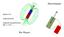
Figure 1. Schematic picture of surface helical domain structure.
|
|
|
- Allyson Barton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 93 (2014) pp Submitted: (2014) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Accepted: doi: / Influence of Magnetic Field of Super High Frequency on Hysteretic Properties of Soft Magnetic Microwires Alexander Chizhik 1, a *, Julian Gonzalez 1,b, Arcady Zhukov 1,2,c, Andrzej Stupakiewicz 3,d, Andrzej Maziewski 3,e 1 Universidad del Pais Vasco, UPV/EHU, San Sebastian, Spain 2 IKERBASQUE, Bilbao, Spain 3 Laboratory of Magnetism, University of Bialystok, Bialystok, Poland a oleksandr.chyzhyk@ehu.es, b julianmaria.gonzalez@ehu.es, c arkadi.joukov@ehu.es, d and@uwb.edu.pl, e magnet@uwb.edu.pl Keywords: Amorphous magnetic wire, Hysteresis, Magnetooptic Kerr effect Abstract. The influence of super high frequency (SHF) circular magnetic field on magnetization reversal in the Co-rich glass covered microwire has been investigated. The study has been performed by magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) technique. It was found that the presence of the SHF field causes the change of the re-magnetization mechanism the rotation of the magnetization is observed instead of domain walls motion. Also the hysteresis loop has an asymmetric shape that confirms the co-existence of the stable and meta-stable helical magnetic states in the surface of microwires. Introduction The optimization of main parameters of sensors based on giant magnetoimpedance (GMI) effect [1] is an actual task of modern electronics. Glass covered microwires is the basic element of this type of magnetic sensors and during last years we directed our efforts to elucidation of fundamental mechanisms of magnetization reversal and domain structure formation in these microwires [2]. Now we understand that the magnetic structure consist of helically magnetized domains (Fig. 1). There are two possible types of this structure: serpentine or elliptic. The present paper is devoted to the study of the magnetization reversal in the presence of electric current of high and super-high frequency. The investigations have been performed using the magneto-optical Kerr effect technique which demonstrated very high efficiency in the study of the surface magnetic properties of cylindrically shaped samples. Experimental Details Figure 1. Schematic picture of surface helical domain structure. The longitudinal impedance was measured with a vector network analyzer (VNA) through the reflection coefficient [3]. The microwire was soldered in microstrip cell (Fig. 2). One wire end was connected to the inner conductor of a coaxial line through a matched microstrip line while the other was connected to the ground plane. The sample holder was placed inside a sufficiently long solenoid that creates a homogeneous magnetic field in the sample. All rights reserved. No part of contents of this paper may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without the written permission of TTP, (ID: /10/14,15:17:34)
2 204 6th Forum on New Materials - Part A Figure. 2 Sample cell (a). Reflection of the light from the microeire (b). The external magnetic field was the sum of axial magnetic field (H AX ) (up to 200 Oe) and super high frequency circular magnetic field (H CIR ) (up to 20 ma). To obtain the surface hysteresis loops MOKE polarizing microscopy was used. First, surface domain imaging was performed by means of MOKE microscope. Magnetic domains are observed because of different in-plane components of the surface magnetization. This difference transforms to black-white contrast when the polarized light reflects from the top of the cylindrically shaped surface of the microwire. Second, the histeresis loops were obtained from the magneto-optic intensity as a result of the MOKE images processing. We studied glass-coated microwire with the nominal composition Co 67 Fe 3.85 Ni 1.45 B 11.5 Si 14.5 Mo 1.7 (metallic nucleus radius is 11.2 µm) supplied by Tamag Ibérica. Experimental Results and Discussion Figure 3. GMI curves.
3 Advances in Science and Technology Vol Fig. 3 demonstrates the dependences of the real part impedance on external magnetic field. According to the classical interpretation, at moderate frequency of 100 MHz the maximum of GMI curve is related to anisotropy filed H k of the sample that can be estimated as 210 A/m. Below H k the impedance is determined by domain walls motion and the rotation of the magnetization. Above H k the surface layer of microwire is saturated and the impedance decreases as the transverse susceptibility decreases. At higher frequencies (>1GHz), the impedance becomes dominated by ferromagnetic resonance with maxima displacing to the high field with increasing frequencies. Figure 4. MOKE hysteresis sloops obtained in the presence of 1MHz electric current. Fig. 4 shows the hysteresis loops obtained in the axial magnetic field and in the presence HF circular magnetic field of 1 MHz. The HF circular magnetic field causes the transformation of the hysteresis loop. It means the strong transformation of the magnetization reversal process. The hysteresis consists of the rotation of the magnetization and the surface domain structure transformation when the HF electric current is small (2mA). Figure 5. Hystereis loops obtained in the presence of electric current of 2 GHz frequency and amplitude (a) 2 ma; (b) 20 ma.
4 206 6th Forum on New Materials - Part A The asymmetric transformation of hysteresis loop takes place for higher amplitude of HF electric current (10 ma). The following increase of the amplitude of electric current (20 ma) induces the change of the mechanism of magnetization reversal. The pure rotation of the magnetization dominates. The HF circular field induces the vibration of the surface magnetization difference from DC circular field. In the presence of axial magnetic field this vibration causes the successive inclination of magnetization towards the circular direction. In such a way the HF field stabilizes the inclined meta-stable helical structure. The degree of the inclination depends on the value of the frequency. Figure 6. The MOKE hysteresis loops obtained in the presence of SHF electric current of 20 ma amplitude and frequency band of 0.1 GHz 3 GHz. Fig. 5 presents the MOKE hysteresis loops obtained in presence of electric current of 2 GHz frequency range. The observed local laydown could be related to the effect of the local domain disappearance. The helical magnetic states are very sensitive to SHF circular field. The increase of circular field results in competition between meta-stable helical structures. Also SHF circular field makes preferable the DW propagation or domain nucleation. The reason of the observed effects is determined mainly by the co-existence of different helical states in the microwire. This co-existence is realized in the domain structure in which the angle of the DW changes the direction in the length of the wire. The DWs which divides different helical states have different inclination