Some Families of Organic Compounds HL
|
|
|
- Flora Barton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Organic Chemistry 22. Types of Reactions in Organic Chemistry Objectives Addition Reactions -explain what is meant by an addition reaction -write balanced equations using structural formula for the reactions of the alkenes with hydrogen, chlorine, bromine, water and hydrogen chloride -outline the industrial importance of: products of the addition reactions of ethene with chlorine, bromine, water and hydrogen chloride hydrogenation of vegetable oils -describe the mechanisms of ionic addition (addition of HCl, Br 2, Cl 2, only to ethene) -describe the evidence for this mechanism as: the reaction of ethene with bromine water containing sodium chloride results in the formation of 2-bromoethanol 1- bromo-2-chloroethane and 1,2-dibromoethane -explain what is meant by addition polymerisation -outline the polymerisation reaction of ethane and propene (reaction mechanism not required). -account for the unreactivity of benzene with regard to addition reactions relative to ethene -account for the use of alkenes as raw materials in the industrial manufacture of plastics -outline the range and scope of the petrochemical industry -list two synthetic products of the petrochemical industry (structures not required unless specified elsewhere on the syllabus) Substitution Reaction -define substitution reaction -recognise halogenation of alkanes as a substitution reaction -write balanced equations using structural formula for the halogenations of alkanes -describe the mechanism of free radical substitution (monochlorination of methane and ethane only) -discuss the evidence for the mechanism of free radical substitution use of ultraviolet light even for a very short period causes a chain reaction formation of trace quantities of ethane and butane in the monochlorination of methane and ethane, respectively these reactions are speeded up by the addition of a known source of free radicals, such as tetraethyllead -explain what is meant by esterification -explain what is meant by base hydrolysis of esters -write balanced equations using structural formulas to illustrate base hydrolysis of esters -prepare a sample of soap (structures of reactants and products required) -discuss the manufacture of soap (structures of reactants and products required) Elimination Reactions -explain what is meant by an elimination reaction -explain what is meant by a dehydration reaction write balanced equations using structural formula for the dehydration of alcohols Redox Reactions Page 1 of 9
2 -write balanced half equations using structural formula for the oxidation (using KMnO 4 or Na 2Cr 2O 7) of: alcohols to(i) aldehydes and (ii) acids aldehydes to acids -carry out calculations involving percentage yield of ethanal (the balanced equation will be given) -demonstrate the properties of ethanal (limited to reactions with (i) acidified potassium manganate(vii) solution, (ii) Fehling s reagent and (iii) ammoniacal silver nitrate) -relate the production of ethanal to the metabolism of ethanol in the human body -carry out calculations involving percentage yield of ethanoic acid (the balanced equation will be given) -carry out diagnostic tests on ethanoic acid (limited to reactions with sodium carbonate, magnesium and ethanol) -account for the lower susceptibility of ketones than aldehydes to oxidation -write balanced equations using structural formulas for the reduction of carbonyl compounds using a H 2/Ni catalyst -recall that combustion is a reaction common to most organic compounds -recall that the fully halogenated alkanes are non-flammable, relate this property to their use in flame retardants and fire extinguishers -oxidise phenylmethanol (benzyl alcohol) to benzoic acid using potassium permanganate under basic conditions. -recall that benzaldehyde is a constituent of almond kernels (structure of benzaldehyde not required) -purify a sample of benzoic acid by recrystallisation outline the use of melting point to confirm purity determine the melting point of benzoic acid Reactions as acids -write balanced equations using structural formulas for the reactions of alcohols with sodium -account for the acidic nature of the carboxylic acid group -write balanced equations using structural formulas for the reactions of carboxylic acids with magnesium, with sodium hydroxide and with sodium carbonate ADDITION REACTIONS Organic synthesis: principles and examples -recall that chemical synthesis involves (i) bond breaking and (ii) bond forming -describe the organic synthesis of PVC from ethene (structures and synthetic route not required) -work out reaction schemes of up to three conversions recalling familiar reactions Def n : An addition reaction is one in which two substances react to form a single substance. General Notes on add n reactions: 1. Always will occur on a double/triple bond. 2. Geometry will change from planar (unsaturated C-C bonds) to tetrahedral (saturated C-C bonds). 3. Benzene does not undergo addition reactions as its delocalised electrons make it very stable and unreactive. Uses of add n reactions: 1. Hydrogenation of vegetable oils. Forms margarine. H 2 (with Ni catalyst) added to unsaturated oils to partially saturate them. This is also a reduction reaction as we are adding hydrogen. 2. Polymerisation reactions to make long chains of carbons we call plastics. Page 2 of 9
3 Ethene is often seen as the most important organic chemical, as it undergoes many addition reactions to form different organic compounds. Example we need to know are: The last example, called the Bromination of Ethene needs to be study in more detail. We need to know the mechanism of the reaction: Overall this type of reaction is known as Ionic Addition. Def n : The mechanism of a reaction is the detailed step-by-step description of how the reaction occurs. Step 1: Polarisation The C=C double bond in ethane has a high concentration of negative charge. As the Br 2 approaches the ethene, the electrons are repelled away from the ethene, polarising the Br 2. Page 3 of 9
4 Step 2: Heterolytic Fission: The polarisation eventually becomes so great, the molecule splits into Br - and Br +. We call this heterolytic fission because the Br - took all 2 electrons from the Br-Br bond. Step 3: Carbonium Ion Formation: The Br + attacks the electron rich C=C double bond. This forms a carbonium ion (positive charge on C) Step 4: Ionic Attack The Br - ion attacks the carbonium ion, forming 1,2-dibromoethane. Evidence for this mechanism: If this reaction is carried out in bromine water with some Cl - ions added, we see the normal 1,2-dibromoethane product being formed, but two other products form also; 1-bromo-2-chloroethane and 2-bromoethanol. These form because of the Cl - or the OH - (from water s self-ionisation) can replace the Br - in step 4. TO WRITE THE MECHANISM FOR THE ADDITION OF CL 2 OR HCL, SIMPLY REPLACE THE BR 2! Polymerisation reactions are also a type of addition reaction. Def n : Polymers are long chain molecules made by joining many small molecules (monomers). Polymers are made up of many repeating units. Page 4 of 9
