Hiromu Fuse 2017/02/04(Sat) Introduction Novel cross coupling was reported! Highly selective sp 3 C-H functionalization!
Nitrogen Centered Radical Ligands Nagashima Nozomu
 1 Nitrogen Centered Radical Ligands 2015. 7. 4. Nagashima Nozomu 1. Introduction 2 3 Aminyl radical 1) D. E. Wiliams, JACS, 1966, 88, 5665 2) Y. Teki et al. JOC, 2000, 65, 7889 Sterically protected aminyl
1 Nitrogen Centered Radical Ligands 2015. 7. 4. Nagashima Nozomu 1. Introduction 2 3 Aminyl radical 1) D. E. Wiliams, JACS, 1966, 88, 5665 2) Y. Teki et al. JOC, 2000, 65, 7889 Sterically protected aminyl
C H activation of aliphatic amines without unnecessary mask M2 Takaya Togo
 C H activation of aliphatic amines without unnecessary mask 2017.11.25 M2 Takaya Togo 1 Outline 1.Introduction 2.Free amines as DG Discovery of new activation mode Mechanistic studies Application of the
C H activation of aliphatic amines without unnecessary mask 2017.11.25 M2 Takaya Togo 1 Outline 1.Introduction 2.Free amines as DG Discovery of new activation mode Mechanistic studies Application of the
2.2.7 Research Area Oxidative Coupling Reactions Methods and Mechanisms (M. Klußmann)
 2.2.7 Research Area Oxidative Coupling Reactions Methods and Mechanisms (M. Klußmann) Involved: E. Böß, P. Karier, K. M. Jones, T. Hillringhaus, C. Schmitz, J. Demaerel, B. Schweitzer-Chaput, N. Gulzar,
2.2.7 Research Area Oxidative Coupling Reactions Methods and Mechanisms (M. Klußmann) Involved: E. Böß, P. Karier, K. M. Jones, T. Hillringhaus, C. Schmitz, J. Demaerel, B. Schweitzer-Chaput, N. Gulzar,
Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage (C-C Activation) Group Meeting Timothy Chang
 Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage (C-C Activation) Group Meeting 01-15-2008 Timothy Chang Outlines - Fundamental considerations, C-H versus C-C activation - Orbital interactions -
Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage (C-C Activation) Group Meeting 01-15-2008 Timothy Chang Outlines - Fundamental considerations, C-H versus C-C activation - Orbital interactions -
An Overview of Organic Reactions. Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants:
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
ummary Manipulating Radicals
 Manipulating Radicals ummary Modern catalysis research tries to address issues such as material scarcity, sustainability or process costs. One solution is to replace expensive and scarce noble metal catalysts
Manipulating Radicals ummary Modern catalysis research tries to address issues such as material scarcity, sustainability or process costs. One solution is to replace expensive and scarce noble metal catalysts
Catalysis Lectures W.H. Green 5.68J/10.652J Spring Handouts: Norskov et al., J. Catalysis Imbihl and Ertl, Chem. Rev. (partial) Homework
 Catalysis Lectures W.H. Green 5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Handouts: Norskov et al., J. Catalysis Imbihl and Ertl, Chem. Rev. (partial) Homework Major points: 1) Why reactions have barriers, and how catalysts
Catalysis Lectures W.H. Green 5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Handouts: Norskov et al., J. Catalysis Imbihl and Ertl, Chem. Rev. (partial) Homework Major points: 1) Why reactions have barriers, and how catalysts
Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) H Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group
 Literature eport Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group eporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Yue Ji Date: 2016-04-05 Yu, J.-Q. et al. Science 2016, 351, 252-256. Scripps esearch
Literature eport Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group eporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Yue Ji Date: 2016-04-05 Yu, J.-Q. et al. Science 2016, 351, 252-256. Scripps esearch
Oxidative couplings of two nucleophiles
 Oxidative Couplings of Hydrocarbons Oxidative couplings of two nucleophiles Oxidants involved: O 2 H 2 O 2 high h valent metals(copper salts) halides(iodine(Ⅲ) oxidants) Lei, A. W. Chem. Rev., 2011, 111,
Oxidative Couplings of Hydrocarbons Oxidative couplings of two nucleophiles Oxidants involved: O 2 H 2 O 2 high h valent metals(copper salts) halides(iodine(Ⅲ) oxidants) Lei, A. W. Chem. Rev., 2011, 111,
Preparation of alkenes
 Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH.8 - HALOALKANES, HALOGENATION AND RADICALS
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKYL HALIDES Alkyl halides are named by naming them as a substituent before the root chain and indicating their location. Prefixes: -F, -Cl -Br -I Alkyl halides have NO
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKYL HALIDES Alkyl halides are named by naming them as a substituent before the root chain and indicating their location. Prefixes: -F, -Cl -Br -I Alkyl halides have NO
The Study of Chemical Reactions. Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order.