angles. Fig. 6 presents the MOKE hysteresis loops obtained in the presence of SHF electric current of 20 ma amplitude and frequency band of 0.1 GHz 3 GHz. Fig. 6(a) shows the hysteresis loops for 0.1 GHz and 1 GHz. For such high value of electric current the shape of the curves is interpreted in the following way: one of the surface circular domains is in an advantageous state in the presence of SHF circular magnetic field. The curve demonstrates the rotation of the magnetization in this advantageous domain. The circular field of 1 GHz induces higher inclination of the circular magnetization toward the circular direction. It is the reason of the observed acceleration of the rotation of the magnetization. For the frequency of 2 and 3 GHz (Fig. 6(b)) the pure rotation of the magnetization is also observed, but the direction of the rotation differs from the case of 1 GHz: now the other circular domain is the advantageous one. This effect could be explained in supposition of the existence of small initial helicality of surface magnetic structure. The increase of the amplitude of the vibration of the magnetization is induced by SHF field. When the vibrating circular magnetization overcomes
5 Advances in Science and Technology Vol the axial direction of the microwire the meta-stable advantageous domain change the sign to the opposite one. Generally the effect observed in this frequency band could be interpreted in the frame of low field absorption and splitting between giant magnetoimpedance and ferromagnetic resonance. Conclusions The process of surface magnetization reversal was studied in glass covered microwires in the presence of electric current of MHz-GHz range. Now it is clear that the circular magnetic field affects the magnetization reversal even at SHF range. The real mechanism of the magnetization reversal depends on the amplitude of the SHF electric current. The circular magnetic field induces the meta-stable inclined helical state. The frequency and the amplitude of the SHF field determine the sign and the degree of the helicality of the meta-stable states. References [1] A. Zhukov, V. Zhukova, Magnetic Properties and Applications of Ferromagnetic Microwires with Amorphous and Nanocrystalline Structure, Nova Science Publishers, New York, [2] A. Chizhik, J. Gonzalez, Magnetic Microwires. A Magneto-Optical Study, Pan Stanford Publishing, Singapore, [3] M. Ipatov, A. Chizhik, V. Zhukova, J. Gonzalez, A. Zhukov, Correlation of surface domain structure and magneto-impedance in amorphous microwires, Journal of Applied Physics 109 (2011)
Vortex magnetic structure in circularly magnetized microwires as deduced from magneto-optical Kerr measurements
 Vortex magnetic structure in circularly magnetized microwires as deduced from magneto-optical Kerr measurements Item Type Article Authors Ivanov, Yurii P.; del Real, R. P.; Chubykalo-Fesenko, O.; Vázquez,
Vortex magnetic structure in circularly magnetized microwires as deduced from magneto-optical Kerr measurements Item Type Article Authors Ivanov, Yurii P.; del Real, R. P.; Chubykalo-Fesenko, O.; Vázquez,
P. Gawroński and K. Kułakowski
 Stable states of systems of bistable magnetostrictive wires against applied field, applied stress and spatial geometry P. Gawroński and K. Kułakowski AGH-University of Science and Technology Kraków, Poland
Stable states of systems of bistable magnetostrictive wires against applied field, applied stress and spatial geometry P. Gawroński and K. Kułakowski AGH-University of Science and Technology Kraków, Poland
STATIC TORQUE MEASUREMENT USING GMI STRAIN GAUGE
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials Vol. 6, No. 2, June 2004, p. 699-703 STATIC TORQUE MEASUREMENT USING GMI STRAIN GAUGE T. Uchiyama, F. Borza *, T. Meydan Wolfson Centre for Magnetics Technology,
Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials Vol. 6, No. 2, June 2004, p. 699-703 STATIC TORQUE MEASUREMENT USING GMI STRAIN GAUGE T. Uchiyama, F. Borza *, T. Meydan Wolfson Centre for Magnetics Technology,
PSI AP Physics C Sources of Magnetic Field. Multiple Choice Questions
 PSI AP Physics C Sources of Magnetic Field Multiple Choice Questions 1. Two protons move parallel to x- axis in opposite directions at the same speed v. What is the direction of the magnetic force on the
PSI AP Physics C Sources of Magnetic Field Multiple Choice Questions 1. Two protons move parallel to x- axis in opposite directions at the same speed v. What is the direction of the magnetic force on the
MOKE: Principles and Measurement. Corbyn Mellinger Dr. Xu Group June 10, 2016
 MOKE: Principles and Measurement Corbyn Mellinger Dr. Xu Group June 10, 2016 Common Magneto-optical Effects Faraday Effect: magnetization of material affects transmission of polarized light Kerr Effect:
MOKE: Principles and Measurement Corbyn Mellinger Dr. Xu Group June 10, 2016 Common Magneto-optical Effects Faraday Effect: magnetization of material affects transmission of polarized light Kerr Effect:
ARTICLE IN PRESS Sensors and Actuators A xxx (2012) xxx xxx
 G Model ARTICLE IN PRESS Sensors and Actuators A xxx (2012) xxx xxx Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Sensors and Actuators A: Physical jo u rn al hom epage: www.elsevier.com/locate/sna
G Model ARTICLE IN PRESS Sensors and Actuators A xxx (2012) xxx xxx Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Sensors and Actuators A: Physical jo u rn al hom epage: www.elsevier.com/locate/sna
Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields Sources
 Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields Sources All known magnetic sources are due to magnetic dipoles and inherently macroscopic current sources or microscopic spins and magnetic moments Goals for Chapter 28 Study
Chapter 28 Magnetic Fields Sources All known magnetic sources are due to magnetic dipoles and inherently macroscopic current sources or microscopic spins and magnetic moments Goals for Chapter 28 Study
Metacomposite characteristics and their influential factors of polymer composites containing orthogonal ferromagnetic microwire arrays
 Metacomposite characteristics and their influential factors of polymer composites containing orthogonal ferromagnetic microwire arrays Y. Luo 1, H.X. Peng 1,a), F.X. Qin 2,b), M. Ipatov 3, V. Zhukova 3,
Metacomposite characteristics and their influential factors of polymer composites containing orthogonal ferromagnetic microwire arrays Y. Luo 1, H.X. Peng 1,a), F.X. Qin 2,b), M. Ipatov 3, V. Zhukova 3,
Dynamics of a magnetic nanoparticle with cubic anisotropy in a viscous liquid
 Dynamics of a magnetic nanoparticle with cubic anisotropy in a viscous liquid N. A. Usov 1,2,4, M. L. Fdez-Gubieda 2, A. Muela 3 and J. M. Barandiarán 2 1 IKERBASQUE, The Basque Foundation for Science,
Dynamics of a magnetic nanoparticle with cubic anisotropy in a viscous liquid N. A. Usov 1,2,4, M. L. Fdez-Gubieda 2, A. Muela 3 and J. M. Barandiarán 2 1 IKERBASQUE, The Basque Foundation for Science,
MAGNETIC PROBLEMS. (d) Sketch B as a function of d clearly showing the value for maximum value of B.