5 ELIMINATION REACTIONS Def n : An elimination reaction is one in which a small molecule is removed from a larger molecule, leaving a double bond on the larger molecule. General Notes on elim n reactions: 1. Geometry changes from tetrahedral to planar as a double bond is formed. 2. Generally involved the removal of a water molecule (H 2O) these are also called dehydration reactions. This example is the reaction you carried out when producing ethene gas. Notice that water is removed from the ethanol. Know that Al 2O 3 and heat is used to remove water in a dehydration reaction. SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS Def n : A substitution reaction is one in which an atom (or group of atoms) in a molecule is replaced with another atom (or group of atoms). There are 2 main types we study: 1. Halogenation of Alkanes This involves substituting hydrogen atoms in alkanes with halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, etc.). Fully halogenated alkanes e.g. CCl 4 are used as flame retardants. Less common now as they damage the ozone layer. We need to know the overall reaction, and the detailed mechanism for the monochlorination of methane/ethane. The mechanism for the monochlorination of methane is shown below. This mechanism is called free-radical substitution. Step 1: Homolytic Fission UV light is used to break the Cl-Cl bond. Each Cl atom receives 1 of the 2 electrons from the bond. This forms 2 Cl radicals which are very reactive. Step 2: Propogation One of the Cl radicals attacks the methane molecule to form HCl and a methyl radical. Step 3: Propogation The methyl radical attacks a new Cl 2 molecule to form a molecule of chloromethane and a Cl radical. The Cl radical now undergoes Step 2 again, and this forms a chain reaction between Steps 2 and 3. Page 5 of 9
6 Step 4: Termination When most of the reactants have been used up during Steps 2 and 3, there are only a small number of Cl radicals and methyl radicals left over. These combine to form Cl 2, chloromethane and ethane. Note: The mechanism for the monochlorination of ethane is identical. Practice writing it out. The italics shown in the table below refer to the evidence for the monochlorination of ethane. Evidence for this mechanism: Evidence Reaction takes place when exposed to UV light For every photon of UV light used, thousands of chloromethane molecules are formed Ethane is found in the products (butane) Adding tetramethyllead (tetraethyllead), which is a source of free radicals, increases the rate of the reaction Addition of an inhibitor, like O 2, slows down the reaction Explanation Suggests a free-radical mechanism whereby Cl 2 is broken down into Cl radicals. Suggests a chain reaction is involved. Methyl (ethyl) radicals must have been present, as ethane (butane) forms when two methyl radicals combine. Only a reaction which uses free radicals would be sped up by adding free radicals. Shows a chain reaction is taking place, as O 2 combines with free radicals, stopping the chain reaction. 2. Esterification When a carboxylic acid is reacted with an alcohol (with a small amount of H 2SO 4 as a catalyst), an ester is formed. This is a substitution reaction as the H on the OH of the carboxylic acid has been substituted with an alkyl (methyl-, ethyl-, etc.) group. Notice that this is an equilibrium reaction. This means that the reverse reaction can also occur. To do this, we simply need to add water. This is called hydrolysis. Hydrolysis of esters can also be carried out using a base e.g. NaOH or KOH. This results in the formation of the sodium/potassium salt of the carboxylic acid. These salts are known to us as soaps. This process of base hydrolysis is also called saponification. You carried out this reaction when you prepared a sample of soap: How does soap work? Soap molecules contain a long, non-polar carbon chain which will dissolve oils (e.g. from skin). The opposite end of the molecule contains a polar COO - Na + which will dissolve salts from sweat and will also dissolve in water. This allows soap to pick up oils and salts and then be washed down the drain. Page 6 of 9
7 REDOX REACTIONS General Notes on redox reactions: 1. Oxidation is the addition of O or the removal of H. 2. Reduction is the removal of O or the addition of H 3. Oxidation carried out using either: a. Acidified Sodium Dichromate (Na 2Cr 2O 7/H + ) Cr(VI) [orange] gets reduced to Cr(III) [green]. b. Acidified Potassium Permanganate (KMnO 4/H + ) Mn(VII) [purple] gets reduced to Mn(II) [colourless]. 4. Reduction is carried out using Hydrogen gas and a Nickel catalyst (H 2/Ni) Primary Alcohols Primary alcohols get oxidised to aldehydes. If there is excess oxidising agent present, the aldehydes can then be further oxidised to carboxylic acids. Carboxylic acids get reduced to aldehydes. If there is excess reducing agent, the aldehydes can be further reduced to alcohols. Note that all of the changes happen at the terminal carbon (the carbon at the end), where the oxygen atom was. Secondary Alcohols Secondary alcohols get oxidised to ketones. They cannot be oxidised any further. This is because the carbon with the oxygen is not at the end of the molecule. Thus we form a ketone rather than an aldehyde. As carboxylic acids can only have the COOH on the terminal carbon, a ketone can never be oxidised to a carboxylic acid. Page 7 of 9
8 Ketones get reduced to secondary alcohols. Organic Redox reactions in everyday life 1. A bottle of wine left open to the air will start to taste vinegary after some time. This is because oxygen in the air oxidises the ethanol in the wine to ethanoic acid. 2. When ethanol is consumed, the liver works hard to break it down, as it is a foreign toxin to the body. The liver oxidises the ethanol to ethanal, which is even more toxic! The ethanal is what causes some of the bad symptoms of a hangover. Eventually, when given enough time, the ethanal is further oxidised by the liver to carbon dioxide and water, which are excreted through the lungs and urine. 3. Old-style breathalysers (these can still be bought in your local pharmacy!) contained potassium dichromate crystals [Cr(VI) - orange]. If alcohol was in a person s system and they breathed through a tube containing the crystals, the ethanol in the breath would be oxidised. This would reduce the Cr(VI) [orange] to Cr(III) [green], showing that ethanol was present. REACTIONS AS ACIDS Alcohols reacting with Sodium The H on the OH of an alcohol can act as an acid when reacted with the extremely reactive metal, sodium. This forms the sodium salt of the alcohol, and hydrogen gas. H H H C C O H H H Ethanol H + Na H C C O Na H 2 H H H Sodium Ethoxide The Acidic nature of the Carboxylic Acids Why is the H on the COOH group acidic (why can it dissociate)? There are 2 reasons: 1. Inductive effect Because the O in the C=O is very electronegative, the C is left with a slight positive charge. This draws electron density towards the C and away from the OH, allowing the H to dissociate. Page 8 of 9
9 2. Stability of the carboxylate ion When the H of the OH dissociates to form a H + we are left with a carboxylate ion COO -. The negative charge is not localised to just one of the oxygens and is instead delocalised between the two of them. This delocalised structure gives the carboxylate ion extra stability, allowing the H + to easily dissociate. Common reactions with carboxylic acids: 1. Acid + Base Salt + Water e.g. CH 3COOH + NaOH CH 3COONa + H 2O 2. Acid + Carbonate Salt + Carbon Dioxide + Water 2CH 3COOH + Na 2CO 3 2CH 3COONa + CO 2 + H 2O 3. Acid + Metal Salt + Hydrogen 2CH 3COOH + Mg (CH 3COO) 2Mg H 2 SYNTHESIS OF PVC FROM ETHENE Step 1: Ethene and chlorine react to form 1,2-dichloroethane. (Addition reaction of which we know the mechanism) Step 2: Heat is used to thermally crack the 1,2-dichloroethane into chloroethene and HCl. Step 3: The chloroethene undergoes a polymerisation reaction to form polychloroethene (PVC) Page 9 of 9
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds. Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Chemistry 2.5 AS WORKBOOK. Working to Excellence Working to Excellence
 Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Definition: A hydrocarbon is an organic compound which consists entirely of hydrogen and carbon.