 The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
Reactivity within Confined Nano-spaces
 Reactivity within Confined Nano-spaces Larry Wolf Group Meeting 11-17-09 Encapsulating Cyclobutadiene hemicarcerand Anslyn, E. V; Dougherty, D. A. Modern Physical Organic Chemistry Cram. D. J. et. al.
Reactivity within Confined Nano-spaces Larry Wolf Group Meeting 11-17-09 Encapsulating Cyclobutadiene hemicarcerand Anslyn, E. V; Dougherty, D. A. Modern Physical Organic Chemistry Cram. D. J. et. al.
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
CHAPTER 7. Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination
 CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
Lecture 11 Organic Chemistry 1
 EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
Figure 1. Oxidation by iron-oxo complex. supported by porous solid
 Oxidation of Ethane to Ethanol by N 2 O in a Metal-Organic Framework with Coordinatively Unsaturated Iron(II) Sites Long, J.R, et al., Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 590. Mechanism of Oxidation of Ethane to Ethanol
Oxidation of Ethane to Ethanol by N 2 O in a Metal-Organic Framework with Coordinatively Unsaturated Iron(II) Sites Long, J.R, et al., Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 590. Mechanism of Oxidation of Ethane to Ethanol
Student Manual for Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation Using a Copper(I)/TEMPO Catalyst System
 Student Manual for Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation Using a Copper(I)/TEMPO Catalyst System icholas J. Hill, Jessica M. Hoover and Shannon S. Stahl* Department of Chemistry, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1101
Student Manual for Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation Using a Copper(I)/TEMPO Catalyst System icholas J. Hill, Jessica M. Hoover and Shannon S. Stahl* Department of Chemistry, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1101
sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito
 1 sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito 2016. 1. 30 1. Introduction 2 About Carbene 3 Brief history of carbene (~2000) Carbene Neutral compounds featuring a divalent carbon atom with only
1 sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito 2016. 1. 30 1. Introduction 2 About Carbene 3 Brief history of carbene (~2000) Carbene Neutral compounds featuring a divalent carbon atom with only
CHEMICAL KINETICS C.H. BAMFORD C.F.H. TIPPER WSSSKUH EDITED BY
 CHEMICAL KINETICS EDITED BY C.H. BAMFORD M.A., Ph.D., Sc.D. (Cantab.), F.R.I.C., F.R.S. Campbell-Brown Professor of Industrial Chemistry, Uniuersity of Liverpool AND C.F.H. TIPPER Ph.D. (Bristol), D.Sc.
CHEMICAL KINETICS EDITED BY C.H. BAMFORD M.A., Ph.D., Sc.D. (Cantab.), F.R.I.C., F.R.S. Campbell-Brown Professor of Industrial Chemistry, Uniuersity of Liverpool AND C.F.H. TIPPER Ph.D. (Bristol), D.Sc.
Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Relative Reactivity of carbonyls: Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes
 Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Weak nucleophiles, such as water, alcohols, and amines, require acid or base catalysis to undergo addition to carbonyl compounds Relative Reactivity
Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Weak nucleophiles, such as water, alcohols, and amines, require acid or base catalysis to undergo addition to carbonyl compounds Relative Reactivity
Anti-Markovnikov Olefin Functionalization
 Anti-Markovnikov Olefin Functionalization ~Prof. Robert H. Grubbs Work~ 4 th Literature Seminar July 5, 2014 Soichi Ito (D1) Contents 1. Introduction Flow of Prof. Grubbs Research Markovnikov s Rule Wacker
Anti-Markovnikov Olefin Functionalization ~Prof. Robert H. Grubbs Work~ 4 th Literature Seminar July 5, 2014 Soichi Ito (D1) Contents 1. Introduction Flow of Prof. Grubbs Research Markovnikov s Rule Wacker
Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides
 Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides Alcohols Structure and Bonding Enols and Phenols Compounds having a hydroxy group on a sp 2 hybridized carbon enols and phenols undergo different reactions than alcohols. Chapter
Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides Alcohols Structure and Bonding Enols and Phenols Compounds having a hydroxy group on a sp 2 hybridized carbon enols and phenols undergo different reactions than alcohols. Chapter
Organometallic Catalysis
 Organometallic Catalysis The catalysts we will study are termed homogeneous catalysts as they are dissolved in th e same solvent as the substrate. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysts, such as palladium
Organometallic Catalysis The catalysts we will study are termed homogeneous catalysts as they are dissolved in th e same solvent as the substrate. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysts, such as palladium
Hydrogen-Mediated C-C Bond Formation
 EPFL - ISIC - LSPN Hydrogen-Mediated C-C Bond Formation History and selected examples The Research of Prof. Michael Krische (University of Texas at Austin) LSPN Group Seminar Mathias Mamboury Table of
EPFL - ISIC - LSPN Hydrogen-Mediated C-C Bond Formation History and selected examples The Research of Prof. Michael Krische (University of Texas at Austin) LSPN Group Seminar Mathias Mamboury Table of
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Amines Reading Study Problems Key Concepts and Skills Lecture Topics: Amines: structure and nomenclature
 Amines Reading: Wade chapter 19, sections 19-1-19-19 Study Problems: 19-37, 19-39, 19-40, 19-41, 19-44, 19-46, 19-47, 19-48, 19-51, 19-54 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain how the basicity of amines varies
Amines Reading: Wade chapter 19, sections 19-1-19-19 Study Problems: 19-37, 19-39, 19-40, 19-41, 19-44, 19-46, 19-47, 19-48, 19-51, 19-54 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain how the basicity of amines varies
Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3
 Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3 1. Carbon-carbon bonds are not easily broken. Which bond in the following compound would be the least difficult to break homolytically? 2. Which of the following molecules
Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3 1. Carbon-carbon bonds are not easily broken. Which bond in the following compound would be the least difficult to break homolytically? 2. Which of the following molecules
Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis
 rganometallic hemistry and omogeneous atalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N8 Kashiwa ampus, December 11, 2009 Types of reactions in the coordination sphere of T 3. Reductive elimination X-L n -Y L n +
rganometallic hemistry and omogeneous atalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N8 Kashiwa ampus, December 11, 2009 Types of reactions in the coordination sphere of T 3. Reductive elimination X-L n -Y L n +
Ch 18 Ethers and Epoxides
 Ch 18 Ethers and Epoxides Ethers (R-O-R ) are compounds with two organic groups attached to an sp 3 oxygen. Epoxides are cyclic ethers where the sp 3 O is a part of a 3-membered ring. Thiols (R-S-H ) and
Ch 18 Ethers and Epoxides Ethers (R-O-R ) are compounds with two organic groups attached to an sp 3 oxygen. Epoxides are cyclic ethers where the sp 3 O is a part of a 3-membered ring. Thiols (R-S-H ) and
The Mechanistic Studies of the Wacker Oxidation. Tyler W. Wilson SED Group Meeting
 The Mechanistic Studies of the Wacker xidation Tyler W. Wilson SE Group Meeting 11.27.2007 Introduction xidation of ethene by (II) chloride solutions (Phillips, 1894) -First used as a test for alkenes
The Mechanistic Studies of the Wacker xidation Tyler W. Wilson SE Group Meeting 11.27.2007 Introduction xidation of ethene by (II) chloride solutions (Phillips, 1894) -First used as a test for alkenes
Chapter 15. Free Radical Reactions