 PHYS2012/2912 MAGNETC PROBLEMS M014 You can investigate the behaviour of a toroidal (dough nut shape) electromagnet by changing the core material (magnetic susceptibility m ) and the length d of the air
PHYS2012/2912 MAGNETC PROBLEMS M014 You can investigate the behaviour of a toroidal (dough nut shape) electromagnet by changing the core material (magnetic susceptibility m ) and the length d of the air
Determination of Mechanical Force between two Planar Inductors in the Problem of Electrodynamic Excitation of Seismic Waves
 Journal of Siberian Federal University. Mathematics & Physics 2014, 7(3), 389 397 УДК 621.318.38 Determination of Mechanical Force between two Planar Inductors in the Problem of Electrodynamic Excitation
Journal of Siberian Federal University. Mathematics & Physics 2014, 7(3), 389 397 УДК 621.318.38 Determination of Mechanical Force between two Planar Inductors in the Problem of Electrodynamic Excitation
MSE 7025 Magnetic Materials (and Spintronics)
 MSE 7025 Magnetic Materials (and Spintronics) Lecture 10: Characterization Techniques Episode I: VSM and MOKE Chi-Feng Pai cfpai@ntu.edu.tw Course Outline Time Table Week Date Lecture 1 Feb 24 Introduction
MSE 7025 Magnetic Materials (and Spintronics) Lecture 10: Characterization Techniques Episode I: VSM and MOKE Chi-Feng Pai cfpai@ntu.edu.tw Course Outline Time Table Week Date Lecture 1 Feb 24 Introduction
Technique for the electric and magnetic parameter measurement of powdered materials
 Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIV 41 Technique for the electric and magnetic parameter measurement of powdered materials R. Kubacki,. Nowosielski & R. Przesmycki Faculty of Electronics,
Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIV 41 Technique for the electric and magnetic parameter measurement of powdered materials R. Kubacki,. Nowosielski & R. Przesmycki Faculty of Electronics,
Introduction. Concept of shielding
 Shielding Introduction Concept of shielding Shielding of a metal shield (theory) For E field SE.. 2log E E i t For H field SE.. 2log H H i t Do they be equal? Shielding of a metal shield (theory) It depends.
Shielding Introduction Concept of shielding Shielding of a metal shield (theory) For E field SE.. 2log E E i t For H field SE.. 2log H H i t Do they be equal? Shielding of a metal shield (theory) It depends.
Techniques for inferring M at small scales
 Magnetism and small scales We ve seen that ferromagnetic materials can be very complicated even in bulk specimens (e.g. crystallographic anisotropies, shape anisotropies, local field effects, domains).
Magnetism and small scales We ve seen that ferromagnetic materials can be very complicated even in bulk specimens (e.g. crystallographic anisotropies, shape anisotropies, local field effects, domains).
Angular dependence of the magnetization reversal in exchange biased Fe/MnF 2. Elke Arenholz
 Angular dependence of the magnetization reversal in exchange biased Fe/MnF 2 Elke Arenholz Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720 Kai Liu Department of Physics,
Angular dependence of the magnetization reversal in exchange biased Fe/MnF 2 Elke Arenholz Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720 Kai Liu Department of Physics,
DEHRADUN PUBLIC SCHOOL I TERM ASSIGNMENT SUBJECT- PHYSICS (042) CLASS -XII
 Chapter 1(Electric charges & Fields) DEHRADUN PUBLIC SCHOOL I TERM ASSIGNMENT 2016-17 SUBJECT- PHYSICS (042) CLASS -XII 1. Why do the electric field lines never cross each other? [2014] 2. If the total
Chapter 1(Electric charges & Fields) DEHRADUN PUBLIC SCHOOL I TERM ASSIGNMENT 2016-17 SUBJECT- PHYSICS (042) CLASS -XII 1. Why do the electric field lines never cross each other? [2014] 2. If the total
MEASURE THE COMPLEX PERMEABILITY OF FER- ROMAGNETIC THIN FILMS: COMPARISON SHORTED MICROSTRIP METHOD WITH MICROSTRIP TRANS- MISSION METHOD
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 173 181, 2009 MEASURE THE COMPLEX PERMEABILITY OF FER- ROMAGNETIC THIN FILMS: COMPARISON SHORTED MICROSTRIP METHOD WITH MICROSTRIP TRANS- MISSION
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 173 181, 2009 MEASURE THE COMPLEX PERMEABILITY OF FER- ROMAGNETIC THIN FILMS: COMPARISON SHORTED MICROSTRIP METHOD WITH MICROSTRIP TRANS- MISSION
MAGNETIC MATERIAL CHARACTERIZATION BY OPEN SAMPLE MEASUREMENTS
 MAGNETIC MATERIAL CHARACTERIZATION BY OPEN SAMPLE MEASUREMENTS VALENTIN IONIŢĂ, LUCIAN PETRESCU Key words: Magnetic material characterization, Open sample measurements, Correction of experimental data.
MAGNETIC MATERIAL CHARACTERIZATION BY OPEN SAMPLE MEASUREMENTS VALENTIN IONIŢĂ, LUCIAN PETRESCU Key words: Magnetic material characterization, Open sample measurements, Correction of experimental data.
AISSCE 2016 EXPECTED (SURE SHORT) QUESTIONS WEIGHTAGE-WISE 2016
 CLASS: XII AISSCE 2016 Subject: Physics EXPECTED (SURE SHORT) QUESTIONS WEIGHTAGE-WISE 2016 Q3 Section A ( 1 Mark ) A force F is acting between two charges placed some distances apart in vacuum. If a brass
CLASS: XII AISSCE 2016 Subject: Physics EXPECTED (SURE SHORT) QUESTIONS WEIGHTAGE-WISE 2016 Q3 Section A ( 1 Mark ) A force F is acting between two charges placed some distances apart in vacuum. If a brass
Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 28 To determine the
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 28 To determine the
Magneto Optical Kerr Effect Microscopy Investigation on Permalloy Nanostructures
 Magneto Optical Kerr Effect Microscopy Investigation on Permalloy Nanostructures Zulzawawi Bin Haji Hujan A thesis submitted for the degree of MSc by research University of York Department of Physics January
Magneto Optical Kerr Effect Microscopy Investigation on Permalloy Nanostructures Zulzawawi Bin Haji Hujan A thesis submitted for the degree of MSc by research University of York Department of Physics January
θ θ θ θ current I Fig. 6.1 The conductor and the magnetic field are both in the plane of the paper. State
 3 1 (a) A straight conductor carrying a current I is at an angle θ to a uniform magnetic field of flux density B, as shown in Fig. 6.1. magnetic field, flux density B θ θ θ θ current I Fig. 6.1 The conductor
3 1 (a) A straight conductor carrying a current I is at an angle θ to a uniform magnetic field of flux density B, as shown in Fig. 6.1. magnetic field, flux density B θ θ θ θ current I Fig. 6.1 The conductor
CBSE Examination Paper
 CBSE Examination Paper Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks: 70 General Instructions: Same as CBSE Examination Paper SET I 1. Using the concept of force between two infinitely long parallel current carrying
CBSE Examination Paper Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks: 70 General Instructions: Same as CBSE Examination Paper SET I 1. Using the concept of force between two infinitely long parallel current carrying
HIGH SENSITIVITY TRIAXIAL MAGNETIC FIELD TRANSDUCER, BASED ON THE PHASE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GMI EFFECT
 XIX IMEKO World Congress Fundamental and Applied Metrology September 6 11, 2009, Lisbon, Portugal HIGH SENSITIVITY TRIAXIAL MAGNETIC FIELD TRANSDUCER, BASED ON THE PHASE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GMI EFFECT
XIX IMEKO World Congress Fundamental and Applied Metrology September 6 11, 2009, Lisbon, Portugal HIGH SENSITIVITY TRIAXIAL MAGNETIC FIELD TRANSDUCER, BASED ON THE PHASE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GMI EFFECT
Friction Drive Simulation of a SAW Motor with Slider Surface Texture Variation
 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 54 (28) pp 366-371 online at http://www.scientific.net (28) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online available since 28/Sep/2 Friction Drive Simulation of a SAW
Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 54 (28) pp 366-371 online at http://www.scientific.net (28) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online available since 28/Sep/2 Friction Drive Simulation of a SAW