 Hydrocarbons Definition: A hydrocarbon is an organic compound which consists entirely of hydrogen and carbon. It is important to note that carbon atoms have 4 free bonds and that hydrogen has 1 free bond.
Hydrocarbons Definition: A hydrocarbon is an organic compound which consists entirely of hydrogen and carbon. It is important to note that carbon atoms have 4 free bonds and that hydrogen has 1 free bond.
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level. Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis
 OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
Organic Chemistry Review: Topic 10 & Topic 20
 Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Chemistry. Chapter 10
 Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 10.1 Homologous Series Overview We Are Here Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds. From the very simple: methane To the very complex:
Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 10.1 Homologous Series Overview We Are Here Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds. From the very simple: methane To the very complex:
4. Carbon and Its Compounds
 4. Carbon and Its Compounds Covalent bonds The bonds formed by the sharing of electrons are known as covalent bonds. In covalent bonding, both the atoms (that are participating in the bonding) share electrons,
4. Carbon and Its Compounds Covalent bonds The bonds formed by the sharing of electrons are known as covalent bonds. In covalent bonding, both the atoms (that are participating in the bonding) share electrons,
3.2.8 Haloalkanes. Nucleophilic Substitution. 267 minutes. 264 marks. Page 1 of 36
 3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
Question Bank Organic Chemistry II
 Question Bank Organic Chemistry II 1. What are saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Classify the following as saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. CH 4, C 2 H 2, C 2 H 6, C 3 H 6, C 3 H 4 Ans. Compounds
Question Bank Organic Chemistry II 1. What are saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Classify the following as saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. CH 4, C 2 H 2, C 2 H 6, C 3 H 6, C 3 H 4 Ans. Compounds
Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL
 Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Understandings: A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ
Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Understandings: A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ
Carbon and its Compounds
 CHAPTER4 Carbon and its Compounds Multiple Choice Questions 1. Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of carbon monoxide only carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide carbon dioxide only coal
CHAPTER4 Carbon and its Compounds Multiple Choice Questions 1. Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of carbon monoxide only carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide carbon dioxide only coal
Organic Chemistry. Alkanes are hydrocarbons in which the carbon atoms are joined by single covalent bonds.
 Organic Chemistry Organic compounds: The branch of chemistry which deals with the study of carbon compounds is called organic chemistry. Catenation: The carbon atom has a property to undergo self linking
Organic Chemistry Organic compounds: The branch of chemistry which deals with the study of carbon compounds is called organic chemistry. Catenation: The carbon atom has a property to undergo self linking
Organic Chemistry. REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling
 Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY
 WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY enthalpy change of reaction, enthalpy change of combustion and standard molar enthalpy change of formation, Δ fh ϴ Hess s law and energy cycles concept
WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY enthalpy change of reaction, enthalpy change of combustion and standard molar enthalpy change of formation, Δ fh ϴ Hess s law and energy cycles concept
10.2 ALCOHOLS EXTRA QUESTIONS. Reaction excess conc, H SO 180 C
 10.2 ALOOLS EXTRA QUESTIONS 1. onsider the reaction scheme below which starts from butanone. N Reaction 1 3 2 3 3 2 3 O Reaction 2 O A 3 O B 2 3 excess conc, SO 180 2 4 but 1 ene and but 2 ene (a) When
10.2 ALOOLS EXTRA QUESTIONS 1. onsider the reaction scheme below which starts from butanone. N Reaction 1 3 2 3 3 2 3 O Reaction 2 O A 3 O B 2 3 excess conc, SO 180 2 4 but 1 ene and but 2 ene (a) When
Alcohols. Ethanol Production. 182 minutes. 181 marks. Page 1 of 25
 3..10 Alcohols Ethanol Production 18 minutes 181 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Ethanol is produced commercially by fermentation of aqueous glucose, C 6 H 1 O 6 State two conditions, other than temperature, which
3..10 Alcohols Ethanol Production 18 minutes 181 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Ethanol is produced commercially by fermentation of aqueous glucose, C 6 H 1 O 6 State two conditions, other than temperature, which
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide.
 Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
ORGANIC REACTIONS 14 APRIL 2015 Section A: Summary Notes
 ORGANIC REACTIONS 14 APRIL 2015 Section A: Summary Notes 1. Combustion Alkanes are very important fossil fuels. The combustion of alkanes is very exothermic and carbon dioxide and water are produced. General
ORGANIC REACTIONS 14 APRIL 2015 Section A: Summary Notes 1. Combustion Alkanes are very important fossil fuels. The combustion of alkanes is very exothermic and carbon dioxide and water are produced. General
3.2.9 Alkenes. Addition Reactions. 271 minutes. 268 marks. Page 1 of 35
 ..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
15.1: Hydrocarbon Reactions
 15.1: Hydrocarbon Reactions Halogenation An alkane will react with a halogen to produce a halalkane and the corresponding hydrogen halide. The catalyst is ultraviolet radiation. Reaction 1 methane chlorine
15.1: Hydrocarbon Reactions Halogenation An alkane will react with a halogen to produce a halalkane and the corresponding hydrogen halide. The catalyst is ultraviolet radiation. Reaction 1 methane chlorine
Topic 2 Organic Chemistry
 Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg Pg. 20 Topic 2 Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds, which are found in living things or are derived from living things. The basis of
Form 5 Chemistry Notes Ms. R. Buttigieg Pg. 20 Topic 2 Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds, which are found in living things or are derived from living things. The basis of
IGCSE SEPARATE SCIENCES TOPIC C14: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY REVISION NOTES
 IGCSE SEPARATE SCIENCES TOPIC C14: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY REVISION NOTES Organic chemistry is the chemistry of a huge number of compounds containing carbon. Carbon atoms are in group 4 which means they form
IGCSE SEPARATE SCIENCES TOPIC C14: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY REVISION NOTES Organic chemistry is the chemistry of a huge number of compounds containing carbon. Carbon atoms are in group 4 which means they form
Synthesis and Sustainable Chemistry
 Synthesis and Sustainable Chemistry Considering % yield and % Atom Economy: high % yield means very efficient conversion from reactants to products increasing % yield means more efficient use of starting
Synthesis and Sustainable Chemistry Considering % yield and % Atom Economy: high % yield means very efficient conversion from reactants to products increasing % yield means more efficient use of starting
CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS
 CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 Mark] 1. Give the names of the following functional groups: (i) OH (ii) COOH Ansswer. (i) Alcohol group (ii) Carboxylic acid group 2. What is
CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 Mark] 1. Give the names of the following functional groups: (i) OH (ii) COOH Ansswer. (i) Alcohol group (ii) Carboxylic acid group 2. What is
Mechanisms. . CCl2 F + Cl.
 Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Organic Chemistry. Dr. Catherine Tan. (IGCSE Chemistry Syllabus )
 Organic Chemistry (IGCSE Chemistry Syllabus 2016-2018) Number of carbon(s) Root Alkanes Alkenes Alcohols Carboxylic acids 1 Meth- Methane Methene Methanol Methanoic acid 2 Eth- Ethane Ethene Ethanol Ethanoic
Organic Chemistry (IGCSE Chemistry Syllabus 2016-2018) Number of carbon(s) Root Alkanes Alkenes Alcohols Carboxylic acids 1 Meth- Methane Methene Methanol Methanoic acid 2 Eth- Ethane Ethene Ethanol Ethanoic
CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL
 *P15* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2009 CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in all These must include at least two questions from Section A All questions carry
*P15* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2009 CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in all These must include at least two questions from Section A All questions carry
Some Families of Organic Compounds HL
 Name: Organic Chemistry 22. Some Families of Organic Compounds Objectives -define tetrahedral carbon -explain what is meant by the term alcohol -describe the alcohols as a homologous series of organic
Name: Organic Chemistry 22. Some Families of Organic Compounds Objectives -define tetrahedral carbon -explain what is meant by the term alcohol -describe the alcohols as a homologous series of organic
Page (Extra space) (4) Benzene can be converted into amine U by the two-step synthesis shown below.
 Q1. The hydrocarbons benzene and cyclohexene are both unsaturated compounds. Benzene normally undergoes substitution reactions, but cyclohexene normally undergoes addition reactions. (a) The molecule cyclohexatriene
Q1. The hydrocarbons benzene and cyclohexene are both unsaturated compounds. Benzene normally undergoes substitution reactions, but cyclohexene normally undergoes addition reactions. (a) The molecule cyclohexatriene
MOSTLY ALCOHOLS. Question 2, 2017 The structure of a molecule of an organic compound, threonine, is shown below.
 MOSTLY ALCOHOLS Modified Question 1, 2017 A chemistry class was learning about the chemistry of haloalkanes. They were researching the effect of heat and concentrated potassium hydroxide in ethanol, conc.
MOSTLY ALCOHOLS Modified Question 1, 2017 A chemistry class was learning about the chemistry of haloalkanes. They were researching the effect of heat and concentrated potassium hydroxide in ethanol, conc.
17 Alcohols H H C C. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 H H. Bond angles in Alcohols. Boiling points. Different types of alcohols H 2 C CH 2 CH 2
 17 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
17 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
CHAPTER 15: Hydrocarbons
 CHAPTER 15: Hydrocarbons 15.1 Introduction to Alkanes 15.2 Reactions of Alkanes 15.3 Introduction to Alkenes 15.4 Reactions of Alkenes 15.5 Uses of Hydrocarbons Learning outcomes: (a) show awareness of
CHAPTER 15: Hydrocarbons 15.1 Introduction to Alkanes 15.2 Reactions of Alkanes 15.3 Introduction to Alkenes 15.4 Reactions of Alkenes 15.5 Uses of Hydrocarbons Learning outcomes: (a) show awareness of
Name Date Class. aryl halides substitution reaction
 23.1 INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Section Review Objectives Explain how organic compounds are classified Identify the IUPAC rules for naming halocarbons Describe how halocarbons can be prepared Vocabulary
23.1 INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Section Review Objectives Explain how organic compounds are classified Identify the IUPAC rules for naming halocarbons Describe how halocarbons can be prepared Vocabulary
JUNIOR COLLEGE CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT EXPERIMENT 14 SECOND YEAR PRACTICAL. Name: Group: Date:
 JUNIOR COLLEGE CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT EXPERIMENT 14 SECOND YEAR PRACTICAL Name: Group: Date: This practical will serve as (i) an introduction to aromatic chemistry and (ii) a revision of some of the reactions
JUNIOR COLLEGE CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT EXPERIMENT 14 SECOND YEAR PRACTICAL Name: Group: Date: This practical will serve as (i) an introduction to aromatic chemistry and (ii) a revision of some of the reactions
Assessment Schedule 2016 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds (91165)
 NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2016 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2016 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds (91165) Evidence Statement ONE (a) (i) 2-iodohexane
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2016 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2016 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds (91165) Evidence Statement ONE (a) (i) 2-iodohexane