 Grossman, CE 230 Chapter 15. Free Radical Reactions A free radical is a species containing one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are electrondeficient species, but they are usually uncharged, so
Grossman, CE 230 Chapter 15. Free Radical Reactions A free radical is a species containing one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are electrondeficient species, but they are usually uncharged, so
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
II. 1. TRANSFORMATIONS UNDER THE ACTION OF HEAT OR IRRADIATION
 CHAPTER II HYDROCARBON TRANSFORMATIONS THAT DO NOT INVOLVE METALS OR THEIR COMPOUNDS n this chapter we will briefly survey the main types of hydrocarbon transformations that occur without the participation
CHAPTER II HYDROCARBON TRANSFORMATIONS THAT DO NOT INVOLVE METALS OR THEIR COMPOUNDS n this chapter we will briefly survey the main types of hydrocarbon transformations that occur without the participation
What are radicals? H. Cl. Chapter 10 Radical Reactions. Production of radicals. Reactions of radicals. Electronic structure of methyl radical
 What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
Organic Chemistry Lecture 2 - Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Substitutions
 ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
Oxygen Reduction Reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Oxygen Reduction Reaction Oxygen is the most common oxidant for most fuel cell cathodes simply
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Oxygen Reduction Reaction Oxygen is the most common oxidant for most fuel cell cathodes simply
Homogeneous Catalysis - B. List
 omogeneous Catalysis - B. List 2.2.2 Research Area "rganocatalytic Asymmetric α-alkylation of Aldehydes" (B. List) Involved:. Vignola, A. Majeed Seayad bjective: α-alkylations of carbonyl compounds are
omogeneous Catalysis - B. List 2.2.2 Research Area "rganocatalytic Asymmetric α-alkylation of Aldehydes" (B. List) Involved:. Vignola, A. Majeed Seayad bjective: α-alkylations of carbonyl compounds are
10/26/2010. An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene. to Ethylene
 6.5 An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene Addition of water to ethylene Typical polar process Acid catalyzed addition reaction (Electophilic addition reaction) Polar Reaction All
6.5 An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene Addition of water to ethylene Typical polar process Acid catalyzed addition reaction (Electophilic addition reaction) Polar Reaction All
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122)
 Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Amines. Amines are organic compounds containing a nitrogen functionality. primary secondary tertiary quaternary
 Amines Amines are organic compounds containing a nitrogen functionality Depending upon the number of alkyl, or aryl, groups attached to nitrogen determines its classification, or order 2 primary secondary
Amines Amines are organic compounds containing a nitrogen functionality Depending upon the number of alkyl, or aryl, groups attached to nitrogen determines its classification, or order 2 primary secondary
Reductive Elimination from High-Valent Palladium. Kazunori Nagao MacMillan Group Meeting
 Reductive Elimination from igh-valent Palladium Kazunori agao MacMillan Group eting Why do people focus on rging with C activation Facile reductive elimination DG C palladacycle oxidant complex C etero
Reductive Elimination from igh-valent Palladium Kazunori agao MacMillan Group eting Why do people focus on rging with C activation Facile reductive elimination DG C palladacycle oxidant complex C etero
75. A This is a Markovnikov addition reaction. In these reactions, the pielectrons in the alkene act as a nucleophile. The strongest electrophile will
 71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSGNED READNGS: TODAY S CLASS: Sections 4.1 4.6 NEXT CLASS: rest of Ch.4 http://artsandscience.concordia.ca/facstaff/p-r/rogers
CEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSGNED READNGS: TODAY S CLASS: Sections 4.1 4.6 NEXT CLASS: rest of Ch.4 http://artsandscience.concordia.ca/facstaff/p-r/rogers
CHAPTER 2. Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
 CHAPTER 2 Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules 2-1 Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Simple Chemical Processes Chemical thermodynamics: Is concerned with the extent that
CHAPTER 2 Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules 2-1 Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Simple Chemical Processes Chemical thermodynamics: Is concerned with the extent that
Learning Guide for Chapter 15 - Alcohols (II)
 Learning Guide for Chapter 15 - Alcohols (II) I. Introduction to alcohol reactivity II. Reactions of alcohols with acids III. Reactions of alcohols with electrophiles alogenated phosphorus and sulfur compounds