Chapter 19. Magnetism
 Chapter 19 Magnetism The figure shows the path of a negatively charged particle in a region of a uniform magnetic field. Answer the following questions about this situation (in each case, we revert back
Chapter 19 Magnetism The figure shows the path of a negatively charged particle in a region of a uniform magnetic field. Answer the following questions about this situation (in each case, we revert back
Surface Plasmon Resonance. Magneto-optical. optical enhancement and other possibilities. Applied Science Department The College of William and Mary
 Surface Plasmon Resonance. Magneto-optical optical enhancement and other possibilities Applied Science Department The College of William and Mary Plasmonics Recently surface plasmons have attracted significant
Surface Plasmon Resonance. Magneto-optical optical enhancement and other possibilities Applied Science Department The College of William and Mary Plasmonics Recently surface plasmons have attracted significant
Subject Area Competencies and Skills (22nd Edition)
 Science Education (Physics) Program Requirements Physics 6-12 "C" below indicates where content is covered through coursework 1. Knowledge of the nature of scientific investigation and instruction in physics
Science Education (Physics) Program Requirements Physics 6-12 "C" below indicates where content is covered through coursework 1. Knowledge of the nature of scientific investigation and instruction in physics
Chapter 8 Magnetic Resonance
 Chapter 8 Magnetic Resonance 9.1 Electron paramagnetic resonance 9.2 Ferromagnetic resonance 9.3 Nuclear magnetic resonance 9.4 Other resonance methods TCD March 2007 1 A resonance experiment involves
Chapter 8 Magnetic Resonance 9.1 Electron paramagnetic resonance 9.2 Ferromagnetic resonance 9.3 Nuclear magnetic resonance 9.4 Other resonance methods TCD March 2007 1 A resonance experiment involves
Supplementary Figure 1. Magnetic domain configuration under out-of-plane field application. (a), (b) MTXM images showing magnetic domain state
 Supplementary Figure 1. Magnetic domain configuration under out-of-plane field application. (a), (b) MTXM images showing magnetic domain state acquired at a given out-ofplane magnetic field. Bright and
Supplementary Figure 1. Magnetic domain configuration under out-of-plane field application. (a), (b) MTXM images showing magnetic domain state acquired at a given out-ofplane magnetic field. Bright and
Supplementary Figure 1. Optical and magneto-optical responses for 80 nm diameter particles
 Supplementary Figure 1 Optical and magneto-optical responses for 80 nm diameter particles The schematics on the left illustrate the direction of incident polarization and the induced dipole moments that
Supplementary Figure 1 Optical and magneto-optical responses for 80 nm diameter particles The schematics on the left illustrate the direction of incident polarization and the induced dipole moments that
DIRECTIVITY AND SENSITIVITY OF HIGH FREQUENCY CARRIER TYPE THIN-FILM MAGNETIC FIELD SENSOR
 DIRECTIVITY AND SENSITIVITY OF HIGH FREQUENCY CARRIER TYPE THIN-FILM MAGNETIC FIELD SENSOR M. Yamaguchi a, M. Takezawa a, H. Ohdaira b, K. I. Arai a, and A. Haga b a Research Institute of Electrical Communication,
DIRECTIVITY AND SENSITIVITY OF HIGH FREQUENCY CARRIER TYPE THIN-FILM MAGNETIC FIELD SENSOR M. Yamaguchi a, M. Takezawa a, H. Ohdaira b, K. I. Arai a, and A. Haga b a Research Institute of Electrical Communication,
Electromagnetic fields Learning outcome
 Electromagnetic fields Learning outcome At the end of this lecture you will be able to: List the most important electromagnetic field quantities Explain what these quantities describe Calculate some of
Electromagnetic fields Learning outcome At the end of this lecture you will be able to: List the most important electromagnetic field quantities Explain what these quantities describe Calculate some of
Electrodynamic passive magnetic bearing using reluctance forces
 Electrodynamic passive magnetic bearing using reluctance forces Keywords Jan Sandtner, Hannes Bleuler: École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne EPFL, Switzerland Département de microtechnique DMT, Institut
Electrodynamic passive magnetic bearing using reluctance forces Keywords Jan Sandtner, Hannes Bleuler: École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne EPFL, Switzerland Département de microtechnique DMT, Institut
Problem 2: 25 points The space between the conductors of a long coaxial cable used to transmit television signals has an inner radius r 1 =0:15 mm and
 Physics 272. Practice Final Exam On the nal exam there will be 8 problems. The nal exam is Thursday May 12th, 9:45-11:45 a.m. in WAT 112 Problem 1: 25 points A sphere has a volume charge density (r) =
Physics 272. Practice Final Exam On the nal exam there will be 8 problems. The nal exam is Thursday May 12th, 9:45-11:45 a.m. in WAT 112 Problem 1: 25 points A sphere has a volume charge density (r) =
Stress effect on magnetoimpedance (MI) in amorphous wires at GHz frequencies and application to stress-tunable microwave composite materials
 Stress ect on magnetoimpedance (MI) in amorphous wires at G frequencies and application to stress-tunable microwave composite materials L. V. Panina a), S. I. Sandacci, and D. P. Makhnovskiy b) School
Stress ect on magnetoimpedance (MI) in amorphous wires at G frequencies and application to stress-tunable microwave composite materials L. V. Panina a), S. I. Sandacci, and D. P. Makhnovskiy b) School
Dpto. de Química Inorgánica, Universidad del País Vasco, UPV/EHU, P.O. Box. 644, E-48080, Bilbao, Spain.
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles Prepared by Seeded-Growth Route for Hyperthermia: Electron Magnetic Resonance
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles Prepared by Seeded-Growth Route for Hyperthermia: Electron Magnetic Resonance
High School Curriculum Standards: Physics
 High School Curriculum Standards: Physics Students will understand and apply scientific concepts, principles, and theories pertaining to the physical setting and living environment and recognize the historical
High School Curriculum Standards: Physics Students will understand and apply scientific concepts, principles, and theories pertaining to the physical setting and living environment and recognize the historical
Direct observation of the skyrmion Hall effect
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS3883 Direct observation of the skyrmion Hall effect Wanjun Jiang 1,2,3, *,, Xichao Zhang 4,*, Guoqiang Yu 5, Wei Zhang 1, Xiao Wang 6, M. Benjamin Jungfleisch
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHYS3883 Direct observation of the skyrmion Hall effect Wanjun Jiang 1,2,3, *,, Xichao Zhang 4,*, Guoqiang Yu 5, Wei Zhang 1, Xiao Wang 6, M. Benjamin Jungfleisch
Unidirectional spin-wave heat conveyer
 Unidirectional spin-wave heat conveyer Figure S1: Calculation of spin-wave modes and their dispersion relations excited in a 0.4 mm-thick and 4 mm-diameter Y 3 Fe 5 O 12 disk. a, Experimentally obtained
Unidirectional spin-wave heat conveyer Figure S1: Calculation of spin-wave modes and their dispersion relations excited in a 0.4 mm-thick and 4 mm-diameter Y 3 Fe 5 O 12 disk. a, Experimentally obtained
Self Field Measurements by Hall Sensors on the SeCRETS Long Sample CICCs in SULTAN
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON APPLIED SUPERCONDUCTIVITY, VOL. 12, NO. 1, MARCH 2002 1667 Self Field Measurements by Hall Sensors on the SeCRETS Long Sample CICCs in SULTAN Yu. A. Ilyin, A. Nijhuis, H. H. J. ten
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON APPLIED SUPERCONDUCTIVITY, VOL. 12, NO. 1, MARCH 2002 1667 Self Field Measurements by Hall Sensors on the SeCRETS Long Sample CICCs in SULTAN Yu. A. Ilyin, A. Nijhuis, H. H. J. ten
Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998.
![Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998. Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998.](/thumbs/90/104152266.jpg) Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/9803101v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998 A. D. Kent a, U. Ruediger a, J. Yu a, S. Zhang a, P. M. Levy a
Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/9803101v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998 A. D. Kent a, U. Ruediger a, J. Yu a, S. Zhang a, P. M. Levy a
Chapter 19. Magnetism. 1. Magnets. 2. Earth s Magnetic Field. 3. Magnetic Force. 4. Magnetic Torque. 5. Motion of Charged Particles. 6.
 Chapter 19 Magnetism 1. Magnets 2. Earth s Magnetic Field 3. Magnetic Force 4. Magnetic Torque 5. Motion of Charged Particles 6. Amperes Law 7. Parallel Conductors 8. Loops and Solenoids 9. Magnetic Domains
Chapter 19 Magnetism 1. Magnets 2. Earth s Magnetic Field 3. Magnetic Force 4. Magnetic Torque 5. Motion of Charged Particles 6. Amperes Law 7. Parallel Conductors 8. Loops and Solenoids 9. Magnetic Domains
NR/RR. Set No. 2 CODE NO: NR/RR210204
 Set No. 2 II B.Tech I Semester Examinations,May 2011 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS Electrical And Electronics Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
Set No. 2 II B.Tech I Semester Examinations,May 2011 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS Electrical And Electronics Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
Infrastructure of Thin Films Laboratory in Institute of Molecular Physics Polish Academy of Sciences
 Infrastructure of Thin Films Laboratory in Institute of Molecular Physics Polish Academy of Sciences Outline Sample preparation Magnetron sputtering Ion-beam sputtering Pulsed laser deposition Electron-beam
Infrastructure of Thin Films Laboratory in Institute of Molecular Physics Polish Academy of Sciences Outline Sample preparation Magnetron sputtering Ion-beam sputtering Pulsed laser deposition Electron-beam
01 Development of Hard Disk Drives
 01 Development of Hard Disk Drives Design Write / read operation MR / GMR heads Longitudinal / perpendicular recording Recording media Bit size Areal density Tri-lemma 11:00 10/February/2016 Wednesday
01 Development of Hard Disk Drives Design Write / read operation MR / GMR heads Longitudinal / perpendicular recording Recording media Bit size Areal density Tri-lemma 11:00 10/February/2016 Wednesday
Exchange Splitting of Backward Volume Spin Wave Configuration Dispersion Curves in a Permalloy Nano-stripe
 760 PIERS Proceedings, Kuala Lumpur, MALAYSIA, March 27 30, 2012 Exchange Splitting of Backward Volume Spin Wave Configuration Dispersion Curves in a Permalloy Nano-stripe G. Venkat 1, A. Prabhakar 1,
760 PIERS Proceedings, Kuala Lumpur, MALAYSIA, March 27 30, 2012 Exchange Splitting of Backward Volume Spin Wave Configuration Dispersion Curves in a Permalloy Nano-stripe G. Venkat 1, A. Prabhakar 1,
Material and Design Requirements for Advanced Concentrators
 Advances in Science and Technology Online: 2010-10-27 ISSN: 1662-0356, Vol. 74, pp 237-242 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ast.74.237 2010 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Material and Design Requirements
Advances in Science and Technology Online: 2010-10-27 ISSN: 1662-0356, Vol. 74, pp 237-242 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ast.74.237 2010 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Material and Design Requirements
Marking Scheme PHYSICS SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER Section- A
 Marking Scheme PHYSICS SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER-2018 Section- A 1. As V A V B = V B V C magnitude of work done is same. (1) 2. I = (1) 3. Factors are : (i) magnetic permeability of the medium (1/2) (ii) electric
Marking Scheme PHYSICS SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER-2018 Section- A 1. As V A V B = V B V C magnitude of work done is same. (1) 2. I = (1) 3. Factors are : (i) magnetic permeability of the medium (1/2) (ii) electric
NYS STANDARD/KEY IDEA/PERFORMANCE INDICATOR 5.1 a-e. 5.1a Measured quantities can be classified as either vector or scalar.
 INDICATOR 5.1 a-e September Unit 1 Units and Scientific Notation SI System of Units Unit Conversion Scientific Notation Significant Figures Graphical Analysis Unit Kinematics Scalar vs. vector Displacement/dis
INDICATOR 5.1 a-e September Unit 1 Units and Scientific Notation SI System of Units Unit Conversion Scientific Notation Significant Figures Graphical Analysis Unit Kinematics Scalar vs. vector Displacement/dis
Two-Temperature EPR Measurements of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Paweł Szroeder, Franciszek Rozpłoch and Waldemar Marciniak
 Solid State Phenomena Vol. 94 (2003) pp 275-278 (2003) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.94.275 Two-Temperature EPR Measurements of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Paweł
Solid State Phenomena Vol. 94 (2003) pp 275-278 (2003) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.94.275 Two-Temperature EPR Measurements of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Paweł
The GENERATION, MEASURING TECHNIQUE AND APPLICATION OF PULSED FIELDS. R.Grössinger
 High Magnetic Fields The GENERATION, MEASURING TECHNIQUE AND APPLICATION OF PULSED FIELDS R.Grössinger Coworker: M. Küpferling, H.Sassik, R.Sato, E.Wagner, O.Mayerhofer, M.Taraba ƒ1 Content CONTENT Generation
High Magnetic Fields The GENERATION, MEASURING TECHNIQUE AND APPLICATION OF PULSED FIELDS R.Grössinger Coworker: M. Küpferling, H.Sassik, R.Sato, E.Wagner, O.Mayerhofer, M.Taraba ƒ1 Content CONTENT Generation
Magnetic domain theory in dynamics
 Chapter 3 Magnetic domain theory in dynamics Microscale magnetization reversal dynamics is one of the hot issues, because of a great demand for fast response and high density data storage devices, for
Chapter 3 Magnetic domain theory in dynamics Microscale magnetization reversal dynamics is one of the hot issues, because of a great demand for fast response and high density data storage devices, for
B for a Long, Straight Conductor, Special Case. If the conductor is an infinitely long, straight wire, θ 1 = 0 and θ 2 = π The field becomes
 B for a Long, Straight Conductor, Special Case If the conductor is an infinitely long, straight wire, θ 1 = 0 and θ 2 = π The field becomes μ I B = o 2πa B for a Curved Wire Segment Find the field at point
B for a Long, Straight Conductor, Special Case If the conductor is an infinitely long, straight wire, θ 1 = 0 and θ 2 = π The field becomes μ I B = o 2πa B for a Curved Wire Segment Find the field at point
Neutron Reflectometry of Ferromagnetic Arrays
 Neutron Reflectometry of Ferromagnetic Arrays Z.Y. Zhao a, P. Mani a, V.V.Krishnamurthy a, W.-T. Lee b, F. Klose b, and G.J. Mankey a a Center for Materials for Information Technology and Department of
Neutron Reflectometry of Ferromagnetic Arrays Z.Y. Zhao a, P. Mani a, V.V.Krishnamurthy a, W.-T. Lee b, F. Klose b, and G.J. Mankey a a Center for Materials for Information Technology and Department of
Physics 208 Exam 3 Nov. 28, 2006
 Name: Student ID: Section #: Physics 208 Exam 3 Nov. 28, 2006 Print your name and section clearly above. If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name. Your final answer must be placed in
Name: Student ID: Section #: Physics 208 Exam 3 Nov. 28, 2006 Print your name and section clearly above. If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name. Your final answer must be placed in
Magnetic Force Microscopy practical
 European School on Magnetism 2015 From basic magnetic concepts to spin currents Magnetic Force Microscopy practical Organized by: Yann Perrin, Michal Staňo and Olivier Fruchart Institut NEEL (CNRS & Univ.