I can calculate the rate of reaction from graphs of a changing property versus time, e.g. graphs of volume against time
 UNIT 1 CONTROLLING THE RATE OF REACTION I can calculate the rate of reaction from graphs of a changing property versus time, e.g. graphs of volume against time I can use the reciprocal of to calculate
UNIT 1 CONTROLLING THE RATE OF REACTION I can calculate the rate of reaction from graphs of a changing property versus time, e.g. graphs of volume against time I can use the reciprocal of to calculate
AS Organic Chemistry Revision. Part 1
 AS Organic Chemistry Revision. Part 1 2.2 Nomenclature and isomerism in organic compounds 2.2.1 understand the terms empirical, molecular and structural formulae, homologous series and functional groups;
AS Organic Chemistry Revision. Part 1 2.2 Nomenclature and isomerism in organic compounds 2.2.1 understand the terms empirical, molecular and structural formulae, homologous series and functional groups;
Alkanes and Alkenes. The Alkanes
 Alkanes and Alkenes The Alkanes Alkanes are hydrocarbons (i.e. compounds of carbon and hydrogen only). They are called saturated hydrocarbons because they contain no double bonds, and so cannot undergo
Alkanes and Alkenes The Alkanes Alkanes are hydrocarbons (i.e. compounds of carbon and hydrogen only). They are called saturated hydrocarbons because they contain no double bonds, and so cannot undergo
Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry
 Lesmahagow High School AHChemistry Organic Chemistry& Instrumental Analysis Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Organic Chemistry and Instrumental Analysis Alkanes, Alkenes and
Lesmahagow High School AHChemistry Organic Chemistry& Instrumental Analysis Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Organic Chemistry and Instrumental Analysis Alkanes, Alkenes and
UNIT 2 REVISION CHECKLIST. a) understand that reactions are either exothermic or endothermic and apply the sign convention
 UNIT 2 REVISION CHECKLIST Topic 2.1 Energetics a) understand that reactions are either exothermic or endothermic and apply the sign convention b) define the term enthalpy change, recall what standard conditions
UNIT 2 REVISION CHECKLIST Topic 2.1 Energetics a) understand that reactions are either exothermic or endothermic and apply the sign convention b) define the term enthalpy change, recall what standard conditions
AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS TOPIC 4.11 STRUCTURE DETERMINATION BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
 AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS TOPIC 4.11 STRUCTURE DETERMINATION BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS 1 1. Consider the following reaction sequence. CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 Step 1
AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS TOPIC 4.11 STRUCTURE DETERMINATION BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS 1 1. Consider the following reaction sequence. CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 Step 1
MONICA COACHING CENTRE An Institute For Science Classes JALANDHAR, PUNJAB CARBON AND COMPOUNDS
 CARBON AND COMPOUNDS The atmosphere has only 0.03% of carbon dioxide. The number of electrons lost or gained by an atom to complete its octet (or duplet) is called its valency. It depends on the number
CARBON AND COMPOUNDS The atmosphere has only 0.03% of carbon dioxide. The number of electrons lost or gained by an atom to complete its octet (or duplet) is called its valency. It depends on the number
HYDROCARBONS. Section A
 MCQs Section A Q1The products obtained by cracking an alkane, X, are methane, ethene and propene. The mole fraction of ethene in the products is 0.5. What is the identity of X? A C6H14 B C8H18 C C9H20
MCQs Section A Q1The products obtained by cracking an alkane, X, are methane, ethene and propene. The mole fraction of ethene in the products is 0.5. What is the identity of X? A C6H14 B C8H18 C C9H20
1. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? O A. CH CH CH O B. CH CCH O C. CH CH COH O D. CH COCH
 1. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? O A. CH CH CH 3 2 O B. CH CCH 3 3 O C. CH CH COH 3 2 O D. CH COCH 3 3 2. What product results from the reaction of CH 2 ==CH 2 with Br 2? A. CHBrCHBr B.
1. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? O A. CH CH CH 3 2 O B. CH CCH 3 3 O C. CH CH COH 3 2 O D. CH COCH 3 3 2. What product results from the reaction of CH 2 ==CH 2 with Br 2? A. CHBrCHBr B.
pent-2-ene CH 3CH = CHCH 2CH 3 3-methylbut-1-ene (CH 3) 2CHCH = CH 2 2-methylbut-2-ene (CH 3) 2C = CHCH 3 2-methylbut-1-ene H 2C = C(CH 3)CH 2CH 3
 Q1.The following table gives the names and structures of some structural isomers with the molecular formula C 5H 10. Name of isomer Structure 1 pent-2-ene CH 3CH = CHCH 2CH 3 2 cyclopentane 3 4 5 3-methylbut-1-ene
Q1.The following table gives the names and structures of some structural isomers with the molecular formula C 5H 10. Name of isomer Structure 1 pent-2-ene CH 3CH = CHCH 2CH 3 2 cyclopentane 3 4 5 3-methylbut-1-ene
QUESTIONSHEETS ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS I FREE RADICAL SUBSTITUTION I FREE RADICAL SUBSTITUTION II ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION TO SYMMETRICAL ALKENES
 CHEMISTRY QUESTIONSHEETS AS Level AS TOPIC 14 ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS I Questionsheet 1 Questionsheet 2 Questionsheet 3 Questionsheet 4 Questionsheet 5 Questionsheet 6 Questionsheet 7 Questionsheet
CHEMISTRY QUESTIONSHEETS AS Level AS TOPIC 14 ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS I Questionsheet 1 Questionsheet 2 Questionsheet 3 Questionsheet 4 Questionsheet 5 Questionsheet 6 Questionsheet 7 Questionsheet
22 & 23 Organic Chemistry
 22 & 23 rganic hemistry These two rganic hemistry chapters play a very important role on the Leaving ertificate hemistry examination paper. Firstly, these chapters cover six Mandatory Student Experiments.
22 & 23 rganic hemistry These two rganic hemistry chapters play a very important role on the Leaving ertificate hemistry examination paper. Firstly, these chapters cover six Mandatory Student Experiments.
# Ans Workings / Remarks
 # Ans Workings / Remarks 1 B Atomic mass and temperature affects the rate of diffusion of gas. The lower the atomic mass, the lighter the substance. The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of collision
# Ans Workings / Remarks 1 B Atomic mass and temperature affects the rate of diffusion of gas. The lower the atomic mass, the lighter the substance. The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of collision
CHEMISTRY CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS
 CHEMISTRY CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS Carbon is a versatile element. In earth s crust, carbon is 0.02% and found in form of minerals. Atmosphere has 0.03% of Carbon dioxide. All living structures are carbon
CHEMISTRY CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS Carbon is a versatile element. In earth s crust, carbon is 0.02% and found in form of minerals. Atmosphere has 0.03% of Carbon dioxide. All living structures are carbon
Q1. The following pairs of compounds can be distinguished by simple test tube reactions.
 Q1. The following pairs of compounds can be distinguished by simple test tube reactions. For each pair of compounds, give a reagent (or combination of reagents) that, when added separately to each compound,
Q1. The following pairs of compounds can be distinguished by simple test tube reactions. For each pair of compounds, give a reagent (or combination of reagents) that, when added separately to each compound,
Instructions: Cut individually and fold/glue. Can be either laminated or folded around cardboard.