Learning Guide for Chapter 15 - Alcohols (II) I. Introduction to alcohol reactivity II. Reactions of alcohols with acids III. Reactions of alcohols with electrophiles alogenated phosphorus and sulfur compounds
The problem is that your product still has a-protons, and can keep on forming enolates to get more methyl groups added:
 Lecture 14 ovember 3, 2011 OK I want to continue briefly with the topic of proline catalysis that we discussed last time. In particular, the idea of using secondary amines to catalyze carbonyl chemistry
Lecture 14 ovember 3, 2011 OK I want to continue briefly with the topic of proline catalysis that we discussed last time. In particular, the idea of using secondary amines to catalyze carbonyl chemistry
Transition Metal Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Activation
 literature seminar 2 H. Mitsunuma(M1) 2010/09/08 Transition tal Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Activation 0. Introduction Currently, selective C-H and C-C bond activation by transition metal complexes has
literature seminar 2 H. Mitsunuma(M1) 2010/09/08 Transition tal Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Activation 0. Introduction Currently, selective C-H and C-C bond activation by transition metal complexes has
Formation and Reactivity of Nitrenes with Silver Catalysts for C-H H Bond Amination. Joseph Scanlon Ripon College
 Formation and Reactivity of Nitrenes with Silver Catalysts for C-H H Bond Amination Prasoon Saurabh, Kelcey Anderson, Joseph Scanlon Ripon College Why we want C-N C N bonds More chemically reactive than
Formation and Reactivity of Nitrenes with Silver Catalysts for C-H H Bond Amination Prasoon Saurabh, Kelcey Anderson, Joseph Scanlon Ripon College Why we want C-N C N bonds More chemically reactive than
Chapter 24. Amines. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 Chapter 24. Amines Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Amines Organic Nitrogen Compounds Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3, Nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons, making amines
Chapter 24. Amines Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Amines Organic Nitrogen Compounds Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3, Nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons, making amines
Scission of Dinitrogen by a Molybdenum(III) Xylidene Complex. CHM 5.33 Fall 2005
 Scission of Dinitrogen by a Molybdenum(III) Xylidene Complex CHM 5.33 Fall 2005 Introduction The experiment is based on research performed in the laboratory of Professor Cummins during the early 90 s.
Scission of Dinitrogen by a Molybdenum(III) Xylidene Complex CHM 5.33 Fall 2005 Introduction The experiment is based on research performed in the laboratory of Professor Cummins during the early 90 s.
Morita Baylis Hillman Reaction. Aaron C. Smith 11/10/04
 Morita Baylis Hillman Reaction Aaron C. Smith 11/10/04 Outline 1. Background 2. Development of Asymmetric Variants 3. Aza-Baylis Hillman Reaction 4. Applications of Baylis Hillman Adducts Outline 1. Background
Morita Baylis Hillman Reaction Aaron C. Smith 11/10/04 Outline 1. Background 2. Development of Asymmetric Variants 3. Aza-Baylis Hillman Reaction 4. Applications of Baylis Hillman Adducts Outline 1. Background
CHEM Lecture 7
 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
1. Which of the following compounds is the weakest base?
 I. Multiple-choice Questions Fall 2018 1. Which of the following compounds is the weakest base? a. C3C2 b. C3C2 c. N3 d. C3 e. N2 2. Which of the following functional groups is indicated by a strong and
I. Multiple-choice Questions Fall 2018 1. Which of the following compounds is the weakest base? a. C3C2 b. C3C2 c. N3 d. C3 e. N2 2. Which of the following functional groups is indicated by a strong and
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW
 REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Text Sections (N0 1.9, 9-11) Homework: Chapter 1:
 CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
Hydrides and Dihydrogen as Ligands: Hydrogenation Catalysis
 Hydrides and Dihydrogen as Ligands: Hydrogenation Catalysis Synthesis of Organometallic Complex Hydrides Reaction of MCO with OH -, H -, or CH 2 CHR 2 M(CO) n + OH - = M(CO) n-1 (COOH) - = HM(CO) n-1 -
Hydrides and Dihydrogen as Ligands: Hydrogenation Catalysis Synthesis of Organometallic Complex Hydrides Reaction of MCO with OH -, H -, or CH 2 CHR 2 M(CO) n + OH - = M(CO) n-1 (COOH) - = HM(CO) n-1 -
Chapter 10 Free Radicals
 hapter 10 Free Radicals This is an example of a free radical reaction. A radical is a species that has a free unpaired electron. There are several examples of stable radicals, the most common of which
hapter 10 Free Radicals This is an example of a free radical reaction. A radical is a species that has a free unpaired electron. There are several examples of stable radicals, the most common of which
This reactivity makes alkenes an important class of organic compounds because they can be used to synthesize a wide variety of other compounds.