European School on Magnetism 2015 From basic magnetic concepts to spin currents Magnetic Force Microscopy practical Organized by: Yann Perrin, Michal Staňo and Olivier Fruchart Institut NEEL (CNRS & Univ.
Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: Section Number:
 Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: E-mail: Section Number: No calculators are allowed in the test. Be sure to put a box around your final answers and clearly
Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: E-mail: Section Number: No calculators are allowed in the test. Be sure to put a box around your final answers and clearly
Chapter 22, Magnetism. Magnets
 Chapter 22, Magnetism Magnets Poles of a magnet (north and south ) are the ends where objects are most strongly attracted. Like poles repel each other and unlike poles attract each other Magnetic poles
Chapter 22, Magnetism Magnets Poles of a magnet (north and south ) are the ends where objects are most strongly attracted. Like poles repel each other and unlike poles attract each other Magnetic poles
Structural and Thermal Characterization of Polymorphic Er 2 Si 2 O 7 Asghari Maqsood
 Key Engineering Materials Online: 202-05-4 ISSN: 662-9795, Vols. 50-5, pp 255-260 doi:0.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.50-5.255 202 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Structural and Thermal Characterization
Key Engineering Materials Online: 202-05-4 ISSN: 662-9795, Vols. 50-5, pp 255-260 doi:0.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.50-5.255 202 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Structural and Thermal Characterization
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents), Ampere s Law is introduced
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents), Ampere s Law is introduced
Chapter 30 Sources of the magnetic field
 Chapter 30 Sources of the magnetic field Force Equation Point Object Force Point Object Field Differential Field Is db radial? Does db have 1/r2 dependence? Biot-Savart Law Set-Up The magnetic field is
Chapter 30 Sources of the magnetic field Force Equation Point Object Force Point Object Field Differential Field Is db radial? Does db have 1/r2 dependence? Biot-Savart Law Set-Up The magnetic field is
Experiment and Simulation Study on A New Structure of Full Optical Fiber Current Sensor
 2017 2nd International Conference on Computational Modeling, Simulation and Applied Mathematics (CMSAM 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-499-8 Experiment and Simulation Study on A New Structure of Full Optical Fiber
2017 2nd International Conference on Computational Modeling, Simulation and Applied Mathematics (CMSAM 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-499-8 Experiment and Simulation Study on A New Structure of Full Optical Fiber
1.50 m, and a speed of 750 km/hr. What is the distance between adjacent crests of these waves? A) 9000 m B) 32,400 m C) 2500 m D) 9000 km E) 32,400 km
 Exam Physics 3 -TTh - Fall 2016 Name Email Perm# Tel # Remember to write all work in your Bluebook as well as put the answer on your Scantron MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
Exam Physics 3 -TTh - Fall 2016 Name Email Perm# Tel # Remember to write all work in your Bluebook as well as put the answer on your Scantron MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 28 Looking forward
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 28 Looking forward
Downloaded from
 Question 4.1: A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil? Number of turns
Question 4.1: A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil? Number of turns
Design of an RF Photo-Gun (PHIN)
 Design of an RF Photo-Gun (PHIN) R. Roux 1, G. Bienvenu 1, C. Prevost 1, B. Mercier 1 1) CNRS-IN2P3-LAL, Orsay, France Abstract In this note we show the results of the RF simulations performed with a 2-D
Design of an RF Photo-Gun (PHIN) R. Roux 1, G. Bienvenu 1, C. Prevost 1, B. Mercier 1 1) CNRS-IN2P3-LAL, Orsay, France Abstract In this note we show the results of the RF simulations performed with a 2-D
Adouble-layered (DL) perpendicular anisotropy system
 1200 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 41, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 Methodology for Investigating the Magnetization Process of the Storage Layer in Double-Layered Perpendicular Magnetic Recording Media Using
1200 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 41, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 Methodology for Investigating the Magnetization Process of the Storage Layer in Double-Layered Perpendicular Magnetic Recording Media Using
Advanced Lab Course. Tunneling Magneto Resistance
 Advanced Lab Course Tunneling Magneto Resistance M06 As of: 015-04-01 Aim: Measurement of tunneling magnetoresistance for different sample sizes and recording the TMR in dependency on the voltage. Content
Advanced Lab Course Tunneling Magneto Resistance M06 As of: 015-04-01 Aim: Measurement of tunneling magnetoresistance for different sample sizes and recording the TMR in dependency on the voltage. Content
Magnetic Force on a Moving Charge
 Magnetic Force on a Moving Charge Electric charges moving in a magnetic field experience a force due to the magnetic field. Given a charge Q moving with velocity u in a magnetic flux density B, the vector
Magnetic Force on a Moving Charge Electric charges moving in a magnetic field experience a force due to the magnetic field. Given a charge Q moving with velocity u in a magnetic flux density B, the vector
physics 590 ruslan prozorov magnetic measurements Nov 9,
 physics 590 ruslan prozorov magnetic measurements Nov 9, 2009 - magnetic moment of free currents Magnetic moment of a closed loop carrying current I: Magnetic field on the axis of a loop of radius R at
physics 590 ruslan prozorov magnetic measurements Nov 9, 2009 - magnetic moment of free currents Magnetic moment of a closed loop carrying current I: Magnetic field on the axis of a loop of radius R at
Surface Magnetic Non-Destructive Testing
 Surface Magnetic Non-Destructive Testing Evangelos Hristoforou 1,*, Konstantinos Kosmas 1 and Eleftherios Kayafas 2 1 School of Mining and Metallurgy Engineering, National Technical University of Athens,
Surface Magnetic Non-Destructive Testing Evangelos Hristoforou 1,*, Konstantinos Kosmas 1 and Eleftherios Kayafas 2 1 School of Mining and Metallurgy Engineering, National Technical University of Athens,
Optical properties of spherical and anisotropic gold shell colloids
 8 Optical properties of spherical and anisotropic gold shell colloids Core/shell colloids consisting of a metal shell and a dielectric core are known for their special optical properties. The surface plasmon
8 Optical properties of spherical and anisotropic gold shell colloids Core/shell colloids consisting of a metal shell and a dielectric core are known for their special optical properties. The surface plasmon
Properties and applications of ferromagnetic nanostructures
 Properties and applications of ferromagnetic nanostructures Diego Bisero, Lucia Del Bianco, Federico Spizzo Magnetism Experimental group Outline 1.Nanostructures: some examples 2.Why ferromagnetic nanostructures?