 NCEA Chemistry 3.5 Flash Cards Instructions: Cut individually and fold/glue. Can be either laminated or folded around cardboard. Ideas for Use: 1. Group reactants (or products) into functional groups 2.
NCEA Chemistry 3.5 Flash Cards Instructions: Cut individually and fold/glue. Can be either laminated or folded around cardboard. Ideas for Use: 1. Group reactants (or products) into functional groups 2.
Organic Chemistry. Why are these compounds called Organic. What is a Hydrocarbon? Questions: P167 Read
 Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Isomerism and Carbonyl Compounds
 Isomerism and Carbonyl Compounds 18 Section B Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 7 Esters have many important commercial uses such as solvents and artificial flavourings in foods. Esters can
Isomerism and Carbonyl Compounds 18 Section B Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 7 Esters have many important commercial uses such as solvents and artificial flavourings in foods. Esters can
Q1. Which one of the following is least likely to occur in the reaction between methane and chlorine?
 Q1. Which one of the following is least likely to occur in the reaction between methane and chlorine? A B C D C 4 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 Cl + C 3 + Cl 2 C 3 Cl + Cl C 3 Cl + Cl C 2 Cl + Cl (Total 1
Q1. Which one of the following is least likely to occur in the reaction between methane and chlorine? A B C D C 4 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 Cl + C 3 + Cl 2 C 3 Cl + Cl C 3 Cl + Cl C 2 Cl + Cl (Total 1
Alkanes are aliphatic saturated hydrocarbons (no C=C double bonds, C and H atoms only). They are identified by having a ane name ending.
 Alkanes Alkanes are aliphatic saturated hydrocarbons (no = double bonds, and atoms only). They are identified by having a ane name ending. The alkanes have similar chemistry to one another because they
Alkanes Alkanes are aliphatic saturated hydrocarbons (no = double bonds, and atoms only). They are identified by having a ane name ending. The alkanes have similar chemistry to one another because they
BIOB111 - Tutorial activities for session 8
 BIOB111 - Tutorial activities for session 8 General topics for week 4 Session 8 Physical and chemical properties and examples of these functional groups (methyl, ethyl in the alkyl family, alkenes and
BIOB111 - Tutorial activities for session 8 General topics for week 4 Session 8 Physical and chemical properties and examples of these functional groups (methyl, ethyl in the alkyl family, alkenes and
Topic 10 Organic Chemistry. Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School
 Topic 10 Organic Chemistry Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School -Alkanes: have low reactivity and undergo free radical substitution. -Alkenes: are more reactive than alkanes, since
Topic 10 Organic Chemistry Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School -Alkanes: have low reactivity and undergo free radical substitution. -Alkenes: are more reactive than alkanes, since
video 14.4 isomers isomers Isomers have the molecular formula but are rearranged in a structure with different properties. Example: Both C 4 H 10
 video 14.4 isomers isomers Isomers have the molecular formula but are rearranged in a structure with different properties. Example: Both C 4 H 10 Butane Methylpropane 1 match the isomers drawing an isomer
video 14.4 isomers isomers Isomers have the molecular formula but are rearranged in a structure with different properties. Example: Both C 4 H 10 Butane Methylpropane 1 match the isomers drawing an isomer
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry Specimen Paper for first teaching
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry Specimen Paper for first teaching
Organic Chemistry. Unit 10
 Organic Chemistry Unit 10 Halides Primary Carbons Secondary Carbons Tertiary Carbons IMPORTANCE?? REACTIONS!! Benzene C6H6 Aromatic functional group - C6H5 (IUPAC name - phenyl) Substitution Reactions
Organic Chemistry Unit 10 Halides Primary Carbons Secondary Carbons Tertiary Carbons IMPORTANCE?? REACTIONS!! Benzene C6H6 Aromatic functional group - C6H5 (IUPAC name - phenyl) Substitution Reactions
A.M. WEDNESDAY, 3 June hours
 Candidate Name Centre Number 2 Candidate Number GCE AS/A level 1092/01 New AS CEMISTRY C2 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this examination paper, you will need a: calculator; Data Sheet containing
Candidate Name Centre Number 2 Candidate Number GCE AS/A level 1092/01 New AS CEMISTRY C2 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this examination paper, you will need a: calculator; Data Sheet containing
C11.1 Organic Chemistry Quiz Questions & Answers. Parts 1 & 2; all sets Parts 3 & 4; Sets 1 & 2 only
 C11.1 Organic Chemistry Quiz Questions & Answers Parts 1 & 2; all sets Parts 3 & 4; Sets 1 & 2 only C11.1 Organic Chemistry Part 1 1. Define a mixture. 2. Define crude oil. 3. Define a hydrocarbon. 4.
C11.1 Organic Chemistry Quiz Questions & Answers Parts 1 & 2; all sets Parts 3 & 4; Sets 1 & 2 only C11.1 Organic Chemistry Part 1 1. Define a mixture. 2. Define crude oil. 3. Define a hydrocarbon. 4.
EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES. 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction....
 EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction. C 6 H 5 3 + Cl 2 C 6 H 5 2 Cl + HCl Write an equation for the initiation
EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction. C 6 H 5 3 + Cl 2 C 6 H 5 2 Cl + HCl Write an equation for the initiation
Chapter 16. Answers to examination-style questions. Answers Marks Examiner s tips. 1 (a) (i) C 6 H 12 O 6 2C 2 H 5 OH + 2CO 2 (ii) fermentation
 Chapter 6 (a) (i) C 6 O 6 C 5 O + CO (ii) fermentation (b) (i) C 5 O + 3O CO + 3 O (ii) CO or carbon monoxide or C or carbon (a) (i) potassium (or sodium) dichromate(vi) or correct formula or potassium
Chapter 6 (a) (i) C 6 O 6 C 5 O + CO (ii) fermentation (b) (i) C 5 O + 3O CO + 3 O (ii) CO or carbon monoxide or C or carbon (a) (i) potassium (or sodium) dichromate(vi) or correct formula or potassium
Atoms, Elements, Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures. Compounds and Mixtures. Atoms and the Periodic Table. Atoms and the.