 This reactivity makes alkenes an important class of organic compounds because they can be used to synthesize a wide variety of other compounds. Mechanism for the addition of a hydrogen halide What happens
This reactivity makes alkenes an important class of organic compounds because they can be used to synthesize a wide variety of other compounds. Mechanism for the addition of a hydrogen halide What happens
Metalloporphyrin. ~as efficient Lewis acid catalysts with a unique reaction-field~ and. ~Synthetic study toward complex metalloporphyrins~
 Metalloporphyrin ~as efficient Lewis acid catalysts with a unique reaction-field~ and ~Synthetic study toward complex metalloporphyrins~ Literature Seminar Kenta Saito (D1) 1 Topics Chapter 1 ~as efficient
Metalloporphyrin ~as efficient Lewis acid catalysts with a unique reaction-field~ and ~Synthetic study toward complex metalloporphyrins~ Literature Seminar Kenta Saito (D1) 1 Topics Chapter 1 ~as efficient
10. Alkyl Halides. What Is an Alkyl Halide. An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen
 10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
Investigation of the Role and Form. Formation. Michael Enright
 Investigation of the Role and Form of Silver Catalysts in C N Bond Formation Michael Enright Ripon College Importance Carbon Nitrogen Bonds Medicine Biological compounds Make C N bonds whenever we want
Investigation of the Role and Form of Silver Catalysts in C N Bond Formation Michael Enright Ripon College Importance Carbon Nitrogen Bonds Medicine Biological compounds Make C N bonds whenever we want
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides"
 Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides The (E)-(Z) System for Designating Alkene Diastereomers The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog convention is used to assign
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides The (E)-(Z) System for Designating Alkene Diastereomers The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog convention is used to assign
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Sonogashira: in situ, metal assisted deprotonation
 M.C. White, Chem 253 Cross-Coupling -120- Week of ctober 11, 2004 Sonogashira: in situ, metal assisted deprotonation catalytic cycle: ' (h 3 ) n d II The first report: h Sonogashira T 1975 (50) 4467. h
M.C. White, Chem 253 Cross-Coupling -120- Week of ctober 11, 2004 Sonogashira: in situ, metal assisted deprotonation catalytic cycle: ' (h 3 ) n d II The first report: h Sonogashira T 1975 (50) 4467. h
D. X. Hu Towards Catalytic Enantioselective Halogenation of Alkenes Burns Group
 D. X. Hu Towards Catalytic Enantioselective Halogenation of Alkenes Burns Group Literature Review Organic Synthesis 10, 20, 50 Years from Now? Catalytic Enantioselective Halogenation October 6 th, 2012
D. X. Hu Towards Catalytic Enantioselective Halogenation of Alkenes Burns Group Literature Review Organic Synthesis 10, 20, 50 Years from Now? Catalytic Enantioselective Halogenation October 6 th, 2012
Olefin Metathesis ROMP. L n Ru= ROMP n RCM. dilute
 lefin Metathesis MP: ing-opening metathesis polymerization Thermodynamically favored for 3,4, 8, larger ring systems Bridging groups (bicyclic olefins) make ΔG polymerization more favorable as a result
lefin Metathesis MP: ing-opening metathesis polymerization Thermodynamically favored for 3,4, 8, larger ring systems Bridging groups (bicyclic olefins) make ΔG polymerization more favorable as a result
Oxidative Addition oxidative addition reductive elimination
 Oxidative Addition We have seen how neutral ligands such as C 2 H 4 or CO can enter the coordination sphere of a metal by substitution. We now look at a general method for simultaneously introducing pairs
Oxidative Addition We have seen how neutral ligands such as C 2 H 4 or CO can enter the coordination sphere of a metal by substitution. We now look at a general method for simultaneously introducing pairs
Module9. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy - Chemical shift - Integration of signal area
 1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
https://cuvillier.de/de/shop/publications/766
 Jelena Jenter (Autor) Nitrogen Donor Ligands in the Coordination Chemistry of the are Earth and Alkaline Earth Metals Synthesis - Structures - Catalysis https://cuvillier.de/de/shop/publications/766 Copyright:
Jelena Jenter (Autor) Nitrogen Donor Ligands in the Coordination Chemistry of the are Earth and Alkaline Earth Metals Synthesis - Structures - Catalysis https://cuvillier.de/de/shop/publications/766 Copyright:
Chapter 15: Enyzmatic Catalysis
 Chapter 15: Enyzmatic Catalysis Voet & Voet: Pages 496-508 Slide 1 Catalytic Mechanisms Catalysis is a process that increases the rate at which a reaction approaches equilibrium Rate enhancement depends