Properties and applications of ferromagnetic nanostructures Diego Bisero, Lucia Del Bianco, Federico Spizzo Magnetism Experimental group Outline 1.Nanostructures: some examples 2.Why ferromagnetic nanostructures?
Electromagnetic Theory: PHAS3201, Winter 2008 Preliminaries D. R. Bowler drb/teaching.
 Electromagnetic Theory: PHA3201, Winter 2008 Preliminaries D. R. Bowler david.bowler@ucl.ac.uk http://www.cmmp.ucl.ac.uk/ drb/teaching.html 1 yllabus The course can be split into three main areas: electric
Electromagnetic Theory: PHA3201, Winter 2008 Preliminaries D. R. Bowler david.bowler@ucl.ac.uk http://www.cmmp.ucl.ac.uk/ drb/teaching.html 1 yllabus The course can be split into three main areas: electric
Electromagnetism. Topics Covered in Chapter 14:
 Chapter 14 Electromagnetism Topics Covered in Chapter 14: 14-1: Ampere-turns of Magnetomotive Force (mmf) 14-2: Field Intensity (H) 14-3: B-H Magnetization Curve 14-4: Magnetic Hysteresis 14-5: Magnetic
Chapter 14 Electromagnetism Topics Covered in Chapter 14: 14-1: Ampere-turns of Magnetomotive Force (mmf) 14-2: Field Intensity (H) 14-3: B-H Magnetization Curve 14-4: Magnetic Hysteresis 14-5: Magnetic
Warsaw University of Technology Electrical Department. Laboratory of Materials Technology KWNiAE
 Warsaw University of Technology Electrical Department Laboratory of Materials Technology KWNiAE Practice 6 Analysis of Ferromagnetic Materials 1. Introduction In each atom of every known material there
Warsaw University of Technology Electrical Department Laboratory of Materials Technology KWNiAE Practice 6 Analysis of Ferromagnetic Materials 1. Introduction In each atom of every known material there
ONE CENTURY LATER: REMARKS ON THE BARNETT EXPERIMENT
 ONE CENTURY LATER: REMARKS ON THE BARNETT EXPERIMENT Alexander L. Kholmetskii Department of Physics Belarus State University 4, F. Skorina Avenue 220080 Minsk, Belarus E-mail: kholm@bsu.by Abstract The
ONE CENTURY LATER: REMARKS ON THE BARNETT EXPERIMENT Alexander L. Kholmetskii Department of Physics Belarus State University 4, F. Skorina Avenue 220080 Minsk, Belarus E-mail: kholm@bsu.by Abstract The
Modelling of the Ultrasonic Shot Peening Process. C. Pilé, M. François, D. Retraint, E. Rouhaud and J. Lu
 Materials Science Forum Online: 5-7-15 ISSN: 1-975, Vols. 9-91, pp 7-7 doi:1.8/www.scientific.net/msf.9-91.7 5 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Modelling of the Ultrasonic Shot Peening Process C. Pilé,
Materials Science Forum Online: 5-7-15 ISSN: 1-975, Vols. 9-91, pp 7-7 doi:1.8/www.scientific.net/msf.9-91.7 5 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Modelling of the Ultrasonic Shot Peening Process C. Pilé,
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 5 (217-18) SUBJECT: PHYSICS (43) BLUE PRINT : CLASS XII UNIT VSA (1 mark) SA - I (2 marks) SA II (3 marks) VBQ (4 marks) LA (5 marks) Total I
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 5 (217-18) SUBJECT: PHYSICS (43) BLUE PRINT : CLASS XII UNIT VSA (1 mark) SA - I (2 marks) SA II (3 marks) VBQ (4 marks) LA (5 marks) Total I
PHYS 1444 Section 501 Lecture #17
 PHYS 1444 Section 501 Lecture #17 Wednesday, Mar. 29, 2006 Solenoid and Toroidal Magnetic Field Biot-Savart Law Magnetic Materials B in Magnetic Materials Hysteresis Today s homework is #9, due 7pm, Thursday,
PHYS 1444 Section 501 Lecture #17 Wednesday, Mar. 29, 2006 Solenoid and Toroidal Magnetic Field Biot-Savart Law Magnetic Materials B in Magnetic Materials Hysteresis Today s homework is #9, due 7pm, Thursday,
Prentice Hall. Physics: Principles with Applications, Updated 6th Edition (Giancoli) High School
 Prentice Hall Physics: Principles with Applications, Updated 6th Edition (Giancoli) 2009 High School C O R R E L A T E D T O Physics I Students should understand that scientific knowledge is gained from
Prentice Hall Physics: Principles with Applications, Updated 6th Edition (Giancoli) 2009 High School C O R R E L A T E D T O Physics I Students should understand that scientific knowledge is gained from
Chapter 4 - Moving Charges and Magnetism. Magnitude of the magnetic field at the centre of the coil is given by the relation,
 Question 4.1: A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil? Number of turns
Question 4.1: A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil? Number of turns
NEGATIVE MAGNETOSTRICTIVE DELAY LINES USED IN SENSING APPLICATIONS
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials Vol. 6, No. 2, June 4, p. 593-598 NEGATIVE MAGNETOSTRICTIVE DELAY LINES USED IN SENSING APPLICATIONS C. Petridis, P. Tsiklidis, A. Ktena, E. Hristoforou
Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials Vol. 6, No. 2, June 4, p. 593-598 NEGATIVE MAGNETOSTRICTIVE DELAY LINES USED IN SENSING APPLICATIONS C. Petridis, P. Tsiklidis, A. Ktena, E. Hristoforou
11/21/2011. The Magnetic Field. Chapter 24 Magnetic Fields and Forces. Mapping Out the Magnetic Field Using Iron Filings
 Chapter 24 Magnetic Fields and Forces Topics: Magnets and the magnetic field Electric currents create magnetic fields Magnetic fields of wires, loops, and solenoids Magnetic forces on charges and currents
Chapter 24 Magnetic Fields and Forces Topics: Magnets and the magnetic field Electric currents create magnetic fields Magnetic fields of wires, loops, and solenoids Magnetic forces on charges and currents
Torque on a Current Loop
 Today Chapter 19 Magnetism Torque on a current loop, electrical motor Magnetic field around a current carrying wire. Ampere s law Solenoid Material magnetism Clicker 1 Which of the following is wrong?