 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components
Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components
Organic Chemistry Worksheets
 Highlight the single longest, continuous carbon-carbon chain. Note the alkyl branches that are connected to the root chain. Count the carbons in the root chain, starting from the end closest to the alkyl
Highlight the single longest, continuous carbon-carbon chain. Note the alkyl branches that are connected to the root chain. Count the carbons in the root chain, starting from the end closest to the alkyl
Organic Mechanisms 1
 Organic Mechanisms 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Chemical properties of alkanes 314 Chemical properties of alkenes 318 Bonding in alkenes 320 Bonding
Organic Mechanisms 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Chemical properties of alkanes 314 Chemical properties of alkenes 318 Bonding in alkenes 320 Bonding
Replace one H with a Br for every mole of Br 2
 Substitution A substitution reaction occurs when a hydrogen atom is removed from a hydrocarbon and replaced by a halide substituent. When a bromine molecule absorbs energy, the covalent bond is broken
Substitution A substitution reaction occurs when a hydrogen atom is removed from a hydrocarbon and replaced by a halide substituent. When a bromine molecule absorbs energy, the covalent bond is broken
Module 2A Alcohols and halogenoalkanes
 Module 2A Alcohols and halogenoalkanes Making ethanol Ethanol is made in 1 of 2 ways: 1) Hydration of ethene: This is a reversible reaction and only about 5% of ethene is converted to ethanol. Unreacted
Module 2A Alcohols and halogenoalkanes Making ethanol Ethanol is made in 1 of 2 ways: 1) Hydration of ethene: This is a reversible reaction and only about 5% of ethene is converted to ethanol. Unreacted
1 Alkane C n H 2n+2 2 Alkene C n H 2n
 CLASS-10 PYSICAL SCIENCES 2014-2015 NEW TEXT BOOK 14. CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS Questions and Answers 1. Name the simplest hydrocarbon. A. Methane (C 4 ) is the simplest hydrocarbon. 2. What are the general
CLASS-10 PYSICAL SCIENCES 2014-2015 NEW TEXT BOOK 14. CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS Questions and Answers 1. Name the simplest hydrocarbon. A. Methane (C 4 ) is the simplest hydrocarbon. 2. What are the general
Downloaded from
 1. mark questions CHEMISTRY CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS 1. Name of the organic compound, which can be produced by fermentation of sugar and is a constituent of beer. 2. Name the main products formed when
1. mark questions CHEMISTRY CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS 1. Name of the organic compound, which can be produced by fermentation of sugar and is a constituent of beer. 2. Name the main products formed when
ORGANIC REACTIONS 11 MARCH 2014
 ORGANIC REACTIONS 11 MARCH 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at the chemical reactions of organic molecules Summary Organic molecules can undergo several important chemical reactions. 1.
ORGANIC REACTIONS 11 MARCH 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at the chemical reactions of organic molecules Summary Organic molecules can undergo several important chemical reactions. 1.
Organic Reactions. Recognize organic reactions: substitution, addition, esterification, combustion, fermentation, and saponification.
 Why? Organic Reactions Many organic reactions lead to products we use everyday. Organic reactions can be categorized by looking at the reactants used and the products formed. Soap, alcohol, fragrances,
Why? Organic Reactions Many organic reactions lead to products we use everyday. Organic reactions can be categorized by looking at the reactants used and the products formed. Soap, alcohol, fragrances,
dihalogenoalkane H 2, Nickel Catalyst KOH alcoholic HBr, HCl Br Cl Elimination KOH aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution
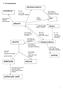 7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
UNIT 2: CHEMICAL BONDING, APPLICATION OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOUNDATION TIER SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS
 GCSE CHEMISTRY Sample Assessment Materials 71 Surname Other Names Centre Number Candidate Number GCSE CHEMISTRY UNIT 2: CHEMICAL BONDING, APPLICATION OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOUNDATION
GCSE CHEMISTRY Sample Assessment Materials 71 Surname Other Names Centre Number Candidate Number GCSE CHEMISTRY UNIT 2: CHEMICAL BONDING, APPLICATION OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOUNDATION
Unit 7 Part 3 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Simple Reactions of Hydrocarbons UNIT 7 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 Unit 7 Part 3 Introduction to Organic hemistry Simple Reactions of ydrocarbons UNIT 7 INTRODUTION TO ORGANI EMISTRY PART 3 SIMPLE REATIONS OF YDROARBONS ontents 1. Alkanes 2. Alkenes 3. Alkynes 4. Benzene
Unit 7 Part 3 Introduction to Organic hemistry Simple Reactions of ydrocarbons UNIT 7 INTRODUTION TO ORGANI EMISTRY PART 3 SIMPLE REATIONS OF YDROARBONS ontents 1. Alkanes 2. Alkenes 3. Alkynes 4. Benzene
THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKANES
 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKANES Information taken from a presentation by: KNOCKHARDY PUBLISHING General ALKANES members of a homologous series general formula is C n H 2n+2 for non-cyclic alkanes
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKANES Information taken from a presentation by: KNOCKHARDY PUBLISHING General ALKANES members of a homologous series general formula is C n H 2n+2 for non-cyclic alkanes
CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS
 CARBN AND ITS CMPUNDS Catenation: The unique property of carbon atom to form covalent bonds with other carbon atoms giving rise to large molecules is called catenation. The compounds formed may have long
CARBN AND ITS CMPUNDS Catenation: The unique property of carbon atom to form covalent bonds with other carbon atoms giving rise to large molecules is called catenation. The compounds formed may have long
C. CH CH COH CH CCH. 6. Which substance(s) could be formed during the incomplete combustion of a hydrocarbon?
 1. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? O O A. CH 3CH 2 CH B. CH 3CCH3 C. CH 3CH 2 COH D. CH COCH 2. What product results from the reaction of CH 2 ==CH 2 with Br 2? A. CHBrCHBr B. CH 2 CHBr C.
1. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? O O A. CH 3CH 2 CH B. CH 3CCH3 C. CH 3CH 2 COH D. CH COCH 2. What product results from the reaction of CH 2 ==CH 2 with Br 2? A. CHBrCHBr B. CH 2 CHBr C.