Chapter 15: Enyzmatic Catalysis Voet & Voet: Pages 496-508 Slide 1 Catalytic Mechanisms Catalysis is a process that increases the rate at which a reaction approaches equilibrium Rate enhancement depends
Classifying Organic Chemical Reactions
 Chemical Reactivity Organic chemistry encompasses a very large number of compounds ( many millions ), and our previous discussion and illustrations have focused on their structural characteristics. Now
Chemical Reactivity Organic chemistry encompasses a very large number of compounds ( many millions ), and our previous discussion and illustrations have focused on their structural characteristics. Now
The Final Learning Experience
 Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #5 Reactions of Alcohols and Related Reactions The Final Learning Experience Wednesday, December 20, 2000, 1:00-3:00 Name:
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #5 Reactions of Alcohols and Related Reactions The Final Learning Experience Wednesday, December 20, 2000, 1:00-3:00 Name:
CHEMISTRY Topic #8: Oxidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay
 CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #8: xidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay xidation States of Carbon Carbon can have any oxidation state from -4 (C 4 ) to +4 (C 2 ). As a general rule, increasing
CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #8: xidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay xidation States of Carbon Carbon can have any oxidation state from -4 (C 4 ) to +4 (C 2 ). As a general rule, increasing
LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
CHEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #14 Thurs., Oct.20, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: NEXT LECTURE: Sections 4.7-4.10 finish Ch.4,
Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X. Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): R + X X 2.
 Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions
 Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions A Primer on MO Theory σ-bonding in Organotransition Metal Complexes M-C Bond Energies in Organotransition Metal Complexes Thermodynamic Predictions
Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions A Primer on MO Theory σ-bonding in Organotransition Metal Complexes M-C Bond Energies in Organotransition Metal Complexes Thermodynamic Predictions
Ethers can be symmetrical or not:
 Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides 175 Physical Properties Ethers can be symmetrical or not: linear or cyclic. Ethers are inert and make excellent solvents for organic reactions. Epoxides are very
Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides 175 Physical Properties Ethers can be symmetrical or not: linear or cyclic. Ethers are inert and make excellent solvents for organic reactions. Epoxides are very
Alcohols: Contain a hydroxy group( OH) bonded to an sp 2 or sp 3 hybridized
 Lecture Notes hem 51B S. King hapter 9 Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides I. Introduction Alcohols, ether, and epoxides are 3 functional groups that contain σ-bonds. Alcohols: ontain a hydroxy group( ) bonded
Lecture Notes hem 51B S. King hapter 9 Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides I. Introduction Alcohols, ether, and epoxides are 3 functional groups that contain σ-bonds. Alcohols: ontain a hydroxy group( ) bonded
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
Ch 16 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Ch 16 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Mechanism - Aromatic rings typically undergo substitution, where an H is replaced with an electrophile (E+). - The rings do not typically undergo addition across
Ch 16 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Mechanism - Aromatic rings typically undergo substitution, where an H is replaced with an electrophile (E+). - The rings do not typically undergo addition across
Unraveling the Mechanism of Water Oxidation by Ruthenium-Oxo Complexes
 Unraveling the Mechanism of Water xidation by thenium-xo Complexes Casseday Richers Literature Seminar ovember 20, 2007 The oxidation of water to dioxygen and protons represents one half the watersplitting
Unraveling the Mechanism of Water xidation by thenium-xo Complexes Casseday Richers Literature Seminar ovember 20, 2007 The oxidation of water to dioxygen and protons represents one half the watersplitting
Lecture 4 Chapter 13 - Polymers. Functional Groups Condensation Rxns Free Radical Rxns
 Lecture 4 Chapter 13 - Polymers Functional Groups Condensation Rxns Free Radical Rxns Chemistry the whole year on one page Last semester Basic atomic theory Stoichiometry, balancing reactions Thermodynamics