Today Chapter 19 Magnetism Torque on a current loop, electrical motor Magnetic field around a current carrying wire. Ampere s law Solenoid Material magnetism Clicker 1 Which of the following is wrong?
MAGNETIC FIELDS AND UNIFORM PLANE WAVES
 MAGNETIC FIELDS AND UNIFORM PLANE WAVES Name Section 1. (8 Pts) 2. (8 Pts) 3. (8 Pts) 4. (6 Pts) 5. (6 Pts) 6. (4 Pts) 7. (20 Pts) 8. (20 Pts) 9. (20 Pts) Total Notes: 1. Please read over all questions
MAGNETIC FIELDS AND UNIFORM PLANE WAVES Name Section 1. (8 Pts) 2. (8 Pts) 3. (8 Pts) 4. (6 Pts) 5. (6 Pts) 6. (4 Pts) 7. (20 Pts) 8. (20 Pts) 9. (20 Pts) Total Notes: 1. Please read over all questions
A detailed study of magnetization reversal in individual Ni nanowires
 A detailed study of magnetization reversal in individual Ni nanowires Item Type Article Authors Vidal, Enrique Vilanova; Ivanov, Yurii P.; Mohammed, Hanan; Kosel, Jürgen Citation A detailed study of magnetization
A detailed study of magnetization reversal in individual Ni nanowires Item Type Article Authors Vidal, Enrique Vilanova; Ivanov, Yurii P.; Mohammed, Hanan; Kosel, Jürgen Citation A detailed study of magnetization
HALL EFFECT AND MAGNETORESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON PERMALLOY Py THIN FILMS AND Py/Cu/Py MULTILAYERS
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, Vol. 4, No. 1, March 2002, p. 79-84 HALL EFFECT AND MAGNETORESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON PERMALLOY Py THIN FILMS AND Py/Cu/Py MULTILAYERS M. Volmer, J. Neamtu
Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, Vol. 4, No. 1, March 2002, p. 79-84 HALL EFFECT AND MAGNETORESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON PERMALLOY Py THIN FILMS AND Py/Cu/Py MULTILAYERS M. Volmer, J. Neamtu
Kerr effect in Sr 2 RuO 4 and other unconventional superconductors
 Kerr effect in Sr 2 RuO 4 and other unconventional superconductors Students: Jing Xia Elizabeth Schemm Variety of samples: Yoshi Maeno (Kyoto University) - Sr 2 RuO 4 single crystals D. Bonn and R. Liang
Kerr effect in Sr 2 RuO 4 and other unconventional superconductors Students: Jing Xia Elizabeth Schemm Variety of samples: Yoshi Maeno (Kyoto University) - Sr 2 RuO 4 single crystals D. Bonn and R. Liang
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON. SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, SPORTS and SCIENCES BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER /2018
 ENG018 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, SPORTS and SCIENCES BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING MODULE NO: EEE6002 Date: 17 January 2018 Time: 2.00 4.00 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: There are six questions.
ENG018 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, SPORTS and SCIENCES BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING MODULE NO: EEE6002 Date: 17 January 2018 Time: 2.00 4.00 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: There are six questions.
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 15 Chapter 27 sec. 3-5 Fall 2016 Semester Professor Koltick Magnetic Fields B = μ 0 4π I dl r r 2 = μ 0 4π I dl r r 3 B = μ 0 2I 4π R B = μ 0 2 IR 2 R 2 + z 2
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 15 Chapter 27 sec. 3-5 Fall 2016 Semester Professor Koltick Magnetic Fields B = μ 0 4π I dl r r 2 = μ 0 4π I dl r r 3 B = μ 0 2I 4π R B = μ 0 2 IR 2 R 2 + z 2
arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.ins-det] 3 Apr 2003
![arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.ins-det] 3 Apr 2003 arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.ins-det] 3 Apr 2003](/thumbs/89/100394661.jpg) GIANT MAGNETO-IMPEDANCE AND ITS APPLICATIONS C. Tannous and J. Gieraltowski Laboratoire de Magnétisme de Bretagne, arxiv:physics/0208035v2 [physics.ins-det] 3 Apr 2003 CNRS UMR-6135, Université de Bretagne
GIANT MAGNETO-IMPEDANCE AND ITS APPLICATIONS C. Tannous and J. Gieraltowski Laboratoire de Magnétisme de Bretagne, arxiv:physics/0208035v2 [physics.ins-det] 3 Apr 2003 CNRS UMR-6135, Université de Bretagne
ELECTROMAGNETISM. Second Edition. I. S. Grant W. R. Phillips. John Wiley & Sons. Department of Physics University of Manchester
 ELECTROMAGNETISM Second Edition I. S. Grant W. R. Phillips Department of Physics University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Flow diagram inside front cover
ELECTROMAGNETISM Second Edition I. S. Grant W. R. Phillips Department of Physics University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Flow diagram inside front cover
Chapter 19. Magnetism
 Chapter 19 Magnetism Magnetic Fields and Forces Fundamentally they do not exist If we had special relativity we would find there is no such thing as a magnetic field. It is only a relativistic transformation
Chapter 19 Magnetism Magnetic Fields and Forces Fundamentally they do not exist If we had special relativity we would find there is no such thing as a magnetic field. It is only a relativistic transformation
1 Introduction + = Bdipole
 Design and fabrication of a 2.5T superconducting dipole prototype based on tilted solenoids CHEN Yu-Quan( 陈玉泉 ) 1,2:1) MA Li-Zhen( 马力祯 ) 1 WU-Wei( 吴巍 ) 1 WU Bei-Min( 吴北民 ) 1 YANG Tong-Jun( 杨通军 ) 1 LIANG
Design and fabrication of a 2.5T superconducting dipole prototype based on tilted solenoids CHEN Yu-Quan( 陈玉泉 ) 1,2:1) MA Li-Zhen( 马力祯 ) 1 WU-Wei( 吴巍 ) 1 WU Bei-Min( 吴北民 ) 1 YANG Tong-Jun( 杨通军 ) 1 LIANG
PHYSICS. Chapter 29 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 29 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 29 The Magnetic Field IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about magnetism and the magnetic field.
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 29 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 29 The Magnetic Field IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about magnetism and the magnetic field.
Estimating Probability of Detection Curves Related to Eddy Current Sender Receiver Probes
 5 th European-American Workshop on Reliability of NDE Lecture 9 Estimating Probability of Detection Curves Related to Eddy Current Sender Receiver Probes Anders ROSELL 1, 2, Gert PERSSON 2, Håkan WIRDELIUS
5 th European-American Workshop on Reliability of NDE Lecture 9 Estimating Probability of Detection Curves Related to Eddy Current Sender Receiver Probes Anders ROSELL 1, 2, Gert PERSSON 2, Håkan WIRDELIUS