Le Lycee Mauricien. Proposed Syllabus Chemistry (5070) - Form 5
 Le Lycee Mauricien Proposed Syllabus 2017 Chemistry (5070) - Form 5 First Term 1. Metals Properties of metals - Physical properties of metals - Structure of alloys and uses Reactivity Series - Place metals
Le Lycee Mauricien Proposed Syllabus 2017 Chemistry (5070) - Form 5 First Term 1. Metals Properties of metals - Physical properties of metals - Structure of alloys and uses Reactivity Series - Place metals
Wednesday 16 January 2013 Morning
 Wednesday 16 January 2013 Morning AS GCE CEMISTRY A F322/01 Chains, Energy and Resources *F314440113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry A (inserted)
Wednesday 16 January 2013 Morning AS GCE CEMISTRY A F322/01 Chains, Energy and Resources *F314440113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry A (inserted)
UNIT 12 - TOPIC 3 ORGANIC REACTIONS
 UNIT 12 - TOPIC 3 ORGANIC REACTIONS Name: ESSENTIALS: Know, Understand, and Be Able To Types of organic reactions include: addition substitution combustion polymerization esterfication fermentation saponification
UNIT 12 - TOPIC 3 ORGANIC REACTIONS Name: ESSENTIALS: Know, Understand, and Be Able To Types of organic reactions include: addition substitution combustion polymerization esterfication fermentation saponification
Name/CG: 2012 Term 2 Organic Chemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question
 Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
IB Topics 10, 20 & 21 MC Practice
 IB Topics 10, 20 & 21 MC Practice 1. What is the major product of the reaction between HCl and but-2-ene? 1,2-dichlorobutane 2,3-dichlorobutane 1-chlorobutane 2-chlorobutane 2. Which compound can be oxidized
IB Topics 10, 20 & 21 MC Practice 1. What is the major product of the reaction between HCl and but-2-ene? 1,2-dichlorobutane 2,3-dichlorobutane 1-chlorobutane 2-chlorobutane 2. Which compound can be oxidized
Types of reactions: addition, elimination and substitution reactions
 OpenStax-NX module: m39090 1 Types of reactions: addition, elimination and substitution reactions Free igh School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-NX and licensed under the reative
OpenStax-NX module: m39090 1 Types of reactions: addition, elimination and substitution reactions Free igh School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-NX and licensed under the reative
OCR AS Chemistry A H032 for first assessment in Complete Tutor Notes. Section: Boomer Publications
 R AS hemistry A 032 for first assessment in 2016 omplete Tutor Notes www.boomerchemistry.com Section: 4.2.1 Alcohols 4.2.2 aloalkanes 2015 Boomer Publications page 145 page 152 40 Alcohols Page 155 Ethanol
R AS hemistry A 032 for first assessment in 2016 omplete Tutor Notes www.boomerchemistry.com Section: 4.2.1 Alcohols 4.2.2 aloalkanes 2015 Boomer Publications page 145 page 152 40 Alcohols Page 155 Ethanol
Practice Packet Unit 11: Organic Chemistry
 Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Practice Packet Unit 11: Organic Chemistry www.mrpalermo.com 1 LESSON 1: Introduction to Organic Chemistry 1. How many times does carbon bond and why? 2. A student investigated
Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Practice Packet Unit 11: Organic Chemistry www.mrpalermo.com 1 LESSON 1: Introduction to Organic Chemistry 1. How many times does carbon bond and why? 2. A student investigated
Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms
 Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Dr. Solomon Derese 1 A chemical reaction is the transformation of one chemical or collection of chemicals into another
Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Dr. Solomon Derese 1 A chemical reaction is the transformation of one chemical or collection of chemicals into another
CHEMISTRY FOR THE IB DIPLOMA CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS
 10 rganic chemistry Revision checklist I am able to: explain, using an example, what is meant by the term homologous series sketch a graph of boiling point against number of carbons for the straight-chain
10 rganic chemistry Revision checklist I am able to: explain, using an example, what is meant by the term homologous series sketch a graph of boiling point against number of carbons for the straight-chain
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Atomic Structure Recall the different charges of the particles that make up an atom. Describe why atoms have no overall charge. Use the periodic table to identify
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Atomic Structure Recall the different charges of the particles that make up an atom. Describe why atoms have no overall charge. Use the periodic table to identify
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
AQA Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Alkyl phenyl ketones are usually named by adding the acyl group as prefix to phenone.
 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones Aldehydes: Often called by their common names instead of IUPAC names. Ketones: Derived by naming two alkyl or aryl groups bonded
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones Aldehydes: Often called by their common names instead of IUPAC names. Ketones: Derived by naming two alkyl or aryl groups bonded
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80
 ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2011 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2011 Time: 1½ hrs Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will NOT be allowed to
FACTFILE: GCSE CHEMISTRY: UNIT 2.5
 FACTFILE: GCSE CHEMISTRY: UNIT Organic Chemistry Learning outcomes Student should be able to:.1 demonstrate knowledge and understanding that carbon can form four covalent bonds and there is a large number
FACTFILE: GCSE CHEMISTRY: UNIT Organic Chemistry Learning outcomes Student should be able to:.1 demonstrate knowledge and understanding that carbon can form four covalent bonds and there is a large number
Inter-conversions of carbon compounds Inter-conversions between the functional groups Considerations in planning a synthetic route
 Chapter 45 Inter-conversions of carbon compounds 45.1 Inter-conversions between the functional groups 45.2 Considerations in planning a synthetic route 45.3 Laboratory preparation of simple carbon compounds
Chapter 45 Inter-conversions of carbon compounds 45.1 Inter-conversions between the functional groups 45.2 Considerations in planning a synthetic route 45.3 Laboratory preparation of simple carbon compounds
Organic Chemistry. Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon.
 Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. In this chapter we will discuss the structural features of organic molecules, nomenclature, and a
Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. In this chapter we will discuss the structural features of organic molecules, nomenclature, and a
Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline
 Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Slide 2 Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of and its compounds. The major sources of carbon are the fossil fuels: petroleum, natural gas,
Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Slide 2 Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of and its compounds. The major sources of carbon are the fossil fuels: petroleum, natural gas,
2.1. The Main Types of Organic Reactions. Addition, Substitution, and Elimination Reactions
 The Main Types of rganic Reactions Figure 2.1(A) shows raw fruit. The crisp, sharp-tasting fruit becomes soft and sweet when it is cooked. Figure 2.1(B) shows a chemist accelerating the tranformation of
The Main Types of rganic Reactions Figure 2.1(A) shows raw fruit. The crisp, sharp-tasting fruit becomes soft and sweet when it is cooked. Figure 2.1(B) shows a chemist accelerating the tranformation of
Worksheet Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary
 Worksheet 10.1 Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary Addition elimination reaction A reaction in which two molecules combine with the release of a small molecule, often water. This type of reaction is
Worksheet 10.1 Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary Addition elimination reaction A reaction in which two molecules combine with the release of a small molecule, often water. This type of reaction is