Lecture 4 Chapter 13 - Polymers Functional Groups Condensation Rxns Free Radical Rxns Chemistry the whole year on one page Last semester Basic atomic theory Stoichiometry, balancing reactions Thermodynamics
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Ethers. Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, & Sulfides. General Formula: Types: a) Symmetrical: Examples: b) Unsymmetrical: Examples: Physical Properties:
 Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture Notes Examination 1 Materials Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, & Sulfides Ethers General Formula: Types: a) Symmetrical: Examples: b) Unsymmetrical: Examples: Physical Properties:
Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture Notes Examination 1 Materials Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, & Sulfides Ethers General Formula: Types: a) Symmetrical: Examples: b) Unsymmetrical: Examples: Physical Properties:
Organic Chemistry. Radical Reactions
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Radical Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Radical Reactions by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
Construction of C-C or C-N Bond via C-H Activation ~Chemistry of Yong-Qiang Tu~
 Literature Seminar 2010.5.26 Yao u(2) Construction of C-C or C-N Bond via C-H Activation ~Chemistry of Yong-Qiang Tu~ Contents: 1. Yong-Qiang Tu's Profile 2.LatestWorkofProfessorTu 2-1. C-H Activation
Literature Seminar 2010.5.26 Yao u(2) Construction of C-C or C-N Bond via C-H Activation ~Chemistry of Yong-Qiang Tu~ Contents: 1. Yong-Qiang Tu's Profile 2.LatestWorkofProfessorTu 2-1. C-H Activation
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions"
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
I5 ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTIONS OF
 Section I Aromatic chemistry I5 ELECTPILIC SUBSTITUTINS F MN-SUBSTITUTED AMATIC INGS Key Notes ortho, meta and para substitution Substituent effect eaction profile Activating groups inductive o/p Deactivating
Section I Aromatic chemistry I5 ELECTPILIC SUBSTITUTINS F MN-SUBSTITUTED AMATIC INGS Key Notes ortho, meta and para substitution Substituent effect eaction profile Activating groups inductive o/p Deactivating
Bio-inspired C-H functionalization by metal-oxo complexes
 1 Literature Seminar Bio-inspired C-H functionalization by metal-oxo complexes 2016. 7. 23. Nagashima Nozomu 2 C-H functionalization by enzymes Enzymes enable aliphatic C-H functionalization 3 P450 oxidation
1 Literature Seminar Bio-inspired C-H functionalization by metal-oxo complexes 2016. 7. 23. Nagashima Nozomu 2 C-H functionalization by enzymes Enzymes enable aliphatic C-H functionalization 3 P450 oxidation
Recommended Reading: 23, 29 (3rd edition); 22, 29 (4th edition) Ch 102 Problem Set 7 Due: Thursday, June 1 Before Class. Problem 1 (1 points) Part A
 Recommended Reading: 23, 29 (3rd edition); 22, 29 (4th edition) Ch 102 Problem Set 7 Due: Thursday, June 1 Before Class Problem 1 (1 points) Part A Kinetics experiments studying the above reaction determined
Recommended Reading: 23, 29 (3rd edition); 22, 29 (4th edition) Ch 102 Problem Set 7 Due: Thursday, June 1 Before Class Problem 1 (1 points) Part A Kinetics experiments studying the above reaction determined
Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways
 Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways 1. Reaction a. Thermodynamics b. Kinetics 2. Enzyme a. Structure and Function b. Regulation of Activity c. Kinetics d. Inhibition 3. Metabolic Pathways a. REDOX
Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways 1. Reaction a. Thermodynamics b. Kinetics 2. Enzyme a. Structure and Function b. Regulation of Activity c. Kinetics d. Inhibition 3. Metabolic Pathways a. REDOX
An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A
 An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A How many nonequivalent protons does the following structure have? 4 Reading from left to right,
An unknown molecule A has 4 signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum. Which of the following corresponds to molecule A How many nonequivalent protons does the following structure have? 4 Reading from left to right,
Lecture Topics: I. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
CH 3 TMG, DMF N H 3 CO 2 S. (PPh 3 ) 2 Pd 0
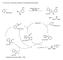 1. (a) rovide a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I S 2 C 3 C 3 ( 3 ) 2 2, CuI C 3 TMG, DMF 3 C 2 S TMG = Me 2 Me 2 ICu ( 3 ) 2 0 I S 2 C 3 S 2 C 3 Cu I 3 3 3 C 2 S I 3 3 3 C 2 S 3
1. (a) rovide a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I S 2 C 3 C 3 ( 3 ) 2 2, CuI C 3 TMG, DMF 3 C 2 S TMG = Me 2 Me 2 ICu ( 3 ) 2 0 I S 2 C 3 S 2 C 3 Cu I 3 3 3 C 2 S I 3 3 3 C 2 S 3
